Page 1

W
N-200USB
W
ireless 11n USB Dongle
User’s Manual
Page 2

Copyright and Disclaimer
Copyright & Disclaimer
No part of this publication may be reproduced in any form or by any means, whether
electronic, mechanical, photocopying, or recording without the written consent of OvisLink
Corp.
OvisLink Corp. has made the best effort to ensure the accuracy of the information in this
user’s guide. However, we are not liable for the inaccuracies or errors in this guide.
Please use with caution. All information is subject to change without notice
All Trademarks are properties of their respective holders.
AirLive WN-200USB User’s Manual
Page 3

Table of Contents
Table of Contents
1. Introduction ................................................................................................1
1.1 Overview..............................................................................................1
1.2 How to Use This Guide........................................................................1
1.3 Driver/Utility Upgrade and Tech Support..............................................1
1.4 Features...............................................................................................2
2. Installing the WN-200USB .........................................................................3
1.1 Requirement ........................................................................................3
2.2 Package Content .................................................................................3
2.3 Knowing your WN-200USB..................................................................4
2.4 Software Installation.............................................................................4
2.5 Hardware Installation ...........................................................................8
2.6 LED Table ............................................................................................9
3. Configuration of WN-200USB .................................................................10
3.1 Important Information.........................................................................10
3.2 Using AirLive Wireless LAN Utility .....................................................10
3.2.1 Status Information......................................................................................10
3.2.2 Menu Structure of AirLive Wireless LAN Utility ..........................................11
3.2.3 Network Screen .........................................................................................12
3.2.4 Profile Screen ............................................................................................16
3.2.5 Advance Screen ........................................................................................22
3.2.6 Statistics Screen ........................................................................................24
3.2.7 WMM Screen.............................................................................................26
3.2.8 WPS Screen ..............................................................................................27
3.2.9 Radio on/off Button....................................................................................29
3.2.10 About Screen ...........................................................................................29
3.3 Using Windows Zero Configuration ...................................................30
4. Troubleshooting.......................................................................................34
5. Specifications...........................................................................................36
6. Network Glossary ....................................................................................38
i
AirLive WN-200USB User’s Manual
Page 4
1. Introduction
1. Introduction
1
1.1 Overview
The WN-200USB provides a wireless network interface for your Notebook or PC. Besides
common wireless standard 802.11b/g, WN-200USN is also able to access 802.11n
wireless network whose data transfer is up to 150Mbps.
1.2 How to Use This Guide
WN-200USB is a wireless 11n USB dongle. It is recommended that you read through the
entire user’s guide whenever possible. The user guide is divided into different chapters.
You should read at least go through the first 3 chapters before attempting to install the
device.
Recommended Reading
Chapter 1: This chapter explains the basic information for WN-200USB. It is a must read.
Chapter 2: This chapter is about hardware installation. You should read through the
entire chapter.
Chapter 3: This chapter is about windows utility installation. You also should read
through the entire chapter.
Chapter 4: If any trouble in using WN-200USB, you can refer to this chapter
Chapter 5: This chapter show technical specification of WN-200USB.
Chapter 6: Explanation on network technical terms from A to Z. Highly recommended for
reference when you encounter an unfamiliar term.
1.3 Driver/Utility Upgrade and Tech Support
If you encounter a technical issue that can not be resolved by information on this guide, we
1
AirLive WN-200USB User’s Manual
Page 5

1. Introduction
recommend that you visit our comprehensive website support at www.airlive.com. The
tech support FAQ are frequently updated with latest information.
In addition, you might find new driver/utility that either increase software functions or
provide bug fixes for WN-200USB. You can reach our on-line support center at the
following link:
http://www.airlive.com/support/support_2.jsp
Since 2009, AirLive has added the “Newsletter Instant Support System” on our website.
AirLive Newsletter subscribers receives instant email notifications when there are new
download or tech support FAQ updates for their subscribed AirLive models. To become
an AirLive newsletter member, please visit: http://www.airlive.com/member/member_3.jsp
1.4 Features
Compatible with Draft IEEE 802.11n, 802.11b and 802.11g 2.4GHz
Data transmission rate is up to 150Mbps
Supports Turbo Mode which can enhance the data transmission rate within the specific
wireless network
Supports WMM (Wi-Fi Multimedia) function (IEEE 802.11e QoS standard) and can
meet the requirement of the multi-media data bandwidth
Supports 64/128-bit WEP, WPA (TKIP with IEEE802.1x) and WPA2 (AES with IEEE
802.1x) functions for high level security
Supports CCX v5 (Cisco Compatible Extensions) for the radio monitoring and fast
roaming
Automatic fallback which increases the data security and reliability
Supports USB 2.0 interface
AirLive WN-200USB v2 User’s Manual
2
Page 6

2. Installing the
2. Installing the WN-200USB
2
This chapter describes the software and hardware installation procedure for the
WN-200USB. For utility configuration, please go to chapter 3 for more details.
WN-200USB
1.1 Requirement
It is important to make sure that you have the below requirement before installing the
WN-200USB.
Your operation system of PC or Notebook is Windows 2000/XP/Vista.
Available USB port.
CD-ROM drive.
IEEE802.11b, IEEE802.11g or IEEE802.11n wireless LAN.
2.2 Package Content
Unpack the contents of the WN-200USB and verify them against the checklist below.
One unit of WN-200USB
User Guide (CD-ROM)
Quick Installation Guide
WN-200USB User Guide (CD-ROM) Quick Installation Guide
Compare the contents of your WN-200USB package with the standard checklist above. If
any item is missing or damaged, please contact your local dealer for service.
3
AirLive WN-200USB User’s Manual
Page 7

2.3 Knowing your WN-200USB
Below are descriptions and diagrams of the product:
2. Installing the WN-200USB
2.4 Software Installation
You should install the supplied software BEFORE inserting the WN-200USB.
1. Insert the CD-ROM into the drive on your PC or Notebook.
2. The main screen of AutoRun CD will appear automatically. If not, please run
“D:\autorun.exe” where D is the letter of your CD-ROM drive. Select Install Driver &
Utility to start installation
AirLive WN-200USB User’s Manual
4
Page 8
2. Installing the WN-200USB
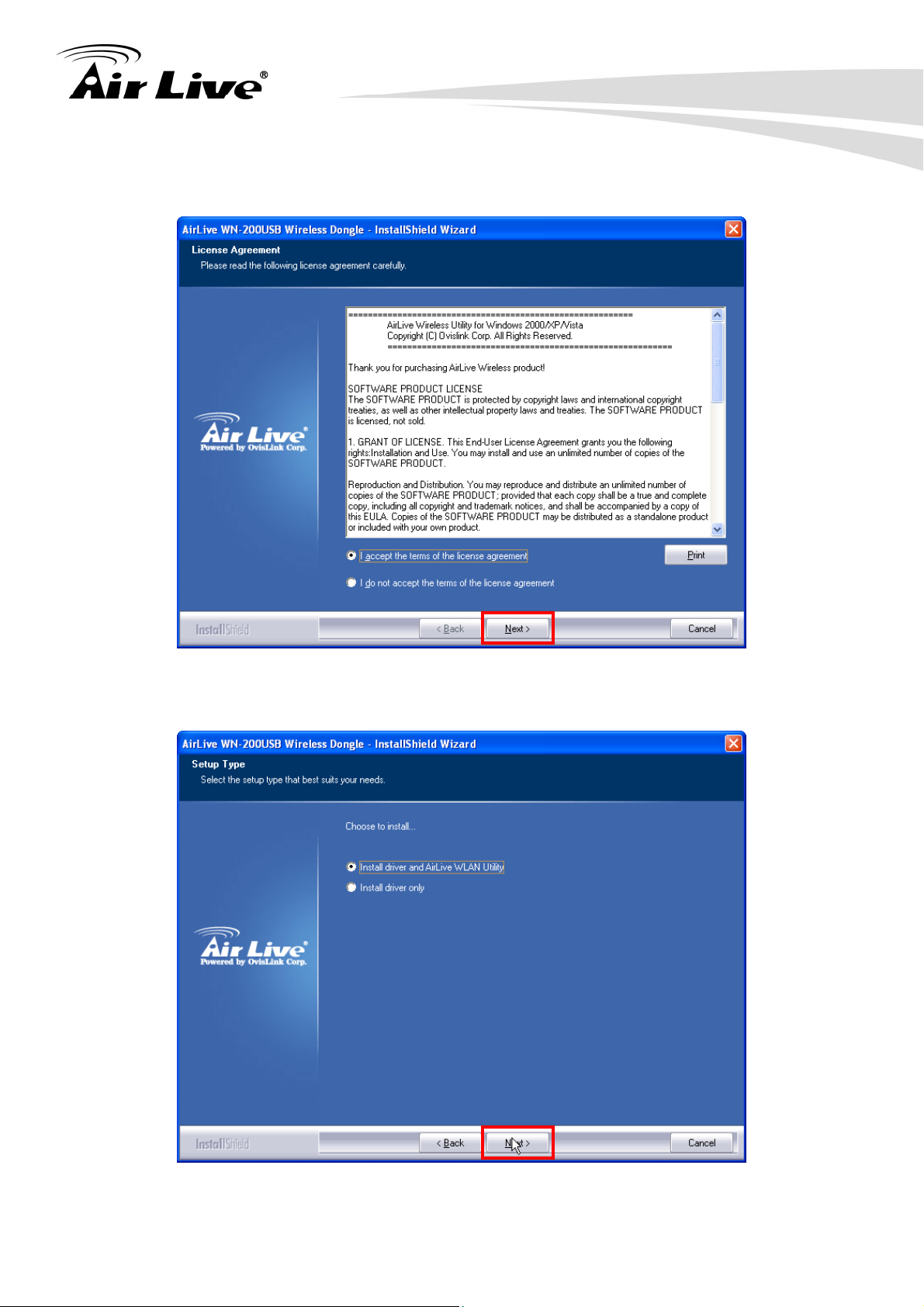
3. Please read the end user license agreement and click “I accept the terms of the license
agreement” then click “Next” button to accept license agreement.
4. It is recommended that users choose “install driver and AirLive WLAN utility”. If you want
to update the driver only, choose “Install driver only”. Click “Next” to continue.
5
AirLive WN-200USB User’s Manual
Page 9

