ANALOG DEVICES SSM2211 Service Manual
Low Distortion, 1.5 W Audio
www.BDTIC.com/ADI
FEATURES
1.5 W output with THD + N < 1%
Differential bridge-tied load output
Single-supply operation: 2.7 V to 5.5 V
Functions down to 1.75 V
Wide bandwidth: 4 MHz
Highly stable phase margin: >80°
Low distortion: 0.2% THD + N @ 1 W output
Excellent power supply rejection
APPLICATIONS
Portable computers
Personal wireless communicators
Hands-free telephones
Speaker phones
Intercoms
Musical toys and talking games
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
The SSM22111 is a high performance audio amplifier that
delivers 1 W rms of low distortion audio power into a bridgeconnected 8 Ω speaker load (or 1.5 W rms into a 4 Ω load).
The SSM2211 operates over a wide temperature range and is
specified for single-supply voltages between 2.7 V and 5.5 V.
When operating from batteries, it continues to operate down to
1.75 V. This makes the SSM2211 the best choice for unregulated
applications, such as toys and games.
Featuring a 4 MHz bandwidth and distortion below 0.2% THD
+ N @ 1 W, superior performance is delivered at higher power
or lower speaker load impedance than competitive units.
Furthermore, when the ambient temperature is at 25°C, THD +
N < 1%, and V
delivers a 1.5 W output.
1
Protected by U.S. Patent No. 5,519,576.
Rev. E
Information furnished by Analog Devices is believed to be accurate and reliable. However, no
responsibility is assumed by Analog Devices for its use, nor for any infringements of patents or other
rights of third parties that may result from its use. Specifications subject to change without notice. No
license is granted by implication or otherwise under any patent or patent rights of Analog Devices.
Trademarks and registered trademarks are the property of their respective owners.
= 5 V on a four-layer PCB, the SSM2211
S
Power Amplifier
SSM2211
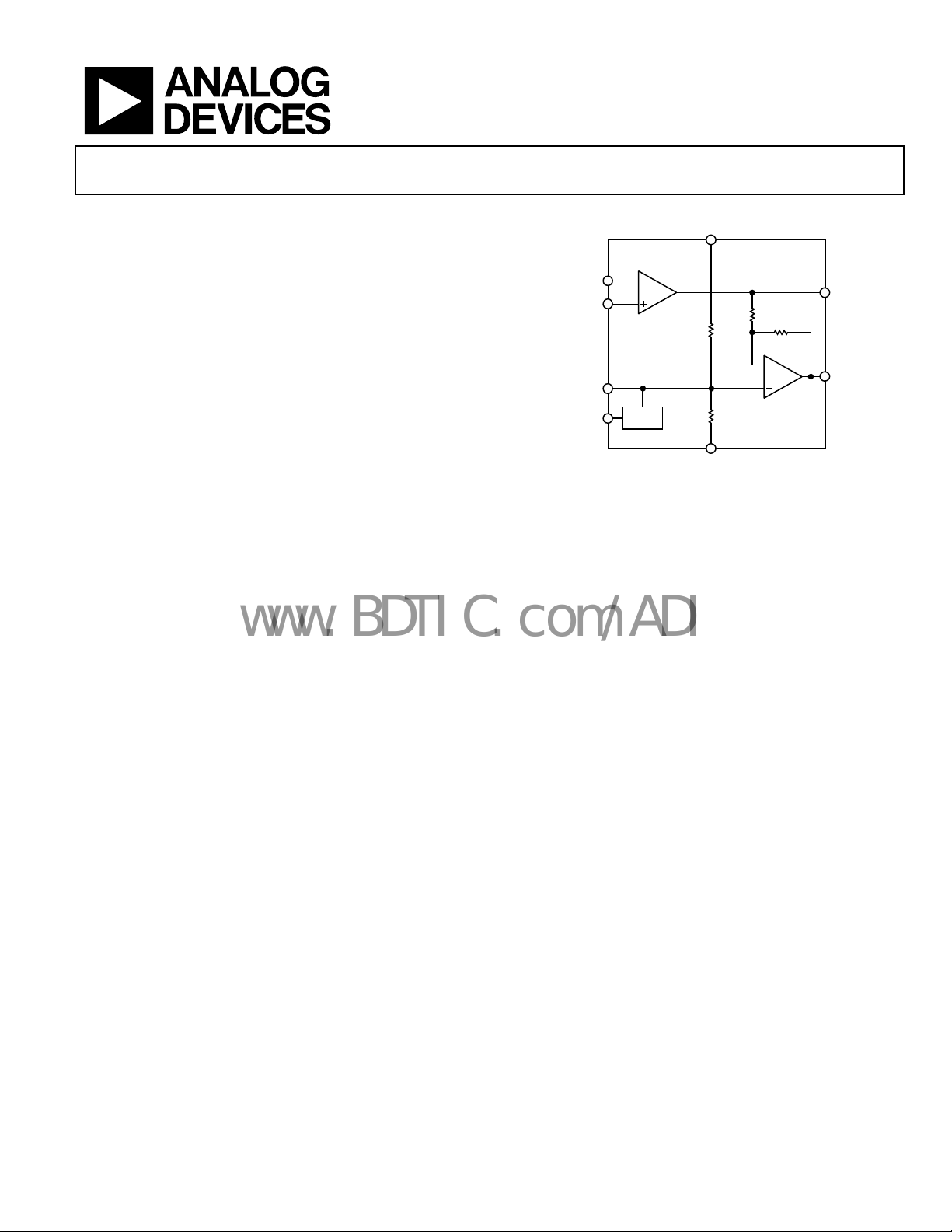
FUNCTIONAL BLOCK DIAGRAM
IN–
IN+
BYPASS
SHUTDOWN
The low differential dc output voltage results in negligible
losses in the speaker winding and makes high value dc blocking
capacitors unnecessary. The battery life is extended by using
shutdown mode, which typically reduces quiescent current
drain to 100 nA.
The SSM2211 is designed to operate over the −40°C to +85°C
temperature range. The SSM2211 is available in 8-lead SOIC
(narrow body) and LFCSP (lead frame chip scale) surfacemount packages. The advanced mechanical packaging of the
LFCSP models ensures lower chip temperature and enhanced
performance relative to standard packaging options.
Applications include personal portable computers, hands-free
telephones and transceivers, talking toys, intercom systems, and
other low voltage audio systems requiring 1 W output power.
One Technology Way, P.O. Box 9106, Norwood, MA 02062-9106, U.S.A.
Tel: 781.329.4700 www.analog.com
Fax: 781.461.3113 ©2008 Analog Devices, Inc. All rights reserved.
BIAS
SSM2211
V– (GND)
Figure 1.
A
V
OUT
V
B
OUT
00358-001

SSM2211
www.BDTIC.com/ADI
TABLE OF CONTENTS
Features .............................................................................................. 1
Applications ....................................................................................... 1
Functional Block Diagram .............................................................. 1
General Description ......................................................................... 1
Revision History ............................................................................... 2
Electrical Characteristics ................................................................. 3
