Page 1
In the absence of confirmation by device specification sheets, SHARP takes no responsibility for any defects that may occur in equipment using any SHARP devices shown in
catalogs, data books, etc. Contact SHARP in order to obtain the latest device specification sheets before using any SHARP device.
1
DESCRIPTION
The LZ23BP2 is a 1/3-type (6.0 mm) solid-state
image sensor that consists of PN photo-diodes and
CCDs (charge-coupled devices). With approximately 350 000 pixels (695 horizontal x 504
vertical), the sensor provides a stable highresolution color image. All pixel signals can be read
independently via the vertical shift register and
horizontal shift register.
FEATURES
• Progressive scan
• Square pixel
• Compatible with VGA format
• Number of effective pixels : 659 (H) x 494 (V)
• Number of optical black pixels
– Horizontal : 2 front and 34 rear
– Vertical : 8 front and 2 rear
• Number of dummy bits
– Horizontal : 16
– Vertical : 4
• Pixel pitch : 7.4 µm (H) x 7.4 µm (V)
• R, G, and B primary color mosaic filters
• Low fixed-pattern noise and lag
• No burn-in and no image distortion
• Blooming suppression structure
• Built-in output amplifier
• Built-in overflow drain voltage circuit and reset
gate voltage circuit
• Variable electronic shutter (1/30 to 1/10 000 s)
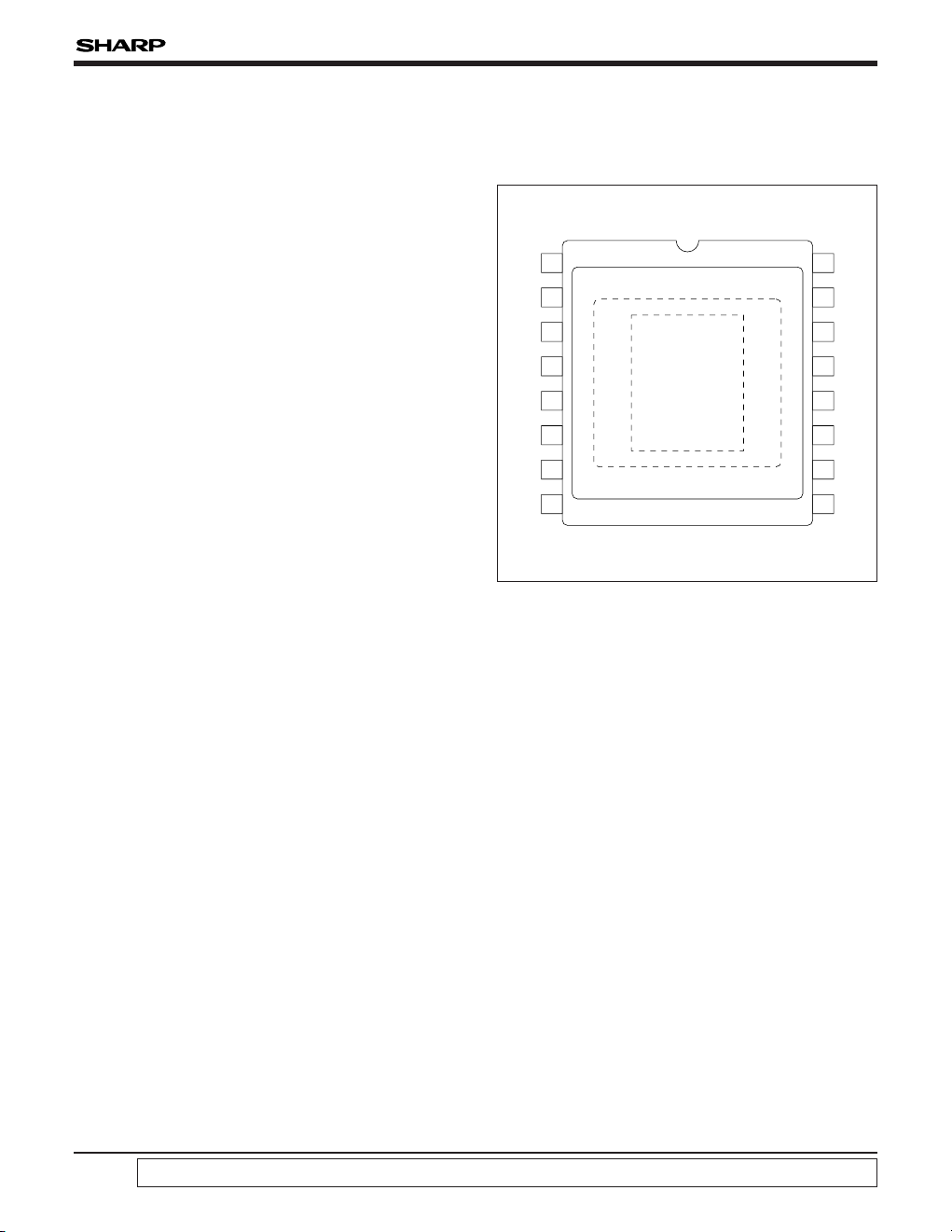
• Package :
16-pin half-pitch WDIP [Ceramic]
(WDIP016-N-0450)
Row space : 11.43 mm
PIN CONNECTIONS
PRECAUTIONS
• The exit pupil position of lens should be more
than 25 mm from the top surface of the CCD.
