Page 1

K
Administrator’s Guide
for the Workgroup Server 9150/120
Page 2

K Apple Computer, Inc.
© 1995 Apple Computer, Inc. All rights reserved. Under
the copyright laws, this manual may not be copied, in
whole or in part, without the written consent of Apple.
Your rights to the software are governed by the
accompanying software license agreement.
The Apple logo is a trademark of Apple Computer, Inc.,
registered in the United States and other countries. Use of
the “keyboard” Apple logo (Option-Shift-K) for
commercial purposes without the prior written consent of
Apple may constitute trademark infringement and unfair
competition in violation of federal and state laws.
Every effort has been made to ensure that the information
in this manual is accurate. Apple is not responsible for
printing or clerical errors.
Apple Computer, Inc.
1 Infinite Loop
Cupertino, CA 95014-2084
(408) 996-1010
Apple, the Apple logo, Apple Super Drive, AppleShare,
AppleTalk, EtherTalk, LaserWriter, LocalTalk, Macintosh,
PlainTalk, and StyleWriter are trademarks of Apple
Computer, Inc., registered in the United States and
other countries.
AppleCD, Apple Desktop Bus, AppleScript, AppleSearch,
Balloon Help, Disk First Aid, Finder, GeoPort, Mac,
MacTest, Power Macintosh, PowerTalk, QuickDraw, and
QuickTime are trademarks of Apple Computer, Inc.
Adobe, Adobe Illustrator, and PostScript are trademarks of
Adobe Systems Incorporated, which may be registered in
certain jurisdictions.
Creo is a registered trademark of Creo Systems Inc.
Helvetica and Times are registered trademarks of
Linotype Company.
IBM is a registered trademark and PowerPC is a
trademark of International Business Machines
Corporation, used under license therefrom.
Macintosh Basics was developed using VideoWorks
Interactive. VideoWorks Interactive is a trademark of
Macromedia, Inc. (formerly MacroMind, Inc.).
Microsoft is a registered trademark, and Windows is a
trademark, of Microsoft Corporation.
Motorola is a registered trademark of Motorola
Corporation.
NuBus is a trademark of Texas Instruments.
QuarkXPress is a registered trademark of Quark, Inc.
Retrospect Remote is a trademark of Dantz
Development Corporation.
Simultaneously published in the United States and Canada.
Mention of third-party products is for informational
purposes only and constitutes neither an endorsement nor
a recommendation. Apple assumes no responsibility with
regard to the performance or use of these products.
Page 3

Con tents
Preface Abou t This Gui de / xi
Communications regulation information / viii
Laser information / ix
1Setting Up Your Ser ver / 1
Your server at a glance / 2
Security issues / 4
Physically isolating the system / 4
Using a locking cable / 4
Using the key lock switch / 5
Replacing lost keys /6
Attaching the rubber feet / 6
Installing an expansion card or internal SCSI device / 7
Connecting a monitor / 7
Connecting the monitor’s power cord / 7
Connecting the monitor cable / 9
Connecting the mouse and keyboard / 10
Connecting other devices / 10
Plugging in the server / 11
Turning the server on / 12
Problems turning on your server? / 15
Setting the system time and date / 15
Turning the server off / 16
Page 4

2Connecting to the Network / 17
Connecting to an Ethernet network / 18
Connecting to thin coaxial Ethernet / 19
Connecting to twisted-pair Ethernet / 20
Connecting to other types of Ethernet / 21
Connecting to a LocalTalk network / 22
If you need to switch the network connection / 23
3Expanding Your Server and Connecting Other Equipment / 25
Installing an expansion card / 27
Power requirements / 27
Installing the card / 27
Expanding memory / 33
Connecting hard disks and other SCSI devices / 33
Setting the SCSI ID number / 34
Installing internal disk drives / 35
Connecting an external SCSI device / 45
Installing a device driver / 48
Do you need to initialize a hard disk? / 48
iv Contents
Connecting a printer / 49
Connecting an additional monitor / 49
Connecting a trackball or other input device / 50
Connecting a microphone / 50
Connecting a GeoPort Telecom Adapter or modem / 51
4Using Software With Your Server / 53
Using Power Macintosh programs / 54
Virtual memory / 54
Shared libraries / 54
Using older Macintosh programs / 55
Page 5

Using server application programs / 56
Setting the system time and date / 56
Order of installing and starting programs / 56
Setting up your server to restart programs automatically / 56
Additional capabilities for your server system / 58
Backing up your files / 58
5Using a DATDrive and Tape Cassettes / 59
Compatible tapes / 60
Tapes supplied with the server / 60
Starting up the tape drive / 60
Inserting tape cassettes / 61
Status lights / 62
The caution signal / 62
Removing tape cassettes / 63
Forcing the ejection of a tape cassette / 63
Locking a cassette / 63
Avoiding high humidity / 63
Cleaning the tape-drive heads / 64
6Troubleshooting / 65
When you run into trouble / 65
Take your time / 65
Start over / 66
Solutions to common problems / 67
When you need to reinstall system software / 76
Reinstalling system software / 76
Starting up from the CD-ROM drive / 77
Starting up from the floppy drive / 77
About using the Installer program / 78
Creating startup floppy disks / 80
Contents v
Page 6

What to do if your server’s performance decreases / 82
Doing a clean installation of system software / 82
If there’s a problem with your CD-ROM drive software / 85
Repairing a damaged disk / 86
Try these suggestions first /87
How to test a hard disk / 87
How to repair a hard disk or floppy disk / 88
If Disk First Aid cannot correct the problem / 90
Appendi x A Safety, Maintenance, and Health Information / 91
Important server safety instructions / 91
Handling your computer equipment / 92
Handling the monitor / 93
Handling the keyboard / 94
Handling floppy disks / 94
Ejecting a disk / 95
If you can’t eject a floppy disk / 95
Power supply / 95
Cleaning your equipment / 96
Cleaning the server case / 96
Cleaning the monitor / 96
Cleaning the mouse / 96
Health-related information about computer use / 98
Musculoskeletal discomfort / 98
Eye fatigue / 99
Arranging your office / 100
Avoiding fatigue / 101
What about electromagnetic emmissions? / 102
Appendi x BGetting Help/103
Learning the basics / 104
Reviewing the basics / 105
Getting answers in Macintosh Guide / 106
vi Contents
Page 7

Getting answers with the Topics button / 107
Getting answers with the Index button / 109
Getting answers with the Look For button / 110
Tips for using Macintosh Guide / 112
Identifying objects on the screen / 113
Learning useful shortcuts / 114
Appendi x C Special Keys on Your Keyboard / 117
Appendi x D Using Stereo Audio / 119
About your server’s sound ports / 120
Connecting an audio device / 121
Choosing audio input options / 121
Choosing audio output options / 122
Recording an alert sound / 124
Connecting external stereo speakers / 124
Playing audio CDs / 125
Index / 127
Contents vii
Page 8

Communications regulation inform ation
FCC statement
DOC statement
VCCI statement
This equipment has been tested and found
comply with the limits for a Class A digital device
pursuant to Part 15 of the Federal Communications
Commission (FCC) rules. These limits are
designed to provide reasonable protection against
such interference when the equipment is operated
in a commercial environment. This equipment
generates, uses, and can radiate radio-frequency
energy and, if not installed and used in accordance
with the instructions in this manual, may cause
interference to radio communications. Operation
of this equipment in a residential area is likely to
cause interference, in which case the user, at the
user’s own expense, will be required to correct the
interference.
DOC Class A Compliance
This digital apparatus does not exceed the Class A
limits for radio noise emissions from digital
apparatus set out in the radio interference regulations
of the Canadian Department of Communications.
to
IMPORTANT
product are not authorized by Apple Computer,
Inc., and could void the FCC certification and
negate your authority to operate the product. This
product was tested for FCC compliance under
conditions that included the use of shielded cables
and connectors between system components. It is
important that you use shielded cables and
connectors to reduce the possibility of causing
interference to radios, television sets, and other
electronic devices. For Apple peripheral devices,
you can obtain the proper shielded cables through
an Apple-authorized dealer. For non-Apple
peripheral devices, contact the manufacturer or
dealer for assistance.
Observation des normes—Classe A
Le présent appareil numérique n’émet pas de bruits
radioélectriques dépassant les limites applicables
aux appareils numériques de la Classe A prescrites
dans les règlements sur le brouillage
radioélectrique édictés par le Ministère des
Communications du Canada.
Changes or modifications to this
CE statement
This equipment has been designed, tested, and found
compliant with the Class A limits for Information
Technology Equipment of EN55022. These limits
are designed to provide reasonable protection
against radio interference when the equipment is
operated in a commercial environment.
viii Communications regulation information
This equipment generates, uses, and may radiate
radio-frequency energy and, if not installed and
used in accordance with the instruction manual,
may result in interference to radio communications.
Operation of this equipment in a residential area
may cause radio interference, in which case the
user will be required to correct the interference at
his own expense.
Page 9

Laser information
WARNING
Making adjustments or performing procedures other than
those specified in your equipment’s documentation may result in
hazardous exposure.
WARNING
Do not attempt to disassemble the cabinet containing the laser.
The laser beam used in this product is harmful to the eyes. The use of
optical instruments, such as magnifying lenses, with this product
increases the potential hazard to your eyes. For your safety, have this
equipment serviced only by an Apple-authorized service provider.
Your computer is a Class 1 laser product. The following Class 1 and service
warning labels are on the CD-ROM drive inside the computer. The Class 1
label indicates that the drive meets minimum safety requirements.
Class 1 label
Laser information ix
Page 10

Page 11

Preface Ab o ut T his Guide
This guide tells you how to set up your Workgroup Server 9150/120 and
connect it to a LocalTalk or Ether net network. The guide also pr ovides
information about expanding your server, using software, and troubleshooting
problems that may arise.
Note: For easier reading, the Workgroup Server 9150/120 will be referred to
as the Workgroup Server 9150 throughout the remainder of this guide.
About your Workgroup Server 9150 and Power Macintosh software
Your Workgroup Server 9150 is powered by the new PowerPC microprocessor
(or “chip”). This microprocessor was designed by Apple Computer, Inc.,
Motorola, Inc., and IBM Corporation. The PowerPC microprocessor uses
Reduced Instruction Set Computer (RISC) technology to deliver very high
performance at the lowest possible cost. The PowerPC RISC microprocessor
represents the state of the art in microprocessor design.
Your Workgroup Server 9150 will run almost all of your existing Macintosh
software, but for best performance and greatest speed, look for software programs
designed especially for Power Macintosh computers. You’ll find Power
Macintosh programs at any software store that carries products for Macintosh.
Page 12

Who s h ould read this guide
This guide is intended for the person who sets up the server and connects it to
an existing network. You should be familiar with basic Macintosh terms,
concepts, and techniques. If you’re new to the Macintosh environment, see
Appendix B, “Getting Help,” after setting up your server system. You also
need to know some details of your existing network to choose the appropriate
procedures for connecting the server to your network.
What this guide contains
Here’s a brief summary of what you’ll find in this guide:
m Chapter 1, “Setting Up Your Server,” explains how to connect the monitor,
keyboard, and mouse, and how to start up your server for the first time.
m Chapter 2, “Connecting to the Network,” describes how to connect the
server to an Ethernet or LocalTalk network.
m Chapter 3, “Expanding Your Server and Connecting Other Equipment,”
describes how to install an expansion card, add memory to the server, and
connect additional internal and external devices.
m Chapter 4, “Using Software With Your Server,” discusses running Power
Macintosh software and server application programs (including network
services).
xii Preface
m Chapter 5, “Using a DAT Drive and Tape Cassettes,” explains the use of the
optional DAT drive and describes the types of tape cassettes that are
appropriate for use with the drive.
m Chapter 6, “Troubleshooting,” helps you solve problems with the server.
This chapter also explains how to reinstall system software.
m Appendix A, “Safety, Maintenance, and Health Information,” suggests how
you can create a healthful and safe server environment and keep your server
equipment in good working order.
Page 13

m Appendix B, “Getting Help,” describes how to u s e t h e va r i o u s k i n d s o f o n -
screen help available in the Guide menu.
m Appendix C, “Special Keys on Your Keyboard,” describes the uses of unique
keys as shortcuts for menu commands and alternatives to using the mouse.
m Appendix D, “Using Stereo Audio,” explains how to use your server’s
stereo audio capabilities.
How to use this guide
Familiarize yourself with your server’s basic components. See the section
“Your Server at a Glance” in Chapter 1.
Consider security issues and placement of your server. Read the section
“Security Issues” in Chapter 1 for important information about protecting your
server from unauthorized access.
If you want to add an expansion card or internal drive to the server: Install the
card or internal device according to the instructions in Chapter 3, “Expanding
Your Server and Connecting Other Equipment.” Then return to Chapter 1 to
connect the monitor and keyboard.
If you want to connect external peripheral devices to your server: After you
connect the monitor and keyboard to the server, as described in Chapter 1, turn
to the appropriate instructions in Chapter 3, then return to Chapter 1.
Connect to the network to complete the setup process. See Chapter 2,
“Connecting to the Network,” for details.
If you are new to Macintosh: After setting up the hardware and turning your
server on, refer to Appendix B, “Getting Help,” to learn how to use the
features of Macintosh system software and application programs.
Be sure to read other sections of the book that are relevant to your work
environment. Also, be sure to keep this book in a handy location; if you
experience problems while using your server, you may need to refer to
Chapter 6, “Troubleshooting.”
Preface xiii
Page 14

For on -scree n help and information
There are several valuable sources of help and information that you can view
directly on your server’s monitor screen, as described in this section.
Workgroup Server Read Me
It is important that you read the Workgroup Server Read Me file, which
contains late-breaking information about your server. This file is located on the
server’s hard disk and on the Workgroup Server Software CD-ROM disc. You
may want to print this file for future reference.
The Guide menu
Starting with system software version 7.5, you have instant access to new
kinds of help when using your system and application programs. You can see
your options in the Guide (h) menu in the upper-right corner of the screen.
xiv Preface
You’ll find the instructions available in Macintosh Guide particularly useful
when you have questions or encounter problems with your system software.
For more details on the types of on-screen help available, refer to Appendix B,
“Getting Help,” and explore your options in the Guide menu.
Workgroup Server Electronic Library
For your convenience, electronic versions of your server’s documentation are
provided on your server’s hard disk and on the Workgroup Server Software
CD-ROM disc. You’ll find these documents in a folder called the Electronic
Library. To read a document, just double-click to open it. You’ll find on-screen
help available in the document.
Page 15

The Electronic Library folder contains electronic versions of the
following documents:
m this book, the Administrator’s Guide
m the Technical Information booklet for the Workgroup Server 9150
m the Apple RAID Software Administrator’s Guide
m other user’s guides for software that may have come with your server
Other reference material
In addition to this guide, you may need to consult the following sources
of information.
m Technical Information See this booklet for the technical specifications of
your server.
m The user’s guide for the CD-ROM drive that came with your server. See this
guide for information about using CD-ROM discs, playing audio compact
discs and audio tracks on CD-ROM discs, and working with Photo CD discs.
m For information about server application programs included with your
Workgroup Server 9150, such as Apple RAID Software and Retrospect
Remote, refer to the documentation for those programs included in the
server accessory kit.
m There are a number of network services, such as AppleShare, AppleSearch,
and Apple Remote Access, that can be installed on your Workgroup
Server 9150. Refer to the documentation included with those services for
installation and operation information.
m For late-breaking information about your server and system software, see
the Workgroup Server Read Me file, located on the server’s hard disk and
on the Workgroup Server Software CD-ROM disc.
Preface xv
Page 16

