Page 1

Xsan
Administrator’s Guide
Includes information for managing Xsan
volumes in a storage area network using
Xsan Admin or the command line
Page 2

Apple Computer, Inc.
© 2004 Apple Computer, Inc. All rights reserved.
The owner or authorized user of a valid copy of Xsan
software may reproduce this publication for the purpose
of learning to use such software. No part of this
publication may be reproduced or transmitted for
commercial purposes, such as selling copies of this
publication or for providing paid for support services.
The Apple logo is a trademark of Apple Computer, Inc.,
registered in the U.S. and other countries. Use of the
“keyboard” Apple logo (Option-Shift-K) for commercial
purposes without the prior written consent of Apple
may constitute trademark infringement and unfair
competition in violation of federal and state laws.
Apple, the Apple logo, Mac, Macintosh, Mac OS, Power
Mac, and Xserve are trademarks of Apple Computer, Inc.,
registered in the U.S. and other countries. Finder and
Xsan are trademarks of Apple Computer, Inc.
UNIX is a registered trademark in the United States and
other countries, licensed exclusively through
X/Open Company, Ltd.
StorNext and ADIC are registered trademarks of
Advanced Digital Information Corporation.
019-0192/08-27-04
Page 3

3
Contents
Preface 7 About This Book
8
Notation Conventions
Chapter 1 9 Overview of Xsan
9
What Is Xsan?
10
Xsan Storage Area Networks
11
11
11
12
12
13
13
14
15
15
15
15
16
16
Shared SAN Volumes
Controllers and Clients
SAN Connections
How Xsan Storage Is Organized
LUNs (RAID Arrays)
Storage Pools
Volumes
Folders With Affinities
How Xsan Utilizes Available Storage
Metadata and Journal Data
Striping at a Higher Level
Security
Expanding Storage
Xsan Capacities
Chapter 2 17 Setting Up a Storage Area Network
18
Hardware and Software Requirements
18
18
19
19
20
20
21
22
27
27
Supported Computers
Supported Storage Devices
Fibre Channel Fabric
Ethernet TCP/IP Network
Directory Services
Outgoing Mail Service
Planning Your SAN
Planning Considerations and Guidelines
Connecting Computers and Storage Devices
Preparing LUNs (RAID Arrays and Slices)
3
Page 4

28
Using the Xsan Admin Application
28
28
28
28
28
29
30
38
38
39
Installing Xsan Admin Separately
Connecting Through a Firewall
Xsan Admin Preferences
Getting Help
Using the Command Line
SAN Setup Summary
Setting Up an Xsan Storage Area Network
Renaming a SAN
Deleting a SAN
Setting Up Additional SANs
Chapter 3 41 Managing SAN Storage
42
Adding Storage
43
44
45
46
47
47
48
48
49
49
50
51
52
52
53
54
55
56
56
Adding LUNs to a Storage Pool
Adding a Storage Pool to a Volume
Adding a Volume to a SAN
Assigning a Storage Pool Affinity to a Folder
Assigning an Affinity to a Folder Within a Folder
Removing an Affinity
Changing Storage Pool Settings
Renaming a Storage Pool
Setting Storage Pool Access Permissions
Choosing the Types of Files Stored on a Storage Pool
Setting Storage Pool Stripe Breadth
Setting the Selection Method for Multiple Connections
Changing Volume Settings
Renaming a Volume
Setting the Volume Allocation Strategy
Setting the Block Allocation Size
Defragmenting a Volume
Checking the Integrity of a Volume
Repairing a Volume
Chapter 4 57 Managing Clients and Users
58
Adding a Client
58
Adding a Client to a StorNext SAN
59
Mounting a Volume on a Client
59
Controlling Client and User Access
59
60
60
60
4
Controlling Access to Folders on Volumes
Unmounting a Volume From a Client
Restricting a Client to Read-Only Access
Removing a Client From a SAN
Contents
Page 5

60
61
61
62
Removing Xsan Software From a Computer
Setting User and Group Quotas
About Xsan Quotas
Checking Quota Use
Chapter 5 63 Managing Metadata Controllers
64
Adding a Controller
64
Setting Controller Failover Priority
65
Switching to a Standby Controller
66
Finding Out Which Controller Is Hosting a Volume
66
Listing the Volumes Hosted by a Controller
67
Changing a Controller’s IP Address
68
Upgrading Controller Software
68
Monitoring Controller Status
Chapter 6 69 Monitoring SAN Status
70
Checking Free Space on a SAN Volume
70
Checking Free Space on a Storage Pool
71
Checking User Quota Use
71
Viewing Controller CPU and Network Utilization Graphs
72
Setting Up Status Notifications
72
Checking Status of File System Processes
73
Viewing Logs
73
Checking Volume Clients
74
Checking for Fibre Channel Connection Failures
74
Checking the State of Xserve RAID Systems
Chapter 7 75 Solving SAN Problems
75
75
75
75
75
76
77
77
77
77
You Can’t Install the Xsan Software
Some Computers Aren’t Listed During Setup
You Can’t Connect to a SAN Computer From Xsan Admin
Xserve RAID Systems Aren’t Accessible Over Fibre Channel
You Can’t Mount a Volume on a Client
You Can’t Add a Storage Pool
After Slicing, Some LUNs Aren’t Listed in Xsan Admin
Problems Using Command-Line Tools
SAN User Sees Error Code –1425
LUN Doesn’t Have as Much Space as Expected
Appendix A 79 Combining Xsan and StorNext Clients and Controllers
79
Compatible Software Versions
79
Licensing
79
Terminology
80
Adding Macintosh Clients to a StorNext SAN
Contents
5
Page 6

81
Using Xsan Controllers With StorNext Clients
Appendix B 83 Using the Command Line
83
Using the Shell Commands
83
83
84
84
85
88
Working on Remote Computers
Viewing the Man Pages
Notation Conventions
The Commands
Viewing or Changing Volume and Storage Pool Settings (
Copying Files or Folders (
89 Checking or Repairing a Volume (cvfsck)
90 Labeling LUNs (cvlabel)
91 Creating a Folder With an Affinity (cvmkdir)
91 Creating and Pre-Allocating a File (cvmkfile)
92 Initializing a Volume (cvmkfs)
92 Viewing Storage Pool Information (cvsginfo)
92 Applying Volume Configuration Changes (cvupdatefs)
93 Starting a Volume Controller (fsm)
93 Starting a Port Mapper Process (fsmpm)
93 Defragmenting a File, Directory, or Volume (snfsdefrag)
95 Mounting an Xsan Volume
95 Unmounting an Xsan Volume
95 Viewing Logs
96 The Configuration Files
96 The Volume Configuration File
10 2 The Volume Auto-Start List
10 4 The Controller List
cvcp)
cvadmin
)
Glossary 10 7
Index 111
6
Contents
Page 7

About This Book
Use this guide to learn how to set up and manage Xsan
volumes on a storage area network.
This guide shows how to use Xsan to combine Xserve RAID arrays and slices into large,
easy-to-expand volumes of storage that clients use like local disks but are actually
shared over a high-speed Fibre Channel fabric.
Chapter 1 provides an overview of Xsan and how you can use it to organize RAID arrays
and storage pools into shared volumes of storage.
Chapter 2 includes hardware and software requirements, SAN planning guidelines, and
basic steps for setting up an Xsan SAN.
Chapter 3 contains instructions for adding storage to a SAN, creating folders with
affinities, changing volume and storage pool settings, and checking, defragmenting,
and repairing SAN volumes.
Preface
Chapter 4 shows how to add client computers to a SAN, mount volumes on clients,
control client and user access to SAN files, and control user space using quotas.
Chapter 5 contains information on managing metadata controllers.
Chapter 6 includes instructions for monitoring and automatically reporting the
condition of a SAN.
Chapter 7 lists solutions to common problems you might encounter.
Appendix A contains information to help you join Xsan controllers or clients together
with ADIC StorNext controllers or clients in the same SAN.
Appendix B describes available command-line utilities and configuration files to help
you manage an Xsan SAN using Terminal.
7
Page 8

Notation Conventions
The following conventions are used in this book wherever shell commands or other
command-line items are described.
Notation Indicates
monospaced font A command or other terminal text
$ A shell prompt
[text_in_brackets] An optional parameter
(one|other) Alternative parameters (type one or the other)
underlined
[...] A parameter that may be repeated
<anglebrackets> A displayed value that depends on your SAN configuration
A parameter you must replace with a value
8 Preface About This Book
Page 9
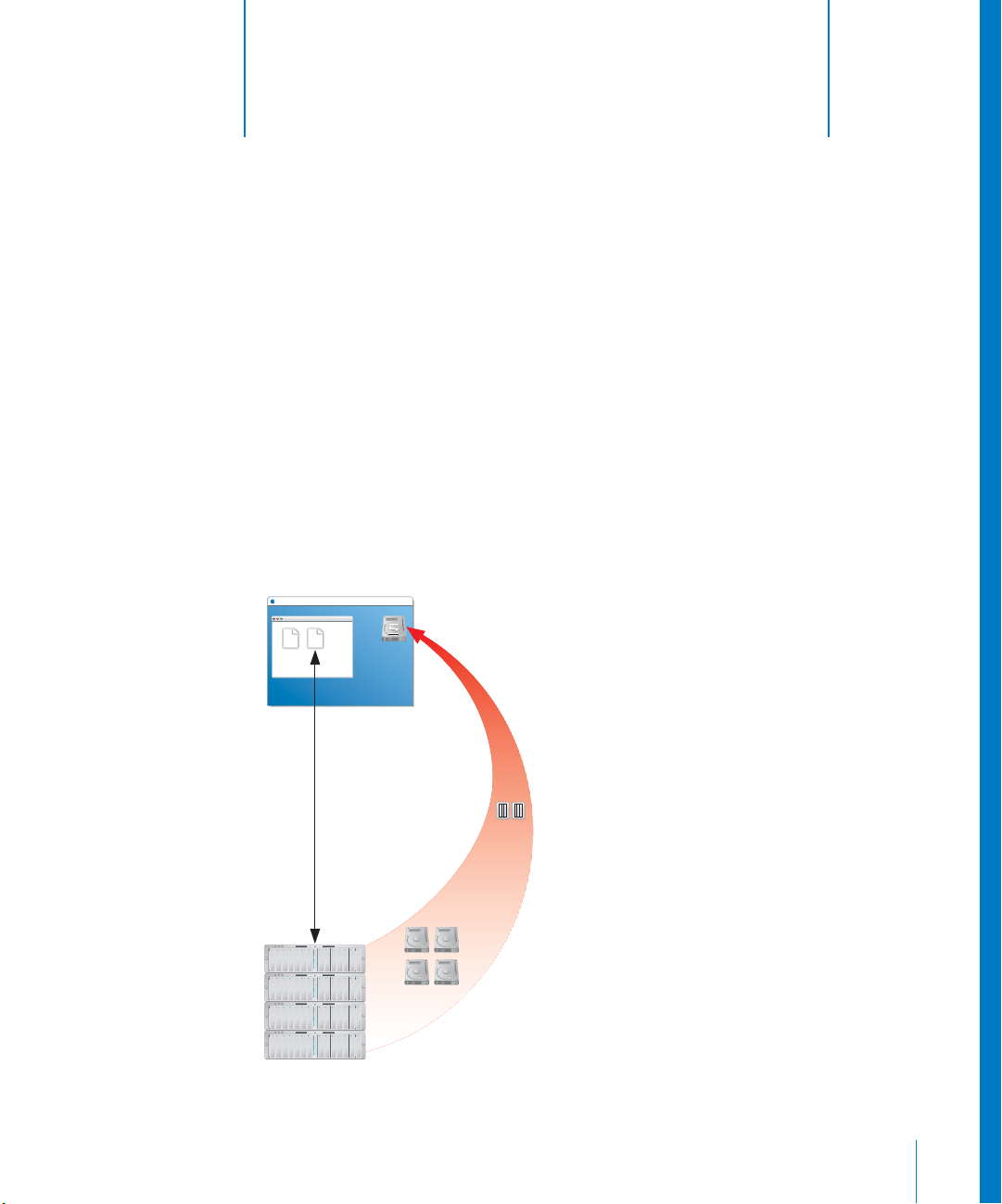
1 Overview of Xsan
1
This chapter gives you an overview of Xsan and storage
area networks.
Read this chapter for an overview of Xsan and how you can use it to set up a storage
area network (SAN) to provide fast, shared storage.
What Is Xsan?
Xsan is a storage area network file system and a management application (Xsan Admin)
you can use to provide users or applications on client computers with shared highspeed access to expandable storage.
Volumes
SAN vol
Xsan lets you
Fibre
Channel
9
combine RAID arrays
into volumes clients
use like local disks.
RAID
arrays (LUNs)
Storage
pools
Page 10
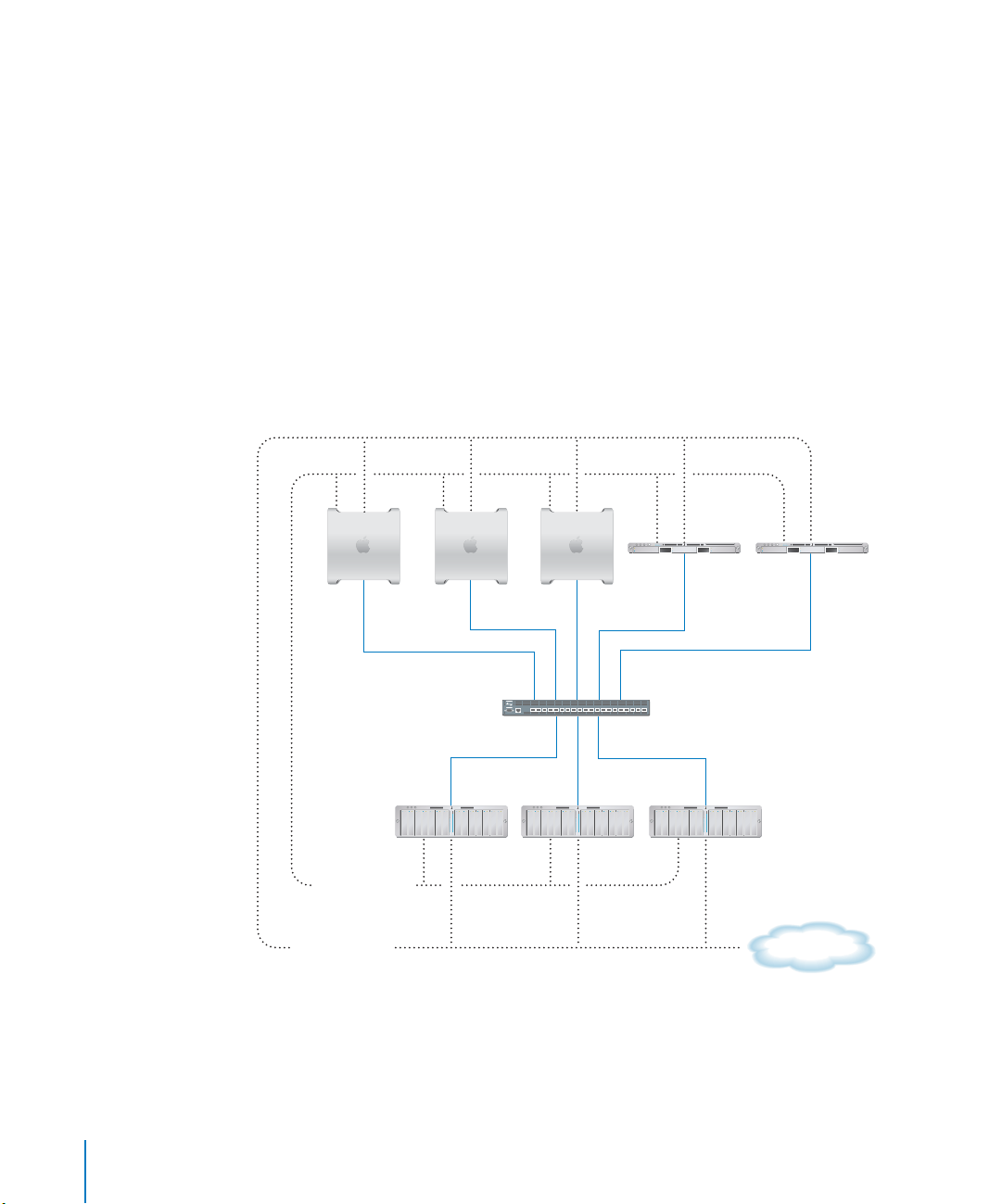
Xsan Storage Area Networks
A storage area network is a way of connecting computers to storage devices that gives
users very fast access to files and gives administrators the ability to expand storage
capacity as needed without interrupting users.
An Xsan SAN consists of:
• Volumes of shared storage, stored on Xserve RAID systems, available to clients as
mounted volumes that they can use like local disks
• At least one computer acting as a metadata controller that coordinates access to the
shared volumes
• Client computers that access storage in accordance with established permissions and
quotas
• Underlying Fibre Channel and Ethernet networks
The following illustration shows the physical components of a typical Xsan SAN.
Clients
Ethernet - TCP/IP
(Private)
Ethernet - TCP/IP
(Public)
Metadata
controller
Fibre
Channel switch
Standby
controller
Xserve RAID
storage
Intranet/
Internet
10 Chapter 1 Overview of Xsan
Page 11

