Page 1

Arria V SoC Development Kit User Guide
Arria V SoC Development Kit
User Guide
101 Innovation Drive
San Jose, CA 95134
www.altera.com
UG-01147-1.1
Feedback Subscribe
Page 2

© 2014 Altera Corporation. All rights reserved. ALTERA, ARRIA, CYCLONE, HARDCOPY, MAX, MEGACORE, NIOS, QUARTUS and STRATIX words and logos
are trademarks of Altera Corporation and registered in the U.S. Patent and Trademark Office and in other countries. All other words and logos identified as
trademarks or service marks are the property of their respective holders as described at www.altera.com/common/legal.html. Altera warrants performance of its
semiconductor products to current specifications in accordance with Altera's standard warranty, but reserves the right to make changes to any products and
services at any time without notice. Altera assumes no responsibility or liability arising out of the application or use of any information, product, or service
described herein except as expressly agreed to in writing by Altera. Altera customers are advised to obtain the latest version of device specifications before relying
on any published information and before placing orders for products or services.
ISO
9001:2008
Registered
June 2014 Altera Corporation Arria V SoC Development Kit
User Guide
Page 3

Contents
Chapter 1. About This Kit
Kit Features . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1–1
Before You Begin . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1–1
Inspect the Boards . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1–1
References . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1–2
Chapter 2. Software Installation
About the Quartus II Software . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2–1
Installing the Quartus II Subscription Edition Software . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2–2
Activating Your License . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2–2
Installing the Altera SoC Embedded Development Suite (EDS) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2–3
Installing the Development Kit . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2–3
Installing the USB-Blaster II Driver . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2–4
Chapter 3. Board Setup and Defaults
Setting Up the Board . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3–1
Factory Default Switch and Jumper Settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3–1
Restoring the MAX V CPLD to the Factory Settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3–6
Restoring the CFI Flash Device to the Factory Defaults . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3–6
Chapter 4. Board Update Portal
Connecting to the Board Update Portal Web Page . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4–1
Chapter 5. Board Test System
Preparing the Board for the Board Test System . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5–2
Running the Board Test System . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5–2
Using the Board Test System . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5–3
The Configure Menu . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5–3
The System Info Tab . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5–3
Board Information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5–4
JTAG Chain . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5–4
The GPIO Tab . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5–5
Character LCD . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5–5
User DIP Switch . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5–5
User LEDs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5–6
Push Button Switches . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5–6
The I2C Tab . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5–6
EEPROM . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5–7
RTC . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5–7
The DDR3 A and DDR3 B Tabs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5–8
Start . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5–8
Stop . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5–8
Performance Indicators . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5–8
Error Control . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5–9
Number of Addresses to Write and Read . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5–9
The XCVR Tab . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5–10
SFP A, SFP B, SMA . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5–10
The FMC A Tab . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5–12
June 2014 Altera Corporation Arria V SoC Development Kit
User Guide
Page 4

iv Contents
XCVR 10G and CMOS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5–12
The FMC B Tab . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5–14
FMC 10G, FMC 6G, CMOS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5–14
The Power Monitor . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5–16
U46, U60, U50 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5–16
Controls . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5–17
The Clock Control . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5–17
Serial Port Registers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5–18
fXTAL . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5–18
Target Frequency . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5–18
Default . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5–19
Set New Frequency . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5–19
Configuring the FPGA Using the Quartus II Programmer . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5–19
Before Configuring . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5–19
Configuring the FPGA . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5–19
Appendix A. Programming Flash Memory
CFI Flash Memory . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . A–1
CFI Flash Memory Map . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . A–1
Programming CFI Flash Using the Quartus II Programmer . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . A–1
Converting .sof to .pof . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . A–3
Quad SPI Flash Memory . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . A–3
Programming Quad SPI Flash using the Quartus II Programmer . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . A–3
SD Card Memory . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . A–4
The SD Card Default HPS Boot Source . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . A–4
Additional Information
Document Revision History . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Info–1
How to Contact Altera . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Info–1
Typographic Conventions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Info–1
Arria V SoC Development Kit June 2014 Altera Corporation
User Guide
Page 5

Kit Features
f For a complete list of this kit’s contents and capabilities, refer to the Arria V SoC
1. About This Kit
The Altera® Arria®V system on a chip (SoC) Development Kit is a complete design
environment that includes both the hardware and software you need to develop
Arria V SoC designs.
This section briefly describes the kit contents.
Development Kit page.
The Arria V SoC Development Kit includes the following hardware:
■ Arria V development board—A development platform that allows you to develop
and prototype hardware designs running on the Arria V SoC.
■ MicroSD flash memory card.
■ Loopback FPGA mezzanine card (FMC) daughter card.
■ Power supply and cables—The kit includes the following items:
Before You Begin
Before using the kit or installing the software, check the kit contents and inspect the
boards to verify that you received all of the items listed in Quick Start Guide printout in
the box. If any of the items are missing, contact Altera before you proceed.
Inspect the Boards
To inspect each board, perform these steps:
f For detailed information about the board components and interfaces, refer
to the Arria V SoC Development Board Reference Manual.
■ Power supply and AC adapters for North America/Japan, Europe, and the
United Kingdom.
■ One micro USB and two mini USB cables.
■ Ethernet cable.
1. Place the board on an anti-static surface and inspect it to ensure that it has not been
damaged during shipment.
c Without proper anti-static handling, you can damage the board.
2. Verify that all components on the boards appear in place and intact.
June 2014 Altera Corporation Arria V SoC Development Kit
User Guide
Page 6
1–2 Chapter 1: About This Kit
Before You Begin
1 In smaller applications with the Arria V development board, a heat sink is not
necessary. However, under extreme conditions (or for engineering sample silicon), the
board might require additional cooling to stay within operating temperature
guidelines. The board has two holes near the FPGA that accommodate many different
heat sinks, including the Dynatron V31G. You can perform power consumption and
thermal modeling to determine whether your application requires additional cooling.
For information about measuring board and FPGA power in real time, refer to “The
Power Monitor” on page 5–16.
f For more information about power consumption and thermal modeling,
refer to AN 358: Thermal Management for FPGAs.
References
Use the following links in Tab le 1– 1 to check the Altera website for other related
information:
Table 1–1. Related Links and Documents
Altera Website Link Information
Arria V SoC Development Kit page Latest board design files and reference designs.
Open-source community website supporting SoC
RocketBoards.org
ARM Cortex-A (SoC) On the dual-core ARM Cortex-A9 MPCore processor.
Getting Started for Software Developers Developing software for the Arria V SoC.
SoC Development Kit Hardware Developer
Resource Center
Altera SoC Embedded Design Suite User
Guide
GSRD User Manual page on
RocketBoards.org
ARM Development Studio 5 (DS-5) Altera
Edition Toolkit
Arria V SoC Development Board Reference
Manual
Development Board Daughtercards Additional daughter cards available for purchase.
Documentation: Arria V Devices Arria V device documentation.
Devices Purchase devices from the eStore.
Capture CIS Symbols Arria V OrCAD symbols.
Embedded Processing Nios II 32-bit embedded processor solutions.
development including Altera and Partner SoC
development kit targets and related designs and
documentation.
Developing SoC Hardware designs on the
development kit.
Includes information on the Installing the SoC EDS
and ARM DS-5. Preloader user guide. Hard
Processor System (HPS) Flash programmer. Bare
Metal and Linux Compiler. Yocto plugin. Debugging.
The Golden System Reference Design (GSRD)
demonstrates the HPS ability to communicate
between HPS to the FPGA logic via the AXI Bridge
interfaces.
As a part of the Altera SoC EDS, the ARM DS-5 Altera
Edition Toolkit provides a comprehensive set of
embedded development tools for Altera SoCs.
Complete information about the development board.
Arria V SoC Development Kit June 2014 Altera Corporation
User Guide
Page 7

This chapter explains how to install the following software:
■ Quartus II Subscription Edition Software (optional)
■ Altera SoC Embedded Development Suite (EDS)
■ Arria V SoC Development Kit software
■ On-Board USB-Blaster™ II driver
1 If you do not need to develop FPGA designs, you do not need to download the
Quartus II software. For example, when you only want to write software for the SoC
HPS. Installing the SoC EDS software, along with USB-II Blaster drivers, provides a
development kit JTAG programming environment.
About the Quartus II Software
Your kit includes a license for the Development Kit Edition (DKE) of the Quartus II
software (Windows platform only). For one year, this license entitles you to most of
the features of the Subscription Edition (excluding the IP Base Suite).
2. Software Installation
1 After the year, your DKE license will no longer be valid and you will not be permitted
to use this version of the Quartus II software. To continue using the Quartus II
software, you should download the free Quartus II Web edition or purchase a
subscription to Quartus II software. For more information, refer to the Design
Software page of the Altera website.
The Quartus II Development Kit Edition (DKE) software includes the following items:
■ Quartus II Software—The Quartus II software, including the Qsys system
integration tool, provides a comprehensive environment for network on a chip
(NoC) design. The Quartus II software integrates into nearly any design
environment and provides interfaces to industry-standard EDA tools.
■ MegaCore
®
IP Library—A library that contains Altera IP MegaCore functions. You
can evaluate MegaCore functions by using the OpenCore Plus feature to do the
following:
■ Simulate behavior of a MegaCore function within your system.
■ Verify functionality of your design, and quickly and easily evaluate its size and
speed.
■ Generate time-limited device programming files for designs that include
MegaCore functions.
■ Program a device and verify your design in hardware.
1 The OpenCore Plus hardware evaluation feature is an evaluation tool for
prototyping only. You must purchase a license to use a MegaCore function
in production.
June 2014 Altera Corporation Arria V SoC Development Kit
User Guide
Page 8

