Precision Picoampere Input Current
a
FEATURES
Low Offset Voltage: 50 V max
Low Offset Voltage Drift: 0.5 V/ⴗC max
Very Low Bias Current
25ⴗC: 100 pA max
–55ⴗC to +125ⴗC: 450 pA max
Very High Open-Loop Gain: 2000 V/mV min
Low Supply Current (per Amplifier): 625 A max
Operates from ⴞ2 V to ⴞ20 V Supplies
High Common-Mode Rejection: 120 dB min
APPLICATIONS
Strain Gage and Bridge Amplifiers
High Stability Thermocouple Amplifiers
Instrumentation Amplifiers
Photo-Current Monitors
High Gain Linearity Amplifiers
Long-Term Integrators/Filters
Sample-and-Hold Amplifiers
Peak Detectors
Logarithmic Amplifiers
Battery-Powered Systems
Quad Operational Amplifier
OP497
PIN CONNECTIONS
16-Lead Wide Body SOIC
(S-Suffix)
OUT D
1
OUT A
–IN A
2
+
–
3
+IN A
V+
4
OP497
5
+IN B
–IN B
OUT B
NC
–
+
6
7
8
NC = NO CONNECT
14-Lead Plastic Dip
(P-Suffix)
14-Lead Ceramic Dip
(Y-Suffix)
16
–IN D
15
+
–
+IN D
14
V–
13
+IN C
12
–
+
11
10
9
–IN C
OUT C
NC
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
The OP497 is a quad op amp with precision performance in the
space-saving, industry standard 16-lead SOlC package. Its combination of exceptional precision with low power and extremely
low input bias current makes the quad OP497 useful in a wide
variety of applications.
Precision performance of the OP497 includes very low offset,
under 50 µV, and low drift, below 0.5 µV/°C. Open-loop gain
exceeds 2000 V/mV ensuring high linearity in every application.
Errors due to common-mode signals are eliminated by the OP497’s
common-mode rejection of over 120 dB. The OP497’s power
supply rejection of over 120 dB minimizes offset voltage changes
experienced in battery-powered systems. Supply current of the