2. Installing the WN-200USB
5. It’s recommended to select “AirLive Wireless LAN Utility”, which provides fully access to
all functions of this wireless network card. If you prefer to use the wireless configuration
tool provided by Windows XP or Vista, please select “Microsoft Zero Configuration Tool”
then click “Next”.
6. You will see the following message, please click “Install” to start utility installation.
AirLive WN-200USB User’s Manual
6
Page 10
2. Installing the WN-200USB
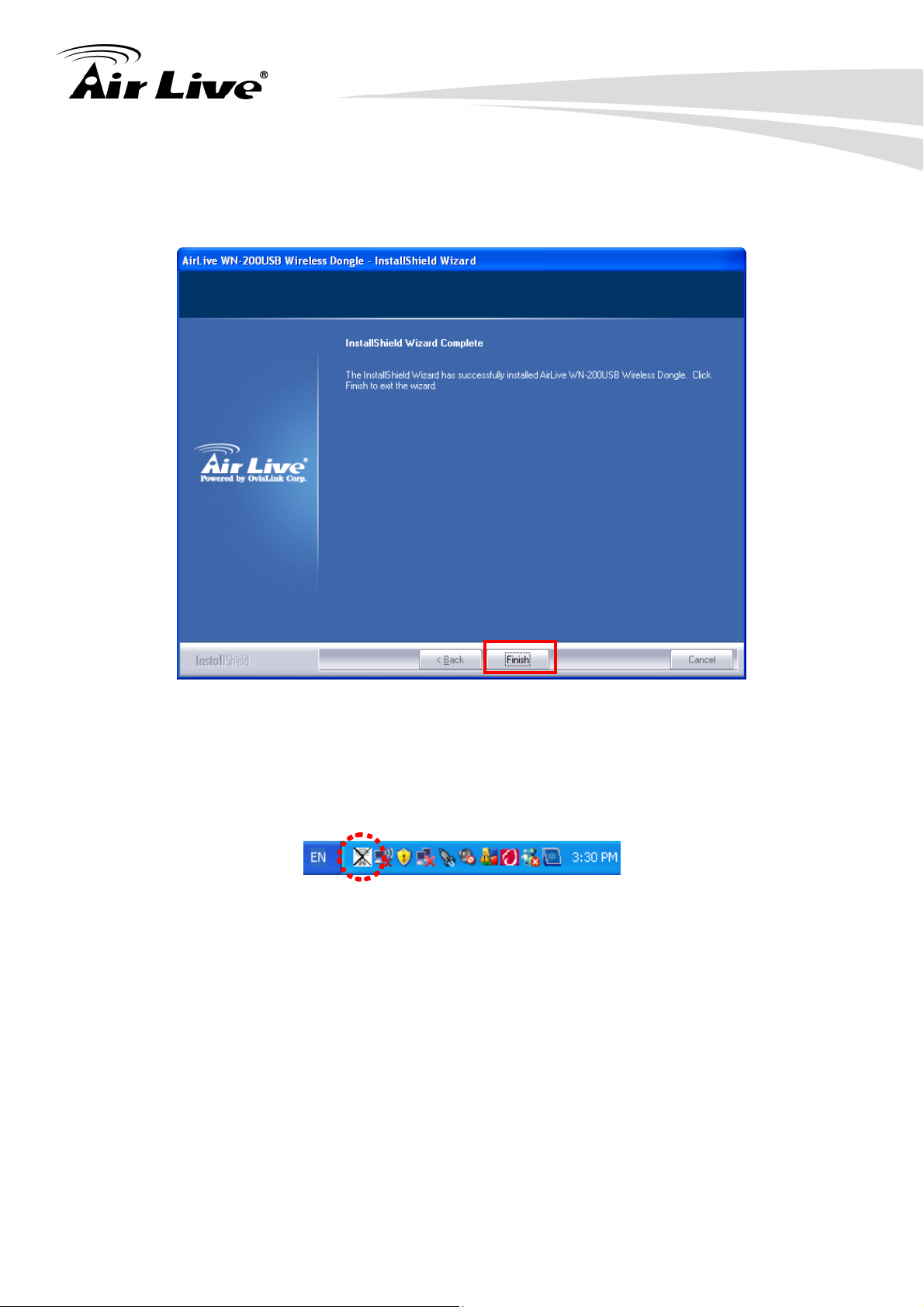
7. Please wait while the install procedure is running. When you see this message, please
click “Finish” to complete the driver installation process.
8. After installation is complete, wireless configuration utility will be shown in the desktop of
your computer automatically. You will also see an icon at the lower-right corner of your
windows system. If you put the mouse cursor on the icon, the status of wireless card will
be displayed as a popup balloon.
Users can easily check current status of WN-200USB in system tray, as shown below.
7
AirLive WN-200USB User’s Manual
Page 11
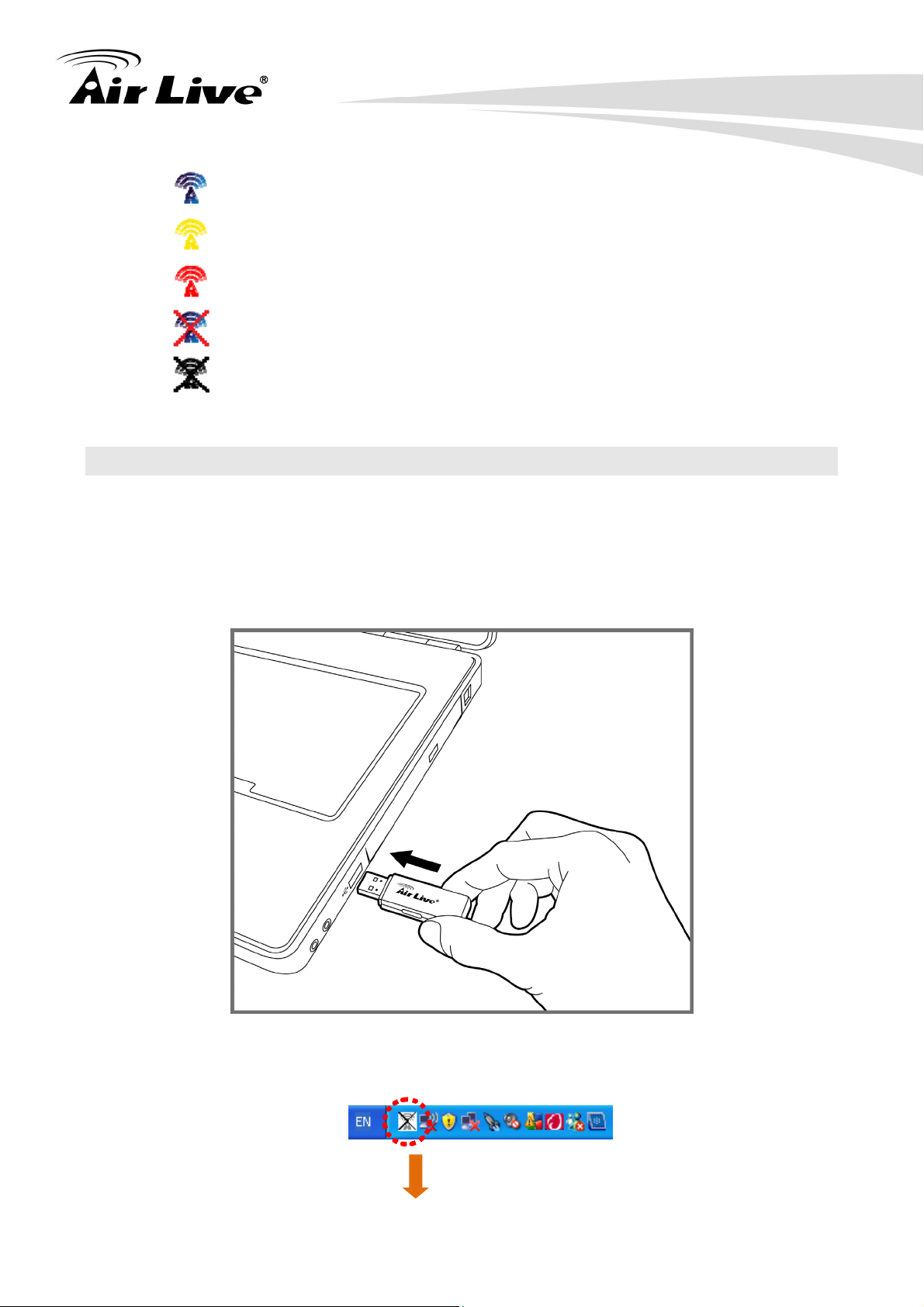
Wireless connection is established, good signal reception.
Wireless connection is established, normal signal reception
Wireless connection is established, weak signal reception
No connection to the WN-200USB.
The WN-200USB is unplugged.
2.5 Hardware Installation
2. Installing the WN-200USB
Please follow the following instructions to install your new wireless network card:
1. Insert the WN-200USB into an available USB 2.0 port of your PC/Notebook when
PC/Notebook is power-on status. Never use force to insert the WN-200USB, if you feel
it’s stuck, flip the dongle over and try again.
2. Once inserting the WN-200USB properly, the icon in system tray will change from
“unplugged” status to “wireless connection is established” status.
AirLive WN-200USB User’s Manual
8
Page 12