Where to find answer s
When you have questions about using your server, there are several places you
can look for answers.
In this book
Use this book to help you set up your server and learn about
Administrator’s Guide
it, or to find solutions to problems.
In the Guide menu
The Guide menu (marked with the hicon) is your main source
of information about system software. To learn how to get
different kinds of help from the Guide menu, see Appendix B in
this book.
In other manuals
For answers to questions about other equipment or about
application programs you have purchased, see the manuals that
came with the equipment or programs.
xvi Preface
From Apple’s customer support hotline
If you can’t find an answer in any of the materials provided,
call the customer support hotline. (The phone number for the
hotline is in the service and support information that came with
your server.)
Page 17

1 Setting Up Your Server
Setting up your server involves connecting a monitor, mouse, and keyboard,
expanding your system to suit your needs, and connecting to the network.
First, acquaint yourself with your server’s features, as shown in the first
section, “Your Server at a Glance.” Also, be sure to read the section “Security
Issues” for important information about protecting your server from
unauthorized access. Then, if you want to install an expansion card or install
other internal devices, see the appropriate sections in Chapter 3 before
returning to the setup procedures in this chapter. Once you’ve connected the
monitor, mouse, and keyboard, you may need to refer to Chapter 3 again if
you want to connect any external devices.
You complete the setup process by configuring your network connection, as
described in Chapter 2.
Page 18
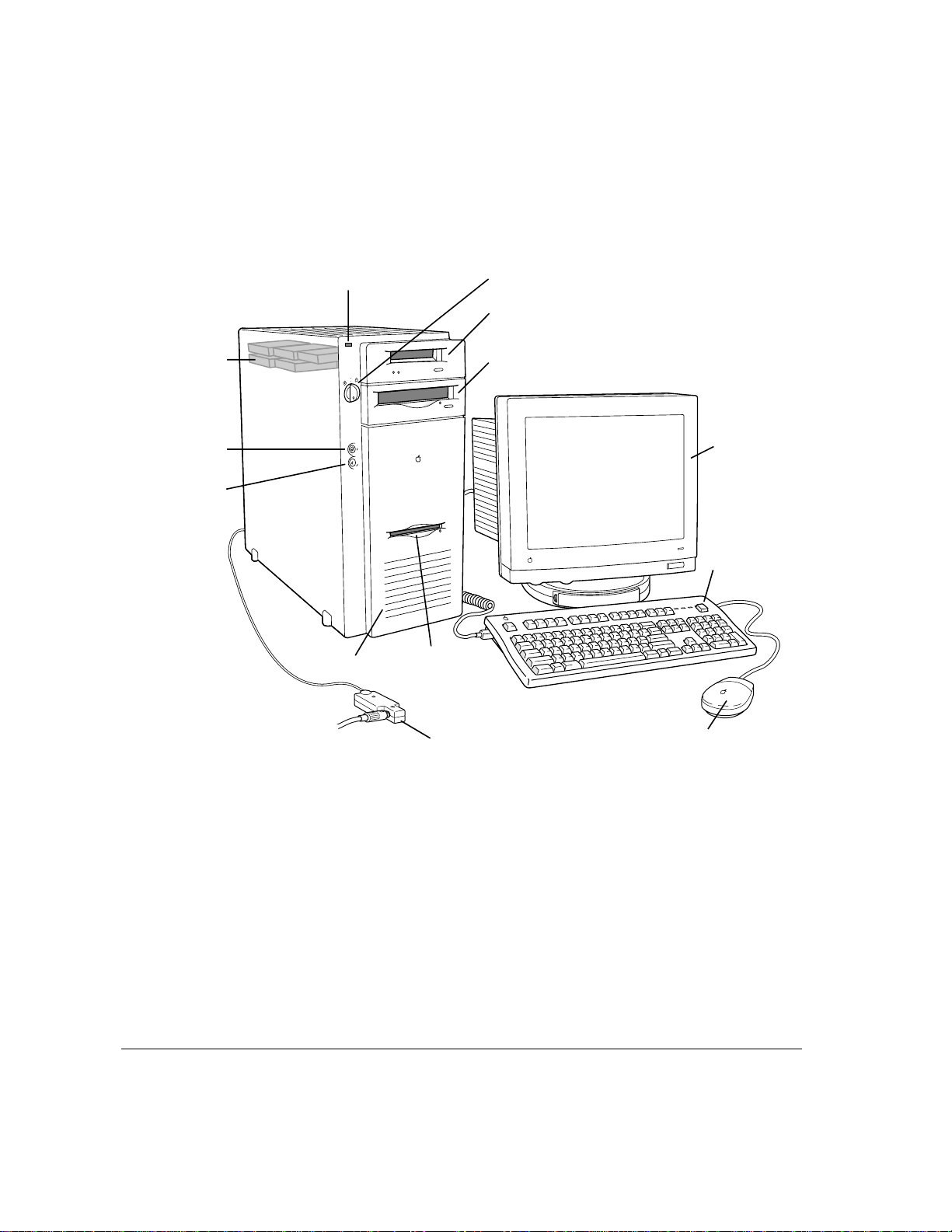
Your server at a glance
The following figure shows the basic components of your Workgroup
Server 9150, assembled and connected to a network.
Key lock switchPower light
DAT drive
(optional)
Startup hard
disk drive
(additional drives
are optional)
Interrupt switch
Reset switch
¥
P
Speaker
ª
To the
network
Floppy disk drive
Media adapter
(transceiver)
CD-ROM drive
Monitor
Power On key
Mouse
2 Chapter 1 / Setting Up Your Server
Page 19
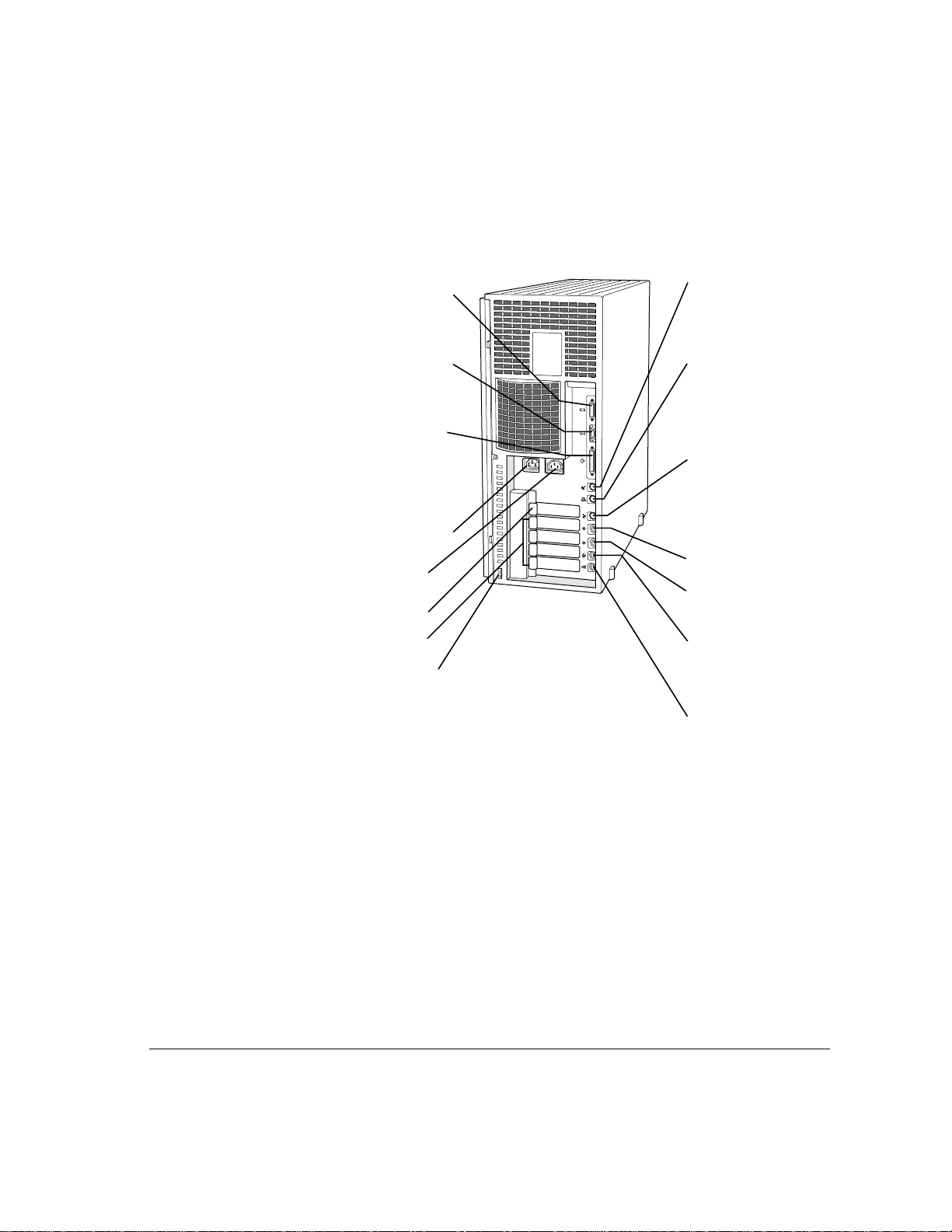
The ports on the back of the Workgroup Server 9150 and the icons that identify
them are shown in the following figure. During setup, you’ll connect hardware
to some of these ports.
W
Monitor port
Connects your monitor
to your server.
™
Modem port
(GeoPort)
Connects an external
modem to your server.
Ethernet port
Connects your server to
a high-speed network.
SCSI port
Connects your server
to SCSI devices, such
as hard disk drives,
scanners, and printers.
Power plug
Monitor power socket
Processor-direct slot (1)
NuBus slots (4)
Security lock port
G
g
≤
F
Printer port
[
Connects your server
to a printer, LocalTalk
network, or GeoPort
Adapter.
V
ADB port
Connects your server
to input devices,
such as a keyboard
or a trackball.
0
Line input ports
Connect your server to
)
an audio source, such
as a stereo system.
Sound input port
≈
Connects your server
to a microphone.
Sound output port
_
Connects your server
to sound output
devices, such as a
pair of headphones
or speakers.
Your server at a glance 3
Page 20

Security issues
The Workgroup Server 9150 lets you concentrate valuable or sensitive
information on one system that can be physically isolated and more carefully
monitored than would be possible if that information were stored on personal
computers. Before you set up the server, you may want to consider three
measures that you can take to secure the hardware components: physically
isolating the system, using a locking cable to secure the system, and using the
server’s key lock switch.
Physically isolating the system
It is important to note that even if software security features (such as password
protection or locking screen savers) are in use on the server, it is still possible
to disconnect peripheral devices—such as hard disks, which may contain
confidential information—from your server system. There is no better way to
protect hardware components than by physically isolating the server—locking
it either in a well-ventilated cabinet or in a room with controlled access.
Depending on your security needs, the nature of the data stored on the server
may warrant the effort.
Using a locking cable
As an alternative to isolating the system completely in an area of controlled
access, you can purchase a locking cable and attach it to your server. The back
panel has a built-in port for a locking cable. Follow the instructions supplied
with the locking cable to attach it to your server.
4 Chapter 1 / Setting Up Your Server
Page 21
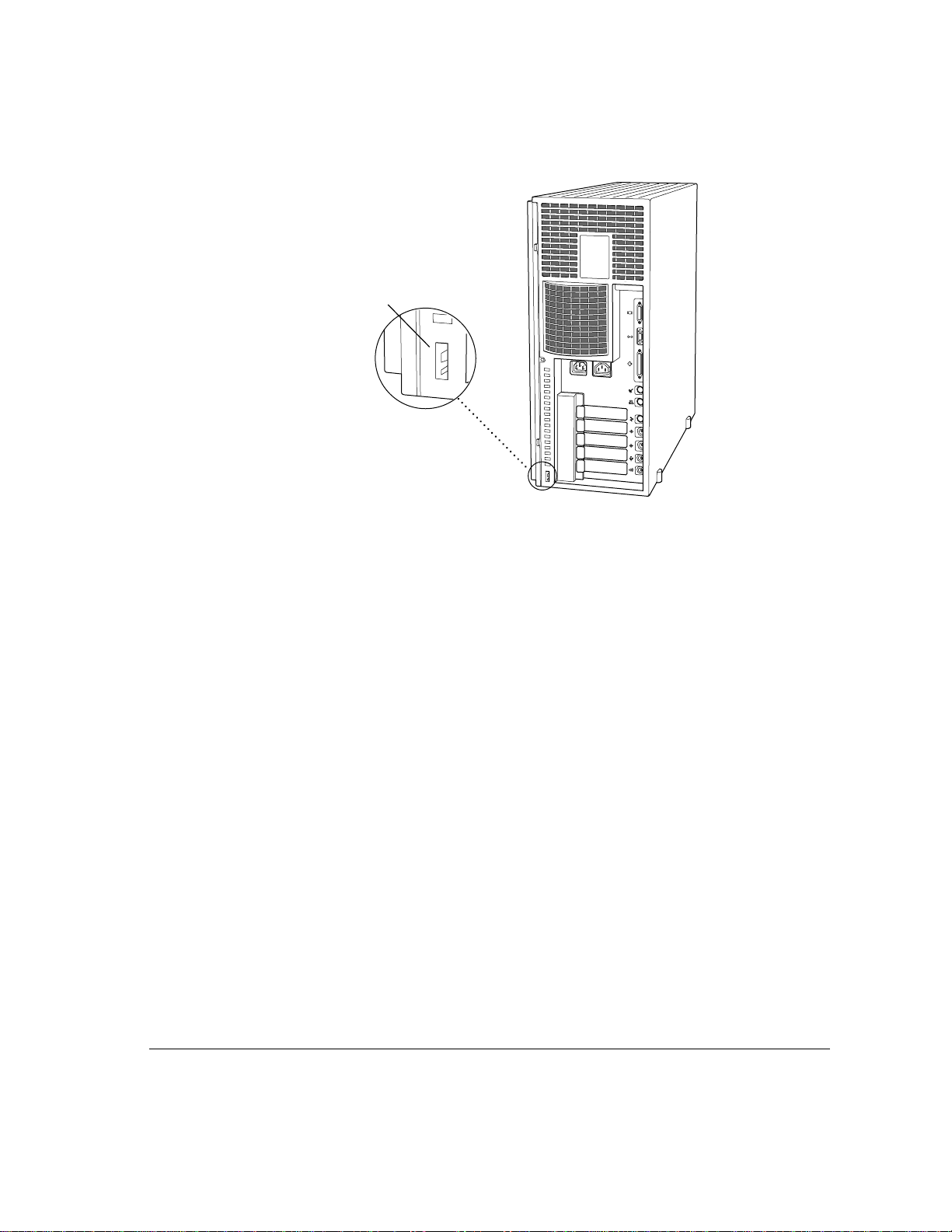
Security lock port
F
F
By itself, a locking cable cannot prevent unauthorized use of the server, but it
can prevent the server (and its peripheral devices if they are also secured by
locking cables) from being removed.
In combination with the key lock switch, a locking cable ensures that the system
is secure physically and that only the person with the key can operate it locally.
Using the key lock switch
The key lock switch is a physical lock on the front panel of the Workgroup
Server 9150. When you turn the key to the “secure” position, the Apple
Desktop Bus (ADB) devices (that is, the keyboard and mouse) and floppy
disk drive become inoperable. This means that the server cannot be operated
locally; the server can be operated only by special (remote-access) software
that makes it possible to control the server from another computer on the
network. See “Turning the Server On” later in this chapter for more details
about using the key lock switch.
Security issues 5
Page 22
Replacing lost keys
Be sure to store the Workgroup Server 9150 keys in a safe place. Because lost
keys are difficult to replace, you may want to make duplicates of your keys. If
you lose both keys, the following solutions are available:
m Contact a locksmith. Most locksmiths can create a new set of keys directly
from the key lock switch.
m Contact your Apple-authorized service provider for assistance. The service
provider can order additional keys from the lock manufacturer. (The lock
manufacturer will accept calls only from Apple-authorized service providers.)
m As an alternative to ordering new keys, the service provider can replace the
key lock switch on your Workgroup Server 9150 and provide new keys.
Attaching the rubber feet
The Workgroup Server 9150 comes with six rubber feet that need to be
attached to the bottom of the server.
For each foot, peel off the adhesive backing and press the foot into one of the
m
indentations on the bottom of the computer.
6 Chapter 1 / Setting Up Your Server
Page 23

