Page 1
OPERATING MANUAL
MULTIPLE OUTPUT LINEAR SYSTEM
DC POWER SUPPLY
AGILENT MODELS 6625A, 6626A,
6628A, and 6629A
Agilent Part No 06626-90001
Microfiche Part No. 06626-90002 Printed in Malaysia
September, 2004
Page 2
CERTIFICATION
Agilent Technologies certifies that this product met its published specifications at time of shipment from the factory. Agilent
Technologies further certifies that its calibration measurements are traceable to the United States National Bureau of
Standards, to the extent allowed by the Bureau's calibration facility, and to the calibration facilities of other International
Standards Organization members.
WARRANTY
This Agilent Technologies hardware product is warranted against defects in material and workmanship for a period of one
year from date of delivery. Agilent software and firmware products, which are designated by Agilent for use with a
hardware product and when properly installed on that hardware product, are warranted not to fail to execute their
programming instructions due to defects in material and workmanship for a period of 90 days from date of delivery. During
the warranty period Agilent Technologies will, at its option, either repair or replace products which prove to be defective.
Agilent does not warrant that the operation of the software, firmware, or hardware shall be uninterrupted or error free.
For warranty service, with the exception of warranty options, this product must be returned to a service facility designated
by Agilent. Customer shall prepay shipping charges by (and shall pay all duty and taxes) for products returned to Agilen t
for warranty service. Except for products returned to Customer from another country, Agilent shall pay for return of
products to Customer.
Warranty services outside the country of initial purchase are included in Agilent's product price, only if Customer pays
Agilent international prices (defined as destination local currency price, or U.S. or Geneva Export price).
If Agilent is unable, within a reasonable time to repair or replace any product to condition as warranted, the Customer shall
be entitled to a refund of the purchase price upon return of the product to Agilent.
LIMITATION OF WARRANTY
The foregoing warranty shall not apply to defects resulting from improper or inadequate maintenance by the Customer,
Customer-supplied software or interfacing, unauthorized modification or misuse, operation outside of the environmental
specifications for the product, or improper site preparation and maintenance. NO OTHER WARRANTY IS EXPRESSED
OR IMPLIED. Agilent SPECIFICALLY DISCLAIMS THE IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY AND
FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE.
EXCLUSIVE REMEDIES
THE REMEDIES PROVIDED HEREIN ARE THE CUSTOMER'S SOLE AND EXCLUSIVE REMEDIES. Agilent
SHALL NOT BE LIABLE FOR ANY DIRECT, INDIRECT, SPECIAL, INCIDENTAL, OR CONSEQUENTIAL
DAMAGES, WHETHER BASED ON CONTRACT, TORT, OR ANY OTHER LEGAL THEORY.
ASSISTANCE
The above statements apply only to the standard product warranty. Warranty options, extended support contracts, product
maintenance agreements and customer assistance agreements are also available. Contact your nearest Agilent
Technologies Sales and Service office for further information on Agilent's full line of Support Programs.
Copyright 2000, 2004 Agilent Technologies Edition 1___January, 1993
Update 1___February, 2000
Update 2___September, 2004
2
Page 3
SAFETY SUMMARY
The following general safety precautions must be observed during all phases of operation, service, and repair of this
instrument. Failure to comply with these precautions or with specific warnings elsewhere in this manual violates safety
standards of design, manufacture, and intended use of the instrument. Agilent Technologies assumes no liability for the
customer’s failure to comply with these requirements.
BEFORE APPLYING POWER.
Verify that the product is set to match the available line voltage and the correct fuse is installed.
GROUND THE INSTRUMENT.
This product is a Safety Class 1 inst rument (provided with a protective earth terminal). To minimize shock hazard, th e instrument chassis
and cabinet must be connected to an electrical ground. The instrument must be connected to the ac power supply mains through a threeconductor power cable, with the third wire firmly connected to an electrical ground (safety ground) at the power outlet. For instruments
designed to be hard-wired to th e ac power lines (supply mains), conn ect the protective earth terminal to a protect ive conductor before any
other connection is made. Any interruption of the protective (grounding) conductor or disconnection of the protective earth terminal will
cause a potential shock h azard that could result in personal inju ry. If the instrument is to be energized via an external autotransformer for
voltage reduction, be certain that the autotransfo r mer common terminal is connect ed to the neutral (earthed pole) of the ac power lines
(supply mains).
FUSES.
Only fuses with the required rated current, voltage, and specified type (normal blow, time delay, etc.) should be used. Do not use repaired
fuses or short circuited fuseholders. To do so could cause a shock or fire hazard.
DO NOT OPERATE IN AN EXPLOSIVE ATMOSPHERE.
Do not operate the instrument in the presence of flammable gases or fumes.
KEEP AWAY FROM LIVE CIRCUITS.
Operating personnel must not remove instrument covers. Component replacement and internal adjustments must be made by qualified
service personnel. Do not replace components with power cable connected. Under certain conditions, dangerous voltages may exist even
with the power cable removed. To avoid injuries, always disconnect power, discharge circuits and remove external voltage sources before
touching components.
DO NOT SERVICE OR ADJUST ALONE.
Do not attempt internal service or adjustment unless another person, capable of rendering first aid and resuscitation, is present.
DO NOT EXCEED INPUT RATINGS.
This instrument may be equipped with a line filter to reduce electromagnetic interference and must be connected to a properly grounded
receptacle to minimize electric shock hazard. Operation at line voltages or frequencies in excess of those stated on the data plate may
cause leakage currents in excess of 5.0 mA peak.
SAFETY SYMBOLS.
Instruction manual symbol: the product will be marked with this symbol when it is necessary for the user to refer to the
instruction manual (refer to Table of Contents) .
Indicates hazardous vo ltages.
Indicate earth (ground) terminal.
The WARNING sign denotes a hazard. It calls attention to a procedure, practice, or the like, which, if not correctly
performed or adhered to, could result in personal injury. Do not proceed beyond a WARNING sign until the
indicated conditions are fully understood and met.
The CAUTION sign denotes a hazard. It calls attention to an operating procedure, or th e like, which, if not correctly
performed or adhered to, coul d result in damage to or destruction of part or all of the product. Do not proceed
beyond a CAUTION sign until the indicated conditions are fully understood and met.
DO NOT SUBSTITUTE PARTS OR MODIFY INSTRUMENT.
Because of the danger of introducing additional hazards, do not install substitute parts or perform any unau t horized modification to the
instrument. Return the instrument to an Agilent Technologies Sales and Service Office for service and repair to ensure that safety features
are maintained.
Instruments which appear damaged or defective should be made inoperative and secured against unintended operation until they can be
repaired by qualified service personnel
3
Page 4

SAFETY SUMMARY (continued)
GENERAL
Any LEDs used in this product are Class 1 LEDs as per IEC 825-1.
This ISM device complies with Canadian ICES-001. Cet appareil ISM est conforme à la norme NMB-001 du Canada.
ENVIRONMENTAL CONDITIONS
This instrument is intended for indoor use in an installation category II, pollution degree 2 environment. It is designed to
operate at a maximum relative humidity of 95% and at altitudes of up to 2000 meters. Refer to the specifications tables for the
ac mains voltage requirements and ambient operatin g temperature range.
SAFETY SYMBOL DEFINITIONS
Symbol Description Symbol Description
Direct current Terminal for Line conductor on permanently
installed equipment
Alternating current Caution, risk of electric shock
Both direct and alternating current Caution, hot surface
Three-phase alternating current Caution (refer to accompanying documents)
Earth (ground) terminal In position of a bi-stable push control
Protective earth (ground) terminal Out position of a bi-stable push control
Frame or chassis terminal On (supply)
Terminal for Neutral conductor on
permanently installed equipment
Terminal is at earth potential
(Used for measurement and control
circuits designed to be operated with
one terminal at earth potential.)
Herstellerbescheinigung
Diese Information steht im Zusammenhang mit den Anforderungen der
Maschinenläminformationsverordnung vom 18 Januar 1991.
* Schalldruckpegel Lp <70 dB(A) * Am Arbeitsplatz * Normaler Betrieb
* Nach EN 27779 (Typprüfung).
Manufacturer’s Declaration
This statement is provided to comply with the requirements of the German Sound Emission Directive,
from 18 January 1991.
* Sound Pressure Lp <70 dB(A) * At Operator Position * Normal Operation
* According to EN 27779 (Type Test).
Off (supply)
Standby (supply)
Units with this symbol are not completely
disconnected from ac mains when t his switch is
off. To completely disconnect the unit from ac
mains, either disconnect the power cord or have
a qualified electrician install an external switch.
4
Page 5

DECLARATION OF CONFORMITY
According to ISO/IEC Guide 22 and CEN/CENELEC EN 45014
Manufacturer’s Name and Address
Responsible Party
Agilent Technologies, Inc. Agilent Technologies (Malaysia) Sdn. Bhd
550 Clark Drive, Suite 101
Budd Lake, New Jersey 07828
USA
Declares under sole responsibility that the product as originally delivered
Product Names a) Multiple Output 40 W and 80 W system dc Power Supplies
Model Numbers a) 6621A, 6622A, 6623A; 6624A, 6627A
Product Options This declaration covers all options and customized products based on the above
Complies with the essential requirements of the Low Voltage Directive 73/23/EEC and the EMC
Directive 89/336/EEC (including 93/68/EEC) and carries the CE Marking accordingly.
EMC Information ISM Group 1 Class A Emissions
As detailed in Electromagnetic Compatibility (EMC), Certificate of Conformance Number
Assessed by: Celestica Ltd, Appointed Competent Body
Safety Information and Conforms to the following safety standards.
This DoC applies to the above-listed products placed on the EU market after:
Alternate Manufacturing Site
Malaysia Manufacturing
Bayan Lepas Free Industrial Zone, PH III
11900 Penang,
Malaysia
b) Multiple Output 25 W and 50 W precision system dc Power Supplies
b) 6625A; 6626A; 6628A; 6629A
(and other customized products based upon the above)
products.
CC/TCF/00/076 based on Technical Construction File (TCF) HPNJ3, dated
Oct. 29, 1997
Westfields House, West Avenue
Kidsgrove, Stoke-on-Trent
Straffordshire, ST7 1TL
United Kingdom
IEC 61010-1:2001 / EN 61010-1:2001
UL 1244
CSA C22.2 No. 1010.1:1992
January 1, 2004
Date Bill Darcy/ Regulations Manager
For further information, please contact your local Agilent Technologies sales office, agent or distributor.
Authorized EU-representative: Agilent Technologies Deutschland GmbH, Herrenberger Straβe 130, D
71034 Böblingen, Germany
Revision: B.00.00 Issue Date: Created on 11/24/2003 3:33
PM
Document No. 662xA.11.24.doc
5
Page 6

WHAT THIS MANUAL CONTAINS
It contains information relating to the installation, operation, and programming of these supplies as outlined below.
Maintenance and troubleshooting instructions are given in a separate Service Manual (Agilent Part No. 06626-90003).
Chapter 1.--General Information
Chapter 1 contains a general description of the power supplies as well as instrument specifications and information
concerning options and accessories.
Chapter 2.--Installation Procedures
Chapter 2 contains information to prepare the supply for use. Included in this chapter are power requirements, line voltage
conversion, and GP-IB interface connections.
Chapter 3.--Getting Started
Chapter 3 contains a brief description of the supply’s front panel controls and indicators and describes how to turn on the
supply and to check it’s operation. An introd uction to remote operation over the GP-IB is also given to help a first time user
get started quickly.
Chapter 4.--Output Connections and Opera ting Information
Chapter 4 contains information about making connections to the supply’s output terminals. General operating information is
also provided.
Chapter 5.--Remote Operation
Chapter 5 contains all of the information required to op erate the supply remotely via a GP-IB computer. All of the
commands that can be used to program the supplies are described.
Chapter 6.--Local Operation
Chapter 6 contains instructions on using all of the front panel controls and indicators.
Appendix A--Calibration Procedure
Appendix A contains programming steps and procedures that are required to calibrate your power supply. It is
recommended that the power supply be calibrated yearly.
Appendix B--Programming with Series 200/300 Computer
Appendix B contains Series 200/300 Computer programming examples (in Agilent extended BASIC language) for your
Power Supply’s most fr e quently used functions.
Appendix C--Command Summary
Appendix C contains an alphabetical listing of all commands that can be sent to a supply.
Appendix D--Error Messages
Appendix D contains a listing and brief explanation of all error codes and messages for all programming and hardware
errors.
Appendix E - Manua l Backdating
Appendix E contains backdating in formation for units with Serial numbers lower than those listed on the title page.
6
Page 7

1 General Information
Introduction...................................................................................................................................................11
Safety Considerations....................................................................................................................................11
Instrument and Manual Identification...........................................................................................................11
Options..........................................................................................................................................................11
Accessories....................................................................................................................................................12
Description ...................................................................................................................................................12
Basic Operation.............................................................................................................................................14
GP-IB Board..............................................................................................................................................14
Output Boards............................................................................................................................................15
Specifications................................................................................................................................................15
Qualifying Conditions...............................................................................................................................15
Definitions.................................................................................................................................................15
2 Installation
Introduction...................................................................................................................................................25
Initial Inspection............................................................................................................................................25
Location and Cooling....................................................................................................................................25
Input Power Requirements............................................................................................................................26
Line Fuse.......................................................................................................................................................27
Power Cord....................................................................................................................................................28
Line Voltage Conversion...............................................................................................................................29
GP-IB Interface Connection.............. ............................................................................................................29
Table Of Contents
3 Getting Started
Introduction ..................................................................................................................................................31
Front Panel Controls and Indicators..............................................................................................................31
Turning On Your Supply...............................................................................................................................36
Normal Self Test Indications.....................................................................................................................36
Self Test Errors..........................................................................................................................................37
Checking Out Your Supply Using Local Control..........................................................................................37
Voltage Test..............................................................................................................................................38
Overvoltage Test.......................................................................................................................................38
Current Test...............................................................................................................................................38
Changing Resolution Range......................................................................................................................39
Introduction To Remote Operation....... ........................................................................................................39
Enter/Output Statements............................................................................................................................40
Reading the GP-IB Address......................................................................................................................40
Changing the GP-IB Address....................................................................................................................40
Sending a Remote Command....................................................................................................................41
Getting Data from the Supply....................................................................................................................41
Often Used Commands..............................................................................................................................41
Returning the Supply to Local Mode........................................................................................................43
4 Output Connections and Operating Information
Introduction ..................................................................................................................................................45
Output Ranges...............................................................................................................................................45
Operating Quadrants..................................................................................................................................46
Operating Range........................................................................................................................................47
Protection Features........................................................................................................................................48
Connecting The Load....................................................................................................................................49
Wire Size Selection...................................................................................................................................49
Multiple Loads.............................. ............................................................................................................50
7
Page 8

Positive and Negative Voltages.................................................................................................................51
Remote Voltage Sensing............................................................................................................................... 51
Remote Sense Connections.......................................................................................................................52
Output Noise Considerations.....................................................................................................................53
Programming Response Time with an Output Capacitor..........................................................................53
Open Sense Leads......................................................................................................................................54
Overvoltage Trigger Connections.................................................................................................................54
External Trigger Circuit............................................................................................................................54
Power Supply Protection Considerations .......................... ...........................................................................55
Battery Charging........................... ............................................................................................................55
Capacitive Load Limitation.......................................................................................................................56
Parallel Operation..........................................................................................................................................56
CV Operation............................................................................................................................................57
CC Operation.............................................................................................................................................58
Remote Sensing.........................................................................................................................................58
Specifications for Parallel Operation.........................................................................................................58
Series Operation............................................................................................................................................59
CV Operation............................................................................................................................................59
CC Operation.............................................................................................................................................60
Remote Sensing.........................................................................................................................................60
Specifications for Series Operation...........................................................................................................60
Bi-Polar Operation....................................................................................................................................61
5 Remote Operation
Introduction ..................................................................................................................................................63
GP-IB Operation............................................................................................................................................63
Interface Functions....................................................................................................................................63
GP-IB Address Selection...........................................................................................................................64
Power-On Service Request (PON)............................................................................................................65
Programming Syntax.....................................................................................................................................65
Numeric Data............................................................................................................................................67
Order of Execution....................................................................................................................................70
Terminators................................ ...............................................................................................................70
Initial Conditions...........................................................................................................................................71
Power Supply Commands.......................................................................................................... ...................71
Voltage Programming...............................................................................................................................71
Current Programming................................................................................................................................73
Range Programming..................................................................................................................................73
Output On/Off.................................... .......................................................................................................74
Overvoltage Protection..............................................................................................................................74
Overcurrent Protection........................... ...................................................................................................75
Multiple Output Storage and Recall..........................................................................................................75
The Clear Command..................................................................................................................................76
Status Reporting........................................................................................................................................76
Service Request Generation....................... ...............................................................................................79
Reprogramming Delay............................. .................................................................................................80
Display On/Off.......................................................................................................................................... 81
Other Queries.............................................................................................................................................82
Table Of Contents (continued)
6 Local Operation
Introduction ..................................... .............................................................................................................85
Local Mode....................................................................................................................................................85
8
Page 9

Table Of Contents (continued)
Local Control Of Output Functions............................................................................................................... 85
General........................................... ...........................................................................................................85
Setting Voltage and Voltage Range...........................................................................................................86
Setting Current and Current Range............................................................................................................87
Enabling/Disabling an Output...................................................................................................................87
Setting Overvoltage Protection..................................................................................................................88
Resetting Overvoltage Protection..............................................................................................................88
Enabling/Disabling Overcurrent Protection..............................................................................................88
Resetting Overcurrent Protection..............................................................................................................88
Local Control Of System Functions..............................................................................................................88
Setting the Supply’s GP-IB Address..........................................................................................................88
Displaying Error Messages........................................................................................................................89
Storing and Recalling Voltage and Current. Settings for all Outputs........................................................89
A Alignment Procedures
Introduction...................................... .............................................................................................................91
Test Equipment and Setup Required.............................................................................................................91
Calibration Program......................................................................................................................................91
Alignment Program.......................................................................................................................................95
B Programming With a Series 200/300 Computer
Introduction ................................................................................................................................................103
I/O Path Names...................... .....................................................................................................................103
Voltage and Current Programming.............................................................................................................103
Voltage and Current Programming With Variables... .................................................................................104
Voltage and Current Readback....................................................................................................................104
Programming Power Supply Registers........................................................................................................105
Present Status...................... ....................................................................................................................105
Service Request and Serial Poll...............................................................................................................106
Error Detection .................... ...................................................................................................................107
Stored Operating States...........................................................................................................................108
C Command Summary
Introduction.................................................................................................................................................109
D Error Messages
Introduction.................................................................................................................................................117
Power-On Self Test Messages.....................................................................................................................117
Error Responses...........................................................................................................................................117
Test Responses............................................................................................................................................117
E Manual Backdating
Introduction ................................................................................................................................................121
Make Changes.................…………………………………………………………………………………...121
Agilent Sales and Support Office
Contacts ......................................................................................................................................................122
9
Page 10

Page 11

1
General Information
Introduction
This chapter contains a general description of your power supply as well as its performance specifications. Information
about options, accessories, and GP-IB cables is also provided. This manual describes the Agilent 6625A, 6626A, 6628A,
and Agilent 6629A power supplies. Unless stated otherwise, the information in this manual applies to all of these models.
Information that is specific to one model only is identified as such in this manual.
Safety Considerations
This product is a Safety Class 1 instrument, which means that it is provided with a protective earth terminal. This terminal
must be connected to a power source that has a 3-wire ground receptacle. Review the instrument and this manual for safety
markings and instructions b e fore operation. Refer to the Safety Summary page at the beginning of this manua l for a
summary of general safety information. Safety information for specific procedures is located at appropriate places in this
manual.
Instrument and Manual Identification
Agilent Technologies power supplies are identified by a two-part serial number, i.e. 2601A-00101. The first part of the
serial number (the prefix) is a number/letter combination that denotes either the date of manufacture or the date of a
significant design change. It also indicates the country of origin. (Starting at 1960, 26 = 1986; 01 = the first week of the
year; A = U.S.A.) The second part of the serial number is a different sequential number assigned to each instrument starting
with 00101.
Options
Options 100,120, 220, and 240 simply determine which line voltage is selected at the factory. For information about
changing the li ne voltage setting, see line voltage conversion para graph on page 29.
Option 750 consists of a fault indicator (FLT) and remote inhibit (INH) circuit and relay control, which provide additional
shutdown protection should either the GP-IB and/or controller fail. This Option is described in a separate document
entitled, ’’Appendix E Option 750 Operating Instructions for the Multiple Output Linear System DC Power Supply, Agilent
Models 6621A, 6622A, 6623A, 6624A, and 6627A’’ (Agilent P/N 5957-6372).
#100 Input power, 100 Vac, 47-66 Hz
#120 Input power, 120 Vac, 47-66 Hz
#220 Input power, 220 Vac, 47-66 Hz
#240 Input power, 240 Vac, 47-66 Hz
#750 Fault (FLT) Remote Inhibit (INH) and Relay Control
#908 One rack mount kit (5062-3977)
#909 One rack mount kit with handles (5062-3983)
#0L2 One extra operating manual
#0B3 One service manual
General Information
11
Page 12
Accessories
10833A GP-IB cable, 1 m (3.3 ft)
10833B GP-IB cable, 2 m (6.6 ft)
10833C GP-IB cable, 4 m (13.2 ft)
10833D GP-IB cable, 0.5 m (1.6 ft)
10834A GP-IB connector extender
Slide mount kit (1494-0059)
Description
The Agilent power supply features a combination of programming capabilities and linear power supply performance that
make them ideal for systems applications. The models in this family offer a total of up to 200 watts of output power, with
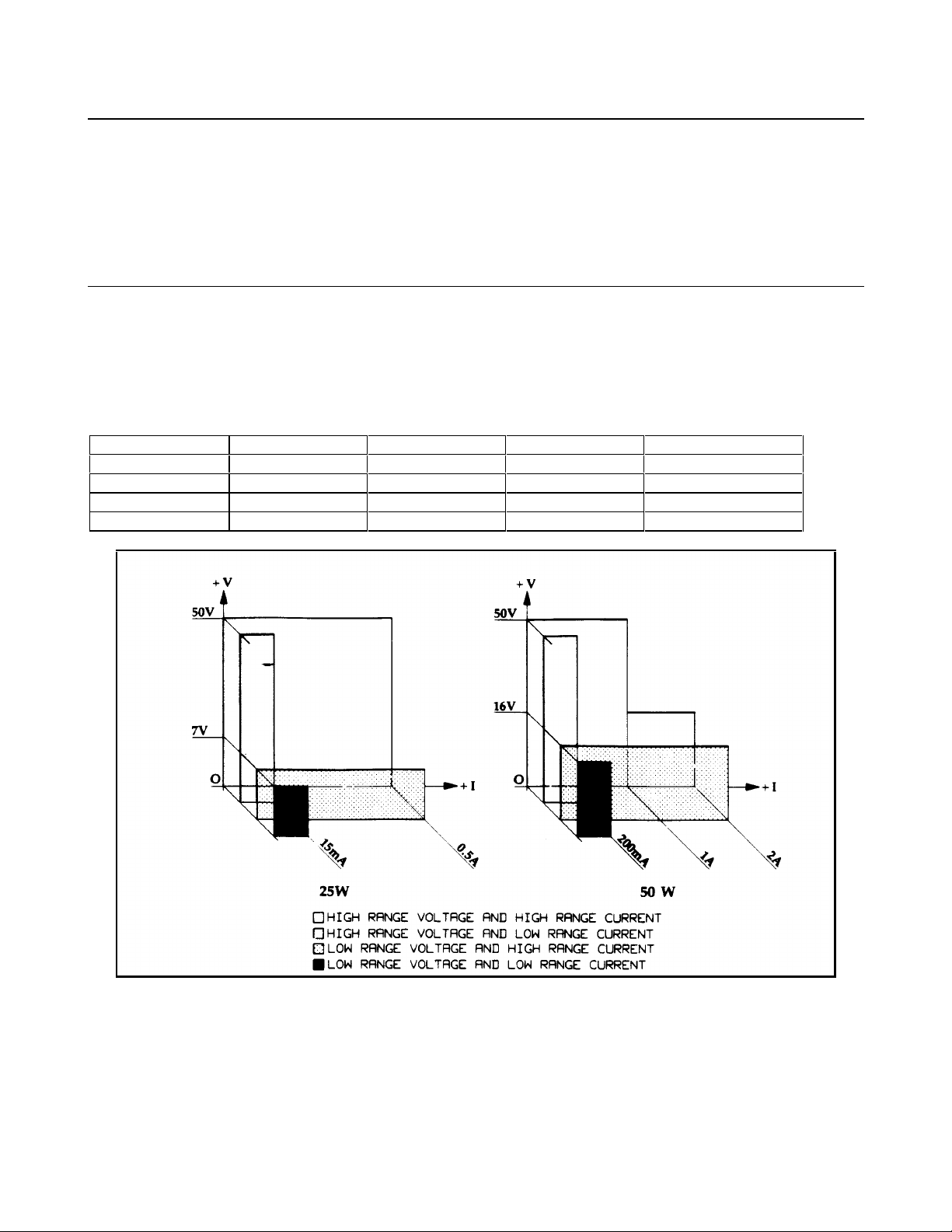
voltages up to 50 volts and currents up to 2 amps. The output combinations that correspond to each model are shown in
Table 1-1. Each isolated output has a high resolution and standard resolution range, as shown in Figure 1-1.
Table 1-1 Output Combinations Available
Model Output 1 Output 2 Output 3 Output 4
Agilent 6625A 25 W 50 W -- -Agilent 6626A 25 W 25 W 50 W 50 W
Agilent 6628A 50 W 50 W -- -Agilent 6629A 50 W 50 W 50 W 50W
Figure 1-1. Output Operating Range
Output 2 of the Agilent 6625A and outputs 3 and 4 of the Agilent 6626A and all outputs of the Agilent 6628A and Agilent
6629A have an "L’’ shaped characteristic. The L shaped characteristic allows you to use the same output to power loads
with different voltage and current requirements. The power supply automatically selects one of the operating ranges based
on the last parameter (voltage or current) that is set. If a high resolution o r a standard resolution application is required for
either voltage or current, VRSET and IRSET should be used (see Appendix C-Command Summary). Additionally, each
output contains an active downprogrammer, which means that voltage downprogramming can be accomplished as quickly
as upprogramming, even without a load.
12
General Information
Page 13