2. Installing the WN-200USB
2.6 LED Table
The LED Indicators gives real-time information of systematic operation status. The
following table provides descriptions of LED status and their meaning.
LED Color Status Description
● Green
LNK/ACT
ON Associated with the network
OFF Not associated with the network
Blink Data being transferred
9
AirLive WN-200USB User’s Manual
Page 13

3. Configuration of WN-200USB
3. Configuration of
3
The WN-200USB offers two different types of management interface. You can configure
through AirLive Wireless LAN Utility and built-in Windows Zero Configuration (WZC) which
dynamically selects a wireless network to connect. In this chapter, we will introduce how
to apply these two methods to make use of WN-200USB.
WN-200USB
3.1 Important Information
Before using the AirLive Utility, please make that your have referred to Chapter 2.4 and
Chapter 2.5 to install AirLive Utility and insert WN-200USB into a available USB port.
3.2 Using AirLive Wireless LAN Utility
If the Wireless Utility program is running, you can double-click the icon in the System Tray
or right-click the icon and select "Launch Config Utility" to open the application.
3.2.1 Status Information
The menu options available from the System Tray icon are:
Launch Config Utility: This will display the main screen of the Utility.
Use Zero Configuration as configuration Utility: Wireless Zero Configuration
(WZC), is a service of Microsoft Windows which dynamically selects a wireless
network to connect.
Exit: Terminate the connection to the WN-200USB.
AirLive WN-200USB User’s Manual
10
Page 14
3. Configuration of WN-200USB
Double-click the Icon to execute the utility, where you can select the Wireless network you
wish to join.
3.2.2 Menu Structure of AirLive Wireless LAN Utility
The menu structure of AirLive Wireless LAN Utility is divided into two parts: Top Menu and
Setup Area.
Top Menu: You can select a setup function (Profile, Network, etc.) from top menu,
and corresponding configuration items will be displayed at Setup area.
Setup Area: Once clicking one of the functions from Top Menu, the related
configurations will be displayed in Setup Area
11
AirLive WN-200USB User’s Manual
Page 15
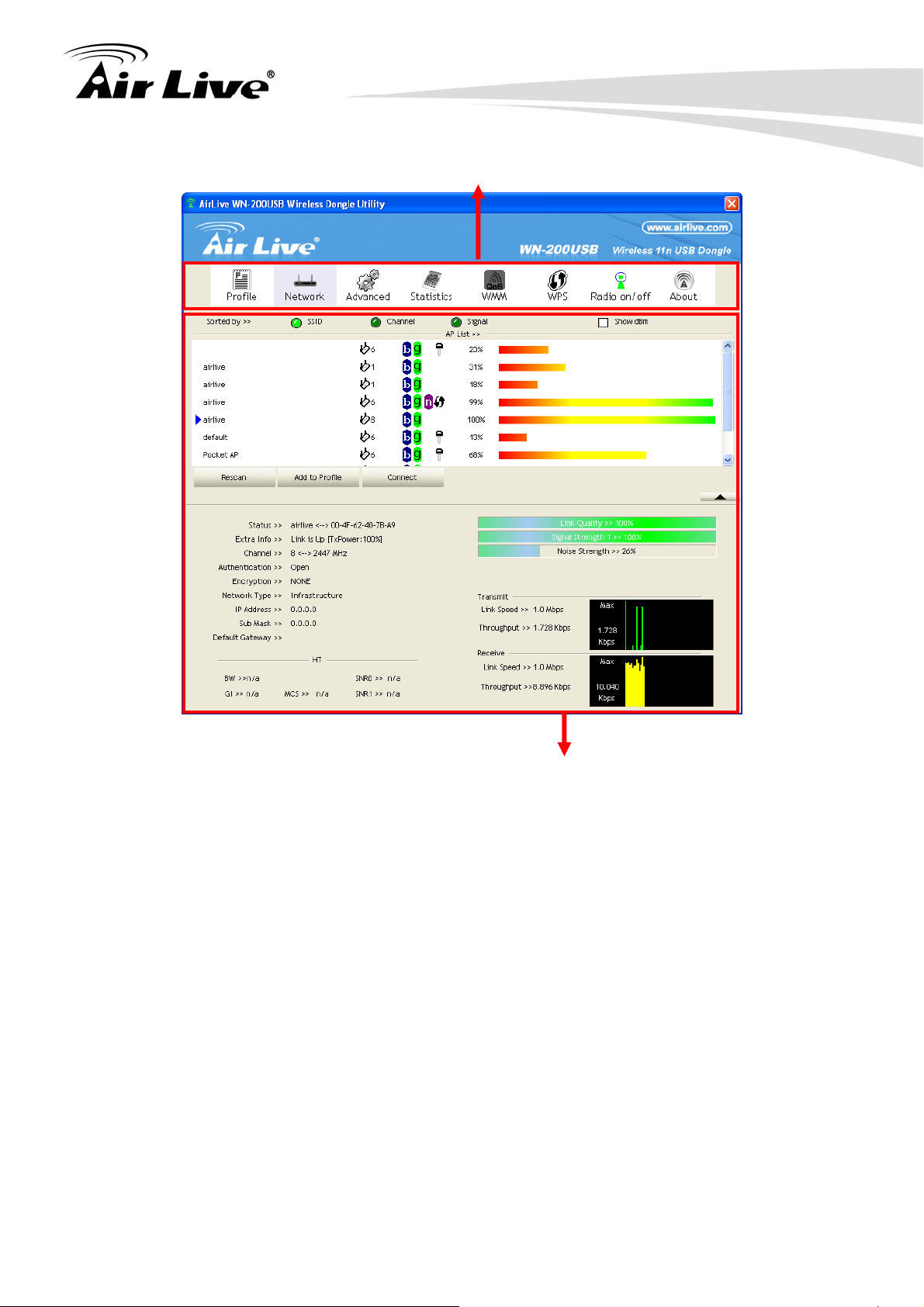
3. Configuration of WN-200USB
Top Menu
Setup Area
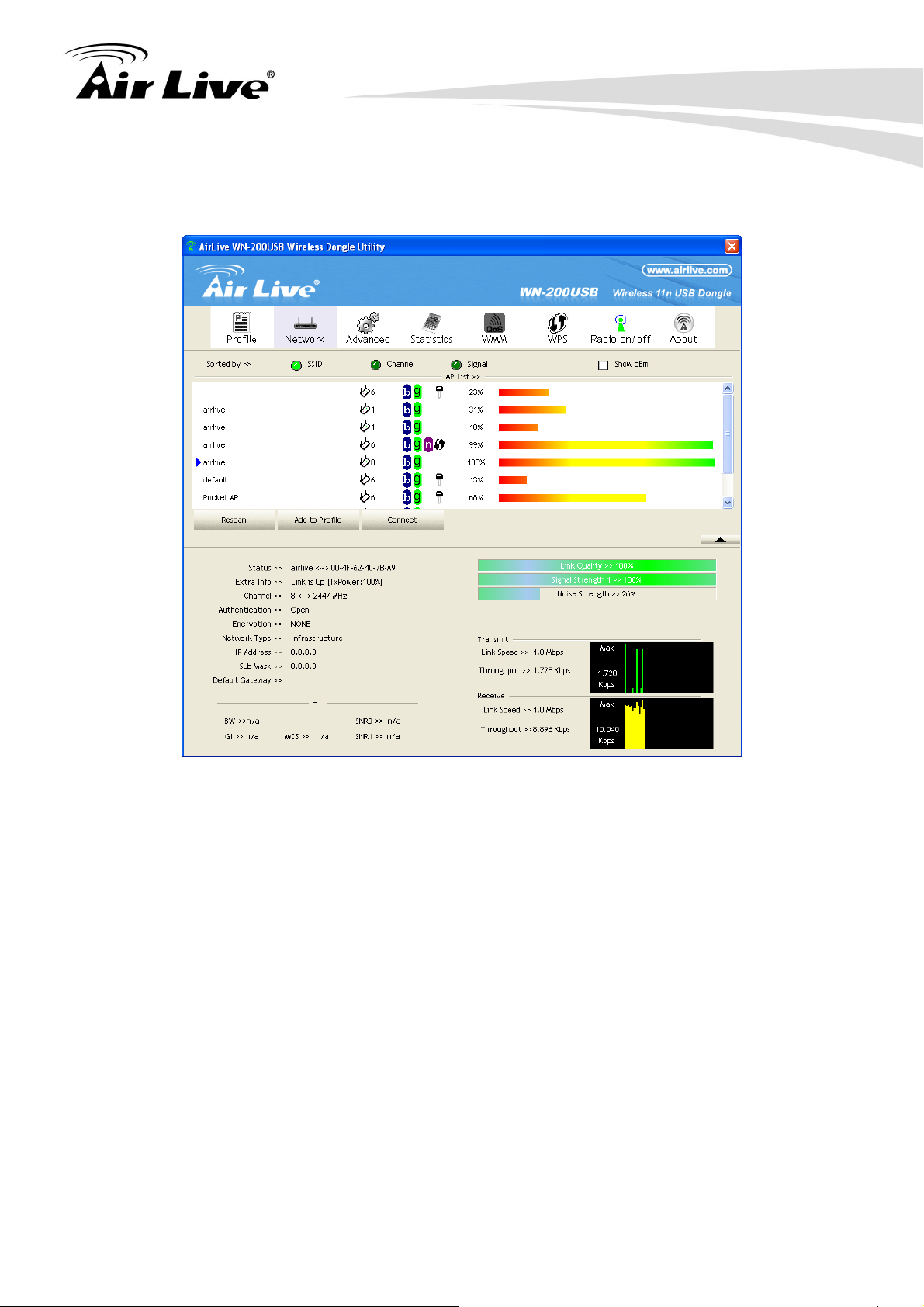
3.2.3 Network Screen
This screen is displayed when you double-click the system tray icon. You can also click the
Network tab in the Top Menu
When you open the utility program, it will scan all the channels to find all the access
points/stations within the accessible range and automatically connect to one of the wireless
devices which have the highest signal strength.
AirLive WN-200USB User’s Manual
12
Page 16

