Page 1

Cyclone III LS FPGA Development Kit
User Guide
101 Innovation Drive
San Jose, CA 95134
www.altera.com
Document Version: 1.0
Document Date: October 2009
Page 2

Copyright © 2009 Altera Corporation. All rights reserved. Altera, The Programmable Solutions Company, the stylized Altera logo, specific device designations, and all other
words and logos that are identified as trademarks and/or service marks are, unless noted otherwise, the trademarks and service marks of Altera Corporation in the U.S. and other
countries. All other product or service names are the property of their respective holders. Altera products are protected under numerous U.S. and foreign patents and pending applications, maskwork rights, and copyrights. Altera warrants performance of its semiconductor products to current specifications in accordance with Altera's standard warranty,
but reserves the right to make changes to any products and services at any time without notice. Altera assumes no responsibility or liability arising out of the application or use of
any information, product, or service described herein except as expressly agreed to in writing by Altera Corporation. Altera customers are advised to obtain the latest version of
device specifications before relying on any published information and before placing orders for products or services
.
UG-01071-1.0
Page 3

Contents
Chapter 1. About This Kit
Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1–1
Kit Features . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1–1
Hardware . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1–1
Software . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1–1
Chapter 2. Getting Started
Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2–1
Before You Begin . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2–1
Inspect the Board . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2–1
References . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2–1
Chapter 3. Software Installation
Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3–1
Installing the Altera Complete Design Suite . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3–1
Licensing Considerations . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3–1
Installing the Cyclone III LS FPGA Development Kit . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3–2
Installing the USB-Blaster Driver . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3–2
Chapter 4. Development Board Setup
Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4–1
Setting Up the Board . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4–1
Factory Default Switch Settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4–2
Chapter 5. Board Update Portal
Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5–1
Connecting to the Board Update Portal Web Page . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5–1
Using the Board Update Portal to Update User Designs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5–2
Chapter 6. Board Test System
Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6–1
Preparing the Board . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6–3
Running the Board Test System . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6–3
October 2009 Altera Corporation Cyclone III LS FPGA Development Kit User Guide
Page 4

iv
Using the Board Test System . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6–3
The Configure Menu . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6–4
The Config Tab . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6–4
MAX-II Registers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6–4
JTAG Chain . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6–6
Board Information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6–6
Flash Memory Map . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6–6
The GPIO Tab . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6–6
Character LCD . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6–7
User Dip Switch . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6–7
User LEDs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6–7
Pushbutton Switches . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6–8
The SRAM&Flash Tab . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6–8
SRAM . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6–8
Flash . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6–9
The DDR2 Tab . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6–9
Port . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6–10
Start . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6–10
Stop . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6–10
Performance Indicators . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6–10
Error Control . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6–11
Number of addresses to write / read . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6–11
Data Type . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6–11
Read/Write control . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6–11
The HSMC Tab . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6–11
Status . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6–12
Data Type . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6–13
Error Control . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6–13
Start . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6–13
Stop . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6–13
Performance Indicators . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6–13
The Power Monitor . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6–13
MAX II Information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6–14
Power Information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6–15
Power Graph . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6–15
Graph Settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6–15
Reset . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6–15
Calculating Power . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6–15
Configuring the FPGA Using the Quartus II Programmer . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6–16
Appendix A. Programming the Flash Memory Device
Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . A–1
CFI Flash Memory Map . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . A–1
Preparing Design Files for Flash Programming . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . A–2
Creating Flash Files Using the Nios II EDS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . A–2
Programming Flash Memory Using the Board Update Portal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . A–3
Programming Flash Memory Using the Nios II EDS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . A–3
Restoring the Flash Device to the Factory Settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . A–4
Restoring the MAX II CPLD to the Factory Settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . A–5
Additional Information
Revision History . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Info–1
How to Contact Altera . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Info–1
Cyclone III LS FPGA Development Kit User Guide October 2009 Altera Corporation
Page 5

Typographic Conventions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Info–1
v
October 2009 Altera Corporation Cyclone III LS FPGA Development Kit User Guide
Page 6

vi
Cyclone III LS FPGA Development Kit User Guide October 2009 Altera Corporation
Page 7

Introduction
Kit Features
1. About This Kit
The Altera® Cyclone® III LS FPGA Development Kit is a complete design
environment that includes both the hardware and software you need to develop
Cyclone III LS FPGA designs. The board and the one-year license for
software provide everything you need to begin developing custom Cyclone III LS
FPGA designs. The following list describes what you can accomplish with the
dev
elopment kit:
Develop and test memory subsystems consisting of DDR2 memory
Take advantage of the modular and scalable design by using the high-speed
mezzanine card (HSMC) connectors to interface to over 20 different HSMCs
provided by Altera partners
the Quartus® II
This section briefly describes the Cyclone III LS FPGA Development Kit contents.
Hardware
Cyclone III LS FPGA development board—A development platform that allows
you to develop and prototype hardware designs running on the Cyclone III LS
EP3CLS200 FPGA.
For detailed information about the board components and interfaces, refer to the
Cyclone III LS FPGA Development Board Reference Manual.
Power supply and cables—The development kit includes the following items:
Power supply and AC adapters for North America/Japan, Europe, and the
United Kingdom
USB cable
Ethernet cable
Software
Altera Complete Design Suite DVD—A DVD that includes the following items:
Quartus II Software—The Quartus II software, including the SOPC Builder
system development tool, provides a comprehensive environment for
system-on-a-programmable-chip (SOPC) design. The Quartus II software
integrates into nearly any design environment and provides interfaces to
industry-standard EDA tools.
© October 2009 Altera Corporation Cyclone III LS FPGA Development Kit User Guide
Page 8

1–2 Chapter 1: About This Kit
Kit Features
f The kit includes a development kit edition (DKE) license for the Quartus II
software (Windows platform only). This license entitles you to all the
features of the subscription edition for a period of one year. After the year,
you must purchase a renewal subscription to continue using the software.
For more information, refer to the Altera website (www.altera.com).
MegaCore
®
IP Library—A library that contains Altera IP MegaCore functions.
You can evaluate MegaCore functions by using the OpenCore Plus feature to
do the following:
Simulate behavior of a MegaCore function within your system
Verify functionality of your design, and quickly and easily evaluate its size
and speed
Generate time-limited device programming files for designs that include
MegaCore functions
Program a device and verify your design in hardware
1 The OpenCore Plus hardware evaluation feature is an evaluation tool for
prototyping only. You must purchase a license to use a MegaCore function
in production.
f For more information about OpenCore Plus, refer to AN 320: OpenCore
Plus Evaluation of Megafunctions.
Nios
®
II Embedded Design Suite (EDS)—A full-featured set of tools that allow
you to develop embedded software for the Nios II processor which you can
include in your Altera FPGA designs.
Cyclone III LS FPGA Development Kit CD-ROM—A CD-ROM that includes all
the documentation and design examples for the kit.
f Use the following links to check the Altera website to ensure you have the latest
software versions:
For the Altera Complete Design Suite, refer to the Quartus II Subscription Edition
Download page.
For the Cyclone III LS FPGA Development Kit, refer to the Cyclone III LS FPGA
Development Kit page.
Cyclone III LS FPGA Development Kit User Guide © October 2009 Altera Corporation
Page 9

Introduction
f For complete information about the development board, refer to the Cyclone III LS
2. Getting Started
This user guide leads you through the following Cyclone III LS FPGA development
board setup steps:
Inspecting the contents of the kit
Installing the Altera Complete Design Suite DVD software
Setting up, powering up, and verifying correct operation of the development
board
Configuring the Cyclone III LS FPGA
Running the Board Test System designs
FPGA Development Board Reference Manual.
Before You Begin
Before using the kit or installing the software, check the kit contents and inspect the
board to verify that you received all of the items listed in this section. If any of the
items are missing, contact Altera before you proceed.
Inspect the Board
To inspect the board, perform the following steps:
1. Place the board on an anti-static surface and inspect it to
2. Verify that all components are on the board and appear intact.
1 In typical applications with the Cyclone III LS FPGA development board, a heat sink
is not necessary. However, under extreme conditions or for engineering sample silicon
the board might require additional cooling to stay within operating temperature
guidelines. You can perform power consumption and thermal modeling to determine
whether your application requires additional cooling.
f For more information about power consumption and thermal modeling, refer to
AN 358: Thermal Management for FPGAs.
ensure that it has not been
damaged during shipment.
c Without proper anti-static handling, you can damage the board.
References
Use the following links to check the Altera website for the following other related
information:
© October 2009 Altera Corporation Cyclone III LS FPGA Development Kit User Guide
Page 10