Absolute Maximum Ratings ............................................................ 5
Thermal Resistance ...................................................................... 5
ESD Caution .................................................................................. 5
Pin Configurations and Function Descriptions ........................... 6
Typical Performance Characteristics ............................................. 7
Product Overview ........................................................................... 14
Thermal Performance—LFCSP ................................................ 14
Typical Applications ....................................................................... 15
Bridged Output vs. Single-Ended Output Configurations ... 15
Speaker Efficiency and Loudness ............................................. 15
Power Dissipation....................................................................... 16
Output Voltage Headroom ........................................................ 17
Automatic Shutdown-Sensing Circuit ..................................... 17
Shutdown-Circuit Design Example ......................................... 18
Start-Up Popping Noise ............................................................. 18
SSM2211 Amplifier Design Example .................................. 18
Single-Ended Applications ........................................................ 19
Driving Two Speakers Single Endedly ..................................... 19
Evaluation Board ........................................................................ 20
LFCSP PCB Considerations ...................................................... 20
Outline Dimensions ....................................................................... 21
Ordering Guide .......................................................................... 22
REVISION HISTORY
4/08—Rev. D to Rev. E
Changes to Features .......................................................................... 1
Changes to General Description .................................................... 1
Changes to Supply Current in Table 1 and Table 2 ...................... 3
Changes to Supply Current in Table 3 ........................................... 4
Changes to Absolute Maximum Ratings ....................................... 5
Changes to Figure 41 ...................................................................... 14
Changes to Equation 7, Equation 8, and Equation 10 ............... 16
Changes to Figure 47 ...................................................................... 17
Changes to Automatic Shutdown-Sensing Circuit Section ...... 18
Changes to SSM2211Amplifier Design Example Section ......... 19
Changes to Driving Two Speakers Single Endedly Section ...... 20
Changes to Figure 50 ...................................................................... 20
Changes to Evaluation Board Section .......................................... 20
Changes to Figure 51 ...................................................................... 20
Changes to Ordering Guide .......................................................... 22
11/06—Rev. C to Rev. D
Updated Format .................................................................. Universal
Changes to General Description .................................................... 1
Changes to Electrical Characteristics ............................................ 3
Changes to Absolute Maximum Ratings ....................................... 5