OP497 is under 625 µA per amplifier, and it can operate with
supply voltages as low as ±2 V.
The OP497 utilizes a superbeta input stage with bias current cancellation to maintain picoamp bias currents at all temperatures.
This is in contrast to FET input op amps whose bias currents start
in the picoamp range at 25°C, but double for every 10°C rise in
temperature, to reach the nanoamp range above 85°C. Input bias
current of the OP497 is under 100 pA at 25°C and is under 450
pA over the military temperature range.
Combining precision, low power, and low bias current, the
OP497 is ideal for a number of applications, including instrumentation amplifiers, log amplifiers, photo-diode preamplifiers,
and long-term integrators. For a single device, see the OP97; for a
dual device, see the OP297.
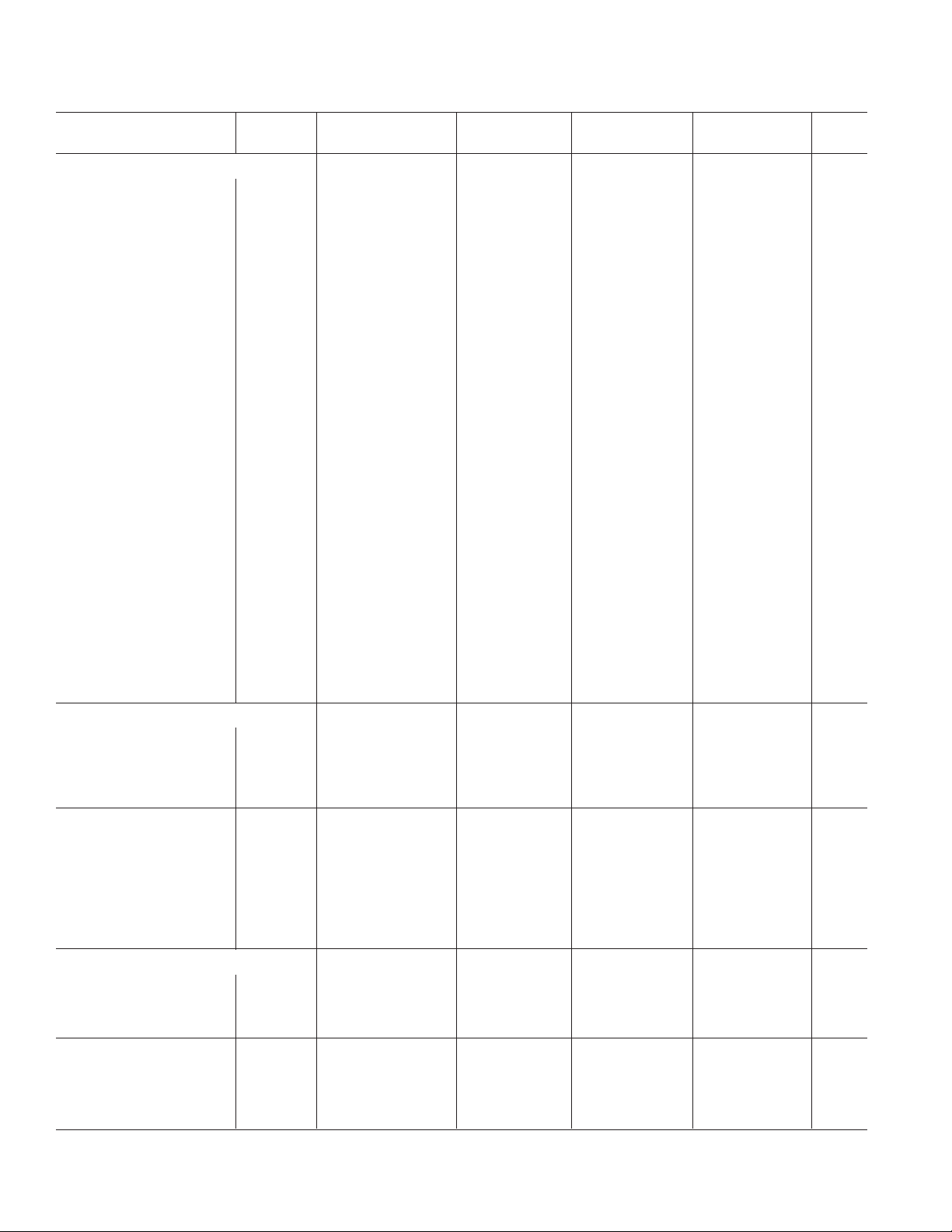
OUT A
1
–IN A
2
+–+
+IN A
V+
+IN B
–IN B
OUT B
1000
100
INPUT CURRENT – PA
10
–75 –50 –25 0 25 50 75 100 125
–
3
4
OP497
5
–
+–+
6
7
TEMPERATURE – C
OUT D
14
–IN D
13
+IN D
12
V–
11
+IN C
10
–IN C
9
OUT C
8
VS = ⴞ15V
V
CM
–I
B
+I
B
I
OS
Input Bias, Offset Current vs. Temperature
= 0V
REV. D
Information furnished by Analog Devices is believed to be accurate and
reliable. However, no responsibility is assumed by Analog Devices for its
use, nor for any infringements of patents or other rights of third parties that
may result from its use. No license is granted by implication or otherwise
under any patent or patent rights of Analog Devices.
One Technology Way, P.O. Box 9106, Norwood, MA 02062-9106, U.S.A.
Tel: 781/329-4700 www.analog.com
Fax: 781/326-8703 © Analog Devices, Inc., 2002
OP497–SPECIFICATIONS
(@ VS = 15 V, TA = 25ⴗC, unless otherwise noted.)
