Analog Devices AD712JN, AD712CN, AD712BQ, AD712AQ, AD712TQ-883B Datasheet
...
Dual-Precision, Low-Cost,
a
FEATURES
Enhanced Replacement for LF412 and TL082
AC PERFORMANCE
Settles to 0.01% in 1.0 s
16 V/s Min Slew Rate (AD712J)
3 MHz Min Unity Gain Bandwidth (AD712J)
DC PERFORMANCE
0.30 mV Max Offset Voltage: (AD712C)
5 V/C Max Drift: (AD712C)
200 V/mV Min Open-Loop Gain (AD712K)
4 V p-p Max Noise, 0.1 Hz to 10 Hz (AD712C)
Surface Mount Available in Tape and Reel in
Accordance with EIA-481A Standard
MIL-STD-883B Parts Available
Single Version Available: AD711
Quad Version: AD713
Available in Plastic Mini-DIP, Plastic SOIC, and
Hermetic CERDIP
PRODUCT DESCRIPTION
The AD712 is a high-speed, precision monolithic operational
amplifier offering high performance at very modest prices. Its
very low offset voltage and offset voltage drift are the results of
advanced laser wafer trimming technology. These performance
benefits allow the user to easily upgrade existing designs that use
older precision BiFETs and, in many cases, bipolar op amps.
The superior ac and dc performance of this op amp makes it
suitable for active filter applications. With a slew rate of 16 V/ms
and a settling time of 1 ms to ± 0.01%, the AD712 is ideal as a
buffer for 12-bit D/A and A/D converters and as a high-speed
integrator. The settling time is unmatched by any similar IC
amplifier.
The combination of excellent noise performance and low input
current also make the AD712 useful for photo diode preamps.
Common-mode rejection of 88 dB and open loop gain of
400 V/mV ensure 12-bit performance even in high-speed unity
gain buffer circuits.
The AD712 is pinned out in a standard op amp configuration
and is available in seven performance grades. The AD712J and
AD712K are rated over the commercial temperature range of
0∞C to 70∞C. The AD712A, AD712B, and AD712C are rated
over the industrial temperature range of –40∞C to +85∞C. The
AD712S and AD712T are rated over the military temperature
range of –55∞C to +125∞C and are available processed to MILSTD-883-B, Rev. C.
Extended reliability PLUS screening is available, specified over
the commercial and industrial temperature ranges. PLUS
High-Speed, BiFET Op Amp
AD712
CONNECTION DIAGRAMS
Plastic Mini-DIP (N) Package
SOIC (R) Package and CERDIP (Q) Package
AMPLIFIER NO. 2AMPLIFIER NO. 1
OUTPUT
INVERTING
OUTPUT
NONINVERTING
OUTPUT
1
2
3
V–
4
AD712
screening includes 168-hour burn-in, as well as other environmental and physical tests.
The AD712 is available in an 8-lead plastic mini-DIP, SOIC,
and CERDIP.
PRODUCT HIGHLIGHTS
1. The AD712 offers excellent overall performance at very
competitive prices.
2. Analog Devices’ advanced processing technology and 100%
testing guarantee a low input offset voltage (0.3 mV max,
C grade, 3 mV max, J grade). Input offset voltage is specified
in the warmed-up condition. Analog Devices’ laser wafer drift
trimming process reduces input offset voltage drifts to 5 mV/∞C
max on the AD712C.
3. Along with precision dc performance, the AD712 offers
excellent dynamic response. It settles to ±0.01% in 1 ms and
has a minimum slew rate of 16 V/ms. Thus this device is ideal
for applications such as DAC and ADC buffers which require a
combination of superior ac and dc performance.
4. The AD712 has a guaranteed and tested maximum voltage
noise of 4 mV p-p, 0.1 Hz to 10 Hz (AD712C).
5. Analog Devices’ well-matched, ion-implanted JFETs ensure
a guaranteed input bias current (at either input) of 50 pA
max (AD712C) and an input offset current of 10 pA max
(AD712C). Both input bias current and input offset current
are guaranteed in the warmed-up condition.
