Page 1

WLA-5000AP
A
ccess Point Mode
User’s Guide
Page 2

Copyright Statement
No part of this publication may be reproduced, stored in a retrieval system, or
transmitted in any form or by any means, whether electronic, mechanical,
photocopying, recording or otherwise without the prior writing of the
publisher.
Windows
™
95/98 and Windows
Pentium is trademark of Intel.
All copyright reserved.
™
2000 are trademarks of Microsoft
®
Corp.
1
Page 3

Regulatory Information
Federal Communication Commission Interference Statement
This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a Class B
digital device, pursuant to Part 15 of the FCC Rules. These limits are designed to
provide reasonable protection against harmful interference in a residential installation.
This equipment generates, uses and can radiate radio frequency energy and, if not
installed and used in accordance with the instructions, may cause harmful
interference to radio communications. However, there is no guarantee that
interference will not occur in a particular installation. If this equipment does cause
harmful interference to radio or television reception, which can be determined by
turning the equipment off and on, the user is encouraged to try to correct the
interference by one of the following measures:
- Reorient or relocate the receiving antenna.
- Increase the separation between the equipment and receiver.
- Connect the equipment into an outlet on a circuit different from that to which the
receiver is connected.
- Consult the dealer or an experienced radio/TV technician for help.
FCC Caution: To assure continued compliance, (example - use only shielded
interface cables when connecting to computer or peripheral devices) any changes or
modifications not expressly approved by the party responsible for compliance could
void the user’s authority to operate this equipment. This device complies with Part 15
of the FCC Rules. Operation is subject to the following two conditions: (1) This device
may not cause harmful interference, and (2) this device must accept any interference
received, including interference that may cause undesired operation.
IMPORTANT NOTE:
FCC Radiation Exposure Statement:
radiation exposure limits set forth for an uncontrolled environment. This equipment
should be installed and operated with minimum distance 20cm between the radiator &
your body.
This transmitter must not be co-located or operating in conjunction with any
other antenna or transmitter.
This equipment complies with FCC
2
Page 4
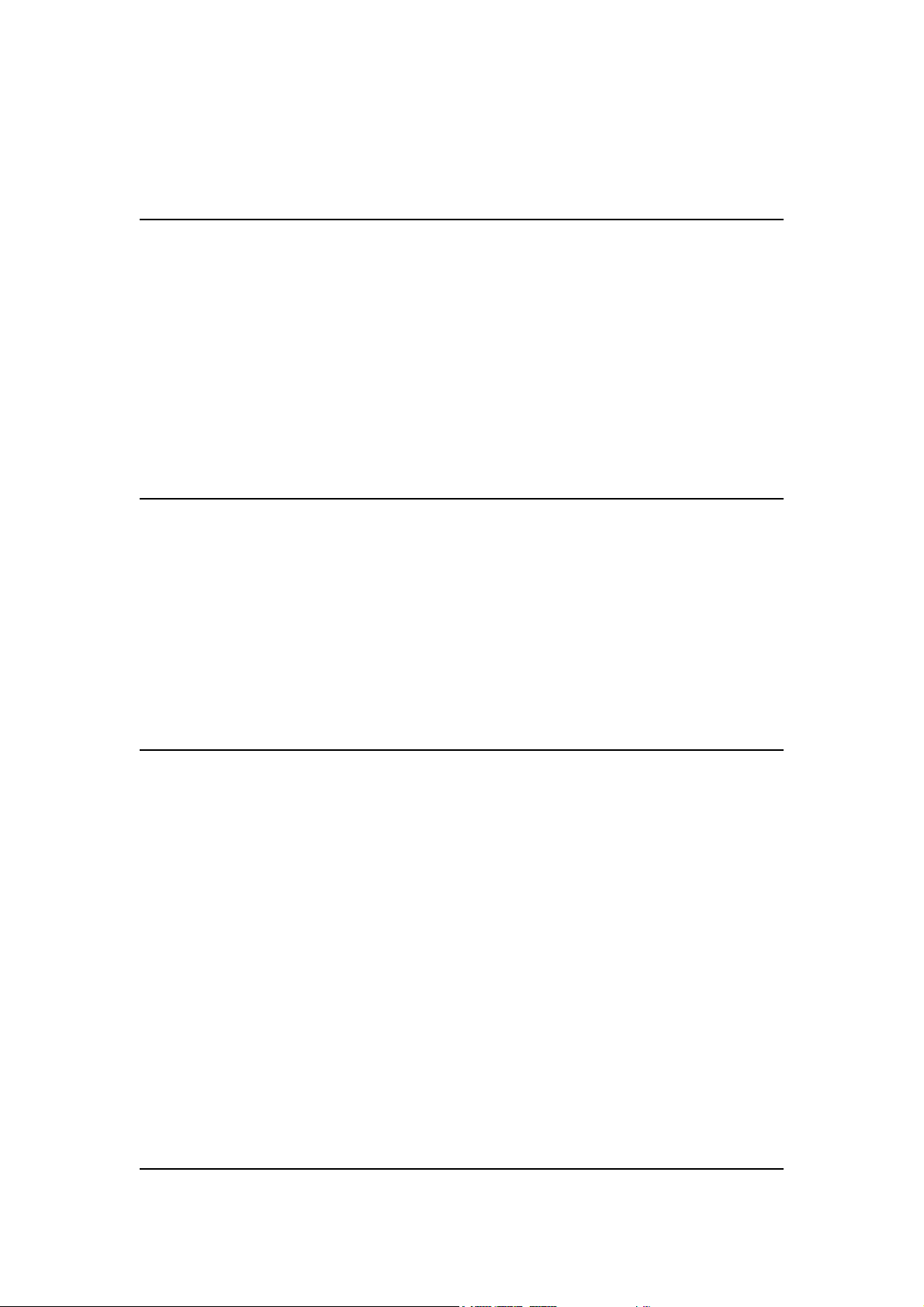
Table of Contents
1. INTRODUCING THE WLA-5000AP 802.11 A/G ACCESS POINT 5
1.1 OVERVIEW 5
1.2 FEATURES 6
1.3 NETWORK CONFIGURATION EXAMPLES 7
1.3.1 AS AN ACCESS POINT 7
1.3.2 AS A STAND-ALONE REPEATER 8
1.3.3 AS A POINT TO MULTI-POINTS BRIDGE 8
1.4 SET UP THE DEVICE 9
2. INSTALL THE WLA-5000AP 802.11 A/G ACCESS POINT 10
2.1 WHAT’S IN THE BOX? 10
2.2 CONNECT THE CABLES 10
2.3 CONFIGURATION STEPS 11
2.4 SET UP A WIRELESS CLIENT AS A DHCP CLIENT 12
2.5 A LOOK AT THE FRONT PANEL 13
2.6 CONNECT MORE DEVICES THROUGH A HUB 13
3. BASIC CONFIGURATION OF THE 802.11A/G ACCESS POINT 14
SETUP WIZARD 15
3.1
3.1.1 TIME SETTINGS 15
3.1.2 DEVICE IP SETTINGS 16
3.1.3 WIRELESS SETTINGS 17
3.1.4
FINISH SETUP WIZARD AND SAVE YOUR SETTINGS 20
3.2 ADVANCED SETTINGS 21
3.2.1 PASSWORD SETTINGS 21
3.2.2 SYSTEM MANAGEMENT 22
3.2.3 MAC FILTERING SETTINGS 23
3.2.4 WIRELESS SETTINGS 24
3.2.5 OPERATIONAL MODE 25
3.2.6 RADIUS SETTINGS 26
4. MANAGE THE 802.11A/G ACCESS POINT 28
3
Page 5