Installing an expansion card or internal SCSI device
If you purchased any expansion cards or additional internal SCSI devices for
your server, install them now (see “Installing an Expansion Card” and
“Connecting Hard Disks and Other SCSI Devices” in Chapter 3 for
instructions). Otherwise, go on to the next section, “Connecting a Monitor.”
Connecting a monitor
Your server has one monitor port that accepts a monitor with a screen 16
inches or smaller (measured diagonally).
Note: You can use a larger monitor by installing a monitor card. See
“Installing an Expansion Card” in Chapter 3.
This section contains instructions for connecting a monitor to your server. You
can connect many types of monitors to your server, including most standard
monitors. See the Technical Information booklet that came with your server
for a more detailed list. To connect a monitor from a manufacturer other than
Apple, refer also to the instructions that came with the monitor.
Connecting the monitor’s power cord
Monitors have two cords to connect: a power cord and a monitor cable. To
connect the monitor power cord:
1 Place the monitor where you will be using it.
Keep in mind these considerations:
m Allow a few inches for air circulation around the server and monitor.
m Make sure the top of the screen is slightly below eye level when you’re
sitting at the keyboard.
m Position the monitor to minimize glare and reflections on the screen from
overhead lights and windows.
m Consult “Arranging Your Office” in Appendix A for suggestions about
locating your server equipment.
Connecting a monitor 7
Page 24
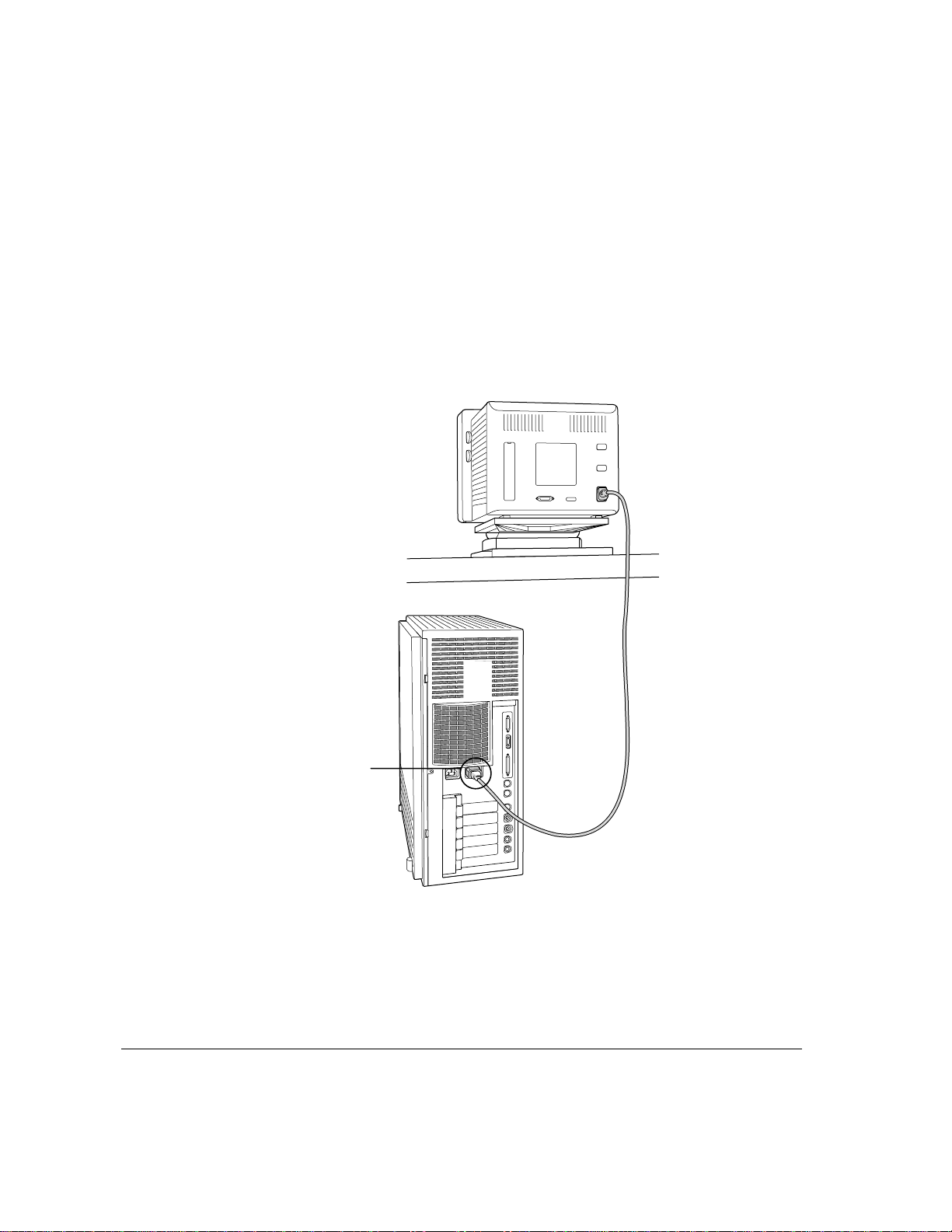
2 Connect the monitor’s power cord to the monitor.
On some monitors, the cord is already attached.
3 Plug in the monitor’s power cord.
Some power cords are designed to plug into the back of your server. You
can also plug the power cord into a grounded electrical outlet (an adapter
may be needed).
Note: Some monitors have to be connected to a grounded power outlet, not to
the server’s power socket. Check the information that came with the monitor.
Plug the monitor power
cord into this socket.
8 Chapter 1 / Setting Up Your Server
Page 25
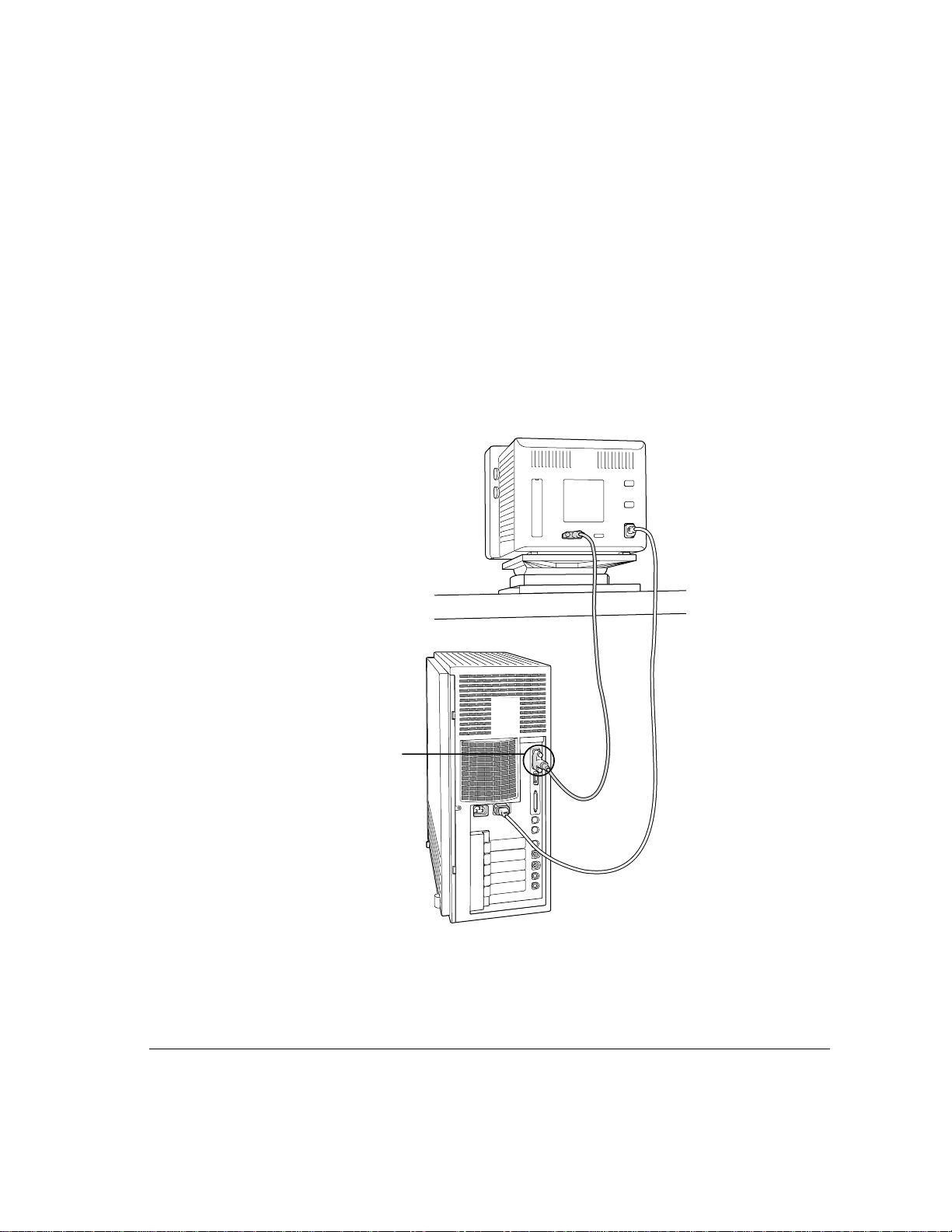
Connecting the monitor cable
After you plug in the monitor’s power cord, connect the monitor cable to the
server’s monitor port.
To connect the monitor cable:
1 Attach the monitor cable to the monitor.
On some monitors, the cable is already attached.
2 Attach the monitor cable to the server’s monitor port.
The monitor port is marked with the icon ™.
Plug the monitor cable
into the monitor port.
Connecting a monitor 9
Page 26