Added Table 6 .................................................................................... 6
Changes to Figure 32 ...................................................................... 11
Changes to the Product Overview Section ................................. 14
Changes to the Output Voltage Headroom Section ................... 17
Changes to the Start-Up Popping Noise Section ........................ 18
Changes to the Evaluation Board Section ................................... 20
Updated Outline Dimensions ....................................................... 21
Changes to Ordering Guide .......................................................... 21
10/04—Data Sheet Changed from Rev. B to Rev. C
Updated Format .................................................................. Universal
Changes to General Description ..................................................... 1
Changes to Table 5 ............................................................................. 4
Deleted Thermal Performance—SOIC Section ........................... 8
Changes to Figure 31 ...................................................................... 10
Changes to Figure 40 ...................................................................... 12
Changes to Thermal Performance—LFCSP Section ................. 13
Deleted Figure 52, Renumbered Successive Figures .................. 14
Deleted Printed Circuit Board Layout—SOIC Section ............. 14
Changes to Output Voltage Headroom Section ......................... 16
Changes to Start-Up Popping Noise Section .............................. 17
Changes to Ordering Guide .......................................................... 20
10/02—Data Sheet Changed from Rev. A to Rev. B
Deleted 8-Lead PDIP ......................................................... Universal
Updated Outline Dimensions ....................................................... 15
5/02—Data Sheet Changed from Rev. 0 to Rev. A
Edits to General Description ........................................................... 1
Edits to Package Type ....................................................................... 3
Edits to Ordering Guide ................................................................... 3
Edits to Product Overview ............................................................... 8
Edits to Printed Circuit Board Layout Considerations ............. 13
Added section Printed Circuit Board Layout
Considerations—LFCSP ................................................................ 14
Rev. E | Page 2 of 24

SSM2211
www.BDTIC.com/ADI
ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS
VDD = 5.0 V, TA = 25°C, RL = 8 Ω, CB = 0.1 µF, VCM = VDD/2, unless otherwise noted.
Table 1.
Parameter Symbol Conditions Min Typ Max Unit
GENERAL CHARACTERISTICS
Differential Output Offset Voltage V
Output Impedance Z
SHUTDOWN CONTROL
Input Voltage High VIH ISY = <100 mA 3.0 V
Input Voltage Low VIL ISY = normal 1.3 V
POWER SUPPLY
Power Supply Rejection Ratio PSRR VS = 4.75 V to 5.25 V 66 dB
Supply Current ISY V
Supply Current, Shutdown Mode ISD Pin 1 = VDD (see Figure 32), −40°C ≤ TA ≤ +85°C 0.1 1 μA
DYNAMIC PERFORMANCE
Gain Bandwidth Product GBP 4 MHz
Phase Margin ΦM 86 Degrees
AUDIO PERFORMANCE
Total Harmonic Distortion THD + N P = 0.5 W into 8 Ω, f = 1 kHz 0.15 %
Total Harmonic Distortion THD + N P = 1.0 W into 8 Ω, f = 1 kHz 0.2 %
Voltage Noise Density en f = 1 kHz 85
AVD = 2, −40°C ≤ TA ≤ +85°C 4 50 mV
OOS
0.1 Ω
OUT
A = V
OUT
B = 2.5 V, −40°C ≤ TA ≤ +85°C 9.5 20 mA
OUT
nV√Hz
VDD = 3.3 V, TA = 25°C, RL = 8 Ω, CB = 0.1 µF, VCM = VDD/2, unless otherwise noted.
Table 2.
