Page 1

Fast Ethernet
Network Interface Card
User Guide
MODEL NO.
3CSOHO100-TX
Page 2

Lifetime Limited
Warranty
3Com’s EtherLink®, Fast EtherLink, OfficeConnect®,
TokenLink®, TokenLink Velocity®, ATMLink™ PCI,
FDDILink™, and Token Ring-in-Fast Ethernet Server
network interface cards have a Lifetime Limited
Warranty. For further details, please see 3Com’s
Limited Warranty statement in this guide.
To ensure the very best 3Com service and
support, take the time to complete the product
registration card.
Page 3

Customers in the countries or regions shown below should send the
completed registration card to the appropriate address. Customers
in other non-U.S. locations should send the registration card to the
U.S. address on the front of the card.
■
Asia
3Com Asia Ltd., Marketing Department
Room 2506-07, 25/F.
Citibank Tower
Citibank Plaza, Central
Hong Kong
■
Australia, New Zealand
3Com Australia, Marketing Department
99 Walker Street
Level 7
North Sydney
New South Wales 2060
Australia
■
Belgium, Netherlands, Luxembourg
3Com Benelux B.V.,
Marketing Department
Nevelgaarde 8-9
3436 ZZ
Nieuwegein
Netherlands
■
France, Israel
3Com France, Marketing Department
Immeuble McKinley
BP 965
1, Avenue de l’Atlantique
91976 Les Ulis Courtaboeuf Cedex
France
■
Italy, Greece, Spain, Portugal, Malta
3Com Mediterraneo Srl,
Marketing Department
Via Michelangelo Buonarroti, 1
20093 Cologno Monzese MI
Italy
■
Japan
3Com Japan, Marketing Department
Shinjuku Sumitomo Building 23F
2-6-1 Nishi Shinjuku, Shinjuku-ku
Tokyo 163-02
Japan
■
Sweden, Finland, Norway,
Denmark
3Com Nordic, Marketing Department
Torshamsgatan 39
Box 1110
164 22 KISTA
Sweden
■
United Kingdom, Eire
3Com UK Ltd., Marketing Department
Pacific House
Third Avenue
Globe Park Marlow-on-Thames
Buckinghamshire, SL7 1YL
England
■
Germany, Austria, Switzerland
3Com GmbH, Marketing Department
Gustav-Heinemann-Ring 123
D-81739 Muenchen
Munich
West Germany
Page 4

OfficeConnect®
Fast Ethernet
Network Interface Card
User Guide
Member of the 3Com OfficeConnect family
http://www.3com.com/
Part No. 09-1569-000
Published October 1998
Page 5

3Com Corporation ■ 5400 Bayfront Plaza ■ Santa Clara, California ■ 95052-8145
Copyright © 1998, 3Com Corporation. All rights reserved. No part of this documentation may be
reproduced in any form or by any means or used to make any derivative work (such as translation,
transformation, or adaptation) without written permission from 3Com Corporation.
3Com Corporation reserves the right to revise this documentation and to make changes in content
from time to time without obligation on the part of 3Com Corporation to provide notification of such
revision or change.
3Com Corporation provides this documentation without warranty, term, or condition of any kind,
either implied or expressed, including, but not limited to, the implied warranties, terms or conditions
of merchantability, satisfactory quality, and fitness for a particular purpose. 3Com may make
improvements or changes in the product(s) and/or the program(s) described in this documentation
at any time.
If there is any software on removable media described in this documentation, it is furnished under a
license agreement included with the product as a separate document, in the hard copy documentation,
or on the removable media in a directory file named LICENSE.TXT or !LICENSE.TXT. If you are unable to
locate a copy, please contact 3Com and a copy will be provided to you.
UNITED STATES GOVERNMENT LEGEND
If you are a United States government agency, then this documentation and the software described
herein are provided to you subject to the following:
All technical data and computer software are commercial in nature and developed solely at private
expense. Software is delivered as “Commercial Computer Software” as defined in DFARS 252.227-7014
(June 1995) or as a “commercial item” as defined in FAR 2.101(a) and as such is provided with only such
rights as are provided in 3Com’s standard commercial license for the Software. Technical data is provided
with limited rights only as provided in DFAR 252.227-7015 (Nov 1995) or FAR 52.227-14 (June 1987),
whichever is applicable. You agree not to remove or deface any portion of any legend provided on any
licensed program or documentation contained in, or delivered to you in conjunction with, this User Guide.
Unless otherwise indicated, 3Com registered trademarks are registered in the United States and may or
may not be registered in other countries.
3Com, the 3Com logo, EtherDisk, and OfficeConnect are registered trademarks of 3Com
Corporation. 3ComFacts is a service mark of 3Com Corporation.
Banyan and VINES are trademarks of Banyan Systems, Incorporated. IBM is a registered trademark of
International Business Machines Corporation. Microsoft, Windows, and Windows NT are trademarks
of Microsoft Corp. Novell and NetWare are trademarks of Novell, Inc.
All other company and product names may be trademarks of the respective companies with which they
are associated.
Guide written by Shelley Spackman. Edited by Nancy Kurahashi. Illustrated by Mary Inden. Produced by
Georgi Felix.
Page 6
C
ONTENTS
A
BOUT THIS GUIDE
Conventions 9
Year 2000 Compliance 10
1
G
ETTING STARTED
What This Guide Covers 11
What This Chapter Covers 11
Understanding Networking 12
Peer-to-Peer Networks 13
Client/Server Networks 14
Ethernet and Fast Ethernet Networking Protocols 14
Understanding Network Interface Cards 15
About the OfficeConnect NIC 15
Required Hardware 16
Required Cabling 16
Required Software 16
2
I
NSTALLING THE NETWORK INTERFACE CARD
Preparing for Installation 17
Inserting the NIC 18
Connecting the NIC to Your Network 20
3
I
NSTALLING THE NETWORK DRIVER
Windows 95 23
Windows 95 Version A 24
Windows 95 Version B 26
Windows 98 28
Windows NT 30
Windows NT 4.0 30
Windows NT 3.51 31
Page 7

Verifying Successful Installation 32
Windows 95 and Windows 98 32
Windows NT 4.0 34
Windows NT 3.51 34
4
T
ROUBLESHOOTING INSTALLATION PROBLEMS
Basic Troubleshooting Tips 35
Interpreting the LEDs 36
Starting the 3Com NIC Diagnostics Program 37
Running the NIC Self-Tests 39
Running the Echo Test 40
Accessing the Help System 43
Viewing Release Notes, Frequently Asked Questions,
and KnowledgeBase Topics 44
Accessing 3Com Support Services 44
Removing NIC Software 46
Windows 95 and Windows 98 46
Windows NT 4.0 47
Windows NT 3.51 47
Frequently Asked Questions 48
5
C
ONFIGURING THE
Displaying Configuration Settings 52
Changing Configuration Settings 54
NIC
A
S
PECIFICATIONS AND CABLING REQUIREMENTS
Specifications 57
Cabling Requirements 57
Unshielded Twisted-Pair Cable 58
10BASE-T Operation 58
10BASE-T Specifications 59
100BASE-TX Operation 59
100BASE-TX Specifications 59
Page 8

B
T
ECHNICAL SUPPORT
Online Technical Services 61
World Wide Web Site 61
3Com FTP Site 61
3Com Bulletin Board Service 62
Access by Analog Modem 62
Access by Digital Modem 62
3ComFacts Automated Fax Service 63
Support from Your Network Supplier 63
Support from 3Com 63
Returning Products for Repair 65
G
LOSSARY
I
NDEX
3COM C
FCC C
FCC D
ORPORATION LIMITED WARRANTY
LASS
B S
ECLARATION OF CONFORMITY
3COM END U
TATEMENT
SER SOFTWARE LICENSE AGREEMENT
Page 9

Page 10

F
IGURES
1
Sample Network 12
2
OfficeConnect NIC 15
3
Inserting the NIC 19
4
Connecting the Network Cable to the NIC 20
5
New Hardware Found Dialog Box 24
6
Update Device Driver Wizard 26
7
Add New Hardware Wizard 28
8
Network Settings Window 31
9
Device Manager Screen 33
10
General Screen 38
11
Diagnostics Screen 39
12
Echo Test Responder Screen 41
13
Echo Test Sender Screen 42
14
Echo Test Statistics Screen 42
15
Support Screen 45
16
General Screen 53
17
NIC Details Screen 53
18
Properties Screen 55
Page 11

T
ABLES
1
Notice Icons 9
2
Text Conventions 10
3
Cable Guidelines 17
4
LED Descriptions 36
5
Frequently Asked Questions 48
6
OfficeConnect NIC Configuration Settings 51
7
Unshielded Twisted-pair Cable Categories 58
Page 12
A
This guide describes how to install, configure, and
troubleshoot the 3Com® OfficeConnect® Fast Ethernet
Network Interface Card (NIC).
This guide is appropriate for anyone who is familiar with
the basic elements of a PC and is interested in connecting a
PC to a network.
If release notes are shipped with your product and the
information there differs from the information in this
guide, follow the instructions in the release notes.
Most user guides and release notes are available in
Adobe Acrobat Reader Portable Document Format (PDF)
or HTML on the 3Com World Wide Web site:
http://www.3com.com/
Conventions
Table 1 and Table 2 list conventions that are used
throughout this guide.
BOUT THIS
GUIDE
Table 1 Notice Icons
Icon Notice Type Description
Information note Important features or instructions
Caution Information to alert you to potential damage to a
Warning Information to alert you to potential personal injury
program, system, or device
Page 13

10 ABOUT THIS GUIDE
Table 2 Text Conventions
Convention Description
Screen displays This typeface represents information as it appears on
the screen.
The words “enter”
and “type”
When you see the word “enter” in this guide, you must
type something, and then press the Return or Enter key.
Do not press the Return or Enter key when an instruction
simply says “type.”
Keyboard key names If you must press two or more keys simultaneously, the
key names are linked with a plus sign (+). Example:
Press Ctrl+Alt+Del
Menu commands
and buttons
Menu commands or button names appear in italics.
Example:
From the Help menu, select Contents.
Words in italics Italics are used to:
■ Emphasize a point.
■ Denote a new term at the place where it is defined in
the text.
■ Identify menu names, menu commands, and software
button names. Examples:
From the Help menu, select Contents.
Click OK.
Year 2000 Compliance
For information on Year 2000 compliance and 3Com
products, visit the 3Com Year 2000 Web page:
http://www.3com.com/products/yr2000.html
Page 14

