Page 1

OfficeConnect
®
Wireless 54 Mbps/108 Mbps
11g Cable/DSL Router
3CRWER100-75, 3CRWER200-75
www.3com.com
Part No. 10014944
Published January 2006
Installation Guide
Guía de instalación
Guide d’installation
Manuale di installazione
Installationsanleitung
Installations Guide
Guia de Instalação
Page 2

Page 3

1
Introduction
INTRODUCTION
This Guide takes you through the basic steps necessary to install and configure
your OfficeConnect Wireless 54 Mbps/108 Mbps 11g Cable/DSL Router, and
establish a connection from your computers to the Internet. Throughout, the
OfficeConnect Wireless 54 Mbps/108 Mbps 11g Cable/DSL Router is simply
referred to as the Router.
• One OfficeConnect Wireless 54 Mbps/108 Mbps 11g Cable/DSL Router
• One power adapter for use with the Router
• Four rubber feet
• One Ethernet cable
• One CD-ROM containing the Quick Installation Guide and the User Guide
• This Installation Guide
• One Support and Safety Information Sheet
• One Warranty Flyer
• Release Note Sheet
• Product Range Sheet
Before starting, you must ensure the following:
• You already have a cable or DSL broadband connection to the Internet
with a suitable modem and that this connection works properly. The
modem must have an Ethernet port for connection to your Router.
• You have a computer that has an Ethernet connection available and is
already correctly configured for communication with the Internet. Your
computer must be able to connect to the Internet via the modem, and
must have a Web browser installed.
• There are no other DHCP server devices on your local network that are
responsible for allocating IP addresses to your computers and other network-connected devices. Your Router will now perform this function by
default.
If one or more of these conditions are not met, refer to the comprehensive Router
User Guide provided on the accompanying CD-ROM for further guidance.
About This Guide:
Your Package Contains:
System Requirements
GB
Page 4
Dimensions and Standards
2
DIMENSIONS AND STANDARDS
Functional: ISO 8802/3, IEEE802.3, IEEE802.11b, 802.11g
Safety: UL60950, CSA22.2 #60950, IEC 60950, EN 60950
EMC: EN 55022 Class B, EN55024, CISPR 22, FCC Part 15 Class B*
ICES-003 Class B, ETSI EN 301 489-17
Radio: CFR 47 FCC Part 15.207, 15.209, 15.247 and 15.249.
ETS 300 328 (2.4 GHz ISM band wide band transmission
systems), RSS-210
Environmental: EN 60068 (IEC 68)
* Refer to Regulatory Notices section in the Support and Safety Information sheet
WARNING: Please read the ‘Important Safety Information’ section in
the Support and Safety Information sheet before you start.
VORSICHT: Bitte lesen Sie den Abschnitt ‘Wichtige
Sicherheitsinformationen’ sorgfältig durch, bevor Sie das Gerät
einschalten.
AVERTISSEMENT: Veuillez lire attentivement la section "Consignes
importantes de sécurité" avant de mettre en route.
Use the four self-adhesive rubber feet to prevent your Router from moving
around on your desk or when stacking with other flat top OfficeConnect
units. Only stick the feet to the marked areas at each corner of the underside
of your Router.
Standards
Dimensions
Using the Rubber Feet
Safety Information
7VA, 23.9 BTU/hr power
requirement
0 to 40ºC (32 to 105ºF)
operating temperature
0 to 90%
(non-condensing)
humidity
41.5 mm
(1.6 in.)
224.8 mm
(8.8 in.)
OfficeConnect Wireless 54 Mbps/108 Mbps
11g Cable/DSL Router 592 g(1.3lb)
Page 5
3
Positioning Your Router
POSITIONING YOUR ROUTER
When positioning your Router, ensure:
• The unit is centrally located to the wireless computers that will connect to
the Router. A suitable location might be on top of a high shelf or similar
furniture to optimise wireless connections to computers in both horizontal
and vertical directions, allowing coverage throughout.
• In order to meet FCC radiation exposure regulations the Router should be
located in a position that maintains a minimum distance of 20 cm (8 inches)
from any personnel (refer to the User Guide for details).
• It is out of direct sunlight and away from sources of heat.