Connecting the mouse and keyboard
You have a choice of several keyboards for your server. They are all connected
the same way.
1 Plug the mouse cable into the port on either side of the keyboard.
Most right-handed people prefer to use the mouse with their right hand; most
left-handed people prefer to use the mouse with their left hand. Plug the
mouse into the port on the side you prefer.
The plug and the port are marked with the same icon (◊). Align the icons
before you insert the plug. The positions of the port and icon on your
keyboard may be different from those pictured.
ADB icon
Note: The ◊ port is called the Apple Desktop Bus (ADB) port.
2 Plug the keyboard cable (both ends are the same) into the other port on the keyboard.
3 Plug the keyboard cable into the port on the back of the server marked with the
Some monitors have a ◊ port to which you can connect the keyboard or
mouse. See the information that came with your monitor.
Connecting other devices
If you want to connect other devices to your server, such as an external hard
disk or a printer, follow the instructions in Chapter 3.
10 Chapter 1 / Setting Up Your Server
◊
icon.
Page 27
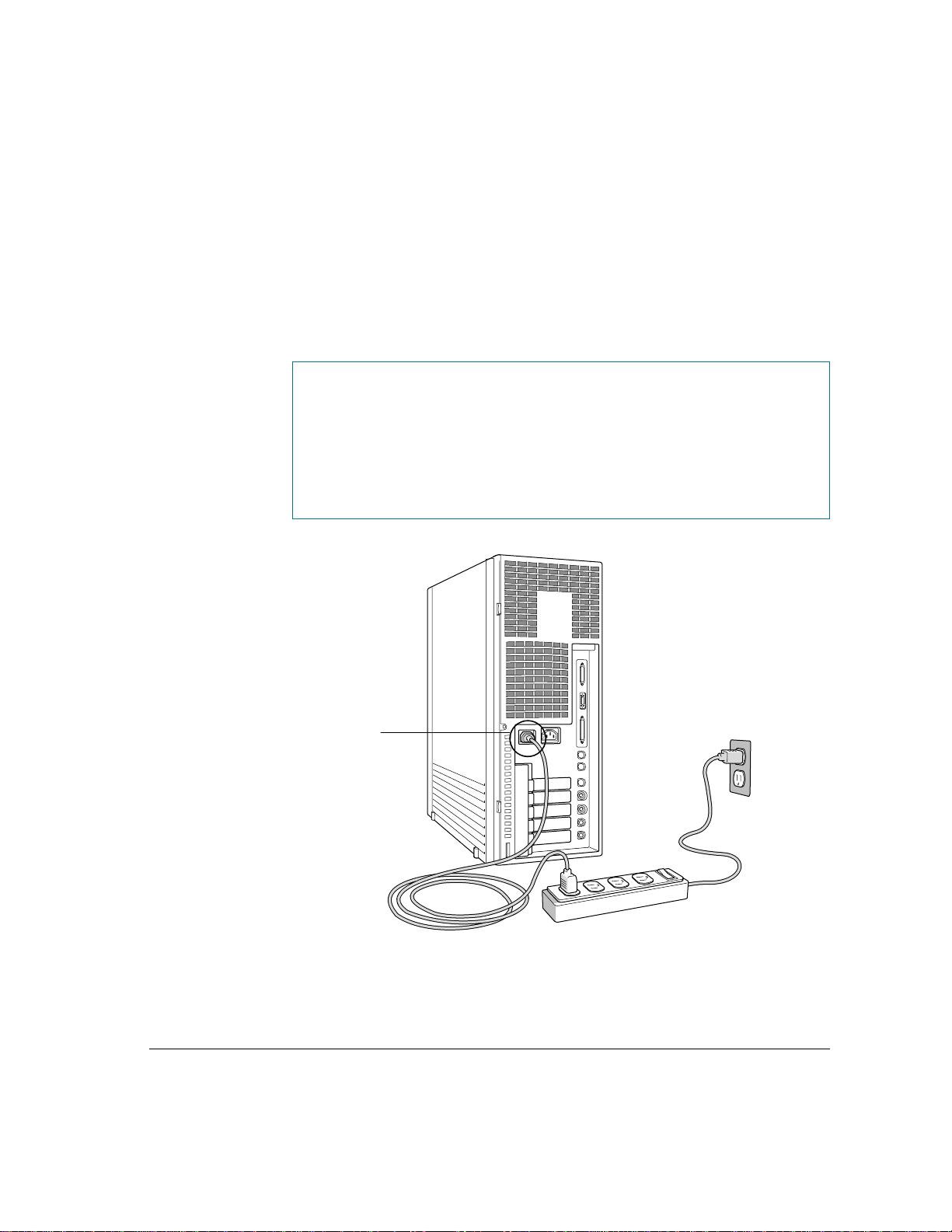
Plugging in the server
To plug in the server:
1 Plug the socket end of the server’s power cord into the recessed power plug (marked
with the symbol ≤) on the back of the server.
2 Plug the other end of the power cord into a three-hole grounded outlet or power strip.
Choose a power outlet to which you have easy access.
WARNING
This equipment is intended to be electrically grounded. Your
server is equipped with a three-wire grounding plug—a plug that has a
third (grounding) pin. This plug will fit only a grounded AC outlet. This
is a safety feature. If you are unable to insert the plug into the outlet, contact
a licensed electrician to replace the outlet with a properly grounded outlet.
Do not defeat the purpose of the grounding plug!
Plug the power cord
into the recessed
power plug.
IMPORTANT
Be sure at least one end of the power cord is within easy reach so
that you can unplug the server when you need to.
Plugging in the server 11
Page 28
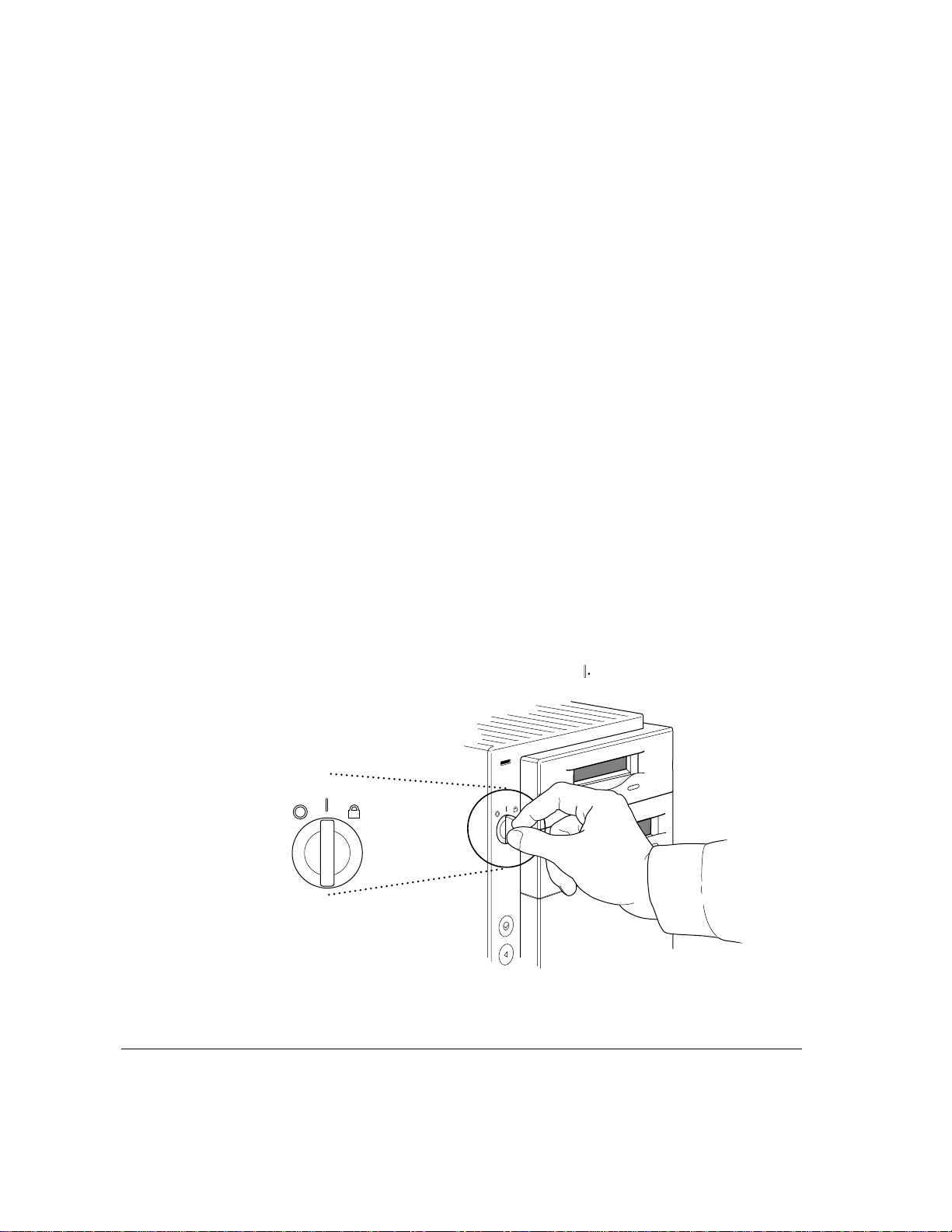
Turning the server on
Before turning the server on, make sure it is in its upright position; the
Workgroup Server 9150 is not designed to run on its side.
To turn on the server for the first time, follow these steps.
1 Turn on the monitor.
See the information that came with your monitor for the location of the power
switch. On Apple monitors, the power switch has this icon: I.
Note: You only need to turn on the monitor once if it is plugged into the
server. From now on, the monitor will turn off automatically when you shut
down the server, and it will turn on automatically when you start up the server.
(If the monitor is not plugged into the server, it must be turned on separately
each time you turn on the server.)
2 Turn on all external devices.
External devices may include hard disk driv es, CD-ROM drives, or tape-backup
drives. The server checks only once—at startup—for the presence of external
devices, so you need to turn on the devices before you turn on the server.
3 Use the key supplied with the server to turn the key lock switch to the “on” position
(straight up).
The “on” position is marked with this symbol: ii.
On
Off
Secure
12 Chapter 1 / Setting Up Your Server
Page 29
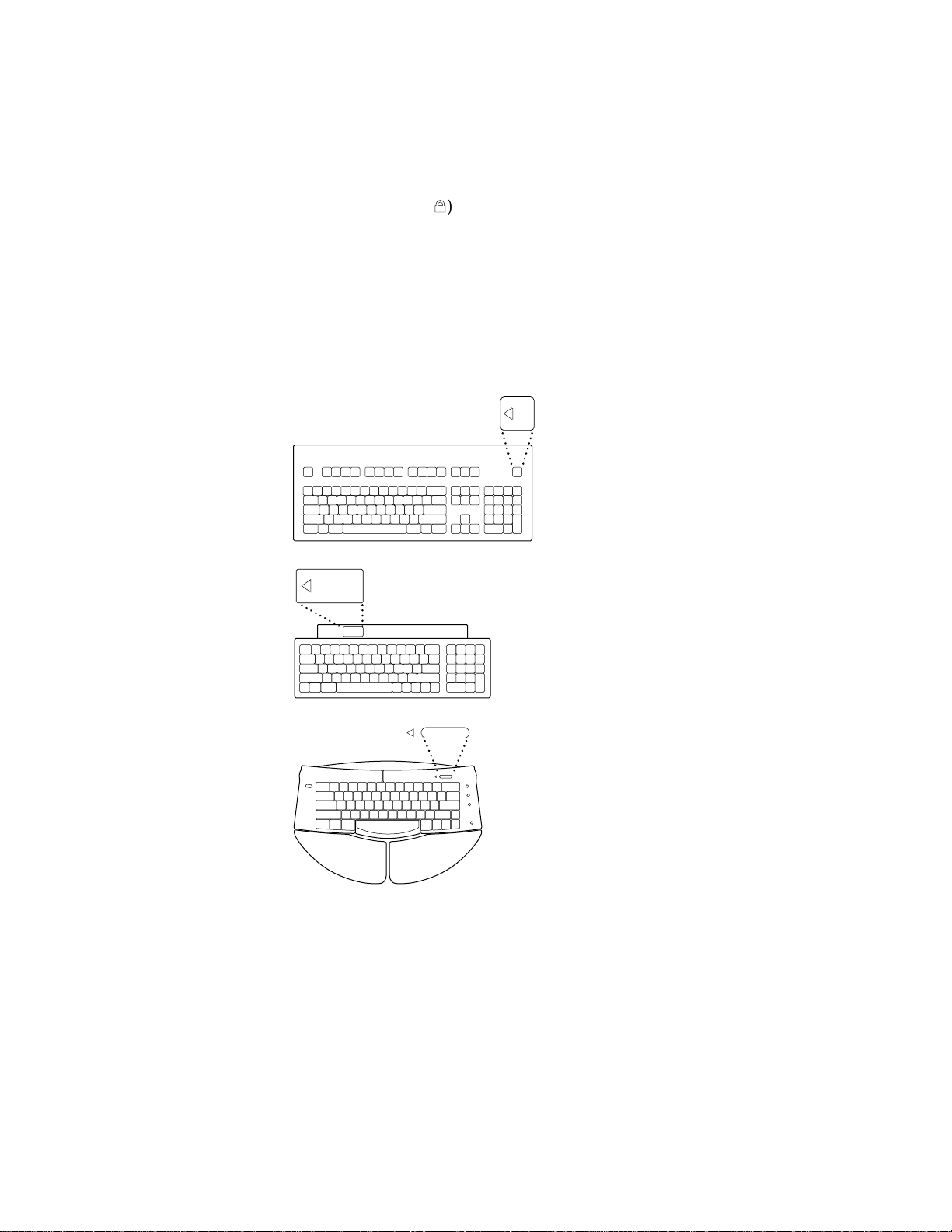
IMPORTANT
with a padlock icon (
When you turn the key to the “secure” position, which is marked
Ç
Ç
), you set the server to start up in remote-access mode,
which locks the keyboard, mouse, and floppy disk drive. Do not turn the key
to the secure position now. For more information on server security, see
“Security Issues” earlier in this chapter.
4 Turn on your server by pressing the Power key.
You’ll find the Power key at the top of the keyboard. You can recognize this
key by the triangle outline.
Turning the server on 13
Page 30

5 Check to see what’s on your screen, then click the OK button to dismiss the dialog box.
m If you see a system message on the desktop, as shown in the following
figure, your system software is already set up correctly.
Startup disk icon
Macintosh desktop
(You may see more
items on your desktop
than those shown here.)
Why the message about your network connection? The Workgroup Server
system software is preset for Ethernet networks. When you start up your
server for the first time (before connecting a network cable), you’ll see a
dialog box alerting you that the system temporarily switched the network
connection from built-in EtherTalk (software for Ethernet) to LocalTalk.
However, if you shut down the server and connect to an Ethernet network
later (as described in Chapter 2), the next time you start up, the system will
automatically make the correct network connection for you.
m If you see a blinking question mark, you need to install system software on
the server’s hard disk. (System software is a set of programs the computer
uses to start itself up.)
See “Reinstalling System Software” in Chapter 6 of this book for
information on installing system software.
m If you see anything else on your screen, or if you see nothing at all, see the
next section, “Problems Turning On Your Server?”
14 Chapter 1 / Setting Up Your Server
Page 31

IMPORTANT
Server Off” later in this chapter. It is very important to use the correct
procedure for shutting down your server before turning it off.
If you need to turn off your server at any point, see “Turning the
Problems turning on your server?
If you don’t see anything on the screen, check these items to see if you can
identify the problem:
m Is the server plugged into a power source? If it is plugged into a power strip,
is the power strip turned on?
m Is the key lock switch in the “on” position?
m Is the power light on the front panel on?
m Are the keyboard and mouse cables connected correctly? (Don’t disconnect
the keyboard or mouse cables while your server is on. You could damage
your equipment.)
m Is the monitor power cord plugged in?
m Is the monitor turned on? (Check the power light on the front of the
monitor.)
m Is the monitor’s cable attached firmly to both the monitor and server?
m Are the brightness and contrast controls on the monitor adjusted correctly?
(On Apple monitors, the brightness control is marked with the symbol ¤,
and the contrast control is marked with the symbol O.)
Setting the system time and date
It’s important that you set the current time and date for your server so that the
system can correctly log system events and record file activity. You set the time
and date in the Date & Time control panel. When setting the time, you can also
specify whether time is displayed on a 12-hour or 24-hour clock. To get stepby-step instructions for setting the system time and date, see the “Setting
Options” topic of Macintosh Guide, available in the Guide (h) menu.
Note: If you’re new to Macintosh, now is a good time to refer to Appendix B,
“Getting Help.”
Setting the system time and date 15
Page 32

Turning the server off
You need to turn off the server to perform the tasks in Chapter 2, “Connecting
to the Network.”
Use the mouse to choose the Shut Down command from the Special menu.
m
Choosing Shut Down readies the hard disk for a fast restart next time you turn
on the server. You will be prompted to save any unsaved work on a disk before
turning the power off.
To turn on the server again, just press the Power On key on the keyboard.
WARNING
the “off” position, you will lose any work you haven’t previously saved
onto a disk. You also risk losing open documents.
IMPORTANT
the following:
m move the server
m connect other equipment to the server
m unplug the server
If you turn the server off by by turning the key lock switch to
Be sure to shut down the server if you need to do any of
16 Chapter 1 / Setting Up Your Server
Page 33

2 Connecting to the Network
The Workgroup Server 9150 contains built-in hardware and software for
connecting the server to two types of networks: LocalTalk and Ethernet. You
connect the server to a LocalTalk network through the printer port. The built-in
Ethernet port on the Workgroup Server 9150 lets you connect the server to a
high-speed Ethernet network. Connecting to either type of network requires a
piece of hardware, which you must purchase separately from your server,
called a transceiver or media adapter for the type of network cables that your
network uses.
Note: With the appropriate communications card and software, you can also
connect your server to other network types, such as a Token Ring or an FDDI
network. See your Apple-authorized dealer for more information.
Page 34

Connecting to an Ethernet network
The built-in Ethernet capabilities of your Workgroup Server 9150 allow you to
connect to any standard Ethernet network using thin coaxial (or “coax”),
10BASE-T twisted-pair, or thick coaxial cables; fiber-optic media; or other
standard Ethernet cables.
To connect the server to an Ethernet network, you need one of the following
Ethernet media adapters for the type of cables that your network uses:
m Apple Ethernet Thin Coax Transceiver
m Apple Ethernet Twisted-Pair Transceiver
m Apple Ethernet AUI Adapter
See your Apple-authorized dealer for more information on Apple Ethernet
media adapters for your Workgroup Server 9150.
WARNING
Do not connect cables to the back of the computer when the
power is on or you may damage your system.
You can connect an adapter and cable for an Ethernet network directly to the
server without installing an expansion card. You can find the Ethernet port on
the back of your server by looking for the Ethernet icon:
Ethernet icon
Ethernet port
The following sections provide the basic instr uctions for connecting your server
at the end of an Ethernet network. However, your server can be connected
anywhere along a network; to do so, though, requires that you temporarily
disconnect the network, which could disrupt existing network services. See the
documentation that came with your media adapter for additional information
about connecting to Ethernet networks.
18 Chapter 2 / Connecting to the Network
Page 35

Connecting to thin coaxial Ethernet
Follow this procedure to connect the server to an Ethernet network that uses
thin coaxial cable. The hardware connection requires an Apple (or Applecompatible) thin coaxial transceiver and a thin coaxial cable.
To connect the server to a thin coaxial network:
1 Make sure that the server is turned off.
2 Attach one end of a thin coaxial cable to one of the posts on the thin coaxial transceiver.
3 Attach the other end of the cable to the last thin coaxial transceiver on the network.
A thin coaxial network must be terminated at the endpoints to function. An Apple
transceiver is self-terminating. A non-Apple transcei v er may require a terminator;
check the documentation that came with the transceiver.
4 Plug the connector on the transceiver into the Ethernet port on the server.
The Workgroup Server is preset to use the system’s network software
connection for Ethernet. When you start up the server, you can use available
network services immediately.
Ethernet port
Ethernet thin coaxial transceiver
Thin coaxial cable
Connecting to an Ethernet network 19
Page 36

Connecting to twisted-pair Ethernet
Follow this procedure to connect the server to a network that implements
Ethernet over twisted-pair cable. The hardware connection requires an Apple
(or Apple-compatible) twisted-pair transceiver and a twisted-pair patch cord
with an RJ-45 telephone-style connector jack. You plug the transceiver into a
standard wall plate that is connected to a centralized 10BASE-T hub.
To connect the server to a twisted-pair network:
1 Make sure that the server is turned off.
2 Plug one end of the twisted-pair patch cord into the transceiver and the other end into an
RJ-45 wall outlet that supports twisted-pair Ethernet.
3 Plug the connector on the transceiver into the Ethernet port on the server.
Note: After you start up the server, check that the green light-emitting diode
(LED) on the twisted-pair transceiver is lit. The LED will confirm that the
server is properly connected to the hub.
The Workgroup Server is preset to use the system’s network software
connection for Ethernet. When you start up the server, you can use available
network services immediately.
20 Chapter 2 / Connecting to the Network
Ethernet port
Ethernet
twisted-pair
transceiver
Wall plate
10BASE-T hub
3-meter patch cord
Page 37

