Page 1
DNAGNITAREPO,NOITALLATSNI
ROFSNOITCURTSNIECIVRES
™ENIPLA
YCNEICIFFEHGIHGNISNEDNOC
TNEVTCERID
RELIOBRETAWTOHDERIF-SAG
As an ENERGY STAR
STAR® guidelines for energy efciency established by the United States Environmental Protection Agency (EPA).
®
Partner, Burnham Hydronics has determined that the Alpine™ Series meets the ENERGY
WaRning: Improper installation, adjustment, alteration, service or maintenance can cause property damage,
injury, or loss of life. For assistance or additional information, consult a qualied installer, service agency or the
gas supplier. This boiler requires a special venting system. Read these instructions carefully before installing.
101602-01R2-9/08
Price - $5.00
Page 2
IMPORTANT INFORMATION - READ CAREFULLY
NOTE: The equipment shall be installed in accordance with those installation regulations enforced in the area where the
installation is to be made. These regulations shall be carefully followed in all cases. Authorities having jurisdiction
shall be consulted before installations are made.
All wiring on boilers installed in the USA shall be made in accordance with the National Electrical Code and/or local regulations.
All wiring on boilers installed in Canada shall be made in accordance with the Canadian Electrical Code and/or local regulations.
The City of New York requires a Licensed Master Plumber supervise the installation of this product.
The Massachusetts Board of Plumbers and Gas Fitters has approved the Alpine™ Series boiler. See the Massachusetts Board of
Plumbers and Gas Fitters website, http://license.reg.state.ma.us/pubLic/pb_pre_form.asp for the latest Approval Code or ask
your local Sales Representative.
The Commonwealth of Massachusetts requires this product to be installed by a Licensed Plumber or Gas Fitter.
The following terms are used throughout this manual to bring attention to the presence of hazards of various risk levels,
or to important information concerning product life.
DangER
indicates an imminently hazardous situation
which, if not avoided, will result in death, serious
injury or substantial property damage.
WaRning
indicates a potentially hazardous situation which,
if not avoided, could result in death, serious injury
or substantial property damage.
indicates a potentially hazardous situation which,
if not avoided, may result in moderate or minor
injury or property damage.
indicates special instructions on installation,
operation, or maintenance which are important
but not related to personal injury hazards.
CaUTiOn
nOTiCE
DangER
DO NOT store or use gasoline or other ammable vapors or liquids in the vicinity of this or any other
appliance.
if you smell gas vapors, nO nOT try to operate any appliance - DO nOT touch any electrical switch or use
any phone in the building. immediately, call the gas supplier from a remotely located phone. Follow the gas
supplier’s instructions or if the supplier is unavailable, contact the re department.
2
Page 3

WaRning
This boiler requires regular maintenance and service to operate safely. Follow the instructions contained
in this manual.
improper installation, adjustment, alteration, service or maintenance can cause property damage, personal
injury or loss of life. Read and understand the entire manual before attempting installation, start-up
operation,
knowledgeable installer or service agency
This boiler must be properly vented.
This boiler needs fresh air for safe operation and must be installed so there are provisions for adequate
combustion and ventilation air.
The interior of the venting system must be inspected and cleaned before the start of the heating season
and
should be inspected periodically throughout the heating season for any obstructions. a clean and
unobstructed venting system is necessary to allow noxious fumes that could cause injury or loss of life
to vent safely and will contribute toward maintaining the boiler’s efciency.
installation is not complete unless a pressure relief valve is installed into the tapping located on left side
of appliance. - See the Water Piping and Trim Section of this manual for details.
This boiler is supplied with safety devices which may cause the boiler to shut down and not re-start
without
unattended in cold weather; or appropriate safeguards and alarms should be installed on the heating
system to prevent damage if the boiler is inoperative.
or service. installation and service must be performed only by an experienced, skilled, and
service. if damage due to frozen pipes is a possibility, the heating system should not be left
This boiler contains very hot water under high pressure. Do not unscrew any pipe ttings nor attempt
to disconnect any components of this boiler without positively assuring the water is cool and has no
pressure. Always wear protective clothing and equipment when installing, starting up or servicing this
boiler to prevent scald injuries. Do not rely on the pressure and temperature gauges to determine the
temperature and pressure of the boiler. This boiler contains components which become very hot when
the boiler is operating. Do not touch any components unless they are cool.
Boiler materials of construction, products of combustion and the fuel contain alumina, silica, heavy metals,
carbon monoxide, nitrogen oxides, aldehydes and/or other toxic or harmful substances which can cause
death or serious injury and which are known to the state of California to cause cancer, birth defects and
other reproductive harm. Always use proper safety clothing, respirators and equipment when servicing
or working nearby the appliance.
Failure to follow all instructions in the proper order can cause personal injury or death. Read all instruc-
tions, including all those contained in component manufacturers manuals which are provided with the
boiler before installing, starting up, operating, maintaining or servicing.
Keep boiler area clear and free from combustible materials, gasoline and other ammable vapors or
liquids.
ll cover plates, enclosures and guards must be in place at all times.
a
nOTiCE
This boiler has a limited warranty, a copy of which is printed on the back of this manual. it is the responsibility
of the installing contractor to see that all controls are correctly installed and are operating properly when the
installation is complete.
3
Page 4

Table of Contents
I. Product Description, Specifications
VIII. Electrical .......................................49
and Dimensional Data....................4
IX. Boiler Stacking ............................. 56
II. Pre-Installation ...............................8
X. Modular Installation ....................58
III. Unpacking Boiler ...........................9
XI. System Start-up ............................66
IV. Venting ......................................... 10
XII. Operation .....................................72
V. Condensate Disposal .................... 29
VI. Water Piping and Trim .................31
XIII. Service and Maintenance .............. 84
XIV. Troubleshooting ...........................88
VII. Gas Piping ....................................46
XV. Repair Parts ..................................91
I. Product Description, Specications and Dimensional Data
Alpine™ Series boilers are condensing high efciency
gas-red direct vent hot water boilers designed for use
in forced hot water space or space heating with indirect
domestic hot water heating systems, where supply water
temperature does not exceed 210°F. These boilers have
special coil type stainless steel heat exchangers, constructed,
tested and stamped per Section IV ‘Heating Boilers’ of
ASME Boiler and Pressure Vessel Code, which provide a
maximum heat transfer and simultaneous protection against
ue gas product corrosion. These boilers are not designed
for use in gravity hot water space heating systems or
systems containing signicant amount of dissolved oxygen
(swimming pool water heating, direct domestic hot water
heating, etc.).
Table 1: Dimensional Data (See Figures 1a & 1B)
Dimension
A - Inch
(mm)
B - Inch
(mm)
C - Inch
(mm)
D - Inch
(mm)
E - Inch
(mm)
Gas Inlet F
(FPT)
Return G
(FPT)
Supply H
(FPT)
Condensate Drain J *
Boiler Two Pipe
CPVC/PVC Vent Connector
- Inch
Approx. Shipping Weight
(LBS)
ALP080 ALP105 ALP150 ALP210 ALP285 ALP399
12-9/16
(320)
5-5/8
(142)
9-5/16
(237)
3 x 3 3 x 4 4 x 4
137 155 182 206 256 304
14
(356)
10-3/4
(273)
5-15/16
* Factory Provided Socket End Compression Pipe Joining Clamp
Boiler Model
19-11/16
(500)
5-13/16
(147)
7-5/16
(186)
16-7/16
(417)
(151)
1/2” 3/4” 1”
1” 1-1/4” 1-1/2”
1” 1-1/4” 1-1/2”
for 3/4” Schedule 40 PVC Pipe
23-15/16
(608)
17-1/8
(435)
21-13/16
(554)
7-5/16
(185)
14-1/8
(358)
18
(456)
12-1/4
(312)
13-1/16
15-13/16
28-7/8
(734)
6-3/16
(157)
(332)
23-3/4
(602)
(402)
4
Page 5
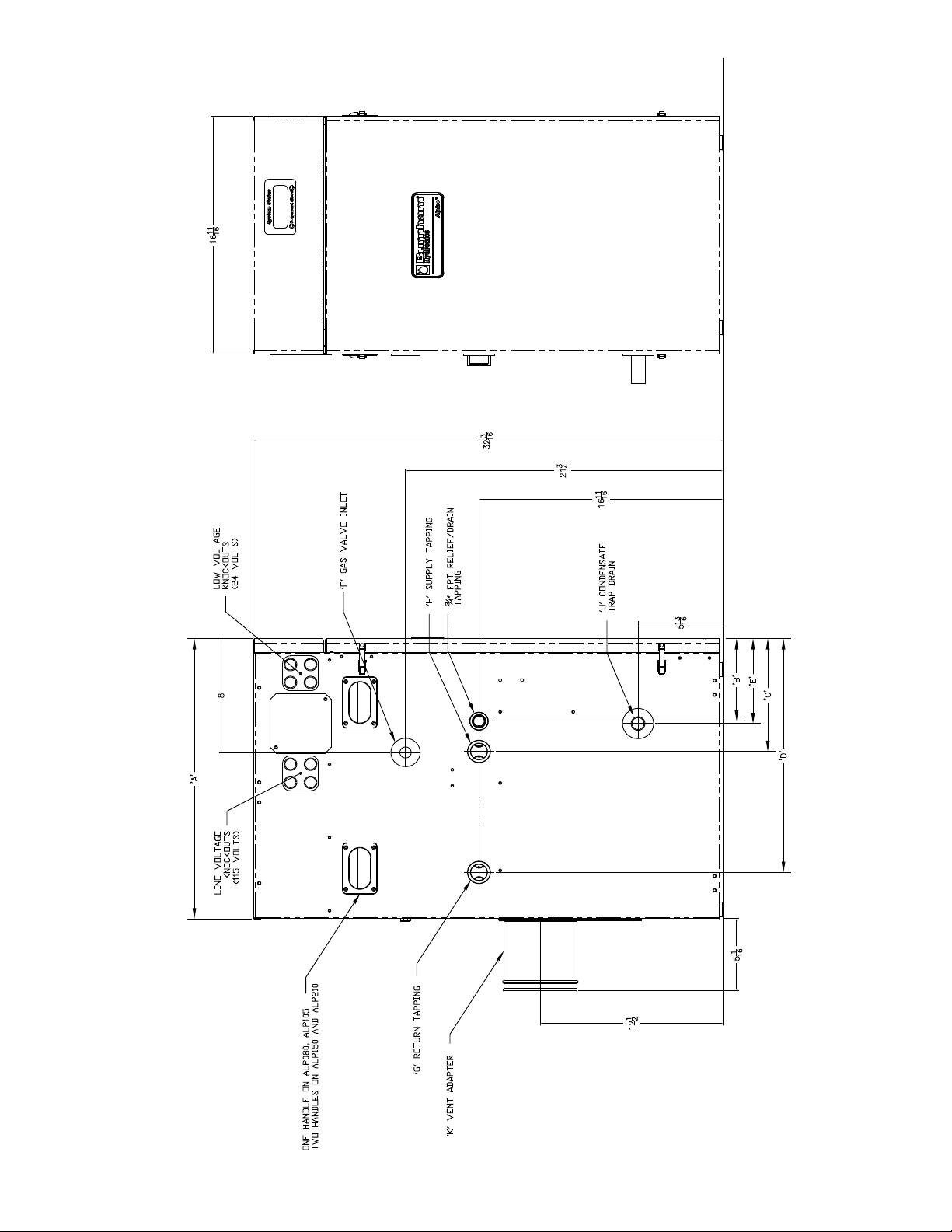
Figure 1a: alpine™ - Models aLP080 thru aLP210
5
Page 6
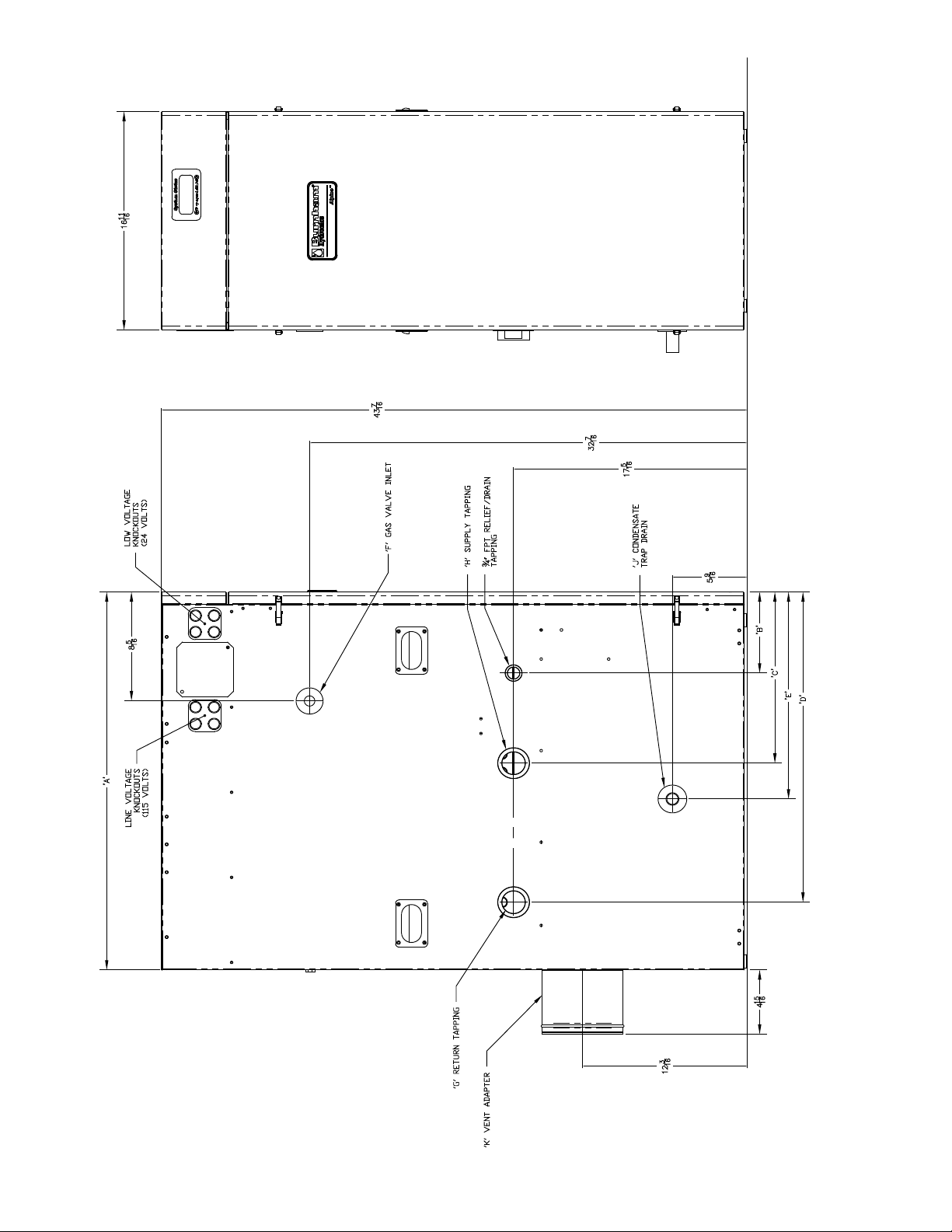
Figure 1B: alpine™ - Models aLP285 thru aLP399
6
Page 7

Table 2a: Rating Data - Models aLP080 thru aLP399 (0 to 2000 Feet Elevation above Sea Level)
alpine Series gas-Fired Boilers
* Model
Number
ALP080 16 80 73 63 95 0.6 7.3
ALP105 21 105 96 83 95 0.7 9.1
ALP150 30 150 138 120 95 1.3 16.4
ALP210 42 210 194 169 95 1.7 21.8
ALP285 57 285 265 230 95 2.4 29.1
ALP399 80 399 377 328 94.1 94.5 3.4 41.8
(MBH)
Min. Max.
** Output
(MBH)
Input
Net I=B=R
Ratings
Water (MBH)
AFUE
%
Thermal
Efciency
(%)
Combustion
Efciency (%)
Boiler Water
Volume
(Gal.)
Heat Transfer
Area
(Sq. Ft.)
* Add Sufx “N” for Natural Gas or Sufx “P” for LP Gas Models.
notes: ** DOE Heating Capacity (ALP080 thru ALP285); Gross Output (ALP399)
Maximum Working Pressure, Water - 30 PSI Shipped from Factory (std.); 50 PSI - Optional (ALP080 thru ALP285)
Maximum Working Pressure, Water - 50 PSI Shipped from Factory (std.); (ALP399)
Maximum Allowable Temperature, Water - 210°F
Boilers are factory shipped as Natural Gas builds and have to be eld adjusted for LP gas application. Refer to ‘System Start-
Up Section of this manual for detailed procedure.
Ratings shown are for installations at sea level and elevations up to 2000 Feet. For elevations above 2000 Feet, ratings should be
reduced at the rate of four percent (4%) for each 1000 Feet above sea level.
Table 2B: Rating Data - Models aLP080 thru aLP399 (2001 to 7000 Feet Elevation above Sea Level)
alpine Series gas-Fired Boilers
Model
Number *
ALP080 27 80 73 63 95 0.6 7.3
ALP105 35 105 96 83 95 0.7 9.1
ALP150 50 150 138 120 95 1.3 16.4
ALP210 70 210 194 169 95 1.7 21.8
ALP285 57 285 265 230 95 2.4 29.1
ALP399 80 399 377 328 94.1 94.5 3.4 41.8
(MBH)
Min. Max.
** Output
(MBH)
* Add Sufx “N” for Natural Gas or Sufx “P” for LP Gas Models.
notes: ** DOE Heating Capacity (ALP080 thru ALP285); Gross Output (ALP399)
Maximum Working Pressure, Water - 30 PSI Shipped from Factory (std.); 50 PSI - Optional
Maximum Allowable Temperature, Water - 210°F
Boilers are factory shipped as Natural Gas builds and have to be eld adjusted for LP gas application. Refer to ‘System Start-
Up Section of this manual for detailed procedure.
For elevations above 2000 Feet, ratings should be reduced at the rate of four percent (4%) for each 1000 Feet above sea level.
Input
Net I=B=R
Ratings
Water (MBH)
AFUE
%
Thermal
Efciency
(%)
Combustion
Efciency (%)
Boiler Water
Volume
(Gal.)
Heat Transfer
Area (Sq. Ft.)
7
Page 8

ii. Pre-installation
WaRning
if you do not follow these instructions exactly,
a re or explosion may result causing property
damage or personal injury.
DangER
Do not install boiler where gasoline or other
ammable vapors or liquids, or sources of
hydrocarbons (i.e. bleaches, cleaners, chemicals,
sprays, paint removers, fabric softeners, etc.) are
used or stored.
nOTiCE
Due to the low water content of the boiler, missizing of the boiler with regard to the heating
system load will result in excessive boiler cycling
and accelerated component failure. Burnham
DOES nOT warrant failures caused by mis-sized
boiler applications. DO nOT oversize the boiler to
the system. Modular boiler installations greatly
reduce the likelihood of boiler oversizing.
A. Installation must conform to the requirements of the
authority having jurisdiction. In the absence of such
requirements, installation must conform to the National
Fuel Gas Code, NFPA 54/ANSI Z223.1, and/or CAN/
CSA B149.1 Installation Codes.
B. Appliance is design certied for installation on
combustible ooring. Do not install boiler on
carpeting.
C. Provide clearance between boiler jacket and
combustible material in accordance with local re
ordinance. Refer to Figure 2 for minimum listed
clearances from combustible material. Recommended
service clearance is 24 inches from left side, front, top
and rear of the boiler. Recommended front clearance
may be reduced to the combustible material clearance
providing:
1. Access to boiler front is provided through a door or
removable front access panel.
2. Access is provided to the condensate trap located
underneath the heat exchanger.
D. Install on level oor. For basement installation provide
a solid base such as concrete, if oor is not level or if
water may be encountered on oor around boiler. Floor
must be able to support weight of boiler, water and all
additional system components.
E. Protect gas ignition system components from water
(dripping, spraying, rain, etc.) during boiler operation
and service (circulator replacement, condensate trap,
control replacement, etc.).
F. Provide combustion and ventilation air in accordance
with applicable provisions of local building codes,
or: USA - National Fuel Gas Code, NFPA 54/ANSI
Z223.1, Air for Combustion and Ventilation;
Canada - Natural Gas and Propane Installation Code,
CAN/CSA-B149.1, Venting Systems and Air Supply for
Appliances.
WaRning
Adequate combustion and ventilation air must
be provided to assure proper combustion.
G. The boiler should be located so as to minimize the
length of the vent system. The PVC combustion
air piping, or the optional concentric vent piping,
containing integral combustion air inlet piping, must
terminate where outdoor air is available for combustion
and away from areas that may contaminate combustion
air. In particular, avoid areas near chemical products
containing chlorines, chloro/uorocarbons, paint
removers, cleaning solvents and detergents. Avoid
areas containing saw dust, loose insulation bers, dry
wall dust etc.
CaUTiOn
avoid operating this boiler in an environment
where saw dust, loose insulation bers, dry wall
dust, etc. are present. if boiler is operated under
these conditions, the burner interior and ports
must be cleaned and inspected daily to insure
proper operation.
8
Page 9

Figure 2: Clearances To Combustible and non-combustible Material
iii. Unpacking Boiler
CaUTiOn
Do not drop boiler.
A. Move boiler to approximate installed position.
B. Remove all crate fasteners.
D. Remove boiler from cardboard positioning sleeve on
shipping skid.
WaRning
installation of this boiler should be undertaken
only by trained and skilled personnel from a
qualied service agency.
C. Lift and remove outside container.
E. Move boiler to its permanent location.
9
Page 10