GETTING STARTED
1
The 3Com® OfficeConnect® Fast Ethernet Network
Interface Card (NIC) allows you to connect your personal
computer (PC) to an Ethernet (10BASE-T) or Fast Ethernet
(100BASE-TX) network.
The OfficeConnect NIC is specifically designed for the
small office/home office environment.
What This Guide Covers
This guide provides all the information you need to install
the OfficeConnect NIC and connect it to a network. It tells
you how to:
■ Insert the NIC into a PC.
■ Attach the PC to a network port on a hub or switch.
■ Install the NIC network driver and diagnostics software
on the PC.
■ Configure the NIC on the PC.
■ Troubleshoot problems you may encounter with
the NIC.
What This Chapter Covers
This chapter provides a brief introduction to networking
and describes the features of your OfficeConnect NIC.
If you’re already familiar with basic networking concepts,
you can start with Chapter 2, “Installing the
Network Interface Card.”
Page 15
12 CHAPTER 1: GETTING STARTED
Understanding Networking
A computer network is a group of computers and other
associated devices, such as printers, fax machines, and
modems, that are connected to one another so they can
share resources and information.
A network allows you to:
■ Share resources — You and others on the network can
share resources, such as a data file or directory, hard
disk drive, printer, scanner, or modem.
■ Exchange information — You can communicate and
exchange information, such as e-mail, with all
designated users on the network.
■ Provide server support — You can store files and
applications in a central location on one PC hard drive,
where they can be accessed by any network users who
have the proper authorization.
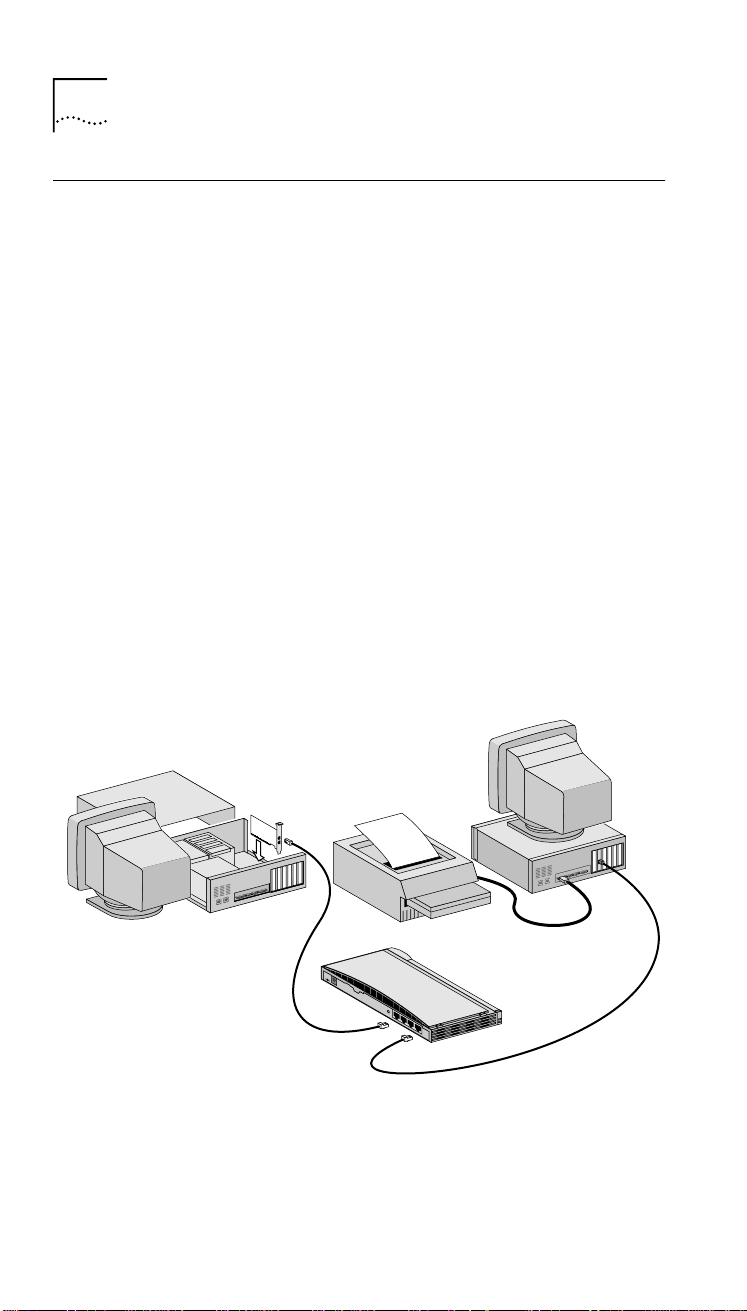
Figure 1 shows a sample network composed of two PCs, a
printer, and a hub.
Computer
1
Figure 1 Sample Network
Printer
10–30 V
1A
D
C
M
A
–
X
+
M
D
I/X
8
Computer
2
Hub
1X
Page 16

Every network requires special software, called a network
operating system (NOS) (such as Windows NT or NetWare),
to control the flow of information between users.
Each PC that you want to connect as part of the network
must have an operating system (such as Windows 95,
Windows 98, or Windows NT) that can communicate with
the NOS.
In a peer-to-peer networking architecture, the operating
system that is installed on each PC acts as the NOS. In a
client/server networking architecture, the operating system
that is installed on each client PC communicates with the
NOS, which is installed on the server PC.
There are two basic types of small business network
architectures: peer-to-peer and client/server.
Peer-to-Peer Networks
A peer-to-peer network is generally suited for home and
small office use. This type of network is the easiest to
install, accommodates up to about five PCs, and is
suitable for sharing applications, data, printers, and
other localized resources.
The PCs on a peer-to-peer network are connected directly to
one other or to a central point, usually a device called a hub.
Unlike a client/server network, a peer-to-peer network allows
users to share information without relying on a centralized
server. Figure 1 is an example of a peer-to-peer network.
The PCs on a peer-to-peer network require an operating
system such as Windows 95 or Windows 98. This operating
system acts as the NOS.
For more information on peer-to-peer networking, see the
Network Assistant CD included in your package.
Understanding Networking 13
Page 17

14 CHAPTER 1: GETTING STARTED
Client/Server Networks
A client/server network is ideal for organizations that
require fast network access for large applications such
as multimedia, databases, and video.
In a client/server network, all shared applications and files
are stored on one central computer known as the server.
Network users (client PCs) can store their own files on their
own PCs, and then use the server to access shared files and
peripherals, such as printers, fax machines, and modems.
The client PCs on a client/server network require an
operating system such as Windows 95, Windows 98, or
Windows NT. The servers on a client/server network require
a NOS such as Windows NT or NetWare.
Ethernet and Fast Ethernet Networking Protocols
Ethernet and Fast Ethernet are local area network (LAN)
protocols, or specifications, that define the signaling of the
network and specify how data is placed on and retrieved
from the network.
Fast Ethernet is the same as Ethernet, except for the speed:
■ Ethernet has a data transfer rate of 10 Mbps (megabits
per second).
■ Fast Ethernet has a data transfer rate of 100 Mbps.
The OfficeConnect NIC is compatible with both Ethernet
and Fast Ethernet networks. It automatically connects to
the network at 10 Mbps or 100 Mbps, depending on the
speed of the connected network hub or switch.
For more information on Ethernet and Fast Ethernet, see
Appendix A.
For more information on networking, see the
Network Assistant CD included in your package.
Page 18

Understanding Network Interface Cards 15
Understanding Network Interface Cards
A network interface card (NIC) is a printed circuit board
that plugs into a PC expansion slot in your computer to
provide a connection to a network.
Once the NIC is installed in your PC, you connect it to the
network media (cabling, such as unshielded twisted-pair
[UTP]), which in turn connects to all the devices on
the network.
About the OfficeConnect NIC
The OfficeConnect NIC is a 10/100 Mbps PCI (Peripheral
Component Interconnect) NIC. It connects your PC to a
10 Mbps Ethernet or 100 Mbps Fast Ethernet network.
Figure 2 OfficeConnect NIC
TX
RJ-45 port
DATA
LEDs
ACT
10
L
N
100
K
The OfficeConnect NIC backplate has three light-emitting
diodes (LEDs):
■ 10 LNK (link)
■ 100 LNK (link)
■ ACT (activity)
Page 19

16 CHAPTER 1: GETTING STARTED
After the NIC is installed, these LEDs show whether there’s
an active connection between the NIC and the network,
and the speed at which you’re connected. (See
“Interpreting the LEDs” in Chapter 4 for more
information.)
Required Hardware
You can install the OfficeConnect NIC in any IBM-compatible
PC with an available PCI expansion slot. Almost all
PCs currently on the market have such slots. (See “Inserting
the NIC” in Chapter 2 for more information about
PCI expansion slots.)
Required Cabling
You need an unshielded twisted-pair cable with RJ-45
connectors on both ends to connect the OfficeConnect NIC
to the network. This cable is not supplied with the NIC.
■ If you’re connecting to a 10 Mbps Ethernet network,
use a Category 3, 4, or 5 UTP cable.
■ If you’re connecting to a 100 Mbps Fast Ethernet
network, use a Category 5 UTP cable.
The maximum Ethernet cable length allowed between
the NIC and the network device to which it is connected
is 328 feet (100 meters).
For more information on cabling, see “Cabling
Requirements” in Appendix A.
Required Software
The OfficeConnect NIC is compatible with the following
operating systems:
■ Windows 95
■ Windows 98
■ Windows NT versions 4.0 and 3.51
You can use the OfficeConnect NIC to connect to both
Microsoft and NetWare network environments.
The EtherDisk diskette included in your package contains the
software (configuration programs, diagnostic programs, and
device drivers) that allows your NIC to work with all of the
operating systems mentioned in this section.
Page 20
INSTALLING THE
2
NETWORK INTERFACE CARD
This chapter explains how to install the OfficeConnect NIC
in your PC and connect it to an Ethernet or Fast Ethernet
network.
Preparing for Installation
Before you install the OfficeConnect NIC, make sure
that you have the following items:
■ OfficeConnect 10/100 Fast Ethernet NIC
■ OfficeConnect EtherDisk diskette
If any of these items are damaged or missing, contact
your shipper or network supplier.
You also need an unshielded twisted-pair (UTP) cable
with RJ-45 connectors on both ends to connect the
OfficeConnect NIC to an Ethernet or Fast Ethernet
network. This cable is not supplied with the NIC.
Table 3 specifies the type of cable that you need for the
type of network that you are connecting to (10 Mbps
Ethernet or 100 Mbps Fast Ethernet).
The maximum distance between any two devices on your
network can be no more than 328 feet (100 meters).
Table 3 Cable Guidelines
Type of
Network
Ethernet
(10BASE-T)
Fast Ethernet
(100BASE-TX)
The next step is to insert the NIC in the PC.
Cable Required
Category 3, 4, or 5 UTP
with RJ-45 connectors on
both ends
Category 5 UTP with RJ-45
connectors on both ends
Maximum
Cable Length
328 ft/100 m
328 ft/100 m
Page 21
18 CHAPTER 2: INSTALLING THE NETWORK INTERFACE CARD
Inserting the NIC
To insert the OfficeConnect NIC in your PC:
1 Remove all jewelry from your hands and wrists.
CAUTION: The NIC is packed in an antistatic container
to protect it during shipment. To avoid damaging any
static-sensitive components on the NIC, before you remove
it from the container, touch the metal chassis of your PC to
discharge static electricity from your body. Also, be careful
to handle the NIC by its edges only.
2 Turn the power off to the PC. Unplug the
power cable. Detach all other cables from the PC.
3 Remove the PC cover.
See your PC documentation for details.
4 Find an empty PCI expansion slot and remove the
corresponding slot cover. Keep the backplate screw.
The OfficeConnect NIC works in a PCI expansion slot. Some
PCs have three types of expansion slots: PCI, ISA, and EISA.
PCI slots are usually white and shorter than the other
expansion slots (see Figure 3). ISA slots are usually black.
EISA slots are usually brown, and are as long as ISA slots. If
you’re not sure what type of expansion slots your PC has,
see your PC documentation for details.
For more information on PCI expansion slots, see
“Frequently Asked Questions” in Chapter 4.
5 Carefully insert the NIC into the slot, pressing firmly
with steady pressure until it’s seated properly.
The NIC’s metal backplate should be positioned so that you
can easily fasten it with the backplate screw. You shouldn’t
be able to see any of the NIC’s edge connector.
Not all PCs have expansion slots positioned on the bottom
of the chassis, as shown in Figure 3. You may be using a PC
with the expansion slots on a vertical panel. If so, follow
the same insertion instructions, except install the NIC
horizontally. If it helps, position the PC on its side
temporarily to insert the NIC securely.
Page 22
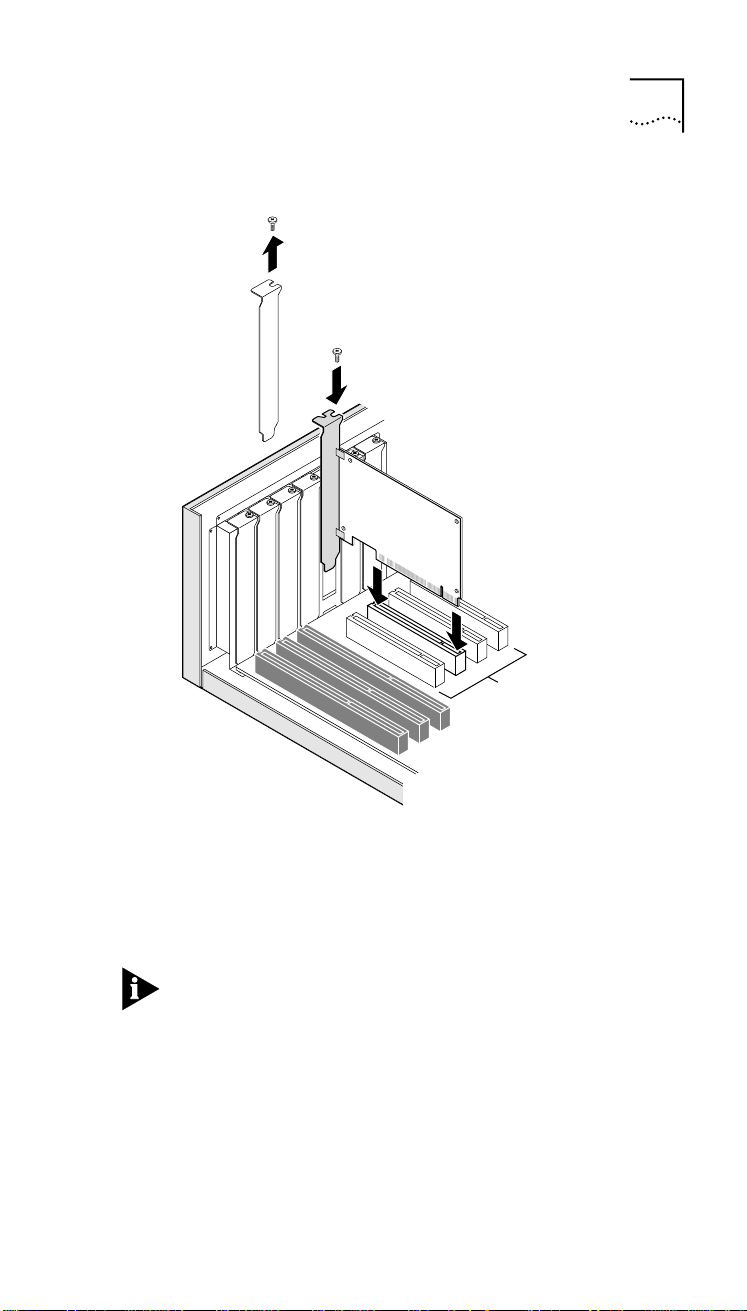
Figure 3 Inserting the NIC
1 Remove slot cover
2 Insert NIC
Inserting the NIC 19
PCI slots
6 Fasten the NIC with the backplate screw you removed
in step 4.
7 Replace the PC cover.
8 Reconnect any cables that you disconnected before
you opened the PC.
Do not turn on the power to the PC.
The next step is to connect the NIC to your network.
Page 23
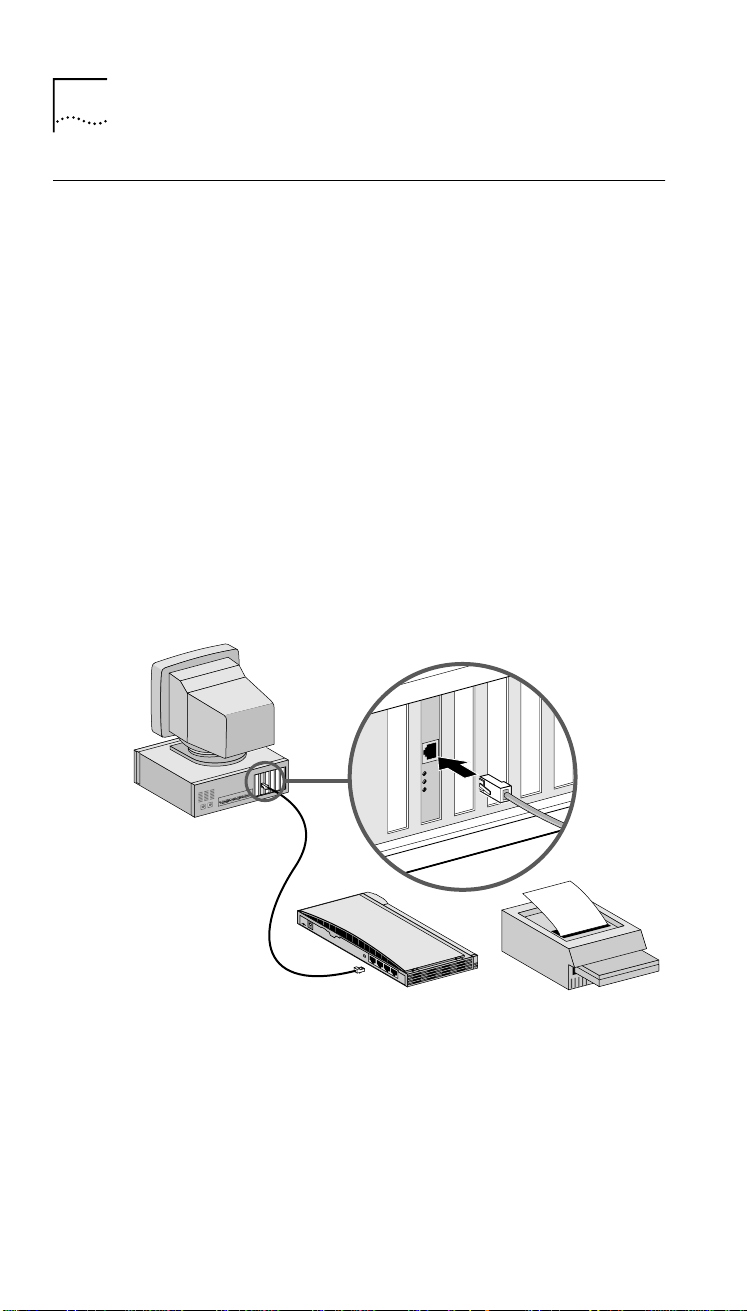
20 CHAPTER 2: INSTALLING THE NETWORK INTERFACE CARD
TX Data
ACT
10
100
L
N
K
Connecting the NIC to Your Network
This section describes how to connect the OfficeConnect
NIC to a network device. For more information on
networking or creating a peer-to-peer network, see
the Network Assistant CD included in your package.
To connect the OfficeConnect NIC to a network device:
1 Using an unshielded twisted-pair (UTP) cable, insert
one of the RJ-45 connectors on the cable into the
RJ-45 port on the installed NIC, as shown in Figure 4.
■ If you’re connecting to a 10 Mbps Ethernet network,
use a Category 3, 4, or 5 UTP cable.
■ If you’re connecting to a 100 Mbps Fast Ethernet
network, use a Category 5 UTP cable.
See Table 3 at the beginning of this chapter or Appendix A
for more information on network cabling requirements.
Figure 4 Connecting the Network Cable to the NIC
RJ-45 port
10–30 V
1A
D
C
M
A
–
X
+
M
D
I/X
8
1X
Hub
or
Printer
Page 24