8
V+
OUTPUT
7
INVERTING
6
INPUT
NONINVERTING
5
INPUT
REV. E
Information furnished by Analog Devices is believed to be accurate and
reliable. However, no responsibility is assumed by Analog Devices for its
use, nor for any infringements of patents or other rights of third parties that
may result from its use. No license is granted by implication or otherwise
under any patent or patent rights of Analog Devices.
One Technology Way, P.O. Box 9106, Norwood, MA 02062-9106, U.S.A.
Tel: 781/329-4700 www.analog.com
Fax: 781/326-8703 © Analog Devices, Inc., 2002
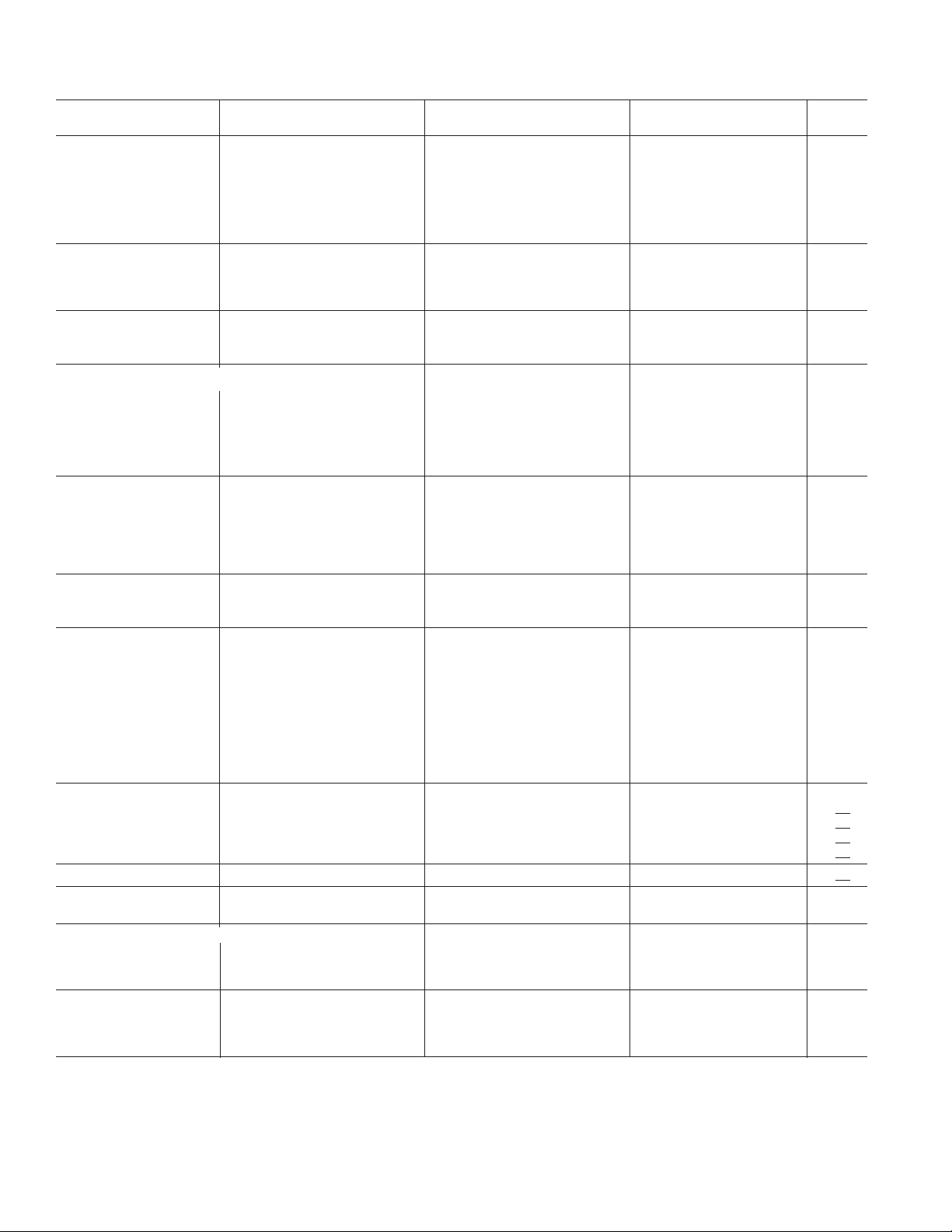
AD712–SPECIFICATIONS
(VS = 15 V @ TA = 25C unless otherwise noted.)