3. Configuration of WN-200USB
SSID
Network Type
Channel
Wireless Mode
Security-Enable
Signal
Rescan
Add to Profile
The SSID (up to 32 printable ASCII characters) is a unique
name identified in a WLAN.
It displays the Network type in use, Infrastructure for BSS,
Ad-Hoc for IBSS network.
The channel used by the Wireless network.
AP support wireless mode. It may support 802.11a, 802.11b,
802.11g or 802.11n wireless mode
Whether AP provides security-enabled wireless network.
This is displayed as percentage (0 ~ 100%) of specified
network.
Click this button to rescan for all Wireless networks.
Click this button to add the selected AP to Profile setting. It
will bring up profile page and save user's setting to a new
profile.
13
AirLive WN-200USB User’s Manual
Page 17
3. Configuration of WN-200USB
Connect
Click this button to connect the Wireless network.
3.2.3.1 Wireless Network Sequence (order)
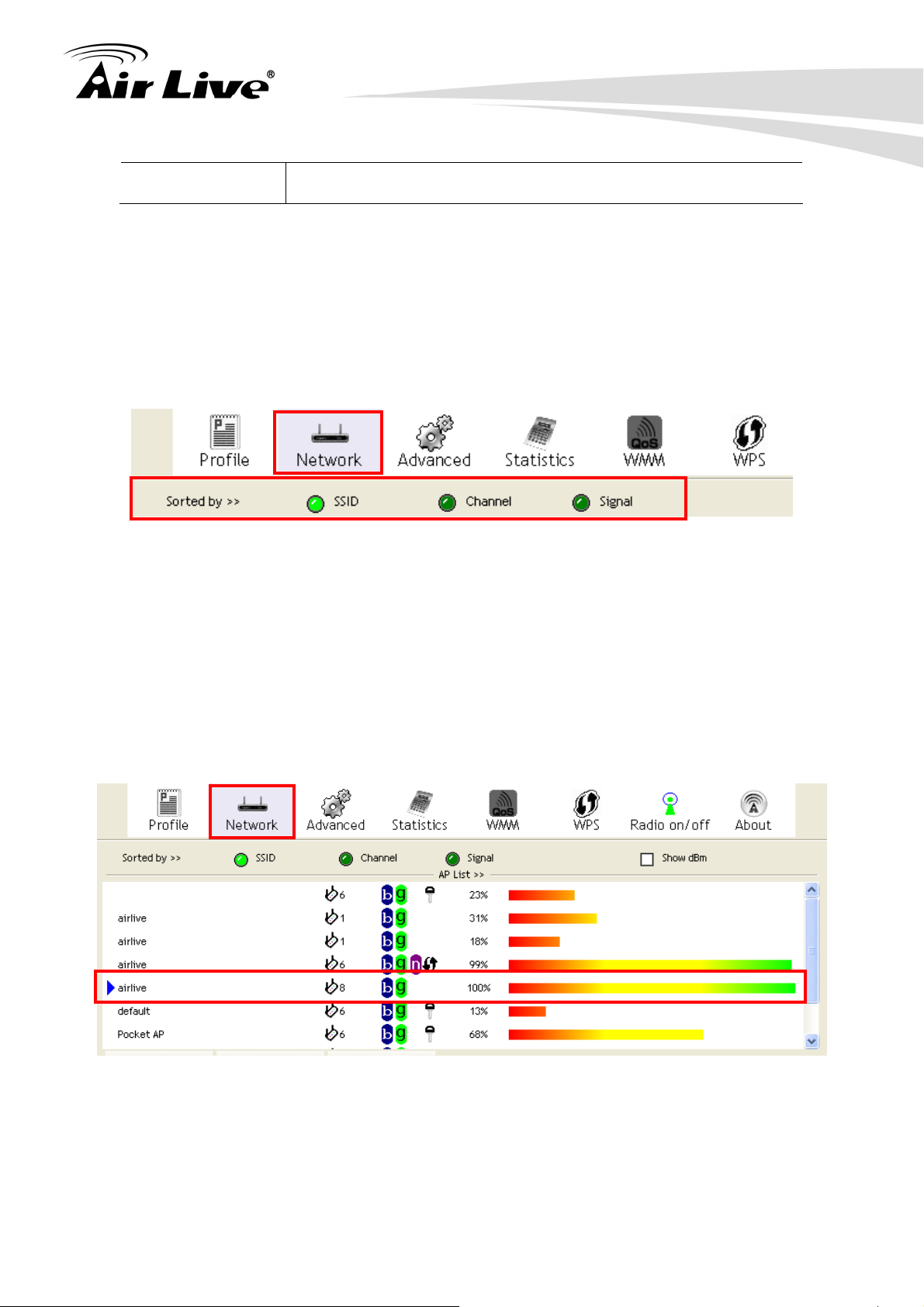
User have three ways (SSID, Channel or Signal) to make order of the wireless network, just
click the radio buttons in left side of Sorted by to arrange the Wireless network in the
desired order.
3.2.3.2 To connect to a wireless network
Click the name of the wireless network to which you want to connect, and then click
“Connect” button to connect chosen wireless network..
Note that once you are connected to a wireless network, the Network screen will identify
the current wireless network with a blue arrow icon, as shown below.
AirLive WN-200USB User’s Manual
14
Page 18

3. Configuration of WN-200USB
It indicates network type is infrastructure mode.
It indicates network type is Ad-hoc mode.
802.11b wireless mode
802.11g wireless mode
802.11n wireless mode
It indicates security-enabled wireless network.
It shows the information of Link Status Section.
It hides the information of Link Status Section.
3.2.3.3 Link Status Screen
The Link Status section displays the detailed information of the current connection. Click
button to show the status screen.
The below table explain each item of them.
Status
Extra Info
Channel
It will indicate the current link status.
It shows the link status.
It displays the current channel in use.
15
AirLive WN-200USB User’s Manual
Page 19

3. Configuration of WN-200USB
Authentication
Encryption
Network Type
IP Address
Subnet Mask
Default Gateway
HT
Link Quality
Signal Strength (1~3)
It will indicate the current authentication mode in use.
It shows the wireless security that the wireless
network is using.
This will indicate "Infrastructure" or "Ad-hoc".
It shows the current IP address on the wireless
interface.
Subnet mask for the current IP address.
Gateway IP address associated with the current IP
address.
It displays current HT status in use (802.11n wireless
card only).
It displays connection quality based on signal strength
and TX/RX packet error rate.
It receives signal strength (1~3), user can choose to
display as percentage or dBm format.
Noise Strength
Link Speed
Throughout
It displays noise signal strength.
It will show current transmit rate and receive rate.
It displays transmits and receive throughput in unit of
Mbps.
3.2.4 Profile Screen
Click “Add to Profile” button on the Network tab, or you can choose “Profile” tab of Top
Menu, then click “Add” button, the Add Profile window will pop up. Users can setup the
general settings, encryption and authentication settings and so on.
AirLive WN-200USB User’s Manual
16
Page 20

3. Configuration of WN-200USB
3.2.4.1 System Config
Profile Name
Enter or select a suitable name for this profile. Each
profile must have a unique name.
17
AirLive WN-200USB User’s Manual
Page 21

3. Configuration of WN-200USB
SSID
Power Save Mode
RTS Threshold
Fragment
Threshold
Network Type
Tx Power
If the desired wireless network is currently available, you
can select its SSID. Otherwise, type in the SSID of the
desired wireless network.
Select either CAM (Constantly Awake Mode) or PSM
(Power Saving Mode).
Select a value within the range of 0 to 2347 bytes
Select the value from 256 to 2346 bytes. The default
value is 2346.
Select the desired option:
z Infrastructure: Select this to connect to an Access
point.
z Ad-Hoc: Select this if you are connecting directly to
another computer.
Select the Tx (transmission) power according to the real
environment.
Preamble
OK button
Cancel button
3.2.4.2 Auth./Encyp.
The preamble defines the length of the CRC (cyclic
redundancy check). Select either Auto or Long Preamble.
Click this button to save the settings and close the page.
The "Cancel" button will discard any data you have
entered and exit the page.
AirLive WN-200USB User’s Manual
18
Page 22

