
Installation and Maintenance Manual IM672-4
Vision™Air Handler
Sizes 003–090
Group: Applied Air
Part Number: IM672
Date: Ju
ly 2007
© 2007 McQuay International

Contents
General Information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3
Receiving and Handling. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3
Unit Storage. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3
Installation Guidelines. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4
Service Clearances . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4
Rigging. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4
Unit Leveling . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
Assembling Sections . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
Ceiling Hung . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
Panels, Frame Channels, and Doors. . . . . . . . . . . 8
Field Mounting Junction Boxes and
Other Components. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
Face and Bypass Section Mounting . . . . . . . . . . . 9
Multizone Assembly. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
Duct Connections. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
Mounting Actuators . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
Piping and Coils. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
Drain Pan Traps. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
Internal Isolation Assembly Adjustment. . . . . . . . 16
Electrical Installation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
Operation Guidelines . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
Startup Checks . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
Fan Wheel Alignment. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
Operating Limits. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
Fan Vibration Levels . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
Service and Maintenance . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 24
Periodic Service and Maintenance . . . . . . . . . . . 24
Ball Bearing Lubrication. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 24
Fan Drive Adjustments. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 24
Fan Drive Belt Adjustment . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 28
Front Load Filter Option . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 29
Filter Gauges . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 29
Maintaining the Coil . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 30
Winterizing Water Coils . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 30
Removing and Replacing Components . . . . . . . . 30
Warranty . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 33
Warranty Return Material Procedure . . . . . . . . . . 33
Replacement Parts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 33
General Information
General Information
Vis ionTM air handlers are not designed to be weather resistant.
Do not install them outdoors.
The system design and installation must follow accepted industry
practice as described in the ASHRAE Handbook, the National
Electric Code, and other applicable standards. Install this
equipment in accordance with regulations of authorities having
jurisdiction and all applicable codes.
Installation and maintenance must be performed by qualified
personnel familiar with applicable codes and regulations and
experienced with this type of equipment. Sheet metal parts,
self-tapping screws, fins, clips, and such items inherently have
sharp edges; the installer should exercise caution.
CAUTION
Sharp edges and coil surfaces are a potential injury hazard.
Avoid contact with them.
ATTENTION
Les bords tranchants et les surfaces des bobines sont un
risque de blessure. Ne les touchez pas.
Receiving and Handling
1 Carefully check items against the bills of lading to verify
all crates and cartons have been received. Carefully inspect
all units for shipping damage. Report damage immediately
to the carrier and file a claim.
2 Vision air handler units are constructed of galvanized or
painted steel and are inspected thoroughly before leaving
the factory. Take care during installation to prevent damage
to units.
3 Take special care when handling the blower section. All
fans are dynamically balanced before leaving the factory.
Rough handling can cause misalignment or a damaged
bearings or shaft. Carefully inspect fans and shaft before
unit installation to verify this has not happened.
4 Handle the zone damper of the multi-zone units with
special care. Zone dampers are set and inspected before
leaving the factory, but should be checked on arrival to the
job to verify the bell arm and connecting rod set screws did
not become loose in shipment.
Screws, bolts, etc., for assembling sections are supplied in a
bag attached to each section. All necessary gasketing is
applied in the factory for section-to-section mounting.
Unit Storage
Store unit on a level surface. If air handling units are stored for
any period of time, periodically rotate the fan wheel to prevent
permanent distortion of drive components. In addition, grease
may settle in the lower part of the bearing, which can lead to
oxidation on the upper portion of the bearing surface. Keep the
fan bearings lubricated.
Store units indoors in a clean, dry environment on a level
surface. Moisture, debris, and minerals can cause permanent
damage to the cabinet and components. Do not allow
coverings to trap moisture on the galvanized surface.
Nomenclature
Model
CAH = Custom modular air handler
CAC = Custom modular component
Nominal unit size
(cataloged size—nominal square foot of coil)
003, 004, 006, 008, 010, 012, 014, 017,
021, 025, 030, 035, 040, 050, 065, 080, 085, 090
Vintage of McQuay air handling unit
CAH 003 G D A C
Unit cross section
C = Standard unit cross section
M = Custom size cross section
Motor location
A = Motor along side of fan housing
D = Motor down stream of belt drive
plenum fan
F = Motor on inline fan
G = Motor downstream of direct drive
plenum fan
T = Motor behind twin fan housing
Unit type/coil position
B = Blow-through cooling coil location
D = Draw-through cooling coil location
H = Heating only
V = Vent only
M = Multizone
McQuay IM 672-4 3
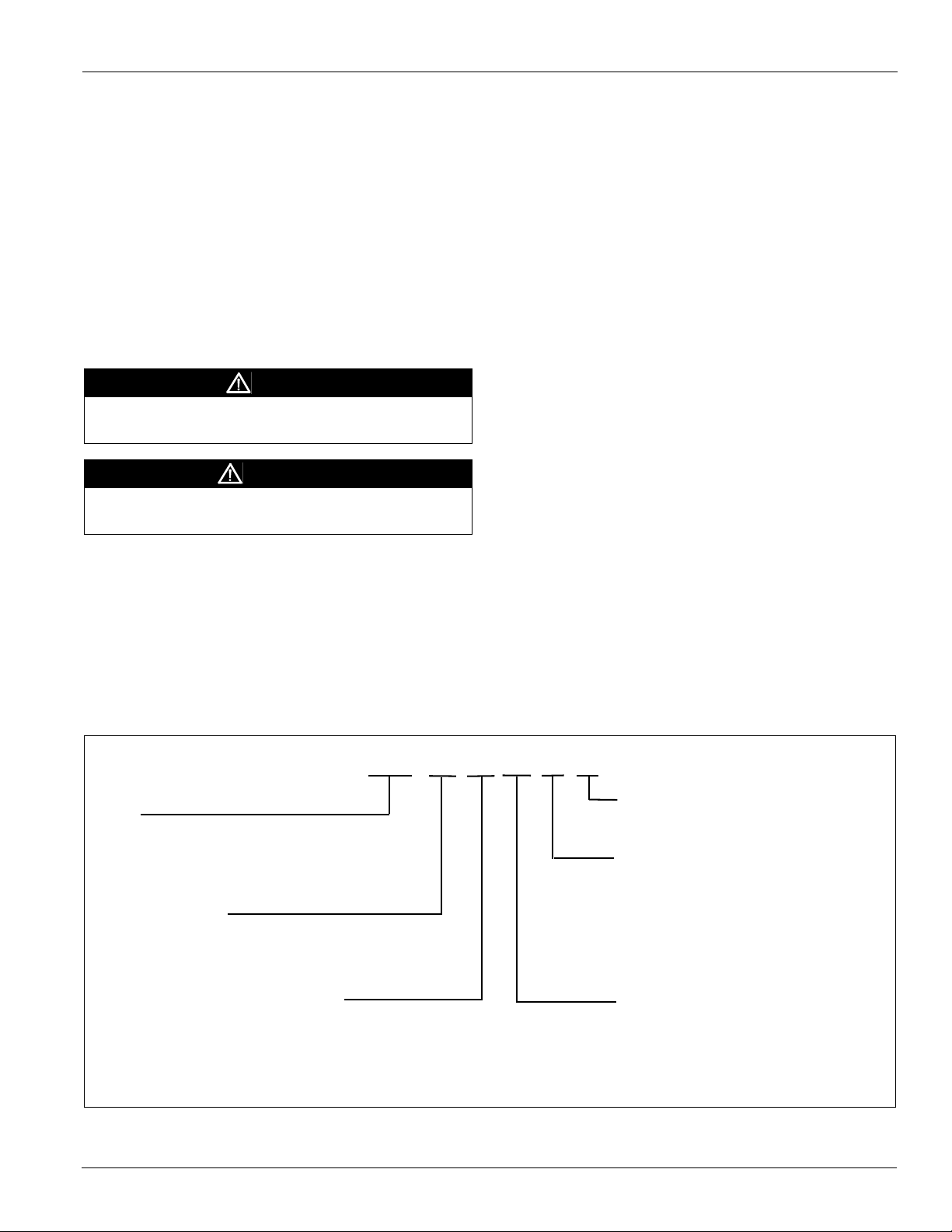
Installation Guidelines
Installation Guidelines
Service Clearances
In addition to providing adequate space around the unit for
piping coils and drains, access to at least one side of the unit is
always required to allow for regular service and routine
maintenance, which includes filter replacement, drain pan
inspection and cleaning, fan bearing lubrication, and belt
adjustment. Provide sufficient space—at least equal to the
length of the coil—on the side of the unit for shaft removal and
coil removal. Space, at least equal to the length of the side coil,
is required for coil removal. Space, at least equal to the fin
height, is required for top coil. See Figure 1 for servicing space
requirements.
For routine maintenance purposes, access normally is obtained
through the access doors or by removing panels. Fan and filter
sections are always provided with a service door on one side of
the unit. If requested, doors can be provided on both sides of
the unit. Optional service doors are available for most section
types and are provided based on customer request.
If component replacement is required, the top panel also can
be removed. If necessary, the unit can be disassembled.
Maintain at least 54" of clearance in front of electrical power
devices (starters, VFDs, disconnect switches and
combination). Electrical power devices that are mounted on
the side of the unit typically are up to 12" deep. See Figure 2.
Figure 1: Servicing Space Requirements
4 . 0 0 " b a s e r a i l e x t e n s i o n
Figure 2: Service Clearance for Electrical Power Devices
1 2 "
5 4 "
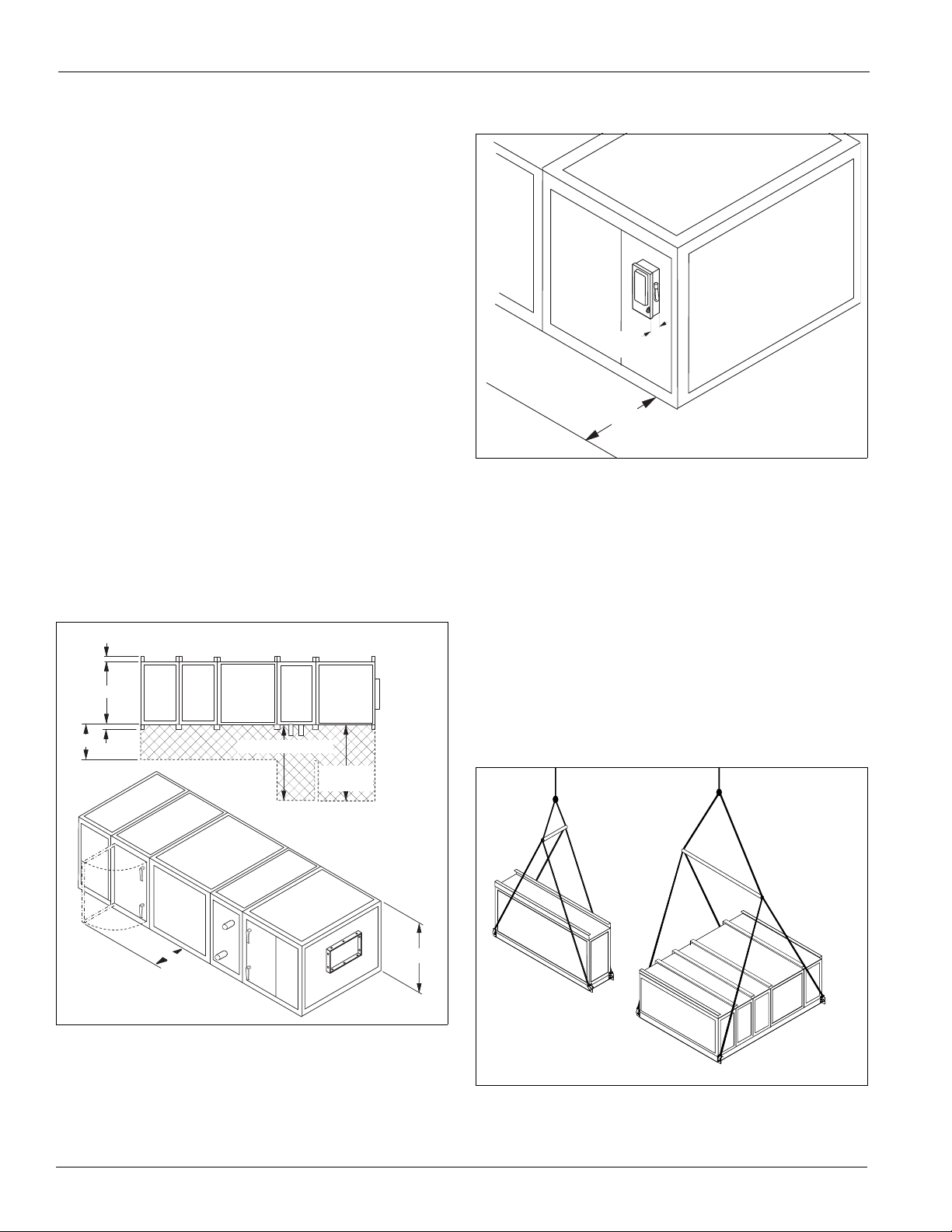
Rigging
Vision handlers ship as separate sections, completely
assembled, or in modules of assembled sections.
be rigged as it ships from the factory. Do not rig units after
assembly.
rail
When a unit is
, it
can be lifted using the 2" diameter lifting holes located in
provided with a factory-installed base
the corners of each shipping section. If a unit does not have a
base rail, rig it using straps or a sling. Fasten the strapping under
the skid that ships with the section.
The unit must
3 0 . 0 0 "
W i d t h
4 . 0 0 "
3 0 . 0 0 "
W i d t h o f c o i l s e c t i o n
W i d t h o f
f a n s e c t i o n
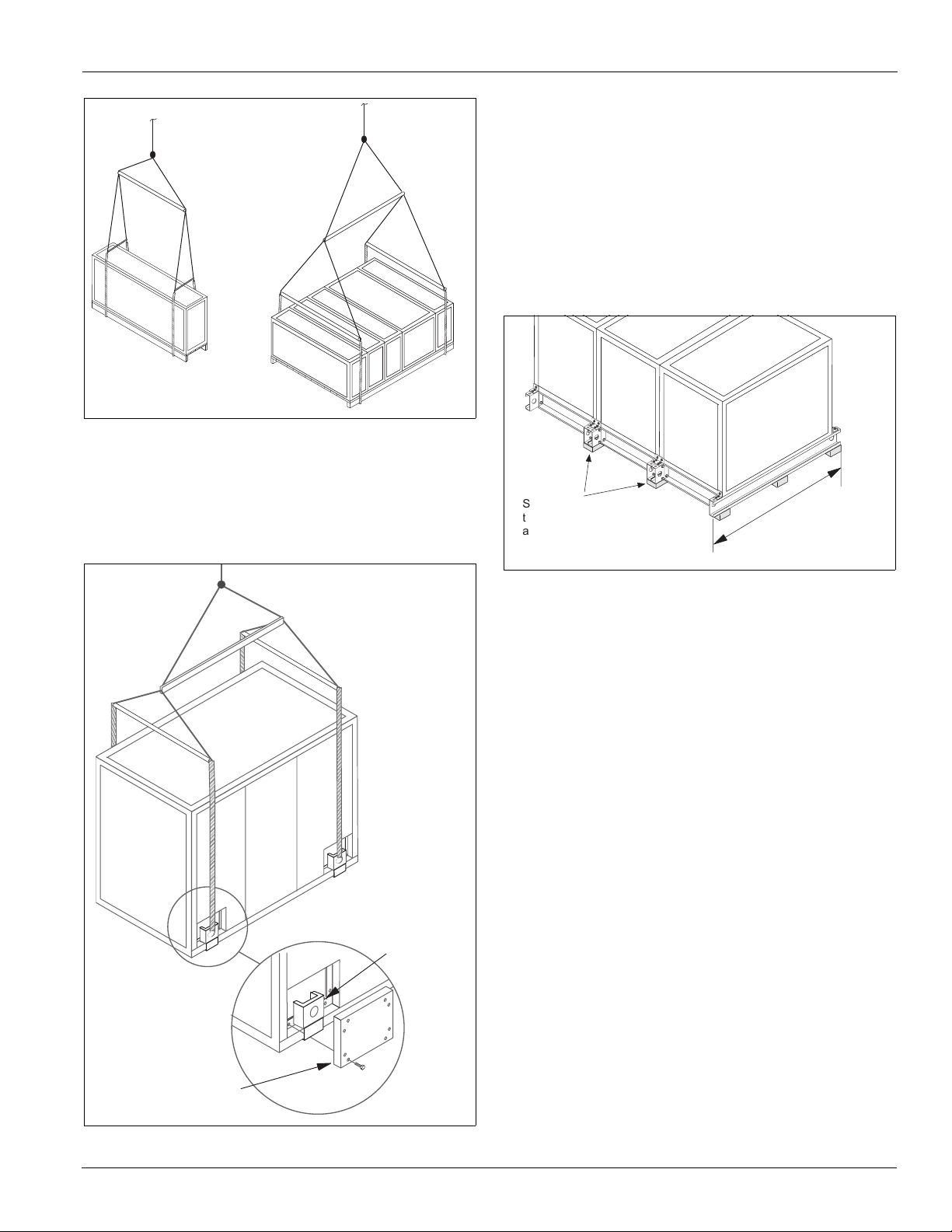
To prevent damage to the unit cabinetry, use spreader bars.
Position spreader bars to prevent cables from rubbing the
frame or panels. Before hoisting into position, test lift for
stability and balance. Avoid twisting or uneven lifting of unit.
Figure 3: Units on Base Rails
H e i g h t
4 McQuay IM 672-4
Installation Guidelines
)
S
t
a
Figure 4: Units on Skids
Fan sections greater than 108" wide that are stacked on another
section are constructed with internal fan support frames that
have integral lifting brackets. After the fan section is placed in
position, remove and discard the lifting brackets. Install the
small panels provided to complete the unit cabinet areas where
the lifting brackets were located.
Figure 5: Fan Sections Stacked on Top of a Lower Section
Unit Leveling
Place the equipment on a flat and level surface. Where the
surface irregularities allow the equipment to distort, shim the
base of the unit a straight line. Uneven or distorted sections
cause misfit or binding of the doors and panels and improper
draining of drain pans.
Units that are over 108" wide must rest on a flat surface
for the entire width of the base rails or must be shimmed at
one or more points along the length of the rails to prevent
distortion or sagging of the support rails. See Figure 6.
Figure 6: Leveling the Unit
h i m s e c t i o n s u n t i l
h e y a r e s t r a i g h t
n d l e v e l
S h i m t o p r e v e n t
d i s t o r t i o n i f w i d t h
i s o v e r 1 0 8 "
I n s t a l l p a n e l s ( 4 )
R e m o v e
l i f t i n g
b r a c k e t s ( 4
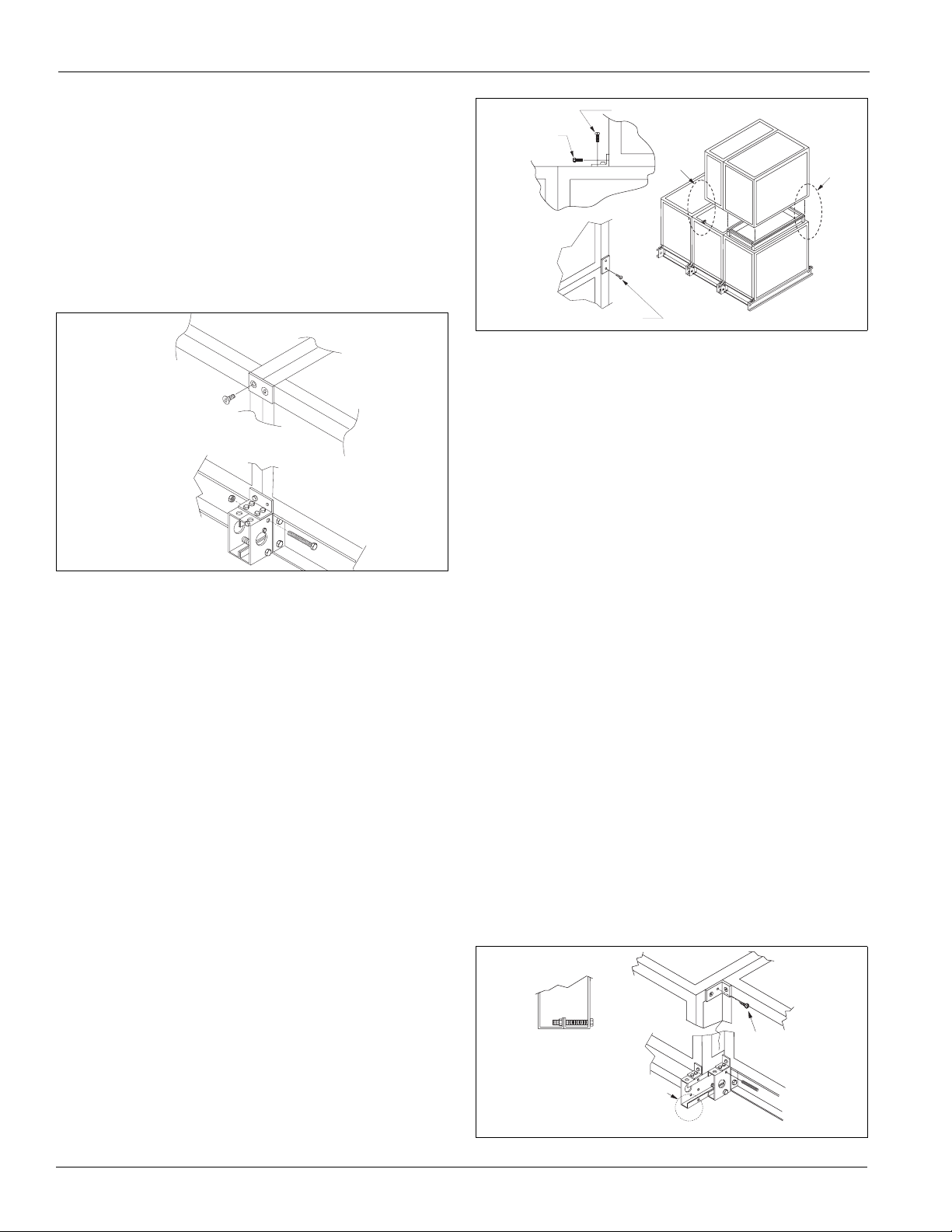
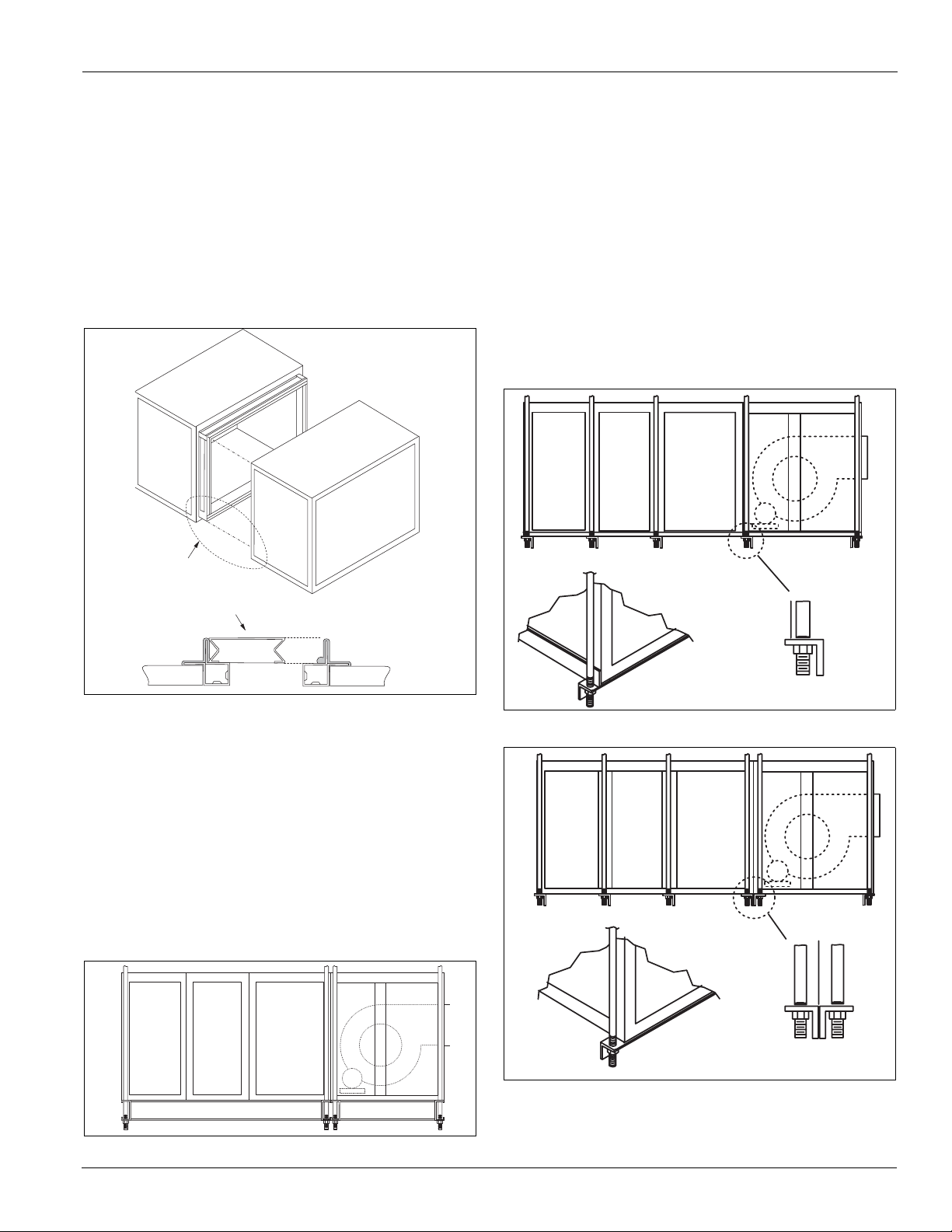
Assembling Sections
External Section-to-Section Mounting
Vision air handling units can ship fully assembled or as
separate shipping sections. Rig units that require field assembly
of shipping sections into position first.
provided with a connection splice joint attached on the leaving
air side of the shipping section. The splice joint is insulated
and provides an air-tight seal between two sections once they
are assembled together. If the splice joint was bent during
shipping or rigging, restore it to its original position. See
Figure 10.
Horizontal Airflow Section Mounting
1 Rig the unit into position and line shipping sections up in
direction of air flow.
2 Pull sections together to fasten. Use a furniture clamp or
straps and a ratchet to help pull the sections together
securely. See Figure 7.
3 If the unit has a factory-installed base rail, first fasten base
rails together using the 3/8"-16 × 5" bolts located in the
splice kit provided with the unit.
a To fasten two shipping sections together, four bolts are
needed (two on each side of the unit). The bolts are run
from one base rail into the other and fastened with a nut.
Complete each section bottom and top before attaching
additional sections.
Shipping sections are
McQuay IM 672-4 5
Installation Guidelines
A
4 If no base rail is provided, fasten the unit in the same
manner on the bottom and top frame channels.
5 Once the sections are positioned together, remove the
fastener in each of the channel corners (on the mating edges
in the channel piece).
6 Place a flat section joining plate (found in the splice kit)
over the two coned holes in the channels, so that the plate
spans the two sections.
7 Replace the fasteners in their original position, through the
joining plate.
Figure 7: Horizontal Joining Sections
T o p
B o t t o m w i t h b a s e r a i l
Vertical Inverted Airflow Section Mounting
For vertical or inverted arrangements, before lifting any top
mounting sections into place, rig into place and fasten together
the bottom tier of sections. Once bottom level sections are in
place and secured, lift stacked components and fasten using
the following procedure:
Note – See “Face and Bypass Section Mounting” on page 9 for
the exception to this procedure.
1 The vertical/inverted section has a splice joint extending
out the top of the bottom joining section. Lower the section
that is to be positioned over the opening over the splice
joint to seal the connection between the two sections.
2 The two sections are fastened together at the four bottom
corners of the mating edge. To fasten the corners located on
the end of the unit (where bottom section and top section
walls are flush with each other), remove the flat head
fasteners in the corners of both sections.
3 Cover the coned holes with a flat joining plate and replace
the flat head fasteners in the holes to secure the joining
plate to both sections. See Figure 8.
4 When one section is deeper than the other, secure the two
sections using an L-shaped joining plate. To secure the
L-shaped bracket, remove the flat head fastener from the
corner, position the bracket over the hole, and replace the
flathead fastener with a 5/16"-18 × 1" bolt. Once the bolt is
in place, secure the bracket to the adjoining section with a
1/4 × 1" drill screw. Repeat the same procedure on both
corners of the unit. See Figure 8.
Figure 8: Vertical Inverted Joining Sections
. 3 1 2 - 1 8
x 1 0 0 b o l t
B
. 2 5 x 1 0 0 d r i l l s c r e w
B
A
R e p l a c e m e n t s c r e w
Extended Coil Section Mounting
The extended coil section is 6" wider than all other sections of
the same unit size. The extension is always located on the coil
connection side of the unit. Because the extended coil section
is wider than other sections, it always ships as a separate
shipping section, and must be joined to other sections in the
field. To join an extended coil section to other components,
first follow the horizontal airflow fastening steps on page 5 to
secure the opposite connection side. To fasten the connection
side, use the following procedure:
1 If the unit has a factory-installed base rail, the extended coil
section base rail is also 6" wider than the adjoining base
rail. Extended coil section base rails on the connection side
are fastened together using the 3/8"-16 by 3" bolts located
in splice kit provided with the unit. See Figure 9.
2 If no base rail is provided, the section is fastened in the
same manner on the bottom and top. Once the sections are
positioned together, remove the fastener in the corner of the
channel piece of the section mating to the extended coil
section. See Figure 9.
3 Place an L-shaped section joining plate (located in the
splice kit) over the coned hole in the channel.
4 Replace the flat head fastener originally used in the corner
with a 5/16"-18 1" bolt and fasten it through the L-shaped
joining plate.
5 Position the L-shaped joining plate so it butts up against the