Shared SAN Volumes
Users and applications see shared SAN storage as local volumes. Xsan volumes are
logical disks made up of groups of RAID arrays. The elements you combine to create an
Xsan volume are described under “How Xsan Storage Is Organized” on page 12.
Controllers and Clients
When you add a computer to an Xsan SAN, you specify whether it will play the role of
client, controller, or both.
Controllers
When you set up an Xsan SAN, you assign at least one computer to act as the
controller. The controller manages the SAN volume metadata, maintains a file system
journal, and controls concurrent access to files. Metadata includes such information as
where files are actually stored and what portions of available storage are allocated to
new files.
For high availability, you can add more than one controller to a SAN, as shown in the
illustration on page 10. If the primary controller fails, the standby controller takes over.
Controllers can also act as clients, so you can use a standby controller as a working
client while the primary controller is operational.
Clients
The computers that users or applications use to access SAN volumes are called clients.
Clients communicate with controllers over the Ethernet network but use Fibre Channel
to send and retrieve file data to and from the RAID systems that provide storage for the
volumes.
SAN Connections
Xsan uses independent networks to connect storage devices, metadata controllers, and
client computers: a Fibre Channel network and one or two Ethernet networks.
User Data Over Fibre Channel
User data is transferred over high-speed Fibre Channel connections.
Metadata Over Ethernet
To eliminate unnecessary traffic on the Fibre Channel connections, controllers and
clients use an Ethernet network to exchange file system metadata. The Xsan Admin
application also uses the Ethernet connection to let you manage the SAN.
Fibre Channel Multipathing
Xsan can take advantage of multiple Fibre Channel connections between clients and
storage. Xsan can alternate between connections for each read and write, or assign
each LUN in a volume to one of the connections when the volume is mounted.
Chapter 1 Overview of Xsan 11
Page 12

How Xsan Storage Is Organized
Users use an Xsan volume the same way they use a local disk. What they don’t see is
that the SAN volume actually consists of numerous physical disks combined on several
levels using RAID techniques.
The following illustration shows an example of how disk space provided by the
individual drive modules in Xserve RAID systems is combined into a volume that users
see as a large local disk.
Shared SAN
volume
Faster
RAID 0
array
Safer
LUN LUN
RAID 5
RAID 5
array
array
LUN LUN
RAID 5
RAID 5
array
array
LUN LUN
RAID 0
RAID 0
array
Affinity Affinity
Storage pool Storage pool
(Striping) (Striping)
LUN LUN
RAID 0
array
array
The following paragraphs describe these storage elements and how you organize them
to create shared Xsan volumes.
LUNs (RAID Arrays)
The smallest storage element you work with in Xsan is a logical storage device called a
LUN (a SCSI logical unit number). In most storage area networks a LUN represents a
group of drives such as a RAID array or a JBOD (just a bunch of disks) device. In Xsan,
LUNs are Xserve RAID arrays or slices.
You create a LUN when you use RAID Admin to create an Xserve RAID array. The
controller hardware and software in the Xserve RAID system combine individual drive
modules into an array based on the RAID scheme you choose. Each array appears on
the network as a separate LUN. If you slice an array, each slice appears as a LUN.
12 Chapter 1 Overview of Xsan
Page 13

One of your first tasks when you set up a SAN volume is to prepare LUNs. If the two
RAID 5 arrays on a new Xserve RAID are not right for your application, you can use RAID
Admin to create arrays based on other RAID schemes. For help choosing schemes for
your LUNs, see “Choosing RAID Schemes for LUNs” on page 23.
The illustration on page 12 shows four Xserve RAID systems hosting two arrays each.
Half of the arrays use a RAID 0 scheme (striping only) for speed while the others use
RAID 5 (distributed parity) to ensure against data loss. Xsan sees the arrays as LUNs that
can be combined to create a volume.
After your Xserve RAID LUNs are set up, you label and initialize them for use with the
Xsan file system using Xsan Admin.
Storage Pools
LUNs are combined to form storage pools. A storage pool in a small volume might
consist of a single RAID array, but storage pools in many volumes consist of multiple
arrays.
Xsan distributes file data in parallel across the LUNs in a storage pool using a RAID 0
(striping) scheme. So, you can improve access speed by distributing available storage
over several LUNs in a storage pool.
You can set up storage pools that have different performance or recoverability
characteristics and assign folders to them using affinities. Users can then select where
to store files based on their need for speed or safety. See “Folders With Affinities” on
page 14.
As an example, the illustration on page 12 shows eight LUNs combined into two
storage pools, one pool consisting of RAID 0 (fast but not recoverable) arrays and the
other made up of RAID 5 (not as fast, but recoverable) arrays. Xsan stripes data across
the four LUNs in each storage pool.
You use Xsan Admin to add available LUNs to specific storage pools.
Volumes
Storage pools are combined to create the volumes that users see. From the user’s
perspective, the SAN volume looks and behaves just like a large local disk, except that:
• The size of the volume can grow as you add underlying arrays or storage pools
• Other users on the SAN can access files on the volume at the same time
In the example illustrated on page 12, two storage pools are combined to create a
single shared volume.
You create volumes and mount them on client computers using the Xsan Admin
application.
Chapter 1 Overview of Xsan 13
Page 14
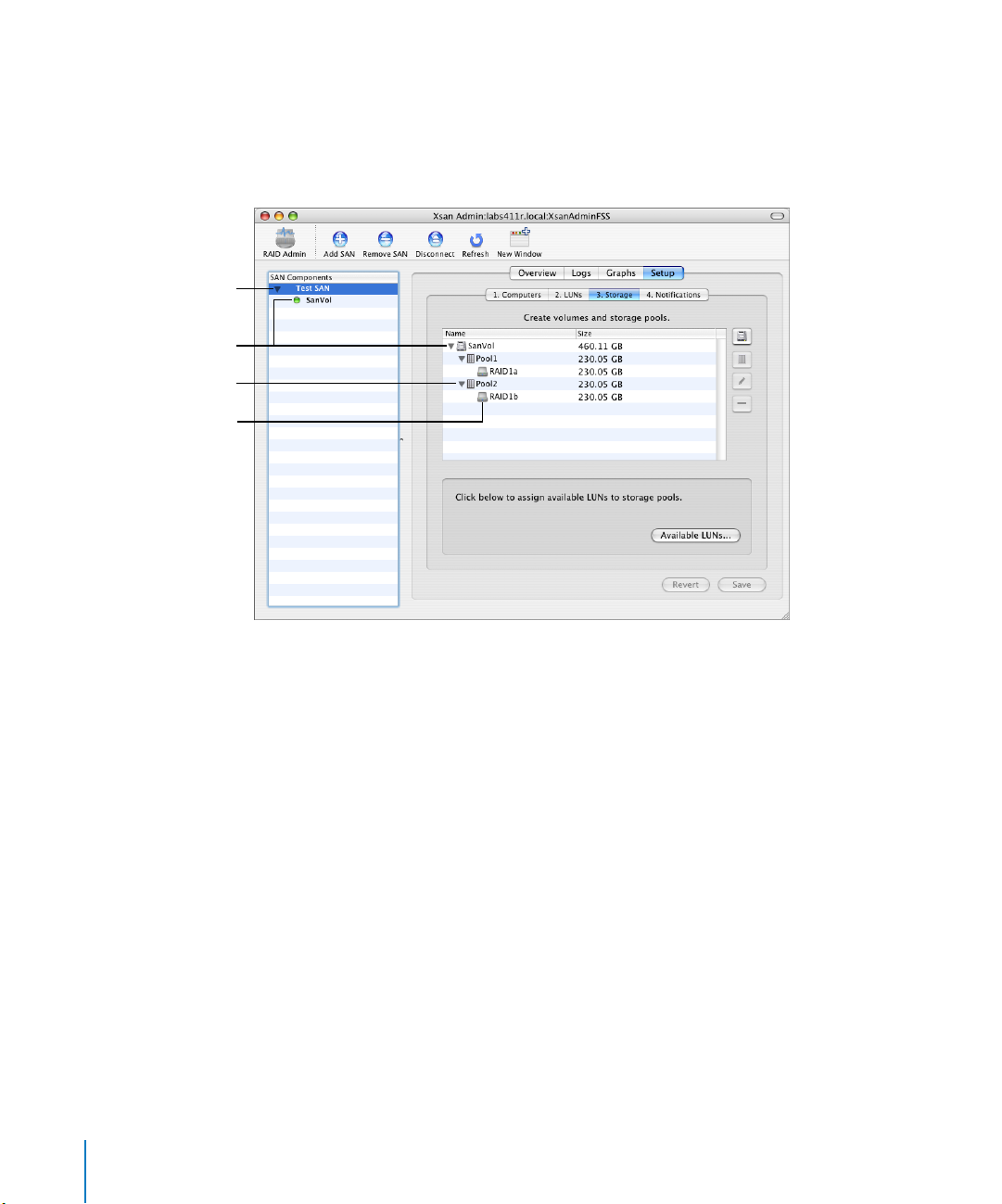
The following screen image shows how LUNs, storage pools, and volumes appear as
you organize them in the Xsan Admin application. This example shows a SAN named
“Test SAN” with a single shared volume named “SanVol.” Storage for the volume is
provided by two storage pools, “Pool1” and “Pool2,” each based on a single LUN. Each
of the LUNs is a 3-disk RAID 5 array on an Xserve RAID using 115 GB drive modules.
SAN
Volume
Storage pool
LUN
Folders With Affinities
To control which storage pool is used to store specific files (for example, to provide
different levels of service for different users or applications), you can associate a folder
on an Xsan volume with one of the storage pools that make up the volume.
If, for example, you set up storage pools with different balances of performance and
data redundancy, users can choose between faster and safer storage by putting files in
the appropriate folder.
In the illustration on page 12, a predefined folder has an affinity for the faster storage
pool that is based on RAID 0 arrays. Any file that a user copies into this folder is
automatically stored on the faster arrays. A second folder is associated with the more
secure RAID 5 storage.
14 Chapter 1 Overview of Xsan
Page 15

How Xsan Utilizes Available Storage
Xsan stores both user files and file system data on SAN volumes, and stripes data across
the LUNs in a volume for better performance.
Metadata and Journal Data
Xsan records information about the files in an Xsan volume using metadata files and
file system journals. File system metadata includes information such as which specific
parts of which disks are used to store a particular file and whether the file is being
accessed. The journal data includes a record of file system transactions that can help
ensure the integrity of files in the event of a failure.
These files are managed by the Xsan metadata controller, but are stored on SAN
volumes, not on the controller itself. By default, metadata and journal data are stored
on the first storage pool you add to a volume. You can use Xsan Admin to choose
where these files are stored when you add storage pools to a new volume.
Striping at a Higher Level
When you write a file to a RAID array using RAID 0 (striping), the file is broken into
segments that are spread across the individual disk drives in the array. This improves
performance by writing pieces of the file in parallel (instead of one piece at a time) to
the individual disks in the array. Xsan applies this same technique at a second, higher
level in the storage hierarchy. Within each storage pool in a volume, Xsan stripes file
data across the individual LUNs that make up the storage pool. Once again,
performance is improved because data is written in parallel.
You can tune SAN performance by adjusting the amount of data written to each LUN in
a storage pool (the “stripe breadth”) to suit a critical application.
Security
As SAN administrator, you can control access to shared volumes in several ways.
First, users cannot browse or mount SAN volumes. Only a SAN administrator can
specify which volumes are mounted on which client computers. One way you can
control access to data is to mount a volume only on appropriate client computers.
To prevent users from modifying data on a volume, you can mount the volume with
read-only access.
You can also control user access to folders on a volume by specifying owner, group,
and general access permissions as you would in the Finder.
You can also set up zones in the underlying Fibre Channel network to segregate users
and volumes.
Chapter 1 Overview of Xsan 15
Page 16

Expanding Storage
You can add free space to an Xsan volume without interrupting the users or
applications that rely on the volume for access to files. There are two ways to add
storage to a volume:
• Add Xserve RAID systems (new LUNs) to existing storage pools
• Add entire new storage pools to volumes
The first method requires you to unmount and remount the volume on clients. The
second method lets you add space without users noticing any change other than the
availability of more space in the volumes they use.
You can also add new volumes to a SAN at any time.
For information on expanding Xsan storage, see “Adding Storage” on page 42.
Xsan Capacities
The following table lists limits and capacities for Xsan volumes.
Parameter Maximum
Number of computers in a SAN (controllers and clients) 64
Number of storage pools in a volume 512
Number of LUNs in a storage pool 32
Number of LUNs in a volume 512
Number of files in a volume 4,294,967,296
Volume size 16 TB
File size 16 TB
Volume name length 70 characters
File or folder name length 251 characters
SAN name length 255 characters
Storage pool name length 255 characters
16 Chapter 1 Overview of Xsan
Page 17

2 Setting Up a Storage Area
Network
This chapter lists requirements, suggests planning tips,
and gives instructions for setting up an Xsan SAN.
This chapter contains:
• Xsan hardware and software requirements (page 18)
• Planning guidelines (page 21)
• SAN setup instructions (page 29)
2
17
Page 18

Hardware and Software Requirements
Your SAN environment needs to satisfy requirements in these areas:
• Supported computers
• Supported storage devices
• Fibre Channel fabric, adapters, and switches
• Ethernet network
• Directory services (optional)
• Outgoing mail service (optional)
Supported Computers
Xsan controller and client computers must meet these minimum requirements:
Systems
• Xserve
• Xserve G5
• Power Mac G4 dual 800 MHz or faster
• Power Mac G5
Memory
• Clients should have a minimum of 256 MB of RAM.
• Controllers should have a minimum of 512 MB of RAM. (For optimum performance,
add an additional 512 MB of RAM for each SAN volume hosted by the controller.)
Supported Operating Systems
• Mac OS X v10.3; version 10.3.5 or later
• Mac OS X Server v10.3; version 10.3.5 or later
Windows, AIX, IRIX, Linux, and Solaris clients must be running ADIC’s StorNext File
System version 2.4.
Supported Storage Devices
This guide assumes you are using Xserve RAID systems for your storage devices.
Important: Be sure to install the latest firmware update on your Xserve RAID systems
before you use them with Xsan.
For demanding applications such as video editing, use Xserve RAID systems that have:
• A full set of 14 Apple Drive Modules
• 512 MB of cache in each controller (1 GB total)
18 Chapter 2 Setting Up a Storage Area Network
Page 19

Fibre Channel Fabric
Unlike file system metadata, which is transferred over Ethernet, actual file content in an
Xsan SAN is transferred over Fibre Channel connections. To set up the connections, you
need:
• Apple Fibre Channel PCI cards for each client and controller computer
• One or more supported Fibre Channel switches
• Fibre Channel cables connecting computers and storage devices to the switches to
form a Fibre Channel fabric
Fibre Channel PCI Cards
Install Apple Fibre Channel PCI cards in all Macintosh computers that will connect to
the SAN.
Fibre Channel Switches
The following Fibre Channel switches have been tested with Xsan, Xserve RAID
systems, and the Apple Fibre Channel PCI card:
• Brocade Silkworm 3200, 3800, 3900, and 12000 series
• QLogic SANbox 2–8, SANbox 2–16, SANbox 2–64, and SANbox 5200
• Emulex SAN Switch 355, 375, and 9200
For the latest additions to this list of qualified switches, see the Xsan webpages at
www.apple.com/xsan.
Fabric Configuration
You must connect the computers, storage devices, and switches in your Fibre Channel
network to form a Fibre Channel “fabric.” In a fabric, Fibre Channel cables connect node
ports (F or N_Port). See the documentation that came with your Fibre Channel switches
for more information.
Note: If you are using a Vixel 355 switch, you must connect Xserve RAID systems to an
FL (arbitrated loop) port on the switch.
You cannot use Fibre Channel Arbitrated Loop (FL ports) with an Xsan SAN, with the
exception noted above for Vixel 355 switches.
Ethernet TCP/IP Network
Computers in the SAN must also be connected to an Ethernet network. Xsan uses this
network instead of the Fibre Channel network to transfer file system metadata,
reserving the Fibre Channel connections for actual file contents.
If the computers in your SAN need to communicate with directory servers, a corporate
or campus intranet, or the Internet, you should connect each SAN client and controller
to two separate Ethernet networks: one private subnet for the SAN and a separate
connection for directory, intranet, or Internet traffic. This is important if you plan to use
the SAN for high-performance applications such as video editing.
Chapter 2 Setting Up a Storage Area Network 19
Page 20

IP Addresses and Domain Names
For best results, assign fixed, non-routed IP addresses to all clients, controllers, and
storage devices connected to the SAN Ethernet network. You can use the following
ranges of IP addresses in your private (non-routed) subnet:
Private address range Associated subnet mask Comments
10.0.0.0 – 10.255.255.255 255.0.0.0 10/8
172.16.0.0 – 172.31.255.255 255.240.0.0 172.16/12
192.168.0.0 – 192.168.255.255 255.255.0.0 192.168/16
Directory Services
If you plan to use user and group privileges to control access to files and folders on the
SAN, you can simplify management by setting up or joining a user and group directory.
Although not required, a central directory lets you manage users and groups on one
computer instead of having to visit all SAN clients and controllers.
If you already have a directory, you can use the Directory Access application on each
controller and client to access the directory for user and group information.
If you don’t use a central directory service, you need to set up users and groups on
each SAN computer.
Important: If you create users and groups on each SAN computer, be sure that 1) each
user or group has a numeric user ID (UID) or group ID (GID) that is unique throughout
the SAN and 2) each user or group defined on more than one computer has the same
UID or GID on each computer.
If you don’t have access to a directory, you can use the directory services in Mac OS X
Server to set up an LDAP directory of SAN users and groups.
Outgoing Mail Service
Xsan can send SAN status notifications via email on your local subnet or corporate
network without using a separate mail server. However, to send notifications outside
your local network, you need an SMTP server to act as a mail gateway. If you don’t have
access to an outgoing mail server, you can use the mail service in Mac OS X Server to
set one up.
20 Chapter 2 Setting Up a Storage Area Network
Page 21

