Page 1
SERVICE GUIDE
for Agilent 6610xA
Power Modules
Serial Numbers:
Agilent Model 66101A: US34440101 and up
Agilent Model 66102A: US34210101 and up
Agilent Model 66103A: US34210101 and up
Agilent Model 66104A: US34450101 and up
Agilent Model 66105A: US34210101 and up
Agilent Model 66106A: US34210101 and up
For instruments with higher serial numbers,
a change page may be included.
For instruments with lower serial numbers,
refer to Appendix A.
Agilent Part No. 5959-3364 Printed in USA
Microfiche Part No. 5959-3365 Update: June, 2000
Page 2
CERTIFICATION
Agilent Technologies certifies that this product met its published specifications at time of shipment from the factory. Agilent
Technologies further certifies that its calibration measurements are traceable to the United States National Bureau of
Standards, to the extent allowed by the Bureau’s calibration facility, and to the calibration facilities of other International
Standards Organization members.
WARRANTY
This Agilent Technologies hardware product is warranted against defects in material and workmanship for a period of three
years from date of delivery. Agilent software and firmware products, which are designated by Agilent Technologies for use
with a hardware product and when properly installed on that hardware product, are warranted not to fail to execute their
programming instructions due to defects in material and workmanship for a period of 90 days from date of delivery. During
the warranty period Agilent Technologies will, at its option, either repair or replace products which prove to be defective.
Agilent Technologies does not warrant that the op eration of the software, firmware, or hardware shall be uninterrupt ed or
error free.
For warranty service, with the exception of warranty options, this product must be returned to a service facility designated
by Agilent Technologies. Customer shall prepay shipping charges (and shall pay all duty and taxes) for products returned to
Agilent Technologies for warranty service. Except for products returned to Customer from another country, Agilent
Technologies shall pay for return of products to Customer.
Warranty services outside the country of initial purchase are included in Agilent Technologies ’ product price, only if
Customer pays Agilent Technologies international prices (defined as destination local currency price, or U.S. or Geneva
Export price).
If Agilent Technologies is unable, within a reasonable time to repair or replace any product to condition as warranted, the
Customer shall be entitled to a refund of the purchase price upon return of the product to Agilent Technologies.
LIMITATION OF WARRANTY
The foregoing warranty shall not apply to defects resulting from improper or inadequate maintenance by the Customer,
Customer-supplied software or interfacing, unauthorized modification or misuse, operation outside of the environmental
specifications for the product, or improper site preparation and maintenance. NO OTHER WARRANTY IS EXPRESSED
OR IMPLIED. AGILENT TECHNOLOGIES SPECIFICALLY DISCLAIMS THE IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF
MERCHANTABILITY AND FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE.
EXCLUSIVE REMEDIES
THE REMEDIES PROVIDED HEREIN ARE THE CUSTOMER’S SOLE AND EXCLUSIVE REMEDIES. AGILENT
TECHNOLOGIES SHALL NOT BE LIABLE FOR ANY DIRECT, INDIRECT, SPECIAL, INCIDENTAL, OR
CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES, WHETHER BASED ON CONTRACT, TORT, OR ANY OTHER LEGAL THEORY.
ASSISTANCE
The above statements apply only to the standard product warranty. Wa rranty options, extended support contracts, product
maintenance agreements and customer assistance agreements are also available. Contact your nearest Agilent
Technologies Sales and Service office for further information on Agilent Technologies’ full line of Support Programs.
2
Page 3
SAFETY SUMMARY
The following general safety precautions must be obser ved during all phas es of oper ation of this power module.
Failure to comply with these precautions or with specific warnings elsewhere in this guide violates safety
standards of design, manufacture, and intended use of the power module. Agilent Technologies assumes no
liability for the user’s failure to comply with these requirements.
GROUND THE POWER MODULE.
When installed in a properly wired mainframe, this product is a Safety Class 1 instrument (provided with a protective earth
terminal). To minimize shock hazard, the mainframe must be connected to an electrical ground. The mainframe must be
connected to the a c power supply mains through a three-conductor power cable , with the third wire firmly connected to an
electrical ground (safety ground) at the power outlet. Any interruption of the protective (grounding) conductor or
disconnection of the protective earth terminal will cause a potential shock hazard that could result in personal injury.
DO NOT EXCEED INPUT RATINGS.
The mainframe is equipped with a power line filter to reduce electromagnetic interference and must be connected to a
properly grounded receptacle to minimize electric shock hazard. Operation at line voltages or frequencies in excess of those
stated on the line rating label may cause leakage currents in excess of 5.0 mA peak.
DO NOT OPERATE IN AN EXPLOSIVE ATMOSPHERE.
Do not operate the power module in the presence of flammable gases or fumes.
BEFORE APPLYING POWER.
Verify that the power module line voltage switch is set to match the available line voltage.
SAFETY SYMBOLS.
Instruction manual symbol: the product will be marked with this symbol when it is necessary for the user to
refer to the instruction manual (refer to Table of Contents) .
Indicates hazardous voltages.
Indicate earth (ground) terminal.
The WARNING sign denotes a hazard. It calls attention to a procedure, practice, or the like, which, if not
correctly performed or adhered to, could result in personal injury. Do not proceed beyond a WARNING
sign until the indicated conditions are fully understood and met.
The CAUTION sign denotes a hazard. It calls attention to an operating procedure, or the like, which, if
not correctly performed or adhered to, could result in damage to or destruction of part or all of the
product. Do not proceed beyond a CAUTION sign until the indicated conditions are fully understood and
met.
Power modules that appear damaged or defective should be made inoperative and secured against unintended operation
until they can be repaired by qualified service personnel.
3
Page 4

Printing History
The current edition of this guide is indicated belo w. Reprints of this guide containing minor corrections and updates may
have the same printing date. New editions are identified by a new printing date and, in some cases, by a new part number.
A new edition incorporates all new or corrected material since the previous edition. Changes to the guide occurring
between editions are covered by change sheets shipped with this guide. Also, if the serial number prefix of your power
module is higher than those listed on the title page of this guide, then it may or may not include a change sheet. That is
because even though the higher serial prefix indicates a design change, that change may not affect the content of the guide.
Edition 1 . . . . October, 1993 (Agilent Model 6610xA)
Update . . . . . June, 2000
Copyright 1993, 2000 Agilent Technologies, Inc.
This document contains proprietary information protected by copyright. All rights are reserved. No part of this document
may be photocopied, reproduced, or translated into another language without pr ior consent of Agilent Techno logies The
information contained in this document is subject to change without notice.
4
Page 5

Table of Contents
Overview.................................................................................................................................................................................. 7
About This Manual............................................................................................................................................................... 7
Related Documents........................................................................................................................................................... 8
Revisions and Updates.......................................................................................................................................................... 8
Manual.............................................................................................................................................................................. 8
Firmware........................................................................................................................................................................... 8
Safety Considerations........................................................................................................................................................... 9
Electrostatic Discharge......................................................................................................................................................... 9
Service Tools and Equipment............................................................................................................................................... 9
Verification and Performance Tests....................................................................................................................................11
Operation Verification Tests...............................................................................................................................................11
Performance Tests..............................................................................................................................................................11
Measurement Techniques............................................................................................................................................... 12
Setup for Most Tests................................................................................................................................................... 12
Current-Monitoring Resistor....................................................................................................................................... 12
Programming.................................................................................................................... .............................................. 12
Constant Voltage (CV) Tests.......................................................................................................................................... 13
CV Setup.....................................................................................................................................................................13
Voltage Programming/Readback Accuracy................................................................................................................13
CV Load Effect........................................................................................................................................................... 13
CV Source Effect........................................................................................................................................................ 14
CV Noise (PARD)...................................................................................................................................................... 14
Transient Recovery Time............................................................................................................................................14
Constant Current (CC) Tests........................................................................................................................................... 15
CC Setup..................................................................................................................................................................... 15
Current Programming/Readback Accuracy................................................................................................................. 15
CC Load and Line Regulation .................................................................................................................................... 15
CC Load Effect........................................................................................................................................................... 16
CC Source Effect........................................................................................................................................................ 16
CC Noise (PARD)......................................................................................................................................................17
Troubleshooting.................................................................................................................................................................... 25
Troubleshooting Sequence..................................................................................................................................................25
Accessing the Flowcharts.................................................................................................................................................... 25
If You Experienced a Selftest Failure or RunTime Error Message................................................................................. 26
If You Experienced Other Problems With the Module................................................................................................... 26
Test Points..........................................................................................................................................................................48
Built-In Test Functions....................................................................................................................................................... 48
EEPROM Troubleshooting and Initialization.....................................................................................................................51
Troubleshooting.............................................................................................................................................................. 51
Initialization.................................................................................................................................................................... 51
Disassembly Procedures..................................................................................................................................................... 56
Removing the Module and Module Connector............................................................................................................... 56
Removing the Cover.......................................................................................................................................................56
Removing the Fan........................................................................................................................................................... 56
Removing the Front Panel Assembly..............................................................................................................................57
Removing the Power Board............................................................................................................................................ 57
Removing the Bias Board............................................................................................................................................... 57
Removing the Front Panel Board.................................................................................................................................... 57
5
Page 6

Installing the Power Board.............................................................................................................................................58
Installing the Bias Board ................................................................................................................................................58
Installing the Front Panel Board and Front Panel Assembly.......................................................................................... 59
Installing the Fan............................................................................................................................................................59
Installing the Cover.........................................................................................................................................................59
Theory of Operation............................................................................................................................................................. 61
AC Input and Bias Supplies................................................................................................................................................ 61
Microprocessor Circuits......................................................................................................................................................61
CV/CC DACs.....................................................................................................................................................................61
CV Amplifier...................................................................................................................................................................... 63
CC Amplifier...................................................................................................................................................................... 63
OR Gates ............................................................................................................................................................................ 63
Pulse-Width Modulator, FETS, and Isolation Transformer................................................................................................ 64
Downprogrammer Circuit................................................................................................................................................... 64
Readback Multiplexer......................................................................................................................................................... 64
OV Circuit..........................................................................................................................................................................65
Replacement Parts................................................................................................................................................................67
Diagrams ............................................................................................................................................................................... 83
Schematic Sheets................................................................................................................................................................ 83
Component Location Diagrams.......................................................................................................................................... 83
Schematic Notes.................................................................................................................................................................84
Manual Backdating............................................................................................................................................................ 97
Index.................................................................................................................................................................................... 99
6
Page 7

1
Overview
About This Manual
This manual is a complete guide for servicing the Agilent 6610xA Power Modules. Troubleshooting information for the
Agilent 66000A MPS Mainframe is provided in the mainframe service manual (see "Related Documents"), which should be
used with this manual.
Note Troubleshooting the Agilent 6610xA Power Modules requires the use of one working Agilent 66000A
MPS Mainframe.
This manual is organized into the following major sections:
■ Overview discusses safety and equipment considerations to be aware of when troubleshooting. It also lists the tools and
equipment required for troubleshooting.
■ Verification and Performance consists of a series of tests that are used to verify....
■ Troubleshooting procedures systematically verify selected circuits to isolate the cause of a problem. Suggestions fo r
remedying the problem are also provided. The following troubleshooting procedures are provided:
❏ Overall
❏ Microprocessor
❏ Error Messages
❏ Overvoltage Circuit
❏ Output Circuit
❏ CV and CC Circuits
❏ Downprogrammer Circuits
❏ DAC Circuit
❏ Readback Circuit
Disassembly procedures are provided at the end of the chapter.
■ Theory of Operation provides a brief description of the overall operation of the power module.
■ Replacement Parts lists part numbers for electrical components and miscellaneous chassis parts.
■ Schematics and component location diagrams are provided as an aid in troubleshooting and repair.
Overview
7
Page 8
Related Documents
The following documents are related to this manual:
Manual Part Number
Agilent 66000A MPS Mainframe
Installation Guide
Agilent Series 6610xA MPS Power
Modules User’s Guide
Agilent Series 6610xA MPS Power
Modules Programming Guide
Agilent Series 66000A MPS
Mainframe Service Manual
Revisions and Updates
66000-90001 Provides product specifications, installation, and
5959-3386
5959-3362
66000-90003 Provides replaceable-parts lists, circuit diagrams, and
Description
connection information.
Describes the operation of the MPS Power Modules.
Describes SCPI programming commands, status
reporting.
verification procedures for the Agilent Series 66000A
MPS Mainframe.
Manual
Agilent Technologies instruments are identified by a two-part, ten-character serial number, such as 3246A-00517. The first
five characters (e.g. 3246A) are the serial prefix, which is the same for all identically made instruments. The last five digits
(e.g. 00517) are a unique serial number assigned to each instrument. If a significant design change is made, the prefix
changes but the last five numbers co ntinue in sequence.
This manual applies to Agilent 6610xA Power Modules with the same serial prefixes and serial numbers equal to or higher
than the ones shown on the title page. If the prefix number on your power module is higher than the one on the title page,
then the module was made after publication of the manual and may have hardware and/or firmware differences not covered
in the manual. If there are such differences, they are documented in one or more "Manual Changes" sheets sent with the
manual.
If the prefix number on your power module is lower than the one on the title page, then the module was made before the
publication of the manual and may have differences not covered in the manual. These differences are documented in
appendix A.
Firmware
This manual applies to p ower modules that run on software revision A.00.01 through A.00.04. Firmware revision A.00.04 is
backward compatible with all previous revisions. The ROM chip (U2) has a label that specifies the firmware revision.
8
Overview
Page 9

Safety Considerations
The Agilent 6610xA Power Modules are Safety Class 1 instruments that connect to a protective earth terminal when
properly installed in an Agilent 66000A MPS Mainframe. Refer to the Safety Summary page at the beginning of this manual
for general safety procedures and the meaning of safety symbols appearing in the manual and on the module.
Electrostatic Discharge
The Modular Power System has components that can be damaged by ESD (electrostatic discharge).
when complete failure does not occur.
When working on the Modular Power System, observe all anti-static work practices. This includes, but is not limited to:
■ Working at a static-free station, such as a table covered with static-dissipative laminate or with a conductive table mat
(Agilent p/n 9300-0797).
■ Using a conductive wrist strap (Agilent p/n 9300-0969 or 9300-0970).
■ Grounding all metal equipment at the station to a single, common ground.
■ Connecting low-impedance test equipment to static sensitive components only when those components have power
applied to them.
■ Removing power from the Modular Power System before removing or installing printed circuit boards.
Failure to observe standard anti-static practices can result in serious degradation of performance even
Service Tools and Equipment
The following tools are required to repair the Agilent 6610xA MPS Modules:
■ T10 TORX driver
■ 7mm HEX NUT drivers
■ #2 POZI driver
■ Slot-head screwdriver - medium
■ DIP component removal tool
■ Soldering iron and solder
■ De-solder removal tool
■ Needle-nose pliers
■ Anti-static work mat and wrist strap
Overview
9
Page 10
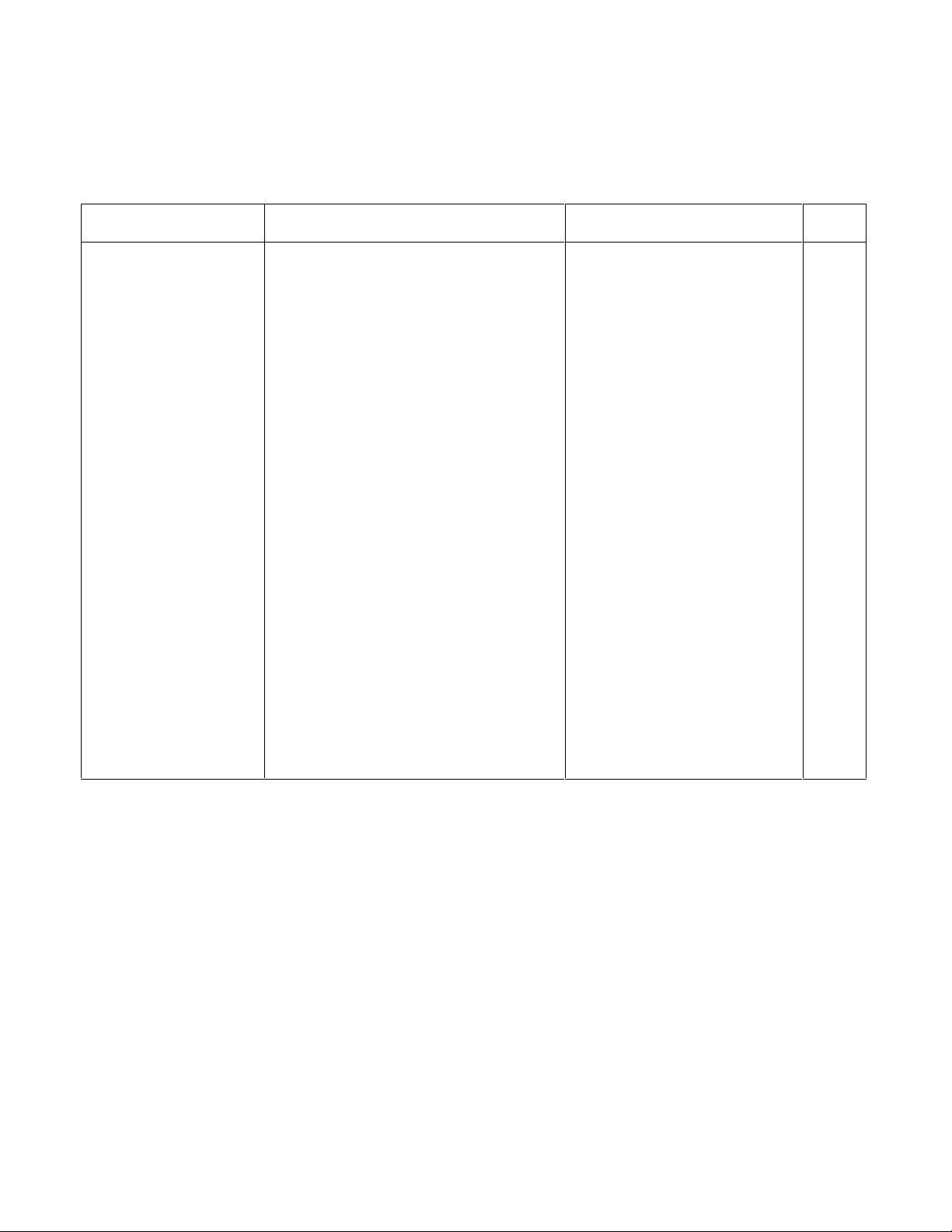
The following equipment is required to verify and troubleshoot the Agilent 6610xA Power Modules:
Table 1-1. Service Test Equipment
Equipment Required Critical Specifications Recommended Model Use
GPIB Controller Full GPIB capabilities HP Series 200/300 computer T
Oscilloscope Sensitivity: 1mV
Agilent 54504A T
Bandwidth Limit: 20MHz
Probe: 1:1 with RF tip
Rms Voltmeter True RMS Band width: 20MHz
Agilent 3400B T
Sensitivity: 100µV
Digital Voltmeter Resolution: 10nV @ 1V (8 1/2 digit) Agilent 3458A Accuracy: 20 ppm V,T
Variable Voltage
Transformer
CC RMS Noise
Resistor (R
)
M
Electronic Load Voltage and current range must exceed range
Adjustable from- 13% to + 6% of input
range. 1KVA min.
Agilent 66101A,102A - 100A (.01 Ω)
2
0.04%
Agilent 66103A,106A - 15A (.01 Ω)
3
0.04%
of module under test.
Power Range: 600W minimum
T
±
Guildline 9230/100
V,T
Guildline 9230/15
±
Agilent 6050A Load mainframe
V,T
and Agilent 60503A module
(240V) or Agilent 60507A module
(120V).
Load Resistor (RL)
Agilent 66101A- 0.1 Ω ± 5% 300W
Agilent 66102A-106A- 1.0 Ω ± 5% 300W
Ohmite C300KR10
Ohmite C300KIR0 T
1
MPS Mainframe Agilent 66000A V,T
MPS Keyboard
4
Agilent 66001A V,T
1 V = Verification; T = Troubleshooting.
2 Guildline Shunt Accuracy determined by Power Coefficient ( ± 0.01% + (0.0004%/watt))
3 Guildline Shunt Accuracy determined by Power Coefficient ( ± 0.01% + (0.002%/watt))
4 Use of the keyboard is recommended for displaying selftest error messages.
10
Overview
Page 11
2
Verification and Performance Tests
This chapter contains test procedures to check the operation of the Agilent 6610xA Power Modules. The required test
equipment is specified in Chapter 1. Sample performance test record sheets are included at the end of the chapter.
Instructions are given for performing the tests either from a GPIB controller or the MPS keyboard. Two types of procedures
are provided: Operation Verification tests and Performance tests.
Operation Verification
Performance
If you encounter failures or out-of-specification test results, see "Troubleshooting Pr ocedures" in Chapter 3 of this manual.
Those procedures will determine if repair and/or calibration is required.
These tests do not check all parameters, but comprise a short procedure to verify that the
power module is performing properly.
These test all the Performance Specifications (not Supplementary Characteristics) listed in
Table 1-1 of the Power Module User’s Guide.
Note The power module must pass the selftest at power-on before the following tests can be performed. If the
module fails selftest, refer to the overall troubleshooting procedures in Chapter 3.
SHOCK HAZARD The tests should only be performed by qualified personnel. During the performance of
these tests, hazardous voltages may be present at the output of the module.
Operation Verification Tests
To assure that the module is operating properly, without testing all specified parameters, perform the following test
procedures:
1. Perform the turn-on and checkout procedures given in Chapter 3 of the Power Module User’s Guide.
2. Perform the Voltage Programming/Readback Accuracy and the Current Programming/Readback Accuracy Performance
Tests in this chapter.
Performance Tests
The following paragraphs provide test procedures for verifying the module’s compliance with the specifications listed in
Table 1-1 of the Power Module User’s Guide. All of the performance test specifications are listed in the Performance Test
Records at the end of this chapter. You can record the actual measured values in the column provided.
Verification and Performance Tests 11
Page 12
Measurement Techniques
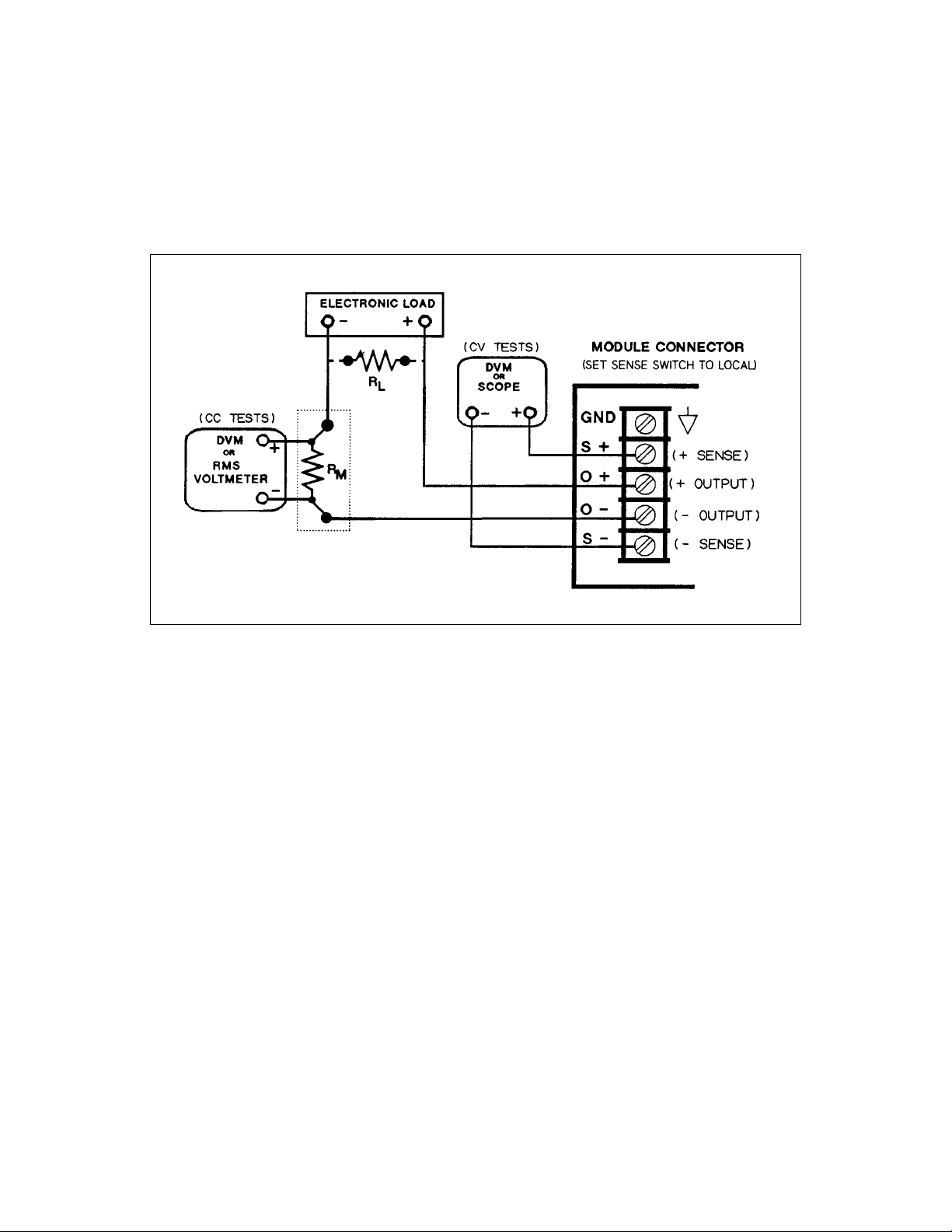
Setup for Most Tests
Most tests are performed at the rear terminals as shown in the following figure. Measure the dc voltage directly at the + S
and - S terminals. Set the connector sense switch for local sensing and use adequate wire gauge for load leads as described
in Chapter 2 of the Power Module User’s Guide.
Figure 2-1. Performance Test Setup
Many of the test procedures require the use of a variable load capable of dissipating the required power (see Table 1-1). If a
variable resistor is used, switches must be used to connect, disconnect, and short the load resistor. For most tests, an
electronic load can be used. The electronic load is considerably easier to use than load resistors but some may not be fast
enough to test transient recove ry time and may be too noisy for the noise (PARD) tests. Fixed load resistors may be used in
place of a variable load, with minor changes to the test procedures in this chapter. Also, if computer controlled test setups
are used, the relatively slow (compared to computers and system voltmeters) settling time and slew rates of the power
module may have to be taken into account. WAIT statements can be used in the test program if the test system is faster than
the module.
Current-Monitoring Resistor
To eliminate output current measurement error caused by voltage drops in the leads and connections, connect the current
monitoring resistor between the output and the load as a four-terminal device (see R
monitoring leads inside the load lead connections directly at the monitoring points on the resistor element.
in Figure 2-1). Connect the current
M
Programming
Table 2-1 lists the programming and current values for each module. You may program the module from the MPS Keyboard
or from a GPIB controller when performing the tests. The test procedures are written assuming that you know how to do
either or both. Complete instructions for remote and local programming are given in the module Power Module
Programming Guide and Power Module User’s Guide.
12 Verification and Performance Tests
Page 13