iV. Venting
WaRning
Failure to vent this boiler in accordance with these instructions could cause products of combustion to
enter the building resulting in severe property damage, personal injury or death.
Do not interchange vent systems or materials unless otherwise specied.
The use of thermal insulation covering pipe and ttings is prohibited.
Do not use a barometric damper, draft hood or vent damper with this boiler.
The use of CPVC is required when venting in chase ways and through interior wall penetrations.
Do not locate vent termination where exposed to prevailing winds. Moisture and ice may form on
surface around vent termination. To prevent deterioration, surface must be in good repair (sealed,
painted, etc.).
Do not locate vent termination where chlorines, chloro/uorocarbons (CFC’s), petroleum distillates,
detergents, volatile vapors or other chemicals are present. Severe boiler corrosion and failure will
result.
The use of cellular core PVC (
Do not locate vent termination under a deck.
Do not reduce size of vent/combustion air pipe diameter.
When installing vent pipe through chimney, no other appliance can be vented into the chimney.
Do not allow low spots in the vent where condensate may pool.
aSTM F891) is prohibited.
A. Vent Guidelines Due to Removal of an Existing
Boiler
For installations not involving the replacement of an
existing boiler, proceed to Step B.
When an existing boiler is removed from a common
venting system, the common venting system is likely
to be too large for proper venting of the remaining
appliances. At the time of removal of an existing
boiler, the following steps shall be followed with each
appliance remaining connected to the common venting
system placed in operation, while the other appliances
remaining connected to the common venting system are
not in operation:
1. Seal any unused openings in the common venting
system.
2. Visually inspect the venting system for proper
size and horizontal pitch and determine there is no
blockage or restriction, leakage, corrosion, and other
deciencies which could cause an unsafe condition.
3. Insofar as is practical, close all building doors and
windows and all doors between the space in which
the appliances remaining connected to the common
venting system are located and other spaces of the
building. Turn on clothes dryers and any appliance
not connected to the common venting system.
Turn on any exhaust fans, such as range-hoods and
bathroom exhausts, so they will operate at maximum
speed. Do not operate a summer exhaust fan. Close
replace dampers.
4. Place in operation the appliance being inspected.
Follow the Lighting (or Operating) Instructions.
Adjust therm
continuously.
5. Test for spillage at the draft hood relief opening
after ve (5) minutes of main burner operation. Use
the ame of a match or candle, or smoke from a
cigarette, cigar or pipe.
6. After it has been determined that each appliance
remaining connected to the common venting system
properly vents when tested as outlined above, return
doors, windows, exhaust fans, replace dampers and
any other gas burning appliance to their previous
conditions of use.
7. Any improper operation of the common venting
system should be corrected so the installation
conforms with the National Fuel Gas Code, NFPA
54/ANSI Z223.1. When resizing any portion of the
common venting system, the common venting
system should be resized to approach the minimum
size as determined using the appropriate tables in
Part II in the National Fuel Gas Code, NFPA 54/
ANSI Z223.1.
ostat so appliance will operate
B. General Guidelines
1. Vent system installation must be in accordance
with National Fuel Gas Code, NFPA 54/ANSI
Z221.3 or applicable provisions of local building
codes. Contact local building or re ofcials about
restrictions and installation inspection in your area.
10
Page 11
2. The Alpine™ is designed to be installed as a Direct
Vent boiler. The air for combustion is supplied
directly to the burner enclosure from outdoors and
ue gases are vented directly outdoors (through wall
or roof).
3. The following combustion air/vent system options
are approved for use with the Alpine™ boilers:
i. Two-Pipe CPVC/PVC Gas Vent/Combustion
Air System (factory standard) - separate
CPVC/PVC pipe serves to expel products of
combustion and separate PVC pipe delivers fresh
outdoor combustion air. Refer to Paragraph C
through F for specic details.
ii. Combination Concentric Gas Vent/
Combustion Air Inlet (optional) - the assembly
consists of inner re resistant polypropylene
vent pipe and outer steel pipe casing. The inner
pipe serves as conduit to expel products of
combustion, while outdoor fresh combustion air
is drawn through the space between the inner and
outer pipes. Refer to Paragraphs G through P for
specic details.
4. Refer to Table 3 and the appropriate drawings to
determine the proper conguration of either factory
standard or optional venting/combustion air system
details.
C. The following information is applicable for Two-
Pipe CPVC/PVC Gas Vent/Combustion Air System
(factory standard).
WaRning
all CPVC vent components (supplied with boiler)
must be used for near-boiler vent piping before
transitioning to Schedule 40 PVC pipe (aSTM
2665) components for remainder of vent system.
CPVC vent components must be used prior to
exit of any closet or conned space.
See
Table 6 for complete list of Burnham Vent
System Components. Use single wall thimble
[Burnham Part No. 102180-01 (3”), 102181-01 (4”)]
when penetrating a combustible wall for vent only.
Horizontal vent pipe must maintain a minimum ¼
1.
inch per foot slope down towards boiler.
2. Use noncombustible ¾ inch pipe strap to support
horizontal runs and maintain vent location and slope
while preventing sags in pipe. Maximum support
spacing is four (4) feet. Avoid low spots where
condensate may pool. Do not penetrate any part of
the vent system with fasteners.
WaRning
all condensate that forms in the vent must be
able to drain back to the boiler.
3.
Vent length restrictions are based on equivalent
length of vent/combustion air pipe (total length
of straight pipe plus equivalent length of ttings).
Maximum vent/combustion air lengths are listed in
Table 7. Do not exceed maximum vent/combustion
air lengths. Table 6 lists equivalent lengths for
ttings. Do not include vent/combustion air
terminals in equivalent feet calculations. See
“Combustion Air/Vent, Equivalent Length Work
Sheet”.
4. Provide minimum service clearance between boiler
back and concentric vent exiting through outside
wall, for concentric vent installation/replacement
and/or ue temperature sensor service/replacement.
5. Do not install venting system components on
the exterior of the building except as specically
required by these instructions. The vent termination
location is restricted as follows (refer to Figures 6
and 9):
a.
Minimum twelve (12) inches above grade plus
normally expected snow accumulation level, or
seven (7) feet above grade, if located adjacent
Table 3: Combustion air/Vent System Options
Option Description
TWO-PiPE
CPVC/PVC
HORizOnTaL
TWO-PiPE
CPVC/PVC
ERTiCaL
V
COnCEnTRiC
HORizOnTaL
COnCEnTRiC
VERTiCaL
Direct Vent (sealed combustion) with both the vent pipe and
combustion air pipe terminating horizontally (through a sidewall)
with individual penetrations for the vent and combustion air
piping and terminals.
Direct Vent (sealed combustion) with both the vent pipe and
combustion air pipe terminating vertically (through the roof) with
individual penetrations for the vent and combustion air piping
and terminals.
Direct Vent (sealed combustion) the concentric vent pipe
terminates horizontally (through a sidewall).
Direct Vent (sealed combustion) the concentric vent pipe
terminates vertically (through the roof).
additional
Vent Kit
Required
no See Table 4 See Figure 6
no See Table 4
o See Table 9 See Figure 13
n
Yes See Table 9 See Figure 19
Components
included with
Boiler
installation
Drawing and
Specication
See Figures
9 and 10
11
Page 12
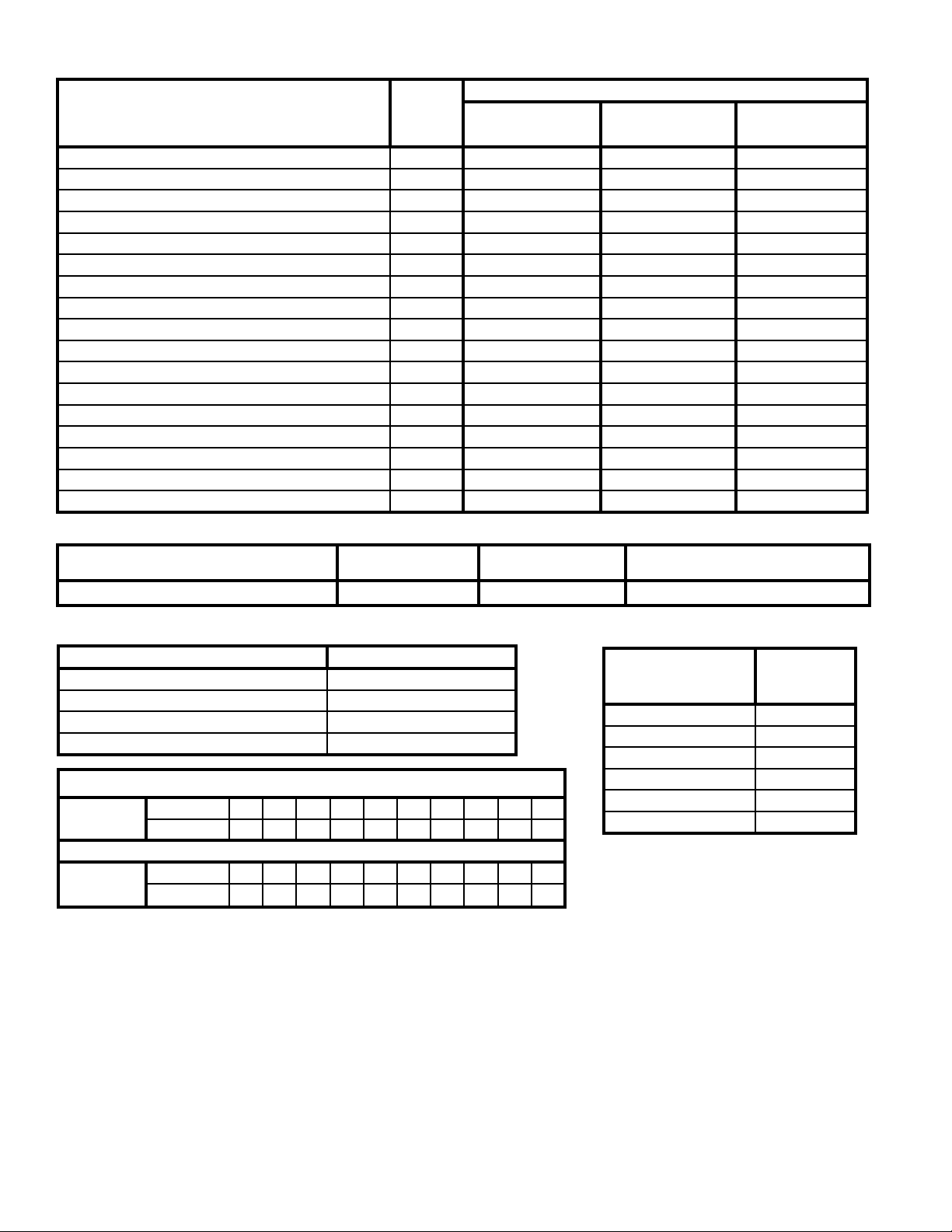
Table 4: Vent System Components included with Boiler
Vent System Components
3” Schedule 40 PVC Tee Combustion Air/Vent Terminal 102190-01 2 1 ---
4” Schedule 40 PVC Tee Combustion Air/Vent Terminal 102190-02 --- 1 2
3” Stainless Steel Rodent Screens 102191-01 2 1 --4” Stainless Steel Rodent Screens 102191-02 --- 1 2
3” x 30” Schedule 40 CPVC Pipe 102193-01 1 1 --4” x 30” Schedule 40 CPVC Pipe 102193-02 --- --- 1
3” Schedule 80 CPVC 90° Elbow 102192-01 1 1 ---
4” Schedule 80 CPVC 90° Elbow 102192-02 --- --- 1
8 oz. Bottle of Transition Cement 102195-01 1 1 1
8 oz. Bottle of Primer 102194-01 1 1 1
Burnham Vent Supplement Manual 102188-01 1 1 1
Two Pipe Vent System Connector for CPVC/PVC 102183-01 1 --- --Two Pipe Vent System Connector for CPVC/PVC 102183-02 --- 1 --Two Pipe Vent System Connector for CPVC/PVC 102183-03 --- --- 1
Two Pipe Vent System Connector for CPVC/PVC Gasket 102185-01 1 1 ---
Two Pipe Vent System Connector for CPVC/PVC Gasket 102185-02 --- --- 1
Silicone Vent Sensor Cap 102153-01 1 1 1
Part
Number
ALP080 & ALP105
(P/N 102189-01)
ALP150 & ALP210
(P/N 102189-02)
ALP285 & ALP399
(P/N 102189-03)
Table 5: Clearances from Vent Piping to Combustible Material
Quantity
Vent Pipe Pipe Direction Enclosure
CPVC/PVC Venting Vertical or Horizontal Enclosed at all Sides 1” Vent/0” Combustion Air
Minimum Clearance To
Combustible Material, Inches
Table 6: Burnham Vent System and Combustion air System Components
Vent System Component Equivalent Length (Ft.)
3” Schedule 40 CPVC Pipe x 30 Inches 2.5
4” Schedule 40 CPVC Pipe x 30 Inches 2.5
3” Schedule 80 CPVC 90° Elbow 5
4” Schedule 80 CPVC 90° Elbow 5
Maximum Number of 90’s and Straight Pipe
Vent Pipe
Combustion
Air Pipe
b. Minimum three (3) feet above any forced
c. Direct Vent - Minimum one (1) foot below, one
d. Minimum four (4) feet horizontally from electric
# of 90’s 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
Feet of Pipe 55 50 45 40 35 30 25 20 15 10
# of 90’s 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
Feet of Pipe 55 50 45 40 35 30 25 20 15 10
to public walkway. Do not install over public
walkway where local experience indicates
appliance ue gas vapor or condensate creates a
nuisance or hazard.
combustion air located within ten (10) feet.
(1) foot horizontally from, or one (1) foot above
any door, window, or gravity air inlet.
meters, gas meters, regulators, and relief valves.
This distance may be reduced if equipment is
protected from damage due to condensation or
vapor by enclosure, overhangs, etc.
e. Minimum twelve (12) inches from overhang or
corner of building.
6. Enclose vent passing through occupied or
unoccupied spaces above the boiler with material
having a re resistance rating of at least equal to the
rating of the adjoining oor or ceiling. Maintain
minimum clearances to combustible materials. See
Figure 2 and Table 5 for details.
Combustion Air
System Component
(Parts by Others)
3” or 4” ID Pipe x 1 Ft. 1
3” or 4” ID Pipe x 2 Ft. 2
3” or 4” ID Pipe x 4 Ft. 4
3” or 4” ID Pipe x 5 Ft. 5
3” or 4” 90° Elbow 5
3” or 4” 45° Elbow 5
*Equivalent Feet of Pipe Based on
Standard 4” PVC Design
Equivalent
Feet of Pipe*
12
Page 13
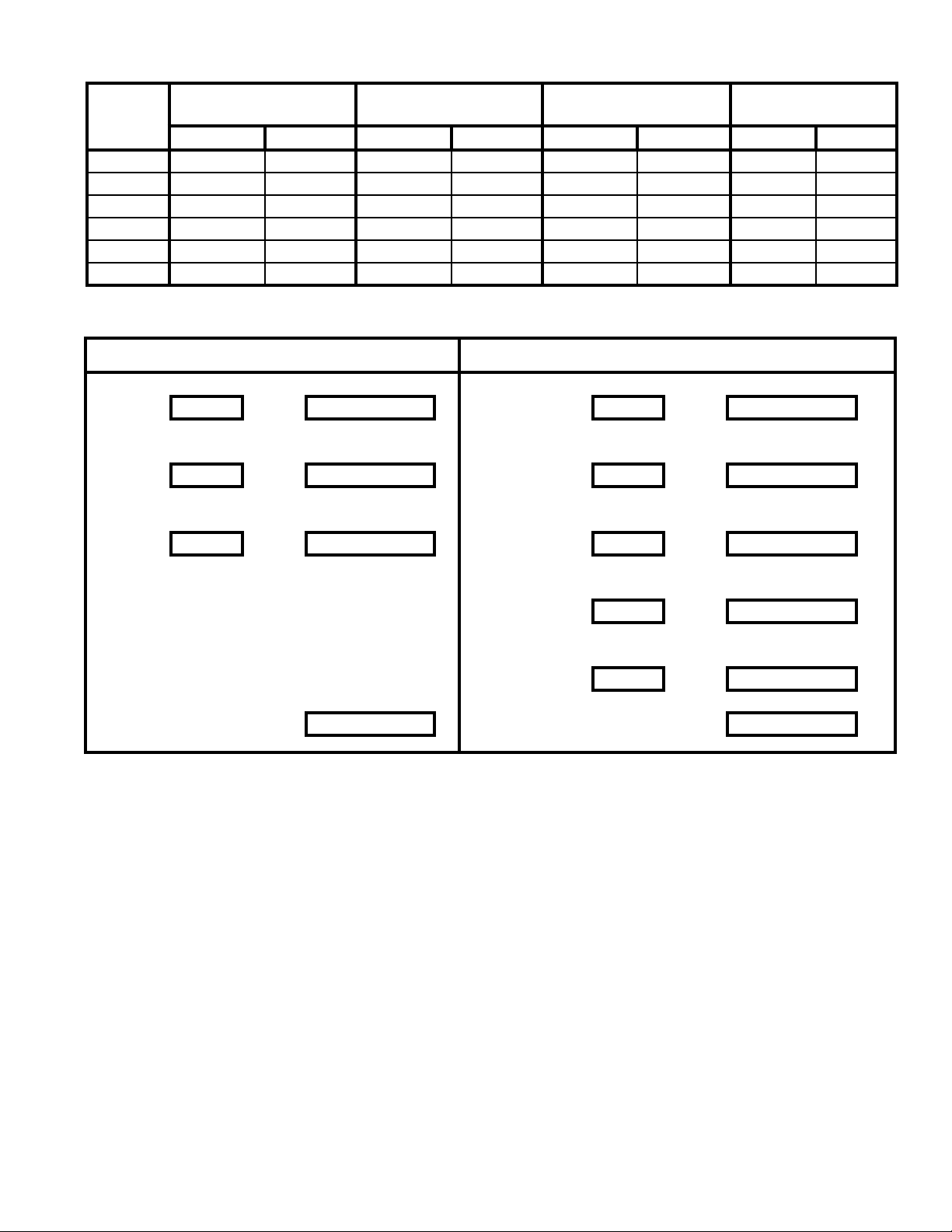
Table 7: Vent/Combustion air Pipe Length
Boiler
Model
ALP080 21-7/8 In. 60 Ft. --- --- 21-7/8 In. 60 Ft. --- --ALP105 21-7/8 In. 60 Ft. --- --- 21-7/8 In. 60 Ft. --- --ALP150 --- --- 21-7/8 In. 60 Ft. 21-7/8 In. 60 Ft. --- --ALP210 --- --- 21-7/8 In. 60 Ft. 21-7/8 In. 60 Ft. --- --ALP285 --- --- 32 In. 60 Ft. --- --- 32 In. 60 Ft.
ALP399 --- --- 32 In. 60 Ft. --- --- 32 In. 60 Ft.
3” Combustion Air Pipe
(Equivalent Length)
Min. Max. Min. Max. Min. Max. Min. Max.
4” Combustion Air Pipe
(Equivalent Length)
3” Vent Pipe
(Equivalent Length)
4” Vent Pipe
(Equivalent Length)
Combustion Air/Vent, Equivalent Length Work Sheet
This sheet is supplied to assist in vent/combustion air, equivalent length calculating
Combustion air Vent
90° elbow(s) PVC Supplied 30” straight CPVC
Quantity = x 5’ = equiv. ft. a. Length ft. = 2.5 x 1 = 2.5 equiv. ft. a.
45° elbow(s) PVC Supplied 90° elbow CPVC
Quantity = x 2.5’ = equiv. ft. b. Quantity = 1 x 5’ = 5 equiv. ft. b.
Straight pipe PVC 90° elbow(s) PVC
Length ft. = x 1 = equiv. ft. c. Quantity = x 5’ = equiv. ft. c.
45° elbow(s) PVC
Quantity = x 2.5’ = equiv. ft. d.
Straight pipe PVC
Length ft. = x 1 = equiv. ft. e.
Total* a.+b.+c. = equiv. ft. Total* a.+b.+c.+d.+e.= equiv. ft.
* Total cannot exceed 60 equiv. ft. length.
Vent and combustion air terminals do not count towards total equiv. ft.
Note: For one or two family dwellings, re
resistance rating requirement may not need to be
met, but is recommended.
7. Plan venting system to avoid possible contact with
plumbing or electrical wires. Start at vent connector
at rear of boiler and work towards vent termination.
8. Design the Vent System to allow a 3/8” of thermal
expansion per 10 feet of CPVC/PVC pipe. Runs of
20 ft. or longer that are restrained at both ends must
use an offset or expansion loop. Refer to Figure 3.
9. Follow all manufacturer instructions and warnings
when preparing pipe ends for joining and using the
primer and the cement.
D. Installation of Two-Pipe CPVC/PVC Gas Vent/
Combustion Air System Connector
The boiler two pipe vent system connector for CPVC/
PVC and gasket are shipped inside the vent carton. The
vent connector mounting hardware - six (6) #8 x ½”
black oxide round head Phillips sheet metal screws - are
shipped inside Miscellaneous Part Carton.
1. Remove the vent connector and gasket from the vent
carton.
2. Locate six mounting screws.
3. Position the vent connector and gasket onto jacket
combination rear/bottom panel and insert vent
connector inner stainless steel vent pipe into the heat
exchanger vent outlet.
4. Align vent connector plate and gasket clearance
holes with rear/bottom panel engagement holes; then
secure the collar and gasket to rear/bottom panel
with six mounting screws. See Figure 4.
5. Flue temperature sensor, factory attached to the
boiler wiring harness, is secured to the boiler rear/
bottom panel with tape.
13
Page 14
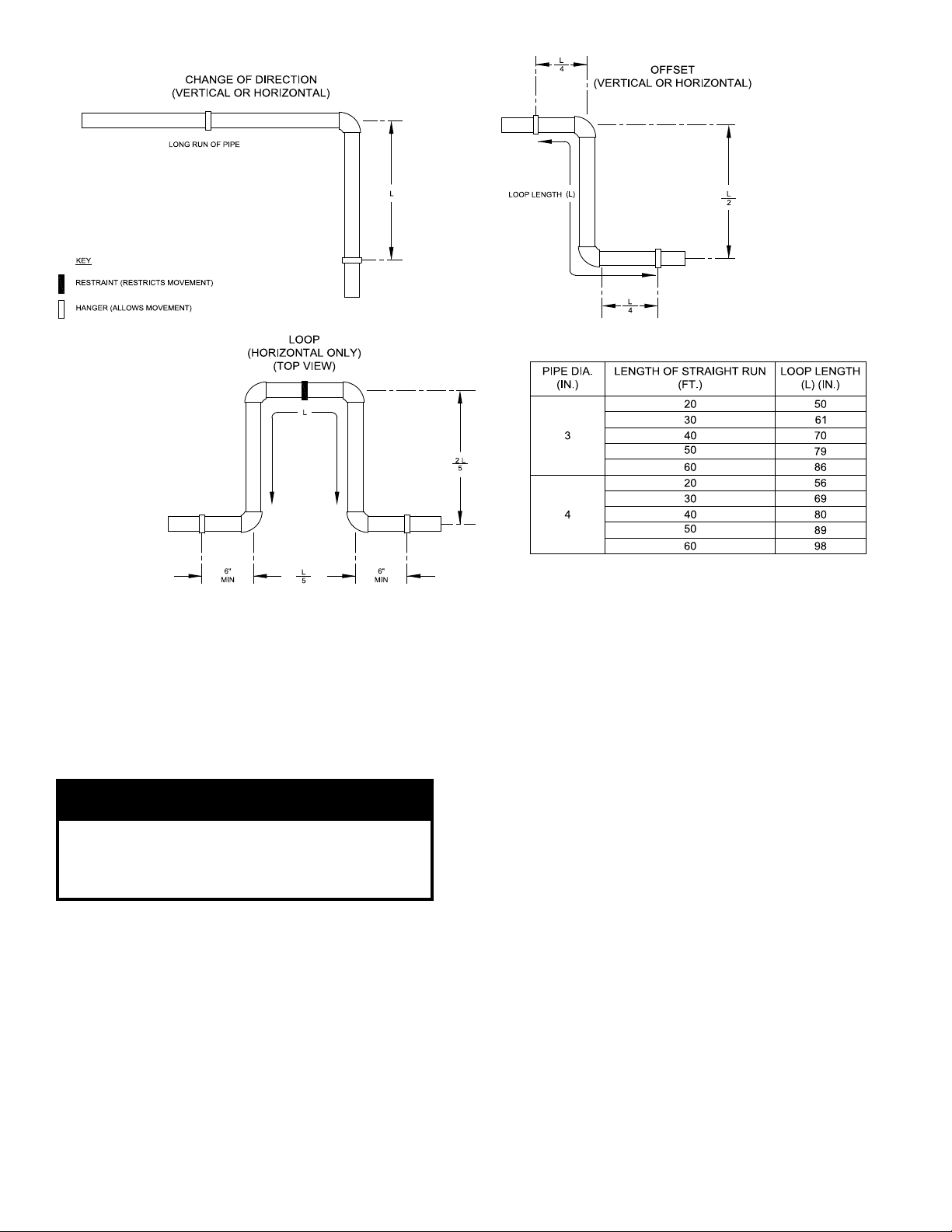
Figure 3: Expansion Loop and Offset
6. Remove the Silicone ue sensor cap from the vent
carton and press onto the two pipe vent system
connector for CPVC/PVC sensor port. Remove
the tape holding the ue sensor and insert the ue
temperature sensor into the ue sensor plug until it
is rmly engaged. See Figure 4.
7. Near-Boiler Vent Piping (see Figure 5):
WaRning
all CPVC vent components (supplied with boiler)
must be used for near-boiler vent piping before
transitioning to Schedule 40 PVC pipe (aSTM
2665) components for remainder of vent system.
a. All CPVC vent components (supplied with
boiler), 30” straight and 90° elbow, must be
used for near-boiler piping before transitioning
to Schedule 40 PVC (ASTM 2665) pipe
components for remainder of vent system.
The CPVC 30” straight section may be cut to
accommodate desired vent conguration for
near-boiler piping, provided both pieces are used
in conjunction with the CPVC 90° elbow, before
any PVC components are used. Ensure that the
CPVC elbow is the rst elbow used in the vent
system as it exits the boiler.
14
b.
Clean all vent and combustion air pipe joints
with primer and secure with transition cement,
(8 oz. bottle of primer and 8 oz. bottle of
transition cement supplied with boiler). Follow
the instructions provided on the primer and
cement.
E. CPVC/PVC Horizontal Venting System
See Figures 3 thru 8.
Vent Piping - Horizontal
1. See Paragraph D for instructions on attaching the
vent system connector to the boiler.
2. Do not exceed maximum vent length. Refer to
Table 7 for pipe diameters and allowable lengths.
3. Horizontal vent pipe must maintain a minimum ¼
inch per foot slope down towards boiler.
4. Use appropriately designed thimbles when passing
through combustible walls (thimble use is optional
for noncombustible walls). Insert thimble through
wall from outside. Secure outside ange to wall
with nails or screws, and seal ID, OD and vent holes
with sealant material. Install inside ange to inside
wall, secure with nails or screws, and seal with
sealant material.
5. For noncombustible wall application when thimble
is not used, size opening such that a minimal
clearance is obtained.
Page 15
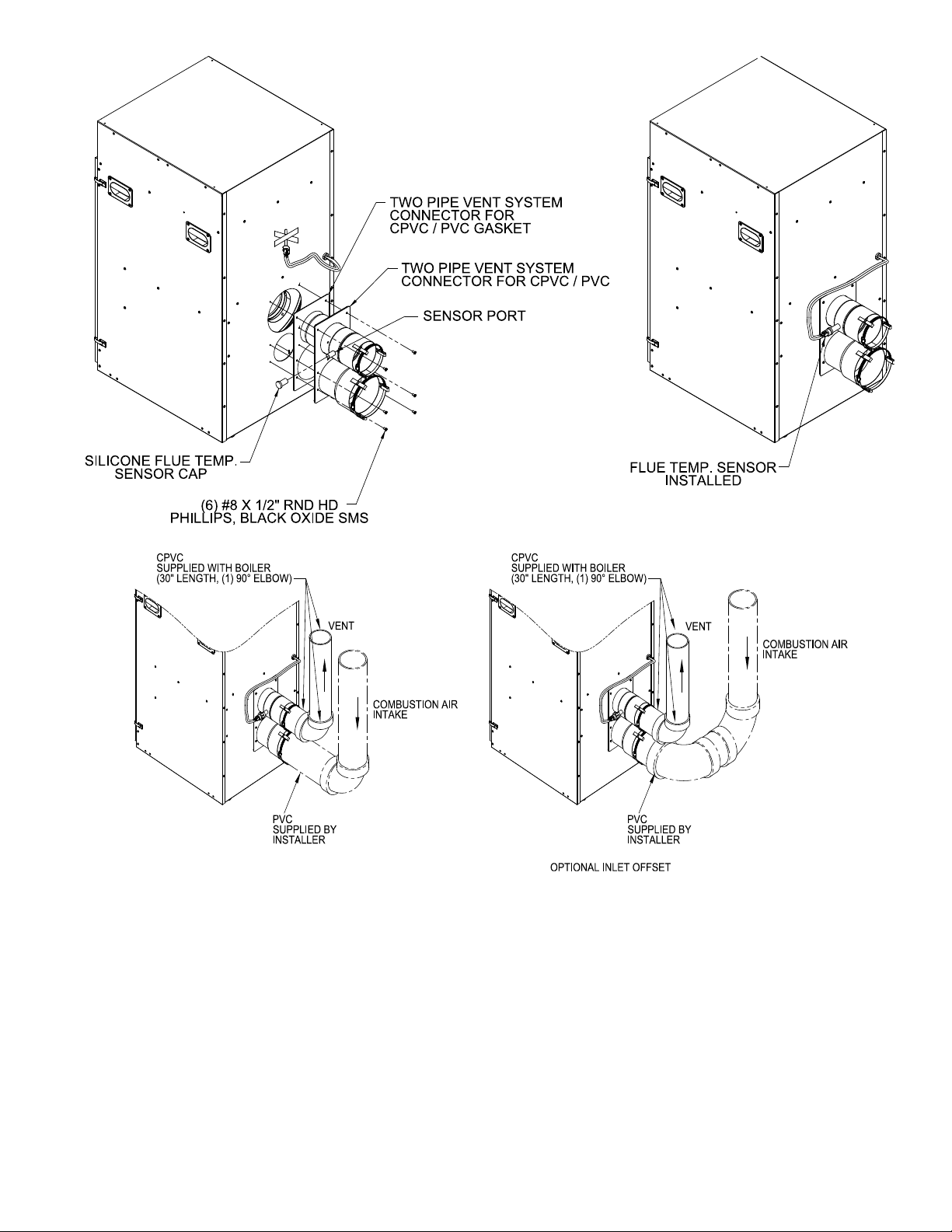
Figure 4: Field installation of Two Pipe Vent System Connector for CPVC/PVC
Figure 5: near-Boiler Vent/Combustion air Piping
6. Install Rodent Screen and Vent Terminal (supplied
with boiler), see Figure 8 for appropriate
conguration.
7. Apply sealant between vent pipe and opening/
thimble to provide weather-tight seal. Sealant
should not restrain the expansion of the vent pipe.
Combustion Air Piping - Horizontal
1. See Paragraph D for instructions on attaching the
vent system connector to the boiler.
2. Do not exceed maximum combustion air length.
Refer to Table 7 for pipe diameters and allowable
lengths.
3. Horizontal combustion air pipe must maintain a
minimum ¼ inch per foot slope down towards
terminal, when possible. If not, slope toward boiler.
4.
It is strongly recommended to locate the combustion
air terminal on the same wall as the vent termination
to prevent nuisance boiler shutdowns. Combustion
air terminal can be installed closer to wall than vent.
5. Start at vent connector (rear boiler jacket) and work
towards the combustion air terminal.
6. Size combustion air wall penetration to allow easy
insertion of combustion air piping.
15
Page 16
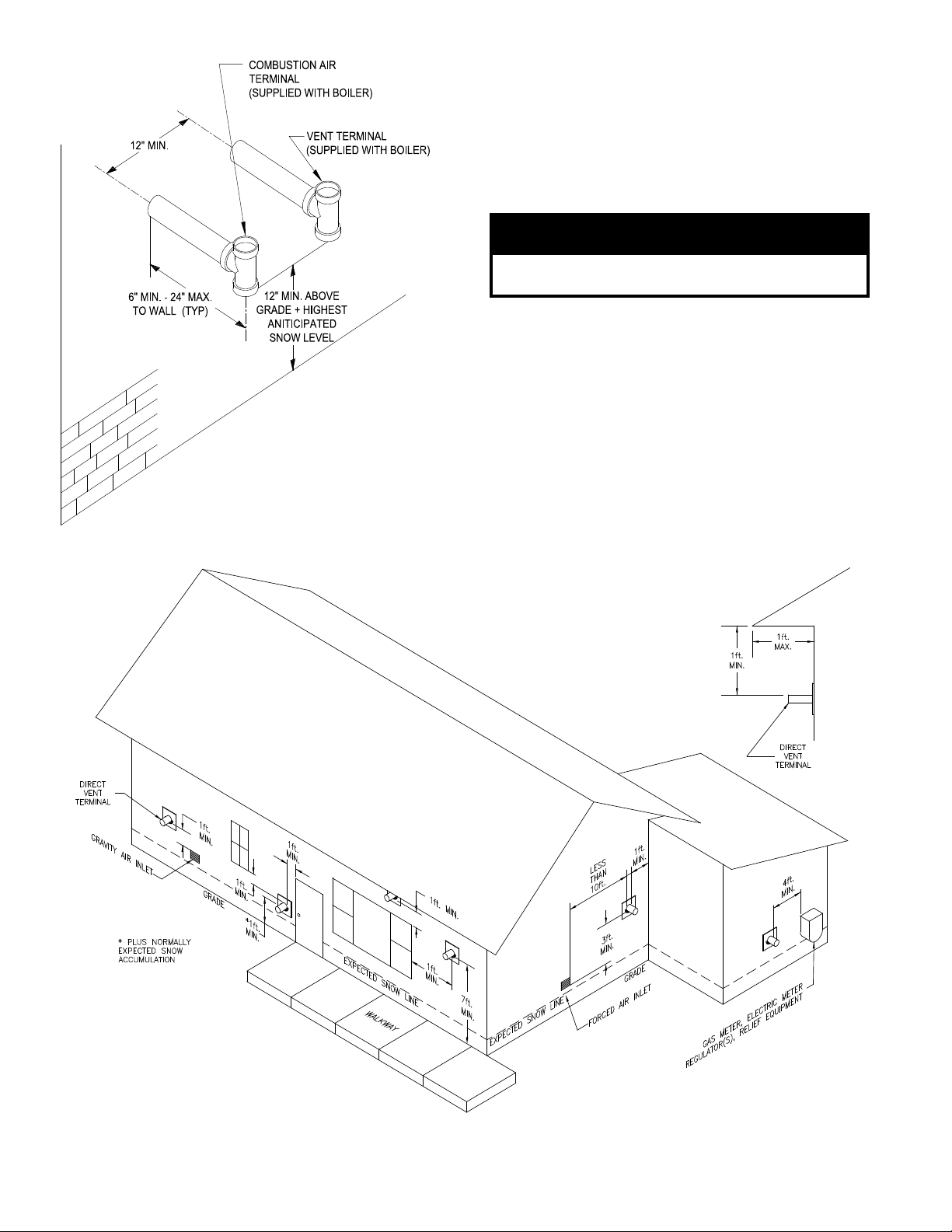
Figure 6 : Direct Vent - Side Wall Terminations
7. Install Rodent Screen and Combustion Air Terminal
(supplied with boiler), see Figure 8 for appropriate
conguration.
8. Apply sealant between vent pipe and opening to
provide weather-tight seal
F. CPVC/PVC Vertical Venting System
Refer to Figures 3, 4, 5, 8, 9 & 10.
nOTiCE
Roof penetrations require the use of roof ashing
and storm collar that are not supplied with boiler.
Vent Piping - Vertical
1. See Paragraph D for instructions on attaching the
vent system connector to the boiler.
2. Do not exceed maximum vent length. Refer to
Table 7 for pipe diameters and allowable lengths.
3. Horizontal vent pipe must maintain a minimum ¼
inch per foot slope down towards boiler.
4. Install re stops where vent passes through oors,
ceilings or framed walls. The re stop must close
the opening between the vent pipe and the structure.
5. Whenever possible, install vent straight through the
roof. Refer to Figures 9 and 10.
16
Figure 7: Location of Vent Terminal Relative to Windows, Doors, grades,
Overhangs, Meters and Forced air inlets (Combustion air Terminal not shown)
Page 17