A F C/G
Parameter Symbol Condition Min Typ Max Min Typ Max Min Typ Max Unit
INPUT CHARACTERISTICS
Offset Voltage Vos 20 50 40 75 80 150 µV
–40°C ≤ +85°C 70 150 120 250
–55°C ≤ +125°C 40 100 80 150 140 300
Average Input Offset
Voltage Drift TCV
OS
T
MIN
– T
MAX
0.2 0.5 0.4 1.0 0.6 1.5 µV/°C
Long-Term Input Offset
Voltage Stability 0.1 0.1 0.1 µV/Mo
Input Bias Current I
B
VCM = 0 V 30 100 40 150 60 200 pA
–40° ≤ T
–55° ≤ T
≤ +85°C 60 200 80 300
A
≤ +125°C 80 450 110 600 130 600
A
Average Input Bias
Current Drift TC
IB
Input Offset Current Ios V
–40° ≤ TA ≤ +85°C 0.3 0.3
–55° ≤ T
CM
–40° ≤ T
–55° ≤ T
≤ +125°C 0.5 0.7 0.7 pA/°C
A
= OV 15 100 30 150 50 200 pA
≤ +85°C 50 200 80 300
A
≤ +125°C 35 400 60 600 90 600
A
Average Input Offset
Current Drift T
Input Voltage Range
1
CIOS
IVR + 13 +14 +13 tl4 +13 +14 V
Common-Mode Rejection CMR V
Large Signal Voltage Gain A
VO
T
– T
MIN
MAX
= ±13 V 120 140 114 135 114 135 dB
CM
T
– T
MIN
MAX
VO = ±10 V,
R
= 2 kΩ 2000 6000 1500 4000 1200 4000 V/mV
L
–40° ≤ T
–55° ≤ T
≤ +85°C 800 2000 800 2000
A
≤ +125°C 1200 4000 1000 3000 800 3000
A
0.2 0.3 0.4 pA/°C
+13 +13.5 +13 +13.5 +13 +13.5
114 130 108 120 108 120
Input Resistance
Differential Mode R
IN
30 30 30 MΩ
Input Resistance
Common Mode R
Input Capacitance C
INCM
IN
500 500 500 GΩ
33 3pF
OUTPUT CHARACTERISTICS
Output Voltage Swing V
O
RL = 2 kΩ±13 ±13.7 ±13 ± 13.7 ± 13 ± 13.7 V
R
= 10 kΩ± 13 ±14 ±13 ± 14 ±13 ±14
L
T
– T
MIN
MAX
RL = 10 kΩ±13 ±13.5 ±13 ± 13.5 ± 13 ± 13.5
Short Circuit I
SC
±25 ±25 ±25 mA
POWER SUPPLY
Power Supply PSRR Vs = ±2 V to ± 20 V 120 140 114 135 114 135 dB
Rejection Ratio Vs = ±2.5 V to ±20 V
T
Supply Current I
SY
(per Amplifier) T
Supply Voltage Range V
S
– T
MIN
MAX
No Load 525 625 525 625 525 625 µA
– T
MIN
MAX
Operating Range ±2 ±20 ±2 ±20 ±2 ± 20 V
T
– T
MIN
MAX
114 130 108 120 108 120
580 750 580 750 580 750
±2.5 ± 20 ±2.5 ±20 ±2.5 ± 20
DYNAMIC PERFORMANCE
Slew Rate SR 0.05 0.15 0.05 0.15 0.05 0.15 V/µS
Gain Bandwidth Product GBW 500 500 500 kHz
Channel Separation CS V
= 20 V
O
p-p,
fo = 10 Hz 150 150 150 dB
NOISE PERFORMANCE
Voltage Noise e
Voltage Noise Density e
n p-p
= 10 Hz 17 17 17 nV/√Hz
n
e
= 1 kHz 15 15 15 nV/√Hz
n
0.1 Hz to 10 Hz 0.3 0.3 0.3 µV/p-p
Current Noise Density in = 10 Hz 20 20 20 fA/√Hz
NOTE
1Guaranteed by CMR Test.
Specifications subject to change without notice.
–2–
REV. D
OP497
WARNING!
ESD SENSITIVE DEVICE
ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATINGS
Supply Voltage . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . ±20 V
Input Voltage
Differential Input Voltage
2
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
2
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
1
20 V
40 V
Output Short-Circuit Duration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Indefinite
Storage Temperature Range
Y Package . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . –65°C to +175°C
P, S Package . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . –65°C to +150°C
Operating Temperature Range
OP497A, C (Y) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . –55°C to +125°C
OP497F, G (Y) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . –40°C to +85°C
OP497F, G (P, S) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . –40°C to +85°C
Junction Temperature
Y Package . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . –65°C to +175°C
P, S Package . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . –65°C to +150°C
Lead Temperature Range (Soldering 60 sec) . . . . . . . . 300°C
Package Type
3
JA
JC
Unit
14-Pin Cerdip (Y) 94 10 °C/W
14-Pin Plastic DIP (P) 76 33 °C/W
16-Pin SOIC (S) 92 23 °C/W
NOTES
1
Absolute Maximum Ratings apply to both DICE and packaged parts, unless
otherwise noted.