2–2 Chapter 2: Software Installation
f For more information about OpenCore Plus, refer to AN 320: OpenCore Plus
Evaluation of Megafunctions.
Installing the Quartus II Subscription Edition Software
f Nios
®
II Embedded Design Suite (EDS)—A full-featured set of tools that
allows you to develop embedded software for the Nios II processor, which
you can include in your Altera FPGA designs.
Installing the Quartus II Subscription Edition Software
Included in the Quartus II Subscription Edition Software are the Quartus II software
(including Qsys), the Nios II EDS, and the MegaCore IP Library. To install the Altera
development tools, perform the following steps:
1. Download the Quartus II Subscription Edition Software from the Quartus II
Subscription Edition Software page of the Altera website. Alternatively, you can
request a DVD from the Altera IP and Software DVD Request Form page of the
Altera website.
2. Follow the on-screen instructions to complete the installation process.
f If you have difficulty installing the Quartus II software, refer to the Altera Software
Installation and Licensing Manual.
Activating Your License
Purchasing this kit entitles you to a one-year license for the Development Kit Edition
(DKE) of the Quartus II software.
1 After the year, your DKE license will no longer be valid and you will not be permitted
to use this version of the Quartus II software. To continue using the Quartus II
software, you should download the free Quartus II Web Edition or purchase a
subscription to Quartus II software.
Before using the Quartus II software, you must activate your license, identify specific
users and computers, and obtain and install a license file.
If you already have a licensed version of the subscription edition, you can use that
license file with this kit. If not, follow these steps:
1. Log on at the myAltera Account Sign In web page, and click Sign In.
2. On the myAltera Home web page, click the Self-Service Licensing Center link.
3. Locate the serial number printed on the side of the development kit box below the
bottom bar code.
The number consists of alphanumeric characters and does not contain hyphens:
for example, 5xxxSoCxxxxxxx.
4. On the Self-Service Licensing Center web page, click the Find it with your License
Activation Code link.
5. In the Find/Activate Products dialog box, enter your development kit serial
number and click Search.
6. When your product appears, turn on the check box next to the product name.
Arria V SoC Development Kit June 2014 Altera Corporation
User Guide
Page 9

Chapter 2: Software Installation 2–3
Installing the Altera SoC Embedded Development Suite (EDS)
7. Click Activate Selected Products, and click Close.
8. When licensing is complete, Altera emails a license.dat file to you. Store the file on
your computer and use the License Setup page of the Options dialog box in the
Quartus II software to enable the software.
To license the Quartus II software, you need your computer’s network interface
card (NIC) ID, a number that uniquely identifies your computer. On the computer
you use to run the Quartus II software, type
to determine the NIC ID. Your NIC ID is the 12-digit hexadecimal number on the
Physical Address line.
For complete licensing details, refer to the Altera Software Installation and Licensing
Manual.
ipconfig /all
at a command prompt
Installing the Altera SoC Embedded Development Suite (EDS)
The Altera SoC EDS is a comprehensive tool suite for embedded software
development on Altera SoC devices. It contains development tools, utility programs,
run-time software, and application examples to expedite firmware and application
software of SoC embedded systems.
As a part of the Altera SoC EDS, the ARM DS-5 Altera Edition Toolkit provides a
comprehensive set of embedded development tools for Altera SoCs.
f For more information, refer to the ARM Development Studio 5 (DS-5) Altera Edition
Toolkit.
f For the steps to install the SoC EDS Tool Suite, refer to the Altera SoC Embedded
Design Suite User Guide.
Installing the Development Kit
Perform these steps:
1. Download the Arria V SoC Development Kit installer from the Arria V SoC
Development Kit page of the Altera website. Alternatively, you can request a
development kit DVD from the Altera Kit Installations DVD Request Form page of
the Altera website.
2. Start the Arria V SoC Development Kit installer .exe for Windows, or unzip the
installation image for Linux.
3. Choose an installation directory that is relative to the Quartus II software
installation directory. Follow the on-screen instructions to complete the
installation process.
4. For the latest issues and release notes, Altera recommends that you review the
readme.txt located in the root directory of the kit installation.
June 2014 Altera Corporation Arria V SoC Development Kit
User Guide
Page 10
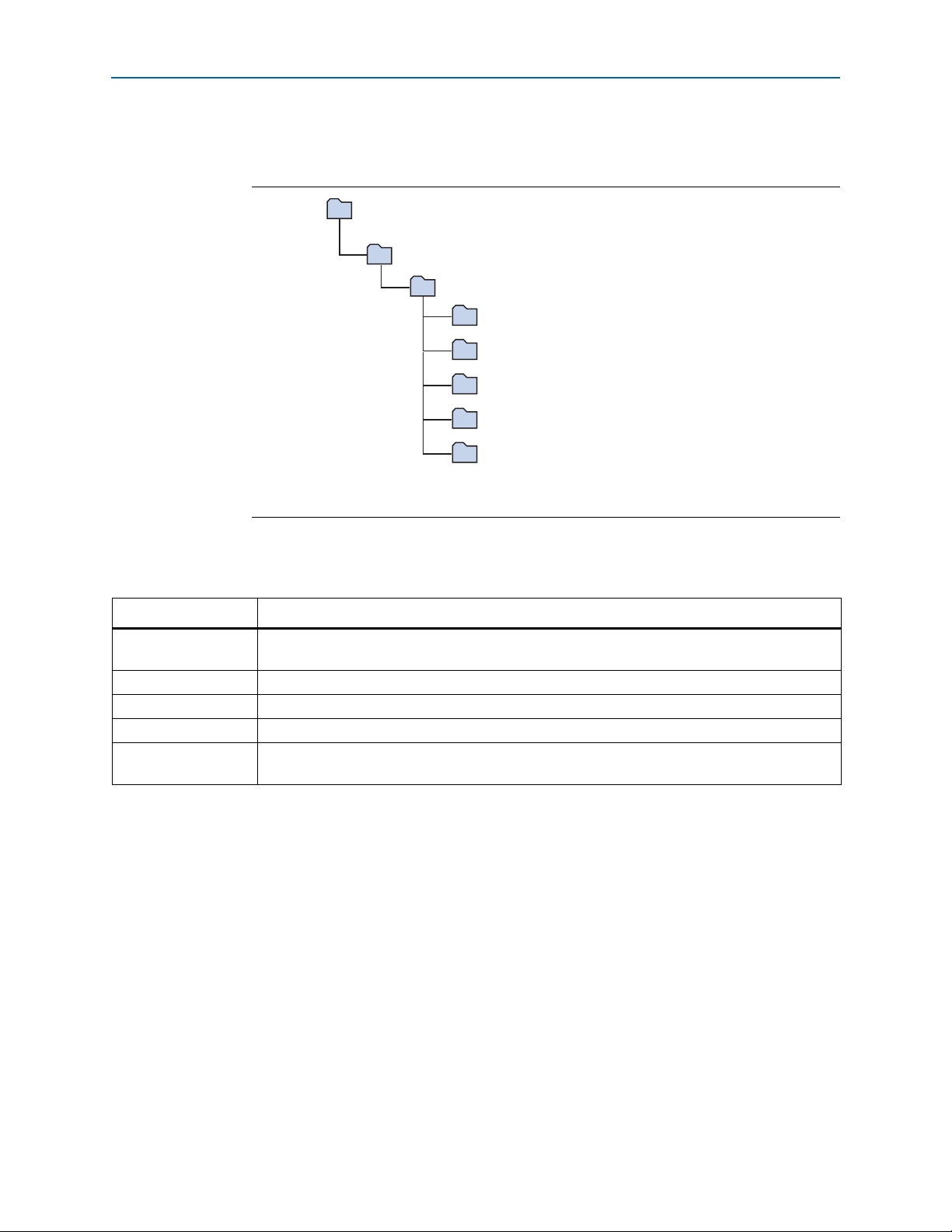
2–4 Chapter 2: Software Installation
<install dir>
documents
board_design_files
The default Windows installation directory is C:\altera\
<version>
\.
examples
factory_recovery
demos
kits
arriaVST_5astfd5kf40es_soc
Installing the USB-Blaster II Driver
The installation program creates the Arria V SoC Development Kit directory structure
shown in Figure 2–1.
Figure 2–1. Arria V SoC Development Kit Installed Directory Structure
Note to Figure 2–1:
(1) Early-release versions might have slightly different directory names.
Tab le 2– 1 lists the file directory names and a description of their contents.
Table 2–1. Installed Directory Contents
Directory Name Description of Contents
board_design_files
Contains schematic, layout, assembly, and bill of material board design files. Use these files as a
starting point for a new prototype board design.
demos Contains demonstration applications.
documents Contains the kit documentation.
examples Contains the sample design files for the Arria V SoC Development Kit.
factory_recovery
Contains the original data programmed onto the board before shipment. Use this data to restore
the board with its original factory contents.
(1)
Installing the USB-Blaster II Driver
The Arria V development board includes integrated USB-Blaster circuitry for FPGA
programming. However, for the host computer and board to communicate, you must
install the On-Board USB-Blaster II driver on the host computer.
f Installation instructions for the On-Board USB-Blaster II driver for your operating
system are available on the Altera website. On the Altera Programming Cable Driver
Arria V SoC Development Kit June 2014 Altera Corporation
User Guide
f For USB-Blaster II configuration details, refer to the On-Board USB-Blaster II page.
Information page of the Altera website, locate the table entry for your configuration
and click the link to access the instructions.
Page 11