Figure 8: Rodent Screen
a. Size roof opening to maintain minimum
clearance of 1 inch from combustible materials.
b. Extend vent pipe to maintain minimum vertical
and horizontal distance of twelve (12) inches
from roof surface. Allow additional vertical
distance for expected snow accumulation.
Provide brace as required.
CaUTiOn
Vertical venting requires the use of roof ashing
and a storm collar to prevent moisture from
entering the structure.
c. Install storm collar on vent pipe immediately
above ashing. Apply Dow Corning Silastic 732
RTV Sealant between vent pipe and storm collar
to provide weather-tight seal.
6.
Install Rodent Screen and Vent Terminal (supplied
with boiler), see Figure 8 for appropriate
conguration.
installation
Figure 9: Direct Vent - Vertical Terminations
Figure 10: Direct Vent - Vertical Terminations with Sloped Roof
Extend vent/combustion air piping to maintain minimum vertical (‘X’) and minimum horizontal (‘Y’) distance of
twelve (12) inches (18 inches Canada) from roof surface. a
snow accumulation.
llow additional vertical (‘X’) distance for expected
17
Page 18
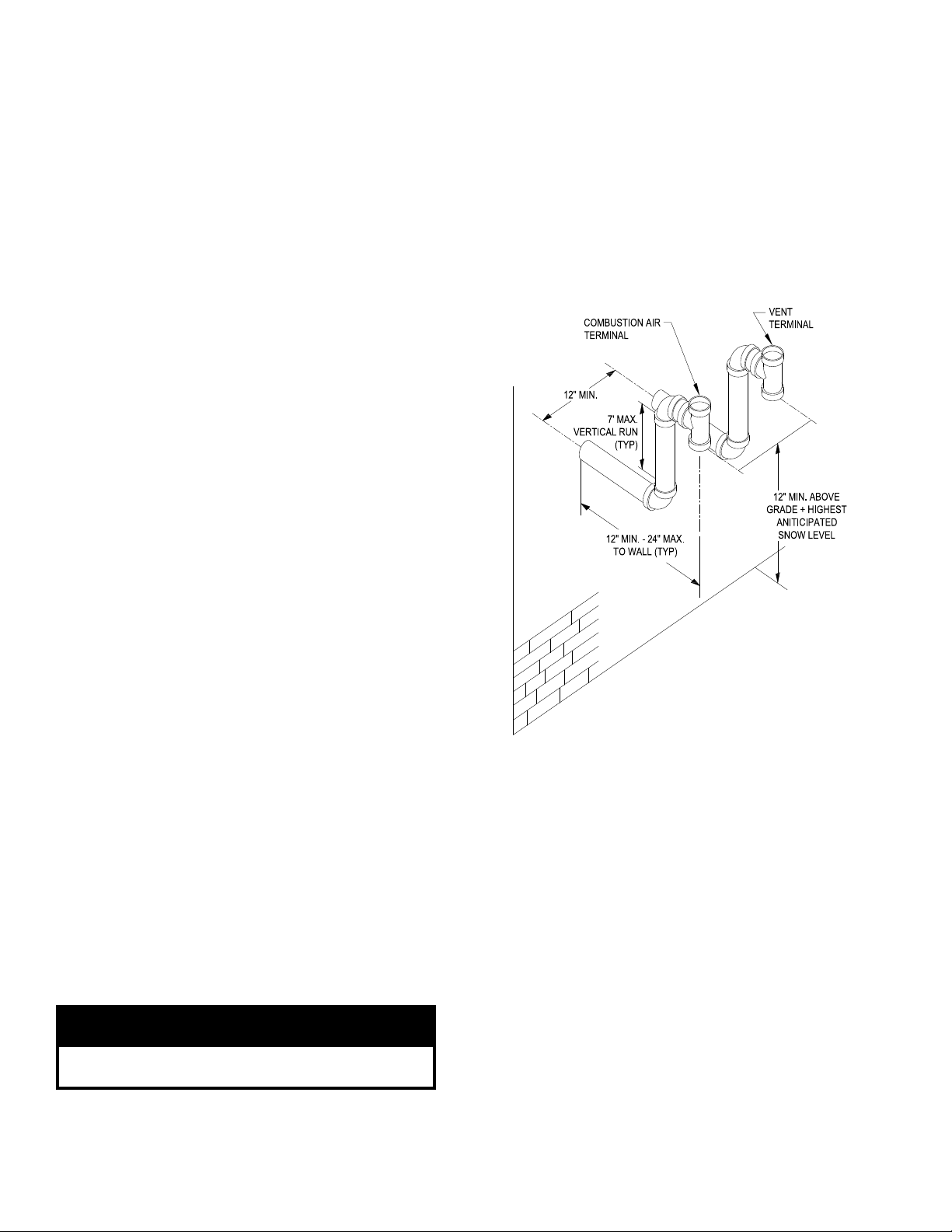
7. Brace exterior piping if required.
Combustion Air Piping - Vertical
1. See Paragraph D for instructions on attaching the
vent system connector to the boiler.
2. Do not exceed maximum combustion air length.
Refer to Table 7 for pipe diameters and allowable
lengths.
3. Horizontal combustion air pipe must maintain a
minimum ¼ inch per foot slope down towards
boiler.
4. Locate combustion air termination on the same roof
location as the vent termination to prevent nuisance
boiler shutdowns. Combustion air terminal can be
installed closer to roof than vent.
5. Start at vent connector on burner enclosure (rear
boiler jacket) and work towards the combustion air
terminal.
6. Size roof opening to allow easy insertion of
combustion air piping and allow proper installation
of ashing and storm collar to prevent moisture
from entering the structure.
a. Use appropriately designed vent ashing
when passing through roofs. Follow ashing
manufacturers’ instructions for installation
procedures.
b. Extend combustion air pipe to maintain
minimum vertical and horizontal distance of
twelve (12) inches from roof surface. Allow
additional vertical distance for expected snow
accumulation. Provide brace as required.
c. Install storm collar on combustion air pipe
immediately above ashing. Apply Dow
Corning Silastic 732 RTV Sealant between
combustion air pipe and storm collar to provide
weather-tight seal.
7. Install Rodent Screen and Combustion Air Terminal
(supplied with boiler), see Figure 8 for appropriate
conguration.
8. Brace exterior piping if required.
G. Optional Snorkel CPVC/PVC Horizontal Vent
System
Refer to Figures 3, 4, 5, 7, 8 and 11.
This installation will allow a maximum of seven (7) feet
vertical exterior run of the vent/combustion air piping
to be installed on the CPVC/PVC horizontal venting
application (Section E).
nOTiCE
Exterior run to be included in equivalent vent/
combustion air lengths.
18
Vent Piping - Snorkel
1. See Paragraph D for instructions on attaching the
vent system connector to the boiler.
2. Do not exceed maximum vent length. Refer to
Table 7 for pipe diameters and allowable lengths.
3. Horizontal vent pipe must maintain a minimum ¼
inch per foot slope down towards boiler
4. After penetrating wall/thimble, install a Schedule
40 PVC 90° elbow so that the elbow leg is in the up
direction.
5. Install maximum vertical run of seven (7) feet of
Schedule 40 PVC vent pipe. See Figure 11.
Figure 11: Direct Vent - Optional Side Wall
Snorkel Terminations
6. At top of vent pipe length install another PVC 90°
elbow so that elbow leg is opposite the building’s
exterior surface.
7. Install Rodent Screen and Vent Terminal (supplied
with boiler), see Figure 8 for appropriate
conguration.
8. Brace exterior piping if required.
Combustion Air Piping - Snorkel
1. See Paragraph D for instructions on attaching the
vent system connector to the boiler.
2. Do not exceed maximum combustion air length.
Refer to Table 7 for pipe diameters and allowable
lengths.
3. Horizontal combustion air pipe must maintain a
minimum ¼ inch per foot slope down towards
terminal, when possible. If not, slope toward boiler.
4. After penetrating wall, install a Schedule 40 PVC
90o elbow so that elbow leg is in the up direction.
Page 19
Remove the collar from the bag and set aside.
5. Install maximum vertical run of seven (7) feet of
Schedule 40 PVC vent pipe. See Figure 11.
6. At top of vent pipe length install another PVC 90°
elbow so that elbow leg is opposite the building’s
exterior surface.
7. Install Rodent Screen and Combustion Air Terminal
(supplied with boiler), see Figure 8 for appropriate
conguration.
8. Brace exterior piping if required.
H. The following information is applicable for
Combination Concentric Gas Vent/Combustion air
System (optional).
I. Field Installation of Boiler Concentric Vent Collar
The Boiler Concentric Vent Collar is shipped inside the
boiler in plastic bag. The Collar mounting hardware
- six (6) #8 x ½” black oxide round head Phillips sheet
metal screws - are shipped inside Miscellaneous Part
Carton.
1.
Release four side draw latches and remove boiler
lower front door assembly to gain access to the Vent
Collar.
Table 8: Concentric Vent Components
Part Number Component Description Size
101493-01 90° Elbow – Long Radius 80/125 mm 5.5
101491-01 45° Elbow - Long Radius 80/125 mm 3.0
101163-01 Cut -To-Length Extension, 500 mm (19-1/2”) 80/125 mm 1.63 **Can be cut
101162-01 Cut -To-Length Extension, 1000 mm (39”) 80/125 mm 3.25 **Can be cut
101485-01 Fixed Extension, 2000 mm (78”) 80/125 mm 3.25 ***Must not be cut
101808-01 Horizontal (Wall) Terminal 80/125 mm *NA Supplied with boiler
101495-01 Vertical Roof Terminal 80/125 mm *NA See Note 1
101496-01 Flat Roof Flashing 80/125 mm
101497-01 Sloped Roof Flashing 80/125 mm See Note 2
101492-01 Support Elbow with Chimney Chase Bracket 80/125 mm 8.5 See Note 3
101498-01 Hanger Wall Bracket 80/125 mm
101548-01 90° Elbow – Long Radius 100/150 mm 8.0
101549-01 45° Elbow - Long Radius 100/150 mm 3.0
101550-01 1 Cut -To-Length Extension, 500 mm (19-1/2”) 100/150 mm 1.63 ** Can be cut
101551-01 Cut -To-Length Extension, 1000 mm (39”) 100/150 mm 3.25 ** Can be cut
101553-01 Fixed Extension, 2000 mm (78”) 100/150 mm 6.5 *** Must not be cut
101809-01 Horizontal (Wall) Terminal 100/150 mm * NA Supplied with boiler
101557-01 Vertical (Roof) Terminal 100/150 mm * NA See Note 1
101558-01 Flat Roof Flashing 100/150 mm
101559-01 Sloped Roof Flashing 100/150 mm See Note 2
101560-01 Support Elbow with Chimney Chase Bracket 100/150 mm 10.0 See Note 3
101561-01 Hanger Wall Bracket 100/150 mm
otes:
n
* NA – do not include vent terminal into total vent length calculations.
** These sections have plain male end and beaded female end. See Figure 11 for details.
*** These sections have beaded male end and beaded female end. See Figure 12 for details.
1. Vertical terminal can be used with either of the roof ashings listed beneath it.
2. Sloped roof ashing suitable for roof angles between 25° and 45°.
3. Used at base of vertical run inside unused masonry chimney.
2.
3. Locate and remove six mounting screws.
4. Position the Collar onto jacket combination rear/
bottom panel and insert collar inner stainless steel
vent pipe into the heat exchanger vent outlet.
Align collar plate clearance holes with rear/bottom
5.
panel engagement holes; then secure the collar to
rear/bottom panel with six mounting screws. See
Figure 12.
6. Flue temperature sensor, factory attached to the
boiler wiring harness, is secured to the boiler rear/
bottom panel with tape.
7. Remove the tape and push the sensor rubber plug
into Concentric Vent Collar sensor port until the
plug is securely engaged. See Figure 12.
The installation of the Concentric Vent Collar is now
completed.
J. General Guidelines - Concentric Venting
1. Vent system installation must be in accordance
with National Fuel Gas Code, NFPA 54/ANSI
Z221.3 or applicable provisions of local building
Component
Equivalent Vent
Length, Ft
Comments
19
Page 20

Figure 12: Field installation of Boiler Concentric Vent Collar
codes. Contact local building or re ofcials about
restrictions and installation inspection in your area.
2.
Horizontal vent pipe must maintain a minimum ¼
inch per foot slope towards the boiler.
3. Use noncombustible ¾ inch pipe strap to support
horizontal runs and maintain vent location and
slope while preventing sags in pipe. Do not restrict
thermal expansion or movement of vent system.
Maximum support spacing is ve (5) feet. Do not
penetrate any part of the vent system with fasteners.
4. Vent length restrictions are based on equivalent
length of vent pipe i.e. total length of straight pipe
plus equivalent length of ttings. See Table 11
for specied vent length details. Do not exceed
maximum vent length. Table 8 lists available
concentric vent components and includes equivalent
vent length for ttings. Do not include vent terminal
into total vent length calculations.
Table 9: Vent System Components included with Boiler
Vent System Components Part Number
80/125mm Horizontal (Wall) Terminal (ALP080 thru ALP210) 101808-01
100/150mm Horizontal (Wall) Terminal (ALP285 thru ALP399) 101809-01
5. Provide and maintain vent pipe minimum clearances
to combustible material. See Figure 2 and Table 10
for details.
6. Provide minimum service clearance between boiler
back and concentric vent exiting through outside
wall, for concentric vent installation/replacement
and/or ue temperature sensor service/replacement,
as follows:
a. For horizontal venting where supplied
Concentric Vent Terminal is attached directly to
installed Boiler Concentric Vent Collar - 6 inches
b. For vertical venting where optional Concentric
Vent 90° long radius elbow is attached to
installed Boiler Concentric Vent Collar - 18
inches
7. Do not install venting system components on the
exterior wall of the building except as specically
required by these instructions. Refer to Figure 7.
Table 10: Clearances from Vent Piping to Combustible Material
Vent Pipe Pipe Direction Enclosure
CPVC/PVC Venting Vertical Or Horizontal Enclosed at All Sides 1” Vent/0” Combustion Air
20
Minimum Clearance To
Combustible Material, Inches
Page 21
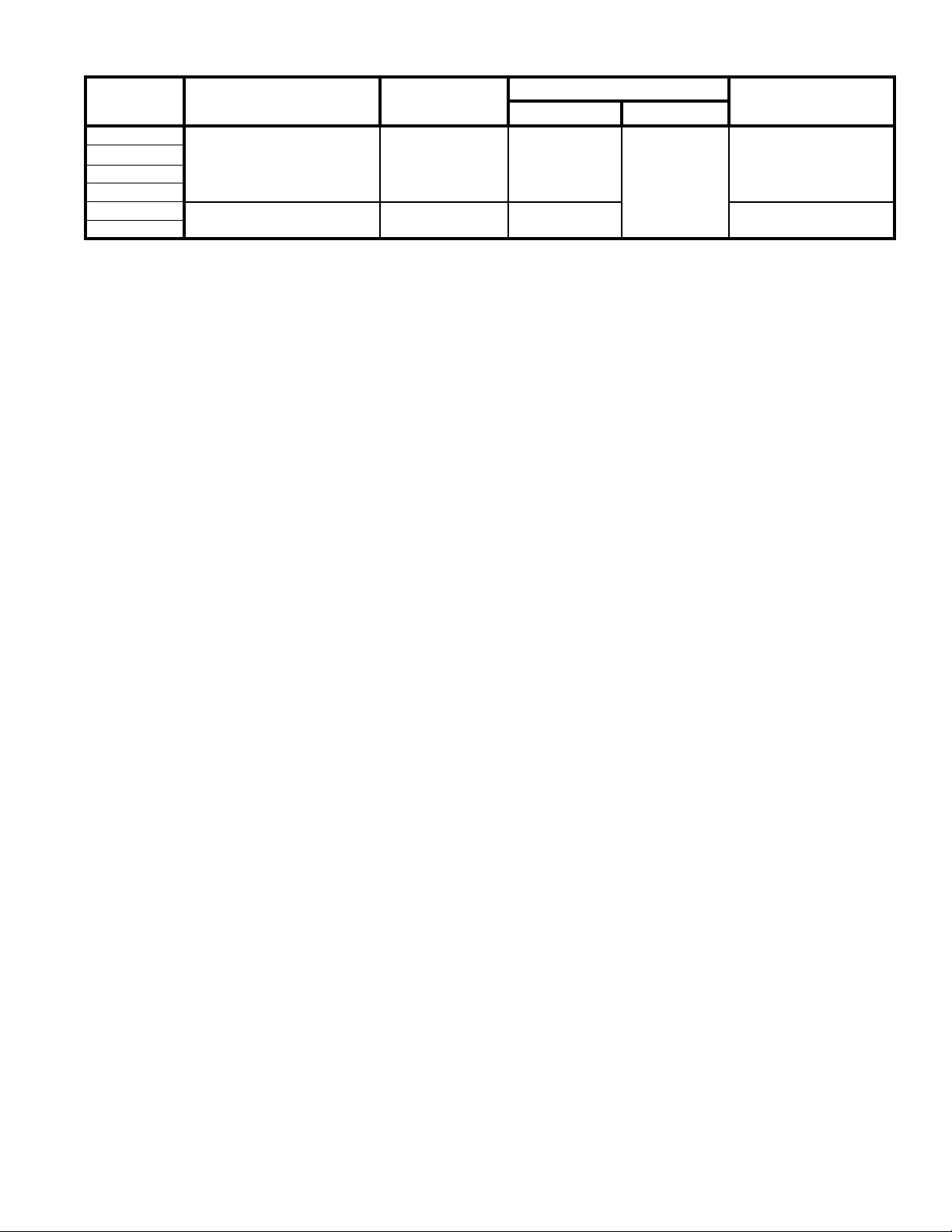
Table 11: Concentric Vent Length
Boiler Model Concentric Vent
ALP080
ALP105
ALP150
ALP210
ALP285
ALP399
ote: * With optional concentric vent components. See Table 10 for details.
n
Factory Supplied
Horizontal (Wall) Terminal
Factory Supplied
Horizontal (Wall) Terminal
Inner/Outer Pipe
Dia., mm
80/125 mm 21-7/8 in
100/150 mm 32 in 6-1/2 in
The direct vent termination location is restricted as
follows:
a. Minimum twelve (12) inches above grade plus
normally expected snow accumulation level, or
minimum seven (7) feet above grade, if direct
vent terminal is located adjacent to public
walkway. Do not install the terminal over public
walkway where local experience indicates that
appliance ue gas vapor or condensate creates a
nuisance or hazard.
b. Minimum three (3) feet above any forced air
inlet located within ten (10) feet.
c. Minimum four (4) feet horizontally from electric
meters, gas meters, regulators and relief valves.
This distance may be reduced if equipment is
protected from damage due to ue gas vapor or
condensation by enclosure, overhang, etc.
d. Minimum twelve (12) inches below, above or
horizontally from any air opening into a building
(window, door or gravity air inlet).
e. Minimum twelve (36) inches horizontally from a
building corner.
f. Minimum twelve (12) inches vertically from any
roof overhang twelve (12) inches or less wide.
If a roof overhang width exceeds twelve (12)
inches the terminal vertical clearance must be
increased to avoid ue vapor condensation.
8. Enclose vent passing through occupied or
unoccupied spaces above the boiler with material
having a re resistance rating of at least equal to the
rating of the adjoining oor or ceiling. Maintain
minimum clearances to combustible materials. See
Figure 2.
Note: For one or two family dwellings, re
resistance rating requirement may not need to be
met, but is recommended.
9. Plan venting system to avoid possible contact with
plumbing or electrical wires. Start at vent connector
on top of boiler and work towards vent terminal.
Concentric Venting - Horizontal Venting
1. Permitted terminals for horizontal venting:
Horizontal (Wall) Terminal, either 80/125 mm (P/N
101808-01) or 100/150 mm (P/N 101809-01) - see
Table 8.
Vent Length
Minimum * Maximum
Total of 60
Equivalent ft.
Wall Opening Diameter
5-1/2 in
2. Concentric Vent components supplied with the boiler
are packed inside boiler carton and include the
following:
a. 80/125 mm Horizontal (Wall) Terminal, Part
Number 101808-01
• Horizontal (Wall) Terminal consists of
Straight section having plain male end with
locking band clamp installed; Terminal
Assembly with offset vent termination,
and Outside Wall Plate, both riveted
on the opposite end; overall length is
approximately 28-1/8”.
• Separate Inside Wall Plate
• Two Hardware Bags (each bag contains
four screws and four anchors) to attach vent
terminal Outside Wall Plate to exterior wall
and Inside Wall Plate to interior wall.
b. 100/150 mm Horizontal (Wall) Terminal, Part
Number 101809-01
• Horizontal Concentric Vent Terminal, which
consists of Straight section having plain
male end with locking band clamp installed;
Terminal Assembly with offset vent
termination, and Outside Wall Plate, both
riveted on the opposite end); overall length
is approximately 31-1/8”.
• Separate Inside Wall Plate.
• Two Hardware Bags (each bag contains
four screws and four anchors) to attach vent
terminal Outside Wall Plate to exterior wall
and Inside Wall Plate to interior wall.
14. Installation of the Boiler Concentric Vent Collar is
covered in Section I above. See Figure 12.
15. For horizontal (side wall) installation, the Horizontal
(Wall) Terminal will extend past outer wall surface
either by 4-1/4” (80/125 mm), or, 5-1/2” (100/150
mm). See Figure 13 “Horizontal (Wall) Terminal
Installation”.
17. For horizontal venting, to install the Horizontal
(Wall) Terminal:
a. Cut a 5-1/2” diameter hole through the exterior
wall opening (for 80/125 mm concentric vent) or
6-1/2” diameter hole (for 100/150 mm concentric
vent) at the planned location of the horizontal
terminal.
21
Page 22
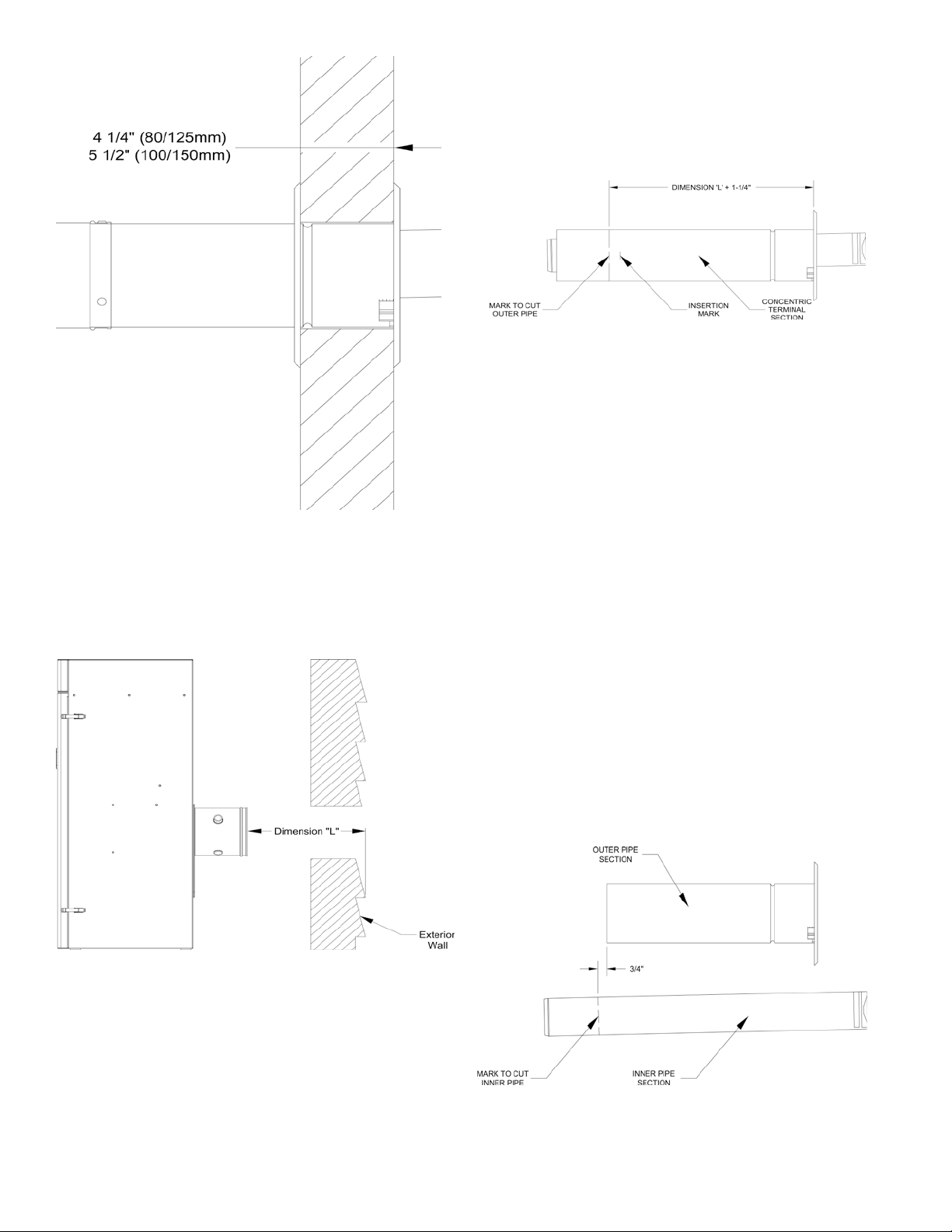
Figure 13: Horizontal (Wall) Terminal installation
b. Measure dimension “L” from exterior wall outer
surface to the end of the last tting (or end of
installed Boiler Concentric Vent Collar). See
Figure 14 ‘Dimension “L”’.
several marks around the outer pipe to establish a
cut line. See Figure 15 ‘ Cutting Outer Pipe’.
d. Carefully cut the outer pipe at the marked line
using aviation shears, a hacksaw etc. Ensure the
pipe is cut square and cut end is deburred.
Figure 15: Cutting Outer Pipe
Mark the end of the Horizontal (Wall) Terminal
e.
inner polypropylene vent pipe to extend ¾” past
the cut end of the outer pipe. To achieve a square
cut of the inner pipe, place several marks around
the inner pipe to establish a cut line.
f.
Cut off the marked end of inner polypropylene
vent pipe with a ne tooth blade hacksaw etc.
and deburr. See Figure 16 “Cutting Inner Pipe.
g. Place a mark around the outer pipe, 1” from cut
edge, towards the attached Outside Wall Plate, to
establish visual insertion line as shown in Figure
16 “Cutting Inner Pipe”.
h. Pass the shortened Horizontal Concentric Vent
from outside, thru earlier cut exterior wall
opening and push in until the attached Outside
Wall Plate is tight against exterior wall surface.
Insure the proper position of the Horizontal
Concentric Vent before securing the Outside Wall
Plate to the wall with provided fasteners. Seal
plate edges with exterior grade sealant to prevent
moisture penetration.
22
Figure 14: Dimension “L”
When factory supplied Horizontal (Wall)
c.
Terminal needs to be shortened, measure
dimension “L” plus 1-¼” from inside of the
attached Outside Wall Plate and mark the
Horizontal (Wall) Terminal outer pipe. To
achieve a square cut of the outer pipe, place
Figure 16: Cutting
inner Pipe
Page 23

