Bacharach HGM-MZ, AGM-MZ, CO2-MZ Owner's Manual

MultiZone Gas Monitors
•HGM-MZ (Halogen)
•AGM-MZ (Ammonia)
•CO2-MZ (Carbon Dioxide)
Installation • Operation • Maintenance
UL 61010-1
CAN/CSA 22.2 No. 61010.1
EN 14624
Instruction P/N: 3015-5074
Rev. 11
August 2013
Product Leadership • Training • Service • Reliability

Multi-Zone Gas Monitors
WARRANTY
Bacharach, Inc. warrants to Buyer that at the time of delivery this Product will be free from defects in material and manufacture and will conform substantially to Bacharach Inc.’s applicable specifications. Bacharach’s liability and Buyer’s remedy under this warranty are limited to the repair or replacement, at
Bacharach’s option, of this Product or parts thereof returned to Seller at the factory of manufacture and shown to Bacharach Inc.’s reasonable satisfaction to have been defective; provided that written notice of the defect shall have been given by Buyer to Bacharach Inc. within two (2) years after the date of delivery
of this Product by Bacharach, Inc.
Bacharach, Inc. warrants to Buyer that it will convey good title to this Product. Bacharach’s liability and Buyer’s remedy under this warranty of title are limited to the removal of any title defects or, at the election
of Bacharach, to the replacement of this Product or parts thereof that are defective in title.
The warranty set forth in Paragraph 1 does not apply to parts that the Operating Instructions designate as having a limited shelf-life or as being expended in normal use (e.g., filters).
THE FOREGOING WARRANTIES ARE EXCLUSIVE AND ARE GIVEN AND ACCEPTED IN LIEU OF (I) ANY AND ALL OTHER WARRANTIES, EXPRESS OR IMPLIED, INCLUDING WITHOUT LIMITATION THE IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY AND FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR
PURPOSE: AND (II) ANY OBLIGATION, LIABILITY, RIGHT, CLAIM OR REMEDY IN CONTRACT OR TORT, WHETHER OR NOT ARISING FROM BACHARACH’S NEGLIGENCE, ACTUAL OR IMPLIED. The remedies of the Buyer shall be limited to those provided herein to the exclusion of any and all other
remedies including, without limitation incidental or consequential damages. No agreement varying or extending the foregoing warranties, remedies or this limitation will be binding upon Bacharach, Inc. unless in writing, signed by a duly authorized officer of Bacharach.
Register your warranty by visiting
www.MyBacharach.com
Product improvements and enhancements are continuous; therefore the specifications and information contained in this document may change without notice.
Bacharach, Inc. shall not be liable for errors contained herein or for incidental or consequential damages in connection with the furnishing, performance, or use of this material.
Patent 6,590,690
Copyright © 2000–2013, Bacharach, Inc., All Rights Reserved
No part of this document may be photocopied, reproduced, or translated to another language without the prior written consent of Bacharach, Inc.
BACHARACH® is a registered trademark of Bacharach, Inc. All other trademarks, trade names, service marks and logos referenced herein belong to their respective owners.
ii |
P/N: 3015-5074 Rev 11 |
|
|
|
Multi-Zone Gas Monitors |
|
|
Table of Contents |
|
SECTION 1. INTRODUCTION............................................................................................................ |
1 |
||
1.1. |
About This Manual ..................................................................................................................... |
1 |
|
1.2. |
Warnings and Cautions .............................................................................................................. |
1 |
|
1.3. |
Safety Precautions..................................................................................................................... |
1 |
|
|
1.3.1. |
Hazardous Areas ........................................................................................................... |
1 |
|
1.3.2. |
Combustible and Flammable Gases................................................................................ |
2 |
|
1.3.3. |
AC Power Supply .......................................................................................................... |
2 |
|
1.3.4. |
Protective Grounding ..................................................................................................... |
2 |
|
1.3.5. |
Explosive Atmosphere ................................................................................................... |
2 |
|
1.3.6. |
Proper Exhaust Venting ................................................................................................. |
2 |
|
1.3.7. |
Accessing the Interior of the Monitor ............................................................................... |
2 |
|
1.3.8. |
Misuse and Modifications to the Instrument ..................................................................... |
3 |
|
1.3.9. |
In Case of Malfunction ................................................................................................... |
3 |
|
1.3.10. Fusing........................................................................................................................... |
3 |
|
|
1.3.11. Installation Category ...................................................................................................... |
3 |
|
|
1.3.12. Altitude Limit.................................................................................................................. |
3 |
|
|
1.3.13. Cleaning ....................................................................................................................... |
3 |
|
1.4. |
Key External Hardware Components .......................................................................................... |
4 |
|
1.5. |
Functional Overview .................................................................................................................. |
4 |
|
|
1.5.1. |
General Description ....................................................................................................... |
4 |
|
1.5.2. |
Communications Options ............................................................................................... |
5 |
|
1.5.3. |
Understanding Monitoring Levels .................................................................................... |
5 |
|
1.5.4. |
Response to the Presence of Multiple Refrigerants (HGM Only) ....................................... |
5 |
|
1.5.5. Suggested Location of Sampling Points .......................................................................... |
5 |
|
|
1.5.6. |
Locating a Remote Display (Optional) ............................................................................. |
6 |
1.6. |
Specifications ............................................................................................................................ |
7 |
|
SECTION 2. INSTALLATION............................................................................................................. |
9 |
||
2.1. |
Installation Considerations.......................................................................................................... |
9 |
|
|
2.1.1. |
Warnings and Cautions .................................................................................................. |
9 |
|
2.1.2. |
Inspection ..................................................................................................................... |
9 |
|
2.1.3. |
Location of the Monitor................................................................................................... |
9 |
|
2.1.4. |
Mounting Instructions ..................................................................................................... |
9 |
2.2. |
Connecting Gas Sample Lines.................................................................................................. |
10 |
|
|
2.2.1. |
Overview..................................................................................................................... |
10 |
|
2.2.2. |
Tubing Considerations ................................................................................................. |
11 |
|
2.2.3. |
Connecting Purge Line................................................................................................. |
11 |
|
2.2.4. |
Connecting Exhaust Line.............................................................................................. |
11 |
|
2.2.5. |
Connecting Sample Intake Lines................................................................................... |
11 |
|
2.2.6. |
Installing an Optional Splitter Kit ................................................................................... |
12 |
|
2.2.7. |
Connecting the Water Trap........................................................................................... |
12 |
2.3. |
Interior Components ................................................................................................................ |
13 |
|
2.4. |
Electrical Wiring....................................................................................................................... |
13 |
|
2.5. |
Connecting Communications Devices ....................................................................................... |
15 |
|
|
2.5.1. |
Remote Display Module (RD) Connection ..................................................................... |
15 |
|
2.5.2. |
Integrating with Building Management Systems............................................................. |
15 |
|
2.5.3. |
Larger Integrated Systems ........................................................................................... |
15 |
|
2.5.4. |
Changing Terminator Switch Settings............................................................................ |
16 |
|
2.5.5. |
Personal Computer ...................................................................................................... |
16 |
2.6. |
Terminating Multiple Monitors ................................................................................................... |
17 |
|
2.7. |
Connecting to a Building Management System .......................................................................... |
17 |
|
2.8. |
PC Software ............................................................................................................................ |
18 |
|
|
2.8.1. |
Operation .................................................................................................................... |
18 |
P/N: 3015-5074 Rev 11 |
iii |

Multi-Zone Gas Monitors
|
2.8.2. |
Saving and Sending Programs ..................................................................................... |
20 |
|
2.8.3. |
Trend Data .................................................................................................................. |
20 |
|
2.8.4. |
Converting the TREND Text File to a Microsoft Excel File .............................................. |
20 |
|
2.8.5. |
Saving and Printing Screens and Logs .......................................................................... |
20 |
|
2.8.6. |
USB Type Laptops....................................................................................................... |
20 |
2.9. |
Optional Current Loop Interfaces .............................................................................................. |
21 |
|
|
2.9.1. |
Optional 4–20 mA DC Outputs...................................................................................... |
21 |
|
2.9.2. |
4-20 mA DC Connections............................................................................................. |
22 |
2.10. Connecting External Alarms ..................................................................................................... |
23 |
||
|
2.10.1. Overview..................................................................................................................... |
23 |
|
|
2.10.2. Connection .................................................................................................................. |
23 |
|
SECTION 3. SETUP PROGRAMMING ............................................................................................. |
25 |
||
3.1. |
Initial Power Up ....................................................................................................................... |
25 |
|
3.2. |
Data Display Screen ................................................................................................................ |
25 |
|
3.3. |
Navigating to the 1st Setup Screen ........................................................................................... |
25 |
|
3.4. Navigating to the 2nd Setup Screen .......................................................................................... |
25 |
||
|
3.4.1. |
Location ...................................................................................................................... |
26 |
|
3.4.2. |
Number of Zones Installed............................................................................................ |
26 |
|
3.4.3. |
Alarm Acknowledge Mode ............................................................................................ |
26 |
|
3.4.4. |
Audible Alarm .............................................................................................................. |
26 |
|
3.4.5. |
Zone Hold ................................................................................................................... |
27 |
|
3.4.6. |
Detection Limit............................................................................................................. |
27 |
|
3.4.8. |
Loop Mode .................................................................................................................. |
27 |
|
3.4.7. |