Connecting to other types of Ethernet
The Apple Ethernet AUI Adapter is a universal adapter that lets you connect the
server to less-common types of industry-standard Ethernet media, such as thick
coaxial or fiber-optic cable. If you are using the Apple Ethernet AUI Adapter,
you also need an Ethernet transceiver for your specific media type, and the
transceiver must have a standard AUI (Attachment Unit Interface) port on it.
To connect the server to an Ethernet transcei v er for other types of Ethernet media:
1 Make sure that the server is turned off.
2 Connect the Ethernet transceiver to the network.
See the documentation for the type of Ethernet transceiver that you have.
3 Plug the transceiver cable from the Ethernet transceiver into the standard AUI port on
the Apple Ethernet AUI Adapter.
4 Plug the adapter’s power cord into a power outlet.
5 Plug the connector on the Apple Ethernet AUI Adapter into the Ethernet port on the server.
The Workgroup Server is preset to use the system’s network software
connection for Ethernet. When you start up the server, you can use available
network services immediately.
Ethernet port
Ethernet transceiver
for other media
Electrical outlet
Apple Ethernet AUI Adapter
Connecting to an Ethernet network 21
Page 38

Connecting to a LocalTalk network
The Apple LocalTalk Locking Connector Kit DIN-8, available from your Appleauthorized dealer, lets you connect the server to an e xisting LocalTalk network by
means of the printer port:
Printer port icon
Printer port
To connect the server to a LocalTalk network:
1Make sure that the server is turned off.
2 Attach the LocalTalk adapter to the printer port.
3 Plug one end of a LocalTalk cable into the LocalTalk adapter.
4 Plug the other end of the cable into the last LocalTalk adapter on the network.
Now that you have made the server’s physical connection to LocalTalk, you
can start up the server.
22 Chapter 2 / Connecting to the Network
Printer port
LocalTalk adapter
LocalTalk cable
Page 39

IMPORTANT
connected to Ethernet), each time you start up the server you’ll see a dialog
box that indicates an error condition. This dialog box informs you that the
system has made a temporary switch from EtherTalk (its preset network
software connection) to LocalTalk. You will see this message until you change
the default setting in the Network control panel. After you turn the server on
(as described in Chapter 1), be sure to continue with the next section in this
chapter to learn how to switch the setting in the Network control panel.
After connecting to a LocalTalk network (if you have not also
If you need to switch the network connection
Your Workgroup Server 9150 includes AppleTalk networking software, which
can run on both Ethernet and LocalTalk networks. (You can also add software
for other networks.) The built-in AppleTalk software for Ethernet networks is
called EtherTalk. Depending on the type of network to which you connect
your server, you may need to change the network connection setting for your
server system.
The Workgroup Server is preset to use the EtherTalk network connection. If
the server is not physically connected to an Ethernet network when you start
up, the system software reports an error condition and temporarily switches to
LocalTalk. If you will not be using an Ethernet network, you need to switch
the connection in the Network control panel to the appropriate network.
Note: The server can be physically connected to more than one network, but
you can use only one network connection at a time.
If you need to switch the network connection 23
Page 40

If you need to switch the server’s network connection, follow these steps:
1 Turn on the server.
2 Choose Control Panels from the Apple (
3 Click the icon of the new network connection that you want to use.
K
) menu and open the Network control panel.
An alert box appears, warning you that you may be disconnected from any
network services (such as network printers) that may be available with your
current network connection. (Your network connection types may be different
from those shown in the following example.)
4 Click OK.
5 Close the Network control panel.
You can now use the network connection you selected.
24 Chapter 2 / Connecting to the Network
Page 41

3 Expanding Your Server
and Connec ting O ther Equipment
This chapter tells you how to expand the capabilities of your serv er by installing
items internally and by connecting external devices.
Page 42

The following figure shows you the location of the Workgroup Server 9150’s
internal components. An external view of the server, depicting the ports to
which you connect other devices, is shown in the section “Your Server at a
Glance” in Chapter 1.
Dynamic RAM
(Optional)
DAT drive
CD-ROM
drive
SIMM connectors
Startup drive
ROM and cache SIMMs
PDS termination card
Floppy disk drive
NuBus slots
WARNING
The processor-direct slot (PDS) must always be occupied by
either the termination card that came with your server or a functional
card such as a video card. Be sure to keep the termination card if you
replace it—you’ll need to reinstall the termination card should you later
remove the replacement card.
26 Chapter 3 / Expanding Your Server and Connecting Other Equipment
PDS card connector
Page 43

Installin g an expans ion car d
You can install printed circuit boards (called cards) for video and graphics
applications, networking and communications, additional processing power,
or other purposes. The cards fit into connectors, called expansion slots, inside
the server.
Your server has four expansion slots designed to accept NuBus™ cards and
one slot that will accept a processor-direct slot (PDS) card. All five slots can
be used simultaneously.
Power requirements
The combined power consumption of expansion cards must not exceed the
limits specified for your Workgroup Server 9150. If you have more than one
expansion card installed, check the information that came with your cards to
make sure that their power consumption is within the limits specified in your
server’s Technical Information booklet.
Installing the card
IMPORTANT
service provider. Check the information that came with the card.
Follow these steps to install an expansion card.
1 Shut down the server, disconnect any attached cables (including the power cord) and
discharge static electricity by turning the key lock switch to the “secure” position and
then back to the “on” position.
IMPORTANT
before opening the server’s cover. Note that when the keyboard is attached and
the power is off, you can discharge static electricity by pressing the Power key.
2 Turn the server on its side, so that the cover is on top.
Some cards may need to be installed by an Apple-authorized
Always be sure to turn off power and discharge static electricity
Installing an expansion card 27
Page 44

3 Remove the cover from the server.
Press the two latches at the rear corners of the case and lift up the back of the
cover. Lift the cover toward you and away from the case. The cover must clear
the guides inside the front of the case.
Latches
WARNING
Be careful that you don’t cut yourself on the sharp metal edges
on the inside of the cover.
28 Chapter 3 / Expanding Your Server and Connecting Other Equipment
Page 45

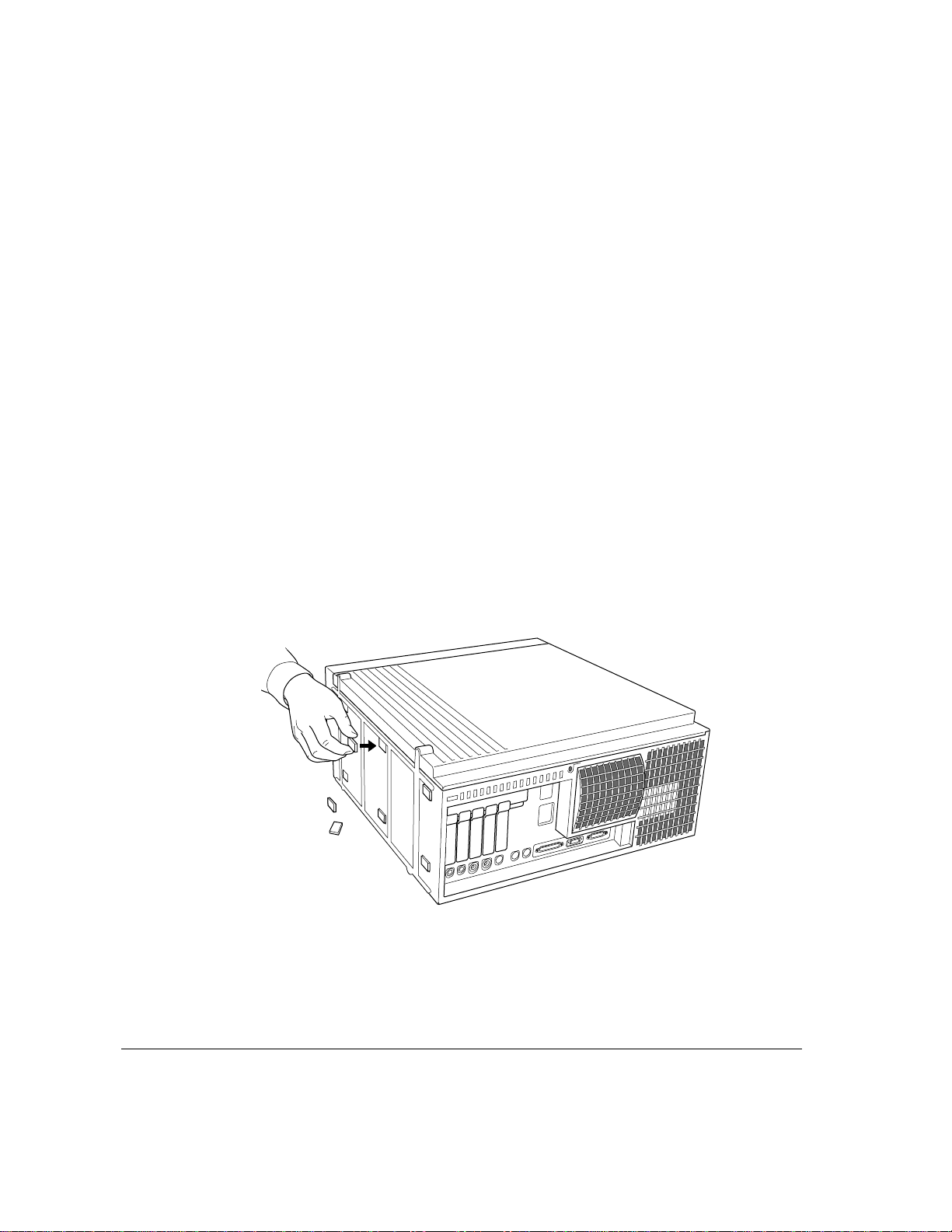
4 If your expansion card has an external connector, push out the cover plate that lines up
with the slot you want to use.
Press down on the clip at the top of the cover plate to release the plate. If you
have difficulty releasing the plate, use a screwdriver to press the clip.
Clip
Plate cover
Installing an expansion card 29
Page 46

5 Touch the metal part of the power supply case inside the server to discharge
static electricity.
Always do this before you touch any parts or install components inside the server.
Power supply case
Power cord
SCSI cable
30 Chapter 3 / Expanding Your Server and Connecting Other Equipment
Page 47

6 If you are installing a PDS card, remove the termination card from the PDS slot.
Remember that the processor-direct slot must always be occupied by either the
PDS termination card or a functional PDS expansion card. Be sure to keep the
termination card in a safe place so that you can replace it if you remove the
PDS expansion card.
7 Remove the card from its static-proof bag.
Hold the card by its edges to avoid touching the connector on the bottom of
the card.
Connector
Installing an expansion card 31
Page 48

8 Align the card over the expansion slot and press down firmly until the connector is seated.
Note: If you are installing an expansion card that is taller than standard size,
you need to remove the expansion card guide on the inside of the cover.
9 Replace the cover on the server.
Note: Before you replace the cover, you may want to add an additional internal
disk drive, as described in “Installing Internal Disk Drives” later in this chapter.
10 Plug the server’s power cord back into a power outlet.
32 Chapter 3 / Expanding Your Server and Connecting Other Equipment
Page 49

Expanding memory
Additional random-access memory (RAM) can be installed in your server. The
Technical Information booklet that came with your server describes how much
additional memory can be installed in the server.
Memory for your server is provided in packages called RAM SIMMs. The
SIMMs must be the correct type for your computer. They should be installed
in pairs of the same size into paired slots in your computer. It is very important
that the RAM SIMMs be correctly installed in your Workgroup Server 9150.
Incorrect installation can result in errors, unpredictable results, and damage to
your equipment and data.
WARNING
an Apple-certified technician install additional RAM. If you attempt to
install additional RAM yourself, any damage you may cause to your
equipment will not be covered by the limited warranty on your server.
To avoid damage to your server, Apple recommends that only
Connecting hard disks and other SCSI devices
This section describes how to install SCSI de vices in and connect them to the
Workgroup Server 9150. The server has two separate SCSI buses: an internal
bus and an external bus. Each bus accommodates seven SCSI devices; thus,
you can connect a total of 14 SCSI devices to your server. The internal bus
handles the built-in startup hard disk drive, CD-ROM drive, (optional) digital
audio tape (DAT) drive, and up to four additional internal disk drives. The
external bus accommodates up to seven external SCSI devices in a chain (such
as hard disks, CD-ROM drives, scanners, printers, and tape-backup drives).
Setting up a SCSI device to use with your server involves
m setting the device’s SCSI ID number
m physically connecting the device to your server
m installing any necessary device drivers
When setting up a SCSI device to use with your serv er, refer to the instructions
that came with the device, as well as the instructions in this section.
Connecting hard disks and other SCSI devices 33
Page 50

Setting the SCSI ID number
As discussed previously, the Workgroup Server 9150 contains two SCSI
buses: an internal bus and an external bus. The devices on each bus must be
assigned unique ID numbers between 0 and 6. That is, each device on the
internal bus must be assigned a unique ID number between 0 and 6, and
likewise for the external bus. This section tells you how to set the ID number
for an Apple SCSI device. When setting a SCSI ID for another manufacturer’s
device, refer to the instructions included with that device.
IMPORTANT
The new SCSI Manager (version 4.3 or later)—an extension to the
Macintosh system software—enables your server to recognize up to 14 SCSI
devices; previously, Macintosh computers were able to recognize only seven
devices. Older SCSI-related applications and utilities may not be able to
recognize more than seven devices, even with the new SCSI Manager. If an
internal device and an external device both have the same ID number, such
software would find only the internal device. If this problem occurs, contact
the distributor of the software.
If you have an Apple SCSI device, set the SCSI ID number as follows:
1 Make sure the device is switched off.
2 Choose a number that doesn’t duplicate the ID of any other SCSI device connected to
your server.
The startup disk’s ID number is preset to 0, the CD-ROM drive’s ID is preset
to 3, and if your server has a DAT drive, its ID is preset to 2. (Your server
itself has the ID number 7.)
The following figure shows the preset ID numbers for these built-in devices.
SCSI ID numbers
0234516
Internal
SCSI
bus
Startup
disk
(Optional)
DAT drive
CD-ROM
drive
34 Chapter 3 / Expanding Your Server and Connecting Other Equipment
Page 51

For devices connected to the external bus, you can assign any number between
0 and 6, provided that each device is uniquely identified.
3 Locate the ID number switch on the back of your SCSI device.
4
4
SCSI ID switch
4 Push the ID switch repeatedly until the number you want appears.
On some SCSI devices, the ID number switch is inside a small hole. Insert a
straightened paper clip to push the switch.
Installing inter nal disk dr ives
This section describes how to install additional internal hard disk drives in
your server.
WARNING
Installing internal disk drives is a difficult procedure. Apple
recommends that an Apple-authorized service provider install additional
drives in order to guarantee the continued coverage of the hardware under
the Apple Limited Warranty. Unless other arrangements ha ve been made,
service providers should install the hardware and run the MacTest Pro
diagnostic to confirm that the hardware is operational.
In addition to the 3.5-inch, half-height drive(s) that you’re installing, you’ll
also need these items:
m a grounding wrist strap and a static mat
m a Phillips screwdriver
m four screws to attach the drive to the bracket
m switches or jumpers as needed to set SCSI IDs f or the drives you are installing
Connecting hard disks and other SCSI devices 35
Page 52