3. Configuration of WN-200USB
Authentication
You MUST select the option to match the Wireless LAN
you wish to join. The available options are:
z Open: Broadcast signals are not encrypted. This
method can be used only with no encryption or with
WEP.
z Shared: Broadcast signals are encrypted using WEP.
This method can only be used with WEP.
z LEAP: Light Extensible Authentication Protocol is a
pre-EAP, Cisco-proprietary protocol. If selected, you
have to enter the identity, password and domain name
of your computer.
z WPA: This version of WPA requires a Radius Server
on your LAN to provide the client authentication
according to the 802.1x standard. Data transmissions
are encrypted using the WPA standard.
z WPA-PSK: PSK means "Pre-shared Key". You must
enter this Passphrase value; it is used for both
authentication and encryption.
z WPA2: This version of WPA2 requires a Radius Server
on your LAN to provide the client authentication
according to the 802.1x standard. Data transmissions
are encrypted using the WPA2 standard.
Encryption
Use 802.1x
z WPA2-PSK: This is a further development of
WPA-PSK, and offers even greater security. You must
enter this Passphrase value; it is used for both
authentication and encryption.
z WPA None: If selected, you can only set encryption
and WPA-Preshared Key settings.
The available options depend on the Authentication
method selected above. The possible options are:
z None: No data encryption is used.
z WEP: If selected, you must enter the WEP data shown
below. This WEP data must match the Access Point or
other Wireless stations.
z AES, TKIP: These options are available with
WPA-PSK, WPA2-PSK, WPA and WPA2. Select the
correct option.
This setting only takes effect when using WPA or WPA2
mode. If enabled, click the 802.1x tab to configure the
related settings.
19
AirLive WN-200USB User’s Manual
Page 23

3. Configuration of WN-200USB
WPA Preshared
Key
For WPA-PSK and WPA2-PSK modes, you need to enter
the desired value (8~63 characters). Data is encrypted
using a 256Bit key derived from this key. Other Wireless
Stations must use the same key.
WEP Key (1~4)
This setting is only available for Open or Shared mode.
There are 2 modes:
z Hex: Only "A~F", "a~f", and "0~9" are allowed to be
entered.
z ASCII: Numerical values, characters or signs are all
allowed to be entered.
3.2.4.3 802.1X
When using WPA or WPA2 mode in Auth. \Encry, the 802.1x tab will show in right side of
Auth. \Encry tab.
AirLive WN-200USB User’s Manual
20
Page 24

3. Configuration of WN-200USB
EAP Method
There are 5 methods in the drop-down list.
z PEAP: Protect Extensible Authentication Protocol. PEAP
transport securely authentication data by using tunneling
between PEAP clients and an authentication server. PEAP
can authenticate wireless LAN clients using only server-side
certificates, thus simplifying the implementation and
administration of a secure wireless LAN.
z TLS-Smart Card: Transport Layer Security. Provides for
certificate-based and mutual authentication of the client and
the network. It relies on client-side and server-side
certificates to perform authentication and can be used to
dynamically generate user-based and session-based WEP
keys to secure subsequent communications between the
WLAN client and the access point.
z TTLS: Tunneled Transport Layer Security. This security
method provides for certificate-based, mutual authentication
of the client and network through an encrypted channel.
Unlike EAP-TLS, EAP-TTLS requires only server-side
certificates.
z EAP-FAST: Flexible Authentication via Secure Tunneling. It
was developed by Cisco. Instead of using a certificate,
mutual authentication is achieved by means of a PAC
(Protected Access Credential) which can be managed
dynamically by the authentication server. The PAC can be
provisioned (distributed one time) to the client either
manually or automatically. Manual provisioning is delivery to
the client via disk or a secured network distribution method.
Automatic provisioning is an in-band, over the air,
distribution.
Tunnel
Authentication
Session
Resumption
Authentication
ID / Password
z MD5-Challenge: Message Digest Challenge. Challenge is
an EAP authentication type that provides base-level EAP
support. It provides for only one-way authentication - there is
no mutual authentication of wireless client and the network.
Select the desired option from the drop-down list.
After reconnecting the signal which broke up, you can enable
the session resumption to reduce the transferring packet to
accelerate the speed.
Enter the required data into the fields.
21
AirLive WN-200USB User’s Manual
Page 25

3. Configuration of WN-200USB
Tunnel ID /
Enter the ID and Password for the tunnel.
Password
Use Client
certificate
Use certificate
chain
Click the checkbox to enable certificate authority server
function.
When the EAP authentication type such as TLS, TTLS or PEAP
is selected and required a certification to tell the client what
server credentials to accept from the authentication server in
order to verify the server, you have to enable this function and
enter the required data in the related fields.
3.2.4.4 General Setting
If you want to do the general settings, please follow the instructions below.
To add a profile
1. On the Profile tab, click “Add” button.
2. Complete and verify the settings on this screen are correct.
3. Click “OK” button.
To delete a profile
1. On the Profile tab, select the profile that you want to delete.
2. Click “Delete”.
To edit a profile
1. On the Profile tab, select the profile that you want to edit.
2. Click ”Edit” button.
3. Change the profile settings as necessary.
4. Click “OK” button.
To enable a profile
1. In the list of available profiles, click the profile that you want to enable.
2. Click “Activate” button.
3.2.5 Advance Screen
AirLive WN-200USB User’s Manual
22
Page 26

3. Configuration of WN-200USB
Click Advanced tab in the Top Menu, you can configure the detailed settings in this page.
Wireless Mode
Enable Tx
Burst
Enable TCP
Window Size
Fast Roaming
at
Select the desired wireless mode.
Tx Burst enables the adapter to deliver better throughput
during a period of time but the function only takes effect when
connecting with the AP which also supports Tx Burst.
The TCP Window is the amount of data which a sender can
send on a particular connection before it gets an
acknowledgement back from the receiver that it has gotten
some of it. When the router or AP which the adapter is
connecting to has set up the TCP Window, you can enable the
parameter to meet the data size for the router or AP
connection. The larger TCP Window the better performance.
When you want to fast roaming to the network nearby without
intercepting the wireless connection especially the adapter is
applied to the multimedia application or a voice call, you can
enable this function.
Show
Authentication
Status Dialog
Select Your
Country
Region Code
When connecting to an AP with authentication, if enabling this
function, it will display dialogs about 802.1x authentication
during the process.
There are 8 kinds of Country Region Codes to choose from.
23
AirLive WN-200USB User’s Manual
Page 27

3. Configuration of WN-200USB
Enable CCX
(Cisco
Compatible
eXtensions)
CCX (Cisco Compatible Extensions) is developed by Cisco for
the radio monitoring and fast roaming.
z Turn on CCKM: During normal operation, LEAP-enabled
client devices mutually authenticate with a new access
point by performing a complete LEAP authentication,
including communication with the main RADIUS server.
When you configure your wireless LAN for fast
re-association, however, LEAP-enabled client devices
roam from one access point to another without involving the
main server. Using Cisco Centralized Key Management
(CCKM), an access point configured to provide Wireless
Domain Services (WDS) takes the place of the RADIUS
server and authenticates the client so quickly that there is
no perceptible delay in voice or other time-sensitive
applications.
z Enable Radio Measurement: When this parameter is
enabled, the Cisco AP can run the radio monitoring through
the associated CCX-compliant clients to continuously
monitor the WLAN radio environment and discover any new
Aps that are transmitting beacons.
Apply
Click this button to save the changes you made.
3.2.6 Statistics Screen
Click Statistics tab in the Top Menu, the page will display the transmitted and received
results.
3.2.6.1 Transmit
AirLive WN-200USB User’s Manual
24
Page 28

3. Configuration of WN-200USB
Frames
Transmitted
Successfully
Frames
Retransmitted
successfully
Frames Fail To
Receive ACK After
All Retries
RTS Frames
Successfully
Receive CTS
RTS Frames Fail
To Receive CTS
Frames successfully sent.
Frames successfully sent with one or more reties.
Frames failed to transmit after hitting retry limit.
Successfully receive CTS (Clear To Send) after sending
RTS (Request To Send) frame.
Failed to receive CTS (Request To Send) after sending RTS
(Clear To Send).
3.2.6.2 Receive
Frames Receive
Successfully
Frames Receive
With CRC Error
Frames received successfully.
Frames received with CRC error.
Frames Dropped
Due To
Out-of-Resource
Frames dropped due to resource problem.
25
AirLive WN-200USB User’s Manual
Page 29

3. Configuration of WN-200USB
Duplicate Frames
Frames received more than twice.
Received
Reset Counter
Click the button to reset counters to zero.
3.2.7 WMM Screen
Click WMM tab in the Top Menu, and you will see the following screen:
WMM Enable
WMM - POWER
SAVE ENABLE
Direct Link Setup
Enable
WMM is short for Wi-Fi Multimedia. It is a standard created
to define quality of service (QoS) in Wi-Fi networks. It is a
precursor to the upcoming IEEE802.11e WLAN QoS draft
standard, which is meant to improve audio, video and voice
applications transmitted over Wi-Fi. WMM adds prioritized
capabilities to Wi-Fi networks and optimizes their
performance when multiple concurring applications, each
with different latency and throughput requirements, compete
for network resources. Click the check box and then click
"Apply" button to apply this function to the system.
Click the check box, and select the desired type of power
saving mode.
Enable the check box and you may start to set MAC
Address, Timeout Value and check the DLS Status. Click
"Apply" button and this setting will be applied to the system.
AirLive WN-200USB User’s Manual
26
Page 30

3. Configuration of WN-200USB
MAC Address
Enter the remote system which you want to connect with.
When you want to enable this function, you have to make
sure that your wireless network supports WMM function and
then enter the MAC address of the adapter which wants to
connect with the remote system.
Timeout Value
The utility performs time-outs so that the program does not
sit idle waiting for input that may never come. Set a value to
apply to the system with WMM.
Apply
Tear Down
Click this button to save the changes you made.
Click this button will disconnect the selected Direct Link
Setup.
3.2.8 WPS Screen
WPS (Wi-Fi Protected Setup) can simplify the process of connecting any device to the
wireless network by using the push button configuration (PBC) on the Wireless Access Point,
or entering a PIN code.
You will use the WPS screen when you try to connect the wireless network with the WPS
function.
WPS AP List
It displays the information of surrounding APs with WPS IE from
last scan result. List information includes SSID, BSSID,
Channel, ID (Device Password ID) and Security-Enabled.
27
AirLive WN-200USB User’s Manual
Page 31