Loop2 Factor ............................................................................................................... |
27 |
|
3.4.9. |
Re-Zero Mode ............................................................................................................. |
28 |
3.5. Navigating to the 3rd Setup Screen........................................................................................... |
28 |
||
|
3.5.1. |
Overview..................................................................................................................... |
28 |
|
3.5.2. |
Baud Rate ................................................................................................................... |
28 |
|
3.5.3. |
Node Address ............................................................................................................. |
28 |
|
3.5.4. |
Password .................................................................................................................... |
28 |
3.6. |
Additional Service Features ...................................................................................................... |
29 |
|
|
3.6.1. |
Service Timeout........................................................................................................... |
29 |
|
3.6.2. |
DET Digipot................................................................................................................. |
29 |
|
3.6.3. |
Node Address ............................................................................................................. |
30 |
|
3.6.4. |
Sensor Temperature Coefficient (For Factory Use Only)................................................. |
30 |
|
3.6.5. |
Password .................................................................................................................... |
30 |
|
3.6.6. |
Acquiring Temperature Coefficient (For Factory Use Only) ............................................. |
30 |
|
3.6.7. |
IR Digipot .................................................................................................................... |
30 |
3.7. |
Establishing the CO2 Sensor Baseline....................................................................................... |
30 |
|
SECTION 4. GENERAL OPERATION .............................................................................................. |
31 |
||
4.1. |
Functional Overview ................................................................................................................ |
31 |
|
4.2. |
The Zone Setup Screen ........................................................................................................... |
31 |
|
|
4.2.1. |
Location ...................................................................................................................... |
31 |
|
4.2.2. |
Gas/Refrigerant Type................................................................................................... |
31 |
|
4.2.3. |
Distance...................................................................................................................... |
32 |
|
4.2.4. |
Zone Temperature ....................................................................................................... |
32 |
|
4.2.5. |
Current Detection Reading ........................................................................................... |
32 |
|
4.2.6. |
Log Interval ................................................................................................................. |
32 |
4.3. |
Navigating to the 2nd Zone Setup Screen ................................................................................. |
32 |
|
|
4.3.1. |
Leak Level .................................................................................................................. |
33 |
|
4.3.2. |
Spill Level ................................................................................................................... |
33 |
|
4.3.3. |
Evacuation Level ......................................................................................................... |
33 |
|
4.3.4. |
Re-Setting the Peak PPM Value ................................................................................... |
33 |
4.4. |
Alarms |
.................................................................................................................................... |
33 |
iv |
P/N: 3015-5074 Rev 11 |
|
|
|
Multi-Zone Gas Monitors |
|
4.4.1. |
Functional Overview .................................................................................................... |
33 |
|
4.4.2. |
Responding to Alarms.................................................................................................. |
34 |
|
4.4.3. |
Alarm Detail Screen ..................................................................................................... |
34 |
|
4.4.4. |
Acknowledging Alarms ................................................................................................. |
35 |
|
4.4.5. |
Silencing an Alarm ....................................................................................................... |
35 |
|
4.4.6. |
Clearing the Alarm Event Log ....................................................................................... |
36 |
4.5. |
System Faults ......................................................................................................................... |
36 |
|
|
4.5.1. |
Functional Overview .................................................................................................... |
36 |
|
4.5.2. |
Navigating to the Fault Screen ...................................................................................... |
37 |
|
4.5.3. |
Critical Faults .............................................................................................................. |
37 |
|
4.5.4. |
Non Critical Faults ....................................................................................................... |
38 |
|
4.5.5. |
Reset to Factory Default Settings.................................................................................. |
38 |
|
4.5.6. |
Clearing System Faults ................................................................................................ |
38 |
|
4.5.7. |
Viewing Fault Log ........................................................................................................ |
39 |
|
4.5.8. |
Viewing Flow Log ........................................................................................................ |
39 |
4.6. |
The Trend Screen.................................................................................................................... |
40 |
|
|
4.6.1. |
Navigating to the Trend Screen .................................................................................... |
40 |
4.7. |
The Calibration Screen............................................................................................................. |
40 |
|
|
4.7.1. |
Overview..................................................................................................................... |
40 |
|
4.7.2. |
Navigating to the Calibration Screen ............................................................................. |
41 |
|
4.7.3. |
Calibration Procedure (HGM and AGM Only)................................................................. |
41 |
|
4.7.4. |
Adjusting Calibration Factor (HGM and AGM Only) ........................................................ |
41 |
|
4.7.4. |
CO2 Atmospheric Concentration ................................................................................... |
42 |
|
4.7.6. |
Programming New Gases (HGM Only).......................................................................... |
42 |
4.8. Zone Hold Mode........................................................................................................................ |
43 |
||
4.9. |
The Diagnostic Screen ............................................................................................................. |
44 |
|
|
4.9.1. |
Navigating to the Diagnostic Screen.............................................................................. |
44 |
|
4.9.2. |
Diagnostic Screen Overview......................................................................................... |
45 |
SECTION 5. MAINTENANCE........................................................................................................... |
47 |
||
5.1. |
Replacement Parts Overview ................................................................................................... |
47 |
|
5.2. |
Replacement Parts and Optional Accessories............................................................................ |
48 |
|
5.3. |
Troubleshooting....................................................................................................................... |
50 |
|
APPENDIX A. RECOMMENDED REFRIGERANT GAS ALARM SETTINGS ..................................... |
53 |
||
APPENDIX B. RS-485 COMMUNICATIONS PROTOCOL ................................................................ |
55 |
||
B.1. |
Overview................................................................................................................................. |
55 |
|
B.2. |
MODBUS RTU Protocol ........................................................................................................... |
55 |
|
B.3. |
MZ MODBUS RTU Operation ................................................................................................... |
55 |
|
|
B.3.1. |
Overview..................................................................................................................... |
55 |
|
B.3.2. |
Protocol Details ........................................................................................................... |
55 |
|
B.3.3. |
MZ Monitor Polling ....................................................................................................... |
56 |
|
B.3.4. |
Network Topologies ..................................................................................................... |
56 |
|
B.3.5. |
Key Comm Protocol Parameters................................................................................... |
56 |
|
B.3.6. |
Summary of Registers.................................................................................................. |
57 |
|
B.3.7. |
System Data Register 0x0010 (16 Dec) (R/W, 54 Bytes) ................................................ |
58 |
|
B.3.8. |
Status Register 0x001 (17 Dec) (R/W, 10 Bytes)............................................................ |
58 |
|
B.3.9. |
Fault Code Table ......................................................................................................... |
59 |
|
B.3.10. |
Zone Data Register 0x12xx (R/W, 78 Bytes).................................................................. |
59 |
|
B.3.11. |
Alarms and Alarm Acknowledge ................................................................................... |
60 |
|
B.3.12. |
Date Time Register 0x0015 (21 Dec) (R/W, 14 Bytes).................................................... |
60 |
|
B.3.13. |
Sensor Data Register 0x0016h (22 Dec) (R, 82 Bytes) ................................................... |
61 |
|
B.3.14. |
Release Zone Hold Register 0x0017h (23 Dec) (W, 10 Bytes) ........................................ |
61 |
|
B.3.15. |
Hold Zone Register 0x0018h (23 Dec) (W, 10 Bytes) ..................................................... |
61 |
|
B.3.16. |
MZ Hold Mode ............................................................................................................. |
61 |
P/N: 3015-5074 Rev 11 |
v |

Multi-Zone Gas Monitors
B.3.17. Fault Log Register 0x1900-01 (6400-6401 Dec) (R, 302 Bytes) ...................................... |
62 |
B.3.18. Flow Log Register 0x001F (31 Dec) (R, 142 Bytes)........................................................ |
62 |
B.3.19. Alarm Log Register 0x1A00-02 (6656-58 Dec) (R, 582 Bytes)......................................... |
62 |
B.3.20. Service Mode Register 0x001B (27 Dec) (W, 10 Bytes).................................................. |
63 |
B.3.21. Release Service Mode 0x001C (28 Dec) (W, 10 Bytes).................................................. |
63 |
B.3.22. MZ Service Mode ........................................................................................................ |
63 |
B.3.23. PPM Register 0x001E (30 Dec) (R, 32 Bytes)................................................................ |
63 |
B.3.24. Zone Log Registers 0x3xyy (R, 1502 Bytes) .................................................................. |
63 |
B.3.25. MODBUS Exception Responses................................................................................... |
64 |
B.3.26. MODBUS Gas Enumeration ......................................................................................... |
64 |
APPENDIX C. SYSTEM MENU MAP............................................................................................... |
65 |
APPENDIX D. AGENCY APPROVALS............................................................................................ |
67 |
APPENDIX E. SERVICE CENTERS ................................................................................................ |
71 |
INDEX ............................................................................................................................................. |
73 |
vi |
P/N: 3015-5074 Rev 11 |
Multi-Zone Gas Monitors
SECTION 1. INTRODUCTION
1.1. About This Manual
Thank you for investing in a Bacharach Multi-Zone Gas Monitor. To assure operator safety and the proper use of the monitor please read this manual. It provides important information on the installation, operation,
maintenance, and servicing of the monitor and display module.
