Page 1

OBD 1350 ProGrade OBDII Scan Tool
en User guide
Page 2

en | 2 | User guide
| OBD 1350
ProGrade OBDII Scan Tool
Serial No: __________________________________
SW ID: _____________________________________
HW Ver: ____________________________________
Boot Ver: ___________________________________
Prod ID: ____________________________________
Board ID: ___________________________________
Burn Date: _________________________________
Record the above information about your tool. The information is available
at Main Menu --> System Setup --> Tool Information. Provide this information when contacting technical support.
If you have questions or concerns contact Technical Support:
Phone: 1-800-228-7667
Email: tech@boschdiagnostics.com
The information, specifications and illustrations in this guide are based on
the latest information available. Bosch reserves the right to make changes
at any time without notice.
580001 | REV. A | 11.2016
Page 3

OBD 1350 ProGrade OBDII Scan Tool | User guide | 3 | en
Table of Contents
1 Safety Precautions ....................... 5
1.1 Read All Instructions ................ 5
1.2 Safety Messages ...................5
2 Important Safety Warnings and Instructions .. 5
3 Getting Started .........................8
3.1 Introduction .......................8
3.2 Download Scanning Suite ............ 8
3.3 OBDII ............................8
3.4 SAE Publications ...................8
3.5 OBDII Data Link Connector (DLC) ...... 8
OBD II Data Link Connector (DLC) Pins .. 9
3.6 OBDII Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs) . 9
Powertrain Codes ...................9
Chassis Codes ......................9
Body Codes ........................ 9
Network Communication Codes ........9
4 Using the Scan Tool .....................10
4.1 The Scan Tool .....................10
4.2 Specifications ..................... 10
Dimensions .......................10
4.3 Display ..........................10
Keypad ..........................10
4.4 Power ...........................11
Internal Battery .................... 11
Vehicle Power ..................... 11
USB Power .......................11
4.5 System Setup .....................11
Changing Measurement Units ......... 11
Changing Auto-Power Off ............12
Quick Test ........................ 12
Print Header ...................... 12
Language Setup ................... 13
Long PID Names ................... 13
Pre-Trigger Setup ..................14
Tool Information ...................14
Display Test ....................... 14
Keypad Test ....................... 15
Memory Test ......................16
Program Mode ....................16
4.6 Vehicle-Specific Features ............16
Review Data ......................16
Recording ........................ 17
Print Data ........................18
4.7 Code Lookup ..................... 19
4.8 Locating the OBD II Data Link Connector
(DLC) 19
4.9 Connect the Tool ..................19
4.10 Vehicle Selection .................. 20
4.11 CodeConnect® Feature ............. 21
4.12 Code Criteria .....................22
4.13 Acronyms ........................ 22
4.14 Component Locator ................23
5 Diagnostic Menu .......................23
5.1 I/M Monitors (Emissions) ........... 24
5.2 Read Codes ......................25
5.3 Erase Codes ...................... 27
5.4 MIL Status ....................... 28
5.5 State OBD Check ..................29
5.6 View Data ........................29
View Entire List .................... 30
Custom List Select ................. 30
5.7 Record Data ...................... 31
5.8 View Freeze Data ..................32
5.9 Drive Cycle Monitor ................33
5.10 O2 Monitor Tests ..................34
5.11 Diagnostic Monitor Tests ........... 35
5.12 On-Board Systems ................. 36
5.13 Vehicle Information ................ 36
5.14 Oil Light Reset .................... 38
5.15 Battery Reset ..................... 39
Battery Information ................. 39
5.16 Charging System Monitor ........... 40
5.17 Modules Present .................. 41
5.18 Fuel Consumption (MPG/KPL) ....... 42
5.19 KOEO On Demand ................. 42
5.20 KOEO Injector Buzz ................ 43
5.21 KOEO Output State ................ 44
5.22 KOER On Demand ................. 44
5.23 KOER Glow Plug ...................45
5.24 KOER Cylinder Contribution ......... 46
6 Troubleshooting ........................ 46
6.1 Error Messages ...................46
6.2 Scan Tool Does Not Power Up ........ 47
6.3 Vehicle Communication Fault ........47
6.4 Operating Error or Erroneous Data .... 47
6.5 Battery Replacement ............... 47
6.6 Tool Self-Tests .................... 47
6.7 Technical Support ................. 47
7 Appendix A—
PID Definitions ............................ 47
8 Appendix B—Glossary ................... 50
9 Limited Warranty .......................55
580001 | REV. A | 11.2016
Page 4

en | 4 | User guide
| OBD 1350
ProGrade OBDII Scan Tool
580001 | REV. A | 11.2016
Page 5
OBD 1350 ProGrade OBDII Scan Tool | User guide | 5 | en
1 Safety Precautions
For your safety, read this manual thoroughly before
operating your scan tool. Always refer to and follow
safety messages and test procedures provided by the
manufacturer of the vehicle or equipment being tested.
The safety messages presented below and throughout
this user’s manual are reminders to the operator to
exercise extreme care when using this test instrument.
1.1 Read All Instructions
Read and understand the user guide
before operating the tool.
Read, understand, and follow all safety messages and
instructions in this manual and on the test equipment.
Safety messages in this section of the manual contain a
signal word with a three-part message and, in some
instances, an icon.
1.2 Safety Messages
Safety messages are provided to help prevent personal
injury and equipment damage. All safety messages are
introduced by a signal word. The signal word indicates
the level of the hazard in a situation. The types of safety
messages are.
DANGER
Indicates a possible hazardous situation
which, if not avoided, will result in death or
serious injury to operator or bystanders.
WARNING
Indicates a possible hazardous situation
which, if not avoided, could result in death
or serious injury to operator or bystanders.
CAUTION
Indicates a possible hazardous situation
which, if not avoided, may result in moderate
or minor injury to operator or bystanders.
IMPORTANT
Indicates a condition which, if not avoided, may
result in damage to test equipment or vehicle.
2 Important Safety Warnings
and Instructions
WARNING
Risk of electric shock.
• Do not exceed voltage limits between
inputs indicated in the Specifications.
• Use extreme caution when working
with circuits that have voltage greater
than 60 volts DC or 24 volts AC.
Electric shock can cause injury.
WARNING
Risk of poisoning.
• Safety goggles and protective clothing must
be worn by the operator and any bystanders.
– Even if everyday glasses have
impact resistant lenses, they are
NOT safety glasses, and may not
provide adequate protection.
• Do not use this scan tool in environments where explosive vapors may
collect. These areas include:
– below-ground pits.
– confined areas.
– areas that are less than 18 inches
above floor.
• Use this scan tool in locations with
mechanical ventilation providing at
least 4 air changes per hour.
• Flammable fuel and vapors can ignite.
• Do not smoke, strike a match, or cause
a spark in the vicinity of the battery.
Battery gases can ignite.
• Avoid making an accidental connection
between the battery terminals. Do not place
uninsulated metal tools on the battery.
• When removing battery cables, remove
the ground cable first.
• Avoid sparks when connecting or disconnecting power leads to the battery.
• Make sure ignition is off, headlights
and other accessories are off and
vehicle doors are closed before disconnecting the battery cables.
– This also helps prevent damage to
on-board computer systems.
• Always disconnect the battery ground
connections before servicing electrical system components.
Explosion can cause injury.
580001 | REV. A | 11.2016
Page 6
en | 6 | User guide
| OBD 1350
ProGrade OBDII Scan Tool
WARNING
Risk of poisoning.
• Use this scan tool in locations with
mechanical ventilation providing at
least 4 air changes per hour. Engine
exhaust contains odorless gas which
can be lethal.
• Route the exhaust outside while
testing with the engine running.
Poisoning can result in death or serious injury.
WARNING
Battery acid is a highly corrosive sulfuric acid.
• Safety goggles and protective gloves must be
worn by the operator and any bystanders.
– Even if your everyday glasses
have impact resistant lenses, they
are NOT safety glasses, and may
not provide adequate protection.
• Make sure someone can hear you or is
close enough to provide aid when
working near a battery.
• Have plenty of fresh water and soap nearby.
– If battery acid contacts skin,
clothing, or eyes, flush exposed
area with soap and water for 10
minutes. Seek medical help.
• Do not touch eyes while working near battery.
Battery acid can burn eyes and skin.
WARNING
Risk of fire.
• Safety goggles and protective clothing must
be worn by the operator and any bystanders.
– Even if your everyday glasses
have impact resistant lenses, they
are NOT safety glasses, and may
not provide adequate protection.
• Do not position your head directly in
front of or over the throttle body.
• Do not pour gasoline down the throttle body when cranking or running the
engine, when working with fuel delivery systems or any open fuel line.
– Engine backfire can occur when
the air cleaner is out of position.
• Do not use fuel injector cleaning solvents
when performing diagnostic testing.
• Keep cigarettes, sparks, open flame
and other sources of ignition away
from vehicle.
• Keep a dry chemical (Class B) fire
extinguisher rated for gasoline, chemical and electrical fires in work area.
Fire can cause death or serious injury.
WARNING
Risk of flying particles.
• Safety goggles and protective gloves must
be worn by the operator and any bystanders while using electrical equipment.
– Electrical equipment or rotating
engine parts can cause flying particles.
– Even if your everyday glasses
have impact resistant lenses, they
are NOT safety glasses, and may
not provide adequate protection.
Flying particles can cause eye injury.
WARNING
Risk of burns.
• Batteries can produce a short-circuit
current high enough to weld jewelry
to metal.
– Remove jewelry such as rings,
bracelets and watches before
working near batteries.
Short circuits can cause injury.
WARNING
Risk of burns.
• Do not remove radiator cap unless
engine is cold.
– Pressurized engine coolant may
be hot.
• Do not touch hot exhaust systems, manifolds, engines, radiators, sample probe.
• Wear insulated gloves when handling
hot engine components.
• Tester leads can become hot after extended
testing in close proximity to manifolds.
Hot components can cause injury.
WARNING
Risk of expelling fuel, oil vapors, hot steam,
hot toxic exhaust gases, acid, refrigerant
and other debris.
• Safety goggles and protective clothing
must be worn by the operator and any
bystanders.
– Even if your everyday glasses
have impact resistant lenses, they
are NOT safety glasses, and may
not provide adequate protection.
• Engine systems can malfunction,
expelling fuel, oil vapors, hot steam,
hot toxic exhaust gases, acid, refrigerant and other debris.
Fuel, oil vapors, hot steam, hot toxic
exhaust gases, acid, refrigerant and other
debris can cause serious injury.
580001 | REV. A | 11.2016
Page 7

OBD 1350 ProGrade OBDII Scan Tool | User guide | 7 | en
P R N D L 2
WARNING
Engine compartment contains electrical
connections and hot or moving parts.
• Keep yourself, test leads, clothing and
other objects clear of electrical connections and hot or moving engine parts.
• Do not wear watches, rings, or loose
fitting clothing when working in an
engine compartment.
• Do not place tools or test equipment
on fenders or other places in engine
compartment.
• Barriers are recommended to help
identify danger zones in test area.
• Prevent personnel from walking
through test area.
Contacting electrical connections and hot
or moving parts can cause injury.
WARNING
Risk of injury.
• The scan tool should be operated by
qualified personnel only.
• Use the scan tool only as described in
the user’s manual.
• Use only manufacturer’s recommended attachments.
• Do not operate the scan tool with
damaged cables.
• Do not operate the scan tool if it has
been dropped or damaged, until examined by a qualified service representative.
Operation of the scan tool by anyone other
than qualified personnel may result in injury.
WARNING
Risk of unexpected vehicle movement.
• Block drive wheels before performing
a test with engine running.
• Unless instructed otherwise:
– set parking brake
– put gear selector in neutral for
manual transmissions
– put gear selector in park for
automatic transmissions
– disconnect release mechanism on
the automatic parking brake
release for testing and reconnect
when testing is completed.
• Do not leave a running engine unattended.
A moving vehicle can cause injury.
CAUTION
Risk of equipment or circuit damage.
• Unless specifically directed by manufacturer, make sure ignition is off before
connecting or disconnecting connectors
or any vehicle electrical terminals.
• Do not create a short between battery
terminals with a jumper wire or tools.
Improper equipment use can cause equipment or circuit damage.
CAUTION
Misdiagnosis may lead to incorrect or
improper repair and/or adjustment.
• Do not rely on erratic, questionable,
or obviously erroneous test information or results.
– If test information or results are
erratic, questionable, or obviously
erroneous, make sure all connections and data entry information
are correct and test procedures
were performed correctly.
– If test information or results are
still suspicious, do not use them
for diagnosis.
Improper repair and/or adjustment may
cause vehicle or equipment damage or
unsafe operation.
DANGER
Some vehicles are equipped with air bags.
• Follow service manual warnings when
working around air bag components
or wiring.
– If service manual instructions are
not followed, an air bag may deploy
unexpectedly, resulting in injury.
– Note an air bag can still deploy
several minutes after ignition key
is off (or even if vehicle battery is
disconnected) because of a
special energy reserve module.
An air bag opening can cause injury.
580001 | REV. A | 11.2016
Page 8
en | 8 | User guide
| OBD 1350
ProGrade OBDII Scan Tool
3 Getting Started
3.1 Introduction
The scan tool was developed by experts in the automotive service industry to help diagnose vehicles and assist
in troubleshooting procedures.
The scan tool monitors vehicle events and retrieves
codes from the vehicle’s control modules to help pinpoint problem areas.
All information, illustrations and specifications contained in this manual are based on the latest information
available from industry sources at the time of publication.
No warranty (expressed or implied) can be made for its
accuracy or completeness, nor is any responsibility
assumed by the manufacturer or anyone connected with
it for loss or damages suffered through reliance on any
information contained in this manual or misuse of
accompanying product. The manufacturer reserves the
right to make changes at any time to this manual or
accompanying product without obligation to notify any
person or organization of such changes.
3.2 Download Scanning Suite
1. Go to http://mactoolsdownloads.service-solutions.
com/ to download the Scanning Suite PC application.
Scanning Suite is NOT required to operate the scan tool.
2. Install the downloaded Scanning Suite application
before connecting the scan tool to the PC.
Some items included with the Scanning Suite are:
• Tool update software
• Print Capture
• Other product information
To be able to use Scanning Suite the PC must meet the
following minimum requirements:
• Microsoft Windows 7, 8, and 10.
• Adobe Acrobat Reader
• Screen Resolution of 800 x 600
– If screen resolution is 800 x 600, in Display
Properties, Settings Tab, set Font Size to
Small Fonts.
3. Use Scanning Suite to determine if any updates are available for your tool by clicking Check for Update button.
4. Check for updates to Use Scanning Suite by clicking
on the Check For Scanning Suite Update button. This
should be done before checking for Tool Updates.
You can also configure the Scanning Suite Frequency (SS
Frequency) to automatically check every xx minutes. The
default frequency is 7 days.
Refer to instructions provided on http://mactoolsdownloads.service-solutions. com/ for how to install Scanning
Suite and Tool updates.
3.3 OBDII
On-board diagnostics version II (OBDII) is a system that
the Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE) developed to
standardize automotive electronic diagnosis.
580001 | REV. A | 11.2016
Beginning in 1996, most new vehicles sold in the United
States were fully OBDII compliant.
Technicians can now use the same tool to test any OBDII
compliant vehicle without special adapters. SAE established guidelines that provide:
• A universal OBDII data link connector, called the
DLC, with dedicated pin assignments.
• A standard location for the DLC, visible under the
dash on driver’s side.
• A standard list of diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs)
used by all manufacturers.
• A standard list of parameter identification (PID) data
used by all manufacturers.
• Ability for vehicle systems to record operating conditions when a fault occurs.
• Expanded diagnostic capabilities that records a
code whenever a condition occurs that affects
vehicle emissions.
• Ability to clear stored codes from the vehicle’s
memory with a scan tool.
3.4 SAE Publications
SAE has published hundreds of pages of text defining a
standard communication protocol that establishes hardware, software, and circuit parameters of OBDII systems. Unfortunately, vehicle manufacturers have different interpretations of this standard communications
protocol. As a result, the generic OBDII communications
scheme varies, depending on the vehicle. SAE publishes
recommendations, not laws, but the Environmental
Protection Agency (EPA) and California Air Resources
Board (CARB) made many of SAE’s recommendations
legal requirements that vehicle manufacturers were
required to phase in over a three-year period. Beginning
in 1994, vehicles with a new engine management computer (about 10% of each manufacturers fleet) were supposed to comply with OBDII standards. For 1995, OBDII
systems were to appear on about 40% of the new vehicles sold in the United States. Some of the 1994-1995
OBDII systems were not fully compliant, so the Government granted waivers to give manufacturers time to
fine-tune their systems. Beginning in 1996, most of the
new vehicles sold in the United States were fully OBDII
compliant.
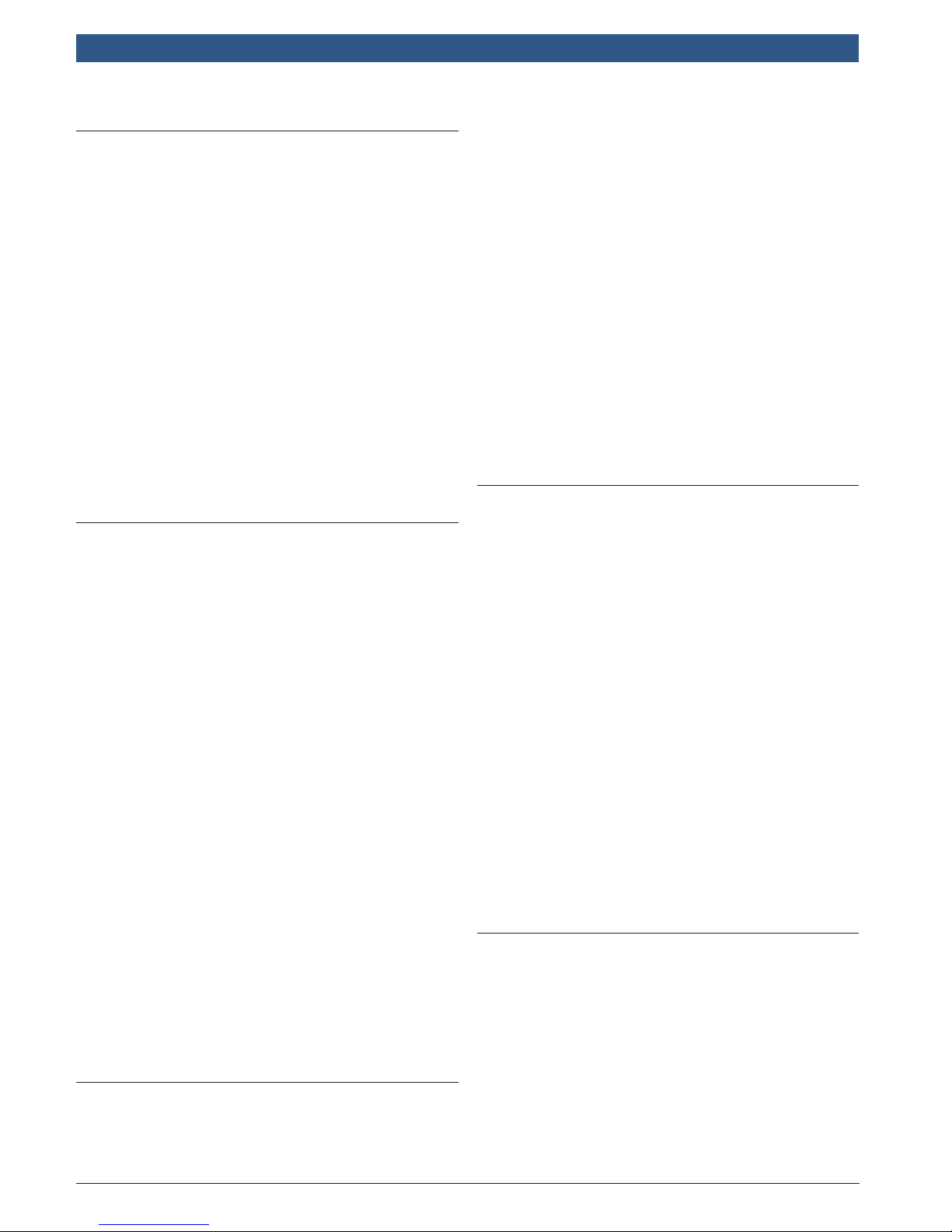
3.5 OBDII Data Link Connector (DLC)
The OBDII data link connector (DLC) allows the scan
tool to communicate with the vehicle’s computer(s).
Beginning in 1996, vehicles sold in the United States use
the J1962 (OBDII) DLC, a term taken from a physical
and electrical specification number assigned by the SAE
(J1962). The DLC should be located under the dashboard on the driver’s side of the vehicle. If the DLC is
not located under the dashboard as stated, a decal
describing its location should be attached to the dashboard in the area the DLC should have been located. For
more information on OBDII connectors, go to http://
www.obdclearinghouse.com/oemdb.
Page 9
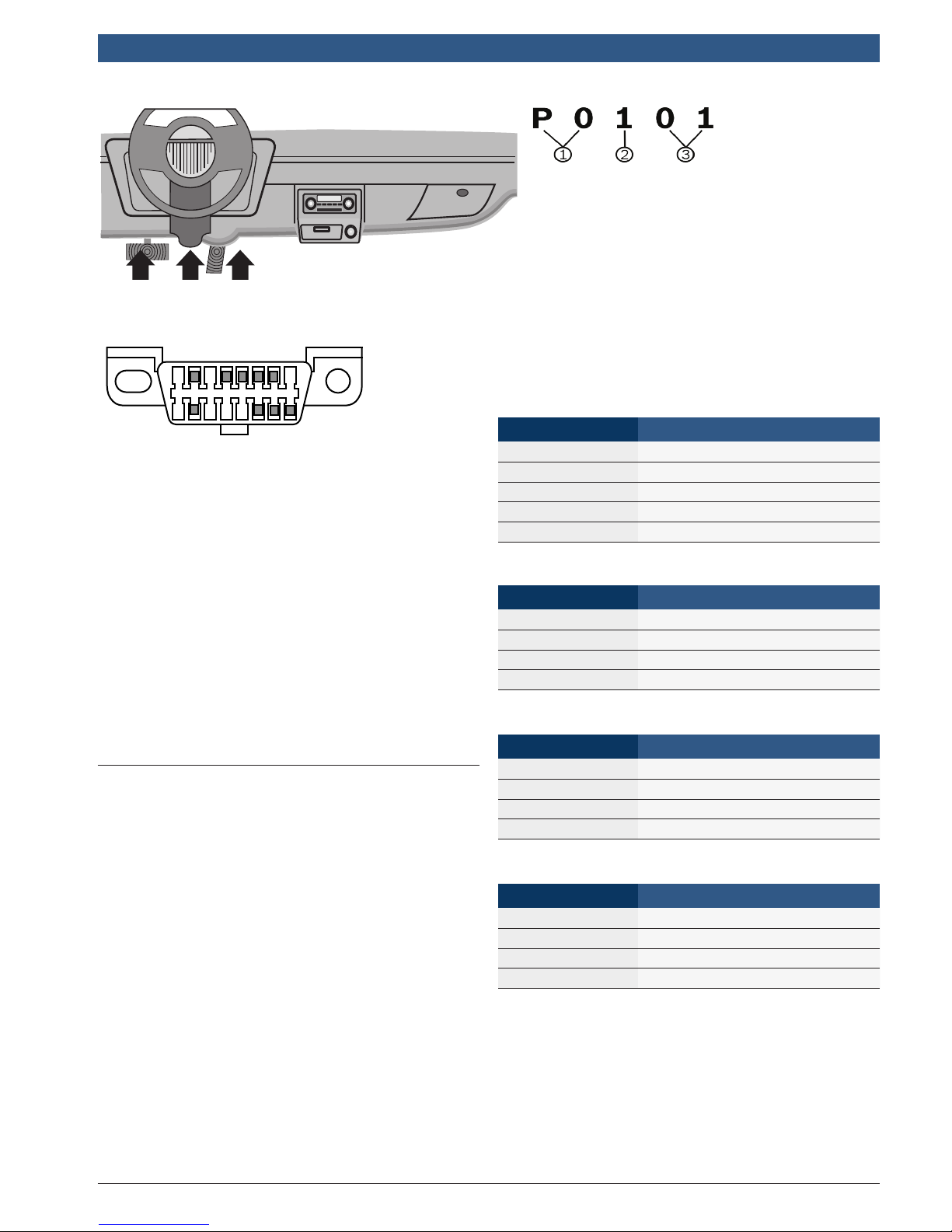
OBD II Data Link Connector (DLC) Pins
9 16
1 8
1. Manufacturer reserved
2. J1850 bus+
3. Manufacturer reserved
4. Chassis ground
5. Signal ground
6. CAN high, J-2284
7. K line, ISO 9141-2 & ISO/DIS 14230-4
8. Manufacturer reserved
9. Manufacturer reserved
10. J1850 Bus-
11. Manufacturer reserved
12. Manufacturer reserved
13. Manufacturer reserved
14. CAN low, J-2284
15. L line, ISO 9141-2 & ISO/DIS 14230-4
16. Battery power
3.6 OBDII Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs)
J2012 and ISO 15031-6 are standards for all DTCs,
established by the SAE, International Organization for
Standardization (ISO) and other governing bodies.
• Codes and definitions assigned by these specifications are known as Generic OBDII codes.
• OBDII requires compliance to these standards for all
cars, light trucks, APVs, MPVs, and SUVs sold in the
United States.
• Codes not reserved by the SAE are reserved for the
manufacturer and referred to as Manufacturer Specific Codes.
DTCs are used to help determine the cause of a problem
or problems with a vehicle.
• DTCs consist of a five-digit alphanumeric code.
• The DTCs format and general code types are shown below.
OBD 1350 ProGrade OBDII Scan Tool | User guide | 9 | en
1. Bx = Body
Cx = Chassis
Px = Powertrain
Ux = Network communication
x - 0, 1, 2, or 3
2. Vehicle specific system
3. Specific fault designation
Example:
P0101 = Mass or volume air flow cir cuit range/perfor-
mance problem
Powertrain Codes
Code Type
P0xxx Generic (SAE)
P1xxx Manufacturer specific
P2xxx Generic (SAE)
P30xx–P33xx Manufacturer specific
P34xx–P39xx Generic (SAE)
Chassis Codes
Code Type
C0xxx Generic (SAE)
C1xxx Manufacturer specific
C2xxx Manufacturer specific
C3xxx Generic (SAE)
Body Codes
Code Type
B0xxx Generic (SAE)
B1xxx Manufacturer specific
B2xxx Manufacturer specific
B3xxx Generic (SAE)
Network Communication Codes
Code Type
U0xxx Generic (SAE)
U1xxx Manufacturer specific
U2xxx Manufacturer specific
U3xxx Generic (SAE)
580001 | REV. A | 11.2016
Page 10