WaRning
The terminal vent portion is offset towards the top
inside the outer pipe of the Horizontal Concentric
Vent Terminal to provide vent pipe pitch towards
the boiler for condensate removal.
See Figure 17 ‘Horizontal (Wall) Terminal Detail’.
it is imperative to properly mount the vent
terminal.
The terminal orientation label is located on the
inside of the terminal Outside Wall Plate. insure
the vent terminal is positioned as shown in
Figure 18 before securing the Outside Wall Plate
to exterior wall.
CaUTiOn
Exterior wall surface must be reasonably at to
attach the Outside Wall Plate. When exterior wall
surface is not at (covered with vinyl or wood
shingle siding etc.) the siding must be removed,
and a at surface build up ash or above siding
exterior surface to secure/seal the terminal
Outside Wall Plate.
Concentric Venting - Vertical Venting
For vertical (through the roof) venting, extend
Vertical (Roof) Terminal to maintain minimum 12
inches vertical and horizontal distance from building
roof surface. Allow additional vertical distance
for expected snow accumulation. Provide brace as
required. See Figure 19 ‘Vertical Concentric Vent
Installation’.
1. For vertical venting, where optional Concentric Vent
90° degree long radius elbow is attached to installed
Boiler Concentric Vent Collar, to install elbow:
a. Remove locking band clamp off the terminal and
set aside.
b. Lubricate the brown gasket inside boiler
concentric vent collar with small amount of
water.
c. Ensure that male end of the elbow inner plastic
pipe is evenly engaged into the gasket all around,
then, push the elbow male end inside boiler
concentric vent collar until the bead on male end
of elbow outer pipe bottoms out inside boiler
vent collar.
Figure 17: Horizontal (Wall) Terminal Detail
i. Install the supplied Inside Wall Plate onto the
shortened Horizontal (Wall) Terminal interior
end and move the plate to cover interior wall
cut opening. Secure the plate with provided
fasteners, then, apply the sealant around plate
sides to seal it to interior wall.
j. Lubricate the brown gasket inside boiler
concentric vent collar or the last section of the
vent pipe with small amount of water.
k. Ensure that inner pipe of the terminal is evenly
engaged into the gasket all around, then push the
termination male end inside boiler concentric
vent collar or the last section of the vent pipe,
until the mark (see Step g) is no longer visible.
l. Re-install locking band clamp onto the joint
to secure the terminal to the collar or the last
section of the vent pipe.
Figure 18: Completing Horizontal (Wall)
erminal installation
T
d. Re-install locking band clamp onto the joint to
secure the elbow to the collar.
e.
Continue installing additional concentric vent
cuttable or non-cuttable piping as required.
2. Additionally, secure elbow to boiler vent collar with
three evenly spaced #8 x ½” sheet metal screws.
Use collar rivets as reference attachment points.
Mark (center punch) each screw location off each
rivet centerline 5/8” towards collar-beaded end. See
Figure 18 ‘Completing Horizontal (Wall) Terminal
Installation’ for details. Drill 1/8” hole thru both
23
Page 24
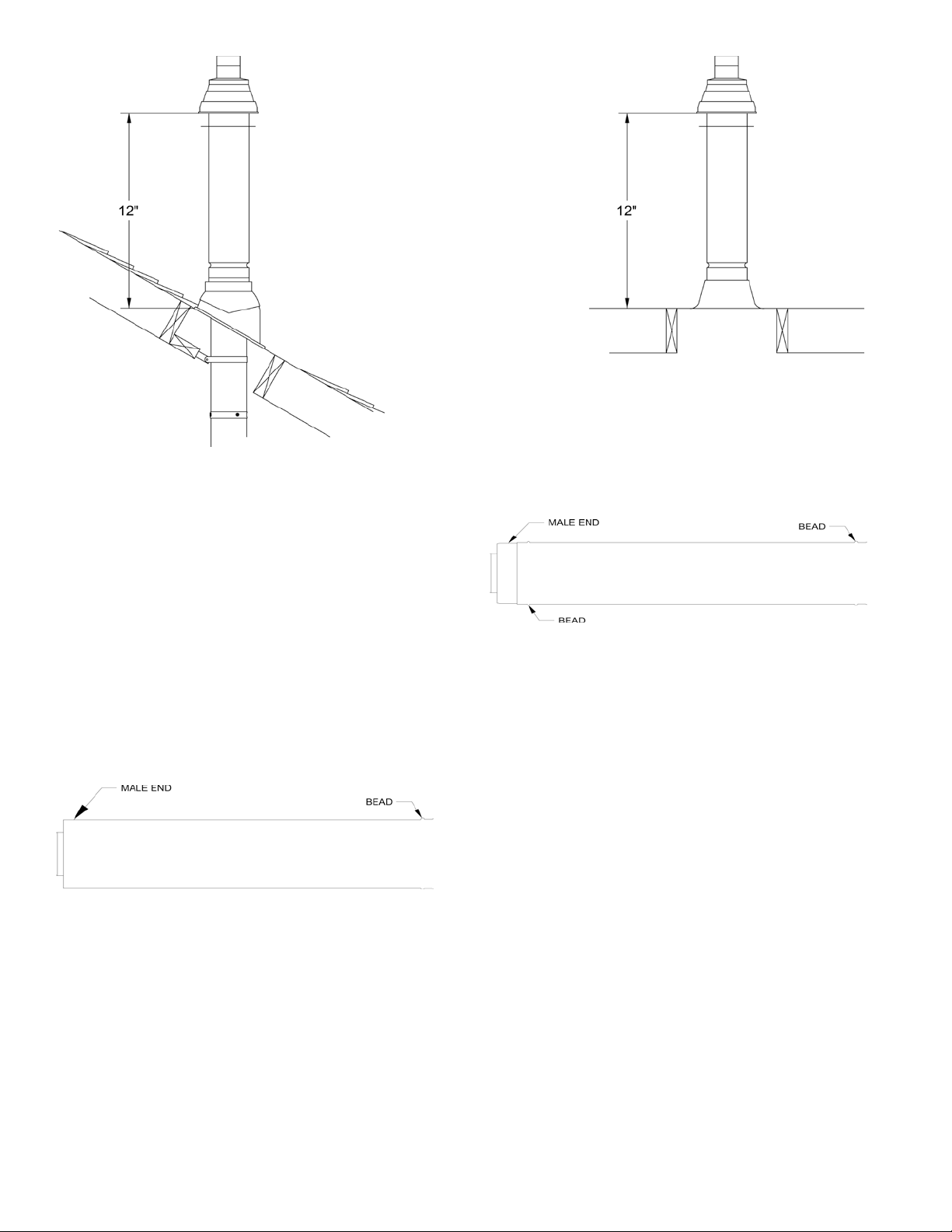
Figure 19: Vertical Concentric Vent installation
outer pipes to start the screw. Use a drill stop or
other means to ensure that the drill bit does not
penetrate more than 3/8” into the outer pipe. Do
not use sheet metal screws longer than ½”.
When Additional Concentric Vent Piping is
needed
1. If additional concentric vent piping is needed:
a. Concentric Vent Cut-To-Length Extension pipes,
identied in Tables 8 and 10 CAN BE CUT
to required length when used as an extension.
These pipes have plain male end and beaded
female end. Always cut the pipe from plain
male end. See Figure 20 ‘Cut-To-Length
Extension (Cuttable)”.
Figure 20: Cut-To-Length Extension (Cuttable)
b. The remaining Concentric Vent Fixed Extensions
shown in Table 8 CANNOT BE CUT. These
pipes have beaded male and beaded female ends.
See Figure 21 ‘Fixed Extension (Non-Cuttable)’.
2. To cut the Concentric Vent Straight pipe to required
length refer to Figure 22 “Cutting Straight Pipe” and
follow the procedure below:
a. Determine the required length of the outer pipe.
When doing this allow an additional 1” of length
for insertion into the female end of the adjoining
pipe. Mark the cut line on the outer pipe.
Figure 21: Fixed Extension (non-Cuttable)
b.
Remove the plastic inner pipe by pulling it out
from the female end.
Cut the OUTER PIPE ONLY at the point
c.
marked in Step (a) using aviation shears, a
hacksaw, or an abrasive wheel cutter. Be careful
to cut the pipe square. Deburr the cut end with a
le or emery cloth.
d. Make an insertion mark 1” from the male end of
the outer pipe.
e. Cut the plastic inner pipe so that it will protrude
3/8” beyond the male end of the outer pipe when
reinstalled in the outer pipe. Use a ne tooth
hacksaw or a PvC saw to cut the plastic pipe and
be careful to cut the pipe square. Deburr the cut
edge of the plastic pipe with a le, razor blade or
ne sandpaper.
f. Reinstall the inner pipe.
3. To join Concentric Vent Pipe refer to Figure 23
“Joining Cuttable Pipe” and Figure 24 “Joining
Non-Cuttable Pipe” and follow the procedure below:
a. Start assembly of the vent system at the boiler.
Lubricate the brown gasket in the boiler vent
collar with a few drops of water.
24
Page 25
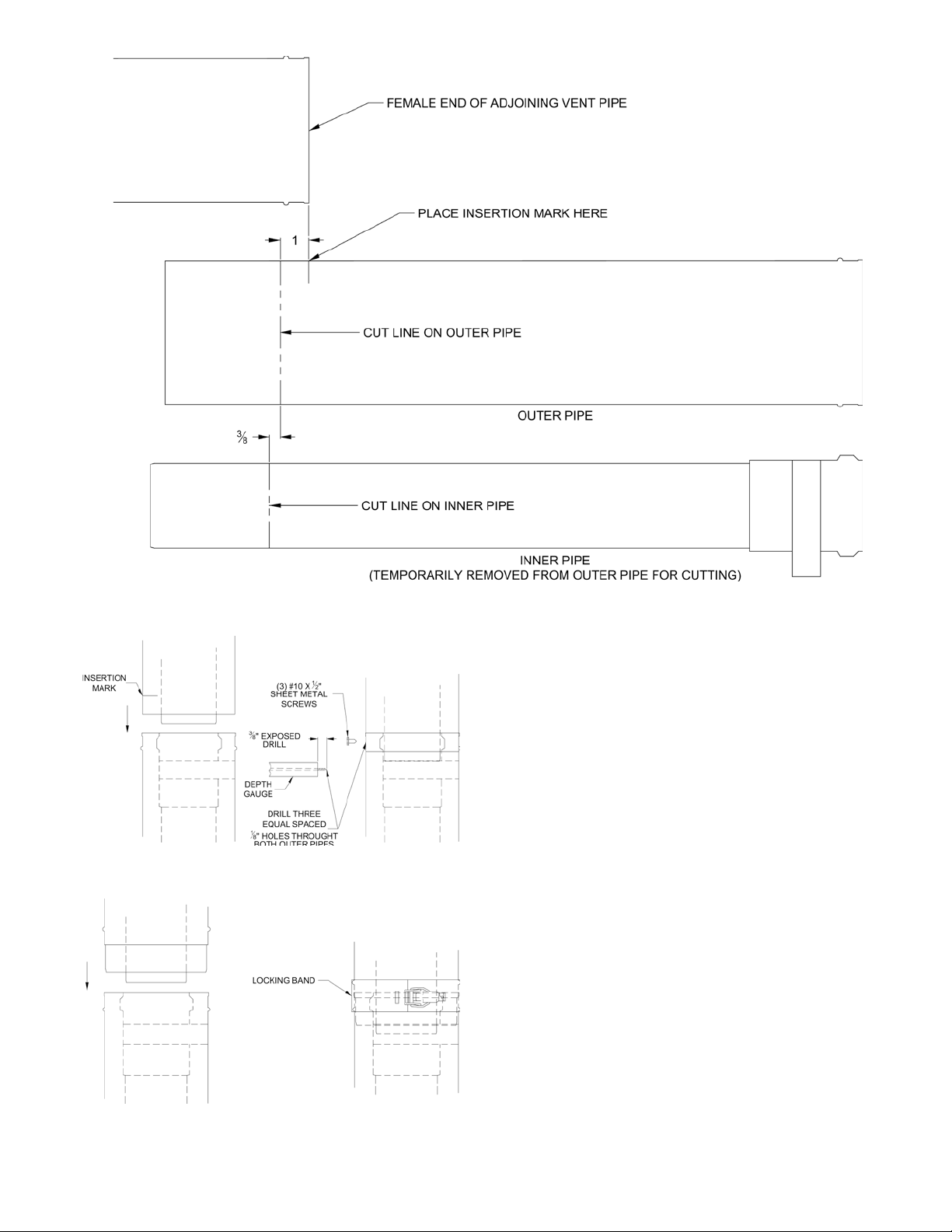
Figure 22: Cutting Straight Pipe
Figure 23: Joining Cuttable Pipe
Figure 24: Joining non-Cuttable Pipe
b. Push the male end of the rst tting into the
boiler collar until it bottoms out. The male end
of cuttable sections should go 1” into the collar
until the insertion mark (made in Step 2d above)
is covered. On other ttings, the bead on the
male pipe will be bottom out on the collar (see
Figure 24).
c.
The male end of cuttable ttings must be held to
the collar with three (3) #10 x 1/2” sheet metal
screws. Drill a 1/8 hole through both outer pipes
to start this screw. Use a drill stop or other
means to ensure that the drill bit does not
penetrate more than 3/8” into the outer pipe.
Do not use a sheet metal screw longer than
1/2” (see Figure 23).
d. Use locking bands (provided with all ttings) to
secure non-cuttable pipe, as well as ttings, to
the boiler collar (see Figure 24).
e. Use the same method to join all remaining vent
components except for the terminal.
Vertical (Roof Terminal Installation
1. Vertical (Roof) Terminal Installation. Refer to
Figures 26, 27 and 28.
In addition to the vertical terminal, either a Flat
Roof Flashing or Sloped Roof Flashing is required
for this installation. Refer to Table 8 ‘Concentric
Vent Components’ for details.
25
Page 26
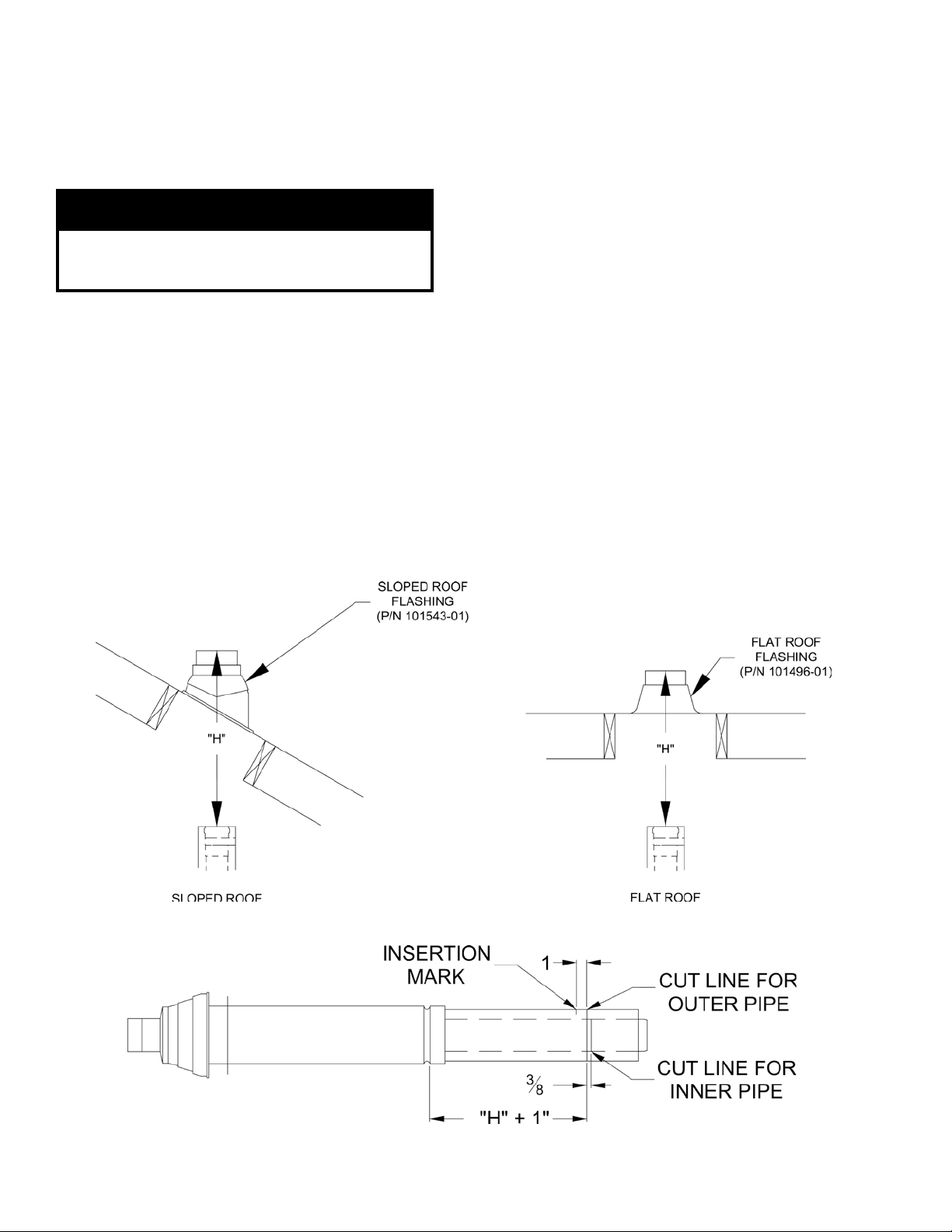
a. Determine the centerline of the terminal location
on the roof. For at roof, cut either 5-1/2”
diameter hole (80/125 mm concentric vent size)
or 6-1/2” diameter hole (100/150 mm concentric
vent size) for the terminal. For sloped roof, cut a
hole in the roof large enough for the terminal to
pass through the roof while remaining plumb.
CaUTiOn
if the boiler is located directly under the hole,
cover it while cutting the hole to prevent debris
from falling onto boiler.
b. Install the roof ashing using standard practice
on the roong system of the structure.
If not already done, assemble the venting system
c.
inside the building. The last section of pipe needs
to be on the same center line as the terminal
and within 19-1/4” of the top edge of the roof
ashing.
Measure distance “H” from the top edge of the
d.
storm collar to the end of the last tting as shown
in Figure 25.
e. Add 1” to distance “H”. Carefully mark this
length on the pipe as shown in Figure 26.
f. Cut the outer pipe only at the point marked in
Step (e) using aviation shears, a hacksaw, or an
abrasive wheel cutter. Be careful to cut the pipe
square. De-burr the cut end with a le or emery
cloth.
g.
Place a mark on the plastic inner pipe 3/8”
beyond the end of the outer pipe (Figure 26).
Use a ne tooth hacksaw to cut the plastic pipe
and be careful to cut the pipe square. De-burr the
cut edge of the plastic pipe with a le or emery
cloth.
h. Make a mark on the terminal section 1” from the
cut end of the outer pipe as shown in Figure 26.
i. Slip the terminal section through the roof from
the outside. Push into the last section of vent
pipe until the mark made in Step (h) is not
longer visible. Secure the terminal to the last
piece of pipe with three #10 x 1/2” sheet metal
screws. Drill a 1/8” hole through both outer
pipes to start these screws. Use a drill stop or
other means to ensure that the drill bit does
not penetrate more than 3/8” into the outer
pipe. Do not use a sheet metal screw longer
than 1/2”.
j. Secure the terminal section to the inside of
the roof structure using the mounting bracket
provided with the terminal (Figure 27).
26
Figure 25: Dimension "H"
Figure 26: Cutting Vertical Terminal
Page 27
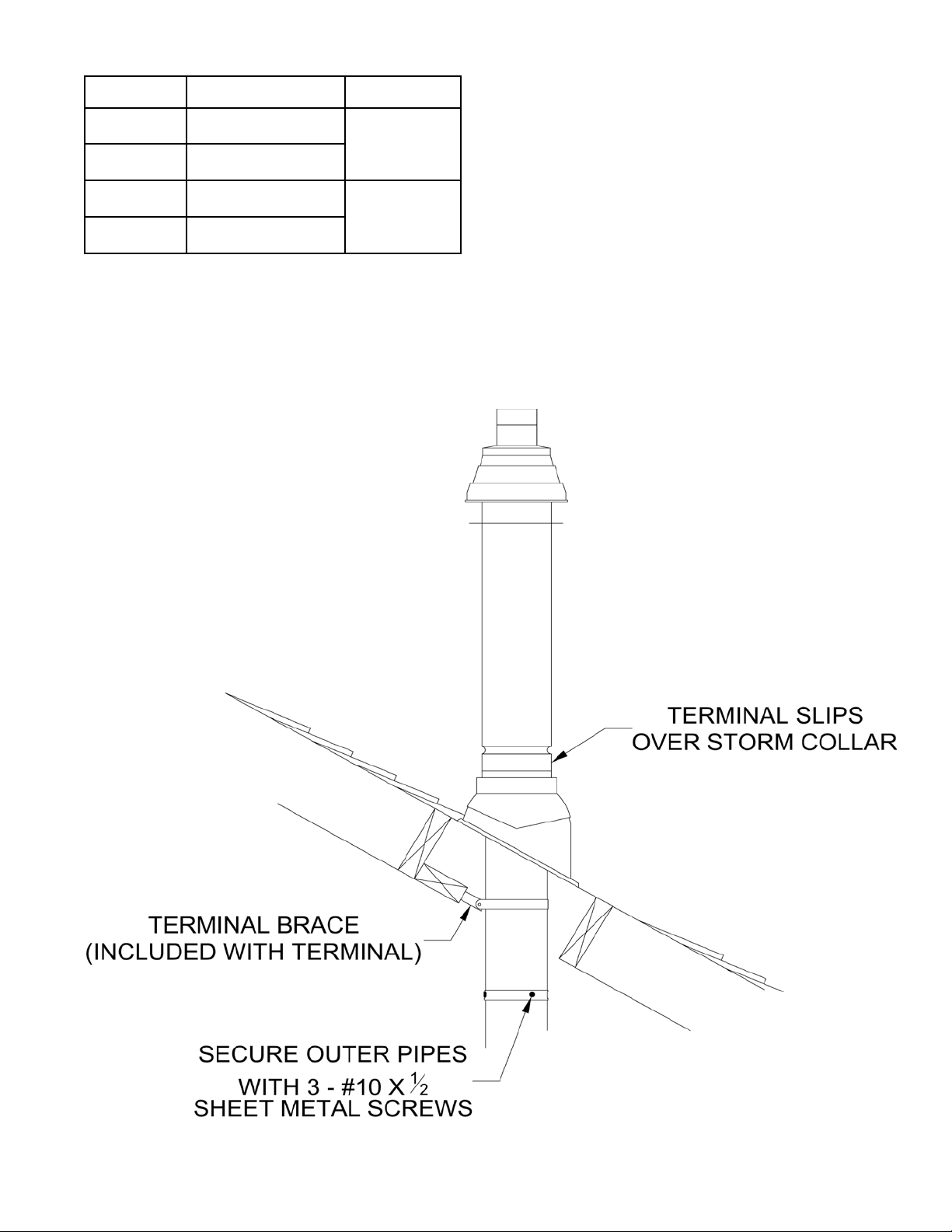
Table 10: Cut-To-Length Extensions (Cuttable)
Part No. Component Description Size
101163-01
101162-01
101550-01
101551-01
Cut-To-Length Extension,
500 mm (19-1/2”)
Cut-To-Length Extension,
1000 mm (39”)
Cut-To-Length Extension,
500 mm (19-1/2”)
Cut-To-Length Extension,
1000 mm (39”)
80/125 mm
100/150 mm
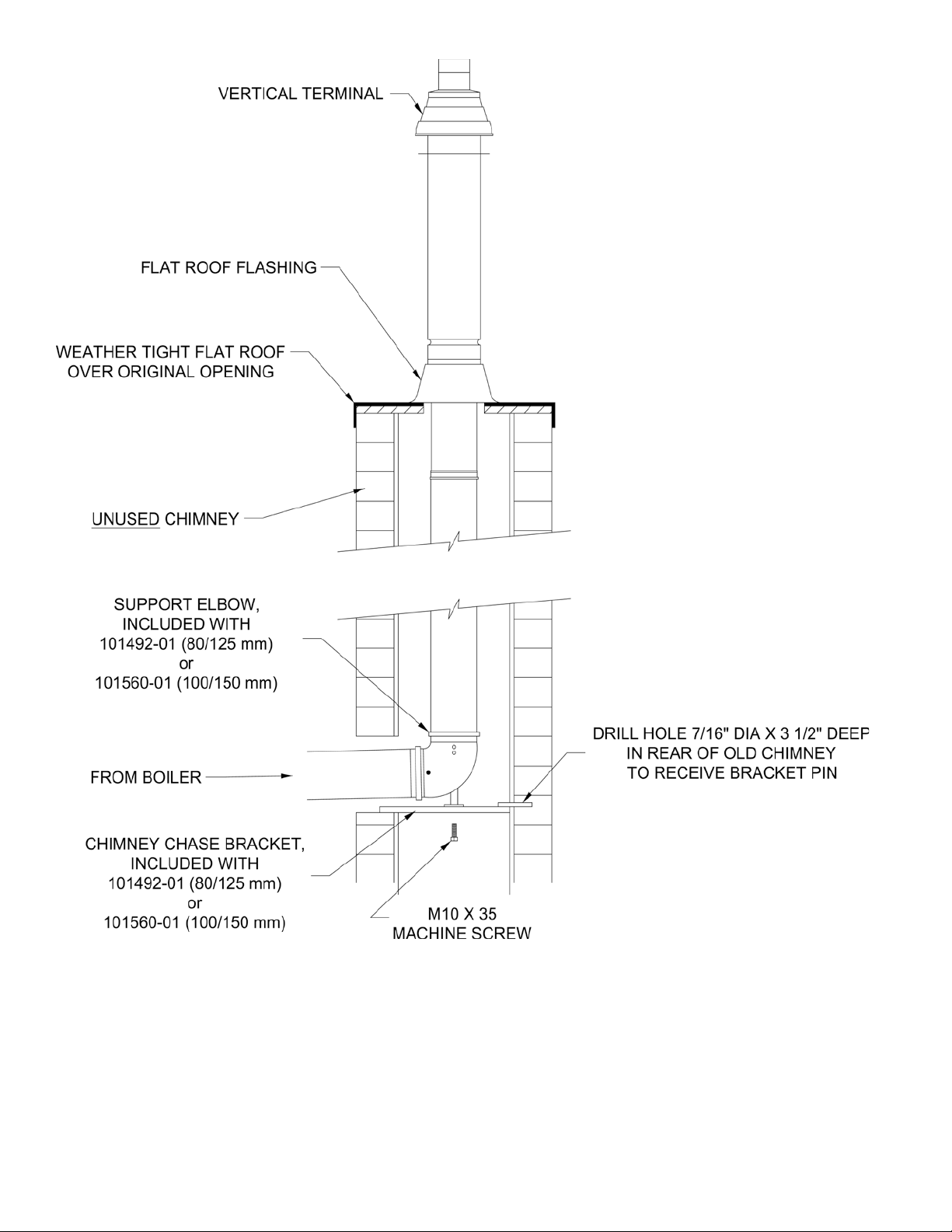
Chimney Chase Installation.
A vertical concentric vent system, either 80/125 mm
or 100/150 mm can be installed in an UNUSED
masonry chimney. Refer to Figure 28.
a. The Chimney chase Support Elbow with
attached Mounting Bracket is used at the base
of the chimney. Refer to Table 8 ‘Concentric
Vent Components’ for details. Slip the elbow
over the M10 x 35 screw in the support bracket.
Determine the desired vertical location of the
support elbow in the chimney and mark the
location of the pin, positioned on the back of
the support bracket, onto the chimney rear wall.
Drill a 7/16” diameter x 3-1/2” deep hole in the
marked location, then, insert the back bracket pin
into the hole. The front of the elbow mounting
bracket should be supported either by bottom of
the opening into chimney or installer supplied
spacer.
b.
Construct a weather-tight at roof to cover
the top of the old chimney. Install the vertical
terminal through this roof using the at roof
ashing.
Figure 27: Completing Vertical Terminal installation
27
Page 28
28
Figure 28: Chimney Chase installation
Page 29

V. Condensate Disposal
A. Condensate Trap and Drain Line.
1. All condensate, which forms in the boiler or vent
system, collects in the sump under heat exchanger
and leaves the boiler through factory installed
condensate trap.
2. The trap allows condensate to drain from sump
while retaining ue gases in the boiler. The trap
has factory installed overow switch, which shuts
down the boiler in the event the drain line becomes
obstructed, preventing proper condensate removal.
Refer to Section XIII “Service and Maintenance”
for condensate trap and condensate overow switch
removal and replacement procedure, if required.
3. Note the following when disposing of the
condensate:
a. Condensate is slightly acidic, typical pH around
3.5 - 4.5. Do not use metallic pipe or ttings in
the condensate drain line. Do not route the drain
line through areas that could be damaged by
leaking condensate.
Do not route or terminate the condensate drain
b.
line in arrears subject to freezing temperatures.
c. If the point of condensate disposal is above the
trap, a condensate pump is required to move
the condensate to the drain. Select a condensate
pump approved for use with condensing
furnaces. If overow from the pump would
result in property damage, select a pump with an
overow switch. Wire this switch in series with
installer provided external high limit, to shut off
the boiler, and, if desired, in series with installersupplied alarm, to trigger an alarm in the event
of overow.
d. Do not attempt to substitute another trap for one
provided with the boiler.
e. In order for boiler to work properly, the boiler
must be leveled during installation.
4. The condensate trap stub is located at boiler left
side, below inlet and outlet water pipe connections.
Refer to Figures 1A and 1B.
5. Condensate trap must be lled up with water,
prior to boiler start-up and before connecting any
condensate line to the boiler, to insure combustion
products cannot escape from operating boiler. To ll
the trap, inject water in the amount of 1 cup (8 uid
ounces) through condensate trap stub opening. Do
not overll the trap.
6. If any additional condensate drain line is needed,
construct the extension from PVC or CPVC
Schedule 40 pipe. The factory supplied ¾” x 5-5/8”
long PVC coupling, located in the Part Carton, must
be used to connect drain line to the condensate trap
stub. Do not over tighten coupling compression nuts
when connecting drain line and condensate trap
stub.
WaRning
Failure to install the condensate trap and
condensate drain in accordance with the above
instructions could cause ue gas to enter the
building, resulting in personal injury or death.
CaUTiOn
Boiler condensate is corrosive. Route
condensate drain line in a manner such
that any condensate leakage will not cause
property damage.
Some jurisdictions may require that
condensate be neutralized prior to disposal.
nOTiCE
Use materials approved by the authority having
jurisdiction.
B. Condensate Neutralizer Installation
1. Some jurisdictions may require that the condensate
be neutralized before being disposed of. Follow
local codes pertaining to condensate disposal.
2. A Condensate Neutralizer Kit (P/N 101867-01)
is available as optional equipment. Follow local
codes and instructions enclosed with the kit for
Condensate Neutralizer installation.
3. Limestone chips will get coated by neutral salts
(product of chemical reaction between limestone
and acidic condensate) and lose neutralizing
effectiveness over time. Therefore, periodic
condensate neutralizer maintenance and limestone
chip replacement must be performed. A pH test or
acid test kits are available from HVAC/plumbing
distributors and should be used to measure
condensate acidity before/after neutralizer thus
indicating a need for service and chip replacement.
29
Page 30

30
Figure 29: Condensate Trap and Drain Line
Page 31

Vi. Water Piping and Trim
WaRning
Failure to properly pipe boiler may result in improper operation and damage to boiler or structure.
install boiler so that the gas ignition system components are protected from water (dripping, spraying,
rain, etc.) during appliance operation and service (circulator replacement, etc.).
nOTiCE
Oxygen contamination of boiler water will cause
corrosion of iron and steel boiler components,
and can lead to boiler failure. Burnham’s Standard
Warranty does not cover problems caused by
oxygen contamination of boiler water or scale
(lime) build-up caused by frequent addition of
water.
Do not ll boiler with softened water to prevent
chloride contamination.
A. Installation of Factory Supplied Piping and Trim
Components
Alpine (ALP) boilers have factory supplied
Miscellaneous Part Carton (P/N 101777-01 – ALP080
thru ALP210; 101777-02 – ALP285; 101777-03
– ALP399), which includes supply piping components,
gas piping components, Temperature & Pressure Gauge,
Pressure Relief Valve and Drain Valve. See Figure 30
“ Factory Supplied Piping and Trim Installation”. Install
these components prior to connecting boiler to system
piping as follows:
Figure 30: Factory Supplied Piping and Trim installation
31
Page 32

1. ALP080 thru ALP285 Boiler Models
a. Locate and remove ¾” NPT x close black nipple,
¾” NPT black tee, ¾” MPT x ¾” FPT Pressure
Relief Valve, ¾” NPT Drain Valve.
b. Install close nipple into tee branch, then, screw
the assembly into boiler left side front ¾”
tapping making sure tee run outlets are in vertical
plane and parallel to boiler side.
c. Mount ¾” MPT x ¾” FPT Pressure Relief Valve
into the tee top outlet.
d. Install Drain Valve into the tee bottom outlet.
2. ALP399 Boiler Model
a. Locate and remove (2) ¾” NPT x close black
nipples, ¾” NPT black tee, ¾” FPT x ¾” FPT
Pressure Relief Valve, ¾” NPT Drain Valve.
b. Install close nipple into tee branch, then, screw
the assembly into boiler left side front ¾”
tapping making sure tee run outlets are in vertical
plane and parallel to boiler side.
c. Install the second close nipple into tee run top
outlet.
d. Mount ¾” FPT x ¾” FPT Pressure Relief Valve
into the tee top outlet.
e. Install Drain Valve into the tee bottom outlet.
3. ALP080 thru ALP210 Boiler Models
a. Locate and remove 1” NPT x 4” long black
nipple, 1” x 1” x 1” NPT black tee, 1” x ¼”
NPT black reducing bushing and Temperature &
Pressure Gauge.
b. Mount the nipple into 1” boiler supply tapping
(see Figure 1A), then, install the tee onto the
nipple, making sure 1” branch outlet is in
horizontal plane and facing the boiler front.
c. Install 1” x ¼” NPT black reducing bushing
into the tee branch, then, put in Temperature &
Pressure Gauge.
4. ALP285 Boiler Model
a. Locate and remove 1¼” NPT x 2” long black
nipple, 1¼” x 1¼” x ¾” NPT black tee, ¾” x ¼”
NPT black reducing bushing and Temperature &
Pressure Gauge.
b. Mount the nipple into 1¼” boiler supply tapping
(see Figure 1B), then, install the tee onto the
nipple, making sure ¾” branch outlet is in
horizontal plane and facing the boiler front.
c. Install ¾” x ¼” NPT black reducing bushing
into the tee branch, then, put in Temperature &
Pressure Gauge.
5. ALP399 Boiler Model
a. Locate and remove 1½” NPT x 2” long black
nipple, 1½” x 1½” x ¾” NPT black tee, ¾” x ¼”
NPT black reducing bushing and Temperature &
Pressure Gauge.
b. Mount the nipple into 1½” boiler supply tapping
(see Figure 1B), then, install the tee onto the
nipple, making sure ¾” branch outlet is in
horizontal plane and facing the boiler front.
c. Install ¾” x ¼” NPT black reducing bushing
into the tee branch, then, put in Temperature &
Pressure Gauge.
32
Page 33

