Page 1
DSBV-D
Motherboard
Page 2

E3043
Second Edition V2
February 2007
Copyright © 2007 ASUSTeK COMPUTER INC. All Rights Reserved.
No part of this manual, including the products and software described in it, may be reproduced, transmitted,
transcribed, stored in a retrieval system, or translated into any language in any form or by any means,
except documentation kept by the purchaser for backup purposes, without the express written permission
of ASUSTeK COMPUTER INC. (“ASUS”).
Product warranty or service will not be extended if: (1) the product is repaired, modied or altered, unless
such repair, modication of alteration is authorized in writing by ASUS; or (2) the serial number of the
product is defaced or missing.
ASUS PROVIDES THIS MANUAL “AS IS” WITHOUT WARRANTY OF ANY KIND, EITHER EXPRESS
OR IMPLIED, INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO THE IMPLIED WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF
MERCHANTABILITY OR FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. IN NO EVENT SHALL ASUS, ITS
DIRECTORS, OFFICERS, EMPLOYEES OR AGENTS BE LIABLE FOR ANY INDIRECT, SPECIAL,
INCIDENTAL, OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES (INCLUDING DAMAGES FOR LOSS OF PROFITS,
LOSS OF BUSINESS, LOSS OF USE OR DATA, INTERRUPTION OF BUSINESS AND THE LIKE),
EVEN IF ASUS HAS BEEN ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGES ARISING FROM ANY
DEFECT OR ERROR IN THIS MANUAL OR PRODUCT.
SPECIFICATIONS AND INFORMATION CONTAINED IN THIS MANUAL ARE FURNISHED FOR
INFORMATIONAL USE ONLY, AND ARE SUBJECT TO CHANGE AT ANY TIME WITHOUT NOTICE, AND
SHOULD NOT BE CONSTRUED AS A COMMITMENT BY ASUS. ASUS ASSUMES NO RESPONSIBILITY
OR LIABILITY FOR ANY ERRORS OR INACCURACIES THAT MAY APPEAR IN THIS MANUAL,
INCLUDING THE PRODUCTS AND SOFTWARE DESCRIBED IN IT.
Products and corporate names appearing in this manual may or may not be registered trademarks or
copyrights of their respective companies, and are used only for identication or explanation and to the
owners’ benet, without intent to infringe.
ii
Page 3

Contents
Notices ........................................................................................................ vii
Safety information .................................................................................... viii
About this guide ......................................................................................... ix
Typography .................................................................................................. x
DSBV-D specications summary .............................................................. xi
Chapter 1: Product introduction
1.1 Welcome! ...................................................................................... 1-1
1.2 Package contents .........................................................................
1.3 Serial number label ......................................................................
1.4 Special features ............................................................................
1.4.1 Product highlights ...........................................................
1.4.2 Innovative ASUS features ...............................................
Chapter 2: Hardware information
2.1 Before you proceed ..................................................................... 2-1
2.2 Motherboard overview .................................................................
2.2.1 Placement direction ........................................................
2.2.2 Screw holes ....................................................................
2.2.3 Support kits for the motherboard ....................................
2.2.4 Motherboard layouts .......................................................
2.2.5 Layout contents ...............................................................
2.3 Central Processing Unit (CPU) ...................................................
2.3.1 Installing the CPU ...........................................................
2.3.2 Installing the CPU heatsink and fan ..............................
2.4 System memory .........................................................................
2.4.1 Overview .......................................................................
2.4.2 Memory congurations ..................................................
2.4.3 Installing a DIMM ..........................................................
2.4.4 Removing a DIMM ........................................................
2.4.5 Installing the optional MemCool FB-DIMM fan .............
2.4.6 Uninstalling the optional MemCool FB-DIMM fan .........
2.5 Expansion slots ..........................................................................
2.5.1 Installing an expansion card .........................................
2.5.2 Conguring an expansion card .....................................
2.5.3 Interrupt assignments ...................................................
2.5.4 PCI-X slots ....................................................................
2.5.5 DDR2 SO-DIMM socket ...............................................
2.5.6 PCI Express x8 slot (x4 link) .........................................
2.5.7 PCI Express x16 slot (x8 link) .......................................
2.6 Jumpers ......................................................................................
1-1
1-1
1-2
1-2
1-4
2-2
2-2
2-2
2-3
2-6
2-7
2-9
2-9
2-12
2-14
2-14
2-14
2-16
2-16
2-17
2-19
2-20
2-20
2-20
2-21
2-22
2-22
2-23
2-23
2-24
iii
Page 4

Contents
2.7 Connectors ................................................................................. 2-29
2.7.1 Rear panel connectors ..................................................
2.7.2 Internal connectors .......................................................
Chapter 3: Powering up
3.1 Starting up for the rst time ........................................................ 3-1
3.2 Turning off the computer .............................................................
3.2.1 Using the OS shut down function ....................................
3.2.2 Using the dual function power switch ..............................
Chapter 4: BIOS setup
4.1 Managing and updating your BIOS ............................................ 4-1
4.1.1 Creating a bootable oppy disk .......................................
4.1.2 Updating the BIOS using the Phoenix
Phlash16 Utility ............................................................... 4-2
4.1.3 ASUS CrashFree BIOS 2 utility ......................................
4.1.4 ASUS Update utility ........................................................
4.2 BIOS setup program ....................................................................
4.2.1 BIOS menu screen ..........................................................
4.2.2 Menu bar .........................................................................
4.2.3 Legend bar ....................................................................
4.2.4 Menu items ...................................................................
4.2.5 Sub-menu items ............................................................
4.2.6 Conguration elds .......................................................
4.2.7 Pop-up window ..............................................................
4.2.8 General help ..................................................................
4.3 Main menu ..................................................................................
4.3.1 System Date ................................................................
4.3.2 System Time .................................................................
4.3.3 Floppy A ........................................................................
4.3.4 IDE Conguration ..........................................................
4.3.5 IDE Channel 0 Master/Slave;
SATA Port 1/2/3/4 .......................................................... 4-15
4.3.6 System Information .......................................................
4.4 Advanced menu .........................................................................
4.4.1 Advanced Processor Options .......................................
4.4.2 Chipset Conguration ...................................................
4.4.3 PCI Conguration ..........................................................
4.4.4 ICH USB Control Sub-Menu .........................................
2-29
2-30
3-2
3-2
3-2
4-1
4-3
4-5
4-8
4-9
4-9
4-10
4-10
4-10
4-10
4-11
4-11
4-12
4-12
4-12
4-12
4-13
4-16
4-18
4-18
4-24
4-26
4-28
iv
Page 5

Contents
4.4.5 Peripheral Devices Conguration ................................. 4-29
4.4.6 ACPI Conguration .......................................................
4.4.7 Power On Conguration ................................................
4.4.8 Hardware Monitor .........................................................
4.5 Server menu ...............................................................................
4.5.1 Console Redirection ......................................................
4.5.2 DMI Event Logging .......................................................
4.6 Security menu ............................................................................
4.7 Boot menu ..................................................................................
4.7.1 Boot Device Priority ......................................................
4.7.2 Boot Features ...............................................................
4.8 Exit menu ....................................................................................
Chapter 5: RAID conguration
5.1 Setting up RAID ............................................................................ 5-1
5.1.1 RAID denitions ..............................................................
5.1.2 Installing hard disk drives ................................................
5.1.3 Setting the RAID item in BIOS ........................................
5.1.4 RAID conguration utilities ..............................................
5.2 LSI Logic Embedded SATA RAID Setup Utility ..........................
5.2.1 Creating a RAID 0 or RAID 1 set ....................................
5.2.2 Creating a RAID 10 set .................................................
5.2.3 Adding or viewing a RAID conguration .......................
5.2.4 Initializing the logical drives ..........................................
5.2.5 Rebuilding failed drives .................................................
5.2.6 Checking the drives for data consistency .....................
5.2.7 Deleting a RAID conguration .......................................
5.2.8 Selecting the boot drive from a RAID set ......................
5.2.9 Enabling the WriteCache ..............................................
®
5.3 Intel
5.4 Global Array Manager ................................................................
Matrix Storage Manager Option ROM Utility ................. 5-30
5.3.1 Creating a RAID 0 set (Stripe) ......................................
5.3.2 Creating a RAID 1 set (Mirror) ......................................
5.3.3 Creating a RAID 10 set (Stripe + Mirror) .......................
5.3.4 Creating a RAID 5 set (Parity) ......................................
5.3.5 Deleting a RAID set ......................................................
5.3.6 Resetting disks to Non-RAID ........................................
5.3.7 Exiting the Intel
®
Matrix Storage Manager .................... 5-37
4-31
4-32
4-33
4-38
4-38
4-40
4-41
4-43
4-43
4-44
4-45
5-1
5-2
5-2
5-2
5-3
5-4
5-10
5-14
5-17
5-22
5-24
5-27
5-28
5-29
5-31
5-33
5-34
5-35
5-36
5-37
5-38
v
Page 6

Contents
Chapter 6: Driver installation
6.1 RAID driver installation ............................................................... 6-1
6.1.1 Creating a RAID driver disk ............................................
6.1.2 Installing the RAID controller driver ................................
6.2 Intel chipset software installation ............................................
6.3 LAN driver installation ...............................................................
6.3.1 Windows 2000/Server 2003 ..........................................
6.3.2 Red Hat/SuSE Linux .....................................................
6.4 VGA driver installation
6.4.1 Windows 2000/Server 2003 ..........................................
6.5 Management applications and utilities installation ................
6.5.1 Running the support CD ...............................................
6.5.2 Drivers menu .................................................................
6.5.3 Management Software menu ........................................
6.5.4 Utilities menu ................................................................
6.5.5 Contact information .......................................................
Appendix: Block diagrams
A.1 DSBV-D block diagram ................................................................A-1
A.2 PHLASH16.EXE and memory managers ....................................
............................................................... 6-18
6-1
6-2
6-11
6-14
6-14
6-17
6-18
6-21
6-21
6-21
6-22
6-22
6-22
A-2
vi
Page 7

Notices
Federal Communications Commission Statement
This device complies with Part 15 of the FCC Rules. Operation is subject to the
following two conditions:
•
This device may not cause harmful interference, and
•
This device must accept any interference received including interference that
may cause undesired operation.
This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a
Class B digital device, pursuant to Part 15 of the FCC Rules. These limits are
designed to provide reasonable protection against harmful interference in a
residential installation. This equipment generates, uses and can radiate radio
frequency energy and, if not installed and used in accordance with manufacturer’
s instructions, may cause harmful interference to radio communications. However,
there is no guarantee that interference will not occur in a particular installation. If
this equipment does cause harmful interference to radio or television reception,
which can be determined by turning the equipment off and on, the user is
encouraged to try to correct the interference by one or more of the following
measures:
•
Reorient or relocate the receiving antenna.
•
Increase the separation between the equipment and receiver.
•
Connect the equipment to an outlet on a circuit different from that to which the
receiver is connected.
•
Consult the dealer or an experienced radio/TV technician for help.
The use of shielded cables for connection of the monitor to the graphics card is
required to assure compliance with FCC regulations. Changes or modications
to this unit not expressly approved by the party responsible for compliance could
void the user’s authority to operate this equipment.
Canadian Department of Communications Statement
This digital apparatus does not exceed the Class B limits for radio noise emissions
from digital apparatus set out in the Radio Interference Regulations of the
Canadian Department of Communications.
This class B digital apparatus complies with Canadian ICES-003.
vii
Page 8

Safety information
Electrical safety
•
To prevent electrical shock hazard, disconnect the power cable from the
electrical outlet before relocating the system.
•
When adding or removing devices to or from the system, ensure that the
power cables for the devices are unplugged before the signal cables are
connected. If possible, disconnect all power cables from the existing system
before you add a device.
•
Before connecting or removing signal cables from the motherboard, ensure
that all power cables are unplugged.
•
Seek professional assistance before using an adapter or extension cord.
These devices could interrupt the grounding circuit.
•
Make sure that your power supply is set to the correct voltage in your area.
If you are not sure about the voltage of the electrical outlet you are using,
contact your local power company.
•
If the power supply is broken, do not try to x it by yourself. Contact a
qualied service technician or your retailer.
Operation safety
•
Before installing the motherboard and adding devices on it, carefully read all
the manuals that came with the package.
•
Before using the product, make sure all cables are correctly connected and the
power cables are not damaged. If you detect any damage, contact your dealer
immediately.
•
To avoid short circuits, keep paper clips, screws, and staples away from
connectors, slots, sockets and circuitry.
•
Avoid dust, humidity, and temperature extremes. Do not place the product in
any area where it may become wet.
•
Place the product on a stable surface.
•
If you encounter technical problems with the product, contact a qualied
service technician or your retailer.
viii
Page 9

About this guide
This user guide contains the information you need when installing and conguring
the motherboard.
How this guide is organized
This user guide contains the following parts:
• Chapter 1: Product introduction
This chapter describes the features of the motherboard and the new
technologies it supports.
• Chapter 2: Hardware information
This chapter lists the hardware setup procedures that you have to perform
when installing system components. It includes description of the switches,
jumpers, and connectors on the motherboard.
• Chapter 3: Powering up
This chapter describes the power up sequence and ways of shutting down
the system.
• Chapter 4: BIOS setup
This chapter tells how to change system settings through the BIOS Setup
menus. Detailed descriptions of the BIOS parameters are also provided.
• Chapter 5: RAID conguration
This chapter provides instructions for setting up, creating, and conguring
RAID sets using the available utilities.
• Chapter 6: Driver installation
This chapter provides instructions for installing the necessary drivers for
different system components.
• Appendix: Reference information
This appendix includes additional information that you may refer to when
conguring the motherboard.
Where to nd more information
Refer to the following sources for additional information and for product and
software updates.
1. ASUS websites
The ASUS website provides updated information on ASUS hardware and
software products. Refer to the ASUS contact information.
2. Optional documentation
Your product package may include optional documentation, such as warranty
yers, that may have been added by your dealer. These documents are not
part of the standard package.
ix
Page 10