Table 2-1. Power Module Voltage and Current Values
Agilent
Model
66101A 8V 8.190V 16A 16.380A 10V
66102A 20V 20.475V 7.5A 7.678A 24V
66103A 35V 35.831V 4.5A 4.607A 42V
66104A 60V 61.425V 2.5A 2.559A 72V
66105A 120V 122.85V 1.25A 1.280A 144V
66106A 200V 204.75V 0.75A 0.768A 240V
Full-Scale
Voltage
Max. Prog.
Voltage
Full-Scale
Current
Max. Prog.
Current
Max. Prog.
Overvoltage
Constant Voltage (CV) Tests
CV Setup
If more than one meter or a meter and an oscilloscope are used, connect each to the terminals by a separate pair of leads to
avoid mutual coupling effects. For constant voltage dc tests, connect only to + S and - S because the module regulates the
output voltage that appears between those terminals, not between the + and - output terminals. Use coaxial cable or shielded
2-wire cable to avoid noise pickup on the test leads.
Voltage Programming/Readback Accuracy
This test verifies that the voltage programming, readback, and front panel display functions are within specifications. Note
that the values read back over the GPIB should be identical to those displayed on the keyboard display.
1. Turn off the power module and connect a digital voltmeter between the + S and--S terminals (see Figure 2-1).
2. Turn on the module and program it for zero volts and the maximum programmable current (see Table 2-1) with the load
off.
3. Record the output voltage readings on the DVM and the keyboard display. The readings should be within the limits
specified in the Performance Test Record Tables under CV PROGRAMMING @ 0 VOLTS, for the particular model
being tested. The CV annunciator should be on and the output current reading should be approximately zero.
4. Program the output voltage to full scale (see Table 2-1).
5. Record the output voltage readings on the DVM and the keyboard display. The readings should be within the limits
specified in the Performance Test Record Tables under CV PROGRAMMING @ FULL SCALE, for the particular
model being tested.
CV Load Effect
This test measures the change in output voltage resulting from a change in output current from full-load to no-load.
1. Turn off the module and connect the output as shown in Figure 2-1 with the DVM connected between the + S and - S
terminals.
2. Turn on the module and program the current to the maximum programmable value and the voltage to the full-scale
value (see Table 2-1).
3. Adjust the load for the full-scale current (see Table 2-1) as indicated on the keyboard display. The front panel CV
annunciator must be on. If it is not, ad just the load so that the output c urrent drops slightly until the annunciator comes
on.
4. Record the output voltage reading on the DVM connected to + S and - S.
5. Open the load and again record the DVM voltage reading.
6. The difference between the DVM readings in steps (4) and (5) is the load effect voltage and should not exceed the
value listed in the Performance Test Record Tables under CV LOAD EFFECT, for the model being tested .
Verification and Performance Tests 13
Page 14

CV Source Effect
This test measures the change in output voltage that results from a change in ac line voltage from the minimum to maximum
value within the line voltage specifications.
1. Turn off the module and c onnect the ac power line through a variable-voltage tr ansformer.
2. Connect the output as shown in Figure 2-1 with the DVM connected between the + S and - S terminals. Set the
transformer to nominal line voltage (either 115Vac or 230Vac).
3. Turn on the module and program the current to the maximum programmable value and the output voltage to the
full-scale value (see Table 2-1).
4. Adjust the load for the full-scale current value (see Table 2-1) as indicated on the keyboard display. The front panel CV
annunciator must be on. If it is not, ad just the load so that the output c urrent drops slightly until the annunciator comes
on.
5. Adjust the transformer to the LOW line voltage (e.g., 87Vac for a 115Vac nominal input, or 174Vac for a 230Vac
nominal input).
6. Record the output voltage reading on the DVM.
7. Adjust the transformer to the HIGH line voltage (e.g., 132Vac for a 115Vac nominal input, or 250Vac for a 230Vac
nominal input).
8. Record the output voltage reading on the DVM.
9. The difference between the DVM readings in steps (6) and (8) is the source effect voltage and should not exceed the
value listed in the Performance Test Record Tables under CV SOURCE EFFECT, for the model being tested.
CV Noise (PARD)
Periodic and random deviations (PARD) in the output (ripple and noise) combine to produce a residual ac voltage
superimposed on the dc output voltage. This test measures CV PARD, specified as the rms or peak-to-peak output voltage
over the frequency range of 20Hz to 20MHz.
1. Turn off the module and connect the output as shown in Figure 2-1 to an oscilloscope (ac coupled) between the + and--
terminals. Set the oscilloscope’s bandwidth limit to 20MHz (30MHz on the Agilent 54504A) and use an RF tip on the
oscilloscope probe.
2. Turn on the module and program the current to the maximum programmable value and the output voltage to the
full-scale value (see Table 2-1).
3. Adjust the load for the full-scale current value (see Table 2-1) as indicated on the keyboard display.
4. The waveform on the oscilloscope should not exceed the peak-to-peak limits in the Performance Test Record Tables
under CV NOISE (PARD), for the model being tested.
5. Disconnect the oscilloscope and connect an ac rms voltmeter in its place. The rms voltage reading should not exceed
the rms limits in the Performance Test Record Tables under CV NOISE (PARD) for the model being tested.
Transient Recovery Time
This test measures the time for the output voltage to recover to within the specified value following a 10% change in the
load current.
1. Turn off the module and connect the output as shown in Figure 2-1 with the oscilloscope across the + S and -S
terminals.
2. Turn on the module and program the output voltage to the full-scale value and the current to the maximum
programmable value (see Table 2-1).
3. Set the load to the Constant Current mode and program the load current to 90% of the power module full-scale rated
current.
4. Set the electronic load’s transient generator frequency to 100Hz and its duty cycle to 50%.
5. Program the load’s transient level to the module’s full-scale current value and turn the transient on.
6. Adjust the oscilloscope for a waveform similar to that in Figure 2-2.
7. The output voltage should return to within 100mV of the nominal value in less than 1ms. Check both loading and
14 Verification and Performance Tests
Page 15
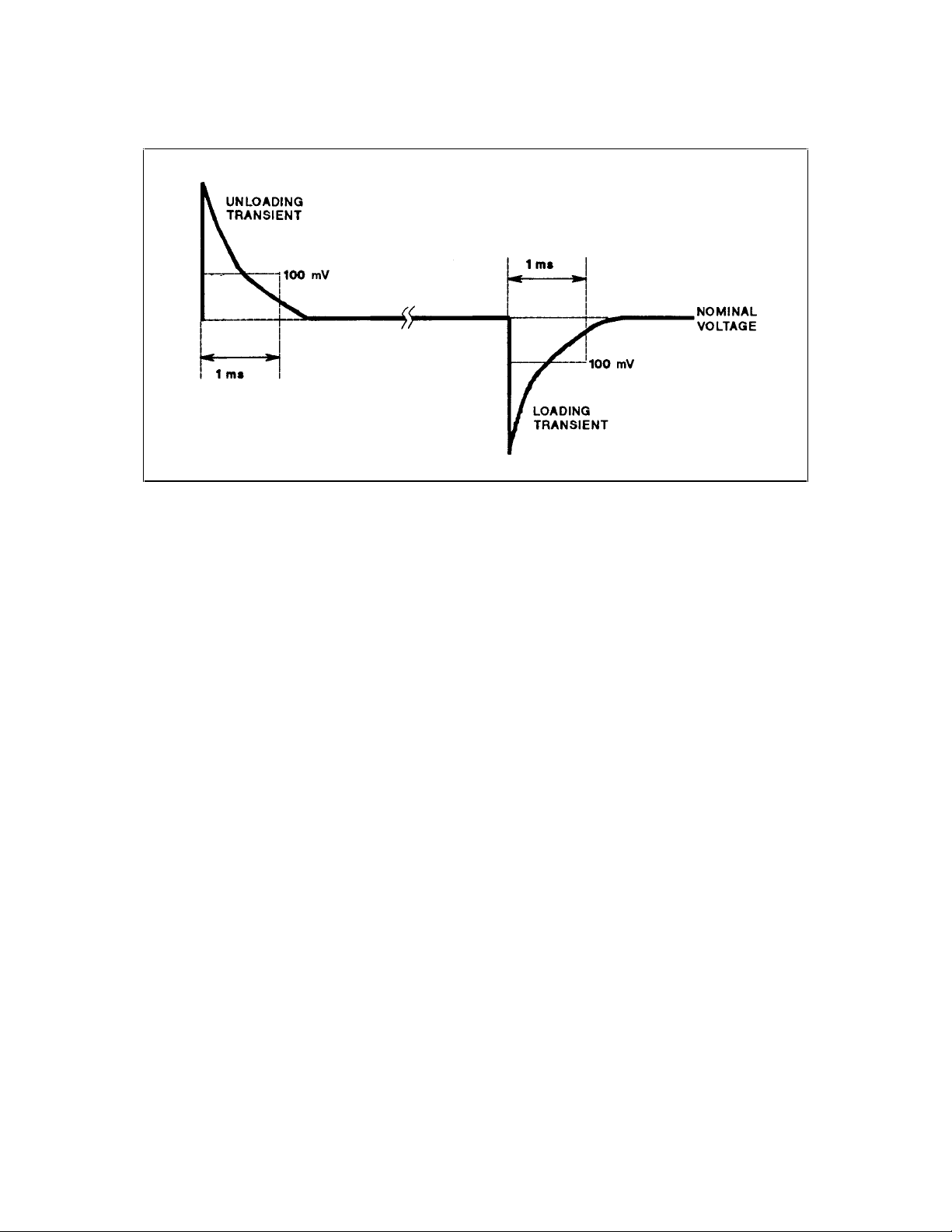
unloading transients by triggering on the positive and negative slope.
Figure 2-2. Transient Response Waveform
Constant Current (CC) Tests
CC Setup
Follow the general setup instructions in the Measurement Techniques paragraph and the specific instructions given in the
following paragrap hs.
Current Programming/Readback Accuracy
This test verifies that the current programming and readback are within specification. The accuracy of the current
monitoring resistor is determined by the power coefficient (see Table 1-1).
1. Turn off the module and connect the current monitoring resistor directly across the output and a DVM across the
resistor. Refer to the "Current Monitoring Resistor" paragraph.
2. Turn on the module and program the output voltage to 5V and the current to zero.
3. Divide the voltage drop (DVM reading) across the current monitoring resistor by its resistance to convert to amps and
record this value as (Io). The actual current (Io) and the reading on the keyboard display should be within the limits
specified in the Performance Test Record Tables under CC PROGRAMMING @ 0 AMPS, for the particular model
being tested.
4. Program the output voltage to 5V and the current to full-scale (see Table 2-1).
5. Divide the voltage drop (DVM reading) across the current monitoring resistor by its resistance to convert to amps and
record this value as (Io). The actual current (Io) and the reading on the keyboard display should be within the limits
specified in the Performance Test Record Tables under CC PROGRAMMING @ FULL SCALE, for the particular
model being tested.
CC Load and Line Regulation
These tests (CC Load Effect and CC Source Effect given below) are tests of the dc regulation of the power module’s output
current. To insure that the values read are not the instantaneous measurement of the ac peaks of the output current ripple,
several dc measurements should be made and the average of these readings calculated.
Verification and Performance Tests 15
Page 16
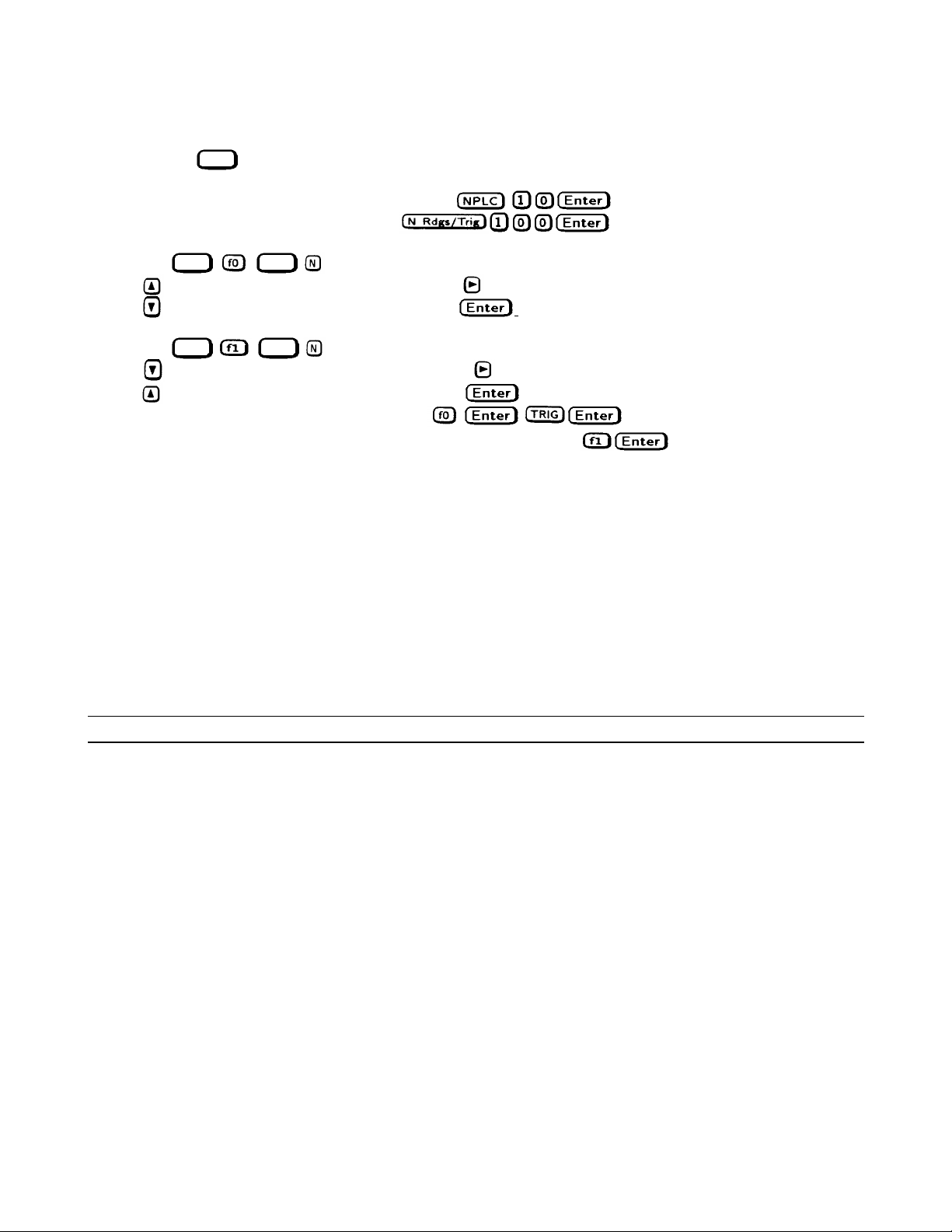
The following steps show how to set up an Agilent 3458A System Voltmeter from its front panel to take a statistical average
of 100 readings.
represents the unlabeled shift key in the FUNCTION/RANGE group.
1. Program 10 power line cycles per samp le by pressing
2. Program 100 samples per trigger by pressing
3. Set up the voltmeter to take measurements in the statistical mode as follows:
4. a. Press
b. Press
c. Press
5. Now set up the voltmeter to read the average value of the measurements as follows:
6. a. Press
b. Press
c. Press
7. Execute the average reading program by pressing
8. Wait for 100 readings and then read the average measurement by pressing
To repeat the measurement, perform steps (7) and (8).
CC Load Effect
This test measures the change in output current for a change in the load from full-scale output voltage to short circuit.
1. Turn off the module and connect the output to be tested as shown in Figure 2-1 with the voltmeter connected across the
2. Turn on the module and program the current to the full-scale current value and the output voltage to the maximum
3. Adjust the load in the CV mode for full-scale voltage as indicated on the keyboard display. Check that the CC
4. Record the output current reading (DVM reading ÷ current monitor resistance value in ohms).
until the MATH function is selected; then press .
until the STAT function is selected; then press .
until the RMATH function is selected; then press .
until the MEAN function is selected; then press .
current monitoring resistor.
programmable voltage value (see Table 2-1).
annunciator is on. If it is not, adjust the load to drop the output voltage slightly until the annunciator c omes on.
.
.
.
.
.
. Record this as your result.
Note You may want to use the average reading program described previously.
5. Short the load switch and record the output current reading.
6. The difference in the current readings in steps (4) and (5) is the load effect and should not exceed the limit specified in
the Performance Test Record Tables under CC LOAD EFFECT, for the particular model being tested.
CC Source Effect
This test measures the change in output current that results when the ac line voltage changes from the minimum to the
maximum value within the specifications.
1. Turn off the module and c onnect the ac power line through a variable-voltage tr ansformer.
2. Connect the output terminals as shown in Figure 2-1 with the voltmeter connected across the current monitoring
resistor. Set the transformer to the nominal line voltage.
3. Turn on the module and program the current to the full-scale value and the output voltage to the maximum
programmable value (see Table 2-1).
4. Adjust the load in the CV mode for full-scale voltage as indicated on the front panel display. Check that the CC
annunciator is on. If it is not, adjust the load to drop the output voltage slightly until the annunciator c omes on.
5. Adjust the transformer to the LOW line voltage (e.g., 87Vac for a 115Vac nominal input, or 174Vac for a 230Vac
nominal input).
6. Record the output current reading (DVM reading ÷ current monitoring resistor in ohms).
16 Verification and Performance Tests
Page 17