If you have a working knowledge of your gas monitor, you will find this manual useful as a reference tool. If you are new to the use of gas monitors, this document is educational in the principles of gas detection and
the proper operation of this device.
1.2. Warning and Caution Conventions
When used in this manual or as labeled on the gas monitor, the following hazard symbols and/or associated words are defined as follows.
WARNING: This symbol and/or the use of the word WARNING indicates a potential
hazard associated with the use of this equipment. It calls attention to a procedure, practice, condition, or the like, which if not correctly performed or adhered to, could result in death or serious injury.
WARNING: This symbol and/or the use of the word WARNING indicates a potential hazard from electrical shock. It calls attention to a procedure, practice, condition, or the like, which if not correctly performed or adhered to, could result in death or serious injury.
CAUTION: This symbol and/or the use of the word CAUTION indicates a potential hazard associated with the use of this equipment. It calls attention to a procedure, practice, condition, or the like, which if not correctly performed or adhered to, could result in minor or
moderate injury.
IMPORTANT: The use of the word IMPORTANT in this manual calls attention to a procedure, practice, condition, or the like, which if not correctly performed or adhered to,
could result in incorrect performance of or damage to the equipment and may void the warranty.
1.3. Safety Precautions
WARNING: This instrument has not been designed to be intrinsically safe for use in areas classified as hazardous locations. For your safety, DO NOT use it in hazardous (classified) locations.
WARNING: This is NOT a safety device. Some gases which this instrument can detect
may be combustible/flammable. When properly configured, this instrument is designed to alarm at concentrations that are lower than the explosive limit of the gas. As such, it is the buyer’s responsibility to initiate an immediate planned response to any gas leaks as soon
as they are detected. This equipment should NEVER be used to measure or sample gases at or above their respective lower explosive limits.
IMPORTANT: The gas monitor uses a universal power supply that is capable of accepting inputs of 100 to 240 VAC, 50/60 Hz. The monitor’s power consumption is 20 Watts. It is
highly recommended that the monitor be connected directly to the AC power source, preferably on its own circuit with UPS or surge protection.
P/N: 3015-5074 Rev 11 |
1 |
Multi-Zone Gas Monitors
WARNING: A switch or circuit breaker must be included in the building installation. The
switch must be in close proximity to the monitor and within easy reach of the operator. The switch must be clearly marked as the disconnecting device for the equipment.
WARNING: Under no circumstances should the monitor be operated without connection to a protective ground. Doing so poses a potential shock hazard and is also a violation of
electrical safety standards applicable to this type of equipment.
WARNING: Do not operate this equipment in the presence of flammable liquids, vapors,
or aerosols. Operation of any electrical instrument in such an environment constitutes a safety hazard.
WARNING: It is imperative that the exhaust port on this instrument be properly vented as described in this manual. Failure to do so may constitute a safety hazard.
WARNING: Extreme care should be exercised when accessing the interior of the monitor. Only qualified electrical maintenance personnel should make connections and perform adjustments. Always remove AC power before opening the monitor’s enclosure.
WARNING: The protection provided by the monitor may be impaired if the monitor is used
in a manner not specified by Bacharach, Inc. Modifications to this monitor, not expressly approved, will void the warranty.
WARNING: Do not continue to use this equipment if there are any symptoms of malfunction or failure. In the case of such occurrence, de-energize the power supply and
contact a qualified repair technician or the nearest Bacharach Service Center.
WARNING: This device uses type “F” fuses (F1 and F2) rated at 1.0 A, 250 VAC. Replace ONLY with Bacharach-approved fuses.
WARNING: Electrical installation should be performed by a certified electrician, and must comply with all applicable NEC/CEC and local electrical safety codes.
IMPORTANT: Use ONLY the provided knockouts for electrical and communications wiring. Drilling into the box will void the warranty.
IMPORTANT: This device is classified as Installation Category II, Pollution Degree II, as defined by UL.
IMPORTANT: This device is designed for operation at or below an altitude of 6,562 ft (2,000 m). Do not operate this device above this altitude limit.
NOTE: To clean the outside of the case use a dry cloth. To avoid shock hazard and/or equipment damage, DO NOT use soap and water.
2 |
P/N: 3015-5074 Rev 11 |

Multi-Zone Gas Monitors
1.4. Key External Hardware Components
Figure 1-1. Multi-Zone Monitor Front View
NOTE: Mounting cutouts are located on the back of the monitor, and are visible from
inside the Multi-Zone monitor. A mounting template is also shipped with the monitor. For mounting information, refer to the mounting instructions on page 8.
Standard Accessories for a 4-Point System
QTY |
Description |
Part Number |
5 |
Line-End Filters |
3015-3420 |
1 |
Charcoal Filter (Halogen Gas Monitor Only) |
3015-3125 |
3 |
End-of-line Water-Stop Filter Assembly |
3015-5512 |
|
|
|
1 |
T-Bolt Bracket (Halogen Gas Monitor Only) |
3015-2969 |
1 |
Multi-Zone Instruction Manual |
3015-5074 |
1.5. Functional Overview
1.5.1.General Description
Gas monitors are specified to support compliance to federal, state and local safety codes governing emissions. Avoiding significant loss reduces equipment replacement costs, maintains equipment efficiency,
promotes safety, and protects the environment.
The Bacharach Multi-Zone Monitor provides continuous monitoring of gas levels in up to 16 separate test zones. The instrument is easily programmed to monitor a variety of gases (dependent on particular model)
and independent leak (small), spill (medium), and evacuation (large) levels may be designated for each zone. The instrument also retains a log of previous readings that can be easily accessed for analysis.
P/N: 3015-5074 Rev 11 |
3 |

Multi-Zone Gas Monitors
An audible alarm and front panel indicators are provided to signal alarm and fault conditions, and relay contacts are provided that can be used to trigger external alarm devices in the event of a system fault, or if a
leak (small), spill (medium), or evacuation (large) level of gas is detected. The system also may be fitted with and optional two-channel 4-20 mA current loop board for connection to remote monitoring equipment.
The multi-zone monitor requires only minor periodic maintenance such as the occasional replacement of
filters. The monitor incorporates active diagnostics that continuously check the system for proper operation. A front panel indicator is provided to alert an operator of system malfunctions, and fault codes are generated that enable the user to identify the cause of the fault.
1.5.2.Communications Options
The multi-zone monitor features full two-way communications via an RS-485 interface. MODBUS RTU is the communications protocol standard. The instrument can be connected directly to a Building
Management System or it may be operated as a stand-alone system.
An RS-232C port is also provided for connection to a PC. This enables the monitor to be setup from a personal computer. Refer to Appendix B for more information on communications protocols.
1.5.3.Understanding Monitoring Levels
Effective use of this instrument requires an understanding of what constitutes reasonable alarm set points for the types of gas being monitored. Manufacturers define allowable exposure levels and threshold limit
values in units of parts per million (ppm). In a good “tight” installation these background levels will be acceptably low and often do not require corrective action. You can reduce nuisance alarms and needless service calls if the alarm levels are set at practical limits. Bacharach has developed recommended
monitoring refrigerant gas levels based on compliance to ANSI/BSR ASHRAE 15-2007 and ASHRAE Safety Code 34-2007. These reference levels are listed in Appendix A.
Setting the monitor at these recommended alarm levels will satisfy the needs of most users. However, the
ppm levels generated by system leaks into the environment are greatly influenced by the volume of air in the sampling area, air circulation, size of the leak, distance to the monitoring point, and a host of other variables. In some cases the set points may need to be adjusted either up or down to achieve effective monitoring.
1.5.4.Response to the Presence of Multiple Refrigerants (HGM Only)
The HGM-MZ is a refrigerant level monitor, not a gas analyzer. You must program the monitor to test for a specific refrigerant, and it will only return accurate concentration readings for that particular refrigerant. If
a leak occurs of another refrigerant gas type, the monitor may return incorrect readings.
Most applications only require detection of a single refrigerant and the problems that are associated with monitoring multiple gases are rarely an issue. If there is a possibility of multiple refrigerants leaking in the
same sampling zone, then you should carefully consider which refrigerant compound you program the unit to monitor.
1.5.5.Suggested Location of Sampling Points
At the point of a leak the gas is nearly pure. As the gas is dispersed into the air, the gas molecules diffuse, causing a dilution of the original concentration. The monitor measures the concentration at the sample collection point. Therefore, if the termination of the collection line is not at the exact point of the leak, the
unit will read a diluted mixture of the gas and air.