extended coil section frame channel. To secure the plate to
the extended coil section, run two 1/4" × 1" drill screws
through the joining plate and into the frame channel.
Figure 9: Extended Coil Section Joining
T o p
V i e w A
B o t t o m
w i t h b a s e r a i l
A
( 2 ) 1 / 4 x 1
D r i l l S c r e w s
6 McQuay IM 672-4
Installation Guidelines
Internal Section-to-Section Mounting
If desired, shipping sections can be fastened together internally.
To fasten internally, run field-provided #10 sheet metal screws or
drill screws (4" long maximum) through the interior frame
channel of one unit into the splice joint of the neighboring section.
The section-to-section splice joint is always provided on the
leaving air side of a shipping section and seals against the
frame channel on the entering-air side of the adjoining section.
Align the splice joint to seat into the mating gasket to provide
an air seal. If the splice joint was bent during shipping or
rigging, restore it to its original position. See Figure 10.
Figure 10: Internal Fastening
Ceiling Hung Using Angle Iron Channel
Install field-provided angle iron or channels per SMACNA
guidelines. When a unit is unitized (ships in one piece), channel
support each component under the unit width.
See Figure 12.
When a unit is sectionalized (ships in multiple sections), channel
support each component under the unit width and provide support
under the full length of the unit base.
See Figure 13. Locate
hanger rods so they do not interfere with access into the unit.
Ceiling suspension using the unit base rails is limited to
unit cabinet widths less than 108". Support units with
cabinets 108" wide and greater with structural members
designed to support the unit at the ends and at intermediate
points along the base rails.
Figure 12: Ceiling Suspended w/o Base Rail (Unitized)
Construction
A
S p l i c e C o l l a r
m u s t b e a l i g n e d
t o s e a l t o g a s k e t .
Ceiling Hung
When a unit is ceiling hung, support it with a base rail, angle iron,
or channel. The Vision air handler is not designed to be suspended
from the top of the unit. Before hanging, rig and completely
assemble the unit. See “Assembling Sections” on page 5.
Ceiling Hung Using Base Rail
The optional base rail provided by the factory has 5/8" diameter
holes in each corner to run hanger rods through. To properly
support the unit and maintain unit integrity, support each
shipping section with hanger rods in each corner. See Figure 11.
Figure 11: Ceiling Suspended with Base Rail
Figure 13: Ceiling Suspended w/o Base Rail—Modular
Construction
McQuay IM 672-4 7
Installation Guidelines
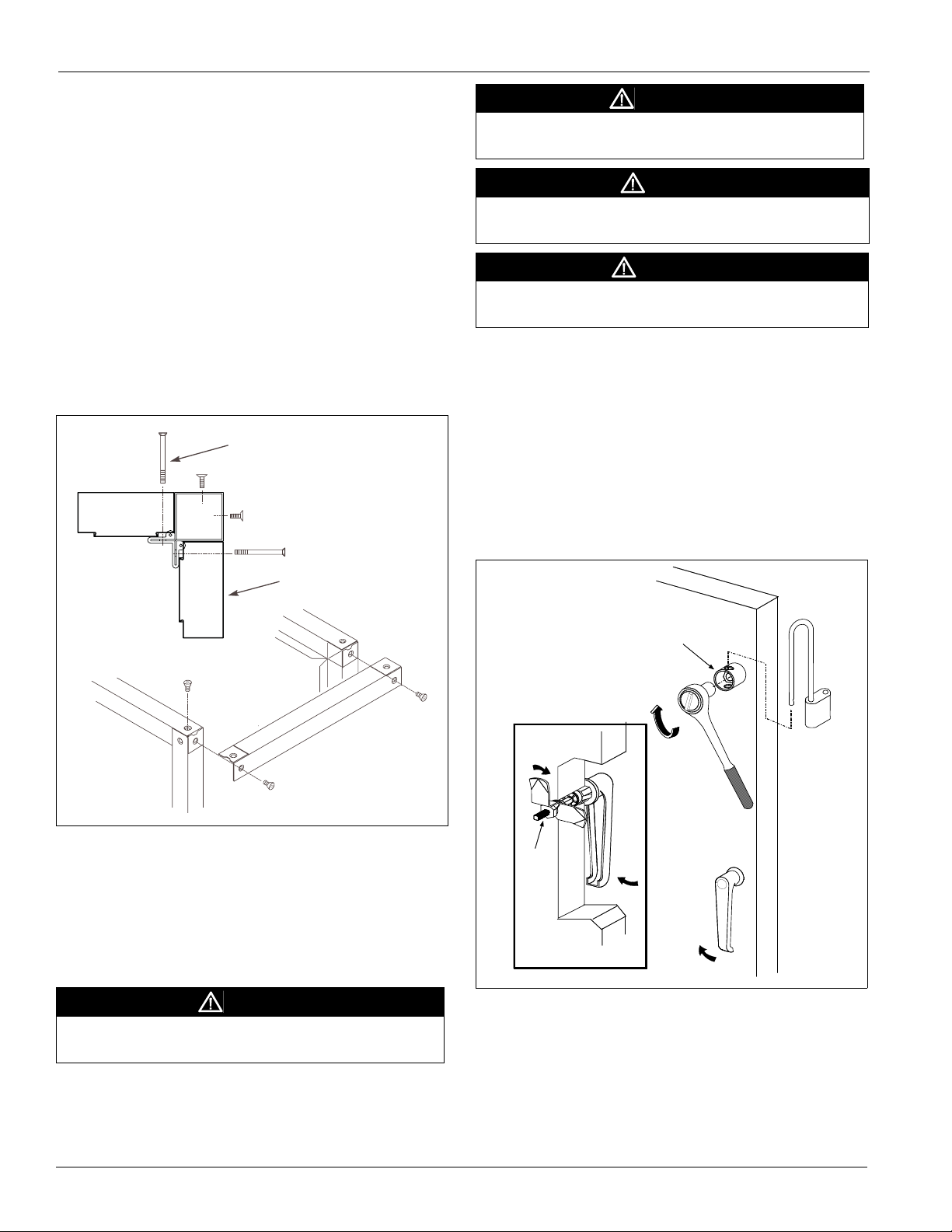
Panels, Frame Channels, and Doors
Panel Removal
To remove a side or top panel, remove the flat head Torx 30
fasteners along the sides of the panel. Lift off the panel after
removing all fasteners.
Frame Channel Removal
Frame channels that run the length of the unit along the top can
be removed to allow access to both the side and top of the unit.
To remove the frame channel, first remove the side panel(s).
Once the side panel is off, remove the flat head Torx 30
fasteners in the corner of the frame channels. Then pull the
frame channel out the side. Remove any panel screws that are
within one inch of the of the frame since they are engaged into
the gasketed flange of the frame. See Figure 14.
Figure 14: Removing Panel Screws
Remove any
panel screws that
engage frame
ATTE NTION
Les bords tranchants et les surfaces des bobines sont un
risque de blessure. Ne les touchez pas.
CAUTION
DO NOT attempt to rotate the cup. Damage to the unit will
occur.
ATTE NTION
NE PAS tenter de faire tourner la cuvette (cup). Ceci va
dendomagger l’unité.
2 Insert 1/2" socket into cup and rotate 1/4 turn clockwise as
shown in Figure 15. If the cup and handle are on the left
side of the door, rotate 1/4 turn counterclockwise.
3 Rotate the door handle 1/4 turn clockwise and then 1/4 turn
counterclockwise to release any internal pressure or
vacuum and open the door. If the cup and handle are on the
left side of the door, rotate the door handle 1/4 turn
counterclockwise and then 1/4 turn clockwise.
4 To prevent air leakage, tighten the door panels by adjusting
the jam nuts.
Remove panel
to remove frame
Fan Section Doors
Note – Opening fan section doors requires using a 1/2" socket
wrench, which satisfies ANSI standards and other codes
that require the “use of tools” to access compartments
containing moving parts or electrical wiring. See
Figure 15.
1 Remove padlock if one is present.
Figure 15: Opening Fan Section Door
Do Not Rotate Cup
Jam
Nuts
View from inside door
OPEN
CAUTION
Sharp edges and coil surfaces are a potential injury hazard.
Avoid contact with them.
8 McQuay IM 672-4
Installation Guidelines
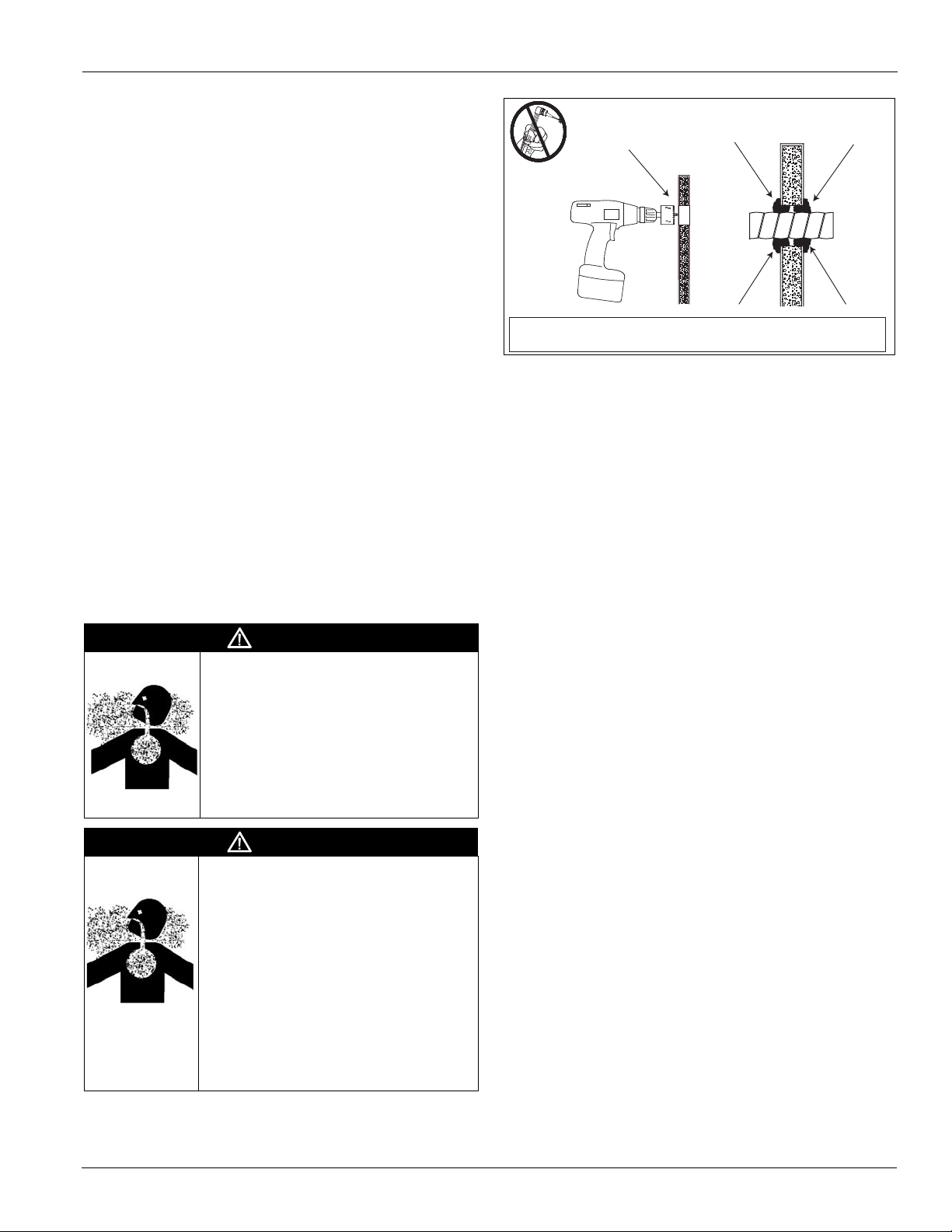
Injected-Foam Insulated Panels
Vision air handlers now are furnished with double-wall,
injected-foam insulated panels. Foam panels are stronger,
more rigid, and lighter than panels with fiberglass insulation.
The insulation R-value is improved to 13. However, foam
insulation can burn when exposed to flame or other ignition
sources and release toxic fumes. Take care in cutting and
sealing all field-cut openings in these panels.
Panel Cutting Procedure
1 Determine the number and location of holes required for
electrical conduit, piping, and control wiring as follows:
• Check that adequate space is available inside the unit for
conduit or pipe routing.
• Do not locate holes in a panel that provides access to key
maintenance components such as filters and fan
assemblies.
• Do not locate where the conduit or piping blocks airflow
or obstructs hinged access doors.
2 Once a proper location is determined, drill a small pilot
hole completely through the panel. Then use a sharp hole
saw or a saber saw and cut from each side of the panel.
3 Seal the double-wall panel on each side with an industrial/
commercial grade silicone sealant or duct seal compound.
It is extremely important to seal each panel hole or
penetration securely so it is airtight, watertight, and so that
there is no exposed insulation.
WARNING
Flame and smoke can cause equipment
damage, severe personal injury, or
death.
Before operating unit, seal all piping and
wiring holes on both inner and outer panels
with an industrial grade silicone sealant or
duct seal compound. Do not use a cutting
torch or expose panel to fire. Panel
damage can occur.
WARNING
Figure 16: Cutting/Sealing Injected-Foam Insulated Panels
Seal completely with silicone
Cut hole from both sides of panel
Prop 65—Substances in fuel or from fuel combustion can cause personal injury or death,
and are known to the State of California to cause cancer, birth defects or other reproductive harm.
sealant or duct seal compound
Field Mounting Junction Boxes and Other Components
For field mounting 4" × 4" or smaller junction boxes to the
standard panel exterior, use a minimum quantity of 4, 3/16"
diameter pop rivets. Do not use self-tapping drill screws.
They will not tighten nor secure properly and panel
damage can occur.
If larger, heavier components require mounting on unit panels,
use through-bolts with flat washers through both outer and
inner panels. To maintain panel integrity, seal both ends with
an industrial/commercial grade silicone sealant or duct seal
compound.
The unit frame channel is another excellent location for
securing heavier components; self-tapping screws are not
acceptable. Ensure that the location permits the full operation
of all access doors and panels and does not interfere with other
vital components.
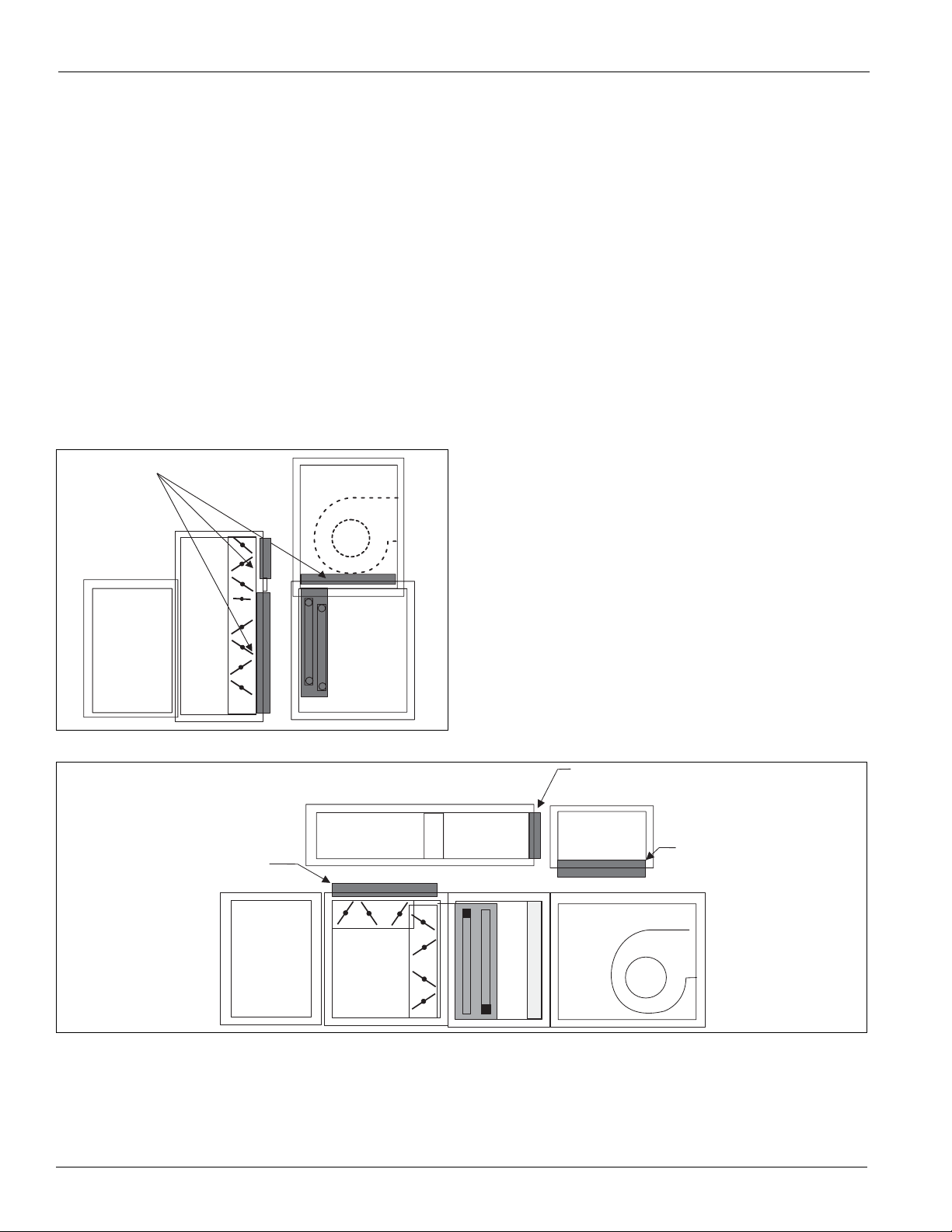
Face and Bypass Section Mounting
Internal face and bypass, and external face and bypass for
sizes 003 to 035 are mounted together using the instructions
for horizontal components and do not require additional
instruction.
La fumée et les flammes peuvent
endommager le matériel et causesr des
blessures graves ou la mort.
Avant d’utiliser le dispositif, obturer tous les
trous de passage de tubulures et de fils
ménagés dans les panneaux intérieurs et
extérieurs au moyen d’une pâte à base de
silicone ou d’un mastic d’étanchéite â
conduits de qualité industrielle.
Ne pas se servir d’un chalumeau
coupeur ni exposer les pannequx à une
flamme nue pour ne pas risquer de les
endommager.
For all size units that bypass directly into a vertical fan section
and for sizes 040 to 090 with external face and bypass, use the
following instructions.
Bypass Into a Vertical Fan Section
Vertical coil sections and the top mounted fan section always
ship separately and must be mounted together at the job site.
The vertical coil section and the bypass duct each has a joining
collar mounted on the leaving air side of the section and duct,
respectively. The mounting collar fits into the side (bypass)
and bottom (vertical coil section) openings in the fan section.
To correctly position the collars in the fan openings, assemble
the fan and coil section first. Use the steps below for assembly.
See Figure 17.
McQuay IM 672-4 9
Installation Guidelines
r
1 Place the vertical coil section in position. If an access
section is positioned downstream from the coil section and
not already assembled to the coil section, secure the two
sections together.
2 Lift the fan section on top of the vertical coil section, taking
care to line up the joining collar in the bottom of the fan
section.
3 For sizes 003 to 035, the bypass duct is integral to the unit
construction and does not require attachment to the bypass
section. For sizes 040 to 090, position and assemble the
bypass duct to the bypass section before joining to the fan.
4 Once the fan is positioned on top of the vertical coil section
and the bypass duct and bypass section are assembled,
position the two assemblies and line up the joining collars
with the openings in the fan and vertical coil section.
5 Once the sections are lined up and in position, secure the
unit together by fastening joining plates to the unit.
Figure 17: Assembly of Fan Coil Sections
Joining
collar
Unit Sizes 040 to 090 External Face and Bypass Duct
Assembly
When unit sizes 040 to 090 are ordered with external face and
bypass, the bypass duct ships separately and must be attached
to the unit in the field. The joining of the bypass duct to the unit
must be done after the unit is assembled. Also, if the bypass
duct is over 90" long, the duct does not ship in one piece and
must be field assembled. The field assembly of the bypass duct
to the unit requires the following steps. See Figure 18.
1 Position the unit shipping sections together and assemble in
the equipment room.
2 After the unit is assembled, lift the duct into position over
the unit. Joining collars are shipped factory assembled to
the unit and duct. There is a joining collar located in the top
of the bypass opening and in the leaving air side of the
bypass duct. These joining collars are used to provide air
seals. Line up the duct with the top openings in the unit.
3 If the bypass duct is longer than 90", the duct ships in more
than one piece and must be field assembled. Place the piece
of duct that has the joining collar on the bottom on top of
the unit first. Once it is in place, position the other piece of
duct. Take care to fit the splice collar into the first piece of
duct and then lower the other end into the bypass opening.
4 Once the duct is positioned correctly, fasten the duct pieces
together with the joining plate provided. To do this, remove
the fasteners in the corners of the duct assemblies, place the
plate over the holes in the corners, and then replace the
fasteners. See Figure 7 on page 6.
Figure 18: Assembly of Bypass Duct to Unit
J o i n i n g C o l l a r
10 McQuay IM 672-4
J o i n i n g C o l l a r
J o i n i n g C o l l a
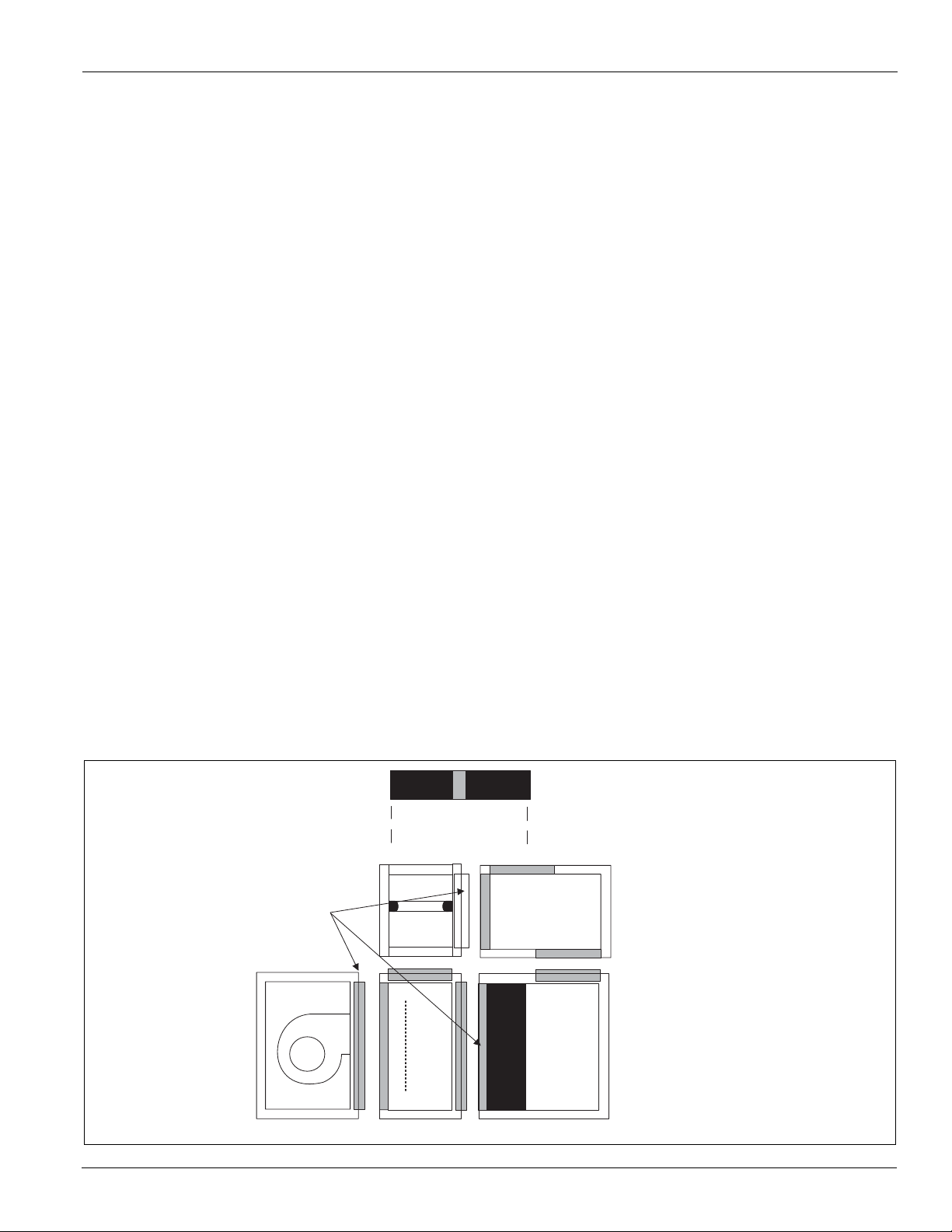
Installation Guidelines
Multizone Assembly
The multizone section may ship completely assembled or it
may ship in numerous pieces. Whether the section ships in a
single piece or multiple pieces depends on customer
requirements and the unit size. When a multizone section is
over 90" high or 90" wide, split it into sections for shipping.
The unit may ship in 1, 2, 3, 4, or 5 separate pieces. Typically,
the multizone damper assembly ships separately (see
“Multizone Damper Assembly” in the next column and
Figure 20 on page 12) and must be attached at the job site.
Attach the damper after the other components are assembled.
Use the instructions below for assembling the multizone
section. See Figure 19.
1 If the diffuser and the cold deck section ship separately,
join them together first. The joining collar mounted in the
diffuser fits into the entering air side of the coil section.
Line up the two sections and fasten together.
2
Once the diffuser and cold deck sections are joined, lift the
hot deck and bypass sections in place on top of the diffuser/
cold deck section. If possible, assemble the hot deck and
bypass section (if there is one) together before lifting on top.
There always is a joining collar in the diffuser. The joining
collar provides the seal between the sections joints. It is
important to line up and fit the collar in the hot deck and
bypass section. For vertical applications, the cold deck also
has a joining collar in the discharge opening. This collar fits
in the bottom of the vertical bypass section.
3 After the components in the multizone are fitted together,
fasten the joining plates to the corners in the unit exterior.
4 If a damper was ordered, assemble it to the section (see
“Multizone Damper Assembly” in the next column and
Figure 20 on page 12).
Note – Verify that the joining collars are aligned to seat into the
gasket. Straighten any collars distorted from shipping or
from rigging.
Multizone Damper Assembly
When a multizone unit is ordered with dampers, depending on
the multizone configuration and size, the damper assembly
may ship separately (all horizontal and units with a total height
over 90").
When the dampers are not factory assembled to the unit, they
ship to the job site on a skid. An assembly kit with screws and
an instruction drawing are included with the damper for field
assembly to the unit.
To assemble:
1 First remove the side plate that encloses insulation from
both sides of the damper assembly.
2 Lift the damper assembly into position. See Figure 20.
3 Fasten the assembly to the frame channels within the
multizone openings.
4 Use caulking to seal up the areas around the unit frame
channel to prevent any air leakage.
5 After caulking, put the side plates back in place and secure.
Damper shaft extensions are provided on both ends of the
damper assembly for actuation. The dampers are linked
together by a linkage bar on both ends of the damper. The
linkage bar is cut at the time of installation to divide the
damper into the required number of zones. See “Multizone
Damper Adjustment” on page 12.
Figure 19: Multizone Sections Assembly
Zone
damper
assembly
Upper unit—heating
Joining
collars
Cooling coilCooling coilDiffuser
McQuay IM 672-4 11
(and optional bypass)