Parameter Min Typ Max Min Typ Max Min Typ Max Unit
AD712J/A/S AD712K/B/T AD712C
INPUT OFFSET VOLTAGE
1
Initial Offset 0.3 3/1/1 0.2 1.0/0.7/0.7 0.1 0.3 mV
to T
T
MIN
MAX
4/2/2 2.0/1.5/1.5 0.6 mV
vs. Temp 7 20/20/20 7 10 3 5 mV/∞C
vs. Supply 76 95 80 100 86 110 dB
to T
T
MIN
MAX
76/76/76 80 86 dB
Long-Term Offset Stability 15 15 15 mV/Month
INPUT BIAS CURRENT
2
VCM = 0 V 25 75 20 75 20 50 pA
= 0 V @ T
V
CM
MAX
0.6/1.6/26 1.7/4.8/77 0.5/1.3/20 1.7/4.8/77 1.3 3.2 nA
VCM = ±10 V 100 100 75 pA
INPUT OFFSET CURRENT
V
= 0 V 10 25 5 25 5 10 pA
CM
VCM = 0 V @ T
MAX
0.3/0.7/11 0.6/1.6/26 0.1/0.3/5 0.6/1.6/26 0.3 0.7 nA
MATCHING CHARACTERISTICS
Input Offset Voltage 3/1/1 1.0/0.7/0.7 0.3 mV
to T
T
MIN
MAX
4/2/2 2.0/1.5/1.5 0.6 mV
Input Offset Voltage Drift 20/20/20 10 5 mV/∞C
Input Bias Current 25 25 10 pA
Crosstalk @ f = 1 kHz 120 120 120 dB
@ f = 100 kHz 90 90 90 dB
FREQUENCY RESPONSE
Small Signal Bandwidth 3.0 4.0 3.4 4.0 3.4 4.0 MHz
Full Power Response 200 200 200 kHz
Slew Rate 16 20 18 20 18 20 V/ms
Settling Time to 0.01% 1.0 1.2 1.0 1.2 1.0 1.2 ms
Total Harmonic Distortion 0.0003 0.0003 0.0003 %
INPUT IMPEDANCE
Differential 3 ¥ 10
12
5.5 3 ¥ 10125.5 3 ¥ 10125.5 WpF
Common Mode 3 ¥ 10125.5 3 ¥ 10125.5 3 ¥ 10125.5 WpF
INPUT VOLTAGE RANGE
Differential
Common-Mode Voltage
3
to T
T
MIN
MAX
4
–VS + 4 +VS – 2 –VS + 4 +VS – 2 –VS + 4 +VS – 2 V
±20 ± 20 ± 20 V
+14.5, –11.5 +14.5, –11.5 +14.5, –11.5
Common-Mode
Rejection Ratio
= ±10 V 76 88 80 88 86 94 dB
V
CM
to T
T
MIN
MAX
= ±11 V 70 84 76 84 76 90 dB
V
CM
T
to T
MIN
MAX
76/76/76 84 80 84 86 90 dB
70/70/70 80 74 80 74 84 dB
INPUT VOLTAGE NOISE 2 2 2 mV p-p
45 45 45 nV/÷
22 22 22 nV/÷
18 18 18 nV/÷
Hz
Hz
Hz
16 16 16 nV/÷Hz
INPUT CURRENT NOISE 0.01 0.01 0.01 pA/÷Hz
OPEN-LOOP GAIN 150 400 200 400 200 400 V/mV
100/100/100 100 100 V/mV
OUTPUT CHARACTERISTICS
Voltage +13, –12.5 +13.9, –13.3 +13, –12.5 +13.9, –13.3 +13, –12.5 +13.9, –13.3 V
±12/± 12/12 +13.8, –13.1 12 +13.8, –13.1 12 +13.8, –13.1 V
Current 25 25 25 mA
POWER SUPPLY
Rated Performance ±15 ± 15 ± 15 V
Operating Range 4.5 18 4.5 18 4.5 18 V
Quiescent Current 5.0 6.8 5.0 6.0 5.0 5.6 mA
NOTES
1
Input Offset Voltage specifications are guaranteed after 5 minutes of operation at TA = 25∞C.