Gases of interest may be heavier or lighter than air and may collect above or below the point of the leak. Therefore sampling point placement is critical and must take into account properties of the target gas and air
flow within the space. In general, sampling points should be located as close as possible to the sources of potential leaks. If this is impractical, then alarm set points for that zone should be adjusted to compensate for the dilution of the gas. General placement guidelines are shown below, but air-flow dynamics should also
be considered (e.g., consider the effects of exhaust fans which tend to draw target gas from the space).
• |
HGM-MZ Halogen |
Mount sampling points 6-18 inches above floor |
• |
AGM-MZ NH3 (Ammonia) |
Mount sampling points 1-2 feet below ceiling |
• |
CO2-MZ CO2 (Carbon Dioxide) |
Mount sampling points 4-6 feet above floor (breathing zone) |
4 |
P/N: 3015-5074 Rev 11 |
Multi-Zone Gas Monitors
DO NOT block any of the zones. Unused zones may be disabled by setting the distance parameter to zero feet in the zone setup screen.
The MZ monitor should be centrally located in the mechanical room and be readily accessible for easy visual monitoring and servicing. The combined length of sample tubing plus exhaust tubing should not exceed 1200 ft (366 m) for any zone. The fresh air purge line should draw from an area that does not
contain any gas. The exhaust line should run to an outside location if possible.
NOTE: The combined length of the purge line and the exhaust line cannot exceed 500 feet.
Ideally, two to three pick up points spaced around each chiller will provide sufficient coverage. It may be necessary to perform a smoke test of the mechanical room to determine the best locations. The smoke test
provides the pattern of air currents present in the mechanical room.
The MZ monitor should be kept dry. When used in a wet or humid area, it is highly recommended to use the optional water stop accessory to avoid internal damage.
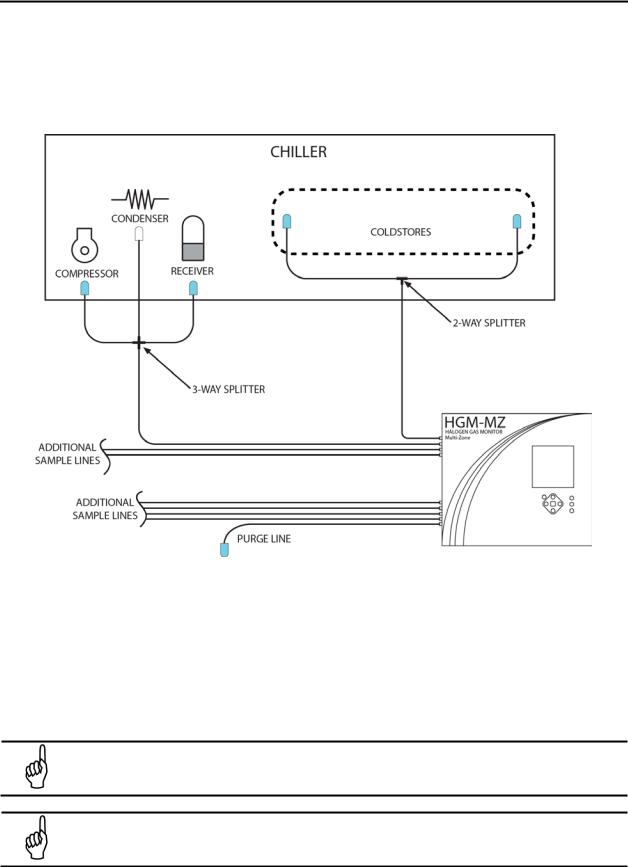
1.5.6.Locating a Remote Display (Optional)
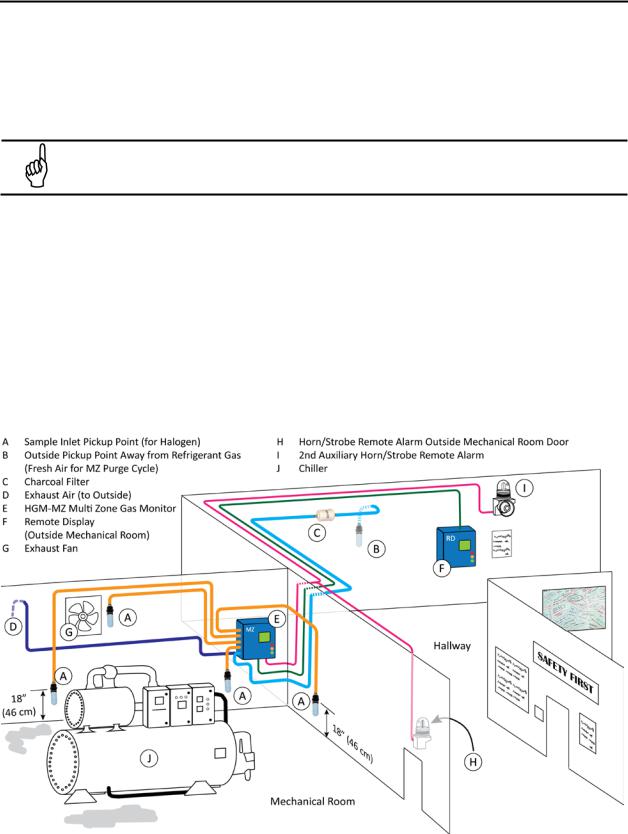
The Remote Display (RD) Module should be mounted outside of the mechanical room, or just inside the room’s doorway if the first option isn’t possible. This is the “split architecture design” for safety of the
operator. The RD can be located up to 4500 feet (1372 m) from the MZ monitor. The RD is the man machine interface by which you program the MZ, acknowledge alarms and observe conditions inside of the mechanical room. Note that there are two additional alarm relay contacts in the RD that can be
programmed to alarm on leak, spill, evacuate, fault, or monitor on conditions.
Figure 1-2. HGM-MZ (Halogen) and RD Placement in a Mechanical Room
P/N: 3015-5074 Rev 11 |
5 |

Multi-Zone Gas Monitors
NOTE: The pickup points located on the floor in the above illustration are examples for
refrigerants which are heavier than air. Placement of pickup points should be determined based on characteristics of the gas being monitored and ambient conditions of the sampling area. (Air=28.9 g/mole, CO2=44.0 g/mole, NH3=17.0 g/mole, and halogens = 100+ g/mole.)
1.6. Specifications
HGM-MZ Specifications
|
Multiple refrigerant gases and multiple area monitoring system for low level continuous |
||
Product Type |
monitoring of CFC, HCFC and HFC refrigerant gases used in most commercial |
||
refrigeration systems. System design supports compliance to the refrigerant monitoring |
|||
|
|||
|
requirements of ANSI/BSR ASHRAE 15-2007 and ASHRAE Safety Code 34-2007. |
||
|
|
||
Sensitivity |
All gases 1 ppm |
||
|
|
||
Measuring Range |
All gases 0 to 10,000 ppm |
||
|
|
||
Accuracy1 |
±1 ppm ±10% of reading from 0-1000 ppm |
||
|
(R11, R22, and R113 ±10 ppm ±15% of reading 0-1000 ppm) |
||
|
CFC: |
HFP, R-11, R-12, R-113, R-114, R-502 |
|
|
HFC: |
R125, R-134a, R236FA, R245Fa, R32, R-404a (HP62), R-407a, R-407c |
|
|
|
(AC9000), R-410a (AZ20), R422a, R422d, R427a, R-507 (AZ50), R-508b |
|
Gas Library |
|
(SUVA95) |
|
HCFC: R-123, R-124, R21, R-22, R227, R-23, R-401a (MP39), R-402a (HP80), |
|||
|
|||
|
|
R-402b (HP81), R-408a, R-409a, R-500, R-503 |
|
|
Halon: |
H1211, H1301, H2402 |
|
|
Other: |
FA188, FC72, H1234YF, N1230, R424A, R426A, R438A, CUSTOM |
|
|
|
|
|
|
AGM-MZ Specifications |
|
|
|
|
Product Type |
The AGM-MZ provides multiple area monitoring system for low level continuous |
|
monitoring of Ammonia gases used in most commercial systems. |
||
|
||
|
|
|
Sensitivity |
20 ppm |
|
|
|
|
Measuring Range |
25 to 10,000 ppm |
|
|
|
|
Accuracy1 |
±10 ppm ±10% of reading from 0-10,000 ppm |
|
Gas Library |
Ammonia (NH3)/R-717 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
CO2-MZ Specifications |
|
|
The CO2-MZ provides multiple area monitoring for low level continuous monitoring of |
|
Product Type |
carbon dioxide gases used in most commercial systems. System design supports |
|
|
compliance to the gas monitoring requirements of ANS/BSR ASHRE 15-1994. |
|
Sensitivity |
10 ppm |
|
|
|
|
Measuring Range |
300-8,000 ppm |
|
|
|
|
Accuracy1 |
±5 PPM ±5% of reading from 300-1000 ppm, ±10% of reading from 1001-3000 ppm |
|
Gas Library |
Carbon Dioxide (CO2)/R-744 |
|
|
|
1 At reference environmental conditions (25°C, 45% RH non-condensing, 1 ATM)
6 |
P/N: 3015-5074 Rev 11 |
|
|
Multi-Zone Gas Monitors |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
General Multi-Zone Specifications |
|
|
|
|
|
Coverage |
4 point standard, expandable to 16 points in 4 point increments |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Detector Type |
Infrared Non-Dispersive |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
3 Indicator lights: |
|
|
|
• Green |
Monitor is powered on. LED glows during normal operation; flashes when |
|
Front Panel |
|
unit is in warm-up mode |
|
|
• Red |
Alarm. LED flashes when any point has exceeded the alarm setting. |
|
|
• Yellow |
Fault. LED flashes when there is a system fault |
|
|
|
|
|
Size (H x W x D) |
12.23" x 13.7" x 4.96" (31.06 cm x 34.80 cm x 12.60 cm) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Weight |
15 lbs. (6.8 kg) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Sampling Mode |
Automatic or manual (hold) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Re-Zero |
Auto or on zone change |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Response Time |
5 to 315 seconds – depending on air line length and number of zones |
|
|
|
|
|
|
System Noise |
Less than 40 dB(A) @ 10 feet (3m) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Monitoring Distance |
1,200 ft (366 m) maximum for combined length of sample + exhaust tubing (each zone) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Conditioned Signal |
Dual optional 4-20 mA DC isolated outputs. Channel 1 = zone area, Channel 2 = PPM |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Alarms |
Four SPDT alarm contacts rated 2A at 250 VAC (inductive) 5 A at 250 VAC (resistive). |
|
|
Three are assigned to PPM level alarms, one assigned to system faults. |
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
Communications |
Full two-way communications with Remote Display Module or Building Management |
|
|
System via RS-485 serial interface. RS-232C communications port standard. |
|
||
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
Power Safety Mode |
Fully automatic system reset. All programmed parameters retained. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Operating Temp |
32 to 122 °F (0 to 50 °C) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Ambient Humidity |
5% to 90% RH (non-condensing) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
AC Power |
100 to 240 VAC, 50/60 Hz, 20 W |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Certification |
UL 61010-1, CAN/CSA 22.2 No. 61010-1 & CE Mark |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Warranty |
2 years from date of shipment |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Altitude Limit |
6,562 ft (2,000 m) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Sensor Life |
7-10 years |
|
|
|
|
|
|
P/N: 3015-5074 Rev 11 |
7 |
Multi-Zone Gas Monitors
SECTION 2. INSTALLATION
2.1. Installation Considerations
2.1.1.Warnings and Cautions
WARNING: Explosion hazard! Do not mount the MZ monitor in an area that may contain flammable liquids, vapors, or aerosols. Operation of any electrical equipment in such an environment constitutes a safety hazard.
