Dell PowerEdge T605 Systems Hardware Owner's Manual

Dell™ PowerEdge™ T605 Systems
Hardware Owner’s Manual
www.dell.com | support.dell.com

Notes, Notices, and Cautions
NOTE: A NOTE indicates important information that helps you make better use of
your system.
NOTICE: A NOTICE indicates either potential damage to hardware or loss of data
and tells you how to avoid the problem.
CAUTION: A CAUTION indicates a potential for property damage, personal injury,
or death.
____________________
Information in this document is subject to change without notice.
© 2007–2009 Dell Inc. All rights reserved.
Reproduction in any manner whatsoever without the written permission of Dell Inc. is strictly
forbidden.
Trademarks used in this text: Dell, the DELL logo, P owerEdg e, and Dell OpenManage are trademarks
of Dell Inc.; AMD and AMD Opter on are registered trademarks and AMD PowerNow! is a trademark
of Advanced Micro Devices; Microsoft, Windows, Windows Server , and MS-DOS are either trademarks
or registered trademarks of Microsoft Corporation in the United States and/or other countries; EMC
is a registered trademark of EMC Corporation; Red Hat and Red Hat Linux are re gistered trademarks
of Red Hat Inc.; UNIX is a registered trademark of The Open Group in the United States and other
countries.
Other trademarks and trade names may be used in this document to refer to either the entities claiming
the marks and names or their products. Dell Inc. disclaims any proprietary interest in trademarks and
trade names other than its own.
Model SCM
September 2009 P/N DR715 Rev. A02

Contents
1 About Your System. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
Other Information You May Need . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
Accessing System Features During Startup
. . . . . . . 12
Front-Panel Features and Indicators . . . . . . . . . . 13
Back-Panel Features and Indicators
Connecting External Devices
Power Indicator Codes
NIC Indicator Codes
LCD Status Messages
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
. . . . . . . . . . 15
. . . . . . . . . . . . 16
Solving Problems Described by
LCD Status Messages
Removing LCD Status Messages
System Messages
Warning Messages
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 32
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 41
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 31
. . . . . . . . . . 32
Diagnostics Messages
Alert Messages
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 41
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 41
Contents 3

2 Using the System Setup Program . . . . . 43
Entering the System Setup Program . . . . . . . . . . . 43
Responding to Error Messages
. . . . . . . . . . . 43
Using the System Setup Program
System Setup Options
Main Screen
Memory Information Screen
CPU Information Screen
SATA Configuration Screen
Integrated Devices Screen
Serial Communication Screen
System Security Screen
Exit Screen
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 44
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 44
. . . . . . . . . . . . 47
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . 48
. . . . . . . . . . . . . 50
. . . . . . . . . . . . . 51
. . . . . . . . . . . 52
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . 53
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 56
System and Setup Password Features
Using the System Password
Using the Setup Password
. . . . . . . . . . . . 56
. . . . . . . . . . . . . 59
. . . . . . . . . . 44
. . . . . . . . . . 56
Disabling a Forgotten Password
Baseboard Management Controller Configuration
Entering the BMC Setup Module
BMC Setup Module Options
. . . . . . . . . . . . . 60
. . . 60
. . . . . . . . . . 61
. . . . . . . . . . . . 61
3 Installing System Components . . . . . . . 63
Recommended Tools . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 64
Inside the System
Front Drive Bezel
Removing the Front Drive Bezel
Installing the Front Drive Bezel
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 64
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 66
. . . . . . . . . . 66
. . . . . . . . . . . 66
4 Contents

Removing an Insert on the Front Drive Bezel . . . 67
Installing an Insert on the Front Drive Bezel
Opening the System
Closing the System
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 68
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 70
Removing and Installing Blank Drive EMI Fillers
Cooling Shrouds
Removing the Expansion Card Shroud
Removing the Processor Shroud
Installing the Processor Shroud
Installing the Expansion Card Shroud
Power Supplies
Removing a Redundant Power Supply
Installing a Redundant Power Supply
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 72
. . . . . . . 72
. . . . . . . . . . 72
. . . . . . . . . . 74
. . . . . . . 75
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 75
. . . . . . . 76
. . . . . . . 77
Removing a Non-redundant Power Supply
. . . . 67
. . . . 71
. . . . 78
Installing a Non-redundant Power Supply
Hard Drives
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 82
Hard Drive Installation Guidelines
Removing a Hard Drive
Installing a Hard Drive
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 82
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 84
Removing a Hot-plug Hard Drive
Installing a Hot-plug Hard Drive
Removing a Hot-plug Hard Drive Blank
Installing a Hot-plug Hard Drive Blank
Diskette Drive
Removing the Diskette Drive
Installing a Diskette Drive
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 91
. . . . . . . . . . . . 91
. . . . . . . . . . . . . 94
. . . . . 81
. . . . . . . . . 82
. . . . . . . . . . 88
. . . . . . . . . . 89
. . . . . . 91
. . . . . . . 91
Contents 5

Optical and Tape Drives . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 97
Removing an Optical or Tape Drive
Installing an Optical or Tape Drive
Expansion Cards
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 108
Removing an Expansion Card
Installing an Expansion Card
SAS Controller Card
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 112
Installing a SAS Controller Card
Removing a SAS Controller Card
RAID Battery
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 115
Installing a RAID Battery
Removing a RAID Battery
Configuring the Boot Device
RAC Card
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 118
. . . . . . . . . 97
. . . . . . . . 101
. . . . . . . . . . . 108
. . . . . . . . . . . 111
. . . . . . . . . 112
. . . . . . . . . 115
. . . . . . . . . . . . . 116
. . . . . . . . . . . . . 117
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . 118
Removing the RAC Card
Installing a RAC Card
Internal USB Memory Key Connector
. . . . . . . . . . . . . 118
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 120
. . . . . . . . . 121
Installing the Optional Internal
USB Memory Key
Integrated TOE
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 123
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 121
Cooling Fans . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 123
Removing the Expansion Card Fan
Installing the Expansion Card Fan
Removing the System Fan
Installing the System Fan
System Memory
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 128
. . . . . . . . . . . . . 125
. . . . . . . . . . . . . 126
General Memory Module Installation Guidelines
Memory Sparing Support
. . . . . . . . . . . . . 129
. . . . . . . . 123
. . . . . . . . 124
128
6 Contents