4.1 DEVICE INFORMATION 28
4.2 SYSTEM LOG 29
4.3 WIRELESS CLIENT TABLE 29
4.4 BRIDGE TABLE 30
4.5 FIRMWARE UPGRADE 30
4.6 CONFIGURATION SAVE AND RESTORE 31
4.7 FACTORY DEFAULT 32
4.8 REBOOT SYSTEM 32
4.9 WHAT IF YOU FORGOT THE PASSWORD? 33
SPECIFICATION 34
4
Page 6

1. Introducing the WLA-5000AP
802.1 1 A/G Access Point
1
1.1 Overview
The WLA-5000AP 802.11A/G ACCESS POINT is an access-point based on IEEE
802.11a/g based 2.4-GHz radio technology. It contains an 802.11a/g and a full-duplex
10/100 LAN interfaces. The 802.11A/G ACCESS POINT can function as a simple
Access Point (AP), and act as the center point of a wireless network supporting a data
rate of up to 54 Mbps. It can also connect these wireless devices to wired network
through the LAN interface.
The 802.11A/G ACCESS POINT can also function in a repeater mode, which is used to
extend the physical coverage of the wireless network. Finally, the 802.11A/G ACCESS
POINT can also function in a Wireless Distribution System (WDS) mode. Multiple
802.11A/G ACCESS POINTs can be configured to operate in the WDS mode to
inter-connect wired LAN segments that are attached to these 802.11A/G ACCESS
POINTs.
Since the 802.11g shares the same 2.4GHz radio band as the 802.11b technology, it can
inter-operate with existing 11Mbps 802.11b devices. Therefore you can protect your
existing investment in 802.11b client cards, and migrate to the high-speed 802.11g
standard as your needs grow.
To address growing security concerns in a wireless LAN environment, different levels of
security can be enabled in the 802.11A/G ACCESS POINT:
To disable SSID broadcast to restrict association to only those client stations that are
already pre-configured with the correct SSID
To enable WEP (Wireless Encryption Protocol) 64, 128, or 156-bit encryption to
protect the privacy of your data.
Support of Access List Control to allow you to grant/deny access to/from specified
wireless stations
Provisioning of centralized authentication through Radius Server(s).
WPA-PSK (Wi-Fi Protected Access, Pre-Shared Key) for home users to provide
authentication, data integrity, and data privacy.
WPA (Wi-Fi Protected Access) works with a RADIUS server to provide stronger
authentication as well as data integrity and privacy.
5
Page 7