WARNING: Shock hazard! Always disconnect AC power before working inside the monitor.
CAUTION: Drilling holes in the MZ enclosure may damage the unit and will void the warranty. Please use the knockouts provided for electrical connections.
CAUTION: The MZ monitor contains sensitive electronic components that can be easily damaged. Do not touch nor disturb any of these components.
2.1.2.Inspection
The MZ monitor has been thoroughly inspected and tested prior to shipment from the factory. Nevertheless, it is recommended that the monitor be re-checked prior to installation. Inspect the outside of the enclosure to make sure there are no obvious signs of shipping damage. Open the enclosure and inspect the interior of
the monitor for loose components that may have become dislodged during shipment. If damage is discovered, please contact the nearest Bacharach Service Center for assistance.
2.1.3.Location of the Monitor
The MZ monitor should be centrally located in the facility and should be easily accessible for visual monitoring and servicing. Combined length of the intake sample line and the exhaust line cannot exceed 1200 feet (366 m) in length, but it is important to remember that sampling cycle time is proportional to the
total number and length of individual sample lines.
Dirt, grease, and oils can adversely affect the operation of the MZ monitor. The monitor should be installed out of direct sunlight in a clean, dry area that is not subject to temperature or humidity extremes. Installation
of the monitor in a mechanical room is acceptable provided reasonable environmental conditions exist. If there is a question, consider installing the unit outside of the mechanical room in a cleaner area of the facility.
NOTE: The mounting location of the monitor should allow it to be easily accessible for visual monitoring and servicing.
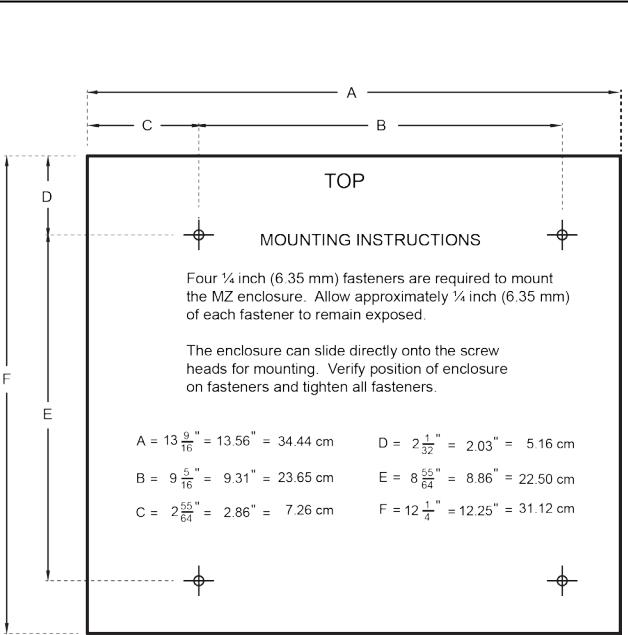
2.1.4.Mounting Instructions
NOTE: The MZ monitor should be installed plumb and level and securely fastened to a rigid mounting surface.
8 |
P/N: 3015-5074 Rev 11 |
Multi-Zone Gas Monitors
The enclosure utilizes keyhole mounting brackets designed for ¼ inch fasteners. Locate the four screws as shown in the diagram below or by using the provided mounting template (P/N 3015-5109). Allow the screw
heads to protrude approximately ¼ inch.
Figure 2-1. MZ Monitor Mounting Specifications
Hold the monitor flat against the mounting surface and allow it to slide down, engaging the screw heads in
the keyhole slots of the mounting brackets. Adjust the screws as necessary to hold the monitor securely against the mounting surface.
2.2. Connecting Gas Sample Lines
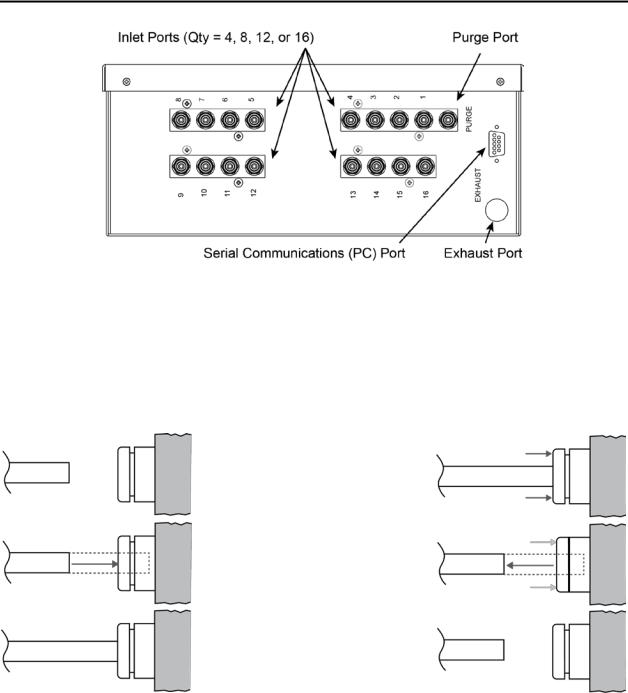
2.2.1.Overview
Individual gas sample lines are run from the MZ monitor to each area of the facility to be monitored.
Additionally, a purge line is installed to provide clean air for resetting the infrared zero baseline. All air, sample, and purge line connections are located on the left side of the enclosure. Refer to the illustration below.
P/N: 3015-5074 Rev 11 |
9 |
Multi-Zone Gas Monitors
Figure 2-2. MZ Monitor Side View
2.2.2.Tubing Considerations
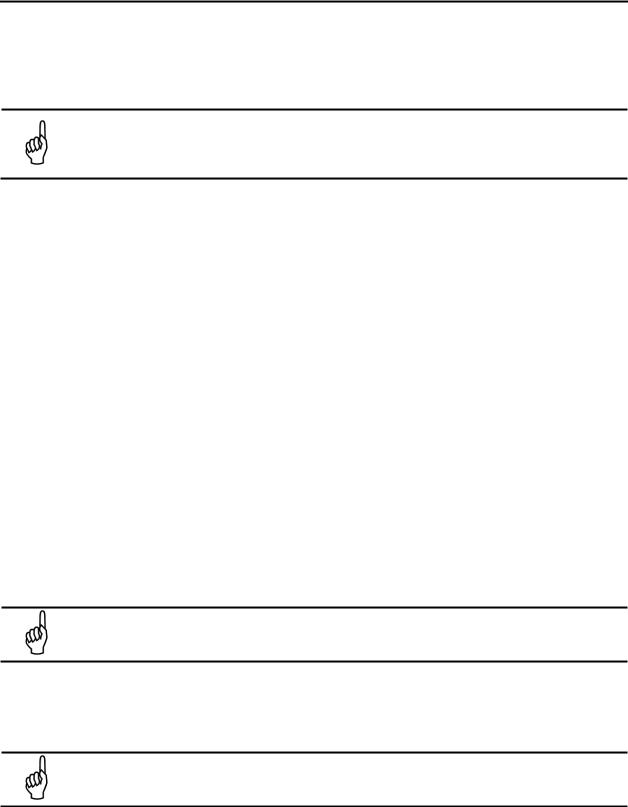
Use ¼” (6.35 mm) outside diameter (0.040” or 1.016 mm wall) flex tubing for all air lines (P/N 3015-3235) or equivalent. The tubing should be clean and free of residual moisture or other contaminants. The tubing should be cut cleanly with a sharp knife and care should be taken not to distort the tubing end.