The power supplies allow up to a 10 volt sense lead drop. This feature makes them ideal for test system applications where
remote sensing is used.
The output voltage and current for any output can be monitored with the front panel display. Output specific error messages
are also displayed. Front panel annunciators show the ope rating status of the instrument. The front pa nel keypad lets you set
and readback the voltage limit, current limit, and overvoltage trip level of any output. With the ke ypad, you can also enable
or disable outputs, enable overcurrent protection, reset overvoltage and overcurrent protection, and return to local operating
mode.
Your multiple output power supply can be b oth a listener and a talker on the GP-IB. (GP-IB is Agilent Technologies’
implementation of IEEE-488). The built-in interface is tailored to the supply, resulting in simpler programming. Voltage
and current settings can be sent directly to the specified output in volts and amps.
Service can be requested from your power supply for up to 10 reasons. The supply responds to a serial poll by identifying
the output on which the fault occurred. Self-contained measurement and readback capability eliminate the need for
externally scanning the outp uts using a separate DVM. Upon command, the supply will measure its output voltage or
current and return the value on the GP-IB. The following functions are implemented via the GP-IB:
Voltage and current programming.
Programmable resolution range.
Voltage and current measurement and readback.
Present and accumulated status readback.
Programmable service request mask.
Programmable overvoltage and overcurrent protection.
Voltage and current range programming.
Storage and recall of programmed voltage and current values for all outputs.
Queries of programmed functions or settings.
Output enable or disable.
Programming syntax erro r detection.
Programmable delay time for service request and OCP mask.
Voltage, current, and overvoltage calibration.
GP-IB interface selftest.
Message display capability on the fro nt pa nel.
Output connections are made to rear panel screw ter minals. Either the positive or negative output terminal can b e grounded,
or the output can be floated up to ± 240 Vdc (includi ng output voltage) from chassis gro und. Output voltage can be locally
or remotely sensed, and identical outputs can be operated in series or parallel combinations for increased output voltage or
current capability. As shipped from the factory, the power supply is jumpered for local sensing.
Your power supply can be calibrated without having to remove the cover or even having to remove it from your system
cabinet. This feature allows you to calibrate the supply at its normal operating temperature. The recommended calibration
interval is one year. Refer to Appendix A of thi s manual for complete calibration details. A calibration security jumper is
available inside the unit. Access is described in the service manual.
General Information
13
Page 14
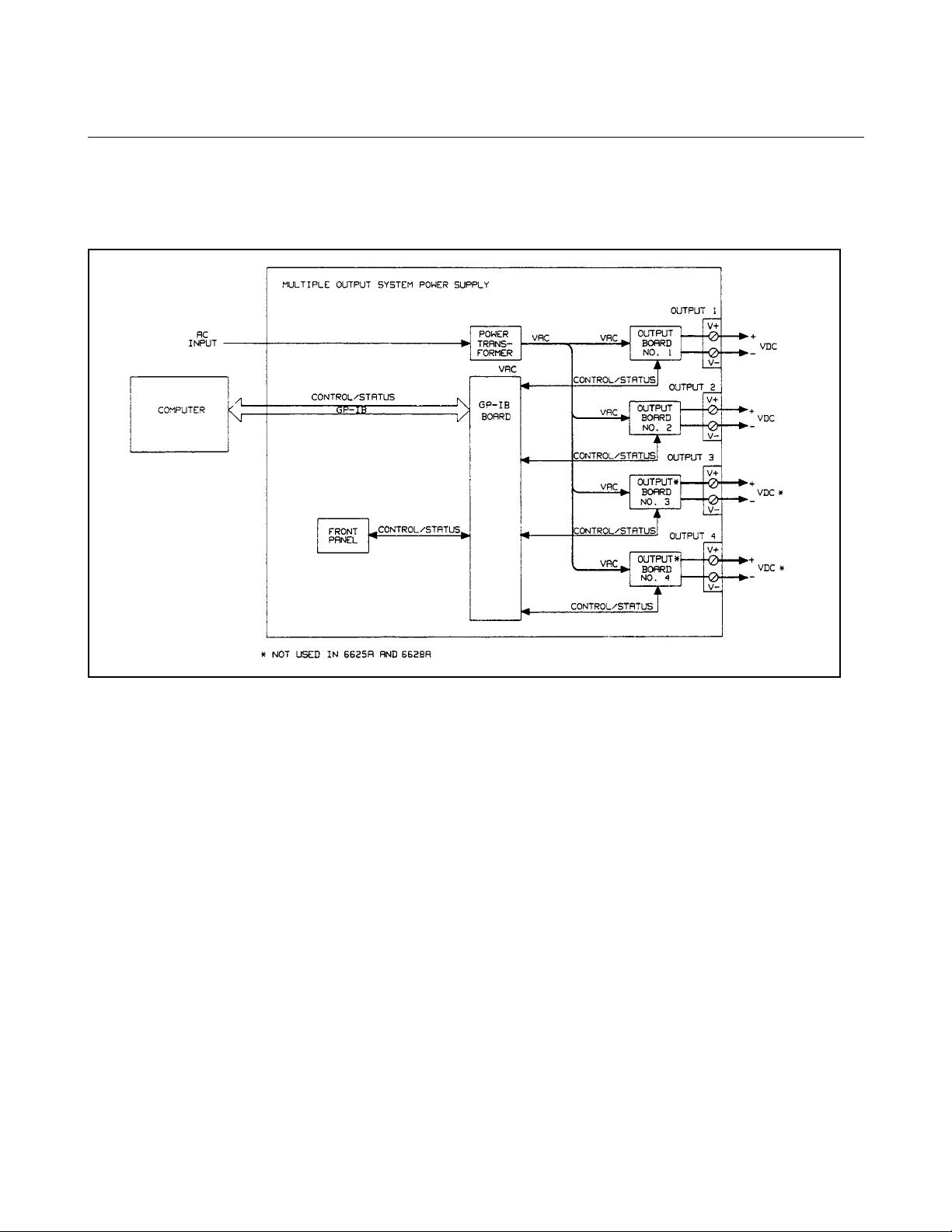
Basic Operation
Figure 1-2 is a block diagram that illustrates the major assemblies contained within the power supply. As shown in the
figure, each supply includes a power transformer, two or more output boards, a GP-IB board, and front panel (display and
control keys).
Figure 1-2. Block Diagram
The appropriate ac input voltage is applied to each output board where it is converted to a raw dc voltage which is
subsequently linearly regulated to become the dc output voltage. The magnitude of the output and the mode of operation are
determined by the load and the data received from the GP-IB computer or from the front panel.
Each power supply model contains one output board for each output that it provides.
GP-IB Board
The GP-IB board provides the interface between the user and the multiple outputs of the power supply. Each output board
is actually an output channel that can be individually selected and controlled over the GP-IB or from the supply’s front
panel. Circuits on the GP-IB board interpret commands from the GP-IB or from the front panel to control the selected
output.
The GP-IB board also processes measurement and status data received from the output boards. This data may be read back
over the GP-IB and/or displayed on the supply’s front panel.
The power supply has no potentiometers. Each output is individually calibrated over the GP-IB using calibration commands
(see Appendix A). Correction factors are calculated by the power supply during calibration and are stored in a non-volatile
memory which is located on the supply’s GP-IB board. The supply contains no batteries.
14
General Information
Page 15

Output Boards
The output boards are linear dc power supplies. Each isolated output operating boundary curve is shown in Figure 1-1.
The ac input to each output board is rectified and applied to a regulator circuit. Each output board employs series regulation
techniques. A regulator element is connected in series with the load and operates in the linear region (between saturation
and cutoff) of the transistor characteristic curve. Regulation is achieved by varying the conduction of the series element in
response to a change in line voltage or circuit load.
The output board receives digital signals from the GP-IB board and converts them to analog signals which program the
output voltage, current, and o vervoltage values. The output may be programmed remotel y over the GP-IB using commands
(see Chapter 5) or locally from the supply’s front panel using the control keys (see Chapter 6).
The output board can be commanded to send measurement and status data back over the GP-IB and/or front panel. The data
is sent back via the supply’s GP-IB board. GP-IB readback capabilities include o utput voltage and current, present a nd
accumulated status, and all programmed settings. The front panel LCD display can indicate the output voltage and current,
the supply’s GP-IB address, error messages, and programmed values. Annunciators on the front panel indicate the operating
status of the selected output (output board).
Specifications
Table l-2 lists the performance specifications for the Agilent 662xA power supplies. Performance specifications describe
the instrument’s warranted performance. The service manual, Option 9l0, contains procedures for verifying the
performance specifications.
Table 1-3 lists the supplemental characteristics for the Agilent 662xA supplies. Supplemental characteristics are type-tested
or typical values, which are based on a product sample and, while representative, are not guaranteed.
Qualifying Conditions
All performance specifications apply over the full operating temperature range of the power supply (0 to 55°C) unless
otherwise specified. All regulation, accuracy, etc. specifications are plus or minus the values listed. All measurements are
made at the rear terminals of the supply with a resistive load and local sensing unless otherwise specified. Voltage
measurements are made from the + S to the - S terminals. Overvoltage measurements are made from the + V to the - V
terminals. + Current refers to the output acting as a current source while - Current refers to the output acting as a current
sink.
Definitions
Load effect
output in question.
Source effect: Maximum steady state change in the regulated output parameter due to a change in the source voltage
within rated values.
Cross regulation: Maximum steady state change in the regulated output parameter due to a change in load resistance on
any other output(s).
Programming accuracy: (Calibration temp ± 5°C) Maximum difference between the programmed value and the actual
output.
: Maximum steady state change in the regulated output parameter due to a change in load resistance on the
Readback accuracy: (Calibration temp ±5°C) Maximum error in reading back an output parameter. Expressed as a
percentage of the reading, plus a constant.
General Information
15
Page 16
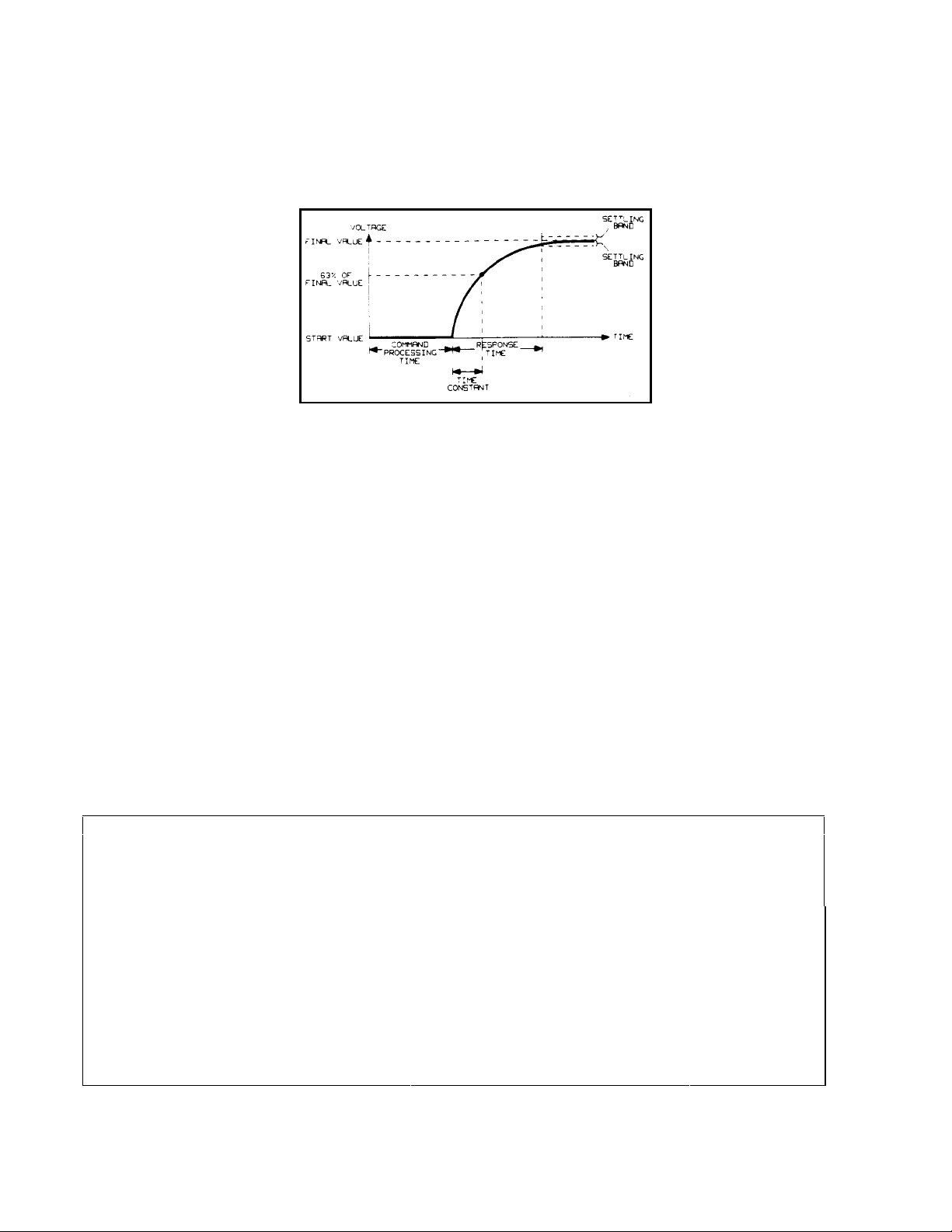
Output response time: Beginning at the time the power supply has finished processing a VSET command (change
output voltage), the maximum time for the output voltage to settle to within a settling band about the final value from any
specified operating point. This value must be added to the command processing time to obtain total programming time (see
Figure 1-3). Time constant is the maximum time required for the voltage to reach 63% of its final value.
Figure 1-3. Output Response Characteristics
Temperature coefficient: Maximum change in the regulated output parameter per °C change in ambient temperature
after a 30 minute warmup. Expressed as a percentage plus a constant per degrees C. (Plus a constant for readback
temperature coefficient).
Long Term Drift: Maximum change of regulated output voltage or current during an 8-hour period following a 30 minute
warmup, with all influence and control quantities maintained constant. Expr essed as a percentage of the setting plus a
constant.
Short Term Drift: Maximum change of regulated output voltage or current within 30 minutes after a line and/or load
change. Expressed as a percentage of the setting plus a constant.
Output Noise (PARD): PARD replaces the former term ripple and noise. PARD is the periodic and random deviation of
dc output voltage or current from its average value, over a specified bandwidth and with all influence and control quantities
maintained constant.
Programming resolution: Average programming step size.
Current Sinking (- Current): Each output can sink as well as source current. The sinking capabilit y is not programmable
and depends upon the output voltage. The current sinking cap ability is described in greater detail in
Chapter 4.
Table 1-2. Specifications
PERFORMANCE SPECIFIC ATIONS: (0 to 55 °C unless otherwise specified)
DC Output Ranges: All outputs will accept voltage programming commands 1% higher than those listed and
current programming commands 3% higher than those listed.
Output Power 25 Watt Output 50 Watt Output
Output Range Lo Range Hi Range Lo Range Hi Range
Output Volts 0-7 V 0-50 V 0-16 V 0-50 V
Output Amps 0-15 mA 0-500 mA 0-200 mA 0-2 A
Load Effect (Regulation):
Voltage 0.5 mV 0.5 mV 0.5 mV 0.5 mV
+ Current 0.005 mA 0.005 mA 0.01 mA 0.015 mA
16
General Information
Page 17

Table 1-2. Specifications (continued)
Source Effect:
Voltage 0.5 mV 0.5 mV 0.5 mV 0.5 mV
+ Current 0.005 mA 0.005 mA 0.01 mA 0.01 mA
Programming Accuracy:
Note: The programming accuracy specifications may degrade slightly when the unit is subjected to an RF field equal
to or greater than 3 volts/meter.
Voltage 0.016% + 1.5 mV 0.016% + 10 mV 0.016% + 3 mV 0.016% + 10 mV
+ Current
OVP 0.13% + 475 mV 0.13% + 475 mV 0.13% + 475 mV 0.13% + 475 mV
Measurement/Readback Accuracy*
Voltage 0.016% + 2 mV 0.016% + 10 mV 0.016% + 3.5 mV 0.016% + 10 mV
±
Current 0.03% + 15 µA 0.03% + 130 µA 0.04% + 250 µA 0.04% + 550 µA
Load Transient Recovery Time :(all outputs)
75 µS maximum to recover to within 75 mV of nominal value following a load change from 0.1 A to 100% of the
maximum rated current
Maximum Output Noise: (PARD) (20 Hz-20 MHz)
0.04% + 15 µA 0.04% + 100 µA 0.04% + 185 µA 0.04% + 500 µA
CV pk-to-pk 3 mV 3 mV 3 mV 3 mV
CV rms 0.5 mV 0.5 mV 0.5 mV 0.5 mV
+CC rms 0.1 mA 0.1 mA 0.1 mA 0.1 mA
AC Input Voltage and Frequency:
Nominal Line l00, 120, 220, or 240 Vac
Amplitude +6% to -13% of nominal line voltage
Frequency 47 to 66 Hz
Note at low line, the supply will operate with up to 3/4 o hm line resistance
*For a ± 5 ° C range about the calibration temperature
Table 1-3. Supplemental Characteristics
Output Power 25 Watt Output 50 Watt Output
Output Range Lo Range Hi Range Lo Range Hi Range
Output Volts 0-7 V 0-50 V 0-16 V 0-50 V
Output Amps 0-15 mA 0-500 mA 0-200 mA 0-2 A
Temperature Coefficient-Programming:
Voltage (0.003%+0.1 mV)
per° C
+ Current
OVP (0.013% + 1 mV)
(0.0035% + 1.5 µA)
per° C
per° C
(0.003%+0.1 mV)
per° C
(0.0035% + 6 µA)
per° C
(0.013% + 2 mV)
per° C
(0.003%+0.1 mV)
per° C
(0.0035% + 30 µA)
per° C
(0.013% + 1 mV)
per° C
(0.003%+0.1 mV)
per° C
(0.0035% + 50 µA)
per° C
(0.013% + 2 mV)
per° C
General Information
17
Page 18

Table 1-3. Supplemental Characteristics (continued)
Output Power 25 Watt Output 50 Watt Output
Output Range Lo Range Hi Range Lo Range Hi Range
Output Volts 0-7 V 0-50 V 0-16 V 0-50 V
Output Amps 0-15 mA 0-500 mA 0-200 mA 0-2 A
Temperature Coefficient-Measurement:
Voltage (0.002% + 0.1 mV)
per° C +0.5 mV
±
Current (0.0025% + 1.5 µA)
per° C + 1 µA
Long Term Drift: (In an 8 hour period following a 30 minute warm up)
Voltage 0.006% + 0.5 mV 0.006% + 2 mV 0.006% + 0.5 mV 0.006% + 2 mV
+ Current
Short Term Drift: (Within 30 minutes after a line and/or load change):
Voltage 0.002 + 0.5 mV 0.002 + 1 mV 0.002 + 0.5 mV 0.002 + 1 mV
+ Current
DC Floating Voltage:
No output terminal may be more that 240 Vdc from any other terminal or from chassis ground. Also, no overvoltage
terminal may be more than 240 Vdc from any other terminal or chassis ground.
Remote Sense Capability: (see pages 50 - 52):
Outputs can maintain specifications with up to 10 volt total in the remote sense lead s.
0.01% + 5 µA 0.01% + 20 µA 0.01% + 40 µA 0.01% + 60 µA
0.01% + 2 µA 0.01% + 20 µA 0.01% + 25 µA 0.01% + 60 µA
(0.002% + 0 .1 mV)
per° C +4 mV
(0.0025% + 10 µA)
per° C + 40 µA
(0.002% + 0 .1 mV)
per° C +1 mV
(0.0025% + 20 µA)
per° C + 15 µA
(0.002% + 0 .1 mV)
per° C +4 mV
(0.0025% + 50 µA)
per° C + 150 µA
AC Input Power
Programming Resolution:
Voltage
+ Current
OVP 230 mV 230 mV 230 mV 230 mV
Readback Resolution:
Voltage
+ Current
- Current
Fixed Overvoltage Protection: (Measured at output terminals +V and -V)
Minimum 56 V 56 V 56 V 56 V
Nominal 60 V 60 V 60 V 60 V
Maximum 64 V 64 V 64 V 64 V
18
General Information
: 550 Watts
460 µV
1 µA 33 µA 13 µA 131 µA
483 µV
1 µA 48 µA 14 µA 160 µA
1 µA 37 µA 14 µA 151 µA
3.2 mV 1 mV 3.2 mV
3.3 mV 1.1 mV 3.3 mV
Page 19