2
Bias Current specifications are guaranteed maximum at either input after 5 minutes of operation at TA = 25∞C. For higher temperatures, the current doubles every 10∞C.
3
Defined as voltage between inputs, such that neither exceeds ± 10 V from ground.
4
Typically exceeding –14.1 V negative common-mode voltage on either input results in an output phase reversal.
Specifications in boldface are tested on all production units at final electrical test. Results from those tests are used to calculate outgoing quality levels. All min and max
specifications are guaranteed, although only those shown in boldface are tested on all production units.
Specifications subject to change without notice.
–2–
REV. E
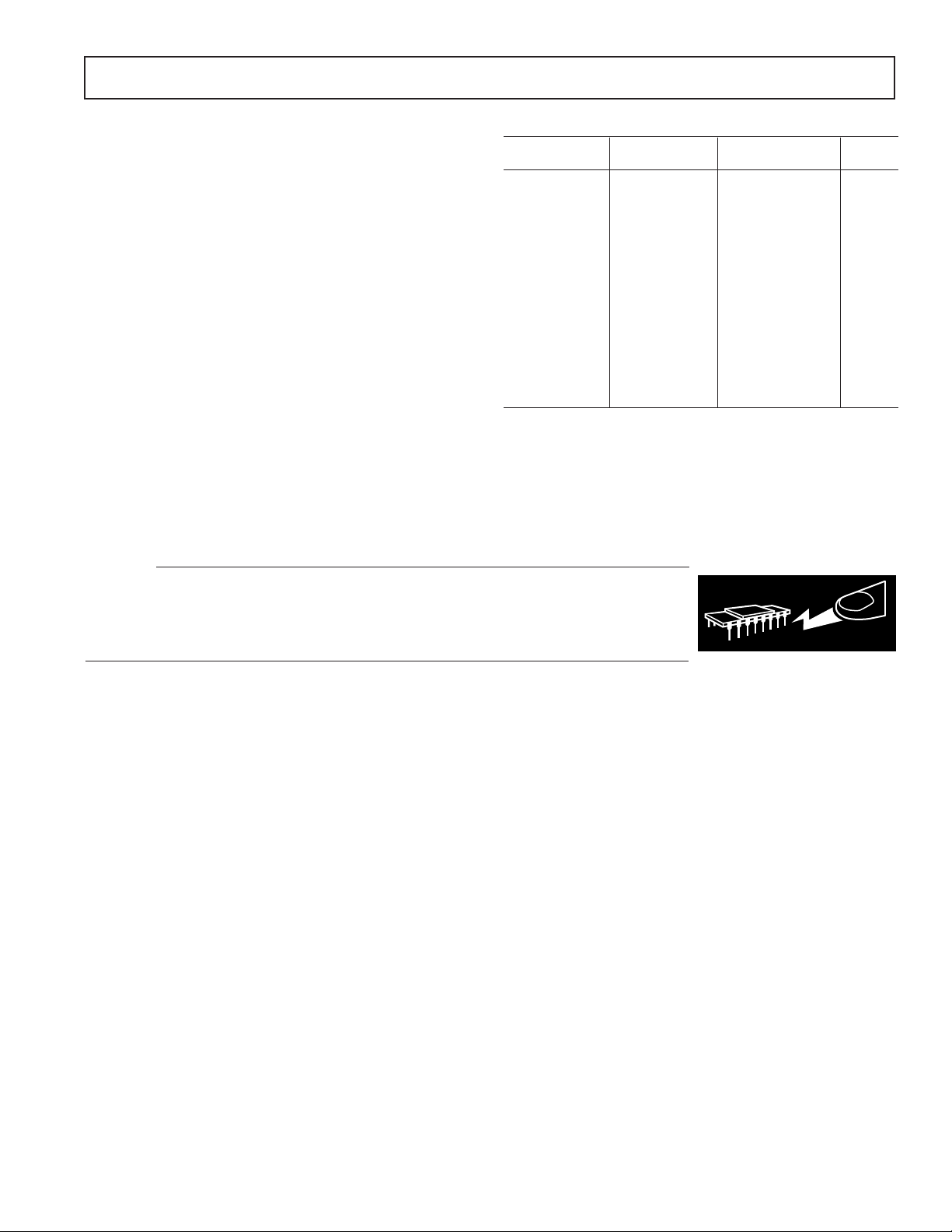
AD712
WARNING!