1.2 Features
Compliant with draft 802.11a, 802.11b and 802.11g standards with roaming
capability.
Support of the standard access point mode for connection to wireless clients.
Support of the repeater mode to extend infrastructure coverage.
Support of the WDS mode for interconnecting LAN segments.
Built-in DHCP Server to assign IP addresses to wired/wireless clients automatically.
Static assignment or DHCP client to set the device IP address.
Multiple security measures: SSID hiding, Access Control List, WEP based encryption
(64, 128, 152 bits), enhanced Security with 802.1x using a primary and a backup
Radius Server with/without dynamic WEP keys, WPA-PSK, and WPA.
Extensive monitoring capability such as event logging, traffic/error statistics
monitoring. Support of remote logging.
Easy configuration and monitoring through the use of a Web-browser based GUI,
SNMP commands from a remote SNMP management station, and UPnP for users to
automatically discover the device.
Setup Wizard for easy configuration/installation.
Configuration file download and restore.
Firmware upgradeable.
6
Page 8
1.3 Network configuration examples
A group of wireless stations communicating with each other is called a Basic Service Set
(BSS) and is identified by a unique SSID.
When an 802.11A/G ACCESS POINT is used, it can be configured to operate in the
following three network configurations
1.3.1 AS AN ACCESS POINT
When configured in the Access Point mode, the 802.11A/G ACCESS POINT allows a
group of wireless stations to communicate with each other through it. Such a network is
called an Infrastructure BSS.
The 802.11A/G ACCESS POINT further provides bridging functions between the
wireless network and the wired LAN network.
When multiple access points are connected to the same LAN segment, stations can roam
from one 802.11A/G ACCESS POINT to another without losing their connections, as
long as they are using the same SSID. See the diagram below.
7
Page 9
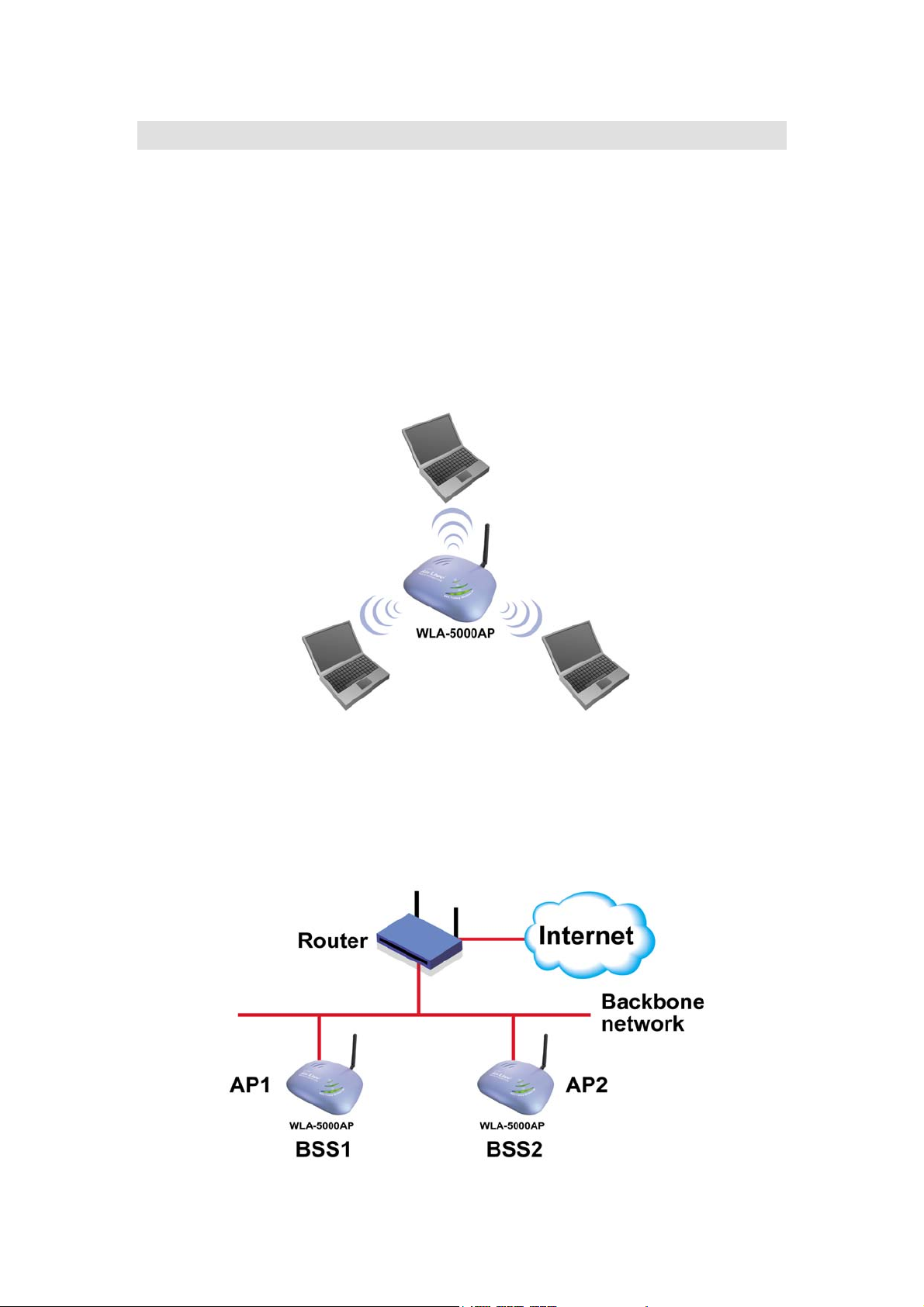
1.3.2 AS A STAND-ALONE REPEATER
The purpose of a repeater is to expand an existing infrastructure BSS. When configured
to operate in the Repeater Mode, the 802.11A/G ACCESS POINTs sit between wireless
stations and a “root” AP whose BSS is being expanded, as shown below:
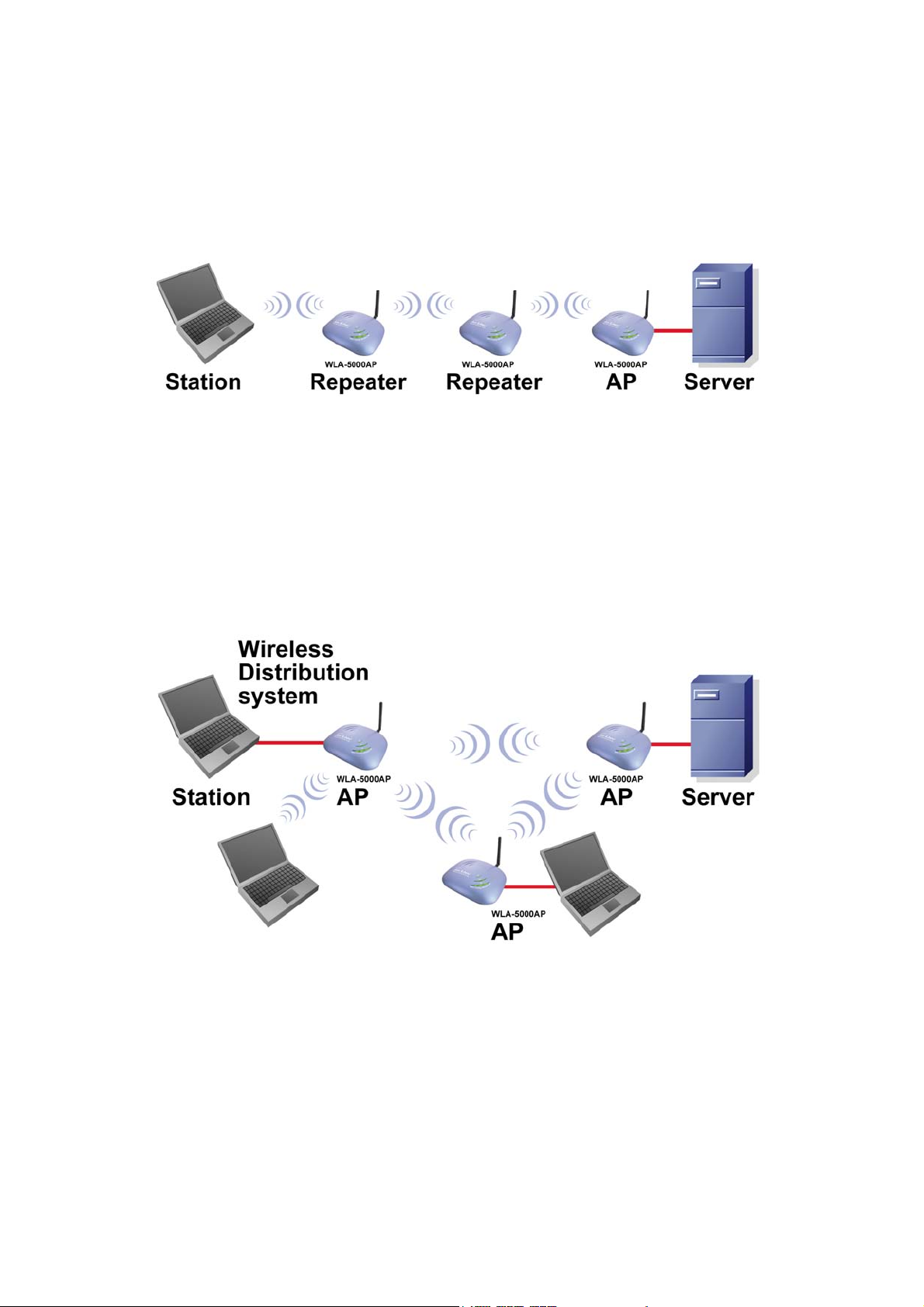
1.3.3 AS A POINT TO MULTI-POINTS BRIDGE
When configured to operate in the Wireless Distribution System (WDS) Mode, the
802.11A/G ACCESS POINT provides bridging functions between the LAN behind it
and separates LANs behind other APs’ operating in the WDS mode. The system will
support up to eight such AP in a WDS configuration.
Note that an 802.11A/G ACCESS POINT running in the WDS mode can also support
wireless stations simultaneously. See the diagram below:
8
Page 10