2
For supply voltages less than ± 20 V, the absolute maximum input voltage is
equal to the supply voltage.
3
HIA is specified for worst-case mounting conditions, i.e., JA is specified for
device in socket for cerdip, P-DIP packages; JA is specified for device soldered
to printed circuit board for SOIC package.
ORDERING GUIDE
Temperature Package Package
Model Range Description Option
OP497AY* –55°C to +125°C 14-Lead Cerdip Q-14
OP497CY* –55°C to +125°C 14-Lead Cerdip Q-14
OP497FP –40°C to +85°C 14-Lead Plastic DIP N-14
OP497FS –40°C to +85°C 16-Lead SOIC R-16
OP497GP –40°C to +85°C 14-Lead Plastic DIP N-14
OP497GS –40°C to +85°C 16-Lead SOIC R-16
*Not for new design; obsolete April 2002.
For a military processed devices, please refer to the Standard
Microcircuit Drawing (SMD) available at www.dscc.dla.mil/
programs.milspec./default.asp.
SMD Part Number ADI Part Number
5962–9452101M2A* OP497BRC
5962–9452101MCA OP497BY
*Not for new designs; obsolete April 2002.
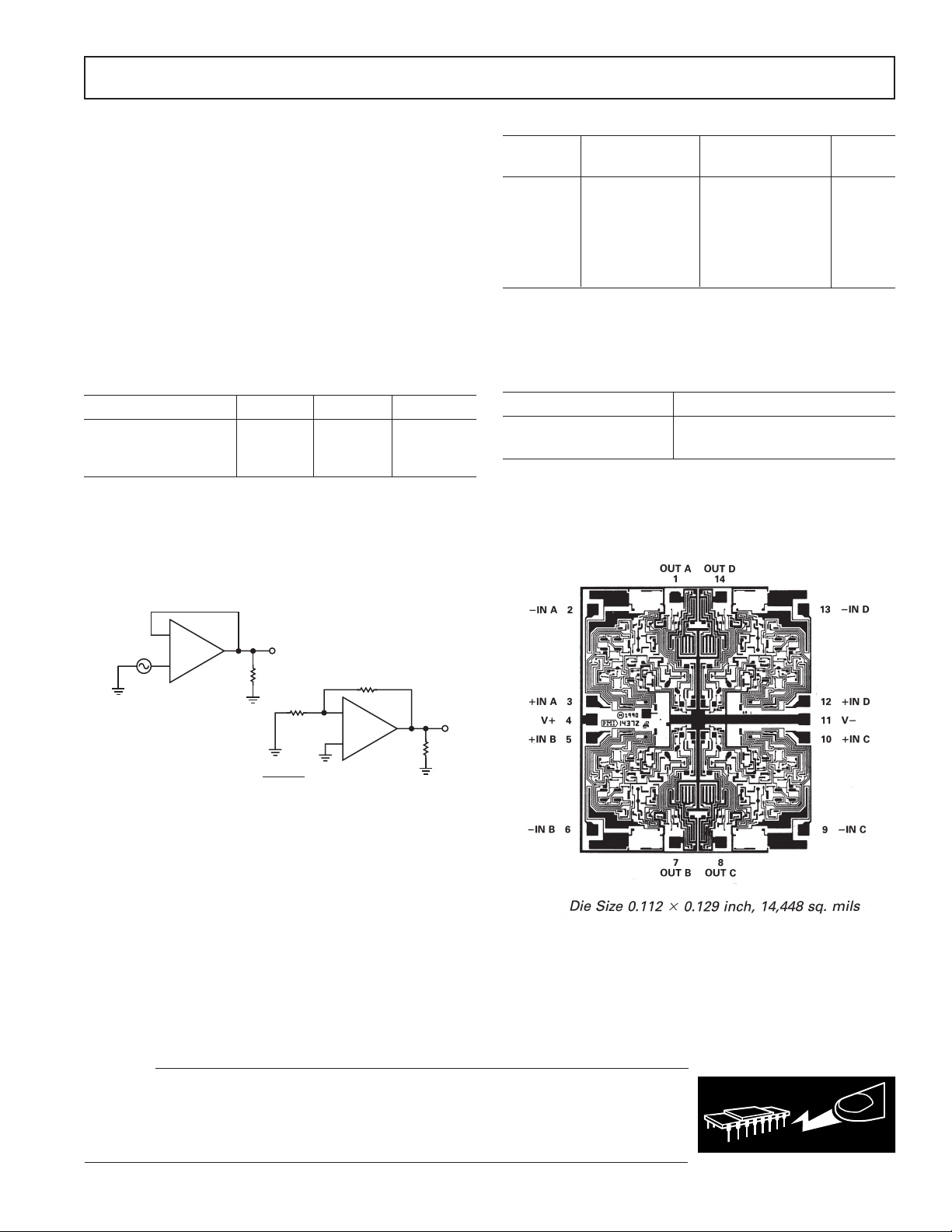
DICE CHARACTERISTICS
–
1/4
OP497
+
CHANNEL SEPARATION = 20 log
V
20V p–p @ 10Hz
1
2k⍀
50⍀
V
1
()
V /10000