3. Configuration of WN-200USB
Rescan
Information
PIN Code
Config Mode
Detail
Connect
Rotate
Click this button to update information on surrounding wireless
network.
Display the information about WPS on the selected network. List
information includes Authentication Type, Encryption Type,
Config Methods, Device Password ID, Selected Registrar, State,
Version, AP Setup Locked, UUID-E and RF Bands.
Enter the PIN code displayed in the following field to the WPS
screen of the access point. When STA is Enrollee, you can use
"Renew" button to re-generate new PIN Code.
Our station role-playing as an Enrollee or an external Registrar.
Information about Security and Key in the credential.
Click this button to connect to the selected network inside
credentials.
Click this button to rotate to connect to the next network inside
credentials.
Disconnect
Export Profile
Delete
PIN
PBC
WPS associate
IE
WPS Probe IE
Click this to stop WPS action and disconnect this active link, and
then select the last profile at the Profile Page of utility if exist. If
there is an empty profile page, the driver will select any
non-security AP.
Export all credentials to Profile.
Click to Delete an existing credential. And then select the next
credential if exist. If there is an empty credential, the driver will
select any non-security AP.
Start to add to Registrar using PIN configuration method. If STA
Registrar, remember that enter PIN Code read from your
Enrollee before starting PIN.
Start to add to AP using PBC configuration method.
Send the association request with WPS IE during WPS setup. It
is optional for STA.
Send the probe request with WPS IE during WPS setup. It is
optional for STA.
Progress Bar
Status Bar
AirLive WN-200USB User’s Manual
Display rate of progress from Start to Connected status.
Display currently WPS Status.
28
Page 32

3.2.9 Radio on/off Button
Yu can turn the radio signal on/off by clicking this button.
The radio signal is on.
3. Configuration of WN-200USB
The radio signal is off.
3.2.10 About Screen
This screen displays details of the traffic sent or received on the current Wireless network.
29
AirLive WN-200USB User’s Manual
Page 33

This tab shows the following information:
z Utility Version, Date
z Driver Version, Date
z EEPROM Version
z Firmware Version
z Phy_Address
3.3 Using Windows Zero Configuration
3. Configuration of WN-200USB
Windows XP and Vista has a built-in wireless network configuration utility, called as
‘Windows Zero Configuration’ (WZC). You can also use WZC to configure your wireless
network parameter:
1. Right-click the icon of AirLive Wireless LAN Utility and select “Use Zero Configuration
as Configuration utility”.
2. Right click Windows Zero Configuration icon and select “View Available Wireless
Networks”. If you can not find the icon, please follow the procedures from step 3 to step
5.
3. Click “Start” button (should be located at the bottom-left corner of windows desktop),
click “Control Panel”, then click “Network and Internet Connections” in Control
Panel.
AirLive WN-200USB User’s Manual
30
Page 34

3. Configuration of WN-200USB
4. Click “Network Connections”.
31
AirLive WN-200USB User’s Manual
Page 35

3. Configuration of WN-200USB
5. Right-click “Wireless Network Connection” (it may have a number as suffix if you have
more than one wireless network card, please make sure you right-click the AirLive
802.11n Wireless Dongle), then select “View Available Wireless Networks”.
6. All wireless access points in proximity will be displayed here. If the access point you
want to use is not displayed here, please try to move your computer closer to the access
point, or you can click ‘Refresh network list’ to rescan access points. Click the access
point you want to use if it’s shown, then click ‘Connect’.
7. If the access point is protected by encryption, you have to input its security key or
AirLive WN-200USB User’s Manual
32
Page 36

3. Configuration of WN-200USB
passphrase here. It must match the encryption setting on the access point.
If the access point you selected does not use encryption, you’ll not be prompted for
security key or passphrase.
8. If you can see ‘Connected’ message, the connection between your computer and
wireless access point is successfully established.
33
AirLive WN-200USB User’s Manual
Page 37

4. Troubleshooting
4. Troubleshooting
4
This section is intended to help you solve the most common problems on the WN-200USB.
Question:
Answer:
====================================================================
Question:
Answer:
I can’t find any wireless access point / wireless device in ‘Site Survey’
function.
z Click “Rescan” for few more times and see if you can find any AP or
wireless device.
z Please move closer to any known AP.
z “Ad hoc” function must be enabled for the wireless device you want
to establish a direct wireless link.
z Please adjust the position of WN-200USB (you may have to move
your computer if you’re using a notebook) and click “Rescan” button
for few more times. If you can find the AP or wireless device you want
to connect by doing this, try to move closer to the place where the AP
or wireless device is located.
Nothing happens when I click “Launch Config Utility”
z Please make sure that WN-200USB is inserted into your computer’s
USB port properly. If the AirLive configuration utility’s icon is black,
WN-200USB is not detected by your computer.
z Reboot the computer and try again.
z Remove the WN-200USB and insert it into another USB port.
z Uninstall the driver and re-install again.
z Contact your local distributor for help.
====================================================================
AirLive WN-200USB User’s Manual
34
Page 38

4. Troubleshooting
Question:
Answer:
I can not establish connection with a certain wireless access point
z Click “Connect” for few more times.
z If the SSID of AP which you want to connect is hidden (nothing
displayed in “SSID” field in “Site Survey” function), you have to input
correct SSID of the AP which you want to connect. Please contact the
owner of AP to ask for correct SSID.
z You have to input correct security key to connect an AP with
encryption. Please contact the owner of AP to ask for correct security
key.
z The AP which you want to connect only allows network cards with
specific MAC address to establish connection. Please go to “About”
tab and write the value of “Phy_Addess” down, then present this
value to the owner of AP, so he/she can add the MAC address of
your network card to his/her AP’s list.
====================================================================
Question:
Answer:
The network is slow/having problem when transferring large files
z Move closer to the place where access point is located.
z Disable “Tx Burst” in “Advanced” tab.
z Enable “WMM” in “WMM” tab if you need to use multimedia /
telephony related applications.
z Disable “WMM – Power Save Enable” in “WMM” tab.
z Please change the wireless channel on your AP or wireless router.
Most of the wireless problems are caused by channel interference.
35
AirLive WN-200USB User’s Manual
Page 39

5. Specifications
5. Specifications
5
This section provides the specifications of WN-200USB, and the following table lists these
specifications.
Chipset
Standard
Bus Type
Data Rate
Operating Channels
Operating Frequency
z Ralink RT3070(MAC/BB/RF)
z IEEE802.11b
z IEEE802.11g
z IEEE802.11n
z USB 2.0
z 802.11n
20 MHz BW(LGI): 65, 58.5, 52, 39, 26, 19.5, 13, 6.5
40 MHz BW(LGI): 135, 121.5, 108, 81, 54, 40.5, 27, 13.5
20 MHz BW(SGI): 72.2, 65, 57.8, 43.3, 28.9, 21.7, 14.4, 7.2
40 MHz BW(SGI): 150, 135, 120, 90, 60, 45, 30, 15
z 802.11g: 54, 48, 36, 24, 18, 12, 9 and 6 Mbps
z 802.11b: 11, 5.5, 2 and 1 Mbps
z 11 for North America, 13 for Europe and Japan
z 2.4 ~ 2.4835 GHz
Modulation
Technique
Media Access
Protocol
Operating Voltage
Security
AirLive WN-200USB User’s Manual
z 802.11n: BPSK, QPSK, 16-QAM, 64-QAM
z 802.11g: OFDM
z 802.11b: CCK,QPSK,BPSK
z CSMA/CA
z 5V +/- 5%
z WPA/WPA2; 128-bit TKIP/AES encryption, 40/64-,
z 802.1x, and EAP-TLS, and PEAP authentication
128-bit WEP shared-key encryption
36
Page 40

5. Specifications
OS Requirements
Produce Weight (g)
Dimensions
z Windows Vista/XP/2000
z
z 440 x 161 x 44 mm
37
AirLive WN-200USB User’s Manual
Page 41

6. Network Glossary
6. Network Glossary
6
The network glossary contains explanation or information about common terms used in
wireless networking products. Some of information in this glossary might be outdated,
please use with caution.
100Base-FX
The IEEE standard defines how to transmit Fast Ethernet 100Mbps data using multi-mode
or single fiber optic cable
100Base-TX
Also known as 802.3u. The IEEE standard defines how to transmit Fast Ethernet 100Mbps
using Cat.5 UTP/STP cable. The 100Base-TX standard is backward compatible with the
10Mbps 10-BaseT standard.
1000Base-SX
Also known as 802.3z. The IEEE standard defines how to transmit gigabit Ethernet data
using multi-mode fiber optic cables. This standard allows transmission distance of 550
meter, which is more than 5 times longer than the 100-meter limitation of 1000Base-T. The
1000Base-SX cannot run in 100Mbps mode.
1000Base-LX
The IEEE standard defines how to transmit gigabit Ethernet data using single mode fiber
optic cables. This standard allows transmission distance of 5km or more using single mode
fiber. The 1000Base-LX cannot run in 100Mbps mode.
1000Base-T
Also known 802.3ab standard. The IEEE standard defines how to transmit Gigabit data
through the use of Cat.5 UTP/STP cable. The 1000Base-T can run in 10/100/1000Mbps
AirLive WN-200USB User’s Manual
38
Page 42