Conventions used in this guide
To make sure that you perform certain tasks properly, take note of the following
symbols used throughout this manual.
DANGER/WARNING
when trying to complete a task.
CAUTION
when trying to complete a task.
IMPORTANT
task.
NOTE:
task.
: Information to prevent damage to the components
: Instructions that you MUST follow to complete a
Tips and additional information to help you complete a
: Information to prevent injury to yourself
Typography
Bold text Indicates a menu or an item to select.
Italics Used to emphasize a word or a phrase.
<Key> Keys enclosed in the less-than and greater than sign means that you must press the
enclosed key.
Example: <Enter> means that you must press
the Enter or Return key.
<Key1+Key2+Key3> If you must press two or more keys
simultaneously, the key names are linked with
a plus sign (+).
Example: <Ctrl+Alt+D>
Command
exactly as shown, then supply the required
item or value enclosed in brackets.
Example: At the DOS prompt, type the
command line:
Means that you must type the command
format A:/S
x
Page 11
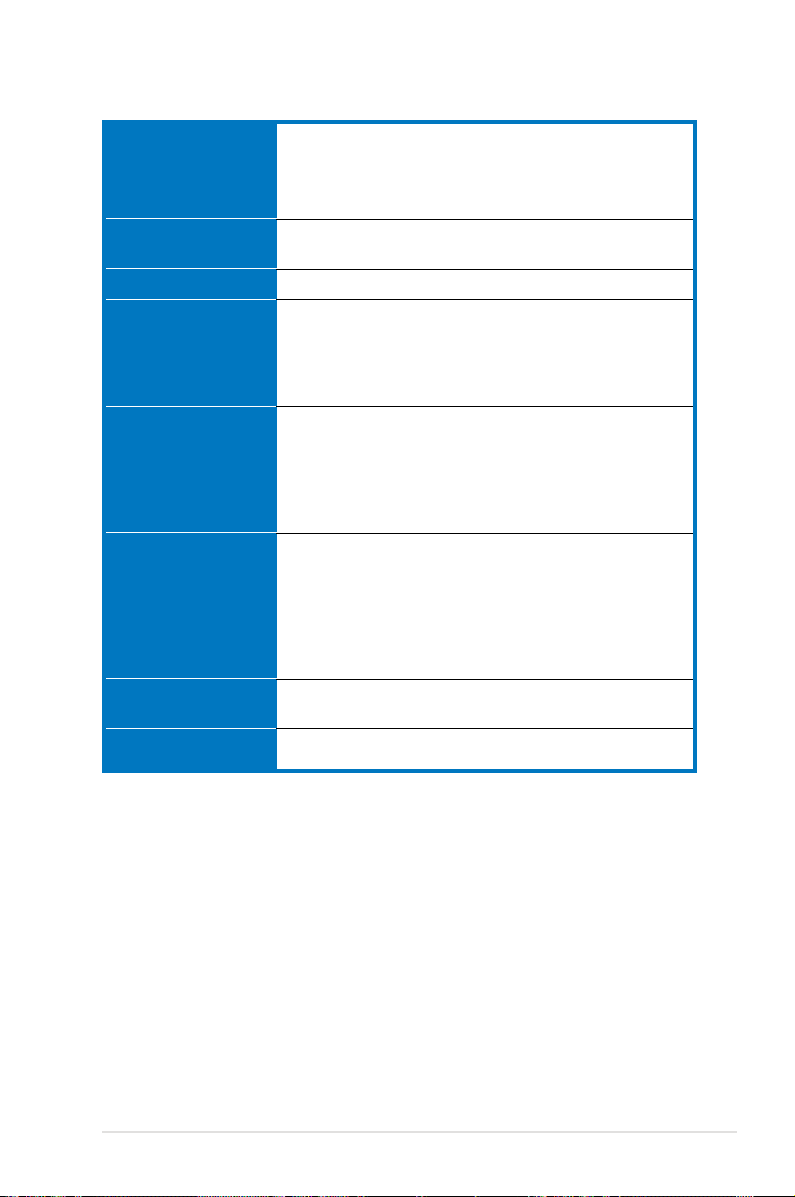
DSBV-D specications summary
CPU
Chipset
Front Side Bus
Memory
Expansion slots
Storage
Discrete graphics
LAN
Dual LGA771 sockets for Intel® Xeon™ Dual Core processors
Supports Intel® Extended Memory 64Technology (EM64T)
Supports Intel® Hyper-Threading Technology (5000 series
support H.T.; 5100/5300 series DO NOT support H.T.)
MCH : Intel® 5000V
ICH : Intel® 6321ESB
1333/1066/667 MHz
Dual-channel memory architecture
6 x 240-pin FB-DIMM sockets support registered ECC
fully buffered DDR2-533/DDR2-667 memory modules
with Advanced Memory Buffer (AMB chip)
Supports 256 MB up to 24 GB system memory
1 x PCI Express™ x16 slot (x8 link)
1 x PCI Express™ x8 slot (x4 link)
3 x PCI-X 133/100 MHz
1 x PCI 33 MHz/32-bit/5V slot
1 x DDR2 SO-DIMM socket for ASUS server management
board 3 series (ASMB3)
Intel® 6321ESB supports:
- 1 x Ultra DMA 100/66/33 channel
- 6 x SATA II (300 MB/s)
- Intel® Matrix Storage with RAID 0, RAID 1, RAID
0+1, and RAID 5 conguration
- LSI MegaRAID controller with RAID 0, RAID 1, and
RAID 0+1 conguration
ATI® ES1000 PCI display controller
- Supports 32 MB display memory
Intel® 82563EB Network Connection (Dual-port)
- Supports Intel I/O Acceleration Technology (IOAT)
(continued on the next page)
xi
Page 12
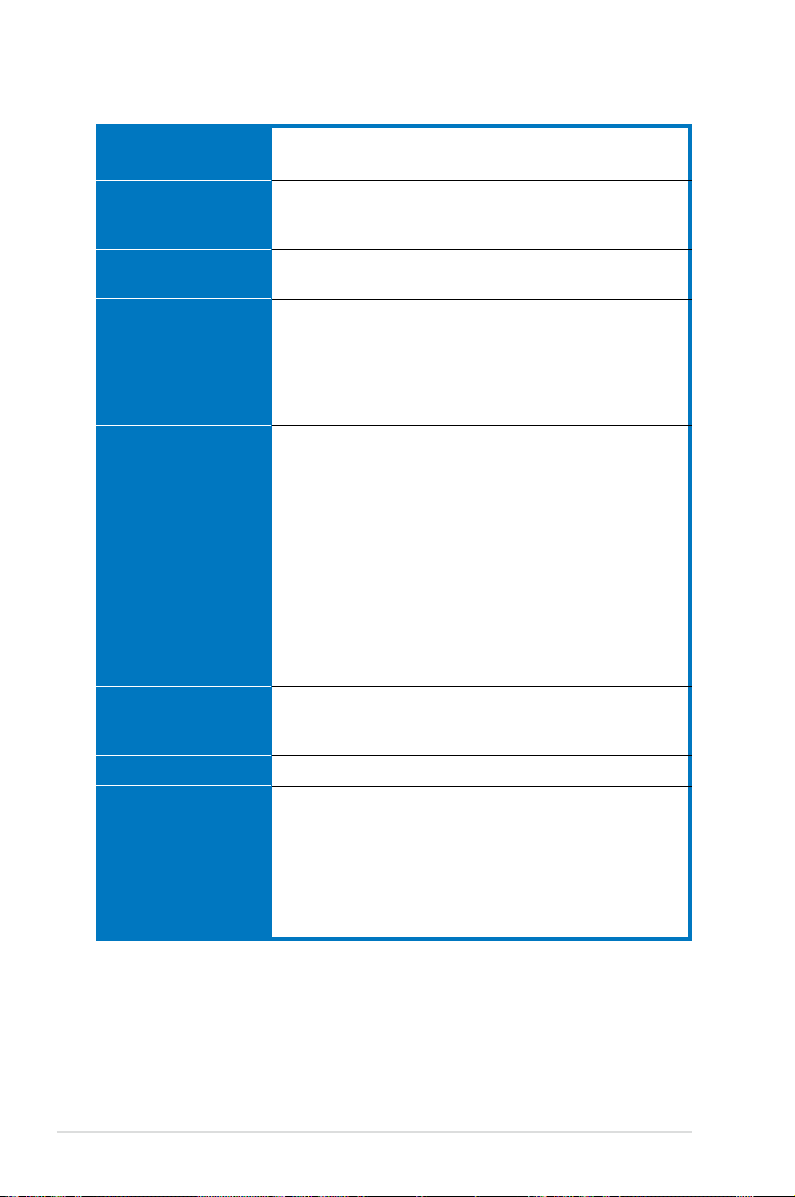
DSBV-D specications summary
USB
Special features
BIOS features
Rear panel
Internal connectors
Power requirement
Form factor
Support CD contents
Intel® 6321ESB supports:
- 4 USB 2.0/1.1 ports (2 on the rear panel, 2 on the front panel)
ASUS Smart Fan Control
ASUS Smart Fan2 Control
ASUS CrashFree BIOS 2
PHOENIX BIOS, 8 Mb FWH, Green, PnP, DMI, WfM2.0,
ACPI 2.0a, SMBIOS 2.3
1 x PS/2 keyboard port (purple)
1 x PS/2 mouse port (green)
2 x USB 2.0 ports
1 x Serial port
1 x VGA port
2 x LAN (RJ-45) ports
1 x Floppy disk drive connector
1 x IDE connector
6 x Serial ATA connectors
1 x Hard disk activity LED connector (4-pin HDLED1)
1 x USB connector (10-1 pin USB34)
1 x Serial port connector (10-1 pin COM2)
1 x Power supply SMBus connector (5-pin PSUMB1)
1 x Parallel port connector (26-1 pin LPT1)
1 x System panel connector (20-1 pin PANEL1)
1 x Auxiliary panel connector (20-2 pin AUX-PANEL1)
SSI power connectors (24-pin, 8-pin, and 4-pin)
CPU (x2), rear (x2), front (x4), and FB-DIMM (x1) fan
connectors
SSI power supply (with 24-pin/4-pin/8-pin 12V plugs)
for LGA771-socket Intel® Xeon Dual Core processors
(Bensley-VS platform)
SSI CEB form factor: 12 in x 10.5 in (30.5 cm x 26.7 cm)
Device drivers
ASUS Update Utility
ASUS Server Web-based Management (ASWM)
ADOBE Acrobat Reader
ASUS Screen Saver
ASUS Flash utility under DOS
*Specications are subject to change without notice.
xii
Page 13

This chapter describes the motherboard
features and the new technologies
it supports.
Product
introduction
1
Page 14

Chapter summary
1
1.1 Welcome! ...................................................................................... 1-1
1.2 Package contents .........................................................................
1.3 Serial number label ......................................................................
1.4 Special features ............................................................................
1-1
1-1
1-2
ASUS DSBV-D
Page 15

1.1 Welcome!
Thank you for buying an ASUS® DSBV-D motherboard!
The motherboard delivers a host of new features and latest technologies, making it
another standout in the long line of ASUS quality motherboards!
Before you start installing the motherboard, and hardware devices on it, check the
items in your package with the list below.
1.2 Package contents
Check your motherboard package for the following items.
Cables
Accessories
Application CDs Support CD 1 1
Documentation User Guide 1 1
Packing Qty. 3pcs per Caton 10pcs per Carton
SATA Signal Cable 6 -SATA Power Cable 3 -2-in-1 (IDE&Floppy) Cable Set 1 -IO Shield 1 1
CEK Spring 2 2
If any of the above items is damaged or missing, contact your retailer.
DSBV-D Retail Pack DSBV-D Bulk Pack
1.3 Serial number label
Before requesting support from the ASUS Technical Support team, you must
take note of the motherboard’s serial number containing 12 characters such as
xxM0Axxxxxxx. See the gure below.
With the correct serial number of the product, ASUS Technical Support team
members can then offer a quicker and satisfying solution to your problems.
DSBV-D
xxM0Axxxxxxx
ASUS DSBV-D 1-1
Page 16
1.4 Special features
1.4.1 Product highlights
Latest processor technology
The motherboard comes with two LGA-771 sockets that support Dual-Core
Intel® Xeon™ processors with 1333/1066/667 MHz Front Side Bus (FSB).
Dual-core processors contain two physical CPU cores to meet demands for
more powerful processing. Intel® Xeon™ processors incorporate the Intel®
Hyper-Threading Technology and Extended Memory 64-bit Technology (EM64T).
The EM64T enables the support for 64-bit operation system, such as 64-bit
Windows® and Linux. See page 2-9 for details.
Intel®
5000V
and Intel® 6321ESB chipset
The Intel® 5000V Memory Controller Hub (MCH) and the Intel® 6321ESB provide
the vital interfaces for the motherboard.
The MCH provides the processor, dual-channel FB-DIMM memory support, and
PCI Express interfaces. The Intel® 6321ESB is a new generation server class I/O
controller hub that provides the interface for PCI 2.3, PCI Express, and PCIX.
Intel® EM64T
The motherboard supports Intel® processors with the Intel® EM64T (Extended
Memory 64 Technology). The Intel® EM64T feature allows your computer to run on
64-bit operating systems and access larger amounts of system memory for faster
and more efcient computing.
Enhanced Intel SpeedStep® Technology (EIST)
The Enhanced Intel SpeedStep® Technology (EIST) intelligently manages the
CPU resources by automatically adjusting the CPU voltage and core frequency
depending on the CPU loading and system speed or power requirement.
FB-DIMM memory support
This motherboard supports fully buffered DIMMs (FB-DIMMs), the latest memory
solution that extends memory capacity and provide high-speed, high-density
system memory peformance. FB-DIMMs use Advanced Memory Buffer (AMB)
chips that transmit signals between the memory modules and controllers with
improved signal integrity and reduced errors. See page 2-14 for details.
1-2 Chapter 1: Product introduction
Page 17
PCI Express™ interface
The motherboard fully supports PCI Express, the latest I/O interconnect technology
that speeds up the PCI bus. PCI Express features point-to-point serial
interconnections between devices and allows higher clockspeeds by carrying data
in packets. This high speed interface is software compatible with existing PCI or
PCI-X specications. See page 2-22 for details.
82563 LAN solution
The motherboard comes with a dual-port 82563EB network connection to provide a
total solution for your networking needs. See page 2-29 for the location of the LAN
ports. See section
2.6 Jumpers
for details on Gigabit LAN settings.
Serial ATA II technology
The motherboard supports the Serial ATA II 3 Gb/s technology through 6321ESB
Serial ATA interfaces. The Serial ATA II specication provides twice the bandwidth
of the current Serial ATA products with a host of new features, including Native
Command Queuing (NCQ), Power Management (PM) Implementation Algorithm,
and Hot Swap. Serial ATA allows thinner, more exible cables with lower pin count
and reduced voltage requirements. See page 2-31 for details.
USB 2.0 technology
The motherboard implements the Universal Serial Bus (USB) 2.0 specication,
dramatically increasing the connection speed from the 12 Mbps bandwidth on USB
1.1 to a fast 480 Mbps on USB 2.0. USB 2.0 is backward compatible with USB 1.1.
See pages 2-29 and 2-32 for details.
Temperature, fan, and voltage monitoring
The CPU temperature is monitored by the W83793G chip to prevent overheating
and damage. The system fan rotations per minute (RPM) is monitored for timely
failure detection. The chip monitors the voltage levels to ensure stable supply of
current for critical components. See page 4-29 for details.
Intel® IOAT
Intel® I/O Acceleration Technology (IOAT) is an integrated server platform I/O
solution that addresses all segments of the server I/O bottleneck problem using
TCP/IP without requiring any modication of existing or future applications.
Intel® IOAT is a system-wide solution that increases CPU efciency and delivers
data to/from applications faster than current server platforms.
ASUS DSBV-D 1-3
Page 18
1.4.2 Innovative ASUS features
CrashFree BIOS 2
This feature allows you to restore the original BIOS data from the support CD in
case when the BIOS codes and data are corrupted. This protection eliminates the
need to buy a replacement ROM chip. See page 4-3 for details.
ASUS Smart Fan technology
The ASUS Smart Fan technology smartly adjusts the fan speeds according to the
system loading to ensure quiet, cool, and efcient operation.
See page 4-31 for details.
ASUS MemCool FB-DIMM Fan Kit (optional)
With this optional fan kit, the platform gets optimal performance and the best
possible FB-DIMM thermal environment.
1-4 Chapter 1: Product introduction
Page 19

This chapter lists the hardware setup
procedures that you have to perform
when installing system components. It
includes description of the jumpers and
connectors on the motherboard.
Hardware
information
2
Page 20

Chapter summary
2
2.1 Before you proceed ..................................................................... 2-1
2.2 Motherboard overview .................................................................
2.3 Central Processing Unit (CPU) ...................................................
2.4 System memory .........................................................................
2.5 Expansion slots ..........................................................................
2.6 Jumpers ......................................................................................
2.7 Switch ..........................................................................................
2.8 Connectors .................................................................................
2-2
2-9
2-14
2-20
2-24
2-32
2-33
ASUS DSBV-D
Page 21
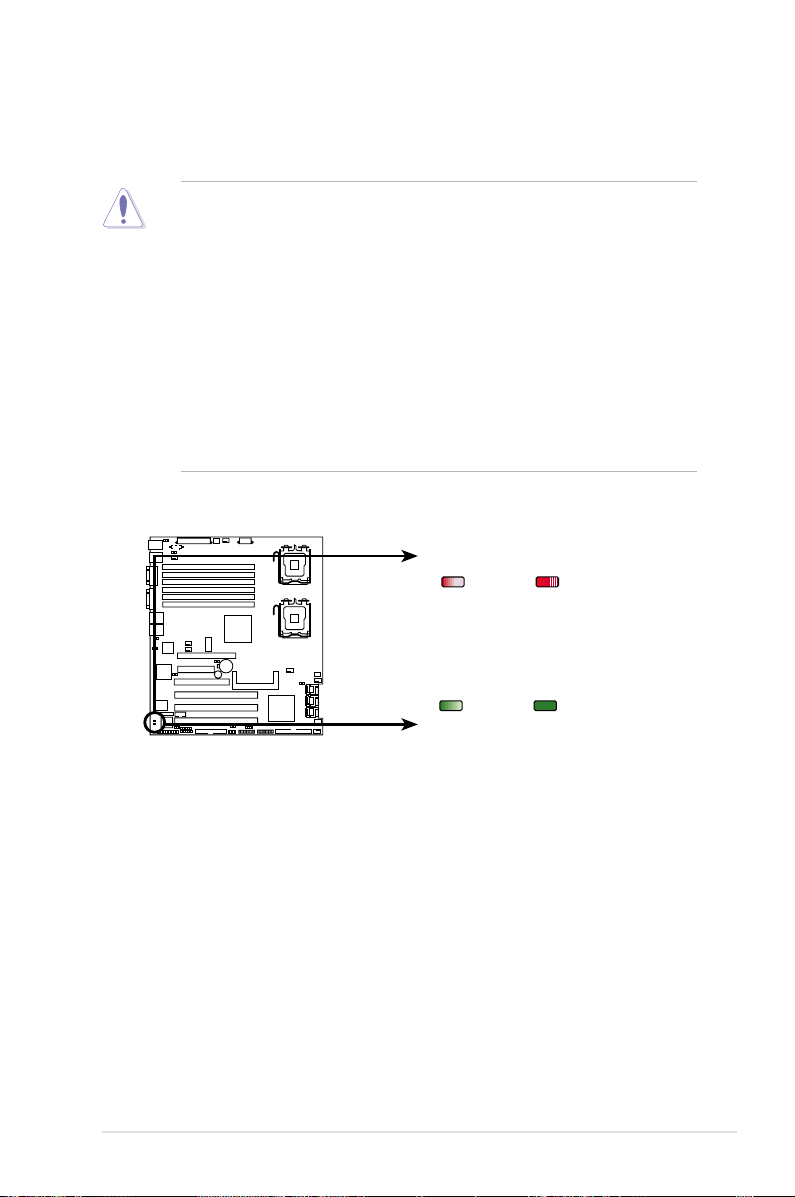
2.1 Before you proceed
DSBV-D
DSBV-D Onboard LED
ON OFF
+12V4LED1
ATX12V2
unplugged
ATX12V2
plugged
ON OFF
SB_PWR1
Standby
Power
Powered
Off
(red)
(green)
Take note of the following precautions before you install motherboard components
or change any motherboard settings.
• Unplug the power cord from the wall socket before touching any
component.
• Use a grounded wrist strap or touch a safely grounded object or
• Hold components by the edges to avoid touching the ICs on them.
• Whenever you uninstall any component, place it on a grounded
• Before you install or remove any component, ensure
Onboard LED
a metal object, such as the power supply case, before handling
components to avoid damaging them due to static electricity.
antistatic pad or in the bag that came with the component.
that the power supply is switched off or the power cord is detached from
the power supply. Failure to do so may cause severe damage to the
motherboard, peripherals, and/or components.
ASUS DSBV-D 2-1
Page 22
2.2 Motherboard overview
DSBV-D
Before you install the motherboard, study the conguration of your chassis to
ensure that the motherboard ts into it.
To optimize the motherboard features, we highly recommend that you install it in an
SSI EEB 3.61 compliant chassis.
Make sure to unplug the chassis power cord before installing or removing
the motherboard. Failure to do so can cause you physical injury and damage
motherboard components!
2.2.1 Placement direction
When installing the motherboard, make sure that you place it into the chassis in the
correct orientation. The edge with external ports goes to the rear part of the chassis
as indicated in the image below.
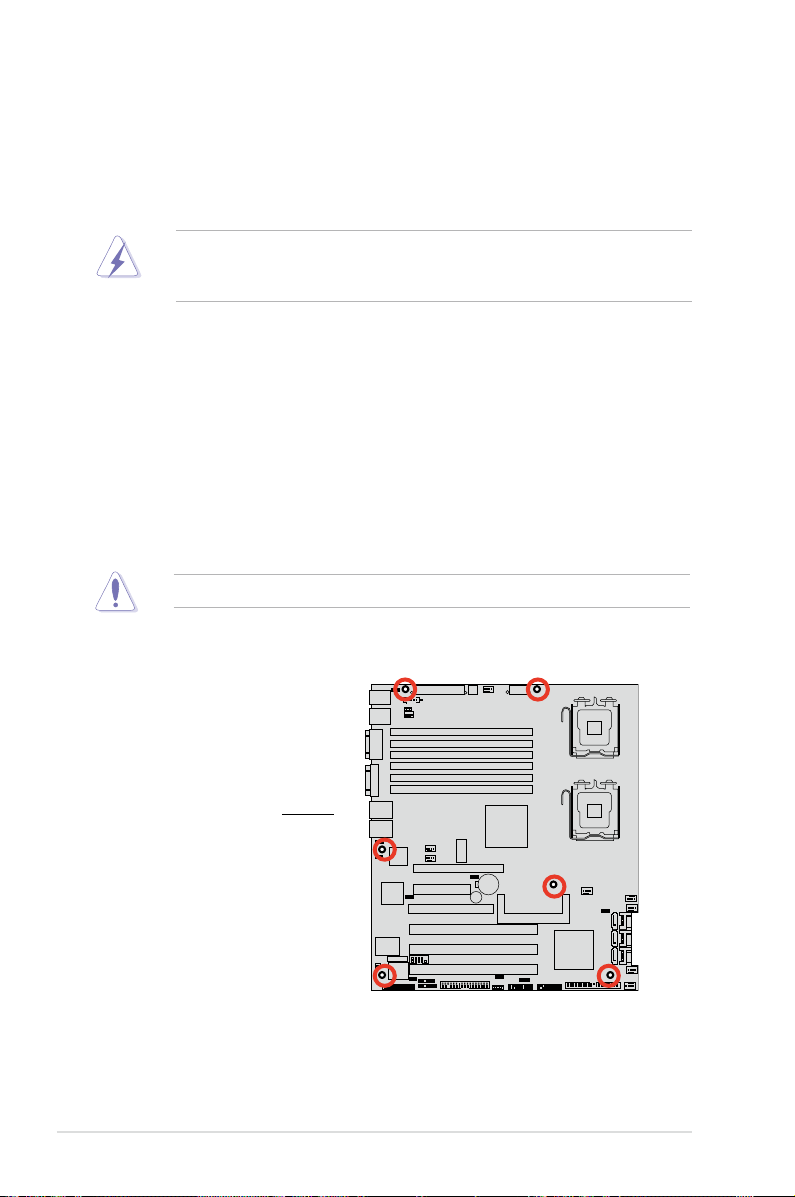
2.2.2 Screw holes
Place six (6) screws into the holes indicated by circles to secure the motherboard
to the chassis.
Do not overtighten the screws! Doing so can damage the motherboard.
Place this side towards
the rear of the chassis
2-2 Chapter 2: Hardware information
Page 23