• Refer to "PRECAUTIONS FOR CCD AREA
SENSORS" for details.
LZ23BP2
1/3-type Progressive-scan Color CCD
Area Sensor with 350 k Pixels
LZ23BP2
1ØV4
2ØV3
3ØV2
4ØV1
5GND
6NC
1
7GND
8
16
15
14
13
12
11
10
9OS
Ø
H2
ØH1
ØRS
PW
OFD
GND
NC
2
OD
16-PIN HALF-PITCH WDIP
TOP VIEW
(WDIP016-N-0450)
Page 2
LZ23BP2
2
PIN DESCRIPTION
ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATINGS
(TA = +25 ˚C)
SYMBOL PIN NAME
OD Output transistor drain
OS Output signals
ØRS Reset transistor clock
Ø
V1, ØV2, ØV3, ØV4 Vertical shift register clock
ØH1, ØH2 Horizontal shift register clock
PW P-well
GND Ground
NC
1, NC2 No connection
PARAMETER SYMBOL RATING UNIT
Output transistor drain voltage V
OD 0 to +18 V
Reset gate clock voltage V
ØRS Internal output V
Vertical shift register clock voltage V
ØV –11.5 to +17.5 V
Horizontal shift register clock voltage VØH –0.3 to +12 V
Voltage difference between P-well and vertical clock V
PW-VØV –29 to 0 V
Storage temperature T
STG –40 to +85 ˚C
Ambient operating temperature T
OPR –20 to +70 ˚C
2
NOTE
NOTES :
1. Do not connect to DC voltage directly. When OFD is connected to GND, connect VOD to GND. Overflow drain clock is
applied below 27 Vp-p.
2. Do not connect to DC voltage directly. When Ø
RS is connected to GND, connect VOD to GND. Reset gate clock is
applied below 8 Vp-p.
3. When clock width is below 10 µs, and clock duty factor is below 0.1%, voltage difference between vertical clocks will be
below 28 V.
Overflow drainOFD
1VInternal outputV
OFDOverflow drain voltage
3V0 to +15VØV-VØVVoltage difference between vertical clocks
Page 3
3
LZ23BP2
RECOMMENDED OPERATING CONDITIONS
PARAMETER SYMBOL MIN. TYP. MAX. UNIT NOTE
Ambient operating temperature T
OPR 25.0 ˚C
Output transistor drain voltage V
OD 14.55 15.0 15.45 V
NOTES :
• Connect NC1 and NC2 to GND directly or through a capacitor larger than 0.047 µF.
1. Use the circuit parameter indicated in "SYSTEM CONFIGURATION EXAMPLE", and do not connect to DC voltage directly.
2. V
PW is set below VØVL that is low level of vertical shift register clock, or is used with the same power supply that is connected
to V
L of V driver IC.
* To apply power, first connect GND and then turn on V
OD. After turning on VOD, turn on PW first and then turn on other powers
and pulses. Do not connect the device to or disconnect it from the plug socket while power is being applied.