6. Network Glossary
speed, and is backward compatible with 10/100Base-TX standard.
802.11a
An IEEE specification for wireless networking that operates in the 5 GHz frequency range
(5.15 GHz to 5.850 GHz) with a maximum of 54 Mbps data transfer rate. The 5 GHz
frequency band is not as crowded as the 2.4 GHz band. In addition, the 802.11a have 12
non-overlapping channels, comparing to 802.11b/g's 3 non-overlapping channels. This
means the possibility to build larger non-interfering networks. However, the 802.11a deliver
shorter distance at the same output power when comparing to 802.11g.
802.3ad
802.3ad is an IEEE standard for bonding or aggregating multiple Ethernet ports into one
virtual port (also known as trunking) to increase the bandwidth.
802.3af
This is the PoE (Power over Ethernet) standard by IEEE committee. 803.af uses 48V
POE standard that can deliver up to 100 meter distance over Ethernet cable.
802.11b
International standard for wireless networking that operates in the 2.4 GHz frequency band
(2.4 GHz to 2.4835 GHz) and provides a throughput up to 11 Mbps.
802.1d STP
Spanning Tree Protocol. It is an algorithm to prevent network from loop topology. Spanning
tree allows a network design to include spare (redundant) links to provide automatic backup
paths if an active link fails, without the danger of bridge loops, or the need for manual
enabling/disabling of these backup links. Bridge loop must be avoided because of flooding
issue in the network.
802.11d
39
AirLive WN-200USB User’s Manual
Page 43

6. Network Glossary
Also known as “Global Roaming”. 802.11d is a standard for use in countries where
systems using other standards in the 802.11 family are not allowed to operate.
802.11e
The IEEE QoS standard for prioritizing traffic of the VoIP and multimedia applications.
The WMM is based on a subset of the 802.11e.
802.11g
A standard provides a throughput up to 54 Mbps using OFDM technology. It also
operates in the 2.4 GHz frequency band as 802.11b. 802.11g devices are backward
compatible with 802.11b devices.
802.11h
This IEEE standard define the TPC (transmission power control) and DFS(dynamic
frequency selection) required to operate WiFi devices in 5GHz for EU.
802.11i
The IEEE standard for wireless security. 802.11i standard includes TKIP, CCMP, and
AES encryption to improve wireless security. It is also know as WPA2.
802.1Q Tag VLAN
In 802.1Q VLAN, the VLAN information is written into the Ethernet packet itself. Each
packet carries a VLAN ID(called Tag) as it traveled across the network. Therefore, the
VLAN configuration can be configured across multiple switches. In 802.1Q spec, possible
4096 VLAN ID can be created. Although for some devices, they can only view in frames
of 256 ID at a time.
802.1x
AirLive WN-200USB User’s Manual
40
Page 44

6. Network Glossary
802.1x is a security standard for wired and wireless LANs. In the 802.1x parlance, there are
usually supplicants (client), authenticator (switch or AP), and authentication server (radius
server) in the network. When a supplicants request a service, the authenticator will pass
the request and wait for the authentication server to grant access and register accounting.
The 802.1x is the most widely used method of authentication by WISP.
Adhoc
A Peer-to-Peer wireless network. An Adhoc wireless network do not use wireless AP or
router as the central hub of the network. Instead, wireless client are connected directly to
each other. The disadvantage of Adhoc network is the lack of wired interface to Internet
connections. It is not recommended for network more than 2 nodes.
Access Point (AP)
The central hub of a wireless LAN network. Access Points have one or more Ethernet
ports that can connect devices (such as Internet connection) for sharing. Multi-function
Access Point can also function as an Ethernet client, wireless bridge, or repeat signals from
other AP. Access Points typically have more wireless functions comparing to wireless
routers.
Cable and Connector Loss
: During wireless design and deployment, it is important to
factor in the cable and connector loss. Cable and connector loss will reduce the output
power and receiver sensitivity of the radio at connector end. The longer the cable length is,
the more the cable loss. Cable loss should be subtracted from the total output power
during distance calculation. For example, if the cable and connector loss is 3dBm and the
output power is 20dBm; the output power at the cable end is only 17dBm.
Client
Client means a network device or utility that receives service from host or server. A client
device means end user device such as wireless cards or wireless CPE.
DHCP
41
AirLive WN-200USB User’s Manual
Page 45

6. Network Glossary
Dynamic Hosting Configuration Protocol. A protocol that enables a server to dynamically
assign IP addresses. When DHCP is used, whenever a computer logs onto the network, it
automatically gets an IP address assigned by DHCP server. A DHCP server can either be a
designed PC on the network or another network device, such as a router.
Encryption
Encoding data to prevent it from being read by unauthorized people. The common
wireless encryption schemes are WEP, WPA, and WPA2.
ESSID (SSID)
The identification name of an 802.11 wireless network. Since wireless network has no
physical boundary liked wired Ethernet network, wireless LAN needs an identifier to
distinguish one network from the other. Wireless clients must know the SSID in order to
associate with a WLAN network. Hide SSID feature disable SSID broadcast,
so users must know the correct SSID in order to join a wireless network.
Firmware
The program that runs inside embedded device such as AP or Switch. Many network
devices are firmware upgradeable through web interface or utility program.
FTP
File Transfer Protocol. A standard protocol for sending files between computer over a
TCP/IP network and the internet.
Fragment Threshold
Frame Size larger than this will be divided into smaller fragment. If there are interferences
in your area, lower this value can improve the performance. If there are not, keep this
parameter at higher value. The default size is 2346. You can try 1500, 1000, or 500
when there are interference around your network.
AirLive WN-200USB User’s Manual
42
Page 46

6. Network Glossary
Full Duplex
The ability of a networking device to receive and transmit data simultaneously. In wireless
environment, this is usually done with 2 or more radios doing load balancing.
Gateway
In the global Internet network, the gateways are core routers that connect networks in
different IP subnet together. In a LAN environment with an IP sharing router, the gateway
is the router. In an office environment, gateway typically is a multi-function device that
integrates NAT, firewall, bandwidth management, and other security functions.
GI
Guard Interval. It’s a measure to protect wireless devices from cross- interference. If there
are two wireless devices using the same or near channel, and they are close enough, radio
interference will occur and reduce the radio resource usability. In an OFDM system, the
length of the guard interval needs to be changed according to the environment to make
efficient use of the communication channels. In General, you will see SGI (Short Guard
Interval) or LGI (Long Interval Guard).
Hotspot
A place where you can access Wi-Fi service. The term hotspot has two meanings in
wireless deployment. One is the wireless infrastructure deployment, the other is the
Internet access billing system. In a hotspot system, a service provider typically need an
authentication and account system for billing purposes, and a wireless AP network to
provide access for customers.
IGMP Snooping
Internet Group Management Protocol. It is a Layer 3 protocol to report IP multicast
memberships to neighboring multicast switches and routers. IGMP Snooping is a feature
that allows an Ethernet Switch to “listen in” on the IGMP conversation between hosts and
routers. When IGMP snooping is enabled in a switch, it prevent hosts on a local network
from receiving traffic for a multicast group they have not explicitly joined. It provides
switches with a mechanism to prune multicast traffic from links that do not contain a
multicast listener (IGMP client).
43
AirLive WN-200USB User’s Manual
Page 47

6. Network Glossary
Infrastructure Mode
A wireless network that is built around one or more access points to provide wireless clients
access to wired LAN / Internet service. The opposite of Infrastructure mode is Adhoc
mode.
IP Address
IP (Internet Protocol) is a Layer 3 network protocol that is the basis of all Internet
communication. An IP address is 32-bit number that identifies each sender or receiver of
information that is sent across the Internet. An IP address has two parts: an identifier of a
particular network on the Internet and an identifier of the particular device (which can be a
server or a workstation) within that network. The new IPv6 specification supports 128-bit IP
address format.
IPsec
IP Security. A set of protocols developed by the IETF to support secure exchange of
packets at the IP layer. IPsec has been deployed widely to implement Virtual Private
Networks (VPNs). IPsec supports two encryption modes: Transport and Tunnel.
Transport mode encrypts only the data of each packet, but leaves the header untouched.
The more secure Tunnel mode encrypts both the header and the payload. On the receiving
side, an IPSec-compliant device decrypts each packet.
LACP (802.3ad) Trunking
Link Aggregation Control Protocol. It is protocol defines how to combine the several
Ethernet ports into one high-bandwidth port to increase the transmission speed. It is also
known as port trunking. Both devices must set the trunking feature to work.
MAC
Media Access Control. MAC address provides Layer-2 identification for network devices.
Each Ethernet device has its own unique address. The first 6 digits are unique for each
device manufacturers. When a network device has MAC access control feature, only the
devices with the approved MAC address can connect with the network.
AirLive WN-200USB User’s Manual
44
Page 48

6. Network Glossary
Mbps
Megabits Per Second. One million bits per second; a unit of measurement for data
transmission.
MESH
Mesh is an outdoor wireless technology that uses Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) and
Wireless Distribution system to achieve self-forming, self-healing, and self-configuring
outdoor network. MESH network are able to take the shortest path to a destination that
does not have to be in the line of site.
MIMO
Multi In Multi Out. A Smart Antenna technology designed to increase the coverage and
performance of a WLAN network. In a MIMO device, 2 or more antennas are used to
increase the receiver sensitivity and to focus available power at intended Rx.
NAT
Network Address Translation. A network algorithm used by Routers to enables several
PCs to share single IP address provided by the ISP. The IP that a router gets from the
ISP side is called Real IP, the IP assigned to PC under the NAT environment is called
Private IP.
Node
A network connection end point, typically a computer.
Packet
A unit of data sent over a network.
Passphrase
45
AirLive WN-200USB User’s Manual
Page 49