ESD SENSITIVE DEVICE
ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATINGS
Supply Voltage . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . ± 18 V
Internal Power Dissipation
2
Input Voltage3 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . ±18 V
Output Short Circuit Duration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Indefinite
Differential Input Voltage . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . +V
Storage Temperature Range (Q) . . . . . . . . . . –65∞C to +150∞C
Storage Temperature Range (N, R) . . . . . . . .–65∞C to +125∞C
Operating Temperature Range
AD712J/K . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 0∞C to 70∞C
AD712A/B/C . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . –40∞C to +85∞C
AD712S/T . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . –55∞C to +125∞C
Lead Temperature Range (Soldering 60 sec) . . . . . . . . . 300∞C
NOTES
1
Stresses above those listed under Absolute Maximum Ratings may cause perma-
nent damage to the device. This is a stress rating only; functional operation of the
device at these or any other conditions above those indicated in the operational
section of this specification is not implied. Exposure to absolute maximum rating
conditions for extended periods may affect device reliability.
2
Thermal Characteristics:
8-Lead Plastic Package: qJA = 165∞C/W
8-Lead Cerdip Package: qJC = 22∞C/W; qJA = 110∞C/W
8-Lead SOIC Package: qJA = 100∞C
3
For supply voltages less than ± 18 V, the absolute maximum input voltage is equal
to the supply voltage.
1
Model Range Description Option
AD712AQ –40∞ C to +85∞C 8-Lead Ceramic DIP Q-8
and –V
S
AD712BQ* –40∞C to +85∞C 8-Lead Ceramic DIP Q-8
S
AD712CN* –40∞C to +85∞C 8-Lead Plastic DIP N-8
AD712JN 0∞C to 70∞C 8-Lead Plastic DIP N-8
AD712JR 0∞C to 70∞C 8-Lead Plastic SOIC R-8
AD712JR-REEL 0∞C to 70∞ C 8-Lead Plastic SOIC R-8
AD712JR-REEL7 0∞C to 70∞C 8-Lead Plastic SOIC R-8
AD712KN 0∞C to 70∞C 8-Lead Plastic DIP N-8
AD712KR 0∞C to 70∞C 8-Lead Plastic SOIC R-8
AD712KR-REEL 0∞C to 70∞C 8-Lead Plastic SOIC R-8
AD712KR-REEL7 0∞C to 70∞C 8-Lead Plastic SOIC R-8
AD712SQ* –55∞C to +125∞C 8-Lead Ceramic DIP Q-8
AD712SQ/883B –55∞C to +125∞C 8-Lead Ceramic DIP Q-8
AD712TQ* –55∞C to +125∞C 8-Lead Ceramic DIP Q-8
AD712TQ/883B* –55∞C to +125∞C 8-Lead Ceramic DIP Q-8
*
Not for new design, obsolete April 2002.
ORDERING GUIDE
Temperature Package Package
CAUTION
ESD (electrostatic discharge) sensitive device. Electrostatic charges as high as 4000 V readily
accumulate on the human body and test equipment and can discharge without detection. Although
the AD712 features proprietary ESD protection circuitry, permanent damage may occur on devices
subjected to high-energy electrostatic discharges. Therefore, proper ESD precautions are
recommended to avoid performance degradation or loss of functionality.