B. Piping System To Be Employed.
Alpine Boiler Head Loss vs. Flow
80
105
150
210
285
399
0
2
4
6
8
10
12
14
16
18
20
0 5 10 15 20 25 30 35 40
Flow Rate (GPM)
Boiler Head Loss (Feet)
Flow,
DT
nOTiCE
Boiler
Head Loss,
Ft. @ 25°F
DT
Maximum
Required
Flow (GPM)
@ 20°F DT
Boiler
Head Loss,
@ 20°F DT
Alpine (ALP) boilers are designed to operate in a closed
loop pressurized system. Minimum pressure in the
boiler must be 12 PSI. Proper operation of the Alpine
(ALP) boiler requires that the water ow through the
Failure to maintain the ow through boiler within
specied limits could result in erratic operation or
premature boiler failure.
boiler remain within the limits shown in Table 11, any
time the boiler is ring.
1. Near boiler piping must isolate ALP boiler from
system piping via closely spaced tees to insure
specied ow range through boiler any time the
boiler is ring:
Table 11: Flow Range Requirement Through Boiler
Boiler
Model
ALP080 1 1 4.2 4.8 4.9 6.4 5.8 8.9 7.3 13.4
ALP105 1 1 5.5 7.0 6.4 9.3 7.7 12.8 9.6 19.1
ALP150 1 1 7.9 5.2 9.2 6.6 11.0 8.9 13.8 12.7
ALP210 1 1 11.1 5.4 12.9 7.1 15.5 9.8 19.4 14.4
ALP285 1¼ 1¼ 15.1 5.9 17.7 7.8 21.2 10.7 26.5 16.0
ALP399 1½ 1½ 21.5 6.1 25.1 7.9 30.2 10.8 37.7 15.9
Notes: Required Flow (GPM) = ** Output (MBH) * 1000/500 * DT
Boiler
Supply
Connection,
Inch, FPT
** Output (MBH) - Select Value for specic Boiler Model from Tables 2A or 2B
Using boiler antifreeze will result in higher uid density and may require larger circulators.
Boiler
Return
Connection,
Inch, FPT
Minimum
Required Flow
(GPM)
@ 35°F DT
Boiler
Head Loss,
Ft.
@ 35°F DT
Required
Flow,
(GPM)
@ 30°F DT
Boiler
Head Loss,
Ft.
@ 30°F DT
Required
(GPM)
@ 25°F
Ft.
33
Page 34
a. The ow rate through the isolated near-boiler
loop is maintained by factory recommended and
installer supplied boiler circulator.
b. The ow rate through the isolated near-boiler
loop is completely independent of the ow rate
through the heating system loop(s).
c. The ow rate through the heating system loop(s)
is controlled by installer sized/provided system
loop circulator(s).
d. This piping arrangement can be used either for
space heating-only applications or space heating
with indirect water heater(s) applications.
i. Space heating only - refer to Table 12A and
Figures 31A or 31B “Near Boiler Piping
- Heating Only” as applicable.
ii. Space heating plus indirect water
heater(s) - refer to Tables 12A, 12B and, as
applicable, to:
• Figures 32A or 32B “Near Boiler Piping Heating Plus Indirect Water Heater”
- when indirect water heater can be piped
as part of near-boiler piping.
• Figures 32C or 32D “Near Boiler Piping -
Heating Plus Indirect Water Heater”
- when indirect water heater must be
piped as a separate heating zone off the
system header.
e. For installations where indirect domestic hot
water heater is combined with space heating,
when sizing an indirect water heater circulator,
compare the specied ow range through an
Alpine model boiler to an indirect water heater
(Alliance SL™) model coil ow rate required to
achieve water heater rating. Refer to Table 12B.
f. When Alliance SL™ model coil ow rate,
required to achieve water heater rating, falls
within the specied ow range for Alpine
boiler model, the Alliance SL™ model can be
piped as part of Alpine near-boiler piping.
Refer to Table 12B, Figures 32A, 32B, 35 and 36
for recommended circulator models, piping and
wiring details.
g. When Alliance SL™ model coil ow rate,
required to achieve water heater rating,
exceeds the specied ow range for Alpine
boiler model, the Alliance SL™/Alpine boiler
combination may result in excessive noise and
boiler heat exchanger erosion, and therefore,
is not recommended. Refer to Table 12B for
details.
h. When Alliance SL™ model coil ow rate,
required to achieve water heater rating, falls
below the specied ow range for Alpine boiler
model, the Alliance SL™ model must be piped
as a separate heating zone off the system
header. The circulator must be sized based on
the Alliance SL™ model coil ow and combined
coil pressure drop and the zone piping total
equivalent length. Refer to Table 12B, Figures
32C, 32D, 37A and 37B for piping and wiring
details.
Table 12a: Recommended Circulator Models for alpine (aLP) Boilers Based on 25°F Temperature Differential
and Up to 75 ft. Equivalent Length Near-Boiler Piping - Space Heating Circulator
Boiler
Model
ALP080 1 1 1 1 5.8 10.3
ALP105 1 1 1 1 7.7 15.1
ALP150 1 1 1 1 11.0 13.1
ALP210 1 1 1¼ 1¼ 15.5 12.7
ALP285 1¼ 1¼ 1½ 1½ 21.5 13.0
ALP399 1½ 1½ 2 2 30.2 12.0
n
otes:
* Circulator Models shown are not equipped with internal ow check valve (IFC).
Boiler Supply
Connection,
Inch, FPT
When selecting Circulators with IFC contact Circulator Manufacturer for sizing information.
Near-Boiler Piping Size shown is based on 2 to 5.5 Ft/Sec. velocity range to avoid potential noise and pipe erosion.
Boiler Return
Connection,
Inch, FPT
Near-Boiler
Piping
Supply Pipe
Size, Inch
Near-Boiler
Piping
Return Pipe
Size, Inch
Flow, GPM
@ 25°F Temp.
Differential
Combined
Boiler & Piping
Loop Head
Loss, Ft.
* Recommended
Circulator
Make & Model
Taco 0010
Grundfos UPS
15-58 FRC
Taco 0014
Grundfos UPS
26-99 FC (second speed)
Taco 0014
Grundfos UP
26-99 FC (rst speed)
Taco 0014
Grundfos UP
26-99 FC (rst speed)
Taco 0013
Grundfos UP
26-99 FC (third speed)
Taco 1400-20
Grundfos UPS
32-80/2 F (second speed)
34
Page 35

Notes
Figure
Reference
Model for
Alliance SL
*Recommended
Circulator Make &
Boiler,
Combined
Coil Head
Alliance SL
Coil
Alliance SL
Models to
Alliance SL
Near-Boiler Piping
installed as Part of
Loss, Ft
& Piping
Loop Head
Alliance SL
Required
Flow Rate
Loss, Ft @
GPM
Required
Flow Rate,
Piping
As Part of
Near-Boiler
be installed
32B
32A or
UPS26-99 FC
Taco 0010 Grundfos
SL27 6 9 19.3
SL35 6 9 19.3
(second speed)
SL50 6 9.5 19.8
SL70 6 10 20.3
SL119 14 17 NA Not Recommended NA Note 1
32B
32A or
UPS26-99 FC
Taco 0010 Grundfos
SL27 6 9 19.3
SL35 6 9 19.3
(second speed)
SL50 6 9.5 19.8
SL70 6 10 20.3
SL119 14 17 NA Not Recommended NA Note 1
32C or 32D Note 2
SL27 6 9 NA Not Recommended
SL35 6 9 NA Not Recommended
SL50 6 9.5 NA Not Recommended
SL70 6 10 NA Not Recommended
32B
32A or
Taco 1400-45
80/2 (max speed)
Grundfos UPS 32-
SL119 14 17 36
Table 12B: Recommended Circulator Models for Alpine (ALP) Boilers and Alliance SL Indirect Water Heaters
Installed as Part of Near-Boiler Piping Up to 75 Ft. Equivalent Length - Indirect Water Heater Circulator
Boiler,
Flow thru
Min Req’d
GPM
Flow,
Max
Flow thru
Allowable
Near-
Boiler
Piping
Near-
Boiler
Piping
Boiler
Return
Boiler
Supply
Boiler
GPM
@ 35°F
Delta T
@ 25°F
GPM
Boiler,
Pipe
Return
Pipe
Supply
Inch, FPT
Connection,
Inch, FPT
Connection,
Model
Delta T
Delta T
@ 20°F
Inch
Size,
Inch
Size,
ALP080 1 1 1 1 7.3 5.8 4.2
ALP105 1 1 1 1 9.6 7.7 5.5
ALP150 1 1 1 1 13.8 11 7.9
erosion and noise.
-seeFigures32Cand32DforalternateIWHpiping.IndirectWaterHeaterCirculatormustbeselectedbyaninstallerbasedonAllianceSLrequiredcoilow
and corresponding coil head loss shown as well as total equivalent length of such separate zone.
NOTES:
Note 1: Required Alliance SL Coil Flow Rate exceeds Max Allowable Flow Rate thru Boiler; this Boiler/Alliance SL combination may result in boiler heat exchanger
Note 2: Required Alliance SL Coil Flow Rate is below Min Required Flow Rate thru Boiler; this Model can only be installed as separate heating zone off system header
Note 3: Combined Head Loss shown corresponds to Min Required Flow Rate thru Boiler.
*CirculatorModelsshownarenotequippedwithinternalowcheckvalve(IFC).
When selecting Circulators with IFC contact Circulator Manufacturer for sizing information.
Near-Boiler Piping Size shown is based on 2 to 5.5 Ft/sec velocity range to avoid potential noise and pipe erosion.
35
Page 36

Notes
Note 3
Figure
Reference
Model for
Alliance SL
*Recommended
Circulator Make &
Boiler,
Combined
Coil Head
Alliance SL
Coil
Alliance SL
Models to
Alliance SL
Near-Boiler Piping
installed as Part of
Loss, Ft
& Piping
Loop Head
Alliance SL
Required
Flow Rate
Loss, Ft @
GPM
Required
Flow Rate,
Piping
As Part of
Near-Boiler
be installed
32C or 32D Note 2
Taco 1400-45
SL27 6 9 NA Not Recommended
SL35 6 9 NA Not Recommended
SL50 6 9.5 NA Not Recommended
SL70 6 10 NA Not Recommended
32B
32A or
80/2 (max speed)
Grundfos UPS 32-
SL119 14 17 29.7
32C or 32D Note 2
SL27 6 9 NA Not Recommended
SL35 6 9 NA Not Recommended
32B
32A or
Taco 1400-45
80/2 (max speed)
Grundfos UPS 32-
SL50 6 9.5 NA Not Recommended
SL70 6 10 NA Not Recommended
SL119 14 19.8 27.0
32C or 32D Note 2
SL27 6 9 NA Not Recommended
SL35 6 9 NA Not Recommended
SL50 6 9.5 NA Not Recommended
SL70 6 10 NA Not Recommended
SL119 14 40.1 NA Not Recommended
Table 12B (continued): Space Heating with Indirect Water Heating - Recommended Circulator Models
for Alpine (ALP) Boilers and Alliance SL Indirect Water Heaters
Installed as Part of Near-Boiler Piping Up to 75 Ft. Equivalent Length
Boiler,
Flow thru
Min Req’d
GPM
Flow,
Max
Flow thru
Allowable
Near-
Boiler
Piping
Near-
Boiler
Piping
Boiler
Return
Boiler
Supply
Boiler
GPM
@ 35°F
Delta T
@ 25°F
GPM
Boiler,
Pipe
Return
Pipe
Supply
Inch, FPT
Connection,
Inch, FPT
Connection,
Model
Delta T
Delta T
@ 20°F
Inch
Size,
Inch
Size,
ALP210 1 1 1-1/4 1-1/4 19.4 15.5 11.1
ALP285 1-1/4 1-1/4 1-1/2 1-1/2 26.5 21.2 15.1
ALP399 1-1/2 1-1/2 2 2 37.7 30.2 21.5
erosion and noise.
-seeFigures32Cand32DforalternateIWHpiping.IndirectWaterHeaterCirculatormustbeselectedbyaninstallerbasedonAllianceSLrequiredcoilow
and corresponding coil head loss shown as well as total equivalent length of such separate zone.
NOTES:
Note 1: Required Alliance SL Coil Flow Rate exceeds Max Allowable Flow Rate thru Boiler; this Boiler/Alliance SL combination may result in boiler heat exchanger
Note 2: Required Alliance SL Coil Flow Rate is below Min Required Flow Rate thru Boiler; this Model can only be installed as separate heating zone off system header
Note 3: Combined Head Loss shown corresponds to Min Required Flow Rate thru Boiler.
*CirculatorModelsshownarenotequippedwithinternalowcheckvalve(IFC).
When selecting Circulators with IFC contact Circulator Manufacturer for sizing information.
Near-Boiler Piping Size shown is based on 2 to 5.5 Ft/sec velocity range to avoid potential noise and pipe erosion.
36
Page 37

Table 13: Fitting and Valve Equivalent Length
Table 13: Fitting and Valve Equivalent Length (cont’d)
Copper Fitting and Sweat Valve Equivalent Length (Ft)
Fitting or Valve
Description
90° Elbow 2.5 3.0 4.0
45° Elbow 1.0 1.2 1.5
Tee (thru ow) 0.5 0.6 0.8
Tee (Branch ow) 4.5 5.5 7.0
Diverter Tee (typical) 23.5 25.0 23.0
Gate Valve 0.3 0.4 0.5
Globe Valve 25.0 36.0 46.0
Angle Valve 5.3 7.8 9.4
Ball Valve (standard port) 4.3 7.0 6.6
Swing Check Valve 4.5 5.5 6.5
Flow-Check Valve (typical) 54.0 74.0 57.0
Buttery Valve 2.7 2.0 2.7
Copper Pipe or Valve Size
1 1¼ 1½
Threaded Fitting and Valve Equivalent Length (Ft)
Fitting or Valve
Description
90° Elbow 2.6 3.5 4.0
Long Radius
Elbow (45° or 90°)
Tee (thru ow) 1.8 2.3 2.7
Tee (Branch ow) 5.3 6.9 8.1
Close Return
Bend
Gate Valve (full open) 0.7 0.9 1.1
Globe Valve (full open) 30.0 39.0 46.0
Angle Valve (full open) 13.0 17.0 20.0
Swing Check Valve
(full open)
Flow-Check Valve
(typical)
Black Threaded Pipe or Valve Size
1 1¼ 1½
1.4 1.8 2.2
4.4 5.8 6.7
8.7 12.0 13.0
42.0 60.0 63.0
NOTE: Table 13 is provided as reference to assist in piping design and species equivalent length of typical piping ttings and
valves.
nOTiCE
The alpine (aLP) boiler heat exchanger is made from stainless steel tubular coil having relatively narrow
waterways. Once lled with water, it will be subject to the effects of corrosion. Failure to take the following
precautions to minimize corrosion and heat exchanger waterways overheating could result in severe boiler
damage.
•
Before connecting the boiler, insure the system is free of impurities, grease, sediment, construction
dust, sand, copper dust, ux and any residual boiler water additives. Flush the system thoroughly and
repeatedly, if needed, with clear water mixed with concentrated rinse agent to remove these contaminants
completely.
•
iron oxide (red oxide sludge Fe2O3) is produced during oxygenation. To minimize any oxygen presence
in the system, the system must be air free and leak tight. Do not connect the boiler to radiant tubing
without an oxygen barrier. Using automatic water rell is not recommended, however, if such rell is
employed, a water meter must be added to evaluate the makeup water volume taken after initial ll and
eliminate any water leakage as early as possible.
•
Maintain the water pressure in the boiler at a minimum of 12 PSi.
•
The boiler water pH must be within 8.2 < pH < 9.5. if the system contains any aluminum components,
pH must be less than 8.5.
•
Black oxide sludge (magnetite Fe3O4) forms as the result of continuous electrolytic corrosion in any
system not protected by an inhibitor.
•
Scale deposit is made up of lime scale contained in most distributed water and settles over the warmest
surfaces of boiler heat exchanger causing subsequent overheating and eventual failure. Water hardness
must be maintained within 3 to 9 grain/gal range.
•
Refer to Section Xiii “Service and Maintenance” for recommended heating system water treatment
products (corrosion/scale inhibitors, cleaners etc) and their suppliers.
37
Page 38

38
Figure 31a: near Boiler Piping - Heating Only (with Central Heating Circulators)
Page 39

Figure 31B: near Boiler Piping - Heating Only (with Central Heating zone Valves)
39
Page 40

40
Figure 32a: near Boiler Piping - Heating Plus indirect Water Heater (with Central Heating Circulators)
Page 41

Figure 32B: near Boiler Piping - Heating Plus indirect Water Heater (with Central Heating zone Valves)
41
Page 42

42
Figure 32C: near Boiler Piping - Heating (with Central Heating Circulators) Plus alternately Piped indirect Water Heater
Page 43

Figure 32D: near Boiler Piping - Heating (with Central Heating zone Valves) Plus alternately Piped indirect Water Heater
43
Page 44

nOTiCE
WaRning
Where it is not possible to install a separate
boiler loop, the system circulator must be
sized to ensure that the ow through boiler
stays within the dened parameters to prevent
overheating when the boiler is red at it’s full
rated input. Install a ow meter to measure the
ow, or re the boiler at full rate and ensure the
boiler DT does not exceed 35°F.
2. Direct connection of Alpine (ALP) boiler to
heating system, similar to a conventional boiler, is
NOT RECOMMENDED because:
The ow rate through system must be the same
a.
as through boiler and fall within limits specied
in Table 11.
Pressure drop through entire system must be
b.
known, added to pressure drop through boiler,
and, a circulator selected to provide required
ow at total calculated pressure drop.
c. It is often very difcult to accurately calculate
the pressure drop through the system.
d. In replacement installations, it may be nearly
impossible to get an accurate measurement of
piping amount and number of ttings in the
system. If system is zoned, the system ow rate
may drop well below recommended minimum
ow when only a single zone is calling for heat.
C. Piping Standard Installation Requirements.
Observe the following guidelines when making the
actual installation of the boiler piping:
1. Pressure Relief Valve (Required) - The relief valve
is packaged loose with boiler and must be installed
in the location shown in Figure 30 “Factory
Supplied Piping and Trim Installation”. The relief
valve must be installed with spindle in vertical
position. Installation of the relief valve must comply
with ASME Boiler and Pressure Vessel Code,
Section IV. The standard factory shipped relief valve
is rated for 30 PSI maximum working pressure.
Optional 50 PSI maximum working pressure
rated relief valve is available. If the valve is to be
replaced, the replacement valve must have a relief
capacity equal or exceeding the boiler DOE Heating
Capacity (models ALP080 thru ALP285) or the
boiler I=B=R Gross Output rating (model ALP399).
Pipe the relief valve discharge to a location where
hot water or steam will not create hazard or property
damage if the valve opens. The end of the discharge
pipe must terminate in an unthreaded pipe. If the
relief valve is not piped to a drain, it must terminate
at least 6” above the oor. Do not run relief valve
discharge piping through an area prone to freezing.
The termination of discharge piping must be in an
area where it will not become plugged by debris.
Pressure relief valve discharge piping must be
piped such that the potential of severe burns
is eliminated. DO nOT pipe in any area where
freezing could occur. DO nOT install any shut-off
valves, plugs or caps. Consult Local Codes for
proper discharge piping arrangement.
2. Circulator (Required) – Usually at least two
circulators will be required to properly install a
Alpine™ Series boiler. See Section B above for
information on sizing the circulators.
Expansion Tank (Required) - If this boiler is
3.
replacing an existing boiler with no other changes
in the system, the old expansion tank can generally
be reused. If the expansion tank must be replaced,
consult the expansion tank manufacturer’s literature
for proper sizing.
4. Fill Valve (Required) – Either manual
(recommended) or automatic ll valve may be used.
However, if automatic rell is employed, a water
meter must be added to evaluate the makeup water
volume taken after initial ll and eliminate any
water leakage as early as possible.
5. Automatic Air Vent (Required) -At least one
automatic air vent is required. Manual vents will
usually be required in other parts of the system to
remove air during initial ll.
6. Manual Reset High Limit (Required by some
Codes) - This control is required by ASME CSD-1
and some other codes. Install the high limit in the
boiler supply piping just above the boiler with no
intervening valves. Set the manual reset high limit
to 200°F. Wire the limit per Figures 36, 37A and
37B in VIII Electrical Section.
7. Flow Control Valve (Strongly Recommended)
- The ow control valve prevents ow through the
system unless the circulator is operating. Flow
control valves are used to prevent gravity circulation
or “ghost ows” in circulator zone systems through
zones that are not calling for heat.
8. Isolation Valves (Strongly recommended) -
Isolation valves are useful when the boiler must be
drained, as they will eliminate having to drain and
rell the entire system.
9. Drain Valve (Required) – Drain valve is packaged
loose with boiler and must be installed in the
location shown in Figure 30 “Factory Supplied
Piping and Trim Installation”.
10. Low Water Cutoff (Required by some Codes)
– LWCO with harness and LWCO transformer are
available as optional components. Order Complete
Kit (Part No. 102097-01) when required.
44
Page 45

D. Special Situation Piping Installation Requirements
Observe the following guidelines when making the
actual installation of the boiler piping for special
situations:
Systems containing high level of dissolved oxygen
1.
– Many hydronic systems contain enough dissolved
oxygen to cause severe corrosion damage to Alpine
(ALP) boiler heat exchanger. Some examples
include but not limited to:
• Radiant systems employing tubing without
oxygen barrier
• Systems with routine additions of fresh water
• Systems open to atmosphere
If the boiler is used in such a system, it must be
separated from oxygenated water being heated with
a heat exchanger as shown in Figure 33. Consult
the heat exchanger manufacturer for proper heat
exchanger sizing as well as ow and temperature
requirements. All components on the oxygenated
side of the heat exchanger, such as the pump
and expansion tank, must be designed for use in
oxygenated water.
2.
Piping with a Chiller - If the boiler is used in
conjunction with a chiller, pipe the boiler and chiller
in parallel. Use isolation valves to prevent chilled
water from entering the boiler.
3. Boiler Piping with Air Handlers - Where the
boiler is connected to air handlers through which
refrigerated air passes, use ow control valves in the
boiler piping or other automatic means to prevent
gravity circulation during the cooling cycle.
Figure
33: isolation of the Boiler From Oxygenated Water with a Plate Heat Exchanger
45
Page 46

Vii. gas Piping
WaRning
Failure to properly pipe gas supply to boiler may
result in improper operation and damage to the
boiler or structure. always assure gas piping is
absolutely leak free and of the proper size and
type for the connected load.
an additional gas pressure regulator may be
needed. Consult gas supplier.
A. Size gas piping. Design system to provide adequate gas
supply to boiler. Consider these factors:
1. Allowable pressure drop from point of delivery to
boiler. Maximum allowable system pressure is ½
psig. Actual point of delivery pressure may be less;
contact gas supplier for additional information.
Minimum gas valve inlet pressure is stamped on
the rating label located in the boiler’s vestibule
compartment.
2. Maximum gas demand. Refer to the boiler’s input as
printed on its rating label. Also consider existing and
expected future gas utilization equipment (i.e. water
heater, cooking equipment).
3. Length of piping and number of ttings. Refer
to Tables 14A (natural gas) or 14B (LP gas) for
maximum capacity of Schedule 40 pipe. Table 15
lists equivalent pipe length for standard ttings.
Specic gravity of gas. Gas piping systems for gas
4.
with a specic gravity of 0.60 or less can be sized
directly from Tables 14A or 14B, unless authority
having jurisdiction species a gravity factor be
applied. For specic gravity greater than 0.60,
apply gravity factor from Table 16. If exact specic
gravity is not shown choose next higher value.
For materials or conditions other than those listed
above, refer to National Fuel Gas Code, NFPA54/ANSI
Z223.1, or size system using standard engineering
methods acceptable to authority having jurisdiction.
B. Connect boiler gas valve to gas supply system.
WaRning
Failure to use proper thread compounds on all
gas connectors may result in leaks of ammable
gas.
Table 14a: Maximum Capacity of Schedule 40 Black Pipe in CFH* (natural gas) For gas Pressures
of 0.5 psig or Less
inlet Pressure 0.5 PSi or less; 0.3 inch W.C. Pressure Drop
Nominal Pipe
Size, In.
½ 0.622 131 90 72 62 55 50 46 42 40 38
¾ 0.824 273 188 151 129 114 104 95 89 83 79
1 1.049 514 353 284 243 215 195 179 167 157 148
1¼ 1.380 1056 726 583 499 442 400 368 343 322 304
1½ 1.610 1582 1087 873 747 662 600 552 514 482 455
2 2.067 3046 2094 1681 1439 1275 1156 1063 989 928 877
2½ 2.469 4856 3337 2680 2294 2033 1842 1695 1576 1479 1397
3 3.068 8584 5900 4738 4055 3594 3256 2996 2787 2615 2470
Inside
Diameter, In.
Length of Pipe, Ft.
10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100
inlet Pressure 0.5 PSi or less; 0.5 inch W.C. Pressure Drop
Nominal Pipe
Size, In.
½ 0.622 172 118 95 81 72 65 60 56 52 50
¾ 0.824 360 247 199 170 151 137 126 117 110 104
1 1.049 678 466 374 320 284 257 237 220 207 195
1¼ 1.380 1392 957 768 657 583 528 486 452 424 400
1½ 1.610 2085 1433 1151 985 873 791 728 677 635 600
2 2.067 4016 2760 2217 1897 1681 1523 1402 1304 1223 1156
2½ 2.469 6401 4400 3533 3024 2680 2428 2234 2078 1950 1842
3 3.068 11316 7778 6246 5345 4738 4293 3949 3674 3447 3256
Inside
Diameter, In.
Length of Pipe, Ft.
10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100
* 1 CFH of Natural Gas is approximately equal to 1 MBH; contact your gas supplier for the actual heating
value of your gas.
46
Page 47

Table 14B: Maximum Capacity of Schedule 40 Black Pipe in CFH* (LP gas) For gas Pressures
of 0.5 psig or Less
inlet Pressure 11.0 inch W.C.; 0.3 inch W.C. Pressure Drop
Nominal Pipe
Size, In.
½ 0.622 88 60 48 41 37 33 31 29 27 25
¾ 0.824 184 126 101 87 77 70 64 60 56 53
1 1.049 346 238 191 163 145 131 121 112 105 100
1¼ 1.380 710 488 392 336 297 269 248 231 216 204
1½ 1.610 1064 732 588 503 446 404 371 346 324 306
2 2.067 2050 1409 1131 968 858 778 715 666 624 590
2½ 2.469 3267 2246 1803 1543 1368 1239 1140 1061 995 940
3 3.068 5776 3970 3188 2729 2418 2191 2016 1875 1760 1662
Inside
Diameter, In.
Length of Pipe, Ft.
10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100
inlet Pressure 11.0 inch W.C.; 0.5 inch W.C. Pressure Drop
Nominal Pipe
Size, In.
½ 0.622 116 80 64 55 48 44 40 38 35 33
¾ 0.824 242 166 134 114 101 92 85 79 74 70
1 1.049 456 314 252 215 191 173 159 148 139 131
1¼ 1.380 937 644 517 442 392 355 327 304 285 269
1½ 1.610 1403 964 775 663 588 532 490 456 427 404
2 2.067 2703 1858 1492 1277 1131 1025 943 877 823 778
2½ 2.469 4308 2961 2377 2035 1803 1634 1503 1399 1312 1239
3 3.068 7615 5234 4203 3597 3188 2889 2658 2472 2320 2191
Inside
Diameter, In.
Length of Pipe, Ft.
10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100
* 1 CFH of LP Gas is approximately equal to 2.5 MBH; contact your gas supplier for the actual heating value
of your gas.
Table 15: Equivalent Lengths of Standard Pipe Fittings & Valves
Nominal
Pipe Size,
Inc.
½ 0.622 0.4 17.3 8.7 4.3 0.7 1.6 3.5 1.6 3.1
¾ 0.824 0.5 22.9 11.4 5.7 1.0 2.1 4.6 2.1 4.1
1 1.049 0.6 29.1 14.6 7.3 1.2 2.6 5.8 2.6 5.2
1¼ 1.38 0.8 38.3 19.1 9.6 1.6 3.5 7.7 3.5 6.9
1½ 1.61 0.9 44.7 22.4 11.2 1.9 4.0 9.0 4.0 8.0
2 2.067 1.2 57.4 28.7 14.4 2.4 5.2 11.5 5.2 10.3
2½ 2.469 1.4 68.5 34.3 17.1 2.9 6.2 13.7 6.2 12.3
3 3.068 1.8 85.2 42.6 21.3 3.6 7.7 17.1 7.7 15.3
Inside
Diameter,
In.
Valves (Screwed) - Fully Open Screwed Fittings
Gate Globe Angle
Swing
Check
45°
Elbow
90°
Elbow
180 Close
Return
Bend
90 Tee
Flow Thru
Run
90 Tee,
Flow Thru
Branch
47
Page 48

Table 16: Specic Gravity Correction Factors
Specic
Gravity
0.60 1.00 0.90 0.82
0.65 0.96 1.00 0.78
0.70 0.93 1.10 0.74
0.75 0.90 1.20 0.71
0.80 0.87 1.30 0.68
0.85 0.81 1.40 0.66
Correction
Factor
Specic
Gravity
Correction
Factor
WaRning
gas supply to boiler and system must be
absolutely shut off prior to installing or servicing
boiler gas piping.
1. Use methods and materials in accordance with local
plumbing codes and requirements of gas supplier. In
absence of such requirements, follow National Fuel
Gas Code, NFPA 54/ANSI Z223.1.
Use thread (joint) compounds (pipe dope) resistant
2.
to action of liqueed petroleum gas.
3. Alpine (ALP) boilers have factory supplied
Miscellaneous Part Carton (P/N 101777-01
- ALP080 thru ALP210; 101777-02 - ALP285;
101777-03 - ALP399), which includes gas piping
components to connect boiler gas valve to gas
supply system. Install these components prior to
connecting boiler to gas supply system piping as
follows:
a. Locate and remove either ½” NPT x 6” long
black nipple and ½” NPT external gas shutoff
valve (ALP080 thru ALP210), or ¾” NPT x
6” long black nipple and ¾” NPT external gas
shutoff valve (ALP285 thru ALP399).
b. Feed the appropriate nipple through factory
installed jacket left side panel grommet (refer
to Figure 1A or 1B for gas supply connection
identication) and screw the nipple into boiler
gas valve inlet port.
c. Mount the appropriate external gas shutoff valve
onto the threaded nipple end outside of the jacket
left side panel.
d. Install sediment trap, ground-joint union and
manual shut-off valve upstream of boiler gas
control valve and outside jacket. See Figure 34.
4. All above ground gas piping upstream from manual
shut-off valve must be electrically continuous and
bonded to a grounding electrode. Do not use gas
piping as grounding electrode. Refer to National
Electrical Code, NFPA 70.
C. Pressure test. See Table 17 for Alpine Min./Max.
Pressure Ratings. The boiler and its gas connection
must be leak tested before placing boiler in operation.
1. Protect boiler gas control valve. For all testing over
½ psig, boiler and its individual shutoff valve must
be disconnected from gas supply piping. For testing
at ½ psig or less, isolate boiler from gas supply
piping by closing boiler’s individual manual shutoff
valve.
2. Locate leaks using approved combustible gas noncorrosive leak detector solution.
DangER
Do not use matches, candles, open ames or
other ignition source to check for leaks.
Table 17: Min./Max. Pressure Ratings
Boiler
Model
No.
ALP080
ALP105
ALP150
ALP210
ALP285
ALP399
Natural/LP
Gas
Max.
Pressure
(in. w.c.)
14 4.0 11.0
Natural Gas
Min. Pressure
Inlet to Gas Valve
(in. w.c.)
Figure 34: Recommended gas Piping
LP Gas
Min. Pressure
Inlet to Gas
Valve
(in. w.c.)
48
Page 49

Viii. Electrical
DangER
Positively assure all electrical connections are unpowered before attempting installation or service of
electrical components or connections of the boiler or building. Lock out all electrical boxes with padlock
once power is turned off.
WaRning
Failure to properly wire electrical connections to the boiler may result in serious physical harm.
Electrical power may be from more than one source. Make sure all power is off before attempting any
electrical work.
Each boiler must be protected with a properly sized over-current device.
n
ever jump out or make inoperative any safety or operating controls.
The wiring diagrams contained in this manual are for reference purposes only. Each boiler is shipped with
a wiring diagram attached to the front door. Refer to this diagram and the wiring diagram of any controls
used with the boiler. Read, understand and follow all wiring instructions supplied with the controls.
A. General. Install wiring and electrically ground boiler
in accordance with authority having jurisdiction or, in
the absence of such requirements, follow the National
Electrical Code, NFPA 70, and/or CSA C22.1 Electrical
Code.
B. A separate electrical circuit must be run from
the main electrical service with an over-current
device/disconnect in the circuit. A service switch is
recommended and may be required by some local
jurisdictions. Install the service switch in the line
voltage “Hot” leg of the power supply. Locate the
service switch such that the boiler can be shut-off
without exposing personnel to danger in the event of
an emergency. Connect the main power supply and
ground to the three (3) boiler wires (black, white and
green) located in the junction box at the inside top of
the boiler jacket.
C. Refer to Figures 35 and 36 or details on the internal
boiler wiring.
1. Line Voltage (120 VAC) Connections (Figure 35)
– The line voltage connections are located in the
junction box on the left side of the vestibule:
nOTiCE
This boiler is equipped with a high water temperature limit located inside the internal wiring of the boiler.
This limit provides boiler shutdown in the event the boiler water temperature exceeds the set point of the
limit control. Certain Local Codes require an additional water temperature limit. In addition, certain types
of systems may operate at temperatures below the minimum set point of the limit contained in the boiler.
If this occurs, install an additional water temperature limit (Honeywell L4006 Aquastat) located in the system
piping as shown in the Water Piping and Trim Section of this manual. Wire as indicated in the Electrical
Section of this manual.
nOTiCE
all wire, wire nuts, controls etc. are installer supplied unless otherwise noted.
49
Page 50