6. Network Glossary
Used much like a password, a passphrase simplifies the WEP encryption process by
automatically generating the WEP encryption keys for the company products.
Port
This word has 2 different meaning for networking.
The hardware connection point on a computer or networking device used for plugging
z
in a cable or an adapter.
The virtual connection point through which a computer uses a specific application on a
z
server.
PPPoE
Point-to- Point Protocol over Ethernet. PPPoE relies on two widely accepted standards:
PPP and Ethernet. PPPoE is a specification for connecting the users on an Ethernet to the
Internet through a common broadband medium, such as a single DSL line, wireless device
or cable modem.
PPTP
Point-to-Point Tunneling Protocol: A VPN protocol developed by PPTP Forum. With
PPTP, users can dial in to their corporate network via the Internet. If users require data
encryption when using the Windows PPTP client, the remote VPN server must support
MPPE (Microsoft Point-To-Point Encryption Protocol) encryption. PPTP is also used by
some ISP for user authentication, particularly when pairing with legacy Alcatel / Thomson
ADSL modem.
Preamble Type
Preamble are sent with each wireless packet transmit for transmission status. Use the
long preamble type for better compatibility. Use the short preamble type for better
performance.
AirLive WN-200USB User’s Manual
46
Page 50

6. Network Glossary
Rate Control
It is an Ethernet switch’s function to control the upstream and downstream speed of an
individual port. Rate control management use “Flow Control” to limit the speed of a port.
Therefore, the Ethernet adapter must also have the flow control enabled. One way to force
the adapter’s flow control on is to set a port to half-duplex mode.
RADIUS
Remote Authentication Dial-In User Service. An authentication and accounting system
used by many Internet Service Providers (ISPs). When you dial in to the ISP, you must
enter your username and password. This information is passed to a RADIUS server, which
checks that the information is correct, and then authorizes access to the ISP system.
Radius typically uses port 1812 and port 1813 for authentication and accounting port.
Though not an official standard, the RADIUS specification is maintained by a working group
of the IETF.
Receiver Sensitivity
Receiver sensitivity means how sensitive is the radio for receiving signal. In general; the
slower the transmission speed, the more sensitive the radio is. The unit for Receiver
Sensitivity is in dB; the lower the absolute value is, the higher the signal strength. For
example, -50dB is higher than -80dB.
RJ-45
Standard connectors for Twisted Pair copper cable used in Ethernet networks. Although
they look similar to standard RJ-11 telephone connectors, RJ-45 connectors can have up to
eight wires, whereas telephone connectors have only four.
Router
An IP sharing router is a device that allows multiple PCs to share one single broadband
connection using NAT technology. A wireless router is a device that combines the
functions of wireless Access Point and the IP sharing router.
47
AirLive WN-200USB User’s Manual
Page 51

6. Network Glossary
RSSI
Receiver Sensitivity Index. RSSI is a value to show the Receiver Sensitivity of the remote
wireless device. In general, remote APs with stronger signal will display higher RSSI
values. For RSSI value, the smaller the absolute value is, the stronger the signal. For
example, “-50db” has stronger signal than “-80dB”. For outdoor connection, signal
stronger than -60dB is considered as a good connection.
RTS
Request To Send. A packet sent when a computer has data to transmit. The computer will
wait for a CTS (Clear To Send) message before sending data.
RTS Threshold
RTS (Request to Send). The RTS/CTS(clear to send) packet will be send before a frame
if the packet frame is larger than this value. Lower this value can improve the
performance if there are many clients in your network. You can try 1500, 1000 or 500
when there are many clients in your AP’s network.
SNMP
Simple Network Management Protocol. A set of protocols for managing complex networks.
The SNMP network contains three key elements: managed devices, agents, and
network-management system (NMS). Managed devices are network devices that contain
SNMP agents. SNMP agents are programs that reside SNMP capable device’s firmware to
provide SNMP configuration service. The NMS typically is PC-based software that can
monitor and control managed devices remotely.
SSH
Developed by SSH Communications Security Ltd., Secure Shell is a program to log into
another computer over a network, to execute commands in a remote machine, and to move
files from one machine to another. It provides strong authentication and secure
communications over insecure channels. It is a replacement for rlogin, rsh, rcp, and rdist.
AirLive WN-200USB User’s Manual
48
Page 52

6. Network Glossary
SSL
Secure Sockets Layer. It is a popular encryption scheme used by many online retail and
banking sites to protect the financial integrity of transactions. When an SSL session
begins, the server sends its public key to the browser. The browser then sends a randomly
generated secret key back to the server in order to have a secret key exchange for that
session. SSL VPN is also known as Web VPN. The HTTPS and SSH management
interface use SSL for data encryption.
Subnet Mask
An address code mask that determines the size of the network. An IP subnet are
determined by performing a BIT-wise AND operation between the IP address and the
subnet mask. By changing the subnet mask, you can change the scope and size of a
network.
Subnetwork or Subnet
Found in larger networks, these smaller networks are used to simplify addressing between
numerous computers. Subnets connect to the central network through a router, hub or
gateway. Each individual wireless LAN will probably use the same subnet for all the local
computers it talks to.
Super A
Super A is an Atheros proprietary turbo mode to increase speed over standard 802.11a
mode. It adds Bursting and Compression to increase the speed. If you live in countries
that prohibit the channel binding technology (i.e. Europe), you should choose “Super-A
without Turbo) if you need more speed than 11a mode
TCP
A layer-4 protocol used along with the IP to send data between computers over the Internet.
While IP takes care of handling the actual delivery of the data, TCP takes care of keeping
track of the packets that a message is divided into for efficient routing through
the Internet.
49
AirLive WN-200USB User’s Manual
Page 53

6. Network Glossary
Turbo A
Turbo A is an Atheros proprietary turbo mode to increase speed over standard 802.11a
mode. It uses channel binding technology to increase speed. There are 2 types of Turbo
A modes: Dynamic Turbo and Static Turbo. In Dynamic Turbo, the channel binding will be
used only if necessary. In Static Turbo, the channel binding is always on. This protocol
may be combined with Super-A model to increase the performance even more. The used
of channel binding might be prohibited in EU countries.
TX Output Power
Transmit Output Power. The TX output power means the transmission output power of
the radio. Normally, the TX output power level limit for 2.4GHz 11g/b is 20dBm at the
antenna end. The output power limit for 5GHz 802.11a is 30dBm at the antenna end..
UDP
User Datagram Protocol. A layer-4 network protocol for transmitting data that does not
require acknowledgement from the recipient of the data.
Upgrade
To replace existing software or firmware with a newer version.
Upload
To send a file to the Internet or network device.
URL
Uniform Resource Locator. The address of a file located on the Internet.
AirLive WN-200USB User’s Manual
50
Page 54

6. Network Glossary
VPN
Virtual Private Network. A type of technology designed to increase the security of
information transferred over the Internet. VPN creates a private encrypted tunnel from the
end user's computer, through the local wireless network, through the Internet, all the way to
the corporate network.
Walled Garden
On the Internet, a walled garden refers to a browsing environment that controls the
information and Web sites the user is able to access. This is a popular method used by
ISPs in order to keep the user navigating only specific areas of the Web
WAN
Wide Area Network. A communication system of connecting PCs and other computing
devices across a large local, regional, national or international geographic area. A WAN
port on the network device means the port (or wireless connection) that is connected to the
Internet side of the network topology.
WEP
Wired Equivalent Privacy. A wireless encryption protocol. WEP is available in 40-bit (64-bit),
108-bit (128-bit) or 152-bit (Atheros proprietary) encryption modes.
Wi-Fi
Wireless Fidelity. An interoperability certification for wireless local area network (LAN)
products based on the IEEE 802.11 standards. The governing body for Wi-Fi is called
Wi-Fi Alliance (also known as WECA).
WiMAX
51
AirLive WN-200USB User’s Manual
Page 55

6. Network Glossary
Worldwide Interoperability for Microwave Access. A Wireless Metropolitan Network
technology that complies with IEEE 802.16 and ETSI Hiperman standards. The orginal
802.16 standard call for operating frequency of 10 to 66Ghz spectrum. The 802.16a
amendment extends the original standard into spectrum between 2 and 11 Ghz. 802.16d
increase data rates to between 40 and 70 Mbps/s and add support for MIMO antennas,
QoS, and multiple polling technologies. 802.16e adds mobility features, narrower
bandwidth (a max of 5 mhz), slower speed and smaller antennas. Mobility is allowed up to
40 mph.
WDS
Wireless Distribution System. WDS defines how multiple wireless Access Point or
Wireless Router can connect together to form one single wireless network without using
wired uplinks. WDS associate each other by MAC address, each device
WLAN
Wireless Local Area Network. A type of local-area network that uses high-frequency radio
waves rather than wires to communicate between nodes. The most popular standard for
WLAN is the 802.11 standards.
WMM
Wi-Fi Multimedia (WMM) is a standard to prioritize traffic for multimedia applications. The
WMM prioritize traffic\ on Voice-over-IP (VoIP), audio, video, and streaming media as well
as traditional IP data over the AP.
WMS
Wireless Management System. An utility program to manage multiple wireless
AP/Bridges.
AirLive WN-200USB User’s Manual
52
Page 56

6. Network Glossary
WPA
Wi-Fi Protected Access. It is an encryption standard proposed by WiFi for advance
protection by utilizing a password key (TKIP) or certificate. It is more secure than WEP
encryption. The WPA-PSK utilizes pre-share key for encryption/authentication.
WPA2
Wi-Fi Protected Access 2. WPA2 is also known as 802.11i. It improves on the WPA
security with CCMP and AES encryption. The WPA2 is backward compatible with WPA.
WPA2-PSK utilizes pre-share key for encryption/authentication.
53
AirLive WN-200USB User’s Manual
 Loading...
Loading...