Installing Memory Modules . . . . . . . . . . . . 131
Removing Memory Modules
Processors
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 134
Removing a Processor
Installing a Processor
System Battery
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 139
Replacing the System Battery
Chassis Intrusion Switch
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 142
. . . . . . . . . . . . 133
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 134
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 137
. . . . . . . . . . . 139
Removing the Chassis Intrusion Switch
Installing the Chassis Intrusion Switch
Power Supply Distribution Board
. . . . . . . . . . . . 144
Removing the Power Supply Distribution Board
Installing the Power Supply Distribution Board
SAS/SATA Backplane
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 149
. . . . . . 142
. . . . . . 143
. . 144
. . 148
Removing the SAS/SATA Backplane
Installing the SAS/SATA Backplane
Control Panel
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 152
Removing the Control Panel
Installing the Control Panel
System Board
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 154
Removing the System Board
Installing the System Board
. . . . . . . . . . . . 152
. . . . . . . . . . . . . 154
. . . . . . . . . . . . 154
. . . . . . . . . . . . 157
. . . . . . . . 149
. . . . . . . . 151
4 Troubleshooting Your System . . . . . . . . 159
Safety First—For You and Your System . . . . . . . . . 159
Start-Up Routine
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 159
Contents 7

Checking the Equipment . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 160
Troubleshooting External Connections
Troubleshooting the Video Subsystem
Troubleshooting the Keyboard
Troubleshooting the Mouse
. . . . . . . . . . . . 162
Troubleshooting Serial I/O Problems
Troubleshooting a Serial I/O Device
Troubleshooting a USB Device
Troubleshooting a NIC
Troubleshooting a Wet System
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 167
. . . . . . . . . . . . . 168
Troubleshooting a Damaged System
Troubleshooting the System Battery
. . . . . . . . . . 161
. . . . . . . . . . 165
. . . . . . . . . . 169
. . . . . . . . . . 170
. . . . . . 160
. . . . . . . . . 164
. . . . . . . 165
Troubleshooting Redundant Power Supplies
. . . . . . 160
. . . . . 171
Troubleshooting System Cooling Problems
Troubleshooting a Fan
Troubleshooting System Memory
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . 172
. . . . . . . . . . . 173
Troubleshooting an Internal USB Key
Troubleshooting a Diskette Drive
Troubleshooting an Optical Drive
Troubleshooting a SCSI Tape Drive
Troubleshooting a Hard Drive
. . . . . . . . . . . 176
. . . . . . . . . . . 178
. . . . . . . . . . 179
. . . . . . . . . . . . . 181
Troubleshooting a Hot-plug Hard Drive
. . . . . . 172
. . . . . . . . . 175
. . . . . . . . 182
Troubleshooting a SAS or SAS RAID Controller
. . . . 184
8 Contents

Troubleshooting Expansion Cards. . . . . . . . . . . . 186
Troubleshooting the Microprocessors
. . . . . . . . . 188
5 Running the System Diagnostics. . . . . . 193
Using Dell PowerEdge Diagnostics . . . . . . . . . . . 193
System Diagnostics Features
When to Use the System Diagnostics
Running the System Diagnostics
System Diagnostics Testing Options
Using the Custom Test Options
Selecting Devices for Testing
Selecting Diagnostics Options
Viewing Information and Results
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . 193
. . . . . . . . . . 194
. . . . . . . . . . . . 194
. . . . . . . . . . 194
. . . . . . . . . . . . . 195
. . . . . . . . . . . 195
. . . . . . . . . . . 195
. . . . . . . . . . 196
6 Jumpers and Connectors . . . . . . . . . . . 197
System Board Jumpers and Connectors . . . . . . . . 197
SAS/SATA Backplane Board Connectors . . . . . . . . 201
Disabling a Forgotten Password
. . . . . . . . . . . . 203
7 Getting Help. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 205
Contacting Dell . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 205
Contents 9

Glossary . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 207
Index . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 223
10 Contents