Installation Guidelines
Figure 20: Multizone Damper Assembly
A i r f l o w
R i g h t h a n d c o i l
D a m p e r b l a d e s
b r o k e n o u t t o
s h o w a i r f l o w
b a l a n c e p l a t e s
b e h i n d t h e m .
R e m o v e a s s e m b l y
i n s u l a t i o n p a n e l
c o v e r f r o m d a m p
t o a l l o w c a u l k i n g .
e r
D r i l l s c r e w i n t o
c a b i n e t f r a m e
w i t h # 1 0 A B x . 5 0
d r i l l s c r e w .
S e a l w i t h c a u l k
o n b o t h s i d e s .
Duct Connections
Use flexible connectors on the outlet and inlet duct
connections of all units. Each zone divider has a W-shaped
duct clip. Insert ductwork into this clip. Figure 21.
Figure 21: Duct connectors
D u c t w o r k
Note – Before connecting to ductwork, read “Multizone Damper
Adjustment” below.
Multizone Damper Adjustment
The installer must clear the damper assemblies of construction
dirt and debris. These materials result in higher torque
requirements and may bend or damage damper components.
Before you begin:
1 Verify that dampers are square and operating smoothly
before ducting.
D u c t c l i p
Z o n e d i v i d e r
I f a i r f l o w b a l a n c e p l a t e s
a r e p r e s e n t , t h e n i n s t a l l
d a m p e r s s o t h a t t h e
p l a t e s a r e o n t h e b o t t o m
o f e a c h z o n e .
1 / 4 A B x . 5 0
O p e n d a m p
t o a l l o w f a s t e n i n g .
e r b l a d e s
b a l a n c e
2 Install duct access panels on the downstream damper for
inspection and maintenance.
If multizone dampers do not close properly, adjust the blades
as follows:
1 Loosen set screws in bell arms for all zones.
2 Close all cold deck dampers tightly.
3 Move bell arms so they are at a 45° angle to the vertical
center when viewing the zone dampers from the cold deck
end of the damper section. See Figure 22.
a Two-deck zone dampers—The cold deck closes when
the bell arms are 45° from the vertical center. The hot
deck closes when the bell arms are 45° clockwise from
the vertical center.
b Three-deck zone dampers—The cold deck closes when
the bell arms are 45° clockwise from the vertical center.
The hot deck closes when the bell arms are 45°
counterclockwise from the vertical center.
4 Tighten set screws on bell arms while holding the dampers
closed.
5 All zone damper blades should close properly. If one or a
few zones do not close completely, repeat the procedure for
these zones.
12 McQuay IM 672-4
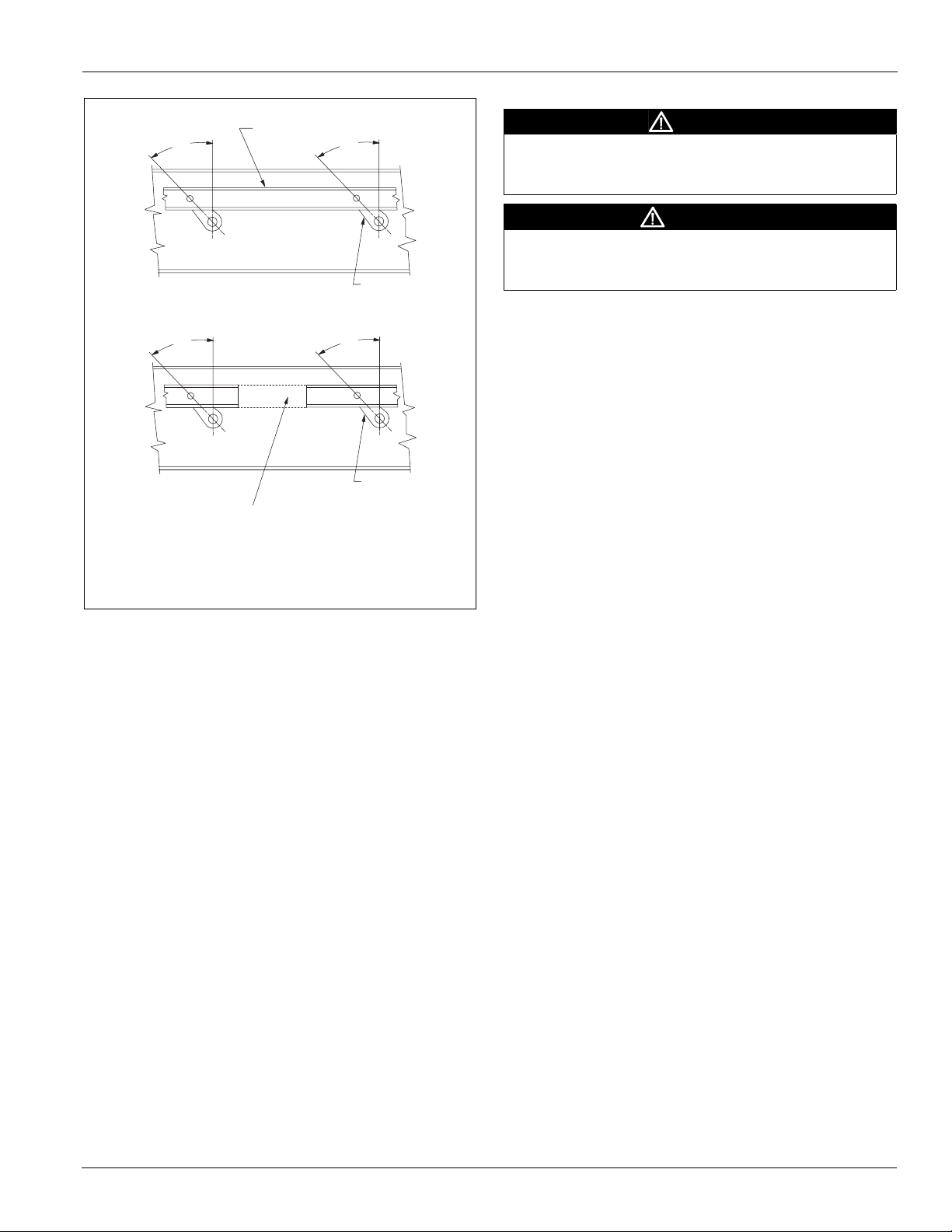
Figure 22: Bell Arms at 45° Angle to Vertical Center
Z o n e d a m p e r l i n k a g e
C o n n . l i n k
4 5 °
4 5 °
B e l l a r m
Installation Guidelines
CAUTION
Maximum damper rotation is 70°. Maximum shaft torque is 205
inches/pound. Greater rotation or torque can cause equipment
damage.
ATTENTION
La rotation maximale des volets est de 70°. Le couple (torque)
maximum de l’arbre est de 205po/lb. Une plus grande rotation
(ou torque) peut endommager l’équipement.
I n s t a l l a t i o n m o d i f i c a t i o n f o r m u l t i p l e z o n e s
4 5 °
To divide the damper section into multiple zones, cut and remove sufficient
connecting link to allow adjacent zones to operate independently.
Note: The damper blades on two-deck dampers seal through several degrees
of shaft rotation.The damper blades can rotate 360° and do not engage a stop.
The hot deck blades are mounted at a 90° to the cold deck blades. Before
installing the zone duct, set up linkages and dampers and adjust. If adjustment
is required and access to the blades is restricted, observe the cold deck blade
position by removing the cabinet panel on the coil section.
4 5 °
B e l l a r m
Multizone, Mixing Box and Economizer Damper
Torque Requirements
On multizone units, the actuator must drive the connection link
for proper damper actuation. Do not activate multiple dampers
must from the shaft extension opposite the connection link.
Mounting Actuators
The installing contractor is responsible for the mounting of all
field-installed actuators. No provisions are made for the
location of these actuators due to the number of options and
arrangements available and the variety of specific applications.
Typically, actuators are mounted inside the cabinet. Provide
proper support for the actuator to avoid excessive stress in the
cabinet, linkage, or damper shafts.
Fresh air and return air dampers can be linked together and
driven from the same actuator if the dampers are the same size.
If the dampers are different sizes, they must be driven by
separate actuators and controlled appropriately. Exhaust
dampers are always driven by a separate actuator.
A typical rotary electric actuator can handle up to 40 sq. ft. of
damper. For pneumatic actuators, allow 5 in-lb per square foot
of damper area.
Face Bypass Damper Torque Requirements
Face and bypass dampers may or may not be linked together.
When dampers are placed before a single bank of coils, they
always are linked together and require a single actuator. When
dampers bypass a stacked or staggered coil, the dampers are
not linked and require multiple actuators.
Unit sizes 040 to 090 provided with external face and bypass,
require three actuators. Other arrangements with stacked or
staggered coils require two actuators. A damper shaft
extension is provided. The shaft extension normally is located
on the drive side of the unit, but can be moved to the other
side.
Face and bypass dampers have a torque requirement of
10 in-lbs per square foot of damper face area.
Piping and Coils
When designing and installing piping:
• Follow applicable piping design, sizing, and installation
information in ASHRAE handbooks.
• Observe all local codes and industry standards.
• Do not apply undue stress at the connection to coil headers;
always use a backup pipe wrench.
• Support pipework independently of the coils.
Water Cooling Coils
• Water supply, water return, drain, and vent connections
extend through the end panel of the coil section. All
connections are labeled on the end panel.
• Water supply and water return connections are typically
male NPT iron pipe.
• When installing couplings, do not apply undue stress to the
connection extending through unit panel. Use a backup
pipe wrench to avoid breaking the weld between coil
connection and header.
• Follow recommendations of the control manufacturer
regarding types, sizing, and installation of controls.
McQuay IM 672-4 13