• Cabling is away from power lines, fluorescent lighting fixtures, and
sources of electrical noise such as radios, transmitters and broadband
amplifiers.
• Water or moisture cannot enter the case of the unit.
• Air flow around the unit and through the vents in the side of the case is
not restricted. We recommend you provide a minimum of 25 mm (1 in.)
clearance.
GB
Page 6
About Your Router
4
ABOUT YOUR ROUTER
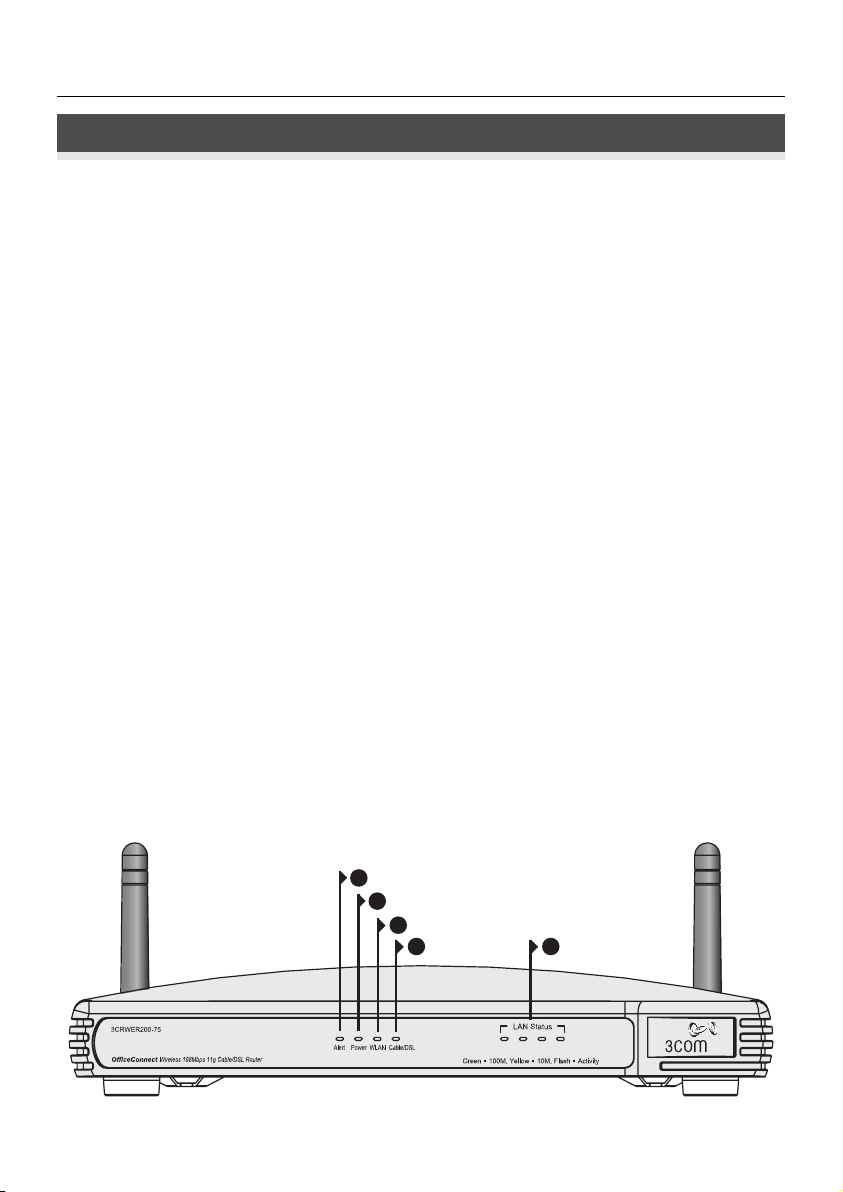
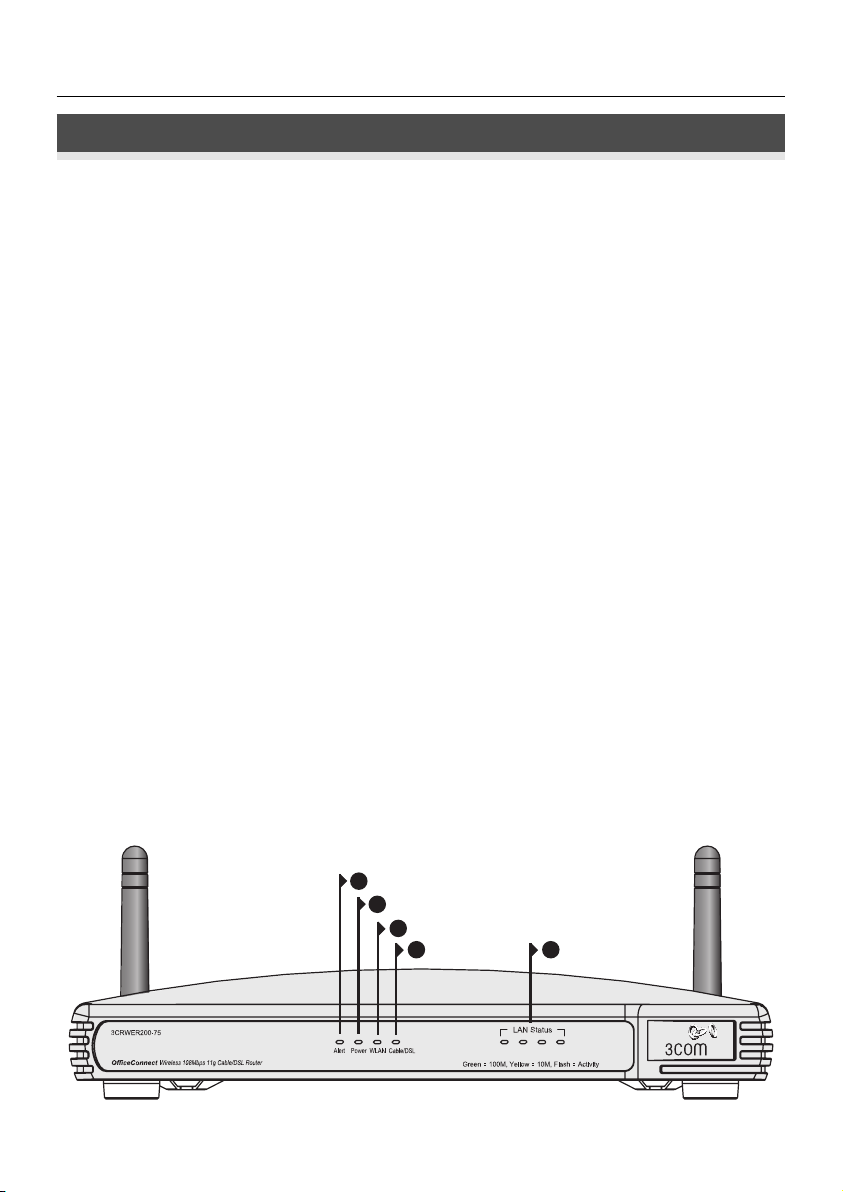
1. Alert LED Orange
Indicates a number of different conditions, as described below.
Off - The Router is operating normally.
Flashing quickly - Indicates one of the following conditions:
• The Router has just been started up and is running a self-test routine, or
• The administrator has invoked the Reset to Factory Defaults command, or
• The system software is in the process of being upgraded
In each of these cases, wait until the Router has completed the current operation and the alert LED is Off.
Flashing slowly - The Router has completed the Reset to Factory Defaults process, and is waiting for you
to reset the unit. To do this, remove power, wait 10 seconds and then re-apply power. The Router will
then enter the start-up sequence and resume normal operation.
On for 2 seconds, and then off - The Router has detected and prevented a hacker from attacking your
network from the Internet.
Continuously on - A fault has been detected with your Router during the start-up process. Refer to the
main User Guide.
2. Power LED Green
Indicates that the Router is powered on.
3. Wireless LAN (WLAN) Status LED Yellow
If the LED is on it indicates that wireless networking is enabled. If the LED is flashing, data is being transmitted or received. If the LED is off, the Wireless LAN has been disabled in the Router, or there is a problem. Refer to the ‘Problem Solving’ section.
4. Four LAN Status LEDs Green (100Mbps link) / Yellow (10Mbps link)
If the LED is on, the link between the port and the next piece of network equipment is OK. If the LED is
flashing, the link is OK and data is being transmitted or received. If the LED is off, nothing is connected,
the connected device is switched off, or there is a problem with the connection (refer the ‘Problem
Solving’ section) The port will automatically adjust to the correct speed and duplex.