Parameter Symbol Conditions Min Typ Max Unit
GENERAL CHARACTERISTICS
Differential Output Offset Voltage V
Output Impedance Z
SHUTDOWN CONTROL
Input Voltage High VIH ISY = <100 μA 1.7 V
Input Voltage Low VIL ISY = normal 1 V
POWER SUPPLY
Supply Current ISY V
Supply Current, Shutdown Mode ISD Pin 1 = VDD (see Figure 32), −40°C ≤ TA ≤ +85°C 0.1 1 μA
AUDIO PERFORMANCE
Total Harmonic Distortion THD + N P = 0.35 W into 8 Ω, f = 1 kHz 0.1 %
AVD = 2, −40°C ≤ TA ≤ +85°C 5 50 mV
OOS
0.1 Ω
OUT
A = V
OUT
B = 1.65 V, −40°C ≤ TA ≤ +85°C 5.2 20 mA
OUT
Rev. E | Page 3 of 24
SSM2211
www.BDTIC.com/ADI
VDD = 2.7 V, TA = 25°C, RL = 8 Ω, CB = 0.1 µF, VCM = VDD/2, unless otherwise noted.
Table 3.
Parameter Symbol Conditions Min Typ Max Unit
GENERAL CHARACTERISTICS
Differential Output Offset Voltage V
Output Impedance Z
SHUTDOWN CONTROL
Input Voltage High VIH ISY = <100 mA 1.5 V
Input Voltage Low VIL ISY = normal 0.8 V
POWER SUPPLY
Supply Current ISY V
Supply Current, Shutdown Mode ISD Pin 1 = VDD (see Figure 32), −40°C ≤ TA ≤ +85°C 0.1 1 μA
AUDIO PERFORMANCE
Total Harmonic Distortion THD + N P = 0.25 W into 8 Ω, f = 1 kHz 0.1 %
AVD = 2 5 50 mV
OOS
0.1 Ω
OUT
A = V
OUT
B = 1.35 V, −40°C ≤ TA ≤ +85°C 4.2 20 mA
OUT
Rev. E | Page 4 of 24
SSM2211
www.BDTIC.com/ADI
ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATINGS
Absolute maximum ratings apply at TA = 25°C, unless
otherwise noted.
Table 4.
Parameter Rating
Supply Voltage 6 V
Input Voltage VDD
Common-Mode Input Voltage VDD
ESD Susceptibility 2000 V
Storage Temperature Range −65°C to +150°C
Operating Temperature Range −40°C to +85°C
Junction Temperature Range −65°C to +165°C
Lead Temperature, Soldering (60 sec) 300°C
Stresses above those listed under Absolute Maximum Ratings
may cause permanent damage to the device. This is a stress
rating only; functional operation of the device at these or any
other conditions above those indicated in the operational
section of this specification is not implied. Exposure to absolute
maximum rating conditions for extended periods may affect
device reliability.
THERMAL RESISTANCE
is specified for the worst-case conditions, that is, a device
θ
JA
soldered in a circuit board for surface-mount packages.
Table 5. Thermal Resistance
Package Type θJA Unit
8-Lead LFCSP_VD (CP-Suffix)1 50 °C/W
8-Lead SOIC_N (S-Suffix)2 121 °C/W
1
For the LFCSP_VD, θJA is measured with exposed lead frame soldered to the PCB.
2
For the SOIC_N, θJA is measured with the device soldered to a four-layer PCB.
ESD CAUTION
Rev. E | Page 5 of 24

SSM2211
www.BDTIC.com/ADI
PIN CONFIGURATIONS AND FUNCTION DESCRIPTIONS
PIN 1
1SHUTDOWN
SHUTDOWN
BYPASS
IN+
IN–
1
SSM2211
2
3
TOP VIEW
(Not to Scale)
4
V
B
8
OUT
V–
7
6
V+
V
A
5
OUT
00358-002
2BYPASS
3IN+
4IN–
INDICATO R
SSM2211
TOP VIEW
(Not to Scale)
Figure 2. 8-Lead SOIC_N Pin Configuration (R-8) Figure 3. 8-Lead LFCSP_VD Pin Configuration (CP-8-2)
Table 6. Pin Function Descriptions
Pin No. Mnemonic Description
1 SHUTDOWN Shutdown Enable.
2 BYPASS Bypass Capacitor.
3 IN+ Noninverting Input.
4 IN− Inverting Input.
5 V
A Output A.