2.2.3 Support kits for the motherboard
For additional protection from motherboard breakage due to the weight of the CPU
heatsinks, your motherboard package comes with CEK springs that you can use as
weight support. Install the CEK springs before installing the motherboard.
If your chassis is SSI EEB 3.61 compliant, we recommend that you use the CEK
springs; otherwise, use the support plates kit.
Each CEK spring has four hooks to match the
designated holes around the CPU area.
Hook
To install the CEK spring:
1. Locate the CPU heatsink holes on
the motherboard.
Socket for CPU2
Socket for CPU1
Heatsink hole
2. Position the CEK spring underneath
the motherboard, then match the
CEK spring hooks to the CPU1
heatsink holes.
ASUS DSBV-D 2-3
Page 24

3. Press the upper spring hooks
inward, then insert to the upper
CPU heatsink holes until they snap
in place.
4. Press the lower spring clips inward,
then insert to the lower CPU
heatsink holes until they snap in
place.
5. If you installed a second CPU,
repeat steps 2 to 4 to install the
CEK spring to the CPU2 heatsink
holes.
The CEK springs appear as shown
when installed.
CEK spring screw hole
2-4 Chapter 2: Hardware information
Page 25

6. Before installing the motherboard
into the chassis, locate the standoffs
that should match the eight (8) CEK
spring screw holes.
Standoffs for CPU1
7. Install the motherboard with the
external I/O ports toward the
chassis rear panel. The CPU
sockets should be right on top of
their respective standoffs.
Standoffs for CPU2
Socket for CPU2
Socket for CPU1
Make sure that the standoffs perfectly match the CEK spring screw holes;
otherwise, you can not install the CPU heatsinks properly.
8. Secure the motherboard with six (6) screws. Refer to section “2.2.2 Screw
holes” for illustration.
ASUS DSBV-D 2-5
Page 26
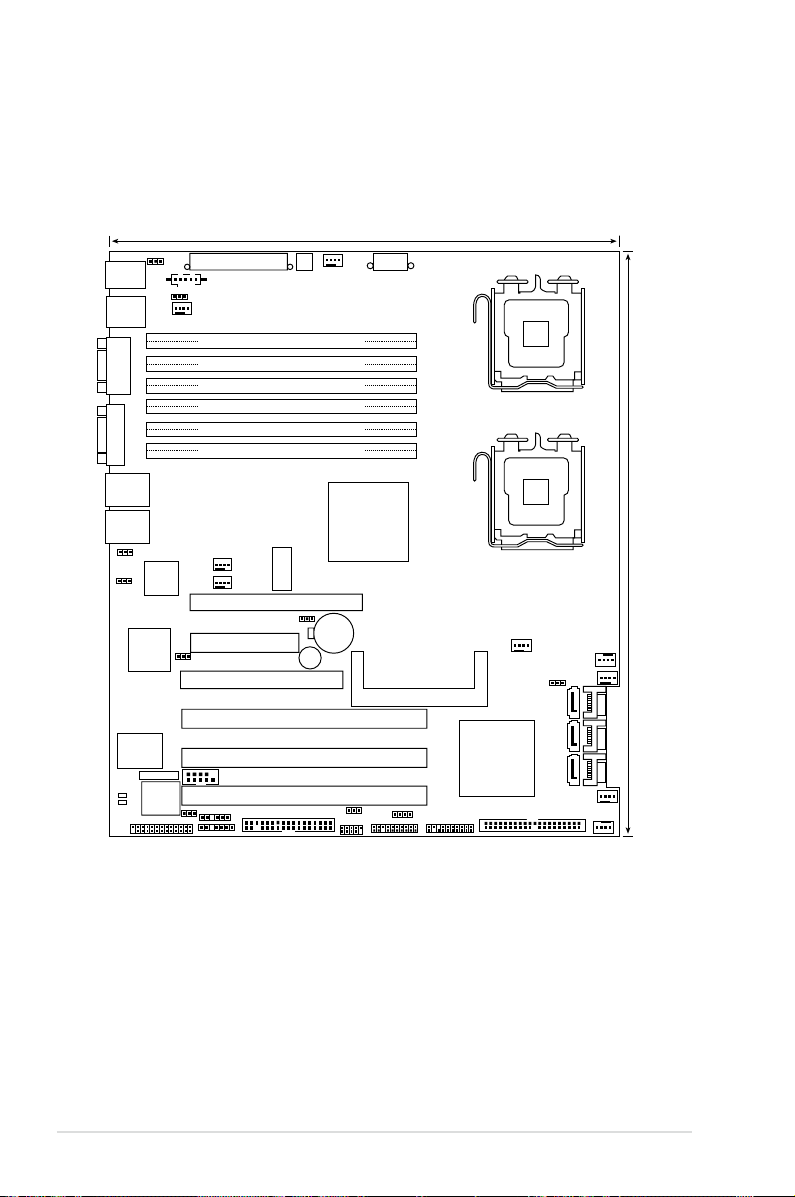
2.2.4 Motherboard layouts
8Mb
FWH
KBPWR1
ATXPWR1
FLOPPY1
ATI
ES1000
BUZZER1
COM2
Super
I/O
CR2032 3V
Lithium Cell
CMOS Power
PANEL1
PS/2
T: Mouse
B: Keyboard
USB1
USB2
RJ-45
(LAN1)
ATX12V1
CPU_FAN1
Intel
®
6321ESB
PSUSMB1
BPSMB1
AUX_PANEL1
HDLED1
USB34
USBPW34
LAN_BW1
LPT1
USBPW12
DSBV-D
ASMB3
Intel
®
5000V
PCIE1
FB-DIMM_00 (64/72 bit, 240-pin module)
26.7cm (10.5in)
30.5cm (12in)
COM1
VGA1
PCIE2
PCIX5
PCIX4
PCI3
PCIX6
REAR_FAN2
ATX12V2
PRI_IDE1
FRNT_FAN2
SATA2
SATA1
SGIOP1
RECOVERY1
VGA_EN1
LAN_EN1
DIP_SW1
RJ-45
(LAN2)
FB-DIMM_01 (64/72 bit, 240-pin module)
FB-DIMM_02 (64/72 bit, 240-pin module)
FB-DIMM_10 (64/72 bit, 240-pin module)
FB-DIMM_11 (64/72 bit, 240-pin module)
FB-DIMM_12 (64/72 bit, 240-pin module)
CPU1
CPU2
FRNT_FAN1
FRNT_FAN4
FRNT_FAN3
CPU_FAN2
REAR_FAN1
CLRTC1
FBD_FAN1
RAID_SEL1
SATA4
SATA3
SATA6
SATA5
Intel
®
82563EB
+12V4LED1
SB_PWR1
DSBV-D
2-6 Chapter 2: Hardware information
Page 27

2.2.5 Layout contents
Slots/Sockets Page
1. CPU sockets 2-9
2. FB-DIMM sockets 2-14
3. PCI-X slots 2-22
4. DDR2 SODIMM socket 2-22
5. PCI Express x8 slot 2-23
6. PCI Express x16 slot 2-23
Jumpers Page
1. Clear RTC RAM (CLRTC1) 2-24
2. LAN bandwidth setting (3-pin LAN_BW1) 2-25
3. USB device wake-up (3-pin USBPW12, USBPW34) 2-25
4. Keyboard power (3-pin KBPWR1) 2-26
5. VGA controller setting (3-pin VGA_EN1) 2-26
6. LAN controller setting (3-pin LAN1_EN1) 2-27
7. Intel® 6321ESB SATA port S/W RAID setting (3-pin RAID_SEL1) 2-27
8. Force BIOS recovery setting (3-pin RECOVERY1) 2-28
Switch Page
1. DIP switches (DIP_SW1) 2-33
Rear panel connectors Page
1. PS/2 mouse port (green) 2-29
2. PS/2 keyboard port (purple) 2-29
3. USB 2.0 ports 1 and 2 2-29
4. Serial (COM1) port 2-29
5. Video Graphics Adapter port 2-29
6. LAN (RJ-45) ports 2-29
ASUS DSBV-D 2-7
Page 28

Internal connectors Page
1. Floppy disk drive connector (34-1 pin FLOPPY1) 2-30
2. IDE connector (40-1 pin PRI_IDE) 2-30
3. Serial ATA connectors (7-pin SATA1, SATA2, SATA3, 2-31
SATA4, SATA5, SATA6 )
4. Hard disk activity LED connector (4-pin HDLED1) 2-31
5. USB connector (10-1 pin USB34) 2-32
6. Serial port connector (10-1 pin COM2) 2-32
7. CPU and system fan connectors (4-pin CPU_FAN1/2, 2-33
REAR_FAN1/2, FRNT_FAN1/2/3/4, FBD_FAN1)
8. Power supply SMBus connector (5-pin PSUSMB1) 2-33
9. SSI power connectors (24-pin ATXPWR1, 8-pin ATX12V1, 2-34
4-pin ATX12V2)
10. Parallel port connector (26-1 pin LPT1) 2-35
11. Backplane SMBus connector (6-1 pin BPSMB1) 2-35
12. Serial General Purpose Input/Output connector 2-36
13. System panel connector (20-1 pin PANEL1) 2-40
14. System panel auxiliary connector (20-2 pin AUX_PANEL1) 2-38
2-8 Chapter 2: Hardware information
Page 29
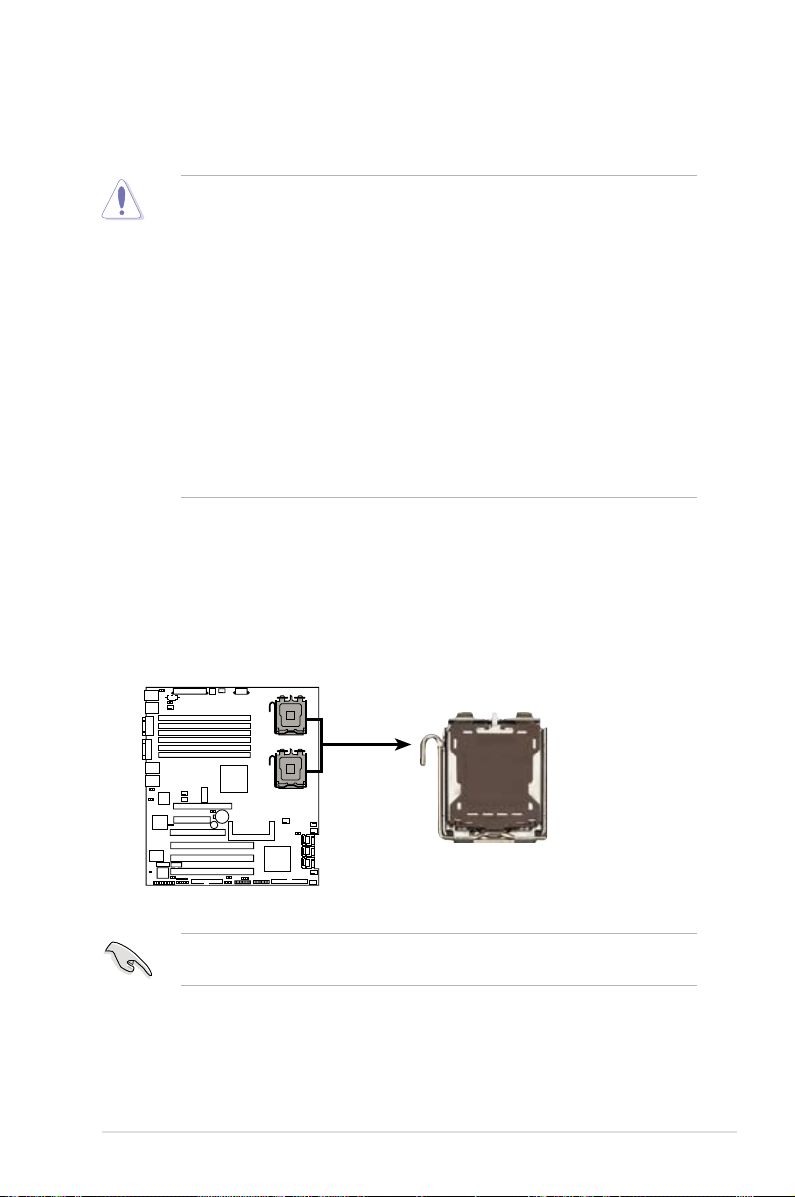
2.3 Central Processing Unit (CPU)
DSBV-D
DSBV-D CPU LGA771
CPU1
CPU2
The motherboard comes with a surface mount LGA771 socket designed for the
Intel® Xeon® Dual Core processor.
• Your boxed Intel® Xeon® LGA771 processor package should
come with installation instructions for the CPU and heatsink. If the
instructions in this section do not match the CPU documentation, follow the
latter.
•
Upon purchase of the motherboard, make sure that the PnP cap is on
the socket and the socket contacts are not bent. Contact your retailer
immediately if the PnP cap is missing, or if you see any damage to the PnP
cap/socket contacts/motherboard components. ASUS will shoulder the cost
of repair only if the damage is shipment/transit-related.
•
Keep the cap after installing the motherboard. ASUS will process Return
Merchandise Authorization (RMA) requests only if the motherboard comes
with the cap on the LGA771 socket.
• The product warranty does not cover damage to the socket contacts
resulting from incorrect CPU installation/removal, or misplacement/loss/
incorrect removal of the PnP cap.
2.3.1 Installing the CPU
To install a CPU:
1. Locate the CPU socket on the motherboard.
ASUS DSBV-D 2-9
Before installing the CPU, make sure that the socket box is facing towards you
and the load lever is on your left.
Page 30
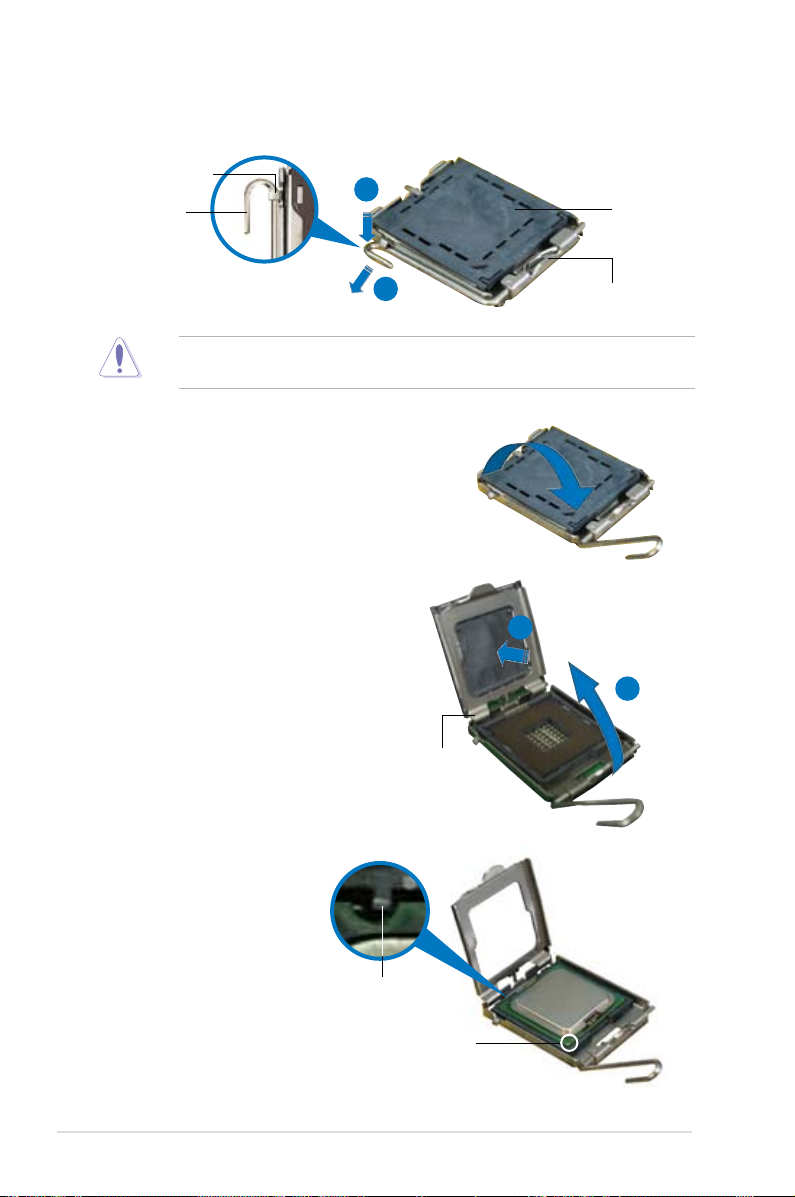
2. Press the load lever with your thumb (A), then move it to the left (B) until it is
released from the retention tab.
Retention tab
A
Load lever
B
To prevent damage to the socket pins, do not remove the PnP cap unless you
are installing a CPU.
3. Lift the load lever in the direction of
the arrow to a 135º angle.
4. Lift the load plate with your
thumb and forenger to a 100º
angle (A), then push the PnP
cap from the load plate window
to remove (B).
PnP cap
This side of the socket box
should face you.
B
A
Load plate
5. Position the CPU over
the socket, making sure
that the gold triangle
is on the bottom-left
corner of the socket.
The socket alignment
key should t into the
Alignment key
CPU notch.
Gold triangle mark
2-10 Chapter 2: Hardware information
Page 31