REV. E
–3–
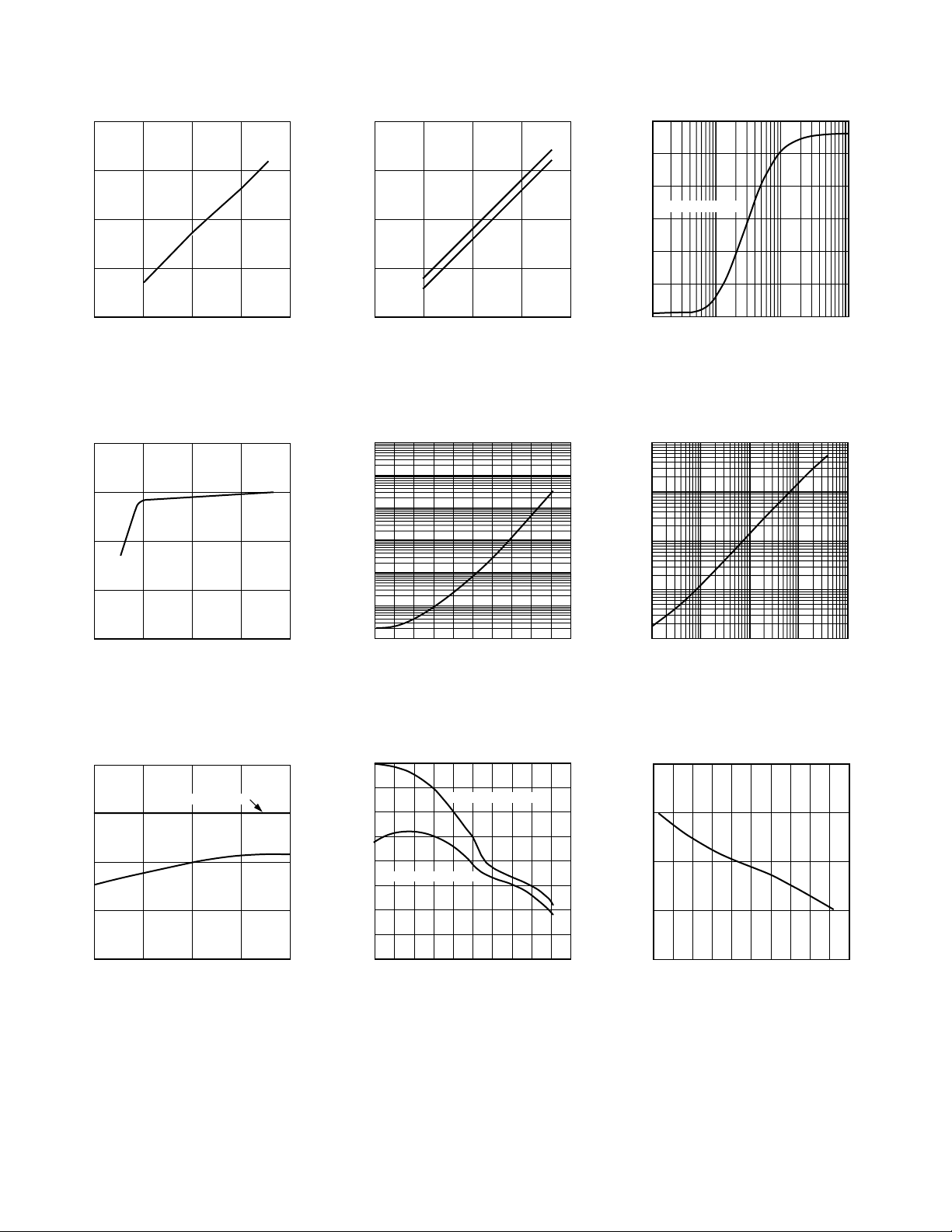
AD712
–Typical Performance Characteristics
20
15
10
R
= 2k
L
25C
5
INPUT VOLTAGE SWING – V
0
0
520
SUPPLY VOLTAGE V
10 15
TPC 1. Input Voltage Swing vs.
Supply Voltage
6
5
4
3
QUIESCENT CURRENT – mA
2
0
520
SUPPLY VOLTAGE V
10 15
TPC 4. Quiescent Current vs.