Note You may want to use the average reading program described previously.
7. Adjust the transformer to the HIGH line voltage (e.g., 132Vac for a 115Vac nominal input, or 250Vac for a 230Vac
nominal input), and record the output current reading.
8. The difference in the current readings in steps (6) and (7) is the CC source effect and should not exceed the values
listed in the Performance Test Record Tables under CC SOURCE EFFECT, for the particular model being tested.
CC Noise (PARD)
Periodic and random deviations (PARD) in the output (ripple and noise) combine to produce a residual ac current as well as
an ac voltage superimposed on the dc output. Constant current (CC) PARD is specified as the rms output current in a
frequency range 20Hz to 20MHz with the module in CC operation.
1. Turn off the module and connect the load resistor (R
) and rms voltmeter as shown in Figure 2-1. Use only a resistive
L
load for this test. Keep leads as short as possible to reduce noise pickup.
2. Check the test setup for noise with the module turned off. Other equipment (e.g. computers, DMM, etc.) may affect the
reading.
3. Turn on the module and program the current to full-scale and the output voltage to the maximum programmable value
(see Table 2-1).
4. The output current should be at the full-scale rating with the CC Mode on.
5. Divide the reading on the rms voltmeter by the shunt resistance to obtain rms current. It should not exceed the values
listed in the Performance Test Record Tables under CC NOISE (Rms) for the particular unit being tested.
Verification and Performance Tests 17
Page 18
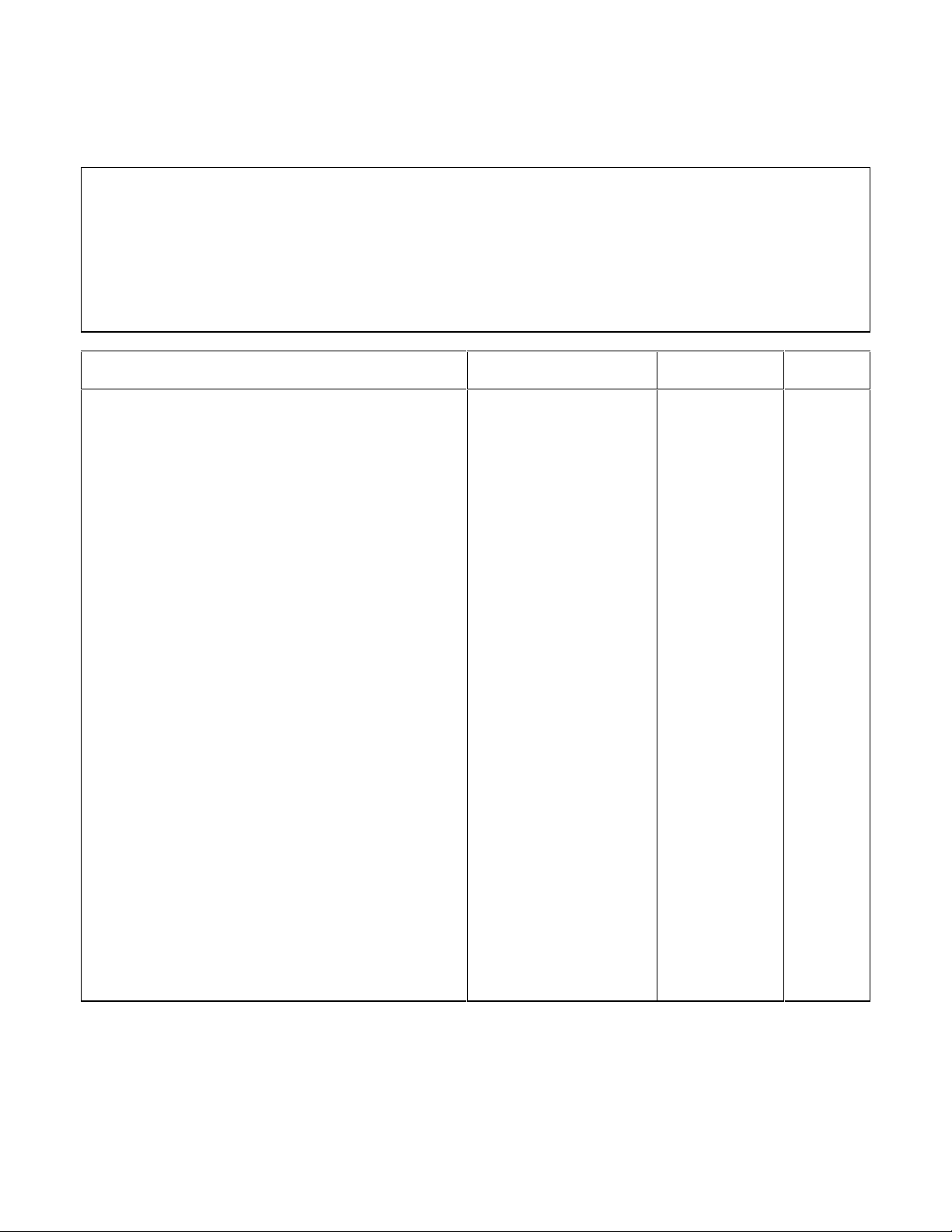
Table 2-2. Performance Test Record for Model Agilent 66101A (8V, 16A)
Pre Cal_____________Post Cal______________
Model Agilent 66101A Temperature___________________________Test Performed
By_______________________
Serial Number_______________________Humidity________________________Date__________________________
Test Description Specification Measurement
Uncertainty
CV PROGRAMMING @ 0 volts
Output Accuracy (DVM Reading)
Display and Readback Accuracy
CV PROGRAMMING @ full-scale
Output Accuracy (DVM Reading)
Display and Readback Accuracy
CV LOAD EFFECT 1mV
CV SOURCE EFFECT 0.5mV
CV NOISE (PARD)
Peak to Peak
Rms
TRANSIENT RECOVERY in 1 ms 100mV 15mV ________
CC PROGRAMMING @ 0 amps
Output Accuracy (Io)
Display and Readback Accuracy
0 ± 3mV
DVM ± 2mV
8V ± 5.4mV
DVM ± 3.6mV
5mV
2mV
0 ± 6mA
Io ± 6mA
1.5µV
1.5µV
88µV
88µV
1µV
1µV
0.87mV
150µV
150µA
150µA
Actual
________
________
________
________
________
________
________
________
________
________
CC PROGRAMMING @ full-scale
Output Accuracy (Io)
Display and Readback Accuracy
CC LOAD EFFECT 0.5mA
CC SOURCE EFFECT 0.75mA
CC NOISE (RMS) 8mA 0.9mA ________
18 Verification and Performance Tests
16A ± 10.8mA
Io ± 9.2mA
2.1mA
2.1mA
15µA
15µA
________
________
________
________
Page 19
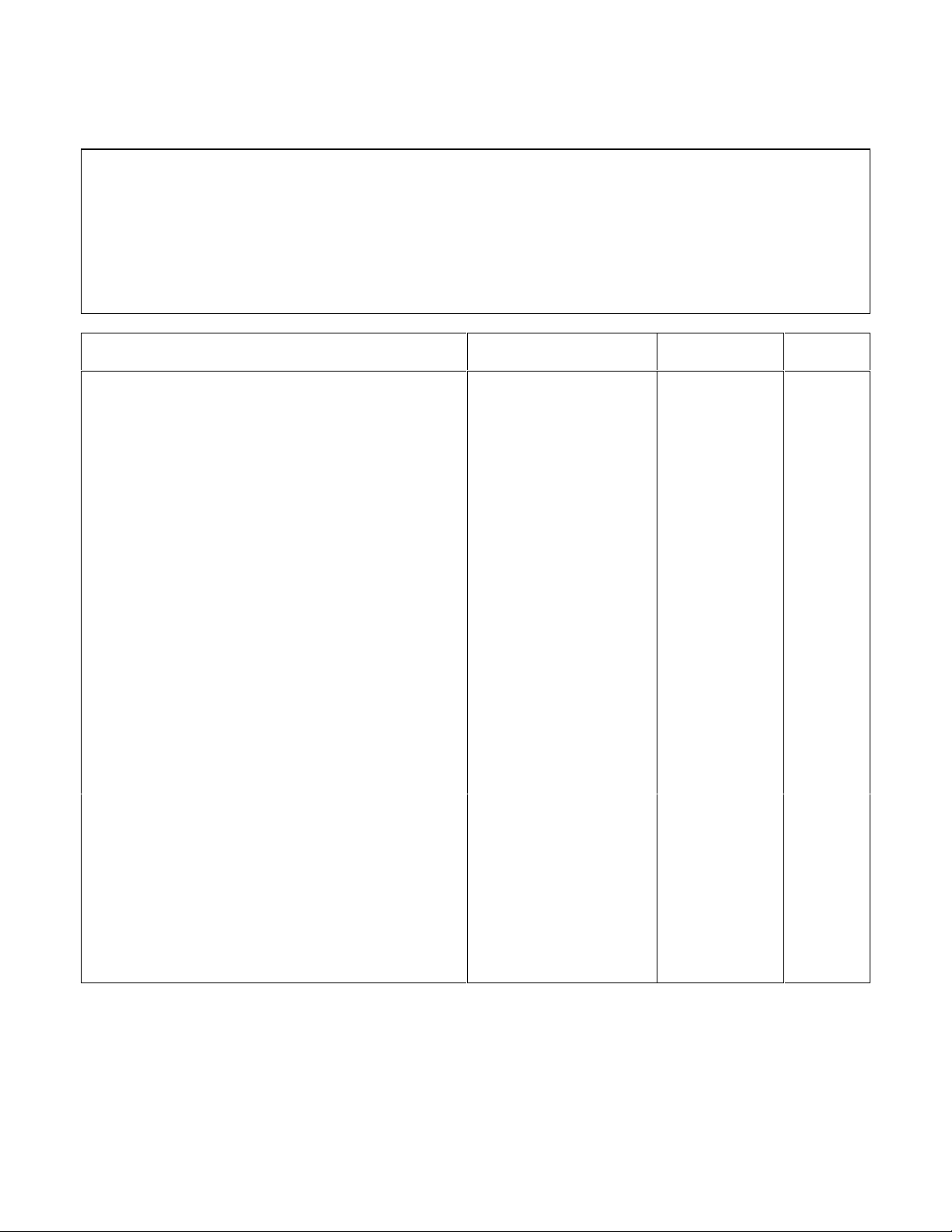
Table 2-3. Performance Test Record for Model Agilent 66102A (20V, 7.5A)
Pre Cal_____________Post Cal______________
Model Agilent 66102A Temperature___________________________Test Performed
By______________________
Serial Number_______________________Humidity________________________Date__________________________
Test Description Specification Measurement
Uncertainty
CV PROGRAMMING @ 0 volts
Output Accuracy (DVM Reading)
Display and Readback Accuracy
CV PROGRAMMING @ full-scale
Output Accuracy (DVM Reading)
Display and Readback Accuracy
CV LOAD EFFECT 1mV
CV SOURCE EFFECT 0.5mV
CV NOISE (PARD)
Peak to Peak
Rms
TRANSIENT RECOVERY in 1 ms 100mV 15mV ________
CC PROGRAMMING @ 0 amps
Output Accuracy (Io)
Display and Readback Accuracy
0 ± 8mV
DVM ± 3mV
20V ± 14mV
DVM ± 7mV
7mV
3mV
0 ± 3mA
Io ± 3mA
1.6µV
1.6µV
335µV
335µV
20µV
20µV
0.872mV
500µV
150µA
150µA
Actual
________
________
________
________
________
________
________
________
________
________
CC PROGRAMMING @ full-scale
Output Accuracy (Io)
Display and Readback Accuracy
CC LOAD EFFECT 0.2mA
CC SOURCE EFFECT 0.5mA
CC NOISE (RMS) 4mA 0.7mA ________
7.5A ± 5.3mA
Io ± 4.5mA
Verification and Performance Tests 19
1mA
1mA
9µA
9µA
________
________
________
________
Page 20
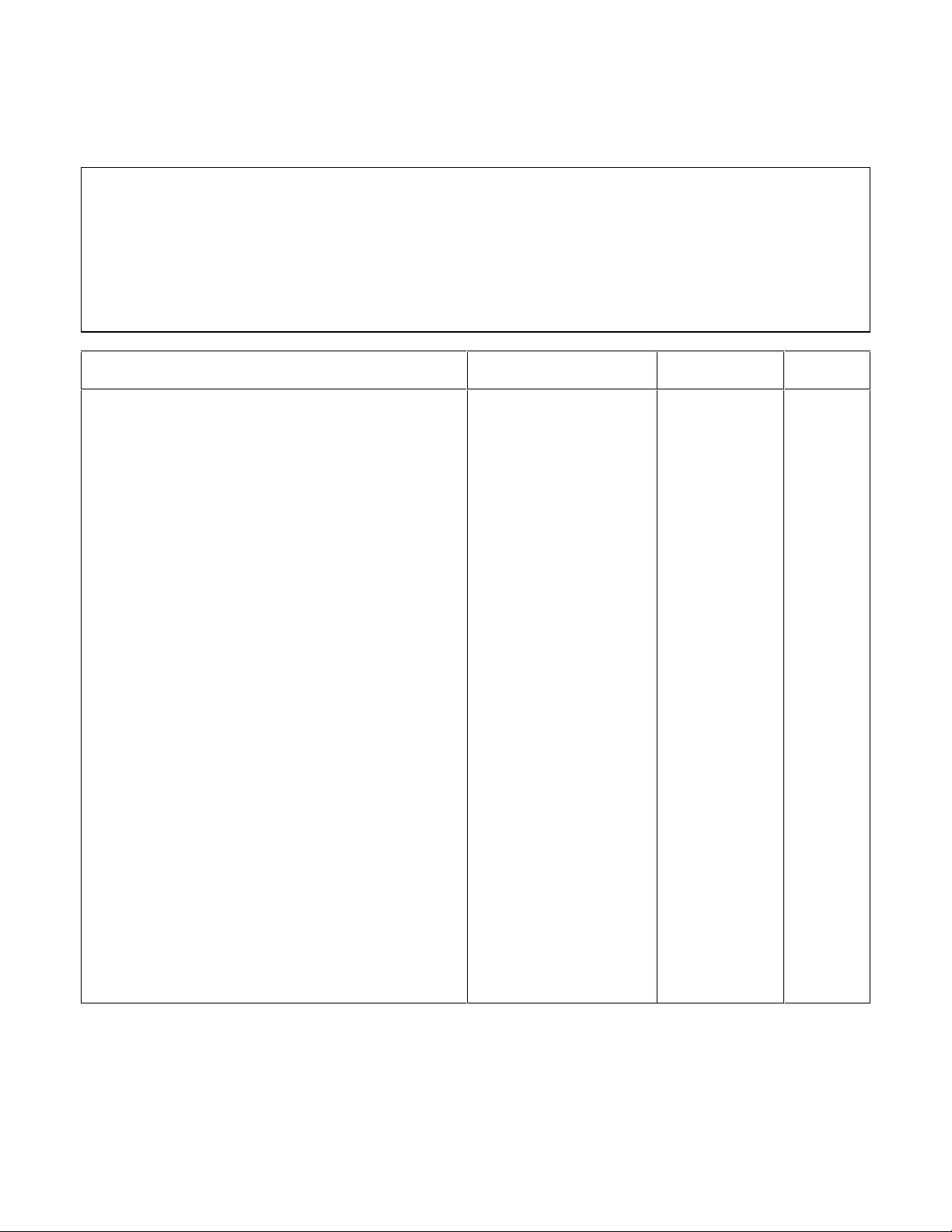
Table 2-4. Performance Test Record for Model Agilent 66103A (35V, 4.5A)
Pre Cal_____________Post Cal______________
Model Agilent 66103A Temperature___________________________Test Performed
By______________________
Serial Number_______________________Humidity________________________Date__________________________
Test Description Specification Measurement
Uncertainty
CV PROGRAMMING @ 0 volts
Output Accuracy (DVM Reading)
Display and Readback Accuracy
CV PROGRAMMING @ full-scale
Output Accuracy (DVM Reading)
Display and Readback Accuracy
CV LOAD EFFECT 1mV
CV SOURCE EFFECT 1mV
CV NOISE (PARD)
Peak to Peak
Rms
TRANSIENT RECOVERY in 1 ms 100mV 15mV ________
CC PROGRAMMING @ 0 amps
Output Accuracy (Io)
Display and Readback Accuracy
0 ± 13mV
DVM ± 8mV
35V ± 23.5mV
DVM ± 15mV
10mV
5mV
0 ± 2mA
Io ± 2mA
1.7µV
1.7µV
526µV
526µV
28µV
28µV
0.90mV
500µV
15µA
15µA
Actual
________
________
________
________
________
________
________
________
________
________
CC PROGRAMMING @ full-scale
Output Accuracy (Io)
Display and Readback Accuracy
CC LOAD EFFECT 0.2mA
CC SOURCE EFFECT 0.3mA
CC NOISE (RMS) 2mA
20 Verification and Performance Tests
4.5A ± 3.4mA
Io ± 2.9mA
0.7mA
0.7mA
3µA
3µA
250µA
________
________
________
________
________
Page 21
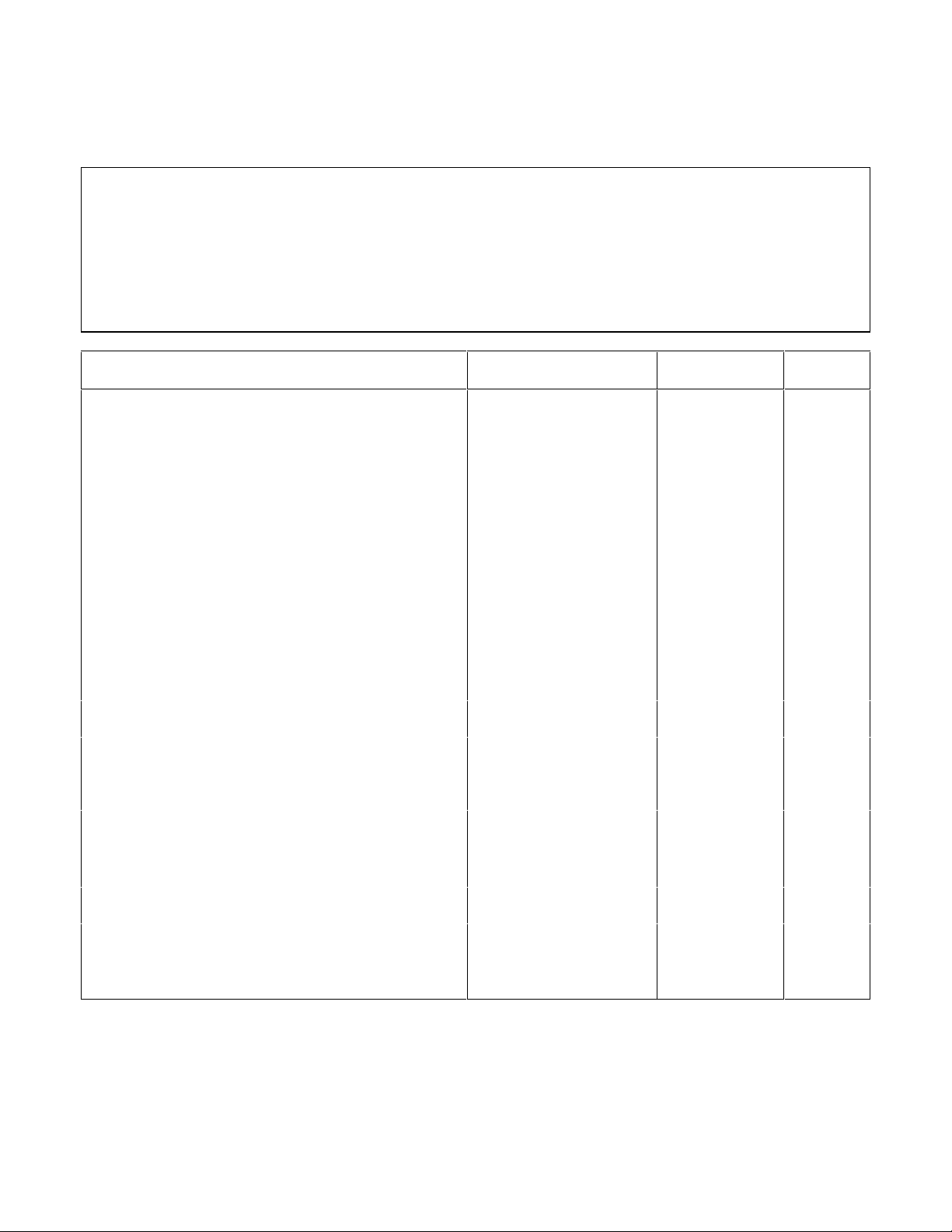
Table 2-5. Performance Test Record for Model Agilent 66104A (60V, 2.5A)
Pre Cal_____________Post Cal______________
Model Agilent 66104A Temperature___________________________Test Performed
By______________________
Serial Number_______________________Humidity________________________Date__________________________
Test Description Specification Measurement
Uncertainty
CV PROGRAMMING @ 0 volts
Output Accuracy (DVM Reading)
Display and Readback Accuracy
CV PROGRAMMING @ full-scale
Output Accuracy (DVM Reading)
Display and Readback Accuracy
CV LOAD EFFECT 2mV
CV SOURCE EFFECT 2mV
CV NOISE (PARD)
Peak to Peak
Rms
1
TRANSIENT RECOVERY in 1 ms 100mV 15mV ________
CC PROGRAMMING @ 0 amps
Output Accuracy (Io)
Display and Readback Accuracy
0 ± 27mV
DVM ± 16mV
60V ± 45mV
DVM ± 28mV
15mV
9mV
0 ± 0.6mA
Io ± 0.6mA
1.8µV
1.8µV
845µV
845µV
40µV
40µV
1.0mV
1.5mV
15µA
15µA
Actual
________
________
________
________
________
________
________
________
________
________
CC PROGRAMMING @ full-scale
Output Accuracy (Io)
Display and Readback Accuracy
CC LOAD EFFECT 0.1mA
CC SOURCE EFFECT 0.1mA
CC NOISE (RMS) 1mA 0.2mA ________
1 18mV Rms when the ac input is between 87 and 104Vac.
2.5A ± 1.4mA
Io ± 1.1mA
Verification and Performance Tests 21
323µA
323µA
2µA
2µA
________
________
________
________
Page 22
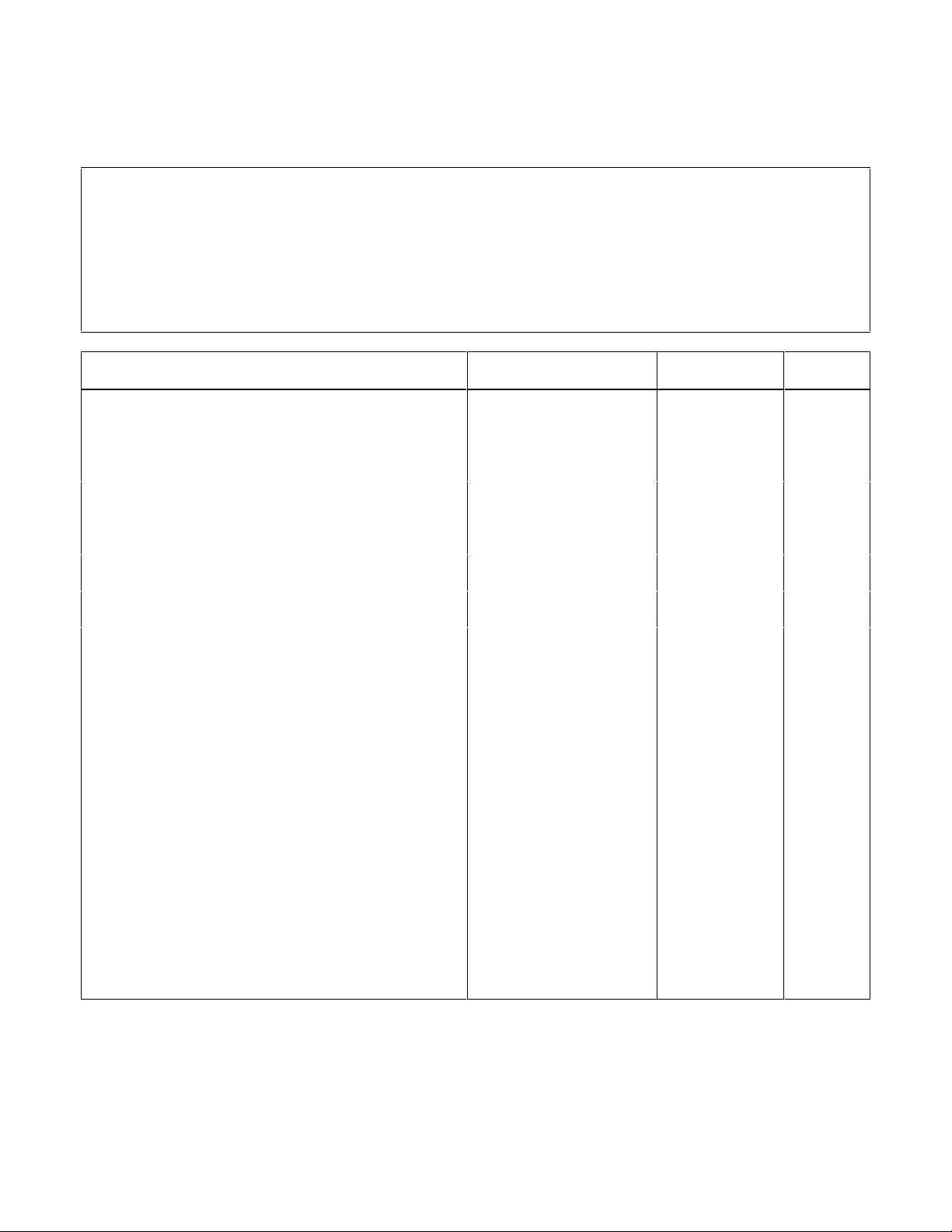
Table 2-6. Performance Test Record for Model Agilent 66105A (120V, 1.25 A)
Pre Cal_____________Post Cal______________
Model Agilent 66105A Temperature___________________________Test Performed
By______________________
Serial Number_______________________Humidity________________________Date__________________________
Test Description Specification Measurement
Uncertainty
CV PROGRAMMING @ 0 volts
Output Accuracy (DVM Reading)
Display and Readback Accuracy
CV PROGRAMMING @ full-scale
Output Accuracy (DVM Reading)
Display and Readback Accuracy
CV LOAD EFFECT 4mV
CV SOURCE EFFECT 3mV
CV NOISE (PARD)
Peak to Peak
Rms
TRANSIENT RECOVERY in 1 ms 100mV 15mV ________
CC PROGRAMMING @ 0 amps
Output Accuracy (Io)
Display and Readback Accuracy
0 ± 54mV
DVM ± 32mV
120V ± 90mV
DVM ± 56mV
25mV
18mV
0 ± 0.6mA
Io ± 0.6mA
2.1µV
2.1µV
1.7mV
1.7mV
230µV
230µV
1.0mV
1.5mV
15µA
15µA
Actual
________
________
________
________
________
________
________
________
________
________
CC PROGRAMMING @ full-scale
Output Accuracy (Io)
Display and Readback Accuracy
CC LOAD EFFECT
CC SOURCE EFFECT
CC NOISE (RMS) 1mA 0.2mA ________
22 Verification and Performance Tests
1.25A ± 975µA
Io ± 850µA
50µA1.4
50µA1.4µA
157µA
157µA
µ
A
________
________
________
________
Page 23
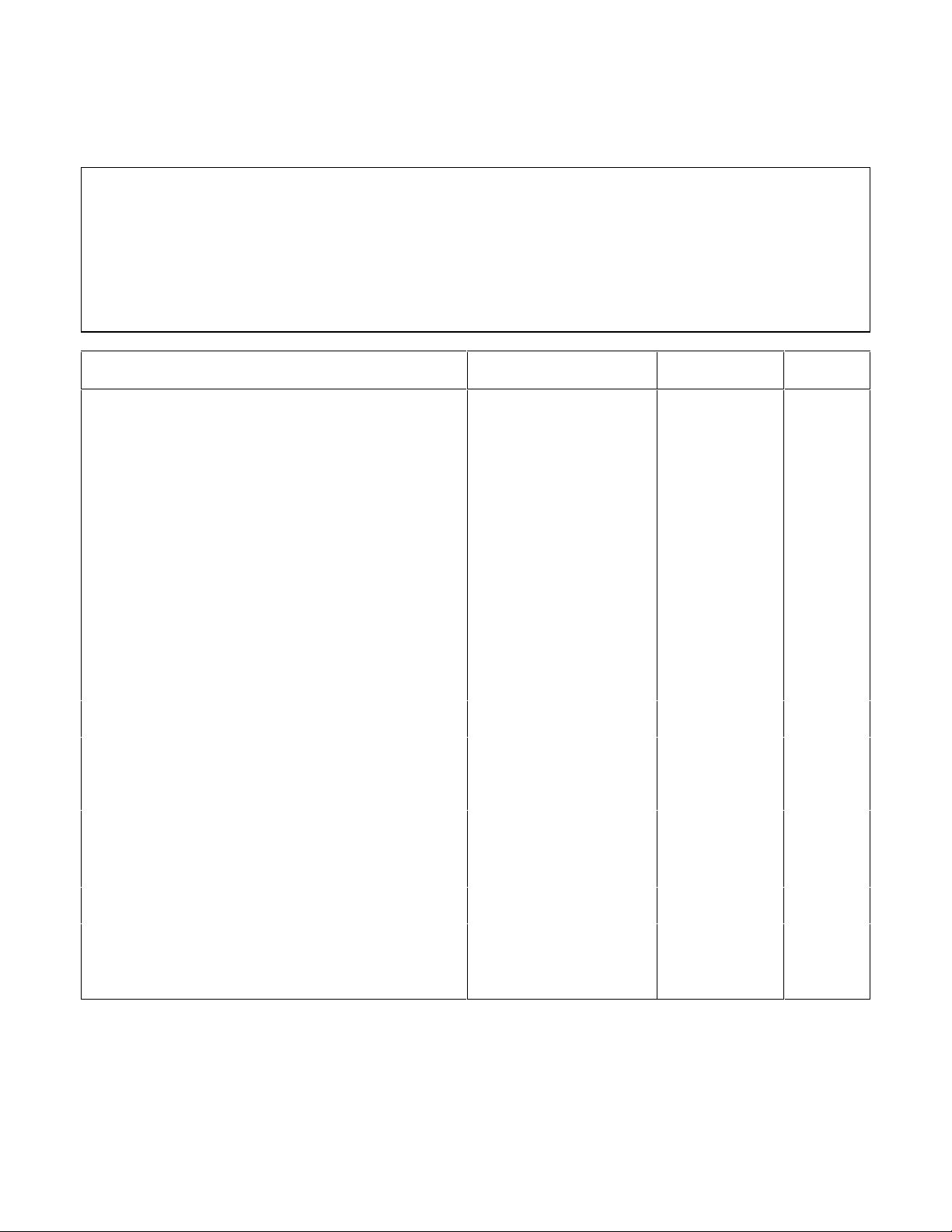
Table 2-7. Performance Test Record for Model Agilent 66106A (200V, 0.75A)
Pre Cal_____________Post Cal______________
Model Agilent 66106A Temperature___________________________Test Performed
By______________________
Serial Number_______________________Humidity________________________Date__________________________
Test Description Specification Measurement
Uncertainty
CV PROGRAMMING @ 0 volts
Output Accuracy (DVM Reading)
Display and Readback Accuracy
CV PROGRAMMING @ full-scale
Output Accuracy (DVM Reading)
Display and Readback Accuracy
CV LOAD EFFECT 7mV
CV SOURCE EFFECT 5mV
CV NOISE (PARD)
Peak to Peak
Rms
TRANSIENT RECOVERY in 1 ms 100mV 15mV ________
CC PROGRAMMING @ 0 amps
Output Accuracy (Io)
Display and Readback Accuracy
0 ± 90mV
DVM ± 54mV
200V ± 150mV
DVM ± 94mV
50mV
30mV
0 ± 0.4mA
Io ± 0.3mA
2.6µV
2.6µV
2.7mV
2.7mV
350µV
350µV
1.5mV
5.0mV
15µA
15µA
Actual
________
________
________
________
________
________
________
________
________
________
CC PROGRAMMING @ full-scale
Output Accuracy (Io)
Display and Readback Accuracy
CC LOAD EFFECT
CC SOURCE EFFECT
CC NOISE (RMS) 1mA 0.2mA ________
0.75A ± 625µA
Io ± 450µA
10µA1
30µA1µA
Verification and Performance Tests 23
100µA
100µA
µ
A
________
________
________
________
Page 24