This chapter explains how to set up the Arria V SoC development board and restore
defaults.
Setting Up the Board
To prepare the board, perform these steps:
1. The development board ships with its board switches preconfigured to support
the design examples in the kit. If you suspect your board might not be currently
configured with the default settings, follow the instructions in “Factory Default
Switch and Jumper Settings” on page 3–1 to return the board to its factory settings
before proceeding.
The development board ships with the Golden System Reference Design binaries
stored in the microSD card.
The microSD card also includes the following:
3. Board Setup and Defaults
■ Hardware reference design FPGA image, Raw Binary File (.rbf) file
■ HPS image preloader U-Boot and Linux images
■ File system and software examples
2. Power up the development board by using the included laptop power supply
plugged into the board.
c Use only the supplied power supply. Power regulation circuitry on the
board can be damaged by power supplies with greater voltage, and a
lower-rated power supply may not be able to provide enough power for the
board.
Alternatively, you can use the an ATX power from a PC by plugging a 4-pin
output from that supply to J33 on the development board.
c Make sure that the ATX supply is off when connecting to the board. Hot-
swap is not supported and may damage the board's power supplies and
other downstream devices.
When configuration is complete, the Config Done LED (D38) illuminates, signaling
that the Arria V device configured successfully.
Factory Default Switch and Jumper Settings
This section shows the factory settings (Figure 3–1) for the Arria V SoC development
board. These settings ensure that the Board Update Portal and Golden System
Reference design function properly.
June 2014 Altera Corporation Arria V SoC Development Kit
User Guide
Page 12
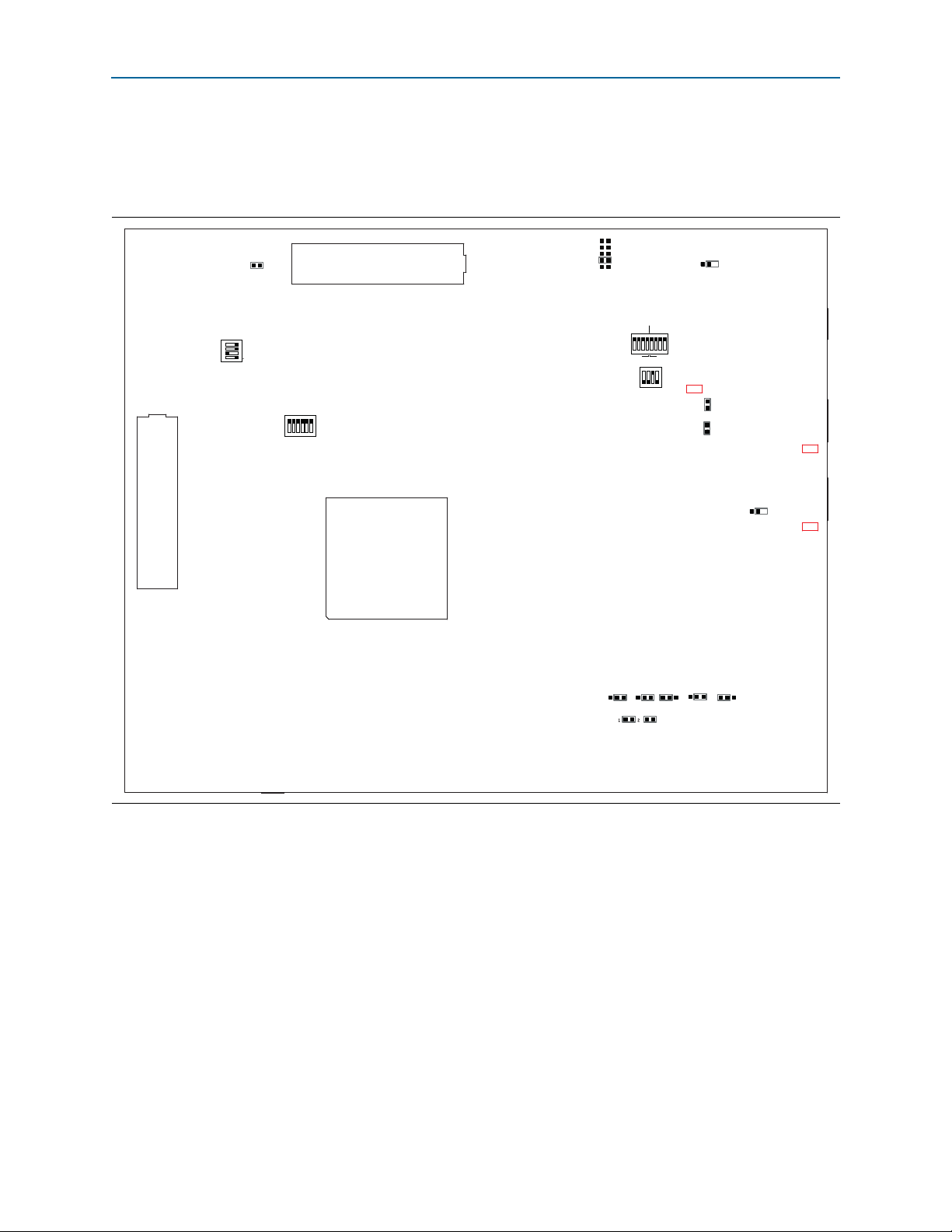
3–2 Chapter 3: Board Setup and Defaults
Arria V SoC
J37
1
0
1
01
0
1
0
J38 J39 J40 J41
CSEL0
J45
SEL1
J46
SEL0
CLK OSC2
CSEL1 BSEL0 BSEL1 BSEL2
1
0
J6
1.2V
FMC VAR
1.5V
1.8V
2.5V
HPS
FPGA
FMC
MAX
SW4
1 2 3 4
ON
SW1
3 2 1 0 3 2 1 0
HPS
J18
J23
J30
Not a jumper
Not a jumper
Not a jumper
Not a jumper
FPGA
ON
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8
J3
FMCB_JTAG_EN
SW2
1 2 3 4
SECURITY
FACT LOAD
Si570
CLK125A
ON
SW3
FMCB
FMCA
01234
MSEL
ON
1 2 3 4 5 6
J7
LMK_OSC_SEL
J28
JTAG_MIC_SEL
J19
JTAG
HPS SEL
J21
JTAG
SEL
Factory Default Switch and Jumper Settings
1 The SD card, Max V system controller, and CFI flash are already programmed with
the factory default files. For more information, refer to Appendix A, Programming
Flash Memory.
Figure 3–1. Switch Locations and Default Settings
Arria V SoC Development Kit June 2014 Altera Corporation
User Guide
Page 13
Chapter 3: Board Setup and Defaults 3–3
Factory Default Switch and Jumper Settings
To restore the switches to their factory default settings, perform these steps:
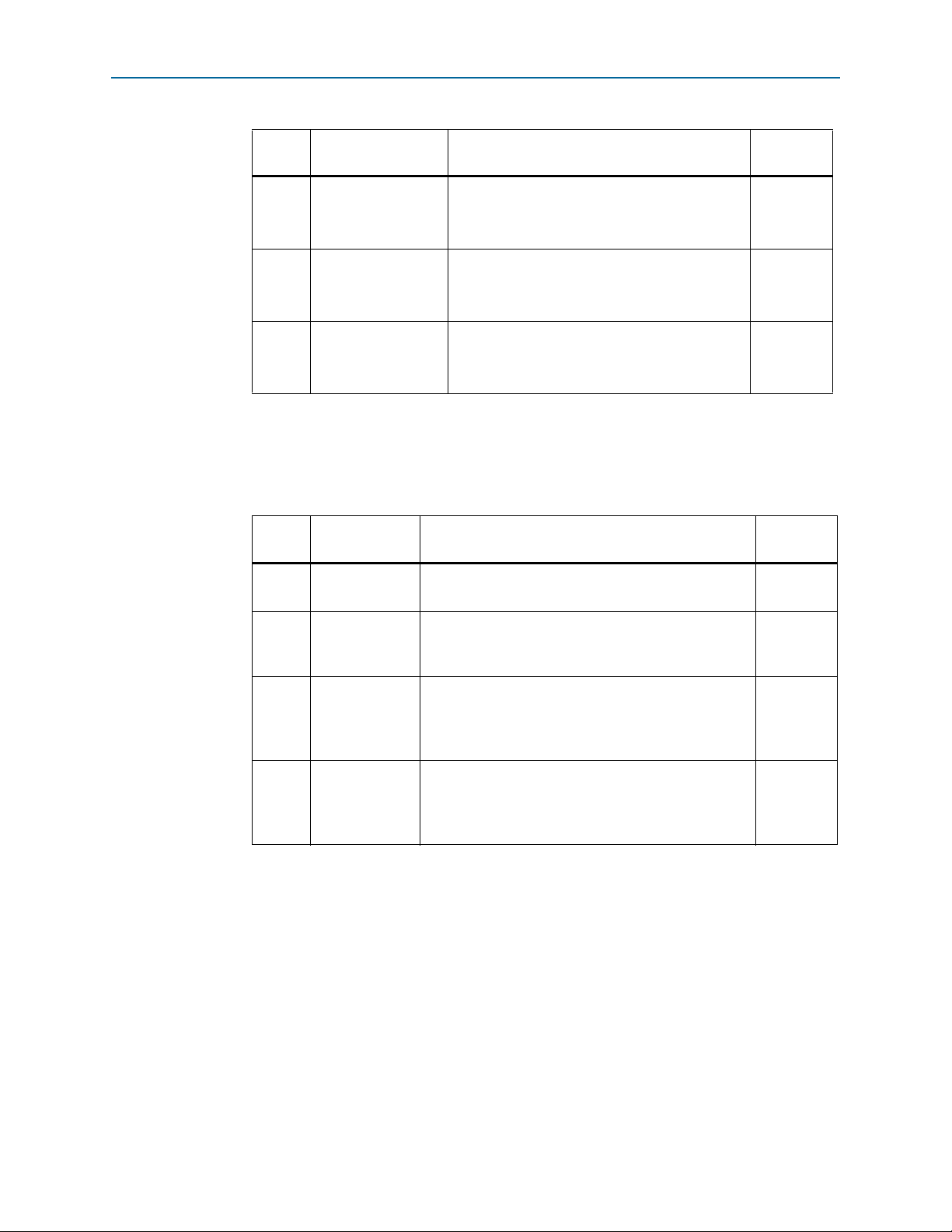
1. Set the DIP switch bank (SW2) to match Table 3–1 and Figure 3–1.
In the following table, ON indicates the switch is to the left according to the board
orientation as shown in Figure 3–1.
Table 3–1. SW2 DIP Switch Settings
Switch
Board
Label
1 CLK125A
2 Si570
3FACT LOAD
4 Security
Function
Switch 1 has the following options:
■ ON (0) = On-board oscillator is disabled.
■ OFF (1) = On-board oscillator is enabled.
Switch 2 has the following options:
■ ON (0) = On-board programmable oscillator is
enabled.
■ OFF (1) = On-board programmable oscillator is
disabled.
Switch 3 has the following options:
■ ON (0) = Load the user design from flash at
power up.
■ OFF (1) = Load the user factory from flash at
power up.
Switch 4 has the following options:
■ ON (0) = On-Board USB Blaster II sends
FACTORY command at power up
■ OFF (1) = On-Board USB Blaster II does not
send FACTORY command at power up
Default
Position
OFF
ON
OFF
OFF
2. Set the DIP switch bank (SW3) to match Table 3–2 and Figure 3–1.
In the following table, up and down indicates the position of the switch with the
board orientation as shown in Figure 3–1.
Important: The default MSEL pin settings are set to all zeroes (ON) to select the fast
passive parallel x16 mode. For power-up configuration from MAX V and CFI
flash, ensure that the MAX V design uses this same mode as does in the design in
the <install dir>\kits\arriaVST_5astfd5kf40es_soc\examples\max5 directory.
Table 3–2. SW3 DIP Switch Settings (Part 1 of 2)
Switch
Board
Label
Function
Default
Position
Switch 1 has the following options:
1 MSEL0
■ ON (up) = MSEL0 is 0.
■ OFF (down) = MSEL0 is 1.
Switch 2 has the following options:
2 MSEL1
■ ON (up) = MSEL1 is 0.
■ OFF (down) = MSEL1 is 1.
ON
ON
June 2014 Altera Corporation Arria V SoC Development Kit
User Guide
Page 14
3–4 Chapter 3: Board Setup and Defaults
Factory Default Switch and Jumper Settings
Table 3–2. SW3 DIP Switch Settings (Part 2 of 2)
Switch
Board
Label
Function
Switch 3 has the following options:
3 MSEL2
■ ON (up) = MSEL2 is 0.
■ OFF (down) = MSEL2 is 1.
Switch 4 has the following options:
4 MSEL3
■ ON (up) = MSEL3 is 0.
■ OFF (down) = MSEL3 is 1.
Switch 5 has the following options:
5 MSEL4
■ ON (up) = MSEL4 is 0.
■ OFF (down) = MSEL4 is 1.
3. Set the DIP switch bank (SW4) to match Table 3–3 and Figure 3–1.
In the following table, up and down indicates the position of the switch with the
board orientation as shown in Figure 3–1.
Table 3–3. SW4 JTAG DIP Switch Settings
Switch
1HPS
2FPGA
3FMCA
Board
Label
Function
■ ON (up) = Do not Include HPS in the JTAG chain.
■ OFF (down) = Include HPS in the JTAG chain
■ ON (up) = Do not Include the FPGA in the JTAG
chain.
■ OFF (down) = Include the FPGA in the JTAG chain.
■ ON (up) = Do not include the FMCA connector in the
JTAG chain.
■ OFF (down) = Include the FMCA connector in the
JTAG chain.
■ ON (up) = Do not include the MAX V system
4MAX
controller in the JTAG chain.
■ OFF (down) = Include the MAX V system controller in
the JTAG chain.
Default
Position
ON
ON
ON
Default
Position
OFF
OFF
ON
OFF
Arria V SoC Development Kit June 2014 Altera Corporation
User Guide
Page 15