2–2 Chapter 2: Getting Started
For the latest board design files and reference designs, refer to the Cyclone III LS
References
FPGA Development Kit page.
For additional daughter cards available for purchase, refer to the Development
Board Daughtercards page.
For the Cyclone III LS device documentation, refer to the Literature: Cyclone III
Devices page.
To purchase devices from the eStore, refer to the Devices page.
For Cyclone III LS OrCAD symbols, refer to the Capture CIS Symbols page.
For Nios II 32-bit embedded processor solutions, refer to the Embedded
Processing page.
Cyclone III LS FPGA Development Kit User Guide © October 2009 Altera Corporation
Page 11

Introduction
This section explains how to install the following software:
Altera Complete Design Suite
Cyclone III LS FPGA Development Kit
USB-Blaster™ driver
Installing the Altera Complete Design Suite
The Altera Complete Design Suite provides the necessary tools used for developing
hardware and software for Altera FPGAs. Included on the Altera Complete Design
Suite DVD are the Quartus II software and the Nios II EDS. The Quartus II software
(
including SOPC Builder) and the Nios II EDS are the primary FPGA development
tools u
sed to create the reference designs in this development kit. To install the Altera
software tools, perform the following steps:
3. Software Installation
1. Insert the Altera Complete Design Suite DVD into your computer.
2.
Follow the installer instructions to complete the installation process.
f If you have difficulty installing the Quartus II software, refer to the Quartus II
Installation & Licensing for Windows and Linux Workstations.
Licensing Considerations
Before using the Quartus II software, you must request a license file from the Altera
Licensing page on the Altera website and install it on your computer. When you
request a license file, Altera emails you a license.da
To license the Quartus II software, you need your computer’s network interface card
(N
IC) ID, a number that uniquely identifies your computer. On the computer you’ll
use to run the Quartus II software, type ipconfig /all at a command
determine the NIC ID. Your NIC ID is the 12-digit hexadecimal number on the
Physical Address line.
To obtain a license, perform the following steps.
1. Go to the Get M
2. Under Development Kit Licenses Request, click Licenses for RoHS-Compliant
Kits.
3. Follow the on-screen instructions to request your license. Altera sends you a
license file through email.
t file that enables the software.
prompt to
y Altera License page on the Altera website.
4. To install your license, refer to Specifying the License File in Quartus II Installation &
Licensing for Windows and Linux Workstations.
© October 2009 Altera Corporation Cyclone III LS FPGA Development Kit User Guide
Page 12
3–2 Chapter 3: Software Installation
<install dir>
cycloneIIILS_3cls200_fpga
documents
board_design_files
The default Windows installation directory is C:\altera\
<version>
\.
examples
factory_recovery
demos
kits
Installing the Cyclone III LS FPGA Development Kit
Installing the Cyclone III LS FPGA Development Kit
To install the Cyclone III LS FPGA Development Kit, perform the following steps:
1. Insert the Cyclone III LS FPGA Development
Kit CD-ROM into your computer.
1 The CD-ROM should start an auto-install process. If it does not, browse to
the CD-ROM drive and double-click on the setup.exe file.
2. Follow the on-screen instructions to complete the installation process.
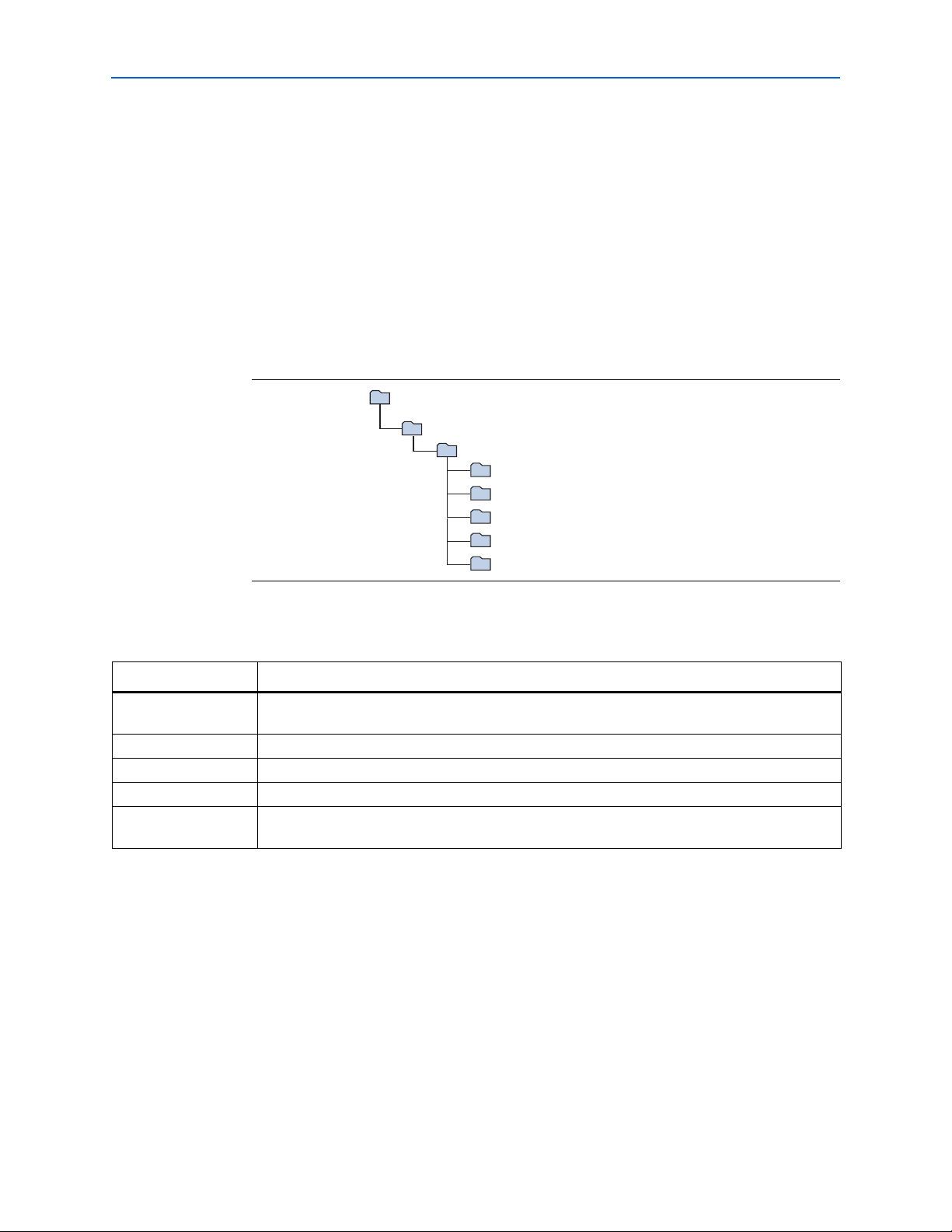
The installation program creates the dir
ectory structure for the Cyclone III LS FPGA
Development Kit files shown in Figure 3–1.
Figure 3–1. Cyclone III LS FPGA Development Kit Installed Directory Structure
Tab le 3–1 lists the file directory names and a description of their contents.
Table 3–1. Installed Directory Contents
Directory Name Description of Contents
board_design_files Contains schematic, layout, assembly, and bill of material board design files. Use these files as a
starting point for a new prototype board design.
demos Contains demonstration applications.
documents Contains the development kit documentation.
examples Contains the sample design files for the Cyclone III LS FPGA Development Kit.
factory_recovery Contains the original data programmed onto the board before shipment. Use this data to restore
the board with its original factory contents.
Installing the USB-Blaster Driver
The Cyclone III LS FPGA development board includes integrated USB-Blaster
circuitry for FPGA programming. However, for the host computer and board to
communicate, you
f Ins
Cyclone III LS FPGA Development Kit User Guide © October 2009 Altera Corporation
tallation instructions for the USB-Blaster driver for your operating system are
available on the Altera website. On the Altera Programming Cable Driver Information
page of the Altera website, locate the table entry for your configuration and click the
link to access the instructions.
must install the USB-Blaster driver on the host computer.
Page 13