en | 10 | User guide
| OBD 1350
ProGrade OBDII Scan Tool
4 Using the Scan Tool
4.1 The Scan Tool
1
11
10
9
8
4
7
9
5
6
4.2 Specifications
Display Color, backlit, QVGA resolution
Operating Temperature
Storage Temperature -20 to 70°C (-4 to 158°F)
Internal Power
External Power 7 to 16 Volts
A minimum of 8.0 V is required for most control modules
to operate properly in a vehicle.
Dimensions
Height Width Depth
6.5 inches 3.75 inches 1.13 inches
165.1 mm 95.25 mm 28.7 mm
2
4.3 Display
The display has a large viewing area for displaying mes-
3
4
sages, instructions, and diagnostic information.
The back-lit liquid crystal display (LCD) is a QVGA pixel
display. Display icons used to help operate the scan tool
are:
• √ Indicates information is available for an item or
multiple items.
0 to 50°C (32 to 122°F)
4-AAA batteries
1. DLC Cable - provides connection for vehicle interface.
2. USB Port - provides a USB connection for the computer.
3. CodeConnect® - allows the operator to access
vehicle-specific repair information.
4. LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys - selects YES or
NO and selects data parameters for custom data
list.
5. ENTER key - selects displayed items.
6. ON/OFF key - turns power ON or OFF.
7. BACK key - goes to the previous screen or
level.
8. MORE INFO key - displays the Diagnostic
Trouble Code (DTC) definition when viewing Freeze
Frame Data. It will display the code setting criteria
when viewing DTC definition.
9. UP and DOWN arrow keys - moves selection
up or down.
10. SOFTKEYS are used to perform the specified
action on the display directly above the key.
11. LCD display (color, backlit, QVGA resolution).
12. Serial Number Plate (on back; not shown) - Located
inside battery compartment, provides serial number
of scan tool.
13. Battery Compartment (on back; not shown) - provides power to the scan tool when reprogramming
from a personal computer or off-vehicle reviewing of
codes and printing.
• Indicates additional information is available by
scrolling up.
• Indicates additional information is available by
scrolling down.
• Indicates internal batteries need replacing or are
not installed.
• Indicates is active.
• Indicates graphical viewing of data items is available in View Data.
• Indicates the key is active.
Keypad
The keypad is used to move through the different menus
of the scan tool. The scan tool’s software is designed for
ease in operating and navigating through menus.
CAUTION
Do not use solvents such as alcohol to clean
keypad or display. Use a mild nonabrasive
detergent and a soft, cotton cloth.
CAUTION
Do not soak keypad as water might find its
way inside the scan tool.
580001 | REV. A | 11.2016
Page 11
OBD 1350 ProGrade OBDII Scan Tool | User guide | 11 | en
4.4 Power
Internal Battery
• Battery power is not required to use tool.
• ON/OFF button on scan tool turns tool on and
off.
• Press and hold ON/OFF for at least 1 second to
turn on scan tool.
• The scan tool will automatically turn OFF after a
user-selectable period of inactivity when powered
from the internal batteries. The default is 2 minutes.
• When powered from the internal batteries, the scan
tool will dim display backlighting.
• The scan tool must be attached to the vehicle to
perform diagnostic functions. The scan tool disables
the diagnostic functions when powered from the
internal batteries.
• Each time the scan tool is powered up, voltage of
the internal battery is checked.
– If voltage is low, the Low Battery Symbol ( )
displays on screen.
– Replace the battery using instructions provided
in Battery Replacement
CAUTION
If the scan tool will not be used for an
extended period of time, remove the batteries to prevent battery leakage from damaging the battery compartment.
Vehicle Power
When the scan tool is connected to the vehicle’s DLC,
the tool is powered by the vehicle and will automatically
turn on once connected.
USB Power
When the tool is connected to a PC via a USB cable (not
provided), the tool will automatically power up. Refer to
“6.2 Scan Tool Does Not Power Up” on page 47 if
there are problems.
4.5 System Setup
System Setup allows:
• Measurement units to be changed.
• Auto-Power off time to be changed.
• Print Header to be turned ON or OFF.
• Scan tool information to be viewed.
• Display to be checked.
• Operation of the keypad to be checked.
• Memory of the tool to be checked.
• Scan tool to be upgraded.
• Language to be changed.
• Quick Test to be turned ON, OFF, or set to the
desired method.
• Long PID names to be turned ON or OFF.
• Change the number of Pre-Trigger frames when
recording data.
From the Diagnostic Menu:
1. Select System Setup.
• Use the DOWN key until System Setup is high-
lighted.
• Press .
Diagnostic Menu
Datastream
Diagnostic Codes
Special Functions
On Demand Tests
Component Locator
Acronyms
Review Data
Print Data
Code Lookup
System Setup
Changing Measurement Units
English is the default measurement unit. Measurement
units can be changed in View and Record Data.
From System Setup screen:
1. Select English/Metric.
• Use the UP and DOWN keys until English/
Metric is highlighted.
• Press .
System Setup
English/Metric
Auto-Power Off
Quick Test
Print Header
Language Setup
Long PID Names
Pre-Trigger Setup
Tool Information
Display Test
2. Select desired measurement unit.
• Use the UP and DOWN keys until the
desired unit is highlighted.
• Press .
Measurement Units
English
Metric
3. Save measurement setting.
• Press .
580001 | REV. A | 11.2016
Page 12
en | 12 | User guide
| OBD 1350
ProGrade OBDII Scan Tool
Changing Auto-Power Off
The Auto-Power Off feature allows the tool to turn off
automatically after a selected amount of time when tool
is not being used. The Auto-Power Off feature will only
turn the tool off when it is operating on battery power.
From System Setup screen:
1. Select Auto-Power Off.
• Use the UP and DOWN keys until Auto-
Power Off is highlighted.
• Press .
System Setup
English/Metric
Auto-Power Off
Quick Test
Print Header
Language Setup
Long PID Names
Pre-Trigger Setup
Tool Information
Display Test
2. Increase or decrease Auto-Power Off time.
• Use the UP key to increase time.
• Use the DOWN key to decrease time.
System Setup
English/Metric
Auto-Power Off
Quick Test
Print Header
Language Setup
Long PID Names
Pre-Trigger Setup
Tool Information
Display Test
2. Select desired Quick Test choice.
• Use the UP and DOWN keys until desired
choice is highlighted.
• Select QuickCheckTM to see the results of I/M
Monitors and Read Codes.
• Select Read All Codes to see the results of all
codes and associated CodeConnect® information. This selection is enabled by default.
Quick Test
Disabled
QuickCheck
Read All Codes
Auto-Power Off
2 minute(s)
Increase time
Decrease time
Press ENTER to continue
3. Save Auto-Power Off time.
• Press .
Quick Test
Quick Test is a feature of the tool that occurs the first
time the tool establishes communication with the vehicle after vehicle selection. Quick Test will display the
results of I/M Monitors and Read Codes.
From System Setup screen:
1. Select Quick Test.
• Use the UP and DOWN keys until Quick
Tes t is highlighted.
• Press .
3. Save Quick Test setting.
• Press .
Print Header
Print Header selection allows the user to turn off the
scan tool printing the currently-selected vehicle prior to
the retrieved vehicle data when selecting items from the
Print Data menu.
For example, if your currently-selected vehicle is a 2008
Chevrolet Corvette W = 6.2L, this information would
print at the top of the page for the data you are printing
From System Setup screen:
1. Select Print Header.
• Use the UP and DOWN keys until Print
Header is highlighted.
• Press .
580001 | REV. A | 11.2016
Page 13