To connect the air lines to the monitor simply push the tubing firmly onto the connector. To remove a line, press the plastic ring on the connector with one hand, then withdraw the tube with your other hand. See below.
The MultiZone monitor uses push- to-connect (PTC) style connectors.
To insert sample lines, firmly push the appropriate tubing into the hole
in the center of the connector until it seats in the connector. Refer to the figures at the left.
To remove tubing from a PTC connector, push and hold the
spring-loaded collar inwards, then simultaneously withdraw the tubing. Refer to the figures at the right.
Figure 2-3. Using PTC Connectors: Connecting (Left) and Disconnecting (Right)
All tubing bends should have a radius of no less than 5” (12.7 cm) to ensure proper airflow. If kinks or obstructions occur in any of the air lines the instrument may not function properly.
2.2.3.Connecting Purge Line
A purge line is an intake line that is required to draw fresh air into the instrument and should not exceed
300 feet (91.44 mm) in length. It is advisable to terminate the purge line outdoors, provided the input is not exposed to rain, snow, ice, exhaust fumes, or other airborne contaminates. If an outdoor installation is impractical, the line should be run to an area inside the facility that you are certain is not contaminated
with ambient gas. If this is not possible, an optional charcoal filter assembly (P/N 3015-3125) can be used
10 |
P/N: 3015-5074 Rev 11 |
Multi-Zone Gas Monitors
with the Halogen Gas Monitor to filter refrigerant from the purge line. It may be mounted adjacent to the monitor. A line-end filter (P/N 3015-3420) should be attached to the end of the purge line when the
charcoal filter is not used. Note that the charcoal filter option must NOT be used in ammonia or CO2 applications.
IMPORTANT (CO2 Only): Because CO2 is present in ambient air, the purge line MUST BE run outside, away from any known sources of CO2 gas. An atmospheric CO2
concentration value can be manually entered by the user in the CAL screen. See CO2
Atmospheric Concentration (page 42).
2.2.4.Connecting Exhaust Line
An exhaust line can be used when it is required to vent gas samples away from the instrument and should not exceed 300 feet (91.44 mm) in length. The exhaust line should terminate in a location that is
completely isolated from the purge line termination point and other areas of the facility that will be monitored. Ideally this line should terminate outdoors in a location that is not exposed to the elements. This line does not require a line-end filter. If the exhaust line terminates outside the building, position the
tubing so that no water or moisture can enter it.
2.2.5.Connecting Sample Intake Lines
The MZ monitor is designed to accommodate up to 16 separate sample intake lines. The standard
configuration of the unit includes one manifold of 4 intake connectors and 1 purge connector. Additional manifolds can be easily installed to increase monitoring capacity (field installation kit P/N 3015-5171, and 4 zone line end filter kit P/N 3015-3411).
Sample intake lines can be up to 1,200 feet (366 m) when no exhaust tubing is used. Otherwise, the combined length of the sample line and the exhaust line cannot exceed 1,200 ft (366 m). All line terminations should be positioned to reduce the possibility of mists, aerosols, oil, water, dust, or other
contaminates being drawn into the instrument. A line-end filter (P/N 3015-3420) should be attached to the end of each sample intake line. General placement guidelines are shown below, but air-flow dynamics should also be considered (e.g., consider the effects of exhaust fans which tend to draw target gas from the
space).
• |
HGM-MZ Halogen |
Mount sampling points 6-18 inches above floor |
• |
AGM-MZ NH3 (Ammonia) |
Mount sampling points 1-2 feet below ceiling |
• |
CO2-MZ CO2 (Carbon Dioxide) |
Mount sampling points 4-6 feet above floor (breathing zone) |
IMPORTANT: DO NOT block any of the zones. Unused zones may be disabled by setting their length parameter to zero in the zone setup screen.
Depending on type of use and location of lines, the end-of-line water stop filter assembly can be used to prohibit moisture from entering the intake lines. Three (3) end-of-line water stop filters are supplied with a
standard unit. Place the end of the intake line into the blue receiver of the end of line water stop and tighten sufficiently.
NOTE: Only one filter assembly, either the line-end filter or end-of-line water stop, should be used for each line.
Please refer to the earlier section Suggested Location of Sampling Points (page 4) to learn more about where to place the ends of the sample intake lines.
P/N: 3015-5074 Rev 11 |
11 |
Multi-Zone Gas Monitors
2.2.6.Installing an Optional Splitter Kit
Splitter kits are made available which allow the MZ unit to take gas sample readings from several sample
points while utilizing just a single zone. These kits are designed for use ONLY in confined/defined spaces with high potential for leaks, such as food cases, cold rooms, refrigeration rack rooms, etc. Bacharach’s 2-way (P/N 3015-5404) and 3-way (P/N 3015-5405) splitter kits are available as optional accessories. Refer
to instruction 3015-5415 (supplied with the kit) for detailed installation instruction.
2.2.7.Connecting the Water Trap
The water trap is an optional accessory for applications that result in water or condensation frequently
entering the intake lines. This is available in a manual style trap (P/N 0007-1655) which is manually emptied once it has become filled. Install the water trap close to the unit for the most effective results. The intake line may be cut where the user finds appropriate (preferably close to monitor). Each side of the
intake line should be inserted into the receivers on either side of the water trap. Secure tightly. A replacement filter (P/N 0007-1656) for the water trap is available and is replaced by unscrewing the clear plastic cup of the water trap, pulling the filter directly out (do not unscrew), and inserting the new filter into
place. Replace the cup of the water trap. If desired, an optional mounting bracket (0007-1657) may be used to secure the water trap in place.
NOTE: The termination filter (P/N 3015-3420) or end-of-line water stop filter (P/N 30155512) should be used, regardless of the presence of a water trap.
IMPORTANT: Extreme or humid temperatures may cause water to condense in the tubes. A water trap is highly recommended for use in these scenarios.
12 |
P/N: 3015-5074 Rev 11 |
Multi-Zone Gas Monitors
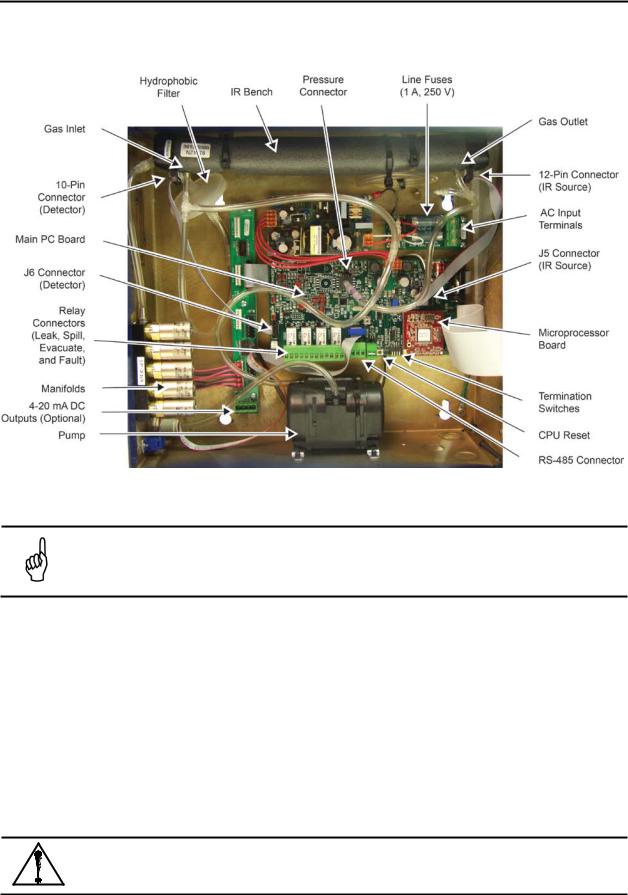
2.3. Interior Components
Figure 2-4. MZ Monitor Interior Components
NOTE: The plastic cable ties surrounding the air pump are to ensure safe handling during
shipping. Please remove before operation. Reinstall a plastic cable around the air pump if the unit is shipped to Bacharach, Inc. for service or repair. This prevents damage during shipping.