Page 25
3
Troubleshooting
This chapter provides troubleshooting and repair information for the Agilent 6610xA Power Modules. Before attempting to
troubleshoot the modules, ensure that the problem is not with an external circuit or application, the mainframe, the GPIB
controller, the application program, or the input power line.
SHOCK HAZARD Most of the troubleshooting procedures given in this chapter are performed with power
applied and protective covers removed. Such maintenance should be performed only by trained
service personnel who are aware of the hazards (for example, tire and electrical shock).
Hazardous voltages are present throughout the P ower and Bias board assemblies. Ac line voltage is present
on some connectors even when the module is not turned on. The dc rail voltage to the module is 310 volts
when the unit is turned on.
Troubleshooting Sequence
1. Verify that the module is at fault.
2. Use the flowcharts to locate the functional block at fault.
3. Troubleshoot the functional block per flowchart instructions.
Selftest routines built into firmware are provided to help isolate a problem to a particular circuit on the board. Once a
problem has been isolate d to a circuit, suggestions are given in the appropriate flowchart as to what component may be at
fault.
This instrument uses components that can be damaged or suffer serious performance degradation as a
result of ESD (electrostatic discharge). Observe the standard anti-static precautions discussed in
Chapter 1 to avoid damage to components.
Accessing the Flowcharts
The following troubleshooting flowcharts are provided to help you identify and isolate a problem to a specific circuit. Once
a problem has been narrowed down, suggestions are provided as to the components that may be responsible fo r the problem.
Refer to the schematic diagrams for detailed information on circuit wiring and component function.
þ Figure 3-1 - Overall Troubleshooting
þ Figure 3-2 - Troubleshooting Microprocessor Circuits
þ Figure 3-3 - Troubleshooting Error Messages
þ Figure 3-4 - Troubleshooting Overvoltage at Turn-on
Troubleshooting 25
Page 26
þ Figure 3-5 - Troubleshooting No Output
þ Figure 3-6 - Troubleshooting High Output
þ Figure 3-7 - Troubleshooting W ill Not Overvoltage
þ Figure 3-8 - Troubleshooting CV Accuracy
þ Figure 3-9 - Troubleshooting CC Accuracy
þ Figure 3-10 - Troubleshooting Downprogrammer
þ Figure 3-11 - Troubleshooting DAC Circuit
þ Figure 3-12 - Troubleshooting Readback Circuits
Oscilloscope waveforms are provided on some flowcharts along with the settings required to generate the waveforms.
Connect the module to ac mains through an isolation transformer when making measurements with an
oscilloscope or any equipment that has the measuring input grounded.
If You Experienced a Selftest Failure or RunTime Error Message
If you experienced a selftest failure or runtime error message as described in Chapter 3 of the Power Module User’s Guide,
disassemble the module and proceed directly to the flowchart in Figure 3-3 "Troubleshooting Error Messages".
If You Experienced Other Problems With the Module
If you experienced problems other than a selftest failure or a runtime error message, disassemble the module and proceed
directly to Figure 3-1 "Overall Troubleshooting".
26 Troubleshooting
Page 27
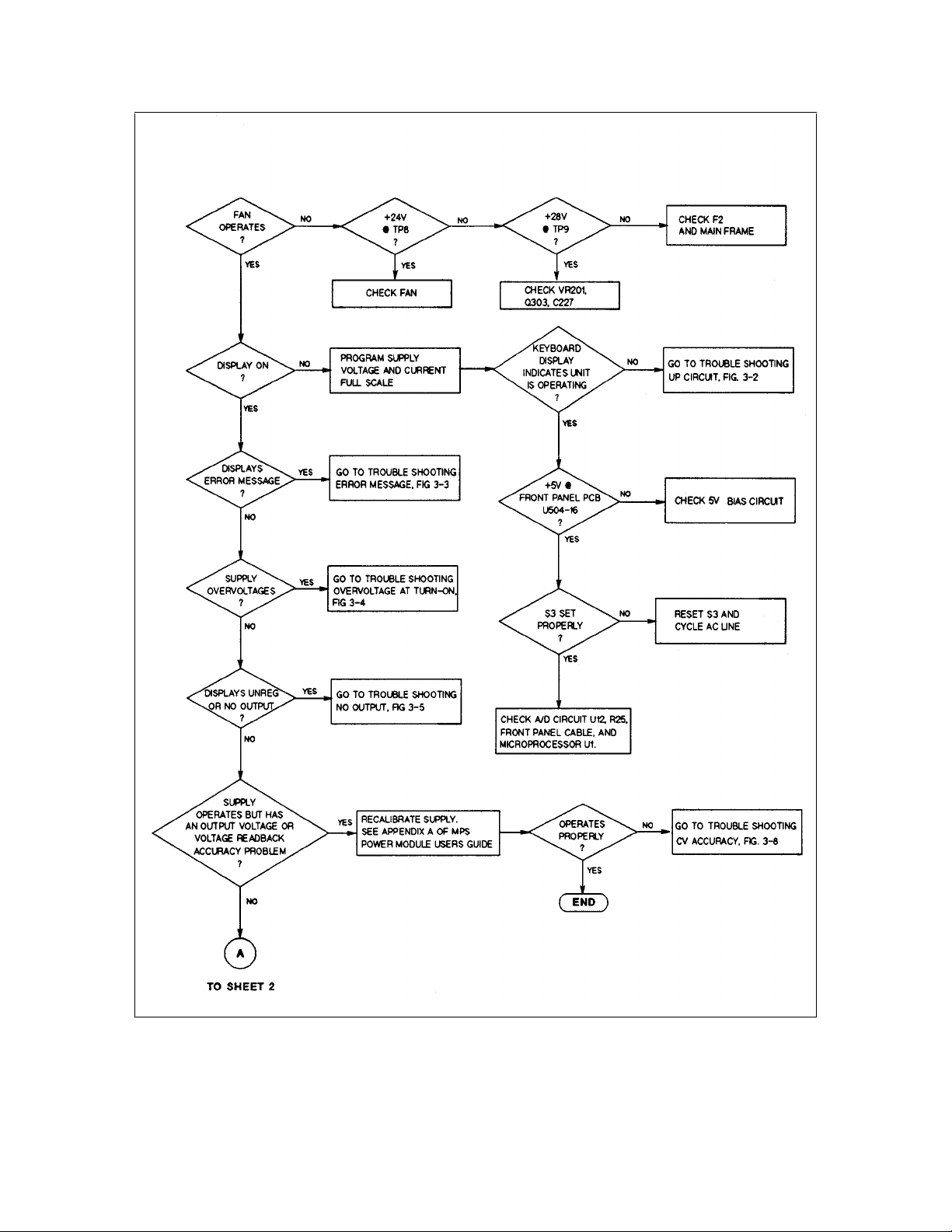
Figure 3-1. Overall Troubleshooting (Sheet 1 of 3)
Troubleshooting 27
Page 28
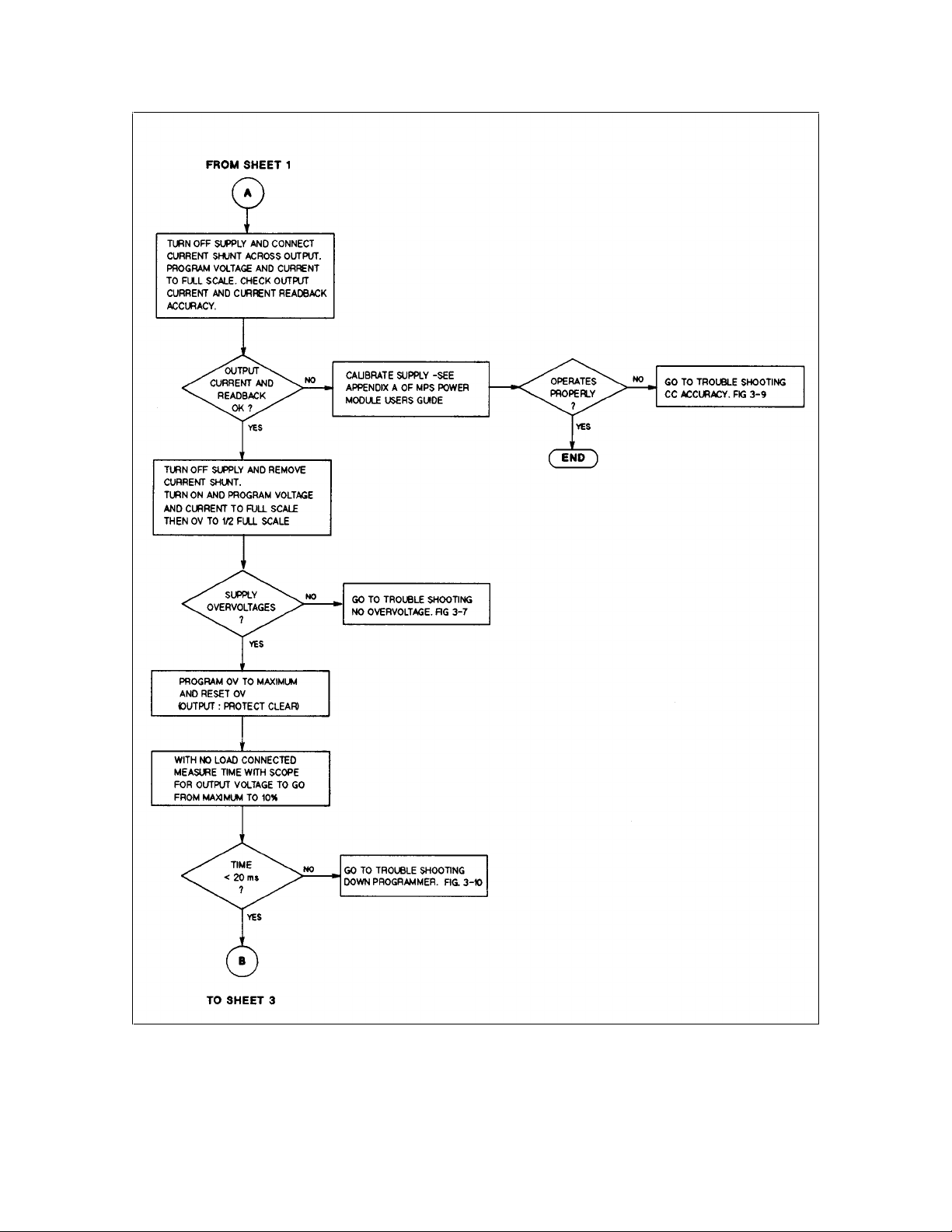
28 Troubleshooting
Figure 3-1. Overall Troubleshooting (Sheet 2 of 3)
Page 29
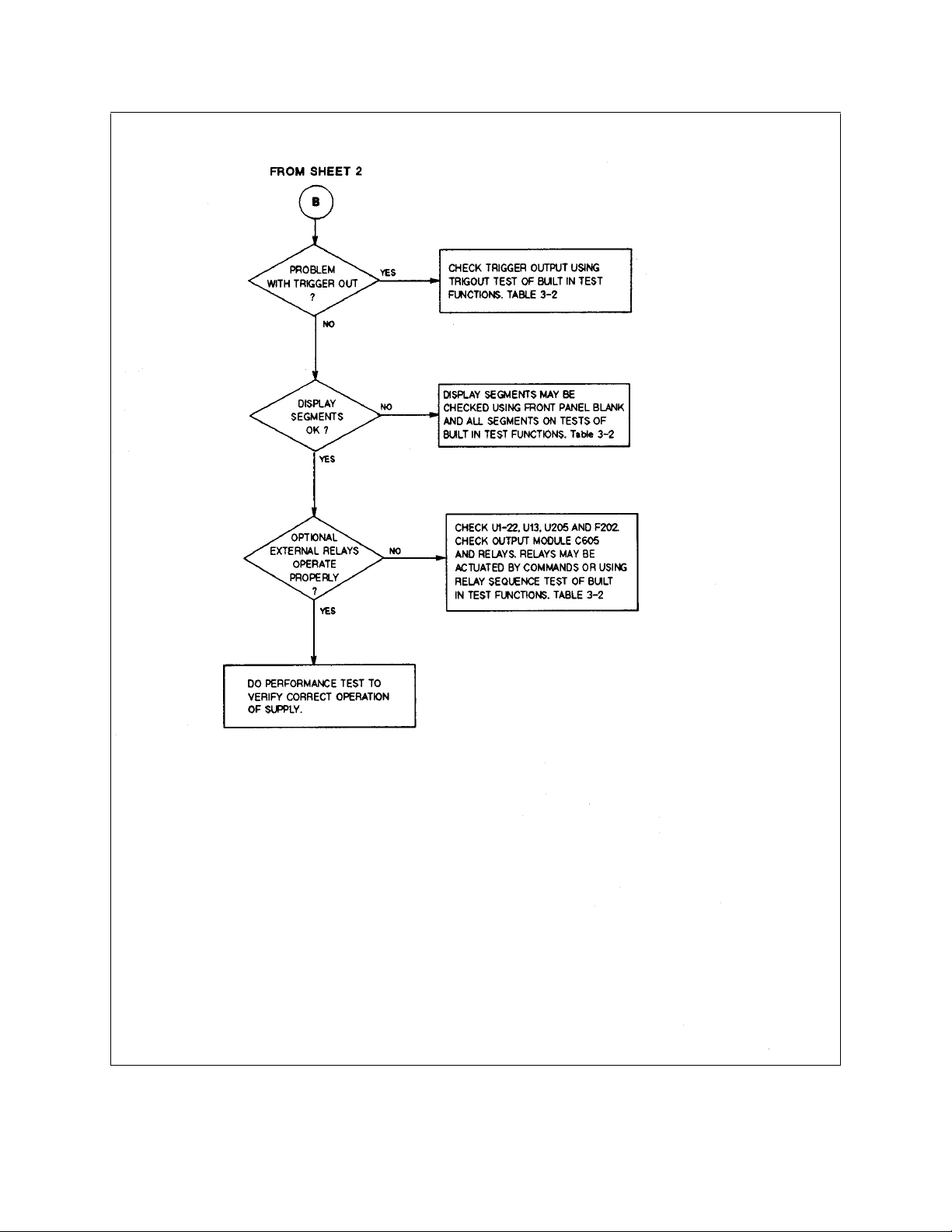
Figure 3-1. Overall Troubleshooting (Sheet 3 of 3)
Troubleshooting 29
Page 30
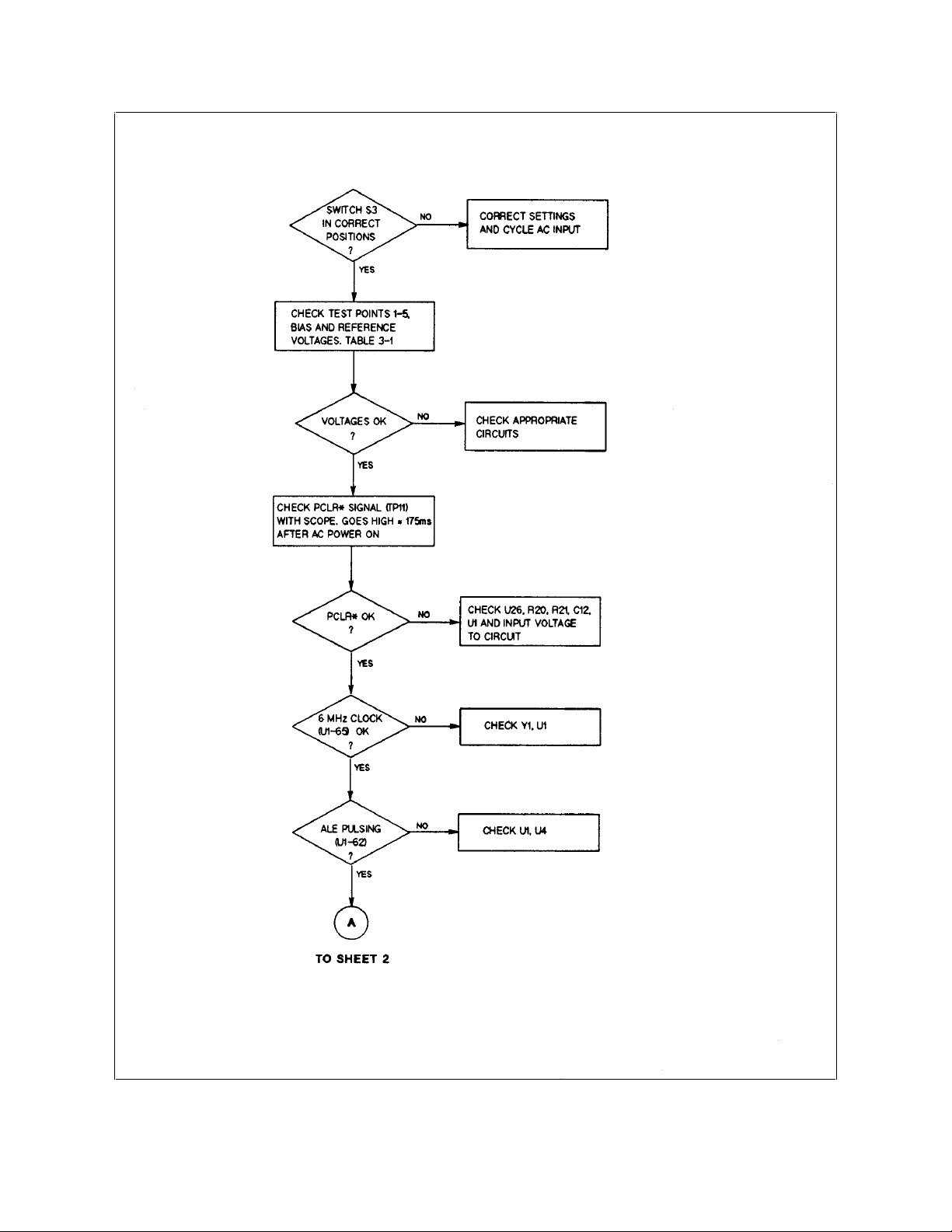
Figure 3-2. Troubleshooting Microprocessor Circuits (Sheet 1 of 2)
30 Troubleshooting
Page 31

Figure 3-2. Troubleshooting Microprocessor Circuits (Sheet 2 of 2)
Troubleshooting 31
Page 32
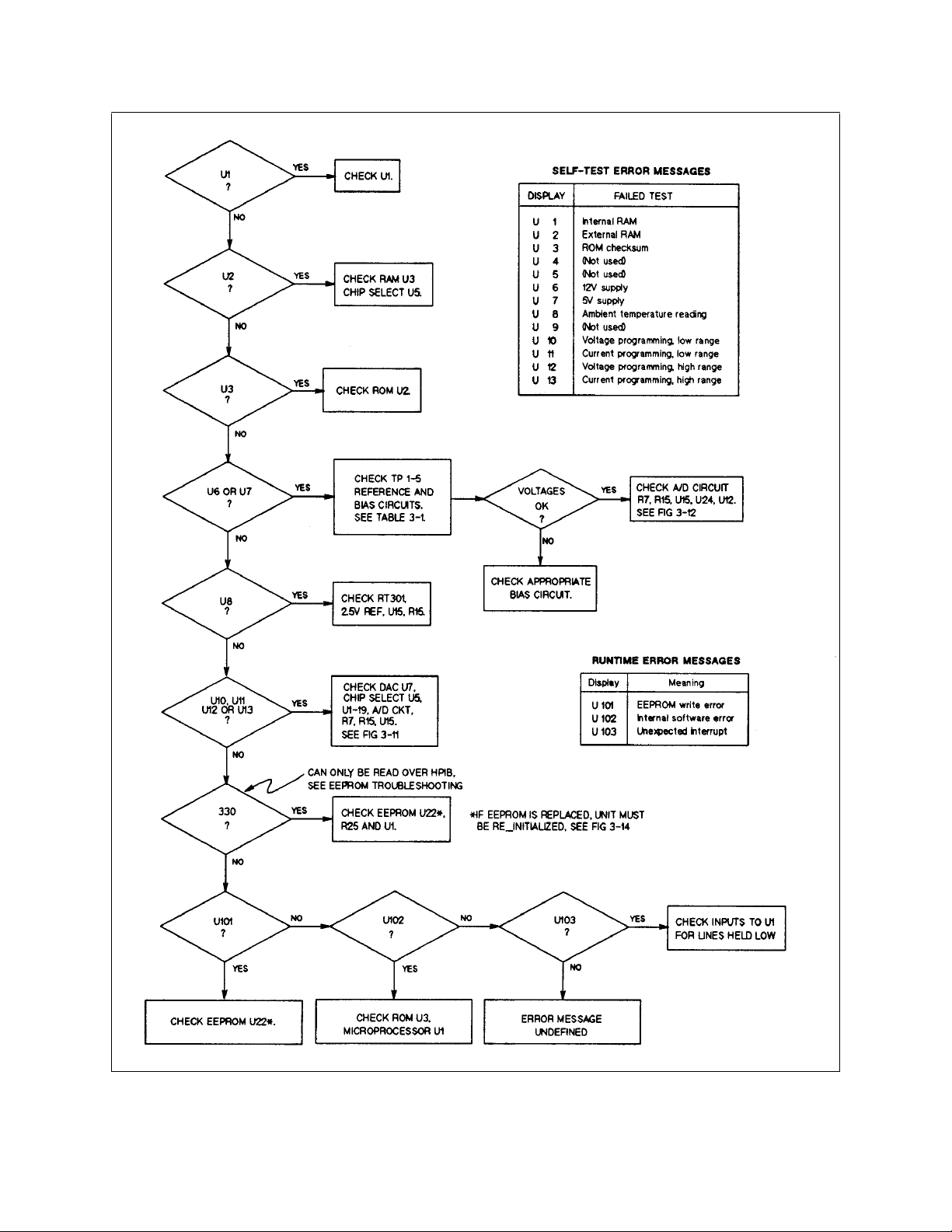
32 Troubleshooting
Figure 3-3. Troubleshooting Error Messages
Page 33

Figure 3-4. Troubleshooting Overvoltage at Turn-On (Sheet 1 of 2)
Troubleshooting 33
Page 34
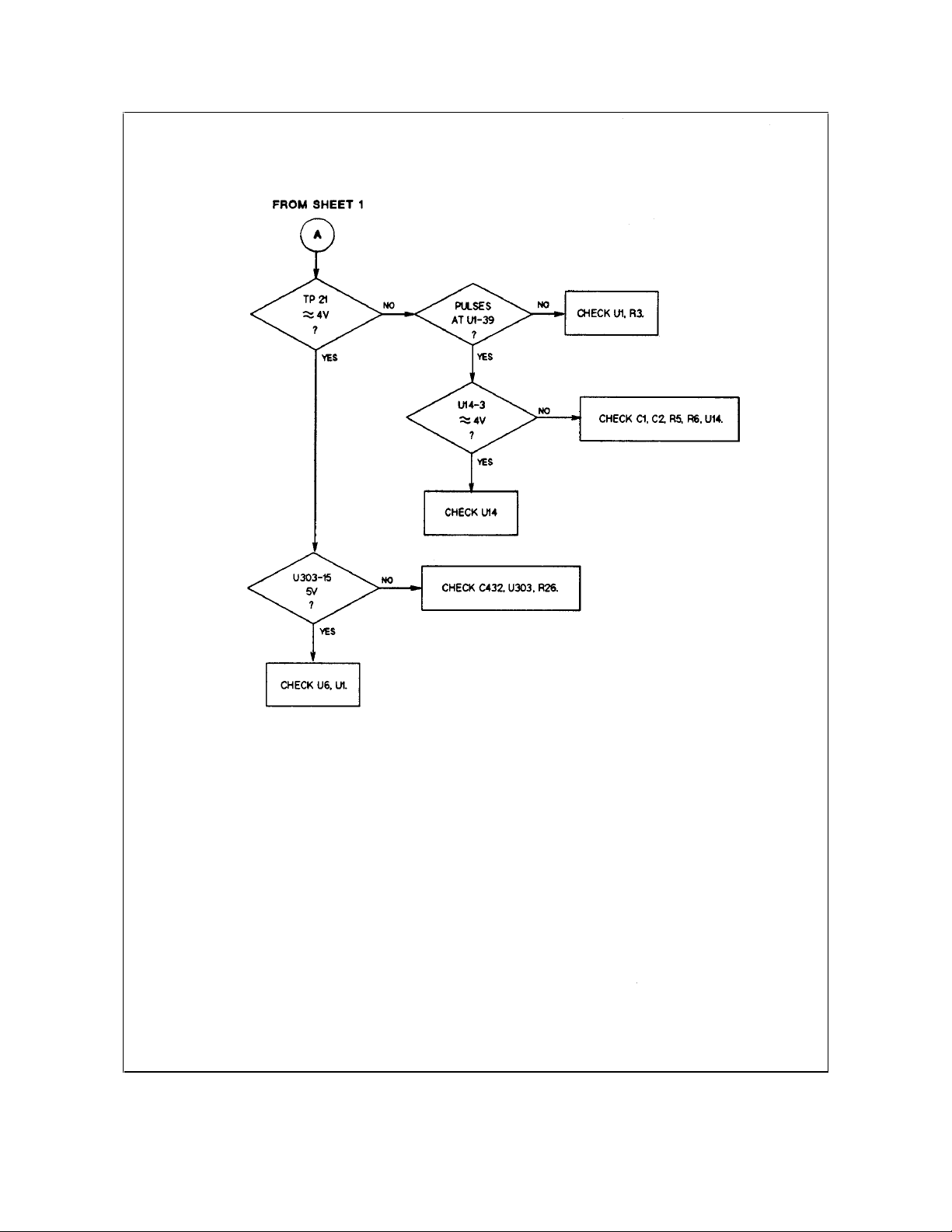
34 Troubleshooting
Figure 3-4. Troubleshooting Overvoltage at Turn-On (Sheet 2 of 2)
Page 35

Figure 3-5. Troubleshooting No Output (Sheet 1 of 5)
Troubleshooting 35
Page 36

36 Troubleshooting
Figure 3-5. Troubleshooting No Output (Sheet 2 of 5)
Page 37
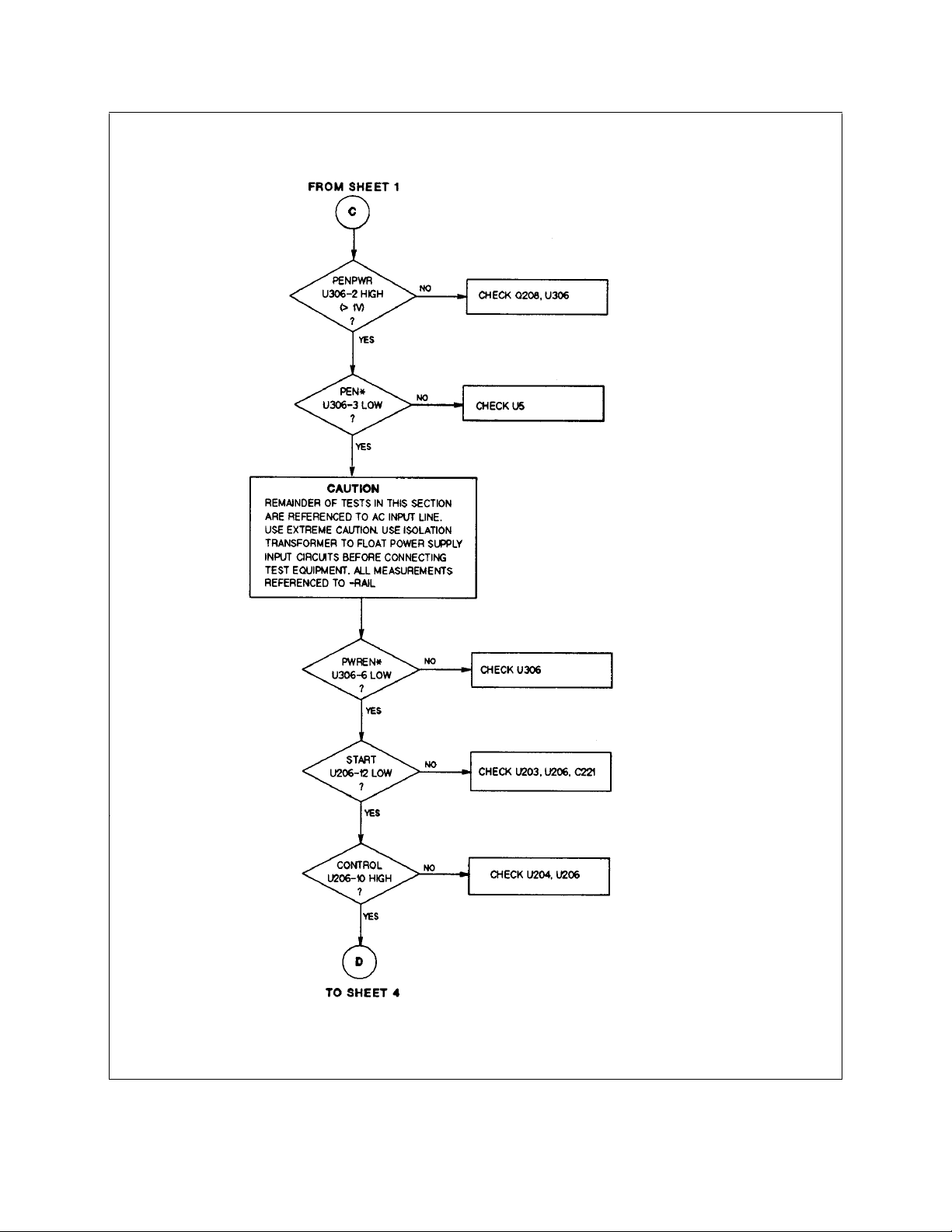
Figure 3-5. Troubleshooting No Output (Sheet 3 of 5)
Troubleshooting 37
Page 38

38 Troubleshooting
Figure 3-5. Troubleshooting No Output (Sheet 4 of 5)
Page 39

Figure 3-5. Troubleshooting No Output (Sheet 5 of 5)
Troubleshooting 39
Page 40
40 Troubleshooting
Figure 3-6. Troubleshooting High Output
Page 41