Introduction
The instructions in this chapter explain how to set up the Cyclone III LS FPGA
development board.
Setting Up the Board
To set up and power up the board, perform the following steps:
1. The Cyclone III LS FPGA development board ships with its board switches
pr
econfigured to support the example designs in the development kit. If you
suspect your board might not be currently configured with the default settings,
follow the instructions in “Factory Default Switch Settings” on page 4–2 to return
the board to its factory settings before proceeding.
2. The development board ships with example designs stored in the flash memory
device. Verify the PGM/USER LOAD switch (SW2.6) is set to the on position to
load the design stored in the factory portion of flash memory. Figure 4–1 shows the
switch location on the Cyclone III LS FPGA development board.
4. Development Board Setup
3. Connect the DC adapter (+16 V, 3.75 A) to the DC power jack (J5) on the FPGA
board and plug the cord into a power outlet.
c Use only the supplied power supply. Power regulation circuitry on the
board can be damaged by power supplies with greater voltage.
4. Set the POWER switch (SW1) to the on position. When power is supplied to the
board, a blue LED (D3) illuminates indicating that the board has power.
The MAX II device on the board contains a parallel flash loader
When the board powers up, the PFL reads one of two designs from flash memory and
configures the FPGA. The PGM/USER LOAD switch (SW2.6) controls which design
to load. When the switch is in the on position, the PFL loads the design from the
factory portion of flash memory. When the switch is in the off position, the PFL loads
the design from the user portion of flash memory.
1 The devel
dir>\kits\cycloneIIILS_3cls200_fpga\examples\max2 directory.
When configuration is complete, the CONF DONE LED (D14) illuminates, signaling
that the Cyclone III LS device configured successfully. If the
Quartus II software INIT_DONE option on, the
illuminates when the device enters user mode.
opment kit includes the MAX II configuration design in the <install
FPGA INIT DONE LED (D14)
(PFL) megafunction.
loaded design has the
f For mor
Flash Loader with the Quartus II Software.
© October 2009 Altera Corporation Cyclone III LS FPGA Development Kit User Guide
e information about the PFL megafunction, refer to AN 386: Using the Parallel
Page 14

4–2 Chapter 4: Development Board Setup
SW2
Board Settings
DIP Switch
OFF = 1
ON = 0
S7
User
DIP Switch
OFF = 1
ON = 0
J11
JTAG Contr ol Jumpers
12345678
OPEN
J12
432
1
ON
(not installed)J18
LCD SEL
EP3CLS200F780
(not installed)
(not installed)
(not installed)
(installed)
Factory Default Switch Settings
Factory Default Switch Settings
This section shows the factory switch settings for the Cyclone III LS FPGA
development board. Figure 4–1 shows the switch bank locations and the default
position of each switch.
Figure 4–1. Switch Locations and Default Settings on the FPGA Development Board
To restore the switches to their factory default settings, perform the following steps:
1. Set DIP switch bank (S7) to match T
able 4–1 and Figure 4–1.
Table 4–1. S7 Dip Switch Settings
Switch Position
1On
2On
3On
4On
2. Set DIP switch bank (SW2) to match Table 4–2 and Figure 4–1.
Table 4–2. SW2 Dip Switch Settings
Switch Position
1On
2On
3On
4On
5Off
6On
7Off
8Off
Cyclone III LS FPGA Development Kit User Guide © October 2009 Altera Corporation
Page 15

Chapter 4: Development Board Setup 4–3
Factory Default Switch Settings
3. Set the board jumpers to match Table 4–3 and Figure 4–1.
Table 4–3. Jumper Settings
Board Reference Shunt Position
J11 pins 1-2 Installed
J11 pins 3-4 Not Installed
J11 pins 5-6 Not Installed
J12 Not Installed
J18 Not Installed
f For more information about the FPGA board settings, refer to the Cyclone III LS FPGA
Development Board Reference Manual.
© October 2009 Altera Corporation Cyclone III LS FPGA Development Kit User Guide
Page 16

4–4 Chapter 4: Development Board Setup
Factory Default Switch Settings
Cyclone III LS FPGA Development Kit User Guide © October 2009 Altera Corporation
Page 17

Introduction
5. Board Update Portal
The Cyclone III LS FPGA Development Kit ships with the Board Update Portal
example design stored in the factory portion of the flash memory on the board. The
de
sign consists of a Nios II embedded processor, an Ethernet MAC, and an HTML
web serve
When you power up the board with the PGM/USER LOAD switch (SW2.6) in the on
position, the Cyclone III LS FPGA configures with the Boar
design. The design can obtain an IP address from any DHCP server and serve a web
page
web page allows you to upload new FPGA designs to the user portion of flash
memory, and provides links to useful information on the Altera website, including
links to kit-specific and design resources.
r.
d Update Portal example
from the flash on your board to any host computer on the same network. The
1 After succ
design from flash memory into the FPGA. To do so, set the PGM/USER LOAD switch
(SW2.6) to the off position and power cycle the board.
The source code for the Board Update Portal design resides in the <insta
dir>\kits\cycloneIIILS_3cls200_fpga\examples di
Portal is corrupted or deleted from the flash memory, refer to “Restoring the Flash
Device to the Factory Settings” on page A–4 to restore the board with its original
factory contents.
essfully updating the flash memory user design, you can load the user
Connecting to the Board Update Portal Web Page
This section provides instructions to connect to the Board Update Portal web page.
1 Be
fore you proceed, ensure that you have the following:
A PC with a connection to a working Ethernet port on a DHCP enabled network.
A separate working Ethernet port connected to the same network for the board.
The Ethernet and power cables that are included in the kit.
To connect to the Board Update Portal web page, perform the following steps:
1. With the board powered down, set the PGM/USER LOAD switch (SW2.6) to the
on p
osition.
ll
rectory. If the Board Update
2. Attach the Ethernet cable from the board to your LAN.
3. Power up the board. The board connects to the LAN’s gateway router, and obtains
an IP address. The LCD on the board displays the IP address.
4. Launch a web browser on a PC that is connected to the same network, and enter
the IP address from the LCD into the browser address bar. The Board Update
Portal web page appears in the browser.
© October 2009 Altera Corporation Cyclone III LS FPGA Development Kit User Guide
Page 18

5–2 Chapter 5: Board Update Portal
5. Click Cyclone III LS FPGA Development Kit on the Board Update Portal web
page and verify that you have the latest version of the development kit software
(the software version also appears on the CD-ROM).
1 If you download new software, double-click the downloaded .exe file to
begin the installation process.
6. Visit the Board Update Portal web page occasionally for documentation updates
and additional new designs not included on the CD-ROM.
f If the Board Update Portal does not connect, refer to the Cyclone III LS FPGA
Development Kit page on the Altera website to determine if you have the latest kit
software.
Using the Board Update Portal to Update User Designs
Using the Board Update Portal to Update User Designs
The Board Update Portal allows you to write new designs to the user portion of flash
memory. Designs must be in the Nios II Flash Programmer File (.f
lash) format.
1 Desi
1 As long as you don’t overwrite the factory image in the flash memory device, you can
gn files available from the Cyclone III LS FPGA Development Kit page on the
Altera website include .flash files. You can also create .flash files from your own
custom design. Refer to “Preparing Design Files for Flash Programming” on page A–2
for information about preparing your own design for upload.
To upload a design over the network into the user portion of flash memory on your
boar
d, perform the following steps:
1. Perform the steps in “Connecting to the Boa
the Board Update Portal web page.
2. In the Hardware File Name field specify the .flash file that you either downloaded
from the Altera website or created on your own. If there is a software component
to the design, specify it in the same manner using the Software File Name field,
otherwise leave the Software File Name field blank.
3. Click Upload. The progress bar indicates the percent complete.
4. To configure the FPGA with the new design after the flash memory upload process
is complete, set the PGM/USER LOAD switch (SW2.6) to the off position and
power cycle the board, or press the PGM_SELECT button (S9) until the
PROGRAM LED1 LED (D30) illuminates and then press the PGM CONFIG button
(S8). Refer to Table 6–1 on page 6–5 for information about the PROGRAM LEDs.
continue to use the Board Update Portal to write new designs to the user portion of
flash memory. If you do overwrite the factory image, you can restore it by following
the instructions in “Restoring the Flash Device to the Factory Settings” on page A–4.
rd Update Portal Web Page” to access
Cyclone III LS FPGA Development Kit User Guide © October 2009 Altera Corporation
Page 19