Connecting the NIC to Your Network 21
2 Insert the other end of the UTP cable into an active
network port.
An active network port may be on a network hub or
switch, or a peripheral device (such as a printer) that is
network-ready (that is, it already has a NIC inside it).
Do not turn on the power to the PC.
The next step is to install the network driver. Go to
Chapter 3.
Page 25

Page 26

INSTALLING THE
3
NETWORK DRIVER
This chapter describes how to install the network driver
in your PC. You must install the network driver so that
the OfficeConnect NIC can transmit and receive data over
the network.
Instructions are provided for the following operating
systems supported by the OfficeConnect NIC:
■ Windows 95
■ Windows 98
■ Windows NT
Go to the appropriate section in this chapter for your
operating system.
If a NIC has already been installed in your PC, you must
remove its network driver before you install the driver for
the OfficeConnect NIC. To find out whether a NIC has
already been installed in your PC, and to remove its driver,
follow the steps in “Removing NIC Software” in Chapter 4.
Windows 95
To install the network driver under Windows 95, you need
the Windows 95 installation files. These files may be on a
CD or diskettes, or they may have been copied to your hard
drive when Windows 95 was installed on your system.
The version of Windows 95 installed on your PC
determines which of the driver installation procedures
to use.
To determine the Windows 95 version installed on your PC:
1 Right-click the My Computer icon, and then
click Properties.
The System Properties window appears.
Page 27

24 CHAPTER 3: INSTALLING THE NETWORK DRIVER
2 Check the version number on the General screen,
under System:
■ If 4.00.950 or 4.00.950A is displayed, follow the
procedure for Windows 95 Version A.
■ If 4.00.950B is displayed, follow the procedure for
Windows 95 Version B.
Windows 95 Version A
To install the network driver in a PC running version A of
Windows 95:
1 Make sure that the NIC is installed in your PC and that
it’s connected to the network, as described in Chapter 2.
2 Turn on the power to the PC.
Windows 95 detects the NIC and displays the
New Hardware Found dialog box (Figure 5), prompting
you for the driver you want to install for your new
hardware.
Figure 5 New Hardware Found Dialog Box
3 Select Driver from disk provided by hardware
manufacturer, and then click OK.
The Install from Disk dialog box appears.
Page 28

Windows 95 25
4 Insert the EtherDisk diskette in drive A and make sure
that A:\ appears in the Copy files from entry box.
5 Click OK.
■ If this is the first time that networking is being installed
on your PC, the Identification tab of the Network
window is displayed. Go to step 6.
■ If networking has already been installed, you’re
prompted for the Windows 95 CD. In this case, go
to step 7.
6 In the specified fields of the Identification tab
screen, enter the following information, and then
click OK:
■ Computer Name — Identifies the computer on the
network for other users. This entry must be a unique
name of 15 characters or fewer, containing no spaces.
■ Workgroup — Identifies the group (for example, your
department name) to which your computer belongs.
If you’re setting up a simple peer-to-peer network,
this entry must be exactly the same for all the PCs in
your network.
■ Computer Description — Displays additional details to
other users on the network about this PC. For example,
you could specify that the PC has a printer attached.
Filling in this field is optional.
7 Insert the Windows 95 CD in the CD-ROM drive, and
then click OK.
If you don’t have the Windows 95 CD, click OK. Enter
the path for the Windows 95 installation files on your PC
(such as C:\WIN95) in the Copying Files entry box, and then
click OK.
Files are copied. You’re prompted to restart your PC.
8 Remove the EtherDisk diskette from drive A, and
then click Yes.
You must reboot your PC to complete the installation.
After Windows restarts, you’re prompted to enter your
name and network password.
Page 29

26 CHAPTER 3: INSTALLING THE NETWORK DRIVER
9 Enter your user name and password, and then
click OK.
The driver installation is complete. To confirm successful
installation, go to “Verifying Successful Installation” later in
this chapter.
Windows 95 Version B
To install the network driver in a PC running version B of
Windows 95:
1 Make sure that the NIC is installed in your PC and that
it’s connected to the network, as described in Chapter 2.
2 Turn on the power to the PC.
Windows 95 detects the NIC. The Update Device Driver
Wizard (Figure 6) starts and prompts you for a diskette
or CD.
Figure 6 Update Device Driver Wizard
3 Insert the EtherDisk diskette in drive A, and then
click Next.
Windows finds the driver and asks if you want to use
this driver.
Page 30

Windows 95 27
4 Click Finish.
The Insert Disk dialog box prompts you for the
OfficeConnect EtherDisk diskette.
5 Click OK.
The Copying Files dialog box appears.
6 Make sure that A:\ appears in the Copying files from
entry box, and then click OK.
■ If this is the first time that networking is being installed
on your PC, the Identification tab of the Network
window is displayed. Go to step 7.
■ If networking has already been installed, you’re prompted
for the Windows 95 CD. In this case, go to step 8.
7 In the specified fields of the Identification tab
screen, enter the following information, and then
click OK:
■ Computer Name — Identifies the computer on the
network for other users. This entry must be a unique
name of 15 characters or fewer, containing no spaces.
■ Workgroup — Identifies the group (for example, your
department name) to which your computer belongs.
If you’re setting up a simple peer-to-peer network,
this entry must be exactly the same for all the PCs in
your network.
■ Computer Description — Displays additional details to
other users on the network about this PC. For example,
you could specify that the PC has a printer attached.
Filling in this field is optional.
8 Insert the Windows 95 CD in the CD-ROM drive, and
then click OK.
If you don’t have the Windows 95 CD, click OK. Enter
the path for the Windows 95 installation files on your PC
(such as C:\WIN95) in the Copying Files entry box, and then
click OK.
Files are copied. You’re prompted to restart your PC.
Page 31

28 CHAPTER 3: INSTALLING THE NETWORK DRIVER
9 Remove the EtherDisk diskette from drive A, and
then click Yes.
You must reboot your PC to complete the installation.
After Windows restarts, you’re prompted for your user
name and password.
10 Enter your user name and password, and then
click OK.
The driver installation is complete. To confirm successful
installation, go to “Verifying Successful Installation” later in
this chapter.
Windows 98
To install the network driver in a PC running Windows 98:
1 Make sure that the NIC is installed in your PC and that
it’s connected to the network, as described in Chapter 2.
2 Turn on the power to the PC.
Windows 98 detects the NIC. The Add New Hardware
Wizard (Figure 7) starts.
Figure 7 Add New Hardware Wizard
Page 32