Table 1-3. Supplemental Characteristics (continued)
High Line Inrush Current: 100 V Opt 120 V Opt 220 V Opt 240 V Opt
Peak Value 85 A 85 A 50 A 50 A
rms Value 6.3A 5.7 A 3.0 A 3.0 A
Fuse Rating 8 A 8 A 4 A 4 A
GP-IB Interface Capabilities:
SH1. AH1, T6, L4, SR1, RL1, PP1, DC1, DT0, C0, E1
Current Sink Capability:
25 Watt output: 0.50 A
50 Watt output: 1.0 A (2.0 A below 16 V)
Command Processing Time: (see Figure 1-3)
7 milliseconds typical (with front p a nel disabled). Using STD and RCL commands allows you to change all the
voltage and current settings in abo ut 1 0 mS (with front panel disabled).
Maximum Output Programming:
Response Time 6 mS 6 mS 6 mS 6 mS
Settling Band 50 mV 50 mV 50 mV 50 mV
Maximum Time
Constant
750 µS 750 µS 750 µS 750 µS
Series and Parallel operation:
Two outputs can be operated directly in parallel or can be connected for straight series operation. Refer to Chapter 4
for more information.
Reactive Load Capability:
All outputs have been designed with the ability to operate with significant reactive loads without instability (refer to
Figures 1-4 through 1-6)
Safety Agency Compliance:
This series of power supplies is designed to comply with the following standards:
IEC 348, UL 1244, and CSA 22.2 No. 231.
Dimensions (all models):
Height 132.6mm (5.22 in)
Width 425.5mm (16.75 in.)
Depth 497.8mm (19.6 in.)
General Information
19
Page 20
Table 1-3. Supplemental Characteristics (continued)
Weight:
Agilent 6625A, 6628A Agilent 6626A, 6629A
Net 15.5 kg (34 lbs.) 17.7 kg (39 lbs.)
Shipping 20.8 kg (46 lbs.) 23 kg (51 lbs.)
Load Cross Regulation:
Voltage 0.25 mV 0.25 mV 0.25 mV 0.25 mV
+ Current 0.005 mA 0.005 mA 0.01 mA 0.01 mA
20
General Information
Page 21
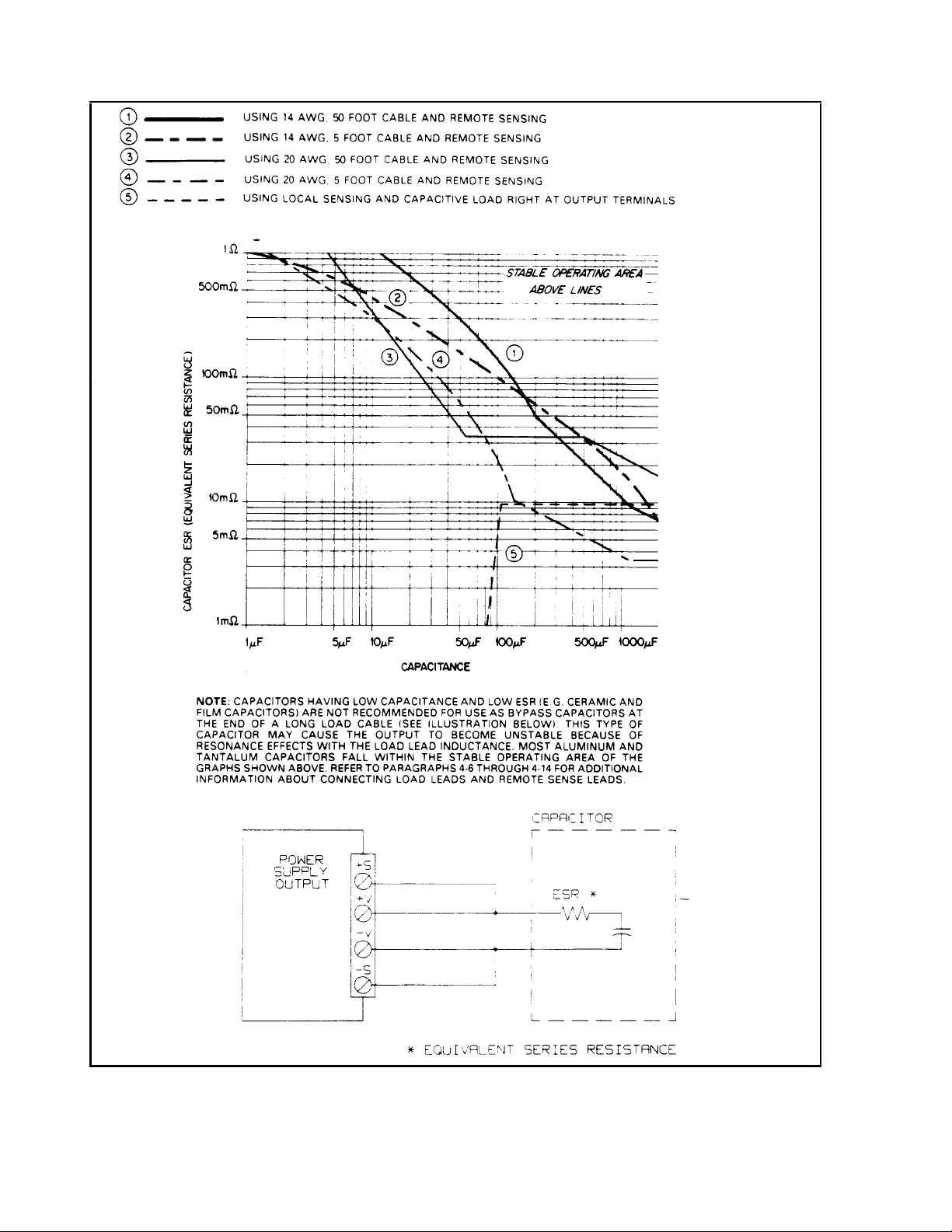
Figure 1-4. CV Operation with Capacitive Load, Stability Graph for all Outputs
General Information
21
Page 22
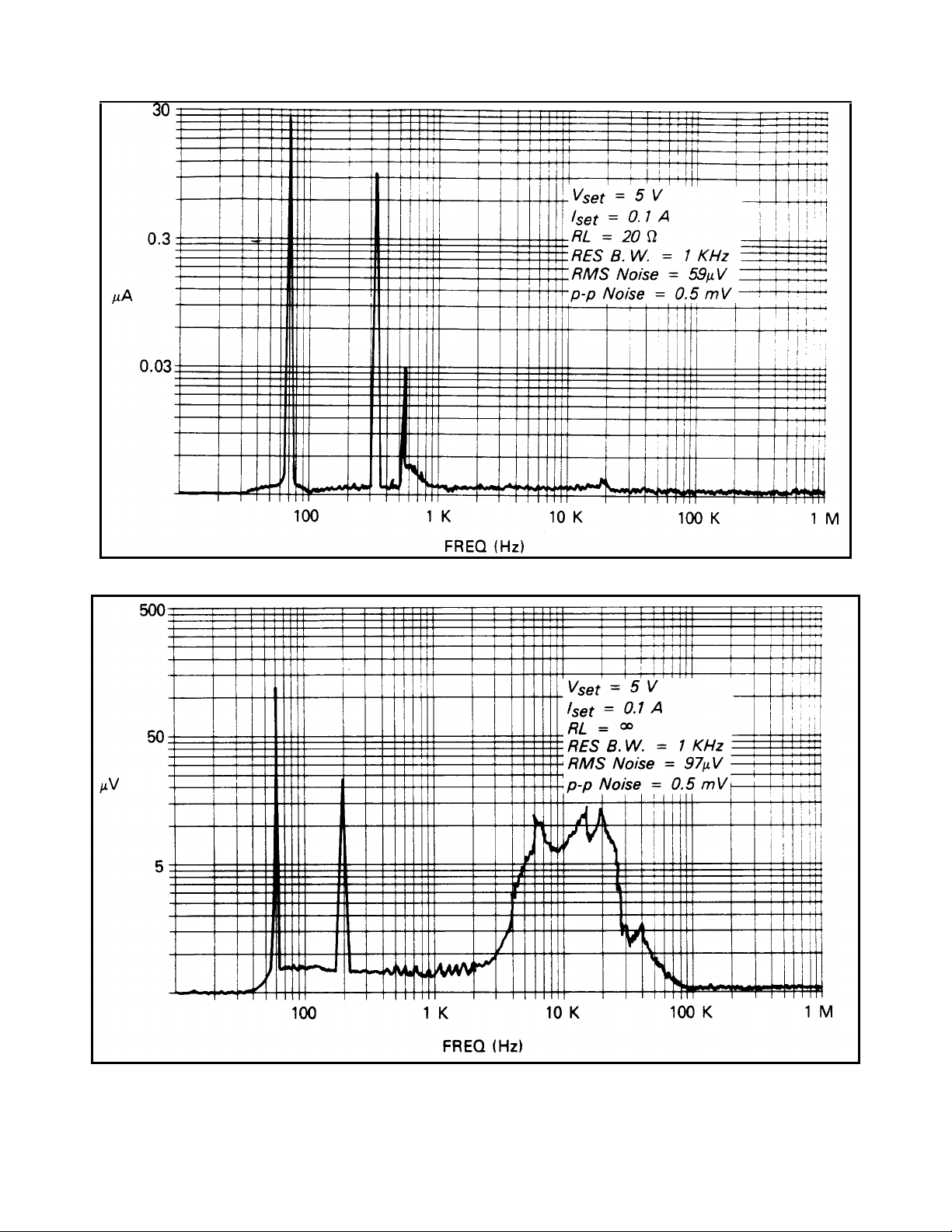
Figure 1-5. Output Noise (Typical) CC Mode
22
General Information
Figure 1-6. Output Noise (Typical) CV Mode
Page 23
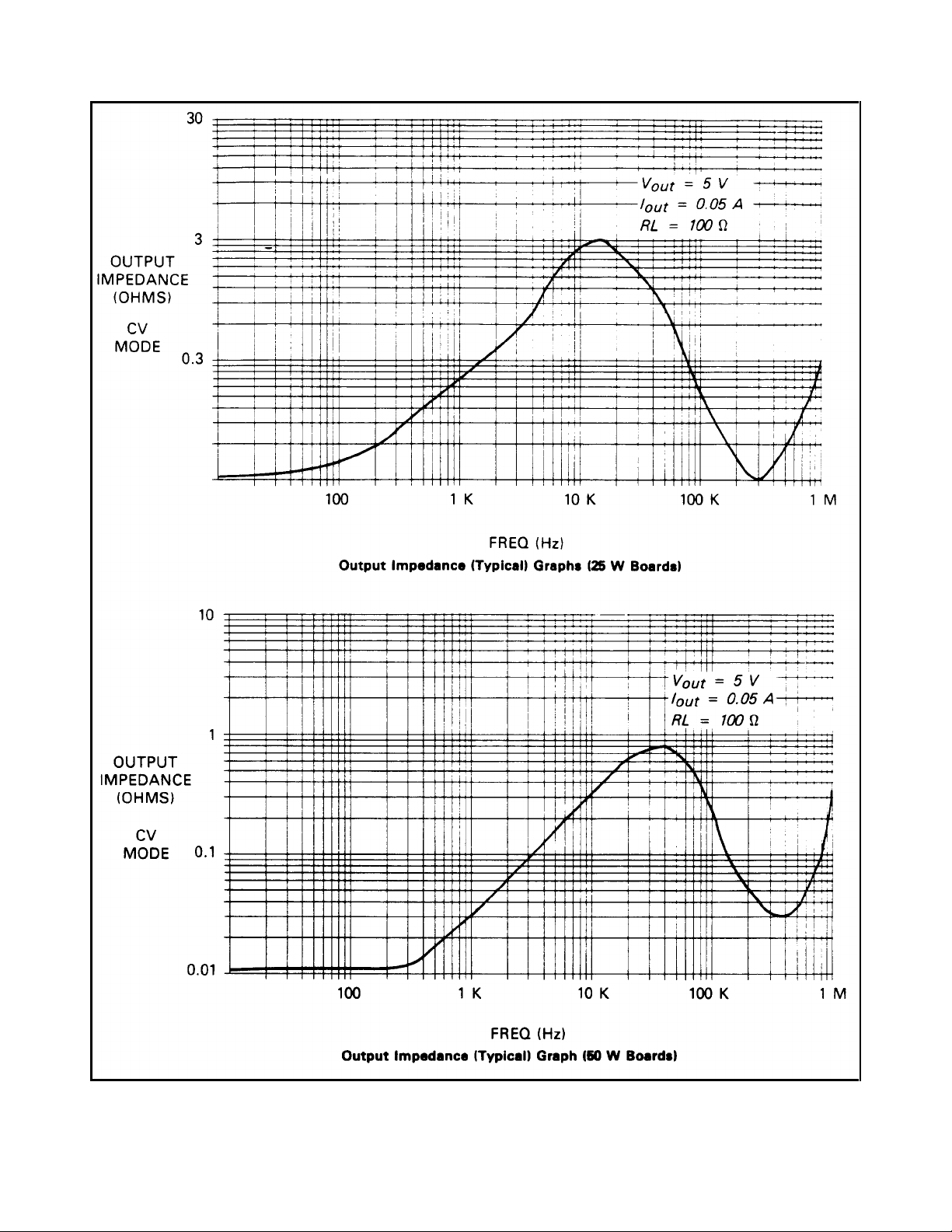
Figure 1-7. Output Impedance (Typical) Graph (See Supplemental Characteristics)
General Information
23
Page 24

Page 25

2
Installation
Introduction
This chapter contains instructions for checking and mounting your power supply, connecting your supply to ac power,
converting it from one line voltage to another, and connecting the GP-IB cable.
The power supply generates operating magnetic fields which may affect the operation of other instruments. If your
instrument is susceptible to magnetic fields, do not locate it in the immediate vicinity of the power supply. Typically, at
three inches from the power supply, the electromagnetic field is less than 5 gauss.
Initial Inspection
Your instrument was thoroughly inspected and tested before it left the factory. As soon as you receive it, remove the power
supply from its packing case and check to make sure it has not been damaged in shipment. Check that there are no broken
connectors or keys, and that the cabinet and panel surfaces are free from dents and scratches. Check the rear panel terminal
blocks and front panel display for any cracks. If damage is found, you should file a claim with the carrier immediately and
notify the Agilent Technologies Sales and Service office nearest you.
Chapter 3 of this manual includes an electrical turn-on check-out procedure which, when carried out successfully, will give
you a high level of confidence that the power supply is operating in accordance with its specifications. Detailed electrical
checks complete with verification procedures are included in the Service Manual.
Keep the original packing materials for the carrier’s inspection if there was damage, or in case any equipment has to be
returned to Agilent Technologie s. Warranty information is printed on the inside cover of this manual. Remember to send a
detailed description of the failure and symptoms when returning the power supply for service. Your Agilent Technologies
Sales and Service office will furnish the address of the neares t service office to which the instrument can be shipped.
Location and Cooling
Your power supply can operate without loss of performance within the temperature range of 0 to 55 ° C (measured at the
fan intake). The fan, located at the rear of the unit, cools the supply by drawing air in through the openings on the rear panel
and exhausting it through openings on the sides. Using Agilent Technologies rack mount kits will not impede the flow of
air.
Because the power supply is fan cooled, it must be installed in a location that allows sufficient space at the rear and the
sides for adequate circulation of air. Either side may be restricted to have as little as 1 inch (25 mm) space.
Figure 2-1 gives the dimensions of the power supply cabinet. These dimensions apply to both models. The cabinet has
plastic feet that are shaped to ensure self-alignment when stacked with other Agilent Technologies System II cabinets. The
feet may be removed for rack mounting.
The power supply can be mounted in a standard 19 inch rack panel or enclosure. Rack mounting accessories for this unit
are listed under options (page 11) o f Chapter 1. Complete installation instruction s are included with each rack mounting kit.
Instrument support rails are required for non-stationary installations. These are normally supplied with the cabinet and are
not included with the rack mounting kits.
Installation
25
Page 26

Figure 2-1. Outline Diagram
Input Power Requirements
You can operate this power supply from a nominal 100 V, 120 V, 220 V or 240 V single phase power source at 47 to 66
Hz. The input voltage range, maximum input current, high line inrush current (PK), and the fuse required for each of the
nominal inputs are listed in Table 2-1. You can check the line voltage setting of your supply by examining the door on the
line module. This is located on the rear panel of your supply as shown in Figure 2-2. The red mark that appears in one of
the four windows on the line module indicates the line voltage setting for which your supply is set.
If necessary, you can convert the supply from one line voltage setting to another by following the instructions under LINE
VOLTAGE CONVERSION (see page 29).
Table 2-1. Input Power
Nominal
Voltage
100 V 6.3 A 85 A 8 AM
120 V Nominal 5.7 A 85 A 8 AM
220 V -13%, +6% 3.0 A 50 A 4 AM
240 V 3.0 A 50 A 4 AM
Line Voltage Range Maximum Input Current
(rms.)
High Line Inrush
Current (PK)
Fuse
Line Fuse
The ac line fuse is located behind the door on the line module (see Figure 2-3). To access the fuse, remove the power cord
and push against the tab on the line module in the direction of the ac input socket. The current rating of the fuse is based on
the line voltage setting of your supply. Table 2-2 gives the Agilent part numbers for the fuses that should be used with
specific line voltages.
Installation26
Page 27
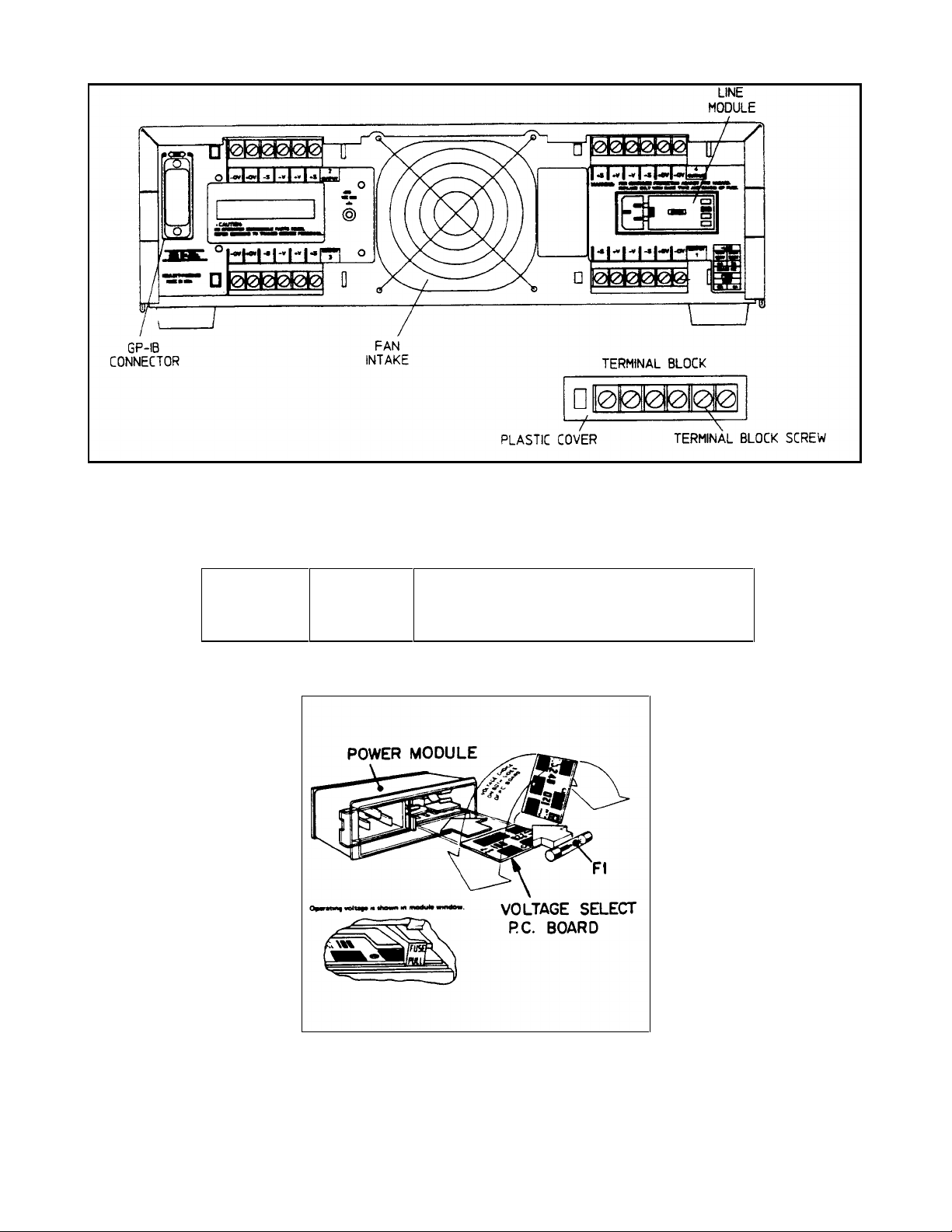
Figure 2-2. Rear Panel Detail (Agilent 6626A Shown)
Table 2-2 Line Fuses
Line
Voltage
100/120 V 8AM 2110-0342
220/240 V 4AM 2110-0055
Note: All fuses are rated for 250 V.
Fuse
Needed
Agilent Part Number (for ¼ X 1¼ in. fuses
only)
Figure 2-3. Line Module Detail
Installation
27
Page 28
Power Cord
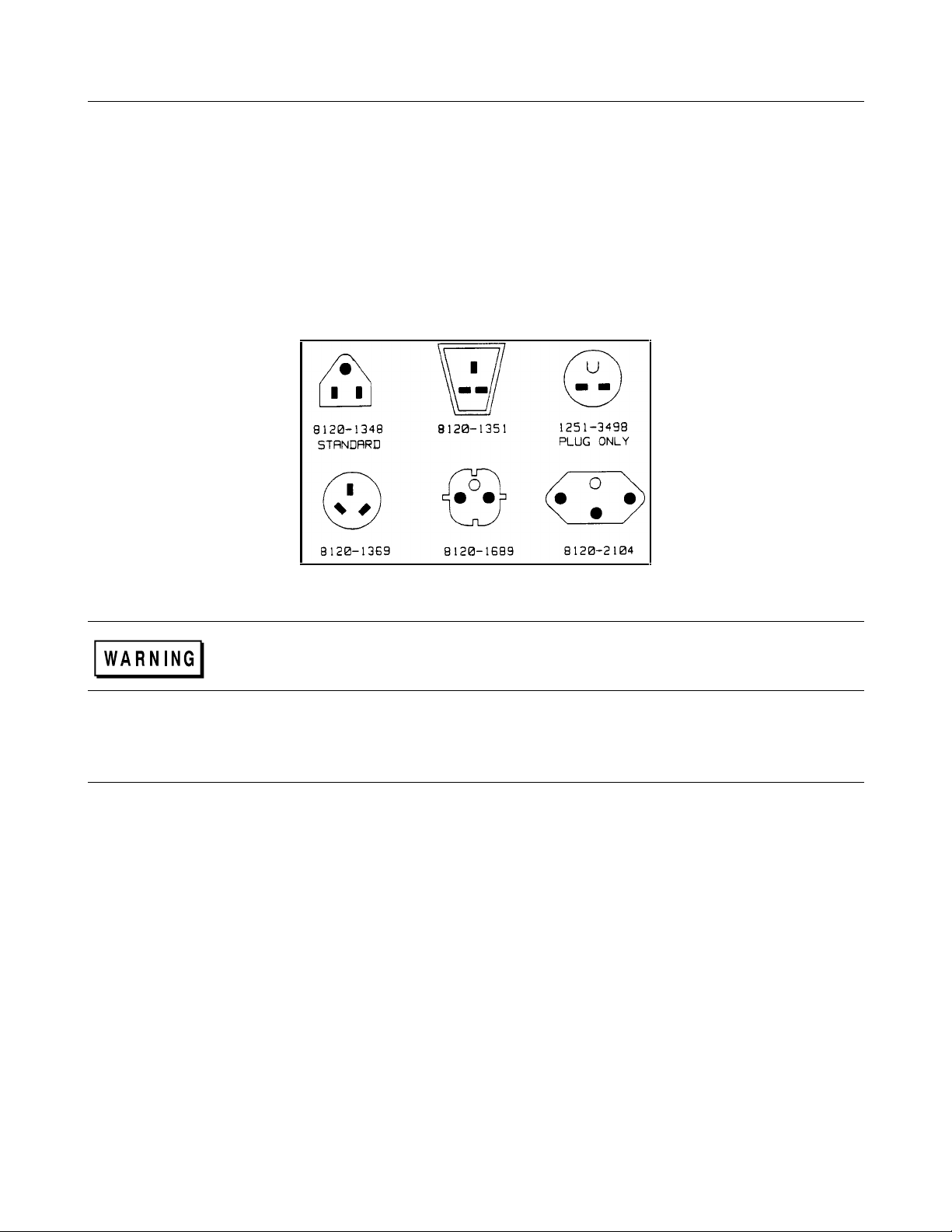
The power supply is shipped from the factory with a power cord that has a plug appropriate for your location. Figure 2-4
shows the standard configuration of plugs used by Agilent Technologies. Below each drawing is the Agilent part number
for the replacement power cord equipped with a plug of that configuration. If a different power cord is required, contact the
nearest Agilent Technologies Sales and Service office.
For your protection, the National Electrical Manufacturer’s Association (NEMA) recommends that the instrument panel and
cabinet be grounded. This power suppl y is equippe d with a three-conductor power cord; the third conductor b e ing the
ground. The power supply is grounded only when the power cord is plugged into an appropriate receptacle. Do not operate
this power supply without adequate cabinet ground connection.
Figure 2-4. Power Cord Plug Configurations
SHOCK HAZARD. Connect the power cord to a grounded receptacle before you connect any
external floating voltages to the supply.
The offset pin on the standard three-prong power cord connector is the ground connection. If a two contact receptacle is
encountered, it must be replaced with a properly grounded three-contact receptacle in accordance with the National
Electrical Code, local codes and ordinances. The work should be done by a qualified electrician.
Line Voltage Conversion
You can change the supply to accept 100 V, 120 V, 220 V and 240 V ac input by adjusting the voltage selector card located
inside of the line module (see Figure 2-3). After you have changed the line voltage, refer to Table 2-2 and check that the
fuse inside the line module is the correct fuse for that line voltage. The procedure is as follows:
1. Turn off power and remove the power cord from the ac input socket on the back of the power supply.
2. To open the line module, move the plastic door on the module aside. If your line voltage change requires a change in the
rating of the fuse, rotate FUSE PULL to the left and re move the fuse.
3. Grasp the voltage select pc board with a pair of needle-nose pliers and slide it out of its slot.
4. To select a voltage, orient the pc board so that the desired voltage appears on the top left side of the board. Push the
board all the way back into its slot. The desired line vo ltage must be visible when the board is installed.
5. Install the correct fuse in the door of the line module if your line voltage change also requires a change in the rating of
the fuse (see Table 2-2).
Installation28
Page 29

FIRE HAZARD. Make sure the replacement fuse is one of the same type (size) and rating (amps) that
is consistent with the voltage level you are operating at. Do not use a sub stitute fuse; use a fuse with
the same Agilent Part number listed in Table 2-2.
6. Close the door of the line module and insert the power cord in the ac input socket. Your power supply is now configured
to operate at the voltage you selected.
GP-IB Interface Connector
The GP-IB connector on the rear panel connects your power supply to your computer and other GP-IB devices (see Figure
2-2). Accessories (page 12) in Chapter 1 lists the cables and cable accessories that are available from Agilent Technologies.
An GP-IB system can be connected together in any configuration (star, linear, or both) as long as the following rules are
observed
1. The total number of devices, including the computer, is no more than 15.
2. The total length of all the cables used is no more than two meters times the number of devices connected together, up to a
maximum of 20 meters.
Note IEEE Std. 488-1978 states that you should exercise caution if your individual cable lengths exceed 4 m.
Do not stack more than three connector blocks together on any GP-IB connector. The resultant leverage can exert excessive
force on the mounting panels. Make sure that all connectors are fully seated and that the lock screws are firmly finger
tightened. Do not use a screwdriver. Use a screwdriver only for the removal of the screws.
Installation
29
Page 30

Page 31

3
Getting Started
Introduction
This chapter is intended for the first time user o f t he supply. It provides four main discussions:
•
Front Panel Controls and Indicators
•
Turning on Yo ur Supply
•
Checking Out Your Supply Using Local Co ntrol
•
Introduction to Remote Operation
First, the supply’s front panel controls and indicators are briefly described. Some of the controls and indicators will be used
in the Turn On And Checkout procedures that follow. Chapter 6 describes how to use all of the front panel controls.
Successful completion of the Turn On And Checkout procedures ensures with a high level of confidence that your supply is
operating properly. Complete performance testing and troubleshooting procedures are given in the Service Manual (Agilent
Part No. 06626-90003).
The checkout procedures are performed locally from the front panel. In addition to checking the ope ration of your supply,
these simple step-by-step checkout procedures will help the first time user become familiar with op e rating the supply from
the front panel.
When you have completed the checkout procedures, you are then introduced to the fundamentals of operating the supply
remotely from a computer. You will learn how to send a command to the supply from the computer and how to get da ta
back to the computer from the power supply. A few of the most often used power supply commands will be described to
help you get started and become familiar with the basics of programming your supply.
After completing this chapter, you can proceed to Chapter 4 to find out how to make load connections to your supply’s
outputs and then to Chapter 5 (Remote Control) and/or Chapter 6 (Local Control) to learn all the details about operating
your supply.
Front Panel Controls and Indicators
The power supply’s controls and indicators are shown in Figure 3-1 and are described in Table 3-1. Note that the front panel
controls are identical for all mode ls except for the number of OUTPUT annunciators (nu mber 3 in Figure 3-1).
Getting Started
31
Page 32