OBD 1350 ProGrade OBDII Scan Tool | User guide | 13 | en
System Setup
English/Metric
Auto-Power Off
Quick Test
Print Header
Language Setup
Long PID Names
Pre-Trigger Setup
Tool Information
Display Test
System Setup
English/Metric
Auto-Power Off
Quick Test
Print Header
Language Setup
Long PID Names
Pre-Trigger Setup
Tool Information
Display Test
2. Select desired Print Header choice.
• Use the UP and DOWN keys until desired
choice is highlighted.
Print Header
ON
OFF
Language Setup
English
Español
Francais
3. Save Language Setup setting.
• Press .
NOTE: When Spanish or French translation is not known,
English will be shown.
Long PID Names
Long PID Names allows the user to enable/disable the tool
scrolling the complete PID name on the bottom line of the
display while viewing Live Data or viewing Freeze Data.
From System Setup screen:
1. Select Long PID Names.
• Use the UP and DOWN keys until Long
PID Names is highlighted.
• Press .
3. Save Print Header setting.
• Press .
Language Setup
Language Setup selection allows the user to change the
language used by the Tool. English is the default language.
From System Setup screen:
1. Select Language Setup.
• Use the UP and DOWN keys until Lan-
guage Setup is highlighted.
• Press .
2. Select desired Language Setup choice.
• Use the UP and DOWN keys until the
desired language is highlighted.
• Press .
System Setup
English/Metric
Auto-Power Off
Quick Test
Print Header
Language Setup
Long PID Names
Pre-Trigger Setup
Tool Information
Display Test
2. Select ON or OFF.
• Use the UP and DOWN keys until the
desired option is highlighted.
• Press .
Long PID Names
ON
OFF
3. Save Long PID Names setting.
• Press .
580001 | REV. A | 11.2016
Page 14
en | 14 | User guide
| OBD 1350
ProGrade OBDII Scan Tool
Pre-Trigger Setup
This function is used to configure how many Pre-Trigger
frames are stored prior to beginning a recording. Pre-Trigger frames are the negative frames when you are playing
back a recording.
From System Setup screen:
1. Select Pre-Trigger Setup.
• Use the UP and DOWN keys until Pre-
Trigger Setup is highlighted.
• Press .
System Setup
English/Metric
Auto-Power Off
Quick Test
Print Header
Language Setup
Long PID Names
Pre-Trigger Setup
Tool Information
Display Test
System Setup
English/Metric
Auto-Power Off
Quick Test
Print Header
Language Setup
Long PID Names
Pre-Trigger Setup
Tool Information
Display Test
2. View information.
• Serial Number (Serial No:)
• Software ID (SW ID:)
• Hardware Version (HW Ver:)
• Boot Version (Boot Ver:)
• Product ID (Prod ID:)
• Board ID (Board ID:)
• Burn Date (Burn Date:)
• Burn Location (Burn Loc:)
2. Increase or Decrease Pre-Trigger Frames.
• Use the UP key to increase frames.
• Use the DOWN key to decrease frames.
• Press .
Pre-Trigger Frames
5 frame(s)
Increase frame
Decrease frame
Press ENTER to continue
3. Save Pre-Trigger frames setting.
• Press .
Tool Information
Tool Information allows the user to view specific tool information that may be needed when contacting customer
service.
From System Setup screen:
1. Select Tool Information.
• Use the UP and DOWN keys until Tool
Information is highlighted.
• Press .
Tool Information
Serial No
SW ID
HW Ver
Boot Ver
Prod ID
Board ID
Burn Date
Burn Loc 04
3. Record Tool Information.
• Space is provided inside the front cover of this
manual to write down the scan tool information.
4. Return to System Setup menu.
• Press
or
• press .
Display Test
The Display Test is used to check the display. The test fills
every pixel of the display with a solid color.
From System Setup screen:
1. Select Display Test.
• Use the UP and DOWN keys until Display
Tes t is highlighted.
• Press .
1284168
5126
01
02
21
33
12/04/14
580001 | REV. A | 11.2016
Page 15
System Setup
English/Metric
Auto-Power Off
Quick Test
Print Header
Language Setup
Long PID Names
Pre-Trigger Setup
Tool Information
Display Test
2. Start Display Test.
• Press .
3. Look for missing spots.
• The first screen displayed says, “Check for
missing spots in the display.”
Display Test
OBD 1350 ProGrade OBDII Scan Tool | User guide | 15 | en
Check for spots in the
display
Press BACK to exit
• Solid red, green, and blue screens are displayed.
• These four screens will continue in succession
until is pressed.
4. Press to exit the test and return to the System
Setup menu.
Keypad Test
The Keypad Test is used to verify that the keys are work-
ing correctly.
From System Setup screen:
1. Select Keypad Test.
• Use the UP and DOWN keys until Keypad
Tes t is highlighted.
• Press .
580001 | REV. A | 11.2016
Page 16
en | 16 | User guide
Quick Test
Print Header
Language Setup
Long PID Names
Pre-Trigger Setup
Tool Information
Display Test
Keypad Test
Memory Test
| OBD 1350
ProGrade OBDII Scan Tool
System Setup
– If no problems were detected, then
“Passed” is displayed.
– If RAM fails, an error message is shown.
– If FLASH fails, a checksum is shown.
Memory Test
INT RAM
INT FLASH
Passed
10ca
2. Press a key.
• Key name or scroll direction should inverse
colors on display.
• will return the tool to the System Setup
screen.
Keypad Test
F3 F4F2F1
CODE
BACK
Press BACK to exit
Memory Test
The Memory Test will test RAM and flash ROM. Run the
Memory Test if the tool has trouble:
• Playing back recorded data.
• Displaying trouble code definitions.
From System Setup screen:
1. Select Memory Test.
• Use the UP and DOWN keys until Memory
Tes t is highlighted.
• Press .
ENTER
Press BACK to exit
2. Return to System Setup menu.
• Press .
Program Mode
The Program Mode is used for updating the scan tool.
Instructions are provided with upgrades. Refer to “3.2
Download Scanning Suite” on page 8.
System Setup
Print Header
Language Setup
Long PID Names
Pre-Trigger Setup
Tool Information
Display Test
Keypad Test
Memory Test
Program Mode
PROGRAM MODE
See User Manual
Connect Tool to PC
with USB Cable
System Setup
Print Header
Language Setup
Long PID Names
Pre-Trigger Setup
Tool Information
Display Test
Keypad Test
Memory Test
Program Mode
• Memory Test may take several minutes to complete.
• Memory Test results display:
580001 | REV. A | 11.2016
• If the Program Mode is entered, is not operational. The tool must be powered off to exit Program Mode and then restarted to continue.
4.6 Vehicle-Specific Features
Review Data
The Review Data function allows the user to view the
information from the previous vehicle tested. The scan
tool can be powered from vehicle or PC using USB to
use the Review Data function.
Page 17
OBD 1350 ProGrade OBDII Scan Tool | User guide | 17 | en
1. Select Review Data.
• Use the UP and DOWN keys until Review
Data is highlighted.
• Press .
Main Menu
Vehicle Diagnostics
Acronyms
Review Data
Print Data
Code Lookup
System Setup
If Review Data is selected from the Main Menu, a Select
Vehicle menu is shown. This menu contains up to 5
previous vehicles, so select which vehicle you wish to
review data.
Select Vehicle
Prev: 06 Accord
Prev: 04 Express 1500
From the Review Data menu:
1. Select Recording.
• Use the UP and DOWN keys until Record-
ing is highlighted.
• The tool can keep up to 5 recordings per vehicle. If the tool has more than one recording,
select a recording to playback.
• Press .
Review Data
✓I/M Monitors
✓DTCs (Codes)
State OBD Check
✓Recording
View Freeze Data
O2 Monitor Tests
Diagnostic Monitor Tests
Vehicle Information
Modules Present
2. Select Playback Recording.
• Use the UP and DOWN keys until Play-
back Recording is highlighted.
• Press .
2. Follow prompts and instructions provided by scan
tool and then select item whose data you wish to
review.
• The Review Data menu shows a checkmark next
to the item(s) that has data.
• If there is not a checkmark next to the item, then
this item can’t be selected until the appropriate
function is run from the Diagnostic Menu.
• See “Recording” on page 17 for detailed
instructions on this function.
Review Data
✓I/M Monitors
✓DTCs (Codes)
✓State OBD Check
✓Recording
View Freeze Data
✓O2 Monitor Tests
✓Diagnostic Monitor Tests
Vehicle Information
Modules Present
Recording
The Recording function is used to play back a recording.
This function is very similar to View Data. The only difference is that View Data is real-time viewing of PIDs, while
Recording is a viewing of previously recorded PIDs.
Playback Options
Playback Recording
Long PID Names
English/Metric
• The recording has frame number and timestamp
(in seconds).
– Negative frames and timestamps indicate
data recorded before trigger event.
– Positive frames and timestamps indicate
data recorded after trigger event.
– Use the UP and DOWN keys to view
recorded PID data within each frame.
– Use the LEFT and RIGHT keys to scroll
back and forth through frames.
– See Appendix A for PID Definitions.
ABSLT TPS(%)
CALC LOAD(%)
COOLANT(°F)
ENG SPEED(RPM)
FUEL SYS 1
FUEL SYS 2
IAT(°F)
IGN ADV(°)
LT FTRM1(%)
Frame:
Throttle position
Time: 0.00
0.0
3.5
95
692
OPEN
OPEN
75
4.5
3.1
580001 | REV. A | 11.2016
Page 18

en | 18 | User guide
| OBD 1350
ProGrade OBDII Scan Tool
– If graphing is available for selected PID, the
“ ” icon is located on the side of the
screen.
– Press to select PIDS to graph.
– Use the UP and DOWN arrow keys
to highlight the second PID to graph
and then press the RIGHT arrow to
select. A maximum of two PIDs can be
graphed. Press to see graph.
• The triangle below the graph indicates the
position of the frame in the graph.
– Use the LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to
scroll back and forth through graph.
– Use the UP and DOWN keys to toggle
back and forth between PIDs.
• Different vehicles communicate at different
speeds and support a different number of PIDs.
Therefore, the maximum number of frames that
can be recorded varies.
Select PIDs to Graph
ABSLT TPS(%)
✓CALC LOAD(%)
COOLANT(°F)
ENG SPEED(RPM)
IAT(°F)
MAF(LB/M)
MAP(”HG)
VEH SPEED(MPH)
• Follow all instructions on PC.
1. Select Print Data.
• Use the UP and DOWN keys until Print
Data is highlighted.
• Press .
Main Menu
Vehicle Diagnostics
Acronyms
Review Data
Print Data
Code Lookup
System Setup
Print Data
Launch PC printing software
application.
Press ENTER to continue
Calculated Engine Load
CALC LOAD(%)
19.4
17.5
Frame: Time:
21 26.8
3. Return to Review Data menu.
• Press .
Print Data
The Print Data function allows the printing of diagnostic
information stored in the scan tool.
• The scan tool’s internal battery power can be
used to print data.
• Use the Print Data function to turn On/Off
printing vehicle information prior to printing
data.
• Make sure you have previously installed the PC
software in Download Scanning Suite.
• Launch Scanning Suite and then start printing
application.
580001 | REV. A | 11.2016
19.2
• On the Print Data menu, Print All prints all data
collected by the scan tool.
Print Data
✓Print All
✓I/M Monitiors
✓DTCs (Codes)
State OBD Check
Recording
View Freeze Data
O2 Monitor Tests
Diagnostic Monitor Tests
Vehicle Information
• When printing a Recording, Start Frame and End
Frame need to be defined.
2. Select Data to Be Printed.
• Use the UP and DOWN keys.
• Press .
• The Print Data menu shows a check mark next
to the items that have data.
• If there isn’t a checkmark next to the item, then
this item can’t be selected until the appropriate
function is run from the Diagnostic Menu.
3. Return to Select Print Data screen.
• Press .
Page 19

4.7 Code Lookup
No DTC definition found. See
service manual
P1575
Code Lookup is used to look up definitions of DTCs
stored in the scan tool.
• If Code Lookup is selected from the Main Menu, the
tool will display Vehicle Selection. Selecting a vehicle in Code Lookup from the Main Menu does not
change the current (previously selected) vehicle. It
is only a temporary change to allow you to lookup
DTC for a vehicle other than the previous vehicle.
• When selecting Code Lookup from the Diagnostic
Menu, the tool goes to the Select Module screen, if
the selected vehicle supports more than one module. Select the desired module to access the Enter
Code screen, since the vehicle was already selected.
• The scan tool does not require power from the
vehicle to perform this function.
From the Main menu:
1. Select Code Lookup.
• Use the UP and DOWN keys until Code
Lookup is highlighted.
• Press .
OBD 1350 ProGrade OBDII Scan Tool | User guide | 19 | en
Code Lookup
0000P
Enter desired code using
keys
Press ENTER when done
P0575
Cruise Control Input Circuit
Vehicle Diagnostics
Acronyms
Review Data
Print Data
Code Lookup
System Setup
2. Select a specific vehicle from US, Europe, or Asia. If
the vehicle is not in the list for the locations listed,
select OBDII/EOBD.
• To select a specific vehicle, see “Vehicle Selec-
tion” section.
OBDII/EOBD
US
Europe
Asia
Prev: 06 Accord
Prev: 04 Express 1500
Prev: 04 Express 1500
Prev: 04 Express 1500
3. Enter code.
• All characters must be entered.
• Only one character can be changed at a time.
• Use the LEFT and RIGHT keys to scroll to
desired digit.
• Use the UP and DOWN keys to change the
selected digit.
• Press .
Main Menu
Vehicle?
• Some vehicles may have an additional screen
asking in which system to look for a code.
• If the definition could not be found, the scan
tool displays “No DTC Definition Found.” See
Service Manual.
4. To look up another DTC, press .
5. Press again to return to the Diagnostic Menu.
4.8 Locating the OBD II Data Link Connector (DLC)
• The OBDII data link connector (DLC) is usually
located under the driver’s side dash.
• Refer to vehicle user manual for DLC location.
• For more information, go to http://www.obdclearinghouse.com/oemdb.
NOTE: When tool is connected to the vehicle’s DLC,
power to the tool comes from the vehicle
4.9 Connect the Tool
1. Locate the OBDII data link connector under the
steering column. If the connector is not there, a
label should be there indicating the whereabouts of
the connector.
2. If necessary, remove the cover from the vehicle
connector.
580001 | REV. A | 11.2016
Page 20

en | 20 | User guide
Select Vehicle
AutoID (>=2000)
Manual (<=1999)
Prev: 06 Accord
Prev: 04 Express 1500
Prev: 04 Express 1500
Prev: 04 Express 1500
2000-04 vehicles may support Aut
| OBD 1350
ProGrade OBDII Scan Tool
3. Turn the ignition switch to the ON position. Do not
start the engine.
4. Plug the OBDII connector attached to the Tool into
the Data Link Connector.
5. The tool will attempt to identify the vehicle. If successful, the vehicle identified will be displayed. If
vehicle couldn‘t be identified, menus will be shown
for you to select the vehicle manually.
The tool can support up to 5 previous vehicles in the
garage. If you already have 5 previous vehicle in your
garage, the tool will display a menu asking you
which previous vehicle to replace with the currently
identified vehicle.
6. Review Quick Test results.
7. Go to Diagnostic Menu by pressing .
4.10 Vehicle Selection
AutoID™ uses the VIN to determine the type of vehicle
the tool is connected to. Vehicle manufactures began
programming the VIN into the vehicle controller in 2000,
but it was not an OBD II mandate until 2005. Vehicles
between 2000 and 2004 may or may not support
AutoID™, but vehicles after 2005 should support
AutoID™. If the tool is on a vehicle newer than database
coverage, the tool will AutoID™ as MY OBD II / EOBD, or
2012 OBD II / EOBD.
From the Main Menu:
1. Use the UP and DOWN keys until Vehicle
Diagnostics is highlighted.
• Press .
Main Menu
Vehicle Diagnostics
Acronyms
Review Data
Print Data
Code Lookup
System Setup
Prev: will be blank.
• Press .
• A Turn Key Off screen will display.
Turn Key Off
Please turn the key off for
10 seconds then turn the key
on.
Press ENTER to continue
3. After 10 seconds, turn key ON.
• If the vehicle is supported, the VIN number and
essential vehicle data will display.
4. Use the LEFT and RIGHT key to select YES or
NO.
• If YES is selected, the Tool may display more
selections to further select the vehicle because
not every aspect of vehicle identification is
contained in the VIN.
• If NO is selected, the Tool proceeds to manual
selection.
• Press .
2. Use the UP and DOWN keys to select
AutoIDTM, Manual or Prev.:
• If the vehicle is a model year 2000 or newer,
select AutoIDTM.
• If the vehicle is 1999 or older, or if the vehicle
is 2000 to 2004 but does not support AutoID™,
select Manual and go to Step 3.
• If the previously tested vehicle listed after
Prev: is desired, select Prev:. If this is the first
580001 | REV. A | 11.2016
time the tool has been used, the space after
VIN 1GCFG15T541238036
2004 Chevrolet
Express 1500
5.3
Is this correct?
Yes
5. If Manual was selected in Step 1, use the UP and
DOWN keys to select:
• OBDII/EOBD
• US
• Europe
• Asia
• Previous Vehicle:
• Press .
No
Page 21

OBD 1350 ProGrade OBDII Scan Tool | User guide | 21 | en
Vehicle Required
Press ENTER to continue
Please verify the tool is
connected to the vehicle with
the ignition key turned on.
Vehicle?
OBDII/EOBD
US
Europe
Asia
Prev: 06 Accord
Prev: 04 Express 1500
Prev: 04 Express 1500
Prev: 04 Express 1500
The OBDII/EOBD selection is provided for vehicles that
are not listed, however, selection of the specific vehicle
is recommended for maximum tool utility.
The previously selected vehicle will appear as the Prev:
menu selection after Asia.
• To select a vehicle other than the previous
vehicle, choose between OBDII/EOBD, US,
Europe, or Asia, and continue making selections
until the vehicle selection is complete.
The following screen only displays when power comes
from vehicle.
• Turn vehicle key OFF for 10 seconds.
• Turn vehicle key back to the ON position.
• Press .
Turn Key Off
Please turn the key off for
10 seconds then turn the key
on.
Press ENTER to continue
• If vehicle power is not detected, a screen is
shown to verify tool connection.
Garage Full
Prev: 05 Tahoe 2WD
Prev: 06 Lancer
Prev: 06 Lancer
Prev: 13 Silverado 2500 HD
Prev: 06 Lancer
Select vehicle To replace
• If the previous vehicle is selected, all stored
vehicle data will be retained until it is overwritten by the corresponding function selected from
the Diagnostic Menu.
4.11 CodeConnect® Feature
CodeConnect® is an experience-based database derived
from millions of phone calls from technicians seeking
assistance diagnosing repair problems on their vehicles.
CodeConnect® brings the technology of professional
technicians to a DIY scan tool. Don’t waste time trying to
find the answer. With the information CodeConnect®
offers, it takes vehicle repairs to the next level. Since you
now know the most probable fix for your problem, you
can decide if you want to tackle the repair yourself, or
bring the vehicle to a local automotive repair facility.
IMPORTANT: For CodeConnect® to work, you must
select your specific vehicle during vehicle selection. A
Global OBD II vehicle selection will not provide any
CodeConnect® information. The power of CodeConnect® is that repair information is vehicle and trouble
code specific and is based on the largest experiencebased database available.
CodeConnect® information is available whenever
is visible on the display. It has the potential of being
displayed while trouble codes are being displayed from
Read Codes or while Viewing Freeze Frame data. Also,
when you print codes to your PC, the CodeConnect®
information, if available, will also be printed.
CodeConnect® information is currently only available in
English, so if your tool is set to Spanish or French, don’t
be alarmed if your DTC text is in one language and your
CodeConnect® information is shown in English.
How to use CodeConnect®:
• If you already have 5 vehicles in your garage, the
tool will display a menu asking you which previous vehicle to replace with the currently identified vehicle.
1. When is shown on the display, press the
key.
2. Scroll through the code-specific repair information.
• Use the UP and DOWN keys to scroll one
line at a time.
• Use the LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to
scroll one screen at a time.
There are 3 levels of reported fixes:
Fix Level Description
Top Reported Fix
More likely to be the solution over other
choices provided
580001 | REV. A | 11.2016
Page 22

en | 22 | User guide
| OBD 1350
ProGrade OBDII Scan Tool
Frequently Reported Fix
Also Reported Fix
P0102
Mass Or Volume Air Flow A
Circuit Low Input
CURRENT
MIL
Since last key cycle
Since DTCs erased
TOP REPORTED FIX
1-Replaced Mass Air Flow (MAF)
Sensor
FREQ REPORTED FIXES
1-Replaced Oxygen (O2) Sensor(
s)
2-Replaced Heated Oxygen Sensor
(HO2S) Bank 1 Sensor 1 (B1S1)
ALSO REPORTED FIXES
1-Replaced ENG 1 Fuse
2-Replaced Evaporative
Emissions (EVAP) Canister
Vent Solenoid/Valve
3-Replaced Ignition Switch
4-Replaced Intake Manifold
5-Repaired Mass Air Flow (MAF)
Sensor Connector
6-Replaced Powertrain Control
Module (PCM)
7-Programmed Powertrain Control
Module (PCM)
8-Cleaned Throttle Body
As likely as other solutions
Less likely than other solutions provided,
but worth considering.
1/2
ECM $10
NOT REQUESTED
PASS/FAIL
PASS/FAIL
Erase FFrameRead
If a vehicle has multiple sets of criteria for the DTC,
a menu is displayed, so that the tool can provide the
most accurate criteria for your specific vehicle.
3. Use the UP and DOWN keys to scroll one line
at a time.
4. Use the LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to scroll a
whole screen at a time.
• To return to the DTC definition screen, press
.
P0102
Mass Or Volume Air Flow A
Circuit Low Input
CURRENT
MIL
Since last key cycle
Since DTCs erased
Erase FFrameRead
NOT REQUESTED
1/2
ECM $10
PASS/FAIL
PASS/FAIL
4.13 Acronyms
The Acronyms function allows the user to view acronyms and abbreviations used by the scan tool.
From the Main Menu or Diagnostic Menu.
1. Select Acronyms.
• Use the UP and DOWN keys until Acro-
nyms is highlighted.
• Press .
Main Menu
Vehicle Diagnostics
Acronyms
Review Data
Print Data
Code Lookup
System Setup
3. To return to the screen from which you pressed the
key, press .
4.12 Code Criteria
The Code Criteria feature will detail the conditions
required for a DTC to be set by the vehicle. The vehicle is
constantly running self-tests on its systems. Code Criteria will describe the conditions under which the vehicle
can initiate the test. These are called “Enable” criterion.
Code Criteria will also describe the the conditions that
will cause a DTC to set. These are called “Failure” criterion. Code Criteria is not available for every DTC. Code
Criteria is currently only available in English, so if your
tool is set to Spanish or French, don’t be alarmed if your
DTC text is in one language and your Code Criteria
information is shown in English.
How to use Code Criteria.
1. When the icon is shown on the display, press the
key.
2. Scroll through the Code Criteria information noting.
580001 | REV. A | 11.2016
2. Select the alphabetical group range for the desired
acronym.
• Use the UP and DOWN keys until the
desired group range is highlighted.
• Press .
Acronyms
# - 24X C
24X S - 5
A - AF 1/1
AF 1/2 - AI
Al - BBA - CA
Ca - CL
Cl - c
C - DIA
3. Select the acronym.
Page 23