Planning Your SAN
It’s easy to add storage to an existing Xsan SAN without interrupting users, but
reorganizing a SAN after you set it up is not so simple. So, it’s important to plan the
layout and organization of your SAN and its storage before you set it up.
An Xsan SAN is composed of:
• Storage devices (usually Xserve RAID systems)
• LUNs (logical unit numbers, usually RAID arrays)
• Storage pools (groups of LUNs)
• Volumes (groups of storage pools visible to users)
• Clients (computers that use volumes)
• Controllers (computers that manage volume metadata)
• Underlying Fibre Channel and Ethernet networks
Before you use Xsan Admin to set up a SAN, decide how you want to organize these
components. Take the time to create a drawing or a table that organizes available
hardware into RAID arrays, storage pools, volumes, client computers, and controllers in
a way that meets both your users’ needs and your needs as SAN administrator.
First, consider these questions:
• How much storage do you need?
• How do you want to present available storage to users?
• What storage organization makes the most sense for user workflow?
• What levels of performance do your users require?
• How important is constant availability?
• What are your requirements for security?
Your answers to the above questions will help you decide the following:
• What RAID schemes should you use for your RAID arrays?
• How many SAN volumes do you need?
• How should individual volumes be organized?
• Which LUNs go in each storage pool?
• Which storage pools make up each volume?
• Which clients, users, and groups should have access to each volume?
• Which computers will act as controllers?
• Do you need standby controllers?
• Do you want to use controllers as clients also?
• Where do you want to store file system metadata and journal data?
• What allocation strategy should you use?
Review the considerations and guidelines on the following pages for help translating
your answers into a suitable SAN design.
Chapter 2 Setting Up a Storage Area Network 21
Page 22

Planning Considerations and Guidelines
The following paragraphs might help you make some of your SAN design decisions.
How Much Storage?
Because it’s easy to add storage to an Xsan SAN without interrupting user work, you
only need to decide on an adequate starting point. You can then add storage as
needed.
Note that the number of Xserve RAID systems you use affects not only available space
but also SAN performance. See “Performance Considerations,” below.
How Should Users See Available Storage?
If you want the users working on a particular project to see a volume dedicated to their
work, create a separate volume for each project. If it’s acceptable for a user to see a
folder for his or her work on a volume with other peoples’ folders, you can create a
single volume and organize it into project folders.
Workflow Considerations
How much file sharing is required by your users’ workflow? If, for example, different
users or groups work on the same files, either simultaneously or in sequence, it makes
sense to store those files on a single volume to avoid having to maintain or hand off
copies. Xsan uses file locking to manage shared access to a single copy of the files.
Performance Considerations
If your SAN supports an application (such as high resolution video capture and
playback) that requires the fastest possible sustained data transfers, design your SAN
with these performance considerations in mind:
• Set up the LUNs (RAID arrays) using a RAID scheme that offers high performance. See
“Choosing RAID Schemes for LUNs” on page 23.
• Group your fastest LUNs in storage pools reserved for the application. Reserve slower
devices for a volume dedicated to less demanding or supporting applications.
• To increase parallelism, spread LUNs across different Xserve RAID controllers. For
example, instead of creating a single 4-disk LUN on one side of an Xserve RAID,
create two 2-disk LUNs, one on each side, and add these LUNs to a storage pool.
Xsan then stripes data across the two LUNs and benefits from simultaneous transfers
through two controllers.
• To increase parallelism in a relatively small storage pool (the size of one or a few
drive modules), create a slice of similar size across all the drives on a controller
instead of creating the storage pool from just one or two drive modules.
• Spread file transfers across as many drives and RAID controllers as possible. Try
creating slices across the drives in RAID systems, then combine these slices into a
storage pool.
• To increase throughput, connect both ports on client Fibre Channel cards to the
fabric and set the multipathing method for the storage pool to Rotate.
22 Chapter 2 Setting Up a Storage Area Network
Page 23

• Store user files, file system metadata, and journal data on separate storage pools, and
create these storage pools using LUNs from different RAID controllers.
• Use a router to isolate the Ethernet network used by the SAN from a company
intranet or the Internet, or better, use a second Ethernet network (including a second
Ethernet card in each SAN computer) for the SAN.
• If your SAN uses directory services, mail services, or other services on a separate
server, use a second, separate Ethernet network to connect SAN computers to that
server.
• As a rule of thumb, consider that a single Xserve RAID controller, after file system
overhead, can transfer roughly 80 MB of user data per second (160 MB per Xserve
RAID system). If your SAN must support an application running on multiple clients
that requires specific throughput on each client, you can use this number to estimate
the number of Xserve RAID systems necessary to support the aggregate transfer rate.
Availability Considerations
If high availability is important for your data, set up at least one standby controller in
addition to your primary controller. Also, consider setting up dual Fibre Channel
connections between each client, controller, and storage device using redundant Fibre
Channel switches.
Important: Losing a metadata controller without a standby can result in the loss of all
data on a volume. A standby controller is recommended.
Also, if you have a standby controller, you can upgrade the Xsan software without
interrupting the SAN. For more information, see “Upgrading Controller Software” on
page 68.
Security Considerations
If your SAN will support projects that need to be completely secure and isolated from
each other, you can create separate volumes for each project to eliminate any
possibility of the wrong client or user accessing files stored on a volume.
As SAN administrator, you control which client computers can use a volume. Clients
can’t browse for or mount SAN volumes on their own. You use Xsan Admin to specify
which clients a volume is mounted on.
You can also assign user and group permissions to folders you create on a volume or
use standard file access permissions to control access to other items.
Choosing RAID Schemes for LUNs
Much of the reliability and recoverability of data in a SAN is not provided by Xsan itself
but by the RAID arrays you combine to create your storage pools and volumes. Before
you set up a SAN, you use RAID Admin to prepare LUNs based on specific RAID
schemes.
Chapter 2 Setting Up a Storage Area Network 23
Page 24

Xserve RAID supports all popular RAID levels. Each RAID scheme offers a different
balance of performance, data protection, and storage efficiency, as summarized in the
following table.
RAID level Storage efficiency Read performance Write performance Data redundancy
RAID 0 Highest Very High Highest No
RAID 1 Low High Medium Yes
RAID 3 High to very high Medium Medium Yes
RAID 5 High to very high High High Yes
RAID 0+1 Low High High Yes
RAID 10, 30, and 50 schemes assume the use of AppleRAID software striping and aren’t
appropriate for use with Xsan, which performs its own striping. For more help choosing
RAID schemes for your arrays, see the Xserve RAID User’s Guide or the Xserve RAID
Technology Overview (at www.apple.com).
Deciding on the Number of Volumes
A volume is the largest unit of shared storage in the SAN. If your users need shared
access to files, you should store those files on the same volume. This makes it
unnecessary for them to pass copies of the files among themselves.
On the other hand, if security is critical, one way to control client access is to create
separate volumes and mount only the authorized volume on each client.
For a more typical balance of security and shared access, a flexible compromise is to
create a single volume and use folder access privileges to control access.
Note: The maximum size of any volume is 16 TB. If you need more than 16 TB of
storage, you need to create more than one volume.
Deciding How to Organize a Volume
You can help users organize data on a volume or restrict users to specific areas of the
volume by creating predefined folders. You can control access to these folders by
assigning access permissions using Xsan Admin.
You can assign folders to specific storage pools using affinities. You can, for example,
create a folder for data that requires fast access and assign that folder to your fastest
storage pool.
Assigning LUNs to Storage Pools
You should set up a storage pool using LUNs that have similar capacity and
performance characteristics.
24 Chapter 2 Setting Up a Storage Area Network
Page 25

To provide high performance, Xsan uses the RAID 0 scheme to stripe data across the
LUNs in a storage pool. This requires that the LUNs in the pool be the same size. If you
set up a storage pool using LUNs of different sizes, Xsan uses available space on each
LUN equal to the capacity of the smallest LUN. If the LUNs vary in size, this can result in
wasted capacity. For example, if you assign 240 GB and 360 GB RAID arrays to a storage
pool, 120 GB of the larger array will not be used. By combining LUNs with similar
capacities, you avoid wasting available storage.
If you want to set up a storage pool for use by a high performance application, assign
similarly high speed LUNs. Assign slower LUNs to a storage pool where you keep data
that doesn’t have critical performance requirements.
Creating storage pools from LUNs that are hosted on different drive modules and
different RAID controllers increases performance by increasing the parallelism of data
transfers. For example, a storage pool consisting of two LUNs, each a single drive
module on the left side of an Xserve RAID, will not be as fast as a similarly sized storage
pool made up of two LUNs that are single slices across all seven drives, one slice on
each controller. In the first case, all transfers go through a single RAID controller to just
two drives; in the second case the same transfer is spread across two RAID controllers
and fourteen drives.
Assigning Storage Pools to Volumes
After you decide how to combine available LUNs into storage pools, assign the storage
pools to the volumes you want to create.
For best performance, create separate storage pools for file system metadata and
journal data.
Note: No storage pool or volume can be larger than 16 TB.
Deciding Which Clients to Mount a Volume On
If you create multiple volumes, decide which volumes should be mounted on which
clients.
Choosing Controllers
You must choose at least one computer to be the SAN controller, the computer that is
responsible for managing file system metadata.
Note: File system metadata and journal data are stored on selected SAN volumes, not
on the controller itself. For more information, see “Choosing Where to Store Metadata
and Journal Data” on page 26.
If you have a small number of clients or if performance is not critical you can use a
single computer as both controller and client. You can even set up a SAN consisting of
a single storage device and a single computer that acts as both controller and client (to
provide network attached storage, for example).
Chapter 2 Setting Up a Storage Area Network 25
Page 26

If high availability is important, you should use at least two controllers, one as the
primary controller and one as a standby. You can specify additional controllers as
needed, and set their failover priorities to determine the order in which they are tried if
the primary controller stops responding.
Choosing Standby Controllers
To be sure that SAN volumes are always available, set up at least one standby controller
that can take over if your primary metadata controller fails. A standby controller also
makes it possible for you to upgrade software on the controllers without interrupting
user access to SAN volumes.
Combining Clients and Controllers
The same computer can function as both a metadata controller and a client. It’s
possible, for example, to set up a SAN consisting of a single Xserve RAID and one
computer that acts as both controller and client. Any computer you specify as a
controller can also act as a client.
If, for example, you don’t have a computer to dedicate as a standby controller, you can
assign a computer that is normally used as a client to take over controller duties if the
primary controller fails.
To keep clients and controllers separate, you can set up client-only computers for your
users.
Choosing Where to Store Metadata and Journal Data
The metadata and journal data that describe a volume are not stored on the volume’s
metadata controller but on the volume itself. By default, they are stored on the first
storage pool in the volume. If the volume consists of more than one storage pool, you
can choose which storage pool is used to store metadata and journal data.
In most cases, storing metadata and journal data on the same storage pool as user data
results in good performance. However, for the best possible performance, consider
storing metadata and journal data on separate storage pools within the volume.
Choosing an Allocation Strategy
The allocation strategy you choose for a volume determines the order in which its
storage pools are filled with data. You can choose round robin, fill, and balance.
If you choose round robin, Xsan writes new data in turn to each storage pool in the
volume.
If you choose fill, Xsan writes all new data to the first storage pool in the volume until
that storage pool is full, then moves to the next storage pool. This is a good choice if
you want to keep a particular storage pool unused as long as possible.
If you choose balance, Xsan writes new data to the storage pool with the most free
space.
26 Chapter 2 Setting Up a Storage Area Network
Page 27

Connecting Computers and Storage Devices
Before you set up your Xsan SAN, connect client computers, controller computers, and
storage devices to the SAN’s Fibre Channel and Ethernet networks. Make sure your
networks meet the requirements summarized under “Fibre Channel Fabric” on page 19
and “Ethernet TCP/IP Network” on page 19.
Preparing LUNs (RAID Arrays and Slices)
Xserve RAID systems usually come preconfigured with two RAID 5 arrays, one on each
side (on each controller). So, out of the box, each Xserve RAID provides two LUNs. If this
suits your needs, no other preparation is needed.
If you want to set up some other combination of RAID arrays or slices, you need to do
so using the RAID Admin utility before you can add the resulting LUNs to your SAN’s
storage pools. For help using RAID Admin, see Using RAID Admin 1.2 and Disk Utility
(available at www.apple.com/server/documentation). For information on choosing a
RAID scheme, see “Choosing RAID Schemes for LUNs” on page 23.
Note: You don’t need to use Disk Utility to format arrays or slices for use with Xsan. The
LUNs are labeled and initialized when you add them to a storage pool using Xsan
Admin. After they are labeled, the LUNs can’t be viewed or modified using Disk Utility.
Be sure to create arrays of similar size if you plan to combine them into the same
storage pool. For more information, see “Assigning LUNs to Storage Pools” on page 24.
Chapter 2 Setting Up a Storage Area Network 27
Page 28

Using the Xsan Admin Application
You use the Xsan Admin application to set up and manage SANs. You can use Xsan
Admin to manage a SAN from any computer that has access to the SAN’s TCP/IP
subnet.
Xsan Admin is installed in /Applications/Server.
Installing Xsan Admin Separately
Xsan Admin is included when you install the Xsan software on SAN controller and
client computers. You can also install just Xsan Admin on any other computer you want
to use to manage the SAN. For help, see page 31.
Connecting Through a Firewall
If there is a firewall between the SAN and the computer you’re using to run Xsan
Admin, you need to open port 311 in the firewall so Xsan Admin can communicate with
the SAN computers.
Xsan Admin Preferences
Open Xsan Admin and choose Xsan Admin > Preferences to adjust these settings:
• The number of states reported by the colored status indicator next to SANs and
volumes in the SAN Components list:
• The use of SSL or digital signatures to secure communications
• The use of DNS to display names instead of IP addresses
• Smoothing of SAN utilization graphs
• Connection alerts
• SAN status refresh interval
• The amount of log information displayed
Getting Help
Xsan Admin includes online help. Choose Help > Xsan Admin Help or click the help
button in any dialog or pane where it appears.
Using the Command Line
If necessary, you can perform many Xsan setup and management tasks from a shell
command prompt. For more information, see Appendix B.
28 Chapter 2 Setting Up a Storage Area Network
Page 29

SAN Setup Summary
You’ll perform the following tasks to set up your first Xsan storage area network. Details
for each task are on the indicated pages.
1 Set up the Fibre Channel network (page 30)
2 Set up the Ethernet network (page 30)
3 Set up SAN users and groups (page 30)
4 Set up RAID arrays (page 30)
5 Install Xsan software on SAN computers (page 31)
6 Log in to the SAN (page 31)
7 Choose a controller and add clients (page 32)
8 Label and initialize available LUNs (page 33)
9 Create volumes (page 34)
10 Add storage pools to volumes (page 35)
11 Add LUNs to storage pools (page 35)
12 (Optional) Set up status notifications (page 36)
13 (Optional) Assign folders to storage pools (page 36)
14 (Optional) Set user and group quotas (page 37)
15 Start the volumes and mount them on clients (page 37)
Chapter 2 Setting Up a Storage Area Network 29
Page 30

Setting Up an Xsan Storage Area Network
Step 1: Set Up the Fibre Channel Network
m
Connect controller computers, client computers, and Xserve RAID storage systems to a
Fibre Channel network. Be sure to configure the switch and make the connections so
that you create a Fibre Channel fabric.
For more information, see the guidelines and requirements under “Fibre Channel
Fabric” on page 19.
Step 2: Set Up the Ethernet Network
m
Connect controller computers, client computers, and Xserve RAID systems to a private
TCP/IP subnet, or to the same subnet of an intranet.
Follow the guidelines summarized under “Ethernet TCP/IP Network” on page 19.
Step 3: Set Up SAN Users and Groups
m
If you already have a centralized directory of users and groups, use the Directory Access
application on each SAN computer to choose that directory for authentication. If you
don’t have a central directory, you can set one up using Workgroup Manager and the
Open Directory service in Mac OS X Server. Otherwise, you need to recreate the same
set of users and groups on each SAN computer.
Important: If you create users and groups individually on each SAN computer, be sure
that each user or group name is assigned the same numeric user ID (UID) or group ID
(GID) on all SAN computers. One way to do this is to create an identical list of users and
groups in the same order on each computer.
Step 4: Create RAID Arrays (Prepare LUNs)
m
New Xserve RAID systems are usually preconfigured as two RAID 5 arrays that are ready
to use as LUNs.To set up some other configuration of LUNs, use the RAID Admin
application to create RAID arrays or slices on your Xserve RAID systems. For help
choosing other RAID schemes, see “Choosing RAID Schemes for LUNs” on page 23.
30 Chapter 2 Setting Up a Storage Area Network
Page 31