6. Close the load plate (A), then
push the load lever (B) until it
snaps into the retention tab.
B
The CPU ts in only one correct orientation. DO NOT force the CPU into the
socket to prevent bending the connectors on the socket and damaging the CPU!
Notes on Intel® Hyper-Threading Technology
• This motherboard supports Intel® Xeon™ CPUs in the 771-land package
with Hyper-Threading Technology.
• Hyper-Threading Technology is supported by Intel
5100/5300 series DO NOT support Hyper-Threading.
• Hyper-Threading Technology is supported under Windows
and Linux 2.4.x (kernel) and later versions only. Under Linux, use the
Hyper-Threading compiler to compile the code. If you are using any other
operating systems, disable the Hyper-Threading Technology item in the
BIOS to ensure system stability and performance.
®
• Installing Windows
• Make sure to enable the Hyper-Threading Technology item in BIOS before
installing a supported operating system.
• For more information on Hyper-Threading Technology, visit www.intel.
com/info/hyperthreading.
2003 Server or later version is recommended.
A
®
5000 series CPU only.
®
XP/2003 Server
To use the Hyper-Threading Technology on this motherboard:
1. Install an Intel
®
Xeon™ CPU that supports Hyper-Threading Technology.
2. Power up the system and enter the BIOS Setup (see Chapter 4: BIOS
setup). Under the Advanced Menu, make sure that the item Hyper-Threading
Technology is set to Enabled. The item appears only if you installed a CPU
that supports Hyper-Threading Technology.
3. Reboot the computer.
ASUS DSBV-D 2-11
Page 32

2.3.2 Installing the CPU heatsink and fan
The Intel® Xeon™ processors require an Intel certied heatsink and fan assembly
to ensure optimum thermal condition and performance.
When you buy a boxed Intel CPU, the package includes the heatsink, fan,
retention brackets, screws, thermal grease, installation manual, and other items
that are necessary for CPU installation.
•
Make sure that you have applied the thermal grease to the top of the CPU
before installing the heatsink and fan.
•
Refer to the installation manual that came with the CPU package for details
on heatsink/fan assembly and installation.
CPU heatsink (top view)
Before installing the CPU heatsinks, ensure that the jumpers DIP_SW1 are set
correctly depending on the pin denition of your CPU fan cables. Refer to page
2-19 for information on these jumpers.
To install the CPU heatsink and fan:
1. Place the heatsink on top of the
installed CPU, making sure that the
four screws on the heatsink align
with the nuts on the support plate.
CPU heatsink (bottom view)
Heatsink screw
2-12 Chapter 2: Hardware information
Page 33

2. Use a Phillips screwdriver to tighten
the four heatsink screws in a
diagonal sequence.
3. Connect the fan cable to the 4-pin
connector labeled CPU_FAN1.
Do not forget to connect the CPU
fan cable! Hardware monitoring
errors may occur if you fail to plug
this connector.
CPU_FAN1
connector
4. Repeat steps 1 to 3 to install the other heatsink if you have installed a second
CPU, then connect the fan cable to the 4-pin connector labeled CPU_FAN2.
ASUS DSBV-D 2-13
Page 34

2.4 System memory
DSBV-D
DSBV-D 240-pin FB-DIMM sockets
FB-DIMM_01
FB-DIMM_00
112 Pins128 Pins
FB-DIMM_10
FB-DIMM_02
FB-DIMM_12
FB-DIMM_11
2.4.1 Overview
The motherboard comes with six fully-buffered DIMM (FB-DIMM) sockets to
support 240-pin FB-DIMM modules. An FB-DIMM module has a different pin-out
from DDR2 DIMMs so you cannot install DDR2 DIMMs on an FB-DIMM socket.
Note that an FB-DIMM socket has an Advanced Memory Buffer (AMB) chip that
allows memory-to-CPU connection at gigabit speed.
The gure illustrates the location of the FB-DIMM sockets:
2.4.2 Memory congurations
You may install 256 MB, 512 MB, 1 GB, 2 GB, and 4 GB registered ECC
FB-DIMMs into the DIMM sockets.
• For optimum compatibility, we recommend that you obtain memory modules
from the same vendor. Refer to the Qualied Vendors List on the ASUS
web site.
• This motherboard does not support memory modules made up of 128 Mb
chips or double-rank x16 memory modules.
• If you are installing only one memory module, install into the white socket
labeled DIMM_00. Installing into any other socket will not work.
2-14 Chapter 2: Hardware information
Page 35

Rank population
MCH
DIMM 01
DIMM 00
DIMM 10
DIMM 02
DIMM 11
DIMM 12
Channel
Slot 0
Slot 1
Ch:0
Slot 2
Slot 0
Slot 1
Ch:1
Slot 2
DIMM installation reference table
No. of DIMMs Slot/s to use
1 DIMM_00
2 DIMM_00, DIMM_10
4 DIMM_00, DIMM_01, DIMM_10, DIMM_11
6 DIMM_00, DIMM_01, DIMM_02, DIMM_10,
• DIMMs in pair means two DIMMs with the same conguration.
• For better performance, same conguration DIMMs should be installed on
DIMM_11, DIMM_12
the same slot number for each channel. For example, you may install the
same type of DIMMs in DIMM_00, and DIMM_10.
ASUS DSBV-D 2-15
Page 36

2.4.3 Memory sparing technology
The Intel® 5000V chipset supports the memory sparing technology. Refer to the
below sections:
Memory Sparing :
At conguration time, a DIMM rank is set aside to replace a defective DIMM rank.
When the error rate for a failing DIMM rank reaches a pre-determined threshold,
the memory sparing function will issue an interrupt and initiate a spare copy. At the
completion of the copy, the failing DIMM rank is disabled and the “spared” DIMM
rank will be used in its place. Refer to
the options of
Branch 0 Rank Sparing
4.4.2 Chipset Conguration
to enable the memory sparing functions.
And the default BIOS setting is disabled.
• The DIMM rank with the largest size will be assigned as spare rank. Data
can only be copied from a smaller sized rank to a larger sized one.
• A DIMM can contain only one or two ranks. To support sparing function, a
DIMM channel should contain at least two ranks.
• When sparing function is enabled, the usable memory size will reduce then
size of the spare ranks.
The following tables show memory congurrations with Memory Sparing function in
Branch 0.
One DIMM per channel (Dual ranks)
and congure
Channel 0 Channel 1
DIMM_00
(2048MB/2 Ranks)
Rank 0
(1024 MB)
Sparing
Memory space
Total Memory
2-16 Chapter 2: Hardware information
1024 MB 1024 MB
Rank 1
(1024 MB)
V V
2048 MB
DIMM_10
(2048MB/2 Ranks)
Rank 0
(1024 MB)
Rank 1
(1024 MB)
Page 37

Two DIMM per channel (Dual ranks)
Channel 0 Channel 1
DIMM_00
(1024MB/2 Ranks)
Sparing
Memory space
Sparing
Memory space
Total Memory
Rank 0
(512 MB)
512 MB 512 MB 512 MB 512 MB
(2048MB/2 Ranks)
Rank 0
(1024 MB)
1024 MB 1024 MB
Rank 1
(512 MB)
DIMM_01
Rank 1
(1024 MB)
V V
4096 MB
Two DIMM per channel (Single rank)
Channel 0 Channel 1
DIMM_00
(512MB/1 Ranks)
Rank 0
(512 MB)
Sparing
Memory space
Sparing
Memory space
Total Memory
512 MB 512 MB
DIMM_01
(1024MB/1 Ranks)
Rank 0
(1024 MB)
V V
1024 MB
DIMM_10
(1024MB/2 Ranks)
Rank 0
(512 MB)
(2048MB/2 Ranks)
Rank 0
(1024 MB)
(512MB/1 Ranks)
(1024MB/1 Ranks)
(512 MB)
DIMM_11
(1024 MB)
DIMM_10
Rank 0
(512 MB)
DIMM_11
Rank 0
(1024 MB)
Rank 1
Rank 1
ASUS DSBV-D 2-17
Page 38

Three DIMMs per channel (Dual ranks)
Channel 0 Channel 1
DIMM_00
(1024/2 Ranks)
Sparing
Memory space
Sparing
Memory space
Sparing
Memory space
Total Memory
Rank 0
(1024 MB)
512 MB 512 MB 512 MB 512 MB
(1024MB/2 Ranks)
Rank 0
(512 MB)
512 MB 512 MB 512 MB 512 MB
(2048MB/2 Ranks)
Rank 0
(1024 MB)
1024 MB 1024 MB
Rank 1
(1024 MB)
DIMM_01
Rank 1
(512 MB)
DIMM_02
Rank 1
(1024 MB)
V V
6144 MB
Three DIMMs per channel (Single ranks)
Channel 0 Channel 1
DIMM_00
(512MB/1 Rank)
Rank 0
(512 MB)
Sparing
Memory space
Sparing
Memory space
Sparing
Memory space
Total Memory
512 MB 512 MB
DIMM_01
(1024MB/1 Rank)
Rank 0
(512 MB)
512 MB 512 MB
DIMM_02
(1024MB/1 Rank)
Rank 0
(1024 MB)
V V
2048 MB
DIMM_10
(1024/2 Ranks)
Rank 0
(1024 MB)
(1024MB/2 Ranks)
Rank 0
(512 MB)
(2048MB/2 Ranks)
Rank 0
(1024 MB)
(512MB/1 Rank)
(1024MB/1 Rank)
(1024MB/1 Rank)
(1024 MB)
DIMM_11
(512 MB)
DIMM_12
(1024 MB)
DIMM_10
Rank 0
(512 MB)
DIMM_11
Rank 0
(512 MB)
DIMM_12
Rank 0
(1024 MB)
Rank 1
Rank 1
Rank 1
2-18 Chapter 2: Hardware information
Page 39

2.4.4 Installing a DIMM
Make sure to unplug the power supply before adding or removing DIMMs or
other system components. Failure to do so may cause severe damage to both
the motherboard and the components.
To install a DIMM:
1. Unlock a DIMM socket by pressing
the retaining clips outward.
2. Align a DIMM on the socket
such that the notch on the DIMM
matches the break on the socket.
3. Firmly insert the DIMM into the
socket until the retaining clips
snap back in place and the DIMM
is properly seated.
• A FB-DIMM is keyed with a notch so that it ts in only one direction. Do not
force a DIMM into a socket to avoid damaging the DIMM.
• Thesockets do not support DDR/DDR2 DIMMs. DO NOT install DDR/DDR2
DIMMs to the FB-DIMM sockets.
2.4.5 Removing a DIMM
To remove a DIMM:
1. Simultaneously press the retaining
clips outward to unlock the DIMM.
Support the DIMM lightly with
your ngers when pressing
the retaining clips. The DIMM
might get damaged when it
ips out with extra force.
1
3
2
1
1
FB-DIMM notch
1
2
2. Remove the DIMM from the socket.
ASUS DSBV-D 2-19
Page 40

2.4.6 Installing the optional MemCool FB-DIMM fan
The FB-DIMMs generate heat during continued operation.
thermal condition and performance, install the optional MemCool FB-DIMM fan.
To install the optional FB-DIMM fan:
1. Locate the three FB-DIMM fan
holes on the motherboard.
To ensure optimum
2. Disengage the fan top cover from the fan base. You can do this by rmly
gripping the top cover by the clamps to release the hooks, then pull up the
top cover carefully until it separates from the fan base.
Do not remove the fan from the
fan base.
Top cover
clamp
Top
cover
hook
Fan
base
3. Position the fan base over the
DIMMs, and insert the fan base
legs into the FB-DIMM holes until
the legs are securely in place.
• For instructional purposes only, no FB-DIMM is installed on any of the slots.
• For 2U or above models, we suggest you to install MemCool FB-DIMM fan
for better cooling effect and system performance.
2-20 Chapter 2: Hardware information
Page 41

4. Position top cover over the fan
base. Insert the top cover legs into
the slot on the fan base legs.
Push down carefully until the legs
are securely in place and the top
cover hooks snap in place.
Make sure the cables pass
through the notch on the fan base
as shown.
5. Connect the fan cable to the
black 4-pin connector labeled
FBD_FAN1.
ASUS DSBV-D 2-21
Page 42

2.4.7 Uninstalling the optional MemCool FB-DIMM fan
1. Unplug the fan cable.
2. Grip the top cover clamps until the
top cover hooks are released, then
carefully lift the top cover while
supporting the fan base with your
free hand.
Top cover
clamp
3. Carefully lift the fan base.
2-22 Chapter 2: Hardware information
Page 43

2.5 Expansion slots
In the future, you may need to install expansion cards. The following sub-sections
describe the slots and the expansion cards that they support.
Make sure to unplug the power cord before adding or removing expansion
cards. Failure to do so may cause you physical injury and damage motherboard
components.
2.5.1 Installing an expansion card
To install an expansion card:
1. Before installing the expansion card, read the documentation that came with
it and make the necessary hardware settings for the card.
2. Remove the system unit cover (if your motherboard is already installed in a
chassis).
3. Remove the bracket opposite the slot that you intend to use. Keep the screw
for later use.
4. Align the card connector with the slot and press rmly until the card is
completely seated on the slot.
5. Secure the card to the chassis with the screw you removed earlier.
6. Replace the system cover.
2.5.2 Conguring an expansion card
After installing the expansion card, congure the it by adjusting the software
settings.
1. Turn on the system and change the necessary BIOS settings, if any. See
Chapter 4 for information on BIOS setup.
2. Assign an IRQ to the card. Refer to the tables on the next page.
3. Install the software drivers for the expansion card.
When using PCI cards on shared slots, ensure that the drivers support “Share
IRQ” or that the cards do not need IRQ assignments. Otherwise, conicts will
arise between the two PCI groups, making the system unstable and the card
inoperable.
ASUS DSBV-D 2-23
Page 44