Note: Your Workgroup Server 9150 has built-in SCSI termination, so be sure
that there are no resistor packs on the drive(s) you are installing.
To install an internal hard disk drive:
1 Shut down the server, disconnect any attached cables (including the power cord) and
discharge static electricity by turning the lock key switch to the “secure” position and
then back to the “on” position.
2 Attach a grounding wrist strap and be sure to use a static mat.
3 Remove the cover from the server.
4 Place the server on its side, with the drive bracket assembly screws visible.
36 Chapter 3 / Expanding Your Server and Connecting Other Equipment
Page 53

5 Disconnect the SCSI cables from the existing drives.
Connecting hard disks and other SCSI devices 37
Page 54

6 Open the cable holder straps and disconnect the power cables from the drives already
installed in the server.
38 Chapter 3 / Expanding Your Server and Connecting Other Equipment
Page 55

7 Remove the bottom two drive bracket screws (the screws closest to the cable holder
straps), then slide the drive assembly up and out of the server.
E
B
D
A
C
Connecting hard disks and other SCSI devices 39
Page 56

8 If you are installing a drive in slot C, D, or E, remove the screws that hold the top bracket
of the drive assembly. Note that if you are adding a drive to slot A or B, you can install
the drive without removing the top bracket.
E
D
C
B
A
9 Make sure that you’ve installed any necessary SCSI ID jumpers or ID switches and that
there are no resistor packs on the drives you are adding. (The Workgroup Server 9150
has built-in SCSI termination.) There are usually three resistor packs; often they are
yellow or orange.
Note: Some newer-model disk drives do not have resistor packs; they use one
jumper to indicate whether SCSI termination is on or off. Be sure to check the
manufacturer’s specifications for your disk drive when setting termination.
40 Chapter 3 / Expanding Your Server and Connecting Other Equipment
Page 57

10 Attach the bottom of the drive to the bracket, using the four screw holes in the bracket plate.
IMPORTANT
Be sure to install drives in the order which they are lettered, filling
slot B before slot C; slot C before slot D; and so on. Because of heat considerations,
it’s important that you use slot E only after the other four slots are filled.
E
D
C
Connecting hard disks and other SCSI devices 41
Page 58

11 Slide the drive assembly back into the server and attach the screws.
E
B
D
A
C
42 Chapter 3 / Expanding Your Server and Connecting Other Equipment
Page 59

12 Connect the power cables and the SCSI cables. Note that the lettered tags on the SCSI
cables match the letters on the drive bracket.
It is important that you place the cables in the cabinet in their original position.
To accomplish this, fold the cables only where there are existing creases.
Connecting hard disks and other SCSI devices 43
Page 60

13 Secure the power cables with the cable holder straps and the cable guide, as shown in the
following figure.
This step is necessary in order to replace the lid.
Cable holder strap
Cable guide
14 Replace the cover and reassemble the server.
44 Chapter 3 / Expanding Your Server and Connecting Other Equipment
Page 61

Connecting an external SCSI device
The SCSI port for connecting external devices to the server is located on the
server’s back panel.
SCSI icon
SCSI port
To connect a SCSI device to your server:
1 Turn off your server.
2 Make sure the SCSI device is switched off.
WARNING
Do not connect or disconnect any device while the device or
your server is turned on. Doing so could damage the device, your server,
or both.
3 Make sure the device has its own, unique ID number between 0 and 6.
See the earlier section “Setting the SCSI ID Number” for details.
Connecting hard disks and other SCSI devices 45
Page 62

4 Use a SCSI cable to connect the device either to the server’s SCSI port or to the last
SCSI device already in the chain.
If the device is the first or only one you’re connecting, use a SCSI system cable
to connect it to the server’s SCSI port.
If the device is not the first one, use a SCSI peripheral interface cable to connect
it to the last device in the chain.
IMPORTANT
To get the best results with SCSI devices, be sure to use highquality SCSI cables and check that the total length of the cables in a SCSI
chain does not exceed 6 meters (20 feet). Use SCSI cables manufactured by
Apple Computer or those of similar quality.
46 Chapter 3 / Expanding Your Server and Connecting Other Equipment
Page 63

5 Make sure that only the last device in the SCSI chain has a terminator.
To ensure accurate transmission of information, a terminator must be at each
end of a SCSI chain. Your server, which is the first device in the external SCSI
chain, has a built-in terminator.
Some external SCSI devices from manuf acturers other than Apple have a built-in
terminator. (Check the information that came with the device.) If the device at
the end of the SCSI chain does not have a built-in terminator, you need to
attach an external terminator.
External SCSI terminator
Have your Apple-authorized service provider remo v e any e xtra b uilt-in terminators.
You can attach or remove external terminators yourself.
Note: If only one external device has a built-in terminator, rearrange the SCSI
chain so that device is at the end.
IMPORTANT
Always turn on any external SCSI devices connected to your
server before turning on the server itself. Otherwise, your server cannot
recognize the SCSI devices.
Connecting hard disks and other SCSI devices 47
Page 64

Installing a device driver
A device driver is software that lets the server communicate with a particular
SCSI device.
Note: If you have set up your server and connected additional devices, but not
yet turned the server on, return to the section “Plugging In the Server” in
Chapter 1 before installing a device driver.
To install a driver:
m
Start up your server, if necessary, and drag the driver icon to the System Folder icon on
your startup disk.
Any drivers needed for a SCSI device are usually on a floppy disk that comes
with the device. (If no drivers come with the device, then it doesn’t need any.)
You may have to restart your server to activate the driver.
Do you need to initialize a hard disk?
You need to initialize a hard disk only in the following cases:
m You’re using specialized disk array management software, such as RAID
(redundant array of independent disks). See the documentation that
accompanied the disk array management software for instructions.
m The disk is new and uninitialized. Your internal hard disk and most external
hard disks are initialized at the factory and do not have to be initialized
again. If you are adding a new non-Apple hard disk to your server, check
your owner’s manual to see if it needs to be initialized.
m You’ve experienced repeated errors using this disk. If problems persist after
you reinitialize the disk, the disk is in need of servicing.
m The disk has been formatted for use with a non-Apple operating system.
48 Chapter 3 / Expanding Your Server and Connecting Other Equipment
Page 65

Connecting a printer
Your server has a printer port, which you use to connect a printer to your computer.
The printer port accepts either a direct cable connection (to printers such as
the StyleWriter II) or a network cable connection (to printers such as a
LaserWriter Pro or LaserWriter Select).
Follow the instructions that came with your printer when connecting it to
your server.
A printer can also be connected to the modem port (GeoPort). You use the
Chooser program to indicate the port you used to connect your printer. (See
the “Printing and Fonts” topic in Macintosh Guide, available in the Guide (h)
menu, for more information on using the Chooser and printing.)
Printer port icon
Printer port
Connecting an additional moni tor
You can use an additional monitor with your server if you install a video
expansion card. See “Installing an Expansion Card” earlier in this chapter
for instructions.
When you connect an additional monitor:
m Make sure that the ventilation openings on the server and the monitors are
clear and unobstructed.
m If there is interference on your screens or on a television or radio near your
server, reposition or separate the affected equipment.
Connecting an additional monitor 49
Page 66

Connecting a trackball or other input device
Your server has an Apple Desktop Bus (ADB) port, which you use to connect
the mouse, the keyboard, and other input de vices such as a trackball, a bar-code
reader, or a graphics tablet.
ADB port icon
ADB port
You can usually connect up to three ADB devices in a chain to a single port. The
exact number depends on how much power the devices require.
IMPORTANT
server must not exceed 500 milliamperes (mA). Information about the power
requirements of the mouse and keyboard are in the Technical Information
booklet that came with your server. Check the information that came with
your other ADB device for power requirements.
Connecting a microphone
Your server has a sound input port, which you can use to connect a microphone.
IMPORTANT
speech recognition programs—do not use the Apple PlainTalk Microphone
with this server.
The total power used by all ADB devices connected to your
The Workgroup Server 9150 is not designed for use with
50 Chapter 3 / Expanding Your Server and Connecting Other Equipment
Page 67

To connect the microphone:
m
Plug the microphone’s connector into the sound input port (marked with the symbol
on the back of the server.
See “Connecting an Audio Device” in Appendix D of this book for more
information about the sound input port.
Connecting a GeoPort Telecom Adapter or modem
Your server has a port, called the GeoPort, which is a serial port designed for
use with devices such as the GeoPort Telecom Adapter. These devices, when
used with appropriate telecommunications software, take advantage of the
server’s built-in modem capabilities. The GeoPort Telecom Adapter comes
with communications and fax software and can be purchased from Appleauthorized dealers.
Modem and GeoPort icon
GeoPort
X
)
You can connect a standard modem to the GeoPort, using a standard
modem cable.
To connect an adapter or modem to your server, follow the instructions that
came with your adapter or modem.
You can also connect a printer to the GeoPort.
Connecting a GeoPort Telecom Adapter or modem 51
Page 68

Page 69

4 Using S oftware With Your Server
This chapter provides important information you need to know about using
your Workgroup Server 9150 with application programs. For instance,
although your server is compatible with most programs intended for use
with Macintosh computers, certain programs are designed especially
for Power Macintosh computers. These kinds of programs take best advantage
of your server’s speed. In addition, the order in which certain programs start
up affects a server’s performance. Be sure to read the information in this
chapter before setting up your server’s application programs.
Page 70

Using Power Ma cintosh p rograms
Programs designed for Power Macintosh computers will provide improved
performance for your server. However, to get the full benefit of this software,
you need to know about two key issues—virtual memory and shared libraries.
Vir tual m emory
Virtual memory is a feature of Macintosh computers that lets you use space on a
hard disk as additional memory . This feature helps you run large programs when
the server does not contain enough random-access memory (RAM). However,
virtual memory will adversely affect the performance of your server application
programs. Do not turn on virtual memory with your Workgroup Server 9150.
Shared libraries
Power Macintosh programs use special files called shared libraries. These files
help Power Macintosh programs to run more efficiently, and can be used by
more than one Power Macintosh program simultaneously. Any necessary
shared libraries are installed automatically in the System Folder when you
install Power Macintosh programs.
Shared libraries are
represented by icons
like this.
If a Power Macintosh program requires a shared library and there is not
enough memory available for the shared library, you’ll see a message that the
program could not be opened because there is not enough system memory
available for the shared library. If this happens, quit programs not in use or
install more memory in your server (see “Expanding Memory” in Chapter 3
for more information).
If a required shared library is missing, you’ll see a message that the program
could not be opened because the shared library could not be found. If this
happens, follow the directions that came with your program to reinstall the
program. If the shared library is still missing, contact the software program’s
manufacturer for assistance.
54 Chapter 4 / Using Software With Your Server
Page 71

Using older Macintosh programs
If you experience problems using an older Macintosh program, it may be
incompatible with your Power Macintosh. You may be able to use your older
program if you change the Memory Manager setting in your Memory control
panel. Follow these steps:
1 Choose Control Panels from the Apple (
2 Turn off Modern Memory Manager.
K
) menu and open the Memory control panel.
Click here to turn
off Modern Memory
Manager.
When you are finished using the program, open the Memory control panel
again and turn Modern Memory Manager back on.
For best performance, contact the program’s manufacturer for an upgrade.
Using older Macintosh programs 55
Page 72

Using se rver app lication programs
Specific server application programs or services, such as AppleShare,
AppleSearch, Apple Remote Access, or Apple RAID Software, may have been
included with your server. Review the documentation that came with the
software before you install these services; you may be required to perform
special procedures that can affect your server system before you use a
particular service. For instance, Apple RAID Software requires you to
reinitialize the hard disks you want to use for storing server data.
Setting the system time and date
As noted in Chapter 1, some server application programs require that your
system clock be set correctly. If you need step-by-step instructions for setting
the system time and date, see the “Setting Options” topic of Macintosh Guide,
available in the Guide (h) menu.
Order of installing and starting programs
Though your server may have come with server application programs or
network services, you may want to install additional software. Note that the
order in which server application programs are installed and started is
important. Be sure to review the documentation, especially product Read Me
files, for all the server application programs you plan to use before installing
and running them. Also, refer to the Workgroup Server Read Me file on your
server system’s hard disk for the most up-to-date news about installing server
application programs.
Setting up your server to restart programs automatically
You can set the Workgroup Server 9150 to start server application programs
(including network services) automatically whenever you start up the server or
whenever the server automatically restarts after a temporary power outage.
56 Chapter 4 / Using Software With Your Server
Page 73

To set up your server to restart server application programs automatically:
1 Create an alias for each program that you want the server to start automatically.
You create an alias by selecting the icon of the program on the desktop and
choosing Make Alias from the File menu.
2 Drag the aliases to the Startup Items folder, located in the System Folder on your
startup disk.
Macintosh computers and servers automatically open documents and programs
(or their aliases) located in the Startup Items folder whenever the computer or
server starts up.
Note: The server opens documents and programs located in the Startup Items
folder in alphabetical or numerical order. Because the order in which server
application programs are started may be important (as described in the
program documentation), you may want to rename the aliases so that the
programs start in the desired order. For example, you can insert a number at
the beginning of each filename. The following figure shows a sample setup.
Add numbers to the
program aliases to set
the order of startup.
Using server application programs 57
Page 74

Additio nal capab ili t ies for your server system
You have the option to install two programs included with your server that
provide new capabilities for your system software:
m PowerTalk, which provides built-in mail and collaboration services
m QuickDraw GX, which gives your computer more powerful
printing capabilities
Because these programs are not designed specifically for use on server systems,
they may reduce your server’s performance. Keep this possibility in mind when
deciding if you want to add these capabilities to your Workgroup Server 9150.
IMPORTANT
want to also use QuickDraw GX, be sure to see the AppleShare Read Me file.
You’ll find Installers for these optional programs in the System Software
Installers folder on the Workgroup Server Software CD-ROM disc.
IMPORTANT
perform repeatedly on your server, is already installed in your system. To
review the available automated tasks, look in the Apple (K) menu. T o learn how
to create new scripts for your server, see the “Using AppleScript” documents
in the AppleScript folder in the Apple Extras folder on your hard disk.
Backing up your file s
Making backup copies of important server files is good protection against
possible damage to the originals. If a backup program was included with your
server, be sure to use it (or another backup program if you prefer) to set up and
schedule a regular, automatic backup of your files. You can also back up your
files manually, by making copies on another hard disk or even on floppy disks,
but such methods are less convenient.
If you use the AppleShare Print Server with your server and you
AppleScript, which allows you to automate many actions you
58 Chapter 4 / Using Software With Your Server
Page 75

5 Using a DAT Drive and Tape Cassettes
You need to read this chapter only if your server includes an internal tapebackup unit.
The internal 3.5-inch DDS-2 DAT drive and accompanying software can perform
full or partial backup and restore procedures for all of the data on your hard
disks. In addition, the drive automatically performs error correction and data
compression of the files that you back up and restore. The error-correction feature
helps ensure a high level of data integrity. The data-compression feature allows
more data to fit on a cassette than do conventional backup mechanisms.
Use Retrospect Remote (or some other backup utility) to back up and restore
data. For information, see the utility’s documentation.
Page 76