Chapter 3: Board Setup and Defaults 3–5
Factory Default Switch and Jumper Settings
4. Set the following jumper blocks to match Tab le 3– 4 and Figure 3–1.
Table 3–4. Default Jumper Settings
Board
Reference
J3 FMCB
Board Label Description
■ SHORT: FMCB is not in the JTAG chain
■ OPEN: FMCB is in the JTAG chain
Variable voltage:
■ 9-10: 1.2 V
J6 FMC
J7 LMK_OSC_SEL
■ 7-8: 1.5 V
■ 5-6: 1.8 V
■ 3-4: 2.5 V
■ 1-2: not valid
■ SHORT: Select to use SMA
■ OPEN: Select to use on-board VCXO
■ SHORT: Controls the HPS from On-Board USB
Blaster II JTAG master.
J19 JTAG HPS SEL
■ OPEN: Controls the HPS from MICTOR-based
JTAG master, such as DSTREAM or Lauterbach
programming cables. Also, sets SW4.1 to ON to
remove the On-Board USB Blaster II from
driving the HPS JTAG input port in this mode.
■ SHORT: The USB Blaster II is the source of the
J21 JTAG SEL
JTAG chain.
■ OPEN: The Mictor is the source of the JTAG
chain.
■ SHORT: JTAG TRST input to HPS driven from
J28 JTAG MIC SEL
the JTAG chain.
■ OPEN: JTAG TRST input to HPS driven from the
MICTOR.
J37 CLKSEL0 Selects the HPS clock settings.
J38 CLKSEL1 Selects the HPS clock settings.
(1)
(1)
J39 BOOTSEL0 Selects the boot mode and source for the HPS.
J40 BOOTSEL1 Selects the boot mode and source for the HPS.
J41 BOOTSEL2 Selects the boot mode and source for the HPS.
(1)
(1)
(1)
Default
Position
SHORT
3-4: 2.5 V
OPEN
SHORT
SHORT
OPEN
SHORT pins
2-3
SHORT pins
2-3
SHORT pins
1-2
SHORT pins
2-3
SHORT pins
1-2
June 2014 Altera Corporation Arria V SoC Development Kit
User Guide
Page 16

3–6 Chapter 3: Board Setup and Defaults
Table 3–4. Default Jumper Settings (Continued)
Restoring the MAX V CPLD to the Factory Settings
Board
Reference
J45, J46 OSC2_CLK_SEL
Note to Tab le 3– 4:
(1) For more information, refer to the Arria V Device Handbook.
Board Label Description
■ 00 (SHORT, SHORT): Selects the on-board
25MHz clock
■ 01 (SHORT, OPEN): Selects SMA
■ 10 (OPEN, SHORT): Selects the on-board
33MHz clock
■ 11 (OPEN, OPEN): none
For more information about the FPGA board settings, refer to the Arria V SoC
Development Board Reference Manual.
Restoring the MAX V CPLD to the Factory Settings
This section describes how to restore the original factory contents to the MAX V
CPLD on the development board. Make sure you have the Nios II EDS installed, and
then perform these steps:
1. Set the board switches to the factory default settings described in “Factory Default
Switch and Jumper Settings” on page 3–1.
Default
Position
SHORT,
SHORT
1 DIP switch SW4.4 includes the MAX V device in the JTAG chain.
2. Launch the Quartus II Programmer.
3. Click Auto Detect.
4. Click Add File and select <install
dir>\kits\arriaVST_5astfd5kf40es_soc\factory_recovery\max<no_ver>.pof.
5. Turn on the Program/Configure option for the added file.
6. Click Start to download the selected configuration file to the MAX V CPLD.
Configuration is complete when the progress bar reaches 100%.
f To ensure that you have the most up-to-date factory restore files and product
information, refer to the Arria V SoC Development Kit page of the Altera website.
Restoring the CFI Flash Device to the Factory Defaults
To program the factory image to the flash device in the Quartus II Programmer, do the
following steps:
1. On the Tools menu in the Quartus II software, click Programmer.
2. In the Programmer window, click Auto-Detect.
1 If you do not see USB Blaster or the board's embedded USB Blaster II listed
next to Hardware Setup, refer to the “Installing the USB-Blaster II Driver”
on page 2–4.
Arria V SoC Development Kit June 2014 Altera Corporation
User Guide
Page 17