2.5.3 Interrupt assignments
Standard interrupt assignments
IRQ Priority Standard Function
0 1 System Timer
1 2 Keyboard Controller
2 — Re-direct to IRQ#9
3 11 Communications Port (COM2)*
4 12 Communications Port (COM1)*
5 13 IRQ holder for PCI steering*
6 14 Floppy Disk Controller
7 15 Printer Port (LPT1)*
8 3 System CMOS/Real Time Clock
9 4 IRQ holder for PCI steering*
10 5 IRQ holder for PCI steering*
11 6 IRQ holder for PCI steering*
12 7 PS/2 Compatible Mouse Port*
13 8 Numeric Data Processor
14 9 Primary IDE Channel
15 10 Secondary IDE Channel
* These IRQs are usually available for ISA or PCI devices.
2-24 Chapter 2: Hardware information
Page 45

2.5.4 PCI-X slots
The PCI-X slots support cards such as a LAN card, SCSI card, USB card, and
other cards that comply with PCI 2.3 and PCI-X 1.0 specications.
PCI-X slot
2.5.5 DDR2 SODIMM socket
The DDR2 SODIMM socket on the
motherboard supports an
ASUS® Server Management Board 3
Series (ASMB3).
SODIMM socket
ASUS DSBV-D 2-25
Page 46

2.5.6 PCI Express x8 slot (x4 link)
The onboard PCI Express x8 slot provides x4 link to the ESB. This slot is designed
for various server class high performance I/O add-on cards like SCSI RAID card,
ber-channel card, etc.
PCI Express x8 slot
2.5.7 PCI Express x16 slot (x8 link)
This motherboard supports PCI Express I/O cards that comply with the PCI
Express specications.
PCI Express x16 slot
2-26 Chapter 2: Hardware information
Page 47

2.6 Jumpers
DSBV-D
DSBV-D Clear RTC RAM
CLRTC1
Normal
(Default)
Clear CMOS
1 2 2 3
1. Clear RTC RAM (CLRTC1)
This jumper allows you to clear the Real Time Clock (RTC) RAM in CMOS.
You can clear the CMOS memory of date, time, and system setup parameters
by erasing the CMOS RTC RAM data. The onboard button cell battery
powers the RAM data in CMOS, which include system setup information such
as system passwords.
To erase the RTC RAM:
1. Turn OFF the computer and unplug the power cord.
2. Remove the onboard battery.
3. Move the jumper cap from pins 1-2 (default) to pins 2-3. Keep the cap
on pins 2-3 for about 5~10 seconds, then move the cap back to pins 1-2.
4. Reinstall the battery.
5. Plug the power cord and turn ON the computer.
6. Hold down the <Del> key during the boot process and enter BIOS setup
to re-enter data.
Except when clearing the RTC RAM, never remove the cap on CLRTC jumper
default position. Removing the cap will cause system boot failure!
ASUS DSBV-D 2-27
Page 48

2. LAN bandwidth setting (3-pin LAN_BW1)
DSBV-D
DSBV-D LAN bandwidth setting
LAN_BW1
Balanced mode
(Default)
Centric mode
2 31 2
DSBV-D
DSBV-D USB device wake up
USBPW12
(Default)
+5V +5VSB
3221
USBPW34
(Default)
+5V +5VSB
3221
This jumper allows you to set the LAN bandwidth setting for more efcient IP
load distribution.
3. USB device wake-up (3-pin USBPW12, USBPW34)
Set these jumpers to +5V to wake up the computer from S1 sleep mode (CPU
stopped, DRAM refreshed, system running in low power mode) using the
connected USB devices. Set to +5VSB to wake up from S4 sleep mode (no
power to CPU, DRAM in slow refresh, power supply in reduced power mode).
• The USB device wake-up feature requires a power supply that can
provide 500mA on the +5VSB lead for each USB port; otherwise, the
system will not power up.
®
• If you are using Windows
up the system from S4 sleep mode.
• The total current consumed must NOT exceed the power supply capability
(+5VSB) whether under normal condition or in sleep mode.
2000, you need to install Service Pack 4 to wake
2-28 Chapter 2: Hardware information
Page 49

4. Keyboard power (3-pin KBPWR1)
DSBV-D
DSBV-D Keyboard power setting
KBPWR1
(Default)
+5V +5VSB
3221
DSBV-D
DSBV-D VGA setting
VGA_EN1
1 2 2 3
Enable
(Default)
Disable
This jumper allows you to enable or disable the keyboard wake-up feature.
Set this jumper to pins 2-3 (+5VSB) to wake up the computer when you press
a key on the keyboard (the default is the Space Bar). This feature requires
an ATX power supply that can supply at least 1A on the +5VSB lead, and a
corresponding setting in the BIOS.
5. VGA controller setting (3-pin VGA_EN1)
These jumpers allow you to enable or disable the onboard VGA controller.
Set to pins 1-2 to activate the VGA feature.
ASUS DSBV-D 2-29
Page 50

6. LAN controller setting (3-pin LAN_EN1)
DSBV-D
DSBV-D LAN1_EN setting
LAN1_EN1
1 2 2 3
Enable
(Default)
Disable
DSBV-D
DSBV-D 6321ESB SATA port S/W RAID setting
RAID_SEL1
3rd party RAID
(Intel® IMSM)
3rd party RAID
(LSI MegaRAID)
(Default)
1 2 2 3
This jumper allows you to enable or disable the onboard Intel
®
6321 Gigabit
LAN controller. Set to pins 1-2 to activate the Gigabit LAN feature.
®
7. Intel
6321ESB SATA port S/W RAID setting
(3-pin RAID_SEL1)
This jumper allows you to select the Serial ATA RAID conguration utility to
use when you create disk arrays. Both utilities are supported by the Intel
®
6321ESB. Place the jumper caps on pins 1-2 if you want to use the LSI
MegaRAID Serial ATA RAID utility (default); otherwise, place the jumper caps
on pins 2-3 to use the Intel® Matrix Storage Manager (IMSM).
2-30 Chapter 2: Hardware information
Page 51

8. Force BIOS recovery setting (3-pin RECOVERY1)
DSBV-D
DSBV-D BIOS recovery setting
RECOVERY1
(Default)
Normal BIOS Recovery
1 2 2 3
This jumper allows you to quickly update or recover the BIOS settings when it
becomes corrupted.
To update the BIOS:
1. Prepare a oppy disk that contains the latest BIOS for the motherboard
and the Phoenix Phlash16 utility. Make sure you download the correct
BIOS for your motherboard model.
2. Set the jumper to pins 2-3.
3. Insert the oppy disk then turn on the system to update the BIOS.
4. Shut down the system.
5. Set the jumper back to pins 1-2.
6. Turn on the system.
ASUS DSBV-D 2-31
Page 52

DSBV-D
DSBV-D DIP switches
DIP_SW1
ON:4-PIN FAN
OFF:3-PIN FAN
SW1:CPU_FAN1
SW2:CPU_FAN2
SW3:FRNT_FAN1
SW4:FRNT_FAN2
SW5:FRNT_FAN3
SW6:FRNT_FAN4
SW7:REAR_FAN1
SW8:REAR_FAN2
ON(Default)OFF
ON
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8
2.7 Switch
1. DIP switches (DIP_SW1)
This switch allows you to set up the fan connections. Set the switch to ON if
you are using a 4-pin fan (PWM fan) cable plug, or to OFF if you are using a
3-pin (PC fan) plug.
The following table shows the corresponding switch for each fan connector.
Switch Fan connector
1 CPU_FAN1
2 CPU_FAN2
3 FRNT_FAN1
4 FRNT_FAN2
5 FRNT_FAN3
6 FRNT_FAN4
7 REAR_FAN1
8 REAR_FAN2
•
If you use a 4-pin fan but set the DIP switch for a 3-pin fan, the fan you
installed may not work.
•
If you use a 3-pin fan but set the DIP switch for a 4-pin fan, the fan controll
will not work and the fan you installed will always run at full speed.
2-32 Chapter 2: Hardware information
Page 53

2.8 Connectors
1
2 3 64 5
2.8.1 Rear panel connectors
1. PS/2
2. PS/2
3.
mouse port (green).
keyboard port (purple).
USB 2.0 ports 1 and 2.
This port is for a PS/2 mouse.
This port is for a PS/2 keyboard.
These two 4-pin Universal Serial Bus (USB) ports
are available for connecting USB 2.0 devices.
4. Serial (COM1) port.
This 9-pin communication port is for pointing devices or
other serial devices.
5. Video Graphics Adapter port.
This port is for a VGA monitor or other VGA-
compatible devices.
6. LAN (RJ-45) ports.
These ports allow Gigabit connection to a Local Area
Network (LAN) through a network hub. Refer to the table below for the LAN
port LED indications.
LAN port LED indications
ACT/LINK LED SPEED LED
Status Description Status Description
OFF No link OFF 10 Mbps connection
GREEN Linked ORANGE 100 Mbps connection
BLINKING Data activity GREEN 1000 Mbps connection
ACT/LINK
LED
LAN port
SPEED
LED
ASUS DSBV-D 2-33
Page 54

2.8.2 Internal connectors
DSBV-D
NOTE: Orient the red markings on
the floppy ribbon cable to PIN 1.
PIN 1
FLOPPY1
DSBV-D Floppy disk drive connector
DSBV-D
DSBV-D IDE connector
PRI_IDE1
PIN 1
NOTE: Orient the red markings
(usually zigzag) on the IDE
ribbon cable to PIN 1.
1. Floppy disk drive connector (34-1 pin FLOPPY1)
This connector is for the provided oppy disk drive (FDD) signal cable. Insert
one end of the cable to this connector, then connect the other end to the
signal connector at the back of the oppy disk drive.
Pin 5 on the connector is removed to prevent incorrect cable connection when
using a FDD cable with a covered Pin 5.
2. IDE connector (40-1 pin PRI_IDE)
This connector is for an Ultra DMA 100/66 signal cable. The Ultra
DMA 100/66 signal cable has three connectors: a blue connector for the
primary IDE connector on the motherboard, a black connector for an Ultra
DMA 100/66 IDE slave device (optical drive/hard disk drive), and a gray
connector for an Ultra DMA 100/66 IDE master device (hard disk drive). If you
install two hard disk drives, you must congure the second drive as a slave
device by setting its jumper accordingly. Refer to the hard disk documentation
for the jumper settings.
• Pin 20 on the IDE connector is removed to match the covered hole on the
Ultra DMA cable connector. This prevents incorrect insertion when you
connect the IDE cable.
• Use the 80-conductor IDE cable for Ultra DMA 100/66 IDE devices.
2-34 Chapter 2: Hardware information
Page 55

3. Serial ATA connectors (7-pin SATA1, SATA2, SATA3, SATA4, SATA5,
DSBV-D
SATA2 SATA1
DSBV-D SATA connectors
SATA4 SATA3
SATA6 SATA5
GND
RSATA_TXP1
RSATA_TXN1
GND
RSATA_RXN1
RSATA_RXP1
GND
GND
RSATA_TXP2
RSATA_TXN2
GND
RSATA_RXN2
RSATA_RXP2
GND
GND
RSATA_TXP3
RSATA_TXN3
GND
RSATA_RXN3
RSATA_RXP3
GND
GND
RSATA_TXP4
RSATA_TXN4
GND
RSATA_RXN4
RSATA_RXP4
GND
GND
RSATA_TXP5
RSATA_TXN5
GND
RSATA_RXN5
RSATA_RXP5
GND
GND
RSATA_TXP6
RSATA_TXN6
GND
RSATA_RXN6
RSATA_RXP6
GND
DSBV-D
DSBV-D storage card activity LED connector
HDLED1
PIN1
ADD_IN_CARD-
NC
NC
ADD_IN_CARD-
SATA6 )
These connectors are for the Serial ATA signal cables for Serial ATA hard disk
drives.
4. Hard disk activity LED connector (4-pin HDLED1)
This connector is used to connect to a hard disk drive active LED connector
on the SCSI or RAID card.
ASUS DSBV-D 2-35
Page 56

5. USB connector (10-1 pin USB34)
DSBV-D
DSBV-D USB connector
USB34
Power
PIN1
USB PortA(-)
GND
Power
USB PortB(-)
USB PortB(+)
GND
NC
DSBV-D
DSBV-D Serial port connectors
PIN1
COM2
This connector is for USB 2.0 ports. Connect the USB module cable to
this connector, then install the module to a slot opening at the back of the
system chassis. This USB connector complies with USB 2.0 specication that
supports up to 480 Mbps connection speed.
The USB port module is purchased separately.
6. Serial port connector (10-1 pin COM2)
This connector is for a serial (COM) port. Connect the serial port module
cable to this connector, then install the module to a slot opening at the back
of the system chassis.
2-36 Chapter 2: Hardware information
The serial port module is purchased separately.
Page 57

7. CPU and system fan connectors (4-pin CPU_FAN1/2, REAR_FAN1/2,
DSBV-D
DSBV-D Fan connectors
CPU_FAN1
CPU_FAN2
REAR_FAN1
REAR_FAN2
FRNT_FAN1
FRNT_FAN2
FRNT_FAN3
FRNT_FAN4
FBD_FAN1
CPU_FAN1 CPU_FAN2
GND
FAN Power
FAN Speed
PWM Control
GND
FAN Power
FAN Speed
PWM Control
REAR_FAN1 REAR_FAN2
GND
FAN Power
FAN Speed
PWM Control
FRNT_FAN1 FRNT_FAN2
FRNT_FAN3 FRNT_FAN4
FBD_FAN1
GND
FAN Power
FAN Speed
PWM Control
GND
FAN Power
FAN Speed
PWM Control
GND
FAN Power
FAN Speed
PWM Control
GND
FAN Power
FAN Speed
PWM Control
GND
FAN Power
FAN Speed
PWM Control
GND
FAN Power
FAN Speed
PWM Control
DSBV-D
DSBV-D Power supply SMBus connector
PSUSMB1
+3.3V Remote Sense
GND
NC
I2CDAT
I2CCLK
FRNT_FAN1/2/3/4, FBD_FAN1)
The fan connectors support cooling fans of 350 mA ~ 740 mA (8.88 W max.)
or a total of 2.1 A ~ 4.44 A (53.28 W max.) at +12V. Connect the fan cables
to the fan connectors on the motherboard, making sure that the black wire of
each cable matches the ground pin of the connector.
Do not forget to connect the fan cables to the fan connectors. Insufcient air
ow inside the system may damage the motherboard components. These are
not jumpers! Do not place jumper caps on the fan connectors!
8. Power supply SMBus connector (5-pin PSUSMB1)
This connector is for the power supply SMB cable, if your power supply
supports the SMBus function.
ASUS DSBV-D 2-37
Page 58

9. SSI power connectors (24-pin ATXPWR1, 8-pin ATX12V1, 4-pin ATX12V2)
DSBV-D
DSBV-D ATX power connectors
8-PIN
GND
12V1
GND
12V1
GND
12V2
GND
12V2
24-PIN Power Connector
ATXPWR1
ATX12V1
+12V DC
GND
+12V DC
GND
4-PIN
ATX12V2
+3 Volts
+3 Volts
Ground
+5 Volts
+5 Volts
Ground
Ground
Power OK
+5V Standby
+12 Volts
-5 Volts
+5 Volts
+3 Volts
-12 Volts
Ground
Ground
Ground
PSON#
Ground
+5 Volts
+12 Volts
+3 Volts
+5 Volts
Ground
These connectors are for SSI power supply plugs. The power supply plugs
are designed to t these connectors in only one orientation. Find the proper
orientation and push down rmly until the connectors completely t.
•
For a fully congured system, we recommend that you use an SSI
12 V-compliant power supply unit (PSU) for LGA771-socket Intel® Xeon
Dual Core processors (Bensley platform).
•
Do not forget to connect the 24+8+4-pin power plugs; otherwise, the system
will not boot up.
•
Use of a PSU with a higher power output is recommended when conguring
a system with more power consuming devices. The system may become
unstable or may not boot up if the power is inadequate.
•
You must install a PSU with a higher power rating if you intend to install
additional devices.
2-38 Chapter 2: Hardware information
Page 59

10. Parallel port connector (26-1 pin LPT1)
DSBV-D
DSBV-D Parallel port connector
LPT1
SPD7GND
SPD6GND
SPD5GND
SPD4GND
SLCT
PEGND
BUSY
ACK#GND
SPD3GND
SPD2SLIN#
SPD1PINIT#
SPD0ERROR#
STB#AFD#
GND
PIN1
DSBV-D
DSBV-D BPSMB connector
BPSMB1
PIN1
12CDAT P2
GND
FAN_PWM
+5V
I2CCLK P2
FAN_DC1
This connector is for a parallel port. Connect the parallel port module cable
to this connector, then install the module to a slot opening at the back of the
system chassis.
11. Backplane SMBus connector (7-1 pin BPSMB1)
This connector allows you to connect SMBus (System Management Bus)
devices. Devices communicate with an SMBus host and/or other SMBus
devices using the SMBus interface.
ASUS DSBV-D 2-39
Page 60

12. Serial General Purpose Input/Output connector (6-1 pin SGPIO1)
DSBV-D
DSBV-D SGPIO connector
SGPIO1
PIN1
GND
SATA_SCLK
SATA_SLOAD
SDATAOUT1
SDATAOUT0
DSBV-D
DSBV-D System panel connector
PANEL1
MLED-GND
NCPOWERBTN#
+5VGND
GNDNC
POWERLED+IDELED+
NCIDELED-
POWERLED-
MLED+NMIBTN#
GNDRESETBTN#
SPKROUTGND
This connector is used to the SGPIO peripherals for the LSI MegaRAID SATA
LED.
13. System panel connector (20-1 pin PANEL1)
This connector supports several chassis-mounted functions.
The system panel connector is color-coded for easy connection.
•
System power LED (Green 3-pin PLED)
This 3-pin connector is for the system power LED. Connect the chassis
power LED cable to this connector. The system power LED lights up
when you turn on the system power, and blinks when the system is in
sleep mode.
2-40 Chapter 2: Hardware information
Page 61