• Black – Line voltage “hot”
• White – “Neutral” for boiler and circulators
• Red – “Heating” circulator “hot”
• Blue – “Indirect Water Heater “ circulator “hot”
• Green – Ground connection
2. Maximum circulator continuous current draw is 2A.
With primary/secondary piping, it may be desirable
to use the boiler to directly control the primary
circulator in addition to the secondary circulator. If
this is done, control both heating circulators using
a relay with a 120VAC coil, such as a Honeywell
R4222, as shown in Figures 37A and 37B. Select a
relay with a contact rating in excess of the combined
draw of the two circulators.
3. Low Voltage Connections (Figure 35) – These
connections are screw terminals located on the
terminal strip next to the junction box on the left:
• Terminals 1 and 8 – “Heating” thermostat
connections
• Terminals 5 and 6 – “External Limit Control”
connections
• Terminals 3 and 4 – “Outdoor Reset Sensor”
connections
• Terminals 2 and 4 – “Domestic Indirect Water
Heater” thermostat connections
• Terminal 7 – “Flame Signal Reading”
• Heat anticipator setting for the thermostat
connection is 0.1 A when thermostat is connected
directly to terminals 1 and 8.
WaRning
When making low voltage connections, make
sure that no external power source is present
in the thermostat or limit circuits. if such a
power source is present, it could destroy the
boiler’s Microprocessor Control (MCBa). One
example of an external power source that could
be inadvertently connected to the low voltage
connections is a transformer in old thermostat
wiring.
4. If the outdoor sensor is connected to terminals 3
and 4, the boiler will adjust the target space heating
set point supply water temperature downwards
as the outdoor air temperature increases. If used,
this sensor should be located on the outside of the
structure in an area where it will sense the average
air temperature around the house. Avoid placing this
sensor in areas where it may be covered with ice or
snow. In general, locations where the sensor will
pick up direct radiation from the sun should also
be avoided. Avoid placing the sensor near potential
sources of electrical noise such as transformers,
power lines, and uorescent lighting. Wire the
sensor to the boiler using 22 gauge or larger wire.
As with the sensor, the sensor wiring should be
routed away from sources of electrical noise. Where
it is impossible to avoid such noise sources, wire
the sensor using a 2 conductor, UL Type CM, AWM
Style 2092, 300Volt 60°C shielded cable. Connect
one end of the shielding on this cable to ground.
50
Page 51
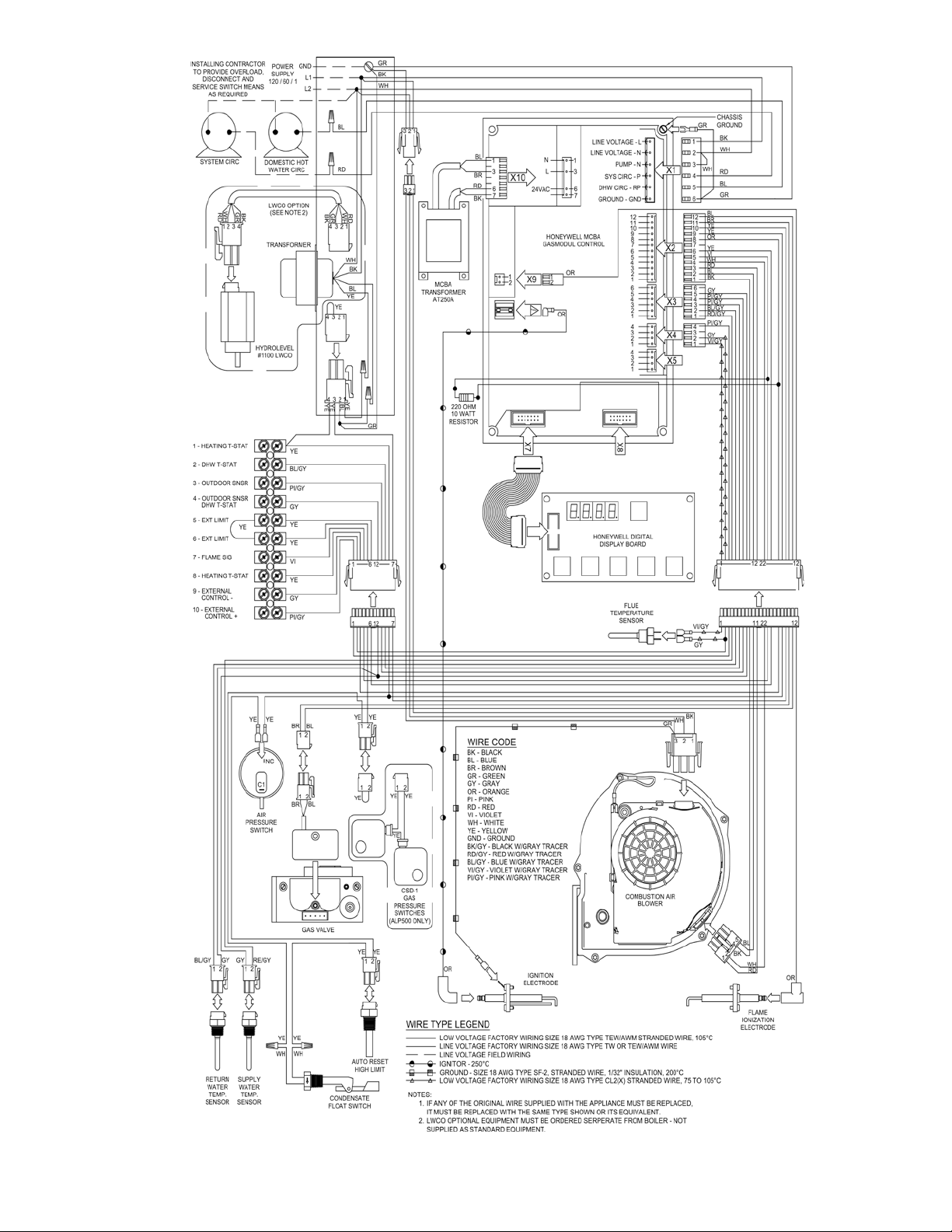
Figure 35: Wiring Connections Diagram
51
Page 52

52
Figure 36: Ladder Diagram
Page 53

Figure 37A: Modied Wiring For DHW Priority When Using Low Flow Circulator Piped Off System Header -
Heating (with Central Heating Circulators) Plus alternately Piped indirect Water Heater
53
Page 54

Figure 37B: Modied Wiring For DHW Priority When Using Low Flow Circulator Piped Off System Header -
Heating (with Central Heating zone Valves) Plus alternately Piped indirect Water Heater
54
Page 55

Figure 38: Wiring for MCBa Modulating Boiler Control Time Delay Relay Box
5. If the boiler installation site may be subject to low
supply voltage conditions or “brownouts”, that
would affect MCBA Modulating Boiler Control
operation, a separate optional Time Delay Relay
Box (P/N 101693-01) installation is strongly
recommended. See Figure 38 “Wiring for MCBA
Modulating Boiler Control Time Delay Relay Box”
and follow the following installation steps:
a.
Turn off power to boiler.
b. Remove 120 volt power wiring, L1, L2 and
ground.
c. Remove cover to MCBA Time Delay Relay Box.
d. Mount MCBA Time Delay Relay Box on secure
surface near boiler.
e. Connect wiring to MCBA Time Delay Relay Box
as per wiring diagram (Figure 38).
f. Connect additional eld wiring (not included
in the kit) from MCBA Time Delay Relay Box
to 120 volt power wiring as per wiring diagram
(Figure 38).
g. Install cover on MCBA Time Delay Relay Box
and restore power to boiler.
h. Measure time from when power is restored until
the boiler actually powers up (LED numbers
will reappear on MCBA display panel). This
MCBA Time Delay Relay Box has a delay on
make timer that delays powering of the boiler for
3 minutes whenever power is lost to the boiler.
Timing should be approximately 3 minutes, but
no longer than 4 minutes.
i. Cycle boiler per installation manual.
55
Page 56

iX. Boiler Stacking
For installations with unusually high space heating
and/or domestic hot water heating loads, where employing
two (2) Alpine (ALP) boilers will offer the benets of
greater operational efciency, oor space savings and boiler
redundancy, the Alpine (ALP) boilers may be installed
stacked one on the top of the other. Refer to Table 18
“Alpine (ALP) Boiler Model Stacking Combinations” for
details.
Table 18: alpine (aLP) Boiler Model
Stacking Combinations
Bottom Boiler Model Top Boiler Model
ALP080 ALP080
ALP105
ALP150
ALP210
ALP285
ALP399
ALP080
ALP105
ALP080
ALP105
ALP150
ALP080
ALP105
ALP150
ALP210
ALP080
ALP105
ALP150
ALP285
ALP080
ALP105
ALP150
ALP210
ALP285
ALP399
A. To eld assemble individual Alpine (ALP) boilers
into a stackable conguration, use the steps below:
1. Position the bottom boiler rst. Refer to Sections II
“Pre-Installation” and III “Unpacking Boiler” of the
manual for details. Always position higher input
boiler model as bottom boiler.
2. Each Alpine (ALP) boiler is factory packaged with
two (2) Stacking Boiler Attachment Brackets (P/N
101679-01) and the bracket mounting hardware [six
(6) self-drilling hex washer head plated #8 x ½”
long screws, P/N 80860743]. Locate and remove
the brackets and the hardware. The Stacking Boiler
Attachments Bracket has three 7/32” diameter holes
punched in a triangular pattern. See Figure 39
“Stacking Boiler Attachment Bracket Placement”.
3. Alpine (ALP) boiler left and right side panels have
a series of dimples at panel top and bottom. These
dimples are positioning dimples for Stacking Boiler
Attachment Bracket mounting screws. Side panel
bottom positioning dimples are evenly spaced
from boiler front and back, while side panel top
positioning dimples follow specic pattern to
compensate for Alpine (ALP) boiler model variable
depth.
4. Position the upper boiler on the top of the bottom
boiler and align boiler front doors and sides ush
with each other.
• Place rst Stacking Boiler Attachment Bracket
onto the upper boiler left side panel, at the panel
lower left corner and align bracket two upper
holes with corresponding side panel lower
dimples.
• The remaining lower bracket hole must align
with a matching bottom boiler left side panel top
positioning dimple.
• Once bracket holes and side panel dimple
alignment is veried, attach the bracket to top
and bottom boiler left side panels with the
mounting screws.
5. Repeat above procedure to install second Stacking
Boiler Attachment Bracket and secure the stacked
boiler right side panels together at the front right
corner.
6. Install the third Stacking Boiler Attachment Bracket
to secure top and bottom boiler left side panels at
the rear left corner. Align the bracket holes with
corresponding positioning dimples in the top boiler
and bottom boiler left side panels, then secure
bracket with the screws.
7. Repeat above procedure to install the forth Stacking
Boiler Attachment Bracket to secure stacked boiler
right side panels at the rear right corner.
B. When installing stackable boiler combinations
observe the following guidelines:
1. Venting - Top and bottom boilers must have their
individual concentric vent piping and vent terminals.
WaRning
no common manifolded venting is permitted.
For side-wall venting individual model vent
terminals must terminate not closer than 12
inches horizontally and three (3) feet vertically
from each other in order to prevent combustion
air contamination. For vertical through the roof
venting, individual vertical vent terminals, if level
with each other, must be spaced no closer than 12
inches horizontally. If vertical terminals cannot end
in one plane, they must be spaced no closer than
three (3) feet horizontally.
Chimney chase concentric venting is permitted for
modules, when stackable, providing concentric
56
Page 57

vertical (roof) vent terminals, if level with
each other, are spaced no closer then 12 inches
horizontally.
If vertical vent terminals cannot end in one plane,
they must be spaced no closer then three (3) feet
horizontally.
Follow instructions in Section IV “Venting” of
the manual for specics of individual boiler vent
termination. Follow instructions in Section V for
each individual boiler ue gas condensate line
construction and condensate disposal. Terminating
individual boiler condensate lines into common
pipe prior to drain disposal is permissible, providing
common pipe has sufcient ow capacity to
handle combined condensate volume of stackable
combination.
2. Gas Piping - Follow instructions in Section VII “Gas
Piping” of the manual for sizing and installation
of an individual boiler. When common gas piping
is sized, insure it will have adequate capacity for
combined input (GPH gas ow) of the selected
stackable boiler combination.
3. Water Piping and Trim - Follow instructions in
Section VI “Water Piping and Trim” of the manual
for system piping and boiler secondary piping
selection/sizing based on combined heating
capacity and/or gross output of the selected
stackable boiler combination. Follow instructions
of Section VI for each individual boiler trim
installation.
4. Electrical - Follow instructions in Section VIII
“Electrical” of the manual to wire individual boilers.
Stackable boilers require a separate, installer
provided, staging control (Tekmar Model 265 or
equivalent) to operate the boilers. Follow control
manufacturer instructions to wire it to the boilers.
Figure 39: Stacking Boiler attachment Bracket Placement
57
Page 58
X. Modular installation
A. General Guidelines
1. Read and follow all venting, combustion air,
water piping, gas piping and electrical instructions
contained in the Installation, Operating and Service
Instructions unless otherwise instructed in this
section.
Consult Local Building Codes or National Fuel Gas
2.
Code, NFPA 54/ANSI Z222.3 for restrictions and
instructions on modular boiler installations.
B. Modular Boiler Venting System Arrangements
Using CPVC/PVC pipe for Individual Module Vent
Piping – (See Figure 40)
1. Each individual module (boiler) must have own
vent pipe and vent terminal. Refer to Section IV
“Venting” of these Instructions for individual
module (boiler) venting guidelines and options.
WaRning
no common manifolded venting (vent piping and
vent terminals) is permitted.
2. The individual module (boiler) maximum vent
length is sixty (60) equivalent feet.
3.
For side wall venting the minimum horizontal
distance between any adjacent individual module
(boiler) vent terminations is twelve (12) inches.
Additional horizontal spacing between any adjacent
individual module (boiler) vent terminations as well
as extending the distance from building surfaces
to vent termination end are recommended to avoid
frost damage to building surfaces where vent
terminations are placed.
CaUTiOn
installing multiple individual module (boiler) vent
terminations too close together may result in
combustion product water vapor condensation
on building surfaces, where vent termination are
placed, and subsequent frost damage. To avoid/
minimize frost damage, extend the distance from
building surfaces to vent termination end and
increase the horizontal distance between adjacent
vent terminations.
4. Individual module (boiler) sidewall vent terminals
must be placed at least twelve (12) inches above the
ground plus the expected snow accumulation.
Multiple individual module vertical vent pipes may
5.
be piped through a common conduit or chase so that
one roof penetration may be made.
The minimum horizontal distance between any
adjacent individual module (boiler) roof vent
58
terminations is one (1) foot.
Using PVC Pipe for Individual Module Combustion
Air Intake Piping – (See Figure 40)
1.
Each individual module (boiler) must have own
combustion air intake pipe and combustion air
intake terminal. Refer to Section IV “Venting” of
these Instructions for individual module (boiler)
combustion air intake guidelines and options.
The individual module (boiler) maximum
2.
combustion air intake pipe length is sixty (60)
equivalent feet.
3.
If possible, locate each individual module (boiler)
both combustion air intake termination and vent
termination on the same side wall, to prevent
nuisance boiler shutdowns.
However, if same side wall placement is
problematic, an individual module (boiler) may
be installed using vertical venting and side wall
combustion air intake termination (or, vice versa)
Using Concentric Combination Venting/Combustion
Air Intake Piping - Inner Polypropylene Vent
Pipe/Outer Combustion Air Intake Steel Pipe Casing
– (See Figure 40)
1. Each individual module (boiler) must have own
concentric vent pipe and vent termination. Follow
Section IV “Venting” of these Instructions for
individual module (boiler) concentric venting
guidelines.
WaRning
no common manifolded concentric venting is
permitted.
2. The individual module (boiler) maximum concentric
vent length is sixty (60) equivalent feet.
3. For sidewall venting any adjacent individual module
(boiler) concentric vent terminals must be spaced no
closer than 12 inches horizontally and three (3) feet
vertically from each other to prevent combustion air
contamination.
Additional horizontal spacing between any
adjacent individual module (boiler) concentric vent
terminations and increased distance from building
surfaces to concentric vent termination end are
recommended to avoid frost damage to building
surfaces where vent terminations are placed.
Individual module (boiler) sidewall concentric
4.
vent terminals must be placed at least twelve (12)
inches above the ground plus the expected snow
accumulation.
5. For vertical through the roof venting any adjacent
individual module (boiler) vertical vent terminals, if
level with each other, must be spaced no closer than
12 inches horizontally.
Page 59

Figure 40: Modular Boiler Direct Vent Termination
59
Page 60

60
Figure 41: Modular Boiler Concentric Vent Termination
Page 61

If vertical vent terminals cannot end in one plane,
they must be spaced no closer than three (3) feet
horizontally.
6. Chimney chase concentric venting is permitted for
modules, when stackable, providing concentric
vertical (roof) vent terminals, if level with
each other, are spaced no closer then 12 inches
horizontally.
If vertical vent terminals cannot end in one plane,
D. Modular Boiler Gas Piping
1. Individual module (boiler) gas pipe sizing specic
details
Individual module (boiler) recommended gas piping.
2.
See Figure 34.
3.
Requirement to install additional gas pressure
regulators to properly regulate gas pressure at the
input of the smallest individual module (boiler).
they must be spaced no closer then three (3) feet
horizontally.
7.
When individual modules (boilers) are installed in
the same horizontal plane, chimney chase vertical
concentric venting is permitted provided:
a. Sufcient inside space available at the base of
the chimney to install multiple chimney chase
brackets and support elbows.
b. Spacing between adjacent vertical vent terminals
is in accordance with paragraph 6 above.
if gas pressure in the building is above ½ psig,
an additional gas pressure regulator is required.
Using one additional regulator for multiple
boilers may result in unsafe boiler operation.
The additional regulator must be able to properly
regulate gas pressure at the input of the smallest
boiler. if the regulator cannot do this, two or
more additional regulators are required. Consult
WaRning
regulator manufacturer and/or local gas supplier
CaUTiOn
installing multiple individual module (boiler)
concentric vent terminations too close together
may result in combustion product water vapor
condensation on building surfaces, where
termination are placed, and subsequent frost
damage. To avoid/minimize frost damage extend
the distance from building surfaces to concentric
vent termination end as well as increase the
horizontal distance between adjacent concentric
vent terminations.
for instructions and equipment ratings.
E. Modular Boiler Electrical
Refer to Section VIII “Electrical” of these Instructions
for:
Individual module (boiler) wiring specic details
1.
2. Individual module (boiler) internal wiring details,
high and low voltage connections
Each individual module (boiler) must be provided with own
fused disconnect and own service switch.
Install modular boiler wiring in accordance with requirements of
authority having jurisdiction. In absence of such requirements,
C. Modular Boiler Water Piping – (See Table 19 and
Figure 42)
Refer to Section VI “Water Piping and Trim” of these
Instructions for:
1. Installation of Factory Supplied Piping and Trim
Components for an individual module (boiler).
2. Regarding an individual module (boiler) piping
system specic details.
3. Selection criteria for individual module (boiler)
space heating and/or DHW circulators.
follow the National Electric Code, NFPA 70 and/or CSA C22.1
Electric Code.
F. Modular Boiler Control Systems – (See Figures 44
and 45)
1. Follow modular boiler control system manufacturer
(Honeywell, Tekmar etc.) instructions to properly
apply a modular control system.
2. Tekmar model 264 and model 265 based control
wiring diagrams (Figures 44 and 45) are provided as
examples of typical modular boiler control system.
3. Additionally, common modular boiler control
systems may use outdoor temperature sensing,
return water temperature sensing or both to stage
Table 19: Modular Boiler Water Manifold Sizing
number of Units
Boiler Model
aLP080 1¼” 1½” 2” 2½” 2½” 2½” 2½”
aLP105 1½” 2” 2” 2½” 2½” 2½” 3
aLP150 2” 2” 2½” 2½” 2½” 3
aLP210 2” 2½” 3
aLP285 2½” 2½” 3
aLP399 2½” 3
2 3 4 5 6 7 8
Recommended Minimum Common Water Manifold Size (nPT)
” 3” 3½” 4” 4”
” 3½” 3½” 4” 5”
” 3” 4” 4” 5” 5”
modular boilers.
” 3½”
”
61
Page 62

62
Figure 42: Modular Boiler Water Piping w/Domestic Hot Water Heater
nOTiCE
installing a low water cutoff in the system piping
of modular boilers is strongly recommended and
may be required by Local Codes.
Page 63

Figure 43: Modular Boiler Water Piping w/Domestic Hot Water Heater (Continued)
63
Page 64

Analog communication signal established
Sequence of Operation
Tekmar 265 Based Control System (or equal)
64
Figure 44: Modular Wiring Diagram w/Tekmar 265 Control
The Tekmar 265 Control (or equal) can control either 3 modulating boilers or 2 modulating boilers and an Indirect Water Heater. When a call for heat is
received by the Tekmar 265 Control, the control will re either one or more boilers in either parallel or sequential ring mode to establish a required reset
water temperature in the system supply main based on outdoor temperature. The boilers will modulate based on an
between the Tekmar 265 Control and each boiler’s MCBA Control. This signal is established by means of a pair of wires from boiler terminal strip to 265
Control utilizing a 500 OHM ¼ watt resistor bridging the conductor connections (the resistors are installer provided and available at any electronic parts store
like Radio Shack, etc.). The boiler(s) and system supply water temperature will be reset together to maintain what is needed to the system. When a call for
Indirect Hot Water is generated to the Tekmar 265, the control will de-energize the zone pump control (ZC terminal), energize the Indirect pump and modulate
the boiler ring to establish a setpoint temperature in the main for the Indirect Heater using Priority. The Tekmar 265 also controls each boiler’s pump and a
post purge of leftover temperature in the boilers will occur at the end of the call for Indirect Hot Water.
Page 65

ekmar 264
Figure 45: Modular Wiring Diagram w/Tekmar 264 Control
Sequence of Operation
Tekmar 264 Based Control System (or equal)
Control. When a call for Indirect Hot Water is generated to the Tekmar 264, the control will de-energize the zone pump control (ZC terminal), energize the
Indirect pump and sequentially re the boilers to establish a setpoint temperature in the main for the Indirect Heater using Priority. The Tekmar 264 Control will
disable the stage ring and post purge the Indirect Pump to reduce the temperature in the Supply Main near the end of the Indirect Mode to a point where it will
need to be when it changes back to Space Heating Mode. The Tekmar 264 Control also has the ability to rotate the lead-lag ring of the boilers to establish
The Tekmar 264 Control (or equal) can control up to four (4) boilers and an Indirect Water Heater by utilizing stage ring. When a call for heat is received
by the Tekmar 264 Control, the control will re either one or more boilers in sequential ring mode to establish a required reset water temperature in the
system supply main based on outdoor temperature. The boilers will modulate on their own based on each boiler’s MCBA Control and will target a setpoint
temperature to supply enough temperature to the system main to satisfy the desired reset water temperature in the main established by the T
equal operating time for each boiler stage.
65
Page 66

Xi. System Start-up
A. Verify that the venting, water piping, gas piping and
electrical system are installed properly. Refer to
installation instructions contained in this manual.
B. Conrm all electrical, water and gas supplies are
turned off at the source and that vent is clear of
obstructions.
C. Conrm that all manual shut-off gas valves between
the boiler and gas source are closed.
WaRning
Completely read, understand and follow all
instructions in this manual before attempting
start up.
D. If not already done, ush the system to remove
sediment, ux and traces of boiler additives. This must
be done with the boiler isolated from the system. Fill
entire heating system with water meeting the following
requirements:
nOTiCE
pH between 8.2 and 9.5.
if system contains aluminum components, pH
must be less than 8.5
Total Dissolved Solids - less than 2500 PPM
Hardness - 3 to 9 grains/gallon.
Pressurize the system to at least 12 PSI. Purge air from
the system.
nOTiCE
If it is required to perform a long term pressure
test of the hydronic system, the boiler should
rst be isolated to avoid a pressure loss due to
the escape of air trapped in the boiler.
To perform a long term pressure test including
the boiler, ALL trapped air must rst be removed
from the boiler.
a loss of pressure during such a test, with no
visible water leakage, is an indication that the
boiler contained trapped air.
3.
Temporarily turn off all other gas-red appliances.
4. Turn on gas supply to the boiler gas piping.
5. Open the eld installed manual gas shut-off valve
located upstream of the gas valve on the boiler.
Conrm that the supply pressure to the gas valve is
6.
14 in. w.c. or less. Refer to Table 21 for minimum
supply pressure.
7. Using soap solution, or similar non-combustible
solution, electronic leak detector or other approved
method. Check that boiler gas piping valves, and
all other components are leak free. Eliminate any
leaks.
DangER
Do not use matches, candles, open ames or
other ignition source to check for leaks.
WaRning
The maximum operating pressure of this boiler
is 30 psig. never exceed this pressure. Do not
plug or change pressure relief valve.
E. Conrm that the boiler and system have no water
leaks.
F. Prepare to check operation.
1. Obtain gas heating value (in Btu per cubic foot)
from gas supplier.
2. Alpine gas valves have inlet and outlet pressure
taps with built-in shut off screw. Turn each
screw from fully closed position three to four
turns counterclockwise to open taps. Connect
manometers to pressure taps on gas valve.
66
8. Purge gas line of air.
G. Operating Instructions
Start the boiler using the lighting instructions, see
Figure 46. After the boiler is powered up, it should go
through the following sequence.
Sequence Display Meaning
1 U.125 Checking internal software
or Blank (power-up only)
2 0.SWT Boiler in standby. SWT = Supply
Water Temp. No call for heat.
(After call for heat from heating
thermostat)
3 A.SWT Self-Check on Start-up
4 5.SWT Blower and circulator on. Check-
ing for adequate air ow.
5 1.SWT Prepurge
6 2.SWT Trial for ignition
7 3.SWT Flame established. Boiler re-
sponding to a call for heat.
Page 67

Alpine™ Series Lighting and Operating Instructions
Figure 46: Lighting instructions
67
Page 68

Figure 47: Burner Flame
H. Purge Air From Gas Train
Upon initial start-up, the gas train will be lled with air.
Even if the gas line has been completely purged of air,
it may take several tries for ignition before a ame is
established. If more than 5 tries for ignition are needed,
it will be necessary to press the reset button to restart
the boiler. Once a ame has been established for the
rst time, subsequent calls for burner operation should
result in a ame on the rst try.
I. Check Burner Flame
Inspect the ame visible through the window. On high
re the ame should be stable and mostly blue (Figure
47). No yellow tipping should be present; however,
intermittent ecks of yellow and orange in the ame are
normal.
J. Check Gas Inlet Pressure
Check the inlet pressure and adjust if necessary. Verify
that the inlet pressure is between the upper and lower
limits shown on the rating plate with all gas appliances
on and off.
WaRning
The outlet pressure for the gas valve has been
factory set and requires no eld adjustment. This
setting is satisfactory for both natural gas and
propane. attempting to adjust the outlet pressure
may result in damage to the gas valve and cause
property damage, personal injury or loss of life.
Table 20: Recommended Combustion Settings,
natural gas
Altitude Range
0 - 7000 Ft.
% O2 Range CO, PPM
2
Less than 75
PPM
68
Boiler
Model
ALP080
ALP105
ALP150
ALP210
ALP285
ALP399
% CO
8.2 - 8.8 5.5 - 6.5
K. Perform Combustion Test
Perform a combustion test. Boilers equipped with a
concentric vent system have a ue gas sample tap
located in the boiler vent collar (under the screw cap).
Insert the analyzer probe in the ue gas sample tap.
Check CO2 (or O2) and CO at both high and low re.
The boiler may be temporarily locked into high or low
re for 15 minutes as follows:
1. To lock the boiler in high re, simultaneously press
and hold the “Mode” button and “+“ button until the
display ashes “H”, indicating that the boiler has
been driven to high re. After this happens, allow
the boiler to operate for approximately 5 minutes
before taking combustion readings.
To lock the boiler in low re, simultaneously press
2.
and hold the “Mode” button and “-“ button until the
display ashes “L”, indicating that the boiler has
been driven to low re. After this happens, allow the
boiler to operate for approximately 5 minutes before
taking combustion readings.
3.
Normal modulation of the boiler should return 15
minutes after the boiler is locked in high or low re.
ypical CO
T
readings are shown in Table 20.
2
WaRning
Each alpine Series boiler is tested at the factory
and adjustments to the air fuel mixture are
normally not necessary. Consult a U.S. Boiler
representative before attempting to make any
such adjustments. improper gas valve or mixture
adjustments could result in property damage,
personal injury, or loss of life.
L. Test External Limits
Test any external limits or other controls in accordance
with the manufacturer’s instructions.
M. Check Thermostat Operation
Verify that the boiler starts and stops in response to
calls for heat from the heating thermostat and indirect
water heater thermostat. Make sure that the appropriate
circulators also start and stop in response to the
thermostats.
Page 69

N. Adjust Supply Water Temperature
As shipped, the heating and indirect water heater set
point supply temperatures are both set to 180°F. If
necessary, adjust these to the appropriate settings for
the type of system to which this boiler is connected. See
Section XII “Operation” of this manual for information
on how to do this.
O. Adjust Thermostats
Adjust the heating and indirect water heater thermostats
to their nal set points.
P. Field Conversion From Natural Gas to LP Gas
Alpine Series boilers are factory shipped as Natural Gas
builds. Follow steps below for eld conversion from
Natural Gas to LP Gas.
WaRning
This conversion should be performed by a
qualied service agency in accordance with the
manufacturer’s instructions and all applicable
codes and requirements of the authority having
jurisdiction. if the information in these instructions
is not followed exactly, a re, an explosion or
production of carbon monoxide may result
causing property damage, personal injury, or loss
of life. The qualied service agency is responsible
for proper conversion of these boilers. The
conversion is not proper and complete until the
operation of the converted appliance is checked
as specied in the Alpine™ Installation, Operating
and Service instructions.
WaRning
These instructions include a procedure for
adjusting the air-fuel mixture on this boiler.
This procedure requires a combustion analyzer
to measure the CO2 (or Oxygen) and Carbon
Monoxide (CO) levels in ue gas. Adjusting the
air-fuel mixture without a proper combustion
analyzer could result in unreliable boiler operation,
personal injury, or death due to carbon monoxide
poisoning.
1. Make sure that the planned fuel conversion is listed
in Table 21. If the planned conversion is not shown
in Table 21, it is not permitted. Refer to Figure
34 to identify the valve used on the model being
converted.
Conversion of Alpine Series boilers from one fuel
2.
to another is accomplished using the throttle screw
on the gas valve. Figure 48 shows the location of
the throttle screw on the Dungs valve. Locate the
throttle on the boiler being converted.
Table 21: Permitted Conversions
Boiler
Model
ALP080
ALP105
ALP150
ALP210
ALP285
ALP399
Gas
Valve
Size
(NPT)
1/2”
3/4”
(Dungs)
Gas Valve Model
GB-WND 055 D01
S00 253082
GB-WND 055 D01
S00 253083
GB-WND 055 D01
S00 253084
GB-WND 057 D01
S00 253085
GB-WND 057 D01
S00 253086
Fuel Converted
From To
Natural
Gas
LP 0 - 7,000 Ft.
3. If conversion is being made on a new installation,
install the boiler in accordance with the installation
instructions supplied with the boiler. If an installed
boiler is being converted, connect the new gas
supply to the boiler, check for gas leaks, and purge
the gas line up to the boiler in accordance with
the National Fuel Gas Code (ANSI Z223.1) or the
requirements of the authority having jurisdiction.
4. Before attempting to start the boiler, make the
number of turns to the throttle screw called for in
Table 22.
Table 22: number of Clockwise Throttle Screw
Turns
Throttle Screw Turns at
Boiler Model Gas Valve
ALP080
ALP105 4
ALP150 3¼
ALP210 4
ALP285
ALP399
Dungs
GB-055
(½” NPT)
Dungs
GB-057
(¾” NPT)
Dungs
GB-057 HO
(¾” NPT)
Altitude Range
0 - 7000 Ft.
2¾
4½
1¾
5. Attempt to start the boiler using the lighting
instructions located inside the lower front cover of
the boiler. If the boiler does not light on the rst
try for ignition, allow to boiler to make at least
four more attempts to light. If boiler still does not
light, turn the throttle counter clockwise in 1/4 turn
increments, allowing the boiler to make at least
three tries for ignition at each setting, until the boiler
lights.
Planned
Installation
Altitude
Range
69
Page 70