87613 5
6626A SYSTEM DC POWER SUPPLY
VOLTS AMPS
45.153 14.235m
1 2 3 4 CV CC UNR OCP ERR RMT ADDR SRQ
LINE
ON
OFF
ENBLD-- OUTPUT --
LCL
SYSTEM OUTPUT ENTRY
ADDR
ERR
STO
RCL
RANGE
V/I
OVSET
OCP
RESET
VOLT
VOLT
CURR
CURR
OUTPUT
SELECT
VSET
ISET
OUTPUT
ON/OFF
789
456
123
0
.
9 4 2
Figure 3-1. Agilent 6626A Front Panel
Table 3-1. Controls and Indicators
Number Controls/Indicators Description Page
1
LCL key
Returns power supply to local mode (unless local
lockout has been received via GP-IB). Also, turns the
power supply’s display on if it was turned off via the
GP-IB.
2
GP-IB Sta tus
Annunciators
(These three
annunciators indicate the
GP-IB status of the
RMT - Indicates that the power supply is operating
under remote control (GP-IB)
ADDR - Indicates that the power supply is addressed to
talk or to listen.
power supply).
SRQ - Indicates that the power supply is requesting
service.
3
OUTPUT
Annunciators
Indicate which output channel has been selected for
front panel control and/or display (Only one output
annunciator can be on at a time.)
4
Power Supply St atus
Annunciators
(These five annunciators
indicate the status of the
power supply).
CV - Indicates that the selected output channel is in the
constant voltage mode.
CC - Indicates that the selected output channel is in the
positive constant current mode ( + CC) o r the negative
current limit ( - CC) mode.
3-13, 5-2,
6-1
3-13, 5-2,
6-1,
3-10, 5-1
5-1, 5-2,
5-3, 5-17
3-7, 3-8,
6-1--6-4
3-8, 4-1,
6-2, 6-3
3-8, 4-1,
6-2, 6-3
ENTER
32
Getting Started
Page 33
Table 3-1. Controls and Indicators (continued)
Number Controls/Indicators Description Page
4 (cont) UNR- Indicates that the selected output channel is
unregulated; i.e., it is not regulated by CV or CC control
loops.
OCP ENBLD - Indicates that the overcurrent protection
function for the selected channel is enabled.
ERR - Indicates that a programming or hardware error
has occurred and that the ERR bit in the serial poll
register has not been cleared
5 Alphanumeric LCD
Display (When power is
turned on, all segments
will be displayed for
approximately 2
seconds).
6 System Control Keys
(These four control keys
affect the entire power
supply and are
independent of the
output selected.) ERR - Displays a programming or hardware error
STO - Used in conjunction with the numeric entry keys
The parameters stored in register 0 are the "power-up"
RCL - Used in conjunction with the numeric entry keys
Normal ly displays the me asured output voltage and
current for the selected channel. When programmed
from the front panel, the function be ing programmed
(e.g. VSET), the output channel (e.g. 2), and the present
value (e.g. 2.250) will be displayed. Error conditions
will be spelled out in alpha characters
ADDR - Displays the power supply’s GP-IB address.
You can change the address using the numeric entry
keys. You cannot query or change the address remotely
(over the GP-IB).
message and clears the ERR bit in the serial poll register
to store the present output conditio ns for all outputs in
the specified internal register (0-10). Each register stores
the following parameters: VSET, VRSET, ISET,
IRSET, and OVSET. In addition, register 0 also stores
OCP, DLY, and MASK parameters. Register 0-3 are
non-volatile.
parameters. These parameters are set upon applying AC
power to the power supply. Note that the STO
command cannot be used over the bus more than once
per non-volatile register (0-3) without cycling the AC
power (OFF and ON). However, these registers can be
used for an unlimited number of times via the front
panel keys without cycling the AC power .
to recall the settings from the specified internal register
(0 to 10). All outputs are set to the recalled values.
4-4
3-8, 6-4,
5-13
4-4, 5-16
3-7--3-10,
4-4, 5-19,
5-20,
6-1--6-4
3-10, 5-2,
6-4
5-1, 5-20
5-1, 5-13
5-1, 5-13
Getting Started
33
Page 34

Table 3-1. Controls and Indicators (continued)
Number Controls/Indicators Description Page
7
Output Contro l K e ys
(These twelve keys are
output dependent).
OUTPUT SELECT - Selects one of the output
channels for local control or display. This key allows the
channels to be selected in forward (Ð) or reverse (Ï)
sequence.
VSET - Displays the selected output’s present voltage
setting. The setting can be changed using the numeric
entry keys, Ñ VOLT, or Ò VOLT keys..
ISET - Displays the selected output’s present current
setting. The setting can be changed using the numeric
entry keys, Ñ CURR, or Ò CURR keys.
OUTPUT ON/OFF - Toggles the selected output on
and off. When off, "DISABLED’’ appears on the
display.
OVSET - Displays the selected output’s overvoltage trip
point. The setting can be changed using the numeric
entry keys.
RANGE V/I - Displays the selected output’s full scale
programming range for voltage and current. This key
also enables the Up/Down keys to change the
programming range.
Up/Down Keys - These keys increment or decrement
the voltage or current settings of the output selected.
The display will be in the metering mo de for the output
selected. When one of the keys is pressed, it will change
the output selected by one least significant bit (LSB). If
the key is pressed and held, it wi ll continually change
the setting until it is released The Ñ VOLT key is
disabled when the supply is in the CC mode. The Ò
CURRENT key is disabled when the supply is in the CV
mode.
These ke ys will also allow you to change the
programmed resolution range of voltage or current after
the RANGE V/I key is depressed.
Ñ VOLT - Increases t he selected output voltage by an
LSB and then a faster rate as the key is kept pressed, or
after the RANGE V/I key has been pressed, sets the
selected output to the high voltage range.
Ò VOLT - Decrease s the selected output voltage by an
LSB and then at a faster rate as the key is kept pressed,
or after the RANGE V/I key has been pressed, sets the
selected output to the low voltage range.
3-7, 3-8,
6-1--6-4
3-8, 3-9,
5-9, 5-11,
6-2
3-8, 5-11,
6-3
5-12, 6-3
3-8, 5-12,
6-4
3-9
3-9, 6-2,
6-3
3-9
3-9, 6-2
3-9, 6-2
34
Getting Started
Page 35

Table 3-1. Controls and Indicators (continued)
Number Controls/Indicators Description Page
7 (cont)
8
9
Tab le 3-1, in addition to providing a brief description of each control and indicator, lists the paragraphs in which the use of
each control and indicator is described. Because most of the functions performed by the front panel controls can also be
performed remotely by power supply commands, the corresponding paragraphs in Chapter 5 (Remote Operation) are listed
in Table 3-1 where applicable.
Numeric Entry Keys
(These keys are used in
conjunction wi th ma n y
of the System Control
and Output Control keys
to enter the desired
values into the power the
metering mode. Supply.
LINE switch
Ñ CURRENT - Increases the selected output current by
an LSB and then at a faster rate as the key is kept
pressed, or after the RANGE V/I key has been pressed ,
sets the selected output to the high current range.
Ò CURRENT - Decreases the selected output current
by an LSB and then at a faster rate as the key is kept
pressed, or after the RANGE V/I key has been pressed ,
sets the selected output to the low current range.
OCP - Toggles the selected output’s overcurrent
protection circuit on and off.
RESET - This key performs the following:
1. Reset the selected output’s overvoltage crowbar (the
cause of the overvoltage must be removed before reset is
successful) .
2. Reset the selected output’s overcurrent condition and
returns the output to its previous settings (the cause of
the overcurrent must be removed before reset is
successful).
3. Return the display to the metering mode from any
other mode (e.g. VSET). In the metering mode, the
measured output voltage and current of the selected
output are displayed .
0 to 9 - Set the value of the specified function and
and (e.g. VSET 1 6.550
.
Ï(backspace) - Erases the previous keystroke.
Depressing this key without setting a
value places the display in
ENTER - Enters the values on the display for the
specified function, initiates the function, and returns the
display to the metering mode. Pressi ng this key without
setting a value will result in retention of the previous
values and returning the display to the metering mode.
Turns ac power on and off.
3-9, 6-3
3-9, 6-3
3-8
3-8
3-8,
6-1--6-5
6-1
3-8,
6-1--6-5
3-6
Getting Started
35
Page 36

Turning On Your Supply
The following paragraphs describe the power-on sequence which includes a self test of most of the power supply’s circuits.
Before you turn on your supply, make sure that :
•
The line module on the rear panel is set to match your input line voltage.
•
The proper fuse is installed and the line cord is plugged in.
If you have any questions concerning installation or p ower requirements, review Chapter 2.
To turn on your sup ply, press the front panel LINE switch. When the power is initially applied, the supply performs a series
of self tests which last about 3 seconds. Included in these tests are checks of circuits on the GP-IB board and on each of the
output boards.
Normal Self Test Indications
If the supply passes the self test, the display will first show all segments of the LCD display with annunciators on as
illustrated in Figure 3-2.
Figure 3-2. Test Pattern of all Display Segments at Power-on
After all segments are displayed, the supply’s GP-IB address will appear for approximately 2 seconds as shown in Figure 3-
3. As shipped from the factory, the power supply’s address is set to 5. You must know this address before you can remotely
program your supply.
Figure 3-3. Typical Address Display During Power-On Self Test
When self test is s ucces sfully completed, the power-up parameters stored in register 0 will be set (see page 89 for a
complete description of the store and recall functions). As shipped from the factory, this non-volatile register co ntains zero
volts and zero current (see Table 5-4 on page 72) for all outputs. Note that the CV annunciator will indicate that the output
is in the constant voltage mode.
36
Getting Started
Page 37

Figure 3-4. Typical Display at Power-On
Self-Test Errors
If the supply fails the power-on self-test, all power supply outputs will remain disabled (off) and the display will indicate
the type of failure and the output channel on which it occurred. Figure 3-5 shows that self-test detected an error in output
channel 3. Error messages that could appear on the display if self-test fails are listed below. Self-test error messages are
explained in Appendix D and troubleshooting procedures are given in the Service Manual. You may also call your Agilent
Sales Office for help.
Power-On Self Test Error Messages
HDW ERR CH "N"
8291 FAILED
TIMER FAILED
CV DAC CH ’’N"
CC DAC CH "N"
OV DAC CH "N"
FUSE CH ’’N"
Note: "N" specifies the failed output channel number: 1,2,3, or 4 as applicable.
Figure 3-5. Sample Self-Test Failure Display
Checking Out Your Supply Using Local Control
The following procedures use the display and keys on the front panel to check each of your power supply’s outputs. No test
equipment, other than a jumper wire (14 AWG), is required to perform these tests. The tests must be repeated for each
output of your particular supply. The checkout consists of voltage, overvoltage, and current tests. It is assumed that power
has already been turned on, the supply has passed the power-on self-test, loads are not connected to any of the supply’s
outputs, and sense clips are connected between the sense terminals and the output terminals.
Note The following procedures are identical for all models and for all outputs. Use the OUTPUT SELECT key
to select an output to be tested. If an output fails any of t he tes ts, refer to the tro ubleshooting section in
the Service Manual.
Getting Started
37
Page 38

Voltage Test
1. Set the voltage of the selected output to 10 V by pressing:
VSET 1 0 ENTER
2. Check that the display reads approximately 10 V and 0 A and the CV annunciator is on indicating that the supply is in
the constant voltage mode o f operation.
Overvoltage Test
1. Program the overvoltage protection (OVP) to 19 V by pressing:
OV 1 9 ENTER
SET
2. Set the voltage to 16 V by pressing:
VSET 1 6 ENTER
3. Check that the display reads approximately 16 V and 0 A.
4. Set the voltage to 20 V by pressing:
VSET 2 0 ENTER
5. Check that the display reads "OVERVOLTAGE’’
6. Reset the supply by pressing:
VSET 1 6 ENTER RESET
7. Check that the display reads approximately 16 V and 0 A.
Current Test
1. Turn off the supply.
2. Remove the barrier block cover from the output to be tested and connect a short circuit (jumper wire) between the + V
and -V terminals of the output being tested.
3. Turn on the supply.
4. Use the
5. Set the voltage to a volts by pressing:
Set the current to 0.01 amps by pressing:
38
Getting Started
to select the output being tested.
VSET 5 ENTER
ISET . 0 1 ENTER
Page 39

6. Check that the display reads approximately 0 volts and the programmable current limit value. Also, check that the front
panel CC annunciator is on indicating that the output is in the constant current mode of operation.
7. Set the current to 0.5 A by pressing:
ISET . 5 ENTER
8. Check that the display reads approximately 0 V and 0.5 A.
9. Enable the overcurrent protection circuit by pressing:
OCP
10. Check that the OCP ENBLD annunciator is on indicating that overcurrent protection is enabled and the display reads
’’OVERCURRENT ’’. When in overcurrent, the output is disabled.
11. Disable the overcurrent protection circuit by pressing:
OCP
12. Reset the output by pressing:
RESET
13. Check that the display reads approximately 0 V and 0.5 A.
14. Turn off the supply and remove the jumper from the output terminals.
Repea t the voltage, overvoltage and curre nt tests given on page 38 for the other output channel(s) using the
Changing Resolution Range
1. Press the RANGE V/I key.
2. Observe the selected output’s full scale programming range for voltage and current in the front panel display.
3. Press either the Ñ or the Ò key. (vo ltage or current)
4. Observe that the selected output’s full scale programming range for voltage and current changes to the high range (if the
Ñ key is pressed) or low range (if the Ò key is pressed). Note that no range cha nge will occur if the Ñ or Ò key is pressed
while the supply is already in the requested range.
Introduction To Remote Operation
The following paragraphs explain the fundamentals of operating the supply remotely from a computer. Only a few
commonly used programming commands will be discussed. Refer to Chapter 5 for a detailed description of all the
commands. The intent of this discussion is to help first time users to quickly become familiar with op e rating their supply
from a computer.
The programming examples that follow assume that a computer is connected to the GP-IB connector on the rear of your
supply (see Chapter 2), power is applied, and loads are not connected to any of the supply’s outputs. The examples used are
primarily for Agilent Series 200/300 computers using Agilent BASIC language. Read the manuals for your particular
computer to find out which statements you must use.
key
Getting Started
39
Page 40

Enter/Output Statements
The programming statements you use to operate your supply from remote depend on your computer and its language. In
particular, you need to know the statements your computer uses to output and enter information. For example, the Agilent
BASIC language statement that ad dresses the power supply to listen and send s the command to the power supply is:
OUTPUT
The Agilent BASIC language statement that addresses the power supply to talk and reads back data from the power supply
is:
ENTER
The supply’s front panel ADDR annunciator is on when the supply is addressed to talk or to listen.
Reading the GP-IB Address
Before you can operate your power supply remotely, you need to know its GP-IB address. The address was displayed
during the power on sequence described in page 36. To see the address, press:
ADDR
A typical address display is shown in Figure 3-6:
The displayed response is the power supply’s GP-IB address. When sending a remote command, you append this address to
the computer’s GP-IB interface select code (normally 7). For example, if the select code is 7 and the power supply’s GP -IB
address is 5, the combination is 705.
Changing the GP-IB Address
Note All examples in this discussion assume a GP -IB address of 5. It is recommended that you retain this
address to simplify programming.
Every device on the GP-IB must have an address. The supply’s address is factory set to decimal 5. Any address from 0
through 30 is a valid address. If you need to change the Agilent 662xA Supply’s address press:
You can now enter a new address. For example, press:
1 4 ENTER
You have now changed the address from 5 to 14. If you want to change the address back to 5, repeat the above procedure
but use 5 instead of 14 in the last step. No te that the address is stored in the power supply’s non-volatile memory and
therefore will be retained through interruption o f the ac li ne power.
Figure 3-6. Typical Address Display
ADDR
40
Getting Started
Page 41

Sending a Remote Command
To send the power supply a remote command, combine your computer’s output statement with the GP-IB interface select
code, the GP-IB device address, and finally, the power supply command. For example, to set the output voltage of output
channel 1 to 2 volts, send:
Getting Data From The Supply
The supply is capable of measuring the values of its output parameters in response to queries. In this example, the query
asks the supply to measure the output voltage at output 1.
When you send a query from remote, the supply does not display the response as it did when you executed the command
from the front panel. Instead, it holds the response in an output buffer. The output buffer is a register that holds information
until it is read by the computer or is replaced with new information.
Note On an Agilent Series 200/300 Computer, the A variable must be declared before you do the following
steps. Refer to your computer’s o perating manual for more information.
Use your computer’s enter statement to get the response from the output buffer. For example, execute:
Followed by:
The ENTER statement enters whatever is in the supply’s output buffer into the computer’s A variable. The DISP statement
displays the A variable’s contents on the computer’s display.
Often Used Commands
The command set contains over sixty commands that allow you to progra m the power supply in a variety of applications.
Within this command set, however, is a small subset of commands that are all you need for most applications. These
commands are: VRSET, IRSET, VSET, ISET, VOUT?, IOUT?, OUT, OVSET, and OCP.
ENTER 705; A
DISP A
Getting Started
41
Page 42

Each of these commands is briefly discussed in the following paragraphs to help you get started in programming your
supply. To know more about these commands, refer to Chapter 5.
The VRSET and IRSET commands select the range the power supply operates in. Two ranges are available for each output
- standard resolution, and high resolution (see Table 1-2).
If the value for voltage or current entered is not within the present ope rating range of the supply, the error annunciator will
indicate an error. Sending ERR?, and addressing the supply to talk, will return the error message (in the case ’’number
range" error would be displayed.
Voltage and Current Programming. You can send voltage and current values to the power suppl y directly in volts or
amps. The following examples use voltage and current values that are within the range of any output that the power supply
provides.
To set the voltage of output 1 to 5 volts, send:
OUTPUT 705; “VSET 1,5”
To set the current o f outpu t 2 to 450 milliamps, send:
OUTPUT 705; ''ISET 2,.450"
Output Voltage and Current Measurement. The power supply has built-in metering circuitry, which allows it to monitor
the output voltage and current of the selected output. You can instruct the supply to return its present output voltage and
current using VOUT? and IOUT? queries respectfully. The metering circuitry is auto-ranging, and will select the pro per
resolution.
To mea sure the output voltage at output 1, send:
OUTPUT 705; "VOUT? 1"
To get the measurement from the output buffer, send:
ENTER 705; A
DISP A
The computer should display a reading of approximately 5 volts .
To measure the output current at output 2, send:
OUTPUT 705: "IOUT? 2''
To get the measurement from the output buffer, send:
ENTER 705; A
DISP A
42
Getting Started
Page 43

Output On/Off. You can turn a specified output on or off. Individual outputs can be controlled as shown below.
To turn off output 1, send:
OUTPUT 705; ’’OUT 1,0"
When an output is turned off, it is set to 0 volts and to the minimum current limit value
To turn on output 1, send:
OUTPUT 705; ’’OUT 1,1"
When an output is turned on it will return to the voltage and current settings determined by the present VSET and ISET
values.
Overvoltage Setting. You can send an overvoltage setting value to the power supply direc t ly in volts. If the output voltage
exceeds this setting, the output crowbar is fired, and the output voltage is quickly downprogrammed and disabled (0 volts
output).
To set the overvoltage value of output 2 to 3.5 volts, send:
OUTPUT 705; “OVSET 2,3.5”
Overcurrent Protection. The output will go to the off state (0 volts and 0 current) when the overcurrent protection (OCP)
feature is enabled and the output is in the + CC mode. To enable the overcurrent protection mode for output 2 send:
OUTPUT 705; ''OCP 2,1"
To disable the overcurrent protection mode for output 2, send:
OUTPUT 705; ''OCP 2,0"
When overcurrent protection is disabled and the output is in + CC mode, the output current will be limited to and will stay
at the ISET value.
Returning the Supply to Local Mode
In the remote mode (RMT annunciator on), the front panel keys have no effect on an y of the suppl y's outputs and only the
computer can control the supply. However, you can still use the front panel display to monitor the output voltage and
current or check any of the present settings (VSET, ISET, OVSET, etc.) of the selected output channel.
If you want to use the front panel keys to chan ge the output settings, you must ret urn the supply to the local mode. You can
return the supply to the local mode (provided that the local lockout command has not been received from the computer) by
pressing the LCL key. A change between the local and remote modes (or vice versa) will not result in a change in the power
supply outputs. Refer to Chapter 6 for additional details on using the LCL key and operating the supply in the local mode.
Getting Started
43
Page 44

Page 45

4
Output Connections and Operating Information
Introduction
This chapter explains how to make connections to the output terminals located on the rear of your power supply. Some
general operating information is included in this chapter to help you und erstand how the power supply operates under
various load conditions. This information ap plies whether you are operating the supply via the front panel or the GP-IB.
Output Ranges
Figure 4-1 identifies the output combinations that are available on the power supply. Each output can operate as a constant
voltage (CV) or constant current (CC) source over a wide variety of output voltage and current combinations. In ad dition,
each output has an active downprogrammer which operates at currents up to approximately 110% of the maximum positive
current rating of the output. This means that each output can actively sink as well as source its maximum rated output
current. At voltages below 2.5 V, a downprogramming resistor continues downprogramming until the voltage reaches
approximately zero volts.
Figure 4-1. Output Combinations
Output Connections and Operating Information
45
Page 46

Operating Quadrants
Figures 4-2A and 4-2B show the operating locus of your power supply in three quadrants. The area in quadrant 1 shows the
operating locus defined by the voltage and current settings of each output. The area in quadrant 2 indicates the locus where
each output can operate as a current sink. You cannot program current limit values in quadrant 2.
46
Output Connections and Operating Information
Figure 4-2. Typical Output Range Characteristics
Page 47

Figure 4-3 shows the current sink characteristics lower voltages in greater detail. The area in quadrant 4 illustrates the
reverse polarity diode characteristics of each output. Do not operate any output with reverse-voltage currents that are
greater than the maximum rating of the output.
Operating Ranges
Notice in Figure 4-2, there are four overlapping areas in quadrant one for both the 25 watt and 50 watt outputs. The Low
Range Voltage and Low Range Current ranges are higher precision than the High Range Voltage and High Range Current
ranges. The voltage and current ranges can be set independently (see page 73). If the high resolution range is programmed,
attempting to program values outside this range will result in a number range error.
The 50 watt output (Figure 4-2B) is different from the 25 watt output (Figure 4-2A), in that there is a power limiting
boundary at 1 amp in the High Voltage/High Current range. As a result, the 50 watt output can be set to no more than 1.03
amps at voltage settings above 16.16 volts, and vice versa.
Setting parameters of voltage or current beyond this power limit boundary, but within the High Voltage/High Current range
will cause the other parameter (voltage or current) to automatically be scaled down to the power limiting boundary (see
pages 71 and 73).
The voltage and current programming resolution of the outputs is affected by the setting of the range. The voltage of the 25
watt output, when programmed to the Low Voltage Range, has a voltage programming resolution of 460 µV. When
programmed above 7 volts, the High Voltage Range must be selected resulting in a programming resolution of 3.2 mV.
The current of the 25 watt output, when programmed to the High Current Range, has a current programming resolution of 1
µA. When programming above 15 mA, the High Current Range must be selected, resulting in a programming resolution of
33 µA.
The voltage of the 50 watt output, when programmed to the High Voltage Range, has a voltage programming resolution of
1 mV. When programming above 16.16 volts, the high range must be selected, resulting in a programming resolution of 3.2
mV.
The current of the 50 watt output, when programmed to the High Current Range, has a current programming resolution of
13 µA. When programmed above 200 mA, the High Current Range must be selected, resulting in a programming resolution
of 131 µA.
The readback range of the outputs is not programmable, and is selected automatically by the power supply.
Figure 4-3. Typical Downprogramming Characteristic Below 2.0 V
Output Connections and Operating Information
47
Page 48

The readback resolution of the 25 watt outputs when metering voltages of 7 volts or below, will be 483 µV. For voltages
above 7 volts, the readback resolution will be 3.3 mV.
The readback resolution of the 25 watt outputs when metering source currents of 15 mA or below, the readback resolution
will be 1 µA. When metering source currents above 15 mA, the readback resolution will be 48 µA.
When metering sink currents of 15 mA or below, the readback resolution of the 25 watt outputs will be 1 µA. When
metering sink currents above 15 mA, the readback resolution will be 37 µA.
When metering voltages of 16 volts, or below, the readback resolution of the 50 watt outputs will be 1.1 µV. For voltages
above 16 volts. the readback resolution will be 3.3 mV.
When metering source currents of 200 mA or below, the readback resolution of the 50 watt outputs will be 14 µA. When
metering source currents above 200 mA, the readback resolution will be 160 µA.
When metering sink currents of 200 mA or below, the readback resolution of the 50 watt outputs will be 14 µA. When
metering sink currents above 200 mA, the readback resolution will be 151 µA.
Protection Features
Protective circuitry within the supply can limit or turn off an output in the e vent of an abnormal condition. The activated
protection feature can be determined by observing the front panel display area. You can also read back the status of the
supply over the GP-IB. The following protection features are implemented:
OVERVOLTAGE -- shorts the output by firing an SCR crowbar and sets zero volts and minimal current on an output if
any of the following conditions are present:
1. The output voltage exceeds the programmed overvoltage trip point.
or
2. The sum of the volta ge fro m the + V output terminal to the +S terminal plus t he voltage from the -S terminal to the -V
output terminal exceeds 10.0 V (applies to remote sensing only).
or
3. A trip signal is received on the output’s OV terminals.
or
4. The output’s fixed overvoltage circuit is activated.
The OV trip point can be programmed up to 55 V. When an overvoltage occurs, the word OVERVOLTAGE appears in the
front panel display and the OV status bit is set for that output. Chapter 5 explains how to program the overvoltage trip level.
A fixed overvoltage threshold of approximately 120% of the maximum rated output voltage is built into each output.
Because the fixed overvoltage circuit is biased from the output terminals, it can be activated and provide protection even
when the supply is not connected to the ac power line.
The OVRST command or front panel RESET key restores the programmed voltage and current values and clears the OV
once the cause of the overvoltage has been eliminated.
OVERCURRENT -- when the overcurrent protection feature is enabled, and the output is sourcing current and enters the +
CC operating mode, the output will be disabled (set to zero volts and minimal current) and the word OVERCURRENT will
appear on the front panel display. In addition, the O C status bit is set for that output. The OCRST command or front panel
RESET key restores the programmed voltage and current values and clears the OC once the cause of the overcurrent
condition has been eliminated. Refer to Chapter 5 for p r ogramming details.
48
Output Connections and Operating Information
Page 49

UNREGULATED OUTPUT -- the supply informs the user when output regulation is not guaranteed. This can occur when
attempting to sink excessive currents below 4 volts on 25 W outputs and 2 volts on 50 W outputs or when operating outputs
in parallel. The UNR annunciator on the front panel and the UNR bit in the status register indicate that the specified output
is unregulated. Line voltage dropout or an incorrectly set ac power module can also cause the output to become
unregulated. If line voltage dropout continues, the supply shuts down and will return to the power-up condition when
normal line voltage is restored.
OVERTEMPERATURE -- shuts do wn the linear pass transistors and downprogrammer of the output that has reached an
unsafe operating temperature. Operation of the other outputs is unaffected. An overtemperature can occur because of
excessively high ambient temperature, a blocked fan, or insufficient space at the sides for adequate air circulation. When an
overtemperature condition occurs, the word OVERTEMP appears in the front panel display and the OT status bit is set.
This circuit resets automatically and restores the output approximately 30 seconds after the temperature drops sufficiently
for safe operation.
ERROR -- if the power supply receives an invalid command either through the front panel or the GP-IB, the ERR
annunciator on the front panel comes on and the ERR bit in the serial poll register is set. The power supply does not execute
the command and remains at previously set values. Pushing the ERR button in local mode displays the error message and
clears the error. The error indicator may also indicate that an instrument failure has occurred. Refer to Appendix D for
further details.
Connecting The Load
Each terminal block cover on the rear panel is secured by a locking tab which snaps into a slot at the left of the terminal
block. To remove, insert a screwdriver into this rectangular slot and move the locking tab to the left. When the loc king tab
releases, gently pull the terminal block cover away from the terminal block. To reinstall the cover, align it over the terminal
block and gently press it in to position until the locking tab engages.
SHOCK HAZARD. Turn off ac power before making rear panel connections. All wires and straps
Each rear terminal block has six M3.5 x 0.6 x 6 mm screws for attaching wires (see Figure 2-2). Load connections to the
supply are made at the + V and -V terminals on each terminal block. Do not connect unterminated wires to the load
terminals. Wires used for load connections must be properly terminated with termination connectors securely attached.
Remember to replace the impact resistant plastic covers (Agilent P/N 06624-20007) over the terminal blocks after making
connections.
Consistent with good engineering practice, all sense and trigger leads connected to the rear terminal blocks should be
twisted and shielded to maintain the instrument’s specified performance.
Wire Size Selection
(ampacity) for various sizes of stranded wire.
Note that the minimum wire size required to prevent overheating may not be large enough to prevent OV trip when remote
sensing and to maintain good regulation. The load wires should be large enough to limit the total voltage drop in both leads
to no more than 10 volts. See Figure 4-6 for total allo wed lo ad lead drop when programming to high voltage setti ngs. With
remote sensing, load regulation is degrad ed 1 mV per 1 V in the - V output terminal load lead. (See Remote Sense
Connections on page 52).
must be properly connected with terminal block screws securely tightened. Replace terminal block
covers before reapplying power.
FIRE HAZARD Select a wire size large enough to carry short-circuit current without overheating.
Two factors must be considered when selecting wire size for load connections: conductor temperature
and voltage drop. To satisfy safety requirements, load wires must be heavy enough not to overheat
while carrying the short-circuit output current of the unit. Table 4-1 lists the current-carrying capacity
Output Connections and Operating Information
49
Page 50