Chapter 3: Board Setup and Defaults 3–7
Restoring the CFI Flash Device to the Factory Defaults
3. Click Add File and open <install
dir>\kits\arriaVST_5astfd5kf40es_soc\factory_recovery\max2_PFL_writer.pof.
4. Turn on the Program/Configure option for the Programmer Object File (.pof) file.
5. Click Start to download the selected configuration file to the MAX V CPLD.
Configuration is complete when the progress bar reaches 100%
6. Click Auto Detect and a flash device should show up attached to the MAX V in
the main window.
7. Double-click the graphic of the flash device in the device chain pane to display the
Device’s Properties dialog box.
8. Select the flash image .pof file: <install
dir>\kits\arriaVST_5astfd5kf40es_soc\factory_recovery\output_file.pof.
9. Once the flash image .pof is attached in the Quartus II Programmer, turn on
Page_1 and Option Bits. (Page_0 is reserved for the GSRD factory design.)
10. Click Start.
11. After the flash writing process has completed, power cycle the board and look for
the MAX CONF DONE LED to turn ON if successful.
12. Altera recommends that you return to the Max V System Controller factory design
after completing the flash writing. To do so, program the Max V with <install
dir>\kits\arriaVST_5astfd5kf40es_soc\factory_recovery\max<version>.pof. For
more information, refer to “Restoring the MAX V CPLD to the Factory Settings”
on page 3–6.
1 The flash writer version blinks the SEL 2, 1, and 0 LEDs and does not support the
Power Monitor, Clock Control, or other logic functions. It should only be used for
configuration.
f To ensure that you have the most up-to-date factory restore files and information
about this product, refer to the Arria V SoC Development Kit page of the Altera
website.
June 2014 Altera Corporation Arria V SoC Development Kit
User Guide
Page 18

3–8 Chapter 3: Board Setup and Defaults
Restoring the CFI Flash Device to the Factory Defaults
Arria V SoC Development Kit June 2014 Altera Corporation
User Guide
Page 19

4. Board Update Portal
The Board Update Portal web page provides links to useful information on the Altera
website. You can use this web page to interact with your board:
■ Blinking LEDs
■ Writing text messages to the LCD
■ Mouse over the board photo to view features
The Board Update Portal web page is served by the web server application running
on the HPS on your board.
Connecting to the Board Update Portal Web Page
Ensure that you have the following items are setup or installed.
■ A PC with a connection to a working Ethernet port on a DHCP enabled network.
■ A separate working Ethernet port connected to the same network for the board.
■ The Ethernet and power cables that are included in the kit.
To connect to the Board Update Portal web page, perform these steps:
1. Ensure that the CSEL and BSEL jumpers (Table 3–4 on page 3–5) and the DIP
switch SW2.3 (Table 3–1 on page 3–3) are in the factory default positions.
2. Attach the Ethernet cable to the HPS Ethernet connector on the upper left of the
board to your LAN.
3. Power up the board. The board connects to the LAN’s gateway router and obtains
an IP address and displays it to the LCD. If no IP address is obtained, the LCD
displays No IP obtained. If the system booted, the LCD displays Hello Tim.
If the LCD displays No IP obtained, your system partially booted, but without
Ethernet access. If you receive the No IP obtained message, Altera recommends that
you install the USB virtual COM port drivers to access the Linux system through a
terminal window.
f For more information, refer to the Configuring Serial Connection section of
the Linux Getting Started page on RocketBoards.org.
1 There are several reasons why your board may fail to get and IP address in
this step:
■ Your port is not active or the cable is not plugged in.
■ You do not have a DHCP server.
■ Your DHCP server ran out of addresses.
■ Your DHCP server was not allowed to respond to the board due to security
filters, such as MAC address filtering.
June 2014 Altera Corporation Arria V SoC Development Kit
User Guide
Page 20

4–2 Chapter 4: Board Update Portal
Connecting to the Board Update Portal Web Page
4. Launch a web browser on a PC that is connected to the same network, and enter
the IP address from the LCD into the browser address bar. The Board Update
Portal web page appears in the browser.
1 You can click Arria V SoC Development Kit on the Board Update Portal web
page to access the kit’s home page for documentation updates and
additional new designs.
f You can also navigate directly to the Arria V SoC Development Kit page of the Altera
website to determine if you have the latest kit software.
Arria V SoC Development Kit June 2014 Altera Corporation
User Guide
Page 21

5. Board Test System
The development kit includes an application called the Board Test System (BTS) and
related design examples. The BTS provides an easy-to-use interface to alter functional
settings and observe the results. You can use the BTS to test board components,
modify functional parameters, observe performance, and measure power usage.
(While using the BTS, you reconfigure the FPGA several times with test designs
specific to the functionality you are testing.)
To install the BTS, follow the steps in “Installing the Development Kit” on page 2–3.
The Board Test System GUI communicates over the JTAG bus to a test design running
in the Arria V device. Figure 5–1 shows the initial GUI for a board that is in the factory
configuration.
1 Look for yellow highlights in the board picture around the corresponding
components for each tab.
Figure 5–1. Board Test System Graphical User Interface
June 2014 Altera Corporation Arria V SoC Development Kit
User Guide
Page 22

5–2 Chapter 5: Board Test System
Several designs are provided to test the major board features. Each design provides
data for one or more tabs in the application. The Configure menu identifies the
appropriate design to download to the FPGA for each tab.
After successful FPGA configuration, the appropriate tab appears that allows you to
exercise the related board features.
The Power Monitor button starts the Power Monitor application that measures and
reports current power information for the board. Because the application
communicates over the JTAG bus to the MAX II device, you can measure the power of
any design in the FPGA, including your own designs.
Preparing the Board for the Board Test System
1 The Board Test System and Power Monitor share the JTAG bus with other
applications like the Nios II debugger and the SignalTap
Analyzer. Because the Quartus II programmer uses most of the bandwidth of the
JTAG bus, other applications using the JTAG bus might time out. Be sure to close the
other applications before attempting to reconfigure the FPGA using the Quartus II
Programmer.
Preparing the Board for the Board Test System
With the power to the board off, follow these steps:
1. Plug the included USB cable from J50 (USB-Blaster II interface) to the host
computer’s USB port.
2. Ensure that the development board switches and jumpers are set to the default
positions as shown in the “Factory Default Switch and Jumper Settings” section
starting on page 3–1.
3. Set the DIP switch (SW2.3) to the user on (0) position.
f For more information about the board’s DIP switch and jumper settings,
refer to the Arria V SoC Development Board Reference Manual.
4. Turn on the power to the board. The board loads the design stored in the user
hardware 1 portion of flash memory into the FPGA. If your board is still in the
factory configuration, or if you have downloaded a newer version of the Board
Test System to flash memory through the Board Update Portal, the design loads
the GPIO, SRAM, and flash memory tests.
®
II Embedded Logic
c To ensure operating stability, keep the USB cable connected and the board
powered on when running the demonstration application. The application
cannot run correctly unless the USB cable is attached and the board is on.
Running the Board Test System
Navigate to the <install
dir>\kits\arriaVST_5astfd5kf40es_soc\examples\board_test_system directory and
run the BoardTestSystem.exe application.
1 To run the BTS in Windows, you can also click Start > All Programs > Altera >
Arria V SoC Development Kit <version> > Board Test System.
Arria V SoC Development Kit June 2014 Altera Corporation
User Guide
Page 23

Chapter 5: Board Test System 5–3
Using the Board Test System
A GUI appears, displaying the application tab that corresponds to the design running
in the FPGA. The Arria V development board’s flash memory ships preconfigured
with the design that corresponds to the GPIO tab.
1 Under two conditions, the BTS displays a message prompting you to configure your
board with a valid BTS design:
■ If you power up your board with the DIP switch (SW2.3) in a position other than
the on (0) position
■ If you load your own design into the FPGA with the Quartus II Programmer
Using the Board Test System
This section describes each control in the BTS.
The Configure Menu
Use the Configure menu to select the design you want to use. Each design example on
this menu tests different board features that corresponds to one or more application
tabs. For example, if you select Configure with GPIO Design, the System Info,
GPIO, and I2C tabs become available for testing.
c The BTS configuration circuit might cause a conflict with the default HPS booting
sequence. Both events program the FPGA. To make sure the operation of the
Configure menu works properly, wait until you see the LCD display Hello Tim before
you use the Configure menu.
Figure 5–2. The Configure Menu
The System Info Tab
The System Info tab shows board’s current configuration. Figure 5–1 on page 5–1
shows the System Info tab. The tab displays the contents of the MAX V registers, the
JTAG chain, the board’s MAC address, the flash memory map, and other details
stored on the board.
The following sections describe the controls on the System Info tab.
June 2014 Altera Corporation Arria V SoC Development Kit
User Guide
Page 24

5–4 Chapter 5: Board Test System
Using the Board Test System
Board Information
The Board information controls display static information about your board.
■ Board Name—Indicates the official name of the board.
■ Part number—Indicates the part number of the board.
■ Serial number—Indicates the serial number of the board.
■ Factory test version—Indicates the version of the Board Test System currently
running on the board.
■ MAC1—Indicates the MAC address of the board's ENET1 10/100 port.
■ MAC2—Indicates the MAC address of the board's ENET2 10/100 port.
■ HPS MAC1—Indicates the MAC address of the board's HPS 10/100/1000
Ethernet port.
■ MAX V ver—Indicates the version of MAX V code currently running on the
board. The MAX V code resides in the <install
dir>\kits\arriaVST_5astfd5kf40es_soc\examples directory. Newer revisions of
this code might be available on the Arria V SoC Development Kit page of the
Altera website.
JTAG Chain
The JTAG chain control shows all the devices currently in the JTAG chain. The
Arria V device is always the first device in the chain. The JTAG chain is normally
mastered by the On-board USB-Blaster II.
1 If you plug in an external USB-Blaster cable to the JTAG header (J35), the On-Board
USB-Blaster II is disabled.
1 JTAG DIP switch bank (SW4) selects which interfaces are in the chain. Refer to
Table 3–3 on page 3–4 for detailed settings.
f For details on the JTAG chain, refer to the Arria V SoC Development Board Reference
Manual. For USB-Blaster II configuration details, refer to the On-Board USB-Blaster II
page.
Arria V SoC Development Kit June 2014 Altera Corporation
User Guide
Page 25