7. Perform a combustion test. Boilers equipped with a
concentric vent system have a ue gas sample tap
located in the boiler vent collar (under the screw
cap).
8. While the burner is at high re adjust the throttle as
needed to obtain the CO
(or O2) settings shown in
2
the Table 23:
• To reduce the CO
(increase the O2) turn the
2
throttle clockwise
• To increase the CO2 (reduce the O2) turn the
throttle counter-clockwise
Make adjustments in increments of 1/8 to 1/4 turn
and allow the boiler at least a minute to respond to
each adjustment before making another. In general,
the CO level will be at its lowest somewhere in the
CO2 range shown in this table.
Table 23: Recommended Combustion Settings,
LP gas
Altitude Range
Boiler
Model
ALP080
ALP105
ALP150
ALP210
ALP285
ALP399
% CO
2
9.5 - 10.1 5.5 - 6.5
0 - 7000 Ft.
% O2 Range CO, PPM
Less than
75 PPM
Verify that the gas inlet pressure is between the
9.
Figure 48: Dungs gas Valve Detail
upper and lower limits shown in Table 24 with all
gas appliances (including the converted boiler) both
6. After the burner lights, force the burner to high re
by simultaneously pressing and holding the “Mode”
button and “+“ button. After a few seconds, the
display should ash “H”, indicating that the boiler
has been driven to high re. Allow the boiler to
operate for approximately 5 minutes before taking
combustion readings. Note: after 15 minutes, the
boiler is automatically released from high re hold.
Be sure to restore high re hold if additional time is
on and off:
10. A label sheet is provided with the boiler for
conversions from natural to LP gas. Once conversion
is completed, apply labels as follows:
• Apply the “Rating Plate Label” adjacent to the
rating plate.
• Apply the “Gas Valve Label” to a conspicuous
area on the gas valve.
needed to obtain high re combustion readings.
WaRning
The pressure regulator has been factory set using precision instruments and must never be adjusted in
the eld. The gas valve outlet pressure is the same for both natural gas and propane. Make sure that
all adjustments are made with the throttle, not the pressure regulator. attempting to adjust the pressure
regulator will result in damage to the gas valve and may cause property damage, personal injury or loss of
life.
70
Page 71

WaRning
The throttle adjustments shown in Table 22 are approximate. The nal throttle setting must be found using
a combustion analyzer. Leaving the boiler in operation with a CO level in excess of the value shown in
Table 23 could result in injury or death from carbon monoxide poisoning.
nOTiCE
if the throttle is very far out of adjustment on the “rich” (counter-clockwise) side, the boiler burner may be
running at 0% Excess Air or even with air deciency.
at 0% Excess air the CO2 readings will be either 11.9% CO2 for natural gas or 13.8% CO2 for LP gas (O2 will
be 0%) and CO level will be extremely high (well over 1000 PPM).
If the burner operates with air deciency, the following phenomena may be observed:
% CO2 will actually drop (% O2 will increase) as the throttle is turned counterclockwise
% CO
If the boiler appears to operate with air deciency, turn the throttle clockwise to increase the amount of
Excess air to the burner.
will actually increase (% O2 will drop) as the throttle is turned clockwise
2
as the throttle is turned clockwise, the CO
level will rise, eventually peaking @ 11.8% or 13.8%, depending
2
of the type of gas being used, before falling (conversely, O2 level will drop to 0% before rising). after this
happens, continue turning the throttle clockwise, until CO2 level drops (or O2 level increases) to the values
shown in Table 20 or Table 23.
Table 24: inlet Pressure Limits
Fuel
Natural Gas 4.0 14.0
LP 11.0 14.0
Inlet Pressure (Inches w.c.)
Min. Max.
• Apply the “Boiler Conversion Label” to a
conspicuous surface on, or adjacent to, the outer
boiler jacket. Fill in the date of the conversion
and the name and address of the company
making the conversion with a permanent marker.
1. Refer to Section XI “System Start-up” of this manual
1
and perform any checks not already completed.
71
Page 72

Xii. Operation
I. Factory Preset Boiler Operating Parameters
(See Table 25 for Parameter Descriptions)
A. The Alpine (ALP) boiler uses a microprocessor based
Honeywell control, known as a “MCBA”, to manage
all boiler functions including ame supervision and
modulation. Two set point or “target” boiler supply
temperatures are stored in the MCBA’s memory;
one for space heating and one for domestic water
production. If an outdoor temperature sensor is
connected to the boiler, the space heating supply set
point will automatically adjust downwards as the
outdoor temperature increases. For more information
on this feature see the discussion on boiler water reset
below.
The MCBA modulates the boiler input by varying the
fan speed. As the fan speed increases, so does the
amount of gas drawn into the blower. As a result, a
fairly constant air-fuel ratio is maintained across all
inputs.
The MCBA determines the input needed by looking
at both current and recent differences between the
supply temperature and the set point temperature.
As the supply temperature approaches the set point
temperature, the fan will slow down and the input drop.
Depending on the model boiler, the minimum input
is between 1/3 (high altitude) and 1/5 (sea level) of
maximum input.
The MCBA also monitors boiler return and ue
temperatures. In addition, all other safety controls,
including the low water cut-off and safety limit, are
connected into the MCBA. The MCBA uses input from
all of these controls to either shut down the boiler when
an unsafe condition exists or, in some cases, to correct
the problem.
B. The display panel has three primary modes of
operation. These are:
1. Standby Mode – Displays boiler’s current status.
This is the default operating mode.
2. Parameter Mode – Used to change control settings
3. Information Mode – Displays boiler operating
temperatures
Under normal conditions, the boiler is in standby mode
and the display looks like that shown in Figure 49. The
three digits to the right of the decimal point are the
boiler’s supply temperature. The digit to the left of the
decimal point is the boiler’s status code. A list of status
codes, and their meanings, is shown in Table 26.
Figure 50 is a map of the menu structure for the control
panel. Push the mode key to move from one mode
to the next. As you change modes, the mode you are
entering is shown on the display:
a. “PArA” for Parameter Mode
b. “Info” for Information Mode
72
c. “Stby” for Standby Mode. Upon entering
standby mode, “Stby” will briey appear on
the display and then the display will show the
boiler’s status along with the supply temperature
(Figure 49).
The
Figure 49: normal Display in Standby Mode
control will return to standby mode from any
other mode if no key is pressed for 20 minutes.
C. In standby mode, it is possible to view both the
heating supply set point temperature and the “domestic
hot water reference set point”. The “domestic hot
water reference set point” plus 45°F equals the boiler
supply set point when it is responding to a call from
the indirect water zone. It is not the actual domestic
hot water set point. The Alpine (ALP) is designed
for use with a storage type indirect water heater such
as the Alliance SL™. The domestic water set point
is controlled by the thermostat on the indirect water
heater. The “default domestic water reference set point”
is 135°F and target boiler supply temperature when
responding to a call from the indirect water heater is
therefore 180°F (135°F +45°F). The default heating
supply set point (parameter 4) is 180°F.
In standby mode it is also possible to turn on or off
either the heating or domestic water zone. There is
normally no reason to turn off either of these zones and
doing so is not recommended.
WaRning
Pushing and holding the “+” while in Standby
Mode will prevent the boiler from responding to
a call for heat. Pushing and holding the “-” while
in Standby Mode will prevent the boiler from
responding to a call for domestic water. if this
happens, “cOFF” or “dOFF” will appear on the
display. To turn back on the heating function,
press and hold “+” until “c” and the set point
temperature appears on the display. To turn back
on the domestic water function, press and hold “-”
until “d” and the set point temperature appears on
the display. after pressing any keys, and before
leaving the installation, verify that the boiler res
in response to a call for heat and domestic water.
Page 73

Table 25: Parameter Descriptions
Access
Code
no
access
Code
needed
Parameter
No.
1 T3set DHW 140
2 DHW system 1 (On)
3 CH system 1 (On)
4 T1top CH Mode 190
5 T1foot CH Mode 130
6 T4 minimum 0
7 T4 maximum 60
8 T4 frost protection * -22
9 T4 correction 0
10 Tblocking 32
11 Booster time 0
12 Tparallel shift 0
13/14 Maximum fanspeed CH 4450 4850 5500 6200 6300 5867
15/16 Maximum fanspeed DHW 4450 4850 5500 6200 6300 5867
17/18 Minimum fanspeed 1125 1250 1300 1375 1450 1267
19 Ignition fanspeed 3000 2300
20 CH postpump time 0
21 DHW postpump time 10.2
22 CH modulation hysteresis on 10
23 CH modulation hysteresis off 2
24 DHW modulation hysteresis on 10
25 DHW modulation hysteresis off 2
26 DHW detection hysteresis on -8
27 DHW detection hysteresis off 10
28 CH blocking time 0
29 DHW blocking time 0
Access Code Required
30 DHW-> CH blocking time 0
31 Modulate back difference T1-T2 54
32 RMCI Address -1
33 Tplus: Setvalue addition for DHW 50
34-1 2nd CH-Circuit (1st digit) 0 (2nd Heating Circuit Off)
34-2 CH Type (2nd digit) 0 (Room Thermostat)
35-1 DHW 3=way valve or pump (1st digit) 1 (Hot Water Pump)
35-2 DHW-type (2nd digit) 3 (Storage Tank without NTC3)
36 Manual fanspeed -1
37-1 PWM-pump level (1st digit) 4
37-2 PWM-pump level (2nd digit) 1
38 Tset hold boiler warm 36
39 Ttop for 2nd CH circuit 190
40 Tfoot for 2nd CH circuit 130
41 Thysteresis for 2nd CH circuit 10
42-1 Pump settings for CH and DHW 0 (CH Normal Pump)
42-2 Minimum Off Cycle (2nd digit) 0 (Not Active)
* Circulator will start when boiler supply sensor will detect temperature 44.6° F or less
Description
Factory Setting
ALP080 ALP105 ALP150 ALP210 ALP285 ALP399
73
Page 74

Figure 50: Basic Menu Tree
74
Page 75

D. Two basic types of errors codes are shown on the
display:
1. Soft Lockout Codes – When a soft lockout occurs,
the boiler will shut down and the display will
alternate between the number “9” and the letter
“b” followed by a two digit service code. A list of
these codes, and their meanings, is shown in Table
29 in Section XIV Troubleshooting. The boiler will
automatically restart once the condition that caused
the lockout is corrected.
Hard Lockout Codes – When a hard lockout occurs,
2.
the boiler will shut down and the display will ash
the letter “E” followed by a two digit service code.
A list of these codes, and their meanings, is shown
in Table 30 in Section XIV Troubleshooting. Once
the condition that caused the lockout is corrected,
the boiler will need to be manually reset using the
RESET button on the display.
Table 23: Boiler Status
First
Digit
0 Burner off - No call for heat or DHW
1 Pre-purge or post-purge
2 Ignition
3 Burner responding to call for heat
4 Burner responding to call for DHW
5 Checking air pressure switch
6 Burner off - Set point temperature has been reached
7 Call for heat ended. 10s heating post pump period
8 Call for DHW ended. 10s DHW post pump period
9 and b
Flashing
Burner off - on soft lockout. See Troubleshooting Section to
determine meaning of error code.
A Boiler responding to call from heating zone
H Burner on - Held in high re
L Burner on - Held in low re
Boiler Status
E. If an outdoor sensor is installed, the boiler will
automatically adjust the heating zone set point
temperature based on the outdoor reset curve in Figure
51. The maximum set point is dened by parameter
4 (factory set to 180°F) when the outdoor temperature
is 0°F or below. The minimum set point temperature
shown is 100°F when the outdoor temperature is 60°F
or above. As the outdoor temperature falls the supply
water target temperature increases. For example,
if the outdoor air temperature is 30°F, the set point
temperature for the supply water is 140°F.
F. An indirect water heater thermostat can be connected
between terminals 2 and 4 on the terminal strip. When
this thermostat closes, the central heating circulator will
be turned off and the DHW circulator will be turned on.
G. An external limit control can be installed between
terminals 5 and 6 on the terminal strip. Be sure to
remove the jumper between terminals 5 and 6 when
adding an external limit control to the system. If the
external limit opens, the boiler will shut down and error
code “b 26” will be displayed. If the limit installed is
a manual reset type, it will need to be reset before the
boiler will operate.
H. The sequence of operation for a Alpine Series boiler
on a call for heat from a thermostat is as described
below:
1. When power is rst turned on, 120V is provided
to the MCBA, the combustion fan and the LWCO
transformer. A separate 50VA transformer,
connected directly to the MCBA, powers all other
low voltage circuits.
2. For the rst few seconds after power-up the control
module goes through a self check.
3. When there is a call for heat, the control module
checks to make sure the air pressure switch is
open. If it is, the combustion fan will be energized
and will ramp up to ignition speed. When the air
pressure switch closes, a 10 second prepurge is
activated.
After the prepurge, the control module energizes
4.
the gas control valve and the spark for 4.5 seconds.
If a ame is established and proved, the control
allows the ame to stabilize for 5 seconds at the
combustion fan ignition speed setting. If the ame
fails to prove, the control module will attempt to
light the burner 4 more times. If a ame is still not
established, the control will lockout.
5. Once the ame stabilization period has ended,
the MCBA allows the burner to modulate. The
actual ring rate is dependent upon the measured
current and recent differences between the set point
temperature and the supply temperature. If an
outdoor sensor is connected to the control module
and the boiler is responding to a call for heat, the set
point temperature will be determined by the outdoor
reset curve shown in Figure 51.
6.
Once the set point temperature is reached, the
MCBA will turn the burner off and allow the
combustion fan to operate in postpurge for 30
seconds before it turns off.
The central heating pump will continue to operate
7.
until the room thermostat has been satised.
8.
A demand for domestic hot water (DHW) is given
priority on Alpine Series boilers. If a call for DHW
is received while the boiler is responding to a call
for heat, the heating circulator is de-energized until
the call for DHW is satised.
75
Page 76

Figure 51: Outdoor Reset Curve
II. Field Adjustable Boiler Operating
Parameters
MCBA control factory programmed operating parameters
will result in satisfactory operation under most conditions.
However, because all systems are different, there may exist
situations where boiler operation may be enhanced by
adjusting a few of these parameters in the eld. A total of
46 eld adjustable parameters are stored in the memory
of the MCBA control. By adjusting these parameters an
installer can ne-tune MCBA operation under different
elds conditions. Refer to Table 25 for the list of adjustable
parameters and their factory settings.
Parameters are numbered from “1” to “42-2”. Parameters
“1” thru “4” are accessible by anyone. Parameters “5” thru
“42-2” require an access code to be viewed and adjusted.
Parameters may be changed by:
• Using the keypad on the boiler as input device to
make adjustments.
• Using personal computer, hooked up to MCBA
control via the GPI PC Interface Kit (P/N 101152-
01), available from US Boiler, as input device to
make adjustments.
Additionally, either the keypad or the personal computer can
be used to obtain information about the boiler current status
and operating history.
A. Adjusting Parameters via Boiler Keypad
Entering the Access Code
1. With boiler running, toggle the Mode key until you
reach the (STBY) Standby mode.
2. Depress and hold the Step key and then quickly
depress and hold the Mode key for 2 - 6 seconds
until the display reads (CODE). Release the Mode
key, then the Step key. The display should show a
‘C’ followed by a random two digit number.
3. Use the + or - keys to scroll to the number 05.
4. Press the Store key momentarily and watch for the
display to blink twice. If the access code has been
successfully entered, the menu tree will be expanded
to include the items shown inside the dashed lines
in Figure 52. Access to parameters 5 - 42 will be
possible by following the instructions in Section
C. After 15 minutes have passed without any keys
being pressed, access to the expanded menu will
end and the access code will need to be reentered to
regain access to parameters 5 - 42.
NOTE: Access Code is not required for Parameters 1
thru 4.
Changing Parameters
1. Toggle the Mode key until you reach (PARA)
Parameter mode.
2. Press the Step key to scroll through the parameters
until you reach the desired parameter number.
3. Use the + or - key to scroll to the desired parameter
setting.
4. Press the Store key momentarily and watch for the
display to blink once. The parameter setting has
now stored it new value.
5. When using the keypad, all parameters show up on
the boiler display as two-digit numbers. This creates
the following special situations:
a. Two parameters are required to dene some
of the fan speeds. For example, the maximum
CH fan speed is dened by Parameters 13 and
WaRning
improper setting of parameters can cause unreliable or unsafe operation, resulting in property damage,
personal injury, or loss of life:
•
Changing parameters should only be attempted by a professional heating service technician.
•
Do not change any parameters not described in this manual without first consulting the
manufacturer.
•
After changing any parameters, carefully conrm proper boiler operation before leaving the installation
site.
76
Page 77

Figure 52: Expanded Menu Tree (Cont’d on next page)
77
Page 78

Figure 52: Expanded Menu Tree (cont’d.)
Figure 53: adjusting Boiler Water Reset Curve
78
Page 79

14; Parameter 13 denes the “thousands” and
hundreds” places and Parameter 14 denes the
“tens” and “ones” places. The ignition fan speed
is only adjustable in increments of hundreds, so
only one parameter (19) is required to dene it.
IMPORTANT: Field adjustment of fan speeds is
not recommended.
b. In some cases one two-digit number denes two
separate parameters. For example, if Parameter
34 is viewed on the boiler display, the “tens
place” is Parameter 34-1 (default value is 0) and
the “ones place” is Parameter 34-2 (default value
is also 0). As viewed on the boiler display, the
factory set Parameter 34 will therefore appear as
“00”. If Parameters 34-2 is changed to accept a
0-10 VDC reading from an AM-4 (see Section
D), Parameter 34 will then read “04” as viewed
on the boiler display.
Common Field Adjustments
Please note that although it is physically possible to
adjust all parameters listed in Table 25 the parameters
shaded gray need not be adjusted in the eld. In case
these parameters are accidentally changed, they should
be restored to default factory settings shown in Table 25
“Parameter Descriptions”.
Parameters permitted to be eld adjusted are non-
shaded ones in Table 25. In order to change these
parameters, three subsequent tasks must be performed:
1. Adjusting the target boiler supply temperature when
responding to call from an indirect water heater The default IWH target supply temperature is 180°F.
Since most indirect water heaters have ratings based
on 180°F boiler supply temperature, it should rarely
be necessary to adjust this parameter.
2. Changing the boiler water reset curve - When an
outdoor temperature sensor is connected to a Alpine
boiler, the MCBA will adjust the target boiler supply
temperature based on outdoor temperature when
the boiler is responding to a call for central heat.
Figure 53 is a graph showing the target boiler supply
temperature as a function of outdoor temperature.
The curve shown in Figure 53 is that obtained with
the factory set parameters. The shape of this curve
may be changed by changing Parameters 4, 5, 6, and
7 as shown in Figure 53. Refer to Part I Section C
for the procedure to change parameters.
If the outdoor sensor is not connected to the boiler,
the target supply temperature is always dened
by Parameter 4 when the boiler is responding to
a call for central heat, regardless of the outdoor
temperature. In this case, the settings of Parameters
5, 6, and 7 are meaningless.
3. Allowing an external control to directly manage
modulation of the boiler. The MCBA control
permits the Alpine to be modulated solely using 0 -
10 VDC signal supplied by an external control,
like multiple - modulating boiler control. When this
function is used, the boiler no longer responds to a
heating thermostat, or an outdoor sensor connected
to a boiler MCBA itself. The boiler will respond
normally to the call from the domestic hot water
thermostat.
In order for the boiler MCBA control to
recognize 0 - 10 VDC signal, Parameter 34-2
(“Room Thermostat” - see Table 25) must be
re-programmed. The factory programmed
default value for Parameter 34 is “0”. It must
be re-programmed to value “4” for MCBA to
recognize 0 - 10 VDC signal. Once this parameter
is changed, the boiler will ignore any call from a
thermostat connected across boiler terminals 1 and 2
(see Figures 35 and 36). It will continue to respond
to a call from the indirect water heater thermostat.
Also, Parameters 2 and 3 (see Table 25) should
be left at factory settings they could be changed
inadvertently (for example, pushing and holding
“+” or “-” key while boiler is in Standby Mode
will change them). If the boiler does not respond
to a call from one or both thermostats, verify that
Parameters 2 and 3 are both “ON”.
4. Communication, Fan Speed and Error Modes
In addition to providing access to all eld adjustable
parameters, entering the access code also provides
access to three additional mode menus using the
boiler keypad. These are shown in Figure 52:
a. Communication Mode - This mode does not
currently have any function.
b. Fan Speed Mode - Allows the user to view the
blower fan speed (ring rate is determined by fan
speed).
c. Error Mode - Pressing STEP while in Error mode
allows the user to see the six most recent error
codes.
79
Page 80

B. Adjusting Parameters via Personal Computer with
GCI Interface
1. Operating System Requirements
The GCI Interface requires a PC computer running a
Windows 98/NT/2000 or XP operating system. In
addition, the PC must have an open serial port.
2. Connecting Personal Computer to MCBA Control
a. Connect the serial cable from the GCI to the
computer.
b. Plug in the GCI.
c. Open the lower front jacket panel. Loosen the
screws holding the control cover and swing down
the control cover so that the control compartment
is open.
d Connect the ribbon cable from the GCI into the
open receptacle on the MCBA next to the ribbon
cable from the boiler display/keypad (Figure 54).
3. Installing GCI Interface Gascom Software
a. Gascom is the name of the software, which
must be installed on personal computer in order
to communicate with MCBA control via GCI
Interface.
b. Insert the Gascom CD in your computer’s
CDROM drive and wait a few seconds for the
software to prompt you to continue setup. Select
“NEXT” to continue the installation. Follow
the prompts to install the software. U.S. Boiler
highly recommends accepting the default
directories recommended.
c. The last screen allows the user to select whether
or not to restart the computer. The computer
must be restarted prior to using the Gascom
program.
d. U.S. Boiler recommends the user register the
software on the date of installation however
registration is not required. Registration gives
the user access to our technical support personnel
online as well as information about software
updates. To register the software click on the
“Gascom Online” icon on the desk top and
select “Registration”. You will be asked to ll
out a short form including your e-mail address.
Once the form is submitted a return e-mail will
be sent to you conrming the information you
entered along with your registration number.
e. Open Gascom by selecting the “Gascom
1.0” icon on the desk top. Before using the
program for the rst time it must be congured
properly to work with the Alpine boiler and
your computer. Go to the menu bar and select
“Gascom” and then “Conguration”. Refer to
the menu tree shown in Figure 55.
i. From the drop down box labeled
“MCBA1400” select the “Standard
HR7A60Hz” option.
ii. From the drop down box labeled “Interface
device” select the “CGI232” option.
iii. The “Communication port” setting is the
serial port on the PC to which the GCI
interface is connected. Most often this serial
port will be “COM1”.
iv. The “Gascom Directory” eld will contain
the correct eld and will not need to be
changed as long as you accepted all of the
default le locations during installation.
Otherwise, you will need to locate the
Gascom directory on your hard drive and
enter the correct path name in this eld.
v. If you wish to access Parameters 5 to 42
enter “05” in the “Access Code” eld (the
access code will need to be entered every
time the Gascom program is reopened).
Changing Parameters
Open the Gascom Program
1. If not already done connect GCI PC Interface, and
install the Gascom software as described in Part II
of this manual and open the Gascom software.
2. Click on the “Parameters” menu on the top of the
screen.
3. Click on “Read from MCBA”. After a few seconds,
a list of parameters and their settings will appear
on the screen. Parameters which are not accessible
are grayed out. If the access code has not been
entered in the conguration screen, this will include
Parameters 5-42. Parameters 43 and above are
always grayed out because they are inaccessible in
the eld.
80
Figure 54: MCBa Control
Page 81

Figure 55: gascom Menu Tree
4. Double-click on the desired parameter. A window
will open with either a eld or a pull down list of
options will appear. Enter or select the desired
value for the parameter.
5. Click OK.
6. Repeat Steps (3) - (5) to change any other desired
parameters.
7. After all parameters have been changed, click on the
“Parameters” menu at the top of the screen and then
click on “Write to MCBA”. After a few seconds,
the display on the boiler will blink. This indicates
that the parameters are written to the control and are
in effect.
Field Adjustable Parameters
Refer to Field Adjustable Parameters under A.
Adjusting Parameters via Boiler Keypad on pages 76
and 79 of this manual.
Using Gascom To Monitor The MCBA
From the Monitor Menu select “Monitor MCBA”.
This will bring up a window which plots the following
information:
1.
Temperatures:
Flow - Actual boiler supply temperature
Return - Actual Boiler return temperature
Outdoor - Temperature being read by outdoor sensor
if it is connected. If it is not, temperature reading is
“-22”.
Fluegas - Flue gas temperature
Set - Target boiler supply temperature
Status:
2.
Room - Room thermostat (“1” = Calling, “0” = Not
Calling)
81
Page 82

Hotwater - Indirect water heater thermostat (“1” =
Calling, “0” = Not Calling)
Pump - Heating circulator (“1” = On, “0” = Off)
Air-switch - Status of air pressure switch (“1” =
Closed, “0” = Open)
Gaspressure - This is actually the status of the high
limit (“1” = Closed, “0” = Open)
GasValve - Status of gas valve (“1” = Open , “0” =
Closed)
Flame - Shows whether the MCBA detects the
presence of the burner ame (“1” = Flame, “0” = No
Flame)
DHW Pump - Indirect water heater circulator (“1” =
On, “0” = Off)
3. RPM:
Fan - Actual speed of fan
Set - Target speed of fan.
Reading the MCBA Error Log
1. The MCBA keeps a log of the last six error codes.
To view these error codes select “Read from
MCBA” from the Error Menu.
2. This data can be saved as a le to disk by selecting
“Save to le” from the Error Menu or printed by
selecting “Print” from the same menu.
3. Error codes can also be removed from the memory
of the MCBA by selecting “Clear in MCBA” from
the Error Menu.
III. Component Test Procedures
A. Flame Signal Check
1. The ame signal can be checked between terminal
number 7 on the low voltage terminal strip and
ground. A good signal reading should be 6 VDC or
greater.
2. If the signal is lower then 6 VDC, check the
continuity of the ground wire between the ignitor
and the junction box. If the ground wire is suspect
replace the ground wire.
3.
If the ground wire is in good condition, remove
the ignitor and ame sensor to inspect the ceramic
insulator for cracks. If none are found, sand off
any oxide deposits which formed on the electrodes.
If the insulator is cracked or the electrode cannot
be properly cleaned, replace the ignitor and ame
sensor. When replacing the ignitor and ame sensor,
be sure to replace the ignitor and ame sensor
gasket as well.
4.
Other problems that can cause a low ame signal
include:
• An improperly adjusted throttle (conrm that the
CO2 is within the limits shown in the installation
manual).
• Fouling of the burner (remove the burner and
clean with compressed air).
• Low inlet gas pressure (verify that gas pressure
is within the limits shown on the rating plate).
• Grounded 24 VAC or sensor wiring (this problem
will result in no ame voltage reading, but will
normally not result in an E02 error because there
is still adequate ame current).
B. NTC Temperature Sensors
1. The supply, return, ue, and outdoor reset sensors
used on the Alpine are of the resistance type.
2. The Table 27 shows the range of resistance values
for these sensors at various temperatures.
82
Page 83

Table 27: nTC Sensor Resistance Values
83
Page 84

Xiii. Service and Maintenance
DangER
This boiler uses ammable gas, high voltage electricity, moving parts, and very hot water under high
pressure. assure that all gas and electric power supplies are off and that the water temperature is cool
before attempting any disassembly or service.
Do not attempt any service work if gas is present in the air in the vicinity of the boiler. never modify,
remove or tamper with any control device.
WaRning
This boiler must only be serviced and repaired by skilled and experienced service technicians.
if any controls are replaced, they must be replaced with identical models.
Read, understand and follow all the instructions and warnings contained in all the sections of this
manual.
i
f any electrical wires are disconnected during service, clearly label the wires and assure that the wires
are reconnected properly.
n
ever jump out or bypass any safety or operating control or component of this boiler.
Read, understand and follow all the instructions and warnings contained in aLL of the component
instruction manuals.
ssure that all safety and operating controls and components are operating properly before placing
a
the boiler back in service.
nOTiCE
Warranty does not cover boiler damage or
malfunction if the following steps are not
performed at the intervals specied.
A. Continuously:
1. Keep the area around the boiler free from
combustible materials, gasoline and other ammable
vapors and liquids.
2. Keep the area around the combustion air inlet
terminal free from contaminates .
3. Keep the boiler room ventilation openings open and
unobstructed.
B. Monthly Inspections:
1. Inspect the vent piping and outside air intake piping
to verify they are open, unobstructed and free from
leakage or deterioration. Call the service technician
to make repairs if needed.
2. Inspect the condensate drain system to verify it is
leak tight, open and unobstructed. Call the service
technician if the condensate drain system requires
maintenance.
3. Inspect the water and gas lines to verify they are
free from leaks. Call the service technician to make
repairs if required.
CaUTiOn
Water leaks can cause severe corrosion damage
to the boiler or other system components.
immediately repair any leaks found.
C. Annual Inspections and Service: In addition to
the inspections listed above the following should be
performed by a service technician once every year.
If equipped, test the low water cutoff by pressing
1.
the “Test” button located at its end. The yellow
light should come on and “E12” should ash on
the display. Push the reset button on the display to
restore normal operation. If the yellow light does
not come on, determine why the low water cutoff is
not working properly.
2. Follow the procedure for turning the boiler off
found in the Alpine™ Series Lighting and Operating
Instructions.
84
Page 85