About Your System
This section describes the physical, firmware, and software interface features
that provide and ensure the essential functioning of your system. The
physical connectors on your system’s front and back panels provide
convenient connectivity and system expansion capability. The system
firmware, programs, and operating systems monitor the system and
component status and alert you when a problem arises. System conditions
can be reported by any of the following:
• Front or back panel indicators
• System messages
• Warning messages
• Diagnostics messages
• Alert messages
This section describes each type of message, lists the possible causes, and
provides steps to resolve any problems indicated by a message. The system
indicators and features are illustrated in this section.
Other Information You May Need
CAUTION: The Product Information Guide provides important safety and
regulatory information. Warranty information may be included within this
document or as a separate document.
• The
• CDs included with your system provide documentation and tools for
• Systems management software documentation describes the features,
• Operating system documentation describes how to install (if necessary),
• Documentation for any components you purchased separately provides
Getting Started Guide
up your system, and technical specifications.
configuring and managing your system.
requirements, installation, and basic operation of the software.
configure, and use the operating system software.
information to configure and install these options.
provides an overview of system features, setting
About Your System 11
• Updates are sometimes included with the system to describe changes to
the system, software, and/or documentation.
NOTE: Always check for updates on support.dell.com and read the updates
first because they often supersede information in other documents.
• Release notes or readme files may be included to provide last-minute
updates to the system or documentation or advanced technical reference
material intended for experienced users or technicians.
Accessing System Features During Startup
Table 1-1 describes keystrokes that may be entered during startup to access
system features. If your operating system begins to load before you enter the
keystroke, allow the system to finish booting, and then restart your system
and try again.
Table 1-1. Keystrokes for Accessing System Features
Keystroke Description
<F2> Enters the System Setup program (see "Entering the System Setup
Program" on page 43).
<F10> Opens the utility partition, allowing you to run the system diagnostics
(see "Running the System Diagnostics" on page 193).
<F11> Enters the boot mode selection screen, allowing you to choose a boot
device.
<F12> Starts PXE boot.
<Ctrl+E> Enters the Baseboard Management Controller (BMC) Management
Utility, which allows access to the system event log (SEL) and
configuration of the remote access controller (RAC) card (see the BMC
User’s Guide for more information on setup and use of BMC).
<Ctrl+C> This keystroke enters the SAS Configuration Utility (see your SAS
controller User’s Guide for more information).
<Ctrl+R> If you have the optional battery-cached SAS RAID controller, this
keystroke enters the RAID configuration utility. For more information,
see the documentation for your SAS controller card.
12 About Your System
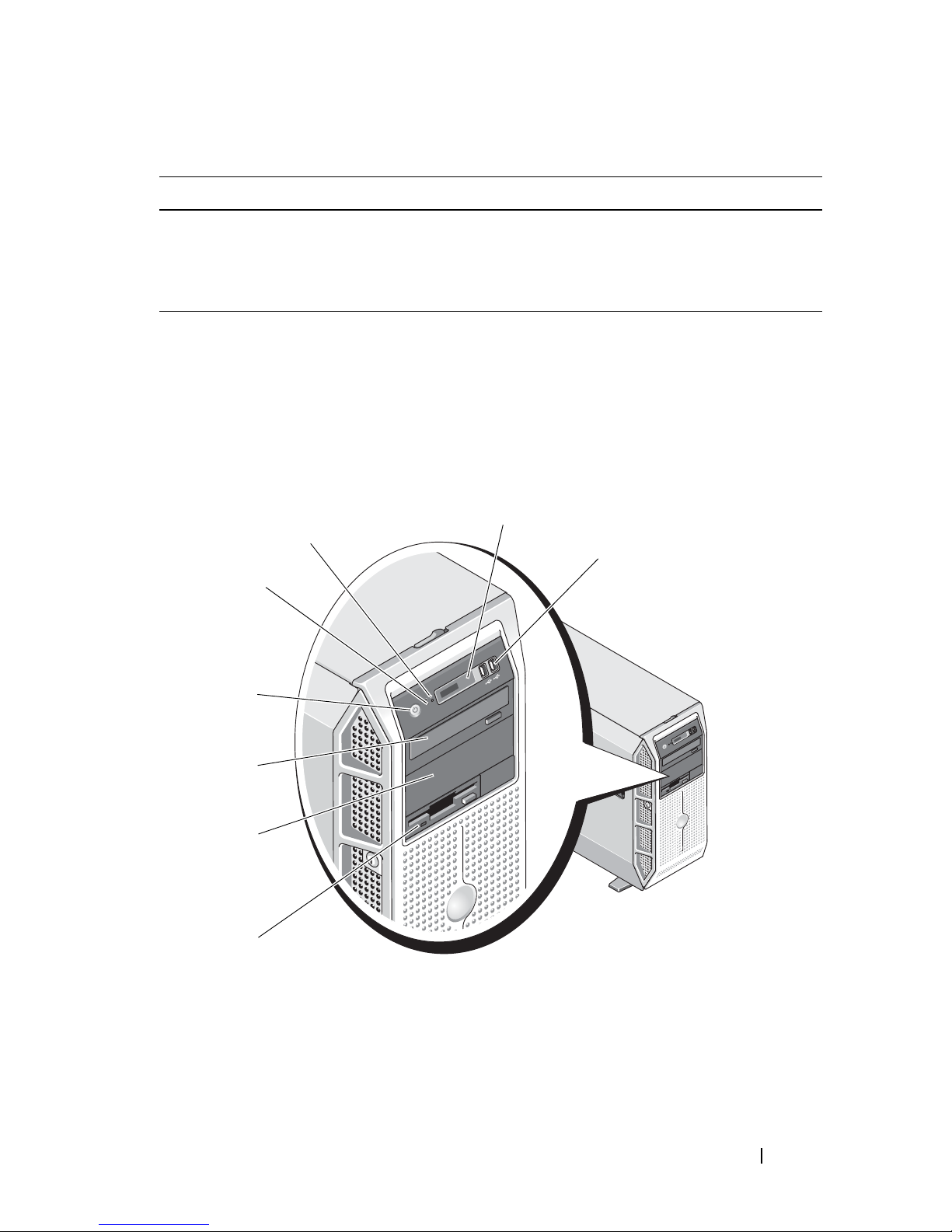
Table 1-1. Keystrokes for Accessing System Features (continued)
8
1
2
4
5
3
6
7
Keystroke Description
<Ctrl+S> If you have PXE support enabled through the System Setup Program
(see "Integrated Devices Screen" on page 51), this keystroke allows you
to configure NIC settings for PXE boot. For more information, see the
documentation for your integrated NIC.
Front-Panel Features and Indicators
Figure 1-1 shows the controls, indicators, and connectors located on the
system's front panel. Table 1-2 provides component descriptions.
Figure 1-1. Front-Panel Features and Indicators
About Your System 13
Table 1-2. Front-Panel Components
Item Component Icon Description
1 3.5-inch drive bay Holds an optional diskette drive.
2 lower 5.25-inch drive
bay
3 upper 5.25-inch drive
Holds an optional optical or tape
backup unit drive.
Holds an optical drive.
bay
4 power button The power button controls the DC
power supply output to the system.
NOTE: If you turn off the system using
the power button and the system is
running an ACPI-compliant operating
system, the system performs a
graceful shutdown before the power
is turned off. If the system is not
running an ACPI-compliant operating
system, the power is turned off
immediately after the power button is
pressed.
5 NMI button Used to troubleshoot software and
device driver errors when using
certain operating systems. This
button can be pressed using the end
of a paper clip.
6 System identification
button
14 About Your System
Use this button only if directed to
do so by qualified support personnel
or by the operating system's
documentation.
The identification buttons on the
front and back panels can be used to
locate a particular system within a
rack. When one of these buttons is
pushed, the LCD panel on the front
and the blue system status indicator
on the back blink until one of the
buttons is pushed again.