2.4.Electrical Wiring
The MZ monitor uses a universal power supply that is capable of accepting inputs of 100 to 240 VAC,
50/60 Hz. The monitor’s power consumption is 20 Watts. It is highly recommended that the monitor be connected directly to the AC power source, preferably on its own circuit. The AC power connection should be completed with UL listed 3-conductor wire (minimum 16 AWG), rated 300 VAC at 105°C.
Locate a convenient service knockout and install electrical conduit in the typical manner.
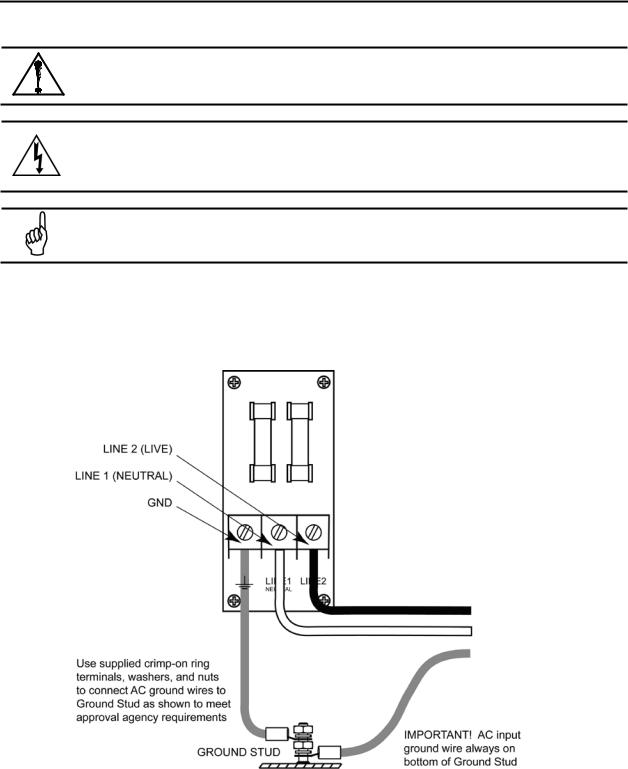
Locate the AC input terminals and ground stud on the inside of the monitor. Secure the incoming AC power neutral (white/blue) and live (black/brown) wires to the LINE 1 and LINE 2 terminals.
Using the supplied crimp-on ring terminals, washers, and nuts, connect the incoming AC power ground wire (green) to the monitor’s AC input ground stud, and then install a separate wire between the ground stud and the GND terminal.
WARNING: Electrical installation should be performed by a certified electrician, and must comply with all applicable NEC/CEC and local electrical safety codes.
P/N: 3015-5074 Rev 11 |
13 |
Multi-Zone Gas Monitors
WARNING: Copper conductors for connection to supply mains must be made in accordance with NEC/CEC and local codes.
WARNING: The AC power ground wire must first be connected to the monitor’s ground
stud. Under no circumstances should this monitor be operated without a protective ground. Doing so poses a potential shock hazard, and is also a violation of electrical safety standards applicable to this type of equipment.
IMPORTANT: Drilling holes in the MZ enclosure may damage the unit and will void the warranty. Please use the knockouts provided for electrical connections.
A switch or circuit breaker rated 1.0 A, 250 VAC must be attached to the monitor’s AC power leads. This
switch must also be located in close proximity to the monitor, and be in easy reach of the operator. This switch should also be clearly marked as the monitor’s main AC disconnect device. The circuit breaker or switch must disconnect all current-carrying conductors (i.e., live and neutral).
Figure 2-5. Multi-Zone AC Input Power and Ground Connections
14 |
P/N: 3015-5074 Rev 11 |
Multi-Zone Gas Monitors
2.5. Connecting Communications Devices
2.5.1.Remote Display Module (RD) Connection
The MZ is connected to the optional RD using a shielded twisted pair instrument cable. The maximum distance between the farthest MZ and RD is 4500 feet.
Use any of the remaining service knockouts to gain access to the interior of the monitor. The RS-485 communications wiring between the MZ and RD must be connected in the following manner:
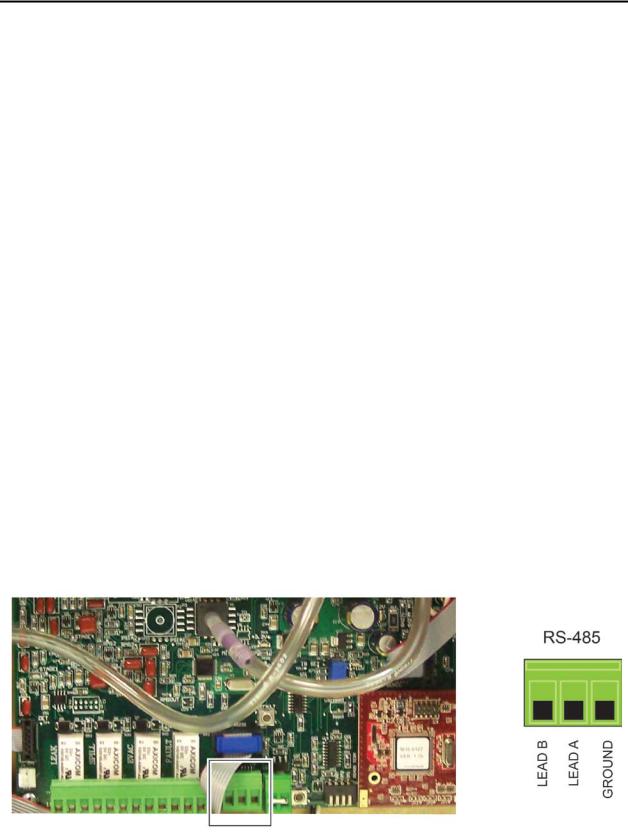
1.Locate the RS-485 connector in the MZ (see Figure 2-3 on page 13).
2.Connect one lead of a twisted shielded pair to the “B” connection point. Note the wire color.
3.Connect the second wire to the “A” connection point. Note the wire color.
4.Connect the ground to the “GND” connection point.
5.Locate the RS-485 connector marked “TO MONITORS” in the RD (see this topic in the RD manual). This connector is located on the bottom of the RD PC board, second from the right.
6.Run the wire to the RD and connect the twisted shielded pair to the RS-485 “TO MONITORS” connector using the same color code as used on the MZ.
2.5.2.Integrating with Building Management Systems
The MZ may be connected directly to a Building Management System using a shielded twisted pair cable. The cable from the Building Management System is connected to the RS-485 connector inside the MZ
monitor. MODBUS RTU is the standard communications protocol.
Use any of the remaining service knockouts to gain access to the interior of the monitor. Locate the RS-485 connector and remove it from the circuit board. Secure the wire leads to the connector orienting them as
shown in the diagram below. Check to make sure that the polarity matches the wiring to the Building Management System. When you are through securing the connections, carefully plug the connector back onto the circuit board.
2.5.3.Larger Integrated Systems
You may also connect the MZ monitor to a Building Management System through a Remote Display. In this case, first connect the MZ to the RD as described above. Then, follow the instructions in the
Communications Connections section of the RD manual for information on how to connect the RD to a Building Management System.
Figure 2-6. RS-485 Connector
P/N: 3015-5074 Rev 11 |
15 |
Multi-Zone Gas Monitors
2.5.4.Changing Terminator Switch Settings
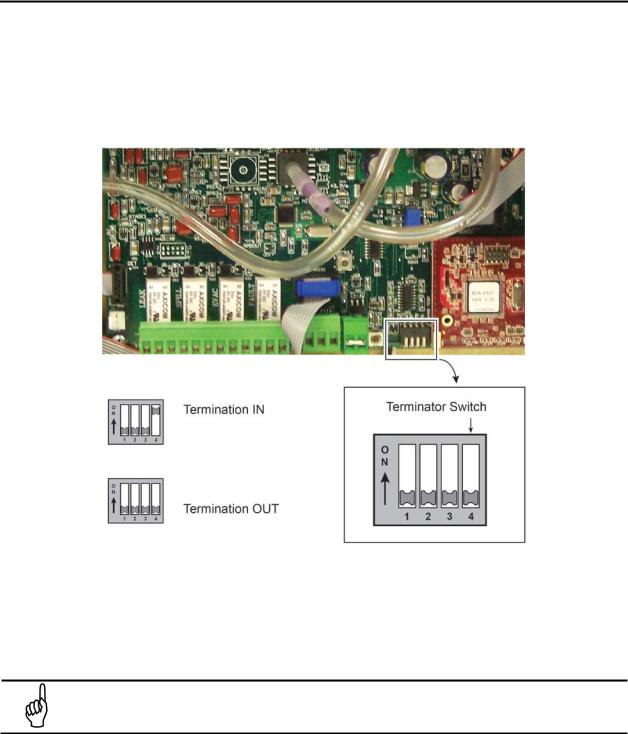
The terminator switch is shipped from the factory in the “OUT” position (no termination). This is the correct
setting if the MZ is to be installed in the middle of a network. If the MZ monitor is connected as a single device or if it is the last device on the network chain, the terminator must be moved to the “IN” position.