Windows 98 29
3 Insert the EtherDisk diskette in drive A, and then
click Next.
4 Select Search for the best driver for your device
(Recommended), and then click Next.
5 Select Floppy disk drives, and then click Next.
Windows finds the driver file for the device.
6 Click Next.
Files are copied.
If the Insert Disk window appears, prompting you to insert
the EtherDisk diskette, click OK.
You’re then prompted for the Windows 98 CD.
7 Insert the Windows 98 CD in the CD-ROM drive, and
then click OK.
If you don’t have the Windows 98 CD, click OK. Enter the
path for the Windows 98 installation files on your PC in the
Copying Files entry box.
Files are copied. The installation is complete when you’re
prompted to click Finish.
8 Click Finish.
You’re prompted to restart the PC.
9 Click Yes to restart the PC.
You must reboot your PC to complete the installation.
The driver installation is complete. To confirm successful
installation, go to “Verifying Successful Installation” later in
this chapter.
Page 33

30 CHAPTER 3: INSTALLING THE NETWORK DRIVER
Windows NT
This section describes how to install the network driver in
a PC running Microsoft Windows NT 4.0 or 3.51.
Windows NT 4.0
To install the network driver in a PC running
Windows NT 4.0:
1 Make sure that the NIC is installed in your PC and that
it’s connected to the network, as described in Chapter 2.
2 Turn on the power to the PC.
3 Double-click the My Computer icon, then the
Control Panel icon, and then the Network icon.
The Network window appears.
4 Click the Adapters tab.
If networking hasn’t been installed on your system before,
Windows NT asks you if you want to install networking. Click
Yes. See the WINNT.TXT file located on the EtherDisk diskette
or your Windows NT documentation for instructions.
5 Click Add.
The Select Network Adapter dialog box appears.
6 Click Have Disk.
The Insert Disk dialog box appears.
7 Insert the EtherDisk diskette in drive A, enter the path
to drive A if it’s not already displayed, and click OK.
The OEM Option dialog box appears.
8 If not already selected, select 3Com OfficeConnect
10/100 Fast Ethernet NIC, and click OK.
Files are copied. The 3Com NIC Diagnostics window appears.
9 Click Close to continue the installation.
The Network screen appears with the OfficeConnect NIC
displayed in the list of network adapters.
10 Click Close.
The driver installation is complete. To confirm successful
installation, go to “Verifying Successful Installation” later in
this chapter.
Page 34

Windows NT 3.51
To install the network driver in a PC running
Windows NT 3.51:
1 Make sure that the NIC is installed in your PC and that
it’s connected to the network, as described in Chapter 2.
2 Turn on the power to the PC.
3 In the Main window of the Program Manager,
double-click the Control Panel icon and then the
Network icon.
The Network Settings window (Figure 8) appears.
Figure 8 Network Settings Window
Windows NT 31
4 Click Add Adapter.
The Add Network Adapter window appears.
5 Click the down arrow to expand the
Network Adapter Card list box, and then scroll down
and select <Other> Requires disk from manufacturer.
6 Click Continue.
The Insert Disk dialog box appears.
7 Insert the EtherDisk diskette in drive A, make sure
that A:\ appears in the entry box, and then click OK.
The Select OEM Option window appears.
Page 35

32 CHAPTER 3: INSTALLING THE NETWORK DRIVER
8 Make sure that 3Com OfficeConnect 10/100
Fast Ethernet NIC is selected, and then click OK.
Files are copied. The 3Com NIC Diagnostics screen appears.
9 Click Close to continue the installation.
The Network Settings window reappears.
10 Click OK in the Network Settings window.
If the TCP/IP Configuration screen appears, enter the
requested information, and then click OK. For help with
this information, click the Help button on the TCP/IP
Configuration screen.
You’re prompted to restart Windows NT.
11 Remove the EtherDisk diskette from drive A.
12 Click Restart Now.
You must reboot your PC to complete the installation.
The driver installation is complete. To confirm successful
installation, go to the next section, “Verifying Successful
Installation.”
Verifying Successful Installation
To confirm that the NIC is installed correctly in your PC,
follow the steps appropriate for your operating system.
Windows 95 and Windows 98
To confirm that the NIC is installed correctly in a PC running
Windows 95 or Windows 98:
1 Right-click the My Computer icon, click Properties,
and then select the Device Manager tab.
A list of devices appears, arranged by type (Figure 9).
Page 36

Verifying Successful Installation 33
Figure 9 Device Manager Screen
2 Double-click Network adapters.
The name of the installed OfficeConnect NIC appears, as
shown in Figure 9.
If a yellow exclamation point (!) or a red X appears next
to the NIC name, the installation wasn’t successful.
Go to “Frequently Asked Questions” in Chapter 4 to
troubleshoot the NIC.
3 Double-click the name of the NIC to display a
description of the NIC and its current status.
The message in the Device status panel confirms that
the OfficeConnect NIC is working properly.
4 Click Cancel to close each dialog box. Then close the
Control Panel and My Computer windows.
You’ve successfully installed and configured the
OfficeConnect NIC.
Page 37

34 CHAPTER 3: INSTALLING THE NETWORK DRIVER
Windows NT 4.0
To confirm that the NIC is installed correctly in a PC running
Windows NT 4.0:
1 Double-click the Network icon in the Control Panel.
2 Click the Adapters tab.
The OfficeConnect NIC should appear in the list of network
adapters. If it doesn’t appear, see Chapter 4 for
troubleshooting information.
Windows NT 3.51
To confirm that the NIC is installed correctly in a PC running
Windows NT 3.51:
1 Double-click the File Manager icon.
2 From the Disk menu, select Connect Network Drive.
The presence of network server names confirms
successful installation.
Page 38

TROUBLESHOOTING
4
INSTALLATION PROBLEMS
This chapter explains how to isolate and solve problems
that may occur when you install the OfficeConnect NIC.
Basic Troubleshooting Tips
If you have trouble installing your OfficeConnect NIC, or if
the installation failed (as described in “Verifying Successful
Installation” in Chapter 3), follow these basic
troubleshooting tips.
CAUTION: Before inserting or removing the NIC from
your PC, turn the power off to the PC and unplug the
power cord.
■ Check the NIC installation by reviewing Chapter 2.
Make sure that the NIC is seated correctly in an
appropriate expansion slot. Check for specific hardware
problems, such as loose or broken connections.
■ Inspect all cables and connections. Check the length
and rating of the cable. Make sure that the cable and
its length comply with 10BASE-T or 100BASE-TX
recommendations. See Table 3 in Chapter 2 or
Appendix A for more information.
■ Make sure that you’re running the latest BIOS for your
PC. If your BIOS hasn’t been upgraded in the previous
12 months, contact your PC manufacturer to obtain
the current version of your BIOS software.
■ Run the NIC self-tests and the Echo test, as described
later in this chapter.
■ Download the latest OfficeConnect NIC driver from the
3Com World Wide Web site and install it in your PC.
Run the NIC self-tests and the Echo test again, using
the same option settings as those used on the failed
NIC. If the tests still fail, the NIC may be defective.
Page 39

36 CHAPTER 4: TROUBLESHOOTING INSTALLATION PROBLEMS
Interpreting the LEDs
The OfficeConnect NIC has three light-emitting diodes
(LEDs) that can help indicate when there are problems
with your network connection.
See Figure 2 in Chapter 1 for a picture of the LEDs.
Table 4 explains the LED states.
Table 4 LED Descriptions
LED State Meaning
10 LNK
(link)
100 LNK
(link)
ACT
(activity)
On
Off
Blinking
On
Off
Flashing
Steady
Off
If the network driver is installed, as described in Chapter 3,
the connection to the 10BASE-T Ethernet network is active.
If the driver is not installed, the NIC is receiving power.
Something is preventing the connection between the NIC
and the network. See the troubleshooting steps following
this table.
The cable polarity is reversed. Try a different
network cable.
If the network driver is installed, as described in Chapter 3,
the connection to the 100BASE-TX Fast Ethernet network
is active.
If the driver is not installed, the NIC is receiving power.
Something is preventing the connection between the NIC
and the network. See the troubleshooting steps following
this table.
Network traffic is present.
Heavy network traffic is present.
No network traffic is present.
If the LNK (10 LNK or 100 LNK) LED is off and the PC is
powered on and the network cable is connected, check
the following:
1 Ensure that the network hub or device to which the
NIC is connected and the cable connecting to your
NIC comply with the 10BASE-T or 100BASE-TX
specifications.
2 Ensure that the network hub or device to which the
NIC is connected is powered on.
Page 40

Starting the 3Com NIC Diagnostics Program 37
Starting the 3Com NIC Diagnostics Program
The 3Com NIC Diagnostics program allows you to run
diagnostic tests, change NIC configuration settings, and
access 3Com support services and Help topics.
This section describes how to use the 3Com NIC
Diagnostics program to help troubleshoot problems
you may encounter with the NIC.
For instructions on changing NIC configuration settings,
see Chapter 5.
The 3Com NIC Diagnostics program is installed
automatically when you install the network driver.
To start the 3Com NIC Diagnostics program:
1 Double-click the 3Com icon in the Windows
system tray.
If the 3Com icon isn’t visible in the system tray, follow
these steps:
a From the Windows Start menu, select Programs.
b Select 3Com NIC Utilities.
c Click 3nicdiag.
For PCs running Windows NT 3.51, from the File menu,
select Run. At the command prompt, enter the path for the
3Com NIC Diagnostics program. The default path is
C:\WINNT35\SYSTEM32\3NICDIAG.EXE.
A warning message appears, stating that your PC will be
disconnected from the network.
This means that no applications other than the 3Com NIC
Diagnostics program can connect to the network while you
run the diagnostics program.
All applications are automatically reconnected to the
network when you exit the diagnostics program. If your
PC doesn’t automatically reconnect to the network, reboot
the PC.
Page 41

38 CHAPTER 4: TROUBLESHOOTING INSTALLATION PROBLEMS
2 Click OK.
The 3Com NIC Diagnostics General screen (Figure 10)
appears.
Figure 10 General Screen
Click the Help button to receive information about the
diagnostic screen that’s currently active.
The General screen displays general information about
the NIC. It also allows you to show or not show the
3Com icon in the Windows system tray by clicking the
Enable Tray Control check box. The 3Com icon provides
quick access to the 3Com NIC Diagnostics program.
3 Click Cancel to exit the 3Com NIC Diagnostics program.
Page 42

Running the NIC Self-Tests
The first tests to run when you have a problem with the
OfficeConnect NIC are the NIC self-tests.
The NIC self-tests can verify that the OfficeConnect NIC is
working correctly by checking the physical components,
connectors, and circuitry on the NIC.
To run the NIC self-tests:
1 Double-click the 3Com icon in the Windows
system tray.
If the 3Com icon isn’t visible in the system tray, follow the
instructions in the previous section, “Starting the 3Com
NIC Diagnostics Program.”
2 Click OK.
The 3Com NIC Diagnostics General screen appears
(Figure 10).
3 Click the Diagnostics tab.
The Diagnostics screen (Figure 11) appears.
Running the NIC Self-Tests 39
Figure 11 Diagnostics Screen
Page 43

40 CHAPTER 4: TROUBLESHOOTING INSTALLATION PROBLEMS
For a description of each test, click the Help button on
the screen or click the question mark (?) at the top of the
screen, move it over the test, and click once. A pop-up box
displays information about the test.
4 Click Start in the Self-Test panel.
A six-test sequence begins. The status of each test (such as
Passed or In Progress) is displayed in the Status column next
to each test as the tests run and are completed.
You can click Stop to stop the tests at any point.
■ If all of the tests are successful, the OfficeConnect NIC
is working correctly.
■ If any test failed, click the question mark (?) at the
top right corner of the screen, move it over the failed
test topic, and click once. A pop-up box displays
information about the test and what to do if it fails.
Running the Echo Test
After you’ve confirmed that the OfficeConnect NIC is
functioning correctly by running the NIC self-tests (as
described in the previous section), verify that the NIC is
transmitting and receiving data over the network by
running the Echo test.
The Echo test checks the ability of the NIC to transmit and
receive data while it’s connected to the network.
To run the Echo test, you need two PCs networked
together.
■ The first PC is used to send data. This is called the
sending PC.
■ The second PC receives data sent from the first PC. This
is called the responding PC.
The two PCs must each have a 3Com OfficeConnect NIC
installed. Also make sure that the network driver is installed.
CAUTION: Running the Echo test while connected to
an active network with more than two computers can
cause intermittent failures within the test. Make sure that
only two computers are connected to the network before
running the Echo test.
Page 44

Running the Echo Test 41
To run the Echo test:
1 On both PCs:
a From the Windows Start menu, select Programs.
b Select 3Com NIC Utilities.
c Click 3nicdiag.
d Click OK.
e Click the Diagnostics tab to display the Diagnostics
screen, shown in Figure 11.
2 On the second PC (the responding PC):
a Click Respond in the Echo Test panel.
The Echo Test Responder screen (Figure 12) appears.
Figure 12 Echo Test Responder Screen
b Click Start.
3 On the first PC (the sending PC):
a Click Send on the Diagnostics screen.
The Echo Test Sender screen (Figure 13) appears.
Page 45