Chapter 5: Board Test System 5–5
Using the Board Test System
The GPIO Tab
The GPIO tab allows you to interact with all the general purpose user I/O
components on your board. You can write to the character LCD, read DIP switch
settings, turn LEDs on or off, and detect push button presses. Figure 5–3 shows the
GPIO tab.
Figure 5–3. The GPIO Tab
The following sections describe the controls on the GPIO tab.
Character LCD
The Character LCD controls allow you to display text strings on the character LCD on
your board. Type text in the text boxes and then click Display.
1 If you exceed the 16 character display limit on either line, a warning message appears.
User DIP Switch
The read-only User DIP switch control displays the current positions of the switches
in the user DIP switch bank. Change the switches on the board to see the graphical
display change accordingly.
June 2014 Altera Corporation Arria V SoC Development Kit
User Guide
Page 26

5–6 Chapter 5: Board Test System
Using the Board Test System
User LEDs
This control displays the current state of the user LEDs. Click the graphical
representation of the LEDs to turn the board LEDs on and off. You can click ALL to
turn on and off all of the user LEDs at once.
Push Button Switches
The read-only Push Button switches control displays the current state of the board
user push buttons. Press a push button on the board to see the graphical display
change accordingly.
The I2C Tab
The I2C tab allows you to read and write 1 kilobit (Kb) to an I2C EEPROM located at
U28 on the development board. Figure 5–4 shows the I2C tab.
Figure 5–4. The I2C Tab
The following sections describe the controls on the I2C tab.
Arria V SoC Development Kit June 2014 Altera Corporation
User Guide
Page 27

Chapter 5: Board Test System 5–7
Using the Board Test System
EEPROM
The serial I2C EEPROM is 32 Kilobits.
■ Start Address—0x0
■ Range—0x1000
■ Read—Reads data from the I
2
C EEPROM.
f For more information on the EEPROM, refer to the Arria V SoC Development Board
Reference Manual.
RTC
Real time clock.
■ RTC Time—Displays current time stored in RTC memory when you click Read. It
is not updated automatically.
■ System Time—Displays current time from PC and is updated automatically.
■ Read—Reads the time from the RTC device on the board.
■ Write System Time to RTC—Writes the time to the RTC device on the board.
June 2014 Altera Corporation Arria V SoC Development Kit
User Guide
Page 28

5–8 Chapter 5: Board Test System
Using the Board Test System
The DDR3 A and DDR3 B Tabs
These tabs allow you to read and write the DDR3 memory on your board. Figure 5–5
shows the DDR3 A tab, which has the same controls has the DDR3 B tab.
Figure 5–5. The DDR3 A Tab
The following sections describe the controls on the DDR3 A tab.
Start
The Start control initiates DDR3 memory transaction performance analysis.
Stop
The Stop control terminates transaction performance analysis.
Performance Indicators
These controls display current transaction performance analysis information collected
since you last clicked Start:
■ Write, Read, and To t al performance bars—Show the percentage of maximum
theoretical data rate that the requested transactions are able to achieve.
Arria V SoC Development Kit June 2014 Altera Corporation
User Guide
Page 29

Chapter 5: Board Test System 5–9
Using the Board Test System
■ Write (MBps), Read (MBps), and Total (MBps)—Show the number of bytes of
data analyzed per second. The data bus is 72 bits wide and the frequency is
400 MHz double data rate (800 Mbps per pin), equating to a theoretical maximum
bandwidth of 3200 Megabits per second or 400 MBps.
Error Control
This control displays data errors detected during analysis and allows you to insert
errors:
■ Detected errors—Displays the number of data errors detected in the hardware.
■ Inserted errors—Displays the number of errors inserted into the transaction
stream.
■ Insert Error—Inserts a one-word error into the transaction stream each time you
click the button. Insert Error is only enabled during transaction performance
analysis.
■ Clear—Resets the Detected errors and Inserted errors counters to zeros.
Number of Addresses to Write and Read
The Number of addresses to write and read control determines the number of
addresses to use in each iteration of reads and writes.
June 2014 Altera Corporation Arria V SoC Development Kit
User Guide
Page 30

5–10 Chapter 5: Board Test System
Using the Board Test System
The XCVR Tab
The XCVR tab allows you to perform loopback tests on the SFP A, SFP B, and SMA
ports. Figure 5–6 shows the XCVR tab.
Figure 5–6. The XCRV Tab
1 To perform these tests you need:
■ Two SFP optical or metal loopback cables to test both at the same time
■ Two matching SMA cables for the SMA loopback
The following sections describe the controls on the XCVR tab.
SFP A, SFP B, SMA
These groups displays the following SFP A, SFP B, SMA status information during the
loopback test:
■ Data rate—Displays the current SFP A, SFP B, SMA data rate in megabytes per
second (MBps).
■ Freq—Displays the data rate frequency in MHz which is equivalent to MBps.
Arria V SoC Development Kit June 2014 Altera Corporation
User Guide
Page 31

Chapter 5: Board Test System 5–11
Using the Board Test System
■ bits—Displays the number of bits transmitted since clicking Start.
■ Inserted errors—Displays the number of errors inserted by clicking Insert Error
button.
■ Detected errors—Displays the number of bit errors detected by the error checking
circuitry.
■ BER—Displays the bit error rate of the interface.
■ PLL lock—Displays Ye s if the SDI PLL is locked.
■ Pattern sync—Displays Ye s if the receiver has detected the input data pattern.
■ Start— Starts the PRBS data test and begins to monitor and update screen with
live test results.
■ Stop—Stops the PRBS data test.
■ Insert Error—Inserts an error into a data stream that is detected by the receiver
when in loopback using the included video cable.
With the Insert Error, there are differences among the three ports:
SFP A—Inserts 4 errors at 1 click due to 4 test blocks control.
SFP B—Inserts 3 errors at 1 click due to 3 test blocks control.
SMA—Inserts 1 error at 1 click.
■ Clear—Clears the Detected errors counter.
■ PMA Setting—Opens the PMA settings window that allows for adjusting the
analog transceiver settings, such as output voltage, loopback settings, and
equalization.
The following settings are available for analysis:
■ Serial Loopback—Routes the selected TX output signal back to the RX input
signal on-chip to verify operation without using an external loopback board.
■ VOD—Specifies the voltage output differential of the transmitter buffer.
■ Pre-emphasis tap
■ Pre—Specifies the amount of pre-emphasis on the pre-tap of the transmitter
buffer.
■ First post—Specifies the amount of pre-emphasis on the first post tap of the
transmitter buffer.
■ Second post—Specifies the amount of pre-emphasis on the second post tap
of the transmitter buffer.
■ Equalizer—Specifies the setting for the receiver equalizer.
■ DC gain—Specifies the DC portion of the receiver equalizer.
■ PRBS—Selects the transmit pattern and sets the receive error detection
circuitry to expect the same pattern for use in loopback testing.
June 2014 Altera Corporation Arria V SoC Development Kit
User Guide
Page 32

5–12 Chapter 5: Board Test System
Using the Board Test System
The FMC A Tab
The FMC A tab allows you to perform loopback tests on the FMC A port. Figure 5–7
shows the FMC A tab.
Figure 5–7. The FMC A Tab
1 For factory testing, you must have an FMC loopback card installed on the FMC
connector for this test to work correctly.
The following sections describe the controls on the FMC A tab.
XCVR 10G and CMOS
■ Data rate—Displays the current XCVR 10G (or CMOS) data rate in megabytes per
second (MBps).
■ Freq—Displays the data rate frequency in MHz which is equivalent to MBps.
■ Bits—Displays the number of bits transmitted since clicking Start.
■ Inserted errors—Displays the number of errors inserted by clicking Insert Error
button.
Arria V SoC Development Kit June 2014 Altera Corporation
User Guide
Page 33

Chapter 5: Board Test System 5–13
Using the Board Test System
■ Detected errors—Displays the number of bit errors detected by the error checking
circuitry.
■ BER—Displays the bit error rate of the interface.
■ PLL lock—Displays Ye s if the SDI PLL is locked.
■ Pattern sync—Displays Ye s if the receiver has detected the input data pattern.
■ Start— Starts the PRBS data test and begins to monitor and update screen with
live test results.
■ Stop—Stops the PRBS data test.
■ Insert Error—Inserts an error into an SDI data stream that is detected by the
receiver when in loopback using the included video cable.
■ Clear—Clears the Detected errors counter.
■ PMA Setting—Opens the PMA settings window that allows for adjusting the
analog transceiver settings, such as output voltage, loopback settings, and
equalization.
■ PRBS (list)—Selects the transmit pattern and sets the receive error detection
circuitry to expect the same pattern for use in loopback testing.
June 2014 Altera Corporation Arria V SoC Development Kit
User Guide
Page 34