1V24.522.5VØOFD
Overflow drain clock
P-well voltage VPW –10.0 VØVL V2
Ground GND 0.0 V
V–8.5–9.0–9.5
V
ØV1L, VØV2L
VØV3L, VØV4L
Vertical shift
register clock
LOW level
INTERMEDIATE level
HIGH level
V
ØV1I, VØV2I
VØV3I, VØV4I
VØV1H, VØV3H 14.55
0.0
15.0 15.45VV
LOW levelHorizontal shift
register clock
V
ØH1L, VØH2L –0.05 0.0 0.05 V
HIGH level VØH1H, VØH2H 4.5 5.0 5.5 V
1V5.55.04.5V
ØRSReset gate clock p-p level
Reset gate clock frequency f
ØRS 12.27 MHz
Horizontal shift register clock frequency fØH1, fØH2 12.27 MHz
Vertical shift register clock frequency
f
ØV1, fØV2
fØV3, fØV4
15.73 kHz
p-p level
Page 4
4
LZ23BP2
CHARACTERISTICS (1/30 s progressive scan readout mode)
(T
A = +25 ˚C, Operating conditions : The typical values specified in "
RECOMMENDED OPERATING CONDITIONS
".
Color temperature of light source : 3 200 K, IR cut-off filter (CM-500, 1 mmt) is used.)
PARAMETER SYMBOL MIN. TYP. MAX. UNIT NOTE
Standard output voltage V
O 150 mV 2
Photo response non-uniformity PRNU 10 % 3
Saturation output voltage V
SAT 500 mV 4
Dark output voltage V
DARK 0.5 3.0 mV 1, 5
Dark signal non-uniformity DSNU 0.5 2.0 mV 1, 6
Sensitivity (green channel) R 245 370 mV 7
Smear ratio SMR –86 –76 dB 9
Image lag AI 1.0 % 10
Blooming suppression ratio ABL 500 11
Output transistor drain current I
OD 4.0 8.0 mA
Output impedance R
O 350 $
Dark noise V
NOISE 0.2 0.3 mV 12
OB difference in level 1.0 mV 1, 13
NOTES :
• Within the recommended operating conditions of VOD,
V
OFD of the internal output satisfies with ABL larger than
500 times exposure of the standard exposure conditions,
and V
SAT larger than 500 mV.
1. T
A = +60 ˚C
2. The average output voltage of G signal under uniform
illumination. The standard exposure conditions are
defined as when Vo is 150 mV.
3. The image area is divided into 10 x 10 segments under
the standard exposure conditions. Each segment's
voltage is the average output voltage of all pixels within
the segment. PRNU is defined by (Vmax – Vmin)/Vo,
where Vmax and Vmin are the maximum and minimum
values of each segment's voltage respectively.
4. The image area is divided into 10 x 10 segments. Each
segment's voltage is the average output voltage of all
pixels within the segment. V
SAT is the minimum
segment's voltage under 10 times exposure of the
standard exposure conditions.
5. The average output voltage under non-exposure
conditions.
6. The image area is divided into 10 x 10 segments under
non-exposure conditions. DSNU is defined by (Vdmax –
Vdmin), where Vdmax and Vdmin are the maximum and
minimum values of each segment's voltage respectively.
7. The average output voltage of G signal when a 1 000
lux light source with a 90% reflector is imaged by a lens
of F4, f50 mm.
8. R
R is defined by VR/VG. RB is defined by VB/VG, where
V
R, VG and VB are the average output voltages of red,
green and blue signals respectively, under the standard
exposure conditions.
9. The sensor is exposed only in the central area of V/10
square with a lens at F4, where V is the vertical image
size. SMR is defined by the ratio of the output voltage
detected during the vertical blanking period to the
maximum output voltage in the V/10 square.
10. The sensor is exposed at the exposure level
corresponding to the standard conditions. AI is defined
by the ratio of the output voltage measured at the 1st
field during the non-exposure period to the standard
output voltage.
11. The sensor is exposed only in the central area of V/10
square, where V is the vertical image size. ABL is
defined by the ratio of the exposure at the standard
conditions to the exposure at a point where blooming is
observed.