3. Inspect the wiring to verify the conductors are in
good condition and attached securely.
CaUTiOn
Label all wires prior to disconnection when
servicing controls. Wiring errors can cause
improper and dangerous operation. Verify
proper operation after servicing.
4. Remove the ignition electrode and inspect it for
oxides. Clean the oxides from the electrode with
steel wool. Do not use sandpaper for the cleaning.
Inspect the ceramic insulator for cracks and replace
the ignitor assembly if necessary. Check the ignitor
electrode spacing gap. Refer to Figure 56 “Ignitor
Electrode Gap” for details.
Figure 56: ignitor Electrode gap
5. Remove the fan/gas valve assembly from the burner
hood. Inspect for lint and dust. If signicant lint
and dust are found, disassemble the fan/gas valve
assembly to expose the swirlplate and fan inlet (see
the exploded diagram in the parts list at the back of
this manual). Vacuum these parts as required, being
careful not to damage the vanes on the swirlplate.
6.
Remove the burner hood to access the burner and
the combustion chamber.
7. Remove the burner and vacuum any dust or lint
from the burner. If the burner shows signs of
deterioration or corrosion, replace it immediately.
Inspect the burner gasket and replace, if necessary.
8. Inspect the heat exchanger, clean and vacuum any
debris found on the surfaces. A soft nylon brush
must be used for cleaning. Remove insulation disc
and clean the surfaces by ushing with clean water.
Drain and ush the inside of the heat exchanger
and condensate collector. Do not use any cleaning
agents or solvents. Re-install insulation disc.
9. Inspect the condensate trap to verify it is open and
free from debris. Inspect condensate line integrity
between boiler and condensate neutralizer (if used)
and condensate neutralizer and the drain. Clean/
repair if needed.
If the condensate neutralizer is used, check pH
before and after the neutralizer to determine
neutralizing effectiveness. Replace limestone chips
and clean out the neutralizer if needed.
10.
Reinstall the burner, burner hood and fan/gas valve
assembly.
1. Reconnect any wiring which has been disconnected.
1
12. Inspect the heating system and correct any other
deciencies prior to restarting the boiler.
13. Follow Section XI System Start-up before leaving
installation.
14. Perform the combustion test outlined in Section XI
System Start-up.
15. Verify that the system PH is between 8.2 and 9.5/.
16. Check for vent terminal obstructions and clean as
necessary.
D. Recommended Heating System Water Treatment
Products:
1. System Cleaning and Conditioning:
a. The following heating system water treatment
products are recommended for an initial existing
heating system sludge removal, initial boiler
cleaning from copper dust, ux residue and any
boiler debris and for preventive treatment as
corrosion/scale inhibitors:
i. Fernox™ Restorer (universal cleaner, sludge
remover, scale remover, ux residue/debris
remover, corrosion inhibitor)
ii. Fernox™ Protector (Alphi 11, CH#, Copal)
(sludge remover, corrosion inhibitor)
Follow manufacturer application procedure
for proper heating system/boiler cleaning
and preventive treatment.
Above referenced products are available
from Cookson Electronics Company, 4100
Sixth Avenue, Altoona, PA 16602, Tel:
(814) 946-1611 and/or selected HVAC
distributors. Contact US Boiler for specic
details.
iii. Equivalent system water treatment products
may be used in lieu of products referenced
above.
2. System Freeze Protection:
a. The following heating system freeze protection
products are recommended for Alpine boilers:
i. Fernox™ Protector Alphi 11 (combined
antifreeze and inhibitor).
Follow manufacturer application procedure
to insure proper antifreeze concentration and
inhibitor level.
Above referenced product is available from
Cookson Electronics Company, 4100 Sixth
Avenue, Altoona, PA 16602, Tel: (814) 9461611 and/or selected HVAC distributors.
Contact US Boiler for specic details.
85
Page 86

b. Equivalent system freeze protection products
may be used in lieu of product referenced
above. In general, freeze protection for new or
existing systems must use specially formulated
glycol, which contains inhibitors, preventing
the glycol from attacking the metallic system
components. Insure that system uid contains
proper glycol concentration and inhibitor level.
The system should be tested at least once a year
and as recommended by the manufacturer of the
glycol solution. Allowance should be made for
expansion of the glycol solution.
CaUTiOn
Use only inhibited propylene glycol solutions
specically formulated for hydronic systems.
Do not use ethylene glycol, which is toxic and
can attack gaskets and seals used in hydronic
systems.
E. Condensate Overow Switch and Condensate Trap
Removal and Replacement:
For removal or replacement of the condensate overow
switch and/or condensate trap follow the steps below.
For parts identication, refer to Section XV “Repair
Parts”.
1. Condensate Overow Switch Removal and
Replacement:
a. Disconnect power supply to boiler.
b. Remove two (2) wire nuts and disconnect
overow switch wire pigtails from boiler wiring.
c. Using pliers, release spring clip securing the
overow switch to condensate trap body and
remove the switch. Note that the switch has
factory applied silicon adhesive seal, which may
have to be carefully cut all around to facilitate
the switch removal.
d. Insure the trap overow switch port is not
obstructed with silicon seal debris, clean as
needed.
e. Apply silicon seal to the replacement switch
threads and install the switch into the trap
body making sure it is properly oriented - the
arrow molded into the switch hex end side
must face down for proper switch operation.
See Figure 57 “Condensate Overow Switch
Orientation” for details.
f. Reconnect the switch wire pigtails to the boiler
wiring and secure with wire nuts.
g.
Restore power supply to boiler. Fill up the trap
(see Section V “Condensate Disposal”) and
verify the switch operation.
2. Condensate Trap Removal and Reinstallation:
a. Disconnect power supply to boiler.
b. Remove two (2) wire nuts and disconnect
overow switch wire pigtails from boiler wiring.
c. Disconnect pressure switch hose from
condensate trap.
d. Disconnect outside condensate compression
tting from condensate trap stab.
e. Using pliers, release spring clip securing the
overow switch to condensate trap body and
remove the switch. Note that the switch has
factory applied silicon adhesive seal, which may
have to be carefully cut all around to facilitate
the switch removal.
f. Using pliers, release spring clip securing
condensate trap body to the heat exchanger
bottom drain stab.
g. Firstly, pull the trap downwards to release from
the heat exchanger bottom drain stab; secondly,
pull the trap end from left side jacket panel
sealing grommet and remove the trap from
boiler.
h. To reinstall the trap, reverse above steps.
i. If the original condensate overow switch is
to be re-used, follow the appropriate switch
removal steps from Condensate Overow Switch
Removal and Replacement procedure above.
j. Insure that fresh silicon sealant is applied to
the overow switch threads, and the switch is
properly oriented relative to the trap body -
the arrow molded into the switch hex side end
must face down for proper switch operation.
See Figure 57 “Condensate Overow Switch
Orientation” for details. Insure that pressure
switch hose is reconnected to the trap.
k. Restore power supply to boiler. Fill up the trap
(see Section V “Condensate Disposal”) and
verify the switch operation.
86
Page 87

Figure 57: Condensate Overow Switch Orientation
87
Page 88

XiV: Troubleshooting
WaRning
Turn off power to boiler before replacing fuses or working on wiring.
A. Troubleshooting problems where no error code is displayed. Refer to Table 28 for problems and possible causes.
Table 28: no Error Code Displayed
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSES
Display Blank, Fan off, LWCO lights off • No 120VAC Power at boiler. Check breaker and wiring between breaker panel and boiler
Display Panel Blank, Fan running
Display reads “U.125” continuously, Fan running
Boiler not responding to call for heat,
Status code on display =”0” (see Figure 50)
Boiler res, but display panel is blank
• Loose 120VAC connection wiring between boiler J-Box and MCBA
• Blown “F1” fuse in MCBA (see Figure 58 for location). Replace with 5A fuse provided
• Defective AT250 transformer
• Blown “F3” fuse in MCBA (see Figure 58 for location). Replace with 4A slow-blow fuse
provided
• Boiler is not seeing call for heat. Check thermostat or zone wiring for loose connection,
miswiring, or defective thermostat/zone control.
• Loose ribbon cable
• Defective display
88
Figure 58: MBCa Fuse Location
Page 89

B. Trouble shooting problems where a soft lockout code is displayed. When a soft lockout occurs, the boiler will shut down
and the display will alternate between the number “9” and the letter “b” followed by a two digit service code. The boiler will
automatically restart once the condition that caused the lockout is corrected.
Table 29: Soft Lockout Codes Displayed
CODE CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSES
• Blockage in intake or vent system.
• Vent and/or intake system not constructed in accordance with Part VI.
b 08 Pressure switch circuit open
b 18
MCBA supply sensor detected temperatures in excess
of 200°F
• Blocked or leaking pressure switch tubing
• Heat exchanger or burner blockage
• Terminals exposed to high winds
• Blockage in condensate trap above vent.
• Heating load at time of error was far below the minimum ring rate of the
boiler
• Defective primary pump or no ow in primary loop (Piping Method 1)
• Control system miswired so that boiler operation is permitted when no zones
are calling
b 19
b 24
b 25 Supply water temperature has risen too quickly
b 26
b 30
b 61 Pressure switch circuit closed with fan off
MCBA return sensor detected temperatures in excess
of 200°F
MCBA is reading a return sensor temperature higher
than the supply sensor temperature. Condition must be
present for at least 75s for this error code to appear.
Boiler safety limit, or external limit wired across
terminals 3&4, is open.
Temperature rise between supply and return is too
high.
• See possible causes for “b18”
• Flow through boiler reversed
• Sensor wiring reversed
• Flow through boiler reversed. Verify correct piping and pump orientation.
• No boiler water ow. Verify that system is purged of air and that appropriate
valves are open.
• Sensor wiring reversed.
• Supply or return sensor defective.
• See possible causes for “b18”
• Inadequate boiler water ow. Verify that pump is operating and that pump
and piping are sized per Part VIII of this manual
• See possible causes for “b18”
• Defective supply sensor.
• Inadequate boiler water ow. Verify that pump is operating and that pump
and piping are sized per Part VIII of this manual
• Blockage in pressure switch hose
• Pressure switch wires shorted together
• Defective pressure switch
• Loose or miswired fan speed harness (if “b61” error code is observed while
fan is running)
b 65 Fan is not achieving set point speed
• Loose or incorrect fan speed control connection
• Defective fan
89
Page 90

C. Trouble shooting problems where a hard lockout
code is displayed. When a hard lockout occurs, the
boiler will shut down and the display will ash the
the condition that caused the lockout is corrected, the
boiler will need to be manually reset using the RESET
button on the display.
letter “E” followed by a two digit service code. Once
Table 30: Hard Lockout Codes Displayed
CODE CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSES
E 00
E 02 Flame failure after 5 tries to restart
E 03 Gas valve error
E 04 Power failure occurred after lockout
E 05
E 06
E 07
E 11
E 12 Low water cut-off circuit open
E 13
E 14
E 15
E 16
E 17
E 18
E 19
E 28
E 29 Blower fan speed has not returned to zero rpm
E 31 Shorted supply temperature sensor
E 32 Shorted return temperature sensor
E 35 Flue gas temperature sensor short circuit
E 36 Supply water temperature sensor circuit open
E 37 Return water temperature sensor circuit open
E 40 Flue gas temperature sensor circuit open
E 44 Internal control failure • Reset the control. If problem reoccurs, replace the MCBA.
E 52 Flue gas temperature over 230°F
E 60 Internal control failure • Reset the control. If problem reoccurs, replace the MCBA.
A ame signal was present when there should
be no ame.
Internal control failure • Reset the control. If problem reoccurs, replace the MCBA.
Internal control failure • Reset the control. If problem reoccurs, replace the MCBA.
MCBA supply sensor detected temperatures in
excess of 200°F for an extended period of time
MCBA return sensor detected temperatures in
excess of 200°F for an extended period of time
Blower is not running when it should or fan speed
signal not being detected by MCBA
• Defective gas valve - make sure inlet pressure is below maximum on rating plate
before replacing valve.
• No gas pressure
• Gas pressure under minimum value shown on rating plate
• Gas line not completely purged of air
• Defective Electrode
• Loose burner ground connection
• Defective Ignition Cable
• Defective gas valve (check for 24 VDC at harness during trial for ignition before
replacing valve)
• Air-fuel mixture out of adjustment - consult factory
• Loose or defective gas valve harness. Check electrical connections.
• Defective gas valve (check for 24 VDC at harness during trial for ignition before
replacing valve)
• Some other error on this list occurred and power to the boiler was then
interrupted. Reset control and see if hard lockout reoccurs.
• If yellow light on LWCO is on, system is low on water
• If neither yellow nor green light is on, check LWCO harness and check for
24VAC across AT140 transformer
• See possible causes for “b18” error. Also, check safety limit for proper operation.
• See possible causes for “b19” error.
• Loose connection in 120 VAC fan wiring
• Loose or miswired fan speed harness
• Defective fan
• Miswired fan speed harness
• Defective fan
• Shorted or miswired supply sensor wiring
• Defective supply sensor
• Shorted or miswired return sensor wiring
• Defective return sensor
• Shorted or miswired ue temp sensor wiring
• Defective ue temp sensor
• Loose or miswired supply sensor wiring
• Defective supply sensor
• Loose or miswired return sensor wiring
• Defective return sensor
• Loose or miswired ue temp sensor wiring
• Defective ue temp sensor
• Heat exchanger needs to be cleaned
• Boiler over-red
• Air-fuel mixture out of adjustment - consult factory
90
Page 91

XV. Repair Parts
All Alpine™ Series Repair Parts may be obtained through your local Burnham Wholesale distributor.
Should you require assistance in locating a Burnham distributor in your area, or have questions regarding
the availability of Burnham products or repair parts, please contact Burnham Customer Service at
(717) 481-8400 or Fax (717) 481-8408.
91
Page 92

Key
Description
No.
1 Heat Exchanger, Burner, Etc. (Key No’s 2 thru 23) 101520-01 101521-01 101522-01 101523-01 101524-01 101525-01
2 Heat Exchanger Assembly 101710-01 101711-01 101712-01 101713-01 101714-01 101715-01
3 Burner Assembly 101717-01 101718-01 101719-01 101720-01 101721-01 101722-01
4 M6x1 Hex Flange Nut (Not Shown) (6) 101724-01
5 Gas/Air Intake Duct Assembly (Not Shown) 101725-01 101725-02
6 Gas/Air Intake Duct Weldment (Not Shown) N/A
7 Burner Plate (Not Shown) 101727-01
Burner Plate Insulation
8
(Warning: Contains RCF, Not Shown)
9 Burner Plate Inner Seal (Not Shown) 101729-01
10 Burner Plate Outer Seal (Not Shown) 101730-01
11 Burner Head (Not Shown) 101731-01 101731-02 101731-03 101731-04 101731-05 101731-06
12 Burner Head Seal (Not Shown) 101732-01
13 Ignitor 101733-01
14 Flame Sensor 101734-01
15 Observation Glass Retaining Plate 101735-01
16 Observation Glass 101736-01
17 Observation Glass Gasket 101737-01
M3x6 mm Socket Hd Thread Forming Screw,
18
T10 Drive (Not Shown)
19 Ignitor Gasket (Not Shown) 101740-01
20 Flame Sensor Gasket (Not Shown) 101741-01
M4x8 mm Socket Hd Cap Thread Forming Screw,
21
X20 Drive (Not Shown)
M5x14 mm Pan Hd Thread Forming Screw, T25 Drive
22
(Not Shown)
23 Insulation Disc (Warning: Contains RCF, Not Shown) 101996-01
31 Air Vent Valve 101586-01
32 Water Temp Sensor (2) 101685-01
33 High Limit 101653-01
42 Wire Harness (Not Shown) 101454-01
ALP080 ALP105 ALP150 ALP210 ALP285 ALP399
(Quantity) Part Number
101728-01
(2) 101738-01
(4) 101739-01
101742-01
92
Page 93

Key
Description
No.
Gas Train Assembly
23
(Key No’s 24 thru 29)
24 Blower 101527-01 101528-01 101529-01 101530-01
25 Blower Inlet Shroud Assembly 101704-01 101704-02 101704-03 101704-04
26 Blower Outlet Gasket 101345-01
27 Blower Mounting Plate N/A
28 Gas Valve 101703-01 101703-03 101703-04 101703-05 101703-06
29 Gas Valve Harness with Plug Included with Gas Valve (Key 28)
ALP080 ALP105 ALP150 ALP210 ALP285 ALP399
101585-01 101585-02 101585-03 101585-04 101585-05 101585-06
(Quantity) Part Number
93
Page 94

94
Key
Description
No.
35 Air Pressure Switch 80160762 101862-01
36 Air Pressure Switch Hose 7016039 7016046
37 Rubber Grommet, Condensate Trap 101595-01
38 Condensate Trap, Blow Molded 101239-01
39 Spring Clip, Condensate Trap (2) 101632-01
40 Blocked Condensate Drain Switch 101587-01
41 Condensate Comp. Fitting 101546-01
ALP080 ALP105 ALP150 ALP210 ALP285 ALP399
(Quantity) Part Number
Page 95

Key
Description
No.
42 Wiring Harness (Not Shown) 101454-01
MCBA Slide Out Assembly
43
(Includes all parts shown)
44 Control Panel, MCBA 101219-01
45A MCBA (programmed - 0-2000’ or 0-7000’) 101866-01 101866-02 101866-03 101866-04
45B MCBA (programmed - 2001 - 7000’) 101866-08 101866-09 101866-10 101866-11 N/A
46 MCBA Transformer 100474-01
47 MCBA Display Board 100450-01
48 MCBA Display Board Cable 101331-01
49 Label, MCBA Display 101609-01
50 MCBA Display Spacer (4) 101636-01
ALP080 ALP105 ALP150 ALP210 ALP285 ALP399
(Quantity) Part Number
101230-01
10186
6-05
101866-06
95
Page 96

96
Key
Description
No.
30 Rubber Grommet, Gas Line 820SOL0001
51 Jacket, Rear/Bottom Panel 101217-01 101217-02 101217-03 101217-04 101764-01 101764-02
52 Lower Front Door Assembly 101227-01 101227-02
53 Draw Latch 101037-01
54 Jacket, Left Side Panel 101215-01 101215-02 101215-03 101215-04 101765-01 101765-02
55 Jacket, Right Side Panel 101216-01 101216-02 101216-03 101216-04 101766-01 101766-02
56 Partition Shelf Assembly 101536-01 101536-02 101536-03 101536-04 101536-05 101536-06
57 Jacket Support Bracket 101593-01
58 Jacket, Top Panel 101218-01 101218-02 101218-03 101218-04 101218-05 101218-06
59 Bracket Assembly, Right Side 101232-01 101232-02 101232-03 101232-04 101232-05 101232-06
60 Side Bracket 101224-01 101224-02 101224-03 101224-04 101224-05 101224-06
61 Junction Box Cover 101326-01
62 Bracket, Rear HX Support 101381-01
63 Bracket, Left Clip 101507-01 101507-02
64 Bracket, Right Clip 101508-01
65 Rubber Pad, Right Clip 101245-01
66 Jacket, Upper Front Panel 101509-01
67 Gasket, Header (All Three) 101240-01 N/A
68 Gasket, Header, 1” NPT N/A 101243-01 N/A
69 Gasket, Header, 1” & 3/4” NPT N/A 101252-01 N/A
70 Gasket, Header, Duo Size N/A 101372-02 101372-03
71 Gasket, Header, Duo Size N/A 101372-01
ALP080 ALP105 ALP150 ALP210 ALP285 ALP399
(Quantity) Part Number
101638-01
Page 97
Key
Description
No.
34 Flue Temp Sensor 101687-01
42 Wire Harness (Not Shown) 101454-01
72 Concentric Vent Collar with Viton Cap 101598-01 101599-01
76 Vent Terminal Kit 101808-01 101809-01
ALP080 ALP105 ALP150 ALP210 ALP285 ALP399
(Quantity) Part Number
97
Page 98

Key No. Description
iSCELLanEOUS PaRTS CaRTOn
M
73 Temperature/Pressure Gauge 8056169
74 External Gas Shut Off Valve 806SOL0005 101615-01
75 Relief Valve 81660363 81660302
77 Boiler Drain Valve 806603061
78 Boiler Stacking Brackets (4) 101679-01
79 Boiler Stacking Bracket Screws (12) 80860743
80 Outdoor Temperature Sensor (1) 101639-01
98
(Quantity) Part Number
ALP080 ALP105 ALP150 ALP210 ALP285 ALP399
101777-01 101777-02 101777-03
Page 99

important Product Safety information
Refractory Ceramic Fiber Product
Warning:
The Repair Parts list designates parts that contain refractory ceramic fibers
(RCF). RCF has been classified as a possible human carcinogen. When
exposed to temperatures about 1805°F, such as during direct flame contact,
RCF changes into crystalline silica, a known carcinogen. When disturbed as a
result of servicing or repair, these substances become airborne and, if inhaled,
may be hazardous to your health.
AVOID Breathing Fiber Particulates and Dust
Precautionary Measures:
Do not remove or replace RCF parts or attempt any service or repair work
involving RCF without wearing the following protective gear:
1. A National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH)
approved respirator
2. Long sleeved, loose fitting clothing
3. Gloves
4. Eye Protection
• Take steps to assure adequate ventilation.
• Wash all exposed body areas gently with soap and water after contact.
• Wash work clothes separately from other laundry and rinse washing
machine after use to avoid contaminating other clothes.
• Discard used RCF components by sealing in an airtight plastic bag. RCF
and crystalline silica are not classified as hazardous wastes in the United
States and Canada.
First aid Procedures:
• If contact with eyes: Flush with water for at least 15 minutes. Seek
immediate medical attention if irritation persists.
• If contact with skin: Wash affected area gently with soap and water.
Seek immediate medical attention if irritation persists.
• If breathing difficulty develops: Leave the area and move to a location
with clean fresh air. Seek immediate medical attention if breathing
difficulties persist.
• Ingestion: Do not induce vomiting. Drink plenty of water. Seek
immediate medical attention.
99
Page 100

e. Boilers installed outside the 48 contiguous United States, the State of Alaska,
and Canada.
f. Damage to the boiler and /or property due to installation or operation of the
boiler that is not in accordance with the boiler installation and operating instruction
manual.
g. Any damage of failure of the boiler resulting from hard water or scale buildup in the
heat exchanger.
h. Any damage caused by improper fuels, fuel additives or contaminated combustion
air that may cause fireside corrosion and/or clogging of the burner or heat
exchanger.
i. Any damage resulting from combustion air contaminated with particulate which
cause clogging of the burner or combustion chamber including but not limited to
sheetrock or plasterboard particles, dirt, and dust particulate. (See Air Ventilation
section of the Installation and Operating Manual furnished with the unit)
j. Any damage, defects or malfunctions resulting from improper operation,
maintenance, misuse, abuse, accident, negligence including but not limited to
operation with insufficient water flow,improper water level, improper water
chemistry,or damage from freezing. (See System Piping, Start up and Checkout,
Operation and Service and Maintenance sections of the Installation and
Operating Manual furnished with the unit)
k. Any damage caused by water side clogging due to dirty systems or corrosion
products from the system.(See System Piping section of the Installation and
Operating Manual furnished with the unit)
l. Any damage resulting from natural disaster.
m. Damage or malfunction due to the lack of required maintenance outlined in the
Service and Maintenance section of the Installation and Operating Manual
furnished with the unit.
6. Exclusive Remedy:U.S. Boiler Company, Inc. obligation forany breach of these
warranties is limited to the repair or replacement of its parts in accordance with the
terms and conditions of these warranties.
7. Limitation of Damages: Under no circumstances shall U.S. Boiler Company,
Inc. be liable for incidental, indirect, special or consequential damages of any kind
whatsoever under these warranties, including, but not limited to, injury or damage to
persons or property and damages for loss of use, inconvenience or loss of time. U.S.
Boiler Company,Inc. liability under these warranties shall under no circumstances
exceed the purchase price paid by the owner for the residential grade water boiler
involved.Some states do not allow the exclusion or limitation of incidental or
consequential damages, so the above limitation or exclusionmay not apply to you.
8. Limitation of Warranties:These warranties set forth the entire obligation of U.S.
Boiler Company,Inc. with respect to any defect in a residential grade stainless
steel water boiler and U.S.Boiler Company, Inc. shall have no expressobligations,
responsibilities or liabilities of any kind whatsoever other than those set forth herein.
These warranties are givenin lieu of all other express warranties.
ALL APPLICABLE IMPLIED WARRAnTIES, If Any, InCLUDIng Any WARRAnTy
Of MERChAnTABILITy OR fITnESS fOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE ARE
ExPRESSLy LIMITED In DURATIOn TO A PERIOD Of OnEyEAR ExCEPT ThAT
IMPLIED WARRAnTIES, If Any, APPLICABLE TO ThE hEAT ExChAngER In A
RESIDEnTIAL STAInLESSSTEEL gRADE WATER BOILER ShALL ExTEnD TO
ThE ORIgInAL OWnER fOR A MAxIMUM Of TWELVE yEARS AT ThE ORIgInAL
PLACE Of InSTALLATIOn.SOME STATES DO nO ALLOW LIMITATIOn On hOW
LOng An IMPLIED WARRAnTy LASTS, SO ThE ABOVE LIMITATIOn MAy nOT
APPLy TO yOU.
In order to assure prompt warranty service, the owner is requested to complete and
mail the attached Warranty Card within ten days after the installation of the boiler,
although failure to comply with this request will not void the owner’srights under these
warranties.
Upon discovery of a condition believed to be related to a defect in material or
workmanship covered by these warranties,the owner should notify the installer, who
will in turn notify the distributor. If this action is not possibleor does not produce a
prompt response, the owner should write to U.S.Boiler Company, Inc., Burnham
hydronics, at P.O.Box 3079, Lancaster,PA 17604, giving full particulars in support
of the claim.
The owner is required to make available for inspection by U.S.Boiler Company, Inc.
or its representative the parts claimed to be defective and, if requested by U.S. Boiler
Company, Inc. to ship these parts prepaid to U.S.Boiler Company, Inc.at the above
address for inspection or repair. In addition, the owner agrees to make all reasonable
efforts to settle any disagreement arising in connection with a claim before resorting
to legal remedies in the courts.
ThIS WARRAnTygIVES yOU SPECIfIC LEgAL RIghTS AnDyOU MAy ALSO
hAVE OThER RIghTS WhICh VARyfROM STATE TO STATE.
Subject to the terms and conditions set forth below, U.S. Boiler Company, Inc.
Lancaster, Pennsylvaniahereby extendsthe followinglimited warranties to the
original owner of a residential grade stainless steel water boiler manufacturedand
shipped on or after november 1, 2007:
U.S.Boiler Company, Inc. warrants to the original owner that its residential grade
stainless steel water boilers comply at the time of manufacture with recognized
hydronic industry standards and requirements then in effect and will be free of
defects in material and workmanship under normal usage for a period of one year
from the date of original installation. If any part of a stainless steel water boiler is
found to be defectivein material or workmanship during this one year period, U.S.
Boiler Company,Inc. will, at its option, repair or replace the defectivepart.
The second through 7th year warranty covers only the heat exchanger. All other
component parts furnished by U.S. Boiler Company,Inc., but purchased from other
manufacturers, shall be limited to their warranties, if any.
U.S.Boiler Company, Inc. warrants to the original owner and at its original place
of installation that the heat exchanger of its residential grade stainless steel water
boilers will remain free from defects in material and workmanship under normal
usage for seven years. If a claim is made under this warranty during the first seven
years from the date of original installation, U.S.Boiler Company, Inc. will, at its
option, repair or replace the heat exchanger. If a claim is made under this warranty
after the expiration of sevenyears and up to twelve years from the date of original
installation, U.S.Boiler Company, Inc. will, at its option and upon payment of the
pro-rated service charge set forth below, repair or replace the stainless steel heat
exchanger. The service charge applicable to a stainless steel heat exchanger
warranty claim is based upon the number of years the heat exchanger has been
in service and will be determined as a percentage of the retail price of the heat
exchanger model involved at the time the warranty claim is made as follows:
nOTE: If the heat exchanger model involvedis no longer available due to product
obsolescence or redesign, the value used to establish the retail price will be the
published price as shown in the Burnham hydronics Repair Parts Price Sheet
where the heat exchanger last appeared or the current retail price of the then
nearest equivalent heat exchanger.
1. Applicability:The limited warranties set forth above are extended only to the
original owner at the original place of installation within the United States and
Canada. These warranties are applicable only to stainless steel water boilers
designated as residential grade by U.S.Boiler Company, Inc.and installed in a
single or two-family residence and do not apply to steam boilers of any kind, any
application other than for space heating or to commercial grade boilers.
2. Components Manufactured by Others: Upon expiration of the one year limited
warranty on residential grade stainless steel water boilers, all boiler components
manufactured by others but furnished by U.S. Boiler Company, Inc. (such as
burners, gas valves and controls) will be subject only to the manufacturer’s
warranty, if any.
3. Proper Installation: The warranties extended by U.S.Boiler Company,Inc. are
conditioned upon the installation of the residential grade stainless steel water boiler
in strict compliance with U.S.Boiler Company, Inc. installation instructions. U. S.
Boiler Company,Inc. specifically disclaims liability of any kind caused by or relating
to improper installation.
4. Proper Use and Maintenance: The warranties extended by U.S.Boiler Company,
Inc. conditioned upon the use of the residential gradestainless steel water boiler for
its intended purposes and its maintenance in accordance with U.S.Boiler Company,
Inc. requirements and hydronics industry standards.
5. This warranty does not cover the following:
a. Expenses for removal or re-installation. The homeowner will be responsible for
the cost of removing and reinstalling the alleged defective part or its replacement
and all labor and material connected therewith, and transportation to and from
U.S.Boiler Company, Inc.
b. Components that are part of the heating system but were not furnished by
U.S.Boiler Company, Inc., as part of the residential boiler.
c. Improper burner adjustment, control settings, care or maintenance.
d. This warranty cannot be considered as a guarantee of workmanship of an
installer connected with the installation of the U.S.Boiler Company, Inc. boiler,
or as imposing on U.S.Boiler Company, Inc.liability of any nature for
unsatisfactory performance as a result of faultyworkmanship in the installation,
which liability is expressly disclaimed.
PROCEDURE FOR OBTAINING WARRANTY SERVICE
ONE YEAR LIMITED WARRANTY ON RESIDENTIAL
STAINLESS STEEL GRADE WATER BOILERS
Limited Warranty
FOR RESIDENTIAL GRADE STAINLESS STEEL WATER BOILERS
TWELVE YEAR LIMITED WARRANTY ON HEAT EXCHANGER
ADDITIONAL TERMS AND CONDITIONS
years in Service 1-7 8 9 10 11 12 13 +
Service Charge
as % of
Retail Price
no
Charge
30 40 50 60 70 100
10/07
100
 Loading...
Loading...