Table 1-2. Front-Panel Components (continued)
Item Component Icon Description
7 LCD panel Provides system ID, status
information, and system error
messages.
The LCD lights blue during normal
system operation. Both the system
management software and the
identification buttons located on
the front and back of the system can
cause the LCD to flash blue to
identify a particular system.
The LCD lights amber when the
system needs attention, and the
LCD panel displays an error code
followed by descriptive text.
NOTE: If the system is connected to
AC power and an error has been
detected, the LCD lights amber
regardless of whether the system has
been powered on.
8 USB connectors (2) Connects USB 2.0-compliant
devices to the system.
Back-Panel Features and Indicators
Figure 1-2 shows the controls, indicators, and connectors located on the
system's back panel.
About Your System 15
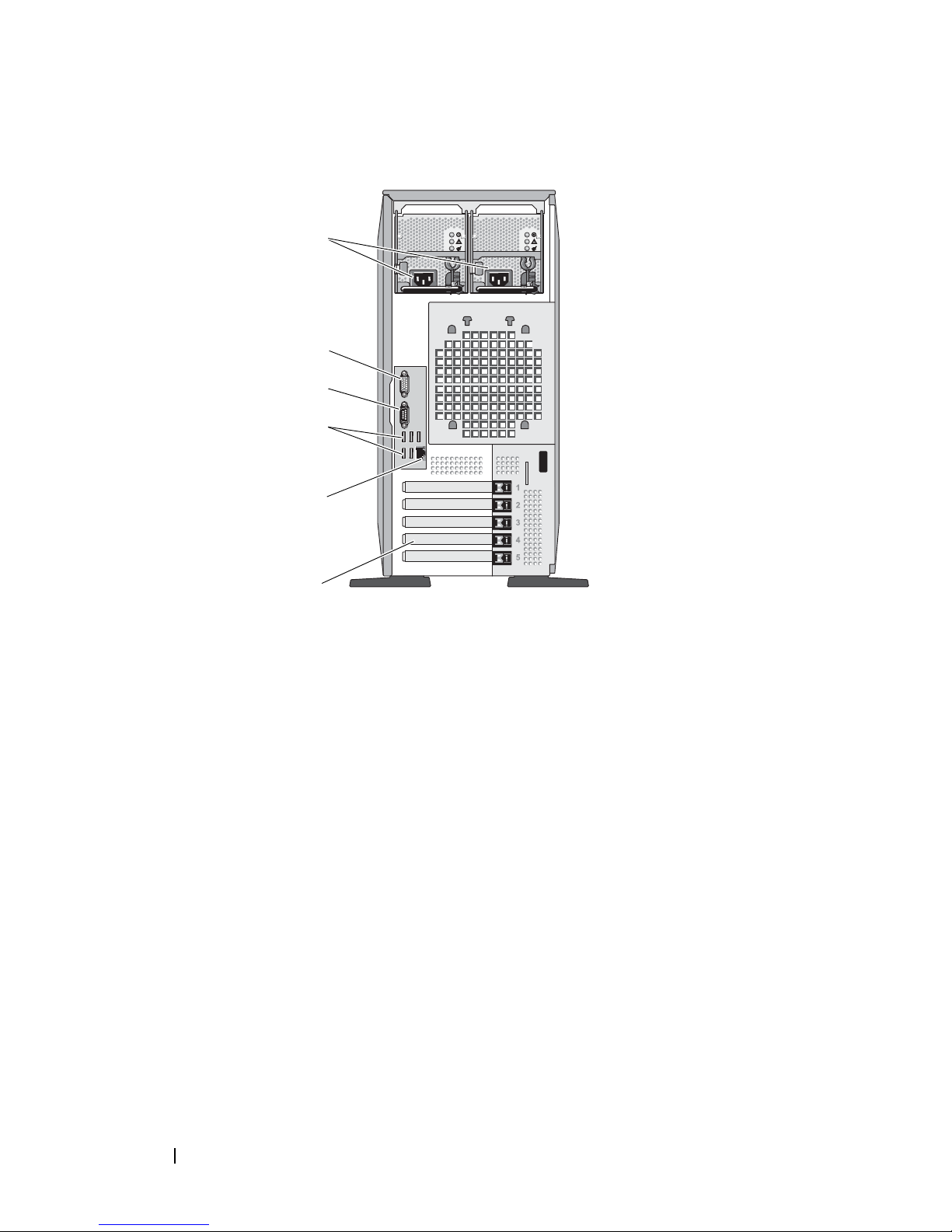
Figure 1-2. Back-Panel Features and Indicators
1
4
5
6
2
3
1 expansion card slots (5) 2 NIC connector
3 USB connectors (5) 4 serial connector
5 video connector 6 power connector(s)
Connecting External Devices
When connecting external devices to your system, follow these guidelines:
• Most devices must be connected to a specific connector and device drivers
must be installed before the device operates properly. (Device drivers are
normally included with your operating system software or with the device
itself.) See the documentation that accompanied the device for specific
installation and configuration instructions.
• Always attach an external device while your system and the device are
turned off. Next, turn on any external devices before turning on the system
(unless the documentation for the device specifies otherwise).
See "Using the System Setup Program" on page 43 for information about
enabling, disabling, and configuring I/O ports and connectors.
16 About Your System
Power Indicator Codes
3
2
1
The power button on the front panel controls the power to the system from
the system's power supplies. The power indicator lights green when the
system is on.
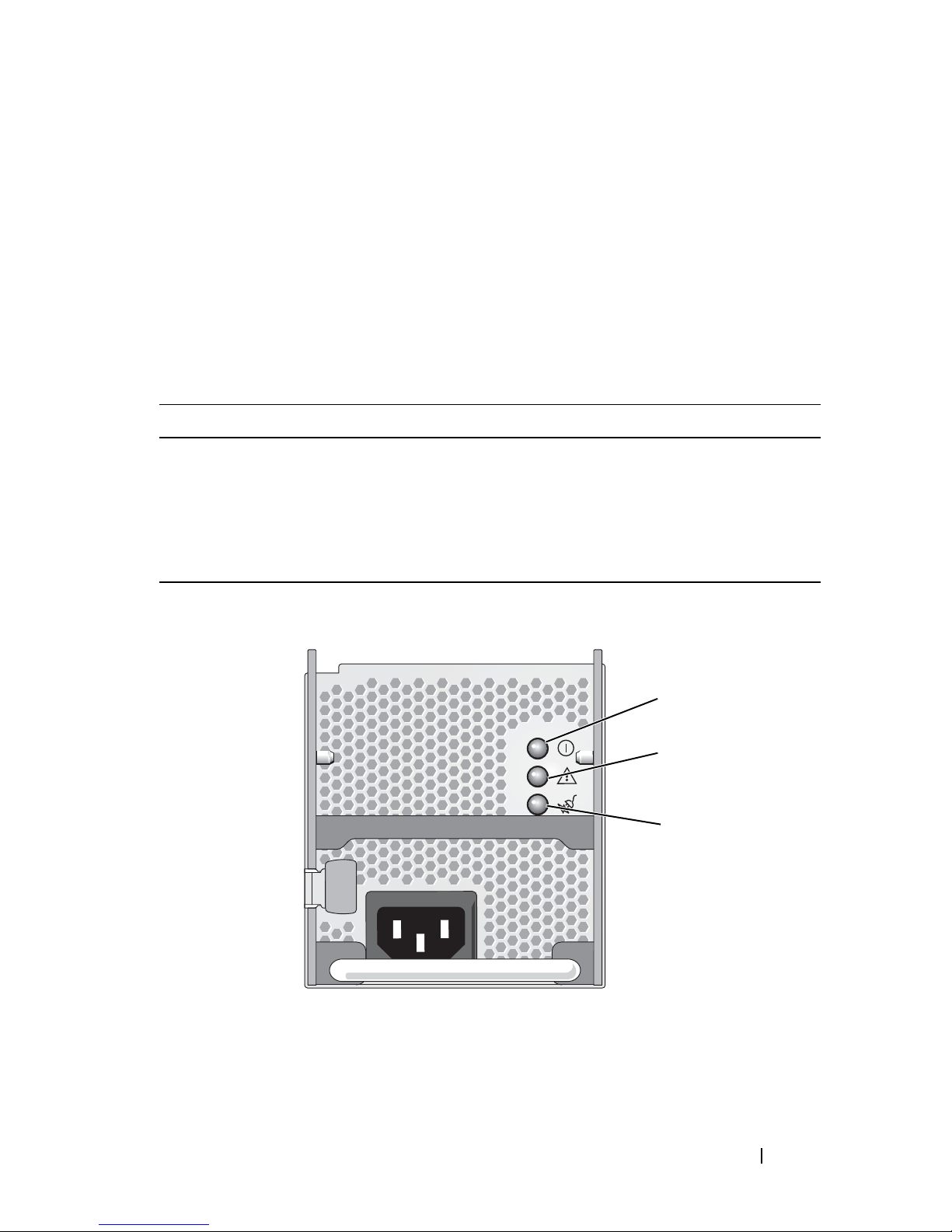
The indicators on the redundant power supplies show whether power is
present or whether a power fault has occurred (see Figure 1-3). Table 1-3 lists
the power supply indicator codes.
Table 1-3. Redundant Power Supply Indicators
Indicator Function
Power supply status Green indicates that the power supply is operational and
providing DC power to the system.
Power supply fault Amber indicates a problem with the power supply.
AC line status Green indicates that a valid AC source is connected to the
power supply and is operational.
Figure 1-3. Redundant Power Supply Indicators
1 power supply status
(DC out is operational)
3 AC line status (AC in is operational)
2 power supply fault
About Your System 17
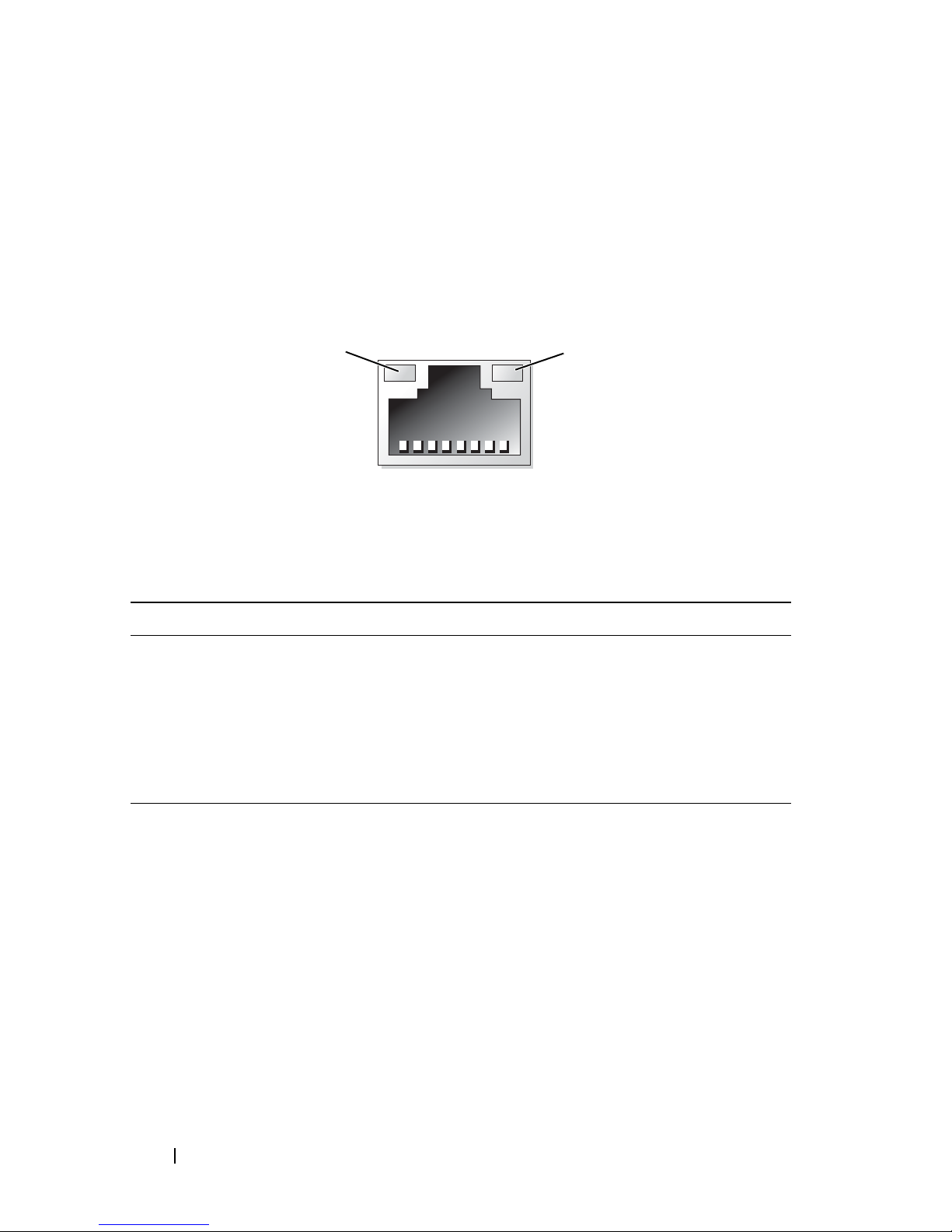
NIC Indicator Codes
1
2
Each NIC on the back panel has an indicator that provides information on
network activity and link status (see Figure 1-4). Table 1-4 lists the NIC
indicator codes.
Figure 1-4. NIC Indicators
1 link indicator 2 activity indicator
Table 1-4. NIC Indicator Codes
Indicator Indicator Code
Link and activity
indicators are off
Link indicator is green The NIC is connected to a valid link partner on the
Activity indicator is
amber blinking
The NIC is not connected to the network.
network.
Network data is being sent or received.
LCD Status Messages
The system's control panel LCD provides status messages to signify when the
system is operating correctly or when the system needs attention.
The LCD lights blue to indicate a normal operating condition, and lights
amber to indicate an error condition. The LCD scrolls a message that
includes a status code followed by descriptive text. Table 1-5 lists the LCD
status messages that can occur and the probable cause for each message. The
LCD messages refer to events recorded in the System Event Log (SEL). For
information on the SEL and configuring system management settings, see
the systems management software documentation.
18 About Your System