Step 5: Install Xsan Software on Clients and Controllers
Take the Xsan installer disc to each controller and client computer connected to the
SAN and install the Xsan software.
To install the Xsan file system and Xsan Admin application:
m
At each computer, insert the disc and double-click the Xsan installer icon.
To install just the file system without Xsan Admin:
m
Click Customize on the final installer window and deselect Xsan Admin.
To install just the Xsan Admin application:
m
On the Xsan installer disc, open the Admin Tools folder, and double-click
XsanAdmin.pkg.
To install Xsan on a computer that has no keyboard or monitor:
1 Log in to a computer that does have a monitor and keyboard and insert the Xsan disc.
2 Open the Terminal application (in /Applications/Utilities).
3 In Terminal, copy the Xsan installer package to the remote computer:
$ scp -r /Volumes/Xsan/install_xsan.mpkg user@remotehost:/tmp/
where user is an administrator user on the remote computer and remotehost is the IP
address or DNS name of the computer you want to install on.
4 Log in to the remote computer:
$ ssh user@remotehost
where user and remotehost are the same as in the previous step.
5 Run the installer on the headless computer:
$ sudo installer -pkg /tmp/Install_Xsan.mpkg -target /
Or, if you want to watch the progress of installation, add the -verbose parameter:
$ sudo installer -verbose -pkg /tmp/Install_Xsan.mpkg -target /
Step 6: Open Xsan Admin and Log In to the SAN
1 Open Xsan Admin on any computer connected to the SAN.
Xsan Admin is in /Applications/Server.
You can open Xsan Admin on any computer attached to the SAN, or on any remote
computer that can reach the SAN’s TCP/IP subnet.
2 When the login dialog appears, use an administrator account to log in to the SAN
computer that will be used as a controller.
3 When the Computers pane appears, type a name for the SAN. (If you don’t see the
Computers pane, click Setup, then click Computers.)
This name appears in the SAN Components list instead of the controller name or
address if you select “Use SAN name in list” in Xsan Admin Preferences.
Chapter 2 Setting Up a Storage Area Network 31
Page 32

Step 7: Set Up Controllers and Clients
All computers on the local network with Xsan installed are listed in the Computers
pane. Your next step is to choose at least one computer to act as metadata controller
and set up the others as clients.
1 Still in the Computers pane, select a computer in the list.
If the computer you’re looking for is not listed, make sure the Xsan software is installed
on it, that it is connected to the SAN’s Ethernet subnet, and that it is turned on and not
set to sleep.
2 If the Authenticate button appears, click it and type an administrator user name and
password for the computer you are adding to the SAN.
3 Click Edit.
4 Type the Xsan software serial number.
You can find the serial number on the Xsan installer disc sleeve.
5 Choose whether the computer will function as a controller or a client.
You must set at least one computer to act as controller for the SAN. Choose from the
Role pop-up menu:
Client: The computer functions as a client only.
Controller: The computer acts as a controller and is also available for use as a client.
There is no controller-only choice. All controllers are capable of acting as clients. To
prevent a controller being used as a client, restrict user logins on or physical access to
the computer.
6 If the computer is a controller, choose its failover priority.
Choose High for the primary controller or the only controller in the SAN. Choose
Medium or Low for standby controllers.
7 Choose the network interface you want to use for metadata communications.
8 Click OK, then repeat these steps for other computers in the list.
9 When you’re through, click Save.
32 Chapter 2 Setting Up a Storage Area Network
Page 33

Step 8: Label and Initialize LUNs (RAID Arrays)
Next, prepare (label and initialize) available LUNs for use with the Xsan file system.
Each LUN represents a RAID array or slice you set up using RAID Admin.
1 In Xsan Admin, click LUNs on the Setup pane.
Responding storage devices are listed by name and size. You should see one LUN for
each RAID array or slice you created on Xserve RAID systems attached to the SAN’s
Fibre Channel network.
If some newly created LUNs are not listed, click Refresh or wait a moment for them to
appear. If they still don’t appear, quit Xsan Admin, restart the computer, and try again.
2 Select a LUN and click Edit.
3 Type a label for the LUN and click OK.
4 Repeat for each unlabeled LUN.
5 Click Save to initialize the LUNs.
You can now organize the LUNs into storage pools and volumes.
Chapter 2 Setting Up a Storage Area Network 33
Page 34

Step 9: Create Volumes
Next, you’ll create the volumes your users will see.
1 In Xsan Admin, click Storage on the Setup pane.
2 Click the New Volume button (next to the empty list).
3 Type a name for the volume.
Use only uppercase letters (A-Z), lowercase letters (a-z), and numbers (0-9). Don’t
include spaces, underscores (_), or hyphens (-). Maximum length: 70 characters.
This is the name users will see in the Finder when the volume is mounted.
4 Unless you have a specific need, leave the maximum log size set to the default value.
This is the amount of space the log file occupies on the controller’s startup disk.
5 Don’t adjust the block allocation size unless you have specific performance tuning
needs.
For optimum performance with Xserve RAID systems, the block allocation size
multiplied by the stripe breadth (which you set for each storage pool you add to the
volume) should equal 1 MB (1048576 bytes). For more information, see “Choosing Block
Allocation Size for a Volume” on page 54.
6 Choose an allocation strategy. This determines the order in which data is written to the
storage pools that make up the volume. You can choose:
Round Robin: New data is written to the next available storage pool in the volume.
Fill: All data is stored on the first storage pool until it is full, then on the next storage
pool.
Balance: New data is written to the storage pool that has the most free space.
7 Click OK.
Repeat these steps if you want to create additional volumes.
Now you’re ready to add storage pools to each volume.
34 Chapter 2 Setting Up a Storage Area Network
Page 35

Step 10: Add Storage Pools to the Volumes
1 Select a volume in the list and click the New Storage Pool button (next to the list).
2 In the storage pool dialog, provide the following information.
Storage Pool Name: Type a name for the storage pool. If the OK button is disabled
after you type a name, the name is reserved. For a list of reserved names, see “You Can’t
Add a Storage Pool” on page 76.
Use For: Choose the type of data to store in the storage pool. Journal data is used by
the controller to ensure the integrity of files in the volume. Metadata is file system
information used by the controller. Journal data and metadata are always stored at
least on the first storage pool in a volume. If this is not the first storage pool in the
volume, you can choose “User data only.” To allow only files saved in a folder that has
an affinity for this storage pool, enable “Only data with affinity.”
Stripe Breadth: Unless you have calculated a different value for performance tuning,
leave this set to the default (64 blocks). Otherwise, change to the amount of data
written, in turn, to each LUN in the storage pool. For optimum performance with
Xserve RAID systems, the stripe breadth multiplied by the block allocation size (which
you set for the volume) should equal 1 MB (1048576 bytes). For more information, see
“Choosing Stripe Breadth for a Storage Pool” on page 50.
Permissions: To prevent users from modifying the contents of the storage pool,
change to Read Only.
Multipath Method: If you have two Fibre Channel connections between each client
computer and Xserve RAID system, choose how Xsan uses the connections. Choose
Rotate to have Xsan alternate between the connections for maximum throughput.
Choose Static to have Xsan assign each LUN in the storage pool alternately to one of
the connections when the volume is mounted.
3 Click OK to return to the list.
4 Repeat for each storage pool you need.
Step 11: Add LUNs (RAID Arrays) to Storage Pools
The final step in preparing storage for the SAN is assigning LUNs to the storage pools in
your SAN volumes:
1 Select a storage pool on the Storage pane and click Available LUNs.
A drawer opens with a list of all the LUNs you initialized on page 33.
2 Drag LUNs from the drawer to the storage pool.
If a new LUN is not the same size as LUNs already in the storage pool, the usable size is
shown next to the LUN in the list.
3 Click Save.
Chapter 2 Setting Up a Storage Area Network 35
Page 36

Step 12: (Optional) Set Up SAN Status Notifications
Xsan can notify you by email or pager when the condition of the SAN changes. If you
don’t want to set up notifications now, you can do it later.
1 On the Notification pane, click the Add button (+) next to the list to add a contact.
2 Double-click the new entry, type an email address or the address of a pager text-
messaging account, and press Return.
3 If the entry is for a pager, select the checkbox in the Page column.
4 Choose the conditions that cause a notification to be sent (next to “Notify if”).
5 Click SMTP Info and enter a sender name and the mail server address.
6 To test notifications, select an address and click Send Test Notification.
Step 13: (Optional) Assign Folders to Storage Pools
If you want to force specific files to be stored in a specific storage pool of a volume,
create a folder with an affinity for that storage pool. Then, files that users put in the
folder are stored only on that storage pool.
1 In Xsan Admin, select a volume in the SAN Components list and click Start Volume.
2 With the volume still selected, click Clients.
3 Select the controller you’re connected to and click Mount Read & Write.
4 Click Affinities.
5 Select the volume the folder will appear on (in the center list, not the list on the left)
and click the Add (+) button next to the list.
6 In the dialog that appears, type a name for the folder, choose the storage pool where
the folder (and all files placed in it) will be stored, and click OK.
If the storage pool you want to use is not listed in the Storage Pool Affinity pop-up
menu, it might not be set to allow user data with affinities. To check, select the SAN in
the SAN Components list on the left, click Setup, and click Storage. Then select the
storage pool, click the Edit button, and check which data types are enabled next to
Use For.
7 Select the new folder and set permissions (below the list).
To change the owner or group, click the Add (+) button and drag a user or group from
the drawer that appears. If users and groups you expect to see are not listed in the
drawer, open Directory Access (in /Applications/Utilities) and make sure you are using
the correct directory for authentication.
8 Click Save.
36 Chapter 2 Setting Up a Storage Area Network
Page 37

Step 14: (Optional) Set User and Group Quotas
You can set up quotas to control how much space in each SAN volume is used by each
user or group.
1 If the volume is not already started, select it in the SAN Components list and click Start
Volume.
2 With the volume still selected, click Quotas.
3 Click the Add (+) button, then drag a user or group from the drawer to the quotas list.
If you don’t see the SAN users in the drawer, open Directory Access (in
/Applications/Utilities) and make sure you’re using the correct directory for user
authentication.
4 Select the user or group in the quotas list and adjust their quota settings in the lower
half of the window.
Soft Quota: The user’s recommended working maximum. The user can exceed this
limit as needed, but only for the length of time specified following “Quota locked after.”
Hard Quota: The absolute maximum amount of storage the user’s data can occupy.
“Quota locked after...”: The length of time the user can exceed their soft quota before
it automatically becomes a hard quota.
Step 15: Start the Volumes and Mount Them on Clients
To make a volume available to a user or application on a client computer, you must use
Xsan Admin to start the volume and mount it on the client. Users logged in to client
computers can’t browse for or mount SAN volumes themselves.
1 In Xsan Admin, select each new volume in the SAN Components list and click Start
Volume.
If you set up affinities or quotas on the volume, you have already started it.
2 With the volume still selected, click Clients.
3 Select a client computer and click Mount Read & Write.
To prevent the client from modifying the volume, click Mount Read Only after you click
Mount Read & Write.
Shift-click computers to mount on more than one at a time.
An icon for the mounted volume appears in the Finder on each client computer.
If you’re unable to mount volumes on any client, try shutting down all clients and
controllers, restarting the controller first and then the clients, and mounting again. If
you still have trouble, check your Fibre Channel switch configuration to be sure that the
SAN’s clients, controllers, and storage devices are in the same Fibre Channel zone.
Chapter 2 Setting Up a Storage Area Network 37
Page 38

Renaming a SAN
SANs are listed by name in the SAN Components list in Xsan Admin. By default, a SAN is
named for the controller you connect to when you set up the SAN. You can change this
name using Xsan Admin.
To change the name of a SAN:
1 Open Xsan Admin (in /Applications/Server).
2 Select the SAN in the SAN Components list.
If the SAN is not listed under SAN Components, click Connect and log in to the SAN’s
controller.
3 Click Setup, then click Computers.
4 Type a name in the SAN Name field and click Save.
5 Choose Xsan Admin > Preferences and select “Use SAN name in list.”
Deleting a SAN
Follow these steps to take a SAN out of service and remove it from Xsan Admin.
To remove a SAN:
1 Open Xsan Admin (in /Applications/Server).
2 Unmount the SAN’s volumes from client computers.
Select each of the SAN’s volumes in the SAN Components list, click Clients, select each
client that has the volume mounted, and click Unmount.
3 Stop the SAN’s volumes.
Select each of the SAN’s volumes in the SAN Components list and click Stop Volume.
4 Select the SAN in the SAN Components list and click Remove SAN.
38 Chapter 2 Setting Up a Storage Area Network
Page 39

Setting Up Additional SANs
You can use Xsan Admin to set up and manage more than one SAN. To add a new SAN,
you connect computers and storage devices to Fibre Channel and Ethernet networks,
identify computers that will act as controllers or clients, organize available storage by
combining Xserve RAID arrays and slices (LUNs) into storage pools and storage pools
into volumes, and mount the resulting volumes on client computers.
If you are setting up a SAN for the first time, see the planning guidelines and more
detailed instructions earlier in this chapter.
To add a SAN:
m
Open Xsan Admin, click Add SAN, and log in to a computer you will use as a controller
for the new SAN. Then set up the SAN as described under “SAN Setup Summary” on
page 29.
Chapter 2 Setting Up a Storage Area Network 39
Page 40

Page 41

3 Managing SAN Storage
This chapter shows how to expand, modify, check, and
repair SAN storage.
This chapter shows how to:
• Add storage to a SAN (page 42)
• Add LUNs to storage pools (page 43)
• Add storage pools to volumes (page 44)
• Add a volume (page 45)
• Create a folder with an affinity for a particular storage pool (page 46)
• Assign an affinity to a folder within a folder (page 47)
• Remove an affinity (page 47)
• Change storage pool settings (page 48)
• Rename a storage pool (page 48)
• Set access permissions (page 49)
• Choose the types of files to store on a storage pool (page 49)
• Set the storage pool stripe breadth (page 50)
• Set the method for choosing a connection (page 51)
• Change volume settings (page 52)
• Rename a volume (page 52)
• Set the storage allocation method (page 53)
• Set the block allocation size (page 54)
• Defragment a volume (page 55)
• Check a volume (page 56)
• Repair a volume (page 56)
3
41
Page 42

Adding Storage
There are several ways you can add storage to a SAN:
• Add RAID arrays (LUNs) to existing storage pools
• Add storage pools to existing volumes
• Add new volumes
The first method requires you to unmount and remount the volume on clients.
The second method lets you increase the available space in an existing SAN volume
without interrupting users who are using the volume. The only change users notice is
additional space available on the volume.
The third option creates a new volume that must be explicitly mounted on client
computers. Clients must then choose to save new files and folders on the new volume,
or copy existing items there, so this option is more likely to disrupt user workflow.
42 Chapter 3 Managing SAN Storage
Page 43

Adding LUNs to a Storage Pool
You can increase the capacity of a SAN volume by adding LUNs (RAID arrays or array
slices) to a storage pool that belongs to the volume.
Choosing Compatible LUNs
Add LUNs that are similar in performance and capacity to the LUNs already in the
storage pool. Mixing LUNs of different sizes or speeds in the same storage pool can
degrade performance and waste capacity.
Note: A storage pool can’t contain more than 32 LUNs and the total number of LUNs in
a volume can’t be greater than 512.
To add a LUN to a storage pool:
1 If you’re adding an Xserve RAID system to host the array, connect it to the SAN’s Fibre
Channel and Ethernet networks.
2 If you haven’t already done so, use RAID Admin to create the RAID array or slice. For
help, see Using RAID Admin and Disk Utility (available at
www.apple.com/server/documentation) or look in the RAID Admin online help.
Note: Don’t use Disk Utility to format the new array. You’ll use Xsan Admin to format
the array for Xsan in Step 6.
3 Open Xsan Admin and select the SAN in the SAN Components list.
4 Click Setup, then click LUNs.
5 Select the new array or slice in the list of available LUNs and click Edit.
6 In the dialog that appears, type a label for the LUN, click OK, and click Save.
The label can’t contain spaces. Only SAN administrators, not users, will see this label.
7 Click Storage, then click Available LUNs.
8 Drag the new LUN to make it the last LUN in the storage pool and click Save.
If the new LUN is not the same size as the existing LUNs, the usable size is shown next
to the LUN in the list.
9 Select the volume in the SAN Components list, click Clients, and unmount and remount
the volume on each client that has it mounted.
Note: To have an existing file redistributed across all of the LUNs in the storage pool
(including the LUN you just added), you must make a new copy of the file. If you are
adding LUNs to speed up access to a file, be sure to duplicate the file so a new copy is
distributed across all available LUNs.
Chapter 3 Managing SAN Storage 43
Page 44

From the Command Line
You can also add LUNs to a storage pool by modifying the associated volume
configuration file and using the
cvlabel command in Terminal. For more information,
see the cvfs_config and cvlabel man pages or “The Volume Configuration File” on
page 96 and “Labeling LUNs (cvlabel)” on page 90.
Adding a Storage Pool to a Volume
You can add free space to a SAN volume by adding a storage pool to the volume.
Note: A volume can’t contain more than 512 storage pools.
To add a storage pool:
1 Prepare the LUNs you’ll use to create the storage pool.
2 Open Xsan Admin and select the SAN in the SAN Components list.
3 Click Setup, then click Storage.
4 Select the volume you’re expanding, then click the Add Storage Pool button (next to
the list).
5 In the dialog that appears, specify:
Storage Pool Name: Type a name for the storage pool. If the OK button is disabled
when you finish typing the name, the name is reserved; try another. For a list of
reserved names, see Chapter 7.
Use For: Choose the types of data that can be stored on the storage pool.
Permissions: Choose the type of access clients have to this storage pool.
Stripe Breadth: Specify how much data is written to or read from each LUN in the
storage pool before moving to the next LUN. This value can affect performance. If
you’re not sure what value to use, use the default (64 blocks) or see “Choosing Stripe
Breadth for a Storage Pool” on page 50.
Multipath Method: Choose Static to use the same connection for access to the
storage pool or Rotate to alternate among the available connections.
6 Click OK.
7 Click Available LUNs, drag LUNs to the storage pool, and click Save.
From the Command Line
You can also add a storage pool by modifying the associated volume configuration file
in Terminal. For more information, see the cvfs_config man page or “The Volume
Configuration File” on page 96.
44 Chapter 3 Managing SAN Storage
Page 45