Introduction
6. Board Test System
The kit includes an example design and application called the Board Test System to
test the functionality of the Cyclone III LS FPGA development board. The application
provides an easy-to-use interface to alter functiona
You can use the application to test board components, modify functional parameters,
observe performance, and measure power usage. The application is also useful as a
reference for designing systems. To install the application, follow the steps in
“Installing the Cyclone III LS FPGA Development Kit” on page 3–2.
The application provides access to the following Cyclone III LS FPGA development
board features:
General purpose I/O (GPIO)
SRAM
Flash memory
l settings and observe the results.
DDR2 memory
HSMC connectors
Programmable oscillator
The application allows you to exercise most of the board components. While using the
appl
ication, you reconfigure the FPGA several times with test designs specific to the
functionality you are testing.
A GUI runs on the PC which communicates over the JTAG bus to a test design
r
unning in the Cyclone III LS device. Figure 6–1 shows the initial GUI for a board that
is in the factory configuration.
© October 2009 Altera Corporation Cyclone III LS FPGA Development Kit User Guide
Page 20

6–2 Chapter 6: Board Test System
Figure 6–1. Board Test System Graphical User Interface
Introduction
Several designs are provided to test the major board features. Each design provides
data for one or more tabs in the application. The Configure menu identifies the
appropriate design to download to the FPGA for each tab.
After successful FPGA configuration, the appr
opriate tab appears and allows you to
exercise the related board features. Highlights appear in the board picture around the
corresponding components.
The Power Mo
nitor button starts the Power Monitor application that measures and
reports current power information for the board. Because the application
communicates over the JTAG bus to the MAX II device, you can measure the power of
any desi
1 The
applications like the Nios II debugger and the SignalTap
gn in the FPGA, including your own designs.
Board Test System and Power Monitor share the JTAG bus with other
®
II Embedded Logic
Analyzer. Because the Quartus II programmer uses most of the bandwidth of the
JTAG bus, other applications using the JTAG bus might time out. Be sure to close the
other applications before attempting to reconfigure the FPGA using the Quartus II
Programmer.
Cyclone III LS FPGA Development Kit User Guide © October 2009 Altera Corporation
Page 21

Chapter 6: Board Test System 6–3
Preparing the Board
Preparing the Board
With the power to the board off, perform the following steps:
1. Connect the USB cable to the board.
2.
Verify the settings for the board settings DIP switch bank (SW2) match Table 4–2
on page 4–2.
3. Set the PGM/USER LOAD switch (SW2.6) to the off position.
4. Verify the settings for the JTAG jumper blocks (J11 and J12) match Table 4–3 on
page 4–3. These settings determine the devices to include in the JTAG chain.
f For more information about the board’s DIP switch and jumper settings,
refer to the Cyclone III LS FPGA Development Board Reference Manual.
5. Turn the power to the board on. The board loads the design stored in the user
portion of flash memory into the FPGA. If your board is still in the factory
configuration or if you have downloaded a newer version of the Board Test
System to flash memory through the Board Update Portal, the design that tests the
GPIO, SRAM, and flash memory loads.
c To ensure operating stability, keep the USB cable connected and the board powered on
when running the demonstration application. The application cannot run correctly
unless the USB cable is attached and the board is on.
Running the Board Test System
To run the application, navigate to the <install
dir>\kits\cycloneIIILS_3cls200_fpga\examples\board_test_system di
run the BoardT
1 On W
1 If you power
indows, click Start > All Programs > Altera > Cyclone III LS FPGA
Development Kit <version> > Board Test System to run the application.
A GUI appears, displaying the application tab that corresponds to the design running
in the FP
preconfigured with the design that corresponds to the Co
SRAM&Flash tabs.
position, or if you load your own design into the FPGA with the Quartus II
Programmer, you receive a message prompting you to configure your board with a
valid Board Test System design. Refer to “The Configure Menu” for information about
configuring your board.
estSystem.exe application.
GA. The Cyclone III LS FPGA development board’s flash memory ships
up your board with the PGM/USER LOAD switch (SW2.6) in the on
rectory and
nfig, GPIO, and
Using the Board Test System
This section describes each control in the Board Test System application.
© October 2009 Altera Corporation Cyclone III LS FPGA Development Kit User Guide
Page 22
6–4 Chapter 6: Board Test System
Using the Board Test System
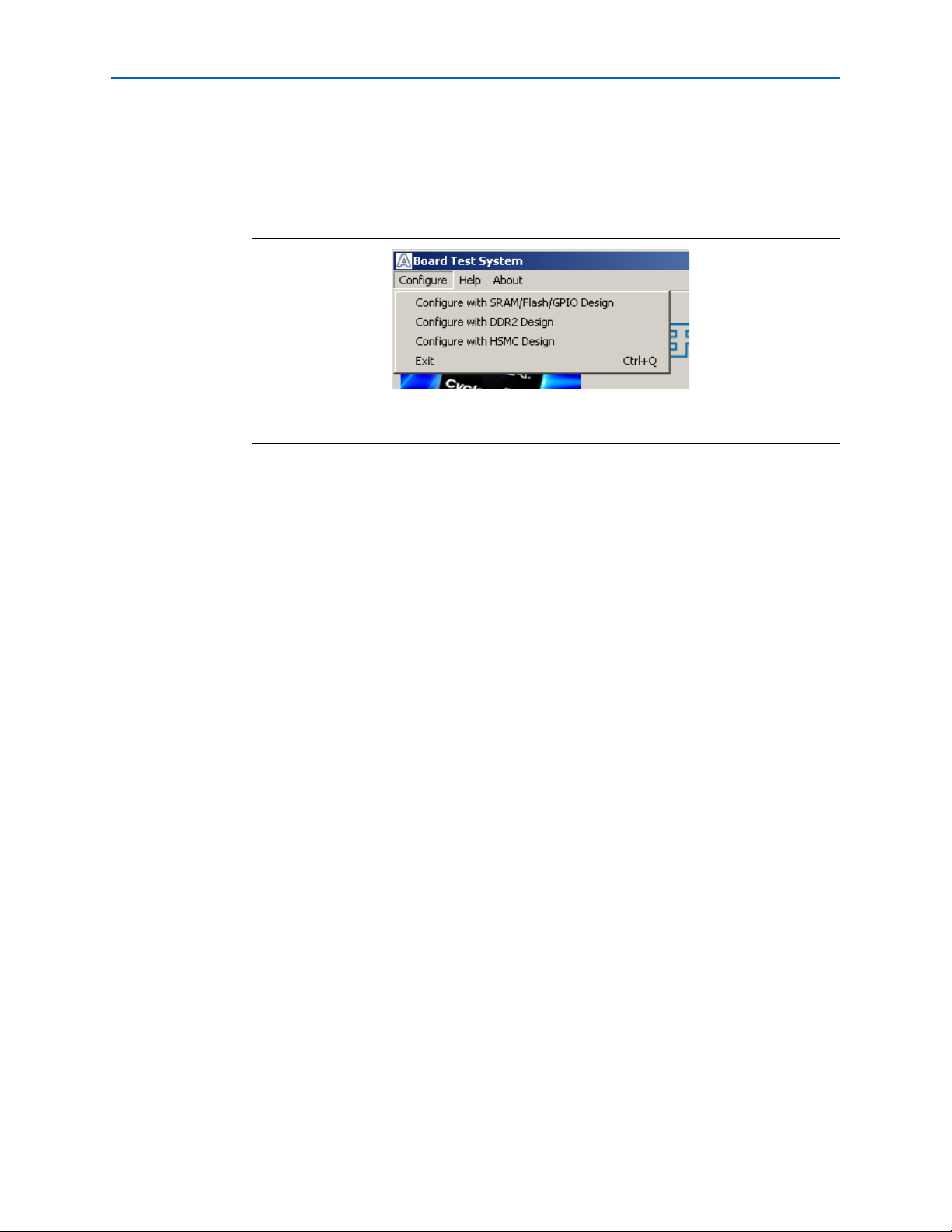
The Configure Menu
Each test design tests different functionality and corresponds to one or more
application tabs. Use the Configure menu to select the design you want to use.
Figure 6–2 shows the Configure menu.
Figure 6–2. The Configure Menu
To configure the FPGA with a test system design, perform the following steps:
The Config Tab
1. On the Configure menu, click the configu
functionality you wish to test.
2. In the dialog box that appears, click Configure to download the corresponding
design’s SRAM Object File (.sof) to the FPGA. The download process usually takes
about a minute.
3. When configuration finishes, click Close to complete the configuration process
and run the design in the FPGA. A corresponding application tab appears in the
GUI that interfaces with the design in the FPGA.
The Config tab shows information about the board’s current configuration.
Figure 6–1 on page 6–2 shows the Config tab.
MAX II registers, the MAX II code version, the JTAG chain, the board’s MAC address,
and the
The following sections describe the controls on the Co
flash memory map.
re command that corresponds to the
The tab displays the contents of the
nfig tab.
MAX-II Registers
These controls allow you to view and change the current MAX II register values as
described in Tabl e 6–1. Changes to the register values with the GUI take effect
immediately. For example, selecting a new frequency in the OCR1 li
changes the clock frequency on the board.
st immediately
Cyclone III LS FPGA Development Kit User Guide © October 2009 Altera Corporation
Page 23
Chapter 6: Board Test System 6–5
Using the Board Test System
Table 6–1. MAX II Registers
Read/Write
Register Name
System Reset
Capability Description
Write only Set to 0 to initiate an FPGA reconfiguration.
(SRST)
Page Select Register
(PSR)
Read / Write Determines which of the two pages of flash memory to use
for FPGA reconfiguration. The flash memory ships with
pages 0 and 1 preconfigured.
Page Select Override
(PSO)
Read / Write When set to 0, the value in PSR determines the page of
flash memory to use for FPGA reconfiguration. When set to
1, the value in PSS determines the page of flash memory to
use for FPGA reconfiguration.
Page Select Switch
(PSS)
Read only Holds the current value of the illuminated PROGRAM LED
(D29-D31) based on the following encoding:
0 = PROGRAM LED0 LED (D31) and corresponds to the
flash memory page for the factory hardware design
1 = PROGRAM LED1 LED (D30) and corresponds to the
flash memory page for the user hardware 1 design
2 = PROGRAM LED2 LED (D29) and corresponds to the
flash memory page for the user hardware 2 design
Oscillator Control
Register 1 (OCR1)
Read / Write Determines the U17 oscillator output frequency based on
the following options:
0 = 100 MHz
1 = 125 MHz
2 = 150 MHz
3 = 156.25 MHz
PSO—Sets the MAX II PSO register. The following options are available:
Use PSR—Allows the PSR to determine the page of flash memory to use for
FPGA reconfiguration.
Use PSS—Allows the PSS to determine the page of flash memory to use for
FPGA reconfiguration.
PSR—Sets the MAX II PSR register. The numerical values in the list corresponds to
the page of flash memory to load during FPGA reconfiguration. Refer to Table 6–1
for more information.
PSS—Displays the MAX II PSS register value. Refer to Table 6 –1 for the list of
available options.
OCR1—Sets the MAX II OCR1 register. Refer to Table 6–1 for the list of available
options.
SRST—Resets the system and reloads the FPGA with a design from flash memory
based on the other MAX II register values. Refer to Tabl e 6–1 for more information.
1 Because the Config tab requires that a specific design is running in the FPGA, writing
a 0 to SRST or changing the PSO value can cause the Board Test System to stop
running.
© October 2009 Altera Corporation Cyclone III LS FPGA Development Kit User Guide
Page 24