Note To prevent tripping of the overvoltage circuit, pick a wire size sufficient to handle the FULL outp ut
current of the unit no matter what the intended load current or current limit setting.
Tab le 4-1 lists the res istivity for various wire sizes and the maximum lengths to limit the voltage drop to 1.0 volts for
various currents.
Table 4-1. Stranded Copper Wire Ampacity and Maximum Wire Lengths to Limit Load Lead Voltage Drop
Wire Size 2 Wire Bundled 4 Wire Bundled Resistivity Drop to 1 V Per Lead
5 A 10 A 20 A
(AWG)
20 7.8 6.9 0.0102 20 10 5
18 14.5 12.8 0.0064 30 15 7.5
16 18.2 16.1 0.0040 50 25 12.5
14 29.3 25.9 0.0025 -- 40 20
12 37.6 33.2 0.0016 -- -- 30
(Cross Section
Area in mm
0.75 9.4 8.3 0.0267 7.4 3.8 1.8
Notes:
1. Ampacities for AWG wires are derived from MIL-W-5088B. Maximum ambient temp: 55°C. Maximum wire temp:
105°C.
2. Ampacities for metric wires are derived from IE Publication 335-1.
3. Ampacity of aluminum wire is approximately 84% of that listed for copper wire.
4. Because of wire inductance considerations, it is recommended that you keep your load leads twisted, tie wrapped, or
bundled together and less than 50 feet (14.7 meters) in length per lead.
5. See Page 49 for information on wire gauge considerations with capacitive loads.
Note The OVP circuit senses at the main output terminals and not on the sense leads. Thus, the voltage sensed
Load lead resistance is an i mportant factor relating to the CV stability of the supply with remote sensing of capacitive
loads. If high capacitance loads are expected, you should not use wire gauges heavier than 12 to 14 AWG for long runs of
load lead. See Figure 1-4 for more information about stability with output capacitors.
Multiple Loads
If you will be sensing the load locally (as shipped from the factory) and are connectin g multiple loads to one output,
connect each load to the output terminals using separate connecting wires (see Figure 4-4). This minimizes mutual coupling
effects and takes full advantage of the power supply's low output impedance. Each pair of wires should be as short as
possible and twisted or bundled to reduce lead inductance and noise pickup.
If load considerations require the use of distribution terminals that are located remotely from the supply, connect the power
supply output terminals to the remote distrib ution terminals by a pair of twisted or bundled wires. Connect each load to the
distribution terminals separately. Remote voltage sensing is recommended under these circumstances. Sense either at the
remote distribution terminals or, if one load is more sensitive than the others, directly at the critical load.
2
)
0.5 7.8 6.9 0.0401 5 2.4 1.2
1 12.7 11.2 0.0200 10 5 2.6
1.5 15.0 13.3 0.0137 14.6 7.2 3.6
2.5 23.5 20.8 0.0082 -- 12.2 6
by the OVP circuit could be as much as 10 V higher than the voltage being regulated at the load. Program
the OVP trip voltage accordingly when using remote sensing. In addition, if the total voltage drop in both
leads exceeds 10 V, a protective circuit will fire the OVP circuit regardless of the OVP setting.
Ampacity Per Wire (Amps)
(Ω/ft)
(Ω/m)
Max Length to Limit Voltage
(feet)
(meters)
50
Output Connections and Operating Information
Page 51

Figure 4-4. Optimum Hookup for Multiple Loads, Local Sensing
Note When a load is connected through relay or switch contacts, contact bounce may activate the overvoltage
circuit and shut down the supply. Therefore, it is recommended that the output be downprogrammed to 0
or turned-off (disabled) before the relay (or switch) contact is opened or closed.
Positive and Negative Voltages
Either positive or negative voltages can be o btained from the supply by grounding (or "commoning") one of the output
terminals. Always use two wires to connect the load to the supply regardless of where or how the system is grounded. This
supply can be operated with any output terminal ± 240 Vdc (including output voltage) from ground.
Remote Voltage Sensing
The power supplies will allow up to a total load lead drop of 10 V.
Because of the unavoidable voltage drop developed in the load leads, the as-shipped terminal block strapping pattern shown
in Figure 4-4 does not provide the best possible voltage regulation at the load. The remote sensing connections shown in
Figure 4-5 improve the voltage regulation at the load by monitoring the voltage there instead of at the supply’s outputs
terminals. This allows the power supply to automatically compensate for the voltage drop in the load lead. Re mote sensing
is especially useful for CV operation with load impedances that vary or have significant lead resistance. It has no effect
during CC operation. Because sensing is independent of other power supply functions, remote sensing can be used
regardless of how the power supply is programmed. Note that with remote sensing, voltage readback monitors the load
voltage at the se nse points.
Output Connections and Operating Information
51
Page 52

The maximum voltage available at the power supply output terminals during remote sensing (see Figure 4-6) is 50.5 volts.
This allows the sum of the voltage acro ss both load leads to equal 10 volts maximum. For lower output voltages refer to
Figure 4-3.
Remote Sense Connections
Remember to turn off the power supply before making or changing any connections on the rear panel terminal blocks.
Connect the unit for remote sensing by first disconnecting the straps between sense and load terminals. Then make your
connections as shown in Figure 4-5. Connect the sense leads as close to the load as possible. See wire size selection
(pages 49 - 50) for information on selection of load lead wire gauge. Best results will be o btained by using the shortest load
leads practical. It is recommended that you keep your load leads under 14.7 meters (50 feet) per lead because of inductance
effects.
Figure 4-5. Remote Voltage Sensing
52
Output Connections and Operating Information
Page 53
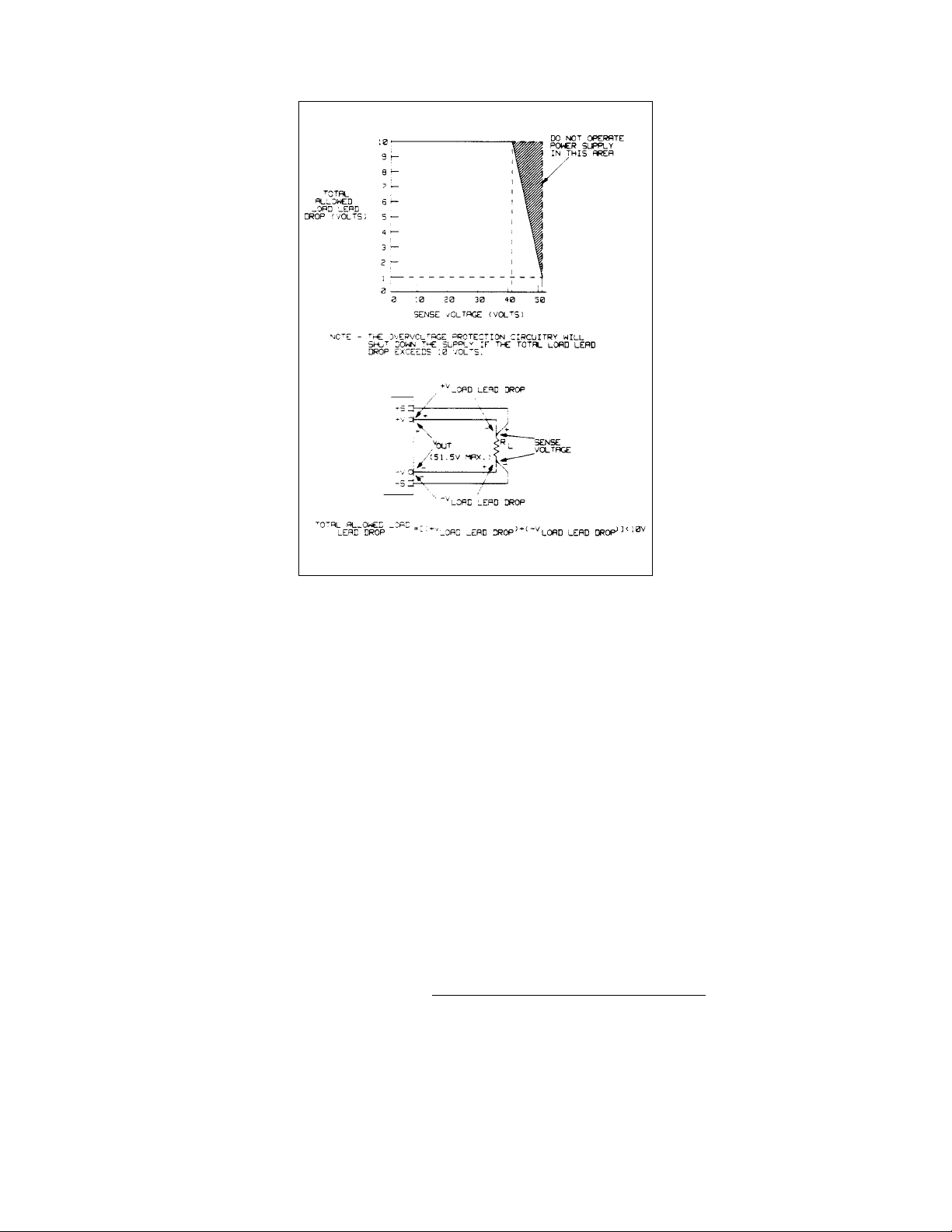
Figure 4-6. Total Allowable Load Lead Voltage Drop (total of both leads) with Remote Sensing
Output Noise Considerations
Any noise picked up on the sense leads will appear at the supply’s output a nd may adversely affect CV load regulation.
Twist the sense leads or use a ribbon cable to minimize the pickup of external noise. In extremely noisy environments it
may be necessary to shield the sense lead s. Ground the shield at the power supply end only; do not use the shield as one of
the sensing conductors.
The noise specifications in Table 1-2 apply at the power supply output terminals when using local sensing. However,
voltage transients may be produced at the load by noise induced in the leads or by load current transients acting on the
inductance and resistance of the load lead. If it is desirable to keep voltage transient levels to a minimum, place an
aluminum or a tantalum capacitor, with an approximate value of 10 µF per foot (30.5 cm) of load lead, right across the load
(see Figure 4-5). Refer to Figure 1-4 for capacitive load stability considerations.
Programming Response Time with an Output Capacitor
Because voltage programming into an external output capacitor may cause the supply to briefly enter CC operating mode,
voltage programming response time may be longer tha n that specified in Table 1-2. Use the following formula to estimate
the additional response time:
Additional Response Time
Added Output Capacitor)(Charge in Vout
()
=
Current Limit Setting
Output Connections and Operating Information
53
Page 54

Open Sense Leads
The sense leads are part of the supply’s feedback path. Connect them in such a way so that they do not inadvertently
become open circuited. The power supply includes protection resistors that reduce the effect of open sense leads during
remote-sensing operation. If the sense leads open during operation, the supply returns to the local sensi ng mode, with the
voltage at the output terminals approximately equal to the programmed value.
Overvoltage Trigger Connections
Each output of your power supply has two OV terminals on its rear panel terminal block. These terminals are labeled +OV
and -OV. By connecting the OV terminals all in parallel as shown in Figure 4-7, an overvoltage shutdown on any one
output will also trigger the overvoltage on the remaining outputs. Any n umber of OV terminals up to eight sets can be
strapped together. Observe polarity when connecting the OV terminals in parallel.
The overvoltage trip point for each output can be set either from the front panel or by remote programming. You can also
externally fire the overvoltage circuit of one or more outputs by applying a 5 volt pulse of at least 50µs to any pair of OV
terminals (see Figure 4-8). As long as all OV terminals are wired together, the outputs will be crowbarred simultaneously .
External Trigger Circuit
Figure 4-8 illustrates a reco mmended external circuit that can be used to provide an OV trip signal to the OV terminals.
This circuit configuration provides good noise immunity and protects against the voltage pulse that is returned from the OV
terminals every time that the overvoltage circuit fires. It can be operated from a wide range of bias voltages provided the
input limiting resistors are chosen as tabulated in the figure. If it is not required to trip the OV with a TTL signal, then a
bias supply, switch, current limiting resistor (R2), and protection diode are all that are required. Note that with the unit off
(ac power removed), the + OV and - OV terminals are inactive.
The internal equi valent OV circuit is shown in Figure 4-9. Note the internal DC blocking capacitor, bleed resistor, and
noise bypass capacitors.
Do not exceed 50 volts maximum between the + OV and the - OV terminals. The OV terminals are
rated at ±240 Vdc (including external OV voltage) from chassis ground or any other output terminals.
Figure 4-7 Overvoltage Connections
54
Output Connections and Operating Information
Page 55

Figure 4-9. Equivalent Internal OV Trigger Circuit
Power Supply Protection Considerations
Battery Charging
If you are using your supply in a battery charging application, it is recommended that a series protection diode be added to
prevent damage to the supply during an overvoltage shutdown. Remember that each output has an overvoltage protection
circuit that fires a crowbar to disable the output for any of the OVERVOLTAGE conditions described on page 48.
Figure 4-10 illustrates t he recom mende d connections and protection circuit for a b a ttery charging application. The diode
will prevent damage to your supp ly that can result from excessive battery current flowing into the supply’s output in the
event of an overvoltage shutdown.
Figure 4-8. External Trigger Circuit
Output Connections and Operating Information
55
Page 56

Figure 4-10. Recommended Protection Circuit for Battery Charging
Capacitive Load Limitation
The programmable overvoltage protection circuit can be used to do wnprogram capacitive loads although it is primarily
intended for use as a protection feature as described on page 48.
Repetitive (over 100 cycles) tripping of the overvoltage circuit with output capacitors greater than 2000
µ
F may result in eventual damage to the supply.
Parallel Operation
Connect in parallel only outputs that have equivalent voltage and curr ent ratings.
Connecting outputs in parallel pro vides a greater current capability than can be o btained from a single output. Because each
output contains an active downprogrammer that is capable of sinking current from only ONE identical output, you can
parallel no more than two outputs. These outputs must have equivalent voltage and current capability. For example, o n the
Agilent 6626A power supply, only outputs 1 and 2 or 3 and 4 may be connected together. On the Agilent 6625A supply,
none of the outputs may be connected together. If you are mixing different model supplies (i.e. an Agilent 6625A and an
Agilent 6626A) be sure to connect only equivalent voltage and current outputs in parallel.
As an example, Figure 4-11 shows how to connect two outputs in parallel to a single load with local sensing. This
configuration applies to both CV and CC operating modes. Connecting the load leads of output 2 directly to the + V and - V
terminals of output 1 keeps the total length of the load leads to a minimum and reduces the number of wire connections that
must be made at the load itself. Connecting the + S and -S terminals of output 2 directly to the sense terminals of output 1
compensates for the IR drop in the interconnecting load leads.
56
Output Connections and Operating Information
Page 57

Figure 4-11. Parallel Connections with Local Sensing
CV Operation
For CV operation, one output must operate in CC mode and the other output must operate in CV mode. Although each
output operates independently of the other, the output that is operatin g in CV mode will be ’’controlling" the voltage
regulation of both outputs. Setti ng the output voltages as outlined in t he following par agraph and configuring the outputs a s
shown in Figure 4-11 will allow output 1 to operate in CV mode and output 2 to operate in CC mode.
To assure that output 2 will be operating in CC mode, yo u must program output 2’s voltage to a hig her value than the
voltage of output 1. One way to accomplish this is to first program output 2 to the maximum allowable voltage setting for
the desired operating range (see Table 4-2 or Figure 4-2). These values are 1% higher than the rated voltage for the
operating range. Then, program output 1 ’s voltage to the desired operating voltage. The lower voltage setting of output 1
will determine the voltage that appears across the load. The current limit point of the paralleled outputs is the sum of both
individual current limit points. The output current of the parallel combination is the algebraic sum of the individual current
readbacks.
The + OV and - OV terminals of output 1 should be wired to the + OV and - OV terminals of output 2. When programming
the overvoltage setpoint, set both outputs to the same overvoltage value. When resetting the overvoltage, first disable both
outputs by using the OUTPUT ON / OFF key or OUT comma nd. Next, reset both overvoltages. Finally, re-ena ble the
outputs with the OUTPUT ON/OFF key or OUT command.
Table 4-2. Maximum Allowable Voltage Setting
Output Type Maximum Low Range Voltage Maximum High Range Voltage
25W 7.07V 50.5V
50W 16.16V 50.5V
Note Below 4 V on 25 W outputs and 2 V on 50 W outputs, the downprogrammer cannot sink the maximum
rated current. (See Figures 4-2 and 4-3). To operate parallel outputs at voltages under 2.5 V, program
both outputs to the same voltage setting. Depending on the load, one output may operate in the
unregulated mode.
Output Connections and Operating Information
57
Page 58

CC Operation
For CC operation, set the output voltages as outlined in CV operation (page 57), or alternatively, program the voltage
settings of both outputs to the same voltage limit point. Then program the current of each output so that the sum of both
currents equals the total desired operating current. The simplest way to accomplish this is to program each output to one
half of the total desired operating current. Both outputs will operate in the CC mode.
Remote Sensing
If it is necessary to remote voltage sense at the load, parallel the sense leads of outp ut 1 with the sense leads of output 2 and
connect to the load as shown in Figure 4-12. The outputs can be programmed as previously described.
Figure 4-12. Parallel Connections with Remote Sensing
Specifications for Parallel Operation
Specifications for outputs operating in parallel can be obtained from the specifications for single outputs. Most
specifications are expressed as a constant or as a percentage (or ppm) plus a constant. For parallel operation, the percentage
portion remains unchanged while constant portions or any constants are changed as indicated below.
Current All parallel specifications referring to current are twice the single output
specification except for programming resolution which is the same for bo th
single output and parallel output operation.
Voltage All parallel specifications referring to voltage are the same as for a single
output except for CV load effect, CV load cross regulation, CV source effect,
and CV short term drift. Below 4 V on 25 W outputs and 2 V on 50 W
outputs, these are all twice the voltage programming accuracy (including the
percentage portion). CV load effect above 4 V on 25 W outputs and 2 V on
50 W outputs, could be twice the load effect specification for a single output.
CV output noise for output voltages less than 4 V on 25 W outputs, and 2 V
on 50 W outputs, may be slightly higher than the output noise for a single
output.
Load Transient Recovery
Time
350 µs maximum to recover within 100 mV of nominal value following a load change
within the range of 0 to full load.
58
Output Connections and Operating Information
Page 59

Series Operation
SHOCK HAZARD. Floating voltages must not exceed 240 Vdc. No output terminal may be more
diode will conduct
Connecting outputs in series provides a greater voltage capability than can be obtained from a single output. Because the
current is the same through each element in a series circuit, outputs connected in series must have equivalent current
ratings. Otherwise, the higher rated output could potentially damage the lower rated output by forcing excessive current
through it under certain load conditions.
Figure 4-13 shows an example of how to connect two outputs in series to a single load with local sensing. This
configuration applies to both CV and CC operating modes. Connecting the + load lead of output 2 directly to the
- V terminal of output 1 completes the series connection between the two outputs. Connecting the + S terminal of output 2
directly to the - S terminal of output 1 and removing the sense jumper (between + S and + V) on output 2 compensates for
the IR drop in the load lead from output 2 to output 1.
than 240 Vdc from chassis ground.
Connect in series only outputs that have equivalent curre nt ratings. Each output has a reverse voltage
protection diode across its output terminals. The current conducted by this diode is not internally
limited by the output. Therefore, never connect an output in such a way that this
current in excess of the rated current of the output since damage could result.
Figure 4-13. Series Connections with Local Sensing
CV Operation
For CV operation, first program the current setting of each output to the desired current limit point. Then program the
voltage of each output so that the sum of both voltages equals the total desired operating voltage. The simplest way to
accomplish this is to program each output to one half of the total desired operating voltage. Both outputs will operate in CV
mode.
Output Connections and Operating Information
59
Page 60
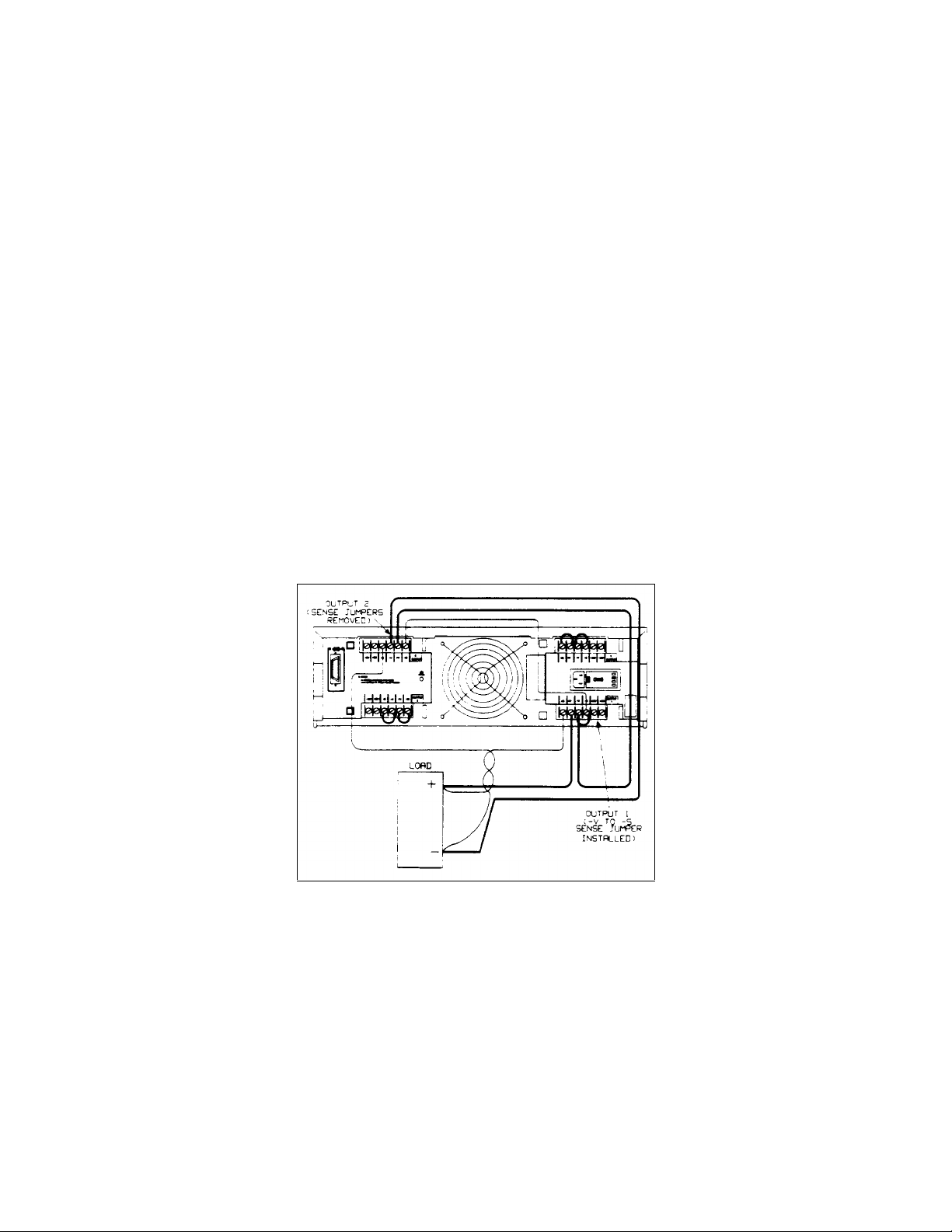
CC Operation
For CC operation, the current setting of each output must be programmed to the desired operating current. The sum of the
voltage settings determines the vo ltage limit point. As an example, one way to program the voltage of the output is to set
the voltage of each output to o ne half of the total voltage limit point. Then, at load voltages less than one half of the total
voltage limit point, one output will operate in CC mode while the other output will be conducting through its i nternal
reverse voltage protection diod e . At load voltages greater than one half the total voltage limit point, the output that was i n
CC mode will change to CV mode while the output that was conducting through its diode will regulate the current in CC
mode and provide the balance of the voltage required b y the load. Note that the total load voltage can be found by adding
the results of reading back the indi vidual series outputs only when neither reverse voltage protection diode is conduc ting.
When this diode is conductin g, the co rresponding output has reverse voltage acro ss it so that its voltage readback may not
be accurate.
When an output is conducting through its reverse voltage p rotection diode, the output will have a reverse voltage across its
output terminals with the - V terminal more positive than the + V terminal. This voltage will be maximum at the rated
current of the output. (See Figure 4-2 for reverse diode characteristic). Note that when an output conducts through this
diode, it will indicate CC mode even though it is not regulating the current or voltage. Also, note that the voltage readback
is not specified to indicate negative voltages although it will operate down to a limit of about - 0.176 V on the 25 W outputs
and -0.392 V on the 50 W outputs. These values will still be indicated even if the actual voltage is more negative.
Remote Sensing
If it is necessary to remote voltage sense at the load, connect the sense leads of output 1 and output 2 as shown in Figure 4-
14. Note that the + sense lead of output 2 must remain connected to the -sense terminal of output 1. The outputs may be set
as previously described.
Figure 4-14 Series Connections with Remote Sensing
Specifications for Series Operation
Specifications for outputs operating in series can be obtained from the specifications for single outputs. Most specifications
are expressed as a constant or a percentage (or ppm) plus a constant. For series operation, the percentage portion remains
unchanged while constant portions or any constants are changed as indicated below.
60
Output Connections and Operating Information
Page 61