OBD 1350 ProGrade OBDII Scan Tool | User guide | 23 | en
• Use the UP and DOWN keys until the
desired acronym is highlighted.
• Press .
Acronyms
# Of Emiss
# Of Pwrt
#CMP/CKP LOSS
#TRP SNC MISF
#TRPS SNC MISF
% Alcohol
% GRADE
% METHANOL
% of Pdl
4. View selected acronym.
• Press to return to the Diagnostic Menu.
# Of Emiss
Number Of Emission Related DTC
4.14 Component Locator
Component Locator provides a vehicle-specific location
of components found on the selected vehicle. It is a
useful companion function to CodeConnect®. CodeCon-
nect® will indicate components that repaired a problem
associated with a DTC, and Component Locator provides the location of the component
Component Locator can be selected from the Diagnos-
tic Menu. Because Component Locator provides vehicle-
specific component locations, a previous vehicle must
be stored in the scan tool.
From the Diagnostic Menu.
1. Select Component Locator.
• Use the UP and DOWN keys until Compo-
nent Locator is highlighted.
component.
• Use the UP and DOWN keys until the
desired group range is highlighted.
• Press .
Component Locator
A - Fuel Injector (No 4
Fuel Injector (No 5 - K
M - W
3. Select the component.
• Use the UP and DOWN keys until the
desired component is highlighted.
• Full component name will scroll on bottom of
screen for the highlighted component.
• Press .
Component Locator
Accelerator Pedal position Sens
Camshaft Position Sensor (Early
Camshaft Position Sensor (Late
Crankshaft Position Sensor
Electronic Brake Control Module
Electronic Brake Control Module
Engine Coolant Temperature Sens
Engine Coolant Temperature Sens
Accelerator Pedal Position Senso
4. View selected component location.
• Press to return to the Diagnostic Menu.
Component Locator
Accelerator Pedal Position
Sensor
-------------------------------Behind Gas Pedal
• Press .
Diagnostic Menu
Datastream
Diagnostic Codes
Special Functions
On Demand Tests
Component Locator
Acronyms
Review Data
Print Data
Code Lookup
System Setup
2. Select the alphabetical group range for the desired
5 Diagnostic Menu
The first time the scan tool links to the vehicle, the
communication protocol is automatically detected, and
is used until the scan tool is turned off or another vehicle is diagnosed.
If an error message displays, make sure the OBDII connector is attached and the ignition key is on. Cycle
ignition key to OFF for 10 seconds, then ON. This may be
required to reset computer. If required, select YES to try
again. If problem still exists, refer to “Error Messages” in
Troubleshooting.
580001 | REV. A | 11.2016
Page 24

en | 24 | User guide
| OBD 1350
ProGrade OBDII Scan Tool
The scan tool keeps data received from the previous 5
vehicle’s selected until any of the following occurs:
• A new vehicle is selected when you already have 5 in
your garage forcing you to select which vehicle you
want to remove from your garage to create space.
• Scan tool is flash programmed to update software.
On initial link to vehicle, scan tool checks the status of
I/M Monitors no matter which function is selected.
IMPORTANT
Review Data, Print Data, Code Lookup, and
System Setup are covered in Section 4 of this
manual. These items are not covered in this
section.
The Diagnostic Menu is broken down into the following
selections:
• Datastream
– View Data
– Record Data
– Component Locator
– Acronyms
– Review Data
– Print Data
– Code Lookup
– System Setup
• Diagnostic Codes
– Read Codes
– Erase Codes
– View Freeze Data
– Component Locator
– Acronyms
– Review Data
– Print Data
– Code Lookup
– System Setup
• Special Functions
– Global OBDII Functions
– I/M Monitors
– Drive Cycle Monitor
– State OBD Check
– MIL Status
– O2 Monitor Tests
– Diagnostic Monitor Tests
– On-Board Systems
– Vehicle Information
– Modules Present
– Charging System Monitor
– Fuel Consumption (MPG/KPL)
– Battery/Charging Services
– Brake Services
– Service Light Reset
– Component Locator
– Acronyms
– Review Data
– Print Data
– Code Lookup
– System Setup
• On Demand Tests
580001 | REV. A | 11.2016
– KOEO On Demand
– KOEO Output State
– KOEO Injector Buzz
– KOER On Demand
– KOER Cylinder Contribution
– KOER Glow Plug
– Component Locator
– Acronyms
– Review Data
– Print Data
– Code Lookup
– System Setup
• Component Locator
• Acronyms
• Review Data
• Print Data
• Code Lookup
• System Setup
Not every function will be on the menus for every vehicle. Some functions are vehicle specific, so they will not
appear on every menu.
5.1 I/M Monitors (Emissions)
The I/M Monitors (Inspection / Maintenance) function is
used to view a snapshot of the operations for the emission system on OBDII vehicles. I/M Monitors is a very
useful function. To guarantee no faults exist make sure
all monitors are ok or n/a and no DTCs exist. Refer to the
vehicles service manual for the drive cycle operation.
During normal driving conditions, the vehicle computer
scans the emission system. After a specific amount of
drive time (each monitor has specific driving conditions
and time required), the computer monitors decide if the
vehicles emission system is working correctly or not as
well as detecting out of range values. When the monitor
status is:
• ok - vehicle was driven enough to complete the
monitor.
• inc (Incomplete) - vehicle was not driven enough to
complete the monitor.
• n/a (not applicable)- vehicle does not support that
monitor.
Depending on vehicle, disconnecting or a discharged
battery may erase DTCs and clear monitor status. Monitors may be reset by:
• Erasing codes
• Vehicle control modules losing power
The I/M Monitors function can be run key on engine
running (KOER) or key on engine off (KOEO).
Extreme weather and/or road conditions can prevent a
monitor from running. Also, some monitors may require
a cold start to complete.
From the Global OBDII Functions Menu.
1. Select I/M Monitors.
• Use the UP and DOWN keys until I/M
Monitors is highlighted.
• Press .
Page 25

Global OBDII Functions
Since DTCs Cleared
Misfire Monitor
Fuel System Mon
Comp Component
Catalyst Mon
Htd Catalyst
Evap System Mon
Sec Air System
A/C Refrig Mon
Oxygen Sens Mon
ok
ok
ok
ok
n/a
inc
n/a
n/a
ok
I/M Monitors
Drive Cycle Monitor
State OBD Check
MIL Status
O2 Monitor Tests
Diagnostic Monitor Tests
On-Board Systems
Vehicle Information
Modules Present
Two types of I/M Monitors test are:
• Since DTCs Cleared - shows status of the monitors
since the DTCs were last erased.
• This Drive Cycle - shows status of monitors since
the start of the current drive cycle. Refer to the
vehicle service manual for more detailed information
on emission-related monitors and their status.
Some vehicles do not support This Drive Cycle. If vehicle supports both types of monitors the I/M Monitors
Menu displays.
I/M Monitors
Since DTCs Cleared
This Drive Cycle
OBD 1350 ProGrade OBDII Scan Tool | User guide | 25 | en
Abbreviations and names for OBDII monitors supported
by the scan tool are shown below. They are required by
the United States Environmental Protection Agency
(EPA). Not all monitors are supported by all vehicles.
Monitors Expanded Name
Misfire Monitor Misfire monitor
Fuel System Mon Fuel System Monitor
Comp Component Comprehensive components monitor
Catalyst Mon Catalyst monitor
Htd Catalyst Heated catalyst monitor
Evap System Mon Evaporative system monitor
Sec Air System Secondary air system monitor
A/C Refrig Mon Air conditioning refrigerant monitor
Oxygen Sens Mon Oxygen sensor monitor
Oxygen Sens Htr Oxygen sensor heater monitor
EGR/VVT Sys Mon
NMHC Cat Mon
Exhaust gas recirculation or variable
valve timing monitor
Non-methane hydrocarbon catalyst mon-
itor
NOX Treat Mon Nitrogen oxide treatment monitor
Boost Pres Mon Boost pressure monitor
Exhst Gas Sensr Exhaust gas sensor
PM Filter Mon Particulate matter filter monitor
3. Return to Global OBDII Functions Menu.
• Press .
2. View summary of monitor status.
• Use the UP and DOWN keys (if required).
Depending on monitor test, one of these two screens
will be present.
OR
This Drive Cycle
Misfire Monitor
Fuel System Mon
Comp Component
Catalyst Mon
Htd Catalyst
Evap System Mon
Sec Air System
A/C Refrig Mon n/a
Oxygen Sens Mon inc
ok
ok
ok
inc
n/a
dis
n/a
5.2 Read Codes
The Read Codes function allows the scan tool to read
the DTCs from the vehicle’s control modules. DTCs are
used to help determine the cause of a problem or problems with a vehicle. These codes cause the control
module to illuminate the malfunction indicator lamp
(MIL) when emission-related or driveability fault occurs.
When referring to the engine control module, MIL is also
known as service engine soon or check engine lamp.
Read Codes can be done with the key on engine off
(KOEO) or with the key on engine running (KOER).
From the Diagnostic Codes Menu:
1. Select Read Codes.
• Use the UP and DOWN keys until Read
Codes is highlighted.
• Press .
2. If more than one module is supported, a menu is
displayed.
• Use the UP and DOWN keys until the
desired choice is highlighted.
• Press .
Diagnostic Codes
Read Codes
Erase Codes
View Freeze Data
Component Locator
Acronyms
Review Data
Print Data
Code Lookup
System Setup
580001 | REV. A | 11.2016
Page 26

en | 26 | User guide
| OBD 1350
ProGrade OBDII Scan Tool
Select Module
OBDII/EOBD
Engine
ABS
Airbag
All of the Above
If no DTCs are present, a message stating “System Pass: No
Faults Detected” is displayed. If All of the Above is selected
from the Select Module menu, all of the codes will be
displayed as if all menu items were selected individually.
Read Codes
No codes found
Press ENTER to continue
3. View and write down the DTCs.
• Use the UP and DOWN keys until the
desired choice is highlighted.
This screen indicates where the Read Codes information
is located.
DTC#
DTC Description
DTC Type
Erase FFrameRead
DTC Number - number of the trouble code found in
vehicle service information.
X of Y - Indication that code x of y is being viewed,
where x is the code being viewed of the total y.
Module - The name of the module (e.g. ABS) or address of
the module (e.g. Mod $28) or both are shown (ABS $28) in
this field. The table below describes modules supported.
Module Description
ECM Engine or powertrain module
TCM Transmission control module
TCCM Transfer case control module
ABS Anti-lock brake system module
HPCM Hybrid powertrain control module
MOD $XX
SRS Supplemental restraint system module
Module address for the OBDII/EOBD module reporting the DTC
X/Y
Module
DTC Description - This area is reserved for the text describing the trouble code listed in the DTC number field.
DTC Type - This area is reserved for providing additional
information about the DTC. Multiple DTC types may be
possible for a given DTC number. Not all vehicles support DTC types. This table describes possible DTC types.
DTC Type Description
Intermittent codes placed in the vehicle’s
memory when the trouble originally oc-
History
curred, and will remain there even if the
trouble has been corrected. If no trouble
after 50 engine warm-up cycles, the DTC
will be erased.
Confirmed codes are reported when a
Confirmed
component, sensor, or other part of the
vehicle is indication a malfunction is present.
Codes transmitted through the PCMs da-
Current
ta stream when a trouble condition is active and cannot be erased. The problem
must be repaired to remove the DTC.
Indicates the current code has been set
Intermittent
at least once but possibly not enough to
cause a history code to be stored.
MIL
Indicates that this DTC has turned on the
MIL light.
Pending codes are also referred to as
continuous monitor or maturing codes.
An intermittent fault causes the control
module to store a code in memory. If the
fault does not occur within a certain num-
Pending
ber of warm-up cycles (depending on vehicle), the code clears from memory. If
fault occurs a specific number of times,
the code matures into a DTC and the MIL
illuminates or blinks. This function can be
used with KOEO or KOER.
Non-MIL
DTC that is not emission-related and did
not turn on the MIL light.
This DTC type also has a number with it
indicating that this is the code number
MIL Code
turning on the MIL. Vehicle service manuals may refer to this number instead of
the one listed in the DTC number field.
Permanent codes are a special type of
confirmed code. Permanent codes began being reported by vehicles around
2010, and therefore not supported by ev-
Permanent
ery vehicle. While Confirmed Codes can
be erased by the Tool, Permanent Codes
cannot. Permanent Codes are erased by
the vehicle when the vehicle has determined the fault is no longer present.
On some vehicles, the code returned by
SCI Hex
the vehicle is not known by the scan tool.
If this happens, the scan tool will display
this type along with the code number.
Active
Stored
DTC that was present at the time of scan
tool request.
DTC that was not present at the time of
scan tool request.
The Read, Erase, FFrame softkeys will execute the corresponding function as if the function was selected from
the menu.
Examples of Read Codes information screens follow.
580001 | REV. A | 11.2016
Page 27

OBD 1350 ProGrade OBDII Scan Tool | User guide | 27 | en
In this example, module (MOD) $18 is reporting the
DTCs.
P0113
Intake Air Temperature Sensor
1 Circuit High Input
Erase FFrameRead
1/3
Mod $18
In this example, the Engine Module is reporting a History
Code. The $10 is the engine module address.
P2270
Torque Converter Clutch
Circuit High
History
Erase FFrameRead
1/3
Eng $10
MIL indicates that this DTC has turned on the MIL light.
P2270
Torque Converter Clutch
Circuit High
Erase FFrameRead
1/3
Eng $10
The screen below shows dashes for the DTC number and
a MIL code of 213. The dashes will be shown if a DTC
number does not exist for the MIL code.
-----
EGR Position High
MIL CODE 213
Erase FFrameRead
1/1
Eng
Active is a DTC that was present at the time of scan tool
request.
P2270
Torque Converter Clutch
Circuit High
MIL
Erase FFrameRead
1/3
Eng $10
Pending indicates a global OBDII/EOBD pending code.
P1501
Vehicle Speed Sensor Out
of Range Self Test
PENDING
Erase FFrameRead
2/3
Mod $18
icon indicates that the key is active. Press the
key to display repair information. Refer to Code-
Connect® in section 3.
Non-MIL is a DTC that is not emission-related and did
not turn on the MIL light.
P0113
Intake Air Temperature Sensor
1 Circuit High
ACTIVE
Erase FFrameRead
1/1
Eng
4. Return to Diagnostic Codes Menu.
• Press .
5.3 Erase Codes
The Erase Codes function deletes DTCs and resets I/M
Monitor data from vehicle’s control module(s). Perform
this function key on engine off (KOEO). Do not start the
engine.
The Erase Codes function may also erase View Freeze
Data, O2 Monitor Tests, and Diagnostic Monitor Test
results depending on vehicle.
The Erase Codes function sets monitors to inc.
Perform Erase Codes function only after systems have been
checked completely and DTCs have been written down.
After servicing the vehicle, erase stored DTCs and verify
no codes have returned. If a DTC returns, problem has
not been fixed or other faults are present.
Permanent DTCs cannot be erased with the Erase Codes
function.
Depending on which monitor sets a code the vehicle
may need to be driven and the monitor ran before concluding that the fault is repaired.
From Diagnostic Codes Menu:
580001 | REV. A | 11.2016
Page 28

en | 28 | User guide
Erase Codes
Press ENTER to continue
Command sent
Codes remaining:0
| OBD 1350
ProGrade OBDII Scan Tool
1. Select Erase Codes.
• Use the UP and DOWN keys until Erase
Codes is highlighted.
• Press .
Diagnostic Codes
Read Codes
Erase Codes
View Freeze Data
Component Locator
Acronyms
Review Data
Print Data
Code Lookup
System Setup
• If diagnostic results and codes are not to be
erased select NO and press .
Erase Codes
Are you sure you want to
erase diagnostic results and
codes?
• Use the UP and DOWN keys until the
desired choice is highlighted.
• Press .
Select Module
OBDII/EOBD
Engine
ABS
Airbag
4. Observe “Command sent” message is displayed.
• Press .
Yes
No
• Selecting NO displays a “Command canceled”
message.
Erase Codes
Command canceled
Press ENTER to continue
2. Select YES to erase diagnostic results and codes.
• Use the LEFT arrow key.
• Press .
Erase Codes
Are you sure you want to
erase diagnostic results and
codes?
5. Return to Diagnostic Codes Menu.
• Press .
5.4 MIL Status
From Global OBDII Functions Menu:
1. Select MIL Status.
• Use the UP and DOWN keys until MIL
Status is highlighted.
• Press .
Global OBDII Functions
I/M Monitors
Drive Cycle Monitor
State OBD Check
MIL Status
O2 Monitor Tests
Diagnostic Monitor Tests
On-Board Systems
Vehicle Information
Oil Light Reset
2. View MIL Status.
• Press to return to Global OBDII Functions
Menu.
3. If more than one module is supported, a menu is
displayed.
580001 | REV. A | 11.2016
Yes
No
Page 29

OBD 1350 ProGrade OBDII Scan Tool | User guide | 29 | en
MIL is ON
MIL lamp should be ON if
engine is running
Press ENTER to continue
MIL is OFF
MIL lamp should be OFF
engine is running
Press ENTER to continue
5.5 State OBD Check
The State OBD Check function is used to display a basic
status of the vehicles OBD system.
• Malfunction indicator lamp (MIL) status
• Codes found
• I/M monitors
Erase Codes deletes DTCs and resets I/M monitors from
vehicle’s computer module(s).
The State OBD Check function has the following areas:
• MIL Status ON or OFF
• Number of Codes Found
• Number of Monitors OK
• Number of Monitors Inc
• Number of Monitors N/A
State OBD Check should be done with the key on
engine running (KOER) due to showing MIL status.
The number of codes found are only Global OBD II codes and
not pending codes.
The number of monitors that are either ok, inc, or na are
only Since DTCs Cleared and not This Drive Cycle.
Refer to Read Codes and I/M Monitors for more
detailed information about the results.
From Global OBDII Functions Menu:
1. Select State OBD Check.
• Use the UP and DOWN keys until State
OBD Check is highlighted.
• Press .
Global OBDII Functions
I/M Monitors
Drive Cycle Monitor
State OBD Check
MIL Status
O2 Monitor Tests
Diagnostic Monitor Tests
On-Board Systems
Vehicle Information
Oil Light Reset
2. View State OBD Check display.
State OBD Check
MIL Status
Codes Found
Monitors OK
Monitors Inc
Monitors N/A
3. Return to Global OBDII Functions Menu.
• Press .
OFF
0
3
4
4
5.6 View Data
The View Data function allows real time viewing of the
vehicle’s computer module’s parameter identification
(PID) data. As the computer monitors the vehicle, information is simultaneously transmitted to scan tool.
View Data allows the following items to be viewed on
the scan tool:
• Sensor data
• Operation of switches
• Operation of solenoids
• Operation of relays
View Data can be shown as:
• Entire Data List
• Custom Data List
Apart from Read Codes, View Data is the most useful
diagnostic function for isolating the cause of a vehicle
operation problem.
From Datastream Menu:
1. Select View Data.
• Use the UP and DOWN keys until View
Data is highlighted.
• Press .
Datastream
View Data
Record Data
Component Locator
Acronyms
Review Data
Print Data
Code Lookup
System Setup
580001 | REV. A | 11.2016
Page 30

en | 30 | User guide
| OBD 1350
ProGrade OBDII Scan Tool
2. Observe while the scan tool validates PID MAP.
• PID MAP validation is the tool asking the vehicle
which PIDs are supported. See Appendix A for a
complete list of PIDs supported by the tool.
• Multiple PIDs may be sent if vehicle is equipped
with more than one computer module (for
example a powertrain control module [PCM]
and a transmission control module [TCM]). The
scan tool identifies them by their identification
names (ID) assigned by manufacturer (i.e. $10
or $1A).
• If one or more control module stops responding,
the scan tool displays a message.
– If continuing, dashes will replace data in
right-hand column.
– If NO is selected, then the scan tool
attempts to re-establish communication
with that module.
Validating PIDs
Waiting for vehicle to
respond
Please Wait
Validating PIDs
Validating PID List
PID 19/329
Please Wait
• Use the UP and DOWN keys.
• See Appendix A for PID definitions.
ABS LOAD(%)
ABSLT TPS($01)
ABSLT TPS($07)
ACC POS D(%)
BARO PRS(”HG)
CALC LOAD(%)
CALC LOAD(%)
CAT TEMP11(°F)
CLR DIST(mi)
CLR DIST(mi)
Absolute Load Value
0.0
6.3
6.3
0.0
29.2
0.0
0.0
73
499
513
If Long PID Names is turned ON, the expanded text for
the PID will scroll on the bottom line of display. See
“Long PID Names” in section 3.
If the icon displays while a PID is selected press
to select PIDs to graph. A maximum of 2 PIDs can
be graphed.
Select PIDs to Graph
✓ABSLT TPS(%)
CALC LOAD(%)
COOLANT(°F)
ENG SPEED(RPM)
EQ RATIO11
IAT(°F)
IGN ADV(°)
LT FTRM1(%)
Throttle Position
• Use the RIGHT arrow key to select/deselect
PIDs. The highlighted PID from when was
pressed is already selected
• Use the LEFT arrow key to deselect all PIDs.
• Press to view graph of selected PIDs.
• When graphing two PIDs, use the UP and
DOWN keys to highlight the desired PID, which
will also display the appropriate scale.
• Press the key to pause the graph. Press
the key again to continue graphing.
View Entire List
View Entire List shows all supported PID data for the
vehicle being tested
From Select Data to View menu:
1. Select Entire Data List.
• Use the UP and DOWN keys until Entire
Data List is highlighted.
• Press .
Select Data to View
Entire Data List
Custom Data List
English/Metric
2. View PIDs on scan tool.
580001 | REV. A | 11.2016
• If the icon displays while a PID is selected
press to view graph.
3. Return to PID screen.
• Press .
4. Return to Select Data to View menu.
• Press .
5. Return to Datastream Menu.
• Press .
Custom List Select
The Custom Data List allows certain PIDs from the View
Entire Data List, such as those PIDs that apply to a
specific driveability symptom or system, to be selected.
From Select Data to View menu:
1. Select Custom List Select.
• Use the UP and DOWN keys until Custom
Data List is highlighted.
• Press .
Page 31