CAUTION: Many repairs may only be done by a certified service technician. You
should only perform troubleshooting and simple repairs as authorized in your
product documentation, or as directed by the online or telephone service and
support team. Damage due to servicing that is not authorized by Dell is not covered
by your warranty. Read and follow the safety instructions that came with the
product.
NOTE: If your system fails to boot, press the System ID button for at least five
seconds until an error code appears on the LCD. Record the code, then see "Getting
Help" on page 205.
Table 1-5. LCD Status Messages
Code Text Causes Corrective Actions
N/A SYSTEM NAME A 62-character string that
can be defined by the user in
the System Setup program.
The SYSTEM NAME
displays under the following
conditions:
• The system is powered on.
• The power is off and
active errors are displayed.
E1000 FAILSAFE,
Call Support
Check the system event log
for critical failure events.
E1114 Temp Ambient Ambient system
temperature is out of
acceptable range.
E1118 CPU Temp
Interface
The BMC is unable to
determine the processor(s)
temperature status.
Consequently, the BMC
increases the processor fan
speed to maximum
as a precautionary measure.
This message is for
information only.
You can change the
system ID and name in
the System Setup
program (see "Entering
the System Setup
Program" on page 43).
See "Getting Help" on
page 205.
See "Troubleshooting
System Cooling
Problems" on page 172.
Turn off power to the
system and restart the
system. If the problem
persists, see "Getting
Help" on page 205.
E1210 CMOS Batt CMOS battery is missing, or
the voltage is out of
acceptable range.
See "Troubleshooting the
System Battery" on
page 170.
About Your System 19