42 CHAPTER 4: TROUBLESHOOTING INSTALLATION PROBLEMS
Figure 13 Echo Test Sender Screen
b Click Start.
The two PCs attempt to transmit data to each other.
Statistics appear in the window, as shown in Figure 14.
Figure 14 Echo Test Statistics Screen
Page 46

Accessing the Help System 43
■ If the values of the Bytes Received, Bytes Transmitted,
Packets Received, or Packets Transmitted statistics
increase, the two PCs are successfully transmitting data
over the network.
■ If the values of the statistics remain at zero, or if there are
excessive collisions, the two PCs aren’t transmitting data
successfully over the network. Check the following:
■ Ensure that the network hub or device to which the
NIC is connected and the cable connecting to your
NIC comply with the 10BASE-T or 100BASE-TX
specifications. (See Appendix A.)
■ Ensure that the network hub or device to which the
NIC is connected is powered on.
For a description of each statistic, click the Help button on
the screen or click the question mark (?) at the top of the
screen, move it over the topic, and click once. A pop-up
box displays information about the statistic.
c Close all open windows when the Echo test is finished.
Accessing the Help System
The OfficeConnect NIC Help system is a Windows Help
application that includes numerous Help topics about the
OfficeConnect NIC.
To access the OfficeConnect NIC Help system:
1 From the Windows Start menu, select Programs.
2 Select 3Com NIC Utilities.
3 Click 3nichelp.
For PCs running Windows NT 3.51, from the File
menu, select Run. At the command prompt, enter the
path for the 3Com NIC Help system. The default path is
C:\WINNT35\SYSTEM32\3NICDIAG.HLP.
The main Help screen appears, displaying information
about the 3Com NIC Diagnostics General screen.
4 Click Help Topics to display a list of Help topics or click
Find to search for a Help topic.
Page 47

44 CHAPTER 4: TROUBLESHOOTING INSTALLATION PROBLEMS
Viewing Release Notes, Frequently Asked Questions,
and KnowledgeBase Topics
The 3Com NIC Diagnostics program contains a substantial
database of support-related and service-related data that
you can access in the following categories: release notes,
frequently asked questions, and KnowledgeBase topics.
To access the support database:
1 Double-click the 3Com icon in the Windows
system tray.
If the 3Com icon isn’t visible in the system tray, follow the
instructions in the section “Starting the 3Com NIC
Diagnostics Program” earlier in this chapter.
2 Click OK.
3 Click the Support tab.
The Support screen appears.
4 Click Release Notes.
The Release Notes Help screen appears.
■ Click the Release Notes link to display tips about
installing and using the OfficeConnect NIC.
■ Click the Frequently Asked Questions link to display
common questions asked by customers and answered
by 3Com support experts.
■ Click the KnowledgeBase link to display OfficeConnect
NIC compatibility topics.
Accessing 3Com Support Services
The Support screen provides access to the 3Com
World Wide Web site, customer support databases (such
as release notes and frequently asked questions), and the
problem report generator.
To access 3Com support services:
1 Double-click the 3Com icon in the Windows
system tray.
If the 3Com icon isn’t visible in the system tray, follow the
instructions in the section “Starting the 3Com NIC
Diagnostics Program” earlier in this chapter.
Page 48

Accessing 3Com Support Services 45
2 Click OK.
3 Click the Support tab.
The Support screen (Figure 15) appears.
Figure 15 Support Screen
■ Click Diagnostics to run the 3Com NIC diagnostic tests.
See “Running the NIC Self-Tests” and “Running the
Echo Test” earlier in this chapter for information on
how to run the 3Com NIC diagnostic tests.
■ Click Release Notes to display customer support
information databases about the OfficeConnect NIC
in three categories: release notes, frequently asked
questions, and the KnowledgeBase.
■ Click BBS Information to display the 3Com BBS
telephone numbers and modem speeds.
■ The http://www.3com.com button displays the
3Com World Wide Web site address.
■ Click Problem Report if you want to generate a
problem report file about an OfficeConnect NIC
problem. You can then e-mail this file to 3Com.
Page 49

46 CHAPTER 4: TROUBLESHOOTING INSTALLATION PROBLEMS
Removing NIC Software
This section describes how to remove a NIC’s network
driver and software from your PC so that you can reinstall
the software or physically remove the NIC from your PC.
If you want to reinstall the OfficeConnect NIC network
driver and software, you must first remove the driver and
software, as described in this section.
Windows 95 and Windows 98
To remove NIC software in a PC running Windows 95
or Windows 98:
1 Double-click the My Computer icon, then the
Control Panel icon, and then the System icon.
2 Click the Device Manager tab.
3 Double-click Network adapters.
4 Select the name of the NIC, for example,
3Com OfficeConnect 10/100 Fast Ethernet
(3CSOHO100-TX) NIC.
5 Click Remove.
6 Click OK to confirm the device removal.
The NIC driver and diagnostic software are removed
from the PC.
You’re prompted to restart the PC.
■ If you’re physically removing the NIC from the PC,
click No. Don’t restart the PC until you shut down the
system, turn the power off, and remove the NIC from
the PC.
■ If you’re reinstalling the NIC software, click Yes.
Page 50

Windows NT 4.0
To remove NIC software in a PC running Windows NT 4.0:
1 Double-click the My Computer icon, then the
Control Panel icon, and then the Network icon.
The Network screen appears.
2 Click the Adapters tab.
3 Select the name of the NIC in the Network Adapters
box, and then click Remove.
4 Click Yes to confirm the removal.
5 Click Close to close the Network screen.
The NIC driver and diagnostic software are removed from
the PC.
You’re prompted to restart the PC.
■ If you’re physically removing the NIC from the PC,
click No. Don’t restart the PC until you shut down the
system, turn the power off, and remove the NIC from
the PC.
■ If you’re reinstalling the NIC software, click Yes to
restart the PC.
Removing NIC Software 47
Windows NT 3.51
To remove NIC software in a PC running Windows NT 3.51:
1 In the Main Program window, double-click
the Control Panel icon, and then the Network icon.
The Network Settings window is displayed.
2 In the Installed Adapter Cards panel, select the name
of the installed NIC and click Remove.
The Network Settings window displays a warning message.
3 Click Yes.
The Network Settings window is displayed again. The NIC
no longer appears in the Installed Adapter Cards panel.
Page 51

48 CHAPTER 4: TROUBLESHOOTING INSTALLATION PROBLEMS
4 Click OK.
The NIC driver and diagnostic software are removed from
the PC.
The Network Settings Change dialog box appears,
prompting you to restart.
■ If you’re physically removing the NIC from the PC, click
No. Don’t restart the PC until you shut down the system,
turn the power off, and remove the NIC from the PC.
■ If you’re reinstalling the NIC software, click Restart Now.
Frequently Asked Questions
Table 5 describes some common questions and answers
about the OfficeConnect NIC.
To view questions and answers online, follow the instructions
in “Viewing Release Notes, Frequently Asked Questions,
and KnowledgeBase Topics” earlier in this chapter.
To view additional questions and answers, see the text files
located in the HELP directory on the EtherDisk diskette.
Table 5 Frequently Asked Questions
Question Answer
Why does the
OfficeConnect NIC
install as a “Generic PCI
Ethernet Controller”
under Other Devices in
the Windows 95/98
Device Manager?
In Windows 95/98,
what should I do if a
yellow exclamation
point (!) appears next
to the NIC name?
(continued)
When Windows 95/98 is installed after the OfficeConnect
NIC has already been installed, Windows 95/98 installs the
NIC as a generic PCI Ethernet controller.
To work around this problem, follow these steps:
1 In the Device Manager, double-click Other Devices.
2 Click PCI Ethernet Controller.
3 Click Remove.
4 Restart your PC.
1 In the Device Manager, double-click Other Devices.
2 Click PCI Ethernet Controller or the duplicate PCI NIC entry.
3 Click Remove.
4 Restart your PC.
Page 52

Frequently Asked Questions 49
Table 5 Frequently Asked Questions (continued)
Question Answer
How do I remove
the 3Com icon from
my Windows
system tray?
Which PCI slot
should I use for my
OfficeConnect NIC?
Do I have to configure
the OfficeConnect NIC?
What interrupts
should I avoid?
Does the OfficeConnect
NIC support
full-duplex?
1 Double-click the 3Com icon to start the 3Com NIC
Diagnostics program.
2 In the bottom-right corner of the main window, click the
Enable Tray Control check box to remove the check mark.
3 Exit the program and the icon will not appear anymore.
3Com PCI NICs, such as the OfficeConnect NIC, are
designed to work in any bus-mastering PCI slot, preferably
slot 1. Normally, slot 1 is marked on the PC motherboard
and is located closest to the computer power supply.
Avoid any PCI slot next to an ISA slot. This is often a
shared slot and does not support bus mastering. The
NICs perform best in those slots that support
bus-mastering data transfers.
Some PCs have three types of expansion slots: PCI, ISA,
and EISA. PCI slots are usually white and shorter than the
other expansion slots (see Figure 3 in Chapter 2). ISA slots
are usually black. EISA slots are usually brown, and are as
long as ISA slots. If you’re not sure what type of expansion
slots your PC has, see your PC documentation for details.
Also refer to your PC manual for information on which
slots support bus-mastering data transfers.
PCI is a self-configuring bus architecture. Most of the
time you only need to install the NIC in your PC; PCI does
the rest. However, on some PCI computers, you may be
required to configure the computer’s BIOS manually after
installing your PCI NIC. Refer to your PC documentation
for more information about your PC’s BIOS.
You should avoid using any interrupts used by ISA/EISA
boards that do not properly support shared interrupts
(level-triggered). If you don’t know or aren’t sure whether
other devices or adapters in your PC support shared
interrupts, then avoid using them.
Avoid using the same interrupt as your local hard drive
(normally IRQ 14 for IDE drives and IRQ 11 for most SCSI
host adapters), because not all hard drives support shared
interrupts at this time. Avoid using 9 because it cascades
with 2.
Yes, the OfficeConnect NIC supports full-duplex operation
at 10 Mbps and 100 Mbps.
Full-duplex is the ability of a device or line to transmit data
simultaneously in both directions (the PC is sending and
receiving data at the same time).
Page 53

Page 54

CONFIGURING THE NIC
5
This chapter describes how to display and change
configuration settings for the OfficeConnect NIC.
Table 6 describes the configurable settings for the
OfficeConnect NIC. The default setting for each option
is in bold in the Available Settings column.
Table 6 OfficeConnect NIC Configuration Settings
Option Description Available Settings
Network Driver
Optimization
Duplex Specifies the duplex mode, which
Media Type Determines the type of media your
.
Specifies how to optimize the network
driver for your network environment.
In a client/server environment, the
network driver may use a larger
percentage of the CPU in order to
improve network throughput. In this
case, select Minimize CPU Utilization.
In peer-to-peer networks, or on
multitasking PCs, it is best to
balance the CPU utilization and the
network performance. In this case,
select Normal.
determines if the NIC transmits data
across the network in both directions
simultaneously (the PC sends and
receives data at the same time)
(full-duplex) or in one direction at a
time (half-duplex). The OfficeConnect
NIC supports full-duplex at 10 Mbps
and 100 Mbps.
Auto Select allows the NIC to
automatically connect at the duplex
mode of the connected hub.
network is using.
Auto Select allows the NIC to
automatically select the type for
you, based on the NIC’s connection
to the hub.
■ Normal
■ Minimized CPU
Utilization
■ Maximized Network
Performance
■ Auto Select
■ Full Duplex
■ Half Duplex
■ 10BASE-T (10Mb/s)
■ 100BASE-TX
(100 Mb/s)
■ Auto Select
Page 55