Adding a Volume to a SAN
A single Xsan SAN can provide multiple shared volumes.
1 Open Xsan Admin and select the SAN in the SAN Components list.
2 Click Setup, then click Storage.
3 Click the Add Volume button next to the list.
4 In the dialog that appears, provide the following information, then click OK.
Volume Name: Type a name for the volume. Use only uppercase letters (A-Z),
lowercase letters (a-z), and numbers (0-9). Don’t include spaces, underscores (_), or
hyphens (-). Maximum length: 70 characters.
Max Log Size: Type the maximum amount of space that the log file for this volume
occupies on the controller’s startup disk.
Allocation Strategy: Choose how storage for files is allocated among the storage pools
that belong to the volume. If you choose Round Robin, each new request for space is
assigned to the next available storage pool in turn. If you choose Fill, all space is
allocated on the first storage pool until it is full, then to the second storage pool, and
so on. If you choose Balance, space is allocated on the storage pool that has the most
free space.
Block Allocation Size: If you’re not sure what value to use, use the default (4 KB) or see
“Choosing Block Allocation Size for a Volume” on page 54.
5 Select the new volume and click the Add Storage Pool button. In the dialog that
appears, provide the following information, then click OK.
Storage Pool Name: Type a name for the storage pool. If the OK button is disabled
when you finish typing the name, the name is reserved; try another. For a list of
reserved names, see Chapter 7.
Use For: Choose the types of data that can be stored on the storage pool.
Permissions: Choose the type of access clients have to this storage pool.
Stripe Breadth: Specify how much data is written to or read from each LUN in the
storage pool before moving to the next LUN. This value can affect performance. If
you’re not sure what value to use, use the default (64 blocks) or see “Choosing Stripe
Breadth for a Storage Pool” on page 50.
Multipath Method: Choose Rotate to have Xsan alternate between the connections
for maximum throughput. Choose Static to have Xsan assign each LUN in the storage
pool alternately to one of the connections when the volume is mounted.
6 Click Available LUNs, drag LUNs to the storage pool, and click Save.
If you haven’t initialized a array, you’ll be asked to type a label for the array.
7 Click Save.
Chapter 3 Managing SAN Storage 45
Page 46

From the Command Line
You can also add a volume by setting up a configuration file. For more information, see
the cvfs_config man page or “The Volume Configuration File” on page 96.
Assigning a Storage Pool Affinity to a Folder
You can set up an affinity between a folder and a storage pool so that files in the folder
are stored only on the specified storage pool.
When you set up storage pools, you group devices with similar performance, capacity,
and data protection schemes. Depending on the devices and the protection schemes
you choose for them, you might end up with some storage pools that are larger, faster,
or better protected than others. Using affinities, you can make sure that an application
or task that needs speed or extra protection stores its files on a suitable storage pool.
Using Xsan Admin, you can assign an affinity to an existing top-level folder or create a
new top-level folder with an affinity. To assign an affinity to a folder within another
folder, you must use a command in Terminal; see the separate topic on assigning an
affinity to a folder within a folder.
To assign a storage pool affinity to a folder:
1 Open Xsan Admin and select the volume that contains the storage pool.
2 If the volume is not started and mounted on the controller, start and mount it.
To start the volume, select it and click Start Volume. To mount the volume, select it,
click Clients, select the controller, and click Mount Read & Write.
3 With the volume still selected, click Affinities.
4 If the folder doesn’t already exist, click the Add button (+) next to the folder list and
type a name for the folder.
If the folder already exists, select it and click the Edit button.
5 Choose the storage pool (where the folder’s contents will be stored) from the Storage
Pool Affinity pop-up menu in the dialog that appears.
If the storage pool you want to use is not listed in the Storage Pool Affinity pop-up
menu, it might not be set to allow user data with affinities. To check, select the SAN in
the SAN Components list on the left, click Setup, and click Storage. Then select the
storage pool, click the Edit button, and check which data types are enabled next to
Use For.
6 Click OK, then click Save.
From the Command Line
You can also assign an affinity to a folder using the
more information, see the cvmkdir man page or “Assigning an Affinity to a Folder
Within a Folder” on page 47.
46 Chapter 3 Managing SAN Storage
cvmkdir command in Terminal. For
Page 47

Assigning an Affinity to a Folder Within a Folder
You can use Xsan Admin to assign an affinity to a folder at the top level of a volume,
but to assign an affinity to a folder that is inside another folder you need to use the
cvmkdir command-line tool.
To assign a storage pool affinity to a folder within a folder:
1 Open Terminal (in /Applications/Utilities).
2 If you are not working at a SAN controller, use SSH to log in to the controller remotely:
$ ssh user@computer
where user is an administrator user on the controller computer and computer is the
controller’s name or IP address.
3 In Terminal, type
$ cd /Library/Filesystems/Xsan/bin
$ sudo ./cvmkdir -k affinity
where affinity is the name of a storage pool in the volume and path is the full path
to the folder on the volume.
For example, to assign an affinity for the storage pool “pool1” to folder “gina audio”
which is inside the folder “projects” on the volume “audio,” you would type
$ sudo ./cvmkdir -k pool1 /Volumes/audio/projects/gina\ audio
path
Removing an Affinity
The way you remove an affinity depends on whether the affected folder is at the top
level of the volume or inside another folder.
To remove a storage pool affinity from a folder:
1 If the folder is at the top level of the volume (not within another folder), open Xsan
Admin, select the volume, click Affinities, double-click the folder and choose Any
Storage Pool from the Storage Pool Affinity pop-up menu.
If the folder is inside another folder on the volume, continue with the next step.
2 Open Terminal (in /Applications/Utilities).
3 If you are not working at a SAN controller, use SSH to log in to the controller remotely:
$ ssh user@computer
where user is an administrator user on the controller computer and computer is the
controller’s name or IP address.
4 In Terminal, type
$ cd /Library/Filesystems/Xsan/bin
$ sudo ./cvmkdir -k ““ path
where path is the full path to the folder on the volume.
Chapter 3 Managing SAN Storage 47
Page 48

Changing Storage Pool Settings
The best way to set up a SAN is to plan its organization carefully before you set it up,
including settings for the storage pools that make up its volumes. You can change
some storage pool settings in an existing SAN, but other changes require the
associated volume to be re-initialized.
Renaming a Storage Pool
It is possible to rename a storage pool, but doing so erases all data on the storage pool
and the volume it belongs to.
Warning: When you rename a storage pool, all data on the storage pool and the
volume to which it belongs is lost.
To rename a storage pool:
1 Unmount the associated volume from all clients.
In Xsan Admin, select the volume, click Clients, select clients in the list, and click
Unmount.
2 Stop the associated volume.
With the volume still selected, click Stop Volume.
3 Rename the storage pool.
Select the SAN, click Setup, click Storage, and double-click the storage pool in the list.
Type the new name and click OK.
4 Click Save.
From the Command Line
You can also modify a storage pool by modifying the associated volume configuration
file in Terminal. For more information, see the cvfs_config man page or “The Volume
Configuration File” on page 96.
48 Chapter 3 Managing SAN Storage
Page 49

Setting Storage Pool Access Permissions
You can set up storage pools for read-write or read-only access. Changing this setting
doesn’t damage existing data on the volume.
To set storage pool access permissions:
1 In Xsan Admin, select the SAN the storage pool belongs to, click Setup, and click
Storage.
2 Double-click the storage pool in the list.
3 Choose Read & Write or Read Only from the Permissions pop-up menu.
4 Click OK, then click Save.
From the Command Line
You can also set read or write access to a storage pool using the cvadmin enable
command in Terminal. For more information, see the cvadmin man page or “Viewing or
Changing Volume and Storage Pool Settings (cvadmin)” on page 85.
Choosing the Types of Files Stored on a Storage Pool
You can limit the files that are stored on a particular storage pool to volume journal
data and metadata, user data, user data with an affinity for that storage pool, or a
combination of these.
Journal data and metadata are always stored on the first storage pool in a volume.
To choose the data types for a storage pool:
1 In Xsan Admin, select the SAN the storage pool belongs to, click Setup, and click
Storage.
2 Double-click the storage pool in the list.
3 Next to Use For, choose the data types to store on the storage pool.
4 Click OK, then click Save.
Chapter 3 Managing SAN Storage 49
Page 50

Setting Storage Pool Stripe Breadth
The default stripe breadth value (64 file system blocks) is adequate for storage pools in
most SAN volumes. However, you can adjust this value along with the file system block
allocation size to tune SAN performance for special applications. For help choosing a
stripe breadth, see “Choosing Stripe Breadth for a Storage Pool,” below.
Warning: When you change a storage pool’s stripe breadth, all data on the storage
pool and the volume to which it belongs is lost.
To set the stripe breadth:
1 In Xsan Admin, select the SAN the storage pool belongs to, click Setup, and click
Storage.
2 Double-click the storage pool in the list.
3 Next to Stripe Breadth, type the new value.
4 Click OK, then click Save.
Choosing Stripe Breadth for a Storage Pool
Xsan uses the storage pool stripe breadth and volume block allocation size together to
decide how to write data to a volume. For most SANs, the default values for storage
pool stripe breadth and volume block allocation size result in good performance.
However, in some cases you might be able to improve read and write performance by
adjusting these values to suit a specific application.
The stripe breadth of a storage pool is the number of file allocation blocks that are
written to a LUN in the pool before moving to the next LUN. To choose an efficient
stripe breadth, you need to consider two other factors:
• The most efficient data transfer size of the LUN storage device (1 MB for Xserve RAID)
• The size of the data blocks written and read by the critical application that uses the
volume (as reflected in the block allocation size for the volume)
Knowing these values, choose a stripe breadth using this formula:
stripe breadth (in blocks) = transfer size (in bytes) / block allocation size (in bytes)
For Xserve RAID systems, which have an optimal transfer size of 1 MB, this becomes:
stripe breadth = 1048576 / block allocation size
If, for example, you are using an application such as Final Cut Pro to move large
amounts of video data, choose the largest block allocation size (512KB) and use the
equation to find the stripe breadth of 2 blocks. Then, Xsan writes 1 MB of data (two
512KB blocks), in turn, to each LUN in your video storage pool.
50 Chapter 3 Managing SAN Storage
Page 51

The Fibre Channel interface in an Xserve RAID caches up to 1 MB of data before
passing the data on to the RAID controller to be written to individual drive modules.
So, to minimize the time data spends waiting in the cache, you want to send data to
the Xserve RAID 1 MB at a time.
Setting the Selection Method for Multiple Connections
If there is more than one Fibre Channel connection to the LUNs in a storage pool, you
can choose whether Xsan uses one connection until it fails or rotates among the
connections. This is called the “multipath method.”
To change the multipath method:
1 In Xsan Admin, select the SAN the storage pool belongs to, click Setup, and click
Storage.
2 Double-click the storage pool in the list.
3 Choose a value from the Multipath Method pop-up menu.
Static: Xsan uses one connection until it fails, then switches to the second connection.
Rotate: Xsan switches to a different connection each time it writes data to the storage
pool. This can improve performance.
4 Click OK, then click Save.
From the Command Line
You can also set the multipath method using the cvadmin multipath command in
Terminal. For more information, see the cvadmin man page or “Viewing or Changing
Volume and Storage Pool Settings (cvadmin)” on page 85.
Chapter 3 Managing SAN Storage 51
Page 52

Changing Volume Settings
You can change some settings for an existing volume, but other changes require the
volume to be re-initialized (you’ll see a warning for these cases).
Renaming a Volume
You can use Xsan Admin to change the volume name users see when the volume is
mounted on their computers.
Warning: Renaming a volume causes all data on the volume to be lost.
To rename a volume:
1 Unmount the volume from clients.
In Xsan Admin, select the volume and click Clients. Then select clients and click
Unmount.
2 Stop the volume.
In Xsan Admin, select the volume and click Stop Volume.
3 Rename the volume.
In Xsan Admin, select the SAN the volume belongs to, click Setup, and click Storage.
Then double-click the volume, type a new name in the Volume Name field, click OK,
and click Save.
Use only uppercase letters (A-Z), lowercase letters (a-z), and numbers (0-9). Don’t
include spaces, underscores (_), or hyphens (-). Maximum length: 70 characters.
4 Start the volume.
Select the volume in the SAN Components list and click Start Volume.
5 Mount the volume on clients.
Select the volume and click Clients. Select clients and click Mount.
52 Chapter 3 Managing SAN Storage
Page 53

Setting the Volume Allocation Strategy
You can set the allocation strategy for a volume to determine the order in which data is
written to the volume’s storage pools.
Warning: When you change a volume’s allocation strategy, all data on the volume
and its storage pools is lost.
To set the allocation strategy:
1 In Xsan Admin, select the SAN the volume belongs to, click Setup, and click Storage.
2 Double-click the volume in the list.
3 Choose a value from the Allocation Strategy pop-up menu.
Round Robin: New data is written to the next available storage pool in the volume.
Fill: All data is stored on the first storage pool until it is full, then on the next storage
pool, and so on.
Balance: New data is written to the storage pool that has the most free space.
4 Click OK, then click Save.
Chapter 3 Managing SAN Storage 53
Page 54

Setting the Block Allocation Size
The default file system block allocation size (4KB) is adequate for most volumes.
However, you can adjust this value along with the stripe breadth of the volume’s
storage pools to tune performance for special applications. For help choosing a block
allocation size, see “Choosing Block Allocation Size for a Volume,” below.
Warning: When you change a volume’s block allocation size, all data on the volume is
lost.
To set the block allocation size:
1 In Xsan Admin, select the SAN the volume belongs to, click Setup, and click Storage.
2 Double-click the volume in the list.
3 Use the up and down arrows to choose a new value for Block Allocation Size.
4 Click OK, then click Save.
Choosing Block Allocation Size for a Volume
Xsan uses the volume block allocation size and storage pool stripe breadth together to
decide how to write data to a volume. For most SANs, the default values for volume
block allocation size and storage pool stripe breadth result in good performance.
However, in some cases you might be able to improve read and write performance by
adjusting these values to suit a specific application.
If the critical application that uses the volume reads and writes small blocks of data,
you might improve performance by choosing a correspondingly small allocation block
size. If, for example, the application reads and writes 16KB blocks of data, you can try
adjusting the block allocation size to 16KB. Then calculate the best corresponding stripe
breadth for the volume’s storage pools using this formula:
stripe breadth (number of blocks) = transfer size (bytes) / block allocation size (bytes)
For Xserve RAID systems, which have an optimal transfer size of 1 MB, this becomes:
stripe breadth = 1048576 / block allocation size
For the block allocation size of 16KB in our example, solving the equation
(1048576/16384) gives you a stripe breadth of 64.
54 Chapter 3 Managing SAN Storage
Page 55

Defragmenting a Volume
When you create a file, Xsan breaks the file into pieces and distributes these pieces
efficiently over the LUNs that make up one of the volume’s storage pools. Over time, as
the file is modified, its pieces can become scattered in less efficient arrangements.
Defragmenting the file reassembles its pieces into the most efficient arrangement.
You can use the snfsdefrag command to defragment a single file, a folder (directory
of files), or an entire volume.
To defragment a file, directory, or volume:
1 Open Terminal (in /Applications/Utilities).
2 If you are not working at the SAN controller computer, use SSH to log in to the
controller remotely:
$ ssh user@computer
where user is an administrator user on the controller computer and computer is the
controller’s name or IP address.
3 Type the snfsdefrag command (in /Library/Filesystems/Xsan/bin).
To defragment one or more individual files:
$ sudo snfsdefrag filename [filename ... ]
To defragment an entire directory:
$ sudo snfsdefrag -r directory
To defragment an entire volume, set directory to the root directory of the volume.
For more information see the snfsdefrag man page or “Defragmenting a File, Directory,
or Volume (snfsdefrag)” on page 93.
Chapter 3 Managing SAN Storage 55
Page 56

Checking the Integrity of a Volume
If SAN users are having trouble accessing files, you can use the cvfsck command to
check the integrity of a volume, its metadata, and files.
To check a volume:
1 Open Terminal (in /Applications/Utilities).
2 If you are not working at the SAN controller computer, use SSH to log in to the
controller remotely:
$ ssh user@computer
where user is an administrator user on the controller computer and computer is the
controller’s name or IP address.
3 Run the cvfsck command-line utility (in /Library/Filesystems/Xsan/bin) twice; once to
check the journal and again to check the volume:
$ sudo cvfsck -j volume
$ sudo cvfsck -n volume
where volume is the name of an Xsan volume.
For more information on using this command, see the cvfsck man page.
Repairing a Volume
If the cvfsck utility reveals problems with a volume, you can use the same command
to repair the volume.
To repair a volume:
1 Stop the volume.
Open Xsan Admin, select the volume, and click Stop Volume.
2 Open Terminal (in /Applications/Utilities).
If you are not working at the SAN controller computer, use SSH to log in to the
controller remotely:
$ ssh user@computer
where user is an administrator user on the controller computer and computer is the
controller’s name or IP address.
3 Run the cvfsck command-line utility (in /Library/Filesystems/Xsan/bin).
$ sudo cvfsck volume
For more information on using this command, see the cvfsck man page.
56 Chapter 3 Managing SAN Storage
Page 57