OBD 1350 ProGrade OBDII Scan Tool | User guide | 31 | en
Select Data to View
Entire Data List
Custom Data List
English/Metric
2. Select View Instructions or Not.
• Use the LEFT and RIGHT keys.
• Press .
Custom Setup
Do you want to view
instructions for creating a
custom data list?
Yes
No
3. Select PIDs to View.
• Use the UP and DOWN keys to move up
and down list.
• The RIGHT arrow selects or deselects data
parameter. All selected data values are marked
with a √ symbol.
• The LEFT arrow deselects all marked data
parameters.
• The key starts recording data or displaying selected data parameters.
• If Long PID Names is turn ON, the expanded text
for the PID will scroll on the bottom line of
display. See “Long PID Names” in section 3.
• Selected PIDs are kept until you exit View Data
and return to the Datastream Menu.
Select Custom List
MIL STATUS
O2S11(V)
O2S12(V)
O2S21(V)
O2S22(V)
OBD2 STAT
PTO STATUS
ST FTRM11(%)
ABS TPS B(%)
MIL STATUS
Throttle Position B
0.0
Off
If the icon displays while a PID is selected press
to view graph. Press to Return to PID
Screen.
Refer to “View Entire List.” on page 4-19 for instructions
on how to select PIDs to graph and how to view graph.
5. Return to Select Data to View Menu.
• Press .
6. Return to Datastream Menu.
• Press .
5.7 Record Data
The Record Data function records PIDs while vehicle is
parked or being driven. The Record Data function is
mainly used for diagnosing intermittent driveability
problems that cannot be isolated by any other method.
The recording time varies. A recording consists of frames
of data before the trigger and several frames after the
trigger.
CAUTION
Two people must be in vehicle when driving.
One to drive and the other to operate the
scan tool.
From Datastream Menu:
1. Select Record Data.
• Use the UP and DOWN keys until Record
Data is highlighted.
• Press .
Datastream
View Data
Record Data
Component Locator
Acronyms
Review Data
Print Data
Code Lookup
System Setup
Malfunction Indicator Lamp Statu
4. View PIDs on scan tool.
• Use the UP and DOWN arrow key.
• See Appendix A for PID Definitions.
2. Follow all instructions on display.
• The scan tool can maintain 5 recordings per
vehicle. If there are already 5 recordings stored,
the scan tool will ask which recording to overwrite.
• Scan tool validates list of global PIDs from
vehicle.
580001 | REV. A | 11.2016
Page 32

en | 32 | User guide
| OBD 1350
ProGrade OBDII Scan Tool
Validating PIDs
Validating PID List
PID 116/329
Please Wait
3. Refer to View Data to setup Custom List or View
Entire List and Pre-Trigger Setup to set the number
of frames to keep prior to triggering the recording.
Select Data to Record
Entire Data List
Custom Data List
Pre-Trigger Setup
4. Press to begin recording.
• Data continues to be saved until either:
– Record memory is full.
– Operator presses .
• Scan tool recording times vary. A recording
consists of frames of data before trigger and
several frames after trigger.
Recording
Record Data
Playback data?
Yes
No
5.8 View Freeze Data
When an emission-related fault occurs, certain vehicle
conditions are recorded by the on-board computer. This
information is referred to as freeze frame data. View
Freeze Data is a snapshot of the operating conditions at
the time of an emission-related fault. View Freeze Data
can be overwritten by faults with a higher priority. If
codes were erased, View Freeze Data may not be stored
in vehicle memory depending on vehicle.
From Diagnostic Codes Menu:
1. Select View Freeze Data.
• Use the UP and DOWN keys until View
Freeze Data is highlighted.
• Press .
Diagnostic Codes
Read Codes
Erase Codes
View Freeze Data
Component Locator
Acronyms
Review Data
Print Data
Code Lookup
System Setup
Collecting pretrigger data
Press ENTER to trigger
recording
Recording
Collecting data for frame #4
Press ENTER to end recording
5. After recording, scan tool displays a prompt to
Playback Data.
• Select NO to return to Datastream Menu.
• Select YES to display recorded data.
• Refer to “Recording” on page 17 for instruc-
tions on how to play back data.
580001 | REV. A | 11.2016
2. Select frame, if more than one frame is present.
• Use the UP and DOWN keys until the
desired frame is highlighted.
• Press .
Select Data to View
P0102 (MOD $10)
Long PID Names
English/Metric
3. View PIDs on scan tool.
• Use the UP and DOWN keys.
• See Appendix A for PID definitions.
Page 33

OBD 1350 ProGrade OBDII Scan Tool | User guide | 33 | en
TROUB CODE
FUEL SYS 1
FUEL SYS 2
CALC LOAD(%)
COOLANT (°F)
ST FTRM1(%)
LT FTRM1(%)
MAP(”HG)
ENG SPEED(RPM)
VEH SPEED(MPH)
Definition that caused Freeze Fra
P2122
N/A
N/A
0.0
-40
0.0
0.0
28.1
0
0
• If Long PID Names is turned on, the expanded
text for the PID will scroll on the bottom line of
the display. See “Long PID Names” on page
13.
• icon indicates that the key is active.
Press the key to display repair information.
Refer to “CodeConnect®” in section 3.
• indicates that the key is active. Press
the key to display the DTC definition of the
DTC that created the Freeze Frame.
4. Select another frame to view (if available).
• Press .
5. Return to Diagnostic Codes Menu.
• Press .
5.9 Drive Cycle Monitor
The Drive Cycle Monitor function is very similar to I/M
Monitors though the Drive Cycle Monitor is used to
view real-time operations of the emissions system on
OBDII vehicles. Drive Cycle Monitor continuously
updates as the vehicle reports operations of the emission system.
CAUTION
Two people must be in vehicle when driving.
One to drive and the other to operate the
scan tool.
From Global OBDII Functions Menu:
1. Select Drive Cycle Monitor.
• Use the UP and DOWN keys until Drive
Cycle Monitor is highlighted.
• Press .
Global OBDII Functions
I/M Monitors
Drive Cycle Monitor
State OBD Check
MIL Status
O2 Monitor Tests
Diagnostic Monitor Tests
On-Board Systems
Vehicle Information
Charging System Monitor
• Two types of drive cycle monitors are:
– Since DTCs Cleared shows status of the
monitors since the Diagnostic Trouble
Codes were last erased.
– This Drive Cycle shows status of monitors
since start of current drive cycle. Refer to
the vehicle service manual for more detailed
information on emission-related monitors
and their status.
– Some vehicles do not support Drive Cycle
Monitor. If vehicle supports both types of
drive cycle monitors the Drive Cycle Moni-
tor menu will display.
Drive Cycle Monitor
Since DTCs Cleared
This Drive Cycle
• Refer to the vehicle service manual for the drive
cycle operation.
Drive Cycle Monitor can be used if you want to drive the
vehicle until all of the monitors are OK.
During normal driving conditions, the vehicle computer
scans the emission system. After a specific amount of
drive time (each monitor has specific driving conditions
and time requirements), the computer monitors will
decide if the vehicle emissions system is working correctly or not as well as detecting out a range of values.
When the monitor status is:
• “ok” - vehicle has been driven enough for function.
• “inc” (incomplete) - vehicle was not driven enough
to complete all of the monitors.
• “n/a” (not applicable) - vehicle does not support
that monitor.
Reset monitors by:
• Erasing codes.
• Vehicle computer module losing power (on some
vehicles).
2. View summary of monitor status.
• Use the UP and DOWN keys (if required).
3. Depending on the drive cycle monitors, either the
This Drive Cycle or the Since DTCs Cleared screen
will display.
This Drive Cycle
Catalyst Mon
Oxygen Sens Mon
Oxygen Sens Htr
EGR/VVT Sys Mon
OR
inc
inc
inc
inc
580001 | REV. A | 11.2016
Page 34

en | 34 | User guide
| OBD 1350
ProGrade OBDII Scan Tool
Since DTCs Cleared
Misfire Monitor
Fuel System Mon
Comp Component
Catalyst Mon
Htd Catalyst
Evap System Mon
Sec Air System
A/C Refrig Mon
Oxygen Sens Mon
• The scan tool display is continuously updated.
Monitors that are “ok” will disappear and only
the “inc” monitors will remain displayed. Monitors designated “n/a” are not displayed.
• When all Monitors are “OK” a screen stating “All
supported monitors are OK” will display.
ok
ok
ok
ok
n/a
inc
n/a
n/a
ok
This Drive Cycle
All supported monitors are OK
Press ENTER to continue
OR
Since DTCs Cleared
• O2 sensors are located before (upstream) and after
(downstream) catalyst(s). Sensors are named (xy) for
their position to both cylinder banks and catalysts.
– The O2 sensor for cylinder bank 1 has prefix 1y
while O2 sensor for cylinder bank 2 has prefix
2y.
– The O2 sensor upstream of catalyst (closest to
engine) has suffix x1 while O2 sensor downstream of catalyst has suffix x2. If vehicle contains more catalysts, O2 sensor downstream of
second catalyst has suffix x3 and O2 sensor
downstream of next catalyst has suffix x4.
– For example, O2S21 is upstream O2 sensor for
cylinder bank 2.
The following O2 Sensor Tests are available:
• Rich-to-lean sensor threshold voltage
• Lean-to-rich sensor threshold voltage
• Low sensor voltage for switch time
• High sensor voltage for switch time
• Rich-to-lean sensor switch time
• Lean-to-rich sensor switch time
• Minimum sensor voltage test cycle
• Maximum sensor voltage test cycle
• Time between sensor transitions
• Sensor period
• Manufacturer specific tests
From Global OBDII Functions Menu:
1. Select O2 Monitor Tests.
• Use the UP and DOWN keys until O2 Moni-
tor Tests is highlighted.
• Press .
All supported monitors are OK
Press ENTER to continue
4. Return to Global OBDII Functions Menu.
• Press .
5.10 O2 Monitor Tests
OBDII regulations require applicable vehicles monitor and
test oxygen (O2) sensors to determine problems related
to fuel and emissions. The O2 Monitor Tests allows
retrieval of completed O2 sensors monitor test results.
• The O2 Monitor Tests is not an on-demand test. O2
sensors are not tested when selected via the menu.
O2 sensors are tested when engine operating conditions are within specified limits.
• If the vehicle communicates using a controller area
network (CAN), O2 Monitor Tests are not supported
by vehicle. A message is displayed. See “Diagnostic
Monitor Tests” in this section to see O2 monitor data.
Global OBDII Functions
I/M Monitors
Drive Cycle Monitor
State OBD Check
MIL Status
O2 Monitor Tests
Diagnostic Monitor Tests
On-Board Systems
Vehicle Information
Charging System Monitor
2. Select O2 sensor.
• Use the UP and DOWN keys until the
desired O2 monitor is highlighted.
• Press .
Select O2 Sensor
O2 Bank1 Sensor1
580001 | REV. A | 11.2016
Page 35

• The O2 sensors located upstream (before catalyst) may perform differently than ones located
downstream (after catalyst).
• Test IDs are shown for unknown O2 sensor
tests.
3. View results of selection.
• Use the UP and DOWN keys.
O2 Bank1 Sensor1
Test $86
MOD
MAX
MEAS
MIN
Test $8D
MOD
MAX
MEAS
MIN
$09
128
128
128
$09
255
128
128
4. Return to O2 Sensor Tests menu.
• Press .
5. Return to Global OBDII Functions Menu.
• Press .
OBD 1350 ProGrade OBDII Scan Tool | User guide | 35 | en
Select Diag Mon Test
Test $03
Test $49
Test $4A
Test $62
Test $76
Test $78
Test $81
Test $9A
Test $9B
Or, refer to appropriate vehicle service manual for
test IDs and definitions.
Select Diag Mon Test
O2 Sensor B1S1
O2 Sensor B1S2
O2 Sensor B2S1
O2 Sensor B2S2
Catalyst B1
Catalyst B2
EGR Mon B1
EVAP (0.090”)
EVAP (0.020”)
5.11 Diagnostic Monitor Tests
The Diagnostic Monitor Test function is useful after
servicing or after erasing a vehicle’s memory. Test
results do not necessarily indicate a faulty component or
system.
• Non-CAN vehicles Diagnostic Monitor Test receives test
results for emission-related powertrain components
and systems that are not continuously monitored.
• CAN vehicles Diagnostic Monitor Test receives test
results for emission-related powertrain components and
systems that are and are not continuously monitored.
• Vehicle manufacturer is responsible for assigning
test and component IDs.
From Global OBDII Functions Menu:
1. Select Diagnostic Monitor Tests.
• Use the UP and DOWN keys until Diagnos-
tic Monitor Tests is highlighted.
• Press .
Global OBDII Functions
I/M Monitors
Drive Cycle Monitor
State OBD Check
MIL Status
O2 Monitor Tests
Diagnostic Monitor Tests
On-Board Systems
Vehicle Information
Charging System Monitor
• Applicable diagnostic monitor tests are dis-
played.
2. Review test results displayed on scan tool.
• Use the UP and DOWN keys until desired
result is highlighted.
• Press .
On Non-CAN vehicles the scan tool displays:
– Test data (test ID)
– Maximum value (MAX)
– Test measurements (MEAS)
– Minimum value (MIN)
– Status (STS)
– Measurements and Specification values are
hexadecimal numbers (i.e., $1A, $FE, $11.)
– Module (MOD)
Test $03
ID
MOD
MAX
MEAS
MIN
STS
• On CAN vehicles scan tool displays:
– Test performed. The test performed can be
$## if test is not defined. Refer to vehicle
service manual for details.
– Measured values and units of measured
(such as volts, amps, and seconds).
– Status of monitor test data.
– Module ID where the monitor test data
came from.
01
$09
---00
00
OK
580001 | REV. A | 11.2016
Page 36

en | 36 | User guide
| OBD 1350
ProGrade OBDII Scan Tool
O2 Sensor B1S1
RICH-LN Thresh
MOD
MAX
MEAS
MIN
STS
$07
0.4497(V)
0.4497(V)
0.4497(V)
OK
3. Return to Select Test menu.
• Press .
4. Return to Global OBDII Functions Menu.
• Press .
5.12 On-Board Systems
The On-Board Systems test allows the scan tool to
control operation of vehicle components, tests or systems.
• Some manufacturers do not allow tools to control
vehicle systems. A vehicle not supporting an onboard system is identified by a message that is
displayed when selected.
• Refer to the vehicle service manual for on-board
systems instructions.
• The manufacturer is responsible for determining the
criteria to automatically stop test. Refer to appropriate vehicle service manual.
From Global OBDII Functions Menu:
1. Select On-Board Systems.
• Use the UP and DOWN keys until On-
Board Systems is highlighted.
• Press .
Global OBDII Functions
I/M Monitors
Drive Cycle Monitor
State OBD Check
MIL Status
O2 Monitor Tests
Diagnostic Monitor Tests
On-Board Systems
Vehicle Information
Charging System Monitor
• A list of on-board systems and components
available for testing are shown on the display.
2. Select test.
• Use the UP and DOWN keys until desired
test is highlighted.
• Press .
On-Board Systems
EVAP System Test
On-Board Systems
Command sent
Press ENTER to continue
3. Return to On-Board Systems menu.
• Press .
4. Return to Global OBDII Functions Menu.
• Press .
5.13 Vehicle Information
The Vehicle Information function allows the scan tool to
request the vehicle’s VIN number, calibration ID(s) which
identifies software version in vehicle control module(s),
calibration verification numbers (CVN(s)) and in-use
performance tracking.
• Vehicle Information function applies to model year
2000 and newer OBDII compliant vehicles.
• The scan tool cannot verify if data is correct for
scanned vehicles.
• CVNs are calculated values required by OBDII regulations.
• The CVN calculation may take several minutes.
• CVNs are reported to determine if emission-related
calibrations have been changed. Multiple CVNs may
be reported for a control module.
• In-use performance tracking, tracks performance of
key I/M Monitors.
From Global OBDII Functions Menu:
1. Select Vehicle Information.
• Use the UP and DOWN keys until Vehicle
Information is highlighted.
• Press .
580001 | REV. A | 11.2016
Page 37