Installation Guidelines
Direct Expansion Coils
• The coil distributor and suction connection extend through
the end panel of the coil section.
• Check nozzle in distributor for proper tonnage.
• When a (field supplied) thermostatic expansion valve is
located outside the unit and connected directly to the
distributor. Do not apply heat to the body of the expansion
valve.
• The thermostatic expansion valve must be the external
equalizer tube type. Connect the 1/4-inch diameter external
equalizer tube provided on the coil to the connection on the
expansion valve.
•
Use care when piping the system, making sure all joints are
tight and all lines are dry and free of foreign material. For
typical refrigerant piping, see condensing unit product manual.
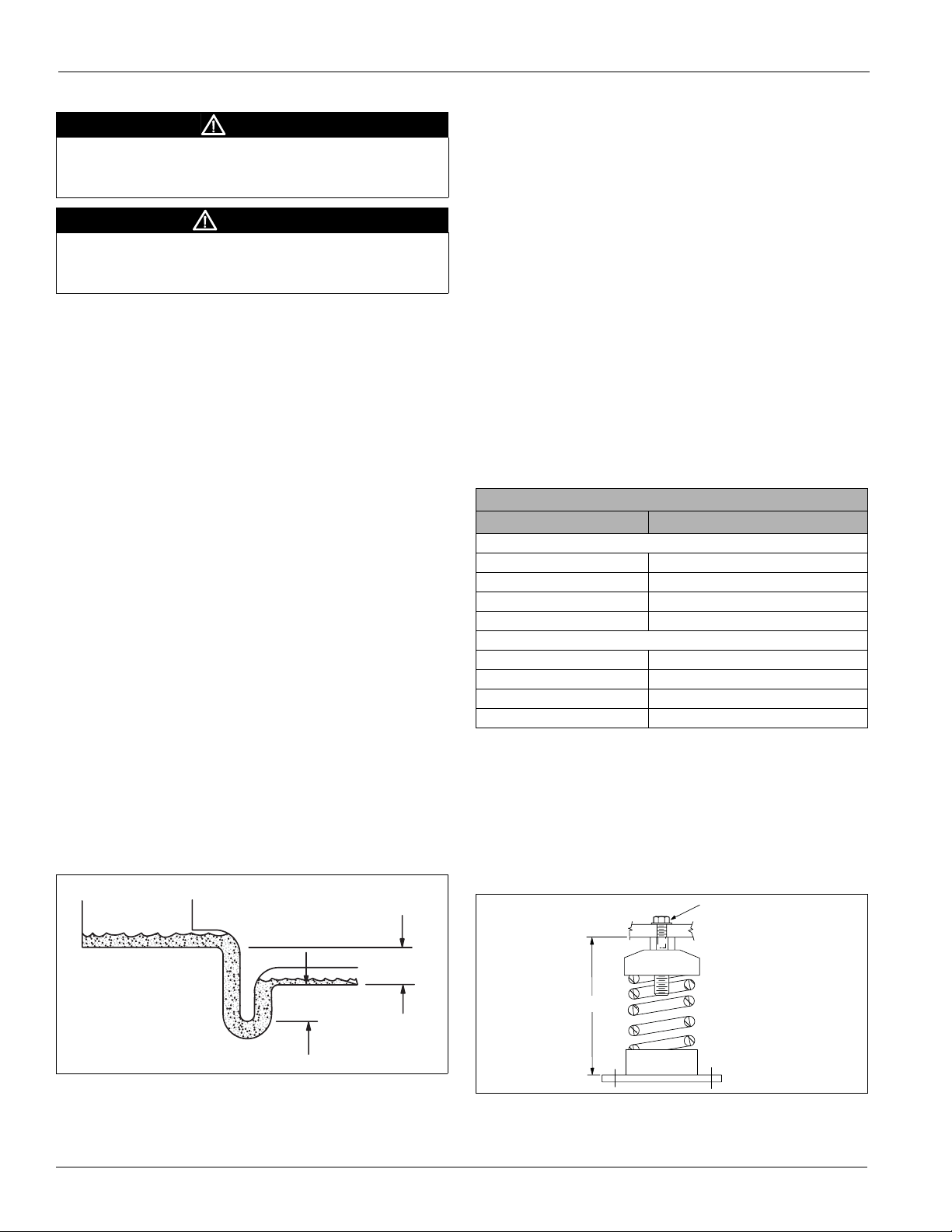
Steam Coils (see Figure 23 on page 15)
Piping
• All steam coils in units are pitched toward return connection.
•
Steam supply and steam return connections typically are male
NPT iron pipe and are labeled on the end panel of coil section.
Connections extend through the coil section end panel.
• When installing couplings, do not apply undue stress to the
connection extending through unit panel. Use a backup
pipe wrench to avoid breaking the weld between coil
connection and header.
• Support piping independently of coils and provide adequate
piping flexibility. Stresses resulting from expansion of
closely coupled piping can cause serious damage.
• Do not reduce pipe size at the coil return connection. Carry
return connection size through the dirt pocket, making the
reduction at the branch leading to the trap.
Coils
• Install vacuum breakers on all applications to prevent
retaining condensate in the coil. Generally, the vacuum
breaker is connected between the coil inlet and the return
main. The vacuum breaker should be open to the
atmosphere, and the trap design should allow venting of
large quantities of air.
• Do not drip supply mains through the coil.
• Do not attempt to lift condensate when using modulating or
on/off control.
Traps
• Size traps in accordance with the manufacturers’
recommendations. Make sure the required pressure
differential is always available. Do not undersize.
• Use float and thermostatic or bucket traps for low pressure
steam. On high pressure steam, use bucket traps. Use
thermostatic traps only for air venting.
• Use bucket traps for on/off control only.
•
Locate traps at least 12 inches below the coil return connection.
• Multiple coil installation.
– Individually trap each coil or group of coils that is
controlled individually trapped.
– Coils in series—use separate traps for each coil, or a bank
of coils.
– Coils in parallel—a single trap can be used, but an
individual trap for each coil is preferred.
– Do not attempt to lift condensate when using modulating
or on/off control.
• With coils arranged for series airflow, use a separate control
on each bank or coil in the direction of airflow.
Valves
• Do not use modulating steam valves on high pressure
systems.
• Properly size modulating valves. Do not undersize.
• Freezing conditions (entering air temperatures below 35°F).
– McQuay strongly recommends 5JA, 8JA, 5RA and 8RA
coils.
– Supply 5 psi steam to coils at all times.
• Do not use modulating valves. Provide control by face and
bypass dampers.
– Consider using two or three coils in series with two
position steam control valves on the coil or coils that
handle 35°F or colder air. Use a modulating valve on the
downstream coil to provide the desired degree of control.
– Thoroughly mix fresh air and return air before it enters the
coil. Also, to obtain true air mixture temperatures,
properly locate temperature control elements.
– As additional protection against freeze-up, install the trap
sufficiently below the coil to provide an adequate
hydrostatic head to remove condensate during an
interruption in the steam pressure. Estimate three feet for
each 1 psi of trap differential required.
– On startup, admit steam to coil ten minutes before
admitting outdoor air.
– Close fresh air dampers if steam supply pressure falls
below the minimum specified.
14 McQuay IM 672-4