•
Hard disk drive activity LED (Red 2-pin IDE_LED)
This 2-pin connector is for the HDD Activity LED. Connect the HDD
Activity LED cable to this connector. The IDE LED lights up or ashes
when data is read from or written to the HDD.
•
System warning speaker (Orange 4-pin SPEAKER)
This 4-pin connector is for the chassis-mounted system warning
speaker. The speaker allows you to hear system beeps and warnings.
•
ATX power button/soft-off button (Yellow 2-pin PWRSW)
This connector is for the system power button. Pressing the power
button turns the system on or puts the system in sleep or soft-off mode
depending on the BIOS settings. Pressing the power switch for more
than four seconds while the system is ON turns the system OFF.
•
Reset button (Blue 2-pin RESET)
This 2-pin connector is for the chassis-mounted reset button for system
reboot without turning off the system power.
•
Message button (Brown 2-pin MLED)
This 2-pin connector is for the message LED which indicates the booting
status. The LED blinks when the system is in the booting process until
the operating system is loaded. Connect the message LED cable to this
connector.
•
Non-Masked Interrupt button (Light blue 2-pin MNIBTN)
This 2-pin connector is for the non-masked interrupt initiation.
ASUS DSBV-D 2-41
Page 62

14. System panel auxiliary connector (20-2 pin AUX_PANEL1)
DSBV-D
DSBV-D System panel auxiliary connector
AUX_PANEL1
I2C_4_DATA#LOCATORLED1+
+5VSBLOCATORLED1-
LAN1_LINKLOCATORBTN#
LAN1_ACTGND
+5VSB
I2C_4_CLK#
GNDGND
LAN2_ACTLOCATORLED2-
LAN2_LINKLOCATORLED2+
CASEOPEN
PIN1
NC
1 2 2
5 43 4
This connector is for additional front panel features including front panel SMB,
locator LED and switch, chassis intrusion, and LAN LEDs.
1 Front panel SMB (6-1 pin FPSMB)
These leads connect the front panel SMBus cable.
2 LAN activity LED (2-pin LAN1_LINKACTLED, LAN2_LINKACTLED)
These leads are for Gigabit LAN activity LEDs on the front panel.
Connect the LAN Activity LED cables to these connectors. The LEDs
blink during a network activity and are always lit when linked.
3 Chassis intrusion (4-1 pin CHASSIS)
These leads are for the intrusion detection feature for chassis with
intrusion sensor or microswitch. When you remove any chassis
component, the sensor triggers and sends a high-level signal to these
leads to record a chassis intrusion event.
4 Locator LED (2-pin LOCATORLED1 and 2-pin LOCATORLED2)
These leads are for the locator LED1 and LED2 on the front panel.
Connect the Locator LED cables to these 2-pin connector. The LEDs
will light up when the Locator button is pressed.
5 Locator Button/Swich (2-pin LOCATORBTN)
These leads are for the locator button on the front panel. This button
queries the state of the system locator.
2-42 Chapter 2: Hardware information
Page 63

This chapter describes the power up
sequence, and ways of shutting down the
system.
Powering up
3
Page 64

Chapter summary
3
3.1 Starting up for the rst time ........................................................ 3-1
3.2 Turning off the computer .............................................................
3-2
ASUS DSBV-D
Page 65

3.1 Starting up for the rst time
1. After making all the connections, replace the system case cover.
2. Be sure that all switches are off.
3. Connect the power cord to the power connector at the back of the system
chassis.
4. Connect the power cord to a power outlet that is equipped with a surge
protector.
5. Turn on the devices in the following order:
a. Monitor
b. System power
6. After applying power, the system power LED on the system front panel case
lights up. For systems withATX power supplies, the system LED lights up
when you press the ATX power button. If your monitor complies with “green”
standards or if it has a “power standby” feature, the monitor LED may light up
or switch between orange and green after the system LED turns on.
The system then runs the power-on self tests or POST. While the tests are
running, the BIOS beeps (see BIOS beep codes table below) or additional
messages appear on the screen. If you do not see anything within 30
seconds from the time you turned on the power, the system may have failed a
power-on test. Check the jumper settings and connections or call your retailer
for assistance.
Phoenix BIOS beep codes
Beep Description Error
Endless beep Memory module missing
One continuous beep followed by VGA controller failure
short beeps
Two short beeps PCI resource assignment error
7. At power on, hold down the <Delete> key to enter the BIOS Setup. Follow the
instructions in Chapter 4.
ASUS DSBV-D 3-1
Page 66

3.2 Turning off the computer
3.2.1 Using the OS shut down function
If you are using Windows® 2000/2003:
1. Click the Start button then click Shut Down...
2. Make sure that the Shut Down option button is selected, then click the OK
button to shut down the computer.
3. The power supply should turn off after Windows
If you are using Windows® XP:
1. Click the Start button then select Turn Off Computer.
2. Click the Turn Off button to shut down the computer.
3. The power supply should turn off after Windows
3.2.2 Using the dual function power switch
While the system is ON, pressing the power switch for less than four seconds puts
the system to sleep mode or to soft-off mode, depending on the BIOS setting.
Pressing the power switch for more than four seconds lets the system enter the
soft-off mode regardless of the BIOS setting.
®
shuts down.
®
shuts down.
3-2 Chapter 3: Powering up
Page 67

This chapter tells how to change
the system settings through the BIOS
Setup menus. Detailed descriptions
of the BIOS parameters are also
provided.
BIOS setup
4
Page 68

Chapter summary
4
4.1 Managing and updating your BIOS ............................................ 4-1
4.2 BIOS setup program ....................................................................
4.3 Main menu ..................................................................................
4.4 Advanced menu .........................................................................
4.5 Server menu ...............................................................................
4.6 Security menu ............................................................................
4.7 Boot menu ..................................................................................
4.8 Exit menu ....................................................................................
4-8
4-12
4-18
4-38
4-41
4-43
4-45
ASUS DSBV-D
Page 69

4.1 Managing and updating your BIOS
The following utilities allow you to manage and update the motherboard Basic
Input/Output System (BIOS) setup:
1. Phoenix Phlash16 BIOS Flash Utility (Updates the BIOS in DOS mode using
a bootable oppy disk.)
2. ASUS CrashFree BIOS 2 (To recover the BIOS using a bootable oppy disk
when the BIOS le fails or gets corrupted.)
3. ASUS Update (Updates the BIOS in Windows
Refer to the corresponding sections for details on these utilities.
Save a copy of the original motherboard BIOS le to a bootable oppy disk in
case you need to restore the BIOS in the future. Copy the original motherboard
BIOS using the ASUS Update or Phoenix Phlash16 BIOS utilities. Refer to page
4-3 for details.
4.1.1 Creating a bootable oppy disk
1. Do either one of the following to create a bootable oppy disk.
DOS environment
a. Insert a 1.44MB oppy disk into the drive.
b. At the DOS prompt, type
®
Windows
XP environment
a. Insert a 1.44 MB oppy disk to the oppy disk drive.
b. Click Start from the Windows
c. Select the 3 1/2 Floppy Drive icon.
d. Click File from the menu, then select Format. A Format 3 1/2 Floppy Disk
window appears.
e. Select Create an MS-DOS startup disk from the format options eld, then
click Start.
format A:/S
®
desktop, then select My Computer.
®
environment.)
then press <Enter>.
Windows® 2000 environment
To create a set of boot disks for Windows® 2000:
a. Insert a formatted, high density 1.44 MB oppy disk into the drive.
®
b. Insert the Windows
ASUS DSBV-D 4-1
2000 CD to the optical drive.
Page 70

c. Click Start, then select Run.
d. From the Open eld, type
D:\bootdisk\makeboot a:
assuming that D: is your optical drive.
e. Press <Enter>, then follow screen instructions to continue.
2. Copy the original or the latest motherboard BIOS le to the bootable oppy
disk.
4.1.2 Updating the BIOS using the Phoenix Phlash16
Utility
The Basic Input/Output System (BIOS) can be updated using the Phoenix
Phlash16 Utility. Follow these instructions to update the BIOS using this utility.
1. Download the latest BIOS le from the ASUS web site. Rename the le to
BIOS.WPH. Save the le to a oppy disk.
Make sure you copy the correct BIOS le for the specic model of your
motherboard. Save only the updated BIOS le in the oppy disk to avoid loading
the wrong BIOS le.
2. Copy the Phoenix Phlash16 (phlash16.exe) utility from the Software folder of
the support CD to the oppy disk with the latest BIOS le.
3. Boot the system in DOS mode using the bootable oppy disk you created
earlier.
4. When the A:> appears, replace the bootable oppy disk with the oppy disk
containing the new BIOS le and the Phoenix Phlash16 Utility.
5. At the prompt, type the following command string:
phlash16 /mode=3 BIOS. WPH.
6. The Phoenix Phlash16 Utility automatically updates the BIOS.
Do not turn off or reset the system during the ashing process!
7. Restart the system after the utility completes the updating process. Make
sure you remove the oppy disk from the drive
4-2 Chapter 4: BIOS setup
Page 71

4.1.3 ASUS CrashFree BIOS 2 utility
The ASUS CrashFree BIOS 2 is an auto recovery tool that allows you to restore
the BIOS le when it fails or gets corrupted during the updating process. You can
update a corrupted BIOS le using a oppy disk.
Prepare a oppy disk before using this utility.
Recovering the BIOS from a oppy disk
To recover the BIOS from a oppy disk:
1. Insert the motherboard oppy disk to a PC, then boot from the support CD;
the screen will show several optional items.
2. Select the item “ Create the emergent BIOS Recovery diskette”.
A) FreeDOS command prompt
B) Create INTEL 6321 MATRIX STORAGE MANAGER for Windows 32 bit
Driver Disk. (Also support AHCI.)
C) Create INTEL 6321 MATRIX STORAGE MANAGER for Windows 64 bit
Driver Disk. (Also support AHCI.)
D) Create INTEL 6321 LSI MegaRAID for Win2k Driver Disk
E) Create INTEL 6321 LSI MegaRAID for WinXP/Win2k3 32 bit
Driver Disk
F) Create INTEL 6321 LSI MegaRAID for WinXP/Win2k3 64 bit
Driver Disk
G) Create the emergent BIOS Recovery diskette
H) ESB2ASFrmwareupdate
Please choose A TO H:
3. After the oppy disk is created, put this disk in the oppy disk drive, then turn
on the machine.
4. The utility displays the following message and automatically checks the oppy
for the recovery information.
RN50 DDR1 A21 BIOS
5. When found, the utility reads the BIOS le and starts ashing the corrupted
BIOS le.
ASUS DSBV-D 4-3
Page 72

Phoenix Phlash16 Utility Version 1.6.1.9
Copyright (c) Phoenix Technologies Ltd., 2005
Performing the following function
Load Image File BIOS.WPH
Verify interface information
Backup system BIOS ROM
Checkashmemorytype(s)
Flash memory block:
Save block
Restore block
Zero out block
Erase block
Program block
Verify block
Flash programming complete
30% Read in
Identifyingashmemoryparttype 00:00:00 (18)
DO NOT shut down or reset the system while updating the BIOS! Doing so can
cause system boot failure!
6. When the utility completes the updating process, a message appears,
informing you that the ash memory has been programmed successfully.
Phoenix Phlash16 Utility Version 1.6.1.9
Copyright (c) Phoenix Technologies Ltd., 2005
Phoenix Phlash16 Status
Performing the following function
Flash memory has been successfully programmed
Load Image File BIOS.WPH
Verify interface information
Backup system BIOS ROM
Checkashmemorytype(s)
Flash memory block:
Save block
Restore block ..........................
Zero out block ..........................
Eraseblock√√√√√√√√√√√√√√√√√√√√√√√√√.
Programblock.√√√√√√√√√√√√√√√√√√√√√√√√√√
Verifyblock.√√√√√√√√√√√√√√√√√√√√√√√√√√
Flash programming complete
PRESS ANY KEY TO RESTART THE SYSTEM
If the system does not restart
TURN THE POWER OFF, THEN ON
Ready to restart the system 00:00:00 (1E)
Flash part: SST49LF008A DeviceID: 5a Mfr.ID: bf
4-4 Chapter 4: BIOS setup
Page 73

7. Press the power button for more than four seconds to turn off the system.
The recovered BIOS may not be the latest BIOS version for this motherboard.
Visit the ASUS website (www.asus.com) to download the latest BIOS le.
4.1.4 ASUS Update utility
The ASUS Update is a utility that allows you to manage, save, and update the
motherboard BIOS in Windows® environment. The ASUS Update utility allows you
to:
• Save the current BIOS le
• Download the latest BIOS le from the Internet
• Update the BIOS from an updated BIOS le
• Update the BIOS directly from the Internet, and
• View the BIOS version information.
This utility is available in the support CD that comes with the motherboard package.
ASUS Update requires an Internet connection either through a network or an
Internet Service Provider (ISP).
Installing ASUS Update
To install ASUS Update:
1. Place the support CD in the optical drive. The Drivers menu appears.
2. Click the Utilities tab, then click Install ASUS Update VX.XX.XX.
3. The ASUS Update utility is copied to your system.
Quit all Windows® applications before you update the BIOS using this utility.
ASUS DSBV-D 4-5
Page 74

Updating the BIOS through the Internet
To update the BIOS through the Internet:
1. Launch the ASUS Update utility from the Windows
> Programs > ASUS > ASUSUpdate > ASUSUpdate. The ASUS Update main
window appears.
®
desktop by clicking Start
2. Select Update BIOS from the
Internet option from the drop-down
menu, then click Next.
4-6 Chapter 4: BIOS setup
3. Select the ASUS FTP site nearest
you to avoid network trafc, or
click Auto Select. Click Next.
Page 75

4. From the FTP site, select the BIOS
version that you wish to download.
Click Next.
5. Follow the screen instructions to
complete the update process.
The ASUS Update utility is
capable of updating itself through
the Internet. Always update the
utility to avail all its features.
Updating the BIOS through a BIOS le
To update the BIOS through a BIOS le:
1. Launch the ASUS Update utility from the Windows
> Programs > ASUS > ASUSUpdate > ASUSUpdate. The ASUS Update main
window appears.
2. Select Update BIOS from a le
option from the drop-down menu,
then click Next.
®
desktop by clicking Start
3. Locate the BIOS le from the Open window, then click Save.
4. Follow the screen instructions to complete the update process.
ASUS DSBV-D 4-7
Page 76

4.2 BIOS setup program
This motherboard supports a programmable Low-Pin Count (LPC) chip that you
can update using the provided utility described in section “4.1 Managing and
updating your BIOS.”
Use the BIOS Setup program when you are installing a motherboard, reconguring
your system, or prompted to “Run Setup.” This section explains how to congure
your system using this utility.
Even if you are not prompted to use the Setup program, you can change the
conguration of your computer in the future. For example, you can enable the
security password feature or change the power management settings. This
requires you to recongure your system using the BIOS Setup program so that the
computer can recognize these changes and record them in the CMOS RAM of the
LPC chip.
The LPC chip on the motherboard stores the Setup utility. When you start up the
computer, the system provides you with the opportunity to run this program. Press
<Del> during the Power-On Self-Test (POST) to enter the Setup utility; otherwise,
POST continues with its test routines.
If you wish to enter Setup after POST, restart the system by pressing
<Ctrl+Alt+Delete>, or by pressing the reset button on the system chassis. You can
also restart by turning the system off and then back on. Do this last option only if
the rst two failed.
The Setup program is designed to make it as easy to use as possible. Being a
menu-driven program, it lets you scroll through the various sub-menus and make
your selections from the available options using the navigation keys.
• The default BIOS settings for this motherboard apply for most conditions
to ensure optimum performance. If the system becomes unstable after
changing any BIOS settings, load the default settings to ensure system
compatibility and stability. Select the Load Default Settings item under the
Exit Menu. See section “4.8 Exit Menu.”
• The BIOS setup screens shown in this section are for reference purposes
only, and may not exactly match what you see on your screen.
• Visit the ASUS website (www.asus.com) to download the latest BIOS le for
this motherboard.
4-8 Chapter 4: BIOS setup
Page 77

4.2.1 BIOS menu screen
Conguration eldsMenu items
General helpMenu bar
Main Advanced Server Security Boot Exit
System Date [04/19/2006]
System Time [15 : 30 : 36]
Floppy A [1.44/1.25 MB 3
IDEConguration
IDE Channel 0 Master [None]
IDE Channel 0 Slave [None]
SATA Port 1 [None]
SATA Port 2 [None]
SATA Port 3 [None]
SATA Port 4 [None]
System Information
F1 Help
ESC Exit
Select Item -/+ Change Values F9 Setup Defaults
↑↓
Select Menu Enter Select Sub-Menu F10 Save and Exit
→←
Sub-menu items
PhoenixBIOS Setup Utility
1/2
”]
ItemSpecicHelp
<Tab>, <Shift+Tab>, or
<Enter>selectseld.
Legend bar
4.2.2 Menu bar
The menu bar on top of the screen has the following main items:
For changing the basic system conguration
Main
Advanced
Server
Security
Boot
Exit
To select an item on the menu bar, press the right or left arrow key on the keyboard
until the desired item is highlighted.
For changing the advanced system settings
For changing the advanced server settings
For changing the security settings
For changing the system boot conguration
For selecting the exit options and loading default settings
ASUS DSBV-D 4-9
Page 78