Compatible tapes
Your internal DAT (digital audio tape) drive is compatible with MRS-quality
DDS (digital data storage) tape cassettes. MRS (Media Recognition System)
cassettes are the highest-quality digital data tape available. Your internal tape
drive requires this level of quality to perform backup operations successfully.
See your Apple-authorized service provider for more MRS-quality DDS tape
cassettes or their compatible substitutes. Compatible cassettes are typically
stamped “Digital Data Storage” and longer-length cassettes (120 meters) need
the “DDS2” designation. If you use cassettes not approved by your Appleauthorized service provider, you void the warranty on your tape drive.
IMPORTANT
as digital audio tape (DAT) cassettes. However, DAT (audio) cassettes have a
different mechanical specification from DDS cassettes. For backing up your
server files, be sure to use only those DA Tcassettes designed for MRS.
Some vendors of computer products may refer to DDS cassettes
Tapes supplied with the server
Two cassettes are supplied with your Workgroup Server 9150. The first is a
blank DDS cassette for backup and restore operations. (The blank tape
included with your system has a maximum storage capacity of 10–14
gigabytes of compressed data.) The second is a cleaning cassette; its operation
is discussed later in this chapter.
Starting up the tape drive
The tape drive receives power and performs a self-test when you start up your
server. During the test, both status lights next to the tape drive opening are solid
green, then the light on the left flashes green and the light on the right turns
off. If no tape is loaded in the tape drive, both status lights turn off. If a tape is
loaded in the tape drive, the light on the left becomes solid green.
60 Chapter 5 / Using a DAT Drive and Tape Cassettes
Page 77

There are two conditions that indicate the self-test has failed. If the light on
the right flashes amber, you may need to clean the tape-drive head as described
in the section “Cleaning the Tape-Drive Heads” later in this chapter. Or, if a
tape is loaded in the tape drive, a flashing amber light may indicate that the
tape is worn and needs to be replaced. If the light on the right becomes solid
amber, the tape drive did not successfully complete its self-test and should not
be used; consult an Apple-authorized service provider.
The status lights are discussed in greater detail later in this chapter.
Inse rting tape cassettes
To use a cassette:
m
Insert it into the tape slot in the front panel of the server, as shown in this figure.
As you insert the cassette, the drive pulls it into place and performs a loading
sequence, which includes threading and rewinding the tape and checking for
error conditions. The loading procedure takes about 30 seconds.
Inserting tape cassettes 61
Page 78

Status lights
Located next to the tape drive opening are two lights that inform you of the
status of tape operations. The light on the left is the tape light, and the light on
the right is the clean light. A solid green tape light indicates normal operation;
a solid amber clean light indicates a warning condition. A flashing green tape
light indicates activity between the tape drive and the SCSI bus. A flashing
amber clean light indicates that the tape in the drive is worn or the tape-drive
head needs to be cleaned.
The following table lists all the possible meanings of the status lights.
Tape light Clean light
(left side) (right side) Meaning
Normal operation
Flash green* Off Cassette loading or unloading, or
self-test in progress
Fast flash green†Off Cassette loaded/read or write activity
Green Off Cassette loading/drive online
Error states
Any Flash amber* Media wear (caution), or clean required
Any Amber Error condition
*Flash means the light flashes
†
Fast flash means the light flashes
1
/2 second on, 1/2 second off.
1
/4 second on, 1/4 second off.
The caution signal
If your tape drive detects problems, it displays a caution signal: the clean light
flashes amber. You can clear the caution signal by ejecting the cassette.
The caution signal may be caused by dirty tape-drive heads, so if this signal
appears, clean the heads and insert the tape again. (Head-cleaning instructions
are given in “Cleaning the Tape-Drive Heads,” later in this chapter.) The caution
signal may also indicate a worn-out tape. If the tape is old or worn, you should
copy its data to a new tape and discard it. If you’re trying to restore data from
a worn tape and the caution signal appears, clean the tape-drive heads, then try
the restore operation again.
62 Chapter 5 / Using a DAT Drive and Tape Cassettes
Page 79

Removing tape cassettes
You can remove a tape cassette at any time by pressing the eject button located
under the tape slot on the right side. You should not press the eject button while
the tape is in use.
Check the Retrospect Remote (or other backup utility’s) documentation to learn
about additional methods for ejecting cassettes while using the backup software.
Forcing th e ejection of a tape cassette
If you need to force the ejection of a tape cassette:
m
Hold the eject button down for at least 5 seconds (perform this step after the server has
started up).
The drive waits 35 seconds for the normal eject procedure to occur, and, if it
does not occur, unthreads the tape and ejects the cartridge.
WARNING
or cause the tape to be invalidly formatted.
Locking a cassette
You can lock a DDS cassette by sliding the tab on the back of the cassette so
that the hole is visible. Once a tape cassette is locked, data can be read from
the cassette but not written to it.
Avoiding high humidi ty
Whenever your tape drive detects water condensation, both status lights glow
solid amber. This w arning signal cancels an y commands in progress. Furthermore,
any commands that access the tape are rejected. The tape drive then unthreads
the tape to prevent tape and tape-head damage.
If you force an eject while the drive is busy, you may lose data
Avoiding high humidity 63
Page 80

To minimize the chance of condensation, adhere to the en vironmental requirements
described in the Technical Information booklet and follow these general
cassette guidelines:
m Use tape cassettes at temperatures between 10˚ C (50˚F) and 35˚ C (95˚ F).
m If you expose the tape cassettes to temperatures outside the operating limits,
you can stabilize them by leaving them in the proper operating temperature
for a minimum of two hours.
Follow these guidelines to avoid temperature problems:
m Avoid exposing cassettes to severe temperature conditions. For example,
don’t store a cassette in a car in bright sunlight.
m Avoid transferring data to or from a tape cassette when the temperature is
changing by more than 10˚ F per hour (roughly 5˚ C per hour).
Cleaning t he tape-drive heads
The most common reason for the display of a caution signal on the front panel
is that the tape-drive heads are dirty. Although your tape drive has a built-in
roller for cleaning the heads during normal operation, you still need to
perform a separate cleaning step as part of preventive maintenance.
Your system comes with a cleaning cassette that you should use to clean the
tape-drive heads after every 25 hours of running time.
Use only a DDS cleaning cassette. When you insert the cleaning cassette into
the drive, the dri v e automatically loads it and cleans the heads. When the cleaning
process is completed, the drive automatically ejects the cassette. Keep a record
of how many times you use the cleaning cassette. After 25 uses, replace it.
The interval at which you clean the tape drive depends on how often you use
it. In general, if you back up daily, you should clean the drive weekly. If you
back up weekly, you should clean the tape drive once a month.
For more information about using the cleaning cassette, refer to the instructions
that came with it. For additional cleaning cassettes, see your Apple-authorized
service provider.
64 Chapter 5 / Using a DAT Drive and Tape Cassettes
Page 81

6 Troubleshooting
Whe n you run into trouble
While you’re using your server, it’s possible that you may experience a
problem such as the pointer “freezing” on the screen, or you may see an error
message or even a bomb icon. If you have trouble with your server, take a
moment to review the solutions to common problems listed in this chapter.
Note: If you have a question or encounter a problem while your system is still
running, you can also check the “Troubleshooting” topic of Macintosh Guide,
available in the Guide (h) menu. For more information on the kinds of on-
screen help available, see Appendix B, “Getting Help,” in this guide.
Take y our time
When you see an error message, you don’t have to tak e action immediately. The
message stays on the screen until you click the OK button or turn off the serv er.
To help diagnose and correct the problem, gather as much information about
the situation as you can before starting over:
m Make a note of exactly what you were doing when the problem occurred.
Write down the message on the screen and its ID number (if any). Also list
the programs you were using and the names of any items you know have
been added to the System Folder since the system software was installed.
This information will help a service person diagnose the problem. (It is
helpful to keep a printed copy of the items in your System Folder. See
instructions for printing a list of files in a window in the “Printing and
Fonts” topic of Macintosh Guide, available in the Guide menu.)
m Check the screen for any clues. Is a menu selected? What programs and
document icons are open? Note anything else that seems relevant.
Page 82

m If you were typing text and were not able to save it before the problem
occurred, you can write down the parts of the text still visible on the screen
so that some of your work will be easy to replace.
m Ask other Macintosh users about the problem you’re having; they may have
a solution for it.
m Find out what actions users were performing on the server (such as
copying large files, launching programs on the server, or installing
programs over the network).
If you need repair service, consult the service and support information that
came with your server for instructions on how to contact an Apple-authorized
service provider or Apple for assistance.
Start over
Often you can eliminate a problem simply by clearing the server’s memory
and starting over.
If you can, save any open documents bef ore restarting the serv er. If your system is
“frozen” and does not respond to any input, or if you have a “bomb” message on
the screen, saving may not be possible. You can try pressing x-Option-Esc to quit
the program in use when the problem occurred; if this works, you can then save
the documents open in other programs before restarting.
To restart your server, try the following steps:
1 If you can, choose Restart from the Special menu or from the dialog box that’s on screen.
2 If you can’t choose Restart, hold down the
On key.
This key combination restarts the server. (Use this key combination only if
choosing Restart from the Special menu does not work.)
3 If nothing happens, look for the reset and interrupt switches on the front of your server
and press the reset switch (the one marked with a triangle).
Pressing the reset switch is like turning the power switch off and then on
again. You will lose any work you haven’t saved. (The interrupt switch is
intended for use by programmers who have debugging software installed.)
66 Chapter 6 / Troubleshooting
x
and Control keys while you press the Power
Page 83

4 If pressing the reset switch does nothing, turn off your server using the key lock switch,
wait at least 10 seconds, then turn it on again.
5 If the key lock switch doesn’t turn off the server, unplug your server.
If you suspect that the problem is with a peripheral device, such as a printer or
external hard disk, turn it off for 10 seconds or more, then turn it on again and
restart the server.
Solutions to commo n problems
This section describes the key symptom for a number of common problems
followed by the steps you can take to solve each problem.
IMPORTANT
Be sure to review the information in the Workgroup Server Read
Me file located on your server’s hard disk and on the Workgroup Server
Software CD-ROM disc. This file contains late-breaking information and tips.
You cannot turn on the server.
See “Problems Turning On Your Server?” in Chapter 1.
The server is turned on but the screen is dark.
The server or the monitor is not getting power, a program has darkened the
screen, or the monitor controls are not adjusted properly.
m If you use a screen-saver program, press a key or move the mouse to turn
off the screen saver.
m Check the monitor’s brightness and contrast controls and turn them up if
necessary.
m Check that the monitor is turned on.
m Check that the power cord and monitor cable are plugged in and firmly
connected to the server and that the electrical outlet has power. The power
light on the server’s front panel should be on.
m If you have more than one monitor, and only one is dark, check that it is set
up correctly in the Monitors control panel.
Solutions to common problems 67
Page 84

A disk icon with a blinking question mark appeared when you started your server.
The blinking question mark indicates that your server cannot find system
software. You may need to repair a damaged disk, or reinstall system software.
m Your server may be having a problem recognizing a SCSI device. Turn off
external SCSI devices and restart.
If the server starts up after you turn off your SCSI devices, read the section
on SCSI devices in Chapter 3 of this manual for information on connecting
SCSI devices and assigning SCSI ID numbers.
m The system software is not installed on the startup hard disk, the system
software is damaged, or the hard disk is not working properly. Start up your
server with the Workgroup Server Software CD-ROM disc (see “Starting Up
From the CD-ROM Drive” later in this chapter). Then refer to “Repairing a
Damaged Disk” at the end of this chapter.
If repairing the disk doesn’t help, follow the instructions in “Reinstalling
System Software” (later in this chapter).
A disk icon with an X appeared and the floppy disk was ejected.
Your server ejected a floppy disk that is not a startup disk.
m Wait a few seconds. The server should start up from its internal hard disk.
Make sure you insert floppy disks only after the server has begun starting up.
68 Chapter 6 / Troubleshooting
Page 85

A “sad Macintosh” icon appeared and the server won’t start up.
Your server cannot start up because of a problem with the system software or
the server hardware.
m Eject any floppy disks (or CD-ROM discs) by turning off the server and
then holding down the mouse button while you turn the server on again. Try
starting up with a different startup disk (such as the Workgroup Server
Software CD-ROM disc). If the “sad Macintosh” icon appears again,
consult the service and support information that came with your server for
instructions on how to contact an Apple-authorized service provider or
Apple for assistance.
You see an error message at startup telling you that the system will use the LocalTalk port.
If you will not be using an Ethernet network, you need to change the setting in
the Network control panel from EtherTalk to the appropriate network. See “If
You Need to Switch the Network Connection” in Chapter 2.
The server’s clock keeps time inaccurately.
Your server has a clock that runs continuously. When the computer is turned off,
a battery keeps the clock running. If your clock begins to keep time inaccurately,
have your Apple-authorized service provider replace the battery.
Solutions to common problems 69
Page 86

The server starts up from the wrong hard disk, or the hard disk icon does not appear on
the desktop.
The startup disk may be slow to start up. Restart the server.
During startup, your server’s operating system finds and mounts attached SCSI
devices that are up and running within 20 seconds. Some very large hard disk
drives (such as 2-gigabyte drives) may take longer than 20 seconds to come up
to speed and therefore may not be recognized by the operating system when
the server is first turned on. Restarting the server enables your system to find
these devices because they will be able to reach full operating speed during the
second startup cycle.
If you still have a problem, try the following:
m If the hard disk is external, make sure it is turned on and its cable is
connected firmly and properly terminated; then restart the server.
m Check the ID numbers of all SCSI equipment connected to your server. See
the information on SCSI devices in Chapter 3 of this book.
m If the hard disk is your startup disk, start up your server with the Workgroup
Server Software CD-ROM disc (see “Starting Up From the CD-ROM
Drive” later in this chapter). Then see “Repairing a Damaged Disk” (later in
this chapter). If repairing the disk doesn’t help, follow the instructions in
“Reinstalling System Software” (also later in this chapter).
IMPORTANT
volumes, you won’t see an icon for it on the desktop until you create at least
one RAID volume on that disk.
Icons do not appear correctly on your screen.
You need to “rebuild the desktop”—a process that helps your server keep track
of files and folders on your hard disks.
m Hold down the Option and x (Command) keys while starting up your
server. Keep holding down the keys until you see a message asking whether
you want to rebuild the desktop. Click OK.
70 Chapter 6 / Troubleshooting
If the hard disk in question has been initialized for use with RAID
Page 87

Your server can’t read a floppy disk.
If you see a message that a floppy disk is unreadable, try one of the following:
m Insert the disk again—sometimes that’s all it takes.
m If the disk has never been used, you may simply need to initialize it. See the
instructions for preparing a disk listed in the “Files” topic of Macintosh
Guide, available in the Guide menu.
m Insert the disk in another computer’s disk drive. If that computer can use the
disk, make a copy of the data and put the copy on a different floppy disk.
m You may need to repair the disk because it is damaged. For information on
testing and repairing disks, see “Repairing a Damaged Disk” later in this
chapter.
If you are trying to use a DOS disk:
m The disk may have been formatted incorrectly on a DOS computer. On DOS
computers it’s possible to format a standard double-sided disk in a highdensity (1440K) format, and vice versa. Disks formatted this way cannot be
read by a Macintosh computer.
When formatting disks on a DOS computer, always format standard doublesided disks in the 720K format. Always format high-density disks in the
1440K format.
If a disk has been formatted incorrectly, use a DOS computer to copy its
contents onto another disk that has been properly formatted.
The pointer doesn’t move when you move the mouse.
The mouse is not connected properly, its signals are not reaching the server, or
there is a software error.
m Make sure the k ey lock switch is in the “on” position (not the “secur e” position).
m Turn off the server by using the key lock switch, check that the mouse cable
is connected properly, then restart the server.
m Clean the mouse (see Appendix A, “Safety, Maintenance, and Health
Information”).
m If you have another mouse or pointing device, try connecting and using it.
(Turn off the server first.) If it works, there is probably something wrong
with your mouse.
Solutions to common problems 71
Page 88

m Restart the server with a different startup disk (such as the Workgroup
Server Software CD-ROM disc). If the mouse works, reinstall system
software on your startup disk.
m If the problem recurs, it may be due to an incompatible program. Make sure
that all programs, desk accessories, and system extensions you’re using are
compatible with the system software.
If none of these procedures solves the problem, consult the service and support
information that came with your server for instructions on how to contact an
Apple-authorized service provider or Apple for assistance.
Typing on the keyboard produces nothing on the screen.
The insertion point hasn’t been set, no text is selected, an application program
is not active, the keyboard is not connected properly, the keyboard’s signals are
not reaching the server, or there is a software error.
m Make sure the k ey lock switch is in the “on” position (not the “secur e” position).
m Make sure that the program you want to use is the active program.
m Place the pointer in the active window and click to set an insertion point or
drag to select text (if applicable).
m Turn off the server by using the key lock switch, then check that the
keyboard cable is connected properly at both ends.
m Turn off the server, then connect the keyboard cable to the other ADB port
(marked with the V icon) on the keyboard. (You may have to unplug the
mouse to do this.) If your keyboard cable is connected to your monitor,
connect it to another ADB port on the monitor or directly to the server’s
ADB port (on the back of the server). If typing still doesn’t work, the
problem is most likely in the keyboard itself.
m If you have access to another keyboard, try using it instead. (Turn off the
server before connecting it.)
m Restart the server with a different startup disk (such as the Workgroup
Server Software CD-ROM disc). If this solves the problem, reinstall system
software on your startup disk.
If none of these procedures solves the problem, consult the service and support
information that came with your server for instructions on how to contact an
Apple-authorized service provider or Apple for assistance.
72 Chapter 6 / Troubleshooting
Page 89