Locate switch #4 and determine its position. If it must be moved, slide the switch to the appropriate position. (Note that switches 1-3 are for service use.)
Figure 2-7. Termination Switches
2.5.5.Personal Computer
The MZ may be connected to a personal computer using the RS-232 interface on the left side of
the enclosure. Software will be provided upon request or as a download from the Bacharach website at http://www.MyBacharach.com/downloads.htm.
NOTE: Refer to the “PC Software” section (section 2.8 on page 18) for details.
16 |
P/N: 3015-5074 Rev 11 |

Multi-Zone Gas Monitors
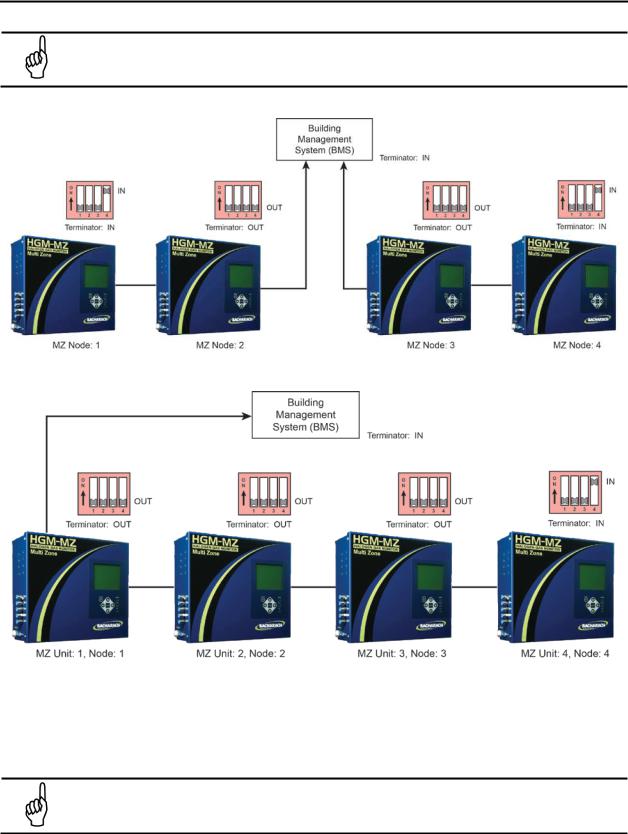
2.6. Terminating Multiple Monitors
Figure 2-8. Termination Settings for a Network of Multiple Monitors and a Remote Display
NOTE: For multiple MZs with Remote Display, the last MZ or RD on either end of the network must have its terminator in the “IN” position, and all other units must have their
terminators in the “OUT” position.
NOTE: For multiple MZs with Remote Display, the total length of the RS-485 cable cannot exceed 4500 feet (1372 m). (Use instrument cable 20 gauge multi-strand shielded and twisted pair – similar or equal to Belden cable #8762.)
2.7. Connecting to a Building Management System
The MZ monitor may be connected to a Building Management System via the RS-485 connector. The node address on each MZ monitor may be set from 1 to 15 in order to identify itself to the Building Management System.
NOTE: Building Management Systems set to a 0 or 1 address both respond to messages from the RD as address 1, therefore you should not have a unit set to 0 and another set to
1 on the same network.
If the MZ network is connected directly to a Building Management System it may not be connected to the RD. However, the RD has two communications ports, an “upstream” port (labeled BMS) and a “downstream” port (labeled TO MONITORS). A BMS node may be connected to the upstream RD port while
the downstream RD port talks to the MZ monitors. In this case, the BMS is talking “through” the RD to the MZ monitors, but not physically on the MZ/RD network.
P/N: 3015-5074 Rev 11 |
17 |
Multi-Zone Gas Monitors
NOTE: User must have two (2) dedicated ports to successfully complete the required setup.
Figure 2-9. Termination Settings for Multiple Monitors Connected to a BMS (Two Trunks)
Figure 2-10. Termination Settings for Multiple Monitors Connected to a BMS (Daisy Chain)
2.8. PC Software
2.8.1.Operation
NOTE: The MZ is compatible with HGM300 PC software version 1.52 and higher.
However, calibration data can only be edited on the front panel of the MZ, not through the PC software or RDM units.
18 |
P/N: 3015-5074 Rev 11 |
Multi-Zone Gas Monitors
NOTE: The PC software is not compatible with 64-bit (or newer) computers.
NOTE: The PC software uses COM1 by default. Therefore, the interface cable should be
connected to the port configured as COM1 on the PC. Also, no other software drivers or devices in the computer may control COM1 when the MZ software is in use. Alternatively, COM2 (for example) may be used by adding a space and the number 2 to the command
line as follows:
C:\pc2HGM.exe 2
When using a USB to serial converter, be sure it has been mapped to COM1 or COM2.
The connection is made through a standard “straight through” serial port connection. A three-wire connection is used (RXD, TXD, and GND). No hardware flow control is used. The MZ software automatically configures COM1 to match the MZ RS-232
communications parameters.
NOTE: Occasionally, the laptop connection will not connect properly and only two beeps
are heard and the program times out. To resolve this, disconnect the RS-232 cable and cycle power on the MZ and the laptop. After both are operational, connect the RS-232 cable and start the software program.
1.Apply power to MZ monitor and allow it to warm up. Note that on CO2 models, a “Clearing Purge Line” message is displayed for approximately 2.5 minutes before warm up begins.
2.Connect RS-232 interface cable to the PC and RS-232 port on the MZ monitor.
3.Insert software disk into the PC.
4.Open the MZ software using Windows Explorer.
5.Upon start up, the program will immediately attempt to download data from the MZ, as indicated by several beeps.
Navigate using your PC keyboard:
•Use the up, down, left, and right arrow keys to navigate through the screen options.
•Use the Enter key to select options.
•Use the Esc key to go back one step.
6.Go to EDIT. From the EDIT Menu, select SYSTEM. The monitors’ LOCATION becomes highlighted. Press Enter to move to the TAG area. Use the Backspace key to remove the existing
tag. Enter a new tag. Press Enter to return to LOCATION. Select the next item to be addressed. Note that you cannot change the “SN” or “FIRMWARE” items. Press the Esc key to return to the menu bar.
7.Go to EDIT. From the EDIT Menu, select ZONES. Select a specific zone to identify and set parameters. When REFRIGERANT is selected (Halogen Monitor), scroll through the gas library to locate and select the gas type for that zone.
8.Setting the Alarms: Select EVAC LEVEL. Use the Backspace key to clear previous setting. Type in the new PPM level. Use the same method to set the spill level and leak level.
9.To close or bypass a zone: Set the DISTANCE to 0 feet.
P/N: 3015-5074 Rev 11 |
19 |

Multi-Zone Gas Monitors
|
IMPORTANT: When a modified parameter (zone, system, or calibration) is sent to the MZ |
|
monitor, please wait for the computer software to indicate that the download is complete |
|
before continuing with any further edits. |
2.8.2. |
Saving and Sending Programs |
• |
When saving to your computer, the program will automatically add “.cfg” to the filename you have |
|
entered. |
• |
To send a saved program to the MZ, open the program and connect the PC to the MZ. From the |
|
monitor, select SEND SETUP and press Enter. The saved program will be sent to the MZ. |
2.8.3. |
Trend Data |
|
|
|
NOTE: Creating a trend data file must be done while connected to the MZ. |
From the computer, select GET TREND DATA. Select the zone that you want to trend and press Enter. The
trend data will appear in a list format. Press Enter again to access the file name screen. Type the file name in for that particular zone. Press Enter. The file will be saved as a text file that can be converted to an Excel file or printed as is.
NOTE: The TREND file must be saved zone by zone, with a filename per zone.
2.8.4.Converting the TREND Text File to a Microsoft Excel File
Open Excel and the desired file. Select “Delimited” format and “Space” as the delimiter. Select “General” as the column data format. The text file will display as an Excel file. When saving, change the file name
extension to “.xls”. Comments or notes may be added to this file as needed and saved.
2.8.5.Saving and Printing Screens and Logs
Open the software while connected to the MZ. After the software receives the program, open the desired screen (e.g., software screen, alarm log, fault log, diagnostic screen, etc.). Use the Alt and Print Screen key combination on the PC keyboard to capture the image and paste it into a Word document. Save and print.
2.8.6.USB Type Laptops
Some laptops have USB ports and no RS-232 9-pin ports. A USB-to-serial converter or PCMCIA-to-serial converter will be required if a PCMCIA slot is available You will be required to purchase a PCMCIA card
that provides an RS-232 output. This is necessary for Windows Vista and higher versions. We recommend the PCMCIA card manufactured by:
SEALEVEL SYSTEMS, INC. 155 TECHNOLOGY PLACE P. O. BOX 830
LIBERTY, SC 29657 PHONE – 864-843-4343 www.sealevel.com
Reference part numbers 2105R USB-to-RS232 or PC-SIO-232 PCMCIA card. A “straight through” RS232 cable and a DB25-to-DB9 adapter will be required to connect the laptop to the HGM-MZ.
20 |
P/N: 3015-5074 Rev 11 |
 Loading...
Loading...