4.2.3 Legend bar
At the bottom of the Setup screen is a legend bar. The keys in the legend bar allow
you to navigate through the various setup menus. The following table lists the keys
found in the legend bar with their corresponding functions.
Navigation Key Function
<F1> Displays the General Help screen
<F9> Loads setup default values
<Esc> Exits the BIOS setup or returns to the main menu from a
Left or Right arrow Selects the menu item to the left or right
Up or Down arrow Moves the highlight up or down between elds
Page Down or – (minus) Scrolls backward through the values for the highlighted eld
Page Up or + (plus) Scrolls forward through the values for the highlighted eld
<Enter> Brings up a selection menu for the highlighted eld
<F10> Saves changes and exit
sub-menu
4.2.4 Menu items
The highlighted item on the menu bar displays the specic items for that menu.
For example, selecting Main shows the Main menu items.
The other items (Advanced, Power, Boot, and Exit) on the menu bar have their
respective menu items.
4.2.5 Sub-menu items
A solid triangle before each item on any menu screen means that the iteam has a
sub-menu. To display the sub-menu, select the item and press <Enter>.
4.2.6 Conguration elds
These elds show the values for the menu items. If an item is user-congurable,
you can change the value of the eld opposite the item. You cannot select an item
that is not user-congurable.
A congurable eld is enclosed in brackets, and is highlighted when selected. To
change the value of a eld, select it then press <Enter> to display a list of options.
Refer to “4.2.7 Pop-up window.”
4-10 Chapter 4: BIOS setup
Page 79

4.2.7 Pop-up window
Select a menu item then press <Enter> to display a pop-up window with the
conguration options for that item.
Main Advanced Server Security Boot Exit
System Date [04/19/2006]
System Time [15 : 30 : 36]
Floppy A [1.44/1.25 MB 3
IDEConguration
IDE Channel 0 Master [None]
IDE Channel 0 Slave [None]
SATA Port 1 [None]
SATA Port 2 [None]
SATA Port 3 [None]
SATA Port 4 [None]
System Information
F1 Help
ESC Exit
Select Item -/+ Change Values F9 Setup Defaults
↑↓
Select Menu Enter Select Sub-Menu F10 Save and Exit
→←
PhoenixBIOS Setup Utility
1/2
Disabled
360 Kb 5
1.2 MB 5
720 Kb 3
1.44/1.25 MB 3
2.88 MB 3
1/4
”
1/4
”
1/2
”
1/2
”
1/2
”
ItemSpecicHelp
<Tab>, <Shift+Tab>, or
”]
<Enter>selectseld.
Pop-up menu
4.2.8 General help
At the top right corner of the menu screen is a brief description of the selected item.
ASUS DSBV-D 4-11
Page 80

4.3 Main menu
When you enter the BIOS Setup program, the Main menu screen appears, giving
you an overview of the basic system information.
Refer to section “5.2.1 BIOS menu screen” for information on the menu screen
items and how to navigate through them.
Main Advanced Server Security Boot Exit
System Date [06/16/2006]
System Time [15 : 30 : 36]
Floppy A [1.44/1.25 MB 3
IDEConguration
IDE Channel 0 Master [None]
IDE Channel 0 Slave [None]
SATA Port 1 [None]
SATA Port 2 [None]
SATA Port 3 [None]
SATA Port 4 [None]
System Information
F1 Help
ESC Exit
Select Item -/+ Change Values F9 Setup Defaults
↑↓
Select Menu Enter Select Sub-Menu F10 Save and Exit
→←
PhoenixBIOS Setup Utility
1/2
”]
ItemSpecicHelp
<Tab>, <Shift-Tab>, or
<Enter>selectseld.
4.3.1 System Date [Day xx/xx/xxxx]
Allows you to set the system date.
4.3.2 System Time [xx:xx:xx]
Allows you to set the system time.
4.3.3 Floppy A [1.44M, 3.5 in.]
Sets the type of oppy drive installed.
Conguration options: [Disabled] [360 Kb 5 1/4”] [1.2 MB 5 1/4”] [720 Kb 3 1/2” ]
[1.44/1.25 MB 3 1/2”] [2.88 MB 3 1/2”]
4-12 Chapter 4: BIOS setup
Page 81

4.3.4 IDE Conguration
Main
IDEConguration
Fixed disk boot sector: [Normal]
S-ATAConguration
PhoenixBIOS Setup Utility
ItemSpecicHelp
Write protects boot sector
on hard disk to protect
against viruses.
F1 Help
ESC Exit
Select Item -/+ Change Values F9 Setup Defaults
↑↓
Select Menu Enter Select Sub-Menu F10 Save and Exit
→←
Fixed disk boot sector [Normal]
Setting this item to [Write Protect] prevents write access to the boot sector on
the hard disk to protect against viruses. The defaul setting [Normal] allows write
access. Conguration options: [Normal] [Write Protect]
S-ATA Conguration
Main
S-ATAConguration
Parallel ATA [Enabled]
Serial ATA [Enabled]
SATA Controller Mode Option [Enhanced]
SATA RAID Enable [Disabled]
SATA AHCI Enable [Disabled]
F1 Help
ESC Exit
Select Item -/+ Change Values F9 Setup Defaults
↑↓
Select Menu Enter Select Sub-Menu F10 Save and Exit
→←
Parallel ATA [Enabled]
Allows you to enable or disable the parallel ATA function.
Conguration options: [Disabled] [Enabled]
PhoenixBIOS Setup Utility
ItemSpecicHelp
Enable the PATA
ASUS DSBV-D 4-13
Page 82

Serial ATA [Enabled]
Allows you to enable or disable the Serial ATA function.
Conguration options: [Disabled] [Enabled]
SATA Controller Mode Option [Enhanced]
Allows selection of the Serial ATA operation mode depending on the operating
system (OS) that you installed. When you set this item to Enhanced Mode,
Serial ATA and Parallel ATA devices are auto-detected and placed in native
IDE mode. Set to Enhanced Mode if you are using native OS, such as
Windows® 2000/XP. When you set this item to Compatible Mode, Serial ATA
and Parallel ATA devices are auto-detected and placed in legacy mode.
Conguration options: [Compatible] [Enhanced]
The following items appear only if you set the
item to [Enhanced].
SATA RAID Enable [Disabled]
Allows you to enable or disable the Serial ATA RAID function.
Conguration options: [Disabled] [Enabled]
SATA AHCI Enable [Disabled]
Allows you to enable or disable the Serial ATA AHCI function.
Conguration options: [Disabled] [Enabled]
• AHCI mode item will support only under Windows environment.
• Due to the driver limitation, you will not nd any SATA driver if you install
Fedora core 4.
SATA Controller Mode Option
4-14 Chapter 4: BIOS setup
Page 83

4.3.5 IDE Channel 0 Master/Slave;
SATA Port 1/2/3/4
Main
IDE Channel 0 Master
Type: [Auto]
Multi-Sector Transfers [Disabled]
LBA Mode Control [Disabled]
32 Bit I/O [Disabled]
Transfer Mode [Standard]
Ultra DMA Mode [Disabled]
PhoenixBIOS Setup Utility
ItemSpecicHelp
Auto = Autotying.
None = Disabling drive.
ATAPI Removable = ATAPI
media (e.g., LS120, USB
Floppy, USB Zip).
CD-ROM = CD-ROM drive.
IDE Removable = IDE
removable media (e.g.,
IDE Zip drive).
Other ATAPI = Other
ATAPI media.
User = You supply the
hard disk drive type.
F1 Help
ESC Exit
Select Item -/+ Change Values F9 Setup Defaults
↑↓
Select Menu Enter Select Sub-Menu F10 Save and Exit
→←
Type [Auto]
Selects the type of IDE drive. Setting to Auto allows automatic selection of the
appropriate IDE device type. Select [CD-ROM] if you are specically conguring a
CD-ROM drive. Select [ATAPI Removable] if your device is either a ZIP, LS-120,
or MO drive. Select [User] to manually enter the parameters of the device.
Conguration options: [Auto] [User] [Other ATAPI] [IDE Removable] [CD-ROM]
[ATAPI Removable]
• Except for 32 Bit I/O item, the following items become user-congurable
when the Type item is not set to [Auto].
• For items that have no sub-menu, you have to use
-/+ for values changing.
Multi-Sector Transfers [Disabled]
Enables or disables data multi-sectors transfers. When set to 2~16 Sectors, the
data transfer from and to the device occurs multiple sectors at a time if the device
supports multi-sector transfer feature. When set to [Disabled], the data transfer
from and to the device occurs one sector at a time.
Conguration options: [Disabled] [2 Sectors] [4 Sectors] [8 Sectors] [16 Sectors]r
LBA Mode Control [Disabled]
Enables or disables the LBA mode. Setting to Enabled enables the LBA mode if the
device supports this mode, and if the device was not previously formatted with LBA
mode disabled. Conguration options: [Disabled] [Enabled]
32 Bit I/O [Disabled]
Enables or disables 32-bit data transfer.
Conguration options: [Disabled] [Enabled]
ASUS DSBV-D 4-15
Page 84

Transfer Mode [Stadard]
Allows you to select the mothod for the data transferring if the hard disk supports
this feature.
Conguration options: [Standard] [Fast PIO 1] [Fast PIO 2] [Fast PIO 3] [Fast PIO 4]
[FPIO 3 / DMA 1] [FPIO 4 / DMA2]
Ultra DMA Mode [Disabled]
When this item is set to [Mode 0-5], the UDMA capability allows improved transfer
speeds and data integrity for supported IDE devices.
Conguration options: [Disabled] [Mode 0] [Mode 1] [Mode 2] [Mode 3] [Mode 4]
[Mode 5]
4.3.6 System Information
This menu gives you an overview of the general system specications. The BIOS
automatically detects the items in this menu.
Main
System Information
Model Name DSBV-D
Model ID 8032A0
ASUS-BIOS
Version 1004
Date 11/15/2006
Processor Information
System Memory Information
PhoenixBIOS Setup Utility
ItemSpecicHelp
The detailed information
for CPUs
F1 Help
ESC Exit
Select Item -/+ Change Values F9 Setup Defaults
↑↓
Select Menu Enter Select Sub-Menu F10 Save and Exit
→←
The items in this menu are non-user congurable.
Model Name/Model ID
Displays the ASUS internal model information.
ASUS BIOS
Displays the BIOS revision and build date.
4-16 Chapter 4: BIOS setup
Page 85

Processor Information
Displays the auto-detected CPU specication.
Main
Processor Information
*** CPU1 :
Brand Intel(R) Xeon(TM) CPU 2.83GHz
Speed 2.800GHz
Ratio Actual 17 Max 17
Cache L1/32 KB L2/4096 KB
ID/uCode 0F64h/02h
PhoenixBIOS Setup Utility
ItemSpecicHelp
All items on this menu
cannotbemodiedinuser
mode. If any items require
changes, please consult
your system Supervisor.
F1 Help
ESC Exit
Select Item -/+ Change Values F9 Setup Defaults
↑↓
Select Menu Enter Select Sub-Menu F10 Save and Exit
→←
System Memory Information
Displays the auto-detected system memory information.
Main
System Memory Information
Speed : DDR2 533
Total Memory: 1024MB
DIMM_00-- 1024MB, AMB Temperature: 18
DIMM_01-- None
DIMM_02-- None
DIMM_10-- None
DIMM_11-- None
DIMM_12-- None
F1 Help
ESC Exit
Select Item -/+ Change Values F9 Setup Defaults
↑↓
Select Menu Enter Select Sub-Menu F10 Save and Exit
→←
PhoenixBIOS Setup Utility
ItemSpecicHelp
All items on this menu
cannotbemodiedinuser
mode. If any items require
changes, please consult
your system Supervisor.
ASUS DSBV-D 4-17
Page 86

4.4 Advanced menu
The Advanced menu items allow you to change the settings for the CPU and other
system devices.
Take caution when changing the settings of the Advanced menu items. Incorrect
eld values can cause the system to malfunction.
Main Advanced Server Security Boot Exit
WARNING: Setting wrong value in below sections may
cause system to malfunction.
Advanced Processor Options
ChipsetConguration
PCIConguration
ICH USB Control Sub-Menu
PeripheralDevicesConguration
ACPIConguration
PowerOnConguration
Hardware Monitor
F1 Help
ESC Exit
Select Item -/+ Change Values F9 Setup Defaults
↑↓
Select Menu Enter Select Sub-Menu F10 Save and Exit
→←
PhoenixBIOS Setup Utility
ItemSpecicHelp
Options for CPU
4.4.1 Advanced Processor Options
The following screens appear when you install Intel® 5000 series CPU.
Advanced
Advanced Processor Options
MultiprocessorSpecication [1.4]
Frequency Ratio [Default]
Hyperthreading: [Enabled]
Intel(R) Virtualization Technology [Enabled]
Machine Checking [Enabled]
Fast String Operations [Enabled]
Compatible FPU Code [Disabled]
Split Lock operations [Enabled]
C1 Enhanced Mode [Enabled]
No Execute Mode Mem Protection [Enabled]
Adjacent Cache Line Prefetch [Enabled]
Set Max Ext CPUID = 3 [Disabled]
Echo TPR [Disabled]
F1 Help
ESC Exit
Select Item -/+ Change Values F9 Setup Defaults
↑↓
Select Menu Enter Select Sub-Menu F10 Save and Exit
→←
Scroll down to display the following item:
Advanced Processor Options
Discrete MTRR Allocation [Disabled]
Intel EIST support: [Enabled]
F1 Help
ESC Exit
Select Item -/+ Change Values F9 Setup Defaults
↑↓
Select Menu Enter Select Sub-Menu F10 Save and Exit
→←
Multiprocessor Specication [1.4]
Allows you to congure the MP Specication revision level.
Conguration options: [1.1] [1.4]
PhoenixBIOS Setup Utility
ItemSpecicHelp
CongurestheMP
Specicationrevision
level. Some operating
systems will require
1.1 for compatibility
reasons.
ItemSpecicHelp
4-18 Chapter 4: BIOS setup
Page 87

Frequency Ratio [Default]
Allows you to select the processor frequency ratio.
Conguration options: [Default] [X 12] [X 13] [X 14] [X 15] [X 16] [X 17]
Hyperthreading: [Enabled]
Allows you to enable or disable the Intel® Hyperthreading Technology feature.
Conguration options: [Disabled] [Enabled]
Intel(R) Virtualization Technology [Enabled]
Conguration options: [Disabled] [Enabled]
Machine Checking [Enabled]
Conguration options: [Disabled] [Enabled]
Fast String Operations [Enabled]
Conguration options: [Disabled] [Enabled]
Compatible FPU Code [Disabled]
Conguration options: [Disabled] [Enabled]
Split Lock operations [Enabled]
Conguration options: [Disabled] [Enabled]
C1 Enhanced Mode [Enabled]
Allows you to enable or disable C1E mode. In C1E mode, the CPU power
consumption is lower when idle. Conguration options: [Disabled] [Enabled]
No Execute Mode Mem Protection [Enabled]
Conguration options: [Disabled] [Enabled]
Adjacent Cache Line Prefetch [Enabled]
Conguration options: [Disabled] [Enabled]
Set Max Ext CPUID = 3 [Disabled]
Enable this item to boot legacy operating systems that cannot support CPUs with
extended CPUID functions. Conguration options: [Disabled] [Enabled]
Echo TPR [Disabled]
Conguration options: [Disabled] [Enabled]
Discrete MTRR Allocation [Disabled]
Conguration options: [Disabled] [Enabled]
ASUS DSBV-D 4-19
Page 88

Intel EIST support [Enabled]
Enables or disables EIST support.
Conguration options: [Disabled] [Enabled]
The following screens appear when you install Intel® 5100 series CPU.
Advanced
Advanced Processor Options
MultiprocessorSpecication [1.4]
Numbers of Stop Grant [Per Core]
Intel(R) Virtualization Technology [Enabled]
Machine Checking [Enabled]
Fast String Operations [Enabled]
Compatible FPU Code [Disabled]
Split Lock operations [Enabled]
Thermal Management 2 [Enabled]
C1 Enhanced Mode [Enabled]
No Execute Mode Mem Protection [Enabled]
Adjacent Cache Line Prefetch [Enabled]
Set Max Ext CPUID = 3 [Disabled]
Echo TPR [Disabled]
F1 Help
ESC Exit
Select Item -/+ Change Values F9 Setup Defaults
↑↓
Select Menu Enter Select Sub-Menu F10 Save and Exit
→←
PhoenixBIOS Setup Utility
ItemSpecicHelp
CongurestheMP
Specicationrevision
level. Some operating
systems will require
1.1 for compatibility
reasons.
Scroll down to display the following item:
Advanced Processor Options
Discrete MTRR Allocation [Disabled]
Intel EIST support: [Enabled]
F1 Help
ESC Exit
Select Item -/+ Change Values F9 Setup Defaults
↑↓
Select Menu Enter Select Sub-Menu F10 Save and Exit
→←
ItemSpecicHelp
Multiprocessor Specication [1.4]
Allows you to congure the MP Specication revision level.
Conguration options: [1.1] [1.4]
Numbers of Stop Grant [Per Core]
Conguration options: [Per Core] [Single]
Intel(R) Virtualization Technology [Enabled]
Conguration options: [Disabled] [Enabled]
Machine Checking [Enabled]
Conguration options: [Disabled] [Enabled]
Fast String Operations [Enabled]
Conguration options: [Disabled] [Enabled]
4-20 Chapter 4: BIOS setup
Page 89