2
50k⍀
–
1/4
OP497
+
V
2
Channel Separation Test Circuit
CAUTION
ESD (electrostatic discharge) sensitive device. Electrostatic charges as high as 4000 V readily
accumulate on the human body and test equipment and can discharge without detection. Although
the OP497 features proprietary ESD protection circuitry, permanent damage may occur on devices
subjected to high-energy electrostatic discharges. Therefore, proper ESD precautions are
recommended to avoid performance degradation or loss of functionality.
REV. D
–3–
OP497
–Typical Performance Characteristics
(25ⴗC, Vs = 15 V, unless otherwise noted.)
50
40
30
20
PERCENTAGE OF UNITS
10
0
–80
–100
–20–40–60
INPUT OFFSET VOLTAGE – V
TA = 25ⴗC
= 15V
V
S
V
CM
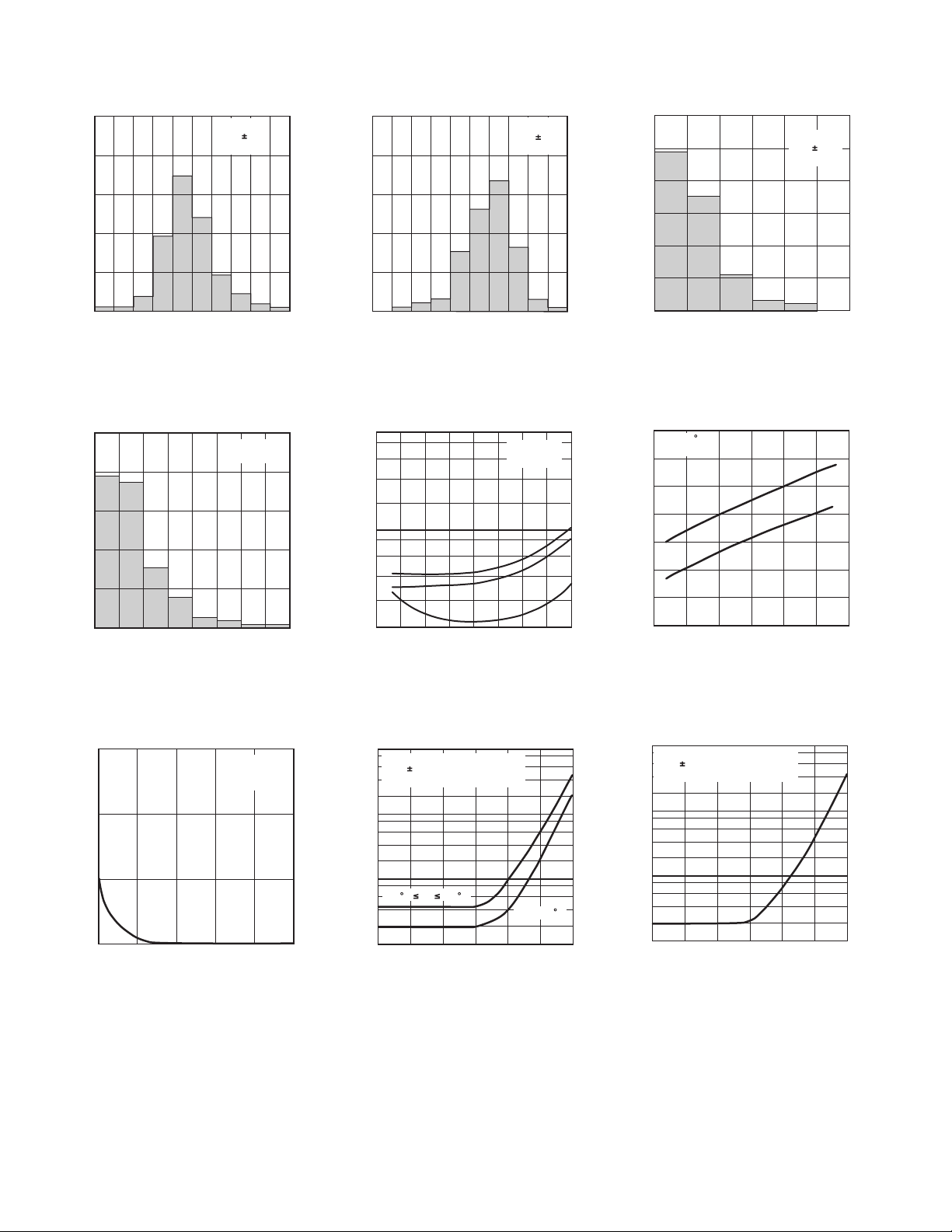
0
TPC 1. Typical Distribution of
Input Offset Voltage
50
40
30
20
PERCENTAGE OF UNITS
10
0
0
0.1
TCVOS – V/ⴗC
VS = ⴞ15V
V
TPC 4. Typical Distribution of
TCV
OS
CM
= 0V
= 0V
50
40
30
20
PERCENTAGE OF UNITS
10
100
80604020
0
–80
–100
INPUT BIAS CURRENT – pA
–20–40–60
TA = 25ⴗC
= 15V
V
S
= 0V
V
CM
0
100
80604020
TPC 2. Typical Distribution of
Input Bias Current
1000