Voltage All series specifications referring to voltage are twice the single output specification
except for programming resolution which is the same as for a single output.
Current All series specifications referring to current are the same as for a single output except
for CC load effect, CC load cross regulation, CC source effect, and CC short term drift
which are twice the current programming accuracy (including the percentage portion).
Load Transient
Recovery Time
Bi-Polar Operation
Figure 4-15 shows an example connecting the outputs of the power supply for bi-polar operation to test power FET’s
(PFET).
Great flexibility is achieved with this setup. The outputs of the po wer supp ly can be programmed as voltage or current
sources provid ing positive or nega tive voltages o r currents. By takin g measurements via internal readback circuitry in the
power supply, the outputs can be used as voltmeters or ammeters.
In order to properly measure the parameters of the PFET, it is desirable to be able to directly regulate any two of the bias
parameters of the PFET, while being able to measure a third. The setup shown in Figure 4-15 allows control of Vds and Ids
while measuring Vgs.
In this example, outputs 3 and 4 are connected to allow bipolar operation. Notice that the - S and - V leads, of outputs 3 and
4, are strapped together. The + S lead of V3 senses the voltage at the drain of the Device Under Test (DUT) and the + S
lead of output 4 senses the voltage at the source of the DUT. Outputs 1 and 2 are strapped to sense the gate to source
voltage.
Load transient recovery time is the same to within approximately twice the voltage
setting band since the output impedances of the series combination add together.
Figure 4-15. Bipolar Operation
Output Connections and Operating Information
61
Page 62

Page 63

5
Remote Operation
Introduction
Chapter 3 introduced you to the basics of remote operation and provided a few simple examples using a Series 200/300
computer as the GP-IB controller. This chapter contains all the information required to control your power supply remotely
and discusses in greater detail how each of the commands can be implemented. The material covered is intended for any
controller capable of using the GP-IB interface functions mentioned in Interface Functions on page 63.
Four major sub-sections are discussed. These are:
1. GP-IB Operation
2. Programming Syntax
3. Initial Cond itions
4. Power Supply Commands
The GP-IB section briefly describes the GP-IB interface functions to get you acquainted with remote programming using
the GP-IB. Under Programming Syntax, the syntax of all commands, the numeric data formats and the programmable
ranges for all models are given. Initial Conditions highlights the initial values of all the parameters at power-on. Power
Supply Commands will describ e all the commands which can be used to program the supply’s functions including status
reporting, error handling, protection features, and voltage and current programming. The power supply command s are
summarized in Appendix C.
The examples are writte n in a generic form to make adaptation to your controller easy. Yo u should be familiar with the use
of your controller and its instruction set and how the power supply commands can be incorporated in your controller
commands. If you are not familiar with the operation of the power supply, you are advised to read through Chapters 2
through 4 first.
GP-IB Operation
Interface Functions
Remote control is i mplemented by the GP-IB. It enables instructions to be sent from an external computer equipped with a
GP-IB interface. The power supply implements the following IEEE-488 Interface Functions:
SH1 - Source Handshake SR1 - Service Request
AH1- Acceptor Handshake RL1 - Remote/Local
T6 - Talker RL1 - Parallel Poll
L4 - Listener DC1 - Device Clear
The source handshake, acceptor handshake, talker and listener functions are implemented by the interface circuits of the
power supply and the controller. The ADDR annunciator indicates when the power supply is addressed to listen or talk.
(The talker function includes the Serial Poll, see page 64).
Service Request. This is a message which can be initiated by the power supply to request service from the controller.
When the supply is requesting service, it asserts the service request (SRQ) line on the GP-IB to interrupt the controller
providing the controller is configured to service interrupts. A service request can be generated whenever there is a fault on
one of the outputs (up to 4 outputs), a programming error has occurred, or at power on providing certain commands are
sent. Service request commands are discussed in detail in Service Request Generation on page 79.
The SRQ annunciator on the front panel display is turned on when the power supply is requesting service from the
computer and remains on until the controller conducts a serial p oll. A serial poll removes the service request and turns off
Remote Operation
63
Page 64

the SRQ annunciator regardless of whether the condition that caused the service request continues to exist. The service
request is also removed when you send the " CLR’’ command (see page 76).
Remote/Local. The power supply can receive programming information either from the GP-IB (remote) or from the front
panel (local). When the power supply is in remote, the state of the supply cannot be changed by using the front panel keys,
although the LCL key will remain enabled. Remote operation takes precedence over local operation, hence if the supply is
accepting commands remotely and you attempt to change it to local operation, the supply will not allow any local settings
and will remain in remote. You can prevent the front panel from sending programming information by sending the local
lockout command. This command is sent only from the GP-IB. If you change from local to remote or vice-versa, there will
be no change in the programmed settings.
Parallel Poll. Parallel Poll allows the controller to receive at the same time one bit of data from each of up to eight
instruments connected to the bus. Agilent power supplies designate bit #6, the RQS bit of the serial po ll register for this
operation. By checking the status of this bit, the computer can quickly determine which instruments on the bus requested
service. Once an instrument is identified, the computer can perform a serial poll to find out the exact cause of the request.
Parallel Poll does not reset this service request bit (RQS) in th e power supply.
Note IEEE-488 does not define what data an instrument should put on a bus in response to parallel poll. Many
instruments such as Agilent Technologies power supplies indicate the state of their RQS bit, but the
operator should not assume that all instrumen ts on the bus respond to parallel poll with their RQS bit.
Unless remotely configured, the power supply will respond with a 1 on one of the GP-IB data lines if it is requesting
service and its address is between 0 and 7. Addresses 0 through 7 define which data line (1 through 8) the supply will
respond on. If the address is set to 8 or greater, the supply will not respond unless remotely configured.
The power supply may be remotely configured to respond with a 0 or 1, on any of the data lines, to indicate that it is
requesting service. This is done in accordance with IEEE-488 1978.
Serial Poll. In a serial poll, the controller polls each instrument on the bus one at time. The power supply responds by
placing the contents of the eight-bit serial poll register on the GP-IB data lines. The Serial Poll register is discussed on
page 78 and defines the function of each of the bits. After the serial poll, the service request is cleared and the SRQ
annunciator at the front panel is reset (off). However, the cond ition that generated the service request may still be present.
See page 79.
Device Clear. The Device clear command is typically used in systems to send all devices in the system to a known state
with a single command. It may be implemented as an addressed or an unaddressed command. The power supply CLR
command performs the same function as Device Clear (see page 76).
GP-IB Address Selection
You can find out the present address or change the address of the supply by using the front panel ADDR key as described
in Chapter 3. Any address 0 through 30 is a valid address. If you program an address outside this range you will get a
number range error.
Note Care should be taken to not select the co ntroller address.
64
Remote Operation
Page 65

Power-On Service Request (PON)
The power supply can request service from the controller when the power is turned on. This request can be enabled or
disabled by sending a PON command (see page 80). When the request is enabled, the supply can generate an SRQ at
power-on or when there is a momentary loss in power. You can execute a serial poll to clear the service request. Table 5-7
details the conditions under which a PON command will generate an SRQ.
Note T he power supply has a non-volatile memory in which it stores certain system variables. Some of these
variables are the calibration constants, the present supply address, and the present setting of the PON
command.
Programming Syntax
The following paragraphs describe the syntax of the device command that is used to program your power supply. As shown
in Figure 5-1, the device command is a specific part of the program statement that your computer will accept. The first part
of the statement is computer as well as programming language specific. Figure 5-1 shows the structure of a typical
programming statement for an Agilent Series 200/300 computer. If you are using a different computer or programming
language, refer to your computer programming manual to determine the correct syntax for this portion of the program
statement. This section of the manual is only concerned with the device command portion (the part inside the quotes for
Series 200/300 computers with BASIC) of the program statement.
Figure 5-1. Typical Program Statement for Series 200 Computers
Table 5-1. Power Supply Commands
Command Header Output
Channel
Query accumulated status register ASTS? 1, 2, 3, 4 --- Q2
Return power supply to turn on state CLR --- --- C1
Turn calibration mode on or off CMODE --- 0,1 (OFF,ON) C2
Query if calibration mode is on CMODE? 1, 2, 3, 4 See Table 5-4 Q1
Set the state of outputs at power on DCPON --- 0,1 (OFF, ON) CC+
Query outputs power on state DCPON? --- ---
Set the reprogra mming delay time DLY 1, 2, 3, 4 0-32 C4
Query the setting of the delay time DLY? 1, 2, 3, 4 --- Q2
Turn front panel display on or off DSP --- 0,1(OFF,ON) C2
Display a string on front panel DSP --- ’’ST R I N G ’’ C6
Query if fro nt panel display is on DSP? --- --- Q1
Data Range
(Fig. 5-2)
2,3 (OFF, ON) CC-
Syntax
Remote Operation
65
Page 66

Table 5-1. Power Supply Commands (continued)
Command Header Output
Channel
Query present hardware error ERR? --- See Table 5-8 Q1
Query fault register FAULT? 1, 2, 3, 4 --- Q2
Query the model number of supply ID? --- --- Q1
Program the I DAC in counts IDAC 1, 2, 3, 4 See Service Manual C4
Query setting of I DAC in counts IDAC? 1, 2, 3, 4 --- Q2
Send data to calibrate I circuits IDATA 1, 2, 3, 4 See Table 5-4 C5
Sets output to high I cal. value IHI 1, 2, 3, 4 See Table 5-4 C3
Sets output to low I cal. value ILO 1, 2, 3, 4 See Table 5-4 C3
Query measured I output IOUT? 1, 2, 3, 4 See Table 5-4 Q2
Used to Calibrate I readback circuits IRDAT 1, 2, 3, 4 See Table 5-4 C5
Set output to + I readback high cal value IRHI 1, 2, 3, 4 See Table 5-4 C3
Set output to - I readback high cal value IRHN 1, 2, 3, 4 See T able 5-4 C3
Set output to - I readback low cal value IRLN 1, 2, 3, 4 See Table 5-4 C3
Set output to + I readback low cal value IRLO 1, 2, 3, 4 See Table 5-4 C3
Set full scale current range of output IRSET 1, 2, 3, 4 See Table 5-4 C4
Query full scale current range ISET? 1, 2, 3, 4 See Table 5-4 Q2
Set current of an output ISET 1, 2, 3, 4 See Table 5-4 C4
Query current of an output ISET? 1, 2, 3, 4 See Table 5-4 Q2
Increase or decrease output current by value ISTEP 1, 2, 3, 4 See Table 5-4 C4
Select which output will be metered METER --- 1-4 C2
Query which output is being metered METER? --- --- Q1
Send data to calibrate -I readback NIDAT 1, 2, 3, 4 See Table 5-4 C5
Enable overcurrent protection OCP 1, 2, 3, 4 0,1 (OFF,ON) C4
Query if OCP is enabled OCP? 1, 2, 3, 4 --- Q2
Reset overcurrent protection OCRST 1, 2, 3, 4 --- C3
Turn output on or off OUT 1, 2, 3, 4 0,1 (OFF,ON) C4
Query if output is on or off OUT? 1, 2, 3, 4 --- Q2
Perform overvoltage calibratio n OVCAL 1, 2, 3, 4 See Table 5-4 C3
Reset overvoltage circuit OVRST 1, 2, 3, 4 --- C3
Set overvoltage trip value OVSET 1, 2, 3, 4 See Table 5-4 C4
Query overvoltage trip value OVSET? 1, 2, 3, 4 See Table 5-4 Q2
Enable power on service request PON --- 0,1 (OFF,ON) C2
Query if PON is enabled PON? 1, 2, 3, 4 --- Q1
Recall voltage and current settings RCL --- 0-10 C2
Set readback DAC to a number of counts RDAC 1, 2, 3, 4 See Service Manual C4
Query readback DAC count setting RDAC? 1, 2, 3, 4 --- Q2
Query revision date of ROM ROM? --- Q1
Query revision date of secondary ROM SROM? 1, 2, 3, 4 --- Q2
Set causes for generating a service request SRQ --- 01,2,3 C2
Query causes which will generate an SRQ SRQ? --- --- Q1
Data Range
(Fig. 5-2)
Syntax
66
Remote Operation
Page 67

Table 5-1. Power Supply Commands (continued)
Command Header Output
Channel
Store present output state STO 0-10 C2
Query preset status of output STS? 1, 2, 3, 4 Q2
Perform self test on GP-IB interface TEST? . C1
Set bits in mask register UNMASK 1, 2, 3, 4 0-255 C4
Query bits set i n mask register UNMASK? 1, 2, 3, 4 Q2
Program the volta ge DAC in counts VDAC 1, 2, 3, 4 See Service Manual C4
Querys setting of voltage DAC in counts VDAC? 1, 2, 3, 4 Q2
Send data to calibrate the voltage circuits VDATA 1, 2, 3, 4 See Table 5-4 C5
Set output to high V calibratio n value VHI 1, 2, 3, 4 See Table 5-4 C3
Set output to low V calibration value VLO 1, 2, 3, 4 See Table 5-4 V C3
Query inputs of analog multiplexer VMUX? 1, 2, 3, 4 1-18 C4
Query measured value of an output VOUT? 1, 2, 3, 4 See Table 5-4 Q2
Calibrate the voltage readback circuitry VRDAT 1, 2, 3, 4 See Table 5-4 C5
Set output to V readback high cal value VRHI 1 2, 3, 4 See Table 5-4 C3
Set output to V readback low cal value VRLO 1, 2, 3, 4 See Table 5-4 C3
Set full scale voltage programming range VRSET 1, 2, 3, 4 See Table 5-4 C4
Query full scale voltage programming range VRSET? 1, 2, 3, 4 See Table 5-4 Q2
Set output voltage VSET 1, 2, 3, 4 See Table 5-4 Q2
Query se tting of output voltage VSET? 1, 2, 3, 4 See Table 5-4 Q2
Increase or decrease output voltage by value VSTEP 1, 2, 3, 4 See Table 5-4 C4
Figure 5-2 shows the possible syntax forms for the device commands that are used to program the power supply. Syntax
forms for the calibration commands that are discussed in Appendix A are also included. The oblong shape at the left of the
syntax forms contains the command header which must be entered as shown in Tables 5-1 and 5-2. Commands are accepted
in either uppercase or lowercase letters (ASCII characters). Circles contain characters that must be entered exactly as
shown. Characters such as a space <SP> or a comma are used to separate elements in the command string. Characters such
as a line feed < LF > or a semicolon are used to terminate the command string. Rectangles contain parameters that follow
the command header lines and arrows indicate the correct paths through the syntax diagrams.
Numeric Data
The power supply will accept numeric data in implicit point, explicit po int, or scientific notatio n. A general syntax diagram
for numeric data is included in Figure 5-2. Implicit point notation means that numbers do not contain a decimal point;
integers for example. Numbers written in explicit notation contain a deci mal point, such as 12.35. In scientific notation, the
letter E stands for "10 raised to". For example, 1.2E3 is read as 1.2 times 10 raised to the 3rd power, which equals 1,200.
Plus and minus signs are considered numeric characters and are optional. If you program a number with an accuracy that is
greater than the resolution of the supply, the number will automatically be rounded to the nearest multiple of the power
supply’s resolution. Table 5-1 gives the ranges for numeric data that is sent to the supply.
The power supply will also return nu meric data (ASCII characters) to your computer. The format of the numbers returned
depends upon the type of data requested. Table 5-2 gives the format for data returned to the computer in response to any of
the queries that are listed.
Data Range
(Fig. 5-2)
Syntax
Remote Operation
67
Page 68

68
Remote Operation
Figure 5-2 (Sheet 1 of 2). Syntax Forms For Power Supply Commands
Page 69

Figure 5-2 (Sheet 2 of 2). Syntax Forms For Power Supply Commands
Remote Operation
69
Page 70

Table 5-2. Power Supply Queries
Query Header
(Note 7)
Voltage Setting VSET? 1,2,3,4 SZD.DDD(Note 3) 0(Note 8) Q2
Current Setting ISET? 1,2,3,4 (Note 2) 10 mA (Note 8) Q2
Full Scale Current Range IRSET? 1,2,3,4 (Note 2) High (Note 8) Q2
Full Scale Voltage Range VRSET? 1,2,3,4 ZD.DDD (Note 8) High (Note 8) Q2
Voltage Output VOUT? 1,2,3,4 SZD.DDD (Note 3) -- Q2
Current Output IOUT? 1,2,3,4 (Note 2) -- Q2
OVP Setting OVSET? 1,2,3,4 SZZD.DD 55 V (Note 8) Q2
OC Protection On/Off OCP? 1,2,3,4 ZZD -- Q2
Output On/Off OUT? 1,2,3,4 ZZD -- Q2
Unmask Setting UNMASK? 1,2,3,4 ZZD 0 (Note 8) Q2
Delay Setting DLY? 1,2,3,4 <sp>ZD.DDD .02 (Note 8) Q2
Status STS? 1,2,3,4 ZZD -- Q2
Accumulated Status ASTS? 1,2,3,4 ZD -- Q2
Fault FAULT? 1,2,3,4 ZZD -- Q2
Error ERR? -- ZZD -- Ql
Service Request Se tting SRQ? -- ZZD 0 (OFF) Q1
Power-On SRQ On/Off PON? -- ZZD 0 (OFF) (Note 9) Q1
Display On/Off DSP? -- ZZD 1 (ON) Q1
Model Number ID? -- Agilent 662XA (Note
Selftest TEST? -- ZZD -- Q1
Calibration Mod e CMODE? -- ZZD 0 (OFF) Q1
DC Power On DCPON? -- ZZD 1 (ON) (Note 9) Q1
S = Sign Z = Digit with leading zeros put out as spaces D = Digit < sp > = space
NOTES:
1. Output channels 3 and 4 are not used in all modes. (See Table 5-4).
2. Current is SZD.DDDDD (0.5 A) & SZD.DDDDDD (15 mA) SZD.DDDD(2 A) & SZD.DDDDD
(0.2 A)
3. Voltage can be SZD.DDDD on 7 VR
4. "X" depends upon model.
5. A space is returned for a + sign.
6. All responses are followed by a <CR> and <LF> (EOI asserted with <LF>).
7. Spaces are allowed between the header and the question mark.
8. Unit powers up with values in state register 0. Table 5-3 gives initial factory settings.
9. Factory setting. P owers up to last stored value.
Order of Execution
When you send a set of instructions to the power supply, they are executed in the order in which they are received. The
power supply completes the execution of the present command before executing another command. To send more than one
command within the power supply command string, use a semicolon to separate the commands. This maximizes the rate at
which the power supply accepts commands.
Terminators
Terminators mark the end of a command string. As shown in Figure 5-2, the semicolon, line feed < LF >, and carriage
return line feed < CR > < LF > are the characters that indicate the end of a message to the power supply. When you are
using the Agilent Series 200 computer with BASIC to send a command using the standard format (see Figure 5-1), the
computer automatically sends < CR > < LF > on the data bus following the command.
Channel
(Note 1)
Response
(Notes 5 and 6)
4)
Initial Value Syntax
(Fig.
5-2)
-- Q1
70
Remote Operation
Page 71

Initial Conditions
Immediately after power on from the factory, the power supply automatically undergoes a self-test and sets all parameters
to the values contained in Table 5-3. The values in the first part of the table come from storage register 0 and were stored at
the factory. They will remain until STO 0 is used to change settings of the power on state. When the power supply is again
turned on, it will initialize its output s to the values in storage register 0.
Table 5-3. Initial Conditions
Parameter Inital Value
Voltage 0 V High Range
Current 10 mA High Range
Reprogramming Delay 20 mS
Store/Recall registers:
0-10: Voltage 0 V High Range
Current 10 mA High Range
Over Voltage (OV) 55 V (High Range)
Over Current Protection (OCP) Disabled
UNMASK register
SRQ 0 (Off)
Output Channels On
Front Panel Metering Output #1
Power Supply Address Last stored value (Factory set to 5)
Local Control Enabled
PON bit On
PON SRQ Off (0)
Cal Mode Off
Power Supply Commands
This section discusses the commands which yo u will use to program the supply’s voltage and current, protection circuits,
and enhanced features like storage and recall registers, and reprogramming delay. When programming, you should be
aware that the current, voltage and overvoltage ranges for each output of your supply may differ. Table 5-1 shows these
values for the power supply. If you send values out of these ranges, you will get a number range error. A summary of all
commands appears in Appendix C.
The output voltage of some output channels exceeds the safe operating limit of 42.2 V. To avoid any
tightened and terminal block covers are replaced before reapplying power.
Voltage Programming
To program voltage, send the output channel and the programmed value. In the example below, output l is programmed to 5
V.
The values you send must always be volts. For example if you want to program 450 mi llivolts, convert to volts and then
send the command:
electrical shock, program the voltage to zero volts or turn off ac input power before changing any rear
panel connections. Make certain all straps are properly connected, terminal block screws are securely
0 (cleared)
VSET 1,5
Remote Operation
71
Page 72

VSET 1,.45
If the output cha nnel is operating in constant vo ltage mode (CV annunciator on) then the actua l voltage is the programmed
voltage, but in CC mode of operation (CC annunciator on), the programmed volta ge is the voltage limit for that output.
When programming a value of voltage, the current setpoint will be changed if the total power is greater than the power
boundary (see Figure 4-2).
Example: ISET 4,1.5 sets current to 1.5 A
VSET 4,50 sets voltage to 50 V
Sending the VSET command caused the current ISET to be reduced to 1.03 A. This is an example of power limiting
changing a supply setting. When this occurs, the "couple parameter" bit (see Table 5-5) in the status register is set.
Table 5-4. Programmable Output Range
Model
Output Configuration
6625A / 6628 A 6626A / 6629A
OUTPUT OUTPUTS Low 0-7 V 0-15 mA
(0.460 mV)
1 1 & 2 High 0-50 V 0-0.5 A
(3.2 mV)
OUTPUT OUTPUTS Low 0-16 V 0.2 A
(1.0 mV)
2 3-4 High 0-50 V 0-2 A
(1,2-6628A) 1,2,3,4-6629A) (3.2 mV)
* The maximum programmable voltage values for each range are 1% higher than the rated voltage and the
maximum programmable current values for each range are 3% higher than the rated current.
** Each channel wakes up to values stored in state register 0. The factory set values are shown in the first
part of Table 5-3. All other registers are set to these settings. Vo latile registers 4-10 always power-up to
these conditions.
To readback the programmed voltage setting for output 1, send the query:
and address the supply to talk. If you want to know the value of the actual output voltage of output 1, send the query:
The results are placed on the GP-IB and read into the controller when the supply is addressed to talk.
Note T he power supply will round the VSET and ISET settings to the nearest multip le of their resolution.
Table 5-4 lists the average resolution of these settings.
Operating
Range *
VSET? 1
VOUT? 1
Output Volt
(Avg. Res.)
Output Curr **
(Avg. Res.)
(1 µA)
(33 µA)
(13 µA)
(131 µA)
72
Remote Operation
Page 73

Current Programming
To program the current, send the output channel and the programmed value in amps. In the example below, output 1 is
programmed to 15 mA.
ISET 1,0.015
The value you send must always be i n amps. For examp l e if you want to program 95 milliamps, convert to amps and then
send the command
ISET 1,.095
If the output channel is in constant current (CC) mode of operation, then the actual current is the programmed current but if
the output is in the CV mode, the programmed current is the current limit of that output.
When programming a value of current, the voltage set point can be changed if the total power is greater then the power
boundary (see Figure 4-2).
Example: VSET 4,50 Voltage set to 50 V
ISET 4,2 ISET to 2 A
Sending the ISET command caused the VSET to be reduced to 16.16 V. This is an example where power limiting changes
a supply setting. When this occurs, the "c oupled parameter" bit (see Table 5-5) in the status register is set.
To readback the programmed current for output 1, send the query and addressing the supply to talk.
ISET?
You can also instruct the supply to measure the actual output current at output channel 1 by sending the following query
and address the supply to talk.
IOUT? 1
The results are placed on the GP-IB and read into the controller.
Range Programming
The range can be set by using the VRSET or IRSET commands. The power supply will automatically pick the range that
the value sent will fit into.
Examples: VRSET 1,7 will select the 7 V range
VRSET 1,3.2 will select the 7 V range
VRSET 1,9.0 will select the 50 V range
VRSET 1,50.5 will select the 50 V range
IRSET 1,.015 will select the 15 mA range
IRSET 1,0 will select the 15 mA range
IRSET 1,.020 will select the 0.5 A range
IRSET 1,0.1 will select the 0.5 A range
Note Ranges will accept values up to 1% greater then full scale for voltage and 3 % for current. Larger
numbers will generate a number range error(s).
When going from the high range to the low range, the present setting must be within the boundary of the low range or the
setting will be reduced to the maximum of the low range. If the setting is changed the "couple parameter" bit (see Table
5-5) in the status register will be set to indicate the change.
Remote Operation
73
Page 74

Output On/Off
The OUT command disab les/enables an output channel of the power supply. It will not disturb any other programmed
function nor will it reset the protection circuits. You can control individual ou tputs with the OUT command as shown
below. For example, to disable output channel 1 send the following:
OUT 1,0
To enable outp ut channel 1 send the following command
OUT 1,1
You can find out the present state of output 1 by sending the query:
OUT? 1
and addressing the supply to talk. The response from the supply is either a "0" to indicate output 1 is off or a "1" to indicate
that the output is on. When disabled, the output behaves as if it were programmed to zero volts on the high voltage range
and 10 mA o n the high current range.
Overvoltage (OV) Protection
The programmable OV is a protection feature which can be set by the operator to protect the load against excessive voltage.
When the actual voltage exceeds the programmed overvoltage setting for a given output channel, the OV is tripped. The
OV circuit will fire the SCR crowbar which shorts across the output and the output assumes a low impedance state.
For example, to program the OV of output channel 1 to 9.5 V send the following command:
OVSET 1,9.5
To find out the OV setting for output channel 1 send the following query and address the supply to talk:
OVSET? 1
To enable an outp ut after it went into overvoltage, you must first remo ve the overvoltage condition and then send the OV
reset command.
To reset output 1 send:
OVRST 1
If you send the reset command without first removing the OV conditio n, the supply will fire the OV again.
Note If the programmable OV fails, the supply has a fixed OV circuit which will fire the SCR crowbar if the
voltage exceeds 120% of the maximum rated output. The fixed OV circuit will also fire the SCR crowbar
if the supply is off (line cord disconnected) and an external source is supplying voltage which exceeds
120% of the maximum rated output.
74
Remote Operation
Page 75