1.4 Set up the device
The 802.11A/G ACCESS POINT can be managed remotely by a PC through either the
wired or wireless network. To do this, the WLA-5000AP must first be assigned an IP
address, which can be done using one of the following two methods.
1.4.1 STATIC IP
The default IP address of the LAN interface of an WLA-5000AP is a private IP address of
192.168.1.1, and a network mask of 255.255.255.0. This means IP addresses of other
devices on the LAN should be in the range of 192.168.1.2 to 192.168.1.254.
This IP address can be modified to either a different address in this same subnet or to an
address in a different subnet, depending on the existing network settings (if there is any)
or user’s preference.
1.4.2 AUTOMATIC IP
The WLA-5000AP can also be configured to “obtain” an IP address automatically from a
DHCP server on the network. This address is called “dynamic” because it is only
dynamically assigned to the device, which may change depends on the IP assignment
policy used by the DHCP server on the network. Since the IP address in this case may
change from time to time, this method is not recommended - unless the user uses UPnP
or other management tools that do not depend on a fixed IP address.
9
Page 11

2. Install the WLA-5000AP 802.11
A/G Access Point
2
This section describes the installation procedure for the WLA-5000AP. It starts with a
summary of the content of the package you have purchased, followed by steps of how to
power up and connect the WLA-5000AP. Finally, this section explains how to configure
a Windows PC to communicate with the WLA-5000AP.
2.1 What’s in the box?
The WLA-5000AP package contains the following items:
One WLA-5000AP
One 5V AC power adapter with a barrel connector
CD of the WLA-5000AP User Guide
2.2 Connect the cables
The Back Panel of the WLA-5000AP appears as follows:
Follow these steps to install your WLA-5000AP:
Step 1. Connect a LAN hub to the LAN port on the WLA-5000AP using the supplied
LAN cable.
Step 2. Connect the power adapter to an electrical outlet and the WLA-5000AP.
Note: You can reset the Access Point’s Settings to factory
defaults by pushing a paperclip in the RESET hole.
Push and hold until the lights at the front of the Access
Point are off.
10
Page 12

2.3 Configuration steps
This section describes configuration required for the WLA-5000AP before it can work
properly in your network.
First, it is assumed that in your LAN environment, a separate DHCP server will be
available for assigning dynamic (and often private) IP addresses to requesting DHCP
clients. This means that the WLA-5000AP normally will not need to enable the DHCP
server function.
Additionally, since you need to perform various configuration changes to the 802.11A/G
ACCESS POINT, including the SSID, Channel number, the WEP key, …, etc., it is
necessary to associate a fixed IP address with the 802.11A/G ACCESS POINT, which is
why the 802.11A/G ACCESS POINT will be shipped with a factory default private IP
address of 192.168.1.1 (and a network mask of 255.255.255.0).
Therefore, during the system installation time, you need to build an isolated environment
with the 802.11A/G ACCESS POINT and a PC, and then perform the following steps:
Step 1. Manually change the IP address of the PC to become 192.168.1.3.
Step 2. Connect the PC to the 802.11A/G ACCESS POINT and change its
configuration to a static IP address based on your network environment. For
example, if there is a DHCP server that assigns IP addresses from the range
192.168.23.10 - 192.168.23.254 to DHCP client devices, it can reserve
192.168.23.10 for the 802.11A/G ACCESS POINT and then the address pool
with the DHCP server becomes 192.168.23.11 – 192.168.23.254.
If there is no DHCP server on your network environment, you just have to
make sure that there is no machine in the environment has the same IP address
as another machine.
Please note that after you change the IP address of the ACCESS POINT, the
PC client may not be able to reach the ACCESS POINT. This is because they
may no longer belong to the same IP network address space.
Step 3. Change the setting of the PC back to “obtain IP addresses dynamically”.
Now you can put the 802.11A/G ACCESS POINT and the PC to your
network where the DHCP server is connected. From then on, any wireless
client configured to “obtain IP addresses dynamically” will work with the AP,
with each other, and with devices on the wired LAN network.
11
Page 13