Figure 3-7. Troubleshooting Will Not Overvoltage
Troubleshooting 41
Page 42

42 Troubleshooting
Figure 3-8. Troubleshooting CV Accuracy
Page 43

Figure 3-9. Troubleshooting CC Accuracy
Troubleshooting 43
Page 44

44 Troubleshooting
Figure 3-10. Troubleshooting Downprogrammer
Page 45
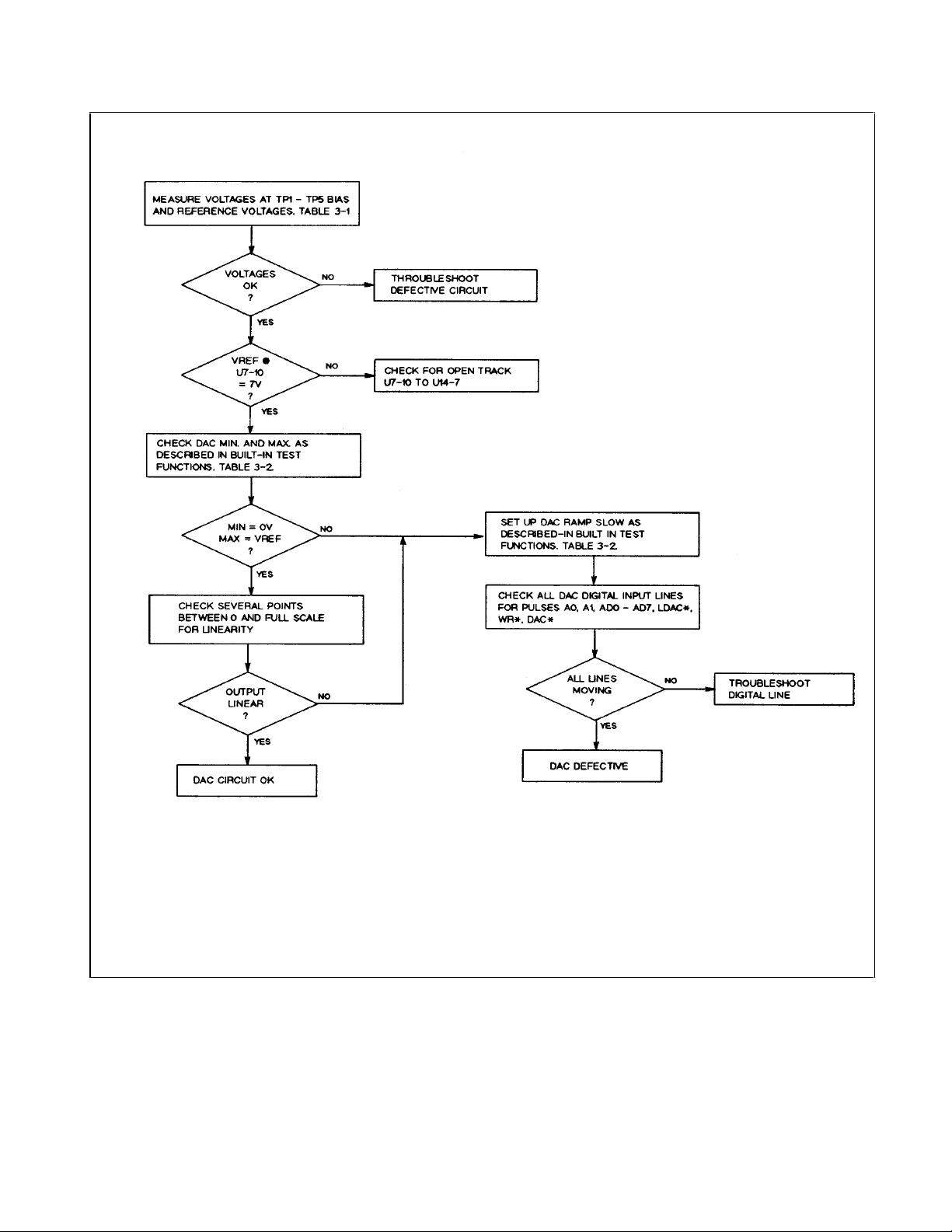
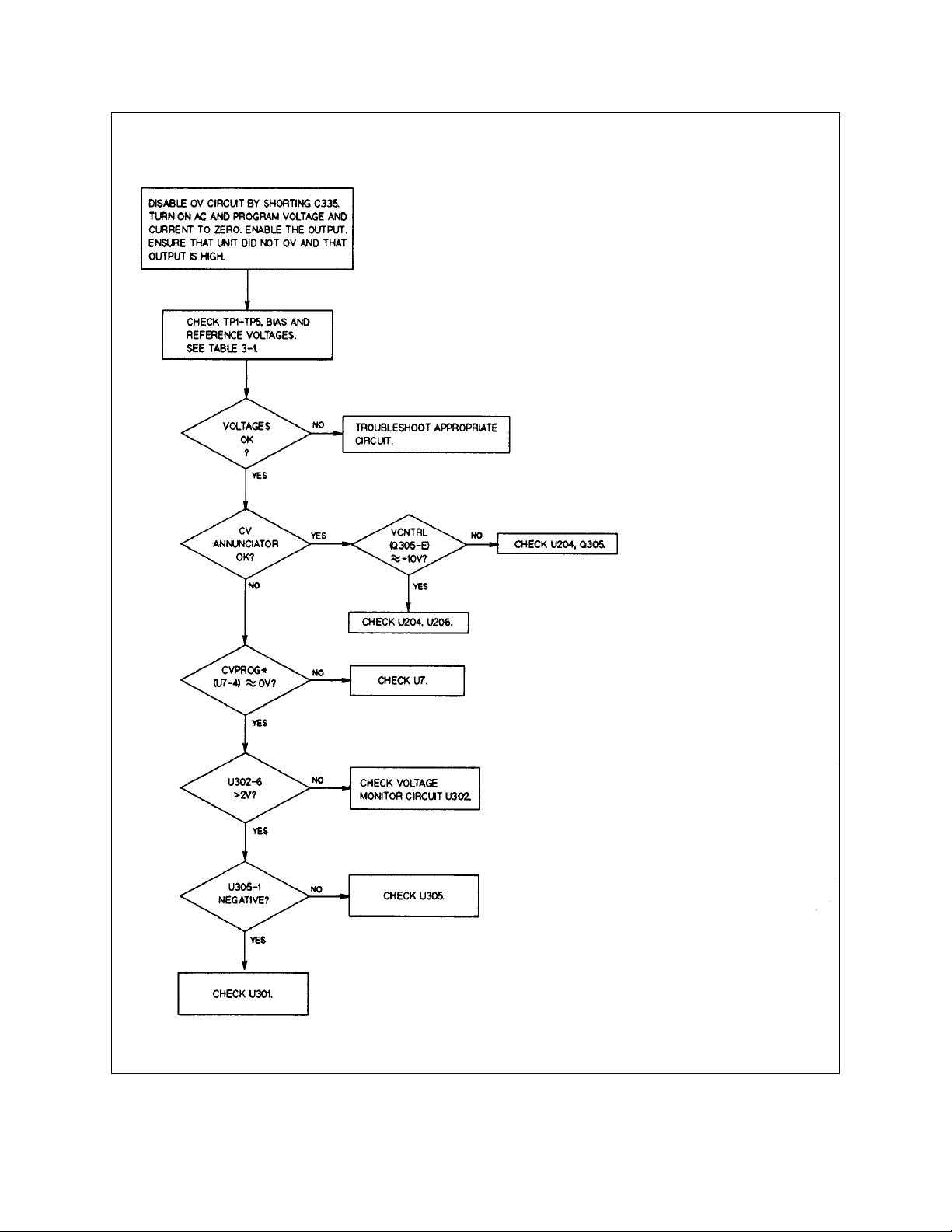
Figure 3-11. Troubleshooting DAC Circuit
Troubleshooting 45
Page 46
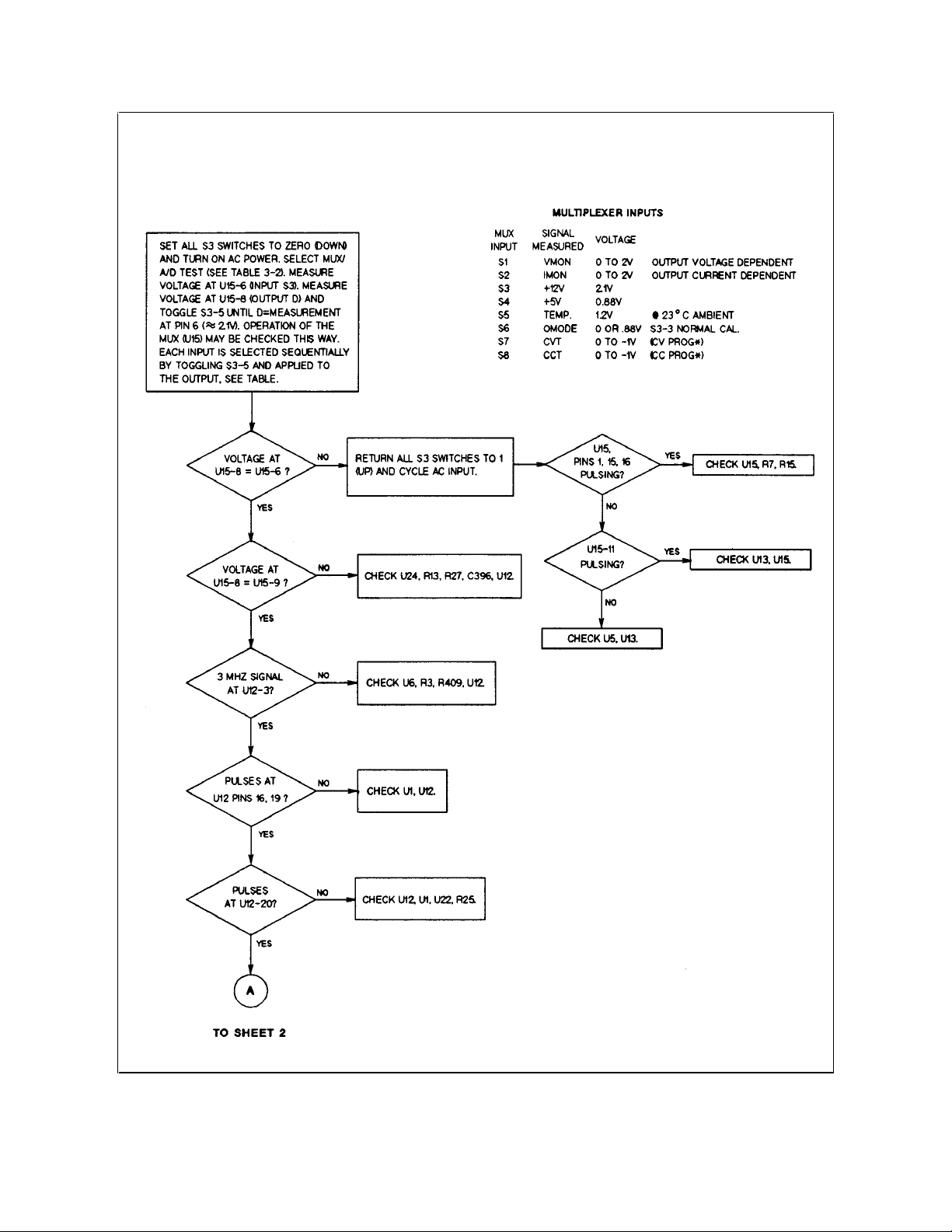
46 Troubleshooting
Figure 3-12. Troubleshooting Readback Circuits (Sheet 1 of 2)
Page 47
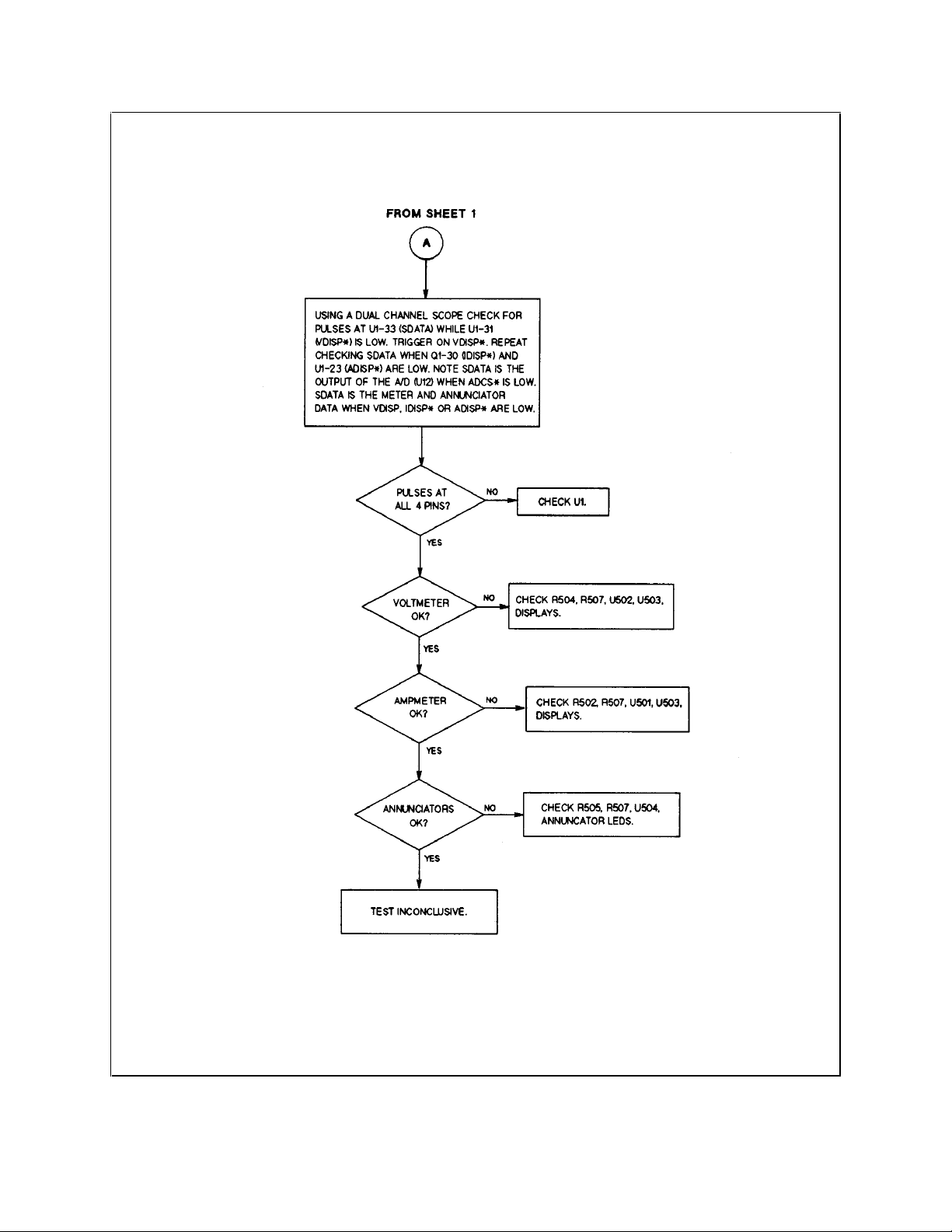
Figure 3-12. Troubleshooting Readback Circuits (Sheet 2 of 2)
Troubleshooting 47
Page 48

Test Points
\
/
The following test points are referenced in the troubleshooting flowcharts. Refer to the component locations diagram in
Chapter 6 for the actual location of the test points on the pc board.
Table 3-1. Test Points
Test Point Description
TP 0
TP 1
TP 2
TP 3
TP 4
TP 5
TP 6
TP 7
TP 8
TP 9
TP 10
TP 11
TP 12
TP 13
TP 14
TP 15
TP 16
TP 17
TP 18
TP 19
TP 20
TP 21
TP 22
Output circuit common (located on inboard side of R303)
+5V (4.8 to 5.2 volts)
+12V (11.4 to 12.6 volts)
+7V (6.7 to 7.3 volts)
+2.5V (2.4 to 2.6 volts)
-12V (-11.4 to -12.6 volts)
+15V (14.25 to 15.75 volts, referenced to the-rail)
l
+5V (4.75 to 5.25 volts, referenced to frame common)
+24V (24.3 to 27.3 volts, referenced to frame common)
+28V (unregulated, referenced to frame common)
Frame common
F
PCLR* (goes low for 175ms at turn-on)
6MHz (microprocessor clock out)
3MHz (A/D clock in)
+ output
-output
0 to-6V (CVPROG)
0 to-6V (CCPROG)
0 to 2V (A/D INPUT)
0 to 2V (VMON)
0 to 2V (IMON)
0 to 4V (OVREF)
-3.4 to -4V (OR GATE, output dependent)
1 Test Equipment must be isolated from ground.
Built-In Test Functions
To aid in troubleshooting, the module configuration switch (S3) can be set to run various test ro utines as described in the
Overall Troubleshooting flowchart. To start the test, set all switches to 0 (down) and turn on ac power. Then set the switch
to perform the selected test as shown in the following table.
48 Troubleshooting
Page 49

Table 3-2. S3 Test Settings
S3 Setting Test Description
8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 Start with blank front panel
0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 Front panel with all segments on
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 VDAC minimum (TP16 = 0V)
0 0 0 1 0 0 0 1 VDAC maximum (TP16 = -VREF)
0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 IDAC minimum (TP17 = 0V)
0 0 0 1 0 0 1 0 IDAC maximum (TP17 = -VREF)
0 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 OVPDAC minimum (TP21 = 0V)
0 0 0 1 0 0 1 1 OVPDAC maximum (TP21 = 4V)
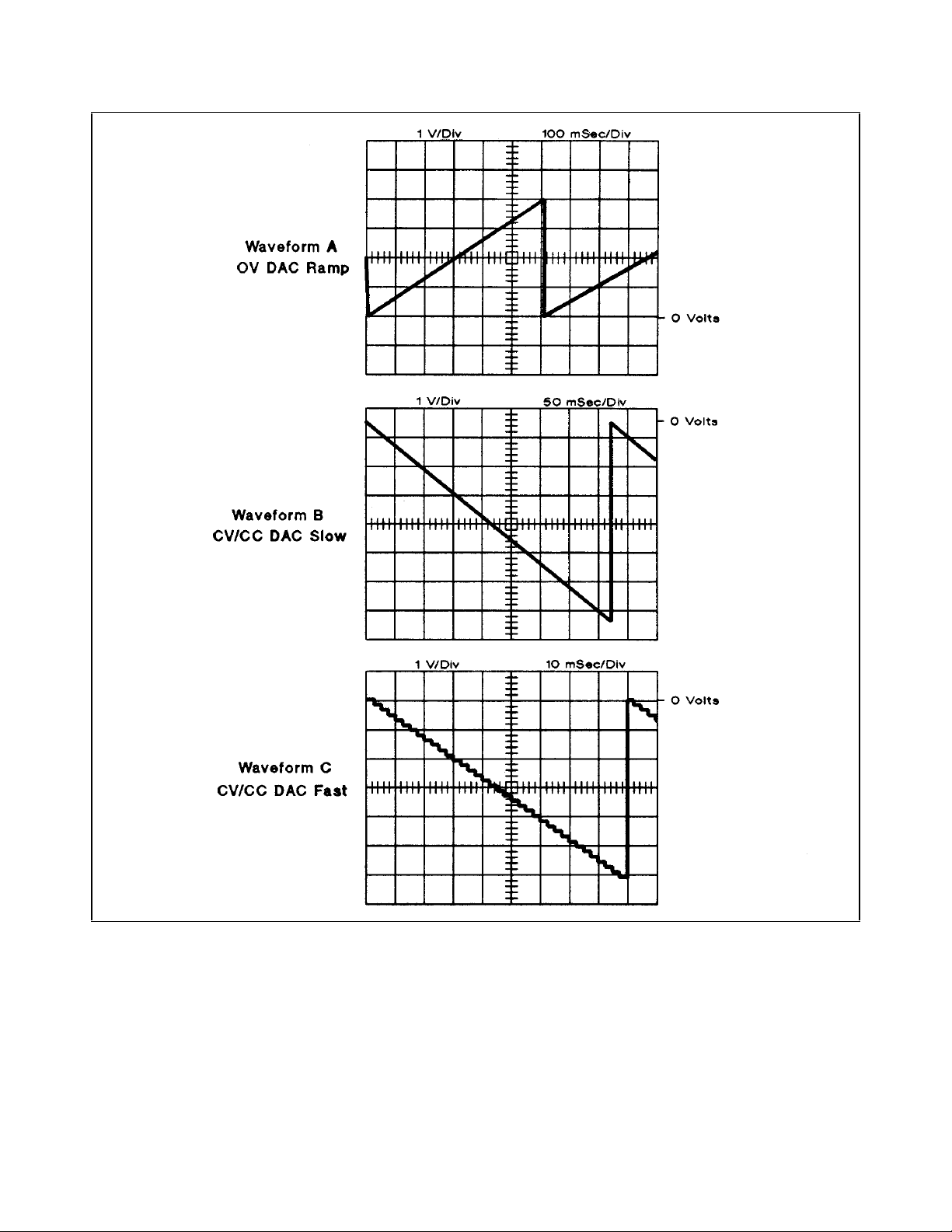
0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 VDAC ramp slow (TP16, see waveform B)
0 0 0 1 0 1 0 0 VDAC ramp fast (TP16, see waveform C)
0 0 0 0 0 1 0 1 IDAC ramp slow (TP17, see waveform B)
0 0 0 1 0 1 0 1 IDAC ramp fast (TP17, see waveform C)
0 0 0 0 0 1 1 0 OVPDAC ramp (TP21, see waveform A)
0 0 0 1 0 1 1 1 MUX/AD (Toggle S3 switch 5 to select input)
0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 SRST* and OVPRST$ pulse
0 0 0 0 1 0 0 1 PWMENhigh
0 0 0 1 1 0 0 1 PWMEN low
0 0 0 0 1 0 1 0 DOCAL pulse
0 0 0 0 1 0 1 1 TRIGOUT (TOUT) pulse
0 0 0 0 1 1 0 0 EEPROM read (U22 pin 4)
2
0 0 0 0 1 1 0 1 Relay sequence (toggle S3 switch 5 to select relay)
0 0 0 0 1 1 1 0 Tx pulses
3
1 Tests multiplexer inputs. First measure voltage at Ul5 pin 4. Toggle S3 switch 5 until voltage at Ul5 pin 8 equals the
voltage at U15 pin 4. Now each time S3 switch 5 is toggled, the multiplexer will sequence through its inputs. The input
of the A/D (Ul2-9) will be equal to the output of the multiplexer. Because the A/D is continually reading, its output
(Ul2-20) should pulse.
2 Continuously reads the contents of location 0 of EEPROM. Check pulses at U22 pin 4.
3 Tests relays K601-K606. Toggling S3 switch 5 sequences through the relays. A relay is off when both ends of the coil
are at +12V. A relay is on when one end is pulled low. A particular relay will energize every 5th toggle on S3 switch 5.
Note that K607 is not tested.
Troubleshooting 49
Page 50
50 Troubleshooting
Figure 3-13. S3 Switch Setting Waveforms
Page 51

EEPROM Troubleshooting and Initialization
Troubleshooting
The power module can detect an EEPROM checksum error. This error is not identified by number, but causes the following
symptoms:
þ The power module starts up with both the VOLTS and AMPS full-scale programming and metering ranges accepting
values up to 1000.
þ Selftest error code 330 is stored in the SCPI error queue where it can be read by the controller (see Chapter 5 in the
Power Module Programming Guide).
þ The *IDN? query returns 0A in the model field.
þ The calibration password is set to 0.
An EEPROM checksum error can occur if there has been an excessive number of write cycles to an EEPROM. This
condition is not recoverable and requires a new EEPROM.
An EEPROM checksum error can also occur due to loss of ac power during a checksum calculation. This condition is very
unlikely, but may be recoverable by performing the following steps from the controller:
þ Enable calibration mode (CAL:STAT ON,0)
þ Save an operating state to EEPROM. (for example, *SAV 2)
Initialization
EEPROM U22 on the power board stores the module’s GPIB address, model number, and other operating and calibration
constants. The EEPROM was initialized with the proper constants at the factory. If you need to re-initialize the module with
the proper o perating constants, run the following program.
After you have initialized the module by running the initialization program, you must calibrate the module as described in
Appendix A of the Power Module User’s Guide.
Troubleshooting 51
Page 52
10 ! Program to initialize EEPROM or move factory preset data in 66101A,
20 ! 66102A, 66103A, 66104A, 66105A and 66106A power supply modules.
30 ! Rev A.00.00 dated May 27, 1993
40 !
50 DIM Init_data(1:39),Model$[6],Idn$[21],Cal_data$[40]
60 INTEGER Addr(1:39),Length(1:39)
70 ASSIGN @Ps TO 70500 ! Supply must be at address 70500
80 CLEAR SCREEN
90 !
100 Eprom_data_addr: ! Data address
110 DATA 2,6,10,14,18,19,20,24,28,32
120 DATA 36,37,38,42,46,50,55,56,57,58
130 DATA 62,66,70,74,,110,l11,112,114,118,119
140 DATA l20,121,122,124,125,126,127,128,130
150 !
160 Eprom_data_len: ! Data for word length
170 DATA 4,4,4,4,1,1,4,4,4,4
180 DATA 1,1,4,4,4,4,1,1,1,4
190 DATA 4,4,4,4,1,1,2,4,1,1
200 DATA 1,1,2,1,1,1,1,1,2
210 !
220 Eprom_data_101a: ! ! EEPROM data for 66101A
230 DATA 409,668,32.2818,8.19,0,66,0,221.586,33.0533,16.38,0
240 DATA 66,4,23.5,19,10,0,255,100,20,66101
250 DATA 3277.35,-1.74536,1772.04,-1.50366,0,0,4,66101,20,150
260 DATA 20,150,28321,40,20,10,83,83,0
270 !
280 Eprom_data_102a: ! ! EEPROM data for 66102A
290 DATA 164.035,32.3969,20.475,0,66,0,440.367,30.0918,7.678,0
300 DATA 66,4,9,5.25,24.0,0,255,100,20,66102
310 DATA 1311.8,.248047,3523.12,-28.4202,0,0,4,66102,20,150
320 DATA 20,150,28321,40,20,10,83,83,0
330 !
340 Eprom_data_103a: ! ! EEPROM data for 66103A
350 DATA 93.7474,32.2944,35.831,0,66,0,735.971,26.127,4.607,0
360 DATA 66,4,4,.93986,5.50002,42,0,255,100,20,66103
370 DATA 749.745,-.725342,5885.92,-54.0496,0,0,4,66103,20,150
380 DATA 20,150,28321,40,20,10,83,83,0
390 !
400 Eprom_data_104a: ! ! EEPROM data for 66104A
410 DATA 54,32.3969,61.425,0,66,0,1320,30.0918,2.559,0
420 DATA 66,4,3,5.25,72.0,0,255,100,20,66104
430 DATA 437,.248047,10569,-28.4202,0,0,4,66104,20,150
440 DATA 20,150,28321,40,20,10,83,83,0
450 !
460 Eprom_data_105a: ! ! EEPROM data for 66105A
470 DATA 27,32.3969,122.85,0,65,0,2640,30.0918,1.28,0
480 DATA 66,4,1.5,5,5.25,144,0,255,100,20,66105
490 DATA 219,.248047,21000,-28.4202,0,0,4,66105,20,150
500 DATA 20,150,28321,40,20,10,82,83,0
Figure 3-14. EEPROM Initialization Program (Sheet 1 of 5)
52 Troubleshooting
Page 53

510 !
520 Eprom_data_106a: ! ! EEPROM data for 66106A
530 DATA 16.4035,32.3969,204.75,0,65,0,4403.67,30.0918,0.768,0
540 DATA 67,4,0.9,5.25,240,0,255,100,20,66106
550 DATA 131.18,.248047,35231.2,-28.4202,0,0,4,66106,20,150
560 DATA 20,150,28321,40,20,10,82,84,0
570 !
580 INPUT “Input Power Supply model number. Example:""66101A""",Model$
590 Model$=TRIM$(UPC$(MODEL$))
600 CLEAR SCREEN
610 !
620 PRINT "The Power Supply Module must be in slot 0. Press ""Continue"""
630 PRINT "to resume program."
640 PAUSE
650 CLEAR SCREEN
660 !
670 RESTORE Eprom_data_addr
680 !
690 FOR I=l T0 39
700 READ Addr(I)
710 NEXT I
720 !
730 RESTORE Eprom_data_len
740 !
750 FOR I=l T0 39
760 READ Length(I)
770 NEXT I
780 !
790 SELECT Model$
800 !
810 CASE "66101A"
820 RESTORE Eprom_data_101a
830 CASE "66102A"
840 RESTORE Eprom_data_102a
850 CASE "66103A"
860 RESTORE Eprom_data_103a
870 CASE "66104A"
880 RESTORE Eprom_data_104a
890 CASE "66105A"
900 RESTORE Eprom_data_105a
910 CASE "66106A"
920 RESTORE Eprom_data_106a
930 CASE ELSE
940 PRINT "Model number not found. Program is for Agilent models"
950 PRINT "66101A through 66106A ONLY"
960 STOP
970 END SELECT
980 !
990 FOR I=l T0 39 ! Read model dependent data
1000 READ Init_data(I)
Figure 3-14. EEPROM Initialization Program (Sheet 2 of 5)
Troubleshooting 53
Page 54

1010 NEXT I
1020 !
1030 OUTPUT @Ps;"*CLS" ! Clears power supply registers
1040 !
1050 OUTPUT @Ps;"CAL;STATE ON," ! Turn on cal mode, "0" passcode
1060 !
1070 GOSUB Ps_error ! Error if passcode is not "0"!
1080 IF Err THEN
1090 OUTPUT @Ps;"*IDN?" ! Get data from model # location
1100 ENTER @Ps;Idn$
1110 Model=VAL(Idn$[POS(Idn$,”,”)+1] )
1120 ELSE
1130 GOTO Start
1140 END IF
1150 !
1160 OUTPUT @Ps;"CAL:STATE ON,";Model ! Turn on cal mode, passcode =
1170 ! data at model number location
1180 !
1190 GOSUB Ps_error ! Error if passcode is not same as
1200 ! data at model # location
1210 IF Err THEN
1220 OUTPUT @Ps;"CAL:STATE ON,";Model$[l,4] ! Turn on cal mode, passcode =
1230 ! model #
1240 GOSUB Ps_error
1250 IF Err THEN
1260 PRINT "Change pass code to the power supply model # or zero. Restart program."
1270 STOP
1280 ELSE
1290 GOTO Start
1300 END IF
1310 END IF
1320 !
1330 Start: !
1340 !
1350 INPUT “Select Initialization (I) or Factory preset replacement (F).”,Sel$
1360 CLEAR SCREEN
1370 SELECT (UPC$(Sel$))
1380 CASE "I" ! Select Initialization
1390 GOTO Init_eeprom
1400 CASE "F" ! Select install new factory data
1410 GOTO Fact_preset
1420 CASE ELSE
1430 BEEP
1440 GOTO Start
1450 END SELECT
1460 !
1470 Init_eeprom: !
1480 PRINT “Initializing EEPROM”
1490 !
1500 FOR I=1 TO 39
Figure 3-14. EEPROM Initialization Program (Sheet 3 of 5)
54 Troubleshooting
Page 55

1510 OUTPUT @Ps;"DIAG:EEPR ’’;Addr(I);’’,’’;Length(I);’’,’’;Init_data(I)
1520 NEXT I
1530 GOTO Cal_off
1540 !
1550 Fact_preset: !
1560 CLEAR SCREEN
1570 PRINT "This program should ONLY be completed if your power supply”
1580 PRINT "EEPROM has been replaced or a component that will effect"
1590 PRINT "the calibration AND the alignment of voltage, overvoltage"
1600 PRINT "and current is complete AND unit has passed the performance"
1610 PRINT "test. Enter C to continue, any other key to abort.”
1620 INPUT Cont_prog$
1630 IF (UPC$(Cont_prog$))< >"C" THEN GOTO Cal_off
1640 !
1650 CLEAR SCREEN
1660 PRINT " Transferring calibration data to factory preset locations."
1670 !
1680 Fact_cal_sour: ! Address of factory calibration data source
1690 DATA 2,6,62,66,20,24,70,74
1700 !
1710 Fact_cal_dest : ! Address of factory calibration data destination
1720 DATA 78,82,86,90,94,98,102,106
1730 !
1740 Fact_cal_len: ! Length of factory calibration data
1750 DATA 4,4,4,4,4,4,4,4,
1760 !
1770 RESTORE Fact_cal_sour
1780 FOR I=1 TO 8
1790 READ Cal_sour_addr(I)
1800 NEXT I
1810 !
1820 RESTORE Fact_cal_dest
1830 FOR I=1 T0 8
1840 READ Cal_dest_addr(I)
1850 NEXT I
1860 !
1870 FOR I=1 T0 8 ! Locations of good data
1880 OUTPUT @Ps;"DIAG:EEPR? ";Cal_sour_addr(I);",";4 ! Read good data
1890 ENTER @Ps;Cal_data$ ! Enter good data
1900 OUTPUT @Ps;"DIAG:EEPR";Cal_dest_addr(I);",";4;",";Cal_data$ ! Write data
1910 NEXT I
1920 !
1930 Cal_off !
1940 CLEAR SCREEN
1950 OUTPUT @Ps;"CaL:STATE OFF" ! Turn off cal mode
1960 !
1970 GOSUB Ps_error ! Check for errors
1980 IF Err THEN
1990 PRINT "An error occurred during the EEPROM read/write, Check for"
2000 PRINT "programming errors. Initialization data may be incorrect."
Figure 3-14. EEPROM Initialization Program (Sheet 4 of 5)
Troubleshooting 55
Page 56

2010 STOP
2020 END IF
2030 !
2040 PRINT "Operation complete. Program stopped."
2050 STOP
2060 !
2070 Ps_error: ! Error handling subroutine
2080 OUTPUT @Ps;"SYST:ERR?" ! Check for errors
2090 ENTER @Ps;Err
2100 RETURN
2110 !
2120 END
Figure 3-14. EEPROM Initialization Program (Sheet 5 of 5)
Disassembly Procedures
This section describes how to disassemble and reassemble the Agilent 6610xA Power Modules. Refer to Chapter 5 for the
component descriptions. Refer to Chapter 1 for the tools required to disassemble and reassemble the unit.
Most of the attaching hardware is metric. Using the wrong fasteners will damage threaded inserts.
Observe all standard anti-static procedures when removing the pc boards from the chassis (see
Chapter 1).
Removing the Module and Module Connector
Before you can disassemble the module, you must first remove the power modules from the mainframe.
1. Use the slot-head screwdriver and release the pull tab at the front of each module.
2. Pull the power module out of the mainframe.
3. To remove the module connector, use the Pozi driver and disconnect the module connectors from the back of the
mainframe.
Removing the Cover
1. Use the T10 driver and remove the seven screws that connect the chassis cover to the chassis.
2. Lift the cover off.
Removing the Fan
1. Carefully unplug the fan cable from the J102 connector on the Power board.
2. Use the T10 driver and 7mm nut driver and remove the two screws that connect the fan to the fan bracket.
3. Remove the fan.
56 Troubleshooting
Page 57