12. The RMS value of the dark noise (after CDS). (100 kHz
to 5.0 MHz, SC trap on.)
13. The difference between the average output voltage of
the effective area and that of the OB area under nonexposure conditions.
80.80.550.3RR
Sensitivity ratio
80.60.40.2R
B
Page 5

LZ23BP2
5
PIXEL STRUCTURE
,
,
,
,
y
y
y
y
659 (H) x 494 (V)
OPTICAL BLACK
(2 PIXELS)
OPTICAL BLACK
(8 PIXELS)
1 pin
OPTICAL BLACK
(2 PIXELS)
OPTICAL BLACK
(34 PIXELS)
COLOR FILTER ARRAY
GBGBG
RGRGR
GBGBG
RGRGR
GBGBG
RGRGR
GBGBG
RGRGR
GBGBG
RGRGR
GBGBG
RGRGR
GBGBG
RGRGR
GBGBG
RGRGR
GBGBG
RGRGR
GBGBG
RGRGR
GBGBG
RGRGR
GBGBG
RGRGR
(1, 494) (659, 494)
(1, 1) (659, 1)
,,,,,,,
yyyyyyy
,,,,,,,
yyyyyyy
,,,,,,,
yyyyyyy
,,,,,,,
yyyyyyy
Page 6

LZ23BP2
6
TIMING CHART
492
493
494
D1
D2
D3
D4
OB1
OB2
OB3
OB4
OB5
OB6
OB7
OB8
1
2
OB2
OB1
OS
Ø
OFD
ØV4
ØV3
ØV2
ØV1
VD
HD
VERTICAL TRANSFER TIMING
525 1 10 20 30
OS
Ø
RS
ØH2
ØH1
HD
OB (34)
OUTPUT (659) 1
πππππππππππ
ØOFD
ØV4
ØV3
ØV2
ØV1
HORIZONTAL TRANSFER TIMING
780, 1 78
107.538
38
73
59
45780 1
52
94
66
83
87
PRE SCAN (16)
80
OB (2)
πππππ
659
Page 7

LZ23BP2
7
ØV4
ØV3
ØV2
ØV1
HD
READOUT TIMING
22.5 µs (276 bits)
32.5 µs (399 bits)
5.05 µs5.05 µs
(62 bits)(62 bits)
63.5 µs (780 bits)
Page 8

LZ23BP2
8
SYSTEM CONFIGURATION EXAMPLE
OD
GND
Ø
V3
ØV2
ØV4
NC2
OFD
Ø
RS
ØH1
ØH2
OS
GND
GND
NC
1
ØV1
PW
V3B
V3A
V1B
V1A
VMa
VH
V4
V2
VL
VMb
POFD
NC
VH
ØH2
V4X
V3X
VH1AX
V2X
VH3AX
+5 V
V
1X
OFDX
ØH1
ØRS
VL (VPW)
CCD
OUT
VOFDH
VH3BX
OFDX
V
2X
V1X
V3X
VDD
GND
V
4X
VH3AX
VH1BX
VH1AX
+
+
1234567812
242322212019181713
11
14
10
15
9
16
10111213141516
76
9
854321
LR36685
LZ23BP2
(*1)(*1)
VOD
270 pF
100 $
1 M$
1 M$
0. 47 µF
0.01 µF
+
+
(*1) ØRS, OFD :
Use the circuit parameter indicated in
this circuit example, and do not connect
to DC voltage directly.
Page 9

PACKAGES FOR CCD AND CMOS DEVICES
9
0.04
1.46
±0.10
Package (Cerdip)
Glass Lid
CCD
Cross Section A-A'
1.25
±0.20
0.60
±0.05
(◊
2
)
11.43
±0.25
0.25
±0.05
(◊2 : Lid's size)
(◊1 : Reference area)
9.2 2.5
0.85
±0.45
0.5 2.5
2.58.4
0.45
±0.45
¬
CCD
1
8
916
12.20
±0.15
10.50
±0.10
(◊2)
0.50R
5.70
±0.15
4-0.20R
MAX.
6.10
±0.15
10.50
±0.10
(◊
2
)
11.40
±0.15
Center of effective imaging area
and center of package
(◊
1
)
(◊
1
)
(◊
1
)
Rotation error of die : ¬ = 1.5˚
MAX.