2.4 Set up a wireless client as a DHCP client
The following will give detailed steps of how to configure a PC or a wireless client to
“obtain IP addresses automatically”.
In the case of using a LAN attached PC, the PC must have an Ethernet interface
installed properly, be connected to the 802.11A/G ACCESS POINT either directly or
through an external LAN switch, and have TCP/IP installed and configured to obtain an
IP address automatically from a DHCP server in the network.
In the case of using a wireless client, the client must also have an 802.11a/b/g wireless
interface installed properly, be physically within the radio range of the 802.11A/G
ACCESS POINT, and have TCP/IP installed and configured to obtain an IP address
automatically from a DHCP server in the network.
Then perform the following steps for either of the cases above. To configure types of
workstations other than Windows 95/98/NT/2000, please consult the manufacturer’s
documentation.
Step 1. From the Win95/98/2000 Start Button, select Settings, then Control Panel.
The Win95/98/2000 Control Panel displays.
Step 2. Double-click on the Network icon.
Step 3. Check your list of Network Components in the Network window
Configuration tab. If TCP/IP has already been installed, go to Step 8.
Otherwise, select Add to install it now.
Step 4. In the new Network Component Type window, select Protocol. In the new
Select Network Protocol window, select Microsoft in the Manufacturers area.
Step 5. In the Network Protocols area of the same window, select TCP/IP, then click
OK. You may need your Win95/98 CD to complete the installation. After
TCP/IP installation is complete, go back to the Network window described in
Step 4.
Step 6. Select TCP/IP in the list of Network Components.
Step 7. Click Properties, and check the settings in each of the TCP/IP Properties
window: Bindings Tab: both Client for Microsoft Networks and File and
printer sharing for Microsoft Networks should be selected. Gateway Tab:
All fields should be blank. DNS Configuration Tab: Disable DNS should
be selected. IP Address Tab: Obtain IP address automatically should be
selected.
Step 8. With the 802.11A/G ACCESS POINT powered on, reboot the PC/wireless
client. After the PC/wireless client is re-booted, you should be ready to
configure the 802.11A/G ACCESS POINT. See Chapter 3.
The procedure required to set a static IP address is not too much different from the
procedure required to set to “obtain IP addresses dynamically” - except that at the end of
step 7, instead of selecting “obtain IP addresses dynamically, you should specify the IP
address explicitly.
12
Page 14

2.5 A look at the front panel
The LEDs on the front of the 802.11A/G ACCESS POINT reflect the operational
status of the unit. The status of the LAN, the wireless, and power can be monitored from
this display.
802.11A/G ACCESS POINT LED Description
Label Wireless LAN POWER
Constant
Light
OFF
FLASH
Link is active Link is active
No Wireless
connection Radio off
XMT/RCV Data XMT/RCV Data
No LAN
connection
Power Normal
Operation
No Power
N/A under
boot-up
2.6 Connect more devices through a hub
The 802.11A/G ACCESS POINT provides an RJ45 LAN interface that you can use to
connect to a PC or an external hub.
13
Page 15

3. Basic Configuration of the
802.11A/G ACCESS POINT
3
This section describes the basic configuration procedure for the 802.11A/G ACCESS
POINT. It describes how to set up the 802.11A/G ACCESS POINT for wireless
connections, and the configuration of the local LAN environment. All basic
configurations may be effected through a standard Web browser such as Microsoft
Internet Explorer. From a PC that has been configured as described in Chapter 2, enter
the IP address of the 802.11A/G ACCESS POINT as the URL in your browser, e.g.
http://192.168.1.1.
Note: The IP address of your PC must be in the same IP subnet as
the 802.11A/G ACCESS POINT.
The Home Page of the 802.11A/G ACCESS POINT screen will appear. Its main menu
displays on the right hand side of the window. The main menu includes the following
choices: Setup Wizard, Device Status, Advanced Settings, System Tools, and Help.
Log On
If you attempt to access a configuration item from the browser menu, an administrator
logon screen, shown below, will appear.
14
Page 16

If you are logging on for the first time, you should use the factory default password
setting “airlive”. The password is always displayed as a string of dots. Click the LOG
ON button to start the configuration session.
3.1 Setup wizard
The Setup Wizard will guide you through a series of configuration screens to set up the
basic functionality of the device. After you finish these screens, press the “FINISH”
button on the last screen to make all your modifications effective. See Chapter 3.1.4.
3.1.1 TIME SETTINGS
After logging on, the time settings page appears. The device time is automatically set to
the local time of the management PC at the first time a connection is made. To modify
the device’s time, modify the appropriate fields, then click NEXT.
15
Page 17