VS = ⴞ15V
= 0V
V
CM
100
–I
INPUT CURRENT – pA
10
0.8
0.70.60.50.40.30.2
–75 –50 –25 0 25 50 75 100 125
B
+I
I
OS
TEMPERATURE – ⴗC
B
TPC 5. Input Bias, Offset
Current vs. Temperature
60
TA = 25ⴗC
50
40
30
20
PERCENTAGE OF UNITS
10
0
0
10
INPUT OFFSET CURRENT – pA
V
S
V
CM
TPC 3. Typical Distribution of
Input Offset Current
70
TA = 25 C
= ⴞ15V
V
S
60
50
40
30
20
INPUT BIAS CURRENT – pA
10
0
–10
–15
COMMON-MODE VOLTAGE – Volts
0
–5
TPC 6. Input Bias Current vs.
Common-Mode Voltage
= 15V
= 0V
50403020
105
60
–I
B
+I
B
15
ⴞ3
ⴞ2
ⴞ1
DEVIATION FROM FINAL VALUE – V
0
0
TIME AFTER POWER APPLIED – Minutes
TA = 25ⴗC
V
V
TPC 7. Input Offset Voltage
Warm-Up Drift
= ⴞ15V
S
= 0V
CM
10000
BALANCED OR UNBALANCED
= 15V
V
S
= 0V
V
CM
1000
100
–55 C T 125 C
A
EFFECTIVE OFFSET VOLTAGE – V
10
10
51
432
100
SOURCE RESISTANCE – ⍀
10k
1k
T = +25 C
100k
A
1M
10M
TPC 8. Effective Offset Voltage
vs. Source Resistance
–4–
100
BALANCED OR UNBALANCED
= 15V
V
S
= 0V
V
CM
10
1
EFFECTIVE OFFSET VOLTAGE – V/ ⴗC
0.1
100 1k 10k 100k
SOURCE RESISTANCE – ⍀
TPC 9. Effective TCVOS vs.
Source Resistance
1M 10M
100M
REV. D
 Loading...
Loading...