Table 1-5. LCD Status Messages (continued)
Code Text Causes Corrective Actions
E1211 ROMB Batt RAID battery is either
missing, bad, or unable to
recharge due to thermal
issues.
E1214
E1216
## PwrGd Specified voltage regulator
has failed.
E1217
E121A 8V PwrGd 8V voltage regulator has
failed.
E121D 1.2V VM Dual
PwrGd
1.2V voltage regulator for
the VM dual signal has
failed.
Reseat the RAID battery
connector (see "Installing
a RAID Battery" on
page 116, and
"Troubleshooting System
Cooling Problems" on
page 172).
See "Getting Help" on
page 205.
Recycle power to the
system or clear the SEL. If
the problem persists, see
"Getting Help" on
page 205.
Recycle power to the
system or clear the SEL. If
the problem persists, see
"Getting Help" on
page 205.
E1227 Linear PwrGd Linear voltage regulator(s)
has failed. Represents status
of multiple voltage
regulators used in the video
and LOM circuitry.
E1229 CPU # VCORE Processor # VCORE voltage
regulator has failed.
E122A CPU VTT PwrGd Processor # VTT voltage has
exceeded the allowable
voltage range.
E122D CPU # VDDIO
1.0V PwrGd
Processor # VDDIO voltage
has exceeded the allowable
voltage range.
20 About Your System
See "Getting Help" on
page 205.
See "Getting Help" on
page 205.
See "Getting Help" on
page 205.
See "Getting Help" on
page 205.

Table 1-5. LCD Status Messages (continued)
Code Text Causes Corrective Actions
E122E CPU # VDDA Processor # VDDA voltage
has exceeded the allowable
voltage range.
E122F 2.5V PwrGd 2.5V voltage regulator has
failed.
E1231 1.2V HTCORE
PwrGd
E1232 VDD 12V PS#
PwrGd
1.2V HTCORE voltage
regulator has failed.
The specified power supply
has failed or has been
removed from the bay while
the system was on.
E1233 Cabled PS
PwrGd
E1234 PCIX-12V
PwrGd
E1235 USB 1.8V
Linear PwrGd
Power supply voltage
regulator failed.
PCI-X -12V voltage regulator
has failed.
1.8V voltage regulator for
the USB linear has failed.
See "Getting Help" on
page 205.
See "Getting Help" on
page 205.
See "Getting Help" on
page 205.
If removed, reinsert the
power supply into the bay
and reconnect to power.
For component failures,
see "Getting Help" on
page 205.
See "Getting Help" on
page 205.
See "Getting Help" on
page 205.
See "Getting Help" on
page 205.
E1236 VID 1.8V Mem
Linear PwrGd
E1237 VID 1.2V
Linear PwrGd
E1238 VID 1.8V
Linear PwrGd
E1239 2.5VAux LOM
Linear PwrGd
E123A 1.2VAux LOM
Linear PwrGd
Linear memory 1.8V voltage
regulator has failed.
1.2V video voltage regulator
has failed.
1.8V video voltage regulator
has failed.
Aux 2.5V voltage regulator
for LOM1 has failed.
1.2V voltage regulator for
LOM has failed.
About Your System 21
See "Getting Help" on
page 205.
See "Getting Help" on
page 205.
See "Getting Help" on
page 205.
See "Getting Help" on
page 205.
See "Getting Help" on
page 205.