4 Managing Clients and Users
This chapter shows how to add, control, and remove
client computers and their users.
Xsan clients are computers that have access to a SAN. Xsan volumes are mounted on
client computers without regard to which user is logged in to the computer.
This chapter show you how to:
• Add a client (page 58)
• Mount a volume on a client (page 59)
• Control client and user access (page 59)
• Control access to folders (page 59)
• Unmount a volume from a client (page 60)
• Restrict a client to read-only access (page 60)
• Remove a client from a SAN (page 60)
• Remove the Xsan software from a client (page 60)
• Set user and group quotas (page 61)
4
57
Page 58

Adding a Client
Before a computer can access a SAN volume, you need to set up that computer as a
SAN client.
To add a client computer to a SAN:
1 If you haven’t already, connect the client computer to the SAN’s Fibre Channel and
Ethernet networks and install the Xsan software.
2 Open Xsan Admin, select the SAN in the SAN Components list, and click Setup.
3 Click Computers, select the new computer in the list, and click Edit.
4 Type an Xsan software serial number.
The serial number is on the Xsan installer disc sleeve.
5 Choose Client or Controller from the Role pop-up menu.
Choose Client if you don’t want the computer to be available as a standby controller for
the SAN.
6 Choose the Ethernet port that the computer uses to communicate with other devices
on the SAN and click OK.
Now you can mount Xsan volumes on the client.
Adding a Client to a StorNext SAN
If you already have an ADIC StorNext File System set up, you can add Macintosh Xsan
clients to it. For more information, see Appendix A.
58 Chapter 4 Managing Clients and Users
Page 59

Mounting a Volume on a Client
A user who is logged in to a client computer can’t mount a SAN volume. A SAN
administrator must use Xsan Admin to mount the volume on the client computer.
To mount an Xsan volume on a client:
1 Open Xsan Admin, select the volume in the SAN Components list, and click Clients.
2 Select the client computer in the list.
3 Click Mount Read & Write.
To prevent the client from modifying the volume, click Mount Read Only after you click
Mount Read & Write.
You only need to mount an Xsan volume on a client once. The volume remains
mounted, even if the user logs out or the client computer is restarted, until you
unmount it or the user on the client unmounts it.
From the Command Line
You can also mount a volume on a client using the
more information, see the mount man page or “Mounting an Xsan Volume” on
page 95.
mount command in Terminal. For
Controlling Client and User Access
You can control access to information on SAN volumes at several levels:
• You can restrict user access to folders on a volume by specifying owner, group, and
general access permissions (folder level).
• You can unmount a SAN volume from selected client computers (volume level).
• You can restrict a client computer to read-only access to a volume (volume level).
• You can remove a client from a SAN (SAN level).
Controlling Access to Folders on Volumes
To restrict user access to specific folders on a SAN volume, assign access permissions to
the folder.
To assign folder access permissions:
1 Make sure the volume is started and mounted on the controller.
To start a volume, select it and click Start Volume. To mount it, select the volume, click
Clients, select the controller, and click Mount Read & Write.
2 In Xsan Admin, select the volume that contains the folder, and click Affinities.
Volumes are listed in the SAN Components list under the SAN to which they belong.
3 Select the folder in the list and specify permissions at the bottom of the window.
4 Click Save.
Chapter 4 Managing Clients and Users 59
Page 60

Unmounting a Volume From a Client
To prevent a client from accessing a volume, you can unmount the volume from the
client. Clients can’t mount SAN volumes themselves; only an administrator can mount a
SAN volume on a client.
To unmount a volume:
1 Open Xsan Admin, select the volume, and click Clients.
2 Select the client computer in the list and click Unmount.
Restricting a Client to Read-Only Access
To prevent a user logged in to a client computer from modifying data on a SAN
volume, you can mount the volume on the client with read-only permissions.
To grant read-only volume access:
1 Open Xsan Admin, select the volume, and click Clients.
2 Select the client computer and click Mount Read Only.
Removing a Client From a SAN
You can remove a client computer from a SAN to prevent it from accessing SAN
volumes.
To remove a client from a SAN:
m
Remove the Xsan software from the client.
Insert the Xsan installer disc and double-click Uninstall_Xsan.pkg.
Removing Xsan Software From a Computer
If you’re no longer going to use a computer on a SAN, you can remove the Xsan
software from the computer.
To uninstall the Xsan software:
m
Insert the Xsan installer disc and double-click Uninstall_Xsan.pkg.
After the software is removed, you can reuse the software and associated serial number
on another computer.
60 Chapter 4 Managing Clients and Users
Page 61

Setting User and Group Quotas
You can set quotas to manage the amount of storage available to a user or group.
To set storage quotas for users and groups:
1 If the volume is not already started, start it.
Open Xsan Admin, select the volume, and click Start Volume.
2 In Xsan Admin, select the volume and click Quotas.
3 If the user or group is not in the list, click the Add (+) button next to the list and drag
users or groups from the drawer to the list.
If the user or group doesn’t appear in the drawer, open Directory Access and make sure
the computer is using the correct directory for authentication.
4 Select the user or group in the list and type their hard quota, soft quota, and grace
period in the fields below the list.
5 Click Save to enforce the specified quotas or Revert to restore the last saved values.
From the Command Line
You can also set user quotas using the cvadmin quotas set command in Terminal.
For more information, see the cvadmin man page or “Viewing or Changing Volume and
Storage Pool Settings (cvadmin)” on page 85.
About Xsan Quotas
Xsan enforces two disk space quotas for each user or group you choose to restrict: a
soft quota and a hard quota. You can set these in combination to establish clear limits
on the amount of storage a user or group can use while still allowing temporary access
to extra space for unexpected storage needs.
You specify quotas individually for each volume in a SAN. A user for whom no quotas
are specified can use all available space on a volume.
Soft Quota
The soft quota is the maximum space a user or group is expected to occupy on a
regular basis. It is “soft” because it can be exceeded by an amount up to the hard quota
for a grace period that you specify.
Hard Quota
The hard quota is an absolute limit on the space a user or group can occupy. Users are
prevented from using more space than specified by their hard quota. If a user tries to
exceed his or her hard quota, he or she sees a message containing the error code -1425.
Grace Period
A user or group can exceed their soft quota without penalty as long as they return
below their soft quota within the grace period you specify.
Chapter 4 Managing Clients and Users 61
Page 62

Soft Quotas Change to Hard Quotas
If a user or group exceeds their soft quota for a time longer than their grace period, the
soft quota is changed to a hard quota, and they will not be able to save additional data
on the volume until they delete old files and return below the soft quota.
Example
Suppose you assign Aldo a soft quota of 75 GB, a hard quota of 100 GB, and a grace
period of 48 hours. Aldo’s files can occupy up to 75 GB of space at any time, for as long
as he needs them. If Aldo is surprised by additional or unusually large files, he can still
copy them to the volume, up to a total of 100 GB. He then has 48 hours to remove files
and return below the 75 GB soft limit. If he is still using more than 75 GB after 48 hours,
Xsan resets his hard quota to 75 GB and he is forced to reduce his storage use. Aldo is
unable to copy or save additional files to the volume until he deletes enough to return
below the 75 GB quota.
Checking Quota Use
See “Checking User Quota Use” on page 71.
62 Chapter 4 Managing Clients and Users
Page 63

5 Managing Metadata Controllers
5
This chapter shows how to add, switch, monitor, and
upgrade Xsan metadata controllers.
Every SAN volume you set up is managed by a metadata controller. To be sure that the
volume is available to clients even if the active controller becomes unresponsive, you
can set up standby controllers, one of which will assume control of the volume if the
primary controller fails.
This chapter shows you how to:
• Add a controller (page 64)
• Set controller failover priority (page 64)
• Switch to a standby controller (page 65)
• Find out which controller is hosting a volume (page 66)
• List the volumes hosted by a controller (page 66)
• Change a controller’s IP address (page 67)
• Upgrade controller software (page 68)
63
Page 64

Adding a Controller
You can add one or more standby controllers to a SAN so that volumes are still
available if the primary controller fails.
Any computer set to act as a controller can also function as a client. So, if you don’t
want to dedicate a computer to act solely as a standby controller, you can use an
existing client.
To add a controller:
1 If you haven’t already, connect the new controller computer to the SAN’s Fibre Channel
and Ethernet networks and install the Xsan software.
2 In Xsan Admin, select the SAN in the SAN Components list and click Setup.
3 Select the new controller in the computer list and click Edit.
4 Choose Controller from the Role pop-up menu.
If this computer has just been added to the SAN, also enter a serial number and choose
the Ethernet interface the controller will use to communicate with other devices on the
SAN.
5 Choose a failover priority and click OK.
Setting Controller Failover Priority
When the primary controller for a volume fails, Xsan uses the failover priorities of the
available standby controllers to decide which one to switch to.
To set a controller’s failover priority:
1 Open Xsan Admin, select the SAN in the SAN Components list, click Setup, then click
Computers.
2 Select the controller in the computer list and click Edit.
3 Choose a failover priority and click OK.
64 Chapter 5 Managing Metadata Controllers
Page 65

Switching to a Standby Controller
You can force an active metadata controller to turn over control of a volume to a
standby controller using the
manager process for the volume.
To switch a volume to a standby controller:
1 Open Terminal (in /Applications/Utilities).
2 If you are not working at the SAN controller computer, use SSH to log in to the
controller remotely:
$ ssh user@computer
where user is an administrator user on the controller computer and computer is the
controller’s name or IP address.
3 In Terminal, type:
$ cd /Library/Filesystems/Xsan/bin
$ sudo ./cvadmin fail volume
where volume is the name of an Xsan volume.
To see a list of volumes hosted by the controller, type:
$ sudo ./cvadmin select
To see which controller is hosting a volume, open Xsan Admin, select the volume, and
click Overview.
cvadmin command or by stopping the file system
Chapter 5 Managing Metadata Controllers 65
Page 66

Finding Out Which Controller Is Hosting a Volume
Control of a particular volume can move from one controller to another as a result of
controller failover. You can use Xsan Admin to find out which controller is currently
hosting a particular volume.
To view a volume’s controller:
m
Open Xsan Admin, select the volume in the SAN Components list, and click Overview.
From the Command Line
You can also find out which controller is hosting a volume using the cvadmin
command in Terminal. For more information, see the cvadmin man page or “Viewing or
Changing Volume and Storage Pool Settings (cvadmin)” on page 85.
Listing the Volumes Hosted by a Controller
You can use the cvadmin command to find out which SAN volumes are being hosted
by a particular controller.
To list hosted volumes:
m
Open Xsan Admin, select a SAN in the SAN Components list, and click Overview.
Controllers and the volumes they are hosting are listed at the bottom of the window.
From the Command Line
You can also find out which volumes are hosted by a controller using the cvadmin
command in Terminal. For more information, see the cvadmin man page or “Viewing or
Changing Volume and Storage Pool Settings (cvadmin)” on page 85.
66 Chapter 5 Managing Metadata Controllers
Page 67

Changing a Controller’s IP Address
Follow these instructions if you need to change the IP address of an Xsan controller.
To change a controller’s IP address:
1 If you have a standby controller in the SAN, switch the active controller’s volumes to
the standby controller. For help, see “Switching to a Standby Controller” on page 65.
If you don’t want to switch the volumes to a standby controller, just stop them: in Xsan
Admin, select the volumes and click Stop Volume.
2 When all volumes are hosted by the standby controller (or stopped, if you don’t have a
standby controller), change the computer’s role to client.
In Xsan Admin, select the SAN, click Setup, and click Computers. Then double-click the
computer and change its role to Client.
3 Change the original controller’s IP address.
If the controller is running Mac OS X Server, you must also run the changeip commandline tool. For more information, see the Mac OS X Server Command-Line Administration
guide at www.apple.com/server/documentation.
4 Restart the computer.
5 Reset the computer to act as a controller with its new IP address.
In Xsan Admin, select the SAN, click Setup, and click Computers. Double-click the
computer in the list and change its role to Controller.
6 Switch control of active volumes back to the primary controller. (If you stopped the
volumes because you have no standby controller, restart them.)
Chapter 5 Managing Metadata Controllers 67
Page 68

Upgrading Controller Software
If your configuration includes a standby controller, you can upgrade the Xsan software
without interrupting the SAN. Xsan controller software is always compatible with the
preceding version of the client software (controllers can be one version ahead of
clients). So, you can upgrade your controllers first and your client computers will
continue to work until it is convenient to upgrade them to the same version.
To upgrade Xsan without interruption:
1 Switch all volumes to a standby controller.
Go to the primary controller, open Terminal, and type:
$ cd /Library/Filesystems/Xsan/bin
$ sudo ./cvadmin fail volume
where volume is the name of an Xsan volume.
To see a list of volumes hosted by the controller, type:
$ sudo ./cvadmin select
To see which controller is hosting a volume:
Open Xsan Admin, select the volume, and click Overview.
2 When all volumes are being hosted by the standby controller, upgrade the software on
the primary controller.
3 When you are finished upgrading the primary controller, use the methods in step 1 to
switch control of active volumes back to the primary controller.
4 Now you can upgrade the standby controller.
Monitoring Controller Status
For information on checking or reporting the status of a controller, see these topics:
• “Viewing Controller CPU and Network Utilization Graphs” on page 71
• “Setting Up Status Notifications” on page 72
• “Checking Status of File System Processes” on page 72
• “Viewing Logs” on page 73
68 Chapter 5 Managing Metadata Controllers
Page 69

6 Monitoring SAN Status
This chapter shows how to check the condition of a SAN
and its components.
This chapter shows how you can check on or automatically report the condition of a
SAN and its components. It includes instructions that explain how to:
• Check free space
• On a volume (page 70)
• On a storage pool (page 70)
• Check user quota use (page 71)
• View CPU and network utilization graphs (page 71)
• Set up status notifications (page 72)
• Check status of file system processes (page 72)
• View logs (page 73)
• Check volume clients (page 73)
• Check for Fibre Channel failures (page 74)
• Check the state of Xserve RAID systems (page 74)
6
69
Page 70

Checking Free Space on a SAN Volume
There are several ways to see how much space is available on a SAN volume.
To see how much free space is available on a volume:
m
If you’re using a computer on which the volume is mounted, select the volume in a
Finder window and look at the size information at the bottom of the window (in
column or list view) or choose File > Get Info.
m
If you’re using a computer on which the volume is not mounted or a computer that
isn’t part of the SAN, open Xsan Admin, connect to a SAN controller, select the volume
in the SAN Components list, and click Overview.
From the Command Line
You can also check volume free space using the cvadmin stat command. For more
information, see the cvadmin man page or “Viewing or Changing Volume and Storage
Pool Settings (cvadmin)” on page 85.
Checking Free Space on a Storage Pool
In addition to checking free space on a volume, you can check free space on the
individual storage pools that make up the volume.
To see how much free space is available on a storage pool:
1 Open Xsan Admin and connect to a SAN controller.
2 Select the volume in the SAN Components list, click Overview, and look in the Storage
Pools list at the bottom of the window.
From the Command Line
You can also check storage pool free space using the cvadmin show command. For
more information, see the cvadmin man page or “Viewing or Changing Volume and
Storage Pool Settings (cvadmin)” on page 85.
70 Chapter 6 Monitoring SAN Status
Page 71

Checking User Quota Use
You can use Xsan Admin to check file system quotas to see how much of their
allotment a user or group is using.
To view quota utilization:
m
Open Xsan Admin, select a volume in the SAN Components list, and click Quotas.
To be sure you’re seeing the latest information, click Refresh at the top of the window.
Xsan Admin lists the following information for each user or group:
Quota: The soft and hard quotas. For example, “75 – 100 MB” indicates a soft quota of
75 MB and a hard quota of 100 MB.
Used: The amount of space the user’s files are occupying.
Quota Status: Green indicates the user or group is below their soft quota. Yellow
indicates usage exceeding the soft quota but for a time within the grace period. Red
indicates that usage now exceeds the hard limit because the soft quota was exceeded
beyond the grace period after which the soft quota was changed to a hard quota.
You can set up Xsan to notify you by email or pager when a user or group exceeds a
specific percentage of their quota. See “Setting Up Status Notifications” on page 72.
For more information on quotas and how to set them, see “Setting User and Group
Quotas” on page 61.
From the Command Line
You can also check user quotas using the cvadmin quotas get command in Terminal.
For more information, see the cvadmin man page or “Viewing or Changing Volume and
Storage Pool Settings (cvadmin)” on page 85.
Viewing Controller CPU and Network Utilization Graphs
You can use Xsan Admin to view graphs of up to 7 days of controller CPU and IP
network utilization data.
1 Open Xsan Admin and connect to the controller.
2 Select the SAN in the SAN Components list and click Graphs.
3 Choose the type of data you want to graph from the Show pop-up menu and choose a
computer from the On pop-up menu. Use the slider at the bottom of the window to
adjust the time period displayed in the graph.
Chapter 6 Monitoring SAN Status 71
Page 72