Removing the Front Panel Assembly
1. Carefully unplug the front panel cable from the J3 connector on the Power board.
2. Spread the bottom of the chassis away from the front panel assembly and lift the assembly out of the chassis.
Removing the Power Board
1. Carefully unplug the front panel cable from the J3 connector, the bias board cables from the J301 and J302 connectors,
and the fan cable from the J102 connector on the Power board.
2. Use the T10 driver and remove the four screws (two toward the back and two near the center) that attach the Power
board to the chassis.
3. Lift up on the top edge of the Power board and carefully remove the board from the chassis.
Removing the Bias Board
Removing the Front Panel assembly first makes it easier to remove the Bias board.
1. Carefully unplug the bias board cables from the J401 and J402 connectors on the Bias board. If you have not already
done so, carefully unplug the front panel cable from the J3 connector on the Power board.
2. Use the T10 driver and remove the two screws at the front that attach the Bias board to the chassis.
3. Lift up on the front edge of the Bias board and carefully remove the board from the chassis.
Removing the Front Panel Board
You must first remove the Front Panel assembly before you can remove the Front Panel board.
1. Separate the two halves of the front panel assembly by releasing the four locking tabs with the flat-bladed screwdriver
(see figure 3-15).
2. Insert the screwdriver into the areas indicated on the figure and press against the tabs to release them.
3. Once separated, you can easily remove the front panel board from the front panel assembly.
4. You can also easily remove the latching mechanism once the front panel assembly is separated.
Troubleshooting 57
Page 58

Figure 3-15. Front Panel Assembly Locking Tabs
Installing the Power Board
1. Insert the tabs along the bottom edge of the board in the corresponding slots on the bottom of the chassis and carefully
install the board in the chassis.
2. Use the T10 driver and insert the four screws (two toward the back and two near the center) that attach the Power board
to the chassis.
3. Connect the front panel cable into the J3 connector, the bias board cables into the J301 and J302 connectors, and the
fan cable into the J102 connector on the Power board.
4. Insert the front panel cable and the bias board cables into the appropriate cable cutout on the fan bracket.
5. To prevent the cover from pinching the cables, route the front panel cable, the longer bias board cable, and the fan
cable between T201 and L201.
Installing the Bias Board
1. Carefully install the Bias board so that T401 is positioned up against the fan bracket.
2. Use the T10 driver and insert the two screws at the front that attach the Bias board to the chassis.
3. Connect the bias board cables into the J401 and J402 connectors on the Bias board.
4. Insert the bias board cables into the appropriate cable cutout on the fan bracket. Route the longer bias cable in between
T201 and L201.
58 Troubleshooting
Page 59

Installing the Front Panel Board and Front Panel Assembly
1. Install the front panel, the front panel board, and the latch assembly in one of the front assembly halves.
2. Make sure that the front panel board is positioned in the slot closest to the front panel.
3. Carefully snap the other half of the front panel assembly together.
4. Insert the tab on the top of the front panel assembly in the corresponding notch on the chassis and position the fro nt
panel assembly into the chassis. The two tabs on the side of the assembly should be positioned in the corresponding
notches on the side of the chassis.
5. Connect the front pane l cable into the J3 connector on the Power board. Route the cable through the cutout on the fa n
bracket and in between T201 and L201.
Installing the Fan
1. Position the fan up against the fan bracket.
Make sure that the arrow on the fan is pointing to the BACK of the module. The airflow must be from
the front of the module to the back of the module.
2. Use the T10 driver and 7mm nut driver and insert the two screws and nuts that connect the fan to the fan bracket. Place
the locking nuts against the fan bracket.
3. Connect the fan cable into the J102 connector on the Power board. Route the cable in between T201 and L201.
Installing the Cover
1. Position the cover over the chassis so that the screw holes and the notches on the front panel assembly notches line up
with the corresponding openings in the cover. Make sure that no cables are being pinched by the cover.
2. Use the T10 driver and insert the seven screws that connect the chassis cover to the chassis
Troubleshooting 59
Page 60

Page 61

Theory of Operation
This chapter provides a brief theory of operation for the Agilent 6610xA Power Modules. Figure 4-1 is a block diagram of
the primary circuit functions of the power modules. The diagram references the schematic sheets where the circuits are
located.
AC Input and Bias Supplies
AC input power is distributed to each module through the backplane connector boa r d on the mainframe. A turn-on relay
inside the module applies ac power from the mainframe to the power module. T his relay receives its bias power from the
mainframe and is opened and closed by a control signal from the mainframe.
The ac input is rectified and filtered in the power module, producing the + and - dc rail. In addition to the dc rail, the ac
input is also applied to a bias transformer, which provides the following bias voltages:
+ 15V (primary)
+ 5V (secondary)
± 12V (secondary)
4
Microprocessor Circuits
All communication between the modules and the controller or keyboard except for the trigger signals is processed by U44
on the mainframe. The primary function of this microprocessor is to distribute the digital signals from controller or
keyboard to the correct module slot in the mainframe.
Microprocessor Ul on the modules communicates with U44 through two data lines -a transmit and a receive line (Tx and
Rx). Associated with Ul is ROM chip U2, RAM chip U3, and EEPROM chip U22.
At turn-on, microprocessor Ul first transfers the calibration constants that are stored in the EEPROM chip of each module
into RAM. It then applies the calibration correction factors in RAM to the voltage or current setting information and
calculates a bit count that it sends to the DACs. The microprocessor directs the data either to the CV or the CC DAC. It is
able to send sixteen data bits to each DAC by first strobing in the upper byte, and then strobing in the lower byte.
CV/CC DACs
Upon receiving data from the microprocessor, the CC and CV DACS output the correct analog output voltage. Both the CC
and the CV DACs output an analog signal in the range of 0 to minus 6 volts (calibrated), which corresponds to the zero to
full-scale output range of the power module’s voltage and current. The DACs are referenced to a regulated 7V bias.
Theory Of Operation 61
Page 62

62 Thoery Of Operation
Figure 4-1. Block Diagram
Page 63

CV Amplifier
The CV amplifier controls the output of the power module when the module is operating in constant voltage mode. The CV
amplifier consists of two stages: an error amplifier stage and a voltage monitor stage. The calibrated CVPROG* signal from
the CV DAC pulls current out of the negative input of the error amplifier at a rate determined by the DAC’s programmed
value. The error amplifier in turn, controls the output of the module.
The output of the module is monitored by the voltage monitor stage. It reduces the module’s output voltage so that the 0 to
full-scale output voltage of the module is represented by a range of 0 to 2 volts at the output of the voltage monitor
amplifier. The voltage monitor amplifier’s output (VMON) is fed through a resistor to develop a current. This current is fed
into the negative input of the error amplifier stage at the same time that current is being pulled out of this input by the
CVPROG* signal from the CV DAC.
When the current pulled out of the error amplifier input by the CV DAC exceeds the current fed into the input by the
voltage monitor, the error amplifier turns on, which turns the output of the module on. When the current pulled out of the
error amplifier input by the CV DAC is less than the current fed into the input by the voltage monitor, the error amplifier
turns off, which turns off the output of the module. When the current pulled out of the error amplifier input by the CV DAC
is equal to the current fed into the input by the voltage monitor, the net current into the error amplifier is zero. At this point,
there is no change on the output voltage of the power module because the output voltage equals the programmed voltage
value.
CC Amplifier
The CC amplifier controls the output of the power module when the module is operating in constant current mode. The CC
amplifier also consists of two stages: an error amplifier stage, and a current monitor stage. The calibrated CCPROG* signal
from the CC DAC pulls current out of the negative input of the error amplifier at a rate determined by the DAC’s
programmed value. The error amplifier in turn, controls the output of the module.
The current monitor stage monitors the current at the output of the module by sensing the voltage drop across current
monitor resistor (RM). The current monitor amplifies this voltage (which is typically in the range of 0 to 50mV) so that the
0 to full-scale current output of the module is represented by a range of 0 to 2 volts at the output of the current monitor
amplifier. The current monitor a mplifier’s output (IMON) is fed through a resistor to develop a c urrent. This current is fed
into the negative input of the error amplifier stage at the same time that current is being pulled out of this input by the
CCPROG* signal from the CC DAC.
When the current pulled out of the error amplifier input by the CC DAC exceeds the current fed into the input by the current
monitor, the error amplifier turns on, which turns on the output of the module. When the current pulled out of the error
amplifier input by the CC DAC is less than the current fed into the input by the current monitor, the error amplifier turns off,
which turns off the output of the module. When the current pulled out of the error amplifier input by the CC DAC is equal to
the current fed into the input by the current monitor, the net current into the error amplifier is zero. At this point, there is no
change on the output current of the power module because the output current equals the programmed current value.
OR Gates
The outputs of the CV and CC amplifiers are "or"ed through two diodes, pro ducing a single pulse-width modulator control
signal (VCNTRL). Whichever of the two signals (CC or CV) is the most negative, with respect to the output of the module,
controls the pulse-width modulator. The pulse-width modulator in turn controls the FETS. The more negative that the
controlling signal is with respect to the output, the harder it causes the pulse-width modulators to turn on the FETs.
Theory Of Operation 63
Page 64

Pulse-Width Modulator, FETS, and Isolation Transformer
The pulse-width modulator controls the FETS. The FETS are arranged in an "H" bridge configuration with the + and - dc
rail at the top and bottom of the H. The 4 FETS are located on each leg of the "H", and the isolation transformer is located
on the horizontal bar of the H. The FETS located diagonally across from each other are alternately turned on and off (Q201
and Q204 are turned on, then off; followed by Q202 and Q203 being turned on, then off).
In this way current flows from the + dc rail through the primary of T201 to the - dc rail. When Q201 and Q204 are on,
current flows through the primary of T201 in one direction. When Q202 and Q203 are on, current flows through the primary
of T201 in the opposite direction. This generates the positive and negative pulses on the secondary winding of T201. The
output of T201 is then rectified and filtered to produce the dc output.
T202, located in series with T201, is part of the peak current limit circuit, which limits the amount of current that can flow
through the FETs. This protects the internal and e xternal circuits from excessive currents that may result when the output of
the module is shorted.
Downprogrammer Circuit
The downprogrammer circuit inter nally dr a ws curre nt through the output rectifier and filte r to keep the FET cir cuits turned
on when the module is programmed to a low or zero output. The maximum current that flows through the downprogrammer
is 10% of the total output current .
The downprogrammer circuit monitors the current at the output of the module and turns off when the output current reaches
1/2 of its full-scale rating.
Additionally, when voltage is programmed to a low value or programmed off, the downprogrammer helps to pull down the
output of the supply to speed up downprogramming time.
Readback Multiplexer
The readback multiplexer and the readback A to D are used to read back information from the module during normal
operation and during selftest. The microprocessor selects an input on the readback multiplexer and reads back data on that
input. The following signals comprise the inputs to the multiplexer:
IMON
VMON
+12V reference
+5V reference
temperature reference
power turn-on switch setting
CV DAC output
CC DAC output
The multiplexer inputs are between 2.5 volts and -2.5 volts, which is the voltage range of the 16-bit readback A to D
converter. The IMON and VMON signals are in the range of 0 to 2 volts, which represents the 0 to full-scale output of the
supply. The readback A to D converter converts the analog signal from the multiplexer to a digital signal, which is returned
to the microprocessor. The microprocessor in turn sends the corrected (calibrated) data to the display.
64 Thoery Of Operation
Page 65

OV Circuit
The OV circuit consists of a comparator that compares the output voltage of the module with an overvoltage reference
signal and shuts down the output when the output of the supply exceeds the overvoltage reference level.
The microprocessor generates the overvoltage reference by putting out a pulse-width modulated signal that is filtered to
produce a 0 to 4 volts reference (OVREF). This reference is proportional to an overvoltage setting of about 0 to 110% of
full scale output and is applied to the + input of the overvoltage comparator.
The output of the supply goes to a voltage divider which steps down the output to a proportional voltage that also ranges
from 0 to 4 volts. This signal is applied to the negative input of the overvoltage comparator. When the voltage at the
negative input exceeds the voltage at the positive input, the output of the comparator changes state, informing the
microprocessor that an overvoltage condition has occurred. The microprocessor then turns off the pulse-width modulators,
which turns off the FETs.
Theory Of Operation 65
Page 66

Page 67
Replacement Parts
Table 5-1 lists the electrical components of the Agilent 6610xA Power Modules’ main, bias, and front panel boards. Table
5-2 lists the mechanical components of the module. Table 5-3 lists all of the components of the connector assembly. These
tables provide the following information:
þ Reference designation
þ Agilent Technologies part number
þ Description of part
You can order parts from your local Agilent Technologies sales office. A list of the regional sales offices is given at the
back of this manual. When ordering parts, include the following information:
þ Agilent Technologies part number
þ Description of the part
þ Quantity desired
þ MPS model number (e.g. Agilent 66101A)
Note The test point and locations diagrams in Chapter 6 identify the location of the electrical components on
the circuit boards.
5
Replacement Parts 67
Page 68

Table 5-1. Agilent 6610xA Power Modules Parts List - Electrical
Reference
Designators
66101A 66101-61022 ASSEMBLY-POWER BOARD
66102A 66102-61022 ASSEMBLY-POWER BOARD
66103A 66103-61022 ASSEMBLY-POWER BOARD
66104A 66104-61022 ASSEMBLY-POWER BOARD
66105A 66105-61022 ASSEMBLY-POWER BOARD
66106A 66106-61022 ASSEMBLY-POWER BOARD
All Models 5060-3358 ASSEMBLY-FAN (REF J102)
Cl, C2 All Models 0160-5422 CAP .047uF 20%
C3 All Models 0180-4136 CAP l0uF 20V
C4-C10 All Models 0160-5422 CAP .047uF 20%
C11, C12 All Models 0180-4136 CAP l0uF 20V
C13, C14 All Models 0160-4807 CAP 33pF 5% l00V
C15-C17 All Models 0160-4822 CAP l000pF 5%
C18 All Models 0180-4136 CAP l0uF 20V
C20-C24 All Models 0160-5422 CAP .047uF 20%
C27 All Models 0160-5422 CAP .047uF 20%
C28 All Models 0160-4281 CAP 2200pF 20%
C192 All Models 0160-5422 CAP .047uF 20%
C201 All Models 0160-4830 CAP 2200pF 10%
C202 All Models 0160-4808 CAP 470pF 5%
C203, C204 All Models 0160-4183 CAP l000pF 20%
C206 All Models 0160-4259 CAP .22uF 10%
C207, C208 All Models 0180-4393 CAP 560uF 250V
C209 All Models 0160-7578 CAP 330pF 630VDC
C210 All Models 0160-4814 CAP 150pF 5%
C211, C212 All Models 0160-5422 CAP .047uF 20%
C213 All Models 0180-4136 CAP l0uF 20V
C214 All Models 0160-7578 CAP 330pF 630VDC
C215 All Models 0160-5422 CAP .047uF 20%
C217-C221 All Models 0160-5422 CAP .047uF 20%
C222 All Models 0160-4803 CAP 68pF 5% 100V
C223 All Models 0160-5422 CAP .047uF 20%
C224 All Models 0160-4801 CAP l00pF 5%
C225, C226 All Models 0160-7578 CAP 330pF 630VDC
C227 All Models 0180-3680 CAP l0uF 50V
C228 All Models 0160-4830 CAP 2200pF 10%
C229 All Models 0160-4833 CAP .022uF 10%
C230 All Models 0160-5098 CAP .22uF 10%
C232 All Models 0160-4439 CAP 4700pF 20%
C301 66101A 0160-7568 CAP 4700pF 250V 5%
66102A 0160-7522 CAP l000pF 630V
66103A 0160-7639 CAP 470pF 1600V
66104A 0160-6838 CAP 2200pF
66105A 0160-7639 CAP 470pF 1600V
66106A 0160-7640 CAP 330pF 1600V
Model Part Number Description
68 Replacement Parts
Page 69

Table 5-1. Agilent 6610xA Power Modules Parts List - Electrical (continued)
Reference
Designators
C303 66101A 0180-4398 CAP 470uF 63V
66102A 0180-4400 CAP 220uF 63V
66103A 0180-4397 CAP l00uF 63V
66104A 0180-3649 CAP 47uF l00VDC
66105A 0180-3648 CAP l0uF 250V
66106A 0180-3169 CAP 4.7uF 250VDC
C304 66101A 0180-4398 CAP 470uF 63V
66102A 0180-4400 CAP 220uF 63V
66103A 0180-4397 CAP l00uF 63V
66104A 0180-3649 CAP 47uF 100V
66105A 0180 3696 CAP 22uF 250V
66106A 0180-3648 CAP l0uF 250V
C305 All Models 0160-4323 CAP .047uF 20%
C306, C307 All Models 0160-4259 CAP .22uF 10%
C307 All Models 0160-4259 CAP .22uF 10%
C308 All Models 0160-4323 CAP .047uF 20%
C309A 66101A-66103A 0160-7562 CAP 6.8uF 63V
66104A-66106A Not Used
C309B 66101A 0160-7562 CAP 6.8uF 63V
66102A, 66103A Not Used
66104A-66106A 0160-5050 CAP l.0uF 250V
C310 All Models 0160-4808 CAP 470pF 5%
C311 66101A, 66104A 0160-4831 CAP 4700pF 10%
66102A, 66103A 0160-7001 CAP 3300pF 100V
66105A 0160-4830 CAP 2200pF 10%
66106A 0160-7001 CAP 3300pF 100V
C312, C313 All Models 0160-4281 CAP 2200pF 20%
C314, C315 All Models 0160-4808 CAP 470pF 5%
C316 All Models 0160-4795 CAP 4.7pF
C317 66101A, 66102A 0160-4831 CAP 4700pF 10%
66103A, 66104A 0160-6616 CAP 6800pF 100V
66105A 0160-4832 CAP .0luF 10%
66106A 0160-5166 CAP .015uF 20%
C318 All Models 0160-4795 CAP 4.7pF
C319 All Models 0160-5467 CAP 0.0luF 63V
C320 All Models 0160-4791 CAP l0pF 5% 100V
C321 66101A 0160-5892 CAP .22uF 10%
66102A-66106A 0160-5468 CAP 0.47uF 50V
C322 All Models
C323 All Models
C324, C325 All Models
C326, C327 All Models 0160-5422 CAP .047uF 20%
C328 All Models 0160-4822 CAP l000pF 5%
C329 All Models 0160 5422 CAP .047uF 20%
C330 All Models 0160-4832 CAP .0luF 10%
C331 66101A, 66102A 0160-4787 CAP 22pF 5% 100V
66103A-66106A 0160-4805 CAP 47pF 5% 100V
Model Part Number Description
0160−4807
0160−5892
0160−4808
CAP 33pF 5% 100V
CAP .22uF 10%
CAP 470pF 5%
Replacement Parts 69
Page 70
Table 5-1. Agilent 6610xA Power Modules Parts List - Electrical (continued)
Reference
Designators
C332, C333 All Models 0160-5422 CAP .047uF 20%
C334 All Models 0160-4807 CAP 33pF 5% 100V
C335 66101A 0160-4831 CAP 4700pF 10%
66102A-66106A 0160-4830 CAP 2200pF 10%
C336 66101A, 66102A 0160-4787 CAP 22pF 5% 100V
66103A-66106A 0160-4805 CAP 47pF 5% 100V
C337 All Models 0160-4830 CAP 2200pF 10%
C338-C341 All Models 0160-5422 CAP .047uF 20%
C342 All Models 0160-5892 CAP .22uF 10%
C343 66101A-66104A 0160-4831 CAP 4700pF 10%
66105A 0160-4833 CAP .022uF l0%
66106A 0160-7001 CAP 3300pF 100V
C346 66101A 0160-4832 CAP .0luF 10%
66102A 0160-6616 CAP 6800pF 100V
66103A, 66104A 0160-4832 CAP .0luF 10%
66105A 0160-4833 CAP .022uF 10%
66106A 0160-4832 CAP .0luF 10%
C347 66101A 0160-4801 CAP l00pF 5%
66102A-66104A 0160-4803 CAP 68pF 5% 100V
66105A 0160-4813 CAP 180pF 5%
66106A 0160-4803 CAP 68pF 5% 100V
C349 66101A-66105A 0160-4812 CAP 220pF 5%
66106A 0160-4808 CAP 470pF 5%
C358 All Models 0160-4830 CAP 2200pF 10%
C395 All Models 0180-4129 CAP luF 35V
C396 All Models 0160-7578 CAP 330pF 630VDC
C397 All Models 0160-4835 CAP .luF 10% 50V
C403 All Models 0160-4183 CAP l000pF 20%
C404 All Models 0160-5422 CAP .047uF 20%
C407 All Models 0180-4136 CAP l0uF 20V
C408-C410 All Models 0180-4129 CAP luF 35V
C411-C413 All Models 0160-4835 CAP .luF 10% 50V
C414, C415 All Models 0160-4822 CAP l000pF 5%
C416 All Models 0160-4808 CAP 470pF 5%
C418 All Models 0160-5422 CAP .047uF 20%
C420-C425 All Models 0160-5422 CAP .047uF 20%
C427A 66101A-66103A 0160-4835 CAP .luF 10% 50V
66104A 0160-4834 CAP .047uF 10%
66105A, 66106A Not Used
C427B 66101A-66103A Not Used
66104A 0160-4834 CAP .047uF 10%
C427B 66105A, 66106A 0160-0269 CAP .luF 20%
C428, C429 66101A-66104A Not Used
66105A, 66106A 0160-0269 CAP .luF 20%
C430 66101A-66106A Not Used
C431, C432 All Models 0160-5422 CAP .047uF 20%
Model Part Number Description
70 Replacement Parts
Page 71

Table 5-1. Agilent 6610xA Power Modules Parts List - Electrical (continued)
Reference
Designators
C433 All Models 0160-4791 CAP l0pF 5% 100V
C434, C435 All Models 0160-5422 CAP .047uF 20%
D201-D204 All Models 1901-1087 DIODE-PWR RECT
D205, D206 All Models 1901-1214 DIODE-PWR RECT
D207, D208 All Models 1901-1098 DIODE-lN4150
D210-D212 All Models 1901-1098 DIODE-lN4150
D215 All Models 1901-1098 DIODE-lN4150
D216, D217 66101A-66103A 1901-1098 DIODE-lN4150
66104A-66106A 1901-1214 DIODE-PWR RECT
D301 66101A-66103A Not Used
66104A 1901-1383 DIODE-P WR RECT
66105A-66106A 1901-1199 DIODE-PWR RECT
D301A 66101A-66105A Not Used
66106A 1901-1199 DIODE-P WR RECT
D302 All Models 1901-1098 DIODE-lN4150
D303, D304 66101A-66103A 5060-3378 ASSY-HS, DIODE (1901-1383)
66104A 1901-1383 DIODE-P WR RECT
66105A-66106A 1901-1199 DIODE-PWR RECT
D303A, D304A 66101A-66105A Not Used
66106A 1901-1199 DIODE-P WR RECT
D314-D316 All Models 1901-1098 DIODE-lN4150
D317, D318 All Models 1901-0880 DIODE GEN PRP
D324, D325 All Models 1901-0880 DIODE GEN PRP
D326 66101A-66103A Not Used
66104A 1901-1383 DIODE-P WR RECT
66105A-66106A 1901-1199 DIODE-PWR RECT
D326A 66101A-66105A Not Used
66106A 1901-1199 DIODE-P WR RECT
Fl All Models 2110-0671 FUSE .125A 125V
F2 All Models 2110-0716 FUSE-SUBMIN .5A
F201 All Models 2110-0056 FUSE 6A 250V, CLIPS (2110-0726)
F202 All Models 2110-0716 FUSE-SUBMIN .5A
J3 All Models 1252-1152 CONNECTOR, To FRONT PANEL
J102 All Models 1252-0063 CONNECTOR, To FAN
J103 All Models 1251-8410 CONNECTOR, To MAINFRAME AC
J301 All Models 1252-0056 CONNECTOR, To BIAS BOARD
J302 All Models 1251-8676 CONNECTOR, To BIAS BOARD
K201 All Models 0490-1781 RELAY 2C 24VDC
Ll All Models 9100-1610 COIL 150nH 20%
L201 All Models 5080-2179 CHOKE-LINE
L202 All Models 5080-2180 CHOKE-INPUT
L203 All Models 9140-0137 COIL lmH 5%
L204-L211 All Models 5080-2251 BEAD-FERRITE
L301 66101A 66101-80001 CHOKE-OUTPUT
L301 66102A 66102-80001 CHOKE-OUTPUT
66103A 66103-80001 CHOKE-OUTPUT
66104A 66104-80001 CHOKE-OUTPUT
66105A 66105-80001 CHOKE-OUTPUT
66106A 66106-80001 CHOKE-OUTPUT
Model Part Number Description
Replacement Parts 71
Page 72

Table 5-1. Agilent 6610xA Power Modules Parts List - Electrical (continued)
Reference
Designators
L302, L303 All Models 5080-2219 CHOKE-OUTPUT
L304 66101A-66103A 9140-1064 CHOKE-OUTPUT
66104A-66106A 5080-2252 CHOKE-OUTPUT
L305, L306 66101A 5080-2251 BEAD-FERRITE
66102A-66106A Not Used
L307 66101A 5080-2251 BEAD-FERRITE
66102A-66105A Not Used
66106A 5080-2251 BEAD-FERRITE
L308 66101A 5080-2251 BEAD-FERRITE
66102A-66106A Not Used
P301 All Models 1252-0167 CONNECTOR, HOOD
Q201-Q204 All Models 5060-3457 ASSY-FET, HS (1855-0510)
Q208 All Models 1854-0087 TRANSISTOR NPN SI
Q301, Q302 66101A-66104A 5060-3382 ASSY-FET, HS (1866-0670)
66105A, 66106A 5060-3466 ASSY-FET, HS (1855-0631)
Q303 All Models 1854-0828 TRANSISTOR NPN SI
Q305 All Models 1853-0086 TRANSISTOR PNP Sl
Q401 All Models 5060-2942 ASSY-REGULATOR, HS (1826-0393)
Q403 All Models 5060-2948 ASSY-REGULATOR, HS (1826-0122)
Q404 All Models 5060-2942 ASSY-REGULATOR, HS (1826-0393)
Rl All Models 0757-0447 RES 16.2K 1%
R2 All Models 0699-2246 RES 25K .05%
R3 All Models 1810-0483 NETWORK-RES SIP
R4 All Models 0699-3414 RES 45K .lW .05%
R5, R6 All Models 0698-3155 RES 4.64K 1%
R7 All Models 1810-0355 NETWORK-RES SIP
R8 All Models 0757-0346 RES 10 1% .125W
R9 66101A-66106A 0757-0346 RES 10 1% .125W
R10 All Models 0698-4123 RES 499 1% .125W
R11 All Models 0698-6619 RES 15K .1%
R12 All Models 0757-0346 RES 10 1% .125W
R13 All Models 0757-0442 RES l0K 1% .125W
R15 All Models 1810-0206 NETWORK-RES SIP
R16 All Models 0757-0280 RES lK 1% .125W
R18, R19 All Models 0698-0082 RES 464 1% .125W
R20 All Models 0698-4202 RES 8.87K 1%
R21 All Models 0698-3155 RES 4.64K 1%
R22 66101A-66103A 0757-0346 RES 10 1% .125W
66104A-66106A 8159-0005 RES-ZERO OHMS
R23 All Models 0698-3155 RES 4.64K 1%
R24 All Models 0757-0430 RES 2.21K 1%
R25 All Models 1810-0279 NETWORK-RES SIP
R26 All Models 1810-0280 NETWORK-RES SIP
R27 All Models 0699-0486 RES 2K .1% .lW F
R28 All Models 0698-3445 RES 348 1% .125W
Model Part Number Description
72 Replacement Parts
Page 73