6–6 Chapter 6: Board Test System
Using the Board Test System
JTAG Chain
This control shows all the devices currently in the JTAG chain. The Cyclone III LS
device is always the first device in the chain.
1 Installing the s
The GPIO Tab
hunt jumper on jumper J11 pins 1-2 includes the MAX II device in the
JTAG chain. Installing the shunt jumper on jumper J12 or setting the anti-tamper DIP
switch SW2.3 to the off position breaks the JTAG chain.
f For information about the anti-tamper design example, refer to <install
dir>\kits\cycloneIIILS_3cls200_fpga\examples\max2\at_example\rea
dme_at_example.txt.
Board Information
MAX-II rev—Indicates the version of MAX II code currently running on the
board. The MAX II code resides in the <install
dir>\kits\cycloneIIILS_3cls200_fpga\examples directory. Newer revisions of
this code might be available on the Cyclone III LS FPGA Development Kit page of
the Altera website.
MAC—Indicates the MAC address of the board.
Flash Memory Map
This control shows the memory map of the flash memory device on your board.
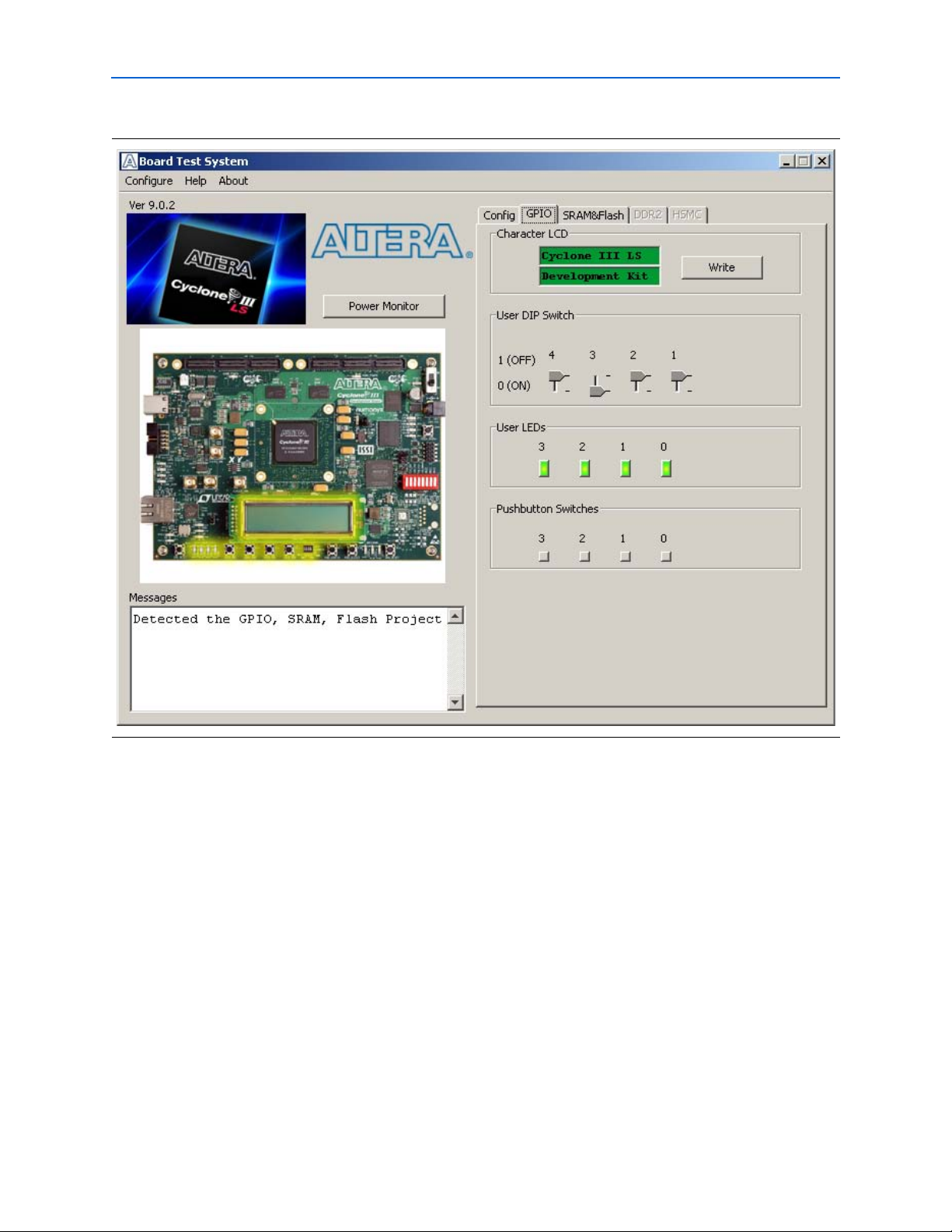
The GPIO tab allows you to interact with all the general purpose user I/O
components on your board. You can write to the LCD, read DIP switch settings, turn
LEDs on or off, and detect push button presses. Figure 6–3 shows the GP
IO tab.
Cyclone III LS FPGA Development Kit User Guide © October 2009 Altera Corporation
Page 25
Chapter 6: Board Test System 6–7
Using the Board Test System
Figure 6–3. The GPIO Tab
The following sections describe the controls on the GPIO tab.
Character LCD
This control allows you to display text strings on the LCD on your board. Type text in
the text boxes and then click Write.
1 If you exceed
the 16 character display limit on either line, a warning message appears.
User Dip Switch
This read-only control displays the current positions of the switches in the user DIP
switch bank (S7). Change the switches on the board to see the graphical display
change accordingly.
User LEDs
This control displays the current state of the user LEDs. Click on the graphical
representation of the LEDs to turn the board LEDs on and off.
© October 2009 Altera Corporation Cyclone III LS FPGA Development Kit User Guide
Page 26