Setting Up Status Notifications
Xsan can send an email or dial a pager to notify you or other administrators when:
• A server or Fibre Channel connection fails
• Free space on a volume falls below a specific percentage
• A user or group exceeds a specific percentage of their hard quota
To send email notifications outside the local network, the controller needs access to an
SMTP server.
To have Xsan send status notifications:
1 Open Xsan Admin, select a SAN in the SAN Components list, click Setup, and click
Notifications.
2 Click the Add (+) button to add an email address or pager number to the list of
contacts.
3 Double-click the new entry in the list, type an email address or the address of a pager
text-messaging account, and press Return.
4 If the entry is for a pager, select the checkbox in the Page column.
5 Choose the conditions that cause a notification to be sent (next to “Notify if”).
6 Click SMTP Info to enter a sender name and the mail server address.
7 Click Save.
8 To test, select an address and click Send Test Notification.
Checking Status of File System Processes
You can use Xsan Admin to see if Xsan file system processes are running.
To see if Xsan processes are running:
m
To check the main controller process, open Xsan Admin, select a SAN, and click
Overview. To check the controller process for a particular volume, select the volume
and click Overview.
From the Command Line
You can also check to see if the file system processes are running using the cvadmin
command in Terminal. For more information, see the cvadmin man page or “Viewing or
Changing Volume and Storage Pool Settings (cvadmin)” on page 85.
72 Chapter 6 Monitoring SAN Status
Page 73

Viewing Logs
You can use Xsan Admin to view diagnostic and informational messages that Xsan has
written to a computer’s system and console logs.
To view the system logs:
m
Open Xsan Admin, select a SAN in the SAN Components list, and click Logs. Use the
Show pop-up menu to change logs and the On pop-up menu to switch to another
computer. To find entries containing specific text, type the text in the Filter field and
press Return.
To view volume logs:
m
Open Xsan Admin, select a volume in the SAN Components list, and click Logs.
From the Command Line
To see the log for a particular volume from the command line, look at the file
/Library/Filesystems/Xsan/data/volume/log/cvlog
where volume is the name of the volume.
Checking Volume Clients
You can use Xsan Admin to see a summary of how many clients are using a volume or
a complete list of those clients.
To see the clients that are using a volume:
m
Open Xsan Admin, select the volume in the SAN Components list, and click Clients.
To see how many clients have a volume mounted:
m
Open Xsan Admin, select the volume in the SAN Components list, and click Overview.
From the Command Line
You can also use the cvadmin who command in Terminal to see a list of volume clients.
For more information, see the cvadmin man page or “Viewing or Changing Volume and
Storage Pool Settings (cvadmin)” on page 85.
Chapter 6 Monitoring SAN Status 73
Page 74

Checking for Fibre Channel Connection Failures
Fibre Channel connection failures or errors are recorded in the system log.
To view the system log:
m
Open Xsan Admin, select a SAN in the SAN Components list, and click Logs. Choose
System Log from the Show pop-up menu and the computer you’re interested in from
the On pop-up menu.
Checking the State of Xserve RAID Systems
You can use the RAID Admin utility to check the condition of Xserve RAID systems and
the arrays, slices, and LUNs they are providing as storage for an Xsan volume.
To see the condition of Xserve RAID systems and LUNs:
m
Open RAID Admin (in /Applications/Server).
74 Chapter 6 Monitoring SAN Status
Page 75

7 Solving SAN Problems
7
This chapter lists solutions to common problems you
might encounter while working with a SAN.
Look here for solutions to common problems you might encounter while setting up,
managing, or using an Xsan SAN.
You Can’t Install the Xsan Software
If the installer says you can’t install the Xsan software on a particular computer, make
sure:
• The computer has Mac OS X v10.3 version 10.3.5 or Mac OS X Server v10.3 version
10.3.5 installed.
Some Computers Aren’t Listed During Setup
If a computer you want to add to the SAN as a controller or client is not listed in Xsan
Admin, make sure:
• You have installed the Xsan software on the computer.
• The computer is powered on.
• The computer is not sleeping and is not set to sleep (in the Energy Saver pane of
System Preferences).
• The computer is in the same TCP/IP subnet as the other SAN components.
You Can’t Connect to a SAN Computer From Xsan Admin
• If there is a firewall between the admin computer and the SAN computer, make sure
TCP port 311 is open.
Xserve RAID Systems Aren’t Accessible Over Fibre Channel
• If you are using a Vixel 355 Fibre Channel switch, connect the Xserve RAID systems to
an FL (arbitrated loop) port on the switch.
• Try restarting the computer that doesn’t see the LUNs.
• Check the configuration of the Fibre Channel switch to be sure the SAN components
are in the same Fibre Channel zone.
You Can’t Mount a Volume on a Client
• Try restarting the client computer, then try again.
75
Page 76

You Can’t Add a Storage Pool
There are some reserved names you can’t use to name a storage pool. If you type one
of these names, the OK button in the storage pool dialog is disabled. Reserved names
are listed in the following table.
Reserved storage pool names
Affinity InodeCacheSize Quotas
AllocationStrategy InodeDeleteMax Read
AttrTokenSize InodeExpandInc Regular
Brls InodeExpandMax Rotate
BrlTime InodeExpandMin Rtios
BufferCacheSize IoHangLimitSecs RtiosReserve
BufferPoolSize Journal Rtmb
BWMFields JournalIcBufNum RtmbReserve
DataMigration JournalIcBufSize RtTokenTimeout
DataMigrationThreadPoolSize JournalSize Sectors
Debug Log SectorSize
DeviceName MaxConnections Static
DirCacheSize MaxLogs StaticInodes
DirFDCacheSize MaxLogSize Status
DirWarp MaxMBPerClientReserve Sticky
Disabled Mbufs StripeBreadth
Disk MbufSize StripeClusters
DiskType MetaData StripeGroup
Enabled MirrorGroup ThreadPoolSize
Exclusive MirrorReadMethod Type
ForcePerfectFit MultiPathMethod WindowSecurity
ForceStripeAlignment No Write
FSBlockSize Node Yes
GlobalSuperUser OpHangLimitSecs
76 Chapter 7 Solving SAN Problems
Page 77

After Slicing, Some LUNs Aren’t Listed in Xsan Admin
• If you slice an array that was previously labeled for use with Xsan, you might need to
remove the old label from the first slice.
To see if the LUN is mounted using its old label, open Terminal and type:
$ sudo cvlabel -l -s
(The cvlabel tool is in /Library/Filesystems/xsan/bin.)
This will show the old label. In the following sample output, the label is sanvol1.
/dev/rdisk4/ [APPLE Xserve RAID 1.20] CVFS “sanvol1” ...
To remove the old label, type:
$ sudo cvlabel -u label
where label is the old label (sanvol1 in the example above).
After you unlabel the LUN, it should appear in the LUNs pane in Xsan Admin.
Problems Using Command-Line Tools
• If you get the response “command not found” when you try to use an Xsan
command-line tool, add /Library/Filesystems/Xsan/bin to your search path or switch
to this directory before you type the command. For example, to use the cvadmin
tool:
$ cd /Library/Filesystems/Xsan/bin
$ sudo ./cvadmin
• If you get the response “Cannot list FSS - reason -Bad file descriptor” when you run
the cvadmin tool, make sure you are using the tool as the root user. Either log in as
the root user or use the sudo command to run the tool. For example:
$ sudo ./cvadmin
• If you get the response “No manual entry for...” when you try to view the man page
for an Xsan command-line tool, you need to add the Xsan man pages directory
/Library/Filesystems/Xsan/man to your man search path. One way to do this is to add
the following line to the file /etc/manpath.config:
OPTIONAL_MANPATH /Library/Filesystems/Xsan/man
SAN User Sees Error Code –1425
• The user is trying to occupy more space than allowed by his or her hard quota.
LUN Doesn’t Have as Much Space as Expected
• To make striping across LUNs possible, Xsan automatically adjusts LUN sizes to make
all LUNs in a storage pool the same size as the smallest LUN in the pool. Xsan doesn’t
use the extra space on larger LUNs when you mix LUNs of different sizes in the same
storage pool.
Chapter 7 Solving SAN Problems 77
Page 78

Page 79

A Combining Xsan and StorNext
Clients and Controllers
A
This appendix shows how to add Macintosh clients to an
existing StorNext File System SAN or connect Windows,
Solaris, AIX, Irix, or Linux clients to an Xsan SAN.
Xsan is fully compatible with ADIC’s StorNext File System, so you can add Macintosh
clients to an existing StorNext SAN or set up Xserve and Xserve RAID systems to act as
controllers and storage for Windows, Solaris, UNIX, AIX, Irix, or Linux clients that are
running StorNext software.
Compatible Software Versions
Xsan clients and controllers are compatible with computers running StorNext File
System version 2.4 and later.
Appendix
Licensing
You license a Macintosh Xsan client or controller using the serial number printed on
the installer disc sleeve that comes in the Xsan package. Licences for StorNext are
purchased separately from ADIC when you buy the StorNext software. Xsan clients do
not use or count against StorNext File System client licenses.
Terminology
Note the following differences in terminology between StorNext and Xsan:
StorNext term Equivalent Xsan term
file system volume
file system server (FSS) controller (or metadata controller)
stripe group storage pool
79
Page 80

Adding Macintosh Clients to a StorNext SAN
If you already have a StorNext File System SAN, you can add a Macintosh client using
Xsan.
To add a Macintosh Xsan client to a StorNext SAN:
1 Connect the Macintosh computer to the SAN’s Ethernet and Fibre Channel networks.
2 Install the Xsan software on the Macintosh computer.
3 License the Xsan software on the Macintosh client.
Open Xsan Admin on the client (in /Applications/Server) and connect to the local
computer. Then select the SAN in the SAN Components list, click Setup, and click
Computers. Double-click the client in the list (in the center of the window) and enter
the serial number.
The serial number is on a sticker on the Xsan installer disc sleeve.
4 Go to an existing StorNext client on the SAN and print a copy of its fsnameservers file.
On SGI IRIX, Sun Solaris, IBM AIX, and Linux StorNext clients, you can find the file in:
/usr/cvfs/config/
On Windows clients, you can find the file in:
\%cvfsroot%\config\
where %cvfsroot% is the directory in which you installed the StorNext software.
5 Back on the Macintosh client, use a text editor such as vi to create a copy of the
fsnameservers file and save it in
/Library/Filesystems/Xsan/config/
Note: To avoid problems caused by different systems using different end-of-line
characters, don’t copy the fsnameservers file to the Macintosh client. Instead, use a text
editor on the Macintosh to recreate the file.
6 Force the Xsan software on the Macintosh to read the new fsnameservers file.
Either restart the Macintosh computer or open Terminal and type this command:
$ sudo kill -HUP ‘cat /var/run/fsmpm.pid’
7 Mount the file system.
If the file system doesn’t mount automatically, type this command in Terminal:
$ sudo mount -t acfs fsname mountpoint
where fsname is the name of the file system and mountpoint is the location where the
file system appears on the Macintosh client (
/Volumes/SanVol, for example).
80 Appendix A Combining Xsan and StorNext Clients and Controllers
Page 81

Using Xsan Controllers With StorNext Clients
You can use ADIC’s StorNext software to access an Xsan SAN from a Windows, UNIX,
AIX, Irix, or Linux computer.
1 Connect the non-Macintosh client to the SAN’s Fibre Channel and Ethernet networks.
2 Install the StorNext File System software on the non-Macintosh client following the
instructions that ADIC provides in the StorNext package.
3 Duplicate the Macintosh Xsan controller’s shared secret file on the non-Macintosh
client.
The shared secret file is named
.auth_secret
On a Macintosh Xsan controller, it is stored in the directory
/Library/Filesystems/Xsan/config/
Copy the file (using the same name) to the non-Macintosh client:
On SGI IRIX, Sun Solaris, IBM AIX, and Linux StorNext clients, put the file in:
/usr/cvfs/config/
On Windows clients, put the file in:
\%cvfsroot%\config\
where %cvfsroot% is the directory where you installed StorNext.
Important: This file contains sensitive information. Secure the file for read/write access
by the root user or Windows administrator only.
4 Place a StorNext license file for your non-Macintosh clients on the Macintosh Xsan
controller.
On the Xsan controller, put the file (named license.dat) in the directory
/Library/Filesystems/Xsan/config/
Contact ADIC to obtain a license file for your non-Macintosh clients.
Appendix A Combining Xsan and StorNext Clients and Controllers 81
Page 82

Page 83

B Using the Command Line
B
This appendix describes Xsan shell commands and
configuration files you can use to work with a SAN from
the command line.
You can use the shell commands and configuration files described here to access, set
up, and manage Xsan SANs, LUNs, storage pools, and volumes from the command line.
Using the Shell Commands
The Xsan command-line utilities are located in
/Library/Filesystems/Xsan/bin
To use a command, type the full path, for example:
$ sudo /Library/Filesystems/Xsan/bin/cvlabel -l -s
Appendix
or change to the directory before typing the command:
$ cd /Library/Filesystems/Xsan/bin
$ sudo ./cvlabel -l -s
or add /Library/Filesystems/Xsan/bin to your shell’s search path.
Working on Remote Computers
To use commands on a remote computer, first use SSH to log in to the other computer:
$ ssh user@computer
where user is a user account on the remote computer and computer is its IP
address or DNS name.
Viewing the Man Pages
UNIX-style man pages describing each of the commands are available in
/Library/Filesystems/Xsan/man
83
Page 84

If you get the response “No manual entry for...” when you try to view a man page,
add the Xsan man pages directory /Library/Filesystems/Xsan/man to your man
search path. One way to do this is to add the following line to the file
/etc/manpath.config on your computer:
OPTIONAL_MANPATH /Library/Filesystems/Xsan/man
Notation Conventions
The following conventions are used throughout the command descriptions.
Notation Indicates
monospaced font A command or other terminal text
$ A shell prompt
[text_in_brackets] An optional parameter
(one|other) Alternative parameters (type one or the other)
underlined
[...] A parameter that may be repeated
<anglebrackets> A displayed value that depends on your SAN configuration
A parameter you must replace with a value
The Commands
Xsan includes the following command-line tools:
Command Description
cvadmin View or change volume and storage pool settings (page 85)
cvcp Copy files or folders (page 88)
cvfsck Check or repair a volume (page 89)
cvlabel View, label, and initialize LUNs (page 90)
cvmkdir Create a folder with an affinity (page 91)
cvmkfile Create and pre-allocate a file (page 91)
cvmkfs Initialize a volume (page 92)
cvsginfo View storage pool information (page 92)
cvupdatefs Apply volume setup changes (page 92)
fsm Start a volume controller process (page 93)
fsmpm Start a port mapper process (page 93)
snfsdefrag Defragment a volume (page 93)
84 Appendix B Using the Command Line
Page 85

Viewing or Changing Volume and Storage Pool Settings (cvadmin)
You can use the cvadmin tool to perform a variety of information and setup tasks
related to Xsan volumes.
To enter interactive mode:
$ sudo cvadmin
To execute commands from a file:
$ sudo cvadmin [-H host] [-F volume] -f cmdfile
To execute a single command and return to the shell prompt:
$ sudo cvadmin [-H host] [-F volume] -e command
Parameter Description
-H host The metadata controller that is hosting the volume. If not provided,
the local computer is assumed.
– the IP address or DNS name of a metadata controller other
host
than the one on which you are logged in.
-F volume
-f cmdfile
-e command
The volume to be the active (“selected”) volume in cvadmin.
volume
Read commands from the specified file.
cmdfile
Execute the specified command and return to the shell prompt.
Otherwise, cvadmin continues to run in interactive mode with the
prompt Xsanadmin>. Available commands are listed under
“cvadmin Commands,” below.
– the name of an Xsan volume
– the name of a text file containing cvadmin commands
Commands available in the cvadmin tool are listed in the following table.
Appendix B Using the Command Line 85
Page 86

cvadmin Commands
cvadmin command Description
activate [volume|index] Choose the “active” volume that you want to work
with interactively.
volume
index
these, use the cvadmin select command without
any parameters)
disable pool
disks [refresh] List LUNs.
down pool
enable pool
fail (volume
filelocks [yes|no] Enable or disable file and record locks. Use the
multipath pool
paths List available LUNs.
quit Exit from cvadmin.
quotas [yes|no] Enable or disable quotas for the active (selected)
quotas get (user|group) name
quotas set (user|group) name
hard
quotacheck Recalculate quota information for the active volume.
soft grace
[read|write] Prevent read or write access to a storage pool.
pool
active volume.
Disallow all access to a storage pool.
[read|write] Allow read or write access to a storage pool.
|index) Cause a volume to fail over to a standby controller.
volume
index
these, use the cvadmin select command without
any parameters)
command without any parameter to see the current
setting for locks.
(rotate|static) Specify how Xsan uses multiple paths to a storage
pool.
volume. Use the command without any parameters to
see the current setting for quotas.
Display current quota information for a user or group.
name
Set quotas for user or group name.
name
hard
soft
grace
– the name of the volume
– the numeric ID of the volume (to see a list of
– the name of a storage pool in the currently
– the name of the volume
– the numeric ID of the volume (to see a list of
– the name of the user or group
– the name of the user or group
– hard quota (bytes)
– soft quota (bytes)
– grace period (minutes)
86 Appendix B Using the Command Line
Page 87

cvadmin command Description
repquota Generate the following quota report files in
/Library/Filesystems/Xsan/data/<vol>:
quota_report.txt – text file
quota_report.csv – comma-delimited file
quota_regen.in – cvadmin commands that will
set up identical quotas on another controller. You can
use cvadmin -f to execute the commands.
repof Create a report of open files on the active volume in
the file /Library/Filesystems/Xsan/data
/<volume>/open_file_report.txt.
select [volume
show [pool
start volume
stat Display information about the active volume.
stop volume
up pool
who Display client information for the active volume.
] Choose the “active” volume that you want to work
with. The name of the currently active volume appears
following the command prompt in interactive mode,
for example: Xsanadmin (Vol1) >.
To see a list of running volumes, leave off the volume
parameter.
volume
] [long] List storage pool information for the active volume.
[on] [controller] Start the volume based on the information in its
configuration file (/Library/Filesystems
/Xsan/config/volume
controller
the volume’s FSM process on.
Stop the active volume and its FSM process.
Allow access to the specified storage pool.
– the name of an Xsan volume
.cfg).
– The address of the controller to start
Appendix B Using the Command Line 87
Page 88