Table 5-1. Agilent 6610xA Power Modules Parts List - Electrical (continued)
Reference
Designators
R29 All Models 0698-0082 RES 464 1% .125W
R201, R202 All Models 0764-0045 RES 22K 5% 2W Mo
R203 All Models 0698-3430 RES 21.5 1% .125W
R204 All Models 0757-0403 RES 121 1% .125W
R205 All Models 0683-0335 RES 3.3 5% .25W
R206, R208 66101A-66103A 0698-3445 RES 348 1% .125W
66104A-66106A 0757-0407 RES 200 1% .125W
R210, R211 All Models 0698-3631 RES 330 5% 2W Mo
R212 All Models 0698-3430 RES 21.5 1%
R213 All Models 0683-0335 RES 3.3 5% .25W
R214 All Models 0757-0403 RES 121 1% .125W
R215-R217 All Models 0757-0442 RES l0K 1% .125W
R218, R219 All Models 0698-3432 RES 26.1 1%
R220 All Models 1810-0203 NETWORK-RES SIP
R221 66101A-66103A 0698-4470 RES 6.98K 1%
66104A-66106A 0757-0290 RES 6.19K 1%
R222 All Models 0757-0449 RES 20K 1% .125W
R223 All Models 0698-3446 RES 383 1% .125W
R224 All Models 0757-0442 RES l0K 1% .125W
R225 All Models 0757-0279 RES 3.16K 1%
R228, R229 All Models 0757-0442 RES l0K 1% .125W
R232 All Models 0757-0442 RES l0K 1% .125W
R234 All Models 0757-0401 RES 100 1% .125W
R235 All Models 0698-3279 RES 4.99K 1%
R236 All Models 0757-0430 RES 2.21K 1%
R237, R238 All Models 0698-3631 RES 330 5% 2W Mo
R239 All Models 0757-0442 RES l0K 1% .125W
R240 All Models 0698-4406 RES 115 1% .125W
R241 All Models 0757-0283 RES 2K 1% .125W
R244 All Models 0698-3159 RES 26.1K 1%
R245, R246 All Models 0698-8827 RES lM 1% .125W
R247 All Models 0757-0280 RES lK 1% .125W
R249 All Models 0757-0462 RES 75K 1% .125W
R250 All Models 0698-4099 RES 139 1% .125W
R301, R302 66101A, 66102A 0811-3896 RES 20 5% l0W
66103A 0811-3897 RES 62 5% l0W
66104A 0811-3896 RES 20 5% l0W
66105A 0811-3891 RES 75 5% l0W
66106A 0811-3892 RES 300 5% l0W
R303 66101A 5080-2217 SHUNT .005 OHMS
66102A 5080-2218 SHUNT .01 OHMS
66103A, 66104A 5080-2224 SHUNT .035 OHMS
66105A 0811-3771 RES .25 OHM 1%
66106A 0811-3772 RES .50 OHM 1%
R304 All Models 0698-3279 RES 4.99K 1%
Model Part Number Description
Replacement Parts 73
Page 74

Table 5-1. Agilent 6610xA Power Modules Parts List - Electrical (continued)
Reference
Designators
R305 66101A 0757-0441 RES 8.25K 1%
66102A 0757-0449 RES 20K 1% .125W
66103A 0757-0123 RES 34.8K 1%
66104A 0698-3572 RES 60.4K 1%
66105A 0757-0467 RES 121K 1%
66106A 0757-0472 RES 200K 1%
R306 66101A 0757-0441 RES 8.25K 1%
66102A 0757-0449 RES 20K 1% .125W
66103A 0757-0123 RES 34.8K 1%
66104A 0698-3572 RES 60.4K 1%
66105A 0757-0467 RES 121K 1%
66106A 0698-6358 RES 100K .1%
R307 All Models 0698-3279 RES 4.99K 1%
R308 66101A-66104A 0757-0472 RES 200K 1%
66105A 0757-0270 RES 249K 1%
66106A 0757-0472 RES 200K 1%
R309 66101A-66104A Not Used
66105A 0811-1732 RES 1 3W 5%
66106A Not Used
R310 66101A 0757-0441 RES 8.25K 1%
66102A 0757-0446 RES 15K 1% .125W
66103A 0757-0444 RES 12.1K 1%
66104A 0757-0946 RES 8.2K 2%
66105A 0698-4444 RES 4.87K 1%
66106A 0698-3498 RES 8.66K 1%
R311 66101A 0757-0458 RES 51.1K 1%
66102A 0757-0462 RES 75K 1% .125W
66103A 0757-0458 RES 51.1K 1%
66104A 0757-0349 RES 22.6K 1%
66105A 0698-4486 RES 24.9K 1%
66106A 0757-0449 RES 20K 1% .125W
R312 All Models 0699-0070 RES 3.16M 1%
R313 66101A 0698-0085 RES 2.61K 1%
66102A 0698-0084 RES 2.15K 1%
66103A 0757-0279 RES 3.16K 1%
66104A, 66105A 0757-0427 RES 1.5K 1%
66106A 0757-0279 RES 3.16K 1%
R314 66101A 0757-0442 RES l0K 1% .125W
66102A 0698-3162 RES 46.4K 1%
66103A 0757-0458 RES 51.1K 1%
66104A 0757-0449 RES 20K 1% .125W
66105A 0757-0461 RES 68.1K 1%
66106A 0757-0469 RES 150K 1%
R315 66101A 0698-4435 RES 2.49K 1%
66102A 0757-0439 RES 6.81K 1%
66103A 0698-3153 RES 3.83K 1%
66104A, 66105A 0698-4435 RES 2.49K 1%
66106A 0757-0440 RES 7.5K 1%
Model Part Number Description
74 Replacement Parts
Page 75

Table 5-1. Agilent 6610xA Power Modules Parts List - Electrical (continued)
Reference
Designators
R316 All Models 0698-8827 RES lM 1% .125W
R317 All Models 0757-0472 RES 200K 1%
R318 All Models 0757-0349 RES 22.6K 1%
R319, R320 All Models 0699-2246 RES 25K .05%
R321 All Models 0699-2248 RES 47.5K .05%
R322 All Models 0699-0070 RES 3.16M 1%
R323 66101A 0811-2568 RES 1 1% 3W
66102A 0811-2455 RES 2 1% 3W
66103A-66105A Not Used
66106A 0698-3433 RES 28.7 1%
R323A 66101A,66102A Not Used
66103A 0698-8822 RES 6.81 1%
66104A 0698-4356 RES 12.7 1%
66105A 0757-0382 RES 16.2 1%
66106A Not Used
R323B 66101A,66102A Not Used
66103A 0698-8822 RES 6.81 1%
66104A 0698-4356 RES 12.7 1%
66105A,66106A Not Used
R324 All Models 0757-0283 RES 2K 1% .125W
R325 66101A-66105A 0699-3415 RES 5K .lW .05%
66106A 0699-3417 RES 3.85K .lW
R326 All Models 0699-3415 RES 5K .lW .05%
R327, R328 66101A 0699-3103 RES 19K .05%
66102A 0699-2248 RES 47.5K .05%
66103A 0699-2879 RES 80K .05% 5PPM .lW
66104A 0699-3446 RES 125K .05%
66105A 0699-3104 RES 250K .125W
66106A 0699-3448 RES 300K .05%
R329, R330 All Models 0757-0280 RES lK 1% .125W
R331 66101A 0698-6362 RES lK .1% .125W
66102A 0698-6631 RES 2.5K .1%
66103A 0698-8184 RES 7.5K 1%
66104A 0699-2246 RES 25K .05%
66105A 0698-6353 RES 50K .1%
66106A 0699-3447 RES 85K .1%
R332 66101A 0698-6362 RES lK .1% .125W
66102A 0698-6631 RES 2.5K .1%
66103A 0698-8184 RES 7.5K 1%
66104A 0699-2246 RES 25K .05%
66105A 0698-6353 RES 50K .1%
66106A 0698-6358 RES 100K .1%
R333 66101A 0698-3159 RES 26.1K 1%
66102A, 66103A 0757-0442 RES l0K 1% .125W
66104A 0757-0443 RES 11K 1% .125W
66105A 0757-0441 RES 8.25K 1%
66106A 0757-0447 RES 16.2K 1%
Model Part Number Description
Replacement Parts 75
Page 76
Table 5-1. Agilent 6610xA Power Modules Parts List - Electrical (continued)
Reference
Designators
R334 66101A-66103A 0698-7933 RES 3.83K .1%
66104A 0698-8607 RES 4.5K .1%
66105A 0698-7933 RES 3.83K .1%
66106A 0698-8607 RES 4.5K .1%
R336 66101A-66103A 0699-3417 RES 3.85K .lW
66104A 0699-3449 RES 4.5K .05%
66105A 0699-3417 RES 3.85K .lW
66106A 0699-3449 RES 4.5K .05%
R337 All Models 1810-0483 NETWORK-RES SIP
R338 66101A, 66102A 0699-3416 RES 100K .lW
66103A 0699-2248 RES 47.5K .05%
66104A 0699-3416 RES 100K .lW
66105A, 66106A 0699-2246 RES 25K .05%
R339 All Models 0698-3430 RES 21.5 1%
R340 66101A 0811-2568 RES 1 1% 3W
66102A 0811-2455 RES 2 1% 3W
66103A-66105A Not Used
66106A 0698-3433 RES 28.7 1%
R340A 66101A, 66102A Not Used
66103A 0698-8822 RES 6.81 1%
66104A 0698-4356 RES 12.7 1%
66105A 0757-0382 RES 16.2 1%
66106A Not Used
R340B 66101A, 66102A Not Used
66103A 0698-8822 RES 6.81 1%
66104A 0698-4356 RES 12.71%
66105A, 66106A Not Used
R341 All Models 0698-3430 RES 21.5 1%
R342 66101A 0757-0462 RES 75K 1% .125W
66102A 0698-3450 RES 42.2K 1%
66103A, 66104A 0757-0470 RES 162K 1%
66105A 0757-0463 RES 82.5K 1%
66106A 0757-0470 RES 162K 1%
R343 66101A 0757-0441 RES 8.25K 1%
66102A 0757-0288 RES 9.09K 1%
66103A 0757-0441 RES 8.25K 1%
66104A 0757-0447 RES 16.2K 1%
66105A 0757-0446 RES 15K 1% .125W
66106A 0757-0447 RES 16.2K 1%
R344 66101A 0698-3450 RES 42.2K 1%
66102A-66106A 0698-4509 RES 80.6K 1%
R345 All Models 0757-0280 RES lK 1% .125W
R346 All Models 0699-2248 RES 47.5K .05%
R347 66101A-66105A 8159-0005 RES-ZERO OHMS
66106A 0699-3416 RES 100K .lW
Model Part Number Description
76 Replacement Parts
Page 77

Table 5-1. Agilent 6610xA Power Modules Parts List - Electrical (continued)
Reference
Designators
R348 66101A, 66102A 0757-0441 RES 8.25K 1%
66103A, 66104A 0757-0444 RES 12.1K 1%
66105A 0698-3136 RES 17.8K 1%
66106A 0698-3159 RES 26.1K 1%
R349 All Models 0757-0472 RES 200K 1%
R350 66101A-66105A 8159-0005 RES-ZERO OHMS
66106A 0698-6358 RES 100K .1%
R351 All Models 0699-2246 RES 25K .05%
R352 All Models 0683-2255 RES 2.2M 5% .25W
R353 66101A 0698-4443 RES 4.53K 1%
66102A 0757-0349 RES 22.6K 1%
66103A 0757-0467 RES 121K 1%
66104A 0698-6376 RES 200K .1%
66105A, 66106A Not Used
R354 All Models 0757-0283 RES 2K 1% .125W
R355 All Models 0757-0442 RES l0K 1% .125W
R359 66101A-66103A 0698-6360 RES l0K .1%
66104A 0698-6320 RES 5K .1% .125W
66105A 0698-6360 RES 10K .1%
66106A 0698-8061 RES 8.25K .1%
R360 66101A 0698-4196 RES 1.07K 1%
66102A 8159-0005 RES-ZERO OHMS
66103A 0698-0064 RES 9.31K 1%
66104A 8159-0005 RES-ZERO OHMS
66105A 0698-7841 RES 164K .1%
66106A 0698-6376 RES 200K .1%
R361 66101A 0698-6619 RES 15K .1%
66102A 0699-2248 RES 47.5K .05%
66103A, 66104A 0698-6359 RES 80K 0.l%
66105A 0698-7841 RES 164K .1%
66106A 0698-8050 RES 256K .1%
R362 All Models 0757-0465 RES 100K 1%
R363 All Models 0699-2246 RES 25K .05%
R364 All Models 0698-3279 RES 4.99K 1%
R365 All Models 0698-6358 RES 100K .1%
R367 66101A, 66102A 0698-8812 RES 1 1% .125W
66103A-66105A Not Used
66106A 0757-0346 RES 10 1% .125W
R368, R369 66101A, 66102A 0698-8812 RES 1 1% .125W
66103A-66106A Not Used
R401 All Models 0699-1069 RES 229 .1%
R402 AU Models 0699-0486 RES 2K .1% .lW F
R406 All Models 0757-0437 RES 4.75K 1%
R407, R408 All Models 0757-0407 RES 200 1% .125W
R409-R411 All Models 0757-0280 RES lK 1% .125W
R416 All Models 8159-0005 RES-ZERO OHMS
R419 All Models 0757-0449 RES 20K 1% .125W
Model Part Number Description
Replacement Parts 77
Page 78

Table 5-1. Agilent 6610xA Power Modules Parts List - Electrical (continued)
Reference
Designators
R420 66101A, 66102A 0698-6358 RES 100K .1%
66103A 0699-2248 RES 47.5K .05%
66104A 0698-6358 RES 100K .1%
66105A, 66106A 0699-2246 RES 25K .05%
R421 All Models 0698-3155 RES 4.64K 1%
R422 All Models 0757-0346 RES 10 1% .125W
R423 All Models 0698-8812 RES 1 1% .125W
R424 All Models 0757-0280 RES lK 1% .125W
R427 66101A-66103A 0698-8812 RES 1 1% .125W
66104A-66106A Not Used
R428 66101A-66105A 0698-8812 RES 1 1% .125W
66106A Not Used
R429 66101A-66103A 0698-8812 RES 1 1% .125W
66104A, 66105A Not Used
66106A 0757-0346 RES 10 1% .125W
R430 All Models 0757-0280 RES lK 1% .125W
RT301 All Models 0837-0397 THERMISTOR
S3 All Models 3101-2243 SWITCH 8-lA
S201 All Models 3101-2966 SWITCH DPDT
T201 66101A 9100-5020 TRANSFORMER-POWER
66102A 9100-5021 TRANSFORMER-POWER
66103A 9100-5022 TRANSFORMER-POWER
66104A 9100-5001 TRANSFORMER-POWER
66105A 9100-5002 TRANSFORMER-POWER
66106A 9100-5003 TRANSFORMER-POWER
T202 All Models 9140-0974 INDUCTOR-FIXED
U1 All Models 1821-1479 MICROPROCESSOR, SOCKET (1200-1274)
U2 All Models 5080-2529 PROGRAMMED-ROM, SOCKET (1200-0567)
U3 All Models 1818-4134 IC-MEMORY, 64K
U4 All Models 1820-2724 IC SN74ALS573BN
U5 AU Models 5080-2236 PROGRAMMED-GAL, SOCKET (1200-0639)
U6 All Models 5080-2530 PROGRAMMED-GAL, SOCKET (1200-0639)
U7 All Models 1826-2402 IC-CONVERTOR AD7837BN
U11 All Models 1826-2284 IC
U12 All Models 1826-2484 IC-CONVERTOR
U13 All Models 1820-3399 IC MC74HC273N
U14 All Models 1826-1409 IC 1013
U15 All Models 1826-1021 ANALOG MULTIPLEXER
U17-U20 All Models 1990-1502 OPTO ISOLATOR
U21 All Models 1820-2110 IC-INTERFACE
U22 All Models 1818-4792 IC-EEPROM
U23 All Models 1820-2110 IC-INTERFACE
U24 All Models 1826-1896 IC-LINEAR
U25 All Models 1990-1502 OPTO ISOLATOR
U26 All Models 1826-2341 IC-VOLTAGE SENSE
U201, U202 All Models 1820-8433 IC PULSE WIDTH MODULATOR
Model Part Number Description
78 Replacement Parts
Page 79

Table 5-1. Agilent 6610xA Power Modules Parts List - Electrical (continued)
Reference
Designators
U203 All Models 1826-2075 IC UC3825N
U204 All Models 1990-1502 OPTO ISOLATOR
U205 All Models 1858-0069 TRANSISTOR ARRAY 18P-DIP
U206 All Models 1826-0175 IC 319
U301 66101A-66103A 1826-0346 IC OP-AMP
66104A-66106A 1826-0962 IC OP-AMP
U302 All Models 1826-1896 IC-LINEAR
U303 All Models 1826-1370 IC 365
U304 All Models 1826-1895 PRECISION OP-AMP
U305 All Models 1826-1553 IC-LINEAR
U306 All Models 1990-1502 OPTO ISOLATOR
U307 All Models 1826-0346 IC OP-AMP
VR201 All Models 1902-0968 DIODE-ZENER 27V 5%
VR302 All Models 1902-0951 DIODE-ZENER
VR304, VR305 All Models 1902-0018 DIODE-ZENER lN941 11.7V
Y1 All Models 0410-2109 CRYSTAL 12.000 MHZ
All Models 5060-3455 ASSEMBLY-BIAS BOARD
C401 All Models 0180-3587 CAP 1000uF 50V
C402 All Models 0180-4273 CAP 1000uF
C404 All Models 0160-5422 CAP .047uF 20%
C405 All Models 0180-3587 CAP 1000uF 50V
C406 All Models 0180-4389 CAP 6800uF 25V
C408, C410 All Models 0180-4129 CAP luF 35V
C411 All Models 0160-4835 CAP .luF 10% 50V
D401, D402 All Models 1901-0731 DIODE-PWR RECT
D402 All Models 1901-0731 DIODE-PWR RECT
F401 All Models 2110-0820 FUSE .5A 250V, HOLDER (2110-0714)
J401 All Models 1252-0056 CONNECTOR, TO POWER BOARD
J402 All Models 1251-8676 CONNECTOR, TO POWER BOARD
Q402 All Models 1826-0527 IC LM337T
Q404 All Models 5060-2942 ASSY-HS, TO-220
R403 All Models 0699-0486 RES 2K .1% .lW F
R404 All Models 0699-1069 RES 229 .1%
R405 All Models 0698-3447 RES 422 1% .125W
R406 All Models 0757-0437 RES 4.75K 1%
S402 All Models 3101-2966 SWITCH DPDT
T401 All Models 9100-4932 TRANSFORMER-BIAS
U401, U402 All Models 1906-0006 DIODE BRIDGE 400V
All Models 5060-3454 ASSEMBLY-FRONT PANEL BOARD
C501, C502 All Models 0160-5422 CAP .047uF 20%
C503, C504 All Models 0160-4833 CAP .022uF 10%
CR501-CR503 All Models 1990-1554 LED GREEN
CR504-CR506 All Models 1990-1553 LED YELLOW
D501-D508 All Models 1990-1492 DISPLAY, LED
D509 All Models 1902-3110 DIODE-ZENER 5.9V 2%
J501 All Models 1252-3844 CONNECTOR, TO POWER BOARD
Model Part Number Description
Replacement Parts 79
Page 80

Table 5-1. Agilent 6610xA Power Modules Parts List - Electrical (continued)
Reference
Designators
R501 All Models 1810-0405 NETWORK RES SIP
R502 All Models 1810-0405 NETWORK RES SIP
R503 All Models 1810-0405 NETWORK RES SIP
R504 All Models 1810-0405 NETWORK RES SIP
R505 All Models 1810-0636 NETWORK RES SIP
R506 All Models 1810-0636 NETWORK RES SIP
R507 All Models 1810-0483 NETWORK RES SIP
U501 All Models 1821-0045 IC DISPLAY DRIVE
U502 All Models 1821-0045 IC DISPLAY DRIVE
U503 All Models 1858-0069 TRANSISTOR ARRAY 18P-DIP
U504 All Models 1820-3344 IC MC74HC595N
Model Part Number Description
All Models 0403-0086 BUMPER FOOT PRESS-IN
All Models 0515-1946 SCREW-MACH, M3 X 0.5 6MM LG, TORX T10 FLT, (REF COVER)
All Models 0515-0430 SCREW-MACH, M3 X 0.5 6MM LG, TORX T10 PAN, (REF PC BD)
All Models 0515-1038 SCREW-MACH, M3 X 0.5 35MM LG, TORX T10 PAN, (REF FAN)
All Models 0535-0031 NUT-HEX W/LKWR, M3 X 0.5, (REF FAN)
All Models 1460-2307 SPRING (REF LATCH)
All Models 5001-6759 CHASSIS
All Models 5001-6760 COVER
All Models 5001-6761 BRACKET-FAN
All Models 5001-6762 INSULATOR
All Models 5040-1677 BEZEL-LEFT
All Models 5040-1678 BEZEL-RIGHT
All Models 5040-1680 LATCH-PLASTIC
All Models 5040-1681 PULLER
All Models 5080-2193 ASSEMBLY-FRONT PANEL CABLE (REF J501/J3)
All Models 5080-2194 ASSEMBLY-BIAS BOARD CABLE (REF J402/J302)
All Models 5080-2195 ASSEMBLY-BIAS BOARD CABLE (REF J401/J301)
All Models 5080-2223 LABEL, AC/S3 SWITCH CONFIG
66101A 66101-40001 PANEL-FRONT
66102A 66102-40001 PANEL-FRONT
66103A 66103-40001 PANEL-FRONT
66104A 66104-40001 PANEL-FRONT
66105A 66105-40001 PANEL-FRONT
66106A 66106-40001 PANEL-FRONT
Model Part Number Description
Table 5-2. Agilent 6610xA Power Modules Parts List - Mechanical
80 Replacement Parts
Page 81

Table 5-3. Output Connector Assembly Parts List
Reference
Designators
5060-3470 ASSEMBLY-OUTPUT CONNECTOR BOARD
C602, C603 0160-5422 CAP .047uF 20%
C604 0160-4281 CAP 2200pF 20%
C605 1810-1379 NETWORK-CAP SIP
J601 1251-8410 CONNECTOR, TO POWER BOARD
J602, J603 1252-4311 CONNECTOR, TO CONNECTOR BOARD
R601 0757-0442 RES l0K 1% .125W
SW1 3101-3133 SWITCH, SLIDE
TB601 0360-2423 TERMINAL BLOCK
VR601-VR603 1902-0968 DIODE-ZENER 27V 5%
5060-3351 ASSEMBLY-OUTPUT RELAY BOARD
C601 0180-4136 CAP l0uF 20V
F601, F602 2110-0757 FUSE .062A
K601-K604 0490-1670 PWR RELAY
K605-K607 0490-1405 RELAY 2C 12 VDC
P602, P603 1252-4310 CONNECTOR, TO CONNECT OR BOARD
R601-R603 0686-3305 RES 33 5% .5W CC
5060-3386 OUTPUT ASSEMBLY-without relays
5060-3387 OUTPUT ASSEMBLY-with relays
1400-0307 Cable Tie
5040-1682 Hood Base
5040-1683 Hood Cover
5080-2220 Hood Label
Part Number Description
Replacement Parts 81
Page 82

Page 83

6
Diagrams
This chapter contains test point and component location diagrams and schematics for troubleshooting the Agilent 6610xA
Power Modules.
SHOCK HAZARD Hazardous voltages are present throughout the Power and Bias board assemblies. Ac line voltage is
present on some connectors even when the module is not turned on. The dc rail voltage to the module is 310 volts when the
unit is turned on.
Schematic Sheets
Foldout #1 front--Power board sheet 1 of 5
back--Power board sheet 2 of 5
Foldout #2 front--Power board sheet 3 of 5
back--Power board sheet 4 of 5
Foldout #3 front--Power board sheet 5 of 5
back--Front panel schematic and component locations
Foldout #4 front--Output connector board schematic and component locations
back--Relay board schematic and component locations
Foldout #5 front--Bias board schematic and component locations
back--Power board component locations and test points
Foldout #6 front--Main board Component coordinates
back--blank
Component Location Diagrams
Component location diagrams are provided for all of the module circuit boards.
The component location diagram for the power board is located on the back of the last foldout sheet (the bias board
schematic) foldout sheet. The diagram is divided into columns and rows designated "x coordinates" and "y coordinates".
The table on the facing page lists all of the components on the Power board and gives the coordinate location of each
component. For example, resistor R201 is located at x coordinate 3.9 and y coordinate 1.4. Refer to Chapter 5 for the part
number and description of each electrical part.
The test points shown on the component location diagram for the power board correspond with the test points that are used
in the troubleshooting procedures of Chapter 3.
The component location diagrams for the bias, front panel, connector, and relay boards are located on the same sheets as
their schematic diagrams.
Diagrams 83
Page 84

Schematic Notes
Notes that apply to all schematic sheets are as follows:
þ All resistors are in ohms +/-1%, 1/8 W, unless otherwise specified.
þ All capacitors are in microfarads unless otherwise specified.
þ Refer to the parts list (Table 5-1) for the values of the resistors and capacitors that are enclosed by a heavy rectangle
on the schematic. Their values differ from model to model. The schematic shows only the values used by Model
66105A.
þ An asterisk negates a signal name. For example,
þ Signal line destinations are given inside the parentheses at the end of the signal lines. For example, PCLR* (S02C5)
on Power board schematic sheet 1 of 5, indicates that the PCLR* signal continues on schematic sheet 2 of 5 at gr id
coordinates C, 5. Coordinates are labeled on the schematic border.
þ Signal lines that are terminated by flags
direction.
þ Signal lines without flags go to another location of the same schematic sheet.
þ Test points on the schematic sheets (e.g. TP22) identify the location of the test points used in the troubleshooting
procedures in Chapter 3.
þ Voltages and waveforms shown on the schematics are obtained when following the troubleshooting procedures in
Chapter 3.
WR appears on the schematic as WR*.
continue onto other sheets. Note that flags do NOT indicate signal flow
84 Diagrams
Page 85
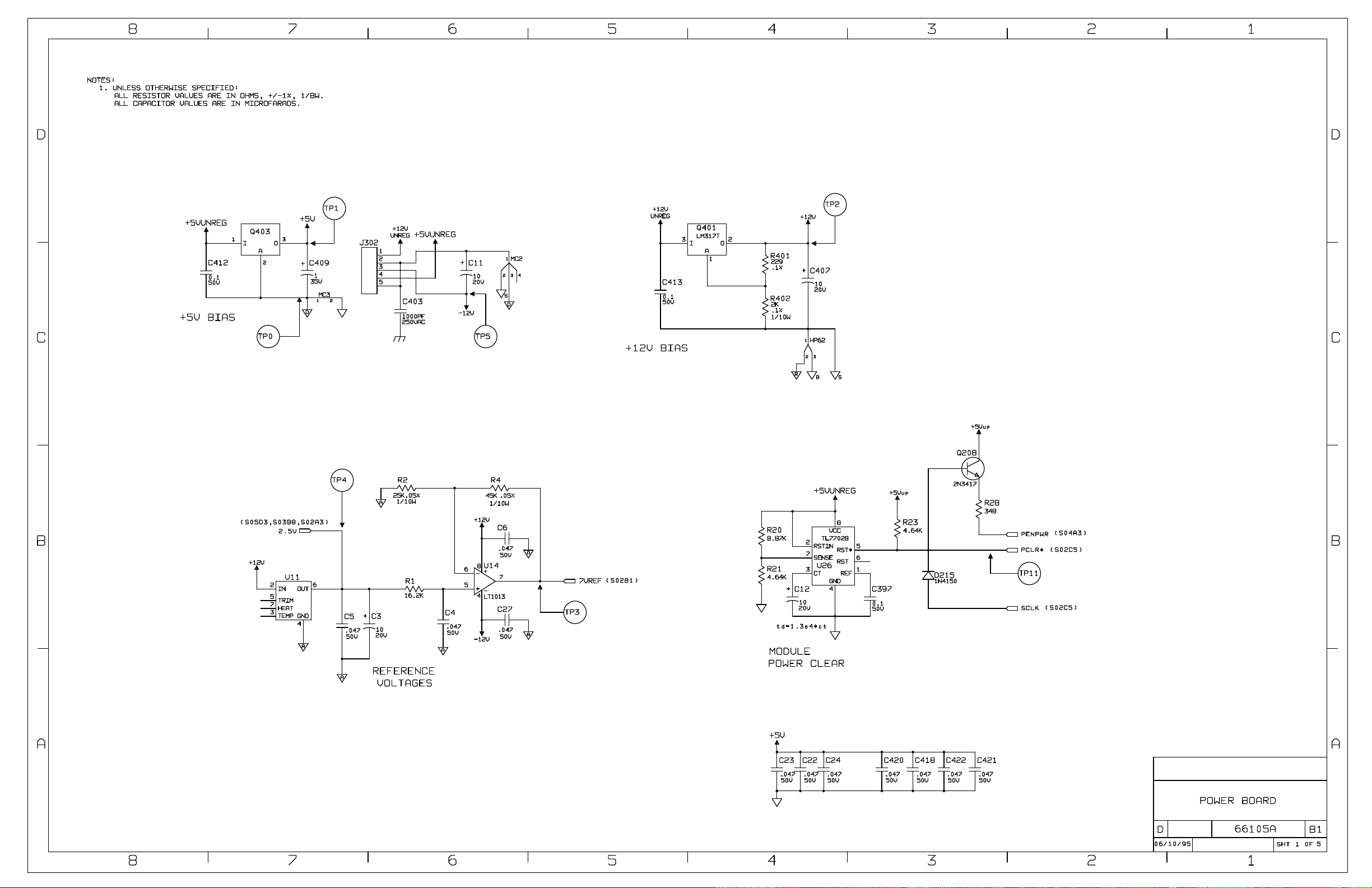
Page 86