Table 1-5. LCD Status Messages (continued)
Code Text Causes Corrective Actions
E123C Planar LOM
PwrGd
Voltage regulator for the
integrated LOM has failed.
E1310 RPM Fan ## RPM of specified cooling
fan is out of acceptable
operating range.
E1313 Fan
Redundancy
The system is no longer fanredundant. Another fan
failure will put the system at
risk of over-heating.
Recycle power to the
system or clear the SEL. If
the problem persists, see
"Getting Help" on
page 205.
See "Troubleshooting
System Cooling
Problems" on page 172.
Check control panel LCD
for additional scrolling
messages (see
"Troubleshooting System
Cooling Problems" on
page 172).
22 About Your System

Table 1-5. LCD Status Messages (continued)
Code Text Causes Corrective Actions
E1414 CPU #
Thermtrip
Specified microprocessor is
out of acceptable
temperature range and has
halted operation.
See "Troubleshooting
System Cooling
Problems" on page 172. If
the problem persists,
ensure that the
microprocessor heat sinks
are properly installed (see
"Troubleshooting the
Microprocessors" on
page 188).
NOTE: The LCD continues
to display this message
until the system’s power
cable is disconnected and
reconnected to the AC
power source, or the SEL is
cleared using either Server
Assistant or the BMC
Management Utility. See
the Dell OpenManage™
Baseboard Management
Controller User’s Guide for
information about these
utilities.
E1418 CPU #
Presence
E141C CPU Mismatch Processors are in a
Specified processor is
missing or bad, and the
system is in an unsupported
configuration.
configuration unsupported
by Dell.
About Your System 23
See "Troubleshooting the
Microprocessors" on
page 188.
Ensure that your
processors match and
conform to the type
described in the
Microprocessor Technical
Specifications outlined in
your system’s Getting
Started Guide.

Table 1-5. LCD Status Messages (continued)
Code Text Causes Corrective Actions
E141F CPU Protocol The system BIOS has
reported a processor
protocol error.
E1421 CPU Init The system BIOS has
reported a processor
initialization error.
E1422 CPU Machine
Chk
The system BIOS has
reported a machine check
error.
E1610 PS # Missing No power is available from
the specified power supply;
specified power supply is
improperly installed or
faulty.
E1614 PS # Status No power is available from
the specified power supply;
specified power supply is
improperly installed or
faulty.
See "Getting Help" on
page 205.
See "Getting Help" on
page 205.
See "Getting Help" on
page 205.
See "Troubleshooting
Redundant Power
Supplies" on page 171.
See "Troubleshooting
Redundant Power
Supplies" on page 171.
E1618 PS #
Predictive
E161C PS # Input
Lost
24 About Your System
Power supply voltage is out
of acceptable range;
specified power supply is
improperly installed or
faulty.
Power source for specified
power supply is unavailable,
or out of acceptable range.
See "Troubleshooting
Redundant Power
Supplies" on page 171.
Check the AC power
source for the specified
power supply. If the
problem persists, see
"Troubleshooting
Redundant Power
Supplies" on page 171.

Table 1-5. LCD Status Messages (continued)
Code Text Causes Corrective Actions
E1620 PS # Input
Range
Power source for specified
power supply is unavailable,
or out of acceptable range.
E1624 PS Redundancy The power supply subsystem
is no longer redundant. If
the last supply fails, the
system will go down.
E1625 PS AC Current Power source is out of
acceptable range.
E1710 I/O Channel
Chk
The system BIOS has
reported an I/O channel
check.
E1711 PCI PERR B##
D## F##
The system BIOS has
reported a PCI parity error
on a component that resides
in PCI configuration space
at bus ##, device ##,
function ##.
Check the AC power
source for the specified
power supply. If the
problem persists, see
"Troubleshooting
Redundant Power
Supplies" on page 171.
See "Troubleshooting
Redundant Power
Supplies" on page 171.
Check the AC power
source.
See "Getting Help" on
page 205.
Remove and reseat the
PCIe expansion cards. If
the problem persists, see
"Troubleshooting
Expansion Cards" on
page 186.
PCI PERR Slot #The system BIOS has
reported a PCI parity error
on a component that resides
in the specified PCIe slot.
About Your System 25
Remove and reseat the
PCIe expansion cards. If
the problem persists, see
"Troubleshooting
Expansion Cards" on
page 186.

Table 1-5. LCD Status Messages (continued)
Code Text Causes Corrective Actions
E1712 PCI SERR B##
D## F##
The system BIOS has
reported a PCI system error
on a component that resides
in PCI configuration space
at bus ##, device ##,
function ##.
PCI SERR Slot #The system BIOS has
reported a PCI system error
on a component that resides
in the specified slot.
E1714 Unknown Err The system BIOS has
determined that there has
been an error in the system,
but is unable to determine
its origin.
E171F PCIE Fatal
Err B## D##
F##
The system BIOS has
reported a PCIe fatal error
on a component that resides
in PCIe configuration space
at bus ##, device ##,
function ##.
Remove and reseat the
PCIe expansion cards. If
the problem persists, see
"Troubleshooting
Expansion Cards" on
page 186.
Remove and reseat the
PCIe expansion cards. If
the problem persists, see
"Troubleshooting
Expansion Cards" on
page 186.
See "Getting Help" on
page 205.
Remove and reseat the
PCIe expansion cards. If
the problem persists, see
"Troubleshooting
Expansion Cards" on
page 186.
PCIE Fatal
Err Slot #
E1810 HDD ## Fault The SAS subsystem has
26 About Your System
The system BIOS has
reported a PCIe fatal error
on a component that resides
in the specified slot.
determined that hard drive
## has experienced a fault.
Remove and reseat the
PCIe expansion cards. If
the problem persists, see
"Troubleshooting
Expansion Cards" on
page 186.
See "Troubleshooting a
Hard Drive" on page 181.