3.1.2 DEVICE IP SETTINGS
The Device IP Settings screen allows you to configure the IP address and subnet of the
device. Although you can rely on a DHCP server to assign an IP address to the
802.11A/G ACCESS POINT automatically, it is recommended that you configure a
static IP address manually in most applications.
If you choose to assign the IP address manually, enable the checkbox of “Assign static IP
to this device” and then fill in the following fields
IP Address and IP Subnet Mask: Default values are 192.168.1.1 and 255.255.255.0
respectively. It is important to note that there are similar addresses falling in the standard
private IP address range and it is an essential security feature of the device. Because of
this private IP address, the device can no longer be accessed (seen) from the Internet.
Gateway IP Address: Enter the IP address of your default gateway.
DNS Server: The Domain Name System (DNS) is a server on the Internet that
translates logical names such as “www.yahoo.com” to IP addresses like 66.218.71.80. In
order to do this, a query is made by the requesting device to a DNS server to provide the
necessary information. If your system administrator requires you to manually enter the
DNS Server addresses, you should enter them here.
Click Next to go to the next screen.
If you choose to use a DHCP Server to acquire an IP address for the 802.11A/G Access
Point automatically, enable the checkbox that says, “Use the DHCP client protocol to
automatically get the IP address for this device”. Then click Next to go to the next screen.
16
Page 18

Again, as a reminder, it is recommended that your 802.11A/G ACCESS POINT should
be assigned a static IP address in order to make it easy for you to manage the device later
on.
3.1.3 WIRELESS SETTINGS
Network ID (SSID): The SSID is the network name used to identify a wireless network.
The SSID must be the same for all devices in the wireless network (i.e. in the same BSS).
Several access points on a network can have the same SSID. The SSID length is up to 32
characters. The default SSID is “airlive”.
Disable SSID Broadcasting: An access point periodically broadcasts its SSID along
with other information, which allows client stations to learn its existence while searching
for access points in a wireless network. Check Disable SSID Broadcasting if you do
not want the device to broadcast the SSID.
Regulatory Domain: Please make sure that your regulatory domain matches your region.
The default value is FCC.
WLAN Mode: The wireless module is IEEE 802.11g and 802.11b compliant, and
choosing “11g/b” allows both 802.11b and 802.11g client stations to get associated.
However, choosing “11g” allows only 802.11g client stations to get associated and get
better overall performance. 802.11a is not compliant with either 802.11b or 802.11g;
choosing “11a” only allows 802.11a client stations to get associated.
Channel: Select a channel from the drop down menu. All devices in a BSS must use the
same channel. You can select Auto to let the system pick up the best channel for you.
17
Page 19

Note: The available channels are different from country to country
and for different WLAN mode.
Security Policy: You can select different security policy to provide association
authentication and/or data encryption.
WEP
WEP allows you to use data encryption to secure your data from being eavesdropped by
malicious people. It allows 3 types of key: 64 (WEP64), 128 (WEP128), and 152
(WEP152) bits. You can configure up to 4 keys using either ASCII or Hexadecimal
format.
Key Settings: The length of a WEP64 key must be equal to 5 bytes, a WEP128 key is 13
bytes, and a WEP152 key is 16 bytes. For WEP64 and WEP128, you can just enter a
pass-phrase and click the GENERATE button to generate the four keys. So you can use
a mnemonic string as the pass-phrase instead of memorizing the four keys.
Key Index: You have to specify which of the four keys will be active.
Once you enable the WEP function, please make sure that both the 802.11A/G
ACCESS POINT and the wireless client stations use the same key.
Note: Some wireless client cards only allow Hexadecimal digits for WEP keys. Please
note that when configuring WEP keys, a WEP128 ASCII key looks like “This is a
key”(13 characters), while a WEP128 Hex key looks like
“54-68-69-73-20-69-73-20-61-20-6b-65-79”(13 bytes).
802.1x
18
Page 20

802.1x allows users to leverage a RADIUS server to do association authentications. You
can also enable dynamic WEP keys (64, 128, 152-bit) to have data encryption. Here you
do not have to enter the WEP key manually because it will be generated automatically
and dynamically.
Note: After you have finished the configuration wizard, you have to
configure the Radius Settings in Advanced Settings in order
to make the 802.1x function work.
WPA-PSK
Wi-Fi Protected Access (WPA) with Pre-Shared Key (PSK) provides better security than
WEP keys. It does not require a RADIUS server in order to provide association
authentication, but you do have to enter a shared key for the authentication purpose. The
encryption key is generated automatically and dynamically.
Pre-shared Key: This is an ASCII string with 8 to 63 characters. Please make sure that
both the 802.11A/G ACCESS POINT and the wireless client stations use the same key.
Encryption Type: There are two encryption types TKIP and CCMP (AES). While
CCMP provides better security than TKIP, some wireless client stations may not be
equipped with the hardware to support it. You can select Both to allow TKIP clients and
CCMP clients to connect to the Access Point at the same time.
Group Rekey Interval: A group key is used for multicast/broadcast data, and the rekey
interval is time period that the system will change the group key periodically. The shorter
19
Page 21

the interval is, the better the security is. 60 seconds is a reasonable time, and it is used by
default.
WPA
Wi-Fi Protected Access (WPA) requires a RADIUS server available in order to do
authentication (same as 802.1x), thus there is no shared key required. The Encryption
Type and Group Rekey Interval settings are the same as WPA-PSK.
3.1.4 FINISH SETUP WIZARD AND SAVE YOUR SETTINGS
After stepping through the Wizard’s pages, you can press the FINISH button for your
modification to take effect. This also makes your new settings saved into the permanent
memory on your system.
Congratulations! You are now ready to use the WLA-5000AP 802.11A/G ACCESS
POINT.
Note: If you change the device’s IP address, as soon as you click on
FINISH you will no longer be able to communicate with your
802.11A/G ACCESS POINT. You need to change your IP
address and then re-boot your computer in order to resume
the communication.
20
Page 22

3.2 Advanced settings
The advanced settings tab on the top row of the window allows you to perform
modifications that normally you may not need to do for general operations except
changing your password from the default factory setting (this is highly recommended for
security purposes).
3.2.1 PASSWORD SETTINGS
The default factory password is “airlive”. To change the password, press the Password
Settings button to enter the Password Settings screen, then enter the current password
followed by the new password twice. The entered characters will appear as asterisks
.
21
Page 23