6–8 Chapter 6: Board Test System
Using the Board Test System
Pushbutton Switches
This read-only control displays the current state of the board user push buttons. Press
a push button on the board to see the graphical display change accordingly.
The SRAM&Flash Tab
The SRAM&Flash tab allows you to read and write SRAM and flash memory on your
board. Figure 6–4 shows the SRAM&
Figure 6–4. The SRAM&Flash Tab
Flash tab.
The following sections describe the controls on the SRAM&Flash tab.
SRAM
This control allows you to read and write the SRAM on your board. Type a starting
address in the text box and click Read. Values starting at the specified address appear
in the table.The base address of SRAM in this Nios II-based BTS design is
0x0D0
0.0000. The valid address range within the 2-MByte SRAM is 0x0000.0000
through 0x001F.FFFF, as shown in the GUI.
Cyclone III LS FPGA Development Kit User Guide © October 2009 Altera Corporation
Page 27

Chapter 6: Board Test System 6–9
Using the Board Test System
1 If you enter an address outside of the 0x0000.0000 to 0x001F.FFFF SRAM address
space, a warning message identifies the valid SRAM address range.
To update the SRAM contents, change values in the table and click Write. The
application writes the new values to SRAM and then reads the values back to
guarantee that the graphical display accurately reflects the memory contents.
Flash
This control allows you to read and write the flash memory on your board. Type a
starting address in the text box and click Read. Values starting at the specified address
appear in the table.The base address of flash memory in this Nios II-based BTS design
is 0x080
through 0x03FF.FFFF, as shown in the GUI.
0.0000. The valid address range within the 64-MByte SRAM is 0x0000.0000
1 If you enter an addr
1 T
The DDR2 Tab
ess outside of the 0x0000.0000 to 0x003F.FFFF flash memory
address space, a warning message identifies the valid flash memory address range.
To update the flash memory contents, change
values in the table and click Wri te. The
application writes the new values to flash memory and then reads the values back to
guarantee that the graphical display accurately reflects the memory contents.
o prevent overwriting the dedicated portions of flash memory, the application limits
the writable flash memory address range to 0x03FE.0000 to 0x003F.FFFF (which
corresponds to the unused flash memory address range shown in Figure 6–1 on
page 6–2 and Table A–1 on page A–1).
The DDR2 tab allows you to read and write the DDR2 memory on your board.
Figure 6–5 shows the DDR2 ta
b.
© October 2009 Altera Corporation Cyclone III LS FPGA Development Kit User Guide
Page 28

6–10 Chapter 6: Board Test System
Figure 6–5. The DDR2 Tab
Using the Board Test System
The following sections describe the controls on the DDR2 tab.
Port
This control directs communication to one of two DDR2 memory ports on your board.
Start
This control initiates DDR2 port transaction performance analysis.
Stop
This control terminates transaction performance analysis.
Performance Indicators
These controls display current transaction performance analysis information collected
since you last clicked Start:
Write, Read, and To t a l performance bars—Show the percentage of maximum data
rate that the requested transactions are able to achieve.
Cyclone III LS FPGA Development Kit User Guide © October 2009 Altera Corporation
Page 29

Chapter 6: Board Test System 6–11
Using the Board Test System
Write(MBytes/s), Read(MBytes/s), and Total(MBytes/s)—Show the number of
bytes of data analyzed per second. Each data bus is 16 bits wide and the frequency
is 167 MHz double data rate (334 Mbps per pin), equating to a theoretical
maximum bandwidth of 668 MBps.
Error Control
These controls track transaction errors detected during analysis:
Detected Errors—Displays the number of transaction errors detected in the
hardware.
Inserted Errors—Displays the number of errors inserted into the transaction
stream.
Insert Error—Inserts a one-word error into the transaction stream each time you
click the button. Insert Error is only enabled during transaction performance
analysis.
Clear—Resets the Detected Errors and Inserted Errors counters to zeros.
Number of addresses to write / read
This control determines the number of addresses to use in each iteration of reads and
writes. Valid values range from 2 to 8,191.
The HSMC Tab
Data Type
This control specifies the type of data contained in the transactions. The following
data types are available for analysis:
PRBS—Selects pseudo-random bit sequences.
Memory—Selects a generic data pattern stored in the on chip memory of the
Cyclone III LS device.
Math—Selects data generated from a simple math function within the FPGA
fabric.
Read/Write control
This control specifies the type of transactions to analyze. The following transaction
types are available for analysis:
Write/Read—Selects read and write transactions for analysis.
Read Only—Selects read transactions for analysis.
Write Only—Selects write transactions for analysis.
The HSMC tab allows you to perform loopback tests on the HSMC A and HSMC B
ports. Figure 6–6 shows the HSMC ta
b.
© October 2009 Altera Corporation Cyclone III LS FPGA Development Kit User Guide
Page 30

6–12 Chapter 6: Board Test System
Using the Board Test System
Figure 6–6. The HSMC Tab
1 You must have the loopback HSMC installed on the HSMC connector that you are
testing for this test to succeed.
The following sections describe the controls on the HSMC tab.
Status
This control displays the following status information during the loopback test:
PLL Lock—Shows the PLL locked or unlocked state.
Channel Lock—Shows the channel locked or unlocked state. When locked, all
lanes are aligned and bonded.
Pattern Sync—Shows the pattern synced or not synced state. The pattern is
considered synced when the start of the data sequence is detected.
Port
This control allows you to specify the type of test to run on the HSMC ports. The
following HSMC port tests are available:
Cyclone III LS FPGA Development Kit User Guide © October 2009 Altera Corporation
Page 31

Chapter 6: Board Test System 6–13
The Power Monitor
HSMA x41 Single Ended Loopback
HSMB x41 Single Ended Loopback
Data Type
This control specifies the type of data contained in the transactions. The following
data types are available for analysis:
PRBS—Selects pseudo-random bit sequences.
Memory—Selects a generic data pattern stored in the on chip memory of the
Cyclone III LS device. This feature is not currently implemented.
Math—Selects data generated from a simple math function within the FPGA
fabric. This feature is not currently implemented.
Error Control
These controls track transaction errors detected during analysis.
Detected Errors—Displays the number of transaction errors detected in the
hardware.
Inserted Errors—Displays the number of errors inserted into the transaction
stream.
Insert Error—Inserts a one-word error into the transaction stream each time you
click the button. Insert Error is only enabled during transaction performance
analysis.
Clear—Resets the Detected Errors and Inserted Errors counters to zeros.
Start
This control initiates HSMC transaction performance analysis.
Stop
This control terminates transaction performance analysis.
Performance Indicators
These controls display current transaction performance analysis information collected
since you last clicked Start:
TX and RX performance bars—Show the percentage of maximum data rate that
the requested transactions are able to achieve.
Tx(MBytes/s) and Rx(MBytes/s)—Show the number of bytes of data analyzed per
second.
The Power Monitor
The Power Monitor measures and reports current power information for the board. To
start the application, click Power Monitor in the Board Test System application.
© October 2009 Altera Corporation Cyclone III LS FPGA Development Kit User Guide
Page 32

6–14 Chapter 6: Board Test System
The Power Monitor
1 You can also run the Power Monitor as a stand-alone application. PowerTool.exe
resides in the <install
dir>\kits\cycloneIIILS_3cls200_fpga\examples\board_test_system directory. On
Windows, click Start > All Programs > Altera > Cyclone III LS FPGA Development
Kit <version> > Power Monitor to start the application.
The Power Monitor communicates to the MAX II device on the board through the
JTAG bus. A power monitor circuit attached to the MAX II device allows you to
mea
sure the power that the Cyclone III LS FPGA device is consuming regardless of
the design currently running. Figure 6–7 shows the Power Monitor.
Figure 6–7. The Power Monitor
The following sections describe the Power Monitor controls.
MAX II Information
These controls display information about the MAX II device.
MAX II Version—
board. The MAX II code resides in the <install
dir>\kits\cycloneIIILS_3cls200_fpga\factory_recovery d
of this code might be available on the Cyclone III LS FPGA Development Kit page of
the Altera website.
Cyclone III LS FPGA Development Kit User Guide © October 2009 Altera Corporation
Indicates the version of MAX II code currently running on the
irectory. Newer revisions
Page 33