52 CHAPTER 5: CONFIGURING THE NIC
Displaying Configuration Settings
Use the 3Com NIC Diagnostics program to display and
change configuration settings for the OfficeConnect NIC.
The 3Com NIC Diagnostics program is automatically
installed when you install the network driver.
To display the current configuration settings for the
OfficeConnect NIC:
1 Make sure that the NIC is installed and is connected
to the network and that the network driver is
installed.
2 Double-click the 3Com icon in the Windows
system tray.
If the 3Com icon isn’t visible in the Windows system tray,
follow these steps:
a From the Windows Start menu, select Programs.
b Select 3Com NIC Utilities.
c Click 3nicdiag.
For PCs running Windows NT 3.51, from the File menu,
select Run. At the command prompt, enter the path for
the 3Com NIC Diagnostics program. The default path is
C:\WINNT35\SYSTEM32\3NICDIAG.EXE.
A warning message appears, stating that your PC will be
disconnected from the network.
This means that no applications other than the 3Com NIC
Diagnostics program will be able to connect to the network
while you run the diagnostics program.
All applications are automatically reconnected to the
network when you exit the diagnostics program. If
your PC doesn’t automatically reconnect to the
network, reboot the PC.
3 Click OK.
The 3Com NIC Diagnostics General screen
(Figure 16) appears.
Page 56

Displaying Configuration Settings 53
Figure 16 General Screen
Click the Help button to receive information about the
diagnostic screen that’s currently active.
4 Click NIC Details.
The NIC Details screen (Figure 17) appears.
Figure 17 NIC Details Screen
Page 57

54 CHAPTER 5: CONFIGURING THE NIC
Each configuration setting is displayed with its current value.
For a description of each setting, click the question mark in
the upper right corner of the screen, drag it to a setting,
and click once. A pop-up box appears, displaying
information for the selected setting.
5 Click OK to exit this screen.
Changing Configuration Settings
To change OfficeConnect NIC configuration settings:
1 Double-click the 3Com icon in the Windows
system tray.
If the 3Com icon isn’t visible in the Windows system tray,
follow these steps:
a From the Windows Start menu, select Programs.
b Select 3Com NIC Utilities.
c Click 3nicdiag.
For PCs running Windows NT 3.51, from the File menu,
select Run. At the command prompt, enter the path for
the 3Com NIC Diagnostics program. The default path is
C:\WINNT35\SYSTEM32\3NICDIAG.EXE.
A warning message appears, stating that your PC will be
disconnected from the network.
This means that no applications other than the 3Com NIC
Diagnostics program will be able to connect to the network
while you run the diagnostics program.
All applications are automatically reconnected to the
network when you exit the diagnostics program. If
your PC doesn’t automatically reconnect to the
network, reboot the PC.
2 Click OK.
3 Click the Properties tab.
The 3Com NIC Diagnostics Properties screen
(Figure 18) appears.
Page 58

Changing Configuration Settings 55
Figure 18 Properties Screen
4 Change the NIC’s configuration:
■ To automatically configure the NIC to nonconflicting
values with your PC, click Optimal Settings.
■ To manually configure the NIC:
a Select an option in the Individual Settings panel.
For a description of each option, see Table 6 at the
beginning of this chapter.
b Click the down arrow in the list box and select a new
value for the option.
c Repeat the process to change any other setting on the
Properties screen.
5 Click OK to save values or Cancel to exit without
saving values.
Page 59

Page 60

SPECIFICATIONS AND
A
This appendix lists the specifications and cable
requirements for the OfficeConnect NIC.
Specifications
Network Interface
10 Mbps Ethernet
10BASE-T
100 Mbps Fast Ethernet
100BASE-TX
Physical Dimensions
Height: 8.57 cm (3.75 in.)
Length: 12.07 cm (4.75 in.)
Environmental Operating Range
Operating temperature: 0˚ to 70 ˚C (32˚ to 158 ˚F)
Humidity: 10 to 90% noncondensing
Power Requirements
Operating voltage: +5 V ± 5% @ 650 mA max
CABLING REQUIREMENTS
Ethernet IEEE 802.3 industry
standard for a 10 Mbps
baseband CSMA/CD local area
network
Ethernet IEEE 802.3u industry
standard for a 100 Mbps
baseband CSMA/CD local area
network
Cabling Requirements
The cable, quality, distance, and connectors must
comply with the Electronic Industries Association/
Telecommunications Industries Association (EIA/TIA)
568 Commercial Building Wiring Standard and the
Technical Services Bulletin TSB38 standards.
Page 61

58 APPENDIX A: SPECIFICATIONS AND CABLING REQUIREMENTS
Unshielded Twisted-Pair Cable
Twisted-pair cable consists of copper wires surrounded by
an insulator. Two wires are twisted together (the twisting
prevents interference problems) to form a pair, and the pair
forms a circuit that can transmit data. A cable is a bundle of
one or more twisted pairs surrounded by an insulator.
Unshielded twisted pair (UTP) is the most commonly used
type of twisted-pair cable. Shielded twisted pair (STP)
provides protection against crosstalk. Twisted-pair cable is
now commonly used in Ethernet, Fast Ethernet, and other
network topologies.
The EIA/TIA defines five categories of unshielded
twisted-pair cable (see Table 7).
Table 7 Unshielded Twisted-pair Cable Categories
Category Use
1 Traditional telephone cable.
2 Data transmissions up to 4 MHz.
3 Voice and data transmission up to 25 MHz. The cable
4 Voice and data transmission up to 33 MHz. The cable
5 Voice and data transmission up to 125 MHz. The cable
typically has four pairs of wires. Category 3 is the
most common type of installed cable found in older
corporate wiring schemes.
normally has four pairs of wire. This grade of UTP
isn’t common.
normally has four pairs of copper wire and three twists
per foot. Category 5 UTP is the most popular cable
used in new installations today.
10BASE-T Operation
10BASE-T is the Institute of Electrical and Electronics
Engineers (IEEE) 802.3 standard for Ethernet signaling over
unshielded twisted-pair wire at 10 Mbps.
Ethernet, as the most widely used network protocol, uses
10BASE-T as its primary cabling scheme. Ethernet’s
characteristics include:
■ A data rate of 10 Mbps
■ A broadcast architecture
■ A specific media-access control (MAC) scheme
Page 62

10BASE-T Specifications
The 10BASE-T name indicates a signaling speed of
10 Mbps and twisted-pair wiring. Base stands for
baseband, which denotes a technique for transmitting
signals as direct-current pulses rather than modulating
them onto separate carrier frequencies.
A wiring topology using 10BASE-T specifies a wiring hub,
cable arranged in a star configuration, and unshielded
twisted-pair cable. Each node has a separate cable run that
must not exceed 100 meters (328 ft) from the node to
the hub.
100BASE-TX Operation
100BASE-TX is the Institute of Electrical and Electronics
Engineers (IEEE) 802.3u standard for Ethernet signaling
over unshielded twisted-pair wire at 100 Mbps.
Fast Ethernet uses 100BASE-TX as its primary cabling
scheme. Fast Ethernet’s characteristics include:
■ A data rate of 100 Mbps
■ A broadcast architecture
■ A specific media-access control (MAC) scheme
Cabling Requirements 59
100BASE-TX Specifications
The 100BASE-TX name indicates a signaling speed of
100 Mbps and twisted-pair wiring. Base stands for
baseband, which denotes a technique for transmitting
signals as direct-current pulses rather than modulating
them onto separate carrier frequencies.
A wiring topology using 100BASE-T specifies a wiring hub,
cable arranged in a star configuration, and unshielded
twisted-pair cable. Each node has a separate cable run that
must not exceed 100 meters (328 ft) from the node to
the hub.
Page 63

Page 64

TECHNICAL SUPPORT
B
3Com provides easy access to technical support information
through a variety of services. This appendix describes
these services.
Information contained in this appendix is correct at time of
publication. For the very latest, 3Com recommends that you
access the 3Com Corporation World Wide Web site.
Online Technical Services
3Com offers worldwide product support 24 hours a day,
7 days a week, through the following online systems:
■ World Wide Web site
■ 3Com FTP site
■ 3Com Bulletin Board Service (3Com BBS)
■ 3ComFacts
SM
automated fax service
World Wide Web Site
Access the latest networking information on the
3Com Corporation World Wide Web site by entering
the URL into your Internet browser:
http://www.3com.com/
This service provides access to online support information
such as technical documentation and software library, as
well as support options ranging from technical education
to maintenance and professional services.
3Com FTP Site
Download drivers, patches, software, and MIBs across the
Internet from the 3Com public FTP site. This service is
available 24 hours a day, 7 days a week.
Page 65

62 APPENDIX B: TECHNICAL SUPPORT
To connect to the 3Com FTP site, enter the following
information into your FTP client:
■ Hostname: ftp.3com.com (or 192.156.136.12)
■ Username: anonymous
■ Password: <your Internet e-mail address>
A user name and password are not needed with Web browser
software such as Netscape Navigator and Internet Explorer.
3Com Bulletin Board Service
The 3Com BBS contains patches, software, and drivers for
3Com products. This service is available through analog
modem or digital modem (ISDN) 24 hours a day, 7 days
a week.
Access by Analog Modem
To reach the service by modem, set your modem to 8 data
bits, no parity, and 1 stop bit. Call the telephone number
nearest you:
Country Data Rate Telephone Number
Australia Up to 14,400 bps 61 2 9955 2073
Brazil Up to 14,400 bps 55 11 5181 9666
France Up to 14,400 bps 33 1 6986 6954
Germany Up to 28,800 bps 4989 62732 188
Hong Kong Up to 14,400 bps 852 2537 5601
Italy Up to 14,400 bps 39 2 27300680
Japan Up to 14,400 bps 81 3 3345 7266
Mexico Up to 28,800 bps 52 5 520 7835
P.R. of China Up to 14,400 bps 86 10 684 92351
Taiwan, R.O.C. Up to 14,400 bps 886 2 377 5840
U.K. Up to 28,800 bps 44 1442 438278
U.S.A. Up to 53,333 bps 1 847 262 6000
Access by Digital Modem
ISDN users can dial in to the 3Com BBS using a digital modem
for fast access up to 64 Kbps. To access the 3Com BBS using
ISDN, use the following number:
1 847 262 6000
Page 66

Support from Your Network Supplier 63
3ComFacts Automated Fax Service
The 3ComFacts automated fax service provides technical
articles, diagrams, and troubleshooting instructions on
3Com products 24 hours a day, 7 days a week.
Call 3ComFacts using your Touch-Tone telephone:
1 408 727 7021
Support from Your Network Supplier
If additional assistance is required, contact your network
supplier. Many suppliers are authorized 3Com service
partners who are qualified to provide a variety of services,
including network planning, installation, hardware
maintenance, application training, and support services.
When you contact your network supplier for assistance,
have the following information ready:
■ Product model name, part number, and serial number
■ A list of system hardware and software, including
revision levels
■ Diagnostic error messages
■ Details about recent configuration changes, if applicable
If you are unable to contact your network supplier, see the
following section on how to contact 3Com.
Support from 3Com
If you are unable to obtain assistance from the 3Com online
technical resources or from your network supplier, 3Com
offers technical telephone support services. To find out more
about your support options, please call the 3Com technical
telephone support phone number at the location nearest you.
When you contact 3Com for assistance, have the following
information ready:
■ Product model name, part number, and serial number
■ A list of system hardware and software, including
revision levels
■ Diagnostic error messages
■ Details about recent configuration changes, if applicable
Page 67

64 APPENDIX B: TECHNICAL SUPPORT
Below is a list of worldwide technical telephone
support numbers:
Country Telephone Number
Asia Pacific Rim
Australia
Hong Kong
India
Indonesia
Japan
Malaysia
New Zealand
Pakistan
Philippines
P.R. of China
Singapore
S. Korea
From anywhere in S. Korea:
From Seoul:
Taiwan, R.O.C.
Thailand
Europe
From anywhere in Europe, call:
From the following European countries, you may use the
toll-free numbers:
Austria
Belgium
Denmark
Finland
France
Germany
Hungary
Ireland
Israel
Italy
Netherlands
Norway
Poland
Portugal
South Africa
Spain
Sweden
Switzerland
U.K.
(continued)
1 800 678 515
800 933 486
61 2 9937 5085
001 800 61 009
0031 61 6439
1800 801 777
0800 446 398
61 2 9937 5085
1235 61 266 2602
10800 61 00137 or 021 6350 1590
800 6161 463
82 2 3455 6455
00798 611 2230
0080 611 261
001 800 611 2000
+31 (0)30 6029900 phone
+31 (0)30 6029999 fax
06 607468
0800 71429
800 17309
0800 113153
0800 917959
0130 821502
00800 12813
1 800 553117
177 3103794
1678 79489
0800 0227788
800 11376
0800 3111206
05 05313416
0800 995014
900 983125
020 795482
0800 55 3072
0800 966197
Page 68