A dialog box with a “bomb” icon appears.
Your system has a software problem.
m Write down what you were doing when the dialog box appeared, and write
down the number on the message, if there is one.
m Restart your server (see “Start Over” earlier in this chapter). Most software
problems are temporary and restarting usually corrects the problem.
m If the problem recurs, check the startup disk and program you are using
when the message appears. Make sure that all programs, desk accessories,
and system extensions you’re using are compatible with the system
software. Reinstalling the system software may correct the problem.
m Sometimes incompatible system extensions or control panels can cause
system software problems. To see if this is the problem, use the Extensions
Manager control panel to turn off individual extensions and then restart the
server. For information on using this control panel to manage system
extensions, see the “Setting Options” topic of Macintosh Guide, available in
the Guide menu. If turning off these programs doesn’t correct the problem,
you may need to reinstall system software.
You can’t start your program or it quits unexpectedly. When you try to open a program,
you see a message that not enough memory is available.
The program needs more memory or the server ran out of memory.
m Quit the programs that you have open and then open the program you want
to use, or restart your server.
m Use the program’s Info window to give it more memory. For more information
see the instructions for making more memory available in the “Working with
Programs” topic of Macintosh Guide, av ailable in the Guide menu.
You see a message that your application program can’t be opened because a file can’t
be found.
Power Macintosh programs use special files called shared libraries. Any
necessary shared libraries should be installed automatically when you install
Power Macintosh programs.
m Follow the directions that came with your program to reinstall the program.
If the shared library is still missing, contact the software program’s
manufacturer for assistance.
Solutions to common problems 73
Page 90

You experience problems using an older Macintosh program.
Some older Macintosh programs are not completely compatible with the
Power Macintosh computers.
m Open the Memory control panel and turn off Modern Memory Manager. For
more detailed instructions, see “Using Older Macintosh Programs” in
Chapter 4 of this guide.
You experience problems using a document from a DOS computer.
If you can’t open a DOS or Windows document using a Macintosh program,
try the following:
m Open the document from within the program by using the Open command
in the program’s File menu.
m Use the PC Exchange control panel to change the document’s type to
one that can be opened by the program. See the information on setting up
your Macintosh to use DOS files in the “Using DOS Files and Disks”
topic of Macintosh Guide, available in the Guide menu.
If a DOS document is displayed incorrectly, or you see strange codes or
characters in the document:
m Your application program may have special procedures for opening and
saving documents with different file formats. See the information that came
with your application program.
m Try opening the document in another program.
Note: Some characters that can be displayed on the server are not accurately
displayed on DOS computers.
You see a message that an application program can’t be found.
The following dialog box appears if you try to open a document created using
software that is not on your hard disk.
74 Chapter 6 / Troubleshooting
Page 91

Normally, you see this message if you try to open a document that came from
another computer with software that is different from yours.
m Some documents can be opened by more than one application program. Try
starting a program that you think might be able to open the document, then
choose the Open command from the program’s File menu to try to open the
document. (Or drag the document to the program’s icon. If the program can
open the document, the program’s icon highlights.)
m Purchase and install the correct software to use the document, or find out if
the original owner of the document can convert it to a form that one of your
programs can use.
m Don’t try to open the files in your System Folder. Most of the System Folder
files are used by your server for internal purposes, and are not intended to
be opened.
m Rebuild your desktop by holding down the Option and x (Command) keys
while starting up your server. Keep holding down the keys until you see a
message asking whether you want to rebuild the desktop. Click OK.
m The application program itself may be damaged. Try reinstalling it.
m If the document is from a DOS computer, use the PC Exchange control
panel. See the information on setting up your Macintosh to use DOS files in
the “Using DOS Files and Disks” topic of Macintosh Guide, available in the
Guide menu.
Your print server is not functioning properly.
You may not be using the correct version of the LaserWriter printer driver
software. If you are running the AppleShare Print Server, you need to use
version 7.2 of the LaserWriter printer software, which is preinstalled on the
server. For more information, see the Read Me file for AppleShare.
You can’t see files on your CD-ROM drive.
If the drive in question is external, be sure that it is properly connected and
terminated. See the section “Connecting Hard Disks and Other SCSI Devices”
in Chapter 3.
There may be a problem with the CD-ROM drive software in your system and
you need to reinstall that software. See the section “If There’s a Problem With
Your CD-ROM Drive Software” later in this chapter.
Solutions to common problems 75
Page 92

Whe n you need to reinstall system software
System software is the set of programs and other files that your server uses to
start itself up, keep track of your files, and run the application programs you
use. System software is kept in the folder called the System Folder. When you
turn on your server, it looks for a startup disk, which is a disk that contains the
system software. The startup disk is usually a hard disk that’s inside your
server, though another hard disk, floppy disk, or CD-ROM disc can also be a
startup disk.
Your server came with all the necessary system software installed on your hard
disk. Unless a problem develops later, you don’t need to reinstall the software.
If a problem with your system software develops, you may see this icon in the
middle of the screen:
If you see this icon, start up your server with the Workgroup Server Software
CD-ROM disc, as described in the section “Starting Up From the CD-ROM
Drive ” later in this chapter. Then refer to “Repairing a Damaged Disk” at the
end of this chapter for information on testing and repairing disks.
If repairing the disk doesn’t help, use the following instructions to start up
your server and reinstall system software.
Reinstalling system software
When you have determined that you need to reinstall system software, you
need to shut down your server and then start it up with another disk and use
the Installer program to reinstall the system software on your server’s hard
disk. Follow the steps provided in this section.
IMPORTANT
reinstall your system software from your backup media. If you used a backup
program to make the copy, see the documentation that came with the program.
76 Chapter 6 / Troubleshooting
If you’ve made a backup copy of your system software, you should
Page 93

Starting up from the CD-ROM drive
You can use the Workgroup Server Software CD-ROM disc to start up your
server from the built-in CD-ROM drive (even if your startup disk is damaged).
1 With your server turned on, place the
ROM drive’s tray with the label facing up, and close the tray.
2 Choose Restart from the Special menu.
3 Immediately press and hold down the “C” letter key. Release the key after the server
starts up.
IMPORTANT
For best performance, start up your server from its internal hard
Workgroup Server Software
CD-ROM disc in the CD-
disk. (You can check that the internal hard disk is selected in the Startup Disk
control panel.) Use the Workgroup Server Software CD-ROM disc only as a
temporary startup system.
Starting up from t h e floppy drive
If you need to do so, you can use floppy disks that contain system software
to start up your server. Use the disks you created with your backup program or
by copying system software from the Workgroup Server Software CD-ROM
disc. See the section “Creating Startup Floppy Disks” later in this chapter for
more information.
Insert the disk named
m
Install Me First
into the floppy drive and start up your server.
IMPORTANT
Make sure you’ve labeled your disks exactly as the Disk Copy
program names them, as described in the section “Creating Startup Floppy
Disks” later in this chapter.
An Installer screen opens automatically to let you reinstall system software on
your hard disk.
Note: If you want to start up your server from a floppy disk without installing
system software, use the disk named Disk Tools.
When you need to reinstall system software 77
Page 94

About using the Installer pro gram
Before you use the Installer, you need to start up your server by following the
instructions in either “Starting Up From the CD-ROM Drive” or “Starting Up
From the Floppy Drive”earlier in this chapter.
How you start using the Installer depends upon where it is located:
m If you started up from the Workgroup Server Software CD-ROM disc, open
the folder named System Software Installers and review the instructions in
the Read Me file before using the Installer programs there.
m If you started up from the floppy disk named Install Me First, the Installer
opens automatically. Depending on the version of system software on the
floppy disk, you may also need to use another Installer to do a system
update after the basic system installation.
After you open the Installer, using it to install system software involves the
following steps:
1 In the Welcome dialog box that appears, click Continue.
The version of system software you install may be later than the one shown in
this example.
78 Chapter 6 / Troubleshooting
Page 95

2 Check that the destination disk indicated in the Installer is the one on which you want to
This is the disk on
which system software
will be installed.
3 Click Install.
install system software.
If not, click the Switch Disk button until the correct disk name appears.
Click to indicate a
different disk.
Note: If you are using the Installer on a hard disk that doesn’t have system
software, the explanatory text on-screen will be slightly different than what’s
shown in this example.
The Easy Install status box appears and keeps you informed of progress
during installation.
If you are installing from floppy disks, follow the instructions asking you to
insert different disks.
4 If you see a message telling you that you need to restart your system, click Restart.
Otherwise, click Quit.
If a message reports that installation was not successful, try installing again.
(Follow the instructions on the screen.)
That’s it. You’ve installed Macintosh system software on your startup disk.
Note: The Installer also has a “custom” feature that lets you install or remove
one or more items. See the Installer’s Help information for more details.
When you need to reinstall system software 79
Page 96

Creating star tup floppy disks
You can create Macintosh system software floppy disks from the Workgroup
Server Software CD-ROM disc. This allows you to have a backup copy of the
system software from which you can start up the server and reinstall the system
software. You need to use the Disk Copy program to make a copy of the
system software. (Dragging system software files to floppy disks does not work
because the Installer expects the files to be in certain places on the floppy disks.)
To copy the software, you’ll need eleven high-density (1.4 megabyte [MB])
floppy disks.
1 Insert the
2 Open the folder named “Disk Images” and locate the Disk Copy icon.
Workgroup Server Software
CD-ROM disc into the CD-ROM drive.
You may need to scroll the window to see the icon.
3 Double-click the Disk Copy icon to start the program.
4 Click anywhere on the screen to remove the explanatory dialog box.
The Disk Copy window appears.
5 In the window, click Load Image File.
A dialog box appears, in which you can select the disk image that you want to
copy. Each image file contains the software for one system software disk.
80 Chapter 6 / Troubleshooting
Page 97

6 Click the name of a disk image, then click Open.
In a few moments a message appears near the top of the window, indicating
that the disk image has been loaded.
7 Click Make A Copy.
8 When you see a message telling you to insert a disk, insert a floppy disk.
If the disk already contains information, you’re asked whether you want to
replace the contents of the disk. Click Duplicate if you want to erase the
information on the disk and replace it with a copy of system software.
Otherwise, eject the disk and insert a different disk.
9 When you see a message telling you that the disk was duplicated successfully, click
Load Image File to copy another disk image or click Quit to leave the program.
The program ejects the disk when it has copied the image.
10 Repeat steps 6 through 9 for each disk image until you have copied all the disk image files.
Store the backup disks in a safe place.
Note: It’s a good idea to label the disks exactly as they are named by the Disk
Copy program. That way, if you need to start up from a floppy disk and
reinstall system software, you can easily follow the directions in “Starting Up
From the Floppy Drive,” earlier in this chapter.
When you need to reinstall system software 81
Page 98

What to do if your server’s performance decreases
If you notice a decrease in your server’s speed and general performance after
adding special software (a control panel, a system extension, or a custom
utility), it may be because your special software does not work well with
Power Macintosh computers.
To see if this is the problem, use the Extensions Manager control panel to turn
off individual programs and extensions, one at a time, and then restart the
server. (For information on using the Extensions Manager control panel, see
the “Setting Options” topic of Macintosh Guide, available in the Guide menu.)
If the computer performs better when a special program or extension is
removed, contact the software’s manufacturer for information or an upgrade.
If you still do not notice an improvement after removing all special programs,
try doing a “clean” installation of system software, as described next.
Doing a clean installation of system software
Performing what is commonly called a “clean” installation of system software
involves repairing any damage to your startup disk and installing new versions
of system software and disk drive software. To do this, you must start up your
server from the Workgroup Server Software CD-ROM disc. There are a
number of steps involved; here’s an overview of the entire process:
m Use the Disk First Aid program to inspect and repair your startup disk.
m Use Apple HD SC Setup to update the startup disk drive software.
m Use a special feature of the Installer to do the clean installation.
WARNING
RAID Software, do not use the following instructions for doing a clean
installation. See the Apple RAID Software Administrator’s Guide for
information about repairing disks and installing system software on
disks containing RAID volumes.
After the clean installation you can experiment with any special sofware you
used with the previous system software to see if you can use it without
decreasing the server’s performance.
82 Chapter 6 / Troubleshooting
If your startup disk has been formatted for use with Apple
Page 99

IMPORTANT
Do a clean installation of system software only if you are sure it’s
acceptable to remove any special control panels, extensions, or custom utilities
you have added to your System Folder. These items will not work when moved
out of the System Folder.
Note: You may have to reinstall some server application programs (including
network services) if you do a clean installation; see your server application
program documentation for details.
Follow these steps to do a clean installation:
1 Start up your server from the
Workgroup Server Software
CD-ROM disc.
If you need instructions, see the section “Starting Up From the CD-ROM
Drive” earlier in this chapter.
2 Open the Utilities folder on the
Disk First Aid icon.
3 In the Disk First Aid window, click the icon of the server’s hard disk.
Workgroup Server Software
disc, then double-click the
Disk icons appear in a box at the top of the Disk First Aid window.
What to do if your server’s performance decreases 83
Page 100

4 Click Repair to begin testing and, if necessary, repairing the startup disk.
5 When the program is finished, choose Quit from the File menu.
6 Double-click the Apple HD SC Setup icon.
WARNING
If your startup disk has been formatted for use with Apple
RAID Software, do not use HD SC Setup to update the disk. See the
Apple RAID Software Administrator’s Guide for information about
repairing disks containing RAID volumes.
7 Click Update to replace the existing startup disk drive software with a new version.
8 When the startup disk software is updated, choose Quit from the File menu.
9 Make sure that at least 20 MB of disk space is available on the startup disk.
If needed, delete unnecessary files until you have 20 MB of space available.
10 Open the Installer program in the System Software Installers folder on the
Server Software
11 If the destination disk named in the Installer screen is not the hard disk on which you
want to do the clean installation, click Switch Disk until the correct name appears.
12 To start the clean installation process, press the Shift-
13 In the dialog box that appears, click the Install New System Folder button and click OK.
CD-ROM disc and click Continue when the Welcome screen appears.
x
x
-K key combination.
Workgroup
The dialog box disappears, and the Install button in the Installer screen
changes to Clean Install.
14 Click Clean Install and follow any instructions that the Installer displays.
15 If a message reports that installation was not successful, repeat the clean
installation procedure.
84 Chapter 6 / Troubleshooting
 Loading...
Loading...