Overcurrent Protection (OCP)
The OCP is a protection feature employed by the power supply to guard against excessive output currents. When the output
enters the + CC mode and the OCP is enabled, the OCP circuit down programs the output voltage and disables the output.
To enable the OCP, for output channel 1, send the command
OCP 1,1
To disable the OCP, send the command
OCP 1,0
You can find out the OCP setting by sending the following query and addressing the power supply to talk.
OCP? 1
The response from the power supply is either a "0’’ to indicate that O CP is off or a ’’1" to indicate that it is on. To reset the
output channel after an overcurrent trip, you can either disable the OCP and send the reset command, or you can reduce the
output current below the programmed current and then send the reset command. To reset output 1, send the command:
OCRST 1
Note The supply can re port a fault cond ition when an output is in overvoltage or overcurrent. Alth ough the
OVRST and OCRST commands re-enable the output, they do not clear the fault register. As a
housekeeping measure, it is advisable to always clear the fault register by querying its value after an OV
or OC reset.
Multiple Output Storage & Recall
The power supply has 11 internal registers (0-10) each of which can store the voltage and current settings of all the outputs.
By storing voltage, volta ge range, current, current range and OV settings for all outputs and recalling them later, you can
have significant savings in programming time. (See Supplemental Characteristic s in Table 1-2). Upon shipment from the
factory, registers (1-10) contain values of 0 volts and 0 current (see Table 5-4).
Registers 0-3 are non-volatile. The y are limited to one STORE each. If more than one STORE is attempted, error 30
(STORE LIMIT) will result. The line must be turned off/on to re-enable these store locations. Register 0 is a special case
that also contains Delay, Mask. When the power supply is turned on, it will access register 0 for power-up settings.
Registers 4-10 (volatile) will be reinitialized to 0 vo lts and 10 mA (max OV & V, I ranges = HIGH) when power is cycled
on/off.
To store voltage and current settings, issue the store (STO) command and specify a register (0-10). For example, to store
the present setting of current and vo ltage of all outputs in register 2, send the following command:
STO 2
To set the power supply to the voltage, voltage ra nge, current, current r ange, and overvoltage settings stored in a register,
issue the recall (RCL) command followed by the desired register. For example to recall settings stored in register 2, send
the following command:
RCL 2
When a register is recalled, the o utputs will be set sequentially (output 1, output 2, etc.). If you attempt to recall a register
outside the 0 to 10 range, you will get a number range error (GP-IB code 5 in Table 5-8).
Remote Operation
75
Page 76

The Clear Command
This command will return the power supply to its power-on state and all parameters are returned to their initial power-on
values except for the following:
1. The store/recall registers are not cleared.
2. The power supply remains addressed to listen.
3. The PON bit in the serial poll register is cleared
To clear the power supply, send the following command:
CLR
Status Reporting
The power supply has the ability to report its internal stat us to the user whenever it is asked to do so . Depending on the type
of status the user requested, the supply will interrogate the status, accumulated status, mask, or fault registers present in
each output. The status register can report status independently (see page 76) or it can work together with the mask and
fault registers to report a fault (see page 77). The accumulated status register records every status condition the output
experienced since the time it was last read (see page 77). Figure 5-3 shows a conceptual model of the operation of these
registers.
The supply has one serial poll register which services all outputs and provides the user with other power supply statusrelated information as discussed in page 78.
Status Register. Each output channel of the power supp ly maintains its present status in an eight bit register. This status
register reports the status of the output c hannel whenever it is queried. A "1" in any of the bit positions indicates that the
condition is true. As long as the cond ition continues to be true, the bit will remain set. Assignments for the b its are shown in
Table 5-5.
Decoding of the reading is based on the weighted number placed on each bit of the eight bit status registers. For example,
bit position 5 in the register has a bit weight of 32 (see Table 5-5). Each bit is assigned to a particular condition and the
corresponding bit weight is used to identify that condition. When set, bit 5 indicates that the associated output is in the
unregulated state. If this is the only bit that is set, the number 32 will be returned when the output’s status register is
queried.
76
Remote Operation
Figure 5-3. Functional Relationship of Status Registers
Page 77

Table 5-5. Bit Assignment for the Status, Astatus, Fault, and Mask Registers
Bit Po sition 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Bit We ight 128 64 32 16 8 4 2 1
Meaning CP OC UNR OT OV -CC +CC CV
Where
CV = Cons tant Voltage Mode
+ CC = Positive Constant Current Mode
- CC = Negative Current Limit Mode
OV = Overvoltage Protection circuit tripped
OT = Over Temperature Protection circuit tripped
UNR = Unregulated Mode
OC = Over Current Protection tripped
CP = Coupled parameter (See Note)
Note: When the range is switched as discussed on page 73, or the power limit is exceeded (see pages 71 &
73), the CP bit is set. It is cleared when you send a voltage, current or range value that causes no other
changes.
To query an output cha nnel for its status, you must specify the output channel. For example, to find out the status at output
2 send the following query and address the supply to talk:
STS? 2
Accumulated Status Register. Each output chan nel of the power supply also maintains a cumulative status i n its
accumulated status (astatus) register. This register records every status condition the power supply output entered since it
was last queried. When queried, it returns a decimal number which is decoded as shown below. The astatus register is reset
to the present value of the status register after it is queried. The bits are assigned as in Table 5-5. Here is an example to help
you decode the decimal number (from 0 to 255) returned when the astatus register is queried. If the output channel was in
overvoltage since the last reading of the astatus register and that channel is presently operating in constant voltage mode,
the reading you will get when you query the register will be 9. To decode this we use Table 5-5.
9 = 8 + 1
OV + CV
For example, to query the astatus register of output 2, send the following query and address the supply to talk
ASTS? 2
The Mask and Fault Register. The fault register works in conjunction with the mask register. These are two eight bit
registers which report any fault cond ition on a particular output channel. The mask register is used to set up the conditions
that generate a fault which is latched in to the fault register. The user can then read the fault register to determine the fault.
When a bit in the fault register is set, the power supply can generate a service request for that output providing the service
request command on fault (SRQ 1 or SRQ 3) was previously sent. See page 79 for a discussion on service request.
To understand how these two registers work, we must include the status register in this discussion. Recall that the status
register takes its input from the power supply and the user cannot chan ge its contents. The mask register takes its inp uts
from the user, and the power supply cannot change its contents. The fault register takes its inputs from both the mask and
the status registers. You can find out the setting of the mask register of output 2 by sending the following query and
addressing the supply to talk:
UNMASK? 2
The response will be a numeric code between 0 and 255 which can be decoded by consulting Table 5-5. You can set the
conditions to generate a fault by setti ng (unmasking) one or more bits in the mask register. The conditions will remain
unmasked until you change them. To unmask conditions i n o utp ut 2 for example, send the following command:
Remote Operation
77
Page 78

UNMASK 2,XXX
where XXX specifies the numeric code (0 to 255) for the unmasked conditions (see Table 5-5). If during operation, the
output experiences any of the previously unmasked conditions, it will set the correspondin g bit(s) in its fault register.
Remember that the bits in the fault register can be set when there is a change in either the status register or the mask
register. Each output has its status, mask, and fault registers arranged as shown in Figure 5-3 and Table 5-5. The mask
register, which is set by the user, is used to specify which bits in the status register are enabled (unmasked) to set bits in the
fault register. A bit is set in the fault register when the corresponding bit in the status register changes from ’’0’’ to ’’1’’ a nd
the corresponding bit in the mask register is a "1". Also, if a bit in the status register is already set and then the
corresponding bit in the mask register is set (unmasked), the corresponding bit in the fault register will be set.
In addition, if both status and mask register bits remain set after the fault regi ster was read (and cleared), the fault register
will remain cleared as long as there are no changes in either the status or mask registers with the following exception.
Executing a VSET, ISET, RCL, OVRST, OCRST, or OUT on/off command, will cause the CV, + CC, - CC, or UNR bit
(as applicable) in the fault register to be set. Note that the fault register is cleared immediately after it is read.
As shown in Figure 5-3, if one or more bits in the fault register of a given output channel are set, then the FAU bit for that
output in the serial poll register will also be set and a service request may be generated (see page 79). To read the fault
register of output 2 and find out which bits are set, send the following query and address the supply to talk:
FAULT? 2
The power supply responds with a number which can be decoded from Table 5-5. For example, the number 9 (8 + 1)
indicates that the OV and the CV bits in the fault register are set.
Note If the condition(s) generating the fault(s) is (are) removed but the fault register is not read, the bit(s) in the
fault register will remain set.
The Serial Poll Register. The serial poll register is an 8 bit register which the supply uses to keep track of its internal
operating status and to determine the operating status of each of its outputs. Table 5-6 defines each bit.
Table 5-6. Bit assignment of the Serial Poll Register
Bit Po sition 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Bit We ight 128 64 32 16 8 4 2 1
Meaning PON RQS ERR RDY FAU 4 FAU 3 FAU 2 FAU 1
The first four bits (0 to 3) in the register tell whether or not a particular output has a fa ult. If t here is a fault in one of the
outputs, then the corresponding FAU bit will be set. Thus if output 1 has a fault, then FAU 1 will be set. In models with
only three outputs, FAU 4 will always be zero and in two o utput models, FAU 3 and FAU 4 will always be zero.
The RDY bit is set when processing is complete and is cleared when the supply is processing commands.
The ERR bit is set when a programming or hardware error occurs and is cleared when the error query (ER R? ) is received.
The error annunciator on the front panel informs the user when this bit is set or cleared.
The RQS bit is set when the power supply generates a service request and cleared after a serial poll is done (see page 79).
The PON bit is set at power on and cleared when a CLR command is sent.
78
Remote Operation
Page 79

Service Request Generation
When operating your supply, you may want it to request service every time a fault or a programming error condition
occurs. To do this you send a service request (SRQ) command. When the condition is true, the power supply responds by
setting the RQS bit in the serial poll register, setting the SRQ annunciator on the front panel, and issuing an SRQ o ver the
GP-IB.
The power supply can generate a service request for any of the following reasons: (refer to Table 5-7)
•
An Output Fault. If there is a fault on one or more of the output channels and you previously sent the SRQ 1 or
SRQ 3 command (see Service Request Enable/Disable information below), then an SRQ will be generated.
•
An Error . If there is an error (see Tables 5-8) and you previously sent the SRQ 2 or SRQ 3 command, (see
Service Request Enable/Disable information below), then the supply will generate a service request.
•
Power-on. At power-on, the PON bit of the serial poll register is set but the supply will only generate an SRQ if
you previously sent a PON 1 command.
•
Input Line Voltage Dropout. Same as power-on cond ition.
To find out the nature of the service request, you must do a serial poll. This will isolate the output that generated the request
by checking which of the FAU bits are set in the case of a fault, or checking to see if the error bit is set in the case of an
error. If the SRQ on faults was set, then send the fault q uery.
FAULT? 2 (using output 2 as an example)
and address the supply to talk if you want to find out which of the conditions you unmasked in Figure 5-3 are true. For
example if the supply was in overvoltage and that condition was unmasked then the response from the fault query will be
"8’’ (see Table 5-5).
Note When you query the fault, the fault register is cleared. Performing a serial poll will reset the RQS bit but
will not clear the fault register.
If the SRQ on error was set then you can send the error query ERR? and address the supply to talk. The response will
identify the error by its code (see Table 5-8).
Service Request Enable/Disable. You can query the status of the service request enable/disable function by sending
the query:
SRQ?
and addressing the power supply to talk. The response from the supply is one of the following:
0, 1, 2, or 3
0--indicates that the service request capability (except for power-on; see page 80) is disabled.
1--indicates that it is enabled for output fault conditions.
2--indicates that it is enabled for error conditions.
3--indicates that it is enabled for both fault and error conditions.
Remote Operation
79
Page 80

The ability to generate service requests can be enabled or disabled using the SRQ command as described below.
To disable the service request capability, except for power-on, send:
SRQ 0
To enable the service request capability for all output faults, send:
SRQ 1
To enable the service request capability for errors, send:
SRQ 2
To enable the service request capability for both faults and errors, send:
SRQ 3
The Power-On Service Request. You can also cause the power supply to request service every time it is switched on
or every time there is a temporary loss in power. To do this send the following command:
PON 1
If you want to disable this facility, send the command.
PON 0
If you want to find out if the power-on SRQ is enabled or disabled, send the following query:
PON?
and address the supply to talk. The supply will respond with a 1 or 0 as discussed above.
Note The power-on (PON) SRQ mode is stored in the non-volatile memory of the supply so that although the
supply may be switched off, it will remember the status of the last PON command at power-on and
respond accordingly.
Table 5-7 summarizes all the co nditions under which a service request will be generated.
Table 5-7. Conditions for Generating a Service Request
Condition Commands Sent State of
• Any
• Power-on
• Error
• Fault
PON SRQ
0 0 0
1 - 1
- 2 or 3 1
-1 or 3 1
RQS Bit
Reprogramming Delay
The power supply may switch modes or become unregulated momentarily after a new output value is programmed.
Because of their short duration, these cases may not ordinarily be considered a fault but the supply will recognize this
deviation and generate a fault signal. To prevent this, the reprogrammin g d e lay feature is implemented.
80
Remote Operation
Page 81

Reprogramming delay will delay the onset of certain fault conditions and prevent the power supply from registering a fa ult
when these conditions are true. When the delay is in effect, the CV, + CC, - CC and UNR bits of the status register are
masked and cannot communicate with t he mask and fault registers and the OCP function. This will prevent the supply from
registering a fault should any of these bits become set during the delay period. Reprogramming delay is initiated when any
of the following functions are executed:
VSET, ISET, RCL, OVRST, OCRST, OUT on/off
At power-on reprogramming delay is set to 20 mS. You can specify new values between 0 and 32 S in steps of 4 mS. If you
specify a value which is not a multiple of 4 mS, the suppl y will round off the set value to the nearest 4 mS multiple.
To program a new value of 80 mS in output 2 for example, send the following:
DLY 2,.08
If you send a value outside the 0 to 32 S range you will get a programming error. You may use the programming response
times in the specifications table to give you an id ea of a typical delay setting. However, the appropriate delay setting will
also depend on load capacitance, load resistance, and current limit setting. See page 53 for output capacitor considerations.
To query the reprogramming delay setting of a particular output channel, send the following query:
DLY? 2 (using output 2 as an example)
and address the supply to talk. The response will be a n umeric value between 0 and 32.
Display On/Off
When the display is on, the commands sent across the GP-IB may experience a slower processing time because the
processor must also spend time to monitor the outputs and update the display. You can shorten your command processing
time by turning off the display. To turn off the display, send the command :
DSP 0
To re-enable the display send the command:
DSP 1
You can also find out the status of the display by sending the following query and addressing the supply to talk:
DSP?
The response will be either a "1’’ or a "0’’.
Message Display Capa bility. The display command can also be used to display messages on the front panel. Messages
may consist of a maximum of twelve alphanumeric characters. Only upper case alpha characters, numbers, and spaces will
be displayed.
For example, to display the message "OUTPUT 2 OK", send the following command:
DSP "OUTPUT 2 OK’’
Note The BASIC programming statement for a series 200/300 computer would be as follows:
OUTPUT 705; "DSP""OUTPUT 2 OK"""
Remote Operation
81
Page 82

Other Queries
In the examples discussed above, you saw how to use queries for each function discussed. The following paragraphs
describe other queries which were not previously covered.
ERROR Query. The power supply can detect both programming and hardware errors. You can use either the front panel
(see page 89) or the GP-IB to find out the type of error. Upon detecting an error, the error annunciator on the front panel
and the ERR bit in the serial poll register will be set. When in local mode the supply will display the error name in response
to pressing the ERR key on the front panel. Over the GP-IB, only the error code will be returned. After a query, the error bit
is cleared. A description of these codes is given in Tables 5-8. To find out what the error is, send the following query and
address the supply to talk:
ERR?
The supply will respond with an error code number (see Table 5-8).
ID Query. If you want to know the model number of the power supply you are working with, you can send the ID? query
over the GP-IB. To do this send the following over the GP-IB and address the supply to talk.
ID?
The supply will respond with its model number.
Test Query. You can get the power supply to perform a limited self-test at any time during its operation by sending the
TEST? query over the GP-IB. This test does not affect the analog control circuits of the supply and it can be performed
while the outputs are connected to external circuits. For tests of the analog control circuits refer to Chapter 3. Responses to
the test query are described in Table 5-9. This test cannot be done from the front panel. To instruct the power supply to
carry out a self-test, send the following query and address the s upply to talk:
TEST?
Calibration Mode Query. To be able to calibrate your power supply, the calibration mode (CMODE) must be turned on
(See Appendix A for a detailed description of the calibration pr ocedure). To find out if the CMODE is on or off, send the
following query over the GP-IB and address the supply to talk:
CMODE?
The supply will respond with a ’’1" which indicates that CMODE. is on or a "0" which indicates that CMODE is o f f.
DCPON. The DCPON command sets the state of all outputs at power-on. You can specify if the outputs wake up enabled
or disabled when the unit is turned on. To enable all outputs at turn-on send:
DCPON 1
To disable all outputs at turn-on send:
DCPON 0
Note that these commands set the output voltage to zero and the output current to a slightly positive value when the
OUTPUT OFF command is issued. Therefore, the constant voltage feedback loop is active and the outputs are in constant
voltage mode when programmed “OFF”.
Starting with firmware revision A.00.04 and later, two additional commands let you set the output current to a slightly
negative val ue when the OUPU T OFF command is issued, causing the outputs to be in constant current mode when
programmed “OFF”. The benefit of being in constant current mode when the output is off is that if the load impedance and
the voltage and current settings are suc h that the unit is forced into constant current mod e at turn on, then the current
feedback loop will be active during the transition to OUTPUT ON, and there will be no output current overshoot due to
mode crossover.
82
Remote Operation
Page 83

To enable all outputs in constant current mode at turn on send: DCPON 2
To disable all outputs in constant c urrent mode at turn-on send: DCPON 3
Table 5-8. Error Messages
Front Panel
Response
NO ERROR 0 This is the response to the ERR? query when there are no errors.
INVALID CHAR 1 You sent the supply a character it did not recognize.
INVALID NUM 2 Format of your number is incorrect. Check number syntax.
INVALID STR 3 or 28 Occurs when you send a command the supply does not understand.
SYNTAX ERROR 4 Either too many parameters are sent without delimiters or the number
NUMBER RANGE 5 An out of range number was sent. Send a new number within the legal range.
NO QUERY 6 Computer addressed the supply to talk, but it did not first request data. Send query
DISP LENGTH 7 Quoted string exceeds the display length of 12 characters. Shorten string to a
GP-IB
Code
Explanation
representation is incorrect. Follow the Syntax Diagram in Figure 5-2. Check spaces
and delimiters.
first then address supply to talk.
maximum of 12 characters.
BUFFER FULL 8 This error may occur if too many numbers are sent. Error #4 or #5 may occur first.
EEPROM ERROR 9 EEPROM is not responding correctly to programming commands. An instrument
failure has occurred and service is required.
HARDWARE ERR 10 An output error has occurred in an unknown output. Service is required.
Remote Operation
83
Page 84

Table 5-8. Error Messages (continued)
Front Panel
Response
HDW ERR CH 1 11 Errors 11 through 14 refer to a specific output where there is an output error.
HDW ERR CH 2 12 Same as in Error #11.
HDW ERR CH 3 13 Same as in Error #11.
HDW ERR CH 4 14 Same as in Error #11.
NO MODEL NUM 15 The interface cannot find its model number. There may be a hardware failure or
CAL ERROR 16 You tried to use either a calibration command with CMODE off or the calibration
UNCALIBRATED 17 There is an incorrect checksum in the EEPROM possibly as a result of incorrect
CAL LOCKED 18 Calibration was attempted with the Calibration Jumper on the GP-IB board in the
GP-IB
Code
Explanation
Service is required.
the instrument may require reprogramming. Service is required.
failed while in CMODE. Enable CMODE and check numbers sent during
calibration. Also, there could be a hardware error.
calibration procedure. Recalibrate, and if the problem persists, your supply has a
hardware failure.
lockout position. Reposition jumper if desired . See Service Manual.
SKIP SELF TST 22 The self test jumper on the GP-IB board is in the Skip Self Test positio n. No self-
test was done. This is for diagnostics only. See Service Manual.
Table 5-9. TEST Responses
Code Explanation
0 This is the response to the TEST? query when there are no errors.
20 The timer has failed self-test. Refer to the troubleshooting section in the Service Manual.
21 The RAM has failed self-test. Refer to the troubleshooting section in the Service Manual.
27 The ROM has failed the checksum test. Refer to the troubleshooting section in the Service Manual.
29 There is an incorrect checksum in the EEPROM for non-volatile state storage. The non-volatile states 0-3
have not been loaded. Store new values, if problem persists , your supply has a hardware failure.
30 The store limit has been reached for CMODE, store states 0-3, DCPON, or SRQ. The power must be
turned off/on to reenable.
84
Remote Operation
Page 85

6
Local Operation
Introduction
Chapter 3 introduced you to the supply’s front panel controls and indicators to help you turn on the supply and perform the
checkout procedures that were given in that chapter. The following paragraphs describe how to use all of the front panel
controls and indicators. Most of the remote operations described in Chapter 5 can also be performed locally from the
supply’s front panel.
Local Mode
In order to use the front panel keys to control the supply, the local mode must be in effect. The local mode is in effect
immediately after power is applied. Table 5-3 lists the initial settings for all of the power supply’s functions when power is
initially applied. When the local mode is in effect (RMT annunciator off), the Output Function, System Functio n, and
Numeric Entry keys on the front panel (see Figure 6-1) can be used to operate the power supply.
In the remote mode (front panel RMT annunciator on), the front panel keys will have no effect on any of the supply’s
outputs and only the computer can con trol the supply. You can, however, still u se the front panel display to view the outp ut
voltage and current readings or the present settings for the selected output channel while t he s upply is in the remote mode.
You can return the supply to the local mode from the remote mode by pressing the LCL key provided that the local lockout
command has not been received from the GP-IB controller. Pressing the LCL key will also turn the supply’s display back
on if it was turned off with a DSP command during remote operation (see page 81). A change between the local and remote
modes will not result in a change in the power supply’s outputs.
Local Control Of Output Functions
The Output Function keys (see Figure 6-1) allow you to control the selected output. Figure 6-1 shows the annunciator arrow
over OUTPUT 2 indicating that output channel 2 is selected. Pressing the OUTPUT SELECT key selects the output
channels in forward (>) or reverse (<) sequence. Note that Figure 6-1 illustrates the front panel for the Agilent 6626A
supply which has four output annunciators. The front panel for Agilent Model 6625 is identical to Figure 6-1 except it has
two output annunciators.
General
The power supply will accept programming values directly in volts and amps. The programmable voltage, current, and
overvoltage ranges for the outputs of each model are given in Table 5-4. The power supply will round off the values
received to the nearest multiple of the resolution for that particular output. If you send a value out of the valid range, it will
not be executed and the ERR annunciator will come on. You can get a readout of the error on the display by pressing the
ERR key. For an out-of-range error, the error message ’’NUMBER RANGE" will be displayed.
When you press the VSET, ISET, or OVSET key, the output selected and the present setting for that function will be
displayed. You can change the setting using the numeric entry keys. Pressing the number keys will cause the present
numeric setting to become blank and be replaced with the new numbers on the display. You can use the Ï key to erase
previous keystro kes if you ma ke a mista ke.
Local Operation
85
Page 86

OUTPUT
ANNUNCIATOR
CHANNEL 1
DISPLAY
LOCAL MODE
KEY
OUTPUT FUNCTION KEYS
6626A SYSTEM DC POWER SUPPLY
VOLTS AMPS
45.153 14.235m
1 2 3 4 CV CC UNR OCP ERR RMT ADDR SRQ
LINE
ON
OFF
ENBLD-- OUTPUT --
LCL
SYSTEM OUTPUT ENTRY
ADDR
ERR
STO
RCL
RANGE
V/I
OVSET
OCP
RESET
VOLT
VOLT
CURR
CURR
OUTPUT
SELECT
VSET
ISET
OUTPUT
ON/OFF
789
456
123
0.
ENTER
SYSTEM FUNCTION KEYS NUMERIC ENTRY KEYS
Figure 6-1. Front Panel (Model 6626A shown)
Pressing the ENTER key will enter the values displayed for the function indicated, initiate that function, and return the
display to the metering mode in which the measured output voltage and current for the selected output are d isplayed.
Pressing the ENTER key without entering numbers will result in retention of the previous values and return to the metering
mode. You can also return to the metering mode at anytime by pressing the RESET key.
The RANGE V/I key is used to display the voltage and current range settings. The key toggles; pressing it will display the
range, pressing it again will put the display back to background metering. The range display shows the largest values of
voltage and current that can be set for the ranges presently set.
The voltage step and current step (arrow keys) are used to change voltage & current settings and voltage & current ranges.
There are 3 modes:
1. To use the step keys to immediately change the output settings, the background metering mode must be in affect.
2. To use the step keys to change the setting, the VSET or ISET key must be pressed first. The step keys can then be used to
adjust the setting. Press the ENTER key to change the actual setting.
3. To use the step keys to change the voltage or current ranges first press the RANGE V/I key. The step keys change the
range as long as the RANGE display is in effect.
Note The step keys change the voltage or current by 1 LSB each time they are pressed. If the key is held down
more than 1 second, the automatic step mode goes into effect. The step rate will start to increase from the
initial value after about 3 seconds.
Setting Voltage and Voltage Range
The selected output’s voltage is programmed locally using the VSET key. For example, program the voltage to 5.25 volts
by pressing:
VSET 5 . 2 5 ENTER
The front panel display then indicates the actual o utput voltage and current for the selected output.
86
Local Operation
Page 87