OUT
6 V+ Positive Supply.
7 V− Negative Supply.
8 V
B Output B.
OUT
8V
7V–
6V+
5V
OUT
OUT
B
A
00358-003
Rev. E | Page 6 of 24
SSM2211
www.BDTIC.com/ADI
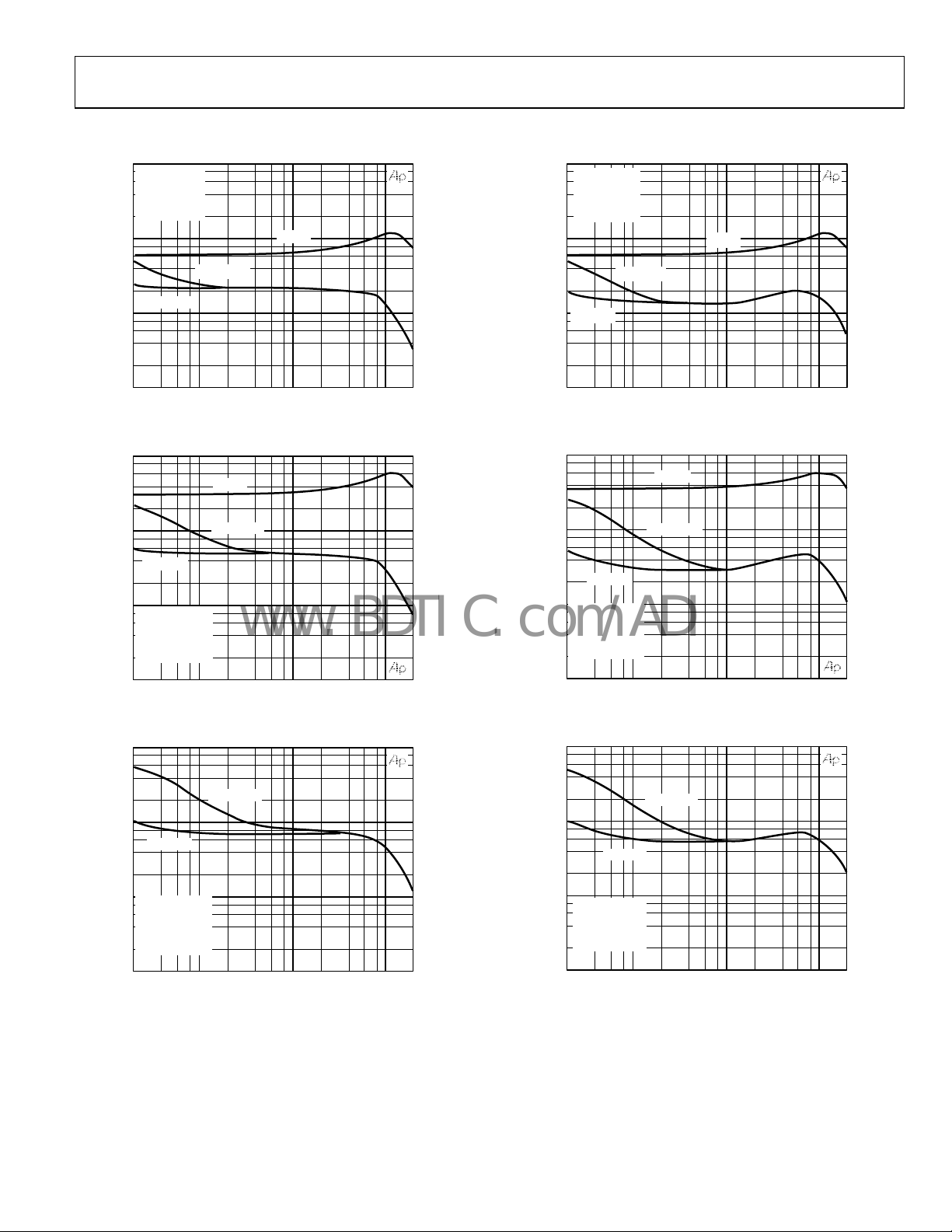
TYPICAL PERFORMANCE CHARACTERISTICS
10
1
TA = 25°C
V
= 5V
DD
A
= 2 (BTL)
VD
R
= 8Ω
L
P
= 500mW
L
CB = 0
10
1
TA = 25°C
V
= 5V
DD
A
= 2 (BTL)
VD
R
= 8Ω
L
P
= 1W
L
CB = 0
CB = 0.1μF
THD + N (%)
CB = 1μF
0.1
0.01
20 100 20k
FREQUENCY (Hz)
1k 10k
Figure 4. THD + N vs. Frequency
10
CB = 0
1
CB = 1μF
THD + N (%)
0.1
TA = 25°C
V
= 5V
DD
A
= 10 (BTL)
VD
R
= 8Ω
L
P
= 500mW
L
0.01
20 100 20k
CB = 0.1μF
1k 10k
FREQUENCY (Hz)
Figure 5. THD + N vs. Frequency
10
00358-004
00358-005
CB = 0.1μF
THD + N (%)
0.1
CB = 1μF
0.01
20 100 20k
FREQUENCY (Hz)
1k 10k
Figure 7. THD + N vs. Frequency
10
CB = 0
1
THD + N (%)
CB = 1μF
0.1
TA = 25°C
V
= 5V
DD
A
= 10 (BTL)
VD
R
= 8Ω
L
P
= 1W
L
0.01
20 100 20k
CB = 0.1μF
1k 10k
FREQUENCY (Hz)
Figure 8. THD + N vs. Frequency
10
00358-007
00358-008
CB = 0.1μF
1
CB = 1μF
THD + N (%)
0.1
TA = 25°C
V
= 5V
DD
A
= 20 (BTL)
VD
R
= 8Ω
L
P
= 500mW
L
0.01
20 100 20k
FREQUENCY (Hz)
1k 10k
00358-006
Figure 6. THD + N vs. Frequency
Rev. E | Page 7 of 24
CB = 0.1μF
1
CB = 1μF
THD + N (%)
0.1
TA = 25°C
V
= 5V
DD
A
= 20 (BTL)