Chapter 6: Board Test System 6–15
The Power Monitor
Power Rail—Selects the power rail to measure. After selecting the desired rail, click
Reset to refresh the screen with new board readings.
f A
table with the power rail is available in the Cyclone III LS FPGA
Development Board Reference Manual.
Power Information
This control displays current, maximum, and minimum power readings for the
following units:
mVolts
mAmps
mWatts
Power Graph
This control displays the mWatt power consumption of your board over time. The
green line indicates the current value. The red line indicates the maximum value read
since the last reset. The yellow line indicates the minimum value read since the last
reset.
Graph Settings
These controls allow you to define the look and feel of the power graph.
Scale Select—Spe
to zoom in to see finer detail. Select a larger number to zoom out to see the entire
range of recorded values.
cifies the amount to scale the power graph. Select a smaller number
Calculating Power
Update Speed—Specifies how o
ften to refresh the graph.
Reset
This control clears the graph, resets the minimum and maximum values, and restarts
the Power Monitor.
The Power Monitor calculates power by measuring two different voltages with the
LT2418 A/D and applying the equation P = V × I to determine the power
consumption. The LT2418 measures the voltage after the appropriate sense resistor
(Vsense) and the voltage drop across that sense resistor (Vdif). The current (I) is
calculated by dividing the measured voltage drop across the resistor by the value of
the sense resistor (I = Vdif/R). Through substitution, the equation for calculating
power becomes P = V × I = Vsense × (Vdif/R) = (Vsense) × (Vdif) × (1/.003).
You can verify the power numbers shown in the Power Monitor with a digital
multimeter
significant digits for an accurate calculation. Measure the voltage on one side of the
resistor (the side opposite the power source) and then measure the voltage on the
other side. The first measurement is Vsense and the difference between the two
measurements is Vdif. Plug the values into the equation to determine the power
consumption.
that is capable of measuring microvolts to ensure you have enough
© October 2009 Altera Corporation Cyclone III LS FPGA Development Kit User Guide
Page 34

6–16 Chapter 6: Board Test System
Configuring the FPGA Using the Quartus II Programmer
Configuring the FPGA Using the Quartus II Programmer
You can use the Quartus II Programmer to configure the FPGA with a specific .sof.
Before configuring the FPGA, ensure that the Quartus II Programmer and the
USB-
Blaster driver are installed on the host computer, the USB cable is connected to
the development board, power to the board is on, and no other applications that use
the JTAG chain are running.
To co n fig ure t h e Cyclone III LS FPGA, perform the following steps:
1. Start the Quartus II Programmer.
2.
Click Add File and select the path to the desired .sof.
3. Turn on the Program/Configure option for the added file.
4. Click Start to download the selected file to the FPGA. Configuration is complete
when the progress bar reaches 100%.
Cyclone III LS FPGA Development Kit User Guide © October 2009 Altera Corporation
Page 35

Introduction
A. Programming the Flash Memory
Device
As you develop your own project using the Altera tools, you can program the flash
memory device so that your own design loads from flash memory into the FPGA on
power up. This appendix describes the preprogrammed contents of the common flash
interface (CFI) flash memory device on the Cyclone III LS FPGA development board
and the Nios II EDS tools involved with reprogramming the user
memory device.
The Cyclone III LS FPGA development board ships with the CFI flash device
preprogrammed with a default factory FPGA configur
Update Portal example design and a default user configuration for running the Board
Test System demonstration. There are several other factory software files written to
the CFI flash device to support the Board Update Portal. These software files were
created using the Nios II EDS, just as the hardware design was created using the
Quar
tus II software.
ation for running the Board
portions of the flash
f For mor
page on the Altera website.
e information about Altera development tools, refer to the Design Software
CFI Flash Memory Map
Tab le A–1 shows the default memory contents of the 512-Mbit (64-MByte) Intel
PC48F4400P0VB00 CFI flash device. For the Boar
update designs in the user memory, this memory map must not be altered.
Table A–1. Byte Address Flash Memory Map
Block Description Size Address Range
Unused 32 KB 0x03FF8000 - 0x03FFFFFF
Unused 32 KB 0x03FF0000 - 0x03FF7FFF
Unused 32 KB 0x03FE8000 - 0x03FEFFFF
Unused 32 KB 0x03FE0000 - 0x03FE7FFF
User software 24,320 KB 0x02820000 - 0x03FDFFFF
Factory software 8,192 KB 0x02020000 - 0x0281FFFF
zipfs (html, web content) 8,192 KB 0x01820000 - 0x0201FFFF
Unused 5,898 KB 0x01280000 - 0x0181FFFF
User hardware 2 6,422 KB 0x00C60000 - 0x0127FFFF
User hardware 1 6,422 KB 0x00640000 - 0x00C5FFFF
Factory hardware 6,422 KB 0x00020000 - 0x0063FFFF
PFL option bits 32 KB 0x00018000 - 0x0001FFFF
Board information 32 KB 0x00010000 - 0x00017FFF
Ethernet option bits 32 KB 0x00008000 - 0x0000FFFF
User design reset vector 32 KB 0x00000000 - 0x00007FFF
d Update Portal to run correctly and
© October 2009 Altera Corporation Cyclone III LS FPGA Development Kit User Guide
Page 36

A–2 Appendix A: Programming the Flash Memory Device
Preparing Design Files for Flash Programming
c Altera recommends that you do not overwrite the factory hardware and factory
software images unless you are an expert with the Altera tools or deliberately
overwriting the factory design. If you unintentionally overwrite the factory hardware
or factory software image, refer to “Restoring the Flash Device to the Factory Settings”
on page A–4.
Preparing Design Files for Flash Programming
You can obtain designs containing prepared .flash files from the Cyclone III LS FPGA
Development Kit page on the Altera website or create .flash file
custom design.
s from your own
The Nios II EDS sof2flash command
line utility converts your Quartus II-compiled
.sof into the .flash format necessary for the flash device. Similarly, the Nios II EDS
elf2
flash command line utility converts your compiled and linked Executable and
Linking Format File (.elf) software design to .flash. After your design files are in the
.flash format, use the Board Update Portal or the Nios II EDS nios2-flashpr
ogrammer utility to write the .flash files to the user hardware and user software
locations of the flash memory.
f For
more information about Nios II EDS software tools and practices, refer to the
Embedded Software Development page on the Altera website.
Creating Flash Files Using the Nios II EDS
If you have an FPGA design developed using the Quartus II software, and software
developed using the Nios II EDS, follow these instructions:
1. On the Windows Start menu, click All Programs > Al
Command Shell.
2. In the Nios II command shell, navigate to the directory where your design files
reside and type the following Nios II EDS commands:
For Quartus II .sof files:
sof2flash --input=<yourfile>_hw.sof --output=<yourfile>_hw.flash --offset=0x0640000 r
For Nios II .elf files:
tera > Nios II EDS > Nios II
elf2flash --base=0x0A000000 --end=0x0BFFFFFF --reset=0x0A820000
--input=<yourfile>_sw.elf --output=<yourfile>_sw.flash
--boot=$SOPC_KIT_NIOS2/components/altera_nios2/boot_loader_cfi.srec r
The resulting .flash files are ready for flash device programming. If your design uses
additional files such as image data or files used by the runtime program, you must
first convert the files to .flash format and concatenate them into one .flash file before
using the Board Update Portal to upload them.
1 The Boar
d Update Portal standard .flash format conventionally uses either
<filename>_hw.flash for hardware design files or <filename>_sw.flash for software
design files.
Cyclone III LS FPGA Development Kit User Guide © October 2009 Altera Corporation
Page 37