5–14 Chapter 5: Board Test System
Using the Board Test System
The FMC B Tab
The FMC B tab allows you to perform loopback tests on the FMC B port. Figure 5–8
shows the FMC B tab.
Figure 5–8. The FMC B Tab
1 For factory testing, you must have an FMC loopback card installed on the FMC
connector for this test to work correctly.
The following sections describe the controls on the FMC tab.
FMC 10G, FMC 6G, CMOS
■ Data rate—Displays the current FMC (or CMOS) data rate in megabytes per
second (MBps).
■ Freq—Displays the data rate frequency in MHz which is equivalent to MBps.
■ Bits—Displays the number of bits transmitted since clicking Start.
■ Inserted errors—Displays the number of errors inserted by clicking Insert Error
button.
Arria V SoC Development Kit June 2014 Altera Corporation
User Guide
Page 35

Chapter 5: Board Test System 5–15
Using the Board Test System
■ Detected errors—Displays the number of bit errors detected by the error checking
circuitry.
■ BER—Displays the bit error rate of the interface.
■ PLL lock—Displays Ye s if the SDI PLL is locked.
■ Pattern sync—Displays Ye s if the receiver has detected the input data pattern.
■ Start— Starts the PRBS data test and begins to monitor and update screen with
live test results.
■ Stop—Stops the PRBS data test.
■ Insert Error—Inserts an error into an SDI data stream that is detected by the
receiver when in loopback using the included video cable.
■ Clear—Clears the Detected errors counter.
■ PMA Setting—Opens the PMA settings window that allows for adjusting the
analog transceiver settings, such as output voltage, loopback settings, and
equalization.
■ PRBS (list)—Selects the transmit pattern and sets the receive error detection
circuitry to expect the same pattern for use in loopback testing.
June 2014 Altera Corporation Arria V SoC Development Kit
User Guide
Page 36

5–16 Chapter 5: Board Test System
The Power Monitor
The Power Monitor
The Power Monitor measures and reports current power information. To start the
application, click Power Monitor in the Board Test System application.
1 You can also run the Power Monitor as a stand-alone application. PowerMonitor.exe
resides in the <install
dir>\kits\arriaVST_5astfd5kf40es_soc\examples\board_test_system directory.
In Windows, click Start > All Programs > Altera > Arria V SoC Development Kit
<version> > Power Monitor to start the application.
The Power Monitor communicates with the MAX V device on the board through the
JTAG bus. A power monitor circuit attached to the MAX V device allows you to
measure the power that the Arria V FPGA is consuming. Figure 5–9 shows the Power
Monitor.
Figure 5–9. The Power Monitor
The following sections describe the Power Monitor controls.
U46, U60, U50
The three groups show the power rail graphs from the three LTC2977 power monitors
on the board:
U46—HPS Power Monitor
Arria V SoC Development Kit June 2014 Altera Corporation
User Guide
Page 37

Chapter 5: Board Test System 5–17
The Clock Control
U60—FPGA Power Monitor 1
U50—FPGA Power Monitor 2
They display the mA power consumption of your board over time.
The green line indicates the current value. The red line indicates the maximum value
read since the last reset.
1 You can enlarge a graph by clicking on it. Click it again to restore the original size.
Temp on 2977
The temperature controls display only the temperature from the power supply
manager, not the FPGA.
Total Power
These controls display the sum of all four rails for each group, U34 and for U26.
Controls
This group contains the following controls:
■ Start—Starts the communication with the board to monitor power.
■ Stop—Stops the communication with the board to monitor power.
■ Update speed—Specifies how often to refresh the graph.
■ Log Results—Specifies that a log file is saved to <install
dir>\kits\arriaVST_5astfd5kf40es_soc\examples\board_test_system.
■ MAX V version—Indicates the version of MAX V code currently running on the
board. The MAX V code resides in the <install
dir>\kits\arriaVST_5astfd5kf40es_soc\factory_recovery and <install
dir>\kits\arriaVST_5astfd5kf40es_soc\examples\max5 directories.
1 Newer revisions of this code might be available on the Arria V SoC
f A table with the power rail information is available in the Arria V SoC Development
Board Reference Manual.
The Clock Control
The Clock Control application sets the Si570 (X2), Si571 (X3), or Si5338 (U31)
programmable oscillators to any frequency between 10 MHz and 810 MHz. The
frequencies support eight digits of precision to the right of the decimal point.
Development Kit page of the Altera website.
The Clock Control application runs as a stand-alone application. ClockControl.exe
resides in the <install
dir>\kits\arriaVST_5astfd5kf40es_soc\examples\board_test_system directory.
To start the application, click Start > All Programs > Altera >
Arria V SoC Development Kit <version> > Clock Control.
June 2014 Altera Corporation Arria V SoC Development Kit
User Guide
Page 38

5–18 Chapter 5: Board Test System
The Clock Control
f For more information about the programmable oscillators and the Arria V
development board’s clocking circuitry and clock input pins, refer to the Arria V SoC
Development Board Reference Manual.
The Clock Control communicates with the MAX V device on the board through the
JTAG bus. The programmable oscillators are connected to the MAX V device through
a 2-wire serial bus. Figure 5–10 shows the Clock Control Si570 tab.
Figure 5–10. The Clock Control
The following sections describe the Si570 tab controls.
Serial Port Registers
The Serial port registers control shows the current values from the Si570 registers.
fXTAL
The fXTAL control shows the calculated internal fixed-frequency crystal, based on the
serial port register values.
For more information about the f
value and how it is calculated, refer to the
XTAL
Si570/Si571 data sheet available on the Silicon Labs website (www.silabs.com).
Target Frequency
The Target frequency control allows you to specify the frequency of the clock. Legal
values are between 10 and 810 MHz with eight digits of precision to the right of the
decimal point. For example, 421.31259873 is possible within 100 parts per million
(ppm). The Target frequency control works in conjunction with the Set New
Frequency control.
Arria V SoC Development Kit June 2014 Altera Corporation
User Guide
Page 39

Chapter 5: Board Test System 5–19
Configuring the FPGA Using the Quartus II Programmer
Default
This control sets the frequency for the oscillator associated with the active tab back to
its default value. This can also be accomplished by power cycling the board.
Set New Frequency
The Set New Frequency control sets the programmable oscillator frequency for the
selected clock to the value in the Target frequency control for the programmable
oscillators. Frequency changes might take several milliseconds to take effect. You
might see glitches on the clock during this time. Altera recommends resetting the
FPGA logic after changing frequencies.
f For more information about these programmable oscillators, refer to the data sheets
available on the Silicon Labs website (www.silabs.com).
Configuring the FPGA Using the Quartus II Programmer
You can use the Quartus II Programmer to configure the FPGA with your SRAM
Object File (.sof) file.
Before Configuring
Ensure the following:
■ The Quartus II Programmer and the USB-Blaster II driver are installed on the host
computer.
■ The USB cable is connected to the development board.
■ Power to the board is on, and no other applications that use the JTAG chain are
running.
If the Quartus II Programmer window is already open, and you power cycle the
board, to detect the JTAG chain, do the following:
■ Click Hardware Setup in the Quartus II Programmer window.
■ Reselect USB-Blaster II in order to properly detect the JTAG chain.
Configuring the FPGA
Perform these steps:
1. Start the Quartus II Programmer.
2. Click Auto Detect to display the devices in the JTAG chain.
3. Click Add File and select the path to the desired .sof.
4. Turn on the Program/Configure option for the added file.
5. Click Start to download the selected file to the FPGA. Configuration is complete
when the progress bar reaches 100%.
June 2014 Altera Corporation Arria V SoC Development Kit
User Guide
Page 40

5–20 Chapter 5: Board Test System
Configuring the FPGA Using the Quartus II Programmer
1 Using the Quartus II Programmer to configure a device on the board causes other
JTAG-based applications such as the Board Test System and the Power Monitor to lose
their connection to the board. Restart those applications after configuration is
complete.
Arria V SoC Development Kit June 2014 Altera Corporation
User Guide
Page 41

A. Programming Flash Memory
This appendix describes programming information for the following memory
devices:
■ Common flash interface (CFI) flash memory
■ Quad serial peripheral interface (quad SPI) flash memory
■ SD card flash memory
The Arria V development board’s flash memory comes preconfigured with the
parallel flash loader (PFL) option bits to support FPGA designs to be written to any of
the three locations (Tab le A– 1). The PFL is disabled by default. Set SW2.3 to ON to
enable FPGA programming from CFI flash memory on power up.
1 There are several other factory software files written to flash memory to support the
Board Update Portal. These software files were created using the Nios II EDS, just as
the hardware design was created using the Quartus II software.
CFI Flash Memory
CFI Flash Memory Map
Tab le A –1 shows the default memory contents of the 512-Mb CFI flash device. For the
Board Update Portal to run correctly and update designs in the user memory, this
memory map must not be altered.
Table A–1. Byte Address Flash Memory Map
Unused 20316 0x02CA.0000 - 0x03FF.FFFF
User hardware 1 23330 0x0166.0000 - 0x02C9.FFFF
Factory hardware (GHRD) 23330 0x0002.0000 - 0x0165.FFFF
PFL option bits 32 0x0001.8000 - 0x00019FFF
Reset vector 96 0x0000.0000 - 0001.7FFFF
c Altera recommends that you do not overwrite the factory hardware images unless
you are an expert with Altera tools. If you unintentionally overwrite the factory
hardware or factory software image, refer to “Restoring the CFI Flash Device to the
Factory Defaults” on page 3–6.
Block Description KB Size Address Range
Programming CFI Flash Using the Quartus II Programmer
You can use the JTAG interface in Altera CPLDs to indirectly program the flash
memory device. The Altera CPLD JTAG block interfaces directly with the logic array
in a special JTAG mode. This mode brings the JTAG chain through the logic array
instead of the Altera CPLD boundary-scan cells (BSC). The PFL megafunction
provides JTAG interface logic to do the following:
June 2014 Altera Corporation Arria V SoC Development Kit
User Guide
Page 42