OBD 1350 ProGrade OBDII Scan Tool | User guide | 37 | en
Global OBDII Functions
I/M Monitors
Drive Cycle Monitor
State OBD Check
MIL Status
O2 Monitor Tests
Diagnostic Monitor Tests
On-Board Systems
Vehicle Information
Oil Light Reset
Vehicle Information
Verify key ON
Engine OFF.
Press ENTER to continue
WORKING
Communicating with the
vehicle
Please Wait
Vehicle Information
Retrieving CALID data. It may
take up to 1.5 minutes.
Press BACK to exit
Vehicle Information
Retrieving IPT data. It may
take up to 1.5 minutes.
Press BACK to exit
2. Select information to view from the menu.
• Use the UP and DOWN keys until desired
selection is highlighted.
• Press .
Vehicle Information
VIN
CVN
CAL ID
IPT
Vehicle Information
Retrieving VIN data. It may
take up to 1.5 minutes.
Press BACK to exit
Vehicle Information
Retrieving CVN data. It may
take up to 1.5 minutes.
Press BACK to exit
• If the selected menu item has data for more
than one module, a menu listing all modules
returning data for that menu item is shown.
3. View information supported by vehicle.
• Use the UP and DOWN keys (if required).
580001 | REV. A | 11.2016
Page 38

en | 38 | User guide
| OBD 1350
ProGrade OBDII Scan Tool
VIN (MOD $09)
1HGCM56866A018504
CVN (MOD $09)
00 5C 02 52
CAL ID (MOD $ 09)
37805-RAD-A590
--------------
IPT (MOD $ 09)
OBDCOND
IGNCNTR
CATCOMP1
CATCOND1
CATCOMP2
CATCOND2
O2SCOMP1
O2SCOND1
Monitor Conditions Encountered
O2SCOMPX
O2SCONDX
EGRCOMP
EGRCOND
AIRCOMP
AIRCOND
EVAPCOMP
EVAPCOND
O2 Sensor Monitor Completion Counts
Bank x
O2 Sensor Conditions Encountered
Counts Bank x
EGR Monitor Completion Condition
Counts
EGR Monitor Conditions Encountered
Counts
AIR Monitor Completion Condition
Counts (Secondary Air)
AIR Monitor Conditions Encountered
Counts (Secondary Air)
EVAP Monitor Completion Condition
Counts
EVAP Monitor Conditions Encountered
Counts
• If message INVALID displays on screen, the data
returned from the vehicle is incorrect, or is not
formatted in accordance with OBDII specifications.
4. Return to Vehicle Information menu.
• Press .
5. Return to Global OBDII Functions Menu.
• Press .
5.14 Oil Light Reset
The Oil Light Reset function allows the scan tool to reset
oil life to 100% and turn off the change oil light. This
function will only appear on the Special Tests menu
when supported by the currently selected vehicle.
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
From Service Light Reset Menu:
1. Select Oil Light Reset.
• Use the UP and DOWN keys until Oil Light
Reset is highlighted.
• Press .
Service Light Reset
Oil Light Reset
• In the above examples, Module $09 returned
data. Scroll down to view information. CVNs are
shown as hexadecimal numbers.
• Abbreviations and names for in-use performance
tracking data supported by the Tool are shown
below. Not all data is supported by all vehicles.
Abbreviated Name
In-Use Perf
Tracking
OBDCOND
Expanded Name
In-Use Performance Tracking
OBD Monitoring Conditions Encountered
Counts
IGNCNTR Ignition Counter
CATCOMPX
CATCONDX
580001 | REV. A | 11.2016
Catalyst Monitor Completion Counts
Bank x
Catalyst Monitor Conditions Encountered
Counts Bank x
2. Follow the instructions displayed. They will vary
depending on the vehicle.
• Press .
Page 39

OBD 1350 ProGrade OBDII Scan Tool | User guide | 39 | en
Oil Light Reset
Cycle key, Turn engine off, Key
on
Press BACK to exit
Press ENTER to continue
3. Reset oil light.
• Press .
Oil Light Reset
Press ENTER to reset
BACK to exit
Press ENTER to continue
4. After the command is sent, the oil light should be
off.
• Press to return to the Service Light Reset
Menu.
Oil Light Reset
battery) or a battery with a different capacity (mAh), the
vehicle may require reprogramming to the new battery
type in addition to performing the battery reset. Reprogramming is not a function of the tool. Consult the
vehicle manual for additional vehicle-specific information.
From the Battery/Charging Services Menu:
1. Select Battery Reset.
• Use the UP and DOWN keys until Battery
Reset is highlighted.
• Press .
Battery/Charging Services
Battery Reset
2. Follow the instructions displayed. They will vary
depending on the vehicle.
• Press .
Battery Reset
Required Whenever:
Battery has been replaced
Otherwise instructed by shop
manual
Command sent
Press ENTER to continue
5.15 Battery Reset
The Battery Reset function allows the scan tool to tell
the vehicle that the battery has been replaced. This
function will only appear on the Special Tests menu
when supported by the currently selected vehicle. Resetting the battery system when a new battery is installed
allows the vehicle to customize charging to the age and
condition of the battery.
Battery Information
The vehicle may contain either a lead-acid battery or an
AGM (absorbed glass mat) battery. Leadacid batteries
contain liquid sulphuric acid and can spill when overturned. AGM batteries also contain sulphuric acid, but
the acid is contained in glass mats between the terminal
plates.
If the original battery is replaced with a different type of
battery (eg. a lead-acid battery is replaced with an AGM
Press ENTER to continue
3. Perform Battery Reset.
• The messages displayed during battery reset
will vary depending on the vehicle.
Battery Reset
(May Take 30 Secs)
Time remaining
0:28
Please Wait
4. Battery Reset Complete.
• Press to return to the Battery/Charging
Services Menu.
580001 | REV. A | 11.2016
Page 40

en | 40 | User guide
| OBD 1350
ProGrade OBDII Scan Tool
Battery Reset
Battery System Reset Complete
Press ENTER to continue
5.16 Charging System Monitor
The Charging System Monitor function allows the scan
tool to provide voltage measurements at the DLC to give
an indication of battery, starter, and alternator performance.
From the Special Functions Menu:
1. Select Charging System Monitor.
• Use the UP and DOWN keys until Charging
System Monitor is highlighted.
• Press .
Special Functions
Global OBDII Functions
Charging System Monitor
Fuel Consumption (MPG/KPL)
Battery/Charging Services
Brake Services
Service Light Reset
Steering Services
Component Locator
Charging System Monitor
DLC KOEO Voltage:
12.2V
Please start the engine
Press BACK to exit
4. When the cranking condition is detected, the scan
tool will begin collecting DLC voltage readings.
• If the engine starts, press .
Charging System Monitor
Collecting data
Press ENTER when the engine
has started
5. If an engine started condition is detected, the scan
tool will collect key on engine running DLC voltages.
Charging System Monitor
2. Turn the ignition key on but do not start the engine.
• Press .
Charging System Monitor
Turn the key on.
Do NOT start the engine.
Press ENTER to continue
3. The DLC voltage is measured at key on engine off.
• The screen below shows a KOEO voltage of
12.2V.
• Start the engine or press to return to the
Diagnostic Menu. The scan tool will monitor the
DLC voltage and progress to step 4 if starter
cranking is detected.
Determining DLC KOER voltage
Press BACK to exit
6. The test results are then displayed.
Test Results
DLC KOEO Voltage
DLC Cranking Voltage
DLC KOER Voltage
ess ENTER to view the data plot.
12.2
10.4
---
580001 | REV. A | 11.2016
Page 41

OBD 1350 ProGrade OBDII Scan Tool | User guide | 41 | en
Test Results
DLC KOEO Voltage
DLC Cranking Voltage
DLC KOER Voltage
ess ENTER to view the data plot.
On the first screen, the scan tool didn’t detect that the
engine had started, so there isn’t a KOER voltage reading.
The second screen did detect that the engine had
started so there is a KOER reading.
The screen on the left shows that the KOEO voltage
before an engine start was attempted was 12.2V. Once
the starter began cranking the engine, a cranking voltage
of 10.4V was measured. After the engine started, a KOER
voltage reading of 14.7V was measured.
• If the KOEO voltage is very low, this could be an
indication of a bad battery, or one that needs to be
charged.
• If the cranking voltage is a lot lower than the KOEO
voltage, than this is an indication of a worn starter.
• If the KOER voltage is not higher than the KOEO
voltage, than this indicates a bad or weak alternator.
After reviewing the test results, Press to view the
data plot.
7. View the data plot.
• The triangle below the graph indicates the
position of the frame in the graph.
• Use the LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to
scroll back and forth through graph.
12.2
10.4
14.7
Global OBDII Functions
O2 Monitor Tests
Diagnostic Monitor Tests
On-Board Systems
Vehicle Information
Oil Light Reset
Charging System Monitor
Modules Present
Component Locator
Acronyms
The types of protocols (communication types) supported by the scan tool are:
• ISO 9141-2 protocol is shown as ISO.
Modules Present
ID Protocol
$40 ISO*
Press ENTER to continue
• SAE J1850 protocol is shown as VPWM or PWM.
Modules Present
ID Protocol
$10 VPWM*
Press ENTER to continue
DLC Pin 16 Voltage
14.7
10.4
Frame: Time:
0 0.00
8. Press to return to the Special Functions
Menu.
5.17 Modules Present
The scan tool identifies the module IDs and communication type for all Global OBD II modules in the vehicle.
From the Global OBDII Functions Menu:
1. Select Modules Present.
• Use the UP and DOWN keys until Modules
Present is highlighted.
• Press .
10.6
OR
Modules Present
ID Protocol
$10 PWM*
Press ENTER to continue
• ISO 15765-4 protocol is shown as CAN.
Modules Present
ID Protocol
$01 CAN*7e9
$00 CAN*7e8
Press ENTER to continue
580001 | REV. A | 11.2016
Page 42

en | 42 | User guide
| OBD 1350
ProGrade OBDII Scan Tool
Since CAN vehicles use module IDs larger than 2 digits,
the scan tool assigns a 2 digit module ID to be used in
place of the actual CAN module ID. The module ID
assigned for the CAN module ID is used in all functions
of the scan tool.
• ISO 14230-4 protocol is shown as K2K (Keyword
2000).
Modules Present
ID Protocol
$10 K2K*
Press ENTER to continue
In the above examples, the * indicates the protocol used
to communicate to the vehicle’s control module.
5.18 Fuel Consumption (MPG/KPL)
The Fuel Consumption function allows the scan tool to
provide information related to fuel consumption for your
current trip. This function is only supported on gasoline
burning vehicles using a Mass Airflow sensor (MAF). It
should not be used for diesel vehicles because the fuel
consumption will be totally inaccurate. This function
depends on the vehicle maintaining a 14.7:1 air/fuel
ratio. Diesel vehicles do not adhere to this ratio and that
is why this function can’t be used.
From the Special Functions Menu:
1. Select Fuel Consumption(MPG/KPL).
• Use the UP and DOWN keys until Fuel
Consumption (MPG/KPL) is highlighted.
• Press .
Special Functions
Global OBDII Functions
Charging System Monitor
Fuel Consumption(MPG/KPL)
Acronyms
Review Data
Print Data
Code Lookup
System Setup
If the vehicle doesn’t use a MAF, the scan tool will display
a message indicating that Fuel Consumption is not
supported.
Fuel Consumption(MPG/KPL)
PIDs required to calculate
Fuel Consumption not
supported by this vehicle
2. The scan tool will now calculate Fuel Consumption.
Fuel Consumption(MPG/KPL)
Instantaneous(MPG)
Average(MPG)
Elapsed Time(H:M:S)
Distance(MI)
Fuel Used(GAL)
Average Speed(MPH)
Reset Metric
36.8
28.8
39:35
33.4
1.11
50.6
Press the Reset key at any time to reset calculation back
to zero. Press the Metric key to change the units from
Miles per gallon to Kilometers per liter.
• Instantaneous – This is an average of fuel consumed over the last 3 or 4 seconds. Instantaneous fuel consumption is only calculated while
the vehicle is moving.
• Average – This is the average fuel consumed
since the reset key was pressed or the fuel
consumption function was selected from the
menu.
• Elapsed Time – This is the total elapsed time in
(H)ours, (M)inutes, and (S)econds, since the
reset key was pressed or the fuel consumption
function was selected from the menu.
• Distance – This is the total distance driven,
since the reset key was pressed or the fuel
consumption function was selected from the
menu.
• Fuel Used – This is the total fuel used, since the
reset key was pressed or the fuel consumption
function was selected from the menu.
• Average Speed – This is the average vehicle
speed, since the reset key was pressed or the
fuel consumption function was selected from
the menu.
3. Return to Special Functions Menu.
• Press .
5.19 KOEO On Demand
The KOEO On Demand is a functional test of the Ford
computer modules and system with the KOEO. It tests
the inputs, outputs, and sensor ranges. Any faults or
DTCs are retrieved by the scan tool.
It is VERY IMPORTANT that each step be performed
when prompted by the scan tool. Failure to follow directions may set DTC(s).
From the On Demand Tests Menu:
1. Select KOEO On Demand.
• Use the UP and DOWN keys until KOEO
On Demand is highlighted.
• Press .
Press ENTER to continue
580001 | REV. A | 11.2016
Page 43

OBD 1350 ProGrade OBDII Scan Tool | User guide | 43 | en
On Demand Tests
KOEO On Demand
KOEO Output State
KOER On Demand
Component Locator
Acronyms
Review Data
Print Data
Code Lookup
System Setup
2. Perform the following:
• Set parking brake.
• Transmission in park (P) or neutral (N).
• Turn A/C off.
• Start engine and let idle until hot.
• Turn ignition key off.
• Wait 10 seconds. Turn key on engine off. Do not
start engine.
• For the 7.3L Powerstroke diesel, depress/hold
throttle during test.
For Gasoline engines, do not touch the throttle during
test.
3. Press to begin the test. The time remaining is
displayed.
KOEO On Demand
Test is running.
Time remaining
2:59
Please Wait
The following system components are tested:
– Electric radiator cooling fan - Avoid cooling fan!
– Fuel pump
– Check engine light
– Idle speed control solenoid
If no DTCs are present, a message stating “No Codes
Found” is displayed.
Read KOEO Codes
No codes found
Press ENTER to continue
P0113
Intake Air Temperature Sensor
1 Circuit High Input
FORD KOEO CODES
Erase FFrameRead
1/1
ECM $10
5. Return to the On Demand Tests Menu.
• Press .
5.20 KOEO Injector Buzz
This test is available on some Ford trucks equipped with
a diesel engine. The KOEO Injector Buzz is a functional
test performed on demand with the ignition key on and
engine off. The test determines if the injector circuits
and solenoids are operating correctly and without faults.
All injectors are buzzed initially (audible feedback of
solenoids energizing the valves) for approximately 2
seconds. Then each injector buzzes individually for
approximately 1 second, in numerical order (1 – 8).
From the On Demand Tests Menu:
1. Select KOEO Injector Buzz.
• Use the UP and DOWN keys until KOEO
Injector Buzz is highlighted.
• Press .
On Demand Tests
KOEO On Demand
KOEO Injector Buzz
KOEO Output State
KOER On Demand
KOER Glow Plug
KOER Cylinder Contribution
Component Locator
Acronyms
Review Data
2. Perform the following:
• Set parking brake.
• Transmission In park (P) or neutral (N).
• Turn A/C off.
• Start engine and let idle until hot.
• Turn ignition key off.
• Wait 10 seconds. Turn key on engine off. Do not
start.
3. Start test.
• Press .
Listen for one long buzz and then 8 short equal buzzes
as each fuel injector is energized.
4. View and write down DTCs.
• Use the UP and DOWN keys.
580001 | REV. A | 11.2016
Page 44

en | 44 | User guide
| OBD 1350
ProGrade OBDII Scan Tool
KOEO Injector Buzz
Test is running.
Time remaining
2:59
Please Wait
4. Return to the On Demand Tests Menu.
• Press .
5.21 KOEO Output State
The KOEO Output State tests the output devices (such
as actuators or relays) controlled by the Ford PCM by
powering them on and off. The voltage and outputs on
suspect devices can be measured and recorded using a
voltmeter. Compare voltages measured with the power
turned on and off to verify operation. Fuel injectors are
not energized by this test.
From the On Demand Tests Menu:
1. Select KOEO Output State.
• Use the UP and DOWN keys until KOEO
Output State is highlighted.
• Press .
KOEO Output State
All But Fans/Injectors
Low Speed Fan
High Speed Fan
• Listen for devices turn on and off.
• Press to change state.
KOEO Output State
All but fans OFF
Press ENTER to change state
Press BACK to exit
4. Return to On Demand Tests Menu.
• Press .
On Demand Tests
KOEO On Demand
KOEO Injector Buzz
KOEO Output State
KOER On Demand
KOER Glow Plug
KOER Cylinder Contribution
Component Locator
Acronyms
Review Data
2. Perform the following:
• Set parking brake.
• Transmission in park (P) or neutral (N).
• Turn A/C off.
• Start engine and let idle until hot.
• Turn ignition key off.
• Wait 10 seconds. Turn key on engine off. Do not
start engine.
For the 7.3L powerstroke diesel, press/release throttle to
toggle outputs.
3. Select an output state.
• Use the UP and DOWN keys.
• Press .
5.22 KOER On Demand
The KOER On Demand is a functional test with the
KOER that checks the Ford control module’s inputs,
outputs, sensor ranges, and operation. Any faults or
DTCs are retrieved by the scan tool.
From the On Demand Tests Menu:
1. Select KOER On Demand.
• Use the UP and DOWN keys until KOER On
Demand is highlighted.
• Press .
On Demand Tests
KOEO On Demand
KOEO Injector Buzz
KOEO Output State
KOER On Demand
KOER Glow Plug
KOER Cylinder Contribution
Component Locator
Acronyms
Review Data
2. Start test.
• Press .
WARNING
Exhaust gases are harmful or fatal. Always
operate vehicle in a well-ventilated area.
580001 | REV. A | 11.2016
Page 45