Figure 23: Piping Arrangements
Installation Guidelines
Float and
thermostatic trap
Vacuum breaker
1/2" check valve
1/4" petcock
for continuous
air venting
1"
min.
12" min.
5GA or 8GA coils. Note that the
addition of a vacuum breaker to
permit the coil to drain during
shutdown.
Check Valve Strainer Gate Valve
High Pressure (over 25 psi)
Steam main
Return main
1/4" petcock
for continuous
High pressure
float or bucket
trap
Return main
air venting
High pressure
bucket trap
5TA, 8TA, or 5HA coils. Condensate is lifted to overhead return
main
Low Pressure (to 25 psi)
Vacuum breaker
1/2" check valve
1" min.
Control valve
modulating
two position
12" min.
Full size of
return conn.
Steam main
5J, 5G, 8J or 8G coils.
Steam main
Vacuum breaker
1/2" check valve
Return main
Vacuum breaker
1/2" check valve
12" min.
Full size of
return conn.
Steam main
12" min.
5JA or 8JA coil. Installed in series.
Note that each coil must have a
separate control valve and trap.
Return main
Steam main
Vacuum breaker
1/2" check valve
Return main
5RA, 8RA, or 5SA coils. Banked two
high, individual trapping of each coil as
shown is preferred.
5RA, 8RA, or 5SA coils. Installed
McQuay IM 672-4 15
Installation Guidelines
Water Heating Coils
CAUTION
Improper installation, use, or maintenance of water
heating coils can cause equipment damage. Read and
follow instructions carefully.
ATTENTION
Si l’installation, l’utilisation ou l’entretien des serpentins
de chauffage à eau sont inadéquats, ceci endommagera
l’équipement. Lire et suivre attentivement les instructions.
• Water supply and water return connections extend through
the end panel of the coil section. All connections are labeled
on the end panel.
• Water supply and water return connections are male NPT
iron pipe.
• When installing couplings, do not apply undue stress to the
connection extending through unit panel. Use a backup pipe
wrench to avoid breaking the weld between the coil
connection and header.
• Follow recommendations of the control manufacturer
regarding types, sizes, and installation of controls.
• Do not use hot water coils with entering air below 40°F.
• If fresh air and return air are to be heated by a hot water coil,
carefully design the system to provide thorough mixing
before air enters the coil.
• To prepare coils for winter operation, see “Winterizing
Water Coils” on page 30.
Drain Pan Traps
Run drain lines and traps full size from the drain pan
connection. Install drain pan trap to allow condensate to drain
freely. On both blow-through and draw-through units, the trap
depth and the distance between the trap outlet and the drain
pan outlet must be twice the static pressure in the drain pan
section under normal operation so the trap remains sealed. See
Figure 24.
Figure 24: Allow Adequate Distance Between Trap Outlet
and Drain Pan Outlet
Pressure (P)
at the drain pan
Internal Isolation Assembly Adjustment
On units with internally isolated fan and motor assemblies, the
assemblies are secured for shipment..
Before Operating the Unit:
Remove the shipping brackets and tie-down bolts (see
Figure 26) and discard. The shipping brackets located on the
opposite drive side of the unit are difficult to access from the
drive side of the unit. Either remove them before the unit is
assembled, or remove the panel on the opposite drive side to
gain access.
The spring isolators under the four corners of the fan and
motor assembly are factory adjusted while the fan was not
running. See Table 1 below. With the unit operating at normal
cfm and static pressure, all the isolators should be at the same
height opening. If adjustments are required, loosen the 1/2"
cap screw on top of the isolator and turn the adjusting bolt to
lower or raise the fan and motor base. Retighten the cap screw
when adjustments are completed.
Table 1: Spring Mount Adjustments
Spring mount adjustment at rest
Fan discharge position Top or bottom horz. (dim "H")
Unit sizes 003–035
13.75
24.25
34.25
43.75
Unit sizes 040–-090
16.00
26.50
36.50
46.00
For models 040 through 090, the isolators should be at equal
height during fan operation (6"). Center the fan outlet in the
outlet panel opening. If adjustment is required, loosen the cap
screw on top of the isolator assembly. Turn the adjustment nut
below the fan frame to lower or raise the fan motor and frame
assembly. Retighten the cap screw on top of the isolator
assembly. See Figure 25.
Figure 25: Adjusting Large Spring Mount Assembly
Adjusting bolt
2P
2P
16 McQuay IM 672-4
6"
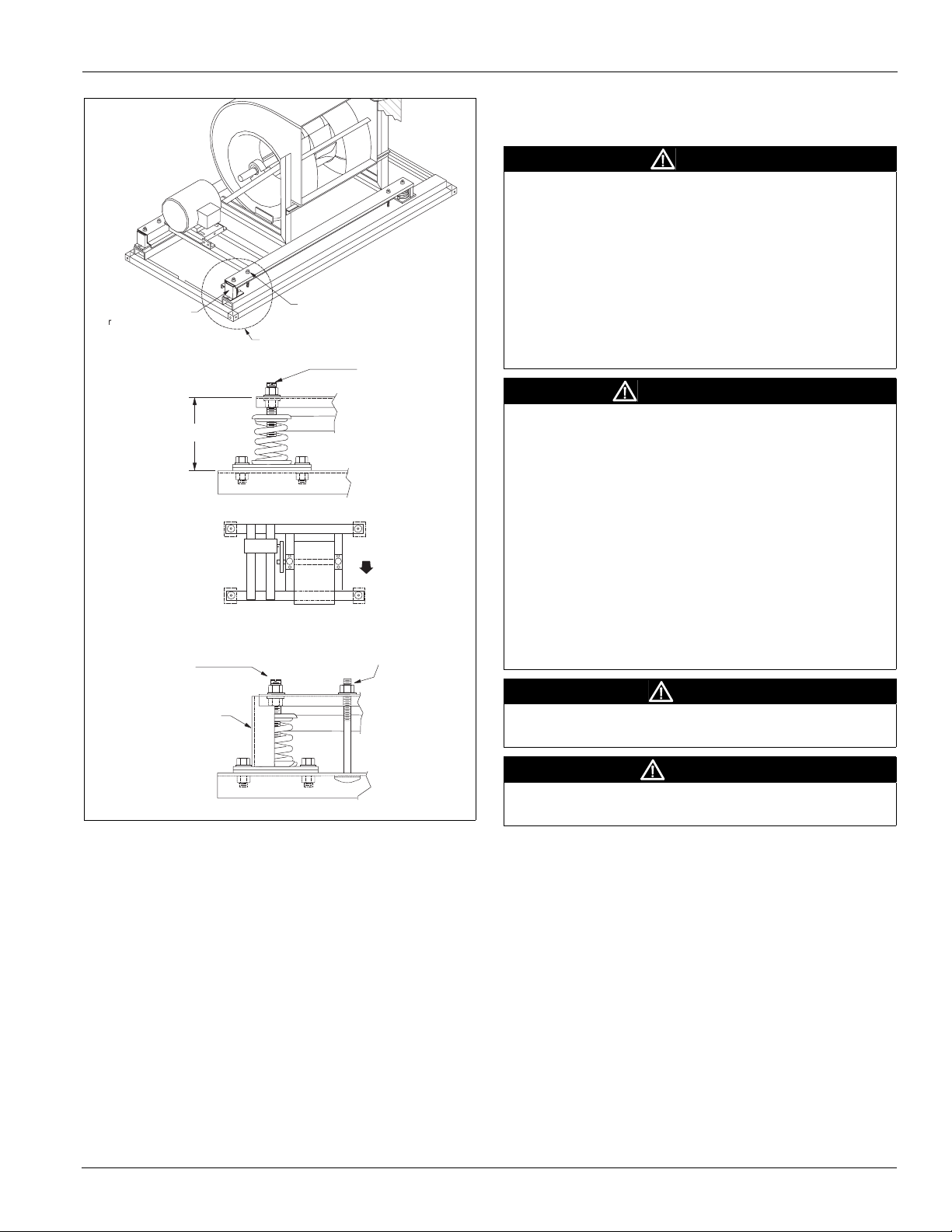
Installation Guidelines
r
Figure 26: Removing Shipping Brackets
Unit sizes 006 - 090
Electrical Installation
Wiring
DANGER
Capacitor hazardous voltage! Failure to disconnect power
and discharge capacitors before servicing will result in serious
injury or death.
Disconnect all electric power (including remote disconnects)
before servicing. Perform lockout/tagout procedures to ensure
that power can not be energized. For variable frequency drives,
S h i p p i n g b r a c k e t
e m o v e a n d d i s c a r d
( T y p i c a l 4 p l a c e s )
D i m " H "
P O S 3
M o t o r
P O S 4
F a n i s o l a t o r p o s i t i o n n u m b e r s
S p r i n g h e i g h t
a d j u s t m e n t s c r e w
S h i p p i n g
b r a c k e t
S h i p p i n g h o l d d o w n
r e m o v e a n d d i s c a r d
( T y p i c a l 4 p l a c e s )
S e e d e t a i l " A "
S p r i n g h e i g h t
a d j u s t m e n t s c r e w
P O S 2
A i r f l o w
F a n
P O S 1
S h i p p i n g h o l d
d o w n s c r e w
or other energy storing components that have been furnished
and mounted by either McQuay, or by others, refer to the
specific manufacturer’s literature for allowable waiting periods
for discharge of capacitors. Verify capacitors have been
discharged using an appropriate voltmeter.
ADVERTISSEMENT
Voltage de condesateur à risquee de danger! À défaut de
débrancher la puissance électrique et de décharger le
condensateur avant de faire le service, il peut en résulter des
blessures sérieuses et même la mort.
Débranchez toute puissance électrique (incluant les
sectionneurs à distance) avant de faire du service. Assurezvous de procéder au cadenassage et à la pose d’avis assurant
que la puissance ne peut être rétablie .
Pour le variateur de fréquence variable ou tout autre
composante pouvant accumuler de l’énergie qui auraient été
fournis et installés par McQuay ou autres, se référer à la
littérature spécifique du manufacturier donnant les périodes
spécifiques d’attente nécessaires pour la décharge du
condensateur. Vérifier que le condensateur est totalement
déchargé avec les voltmètres appropriés.
CAUTION
Use copper conductors only. Failure to use copper
conductors can result in equipment damage.
ATTENTION
D e t a i l A
Utiliser du fil de cuivre seulement. La non utilisation de fil de
cuivre peut causer des dommages à l’équipement.
• Electrical service to the fan must correspond to the rated
voltage on the motor or electrical panel nameplate and
conform to the National Electric Code and local restrictions.
• A door electrical interlock is not provided as standard.
• Thermal motor protection is external to the unit. Unless the
unit is provided with a variable frequency drive (VFD) or a
unit mounted starter, thermal protection and a disconnect
switch provision per electric codes are provided by others.
• When the unit is factory provided with a junction box,
disconnect switch, starter, or a variable frequency drive
(VFD), the components are mounted on the outside of the
unit cabinet. Factory wiring is provided from the device to
the unit internal motor.
• When the unit is provided with a VFD only, refer to the VFD
manual for wire size and torque requirements.
McQuay IM 672-4 17

Operation Guidelines
Operation Guidelines
Startup Checks
When performing startup and service, always take thorough
safety precautions. Only trained, experienced personnel should
perform these functions.
WARNING
Rotating fan. Can cause severe injury or death. Before
servicing fans, lockout and tag out power.
ATTENTION
Risques de dommages dans le moteur du ventilateur
électrique. Si Ia température de l’air a proximité du
ventilateurest élevée, le moteurdu ventilateur électrique peut
chauffer et brûler. Sur les transmetteurs d’air à circulation
transversale ou les transmetteurs dont le ventilateur est en
aval de l’unité de chauffage, régler la température de l’air
sortant de l’unité de chauffage à 40°C (104°F).
AVERTISSEMENT
Ventilateur en rotation. Peut causer des blessures sévères
ou même la mort. Avant d’effectuer l’entretien des ventilateurs,
bloquer et couper la tension.
WARNING
Fire/electric shock hazard. Can cause property damage,
personal injury or death. Wire fan power supply and ground
motor frame in accordance with local electric codes.
AVERTISSEMENT
Risques d´incendie et d’électrocution pouvant causer des
dommages matériels, des blessures et même la mort.
L’alimentation électrique du moteur du ventilateur de même
que la mise à la terre du chàssis du moteur doivent être faits
conformément aux codes d’installations électriques en
vigueur.
WARNING
Fan motor requires overload protection. Failure to provide
motor overload protection can result in fire, property damage,
electric shock, personal injury, or death. Connect motor to an
overload protective device rated in compliance with local
electric codes.
AVERTISSEMENT
Risques d’incendie et d’électrocution pouvant causer des
dommages matériels, des blessures et même la mort.
Connecter au moteur du ventilateur électrique un dispositif de
protection contre les surcharges conforme aux codes
d’installations électriques en vigueur.
CAUTION
Do not overheat fan motor. High air temperatures in the fan
section can cause the fan motor to burnout. On draw-through
air handlers or air handlers with the fan section down the air
stream from the heating section, the discharge air temperature
of the heating section must not exceed 104°F (40°C).
Before Starting the Unit:
Before entering fan section, make sure that fan electrical
power source is disconnected and locked in the OFF position.
1 Check that the unit is completely and properly installed
with ductwork connected.
2 Check that construction debris is removed/filters are clean.
3 Check that all electrical work is complete and properly
terminated.
4 Check that all electrical connections are tight and that the
proper voltage is connected. Phase imbalance must not
exceed 2%.
5 Do not grease ball bearings on the fan shaft and motor
before startup. They are prelubricated.
6 Check tightness of setscrews in bearings and fan wheel(s).
If retightening is needed, position the fan wheel(s) per
Table 2 or Table 3 on page 19. Torque set screws per
Table 6 on page 20.
CAUTION
Equipment damage due to loose fasteners represents
improper start-up and equipment abuse. It is not covered by
the warranty.
ADVERTISSEMENT
Les dommages dus à des attaches installées de façon
inappropriée représentent un démarrage inadéquat et un
abus d’équipement. Ceci n’est pas couvert par la garantie.
7 Check alignment of fan and motor sheaves and belt tension.
Adjust if necessary. Check tightness of sheave setscrews
and/or capscrews. See Figure 39 and Figure 40 on page 28.
8 Leak test the thermal system to verify that connections are
tight.
9 Check that the condensate drain is trapped.
10 Rotate the shaft by hand to be sure it is free.
Fan Startup:
Start and run fan. Observe the rotation. If the fan operates
backward, reverse two legs of the three-phase motor
connections.
18 McQuay IM 672-4