Compatible FPU Code [Disabled]
Conguration options: [Disabled] [Enabled]
Split Lock operations [Enabled]
Conguration options: [Disabled] [Enabled]
Thermal Management 2 [Enabled]
Conguration options: [Disabled] [Enabled]
C1 Enhanced Mode [Enabled]
Allows you to enable or disable C1E mode. In C1E mode, the CPU power
consumption is lower when idle. Conguration options: [Disabled] [Enabled]
No Execute Mode Mem Protection [Enabled]
Conguration options: [Disabled] [Enabled]
Adjacent Cache Line Prefetch [Enabled]
Conguration options: [Disabled] [Enabled]
Set Max Ext CPUID = 3 [Disabled]
Enable this item to boot legacy operating systems that cannot support CPUs with
extended CPUID functions. Conguration options: [Disabled] [Enabled]
Echo TPR [Disabled]
Conguration options: [Disabled] [Enabled]
Discrete MTRR Allocation [Disabled]
Conguration options: [Disabled] [Enabled]
Intel EIST support [Enabled]
Enables or disables EIST support.
Conguration options: [Disabled] [Enabled]
ASUS DSBV-D 4-21
Page 90

The following screens appear when you install Intel® 5300 series CPU.
Advanced
Advanced Processor Options
MultiprocessorSpecication [1.4]
Numbers of Stop Grant [Per Core]
Intel(R) Virtualization Technology [Enabled]
Machine Checking [Enabled]
Fast String Operations [Enabled]
Compatible FPU Code [Disabled]
Split Lock operations [Enabled]
Thermal Management 2 [Enabled]
C1 Enhanced Mode [Enabled]
No Execute Mode Mem Protection [Enabled]
Adjacent Cache Line Prefetch [Enabled]
Set Max Ext CPUID = 3 [Disabled]
Echo TPR [Disabled]
F1 Help
ESC Exit
Select Item -/+ Change Values F9 Setup Defaults
↑↓
Select Menu Enter Select Sub-Menu F10 Save and Exit
→←
PhoenixBIOS Setup Utility
ItemSpecicHelp
CongurestheMP
Specicationrevision
level. Some operating
systems will require
1.1 for compatibility
reasons.
Scroll down to display the following item:
Advanced Processor Options
Discrete MTRR Allocation [Disabled]
Intel EIST support: [Enabled]
F1 Help
ESC Exit
Select Item -/+ Change Values F9 Setup Defaults
↑↓
Select Menu Enter Select Sub-Menu F10 Save and Exit
→←
ItemSpecicHelp
Multiprocessor Specication [1.4]
Allows you to congure the MP Specication revision level.
Conguration options: [1.1] [1.4]
Numbers of Stop Grant [Per Core]
Conguration options: [Per Core] [Single]
Intel(R) Virtualization Technology [Enabled]
Conguration options: [Disabled] [Enabled]
Machine Checking [Enabled]
Conguration options: [Disabled] [Enabled]
Fast String Operations [Enabled]
Conguration options: [Disabled] [Enabled]
Compatible FPU Code [Disabled]
Conguration options: [Disabled] [Enabled]
Split Lock operations [Enabled]
Conguration options: [Disabled] [Enabled]
4-22 Chapter 4: BIOS setup
Page 91

Thermal Management 2 [Enabled]
Conguration options: [Disabled] [Enabled]
C1 Enhanced Mode [Enabled]
Allows you to enable or disable C1E mode. In C1E mode, the CPU power
consumption is lower when idle. Conguration options: [Disabled] [Enabled]
No Execute Mode Mem Protection [Enabled]
Conguration options: [Disabled] [Enabled]
Adjacent Cache Line Prefetch [Enabled]
Conguration options: [Disabled] [Enabled]
Set Max Ext CPUID = 3 [Disabled]
Enable this item to boot legacy operating systems that cannot support CPUs with
extended CPUID functions. Conguration options: [Disabled] [Enabled]
Echo TPR [Disabled]
Conguration options: [Disabled] [Enabled]
Discrete MTRR Allocation [Disabled]
Conguration options: [Disabled] [Enabled]
Intel EIST support [Enabled]
Enables or disables EIST support.
Conguration options: [Disabled] [Enabled]
ASUS DSBV-D 4-23
Page 92

4.4.2 Chipset Conguration
This menu shows the chipset conguration settings. Select an item then press
<Enter> to display a pop-up menu with the conguration options.
Advanced
ChipsetConguration
CrystalBeachCongureEnable [Enabled]
SERR Signal Condition [None]
Demand Scrub Enable [Enabled]
Patrol Scrub Enable [Enabled]
4GB PCI Hole Granularity [256 MB]
Memory Branch Mode [Interleave]
Branch 0 Rank Interleave [4:1]
Branch 0 Rank Sparing [Disabled]
Enhanced x8 Detection [Enabled]
ForceITKCongClocking [Disabled]
FBDIMM(s) Thermal Throttling [Open Loop]
Open Loop Type [Best Performan]
Environment Temperature [025 ºC]
F1 Help
ESC Exit
Select Item -/+ Change Values F9 Setup Defaults
↑↓
Select Menu Enter Select Sub-Menu F10 Save and Exit
→←
Scroll down to display the following item:
Temperature Rise [025 ºC]
FBDIMM(s) Air Flow [2.0]
F1 Help
ESC Exit
Select Item -/+ Change Values F9 Setup Defaults
↑↓
Select Menu Enter Select Sub-Menu F10 Save and Exit
→←
Crystal Beach Congure Enable [Enabled]
Allows you to enable or disable the Conguration/Memory mapped accesses to the
Crystal Beach Conguration space located in Device 8, Fn 0, and Fn 1.
Conguration options: [Disabled] [Enabled]
PhoenixBIOS Setup Utility
ItemSpecicHelp
Select ECC error
conditions that
SERR# be asserted.
SERR Signal Condition [None]
Allows you to select the ECC error that the SERR# asserts.
Conguration options: [None] [Single Bit] [Multiple Bit] [Both]
Demand Scrub Enable [Enabled]
Enables or disables the Demand Scrubbing.
Conguration options: [Disabled] [Enabled]
Patrol Scrub Enable [Enabled]
Enables or disables the Patrol Scrubbing.
Conguration options: [Disabled] [Enabled]
4GB PCI Hole Granularity [256 MB]
Allows you to select the granularity of the PCI hole for PCI resource.
Conguration options: [256 MB] [512 MB] [1.0 GB] [2.0 GB]
4-24 Chapter 4: BIOS setup
Page 93

Memory Branch Mode [Interleave]
Allows you to select the memory branch mode.
Conguration options: [Sequential] [Interleave] [Mirror] [Single channel 0]
Branch 0 Rank Interleave [4:1]
Allows you to select the Branch 0 Rank Interleave.
Conguration options: [1:1] [2:1] [4:1]
Branch 0 Rank Sparing [Disabled]
Allows you to enable or disable the Branch 0 rank/DIMM Sparing feature.
Conguration options: [Disabled] [Enabled]
Enhanced x8 Detection [Enabled]
Allows you to enable or disable the enhanced x8 DRAM UC error detection.
Conguration options: [Disabled] [Enabled]
Force ITK Cong Clocking [Disabled]
Allows you to enable or disable the FBD conguration for ITK test suite.
Conguration options: [Disabled] [Enabled]
FBDIMM(s) Thermal Throttling [Open Loop]
Allows you to disable or set the thermal throttling control.
Conguration options: [Open Loop] [Close Loop] [ASUS MemCool Fan] [Disabled]
Open Loop Type [Best Performance]
Allows you to select the Open Loop Type.
Conguration options: [Best Performance] [Best Acoustic] [User Dene]
The following items appear when you set the
Open Loop Type
to [User Dene].
Environment Temperature [025 ºC]
Allows you to select the Environment Temperature value.
Conguration options: [020 ºC]~[040 ºC]
Temperature Rise [025 ºC]
Allows you to select the Temperature Rise value.
Conguration options: [010 ºC]~[030 ºC]
FBDIMM(s) Air Flow [2.0]
Allows yout to select the Air Flow value.
Conguration options: [1.0] [1.5]~[4.5] [5.0]
ASUS DSBV-D 4-25
Page 94

4.4.3 PCI Conguration
This menu shows the PCI conguration settings. Select an item then press <Enter>
to display the conguration options.
Advanced
PCIConguration
ResetCongurationData [No]
Plug & Play OS [No]
Palette Snooping [Disabled]
PCIE1 Slot
PCIE2 Slot
PCI3 Slot
PCIX4 Slot
PCIX5 Slot
PCIX6 Slot
PhoenixBIOS Setup Utility
ItemSpecicHelp
Select ‘Yes’ if you
want to clear the
Extended System
Conguration
Data (ESCD) area.
F1 Help
ESC Exit
Select Item -/+ Change Values F9 Setup Defaults
↑↓
Select Menu Enter Select Sub-Menu F10 Save and Exit
→←
Reset Conguration Data [No]
This item allows you to clear the Extended System Conguration Data (ESCD)
area. Conguration options: [No] [Yes]
Plug & Play O/S [No]
When set to [No], BIOS congures all the devices in the system. When set to
[Yes] and if you install a Plug and Play operating system, the operating system
congures the Plug and Play devices not required for boot.
Conguration options: [No] [Yes]
Palette Snooping [Disabled]
When set to [Enabled], the palette snooping feature informs the PCI devices that
an ISA graphics device is installed in the system so that the latter can function
correctly. Conguration options: [Disabled] [Enabled]
4-26 Chapter 4: BIOS setup
Page 95

PCIE1/2 Slot; PCI3 Slot; PCIX4/5/6 Slot
Allows you to congure the specic PCI devices.
Advanced
PCIE1 Slot
Optional ROM Scan: [Enabled]
PhoenixBIOS Setup Utility
ItemSpecicHelp
Initialize device
expansion ROM
F1 Help
ESC Exit
Select Item -/+ Change Values F9 Setup Defaults
↑↓
Select Menu Enter Select Sub-Menu F10 Save and Exit
→←
Optional ROM Scan [Enabled]
Allows you to enable or disable the device expansion ROM.
Conguration options: [Enabled] [Disabled]
ASUS DSBV-D 4-27
Page 96

4.4.4 ICH USB Control Sub-Menu
The items in this menu allow you to display the USB conguration settings. Select
an item then press <Enter> to display the conguration options.
Advanced
ICH USB Control Sub-Menu
USB Function [Enabled]
USB 2.0 Controller [Enabled]
Legacy USB Support: [Enabled]
PhoenixBIOS Setup Utility
ItemSpecicHelp
Enable USB host
controller.
F1 Help
ESC Exit
Select Item -/+ Change Values F9 Setup Defaults
↑↓
Select Menu Enter Select Sub-Menu F10 Save and Exit
→←
USB Function [Enabled]
Allows you to enable the USB host controller.
Conguration options: [Disabled] [Enabled]
The following items appear only if you enable the USB Function item.
USB 2.0 Controller [Enabled]
Allows you to enable or disable the USB 2.0 controller. Setting this item to [Enabled]
allows the built-in high speed USB support in the BIOS to turn on automatically
when you install high speed USB devices.
Conguration options: [Disabled] [Enabled]
Legacy USB Support [Enabled]
Allows you to enable or disable support for USB devices on legacy operating
systems (OS). Setting to [Enabled] allows the system to detect the presence of
USB devices at startup. If detected, the USB controller legacy mode is enabled.
if no USB device is detected, the legacy USB support is disabled. Conguration
options: [Disabled] [Enabled]
4-28 Chapter 4: BIOS setup
Page 97

4.4.5 Peripheral Devices Conguration
This menu shows the peripheral devices conguration settings. Select an item
then press <Enter> to display the conguration options.
Advanced
PeripheralDevicesConguration
COM1 port : [Enabled]
Base I/O address: [3F8]
Interrupt: [IRQ 4]
COM2 port: [Enabled]
Mode: [Normal]
Base I/O address: [2F8]
Interrupt: [IRQ 3]
Parallel port: [Enabled]
Base I/O address: [378]
Interrupt: [IRQ 7]
Mode: [ECP]
DMA channel [DMA 3]
Floppy disk controller [Enabled]
F1 Help
ESC Exit
Select Item -/+ Change Values F9 Setup Defaults
↑↓
Select Menu Enter Select Sub-Menu F10 Save and Exit
→←
COM1 port [Enabled]
Allows you to congure COM1 port.
Conguration options: [Disabled] [Enabled] [Auto]
Base I/O address [3F8]
Allows you to select the base I/O address for COM1 port.
Conguration options: [3F8] [2F8] [3E8] [2E8]
PhoenixBIOS Setup Utility
ItemSpecicHelp
Confugure COM1 port
using options:
[Disabled]
Noconguration
[Enabled]
Userconguration
[Auto]
BIOS or OS chooses
conguration
(OS Controlled)
Displayed when
controlled by OS
Interrupt [IRQ 4]
Allows you to set the interrupt for COM1 port.
Conguration options: [IRQ 3] [IRQ 4]
COM2 port [Enabled]
Allows you to congure COM2 port.
Conguration options: [Disabled] [Enabled] [Auto]
Mode [Normal]
Allows you to set the mode for COM2 port.
Conguration options: [Normal] [IR] [ASK-IR]
Base I/O address [2F8]
Allows you to select the base I/O address for COM2 port.
Conguration options: [3F8] [2F8] [3E8] [2E8]
ASUS DSBV-D 4-29
Page 98

Interrupt [IRQ 3]
Allows you to set the interrupt for COM2 port.
Conguration options: [IRQ 3] [IRQ 4]
Parallel port [Enabled]
Allows you to congure the parallel port.
Conguration options: [Disabled] [Enabled] [Auto]
Base I/O address [378]
Allows you to select the base I/O address for the parallel port.
Conguration options: [378] [278] [3BC]
Interrupt [IRQ 7]
Allows you to set the interrupt for the parallel port.
Conguration options: [IRQ 5] [IRQ 7]
Mode [ECP]
Allows you to set the mode for the parallel port.
Conguration options: [Output only] [Bi-directional] [EPP] [ECP]
DMA channel [DMA 3]
Allows you to set the DMA channel for the parallel port.
Conguration options: [DMA 1] [DMA 3]
Floppy disk controller [Enabled]
Allows you to congure the oppy disk controller.
Conguration options: [Disabled] [Enabled] [Auto]
4-30 Chapter 4: BIOS setup
Page 99

4.4.6 ACPI Conguration
This menu shows the Advanced Conguration and Power Interface (ACPI)
conguration settings. Select an item then press <Enter> to display the
conguration options.
Advanced
ACPIConguration
ACPI Version Features [ACPI v1.0]
Headless Mode [Disabled]
ACPI EMS Support [Disabled]
PhoenixBIOS Setup Utility
ItemSpecicHelp
Enable RSDP pointers
to 64-bit Fixed System
Description Tables.
F1 Help
ESC Exit
Select Item -/+ Change Values F9 Setup Defaults
↑↓
Select Menu Enter Select Sub-Menu F10 Save and Exit
→←
ACPI Version Features [ACPI v1.0]
Allows you to enable RSDP pointers to 64-bit xed system description tables.
Conguration options: [ACPI v1.0] [ACPI v2.0] [ACPI v3.0]
Headless Mode [Disabled]
Allows you to enable or disable the headless operation mode through ACPI.
Conguration options: [Disabled] [Enabled]
ACPI EMS Support [Disabled]
Allows you to enable or disable the ACPI EMS support.
Conguration options: [Disabled] [Enabled]
ASUS DSBV-D 4-31
Page 100

4.4.7 Power On Conguration
This menu shows the power conguration settings. Select an item then press
<Enter> to display the conguration options.
Advanced
PowerOnConguration
Restore on AC Power Loss [Last State]
Power On By PS/2 Keyboard [Disabled]
Power On By PS/2 Mouse [Disabled]
Power On By PME# [Disabled]
Power On By RTC Alarm [Disabled]
F1 Help
ESC Exit
Select Item -/+ Change Values F9 Setup Defaults
↑↓
Select Menu Enter Select Sub-Menu F10 Save and Exit
→←
PhoenixBIOS Setup Utility
ItemSpecicHelp
Conguresthesystemstate
after recovering from
power failure.
Restore on AC Power Loss [Last State]
When set to [Power Off], the system goes into “off state” after an AC power
interruption. When set to [Power On], the system turns on automatically after a
power interruption. When set to [Last State], the system goes into whatever was
the system state (on or off) before the power interruption.
Conguration options: [Power Off] [Power On] [Last State]
Power Up By PS/2 Keyboard [Disabled]
Allows you to use specic keys on the PS/2 keyboard to turn on the system. This
feature requires an ATX power supply that provides at least 1A on the +5VSB lead.
Conguration options: [Enabled] [Disabled]
Power Up By PS/2 Mouse [Disabled]
When set to [Enabled], this parameter allows you to use the PS/2 mouse to turn on
the system. This feature requires an ATX power supply that provides at least 1A on
the +5VSB lead. Conguration options: [Enabled] [Disabled]
Power On By PME# [Disabled]
Allows you to enable or disable the PME and onboard LAN to generate a wake-up
event. Conguration options: [Disabled] [Enabled]
Power On By RTC Alarm [Disabled]
Allows you to enable or disable RTC to generate a wake-up event.
Conguration options: [Disabled] [Enabled]
4-32 Chapter 4: BIOS setup
 Loading...
Loading...