Supply Voltage
20
15
10
5
OUTPUT VOLTAGE SWING – V
0
0
520
SUPPLY VOLTAGE V
+V
OUT
–V
OUT
R
= 2k
L
25C
10 15
TPC 2. Output Voltage Swing vs.
Supply Voltage
6
10
7
10
= 0) – Amps
8
10
CM
9
10
10
10
11
10
INPUT BIAS CURRENT (V
12
10
–60
0
TEMPERATURE – C
TPC 5. Input Bias Current vs.
Temperature
30
25
20
15V SUPPLIES
15
10
5
OUTPUT VOLTAGE SWING – V p–p
0
10 100 10k1k
LOAD RESISTANCE –
TPC 3. Output Voltage Swing vs.
Load Resistance
100
10
1.0
0.1
OUTPUT IMPEDANCE –
140–40 –40 20 12040 60 80 100
0.01
1k
10k 100k 1M 10M
FREQUENCY – Hz
TPC 6. Output Impedance vs.
Frequency
100
75
50
25
INPUT BIAS CURRENT – pA
0
–10
MAX J GRADE LIMIT
V
= 15V
S
25C
–5 1005
COMMON MODE VOLTAGE – V
TPC 7. Input Bias Current vs.
Common Mode Voltage
26
24
22
20
18
– OUTPUT CURRENT
16
14
12
SHORT CIRCUIT CURRENT LIMIT – mA
10
–40 –20 0 20 40 60 80 100 120 140
–60
AMBIENT TEMPERATURE – C
+ OUTPUT CURRENT
TPC 8. Short Circuit Current Limit
vs. Temperature
–4–
5.0
4.5
4.0
3.5
UNITY GAIN BANDWIDTH – MHz
3.0
–60 –40 –20 0 20 40 60 80 100 120 140
TEMPERATURE – C
TPC 9. Unity Gain Bandwidth vs.
Temperature
REV. E
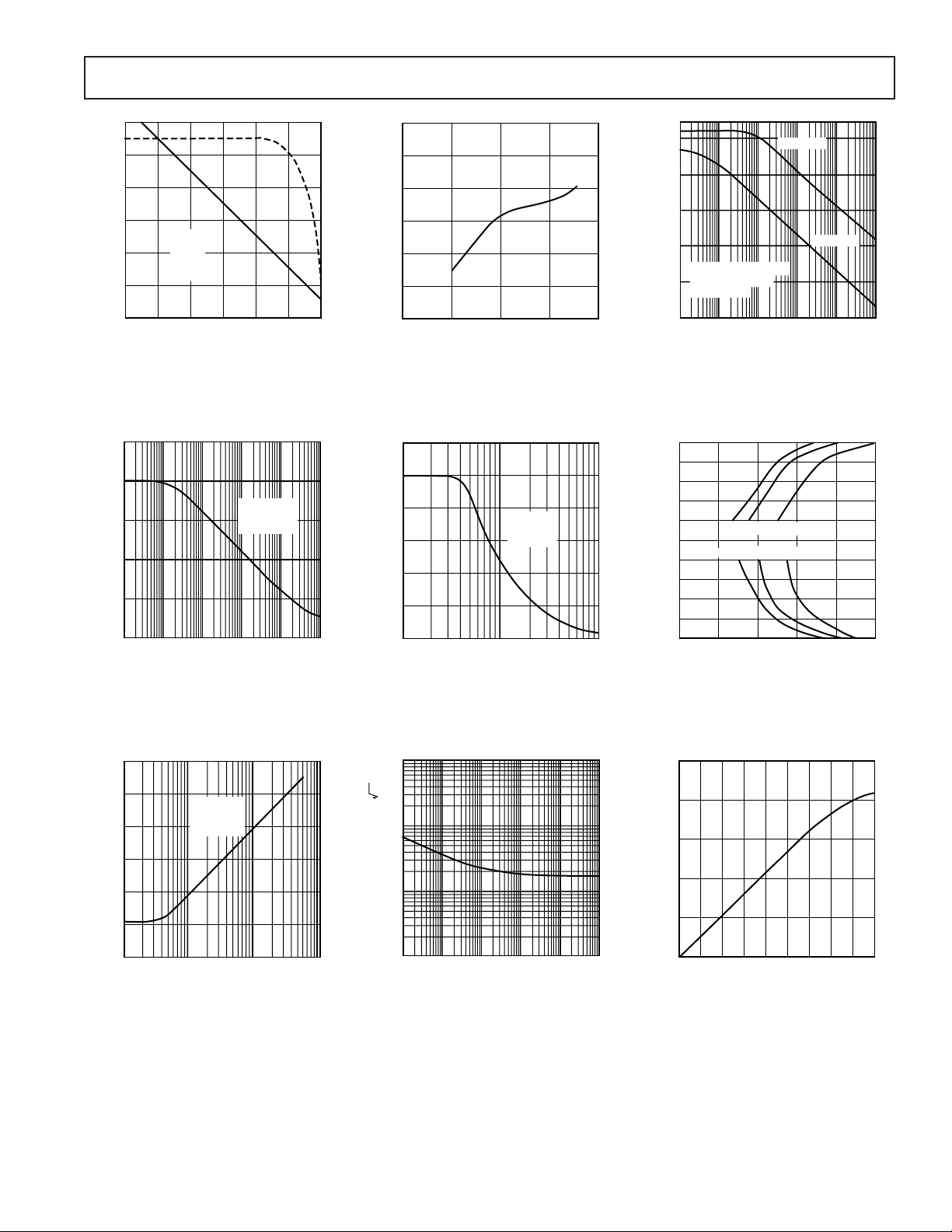
AD712
(
)
100
80
60
40
20
OPEN LOOP GAIN – dB
0
–20
GAIN
PHASE
2k
100pF
LOAD
100 1k 1M10 10k 100k 10M
FREQUENCY – Hz
TPC 10. Open-Loop Gain and
Phase Margin vs. Frequency