Operation Guidelines
O
Note – Variable pitch fan drives usually are provided for
operation in the mid-speed adjustment range. However,
the drives usually ship with the adjustment opened up for
minimum fan speed. Adjust the drives for the proper
airflow. See “Fan Drive Adjustments” on page 24.
After the First 48 Hours of Operation:
1 Disconnect and lock electrical power source.
2 Check tightness of all bearing, wheel, and sheave setscrews
(or capscrews). See Table 6.
3
Recheck belt tension and adjust if necessary. Belts that are
tensioned sufficiently to slip one to two seconds at startup
perform satisfactorily, extending life and reducing vibration. If
retensioning is necessary, be certain to retain sheave
alignment.
Fan Wheel Alignment
Figure 27: Wheel-to-Inlet Tunnel Relationship—Airfoil Type
Fan Wheels (Housed)
E q u a l s p a c i n g
B
a l l a r o u n d
A
A
Table 3: Wheel-to-Inlet Funnel Relationship—Forward
Curved Type Fan Wheels
Forward curved
Unit sizes 003 to 035 Unit sizes 040 to 090
Diameter (in)
9 x 4 0.25 6.35 20 (Class 1 & 2) 0.24 6.10
9 x 7 0.13 3.30 22.38 (Class 1 & 2) 0.41 10.41
9 x 9 0.25 6.35 25 (Class 1 & 2) 0.47 11.94
10 0.22 5.59 27.62 (Class 1 & 2) 0.47 11.94
12 0.35 8.89 30 (Class 1 & 2) 0.47 11.94
15 0.44 11.18 33 (Class 1 & 2) 0.50 12.70
18 0.25 6.35 36 (Class 1 & 2) 0.75 19.05
20 (Class 1 & 2) 0.73 8.54
22 1/2 (Class 1 & 2) 0.59 14.99
24 1/2 (Class 1 & 2) 0.56 14.22
Notes:
1. To obtain rated air performance, dimensional relationship must be held.
2. Adjust dimension C by loosening wheel hub setscrews, shifting wheel(s)
axially as needed, and retightening setscrews
C
(in)C (mm)
Diameter (in)
C
(in)C (mm)
Figure 29: Wheel-to-Inlet Funnel Relationship—Plenum
Fans
Table 2: Wheel-to-Inlet Funnel Relationship—Airfoil Type
Airfoil
Unit sizes 003 to 035 Unit sizes 040 to 090
A
Dia.
(in)A (mm)B (in)B (mm)
13.22 4.56 116 0.21 5.33 20.00 7.19 183 0.31 7.87
14.56 5.06 129 0.21 5.33 22.25 7.69 195 0.33 8.38
16.18 5.62 143 0.21 5.33 24.50 8.56 217 0.31 7.87
17.69 6.90 175 0.22 5.59 27.00 9.47 241 0.63 16.00
21.56 7.59 193 0.24 6.10 30.00 10.47 266 0.39 9.91
24.00 8.45 215 0.23 5.84 33.00 11.75 298 0.38 9.65
36.50 12.78 325 0.38 9.65
40.25 14.31 363 0.50 12.70
Notes:
1. To obtain rated air performance, dimensional relationship must be held.
2. To obtain dimension A, loosen setscrews in wheel hub(s), shifting wheel(s)
axially as needed, and retightening setscrews.
3. To obtain dimension B, loosen screw and washer fasteners around
periphery of funnel(s), shifting funnel radially as required, and re-torquing
fasteners.
A
Dia.
(in)A (mm)A (in)B (mm)
Figure 28: Wheel-to-Inlet Funnel Relationship—Forward
Curved Type Fan Wheels
C
I n l e t
F u n n e l
W h e e l
C
I n l e t
F u n n e l
verlap
Table 4: Wheel-to-Inlet Funnel Relationship—Plenum Fans
Wheel—funnel overlap
Size Overlap
13.5 .120
15 .190
16.5 .250
18.25 .310
20 .380
22.25 .440
24.5 .500
27 .560
30 .620
33 .750
36.5 .810
40.25 .880
44.5 .940
49 1.000
54.25 1.060
60 1.120
McQuay IM 672-4 19
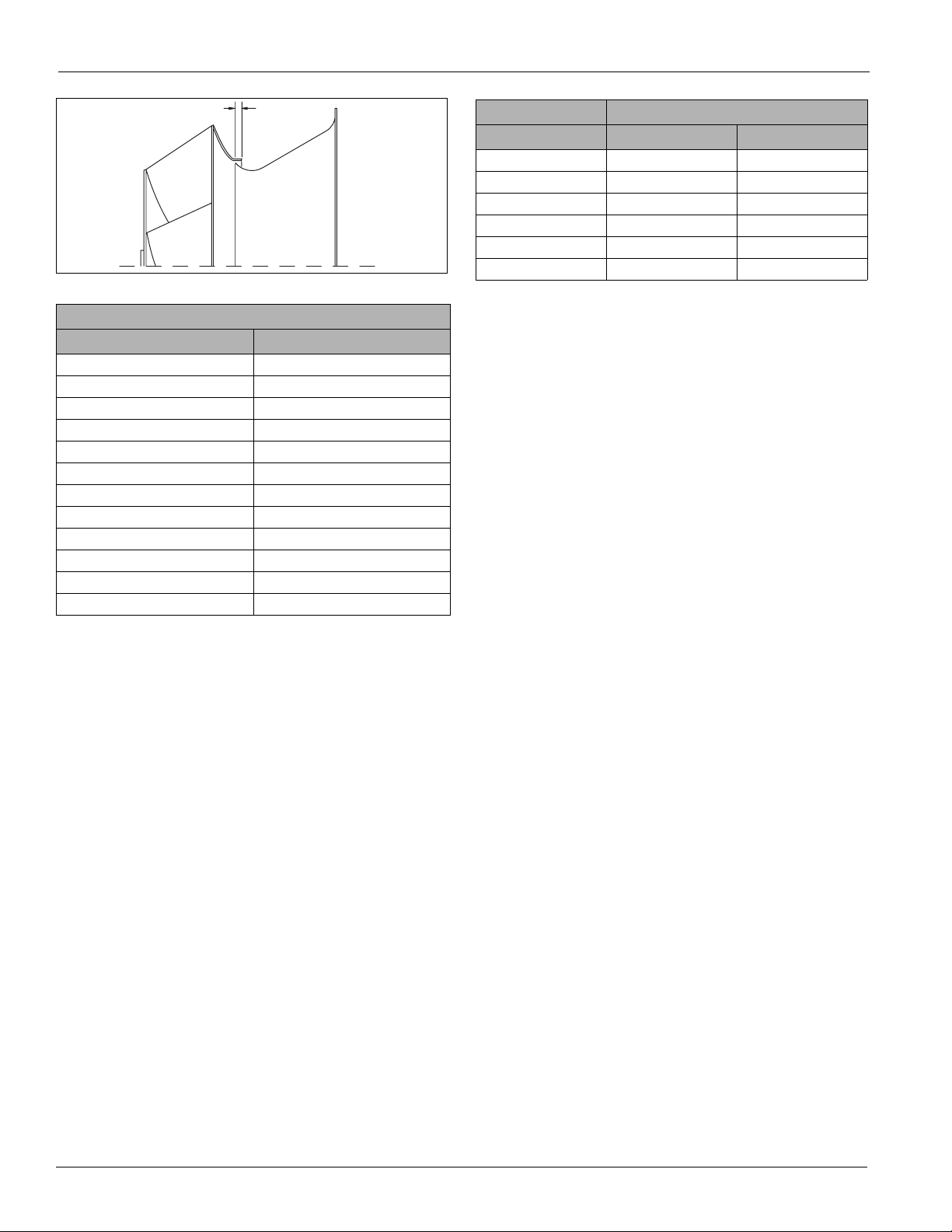
Operation Guidelines
Figure 30: Wheel-to-Inlet Funnel Relationship—Inline Fans
Overlap
Table 5: Wheel-to-Inlet Funnel Relationship—Inline Fans
Wheel—funnel overlap
Size Overlap
150 .375
165 .438
182 .562
200 .625
222 .688
245 .750
270 .812
300 .875
330 1.000
365 1.125
402 1.250
445 1.375
Table 6: Bearing Collar and Wheel Hub Set Screw Torque
set screw Minimum torque
Diameter (in) ft/lbs kg/m.
1/4 5.5 .76
1/16 10.5 1.45
3/8 19.0 2.63
7/16 29.0 4.01
1/2 42.0 5.81
5/8 92.0 12.72
20 McQuay IM 672-4
Operation Guidelines
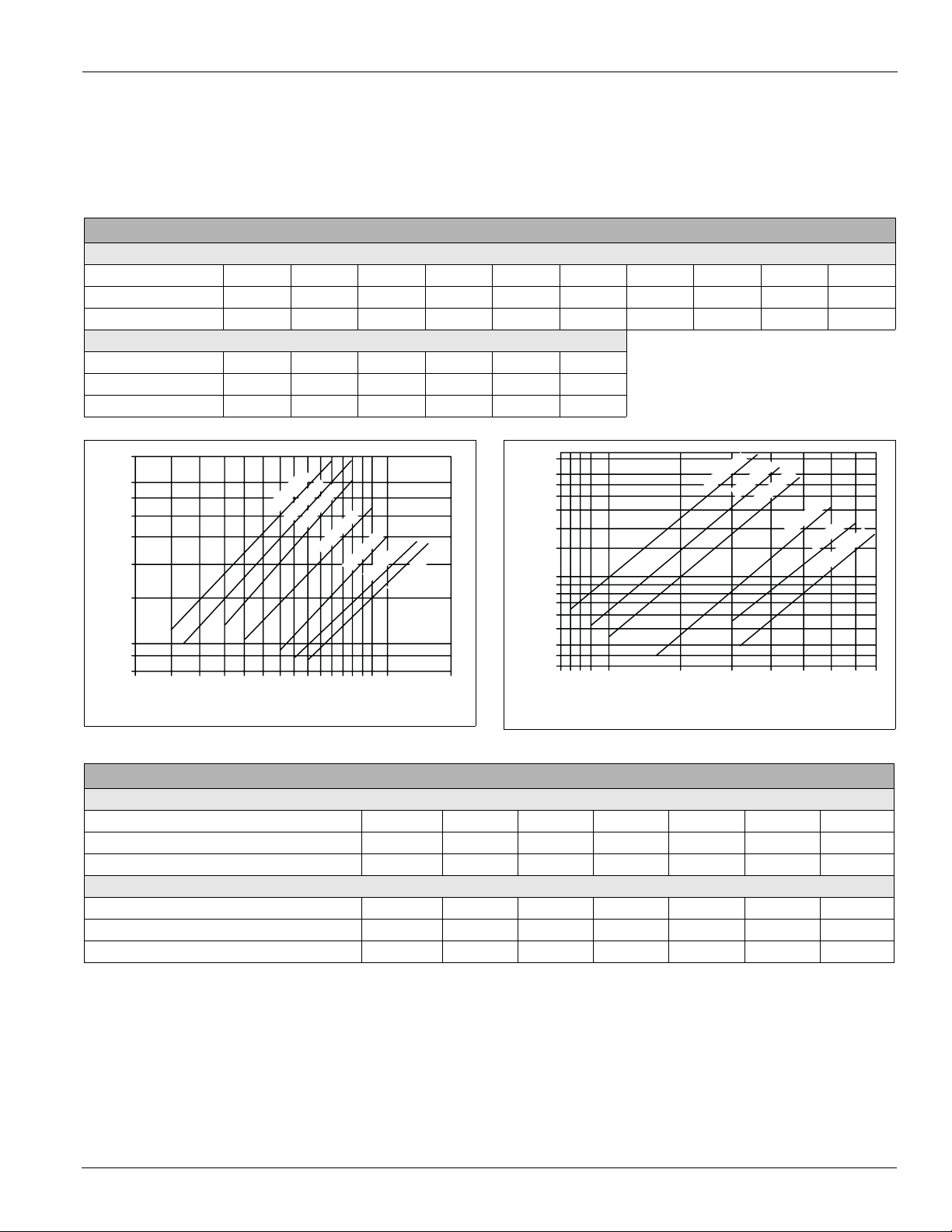
Operating Limits
Do not exceed the operating limits in Table 7. A fan wheel
operated beyond the rpm and temperature limits shown can
suffer permanent distortion or fracture. The resulting
unbalance can cause severe unit vibration.
Table 7: Unit Sizes 003 to 035
Fan operating limits
Forward curved—housed
Diameter 9 × 4 9 × 7 9 × 9 10.62 12.62 15 18 20 22.25 24.50
Maximum rpm Class I N/A 2189 2223 1934 1614 1328 1155 1050 944 858
Maximum rpm Class Il 2244 2854 2896 2518 2091 1725 1450 1200 1030 910
Airfoil—housed
Diameter 13.22 14.56 16.19 19.69 21.56 24.00
Maximum rpm Class I 3000 3000 2300 2000 1700 1500
Maximum rpm Class Il 4335 3918 3457 2858 2427 2255
Figure 31: Torque for FC Variable Inlet Vanes (in–lb) Figure 32: Torque for AF Variable Inlet Vanes (in–lb)
500
400
350
300
250
200
150
Torque (in–lb)
100
90
80
200
250
300
350
Fan speed (rpm)
400
FC36.00
500
450
FC33.00
FC30.25
FC27.62
600
650
550
FC25.00
750
700
800
FC22.38
850
900
1000
FC20.00
1500
450
400
350
300
250
200
150
100
90
80
70
Torque (in–lb)
60
50
40
35
30
750
800
850
900
1000
AF24.00
AF21.56
1500
Fan speed (rpm)
2000
AF19.69
AF16.19
2500
AF14.56
AF13.22
3000
3500
4000
4500
Table 8: Unit Sizes 040 to 090
Fan operating limits
Forward curved—housed
Diameter 20 22.38 25 27.62 30.25 33 36
Maximum rpm Class I 1010 930 790 690 650 600 560
Maximum rpm Class Il 1281 1178 1011 910 835 763 715
Airfoil—housed
Diameter 20 22.25 24.5 27 30 33 36.5
Maximum rpm Class I 2077 1875 1691 1479 1328 1209 1073
Maximum rpm Class Il 2703 2413 2199 1928 1730 1579 1401
McQuay IM 672-4 21

Operation Guidelines
Figure 33: Torque for FC Variable Inlet Vanes (in–lb)
300
250
FC24.50
800
850
FC22.25
900
1000
FC20.00
FC18.00
FC15.00
FC12.62
1500
200
150
100
90
Torque (in–lb)
80
70
60
50
350
400
450
500
600
650
700
550
Fan speed (rpm)
750
2000
Figure 34: Torque for AF Variable Inlet Vanes (in–lb)
2000
1500
1000
900
800
700
600
500
400
350
300
Torque (in–lb)
250
200
150
100
550
600
650
700
750
800
850
AF40.25
900
1000
Fan speed (rpm)
AF38.50
AF33.00
1500
AF30.00
AF27.00
AF24.50
AF22.25
2000
AF20.00
2500
Table 9: Operating Limits—Plenum Fans
Fan operating limits
Plenum fans
Diameter 13.5 15 16.5 18.25 20 22.25 24.5 27 30 33 36.5 40.25 44.50 49 54.25 60
Maximum rpm Class I 2895 2589 2376 2256 2077 1875 1691 1479 1328 1209 1073 972 882 799 725 651
Maximum rpm Class II 3786 3384 3100 2959 2703 2413 2199 1928 1730 1579 1401 1264 1150 1043 938 847
Maximum rpm Class III 4000 4000 3887 3735 3409 3065 2780 2423 2182 1984 1756 1598 1447 1314 1178 1071
3000
Table 10: Operating Limits—Inline Fans, Twin Fans
Fan operating limits
Inline fans
Diameter 18.25 20 22.25 24.5 27 30 33 36.5 40.25 44.50 49 54.25
Maximum rpm Class I 2727 2488 2236 2041 1835 1665 1476 1330 1208 1072 973 880
Maximum rpm Class II 3409 3111 2796 2551 2294 2082 1846 1662 1510 1340 1216 1100
Twin fans
Diameter 9 x 9 10.62 12.62 15 18.12 20
Maximum rpm 2575 2400 2000 1700 1400 1200
Maximum HP 10 15 15 30 40 40
22 McQuay IM 672-4

Operation Guidelines
Figure 35: Torque Requirements at 100% WOV for
SWSI Plenum Fans with NESTED Inlet Vane
5000
4000
3000
2000
1000
Torque (lb./in.)
900
Torque (in-lb)
800
700
600
500
400
300
200
100
600
200
300
400
700
500
Fan Speed (rpm)
800
900
1000
0
0
6
2
4
5
0
9
4
5
4
4
2
0
4
5
6
3
0
3
3
0
0
3
1500
Fan Vibration Levels
Each unit as shipped is trim balanced to operate smoothly. To
provide satisfactory operation after shipping and installation,
use the accepted industry guidelines for field balancing fans.
See Table 11.
Table 11: Vibration Levels
Fan speed (rpm) Vibration
800 or less 5 mils maximum displacement
801 or greater 0.20 in/sec. maximum velocity
Note: Excessive vibration from any cause contributes to premature fan and
motor bearing failure. Monitor overall vibration levels every six months
of operation. An increase in levels is an indication of potential trouble.
Vibration Causes
1 Wheel imbalance
a Dirt or debris on wheel blades
b Loose set screws in wheel hub or bearing-to-shaft
0
7
2
45
2
2000
3000
c Wheel distorted from overspeed
2 Bent shaft
3 Drive faulty
a Variable pitch sheaves—Axial and radial runout of
flanges; uneven groove spacing; out of balance. Also
similar faults in driven sheave.
b Bad V-belts; lumpy, or mismatched; belt tension too
tight or too loose.
4 Bad bearings, loose bearing hold-down bolts
5 Motor imbalance
6 Fan section not supported evenly on foundation
McQuay IM 672-4 23