Country Telephone Number
Latin America
Argentina
Brazil
Chile
Colombia
Mexico
Peru
Puerto Rico
Venezuela
North America 1 800 NET 3Com (1 800 638 3266)
Returning Products for Repair
Before you send a product directly to 3Com for repair, you
must first obtain a Return Materials Authorization (RMA)
number. Products sent to 3Com without RMA numbers will
be returned to the sender unopened, at the sender’s expense.
To obtain an RMA number, call or fax:
Country Telephone Number Fax Number
Asia, Pacific Rim 65 543 6500 65 543 6348
Europe, South Africa,
and Middle East
From the following European countries, you may call the toll-free
numbers; select option 2 and then option 2:
Austria
Belgium
Denmark
Finland
France
Germany
Hungary
Ireland
Israel
Italy
Netherlands
Norway
Poland
Portugal
South Africa
Spain
Sweden
Switzerland
U.K.
(continued)
+ 44 1442 435860 + 44 1442 435718
06 607468
0800 71429
800 17309
0800 113153
0800 917959
0130 821502
00800 12813
1800553117
177 3103794
1678 79489
0800 0227788
800 11376
00800 3111206
05 05313416
0800 995014
900 983125
020 795482
0800 55 3072
0800 966197
Returning Products for Repair 65
AT&T +800 666 5065
0800 13 3266
1230 020 0645
98012 2127
01 800 CARE (01 800 2273)
AT&T +800 666 5065
800 666 5065
AT&T +800 666 5065
Page 69

66 APPENDIX B: TECHNICAL SUPPORT
Country Telephone Number Fax Number
Latin America 1 408 326 2927 1 408 326 3355
U.S.A. and Canada 1 800 NET 3Com
(1 800 638 3266)
1 408 326 7120
Page 70

10BASE-T
100BASE-TX
BIOS
GLOSSARY
Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) 802.3
standard for Ethernet signaling over unshielded
twisted-pair wire at 10 Mbps.
IEEE 802.3u standard for Ethernet signaling over
Category 5 unshielded twisted-pair wire at 100 Mbps.
Basic Input/Output System. Collection of services on a
ROM (read-only memory) chip that enables hardware
and software, operating systems and applications, and
applications and users to communicate with one another.
The BIOS on a PC can be updated and expanded to
handle newer devices and greater demands. To get a
newer BIOS, you replace the ROM chip in your PC with
an upgraded chip.
bus mastering
Method for accessing the PC bus in which a card or
device takes control of the bus in order to send data onto
the bus directly, without help from the central processing
unit (CPU).
client/server network
Networking architecture in which all shared applications
and files are stored on one central computer known as a
server. Network users (known as clients) can store their
own files on their own PCs and then use the server to
access shared files and peripherals, such as printers, fax
machines, and modems.
Ethernet
IEEE standard network protocol that specifies how data
is placed on and retrieved from a common transmission
medium. Ethernet has a transfer rate of 10 Mbps.
Page 71

68 GLOSSARY
Fast Ethernet
100 Mbps technology based on the 10BASE-T Ethernet
network protocol.
full-duplex
Communication setup in which a device or line transmits
data simultaneously in both directions (the PC is sending
and receiving data at the same time).
half-duplex
Communication setup in which a device or line transmits
data in only one direction at a time.
hub
Device that serves as the central location for attaching
wires from workstations. A hub can be passive, when there
is no amplication of the signals; or active, when it is used
like a repeater to provide an extension of the cable that
connects to a workstation.
network
Group of computers and other associated devices, such as
printers, fax machines, and modems, that are connected to
one another so they can share resources and information.
network driver optimization
Driver option that specifies how to optimize performance
of the network driver for your environment.
network operating system (NOS)
System software that runs on the network’s file server, with
a smaller component that runs on each device attached to
the network. Examples of client/server NOSs include Novell
NetWare and Microsoft NT. Examples of peer-to-peer NOSs
include Windows 95 and Windows 98.
NDIS
Network Driver Interface Specification. Defines the network
driver architecture and interfaces that let a PC support
NICs. This architecture provides a standardized way to write
drivers for network NICs.
Page 72

PCI
Peripheral Component Interconnect. Advanced,
high-performance local bus that supports multiple peripheral
devices. A local bus is one that is connected directly to the
PC’s central processing unit (CPU).
peer-to-peer network
Networking architecture in which PCs and other devices,
such as printers and fax machines, are connected directly
to one another or to a central point, usually a hub. Unlike a
client/server network, a peer-to-peer network does not use
a server.
server
PC that provides access to resources or services such as files,
printers, fax machines, and e-mail on a client/server network.
Servers may be distinguished by the elements to which they
control access (for example, on a client/server network there
may be a print server, file server, or communications server).
switch
Device that can direct network traffic among several
Ethernet networks.
GLOSSARY 69
unshielded twisted pair (UTP) cabling
Most commonly used type of twisted-pair cable.
Twisted-pair cable consists of copper wires surrounded by
an insulator. Two wires are twisted together (the twisting
prevents interference problems) to form a pair, and the pair
forms a circuit that can transmit data. A cable is a bundle of
one or more twisted pairs surrounded by an insulator.
Page 73

Page 74

INDEX
Numbers
100BASE-TX
cabling 17
link LED 36
operation 59
specifications 59
10BASE-T
cabling 17
link LED 36
operation 58
specifications 59
3Com bulletin board service (3Com
BBS) 45, 62
3Com icon, in Windows system tray
removing 49
showing 38
3Com NIC Diagnostics program
changing configuration 54
starting 37
3Com support services 44
3Com URL 61
3ComFacts 63
A
accessing
Help 43
online support 44
B
bulletin board service 45, 62
C
cabling
requirements 16, 57
specifications 17
troubleshooting 35
client 13
client/server networks 14
compliance, Year 2000 10
configuration settings
changing 54
default 51
displaying 52
connecting to the network 20
conventions
notice icons, About This Guide 9
text, About This Guide 10
CPU utilization 51
D
default configuration settings 51
determining Windows 95 version 23
diagnostic tests
NIC Echo test 40
NIC self-tests 39
diagnostics program, starting 37
drivers, installing
Windows 95
version A 24
version B 26
Windows 98 28
Windows NT
version 3.51 31
version 4.0 30
duplex mode
changing 54
default setting 51
viewing 52
E
Echo test, running 40
EIA/TIA 568 standards 57
EISA slots 18
environmental operating range 57
Ethernet protocol
characteristics of 58
overview 14
Page 75

72 INDEX
F
Fast Ethernet protocol
characteristics of 59
overview 14
fax service (3ComFacts) 63
frequently asked questions 48
viewing online 44
H
hardware, required 16
Help, accessing 43
hub 13
I
installing drivers
verifying successful installation 32
Windows 95 23
Windows 98 28
Windows NT 30
installing the NIC 17
interrupts 49
ISA slots 18, 49
K
KnowledgeBase, viewing online 44
L
LEDs
description 15
for troubleshooting 36
M
media type
changing 54
default setting 51
viewing 52
MIBs 61
N
network architectures
client/server 14
peer-to-peer 13
network cable, maximum length 17
network driver optimization
changing 54
default setting 51
viewing 52
network interface 57
network interface cards, overview 15
network operating system (NOS) 13
network supplier support 63
network, connecting to 20
networking, overview 12
NIC
configuration settings 51
connecting to the network 20
handling 18
installing drivers 23
installing in the PC 18
LEDs 15, 36
self-tests 39
software, removing 46
specifications 57
NOS (network operating system) 13
O
online support services 44
online technical services 61
operating voltage requirements 57
P
PCI slots 18, 19, 49
peer-to-peer networks 13
physical dimensions 57
power requirements 57
R
release notes, viewing online 44
removing NIC software 46
requirements
cabling 16, 17, 57
hardware 16
software 16
returning products for repair 65
running diagnostic tests 39
S
self-tests, NIC 39
server 13
shielded twisted-pair (STP) cable 58
software, required 16
specifications 57
static electricity 18
STP cable 58
support services 44
system tray, removing 3Com icon
from 49
Page 76

INDEX 73
T
technical support
3Com URL 61
bulletin board service 62
fax service 63
network suppliers 63
product repair 65
tests
Echo 40
NIC 39
troubleshooting 35
cable 35
LEDs 36
running NIC self-tests 39
testing network connection 40
using the 3Com NIC Diagnostics
program 37
twisted-pair cable
100BASE-TX 59
10BASE-T 59
description 58, 69
U
unshielded twisted-pair (UTP)
cable 17, 20, 58
URL 61
V
verifying successful driver
installation 32
viewing online support databases 44
Windows NT
version 3.51
confirming NIC installation 34
installing driver 31
NIC diagnostic tests,
running 39
removing NIC software 47
version 4.0
confirming NIC installation 34
installing driver 30
NIC diagnostic tests,
running 39
removing NIC software 47
Windows system tray
removing 3Com icon from 49
showing 3Com icon 38
World Wide Web (WWW) 61
Y
Year 2000 compliance 10
yellow exclamation point, next to NIC
name 48
W
Windows 95
confirming NIC installation 32
determining the version 23
installing driver 23
NIC diagnostic tests, running 39
removing NIC software 46, 47
Windows 98
confirming NIC installation 32
installing driver 28
NIC diagnostics tests, running 39
removing NIC software 46
Page 77

Page 78

3Com Corporation LIMITED WARRANTY
HARDWARE
3Com warrants its hardware products to be free from defects in workmanship and materials, under
normal use and service, for the following lengths of time from the date of purchase from 3Com or its
authorized reseller:
Network Interface Cards Lifetime
Other hardware products
*unless otherwise specified above
Spare parts and spares kits 90 days
If a product does not operate as warranted above during the applicable warranty period, 3Com shall,
at its option and expense, repair the defective product or part, deliver to Customer an equivalent
product or part to replace the defective item, or refund to Customer the purchase price paid for the
defective product. All products that are replaced will become the property of 3Com. Replacement
products may be new or reconditioned. Any replaced or repaired product or part has a ninety (90) day
warranty or the remainder of the initial warranty period, whichever is longer.
SOFTWARE
3Com warrants that the software programs licensed from it will perform in substantial conformance
to the program specifications therefor for a period of ninety (90) days from the date of purchase from
3Com or its authorized reseller. 3Com warrants the media containing software against failure during the
warranty period. No updates are provided. 3Com’s sole obligation with respect to this express warranty
shall be (at 3Com’s discretion) to refund the purchase price paid by Customer for any defective software
products, or to replace any defective media with software which substantially conforms to applicable
3Com published specifications. Customer assumes responsibility for the selection of the appropriate
applications program and associated reference materials. 3Com makes no warranty or representation
that its software products will meet Customer’s requirements or work in combination with any
hardware or applications software products provided by third parties, that the operation of the software
products will be uninterrupted or error free, or that all defects in the software products will be corrected.
For any third party products listed in the 3Com software product documentation or specifications as
being compatible, 3Com will make reasonable efforts to provide compatibility, except where the
non-compatibility is caused by a “bug” or defect in the third party's product.
1 year*
YEAR 2000 WARRANTY
In addition to the Hardware Products Warranty and Software Products Warranty identified above, 3Com
warrants that all Heritage 3Com products sold or licensed to Customer on and after January 1, 1998
that are date sensitive will continue performing properly with regard to such date data on and after
January 1, 2000, provided that all other products used by Customer in connection or combination
with the 3Com products, including hardware, software, and firmware, accurately exchange date
data with the 3Com products, with the exception of those products identified at 3Com’s Web site,
http://www.3com.com/products/yr2000.html, as not meeting this standard. A product is considered
a “Heritage 3Com product” if it is a member of a product family which was manufactured by 3Com
prior to its merger with US Robotics Corporation. This Year 2000 limited warranty does not apply to
Heritage US Robotics Corporation products. If it appears that any such product does not perform
properly with regard to such date data on and after January 1, 2000, and Customer notifies 3Com
before the later of April 1, 2000, or ninety (90) days after purchase of the product from 3Com or its
authorized reseller, 3Com shall, at its option and expense, provide a software update which would
effect the proper performance of such product, repair such product, deliver to Customer an equivalent
product to replace such product, or if none of the foregoing is feasible, refund to Customer the
purchase price paid for such product.
Any software update or replaced or repaired product will carry a Year 2000 Warranty for ninety
(90) days or until April 1, 2000, whichever is later.
OBTAINING WARRANTY SERVICE
Customer must contact 3Com’s Corporate Service Center or an Authorized 3Com Service Center within
the applicable warranty period to obtain warranty service authorization. Dated proof of purchase may be
required. Products returned to 3Com’s Corporate Service Center must be pre-authorized by 3Com with
a Return Material Authorization (RMA) number marked on the outside of the package, and sent prepaid
and packaged appropriately for safe shipment, and it is recommended that they be insured. The repaired
or replaced item will be shipped to Customer, at 3Com’s expense, not later than thirty (30) days after
receipt of the defective product by 3Com.
Page 79