OBD 1350 ProGrade OBDII Scan Tool | User guide | 45 | en
CAUTION
Keep hands and tools away from fan and
engine during test.
IMPORTANT
Perform each step when prompted by the Scan
Tool. Failure to follow directions may set DTC(s)
in the PCM.
3. Follow the instructions displayed on the tool. If the
steps are not followed correctly, a message displays
asking you to RETRY.
• Set parking brake.
• Transmission in park (P) or neutral (N).
• Turn A/C off.
• Start engine and let idle until hot.
• Turn ignition key off.
• Wait 10 seconds. Start engine and let idle.
If the vehicle is equipped with a manual transmission,
release the clutch.
KOER On Demand
1) Do all test steps:
2) Set parking brake.
3) Trans in P or N.
4) Turn A/C off.
5) Start engine & let idle
until hot.
6) Turn Ign key off.
7) Wait 10 sec. Start engine &
let idle.
Press ENTER to continue
P1127
Heated Oxygen Sensor
Downstream Sensor Not Tested
FORD KOER ON DEMAND
1/4
ECM $10
If no DTCs are present, a message stating “No Codes
Found” is displayed.
7. Return to the On Demand Tests Menu.
• Press .
5.23 KOER Glow Plug
This test is available on some Ford trucks equipped with
a diesel engine. The KOEO Glow Plug is an on-demand
test which activates the glow plug relay and detects any
difference in the amount of current between both banks
of glow plugs. DTCs returned from the test indicate
which bank has failed glow plugs or failed wiring.
WARNING
Exhaust gases are harmful or fatal. Always
operate vehicle in a well-ventilated area.
CAUTION
The KOER glow plug test is done with the
engine running. Do not over-rev the engine.
Observe all safety precautions.
4. Press to continue.
5. The tool prompts you to:
• Work Steering Wheel.
• Pump Brake Pedal.
• Cycle overdrive (OD) cancel switch (on some
automatic transmissions).
KOER On Demand
Work steering wheel,
pump brake pedal,
cycle overdrive cancel switch.
Press ENTER to continue
6. View and write down DTCs.
• Use the UP and DOWN keys.
Battery voltage must be between 11.8 and 14.0 volts for
the Glow Plug Test. To maintain battery voltage, increase
engine RPM. If required, monitor battery voltage during
the test using a voltmeter.
From the On Demand Tests Menu:
1. Select KOER Glow Plug.
• Use the UP and DOWN keys until KOER
Glow Plug is highlighted.
• Press .
On Demand Tests
KOEO On Demand
KOEO Injector Buzz
KOEO Output State
KOER On Demand
KOER Glow Plug
KOER Cylinder Contribution
Component Locator
Acronyms
Review Data
2. Perform the following:
• Set parking brake.
• Transmission in park (P) or neutral (N).
• Turn A/C off.
• Start engine and let idle until hot.
• Turn ignition key off.
• Wait 10 seconds. Turn key on engine off.
580001 | REV. A | 11.2016
Page 46

en | 46 | User guide
| OBD 1350
ProGrade OBDII Scan Tool
If no DTCs are present, a message stating “No
Codes Found” is displayed.
3. View and write down DTCs.
• Use the UP and DOWN keys.
P0340
Camshaft Position Sensor A
Circuit
(Bank 1 Or Single Sensor)
FORD GLOWPLUG CODES
1/4
ECM $10
4. Return to the On Demand Tests Menu.
• Press .
5.24 KOER Cylinder Contribution
This test is available on some Ford trucks equipped with
a diesel engine. The KOER Cylinder Contribution is an
on-demand test performed with the engine running, the
A/C off and engine oil temperature above 76.6°C
(170°F). This test determines that all cylinders are contributing equally to engine performance.
The PCM first tests the cylinders in numeric order (1 –
8) for a bad/weak cylinder. If all cylinders check good, a
4 cylinder test is then executed (if a weak cylinder is
detected in the 8 cylinder test, the four cylinder test will
not be started).
During the test, the engine emits smoke, and the RPM
varies with each check (there is no audible difference in
RPM if a bad/weak cylinder is detected).
WARNING
Exhaust gases are harmful or fatal. Always
operate vehicle in a well-ventilated area.
On Demand Tests
KOEO On Demand
KOEO Injector Buzz
KOEO Output State
KOER On Demand
KOER Glow Plug
KOER Cylinder Contribution
Component Locator
Acronyms
Review Data
2. Perform the following:
• Set parking brake.
• Transmission in park (P) or neutral (N).
• Turn A/C off.
• Start engine and let idle until hot.
• Turn ignition key off.
• Wait 10 seconds. Turn key on engine off.
If no DTCs are present, a message stating “No Codes
Found” is displayed.
3. View and write down DTCs.
• Use the UP and DOWN keys to view DTCs.
P0340
Camshaft Position Sensor A
Circuit
(Bank 1 Or Single Sensor)
FORD CYL CONTRIB CODES
1/4
ECM $10
4. Return to the On Demand Tests Menu.
• Press .
6 Troubleshooting
CAUTION
The KOER cylinder contribution test is
done with the engine running. Set the
parking brake and place the transmission
in PARK or NEUTRAL (automatic transmissions only). Do not over-rev the engine.
Observe all safety precautions.
From the On Demand Tests Menu:
1. Select KOER Cylinder Contribution.
• Use the UP and DOWN keys until KOER
Cylinder Contribution is highlighted.
• Press .
580001 | REV. A | 11.2016
6.1 Error Messages
Check the following if an error message displays:
• Verify ignition key is in the ON and not in the ACCESSORIES position.
• Make sure the DLC Cable is attached to vehicle’s
data link connector (DLC) and scan tool.
• Look at DLC and check for cracked or recessed pins,
or for any substance that could prevent a good
electrical connection.
• Test for continuity between the DLC wiring and the
computer. In an extreme case, there may be a broken wire.
• Check for bent or broken pins.
• With the engine off, check for blown fuses in the
vehicle fuse box.
• Make sure the vehicle’s control module has a good
ground. If the computer case is grounded, then
clean the connection and apply a conductive (dielectric) grease to the mating surfaces.
Page 47

• With the key on engine off (KOEO), verify vehicle
battery voltage is at least 8.0V.
• Verify the control module is not defective. Refer to
the service manual to diagnose the control module.
6.2 Scan Tool Does Not Power Up
OBD 1350 ProGrade OBDII Scan Tool | User guide | 47 | en
LINK ERROR
Check connection! Try
again?
WARNING
Review Safety Messages on page 5
before troubleshooting.
If scan tool will not power up, communicate with vehicle
control module, pass scan tool self-tests, or functions
incorrectly in any other way, do the following:
• Check and replace the batteries (if needed).
• Clean the DLC pins.
• Disconnect and reconnect DLC making sure it is
connected correctly.
• Check vehicle battery to make sure at least 8.0 volts
is present.
• Contact customer service.
• With the engine off, check for blown fuses in the
vehicle fuse box.
6.3 Vehicle Communication Fault
The vehicle’s control module(s) enters into an unrecoverable state.
1. Turn vehicle key to off position.
• Wait 10 seconds.
• Press .
Yes
No
6.5 Battery Replacement
The scan tool requires 4-AAA alkaline batteries to operate without vehicle power.
• When the batteries need to be replaced, the lowbattery icon ( ) is displayed.
• Rechargeable batteries do not last as long as alkaline types and are not recommended.
• Non-rechargeable Lithium (Li) battery can be used.
Though Lithium types last longer than the alkaline
types, they are more expensive.
1. Place display face-down on a non-abrasive surface.
2. Remove battery cover by turning phillips screw
counterclockwise. Slide battery cover off.
3. Remove batteries and properly discard.
4. Install four new AAA Alkaline batteries.
5. Reinstall battery cover by sliding battery cover on.
Install phillips screw turning it clockwise. Do not
overtighten screw.
Vehicle Required
Please verify the tool is
connected to the vehicle with
the ignition key turned on.
Press ENTER to continue
6.4 Operating Error or Erroneous Data
An Operating Error or Erroneous Data occurs if vehicle’s
computer(s) stop(s) communicating with the scan tool.
1. Make selection.
• Use the LEFT and RIGHT keys.
• Press .
6.6 Tool Self-Tests
Tool Self-Tests check the display, keys, and internal
memory.
• Refer to “4 Using the Scan Tool” on page 10 for
the operation procedures for scan tool self-tests.
6.7 Technical Support
Toll-Free Number: 1-800-228-7667.
7 Appendix A—
PID Definitions
Although there are in excess of 300 PIDs, the tool only
displays the PIDs the vehicle supports.
580001 | REV. A | 11.2016
Page 48

en | 48 | User guide
| OBD 1350
ProGrade OBDII Scan Tool
PID PID Description
ABS FRP Absolute Fuel Rail Pressure
ABS LOAD Absolute Load Value
ABS TPS B, C Throttle Position B, C
ABSLT TPS Absolute Throttle Position
ACC POS D Accelerator Pedal D, E, F
ACC POS REL Relative Accelerator Pedal Position
AECD1_TIME1,
TIME 2
AECD10_TIME1,
TIME 2
AECD11_TIME1,
TIME 2
AECD12_TIME1,
TIME 2
AECD13_TIME1,
TIME 2
AECD14_TIME1,
TIME 2
AECD15_TIME1,
TIME 2
AECD16_TIME1,
TIME 2
AECD17_TIME1,
TIME 2
AECD18_TIME1,
TIME 2
AECD19_TIME1,
TIME 2
AECD2_TIME1,
TIME 2
AECD20_TIME1,
TIME 2
AECD3_TIME1,
TIME 2
AECD4_TIME1,
TIME 2
AECD5_TIME1,
TIME 2
AECD6_TIME1,
TIME 2
AECD7_TIME1,
TIME 2
AECD8_TIME1,
TIME 2
AECD9_TIME1,
TIME 2
Total Run Time with EI-AECD #1 Timer
1 Active, #2 Timer Active
Total Run Time with EI-AECD #10
Timer 1 Active, #2 Timer Active
Total Run Time with EI-AECD #11
Timer 1 active, #2 Timer Active
Total Run Time with EI-AECD #12
Timer 1 active, #2 Timer Active
Total Run Time with EI-AECD #13
Timer 1 active, #2 Timer Active
Total Run Time with EI-AECD #14
Timer 1 active, #2 Timer Active
Total Run Time with EI-AECD #15
Timer 1 active, #2 Timer Active
Total Run Time with EI-AECD #16
Timer 1 active, #2 Timer Active
Total Run Time with EI-AECD #17
Timer 1 active, #2 Timer Active
Total Run Time with EI-AECD #18
Timer 1 active, #2 Timer Active
Total Run Time with EI-AECD #19
Timer 1 active, #2 Timer Active
Total Run Time with EI-AECD #2 Timer
1 Active, #2 Timer Active
Total Run Time with EI-AECD #20
Timer 1 active, #2 Timer Active
Total Run Time with EI-AECD #3 Timer
1 Active, #2 Timer Active
Total Run Time with EI-AECD #4 Timer
1 Active, #2 Timer Active
Total Run Time with EI-AECD #5 Timer
1 Active, #2 Timer Active
Total Run Time with EI-AECD #6 Timer
1 Active, #2 Timer Active
Total Run Time with EI-AECD #7 Timer
1 Active, #2 Timer Active
Total Run Time with EI-AECD #8 Timer
1 Active, #2 Timer Active
Total Run Time with EI-AECD #9 Timer
1 Active, #2 Timer Active
ALCOHOL Alcohol Fuel Percent
BARO PRS Barometric Pressure
BAT_PWR Hybrid Battery Pack Remaining Life
BP_A_ACT, B_
ACT
BP_A_CMD, B_
CMD
BP_A_STAT, B_
STAT
Boost Pressure Sensor A, Sensor B
Commanded Boost Pressure A, Pres-
sure B
Boost Pressure A Control Status, B
Control Status
Charge Air Cooler Temperature Bank
CACT 11, 12
1 Sensor 1 supported, Sensor 2
supported
PID PID Description
Charge Air Cooler Temperature Bank
CACT 21,22
2 Sensor 1 supported, Sensor 2
supported
CALC LOAD Calculated Engine Load
CAT TEMP11,
TEMP12
CAT TEMP21,
TEMP22
Cataltic Converter Temp Bank1, Temp
Bank 3
Cataltic Converter Temp Bank2, Temp
Bank 4
CLR DIST Distance since erase
CLR TIME Minutes Run since Erase
CLR TRPS Warmups Since Erase
CMD EQ RAT Commanded Equivalence Ratio
COOLANT Engine Coolant Temp
DPF_REG_AVGD Average Distance Between DPF Regen
DPF_REG_AVGT Average Time Between DPF Regen
DPF_REG_STAT
DPF_REG_TYP
DPF_REGEN_
PCT
DPF1_DP,
DPF2_DP
DPF1_INP,
DPF2_INP
DPF1_INT,
DPF2_INT
DPF1_OUTP,
DPF2_OUTP
DPF1_OUTT,
DPF2_OUTT
ECT 1, 2
Diesel Particulate Filter (DPF) Regen
Status
Diesel Particulate Filter (DPF) Regen
Type
Normalized Trigger for DPF Regen
Diesel Particulate Filter (DPF) Bank 1
Delta Pressure Bank 2 Delta Pressure
Diesel Particulate Filter (DPF) Bank 1
Inlet Pressure, Bank 2 Inlet Pressure
DPF Bank 1 Inlet Temperature Sensor,
Bank 2 Inlet Temperature Sensor
Diesel Particulate Filter (DPF) Bank
1 Outlet Pressure, Bank 2 Outlet
Pressure
DPF Bank 1 Outlet Temperature Sen-
sor, Bank 2 Outlet Temperature Sensor
Engine Coolant Temperature 1, Tem-
perature 2
EGR CMD Comanded EGR
EGR ERR Exhaust Gas Recirculation Error
EGR_A_ACT, B_
ACT
EGR_A_CMD, B_
CMD
EGR_A_ERR, B_
ERR
EGRT 11, 21
EGRT 12, 22
EGT 11, 21
EGT 12, 22
EGT 13, 23
EGT 14, 24
EMIS_SUP
Actual EGR A Duty Cycle / Position, B
Duty Cycle / Position
Commanded EGR A Duty Cycle / Posi-
tion, B Duty Cycle / Position
EGR A Error, B Error
Exhaust Gas Recirculation Tempera-
ture Bank 1 Sensor 1, Bank 2 Sensor 1
Exhaust Gas Recirculation Tempera-
ture Bank 1 Sensor 2, Bank 2 Sensor 2
Exhaust Gas Temperature (EGT) Bank
1 Sensor 1, Bank 2 Sensor 1
Exhaust Gas Temperature (EGT) Bank
1 Sensor 2, Bank 2 Sensor 2
Exhaust Gas Temperature (EGT) Bank
1 Sensor 3, Bank 2 Sensor 3
Exhaust Gas Temperature (EGT) Bank
1 Sensor 4, Bank 2 Sensor 4
Emission requirements to which vehi-
cle is designed
ENG RUN Time Since Engine Start
ENG SPEED Engine RPM
EOT Engine Oil Temperature
580001 | REV. A | 11.2016
Page 49

OBD 1350 ProGrade OBDII Scan Tool | User guide | 49 | en
PID PID Description
EP_1, 2
Exhaust Pressure Sensor Bank 1, Bank
2
EQ RATIO Equivalence Ratio
EVAP PURGE Commanded EVAP Purge
EVAP VP EVAP Vapor Pressure
EVAP VPA Absolute EVAP Vapor Pressure
FRP_A, B Fuel Rail Pressure A, B
FRP_A_CMD, B_
CMD
Commanded Fuel Rail Pressure A, B
FRT_A, B Fuel Rail Temperature A, B
FUEL LEVEL Fuel Level Input
FUEL PRES Fuel Rail Pressure
FUEL SYS 1, 2
Fuel System 1 Loop Status, System 2
Loop Status
FUEL TYPE Fuel Type
FUEL_RATE Engine Fuel Rate
FUEL_TIMING Fueling Injection Timing
GPL_STAT Glow Plug Lamp Status
IAF_A_CMD, B_
CMD
IAF_A_REL, B_
REL
Commanded Intake Air Flow A Control,
B Control
Relative Intake Air Flow A Position, B
Position
IAT Intake Air Temp
IAT 11, 21
IAT 12, 22
IAT 13, 23
Intake Air Temperature Sensor Bank 1
Sensor 1, Bank 2 Sensor 1
Intake Air Temperature Sensor Bank 1
Sensor 2, Bank 2 Sensor 2
Intake Air Temperature Sensor Bank 1
Sensor 3, Bank 2 Sensor 3
ICP_A, B Injection Control Pressure A, B
ICP_A_CMD, B_
CMD
Commanded Injection Control Pres-
sure A, B
IDLE_TIME Total Idle Run Time
IGN ADV Timing Advance
LAMBDA11, 21
LAMBDA12, 22
02 Sensor Lambda Bank 1 Sensor 1,
Bank 2 Sensor 1
02 Sensor Lambda Bank 1 Sensor 2,
Bank 2 Sensor 2
LT FTRM1 Long Term Fuel Trim 1 or 3
LT FTRM2 Long Term Fuel Trim 2 or 4
LT SEC FT1, 2,
3, 4
Long Term Secondary O2 Sensor Fuel
Trim 1, 2, 3, 4
MAF, A, B Mass Air Flow, A, B
MAP, A, B Manifold Absolute Pressure, A, B
MIL DIST MIL_DIST
MIL STATUS Malfunction Indicator Lamp
MIL TIME Minutes Run by MIL activated
MST Manifold Surface Temperature
N/D_STAT Auto Trans Neutral Drive Status
N/G_STAT Manual Trans Neutral Gear Status
NNTE_Stat NOx NTE control area status
NOX 11, 21
NOX 12,22
NOx Sensor Concentration Bank 1
Sensor 1, Bank 2 Sensor 1
NOx Sensor Concentration Bank 1
Sensor 2, Bank 2 Sensor 2
PID PID Description
SCR inducement system actual state
NOX LEVEL HI,
HI1, HI2, HI3,
HI4
10K history HI1 (0-10000 km), 10K history HI2 (10000-20000 km), 10K history HI3 20000-30000 km), 10K history
HI4 (30000-40000 km): NOx emission
too high
NOX_ADS_DESUL
NOX_ADS_REGEN
NWI_TIME
O2S
O2S11_PCT,
O2S21_PCT
O2S12_PCT,
O2S22_PCT
NOx Adsorber Desulfurization Status
NOx Adsorber Regen Status
Total Run Time by the Engien whicle
NOx warning mode is activated
O2 Voltage or Current indicates
Bank / Sensor
02 Sensor Concentration Bank 1 Sensor 1, Bank 2 Sensor 1
02 Sensor Concentration Bank 1 Sen-
sor 2, Bank 2 Sensor 2
OBD2 STAT OBD Status
OUT TEMP Ambient Air Temp
PM 11, PM 21
PM Sensor Mass Concentration Bank
1 Sensor 1, Bank 2 Sensor 1
PNTE_Stat PM NTE control area status
PTO STATUS PTO Status
PTO_STAT Power Take Off (PTO) Status
PTO_TIME Total Run Time With PTO Active
REAG_DEMD
Average Demanded Reagent
Consumption
REAG_LVL Reagent Tank Level
REAG_RATE Average Reagent Consumption
REL FRP Relative Fuel Rail Pressure
REL TPS Relative Throttle Position
RUN_TIME Total Engine Run Time
SCR inducement system actual state
SCR REAG DEV,
DEV1, DEV2,
DEV3, DEV4
10K history DEV1 (0 - 10000 km), 10K
history DEV2 (10000 - 20000 km),
10K history DEV3 (20000 - 30000 km),
10K history DEV4 (30000 - 40000 km):
deviation of reagent consumption
SCR inducement system actual state
SCR REAG
LOW, LOW1,
LOW2, LOW3,
LOW4
10K history LOW1 (0 - 10000 km), 10K
history LOW2 (10000 - 20000 km),
10K history LOW3 (20000 -
30000 km), 10K history LOW4
(30000 - 40000 km): reagent level too
low
SCR REAG WRONG,
WRONG1,
WRONG2,
WRONG3,
WRONG4
SCR SYS ACTIVE
SCR_DIST_1D
SCR inducement system actual state
10K history WRONG1 (0 - 10000 km),
10K history WRONG2 (10000 -
20000 km), 10K history WRONG3
(20000 - 30000 km), 10K history
WRONG4 (30000 - 40000 km): incor-
rect reagent
SCR inducement system actual state:
inducement system active
Distance travelled in current 10K block
(0 - 10000 km)
Distance travelled while induce-
ment system active in current 10K
SCR_DIST_1N,
2N, 3N, 4N
block 1N (0 - 10000 km), 20K block
2N (10 - 20000 km), 30K block 3N
(20 - 30000 km), 40K block 4N
(30 - 40000 km)
580001 | REV. A | 11.2016
Page 50