Service and Maintenance
Service and Maintenance
Periodic Service and Maintenance
1 Check all moving parts for wear every six months.
2 Check bearing collar, sheave, and wheel hub setscrews,
sheave capscrews, and bearing hold-down bolts for
tightness every six months.
3 Annually check and snug all electrical connections. Inspect
for signs of water damage such as corrosion and repair if
necessary. Check ground conductor and connection
integrity. Service if needed.
Ball Bearing Lubrication
1 Motor bearings—All ball bearings are prelubricated and do
not require additional grease at time of installation.
However, periodic cleaning out and renewal of grease is
necessary. Exercise extreme care to prevent foreign matter
from entering the bearing. It also is important to avoid over
greasing. Use a high grade, clean mineral grease with the
following characteristics:
• Melting point over 302°F (150°C)
• Free from oil and soap separation under operating and
storage conditions
• Free of abrasive matter, acid, alkali and moisture
Specific greasing instructions are located on a label
attached to the fan section door.
2 Fan shaft bearings—All ball bearings are prelubricated and
do not require addition of grease at time of installation.
However, periodic renewal of grease is necessary. Bearings
are accessible through access door in fan section. Grease
fittings are located in front of door opening on drive end of
blower section. Apply grease slowly until a very slight
bleeding of grease from the seals is noted. Tie hinged
door(s) open. Do not over lubricate. Wipe off any excess
grease to prevent overheating.
The lubrication interval varies with the period of operation
and temperature of the ambient air. Use the guidelines in
the table below.
Table 12: Lubrication Guidelines
Bearing operating temp range
Temperature
Continuous operation 6 months 4 months 2 months
12-hr. day operation 12 months 12 months 6 months
to 130°F
(54°C)
to 150°F
(66°C)
over 150°F
(66°C)
Table 13: Lubricants Recommended for Fan Shaft Ball
Bearings
Manufacturer Product name
Texaco Lubricants Company Premium RB –30 to 300 –34 to 149
Keystone Ind. Lubricants 81EP-2 0 to 250
Mobil Oil Corporation Mobilith SCH100
Chevron U.S.A. Inc. SRI-2
Exxon Company, U.S.A. Ronex MP
Shell Oil Company Alvania No. 2
Note: Temperature ranges over 225°F are shown for lubricants only. High
temperature applications are not suitable for standard air handler
components.
Tem p. r ang e
°F °C
–
18 to 121
–
40 to 350–40 to 177
–
20 to 325–29 to 163
–
40 to 300–40 to 149
–
20 to 240–29 to 116
Fan Drive Adjustments
WARNING
Before servicing fans, lock out and tag out all power to the
unit. Fans or belts can cause severe personal injury or death.
AVERTISSEMENT
Avant de faire le service sur les ventilateurs,couper et
indiquer que le courant est coupé. Les ventilateurs ou les
courroies peuvent causer des blessures personnelles graves
ou entraîner la mort.
WARNING
Do not open the hinged access door and screw-fastened
access panels while the unit is operating.
strong suction forces can cause severe personal injury or death.
AVERTISSEMENT
Ne pas ouvrir les portes d’accès à charnières et les
panneaux à vis lorsque l’unité fonctionne. Les pièces
mobiles et le niveau de succion peuvent causer des blessures
personnelles graves ou même entraîner la mort.
Upon completion of the air balance, replace the variable
pitched motor sheave with a properly sized, fixed sheave. A
matching fixed sheave provides longer belt and bearing life
and minimizes vibration. Initially, it is best to have a variable
pitched motor sheave for the purpose of air balancing. Once
the balance is achieved, fixed sheaves maintain balancing and
alignment more effectively. Replace the adjustable sheaves
with fixed sheaves.
Moving parts and
With the electrical power disconnected, locked and tagged out,
measure the diameter of the V-belt outer surface where it
passes around the sheave (pitch diameter). Calculate fan speed
from the motor nameplate rpm.
Fan rpm = motor rpm ×
24 McQuay IM 672-4
Measured diameter at motor sheave
Measured diameter at fan sheave

Service and Maintenance
VM and VP Variable Pitch Key Type Sheaves
Mounting
1 Mount all sheaves on the motor or driving shaft with the
setscrews
A toward the motor.
2 Verify that both driving and driven sheaves are in
alignment and that shafts are parallel.
3 Fit internal key D between sheave and shaft and lock
setscrew
A securely in place.
Adjusting
1 Loosen setscrews B and C in moving parts of sheave and
pull out external key
E. (This key projects a small amount
to provide a grip for removing.)
2 To adjust sheave pitch diameter for desired speed, open
moving parts by half or full turns from closed position. Do
not open more than five full turns for
turns for
3 Replace external key E and securely tighten setscrews B
over key and setscrews
B belts.
C into keyway in fixed half of the
A belts or six full
sheave.
4 Put on belts and adjust belt tension. Do not force belts
over grooves. See “Fan Drive Belt Adjustment” on page
28.
5 Make future adjustments by loosening the belt tension and
increasing or decreasing the pitch diameter of the sheave by
half or full turns as required. Readjust belt tension before
starting drive.
6 To provide the same pitch diameter, adjust both halves of
the two-groove sheaves by the same number of turns from
closed position.
7 Verify that all keys are in place and that all se screws are
tight before starting drive. Check setscrews and belt tension
after 24 hours service.
Figure 36: VP Type Sheave Adjustment
A
Single Groove
Key E projects
to provide a grip
for removal.
B
A
Two Groove
C
B
E
D
Do not operate
C
sheeves with flange
projecting beyond
the hub end.
B
D
C
E
McQuay IM 672-4 25

Service and Maintenance
LVP Variable Speed Sheaves
Mounting
1 Slide sheave on motor shaft so that the side of the sheave
with setscrew
A is next to the motor when setscrew A is in
the hub or barrel of the sheave.
2 When setscrew A is at an angle in the center flange B,
mount it away from the motor so that the outer locking ring
and flange can be removed to get to the setscrew.
3 To remove the flange and locking ring:
a Loosen setscrews D.
b Loosen but do not remove capscrews E.
c Remove key F.
Note: This key projects a small amount to provide a grip
for removing.
d Rotate the flange counterclockwise until it disengages
the threads on the sheave barrel.
4 Verify that the driving and driven sheaves are in alignment
and the shafts are parallel. When aligning two-groove
sheaves, allow room between the sheave and motor to
access capscrews
5 Insert key C between the sheave and the shaft and tighten
setscrew
6 If flange and locking ring have been removed, when
A securely.
E.
replacing them make sure that the inner and outer flanges
are open from the closed position by the same amount as
the other flange. Determine this by accurately measuring
the top width of the grooves.
7 Insert key F.
8 Tighten setscrews D and capscrews E.
9 Put on belts and adjust belt tension. Do not force belts
over grooves. See
.
28
“Fan Drive Belt Adjustment” on page
10 Before starting the drive, ensure that all keys are in place
and all setscrews and all capscrews are tight. Check and
retighten all screws and retension belts after approximately
24 hours of service.
Adjusting
1 Slack off belt tension if belts have been installed.
2 Loosen setscrews D.
3 Loosen but do not remove capscrews E.
4 Remove key F.
Note: This key projects a small amount to provide a grip
for removing.
5 Adjust pitch diameter by opening or closing the movable
flanges by half or full turns.
Note: Two-groove sheaves are supplied with both grooves
set at the same pitch diameter.
To provide the same pitch diameter for satisfactory
operation, move both movable flanges the same number of
turns. Do not open sheaves more than five turns for
or six turns for
6 Replace key F.
7 Tighten setscrews D and capscrews E.
8 If belts have been installed, readjust belt tension. If belts
B belts.
A belts
have not been installed, install them and adjust belt tension.
Do not force belts over grooves. See “Fan Drive Belt
Adjustment” on page 28.
9 Before starting the drive, ensure that all keys are in place
and all setscrews and all capscrews are tight. Check and
retighten all screws and retension belts after approximately
24 hours of operation.
Note – Replace variable speed sheaves for 15 hp motors and
greater with a fixed pitch sheave after air balancing to
maintain fan balance integrity. Fixed sheaves furnished
by others.
Figure 37: LVP Type Sheave Adjustment
A
A
E
C
F
D
E
D
B
E
C
A
F
D
A
Section A-A Section A-A
26 McQuay IM 672-4

Service and Maintenance
MVP Variable Speed Sheaves
Mounting:
1 Verify both driving and driven sheaves are in alignment and
the shafts are parallel. The centerline of the driving sheave
must be in line with the centerline of the driven sheave. See
Figure 38.
2 Verify that all setscrews are torqued to the values shown in
Table 14 before starting drive. Check setscrew torque and
belt tension after 24 hours of service.
Adjusting:
1 Adjust motor base forward to release belt tension. Remove
the belts for easier adjustment.
2 Loosen, but do not remove both of the locking setscrews A
in the outer locking ring by using a hex key or torque
wrench with a hex bit.
3 Adjust sheave to desired pitch diameter by turning the outer
locking ring. Use a spanner wrench or drift inserted into the
three holes that are located 120° apart on the ring.
4 Any pitch diameter can be obtained within the sheave
range. One complete turn of the outer locking ring changes
the pitch diameter 0.233".
5 Do not open sheaves more than the following:
• Do not open B sheaves more than 4 3/4 turns for the A
belts or 6 turns for the B belts.
• Do not open C sheaves more than 9 1/2 turns.
• Do not open 5V sheaves more than 6 turns.
• Do not open 8V sheaves more than 8 turns.
6 Tighten BOTH locking screws A in the outer locking ring
before operating the drive. Use a torque wrench and tighten
to the value shown in Table 14.
7
Replace belts and adjust the motor base to tension the belts
properly. See “Fan Drive Belt Adjustment” on page 28
8 Do not loosen any screws other than the two locking screws
A in the outer locking ring when adjusting the sheave pitch.
Do not operate the drive until the locking screws have been
set to the torque specifications.
Table 14: Screw Torque Values
Socket head cap screws
Nominal screw size
(dia–-thds/in)
1/4–20NC 150 12.5 100 87 7.3 3/16 50
5/16–11NC 305 25.4 200 165 13.8 1/4 90
3/8–16NC 545 45.4 350 290 24.2 1/4, 5/16 150, 250
1/2–13NC 1300 108.3 N/A 620 51.7 N/A N/A
5/8–11NC N/A N/A N/A 1225 102.1 N/A N/A
Seating torque Seating torque Seating torque Seating torque Length (L) Seating torque
(in–lbs) (in–lbs) (in–lbs) (in–lbs) (in–lbs) (in–lbs) (in–lbs)
Flat head socket
screws
Lengths equal or greater than dia. For lengths (L)) less than dia.
Hollow head set screws only
.
.
Figure 38: Sheave Adjustment
Must be
parallel
Bearing
Motor
Must be
parallel
Center lines
must coincide
Adjustable
Sheave
McQuay IM 672-4 27
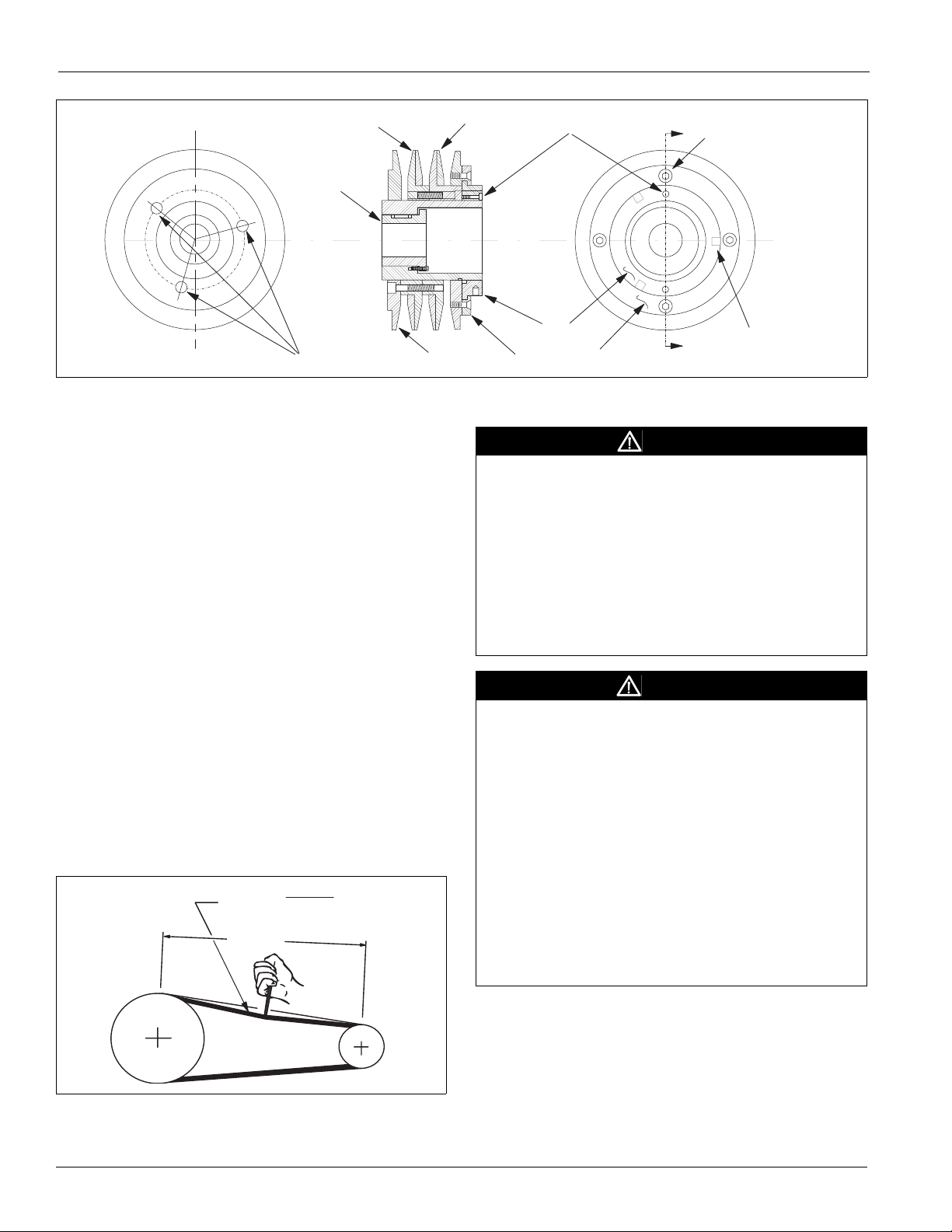
Service and Maintenance
Figure 39: Sheave Adjustment
A d j u s t a b l e
C e n t e r - F l a n g e
S p l i t T a p e r
B u s h i n g
F i x e d
C e n t e r - F l a n g e
( 2 ) L o c k i n g
S e t s c r e w s " A "
F l a t h e a d S o c k e t S c r e w s
( D o N o t R e m o v e )
C a p s c r e w s
( D o N o t R e m o v e )
Fan Drive Belt Adjustment
General Rules of Tensioning
1 The ideal tension is the lowest tension at which the belt
does not slip under peak load conditions.
2 Check tension frequently during the first 24 to 48 hours of
operation.
3 Over tensioning shortens belt and bearing life.
4 Keep belts free from foreign material that can cause
slippage.
5 Inspect V-drive on a periodic basis. Adjust tension if the
belt is slipping. Do not apply belt dressing. This can
damage the belt and cause early failure.
Tension Measurement Procedure
1 Measure the belt span. See Figure 40.
2 Place belt tension checker squarely on one belt at the center
of the belt span. Apply force to the checker, perpendicular
to the belt span, until the belt deflection equals belt span
distance divided by 64. Determine the force applied while
in this position.
3 Compare this force to the values in Table 15.
Figure 40: Drive Belt Adjustment
Deflection =
B
Belt span
64
el
t
s
pan
S t a t i o n a r y
E n d - F l a n g e
O u t e r
L o c k i n g - R i n g
I n n e r L o c k i n g - R i n g
( 3 ) H o l e s f o r
S p a n n e r W r e n c h
o r D r i f t
WARNING
Moving belt and fan can cause severe personal injury or
death. During installation and filter maintenance:
• Verify that the belt and fan guards on plenum fan units are
always in place.
• Lock and tag out fans to prevent accidental start up.
• Do not enter the filter compartment until the fan is
completely stopped.
• Use approved equipment for reaching filters located above
normal reach. Do not step on filter frames or unit
components.
• Floor surfaces must be dry and free of oil or grease.
WARNING
Pendant l’installation et où l’entretien des filtres, une
courroie en mouvement ou un ventilateur en opération
peuvent causer des blessures graves où même causer la
mort.
• S’assurer que les gardes de courroie et de ventilateur sont
toujours en place.
• Verouiller les démarreurs des ventilateurs et afficher un
avis de mise-en-garde afin de prévenir tout accident ou
démarrage.
• Attendre que le ventilateur soit complètement arrêté avant
d’entrer dans l’unité.
• Utiliser seulement des équipements approuvé pour joindre
les bancs de filtres; ne pas mettre soit sur les cadres des
filtres ou même sur toutes composantes de l’unité.
• La surface des planchers doit être sec et libre de toute
trace d'huile et où de graisse.
28 McQuay IM 672-4