Dead- or Defective-on-Arrival. In the event a product completely fails to function or exhibits a defect
in materials or workmanship within the first forty-eight (48) hours of installation but no later than
thirty (30) days after the date of purchase, and this is verified by 3Com, it will be considered deador defective-on-arrival (DOA) and a replacement shall be provided by advance replacement. The
replacement product will normally be shipped not later than three (3) business days after 3Com’s
verification of the DOA product, but may be delayed due to export or import procedures. When an
advance replacement is provided and Customer fails to return the defective product to 3Com within
fifteen (15) days after shipment of the replacement, 3Com will charge Customer for the replacement
product, at list price.
3Com shall not be responsible for any software, firmware, information, or memory data of Customer
contained in, stored on, or integrated with any products returned to 3Com for repair, whether under
warranty or not.
WARRANTIES EXCLUSIVE
IF A 3COM PRODUCT DOES NOT OPERATE AS WARRANTED ABOVE, CUSTOMER’S SOLE REMEDY FOR
BREACH OF THAT WARRANTY SHALL BE REPAIR, REPLACEMENT, OR REFUND OF THE PURCHASE
PRICE PAID, AT 3COM’S OPTION. TO THE FULL EXTENT ALLOWED BY LAW, THE FOREGOING
WARRANTIES AND REMEDIES ARE EXCLUSIVE AND ARE IN LIEU OF ALL OTHER WARRANTIES, TERMS,
OR CONDITIONS, EXPRESS OR IMPLIED, EITHER IN FACT OR BY OPERATION OF LAW, STATUTORY OR
OTHERWISE, INCLUDING WARRANTIES, TERMS, OR CONDITIONS OF MERCHANTABILITY, FITNESS FOR
A PARTICULAR PURPOSE, AND SATISFACTORY QUALITY. 3COM NEITHER ASSUMES NOR AUTHORIZES
ANY OTHER PERSON TO ASSUME FOR IT ANY OTHER LIABILITY IN CONNECTION WITH THE SALE,
INSTALLATION, MAINTENANCE OR USE OF ITS PRODUCTS.
3COM SHALL NOT BE LIABLE UNDER THIS WARRANTY IF ITS TESTING AND EXAMINATION DISCLOSE
THAT THE ALLEGED DEFECT IN THE PRODUCT DOES NOT EXIST OR WAS CAUSED BY CUSTOMER’S OR
ANY THIRD PERSON'S MISUSE, NEGLECT, IMPROPER INSTALLATION OR TESTING, UNAUTHORIZED
ATTEMPTS TO REPAIR OR MODIFY, OR ANY OTHER CAUSE BEYOND THE RANGE OF THE INTENDED
USE, OR BY ACCIDENT, FIRE, LIGHTNING, OR OTHER HAZARD.
LIMITATION OF LIABILITY
TO THE FULL EXTENT ALLOWED BY LAW, 3COM ALSO EXCLUDES FOR ITSELF AND ITS SUPPLIERS ANY
LIABILITY, WHETHER BASED IN CONTRACT OR TORT (INCLUDING NEGLIGENCE), FOR INCIDENTAL,
CONSEQUENTIAL, INDIRECT, SPECIAL, OR PUNITIVE DAMAGES OF ANY KIND, OR FOR LOSS OF
REVENUE OR PROFITS, LOSS OF BUSINESS, LOSS OF INFORMATION OR DATA, OR OTHER FINANCIAL
LOSS ARISING OUT OF OR IN CONNECTION WITH THE SALE, INSTALLATION, MAINTENANCE, USE,
PERFORMANCE, FAILURE, OR INTERRUPTION OF ITS PRODUCTS, EVEN IF 3COM OR ITS AUTHORIZED
RESELLER HAS BEEN ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGES, AND LIMITS ITS LIABILITY
TO REPAIR, REPLACEMENT, OR REFUND OF THE PURCHASE PRICE PAID, AT 3COM’S OPTION. THIS
DISCLAIMER OF LIABILITY FOR DAMAGES WILL NOT BE AFFECTED IF ANY REMEDY PROVIDED HEREIN
SHALL FAIL OF ITS ESSENTIAL PURPOSE.
DISCLAIMER
Some countries, states, or provinces do not allow the exclusion or limitation of implied warranties or
the limitation of incidental or consequential damages for certain products supplied to consumers or the
limitation of liability for personal injury, so the above limitations and exclusions may be limited in their
application to you. When the implied warranties are not allowed to be excluded in their entirety, they
will be limited to the duration of the applicable written warranty. This warranty gives you specific legal
rights which may vary depending on local law.
GOVERNING LAW
This Limited Warranty shall be governed by the laws of the State of California, U.S.A. excluding its
conflicts of laws principles and excluding the United Nations Convention on Contracts for the
International Sale of Goods.
3Com Corporation, 5400 Bayfront Plaza, Santa Clara, CA 95052-8145 (408) 326-5000
FCC CLASS B STATEMENT
This device complies with Part 15 of the FCC Rules. Operation is subject to the following two conditions:
1 This device may not cause harmful interference, and
2 This device must accept any interference received, including interference that may cause
undesired operation.
Page 80

WARNING: This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a Class B digital
device, pursuant to Part 15 of the FCC Rules, and the Canadian Department of Communications
Equipment Standards entitled, “Digital Apparatus,” ICES-003.These limits are designed to provide
reasonable protection against harmful interference in a residential installation. This equipment
generates, uses and can radiate radio frequency energy and, if not installed and used in accordance
with the instructions, may cause harmful interference to radio communications. However, there is
no guarantee that interference will not occur in a particular installation. If this equipment does
cause harmful interference to radio or television reception, which can be determined by turning the
equipment off and on, the user is encouraged to try to correct the interference by one or more of
the following measures:
■ Reorient or relocate the receiving antenna.
■ Increase the separation between the equipment and receiver.
■ Connect the equipment into an outlet on a circuit different from the one which the receiver is
connected to.
■ Consult the dealer or an experienced radio/TV technician for help.
The user may find the following booklet prepared by the Federal Communications Commission helpful:
The Interference Handbook
This booklet is available from the U.S. Government Printing Office, Washington, D.C. 20402. Stock No.
004-000-00345-4.
NOTE: In order to maintain compliance with the limits of a Class B digital device, 3Com requires that
you use quality interface cables when connecting to this device. Changes or modifications not expressly
approved by 3Com could void the user’s authority to operate this equipment. Refer to the manual for
specifications on cabling types.
FCC DECLARATION OF CONFORMITY
We declare under our sole responsibility that the
Model: Description:
3CSOHO100-TX OfficeConnect Fast Ethernet Network Interface Card
to which this declaration relates, is in conformity with the following standards or other normative
documents:
■ ANSI C63.4-1992 Methods of Measurement
■ Federal Communications Commission 47 CFR Part 15, subpart B
15.107 (e) Class B Conducted Limits
15.109 (g) Class B Radiated Emissions Limits
3Com Corporation, 5400 Bayfront Plaza, P.O. Box 58145, Santa Clara, CA 95052-8145
3COM END USER SOFTWARE LICENSE AGREEMENT
IMPORTANT: Read Before Using This Product
YOU SHOULD CAREFULLY READ THE FOLLOWING TERMS AND CONDITIONS BEFORE
USING THIS PRODUCT. IT CONTAINS SOFTWARE, THE USE OF WHICH IS LICENSED BY 3COM
CORPORATION (“3COM”) TO ITS CUSTOMERS FOR THEIR USE ONLY AS SET FORTH BELOW. IF
YOU DO NOT AGREE TO THE TERMS AND CONDITIONS OF THIS AGREEMENT, DO NOT USE THE
SOFTWARE. USING ANY PART OF THE SOFTWARE INDICATES THAT YOU ACCEPT THESE TERMS.
LICENSE: 3Com grants you a nonexclusive license to use the accompanying software program(s) (the
“Software”) subject to the terms and restrictions set forth in this License Agreement. You are not
permitted to lease, rent, distribute or sublicense the Software or to use the Software in a time-sharing
arrangement or in any other unauthorized manner. Further, no license is granted to you in the human
readable code of the Software (source code). Except as provided below, this License Agreement does
not grant you any rights to patents, copyrights, trade secrets, trademarks, or any other rights in respect
to the Software.
Page 81

The Software is licensed to be used on any workstation or any network server owned by or leased to
you, provided that the Software is used only in connection with a 3Com adapter. You may reproduce
and provide one (1) copy of the Software and supporting documentation for each such workstation or
network server on which the Software is used as permitted hereunder. Otherwise, the Software and
supporting documentation may be copied only as essential for backup or archive purposes in support
of your use of the Software as permitted hereunder. You must reproduce and include all copyright
notices and any other proprietary rights notices appearing on the Software and the supporting
documentation on any copies that you make.
NO ASSIGNMENT; NO REVERSE ENGINEERING: You may not transfer or assign the Software and/or
this License Agreement to another party without the prior written consent of 3Com. If such consent is
given and you transfer or assign the Software and/or this License Agreement, then you must at the
same time either transfer any copies of the Software as well as the supporting documentation to the
same party or destroy any such materials not transferred. Except as set forth above, you may not
transfer or assign the Software or your rights under this License Agreement.
Modification, reverse engineering, reverse compiling, or disassembly of the Software is expressly
prohibited. However, if you are a European Community (“EC”) resident, information necessary to
achieve interoperability of the Software with other programs within the meaning of the EC Directive
on the Legal Protection of Computer Programs is available to you from 3Com upon written request.
EXPORT RESTRICTIONS: You agree that you will not export or re-export the Software or
accompanying documentation (or any copies thereof) or any products utilizing the Software or such
documentation in violation of any applicable laws or regulations of the United States and the country
in which you obtained them.
TRADE SECRETS; TITLE: You acknowledge and agree that the structure, sequence and organization
of the Software are the valuable trade secrets of 3Com and its suppliers. You agree to hold such trade
secrets in confidence. You further acknowledge and agree that ownership of, and title to, the Software
and all subsequent copies thereof regardless of the form or media are held by 3Com and its suppliers.
UNITED STATES GOVERNMENT LEGEND: All technical data and computer software are commercial
in nature and developed solely at private expense. The Software is delivered as “Commercial Computer
Software” as defined in DFARS 252.227-7014 (June 1995) or as a “commercial item” as defined in
FAR 2.101(a) and as such is provided with only such rights as are provided in this License Agreement,
which is 3Com’s standard commercial license for the Software. Technical data is provided with limited
rights only as provided in DFAR 252.227-7015 (Nov. 1995) or FAR 52.227-14 (June 1987), whichever is
applicable. You agree not to remove or deface any portion of any legend provided on any licensed
program or documentation delivered to you under this License Agreement.
TERM AND TERMINATION: This license will expire fifty (50) years from the date that you first use the
Software, if it is not earlier terminated. You may terminate it at any time by destroying the Software
and documentation together with all copies and merged portions in any form. It will also terminate
immediately if you fail to comply with any term or condition of this License Agreement. Upon such
termination you agree to destroy the Software and documentation, together with all copies and
merged portions in any form.
GOVERNING LAW: This License Agreement shall be governed by the laws of the State of California
as such laws are applied to agreements entered into and to be performed entirely within California
between California residents and by the laws of the United States. You agree that the United Nations
Convention on Contracts for the International Sale of Goods (1980) is hereby excluded in its entirety
from application to this License Agreement.
LIMITED WARRANTY; LIMITATION OF LIABILITY: All warranties and limitations of liability applicable
to the Software are as stated on the Limited Warranty Card or in the product manual, whether in paper
or electronic form, accompanying the Software. Such warranties and limitations of liability are
incorporated herein in their entirety by this reference.
SEVERABILITY: In the event any provision of this License Agreement is found to be invalid, illegal or
unenforceable, the validity, legality and enforceability of any of the remaining provisions shall not in
any way be affected or impaired and a valid, legal and enforceable provision of similar intent and
economic impact shall be substituted therefor.
ENTIRE AGREEMENT: This License Agreement sets forth the entire understanding and agreement
between you and 3Com, supersedes all prior agreements, whether written or oral, with respect to the
Software, and may be amended only in a writing signed by both parties.
3Com is a registered trademark of 3Com Corporation.
3Com Corporation, 5400 Bayfront Plaza, P.O. Box 58145, Santa Clara, CA 95052-8145. (408) 326-5000
 Loading...
Loading...