100
80
VS = 15V
= 1Vp-p
V
60
CMR – dB
40
20
0
10
100 1k 10k 100k 1M
FREQUENCY – Hz
CM
25C
TPC 13. Common Mode
Rejection vs. Frequency
100
80
60
40
20
0
–20
125
120
115
110
105
PHASE MARGIN – C
OPEN LOOP GAIN – dB
100
95
0
R
= 2k
L
25C
520
SUPPLY VOLTAGE V
10 15
TPC 11. Open-Loop Gain vs. Supply Voltage
30
25
20
15
10
5
OUTPUT VOLTAGE – Volts p–p
0
100k 10M1M
INPUT FREQUENCY – Hz
RL = 2k
25C
V
= 15V
S
TPC 14. Large Signal Frequency
Response
110
100
80
60
40
VS = 15V SUPPLIES
WITH 1V p-p SINE
20
WAVE 25C
POWER SUPPLY REJECTION – dB
0
10
100 1k 10k 100k 1M
SUPPLY MODULATION FREQUENCY – Hz
+ SUPPLY
– SUPPLY
TPC 12. Power Supply Rejection
vs. Frequency
10
8
6
4
2
0
–2
–4
–6
–8
OUTPUT SWING FROM 0V TO VOLTS
–10
0.5
0.1%1%
0.1%1%ERROR
0.7
0.6
SETTLING TIME – s
0.01%
0.01%
0.8 0.9 1.0
TPC 15. Output Swing and Error
vs. Settling Time
–70
–80
–90
–100
THD – dB
–110
–120
–130
100 10k1k
3V RMS
R
L
C
L
FREQUENCY – Hz
TPC 16. Total Harmonic
Distortion vs. Frequency
REV. E
= 2k
= 100pF
100k
1k
Hz
100
10
INPUT NOISE VOLTAGE – nV/
1
FREQUENCY – Hz
1k
TPC 17. Input Noise Voltage
Spectral Density
–5–
25
20
15
10
SLEW RATE – V/s
5
10k 100k100101
0
100
200 300 400 500 600 700 800 9000
INPUT ERROR SIGNAL – mV
AT SUMMING JUNCTION
TPC 18. Slew Rate vs. Input
Error Signal
 Loading...
Loading...