Table 15: Belt Deflection Force (per Browning® specifications)
Sheave diameter (in) Deflection force (lbs)
Cross
section
A, AX
B, BX
5V, 5VX
Smallest
sheave
diameter range
3.0 to 3.6
3.8 to 4.8
5.0 to 7.0
3.4 to 4.2
4.4 to 5.6
5.8 to 8.6
4.4-6.7
7.1-10.9
11.8 -16. 0
rpm
range
1000 to 2500 3.7 5.5 4.1 6.1
2501 to 4000 2.8 4.2 3.4 5.0
100 to 2500 4.5 6.8 5.0 7.4
2501 to 4000 3.8 5.7 4.3 6.4
1000 to 2500 5.4 8.0 5.7 9.4
2501 to 4000 4.7 7.0 5.1 7.6
850 to 2500 4.9 7.2
2501 to 4000 4.2 6.2
860 to 2500 5.3 7.9 7.1 10.5
2501 to 4000 4.5 6.7 7.1 9.1
860 to 2500 6.3 9.4 8.5 12.6
250 to -4000 6.0 8.9 7.3 10.9
500-1749 10.2 15.2
1750-3000 8.8 13.2
3001-4000 5.6 8.5
500-1740 12.7 18.9 14.8 22.1
1741-3000 11.2 16.7 13.7 20.1
500-1740 15.5 23.4 17.1 25.5
1741-3000 14.6 21.8 16.8 25.0
Cross section A, B, 5V Cross section AX, BX, 5VX
Used belt New belt Used belt New belt
Service and Maintenance
Front Load Filter Option
Front loaded filter options require that the filters be removed
and replaced from inside the unit.
To remove filters, rotate the wire clips. This releases both the
prefilter and the final filter. When installing clean filters, check
to verify the filters are fully seated in the frame. See Figure 41.
Figure 41: Frame and Filters with Holding Clips
F i n a l
F i l t e r
F i l t e r
P r e f i l t e r
R o t a t e
W i r e C l i p s
F r a m e
Filter Gauges
Filter gauges indicate pressure drop for installed filters.
Table 16 shows the typical filter pressure drop for clean filters
at rated air flow. The tables also show a final pressure drop for
front loaded filters.
Where a single filter gauge is used, the prefilters can be
removed to check the pressure drop of the final filters.
Figure 42: Filter Gauge
McQuay IM 672-4 29
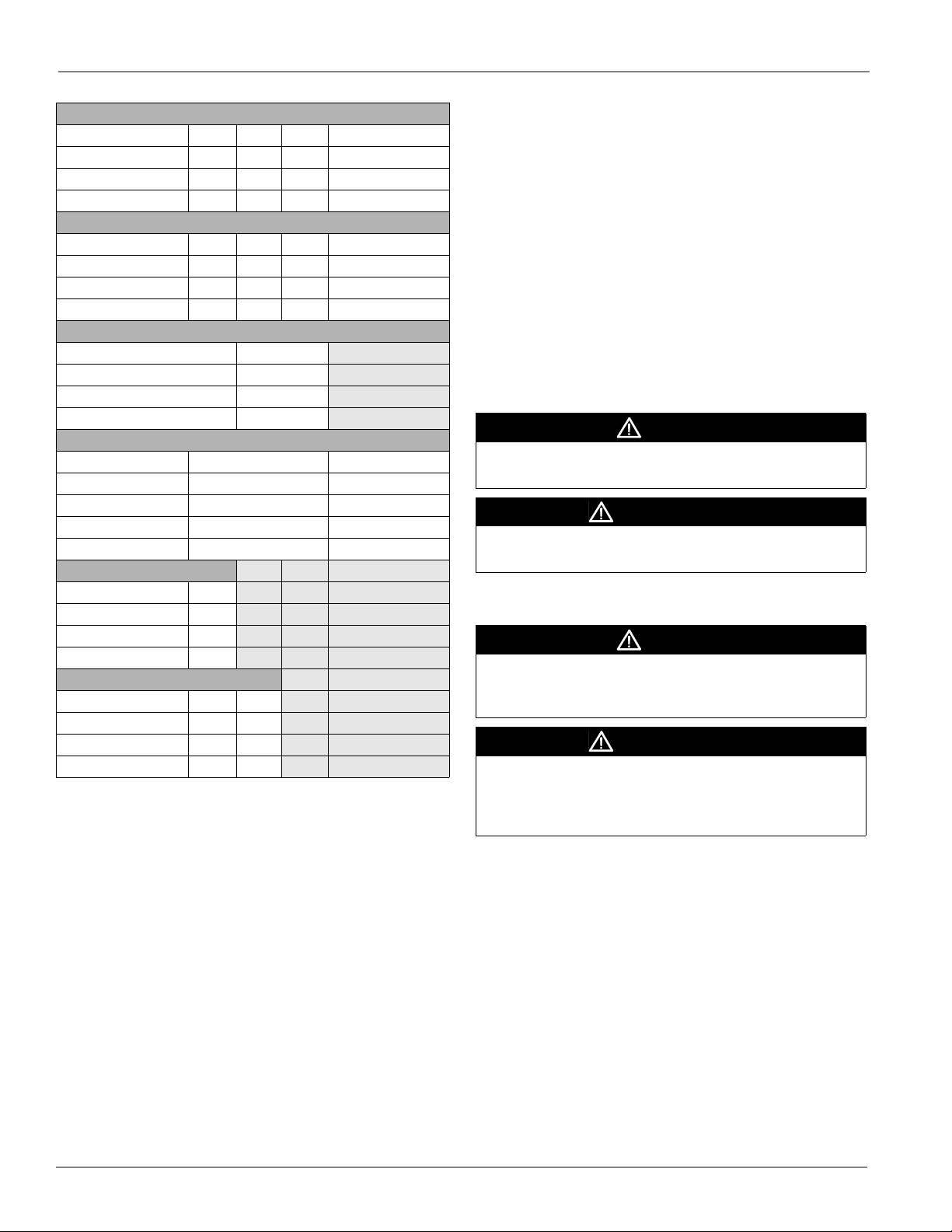
Service and Maintenance
Table 16: Filter Pressure Drops
Bag filters—DriPak 2000
Efficiency 45% 65% 85% 95%
Rated velocity (fpm) 625 500 500 500
Initial pressure drop .20–.26 .21–30 .34–.48 .50–.70
Initial pressure drop 1.0 1.0 1.0 1.0
Cartridge filters—Varicel II MH, 4.25" deep
Efficiency 65% 85% 95% Efficiency
Rated velocity (fpm) 500 500 500 Rated velocity (fpm)
Initial pressure drop .43 .61 .70 Initial pressure drop
Final pressure drop 1.5 1.5 1.5 Final pressure drop
Cartridge filters—Varicel SH, 12" deep
Efficiency 70%
Rated velocity (fpm) 500
Initial pressure drop .39
Final pressure drop 1.2
Pleated panel filters
Type Perfect pleat AMAir 300 4"
Efficiency 30% 30%
Rated Velocity (fpm) 500 625
Initial Pressure Drop .36 .36
Final Pressure Drop 1.0 1.0
5700 filters
Efficiency N/A
Rated velocity (fpm) 500
Initial pressure drop .25
Final pressure drop 1.0
Pleated 62 Plus filters
Size 2" 4"
Efficiency 70% 70%
Initial pressure drop .42 .37
Final pressure drop 1.0 1.0
Maintaining the Coil
1 The coil must be clean to obtain maximum performance.
Check once a year under normal operating conditions and,
if dirty, brush or vacuum clean. Use a chemical coil cleaner
on multiple row coils. Read and follow the chemical
cleaner’s instructions as some cleaners may contain harsh
chemicals. Take care not to damage fins while cleaning.
2 Drain pans in any air conditioning unit may have some
moisture. Algae, etc., can grow due to airborne spores and
bacteria. Periodic cleaning is necessary to prevent this
buildup from plugging the drain and causing the drain pan
to overflow. Also, keep the drain pans clean to prevent the
spread of disease. Cleaning should be performed by
qualified personnel.
3 Dirt and lint can clog the condensate drain, especially with
dirty filters. Inspect twice a year to help avoid overflow.
Winterizing Water Coils
Coils can freeze due to air stratification or failure of outdoor
air dampers and/or preheat controls. Drain all coils as
thoroughly as possible and then treat in the following manner.
• Fill each coil independently with an antifreeze solution
using a small circulating pump and again thoroughly drain.
• Check freezing point of antifreeze before proceeding to next
coil. Due to a small amount of water always remaining in
each coil, there is a diluting effect. The small amount of
antifreeze solution remaining in the coil must always be
sufficient enough to prevent freeze-up.
Note – Carefully read instructions for mixing antifreeze solution
used. Some products have a higher freezing point in their
natural state when mixed with water. McQuay
International is not responsible for the freezing of
coils.
WARNING
Mold can cause personal injury. Clean drain pan regularly
so mold does not develop.
AVERTISSEMENT
La moisissure présente un danger respiratoire. Pour éviter
la moisissure, nettoyer régulièrement le bassin de drainage.
Removing and Replacing Components
WARNING
Before removing any component, lock out and tag out all
power to the unit. Fans and belts can cause severe personal
injury or death.
AVERTISSEMENT
Avant d’enlever toute composante, couper et indiquer que
l’alimentation électrique à l’unité est coupée. Les
ventilateurs et les courroies peuvent entraîner des blessures
personelles graves ou même la mort.
Removing a Panel
To remove a side or top panel:
1 Remove the flat head fasteners located along the sides of
the panel.
2 Once all fasteners are removed, lift off the panel.
Removing a Frame Channel
Frame channels that run the length of the unit along the top can
be removed to allow access to both the side and top of the unit.
To Remove the Frame Channel:
1 First remove any adjoining side and top panel(s).
2 Once the side panel is off, remove the flat head fasteners in
the corner of the frame channels.
30 McQuay IM 672-4

Service and Maintenance
3 Pull the frame channel out the side.
If any top panel fastens into the frame channel (when the
frame channel is 24" or wider in direction of air flow),
remove the fasteners in the top panel before pulling out the
channel.
Removing the Fan Section
The fan shaft, motor, and any drive components can be
removed and replaced through the access door opening. If
required, the side panel can be removed for additional access.
If fan replacement is required, the entire fan assembly can be
pulled out the side of the cabinet. The fan assembly includes
the fan housing, the bearing support, and the fan base.
Removing the Fan Assembly
Remove the side panels and any intermediate supports
1
(follow instructions for side panel removal).
2 Once the panels and any intermediate supports are
removed, disconnect the neoprene bulk head seal that is
attached to the fan discharge.
3 Remove the four discharge angles that hold the neoprene
canvas in place around the discharge opening.
4 Disconnect the fan sled from each of the corner mounts and
pull the entire assembly out the side of the unit.
5 After the fan sled is out, loosen the fan bearings and pull
out the shaft.
6 Disconnect the fan housing from the fan sled, and bearing
support by removing the attaching bolts.
7 Replace the new fan, reconnect the shaft and bearings and
put the fan assembly in the cabinet.
8 Replace panels and fasteners.
2 Remove all screws and remove the access panel.
3 Remove the screws holding the coil in place.
4 Lift and pull the coil out the side.
Installing Single Coils
Slide the coil through the opening in the coil section onto
1
the bottom coil rests.
2 To prevent any air bypass around the coil, place coils up
against the coil bulkheads. See Figure 43.
3 Once the coil is in place, fasten the coil to the section.
4 Caulk the seams between the coil casings and bulkheads.
See Figure 43.
5
If this is an additional coil being installed and not a
replacement, locate the coil supply and return connections
dimensionally. Carefully drill holes in the end panels of the
unit.
6 Remove the brass plugs for the vents and drains on the
connections.
7 Slip the panel over the connections.
8 Replace the brass plugs and panel fasteners.
Figure 43: Single Coil Top Installation/Removal
Opposite
connection
end
Coil
Connection
end
Coil
Removing and Replacing the Coil
The coil can be removed by the side, top, or a combination of
both. The size and configuration of the coil affects how the
coil can be removed. Single banks of coil are fastened only on
the connection side of the unit. Stacked and staggered coils are
fastened on both ends of the coil. See the instructions below
for details to remove each coil type.
Before removing the coil, disconnect all piping. The
instructions below assume the coil is mounted in a
sectionalized coil section where the frame channel can be
removed without affecting other components. If the coil
section is unitized with other components, removing the top
frame channel requires removing additional panels.
Removing Single Coils
Note – Single coils are bolted to the unit on the connection end.
The connection end is held in place with a clamp.
.
1 Disconnect all piping and remove the brass plugs for the
vents and drains located in the connections.
McQuay IM 672-4 31
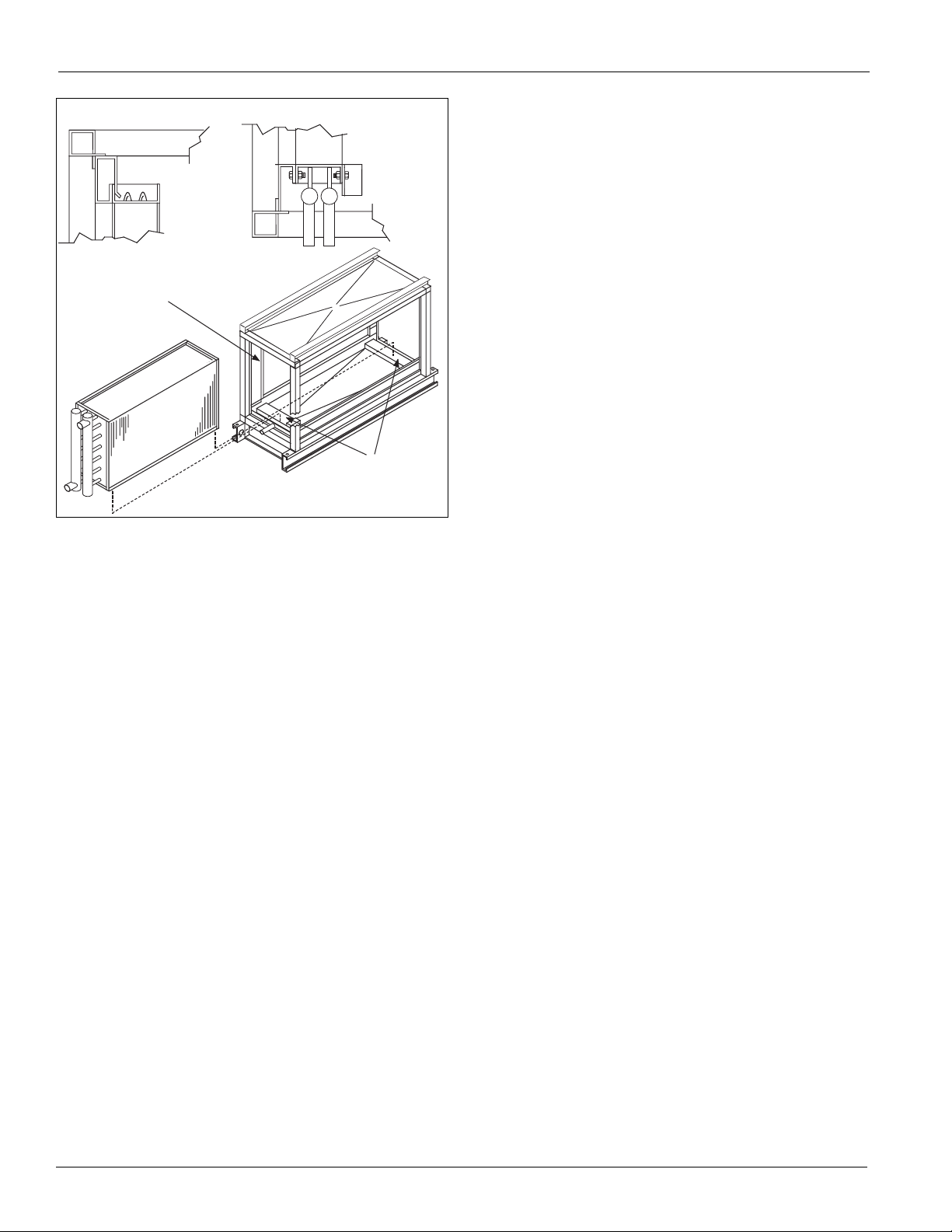
Service and Maintenance
Figure 44: Single Coil Side Installation/Removal
Opposite connection end
Coil
Coil
Bulkhead
Removing Stacked Coils
Note – Top and bottom stacked coils are held together with steel
plate and screws on one side and drain trough and
screws on the other side. Remove the plate and trough
before removing the coils. The coils cannot be removed
attached together.
1 Disconnect all piping and remove the brass plugs for the
Connection end
Coil
Coil
Rests
vents and drains located in the connections.
2 Remove all screws and remove the access panel.
3 Remove the bolts holding the coil in place and then lift and
pull out the coil from the side.
4 Remove the steel plate and the drain trough that holds the
coils together.
5 Remove the bolts on both ends of the top coil holding it in
place and then lift and slide the coil out.
6 Remove the bolts on both ends of the bottom coil holding it
in place and then lift and slide the coil out.
Installing Stacked Coils
1 Slide the bottom coil through the opening in the coil section
onto the bottom coil rests.
2 Place the coil up against the coil bulkheads to prevent any
air bypass around the coil.
3 Once the coil is in place, bolt the coil to the section.
4 Caulk the mounting surface of the steel plate and install the
plate on the coils.
5 Caulk the mounting surface of the drain trough and install
the drain trough on the coils.
6 Caulk the seams between the coil casings and blockoffs.
7 Connect all piping and install the brass plugs for the vents
and drains located in the connections.
8 Install the access panel.
Removing and Installing Staggered Coils
Staggered coils have two banks of coils positioned a few
inches apart in the direction of airflow. Both coils are secured
to the unit on the connection and opposite connection end of
the unit.
1 Disconnect all piping and remove the brass plugs for the
vents and drains located in the connections.
2 To access bolts holding the coils in place, remove the
panels on both the connection and opposite connection end
of the coil section.
3 Each coil is held in place with bolts located in the corners
of the coil side plates. Remove the bolts and then lift and
pull the coil out the side.
4 The bottom coil is fastened to the air block off plate.
Remove the screws attaching this plate to the coil.
5 Once the fasteners holding the coil in place are removed,
pull out the coil from either side of the unit.
6 Install the coils in reverse order of removal.
32 McQuay IM 672-4

Warranty
Warranty
Consult your local McQuay Representative for warranty
details. Refer to Form 933-43285Y. To find your local
McQuay Representative, go to www.mcquay.com.
Warranty Return Material Procedure
Defective material may not be returned without permission of
authorized factory service personnel of McQuay International
in Minneapolis, Minnesota, (763) 553-5330. A “Return
Goods” tag must be included with the returned material. Enter
the required information to expedite handling and prompt
issuance of credits. All parts must be returned to the
appropriate McQuay facility, designated on the “Return
Goods” tag. Transportation charges must be prepaid.
The return of the part does not constitute an order for
replacement. Therefore, a purchase order must be entered
through the nearest McQuay representative. The order should
include part number, model number, and serial number of the
unit involved.
Credit will be issued on customer's purchase order following
an inspection of the return part and upon determination that the
failure is due to faulty material or workmanship during the
warranty period.
Replacement Parts
When writing to McQuay for service or replacement parts,
refer to the model number and serial number of the unit
stamped on the serial plate attached to the unit. If replacement
parts are required, mention the date of installation of the unit
and date of failure, along with an explanation of the
malfunctions and a description of the replacement parts
required.
McQuay IM 672-4 33

McQuay Training and Development
Now that you have made an investment in modern, efficient McQuay equipment, its care should be a high priority.
For training information on all McQuay HVAC products, please visit us at www.mcquay.com and click on training, or
call 540-248-9646 and ask for the Training Department.
Warranty
All McQuay equipment is sold pursuant to its standard terms and conditions of sale, including Limited Product
Warranty. Consult your local McQuay Representative for warranty details. Refer to Form 933-43285Y. To find your
local McQuay Representative, go to www.mcquay.com.
This document contains the most current product information as of this printing. For the most up-to-date product
information, please go to www.mcquay.com.
© 2007 McQuay International • www.mcquay.com • 800-432-1342
 Loading...
Loading...