Table 1-5. LCD Status Messages (continued)
Code Text Causes Corrective Actions
E1811 HDD ## Rbld
Abrt
E1812 HDD ##
Removed
The specified hard drive has
experienced a rebuild abort.
The specified hard drive has
been removed from the
system.
E1914 DRAC5 Conn2
Cbl
E1915 IO55 HTSink
Missing
MCP55 Htsink
Missing
DRAC 5 cable is missing or
disconnected.
Heat sink sensor reports that
the chipset IO55 heat sink is
missing.
Heat sink sensor reports that
the chipset MCP heat sink is
missing.
E1A14 SAS Cable A SAS cable A is missing or
bad.
See "Troubleshooting a
Hard Drive" on page 181.
If the problem persists,
see your RAID
documentation.
Information only.
Reconnect the cable (see
"Installing a RAC Card"
on page 120).
See "Getting Help" on
page 205.
Reseat the cable. If the
problem persists, replace
cable.
E1A15 SAS Cable B SAS cable B is missing or
bad.
E1A15 SAS Cable C SAS cable C is missing or
bad.
If the problem persists,
see "Getting Help" on
page 205.
Reseat the cable. If the
problem persists, replace
cable.
If the problem persists,
see "Getting Help" on
page 205.
Reseat the cable. If the
problem persists, replace
cable.
If the problem persists,
see "Getting Help" on
page 205.
About Your System 27

Table 1-5. LCD Status Messages (continued)
Code Text Causes Corrective Actions
E1A15 SAS Cable D SAS cable D is missing or
bad.
E1A18 PDB Ctrl
Cable
Control cable for the power
distribution board (PDB) is
missing or bad.
E1A19 12V Cable
Fault
Power cable for the PDB or
cabled power supply is
missing or bad. They system
will not turn on.
Reseat the cable. If the
problem persists, replace
cable.
If the problem persists,
see "Getting Help" on
page 205.
Reseat the cable. If the
problem persists, replace
cable.
If the problem persists,
see "Getting Help" on
page 205.
Reseat the cable. If the
problem persists, replace
cable.
If the problem persists,
see "Getting Help" on
page 205.
E1B01 USB#
Overcurrent
Device plugged in the
specified USB port caused
an overcurrent condition.
E2010 No Memory No memory is installed in
the system.
E2011 Mem Config
Err
Memory detected, but is not
configurable. Error detected
during memory
configuration.
E2012 Unusable
Memory
Memory is configured, but
not usable. Memory
subsystem failure.
Reseat the device cable. If
the problem persists,
replace or remove the
device.
Install memory (see
"Installing Memory
Modules" on page 131).
See "Troubleshooting
System Memory" on
page 173.
See "Troubleshooting
System Memory" on
page 173.
28 About Your System

Table 1-5. LCD Status Messages (continued)
Code Text Causes Corrective Actions
E2013 Shadow BIOS
Fail
E2014 CMOS Fail CMOS failure. CMOS RAM
E2015 DMA
Controller
E2016 Int
Controller
The system BIOS failed to
copy its flash image into
memory.
See "Troubleshooting
System Memory" on
page 173.
See "Getting Help" on
not functioning properly.
page 205.
DMA controller failure. See "Getting Help" on
page 205.
Interrupt controller failure. See "Getting Help" on
page 205.
E2017 Timer Fail Timer refresh failure. See "Getting Help" on
page 205.
E2018 Prog Timer Programmable interval
timer error.
See "Getting Help" on
page 205.
E2019 Parity Error Parity error. See "Getting Help" on
page 205.
E201A SIO Err SIO failure. See "Getting Help" on
page 205.
E201B Kybd
Controller
E201C SMI Init System management
Keyboard controller failure. See "Getting Help" on
page 205.
See "Getting Help" on
interrupt (SMI)
page 205.
initialization failure.
E201D Shutdown Test BIOS shutdown test failure. See "Getting Help" on
page 205.
E201E POST Mem Test BIOS POST memory test
failure.
See "Troubleshooting
System Memory" on
page 173. If problem
persists, see "Getting
Help" on page 205.
About Your System 29

Table 1-5. LCD Status Messages (continued)
Code Text Causes Corrective Actions
E201F DRAC Config Dell remote access
controller (DRAC)
configuration failure.
Check screen for specific
error messages.
Ensure that DRAC cables
and connectors are
properly seated. If
problem persists, see your
DRAC documentation.
E2020 CPU Config Processor configuration
failure.
E2021 Memory
Population
Incorrect memory
configuration. Memory
population order incorrect.
Check screen for specific
error messages.
Check screen for specific
error messages (see
"Troubleshooting System
Memory" on page 173).
E2022 POST Fail General failure after video. Check screen for specific
error messages.
E2110 MBE DIMM # & #One of the DIMMs in the
set implicated by "# & #"
has had a memory multi-bit
See "Troubleshooting
System Memory" on
page 173.
error (MBE).
E2111 SBE Log
Disable DIMM
#
E2112 Mem Spare
DIMM #
30 About Your System
The system BIOS has
disabled memory single-bit
error (SBE) logging, and will
not resume logging further
SBEs until the system is
restarted. "#" represents the
DIMM implicated by the
BIOS.
The system BIOS has spared
the memory because it has
determined that the
memory had too many
errors. "# & #" represents
the DIMM pair implicated
by the BIOS.
See "Troubleshooting
System Memory" on
page 173.
See "Troubleshooting
System Memory" on
page 173.
 Loading...
Loading...