3.2.2 SYSTEM MANAGEMENT
Clicking the System Management button to configure system related parameters to for
the 802.11A/G ACCESS POINT.
Management Utility Port Definition: The standard port settings for the HTTP Web
server and the Telnet utility may be replaced by entering new port numbers in these
fields.
Management Session Time-out: This setting specifies the duration of idle time
(inactivity) before a web browser or telnet management session times out. The default
time-out value is 10 minutes.
UPnP: The Universal Plug and Play (UPnP) feature allows a Windows XP/ME PC to
discover this 802.11A/G Access Point and automatically show an icon on the screen.
Then a user can double-click the icon to access this device directly (without having to
find out its IP address).
Syslog: Syslog is an IETF (Internet Engineering Task Force - the Internet standards
body)-conformant standard for logging system events (RFC-3164). When the 802.11A/G
ACCESS POINT encounters an error or warning condition (e.g., a log-in attempt with
an invalid password), it will create a log in the system log table. To be able to remotely
view such system log events, you need to check the Enable Syslog box and configure
the IP address of a Syslog daemon. When doing so, the 802.11A/G ACCESS POINT
will send logged events over network to the daemon for future reviewing.
Syslog server IP address: The IP address of the PC where the Syslog daemon is
running.
22
Page 24

3.2.3 MAC FILTERING SETTINGS
The 802.11A/G ACCESS POINT allows you to define a list of MAC addresses that are
allowed or denied to access the wireless network.
Disable MAC address control list: When selected, no MAC address filtering will be
performed.
Enable GRANT address control list: When selected, data traffic from only the
specified devices in the table will be allowed in the network.
Enable DENY address control list: When selected, data traffic from the devices
specified in the table will be denied/discarded by the network.
To add a MAC address into the table, enter a Mnemonic Name and the MAC Address,
and then click ADD. The table lists all configured MAC Filter entries.
To delete entries, check the corresponding select boxes and then press DELETE
SELECTED.
23
Page 25

3.2.4 WIRELESS SETTINGS
Beacon Interval: The 802.11A/G ACCESS POINT broadcasts beacon frames regularly
to announce its existence. The beacon Interval specifies how often beacon frames are
transmitted in time unit of milliseconds. The default value is 100, and a valid value should
be between 1 and 65,535.
RTS Threshold: RTS/CTS frames are used to gain control of the medium for
transmission. Any unicast (data or control) frames larger than specified RTS threshold
must be transmitted following the RTS/CTS handshake exchange mechanism. The RTS
threshold should have a value between 256-2347 bytes, with a default of 2347. It is
recommended that this value does not deviate from the default too much.
Fragmentation: When the size of a unicast frame exceeds the fragmentation threshold,
it will be fragmented before the transmission. It should have a value of 256-2346 bytes,
with a default of 2346. If you experience a high packet error rate, you should slightly
decrease the Fragmentation Threshold.
DTIM Interval: The 802.11A/G ACCESS POINT buffers packets for stations that
operate in the power-saving mode. The Delivery Traffic Indication Message (DTIM)
informs such power-conserving stations that there are packets waiting to be received by
them. The DTIM interval specifies how often the beacon frame should contain DTIMs.
It should have a value between 1 to 255, with a default value of 3.
24
Page 26

3.2.5 OPERATIONAL MODE
The 802.11A/G ACCESS POINT can be configured to operate in one of the following
three modes as mentioned previously in Chapter 1:
(1) Access Point (2) Repeater (3) Wireless Distribution System (WDS)
When configured as a WDS, you need to further configure the name and MAC address
of its peer WDS devices.
25
Page 27

3.2.6 RADIUS SETTINGS
Radius servers provide centralized authentication services to wireless clients. Two Radius
servers can be defined: one acts as a primary, and the other acts as a backup.
Two user authentication methods can be enabled: one based on MAC address filter, and
the other based on 802.1x EAP authentication.
MAC address filtering based authentication requires a MAC address filter table to be
created in either the 802.11A/G ACCESS POINT (as described in Chapter 3.2.3 MAC
Filtering Settings) and/or the Radius server. During the authentication phase of a
wireless station, the MAC address filter table is searched for a match against the wireless
client’s MAC address to determine whether the station is to be allowed or denied to
access the network.
The Radius server can also be used for 802.1x EAP authentication. IEEE 802.1x is an
IEEE standard that is based on a framework that involves stations to be authenticated
(called Supplicant), an authentication server (a Radius Server) that provides
authentication services, and an authenticator that provides necessary translation and
mediating functions between the authentication server and the stations to be
authenticated. The 802.11A/G ACCESS POINT acts as an authenticator, and it relays
authentication messages between the RADIUS server and client devices being
authenticated.
26
Page 28

IEEE 802.1x EAP authentication is enabled by selecting the Security Policy as 802.1x
or WPA, and this selection is in the Wireless Settings under Setup Wizard.
Enable MAC Address Access Control: Check this option to enable MAC address
access control through a RADIUS server.
Enable Primary/Secondary Server: Check this if you want to enable RADIUS
authentication using the primary/secondary Radius Server. If both are selected, the
primary server will be tried first.
Server IP: The IP address of the RADIUS server.
Port Number: The port number that your RADIUS server uses for authentication. The
default setting is 1812.
Shared Secret: This is used by your RADIUS server in the Shared Secret field in Radius
protocol messages. The shared secret configured in the 802.11A/G ACCESS POINT
must match the shared secret configured in the RADIUS server. The shared secret can
contain up to 64 alphanumeric characters.
Retry Times: The number of times the 802.11A/G ACCESS POINT should attempt to
contact the primary server before giving up.
Reattempt Period: After failed to contact the primary RADIUS server, the 802.11A/G
ACCESS POINT will re-attempt to contact the primary server every this number of
minutes.
27
Page 29