en | 50 | User guide
| OBD 1350
ProGrade OBDII Scan Tool
PID PID Description
SECOND AIR Secondary Air Status
ST FTRM Fuel Trim Bank / Sensor
ST FTRM1, 3 Short Term Fuel Trim1 or 3
ST FTRM2, 4 Short Term Fuel Trim2 or 4
ST SEC
FT1, 2, 3, 4
TAC_A_CMD, B_
CMD
TAC_A_REL, B_
REL
TCA_CINP, TCB_
CINP
TCA_CINT, TCB_
CINT
TCA_COUTT,
TCB_COUTT
TCA_RPM, TCB_
RPM
TCA_TOUTT,
TCB_TOUTT
TCA_TINT, TCB_
TINT
Short Term Secondary O2 Sensor Fuel
Trim 1, 2, 3, 4
Commanded Throttle Actuator A Control, B Control
Relative Throttle A Position, B Position
Turbocharger Compressor Inlet Pressure Sensor A, Pressure Sensor B
Turbocharger A Compressor Inlet Temperature, Turbocharger B
Turbocharger A Compressor Outlet
Temperature, Turbocharger B
Turbocharger A RPM, B RPM
Turbocharger A Turbine Outlet Temperature, Turbocharger B
Turbocharger A Turbine Inlet Tempera-
ture, Turbocharger B
THROT CMD Commanded Throttle Actuator Control
TP G Absolute Throttle Position G
TQ_ACT Actual Engine - Percent Torque
TQ_DD
TQ_MAX1,
MAX2, MAX3,
MAX4, MAX5
Driver's Demand Engine - Percent
Torque
Engine percent torque at
idle point 1, 2, 3, 4, 5
TQ_REF Engine Reference Torque
TROUB CODE Code causing the Freeze Frame
VEH SPEED Vehicle Speed
VGT_A_ACT Variable geometry turbo A position
VGT_A_ACT, B_
ACT
VGT_A_CMD
VGT_A_CMD, B_
CMD
VGT_A_STAT
VGT_A_STAT, B_
STAT
Variable Geometry Turbo A Position,
Turbo B
Commanded variable geometry turbo
A position
Commanded Variable Geometry Turbo
A Position, Turbo B
Variable geometry turbo A control
status
Variable Geometry Turbo A Control
Status, Turbo B
VGT_B_ACT Variable geometry turbo B position
VGT_B_CMD
VGT_B_STAT
Commanded variable geometry turbo
B position
Variable geometry turbo B control
status
VPWR Control Module Voltage
WG_A_ACT Wastegate A position
WG_A_ACT, B_
ACT
Wastegate A Position, B Position
WG_A_CMD Commanded wastegate A control
WG_A_CMD, B_
CMD
Commanded Wastegate A Control, B
Control
WG_B_ACT Wastegate B position
WG_B_CMD Commanded wastegate B control
580001 | REV. A | 11.2016
8 Appendix B—Glossary
A/C:
Air conditioner
A/D:
Analog to digital
A/F:
Air/Fuel ratio. The proportion of air and fuel delivered to
the cylinder for combustion. For example, an A/F ratio of
14:1 denotes 14 times as much air as fuel in the mixture.
Ideally the A/F ratio is 14.7:1.
ABS:
Anti-lock brake system
A/C clutch relay:
The PCM uses this relay to energize the A/C clutch,
turning the A/C compressor on or off.
A/C pressure sensor:
Measures air conditioning refrigerant pressure and
sends a voltage signal to the PCM.
A/C pressure switch:
A mechanical switch connected to the A/C refrigerant
line. The switch is activated (sending a signal to the
PCM) when the A/C refrigerant pressure becomes too
low or high.
Actuator:
Actuators such as relays, solenoids, and motors allow
the PCM to control the operation of vehicle systems.
Air Injection Reaction (AIR) System:
An emission control system operated by the PCM. During cold starts, an air pump injects outside air into the
exhaust manifold to help burn hot exhaust gases. This
reduces pollution and speeds warm-up of oxygen sensors and catalytic converters. After the engine is warm,
the air will either be dumped back to the atmosphere (or
into the air cleaner assembly) or sent to the catalytic
converter.
APP:
Acceleration pedal position (sensor)
ASR:
Acceleration slip regulation
Bank x:
The standard way of referring to the bank of cylinders
containing cylinder #x. In-line engines have only one
bank of cylinders. Most commonly used to identify the
location of oxygen sensors. See O2S, Sensor x, Sensor
x.
BARO:
Barometric pressure sensor. See MAP sensor.
BBV:
Brake boost vacuum (sensor)
BCM:
Body control module
Boost control solenoid:
A solenoid that is energized by the PCM, in order to
control turbo/supercharger boost pressure.
Brake switch signal:
An input signal to the PCM indicating that the brake
pedal is being pressed. This signal is typically used to
Page 51

OBD 1350 ProGrade OBDII Scan Tool | User guide | 51 | en
disengage cruise control systems and torque converter
clutch (TCC) solenoids. See also TCC.
CAM:
Camshaft position sensor. Sends a frequency signal to
the PCM to synchronize fuel injector and spark plug
firing.
Catalytic converter:
Designed to reduce exhaust emissions.
CAN:
Controller area network
CARB:
California air resources board. Governing body for emissions control in California.
CKP REF:
Crankshaft position reference.
CKP:
Crankshaft position. See CPS.
CKT:
Circuit
Closed loop (CL):
A feedback system that uses the O2 Sensor(s) to monitor the results of combustion. Based on the signal(s)
from the O2 sensor(s), the PCM modifies the air/fuel
mixture to maintain optimum performance with lowest
emissions. In closed loop mode, the PCM can fine tune
control of a system to achieve an exact result.
CMP:
Camshaft position sensor
CO:
Carbon monoxide; odorless gas produced by incomplete
combustion.
Code scanner:
A device that interfaces with and communicates information via a data link.
Continuous memory codes:
See pending codes.
CPS:
Crankshaft position sensor. Sends a frequency signal to
the PCM. It is used to reference fuel injector operation
and synchronize spark plug firing on distributorless
ignition systems (DIS).
CTS:
Coolant temperature sensor. A resistance sensor that
sends a voltage signal to the PCM indicating the temperature of the coolant. This signal tells the PCM
whether the engine is cold or warm.
CVRTD:
Continuous variable real time damping
D/R:
Drive/reverse
Data Link Connector (DLC):
Connector providing access and/or control of the vehicle
information, operating conditions, and diagnostic information. Vehicles with OBD II use a 16-pin connector
located in the passenger compartment.
Data stream:
The actual data communications sent from the vehicle’s
PCM to the data connector.
DEPS:
Digital engine position sensor.
Detonation:
See knock.
DI/DIS:
Direct Ignition/Distributorless Ignition System. A system
that produces the ignition spark without the use of a
distributor.
DPFE:
Differential pressure feedback-exhaust gas recirculation
sensor
DTC:
Diagnostic trouble code. An alphanumeric identifier for a
fault condition identified by the on board diagnostic
system.
Duty Cycle:
A term applied to signals that switch between on and
off. Duty cycle is the percentage of time the signal is on.
For example, if the signal is on only one fourth of the
time, then the duty cycle is 25%. The PCM uses duty
cycle type signals to maintain precise control of an
actuator.
EBCM:
Electronic brake control module
EBTCM:
Electronic brake/traction control module
ECM:
Engine control module or electronic control module
ECT:
Engine coolant temperature sensor. See CTS.
EEPROM:
Electrically erasable programmable read only memory
EFE:
Early fuel evaporation
EFI:
Electronic fuel injection. Any system where a computer
controls fuel delivery to the engine by using fuel injectors.
EGR:
Exhaust gas recirculation. The PCM uses the EGR system
to recirculate exhaust gases back into the intake manifold to reduce emissions. EGR is used only during warm
engine cruise conditions.
EOP:
Engine oil pressure (switch)
EOT:
Engine oil temperature (sensor)
EPA:
Environmental protection agency
ESC:
Electronic spark control. An ignition system function that
warns the PCM when knock is detected. The PCM then
retards spark timing to eliminate the knocking condition.
EST:
Electronic spark timing. An ignition system that allows
the PCM to control spark advance timing. The PCM
determines optimum spark timing from sensor information — engine speed, throttle position, coolant tempera-
580001 | REV. A | 11.2016
Page 52

en | 52 | User guide
| OBD 1350
ProGrade OBDII Scan Tool
ture, engine load, vehicle speed, Park/Neutral switch
position, and knock sensor condition.
EVAP:
Evaporative emissions system
FC:
Fan control
Freeze frame:
A block of memory containing DTCs of the vehicle operating conditions for a specific time.
FTP:
Federal test procedure. Strict test of vehicle’s emissions.
Ground (GND):
An electrical conductor used as a common return for an
electric circuit(s) and with a relative zero potential
(voltage).
Hall effect sensor:
Any of a type of sensor utilizing a permanent magnet and
a transistorized Hall Effect switch. Hall Effect type sensors may be used to measure speed and position of the
crankshaft or camshaft — for spark timing and fuel injector control.
HO2S:
Heated oxygen sensor. See O2S.
HVAC:
Heating, ventilation, & air conditioning (system)
I/M:
Inspection and maintenance. An emission control program.
IAC:
Idle air control. A device mounted on the throttle body
which adjusts the amount of air bypassing a closed
throttle so that the PCM can control idle speed.
IAT:
Intake air temperature (sensor)
ICM:
Ignition control module.
IMRC:
Intake manifold runner control
IPC:
Instrument panel cluster
ISC:
Idle speed control. A small electric motor mounted on
the throttle body and controlled by the PCM. The PCM
can control idle speed by commanding the ISC to adjust
its position.
ISO:
International Organization of Standardization also know
as International Standards Organization.
KAM:
Keep alive memory
Knock sensor (KS):
Used to detect engine detonation or knock. The sensor
contains a piezoelectric element and is threaded into the
engine block. Special construction makes the element
sensitive only to engine vibrations associated with detonation.
Knock:
580001 | REV. A | 11.2016
Uncontrolled ignition of the air/fuel mixture in the cylinder. Also referred to as detonation or ping. Knock indicates extreme cylinder pressures or “hotspots” that are
causing the air/fuel mixture to detonate prematurely.
KOEO:
Key ON engine OFF. Turn the ignition key to on, but don’t
start the engine.
KOER:
Key ON engine running. Start the vehicle.
LCD:
Liquid crystal display
LTFT:
Long term fuel trim
M/T:
Manual transmission or manual transaxle.
MAF:
Mass air flow (sensor). Measures the amount and density of air entering the engine and sends a frequency or
voltage signal to the PCM. The PCM uses this signal in
its fuel delivery calculations.
MAP:
Manifold absolute pressure (sensor). Measures intake
manifold vacuum or pressure and sends a frequency or
voltage signal (depending on sensor type) to the PCM.
This gives the PCM information on engine load for control of fuel delivery, spark advance, and EGR flow.
MAT:
Manifold air temperature (sensor). A resistance sensor
in the intake manifold that sends a voltage signal to the
PCM indicating the temperature of the incoming air. The
PCM uses this signal for fuel delivery calculations.
MIL:
Malfunction indicator lamp. The MIL is most commonly
known as the check engine or service engine soon light.
A required on-board indicator to alert the driver of an
emission-related malfunction.
Misfire:
Caused by the air fuel ratio being incorrect.
Monitor:
A test performed by the on-board computer to verify
proper operation of emission-related systems or components.
MPFI or MFI:
Multi-port fuel injection. MPFI is a fuel injection system
using one (or more) injector(s) for each cylinder. The
injectors are mounted in the intake manifold, and fired in
groups rather than individually.
NOx:
Oxides of nitrogen. The system EGR and Camshafts
injects exhaust gases into the intake manifold to reduce
these gases at the tailpipe.
O2S:
Oxygen sensor. Generates a voltage of 0.6 to 1.1 volts
when the exhaust gas is rich (low oxygen content). The
voltage changes to 0.4 volts or less when the exhaust
gas is lean (high oxygen content). This sensor only operates after it reaches a temperature of approximately
349ºC (660ºF). O2 sensors are usually found both
Page 53

OBD 1350 ProGrade OBDII Scan Tool | User guide | 53 | en
upstream and downstream of the catalytic converter.
The PCM uses these sensors to fine tune the air-fuel
ratio and to monitor the efficiency of the catalytic converter. See Bank 1, Bank 2, Sensor 1, Sensor 2.
OBDII:
On-board diagnostics, second generation. OBD II is a
U.S. Government-mandated standard requiring all cars
and light trucks to have a common data connector,
connector location, communication protocol, DTCs and
code definitions. OBD II first appeared on vehicles in
late 1994, and is required to be present on all cars sold
in the US after January 1, 1996.
ODM:
Output device monitor
Open loop (OL):
A control system mode that does not monitor the output
to verify if the desired results were achieved. A fuel
delivery system usually operates in open loop mode
during cold engine warm-up because the oxygen sensors
are not yet ready to send a signal. Without the oxygen
sensor signal, the computer cannot check the actual
results of combustion.
PCM:
Powertrain control module. The brains of the engine and
transmission control systems housed in a metal box with
a number of sensors and actuators connected via a
wiring harness. Its job is to control fuel delivery, idle
speed, spark advance timing, and emission systems. The
PCM receives information from sensors, then energizes
various actuators to control the engine. The PCM is also
known as the ECM (engine control module).
Pending codes:
Also referred to as continuous memory codes and maturing diagnostic trouble codes. Pending codes may be set
by emission related powertrain components and systems. If the fault does not occur after a certain number
of drive cycles, the code is erased from memory.
PID:
Parameter identification. Identifies an address in memory which contains vehicle operating information.
PNP:
Park/neutral position. A switch that tells the PCM when
the gear shift lever is in the park or neutral position.
When in park or neutral, the PCM operates the engine in
an idle mode.
PROM:
Programmable read-only memory. The PROM contains
programming information the PCM needs to operate a
specific vehicle model/engine combination.
PSPS:
Power steering pressure switch
Purge solenoid:
Controls the flow of fuel vapors from the carbon canister
to the intake manifold. The canister collects vapors
evaporating from the fuel tank, preventing them from
escaping to the atmosphere and causing pollution.
During warm engine cruise conditions, the PCM ener-
gizes the Purge Solenoid so the trapped vapors are
drawn into the engine and burned.
PWM:
Pulse width modulated
PZM:
Platform zone module
QDM:
Quad driver module
RAM:
Random access memory
Relay:
An electromechanical device in which connections in one
circuit are switched.
Reluctance sensor:
A type of sensor typically used to measure crankshaft or
camshaft speed and/or position, driveshaft speed, and
wheel speed.
ROM:
Read-only memory. Permanent programming information
stored inside the PCM, containing the information the
PCM needs to operate a specific vehicle model/engine
combination.
RPM:
Revolutions per minute
SAE:
Society of Automotive Engineers
Scan tool:
A device that interfaces with and communicates information on a data link.
SDM:
Sensing and diagnostic module
Sensor x:
A standard term used to identify the location of oxygen
sensors. Sensor 1 is located upstream of the catalytic
converter. See O2S, Bank 1, Bank 2.
Sensor:
Any device that reports information to the PCM. The job
of the sensor is to convert a parameter such as engine
temperature into an electrical signal that the PCM can
understand.
SFI or SEFI:
Sequential fuel injection or sequential electronic fuel
Injection. A fuel injection system that uses one or more
injectors for each cylinder. The injectors are mounted in
the intake manifold and are fired individually.
Solenoid:
A device consisting of an electrical coil which when energized, produces a magnetic field in a plunger, which is
pulled to a central position. A solenoid may be used as
an actuator in a valve or switch.
STFT:
Short term fuel trim
STS:
Service throttle soon
TAC :
Throttle actuator control
TBI:
580001 | REV. A | 11.2016
Page 54

en | 54 | User guide
| OBD 1350
ProGrade OBDII Scan Tool
Throttle body injection. A fuel injection system having
one or more injectors mounted in a centrally located
throttle body, as opposed to positioning the injectors
close to an intake valve port. TBI is also called Central
Fuel Injection (CFI) in some vehicles.
TCC:
Torque converter clutch
TCM:
Transmission control module
TCS:
Traction control system for PCM and brakes
TDC:
Top dead center. When a piston is at its uppermost
position in the cylinder.
TFP:
Transmission fluid pressure
TFT:
Transmission fluid temperature (sensor)
Throttle body:
A device which performs the same function as a carburetor in a fuel injection system. On a throttle body injection (TBI) system, the throttle body is both the air door
and the location of the fuel injectors. On port fuel injection systems (PFI, MPFI, SFI, etc.), the throttle body is
simply an air door. Fuel is not added until the injectors
at each intake port are activated. In each case, the
throttle body is attached to the accelerator pedal.
TPS:
Throttle position sensor. Potentiometer-type sensor
connected to the throttle shaft. Its voltage signal output
increases as the throttle is opened. The PCM uses this
signal to control many systems such as idle speed, spark
advance, fuel delivery, etc.
Traction assist:
Assist in traction with brakes only.
Trip:
Vehicle operation for a period of time so the systems can
be monitored.
TTS:
Transmission temperature sensor. A resistance sensor
mounted in the transmission housing in contact with the
transmission fluid. It sends a voltage signal to the PCM
indicating the temperature of the transmission.
VECI:
Vehicle emission control information. A decal located in
the engine compartment containing information about
the emission control systems found on the vehicle. The
VECI is the authoritative source for determining whether
a vehicle is OBDII compliant.
VIN:
Vehicle identification number. This is the factoryassigned vehicle serial number. This number is stamped
on a number of locations throughout the vehicle, but the
most prominent location is on top of the dashboard on
the driver’s side, visible from outside the car. The VIN
includes information about the car, including where it
was built, body and engine codes, options, and a
sequential build number.
VSS:
Vehicle speed sensor. Sends a frequency signal to the
PCM. The frequency increases as the vehicle moves
faster to give the PCM vehicle speed information used to
determine shift points, engine load, and cruise control
functions.
VTD:
Vehicle theft deterrent
Warm-up cycle:
Warm-up cycle is when the engine coolant temperature
rises at least 40 degrees above that at engine start up.
WOT:
Wide-open throttle. The vehicle operating condition
brought about when the throttle is completely (or
nearly) open. The PCM typically delivers extra fuel to the
engine and de-energizes the A/C compressor at this time
for acceleration purposes. The PCM uses a switch or the
TPS to identify the WOT condition.
580001 | REV. A | 11.2016
Page 55

OBD 1350 ProGrade OBDII Scan Tool | User guide | 55 | en
9 Limited Warranty
THIS WARRANTY IS EXPRESSLY LIMITED TO ORIGINAL RETAIL BUYERS OF BOSCH ELECTRONIC DIAGNOSTIC TOOLS
(“UNITS”).
BOSCH Automotive Service Solutions LLC Units are warranted against defects in materials and workmanship for one year (12 months)
from date of delivery. This warranty does not cover any Unit that has been abused, altered, used for a purpose other than that for which
it was intended, or used in a manner inconsistent with instructions regarding use. The sole and exclusive remedy for any Unit found to
be defective is repair or replacement, the option of BOSCH. In no event shall BOSCH be liable for any direct, indirect, special, incidental
or consequential damages (including lost profit) whether based on warranty, contract, tort or any other legal theory. The existence of a
defect shall be determined by BOSCH in accordance with procedures established by BOSCH. No one is authorized to make any statement or representation altering the terms of this warranty.
DISCLAIMER
THE ABOVE WARRANTY IS IN LIEU OF ANY OTHER WARRANTY, EXPRESS OR IMPLIED, INCLUDING ANY WARRANTY OF MERCHANTABILITY OR FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE.
SOFTWARE
Unit software is proprietary, confidential information protected under copyright law. Users have no right in or title to Unit software
other than a limited right of use revocable by BOSCH. Unit software may not be transferred or disclosed without written consent
of BOSCH. Unit software may not be copied except in ordinary backup procedures.
TECHNICAL SUPPORT
If you have any questions on the operation of the product, please call 1-800-228-7667.
REPAIR SERVICE
• Please contact Technical Support for troubleshooting and service options prior to sending any unit in for repair.
• To send a unit in for repair, go to repairtrack.bosch-automotive.com and follow the online instructions. This web site will also
have the latest Service policies and service center locations. If you do not have internet access, please call 1-800-344-4013.
580001 | REV. A | 11.2016
Page 56

©Bosch Automotive Service Solutions Inc.
3000 Apollo Drive
Brook Park, OH 44142
USA
Telephone: 1-800-228-7667
www.boschdiagnostics.com
 Loading...
Loading...