Page 87

R309
L305
L306
L308
L307
Page 88

Page 89

Page 90

A B C D
+5V
13 53 74
1
R507
2 7
4.7K 5%
1810-1670
81
63
R507
3 6
4.7K 5%
1810-1670
R508
1 8
4.7K 5%
1810-1670
R508
2 7
4.7K 5%
1810-1670
J501
1252-3844
10 PIN
RT < POST
+5V
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
SDATA
SCLK
IDISP
VDISP
ADISP
R507
4.7K 5%
1810-1670
R508
4.7K 5%
1810-1670
+5V
2
C501
X7R16V
0.1 10%
0160-7828
R507
4.7K 5%
1810-1670
100K A
0699-3993
0.1 10%
0160-7828
10K A
0699-3970
X7R16V
C502
0.1 10%
0160-7828
52
54
MODE
51
I/O51
50 66
44
I/O44
46
I/O46
45
I/O45
57
SDI
N13N12N11N7 N8 N9
58
DCLK
59
PRA
61
PRB
N10
48
I/O48
49
I/O49
80
I/O80
R509
16
I/O16
C503
21
I/O21
X7R16V
R510
22
I/O22
3
3320
VCC
U501
A40MX02
A40MX02
GND
7 68
4727
I/O79
I/O78
I/O77
I/O76
I/O75
I/O73
I/O72
I/O71
I/O70
I/O69
I/O67
I/O66CLK
I/O65
I/O64
I/O63
I/O62
I/O23
I/O24
I/O25
I/O26
I/O28
I/O29
I/O30
I/O31
I/O32
I/O34
I/O35
I/O36
I/O37
I/O38
I/O39
I/O40
I/O10
I/O11
I/O12
I/O14
I/O15
79
78
Ia
77
76
Ib
75
73
Ic
72
71
Id
70
69
Ie
67
If
65
64
Ig
63
62
Ih
U502
S0
5
I/O5
S1
6
I/O6
S2
8
I/O8
S3
9
I/O9
23
24
Va
25
26
Vb
28
29
Vc
30
31
Vd
32
34
Ve
35
36
Vf
37
38
Vg
39
40
Vh
CV
1
I/O1
CC
10
ADDR
11
UNR
12
DIS
14
PROT
15
ULN2003AD
1B 1C
2
2B
3
3B
4
4B
5
5B
6
6B
7
7B
E COM
ULN2003AD
1 16
1B 1C
2
2B
3
3B
4
4B
5
5B
6
6B
7
7B
8 9
E COM
1858-0104
U503
1858-0104
161
15
2C
14
3C
13
4C
12
5C
11
6C
10
7C
98
N6
15
2C
14
3C
13
4C
12
5C
11
6C
10
7C
N5
R501
470.0 5%
1810-1979
R501
470.0 5%
1810-1979
R502
1 8
470.0 5%
1810-1979
R502
3 6
470.0 5%
1810-1979
R503
470.05%
1810-1979
R503
470.05%
1810-1979
R504
8 1
470.05%
1810-1979
R504
6 3
470.05%
1810-1979
R505
220.0 5%
1810-1659
R505
2 7
220.0 5%
1810-1659
R505
220.0 5%
1810-1659
R505
4 5
220.0 5%
1810-1659
R506
220.0 5%
1810-1659
R506
2 7
220.0 5%
1810-1659
81
63
18
36
2 7
470.0 5%
1810-1979
4 5
470.0 5%
1810-1979
470.0 5%
1810-1979
470.0 5%
1810-1979
7 2
1810-1979
5 4
1810-1979
1810-1979
1810-1979
81
63
81
R501
R501
R502
R502
R503
470.05%
R503
470.05%
R504
470.05%
R504
470.05%
CR501
1990-1554
CR502
1990-1554
CR503
1990-1554
CR504
1990-1553
CR505
1990-1553
CR506
1990-1553
D505
HDSP-A103
1
C1
2
F
f
3
G
4
e
E
5
D
1
2
3
4
5
HDSP-A103
C1
F
G
e
E
D
1990-1492
f
1990-1492
72
54
27
45
d
D501
d
10
A
a
9
B
b
8
g
C
7
c
DP
6
C6
10
A
a
9
B
b
g
8
C
7
c
DP
6
C6
1
2
3
4
5
1
2
3
4
5
HDSP-A103
C1
F
G
e
E
D
HDSP-A103
C1
F
G
e
E
D
D506
a
f
g
d
1990-1492
D502
a
f
g
d
1990-1492
D507
10
A
9
B
b
8
C
7
c
DP
6
C6
10
A
9
B
b
8
C
7
c
DP
6
C6
1
C1
2
F
3
G
4
E
5
D
1
C1
2
F
3
G
4
E
5
D
HDSP-A103
a
f
g
e
d
1990-1492
D503
HDSP-A103
a
f
g
e
d
1990-1492
10
A
9
B
b
8
C
7
c
DP
6
C6
10
A
9
B
b
8
C
7
c
DP
6
C6
1
C1
2
F
3
G
4
E
5
D
1
C1
2
F
3
G
4
E
5
D
D508
HDSP-A103
a
f
g
e
d
1990-1492
D504
HDSP-A103
a
f
g
e
d
1990-1492
10
A
9
B
b
8
C
7
c
DP
6
C6
10
A
9
B
b
8
C
7
c
DP
6
C6
+5V
D509
1902-1424
1
2
3
4
4
MODULE FRONT PANEL
D
04/01/99
5020-2935
A2
SHEET 1 OF 1
DCBA
Page 91

Page 92
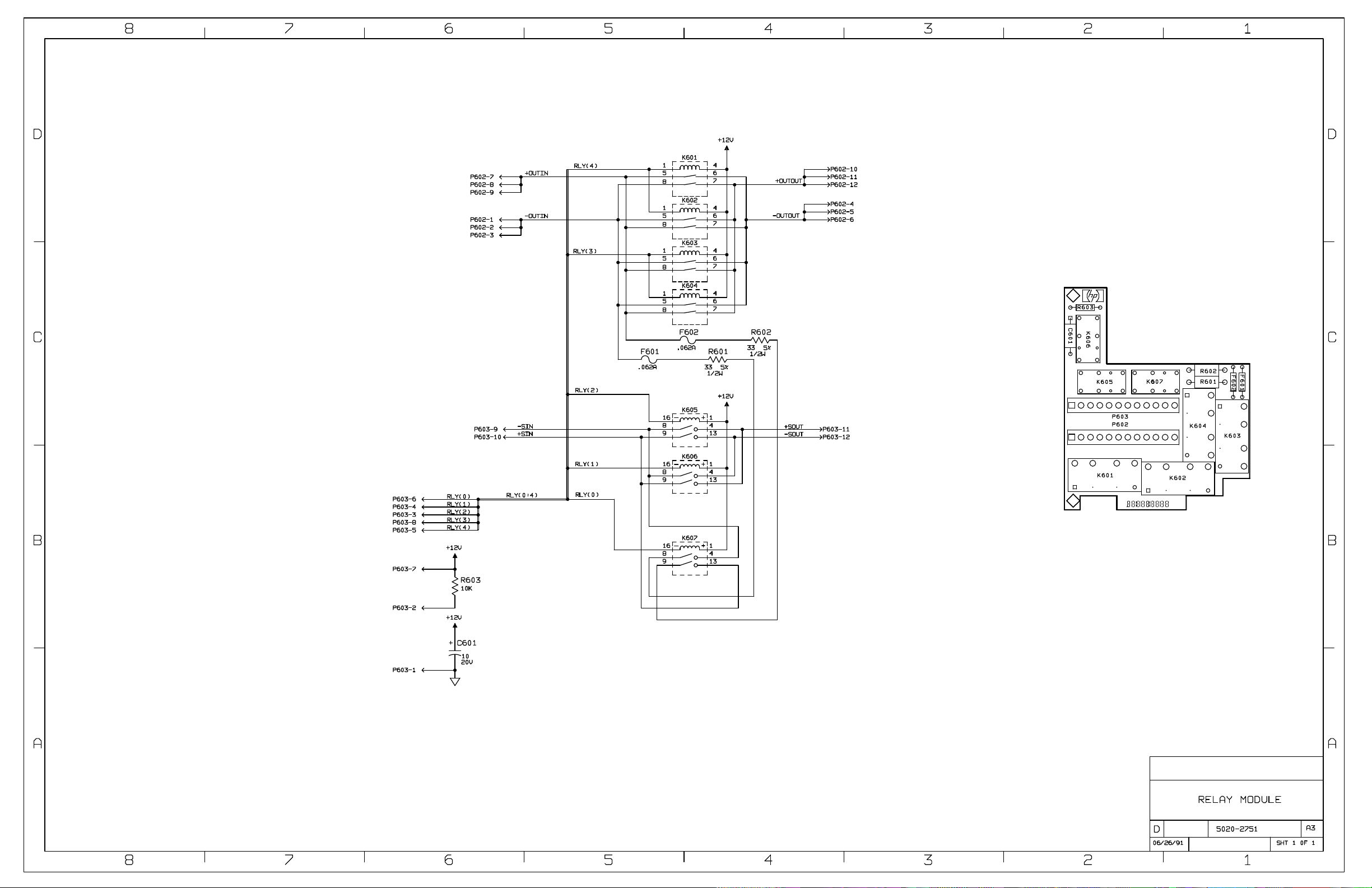
Page 93

Page 94

5
11
0
4
17
18
F
10
22
- I
20
SENSE
15
- OUT
14
19
+ OUT
I
6
1 3
21
16
13
12
9
7 8
Page 95

Main Board Component Coordinates
XY XY XY
C1 8.1 2.2 C220 0.5 2.1 C331 12.7 3.7
C2 8.1 2.0 C221 1.0 3.2 C332 13.7 3.6
C3 8.1 3.1 C222 0.0 2.9 C333 13.4 4.1
C4 7.3 3.0 C223 1.0 2.1 C334 13.2 3.8
C5 8.5 3.4 C224 0.0 2.4 C335 10.9 3.7
C6 7.9 2.1 C225 2.3 3.7 C336 12.2 3.9
C7 9.1 3.7 C226 3.2 3.3 C337 14.2 3.3
C8 9.1 3.6 C227 11.3 2.3 C338 14.9 4.1
C9 9.7 4.0 C228 0.5 2.0 C339 15.4 4.0
C10 9.1 4.0 C229 0.0 1.3 C340 12.2 3.4
C11 6.5 2.7 C230 5.8 3.3 C341 12.7 3.3
C12 7.4 2.4 C232 4.0 2.2 C342 12.2 3.0
C13 8.5 0.4 C301 5.0 3.5 C343 13.6 2.8
C14 8.5 0.3 C302 3.3 4.3 C345 11.0 3.8
C15 9.3 0.4 C303 5.7 4.5 C346 14.1 2.9
C16 10.7 0.9 C304 10.3 4.5 C347 7.2 4.1
C17 8.5 0.6 C305 5.6 3.3 C349 11.6 3.6
C18 9.8 0.6 C306 5.2 3.3 C358 14.7 2.7
C20 8.0 2.5 C307 6.6 4.6 C395 10.9 2.2
C21 8.0 2.4 C308 8.5 4.7 C396 9.6 4.1
C22 5.9 1.9 C309A 15.7 3.4 C397 7.3 2.0
C23 6.9 0.7 C309B 15.6 3.4 C403 6.l 3.3
C24 7.3 1.9 C310 13.5 2.5 C407 8.5 4.2
C27 7.4 2.7 C311 8.5 3.6 C409 6.4 2 .4
C28 5.6 2.3 C312 15.5 2.9 C412 6.4 2.5
C192 6.7 3.5 C313 15.7 3.3 C413 8.0 3.5
C201 1.1 2.6 C314 7.1 3.6 C414 10.2 3.9
C202 0.5 0.9 C315 6.7 3.9 C415 10.2 3.8
C203 10.6 0.0 C316 7.1 4.0 C416 15.4 3.5
C204 7.1 0.0 C317 12.1 3.7 C418 7.9 1.9
C206 4.1 1.8 C318 13.5 3.5 C420 9.1 1.9
C207 1.6 0.6 C319 12.8 3.5 C421 7.5 0.7
C208 1.6 1.8 C320 13.0 2.5 C422 8.2 0.6
C209 2.3 4.8 C321 12.0 3.9 C425 7.1 3.4
C210 0.5 2.3 C322 15.4 3.1 C427A 15.8 3.3
C211 1.6 4.4 C323 12.9 3.3 C427B 15.8 4.1
C212 1.1 3.9 C324 15.4 3.3 C428 12.0 4.7
C213 2.9 2.2 C325 15.4 4.2 C429 5.7 4.9
C214 2.3 4.1 C326 15.4 3.2 C430 9.8 4.5
C215 1.5 3.3 C327 14.3 4.1 C431 14.7 3.3
C217 1.5 2.8 C328 11.0 2.8 C432 9.8 1.7
C218 5.0 1.1 C329 14.1 3.3 C433 13.5 2.9
C219 1.1 2.5 C330 11.0 3.9 C434 13.1 2.7
XY
C435 9.1 4.1
C436 15.5 4.1
C437 15.7 4.1
D201 3.7 2.0
D202 3.7 1.8
D203 2.9 2.0
D204 2.9 1.8
D205 1.6 4.8
D206 1.6 3.7
D207 2.6 4.3
D208 0.5 3.1
D210 2.6 3.2
D211 2.4 2.4
D212 2.4 2.5
D215 7.3 3.1
D216 1.5 4.5
D217 2.5 2.8
D301 3.4 4.7
D302 14.7 2.5
D303 4.6 4.4
D304 4.6 4.7
D314 11.5 3.1
D315 7.7 4.2
D316 11.5 3.2
D317 10.4 4.2
D318 14.1 2.5
D324 12.1 3.3
D325 12.1 3.4
D326 3.4 4.5
Fl 10.4 2.1
F2 10.4 2.0
F201 5.3 0.1
F202 15.4 2.5
J3 5.4 0.6
J102 11.0 2.2
J103 11.3 0.0
J301 0.8 0.7
J302 6.3 2.9
K201 8.0 0.4
L1 9.1 0.4
L201 2.6 0.1
L202 4.7 0.3
L203 2.1 0.0
XY
L301 5.4 3.5
L302 6.3 4.3
L303 13.4 4.2
L304 8.9 4.5
P301 16.2 4.5
Q201 2.2 4.6
Q202 2.2 3.9
Q203 2.2 3.5
Q204 2.1 2.9
Q208 6.7 3.1
Q301 14.3 3.7
Q302 14.9 4.6
Q303 11.1 1.9
Q305 5.5 2.5
Q401 7.9 3.7
Q403 6.7 2.4
R1 7.4 3.0
R2 7.4 2.9
R3 9.7 0.8
R4 7.9 2.8
R5 8.5 2.1
R6 8.0 1.9
R7 9.1 2.0
R8 8.6 3.5
R9 9.7 4.1
R10 8.0 2.3
R11 8.5 2.6
R12 9.1 3.8
R13 9.7 3.7
R15 10.1 2.8
R16 8.6 3.3
R18 10.7 0.8
R19 10.4 1.8
R20 7.3 2.2
R21 6.8 2.1
R22 6.4 2.3
R23 6.8 3.0
R24 10.7 1.0
R25 5.6 0.5
R26 12.5 2.9
R27 8.6 3.9
R28 7.1 4.4
R29 8.5 0.5
XY
R201 3.9 1.4
R202 2.3 0.6
R203 2.6 4.2
R204 2.1 4.2
R205 1.6 4.3
R206 2.2 4.4
R208 2.6 3.3
R210 3.0 4.8
R211 2.8 4.8
R212 2.1 3.1
R213 1.5 3.2
R214 1.9 2.7
R215 0.0 2.5
R216 0.5 2.6
R217 0.5 2.7
R218 1.7 4.0
R219 1.9 2.6
R220 9.8 1.8
R221 0.5 2.2
R222 0.5 1.6
R223 6.4 2.2
R224 0.5 1.9
R225 0.0 3.0
R228 0.5 2.8
R229 0.5 1.5
R232 0.5 1.8
R234 1.1 2.7
R235 0.0 3.2
R236 10.4 2.3
R237 2.8 3.8
R238 3.0 3.1
R239 0.5 1.7
R240 10.3 0.7
R241 0.0 1.2
R242 0.6 0.6
R244 0.5 1.0
R245 0.0 0.7
R246 0.5 0.5
R247 0.5 1.4
R249 0.5 1.1
R250 3.9 0.5
R301 4.4 4.0
R302 3.7 4.0
XY
R303 10.6 4.6
R304 7.1 3.7
R305 6.7 4.1
R306 6.4 4.3
R307 6.7 3.8
R308 7.2 4.0
R310 7.7 3.3
R311 13.5 2.6
R312 13.5 3.2
R313 12.1 3.5
R314 8.0 3.7
R315 14.1 2.6
R316 14.1 2.7
R317 8.5 4.0
R318 13.5 2.8
R319 14.1 3.1
R320 13.5 3.1
R321 13.6 3.0
R322 13.5 3.3
R323 14.1 4.0
R324 14.7 2.6
R325 15.4 2.6
R326 15.4 2.7
R327 14.9 3.0
R328 14.5 3.5
R329 15.4 2.8
R330 14.8 4.2
R331 15.4 2.9
R332 14.0 3.6
R333 12.1 3.8
R334 13.7 3.9
R336 12.2 4.0
R337 14.8 2.5
R338 12.7 3.8
R339 13.7 3.7
R340 13.7 4.0
R341 13.2 4.0
R342 11.0 3.5
R343 12.1 3.0
R344 13.6 3.2
R345 11.0 3.0
R346 12.2 3.6
R347 14.2 3.4
XY
R348 11.5 3.4
R349 11.5 2.9
R350 6.6 4.2
R351 12.7 3.5
R352 16.3 2.5
R353 11.0 3.6
R354 14.7 2.8
R355 8.0 2.8
R359 11.0 3.3
R360 13.9 4.8
R361 14.0 4.3
R362 10.9 4.0
R363 13.5 3.4
R364 12.1 3.1
R365 7.7 3.9
R367 9.8 4.8
R368 9.6 4.8
R369 9.5 4.8
R401 8.5 3.9
R402 8.0 3.8
R407 10.9 3.8
R408 10.9 3.9
R409 9.8 0.3
R410 5.9 2.1
R411 5.9 2.0
R416 11.0 4.0
R419 12.9 3.2
R420 14.1 3.4
R421 13.5 3.0
R422 10.9 1.7
R423 10.9 1.9
R424 9.7 2.3
R427 9.7 4.8
R428 9.4 4.8
R429 9.9 4.8
R430 5.8 2.5
RT301 8.0 2.7
S3 12.4 2.7
S201 0.1 0.0
T201 4.7 2.5
T202 3.2 2.7
U1 8.6 0.7
U2 6.7 0.4
XY
U3 6.0 0.4
U4 7.6 0.8
U5 8.0 0.8
U6 9.6 0.8
U7 9.0 2.0
U11 8.4 2.9
U12 9.6 3.1
U13 7.2 0.8
U14 7.8 2.2
U15 10.5 2.8
U17 9.9 2.4
U18 10.3 1.2
U19 9.9 2.0
U20 10.2 0.8
U21 10.8 1.1
U22 5.2 0.5
U23 10.8 1.5
U24 10.0 3.2
U25 10.3 0.3
U26 7.2 2.6
U201 1.4 4.0
U202 1.4 2.9
U203 1.0 2.3
U204 5.6 1.8
U205 9.6 2.0
U206 l.0 1.4
U301 7.6 3.4
U302 15.4 3.6
U303 10.9 2.8
U304 13.1 3.6
U305 12.9 2.4
U306 5.5 1.3
U307 14.6 2.9
VR201 10.9 2.4
VR302 9.1 3.4
VR304 9.8 2.9
VR305 12.1 3.2
W1 3.4 3.7
W2 9.1 0.3
W3 4.4 3.9
Y1 8.4 0.3
Page 96

Page 97
Manual Backdating
This appendix describes the changes that must be made to this manual to make it comply with module serial numbers lower
than those on the title page. Look for the serial number of your module on the table and make only those changes listed for
that serial number.
Agilent
Model
66101A 3444A 03900-03271 1 66103A 3151A 00155-00149 1,5-7
66102A 3421A 05364-04131 1 3207A 00394-00101 1-3,5,11
66103A 3421A 04175-03501 1 3421A 00760-00369 1,2
CHANGE 1:
CHANGE 2:
CHANGE 3:
CHANGE 4:
CHANGE 5:
Prefix
Number
3444A 03270-01394 1,4 3147A 00148-00141 1,5-8
3421A 01393-01354 1,4 3139A 00140-00101 1,5-8,10
3231A 00516-00360 1,4,5 66104A 3445A 02435-01778 1
3151A 00359-00151 1,4-6 3445A 01777-00840 1,2
3147A 00150-00141 1,4-9 3421A 00839-00795 1-3
3139A 00140-00101 1,4-10 3306A 00421-00395 1-3,5
3226A 00597-00420 1,5 66105A 3421A 01030-00811 1
3204A 00419-00195 1,5,6 3421A 00810-00403 1,2
3151A 00194-00153 1,5-7 3218A 00215-00126 1,2,5,12
3147A 00152-00141 1,5-9 3207A 00126-00101 1,2,5,12,13
3139A 00140-00101 1,5-10 66106A 3421A 00927-00761 1
3226A 00444-00273 1,5 3207A 00222-00101 1,2,5
3204A 00272-00156 1,5,6
Serial Number Make
Changes
In the parts list on page 78 and in the table on schematic sheet 3 of 5, change the part number of U2 to
5080-2235 and U6 to 5080-2237.
In the parts list on page 79, change the part number of U301 to 1826-0346.
In the parts list on page 73 and in the table on schematic sheet 3 of 5,change R301 and R302 to 25
ohms , part number 0811-3890.
In the parts list on page 68 and in the table on schematic sheet 3 of 5,change C301 to 1500pF, part
number 0160-7638.
In the parts list on page 71, change the part number of D301, 303, 304 and 326 to 1901-1199.
In the parts list on page 77 and in the table on schematic sheet 3 of 5,change R360 to zero ohms, part
number 8159-0005.
In the parts list on page 70 and in the table on schematic sheet 3 of 5,change C335 to 2200pF, part
number 0160-4830.
In Table 2-1 on page 13, change the maximum programmable overvoltage to 9.6V.
In the program listing on page 52, change line 240 to read:
DATA 66,4,25,9.25002,9.6,0,255,100,20,66101
In the parts list on page 62, change the part number of the power boards from 6610xA-61022 to
6610xA-61020.
Agilent
Model
Prefix
Number
Serial Number Make
Changes
CHANGE 6:
CHANGE 7:
In the parts list on page 75, change the part number of the output connector board from 5060-3470 to
5060-3350.
In the parts list on page 74, delete bumper foot, part number 0403-0086. Indicate that software revision
A.00.02 applies to these and earlier models.
Backdating 97
Page 98

CHANGE 8:
In the parts list on page 65, change L204 through L211 from part number 5080-2251 to 9170-0442.
CHANGE 9:
CHANGE 10:
CHANGE 11:
CHANGE 12:
CHANGE 13:
On page 67, change R204, R214 to 61.8 ohms, part number 0757-0397. On page 65, delete D216,
D217, part number 1901-1214.
Indicate that software revision A.00.01 applies to these and earlier models.
In the parts list on page 63, change C311 from 0160-4831 to 2200pF, part number 0160-4830. On page
68, change R311 from 0757-0349 to 51.1K part number 0757-0458.
In the parts list on page 68, change R308 from 249K to 200K part number 0757-0472. Delete R309.
In the parts list on page 63, change C303 from 0180-3648 to 0180-4497. On page 71, change R348
from 17.8K to 12.1K part number 0757-0444. Delete R333.
98 Backdating
Page 99

Index
B
backdating....................................................................................................................................................................89
C
component locator.......................................................................................................................................................83
constant current (cc) tests............................................................................................................................................15
constant voltage tests...................................................................................................................................................13
current monitoring.......................................................................................................................................................12
D
disassembly
bias board .............................................................................................................................................................57
cover.....................................................................................................................................................................56
fan.........................................................................................................................................................................56
front panel.............................................................................................................................................................57
front panel board ..................................................................................................................................................57
modules ................................................................................................................................................................56
power board..........................................................................................................................................................57
documents - related........................................................................................................................................................8
E
electrostatic discharge....................................................................................................................................................9
equipment......................................................................................................................................................................9
I
initialization................................................................................................................................................................. 51
installing
bias board .............................................................................................................................................................59
cover.....................................................................................................................................................................59
fan.........................................................................................................................................................................59
front panel board ..................................................................................................................................................59
power board..........................................................................................................................................................58
M
mainframe......................................................................................................................................................................7
P
parts
Bias board - electrical...........................................................................................................................................79
Front Panel board - electrical ...............................................................................................................................79
mechanical............................................................................................................................................................80
output connector...................................................................................................................................................81
Power board - electrical...............................................................................................................................................68
Index 99
Page 100

performance tests.........................................................................................................................................................11
programming values - modules....................................................................................................................................12
R
revision number.............................................................................................................................................................8
run-time error message ................................................................................................................................................26
S
S3 switch settings.........................................................................................................................................................49
schematic
notes .....................................................................................................................................................................84
schematics....................................................................................................................................................................83
bias board .............................................................................................................................................................83
connector board....................................................................................................................................................83
front panel board ..................................................................................................................................................83
power board..........................................................................................................................................................83
relay board............................................................................................................................................................83
selftest failure ..............................................................................................................................................................26
serial number.................................................................................................................................................................8
service manual...............................................................................................................................................................8
shock hazard................................................................................................................................................................25
switch setting waveforms.............................................................................................................................................50
T
test points.....................................................................................................................................................................48
test record - 66101A....................................................................................................................................................18
test record - 66102A....................................................................................................................................................19
test record - 66103A....................................................................................................................................................20
test record - 66104A....................................................................................................................................................21
test record - 66105A....................................................................................................................................................22
test record - 66106A....................................................................................................................................................23
theory...........................................................................................................................................................................61
ac input.................................................................................................................................................................61
bias supplies .........................................................................................................................................................61
CC DAC...............................................................................................................................................................61
CCPROG*............................................................................................................................................................62
CV DAC...............................................................................................................................................................61
CVPROG*............................................................................................................................................................62
downprogrammer..................................................................................................................................................64
FETS ....................................................................................................................................................................64
IMON.............................................................................................................................................................63, 64
isolation transformer.............................................................................................................................................64
microprocessor.....................................................................................................................................................61
OR Gates..............................................................................................................................................................63
OV comparator.....................................................................................................................................................65
readback multiplexer............................................................................................................................................64
turn-on..................................................................................................................................................................61
VCNTRL..............................................................................................................................................................63
VMON............................................................................................................................................................63, 64
tools...............................................................................................................................................................................9
troubleshooting............................................................................................................................................................25
cc accuracy...........................................................................................................................................................43
100 Index
 Loading...
Loading...