Copying Files or Folders (cvcp)
You can use the cvcp command to perform high-speed file copies to or from an Xsan
volume. You can use this command to:
• Copy files or directories
• Copy tar-formatted data to a directory
• Copy a file or directory to a tar-formatted data stream
$ cvcp [options] source destination
Parameter Description
options See “cvcp Command Options,” below.
source
destination
cvcp Command Options
Option Description
-A Turn off pre-allocation.
-b buffers
-k size
-l Copy the targets of symbolic links, not the links.
-n Do not apply command to sub-directories.
-p prefix
-s Allocate on storage pool block boundaries.
-t Specify the number of copy threads.
-v Report all information about file copied.
-x Retain original file permissions in the copy.
-y Retain ownership and group information in the copy. Works only if
-z Retain original modification times in the copy.
The file or folder (directory) to be copied.
Where the copy is created.
Set the number of I/O buffers to use.
buffers
Set the copy buffer size.
size
Only copy files with names that start with the specified prefix.
prefix
the root user is performing the copy.
– the number of buffers to use for the copy
– the buffer size (bytes)
– characters to match with the beginning of the file name
Examples
Copy the file friday to /datasets/data1/july:
$ cvcp friday /datasets/data1/july
Copy directory /data1 and all sub-directories to /datasets/data1, retaining all
permissions and ownerships and displaying files as they are copied:
$ cvcp -vxy data1 /datasets/data1
88 Appendix B Using the Command Line
Page 89

Perform a similar copy as above, but only copy files with names that begin “jul”:
$ cvcp -vxy -p jul data1 /datasets/data1/july
Copy directory /datasets to a tar file named /transfers/data.tar:
$ cvcp . - > /transfers/data
Checking or Repairing a Volume (cvfsck)
You can use the cvfsck command to check or repair an Xsan volume.
$ cvfsck [options] volume
Parameter Description
options See “cvfsck Command Options,” below.
volume
cvfsck Command Options
Option Description
-d Display extra debugging information.
-e Display file extents statistics.
-f Report fragmentation.
-g Print journal recovery log.
-j Perform journal recovery.
-J Display raw journal data.
-K Reset journal. Warning: Resetting the journal might introduce
-l Record problems in the system log.
-n Check volume in read-only mode.
-r Relocate files before changing volume configuration.
-v Display all available information.
-x Report statistics in comma-separated form for use in a spreadsheet.
The name of the volume to check or repair.
metadata inconsistencies. Don’t use unless absolutely necessary.
Appendix B Using the Command Line 89
Page 90

Labeling LUNs (cvlabel)
You can use the cvlabel command to initialize LUNs so they can be added to storage
pools.
To list available LUNs:
$ cvlabel -l [-s] [-v]
To prepare label template file:
$ cvlabel -c
To label a LUN:
$ cvlabel [-v] [-f] [labelfile]
To remove the existing label from a LUN:
$ cvlabel -u lun
Parameter Description
-l List available LUNs.
-s Display device serial numbers.
-v Show progress display.
-c Create a label template file.
-f Relabels LUNs that are already labeled.
labelfile
lun The LUN identified by disk name, for example /dev/disk4.
-u Unlabel the specified volume.
An optional file containing information for each label. You can use
the -c option to create this file, or use this file as a template:
/Library/Filesystems/Xsan/examples
/cvlabels.example
90 Appendix B Using the Command Line
Page 91

Creating a Folder With an Affinity (cvmkdir)
You can use the cvmkdir command to create a folder with an affinity for a particular
storage pool in an Xsan volume.
$ cvmkdir [-k affinity] directory
Parameter Description
-k Optional parameter for specifying the name of the storage pool to
be associated with the directory (folder). If you omit this parameter,
Xsan creates a folder without an affinity.
affinity
directory
The name of a storage pool’s affinity key. In Xsan, this is the same
as the name of the storage pool. You can use the cvadmin show
long command to see a storage pool’s affinity key.
The name of the folder.
Creating and Pre-Allocating a File (cvmkfile)
You can use the cvmkfile command to allocate space for a file on an Xsan volume.
$ cvmkfile [-k affinity] [-p] [-s] [-w] [-z] size(k|m|g) filename
Parameter Description
-k affinity Allocate space for the file on the storage pool with the specified
affinity key.
affinity
as the name of the storage pool)
You can use the cvadmin show long command to see a
storage pool’s affinity key.
-p Force future extensions of the file to be aligned on block
boundaries.
-s Force the file allocation to align with block boundaries.
-w Set file size as indicated by size
-z Set the contents of the file to zeros.
size
(k|m|g) A number specifying the amount of space to allocate to the file.
size
k – kilobytes
m – megabytes
g – gigabytes
filename
The name of the file to allocate.
– the affinity key (in Xsan, the affinity key is the same
.
– a number
Example
Allocate 2 GB of space for the file
$ cvmkfile -k datasets 2g data1
Appendix B Using the Command Line 91
data1 on the storage pool datasets:
Page 92

Initializing a Volume (cvmkfs)
You can use the cvmkfs command to initialize an Xsan volume based on the
information in the corresponding configuration file for the volume (in
/Library/Filesystems/Xsan/config/<vol>.cfg).
Warning: Initializing a volume destroys all existing data on the volume.
$ cvmkfs [-G] [-F] [volume]
Parameter Description
-G Don’t display “Press return to continue” prompts.
-F Don’t display warning and verification prompts. Use this parameter
with caution.
volume
The name of the volume to initialize. This name matches the name
of a configuration (.cfg) file in
/Library/Filesystems/Xsan/config.
Viewing Storage Pool Information (cvsginfo)
You can use the cvgsinfo command to display information about the storage pools in
an Xsan volume.
$ cvsginfo [-l] [-d] file
Parameter Description
-l Display additional information, including number of blocks, disk
names, and striping characteristics.
-d Display additional debugging information.
file
The full path to a file on the volume or of the volume’s root
directory, for example /Volumes/SanVol.
Applying Volume Configuration Changes (cvupdatefs)
You can use the cvupdatefs command to apply configuration file changes to a
volume after you modify the volume’s configuration files.
$ cvupdatefs [-f] volume [configdir]
Parameter Description
-f Update without prompting for confirmation or advising of errors in
the configuration file.
volume
configdir
The volume to update. If you don’t specify a volume, available
volumes are listed for you to choose from.
Location of the volume’s configuration (.cfg) file if it is not in the
default location (/Library/Filesystems/Xsan/config).
92 Appendix B Using the Command Line
Page 93

Starting a Volume Controller (fsm)
You can use the fsm command to start a file system manager process on a controller.
The fsm process manages the volume’s name space, file allocations, and metadata.
$ fsm [volume] [controller]
Parameter Description
volume The volume that the process will manage.
controller
The computer on which the process is started, and which therefore
becomes the volume’s metadata controller.
Starting a Port Mapper Process (fsmpm)
You can use the fsmpm command to start a file system port mapper process on a client
or controller.
$ fsmpm
For more information, see the fsmpm man page.
Defragmenting a File, Directory, or Volume (snfsdefrag)
You can use the snfsdefrag command to defragment a file by reallocating its data in
a single extent. This can improve read and write performance for a file by increasing
disk efficiency and reducing file metadata management overhead.
To defragment a file or directory:
$ snfsdefrag [-D] [-d] [-q] [-s] [-v] [-G group] [-K affinity]
[-k affinity
] [-m count] [-r] target
To report file extents without defragmenting:
$ snfsdefrag -e [-G group] [-K affinity] [-r] target [target] [...]
To display an extent count without defragmenting:
$ snfsdefrag -c [-G group] [-K affinity] [-r] target [target] [...]
To prune a file (remove allocated extents beyond the end of file):
$ snfsdefrag -p [-D] [-v] [-q] [-G group] [-K affinity] [-m count]
[-r] target
[target] [...]
To list files that are candidates for defragmentation:
$ snfsdefrag -l [-D] [-v] [-G group] [-K affinity] [-m count] [-r]
target
Parameter Description
-c Display an extent count but don’t defragment target.
-D Display debugging messages.
-d Operate on files with other than the current depth.
-e Report extents without defragmenting.
[target] [...]
Appendix B Using the Command Line 93
Page 94

Parameter Description
-K affinity
-k affinity
-l List files that might benefit from defragmentation.
-m count
-p Prune instead of defragment.
-q Suppress messages.
-r [target]
-s Allocate new extents on block boundaries.
-v Display all available information and status during
Only operate on files with the specified storage pool affinity.
affinity
as the name of the storage pool)
You can use the cvadmin show long command to see a
storage pool’s affinity key.
Allocate new extents on the storage pool with this affinity.
Only operate on files with more than count extents.
Operate recursively to defragment all files in all directories within
the specified target directory.
defragmentation.
– the affinity key (in Xsan, the affinity key is the same
Examples
Count the extents in file datafile:
$ snfsdefrag -c datafile
List the extents:
$ snfsdefrag -e datafile
Defragment the file datafile:
$ snfsdefrag datafile
Defragment the file datafile only if it has more than two extents:
$ snfsdefrag -m 2 datafile
Defragment every file in the directory /datafolder (or any directory within
/datafolder) that has more than one extent:
$ snfsdefrag -r datafolder
Recover unused pre-allocated disk space assigned to every file in directory
/datafolder:
$ snfsdefrag -rp datafolder
94 Appendix B Using the Command Line
Page 95

Mounting an Xsan Volume
You can use the mount command to mount an Xsan volume on a computer.
1 Either go to the computer and open Terminal, or use SSH to log in to the computer
remotely:
$ ssh user@computer
where user is a user account on the remote computer and computer is its IP
address or DNS name.
2 Create the mount point where the file system will be mounted:
$ mkdir mountpoint
where mountpoint is the directory where the file system is mounted (usually in
/Volumes; for example /Volumes/SanVol).
3 Mount the volume:
$ sudo mount -t acfs volume mountpoint
where volume is the name of the volume and mountpoint is the directory you
created in step 2. For example:
$ sudo mount -t acfs SanVol /Volumes/SanVol
Unmounting an Xsan Volume
You can use the umount command to unmount an Xsan volume on a computer.
1 Either go to the computer and open Terminal, or use SSH to log in to the computer
remotely:
$ ssh user@computer
where user is a user account on the remote computer and computer is its IP
address or DNS name.
2 Unmount the volume:
$ sudo umount mountpoint
where mountpoint is the directory where the volume is mounted (usually
/Volumes/<vol>). For example:
$ sudo umount /Volumes/SanVol
Viewing Logs
The system log to which Xsan writes information about SANs is in
/var/log/system.log
Volume logs are in
/Library/Filesystems/Xsan/data/<volume>/log/cvlog
where <volume> is the name of the specific volume.
Appendix B Using the Command Line 95
Page 96

The Configuration Files
Xsan stores its configuration information in the following files:
File Contents
/Library/Filesystems/Xsan/config/<vol>.cfg Volume settings
/Library/Filesystems/Xsan/config/fsmlist Volume auto-start list
/Library/Filesystems/Xsan/config/fsnameservers Controller list
The Volume Configuration File
The parameters that describe an Xsan volume are stored in the file
/Library/Filesystems/Xsan/config/<vol>.cfg
where <vol> is the name of the volume.
The various parameters in the file and how they are used to define a volume are
described in the cvfs_config man page.
Example Configuration File
# Stornext File System Configuration File Example
#
# Names can be of [A-Z][a-Z][0-9] hyphen (-) and a under-bar (_)
#
# Other things, like user defined strings and pathnames must be enclosed
# by double quotes (").
#
# Comment character (#) can start anywhere and persists to the end of line.
#
#***************************************************************************
# A global section for defining file system-wide parameters.
#***************************************************************************
#
# Global Super User.
#
# If this variable is set to Yes, then any super-user on any client may
# have global access priveleges. If set to No, then the super-user user-id
# can only affect files owned by the super-user.
#
GlobalSuperUser No
#
# The minimum number in file system blocks a file should expand by.
#
InodeExpandMin 8 # 32k initial allocation
#
# The increments an expanding segment should grow by in file system blocks.
#
InodeExpandInc 32 # Increment aggressively (128k)
96 Appendix B Using the Command Line
Page 97

#
# The maximum number in file system blocks a file should expand by.
#
InodeExpandMax 2048 # 8M per expansion (big!)
#
# Align the file system to start on a stripe breadth boundary
#
ForceStripeAlignment Yes
#
# Debug flags
#
# See the debug flags legend in cvadmin (1M)
#
Debug 0
#
# File system block size
#
# - Must be power of two in the range of 4K to 512K.
# - Must be a multiple of the largest sector size of all storage
# devices that are used with this file system configuration.
# - This block size must be evenly divisible into all of your
# striping strategies.
# - Any value greater than 16K degrades metadata operation performance
# (eg. creates/second) but startup time may improve for
# multi-terabyte filesystems.
#
#
FsBlockSize 4K
#
# Inode cache entries - used to reduce I/O for reading inodes.
#
InodeCacheSize 8K
#
# Buffer cache size - used to reduce I/O for reading inodes, directories
# and allocation bitmaps.
#
BufferCacheSize 32M
#
# Maximum clients, and AT connections allowed.
#
MaxConnections 10
Appendix B Using the Command Line 97
Page 98

#
# Maximum log file size
#
MaxLogSize 1M
#
# Client Pool Threads. Number of threads in the message handling pool.
#
ThreadPoolSize 16
#***************************************************************************
# A disktype section for defining disk hardware parameters.
#***************************************************************************
#
# Define types of disks to be configured in number of sectors in size
#
# *** Note - Sector size is 512 bytes. ***
#
[DiskType ST19171FC] # Complete 9.2GB Cuda minus 1M volume header.
Sectors 17780736
SectorSize 512 # Size of a sector (default is 512).
#***************************************************************************
# A disk section for defining disks in the hardware configuration.
#***************************************************************************
#
# The 'Status' keyword indicates the device should initially be UP|DOWN.
#
# The 'Type' keyword must match a name defined in the 'DiskType' keywords.
#
[Disk CvfsDisk0]
Status UP # UP/DOWN
Type ST19171FC # A type defined in a DiskType Section
[Disk CvfsDisk1]
Status UP
Type ST19171FC
[Disk CvfsDisk2]
Status UP
Type ST19171FC
[Disk CvfsDisk3]
Status UP
Type ST19171FC
[Disk CvfsDisk4]
Status UP
Type ST19171FC
98 Appendix B Using the Command Line
Page 99

[Disk CvfsDisk5]
Status UP
Type ST19171FC
[Disk CvfsDisk6]
Status UP
Type ST19171FC
[Disk CvfsDisk7]
Status UP
Type ST19171FC
[Disk CvfsDisk8]
Status UP
Type ST19171FC
[Disk CvfsDisk9]
Status UP
Type ST19171FC
[Disk CvfsDisk10]
Status UP
Type ST19171FC
[Disk CvfsDisk11]
Status UP
Type ST19171FC
[Disk CvfsDisk12]
Status UP
Type ST19171FC
[Disk CvfsDisk13]
Status UP
Type ST19171FC
[Disk CvfsDisk14]
Status UP
Type ST19171FC
[Disk CvfsDisk15]
Status UP
Type ST19171FC
#***************************************************************************
# Storage Pool Definition
#
#***************************************************************************
Appendix B Using the Command Line 99
Page 100

#
# Set up a stripe group for exclusive 8-bit NTSC 525 video use.
#
[StripeGroup VideoGroup1]
Status UP # UP/DOWN
Exclusive Yes # Only allow the affinity described
Affinity 6100_n8 # An affinity name describing this group
Read Enabled # Enable (Disable) reads to the stripe group
Write Enabled # Enable (Disable) writes and space allocation
StripeBreadth 172 # Width of a stripe on a disk in fs blocks
Node CvfsDisk0 0 # A disk name and the placement in the stripe
Node CvfsDisk1 1
Node CvfsDisk2 2
Node CvfsDisk3 3
Node CvfsDisk4 4
#
# Set up a stripe group for exclusive 8-bit PAL 625 video use.
#
[StripeGroup VideoGroup2]
Status UP
Exclusive Yes
Affinity 6100_p8
Read Enabled
Write Enabled
StripeBreadth 204
Node CvfsDisk5 0
Node CvfsDisk6 1
Node CvfsDisk7 2
Node CvfsDisk8 3
Node CvfsDisk9 4
#
# Set up an audio group for the NTSC streams
#
# CCIR-601 525 Audio is read/written in 65536 byte blocks
#
[StripeGroup AudioGroup1]
Status UP
Exclusive Yes
Affinity 6100_n8a
Read Enabled
Write Enabled
StripeBreadth 16
Node CvfsDisk10 0
#
# Set up an audio group for the PAL streams
#
# CCIR-601 625 Audio is read/written in 61440 byte blocks
#
100 Appendix B Using the Command Line
 Loading...
Loading...