3.50
±0.30
1.27
±0.25
1.3
3.37
±0.25
2.75
±0.20
5.29
MAX.
2.23
±0.20
0.46
TYP.
A'
A
0.30
TYP.
P-1.27
TYP.
M0.25
16 WDIP (WDIP016-N-0450)
PACKAGE (Unit : mm)
Page 10

PRECAUTIONS FOR CCD AREA SENSORS
1. Package Breakage
In order to prevent the package from being broken,
observe the following instructions :
1) The CCD is a precise optical component and
the package material is ceramic or plastic.
Therefore,
ø Take care not to drop the device when
mounting, handling, or transporting.
ø Avoid giving a shock to the package.
Especially when leads are fixed to the socket
or the circuit board, small shock could break
the package more easily than when the
package isn’t fixed.
2) When applying force for mounting the device or
any other purposes, fix the leads between a
joint and a stand-off, so that no stress will be
given to the jointed part of the lead. In addition,
when applying force, do it at a point below the
stand-off part.
(In the case of ceramic packages)
– The leads of the package are fixed with low
melting point glass, so stress added to a
lead could cause a crack in the low melting
point glass in the jointed part of the lead.
(In the case of plastic packages)
– The leads of the package are fixed with
package body (plastic), so stress added to a
lead could cause a crack in the package
body (plastic) in the jointed part of the lead.
3) When mounting the package on the housing,
be sure that the package is not bent.
– If a bent package is forced into place
between a hard plate or the like, the package may be broken.
4) If any damage or breakage occurs on the surface of the glass cap, its characteristics could
deteriorate.
Therefore,
ø Do not hit the glass cap.
ø Do not give a shock large enough to cause
distortion.
ø Do not scrub or scratch the glass surface.
– Even a soft cloth or applicator, if dry, could
cause dust to scratch the glass.
2. Electrostatic Damage
As compared with general MOS-LSI, CCD has
lower ESD. Therefore, take the following anti-static
measures when handling the CCD :
1) Always discharge static electricity by grounding
the human body and the instrument to be used.
To ground the human body, provide resistance
of about 1 M$ between the human body and
the ground to be on the safe side.
2) When directly handling the device with the
fingers, hold the part without leads and do not
touch any lead.
Glass cap
Package
Lead
Fixed
Stand-off
Fixed
Lead
Stand-off
Low melting point glass
10
PRECAUTIONS FOR CCD AREA SENSORS
Page 11

3) To avoid generating static electricity,
a. do not scrub the glass surface with cloth or
plastic.
b. do not attach any tape or labels.
c. do not clean the glass surface with dust-
cleaning tape.
4) When storing or transporting the device, put it in
a container of conductive material.
3. Dust and Contamination
Dust or contamination on the glass surface could
deteriorate the output characteristics or cause a
scar. In order to minimize dust or contamination on
the glass surface, take the following precautions :
1) Handle the CCD in a clean environment such
as a cleaned booth. (The cleanliness level
should be, if possible, class 1 000 at least.)
2) Do not touch the glass surface with the fingers.
If dust or contamination gets on the glass
surface, the following cleaning method is
recommended :
ø Dust from static electricity should be blown
off with an ionized air blower. For antielectrostatic measures, however, ground all
the leads on the device before blowing off
the dust.
ø The contamination on the glass surface
should be wiped off with a clean applicator
soaked in Isopropyl alcohol. Wipe slowly and
gently in one direction only.
– Frequently replace the applicator and do not
use the same applicator to clean more than
one device.
◊ Note : In most cases, dust and contamination
are unavoidable, even before the device
is first used. It is, therefore, recommended
that the above procedures should be
taken to wipe out dust and contamination
before using the device.
4. Other
1) Soldering should be manually performed within
5 seconds at 350 °C maximum at soldering iron.
2) Avoid using or storing the CCD at high temperature or high humidity as it is a precise
optical component. Do not give a mechanical
shock to the CCD.
3) Do not expose the device to strong light. For
the color device, long exposure to strong light
will fade the color of the color filters.
11
PRECAUTIONS FOR CCD AREA SENSORS
 Loading...
Loading...