Appendix A: Programming the Flash Memory Device A–3
Programming Flash Memory Using the Board Update Portal
Programming Flash Memory Using the Board Update Portal
Once you have the necessary .flash files, you can use the Board Update Portal to
reprogram the flash memory. Refer to “Using the Board Update Portal to Update User
Designs” on page 5–2 for more information.
1 If you have generated
use the Board Update Portal to upload your design. In this case, leave the Software
File Name field blank.
a .sof that operates without a software design file, you can still
Programming Flash Memory Using the Nios II EDS
The Nios II EDS offers a nios2-flash-programmer utility to program the flash memory
directly. To program the .flash files or any compatible S-Record File (.srec) to the
board using nios2-flash-programmer, perform the following steps:
1. Set the PGM/USER LOAD switch (SW2.6) t
Update Portal design from flash memory on power up.
2. Attach the USB-Blaster cable and power up the board.
3. If the board has powered up and the LCD displays either "Connecting..." or a valid
IP address (such as 152.198.231.75), proceed to step 8. If no output appears on the
LCD is seen or if the CONF DONE LED (D14) does not illuminate, continue to step
4 to load the FPGA with a flash-writing design.
4. Launch the Quartus II Programmer to configure the FPGA with a .sof capable of
flash programming. Refer to “Configuring the FPGA Using the Quartus II
Programmer” on page 6–16 for more information.
5. Click Add File and select <install
dir>\kits\cycloneIIILS_3cls200_fpga\factory_recovery\c3ls200_fpga_bup.sof.
o the on position to load the Board
6. Turn on the Program/Configure option for the added file.
7. Click Start to download the selected configuration file to the FPGA. Configuration
is complete when the progress bar reaches 100%. The CONF DONE LED (D14)
and the four user LEDs (D25-D28) illuminate indicating that the flash device is
ready for programming.
8. On the Windows Start menu, click All Programs > Altera > Nios II EDS > Nios II
Command Shell.
9. In the Nios II command shell, navigate to the <install
dir>\kits\cycloneIIILS_3cls200_fpga\factory_recovery directory (or to the
directory of the .flash files you created in “Creating Flash Files Using the Nios II
EDS” on page A–2) and type the following Nios II EDS command:
nios2-flash-programmer --base=0x08000000 <yourfile>_hw.flash r
10. After programming completes, if you have a software file to program, type the
following Nios II EDS command:
nios2-flash-programmer --base=0x0A000000 <yourfile>_sw.flash r
© October 2009 Altera Corporation Cyclone III LS FPGA Development Kit User Guide
Page 38

A–4 Appendix A: Programming the Flash Memory Device
Restoring the Flash Device to the Factory Settings
11. Set the PGM/USER LOAD switch (SW2.6) to the off position and power cycle the
board, or press the PGM_SELECT button (S9) until the PROGRAM LED1 LED
(D30) illuminates and then press the PGM CONFIG button (S8) to load and run the
user design. Refer to Table 6–1 on page 6–5 for information about the PROGRAM
LEDs.
Programming the board is now complete.
f For mor
e information about the nios2-flash-programmer utility, refer to the Nios II
Flash Programmer User Guide.
Restoring the Flash Device to the Factory Settings
This section describes how to restore the original factory contents to the flash memory
device on the development board. Make sure you have the Nios II EDS installed, and
perf
orm the following instructions:
1. Set the board switches to the factory
Switch Settings” on page 4–2.
2. Launch the Quartus II Programmer to configure the FPGA with a .sof capable of
flash programming. Refer to “Configuring the FPGA Using the Quartus II
Programmer” on page 6–16 for more information.
3. Click Add File and select <install
dir>\kits\cycloneIIILS_3cls200_fpga\factory_recovery\c3ls200_fpga_bup.sof.
4. Turn on the Program/Configure option for the added file.
5. Click Start to download the selected configuration file to the FPGA. Configuration
is complete when the progress bar reaches 100%. The CONF DONE LED (D14)
and the four user LEDs (D25-D28) illuminate indicating that the flash device is
ready for programming.
default settings described in “Factory Default
6. On the Windows Start menu, click All Programs > Altera > Nios II EDS > Nios II
Command Shell.
7. In the Nios II command shell, navigate to the <install
dir>\kits\cycloneIIILS_3cls200_fpga\factory_recovery directory and type the
following command to run the restore script:
./restore.sh r
Restoring the flash memory might take several minutes. Follow any instructions
that appear in the Nios II command shell.
8. After all flash programming completes, cycle the POWER switch (SW1) off then
on.
9. Using the Quartus II Programmer, click Add File and select <install
dir>\kits\cycloneIIILS_3cls200_fpga\factory_recovery\c3ls200_fpga_bup.sof.
10. Turn on the Program/Configure option for the added file.
11. Click Start to download the selected configuration file to the FPGA. Configuration
is complete when the progress bar reaches 100%. The CONF DONE LED (D14)
and the four user LEDs (D25-D28) illuminate indicating the flash memory device
is now restored with the factory contents.
Cyclone III LS FPGA Development Kit User Guide © October 2009 Altera Corporation
Page 39

Appendix A: Programming the Flash Memory Device A–5
Restoring the MAX II CPLD to the Factory Settings
12. Cycle the POWER switch (SW1) off then on to load and run the restored factory
design.
13. The restore script cannot restore the board’s MAC address automatically. In the
Nios II command shell, type the following Nios II EDS command:
nios2-terminal r
and follow the instructions in the terminal window to generate a unique MAC
address.
f To ensure that you have the most up-to-date factory restore files and information
about this product, refer to the Altera Development Kits page on the Altera website.
Restoring the MAX II CPLD to the Factory Settings
This section describes how to restore the original factory contents to the MAX II CPLD
on the development board. Make sure you have the Nios II EDS installed, and
perf
orm the following instructions:
1. Set the board switches to the factory
default settings described in “Factory Default
Switch Settings” on page 4–2.
1 Installing the shunt jumper on jumper J11 pins 1-2 includes the MAX II
device in the JTAG chain. Installing the shunt jumper on jumper J12 or
setting DIP switch SW2.3 to the off position breaks the JTAG chain.
2. Launch the Quartus II Programmer.
3. Click Auto Detect.
4. Click Add File and select <install
dir>\kits\cycloneIIILS_3cls200_fpga\factory_recovery\max2.pof.
5. Turn on the Program/Configure option for the added file.
6. Click Start to download the selected configuration file to the MAX II CPLD.
Configuration is complete when the progress bar reaches 100%.
f To ensure that you have the most up-to-date factory restore files and information
about this product, refer to the Cyclone III LS FPGA Development Kit page on the
Altera website.
© October 2009 Altera Corporation Cyclone III LS FPGA Development Kit User Guide
Page 40

A–6 Appendix A: Programming the Flash Memory Device
Restoring the MAX II CPLD to the Factory Settings
Cyclone III LS FPGA Development Kit User Guide © October 2009 Altera Corporation
Page 41

Additional Information
Revision History
The following table displays the revision history for this user guide.
Date & Document
Version Changes Made Summary of Changes
October 2009
v1.0
How to Contact Altera
Initial release. —
For the most up-to-date information about Altera products, refer to the following
table.
Contact
Contact (Note 1)
Technical support Website www.altera.com/support
Technical training Website www.altera.com/training
Product literature Website www.altera.com/literature
Non-technical support (General) Email nacomp@altera.com
(Software Licensing) Email authorization@altera.com
Note to Table:
(1) You can also contact your local Altera sales office or sales representative.
Method Address
Email custrain@altera.com
Typographic Conventions
This document uses the typographic conventions shown in the following table.
Visual Cue Meaning
Bold Type with Initial Capital
Letters
bold type Indicates directory names, project names, disk drive names, file names, file name
Italic Type with Initial Capital Letters Indicates document titles. For example, AN 519: Stratix IV Design Guidelines.
Italic type Indicates variables. For example, n + 1.
Initial Capital Letters Indicates keyboard keys and menu names. For example, Delete key and the Options
Indicates command names, dialog box titles, dialog box options, and other GUI
labels. For example, Save As dialog box.
extensions, and software utility names. For example, \qdesigns directory, d: drive,
and chiptrip.gdf file.
Variable names are enclosed in angle brackets (< >). For example, <file name> and
<project name>.pof file.
menu.
© October 2009 Altera Corporation Cyclone III LS FPGA Development Kit User Guide
Page 42

Info–2 Additional Information
Typographic Conventions
Visual Cue Meaning
“Subheading Title” Quotation marks indicate references to sections within a document and titles of
Quartus II Help topics. For example, “Typographic Conventions.”
Courier type Indicates signal, port, register, bit, block, and primitive names. For example, data1,
tdi, and input. Active-low signals are denoted by suffix n. For example, resetn.
Indicates command line commands and anything that must be typed exactly as it
appears. For example, c:\qdesigns\tutorial\chiptrip.gdf.
Also indicates sections of an actual file, such as a Report File, references to parts of
files (for example, the AHDL keyword SUBDESIGN), and logic function names (for
example, TRI).
1., 2., 3., and
a., b., c., and so on.
Bullets indicate a list of items when the sequence of the items is not important.
Numbered steps indicate a list of items when the sequence of the items is important,
such as the steps listed in a procedure.
1 The hand points to information that requires special attention.
c
w
A caution calls attention to a condition or possible situation that can damage or
destroy the product or your work.
A warning calls attention to a condition or possible situation that can cause you
injury.
r The angled arrow instructs you to press Enter.
f The feet direct you to more information about a particular topic.
Cyclone III LS FPGA Development Kit User Guide © October 2009 Altera Corporation
 Loading...
Loading...