The voltage step keys can also be use d to change the voltage setting.
VSET ÑVOLT or ÒVOLT then ENTER
The voltage can be set in the immediate execute mode. This mode is in effect when background
metering is in effect. Pressing ÑVOLT or ÒVOLT will change t he setting
and the effect on the voltage and current can be observed on the display.
The voltage range can be changed by using the RANGE V/I key and the voltage step keys.
RANGE V/I ÑVOLT or ÒVOLT
The range will change as soon as one o f t he vo ltage step keys is pressed and the d isplay will be updated. If the voltage
setting is greater then the highest value of t he low range and the range is changed from high to low, the VSET will be
automatically reduced to the maximum voltage of the low range.
Setting Current and Current Range
The selected output’s current is programmed locally using the ISET key. For example, program the current to 1.5 amps by
pressing:
ISET 1 . 5 ENTER
The power supply will accept any programmed current between zero and the minimum programmable current and
automatically set the output to the minimum programmable current without causing a programming error. See Table 5-4.
The current step keys can also be used to change the current setting.
ISET ÑCURR or ÒCURR then ENTER
The current can be set in the immediate execute mode. This mode is in effect when background
metering is in effect. Pressing ÑCURR or ÒCURR will change the setting
and the effect on the voltage and current can be observed on the display.
The current range can be changed by using the RANGE V/I key and the current step keys.
RANGE V/I ÑCURR or ÒCURR
The range will change as soon as one of the current step keys is pressed and the display will be updated. If the current
setting is greater then the highest value of t he low range and the range is changed from high to low, the ISET will be
automatically reduced to the maximum current of the low range.
Enabling/Disabling an Output
The selected output channel can be turned on and off from the front panel. The OUTPUT ON/OFF key toggles the selected
output on and off. When an output is turned off, the message "DISABLED" will be displayed.
The OUTPUT ON/OFF key will not affect any other programmed functions nor will it reset an overvoltage or overcurrent
condition. An output disabled by the OUT PUT ON/OFF key will behave as if it were programmed to zero volts and 10 mA.
Local Operation
87
Page 88

Setting Overvoltage Protection
Programmable overvoltage protection (OVP) guards your load against overvoltage by crowbarring and downprogramming
the power supply output if the programmed overvoltage setting is exceeded.
A fixed OV circuit with a trip level about 20 percent above the maximum programmable voltage acts as a backup to the
programmable OVP. When overvoltage protection is activated, the output is shorted and the message ’’OVERVOLTAGE’’
will appear on the front panel display.
The selected output’s overvoltage setting is programmed locally using the OVSET key. For example, program the
overvoltage to 10.5 volts by pressing:
OVSET 1 0 . 5 ENTER
Resetting Overvoltage Protection
The condition that caused the OVP must fir st b e cleared and then the output can be returned to its previous state by pressing
the RESET key.
Enabling/Disabling Overcurrent Protection
The overcurrent protection feature guards against excessive output currents. When the output goes into the + CC mode and
OCP is enabled, the OCP circuit is activated which downprograms the output voltage and disables the output. For this
condition, the message ’’OVERCURRENT’’ appears on the front panel display.
The selected output’s overcurrent protection feature can be turned on and off from the front panel. The OCP key toggles the
selected output’s overcurrent protection circuit on and off. When it is on (enabled), the OCP ENBLD annunciator will be
on.
Resetting Overcurrent Protection
The condition that activated the OCP circuit must first be cleared and then the output can be returned to its previous state by
pressing the RESET key.
Local Control Of System Functions
The System Function keys consist of the ADDR, ERR, STO, and RCL keys as shown in Figure 6-1. These keys are
independent of the output selected and are used in setting the supply’s GP-IB address, displaying error messages, and
storing/recalling voltage and current settings for all of the supply’s output channels.
Setting the Supply’s GP-IB Address
As described in page 40, before you can operate the supply remotely, you must know its GP-IB address. You can find this
out locally from the front panel by pressing:
ADDR
The supply’s present address will appear in the display. Address 5 is the factory set address.
If you want to leave the address set at 5, you can return to the metering mode by pressing the METER key or you can press
another function key.
If you want to change the address, you can enter a new value.
Any integer from 0 through 30 can be selected.
88
Local Operation
Page 89

For example, you can change the address of your supply to 10 by pressing:
ADDR 1 0 ENTER
Displaying Error Messages
The power supply can detect both programming and hardware errors. Upon detecting an error, the ERR annunciator on the
front panel comes on and the ERR bit in the serial poll register will be set (see page 78).
When an error is detected, you can display the error message by pressing the ERR key. The power supply will return the
error message to the display and clear the error bit. For example, if you program a number that is not within the valid range,
the ERR annunciator will come on. You can d isplay the error message by pressing the ERR key. In this case, the error
message "NUMBER RANGE" will be displayed. Errors generated either locally from the front panel or remotely from the
GP-IB computer can be displayed by pressing the ERR key only when the supply is in the local mode. Pressing the ERR
key also clears the error bit so if you press ERR again, the message "NO ERROR" will appear. All error codes and
associated display messages are listed in Table 5-8.
Storing and Recalling Voltage and Current Settings for All Outputs
As described on page 75, the power supply has 11 internal registers for storing voltage and current settings of all outputs.
At power on each location contains zero volts and the minimum current limit (see initial conditions on page 71).
The STO and RCL keys allow you to stor e and recall voltage and current settings for all your output channels from any of
the 11 internal registers (numbered 0 through 10). For example, you can store the present settings of voltage and current for
all the output channels in internal register 2 by pressing:
STO 2 ENTER
You can change the settings of any of your supply’s outputs any number of times as required and then program them to the
settings stored in internal register 2 by pressing;
RCL 2 ENTER
The internal registers 0-3 will retain the settings when power is turned off. When power is turned off and then on again,
registers 4-10 will be reset to zero voltage and the current to 10 mA. Register 0 is the power on state. The power will be
programmed from values in register 0 at power on.
The advantages in using the i nternal registers are that command processing time is saved and repetitive programming of
different settings is simplified. The STO key can be used in conjunction with the OUTPUT ON/OFF key to store settings
while the outputs are disabled (OFF). These stored settings can be used later to program the outputs to the stored setting s
using the RCL and OUTPUT ON/OFF keys.
Local Operation
89
Page 90

Page 91
A
Alignment Procedures
Introduction
This appendix contains the software alignment procedures for the power supply. These supplies should be aligned twice a
year, or whenever certain repairs are made (see Service Manual).
The equipment that you need and the test setups to perform the alignment are also shown. A listing of the alignment
procedure appears at the end of Appendix A. Refer to Appendix C (Command Summary) for detailed explanations of the
commands used within the alignment program.
Because there are no internal or external hardware adjustments, your power supply can be aligned without removing the
covers or removing it from the cabinet if it is rack mounted. Alignment is performed by measuring actual output values and
sending them to the supply over the GP-IB.
Security against accidental alignment is available. A jumper inside the unit may be moved from NORMAL to CAL
LOCKOUT to disable all alignment commands. Access to this jumper requires opening the unit (see Service Manual).
If a number returned to the power supply is out of range while running the alignment program, the front panel ERR
annunciator will indicate an error. For example, an error will be created if the DMM is connected to measure a current
when a voltage measurement is anticipated by the program.
Note The memory used to store correction constants will accept and store data about 10,000 times, which is
more than sufficient for normal calibrations over the life of the instrument. However, do not put the unit
in a calibration loop that repeatedly turns the calibration mode on and off.
Test Equipment and Setup Required
The following test equipment is required for alignment:
1. A computer connected to the GP-IB connector on the back of the power supply.
2. An Agilent 3458A Digital Multimeter (DMM).
3. A precision 0.1 ohm ±0.003%, 5 A shunt resistor (4 terminal). Recommended--Leeds & Northrop Part Number 4221-B
(in oil bath) or Guildline - Part Number 9330/.l/Agilent (in air).
In line 130, change the constant SHUNT_r to the actual measured value of the shunt being used.
Figures A-1 through A-5 show setups required for aligning the power supply. You will be instructed by the program to
refer to a particular setup. Observe polarity when connecting the DMM.
Calibration Program
The following alignment program can be used as is, provided you have an HP Series 200/300 computer with the BASIC
programming language and an Agilent 3458A DMM. Refer to Appendix C (Command Summary) for further information
on the commands used within the program.
Ali g nment Procedures
91
Page 92

The program contains embedded comments (identified by a leading asterisk {! } ) which explain various sections and
procedures. To reduce keystroking, the program may be shortened to a minimum number of lines by eliminating these
comments.
The alignment program is available on a 5¼ floppy (Agilent P/N 06626-10001) or 3½ inch microfloppy (Agilent P/N
06626-10002). Both disks also contain a verification program, which tests the power supply's output programming and
readback accuracy to ensure that it is aligned correctly.
The program will automatically recognize what model power supply is being tested, the number of outputs the power
supply has, and which type output it is testing. Using this information, the program will calibrate each of the power supply.
After the program has finished calibratin g the power supply, it will store the calibration co nstants and turn off the
calibration mode.
Type in the program and press RUN.
The program first does some "house keeping".
It will clear the screen, and assign a number of Common Variables (lines 100 - 130).
The program next assigns the address of the power supply to 705 (line 160) and the address of the DMM to 722 (line 170).
It will then assign the CRT as the output device (line 180) and the value of the current shunt. Enter the exact measured
value at line 190.
The power supply is sent a CLR command (line 210), which will set it to the turn on state. It will then identify what model
power supply is being tested (lines 220 and 230).
Next it will preset the DMM (line 250) and set the DMM sample (line 260).
It will now place the power supply in calibration mode (line 300).
The program is now ready to perform the calibrations on the power supply.
The program will first perform a subprogram (called at line 360 and performed in lines 3420 - 3630) which will set up the
output parameters of the output under test.
The program will then calibrate its voltage programming and readback circuitry (the subprogram is called at lines 370 and
380, and performed in lines 1430 - 1920). During this subprogram, the controller will pause, and request that the user set up
the power supply and DMM referring to a figure in this Appendix. Press CONTINUE when ready.
Next the overvoltage circuitry will be calibrated (the subprogram is called in line 390, and performed in lines 1960 - 2070).
The current alignment tests on the 2 Amp, 50 W outputs are made using a shunt, be sure that the DMM is connected to the
HI and LO voltage input terminals when the shunt is used.
The current circuitry will be calibrated next (the subprograrn is called in lines 400 and 410, and performed in lines 2110 -
2700). During this subprogram, the controller will pause and request that the user set up the power supply and DMM
referring to a figure in this Appendix. Press CONTINUE when ready.
Finally the program will calibrate its current sink readback circuitry (performed in lines 2740 - 3380).
To perform the current sink readback alignment on the Agilent 6626A, outputs of equivalent current capability are used as
pairs. For example outputs 1 and 2 are used to test each other, the outputs 3 and 4 are used to test each other.
In order to perform the current sink readback alignment on the Agilent 6625A, the program automatically limits the current
of output 2 (the 50 W output) to 0.5 Amps (line 2780).
92
Alignment Procedures
Page 93

After testing of a channel is completed, the pro gram will check if any errors have occurred (the subprogram is called in line
850 and performed in lines 3670 - 3780). If an error has occurred, a message will be sent to the output device (CRT).
After all outputs are tested without errors, the CAL MODE will be turned off, and the calibration constants stored.
Figure A-1
Figure A-2
Figure A-3
Figure A-4
Figure A-1
Figure A-5
Figure A-2
Ali g nment Procedures
93
Page 94

Figure A-3
Figure A-4
94
Alignment Procedures
Figure A-5
Page 95

Alignment Program
10 ! This program called "ALIGN_6626" will align
20 ! the Agilent6625A, 26, 28 and 29A Power Supplies It
30 ! requires an Agilent3458A DMM and a four terminal
40 ! 0.1 ohm current shunt accurate to +/-50 ppm
50 !
60 ! May 06,l989 Rev A.03.01
70 !
80 Clear_screen ! Call program to clear display
90 !
100 COM /Specs/ Vrng_lo,Vrng_hi,Irng_lo,Irng_hi
110 COM /Ps/ Chan,Other_chan,@Ps,Model$[7]
120 COM /Outputs/ No_of_outputs
130 COM /Vm/ @Vm
140 COM /Shunt/ Shunt_r
150 !
160 ASSIGN @Ps TO 705 ! Set Supply address to 705
170 ASSIGN @Vm TO 722 ! Set DMM address to 722
180 PRINTER IS 1 ! Print to the CRT
190 Shunt_r= 1 ! Set value of curr ent shunt
200 !
210 OUTPUT @Ps;"CLR" ! Preset Supply to turn on state
220 OUTPUT @Ps;"ID?" ! Queries Supply model number
230 ENTER @Ps;Model$ ! Enter model number
240 !
250 OUTPUT @Vm;"PRESET NORM;TRIG HOLD" ! Preset DMM
260 OUTPUT @Vm; “NPLC 100” ! Set DMM sample
270 !
280 !
290 !
300 OUTPUT @Ps;"CMODE 1" ! Turn on Supply CAL mode
310 !
320 IF Model$="Agilent6625A" OR Model$='Agilent6628A" THEN No_of_outputs=2
330 IF Model$="Agilent6626A" OR Model$="Agilent6629A" THEN No_of_outputs=4
340 !
350 FOR Chan=1 TO No_of_outputs ! Loop to test all outputs
360 Get_data ! Call program with range data
370 Cal_voltage(Vrng_lo) ! Call program to cal low range voltage
380 Cal_voltage(Vrng_hi) ! Call program to cal high range voltage
390 Cal_overvoltage(Vrng_hi) ! Call program to cal overvoltage
400 Cal_current(Irng_lo) ! Call program to cal low range current
410 Cal_current(Irng hi) ! Call program to cal high range current
420 NEXT Chan ! Test next output
430 !
440 Chan=l ! Select channel to cal sink (-CC)
450 Other_chan=2 ! Select current source channel
460 Get_data ! Call program with range data
470 Cal_sink(Irng_lo,1) ! Call program to cal low range sink
480 ! 1 is + polarity for DMM
490 Chan=2 ! Select channel to cal sink (-CC)
500 Other_chan=l ! Select current source channel
510 Get_data ! Call program with range data
520 Cal_sink(Irng_lo,-1) ! Call program to cal low range sink
Ali g nment Procedures
95
Page 96

Alignment Program (continued)
530 ! -1 is reverse polarity, this saves
540 ! reversing leads as sink channel
550 ! becomes the source for other channel
560 Chan=1 ! Select channel to cal sink (-CC)
570 Other_chan=2 ! Select current source channel
580 Get_data ! Call program with range data
590 Cal_sink(Irng_hi,1) ! Call program to cal high range sink
600 !
610 Chan=2 ! Select channel to cal sink (-CC)
620 Other_chan=1 ! Select current source channel
630 Get_data ! Call program with range data
640 Cal_sink(Irng_hi,-1) ! Call program to cal high range sink
650 !
660 IF No_of_outputs=4 THEN ! Cal outputs 3 & 4
670 Chan=3 ! Select channel to cal sink (-CC)
680 Other_chan=4 ! Select current source channel
690 Get_data ! Call program with range data
700 Cal_sink(Irng_lo,1) ! Call program to cal low range sink
710 !
720 Chan=4 ! Select channel to cal sink (-CC)
730 Other_chan=3 ! Select current source channel
740 Cal_sink(Irng_lo,-1) ! Call program to cal low range sink
750 !
760 Chan=3 ! Select channel to cal sink (-CC)
770 Other_chan=4 ! Select current source channel
780 Cal_sink(Irng_hi,1) ! Call program to cal high range sink
790 !
800 Chan=4 ! Select channel to cal sink (-CC)
810 Other_chan=3 ! Select current source channel
820 Cal_sink(Irng_hi,-1) ! Call program to cal high range sink
830 END IF
840 :
850 Check_error ! Call error checking program
860 Cal_mode_off ! Call program to turn cal mode off
870 !
880 END
890 !
900 !
910 !
920 SUB Clear_screen ! Subprogram to clear display
930 OUTPUT 2;CHR$(255)&CHR$(75); ! Clear screen
940 SUBEND
950 !
960 !
970 !
980 DEF FNDcv ! Function to r at voltage
990 COM /Vm/ @Vm
1000 OUTPUT @Vm;"DCV" ! Set DMM to read DC voltage
1010 TRIGGER @Vm ! Take a voltage reading
1020 ENTER @Vm;Volts ! Enter the voltage
1030 RETURN Volts ! Return voltage reading
1040 FNEND ! End of voltage function
96
Alignment Procedures
Page 97

Alignment Program (continued)
1050 !
1060 !
1070 !
1080 DEF FNDci(I_range) ! Function to read current
1090 COM /Vm/ @Vm
1100 COM /Shunt/ Shunt_r
1110 IF I_range=2 THEN ! 2A must read across shunt
1120 Amps=FNDcv/Shunt_r ! Convert shunt voltage to Amps
1130 ELSE! ! <2A read direct from DMM
1140 OUTPUT @Vm;"DCI" ! Set DMM to read DC current
1150 TRIGGER @Vm ! Take a current reading
1160 ENTER @Vm;Amps ! Enter the current
1170 END IF
1180 RETURN Amps ! Return the current reading
1190 FNEND
1200 !
1210 !
1220 !
1230 SUB Output_on ! Subprogram to turn ON outputs
1240 COM /Ps/ Chan,Other_chan, @Ps, Model$[7]
1250 COM /Outputs/ No_of_outputs
1260 OUTPUT @Ps; OUT l,l;OUT 2,1 ! Turn on outputs 1 & 2
1270 IF No_of_outputs=4 THEN OUTPUT @Ps;"OUT 3,1;OUT 4,1"
1280 ! Turn on outputs 3 & 4
1290 SUBEND
1300 !
1310 !
1320 !
1330 SUB Output_off ! Subprogram to turn OFF outputs
1340 COM /Ps / Chan, Other_chan, @Ps, Mode1$ [ 7 ]
1350 COM /Outputs/ No_of_outputs
1360 OUTPUT @Ps;"OUT 1,0,OUT 2,0" ! Turn off outputs 1 & 2
1370 IF No_of_outputs=4 THEN OUTPUT @Ps; “OUT 3,0;OUT 4,0”
1380 ! Turn off outputs 3 & 4
1390 SUBEND
1400 !
1410 !
1420 !
1430 Cal_voltage : SUB Cal_voltage(V_range) ! Subprogram to cal voltage
1440 COM /Ps/ Chan,Other_chan,@Ps,Model$ [7]
1450 !
1460 IF V_range=50 THEN GOTO Cal_v ! Skip setup instructions
1470 Output_off ! Turn off all outputs
1480 Clear_screen
1490 PRINT "Set up output";Chan;"for voltage calibration
1500 PRINT
1510 PRINT " Use Fig A-1 of the Operating Manual"
1520 PRINT
1530 PRINT “ 3458A input is connected to VOLTAGE terminals”
1540 PRINT
1550 PRINT " The current shunt is NOT used"
1560 PRINT
Ali g nment Procedures
97
Page 98

Alignment Program (continued)
1570 PRINT "Press CONTINUE when ready
1580 PAUSE
1590 Output_on
1600 !
1610 Cal_v: !
1620 Clear_screen
1630 PRINT "Calibrating the";V _range;"volt range programming”
1640 !
1650 OUTPUT @Ps;"VRSET" ;Chan,V_range ! Set voltage range
1660 !
1670 OUTPUT @Ps; VLO";Chan ! Set to low output voltage
1680 WAIT 1 ! Wait for supply to stabilize
1690 Vlo=FNDcv ! Read low voltage
1700 !
1710 OUTPUT @Ps; “VHI” ;Chan ! Set to high output voltage
1720 WAIT 1 ! Wait for supply to stabilize
1730 Vhi=FNDcv ! Read high voltage
1740 !
1750 OUTPUT @Ps; “VDATA” ;Chan, Vlo, Vhi ! Send output voltage data
1760 !
1770 Clear_screen
1780 PRINT "Calibrating the";V_range,'volt range readback"
1790 !
1800 OUTPUT @Ps; VRLO";Chan ! Set low readback voltage
1810 REPEAT ! Wait for supply to finish
1820 UNTIL BIT(SPOLL(@Ps),4) ! Finished when Bit 4 goes true
1830 Vrlo=FNDcv ! Read low output voltage
1840 !
1850 OUTPUT @Ps; “VRHI”;Chan ! Set high readback voltage
1860 REPEAT ! Wait for supply to finish
1870 UNTIL BIT(SPOLL(@Ps),4) ! Finished when Bit 4 goes true
1880 Vrhi=FNDcv ! Read high output voltage
1890 !
1900 OUTPUT @Ps; “VRDAT”; Chan, Vrlo, Vrhi ! Send voltage readback data
1910 !
1920 SUBEND
1930 !
1940 !
1950 !
1960 Cal_overvoltage:SUB Cal_overvoltage(V_range) ! Sub program to cal OV
1970 COM /Ps/ Chan,Other_chan,@Ps,Model$[7]
1980 !
1990 Clear_screen
2000 PRINT "Calibrating the Overvoltage circuit
2010 !
2020 OUTPUT @Ps;"VRSET";Chan,V_range ! Set voltage range
2030 OUTPUT @Ps;"OVCAL";Chan ! Calibrate Overvoltage
2040 REPEAT ! Wait for supply to finish
2050 UNTIL BIT(SPOLL(@Ps),4) ! Finished when Bit 4 goes true
2060 !
2070 SUBEND
2080 !
98
Alignment Procedures
Page 99

Alignment Program (continued)
2090 !
2100 !
2110 Cal_current: SUB Cal_current(I_range) ! Subprogram to cal current
2120 COM /Ps/ Chan,Other_chan,@Ps,Model$[7]
2130 !
2140 IF I_range= .5 THEN GOTO Cal_i ! Skip setup instructions
2150 !
2160 Output_off
2170 !
2180 Clear_screen
2190 PRINT "Set up output";Chan;"for";I_range;”A current calibration”
2200 PRINT
2210 IF I_range=2 THEN ! If the next cal range is 2
2220 ! amps then print this message
2230 PRINT " Use Fig A-3 of the Operating Manual"
2240 PRINT
2250 PRINT “3458A input is connected to VOLTAGE terminals”
2260 PRINT
2270 PRINT “The current shunt IS used”
2280 ELSE ! If not 2 amps then print this
2290 PRINT “Use Fig A-2 of the Operating Manual”
2300 PRINT
2310 PRINT “3458A input is connected to CURRENT terminals”
2320 PRINT
2330 PRINT “The current shunt is NOT used”
2340 END IF
2350 PRINT
2360 PRINT “Press CONTINUE when ready”
2370 PAUSE
2380 Output_on
2390 !
2400 Cal_i : !
2410 Clear_screen
2420 PRINT "Calibrating the";I_range;"A current programming
2430 !
2440 OUTPUT @Ps;"IRSET";Chan,I_range ! Set current range
2450 OUTPUT @Ps;''ILO'';Chan ! Set output current low
2460 WAIT 1 ! Wait for supply to stabilize
2470 Ilo=FNDci(I_range) ! Read low output current
2480 !
2490 OUTPUT @Ps;"IHI";Chan ! Set output current high
2500 WAIT 1 ! Wait for supply to stabilize
2510 Ihi=FNDci(I_range) ! Read high output current
2520 !
2530 OUTPUT @Ps;”IDATA”;chan,Ilo,Ihi ! Set output current data
2540 !
2550 Clear_screen
2560 PRINT 'Calibrating the";I_range;"A current readback"
2570 !
2580 OUTPUT @Ps;"IRLO";Chan ! Set low readback current
2590 REPEAT ! Wait for supply to finish
2600 UNTIL BIT(SPOLL(@Ps),4) ! Finished when Bit 4 goes true
Ali g nment Procedures
99
Page 100

Alignment Program (continued)
2610 Irlo=FNDci(I_range) ! Read low output current
2620 !
2630 OUTPUT @Ps;"IRHI";Chan ! Set high readback current
2640 REPEAT ! Wait for supply to finish
2650 UNTIL BIT(SPOLL(@Ps),4) ! Finished when Bit 4 goes true
2660 Irhi=FNDci(I_range) ! Read high output current
2670 !
2680 OUTPUT @Ps;"IRDAT";Chan,Irlo,Irhi ! Send current readback data
2690 !
2700 SUBEND
2710 !
2720 !
2730 !
2740 Cal_sink SUB Cal_sink(I_range,Polarity) ! Subprogram to cal -CC
2750 COM /Ps/ Chan,Other_chan,@Ps,Model$[7]
2760 !
2770 IF I_range= .5 THEN GOTO Sink_rb ! Skip setup instructions
2780 IF Model$="Agilent6625A" AND I_range=2 THEN I_range= .5
2790 ! If a 6625A, 2A output will be
2800 ! set to 5A to match output 1
2810 IF Chan=2 OR Chan=4 THEN GOTO Sink_rb ! Skip setup instructions
2820 !
2830 Output_off
2840 Clear_screen
2850 PRINT “Set up output';Cha n;”for ;I_range; “A current SINK cal”
2860 PRINT
2870 PRINT “ Connect outputs”;Chan; “and” ;Other_chan; “together as in”
2880 !
2890 IF I range=2 THEN ! If it is 2A output use setup 5
2900 PRINT " Fig A-5 of the Operating Manual'
2910 PRINT
2920 PRINT " 3458A input is connected to VOLTAGE terminals"
2930 PRINT
2940 PRINT " The current shunt IS used for this part"
2950 PRINT " of the alignment"
2960 ELSE ! If not 6626A 2A use setup 4
2970 PRINT “Fig A-4 of the Operating Manual”
2980 PRINT
2990 PRINT “3458A input is connected to CURRENT terminals”
3000 PRINT
3010 PRINT " The current shunt IS NOT used"
3020 END IF
3030 PRINT
3040 PRINT “The sink readback of both outputs”
3050 PRINT “will be aligned with this setup”
3060 !
3070 PRINT
3080 PRINT "Press CONTINUE when ready”
3090 PAUSE
3100 !
3110 Sink_rb
3120 Clear_screen
100
Alignment Procedures
 Loading...
Loading...