VD
R
= 8Ω
L
P
= 1W
L
0.01
20 100 20k
FREQUENCY (Hz)
1k 10k
Figure 9. THD + N vs. Frequency
00358-009
SSM2211
www.BDTIC.com/ADI
10
TA = 25°C
V
= 5V
DD
A
= 2 (BTL)
VD
R
= 8Ω
L
FREQUENCY = 20Hz
C
= 0.1μF
B
1
10
1
TA = 25°C
V
= 3.3V
DD
A
= 2 (BTL)
VD
R
= 8Ω
L
P
= 350mW
L
CB = 0
THD + N (%)
0.1
0.01
20n 0.1 2
10
TA = 25°C
= 5V
V
DD
= 2 (BTL)
A
VD
= 8Ω
R
L
FREQUENCY = 1kHz
C
= 0.1μF
B
1
THD + N (%)
0.1
0.01
20n 0.1 2
10
TA = 25°C
V
= 5V
DD
A
= 2 (BTL)
VD
R
= 8Ω
L
FREQUENCY = 20kHz
C
= 0.1μF
B
1
P
(W)
OUTPUT
Figure 10. THD + N vs. P
P
(W)
OUTPUT
Figure 11. THD + N vs. P
OUTPUT
OUTPUT
THD + N (%)
0.1
CB = 1μF
1
00358-010
0.01
20 100 20k
CB = 0.1μF
FREQUENCY (Hz)
1k 10k
00358-013
Figure 13. THD + N vs. Frequency
10
CB = 0
1
THD + N (%)
1
00358-011
CB = 1μF
0.1
0.01
20 100 20k
CB = 0.1μF
TA = 25°C
V
DD
A
VD
R
= 8Ω
L
P
= 350mW
L
FREQUENCY (Hz)
1k 10k
= 3.3V
= 10 (BTL)
00358-014
Figure 14. THD + N vs. Frequency
10
1
CB = 0.1μF
THD + N (%)
0.1
0.01
20n 0.1 2
P
(W)
OUTPUT
Figure 12. THD + N vs. P
OUTPUT
1
00358-012
Rev. E | Page 8 of 24
CB = 1μF
THD + N (%)
0.1
TA = 25°C
V
= 3.3V
DD
A
= 20 (BTL)
VD
R
= 8Ω
L
P
= 350mW
L
0.01
20 100 20k
FREQUENCY (Hz)
1k 10k
Figure 15. THD + N vs. Frequency
00358-015
 Loading...
Loading...