A–2 Appendix A: Programming Flash Memory
■ Convert the JTAG stream provided by the Quartus II software.
■ Program the CFI flash memory devices connected to the CPLD I/O pins.
CFI Flash Memory
Figure A–1 shows an Altera CPLD configured as a bridge to program the CFI flash
memory device through the JTAG interface.
Figure A–1. Programming the CFI Flash Memory With the JTAG Interface
MAX II CPLD
Quartus II
Software
via JTAG
Configuration Data
PFL
Common
Flash
Interface
CFI Flash
Memory
Altera
FPGA
Altera FPGA Not Used
for Flash Programming
Perform the following steps to program a user design to the flash device in the
Quartus II Programmer:
1 The following flash writing procedure blinks the SEL 2, 1, and 0 LEDs and does not
support the Power Monitor, Clock Control, or other logic functions. It should only be
used for configuration.
1. On the Tools menu in the Quartus II software, click Programmer.
2. In the Programmer window, click Auto-Detect.
1 If you do not see USB Blaster or the board's embedded USB Blaster II listed
next to Hardware Setup, refer to the “Installing the USB-Blaster II Driver”
on page 2–4.
3. Click Add File and open <install
dir>\kits\arriaVST_5astfd5kf40es_soc\factory_recovery\max2_PFL_writer.pof.
4. Turn on the Program/Configure option for the .pof file.
5. Click Start to download the selected configuration file to the MAX V CPLD.
Configuration is complete when the progress bar reaches 100%
6. Click Auto Detect and a flash device should show up attached to the MAX V in
the main window.
7. Double-click the graphic of the flash device in the device chain pane to display the
Device’s Properties dialog box.
8. Select the flash image .pof file generated from the Quartus II Convert
Programming Files dialog box. The default file name is output_file.pof.
9. After the flash image .pof is attached in the Quartus II Programmer, turn on
Page_1 and Option Bits. (Page_0 is reserved for the GSRD factory design.)
Arria V SoC Development Kit June 2014 Altera Corporation
User Guide
Page 43

Appendix A: Programming Flash Memory A–3
Quad SPI Flash Memory
10. Click Start.
11. After the flash writing process has completed, power cycle the board and look for
the MAX CONF DONE LED to turn ON if the writing process is successful.
12. Altera recommends that you return to the Max V System Controller factory design
after completing the flash writing. To do so, program the Max V with <install
dir>\kits\arriaVST_5astfd5kf40es_soc\factory_recovery\max<version>.pof. For
more information, refer to “Restoring the MAX V CPLD to the Factory Settings”
on page 3–6.
f For more information on programming flash memory, refer to Parallel Flash Loader
Megafunction User Guide and Using FPGA-Based Parallel Flash Loader with the
Quartus II Software.
Converting .sof to .pof
To generate a flash programming file, you must use the Quartus II software and
convert .sof files to .pof files.
To convert the files, follow these steps:
1. On the File menu, click Convert Programming Files.
2. For Programming file type, specify Programmer Object File (.pof) and name the
file.
3. For Configuration device, select CFI_512Mb for this kit's CFI device.
4. To add the configuration data, under Input files to convert, select SOF Data.
5. Click Add File and browse to the .sof files you want to add.
If you want to store the data from other .sof files in a different page, click Add SOF
page. Add the .sof files to the new page.
6. Select SOF Data and click Properties to set the page number and name.
7. Under Address mode for selected pages, choose the User Hardware 1 offset as
listed in the memory map in Appendix Table A–1.
Quad SPI Flash Memory
Programming Quad SPI Flash using the Quartus II Programmer
Although the quad SPI flash is not programmed by factory default, you can program
this device using quartus_hps.exe that resides in the quartus/bin directory. To use
this tool, open a command window and change directories to your 13.0 or later
installation (e.g. c:\altera\13.1\quartus\bin). To program an entire file to quad SPI
flash starting at address 0 type:
quartus_hps.exe -c <programming cable index> -o P <flash_boot_image.bin>
For help and more options, type
June 2014 Altera Corporation Arria V SoC Development Kit
quartus_hps.exe --help
User Guide
Page 44

A–4 Appendix A: Programming Flash Memory
SD Card Memory
SD Card Memory
The SD Card Default HPS Boot Source
The SD card is the default boot source for the HPS as selected by the BSEL jumpers.
The socket is designed to accept micro-SD cards. This kit comes with a microSD card,
micro-to-standard SD card adapter, and a USB programming adapter.
To program the SD card, do the following steps:
1. Insert the SD card into the USB Programming adapter and insert the programming
adapter into a USB port on your PC.
2. In Windows, you should see a pop-up window asking what you'd like to do with
the flash device. Click Cancel, but note the drive letter it is mounted as.
You cannot drag and drop files onto the SD card because the file system is
different. You need to use a disk image program or, preferably, use a Cygwin
installation such as the NIOS II Embedded Development System (Nios II EDS).
3. Start the Nios II Command Shell by clicking Start > All Programs > Altera
<version> > Nios II EDS > Nios II Command Shell.
4. At this shell, type the command
The SD card will generally be mounted as sda, sdb, or sdc, etc., depending on other
devices that may be present.
5. To be sure which is correct, remove the card and type
6. Look for what changed since you type the command the first time.
7. Re-insert the SD card, and verify the name once more.
8. Type
dd if=<boot_image_filename.img> of=/dev/<sd_card_name> <enter>
Linux users use the same
1 Be careful using this programming command as it will overwrite whatever
is found on the device pointed to in the
f For more information, refer to the Altera SoC Embedded Design Suite User
Guide and RocketBoards.org.
dd
ls /dev <enter>
commands.
ls /dev <enter>
of
command.
Arria V SoC Development Kit June 2014 Altera Corporation
User Guide
Page 45

This chapter provides additional information about the document and Altera.
Document Revision History
The following table shows the revision history for this document.
Date Version Changes
June 2014 1.1
December 2013 1.0 Initial release.
Corrected J39 BOOTSEL: SHORT pins 1-2.
Updated “Activating Your License” section in Chapter 2.
How to Contact Altera
To locate the most up-to-date information about Altera products, refer to the
following table.
Additional Information
Contact
Technical support Website www.altera.com/support
Technical training
Product literature Website www.altera.com/literature
Nontechnical support (general) Email nacomp@altera.com
Note to Table:
(1) You can also contact your local Altera sales office or sales representative.
(1)
(software licensing) Email authorization@altera.com
Contact Method Address
Website www.altera.com/training
Email custrain@altera.com
Typographic Conventions
The following table shows the typographic conventions this document uses.
Visual Cue Meaning
Bold Type with Initial Capital
Letters
bold type
Italic Type with Initial Capital Letters Indicate document titles. For example, Stratix IV Design Guidelines.
italic type
Indicate command names, dialog box titles, dialog box options, and other GUI
labels. For example, Save As dialog box. For GUI elements, capitalization matches
the GUI.
Indicates directory names, project names, disk drive names, file names, file name
extensions, software utility names, and GUI labels. For example, \qdesigns
directory, D: drive, and chiptrip.gdf file.
Indicates variables. For example, n + 1.
Variable names are enclosed in angle brackets (< >). For example, <file name> and
<project name>.pof file.
June 2014 Altera Corporation Arria V SoC Development Kit
User Guide
Page 46

Info–2 Additional Information
Typographic Conventions
Visual Cue Meaning
Initial Capital Letters
“Subheading Title”
Indicate keyboard keys and menu names. For example, the Delete key and the
Options menu.
Quotation marks indicate references to sections in a document and titles of
Quartus II Help topics. For example, “Typographic Conventions.”
Indicates signal, port, register, bit, block, and primitive names. For example,
tdi
, and
input
. The suffix n denotes an active-low signal. For example,
resetn
data1
.
,
Indicates command line commands and anything that must be typed exactly as it
Courier type
appears. For example,
c:\qdesigns\tutorial\chiptrip.gdf
.
Also indicates sections of an actual file, such as a Report File, references to parts of
files (for example, the AHDL keyword
TRI
example,
).
SUBDESIGN
), and logic function names (for
r An angled arrow instructs you to press the Enter key.
1., 2., 3., and
a., b., c., and so on
■ ■ ■ Bullets indicate a list of items when the sequence of the items is not important.
Numbered steps indicate a list of items when the sequence of the items is important,
such as the steps listed in a procedure.
1 The hand points to information that requires special attention.
h The question mark directs you to a software help system with related information.
f The feet direct you to another document or website with related information.
m The multimedia icon directs you to a related multimedia presentation.
c
w
A caution calls attention to a condition or possible situation that can damage or
destroy the product or your work.
A warning calls attention to a condition or possible situation that can cause you
injury.
The envelope links to the Email Subscription Management Center page of the Altera
website, where you can sign up to receive update notifications for Altera documents.
The feedback icon allows you to submit feedback to Altera about the document.
Methods for collecting feedback vary as appropriate for each document.
c Electromagnetic interference caused by modification of the kit contents is the sole
responsibility of the user.
This equipment is designated for use only in an industrial research environment.
Arria V SoC Development Kit June 2014 Altera Corporation
User Guide
 Loading...
Loading...