4. Manage the WLA-5000AP
802.1 1A/G Access Point
4
This Chapter covers other management aspects of your WLA-5000AP 802.11A/G
ACCESS POINT:
Check Device Information
View System Log
Wireless Client Table
Bridge Table
Upgrade Firmware
Save or Restore Configuration Changes
Reset to Factory Default
Reboot AP
What if you forgot the password?
4.1 Device Information
You can monitor the system status and get general device information from the Device
Information screen:
This is at the left-bottom corner of the Device Status window.
28
Page 30

4.2 System Log
The WLA-5000AP 802.11A/G ACCESS POINT maintains a system log that you can use to
track events that have occurred in the system. Such event messages can sometimes be
helpful in determining the cause of a problem that you may have encountered.
You can select System Log on the left side of the Device Status window to view log events
recorded in the system. The System Log entries are shown in the main screen along with the
log level, the severity level of messages that are being displayed (lower is severer), and the
uptime, which is the amount of time since the 802.11A/G ACCESS POINT was boot-up.
4.3 Wireless Client Table
The wireless client table lists the current wireless clients and its MAC address, state, and
traffic statistics. You can check this table by clicking Wireless Client Table at the left side
of the Device Status window.
29
Page 31

4.4 Bridge Table
The bridge table shows all MAC entries learned from the wired LAN interface, wireless
clients, and WDS peers (if running in the WDS mode). You can check this table by clicking
Bridge Table at the left side of the Device Status window.
4.5 Firmware Upgrade
You can upgrade the firmware of your 802.11A/G ACCESS POINT (the software that
controls your 802.11A/G ACCESS POINT’s operation). Normally, this is done when a new
version of firmware offers new features that you want, or solves problems that you have
encountered with the current version. System upgrade can be performed through the System
Upgrade window as follows:
Step 1 Select System Tools, then Firmware Upgrade from the menu.
30
Page 32

Step 2 To update the 802.11A/G ACCESS POINT firmware, first download the firmware
from the distributor’s web site to your local disk, and then from the above screen
enter the path and filename of the firmware file (or click Browse to locate the
firmware file). Next, Click the Upgrade button to start.
The new firmware will be loaded to your 802.11A/G ACCESS POINT. After a message
appears telling you that the operation is completed, you need to reset the system to have the
new firmware take effect.
Note: It is recommended that you do not upgrade your 802.11A/G
ACCESS POINT unless the new firmware has new features you
need or if it has a fix to a problem that you’ve encountered.
4.6 Configuration Save and Restore
You can save system configuration settings to a file, and later download it back to the
802.11A/G ACCESS POINT by following the steps.
Step 1 Select Configuration Save and Restore from the System Tools menu.
Step 2 Enter the path of the configuration file to save-to/restore-from (or click the Browse
button to locate the configuration file). Then click the SAVE TO FILE button to
save the current configuration into the specified file, or click the RESTORE FROM
FILE button to restore the system configuration from the specified file.
31
Page 33

4.7 Factory Default
You can reset the configuration of your 802.11A/G ACCESS POINT to the factory
default settings. To do it:
Step 1 Select Factory Default from the System Tools menu.
Step 2 Click YES to go ahead and restore the configuration to the factory default.
4.8 Reboot System
You can reset your 802.11A/G ACCESS POINT from the Browser. To reset it:
Step 1 Select Reboot System from the System Tools menu.
Step 2 Click YES to reboot the 802.11A/G ACCESS POINT.
Note: Rebooting the 802.11A/G ACCESS POINT disconnects any
active clients, and therefore will disrupt any current data
traffic.
32
Page 34

4.9 What if you forgot the password?
If you forgot the password, the only way to recover is to clear the device configuration
and return the unit to its original state as shipped from the factory.
You can reset the Access Point’s Settings to factory defaults by pushing a paperclip in the
RESET hole on the back panel. Push and hold for around 2 seconds until the lights at
the front of the Access Point are off. Doing so will clear your current configuration.
33
Page 35

Specification
Product Name
Control Number
OS
Standard
WLAN Network Architecture Type
Wireless Transfer Data Rate for IEEE
802.11a Draft Standard
Wireless Transfer Data Rate for IEEE
802.11g Draft Standard
Wireless Transfer Data Rate for IEEE
802.11b
Physical Specification
Hardware & Antenna
Security
Management
IP Address Assignment
Environmental Specification
EMC Certification
Certificate
IEEE 802.11a/g SOHO Access Point
CA8-4
Linux® 2.4.18
• IEEE 802.11a/b/g
• IEEE 802.1d Spanning Tree
• IEEE 802.1x
• IEEE 802.3u Ethernet protocol
• Infrastructure
• Bridge Mode (WDS)
• Repeater Mode
IEEE 802.11a Standard: 54, 48, 36, 24, 18, 12, 9
& 6 Mbps with auto fallback
IEEE 802.11g Draft Standard: 54, 48, 36, 24, 18,
12, 9 & 6 Mbps with auto fallback
11, 5.5, 2 & 1 Mbps with auto fallback
• External Power Adapter with DC5V/2A Input
• PCB Dimension: 100 mm x 100 mm
• Desktop Instillation
• Wall/Ceiling Mountable
• 1 x RJ45
• 1 x Restore Button
• 1x External Antenna & 1x embedded antenna
• 6 x LED (1 x Power, 2 x LAN, 3 x WLAN)
• WEP 64-bit, 128-bit, 152-bit Encryption
• MAC Access Control for the wireless interface
• EAP & 802.1x support
• Support Primary & secondary RADUIUS server
• WPA and WPA-PSK
• Web-Based Management Tool
• UPnP
• Upload & download test-based configuration
file via HTTP browser
• Firmware upgrade via HTTP browser
• SysLog
• DHCP Client
• Static IP Address
• Operation Temperature: 0
• Storage Temperature: -20
• Operating Humidity: 10% ~80% (without
Condensation)
• FCC
• UL
• TELEC/JTEC
• SRRC/CCC
• DGT
• CE
• Wi-Fi Class 2.4 GHz 802.11a/g (Planning)
0
~400 C.
0
~ 650C
34
 Loading...
Loading...