OfficeConnect Wireless 54 Mbps/108 Mbps 11g Cable/DSL Router - front.
1
2
3
5 4
Page 7
5
About Your Router
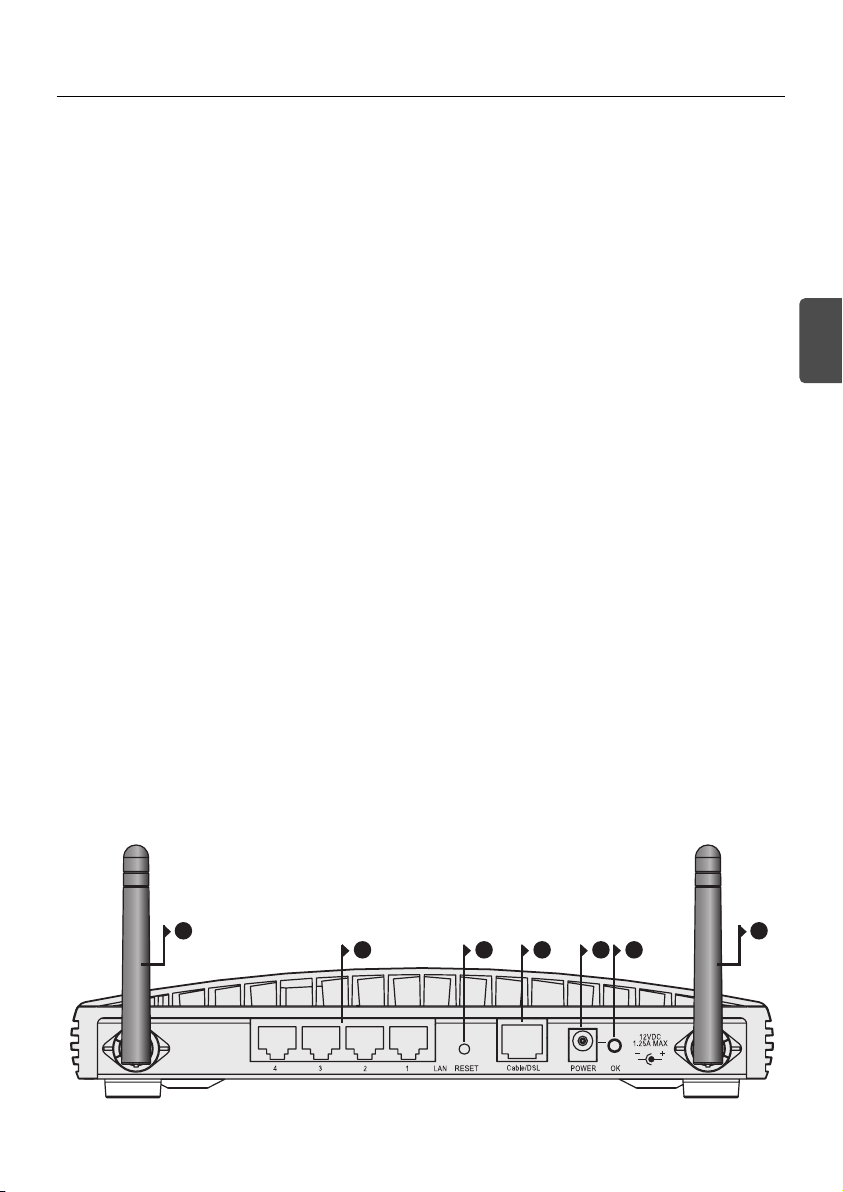
5. Cable/DSL Status LED Green (100Mbps link) / Yellow (10Mbps link)
If the LED is on, the link between the Router and the cable or DSL modem is OK. If the LED is flashing,
the link is OK and data is being transmitted or received. If the LED is off, nothing is connected, the
modem is switched off or there is a problem (refer to the ‘Problem Solving’ section).
6. Wireless Antennae
The antennae on the product should be placed in a ‘V’ position when initially installed.
CAUTION: Do not force the antennae beyond their mechanical stops. Rotating the antennae further may
cause damage.
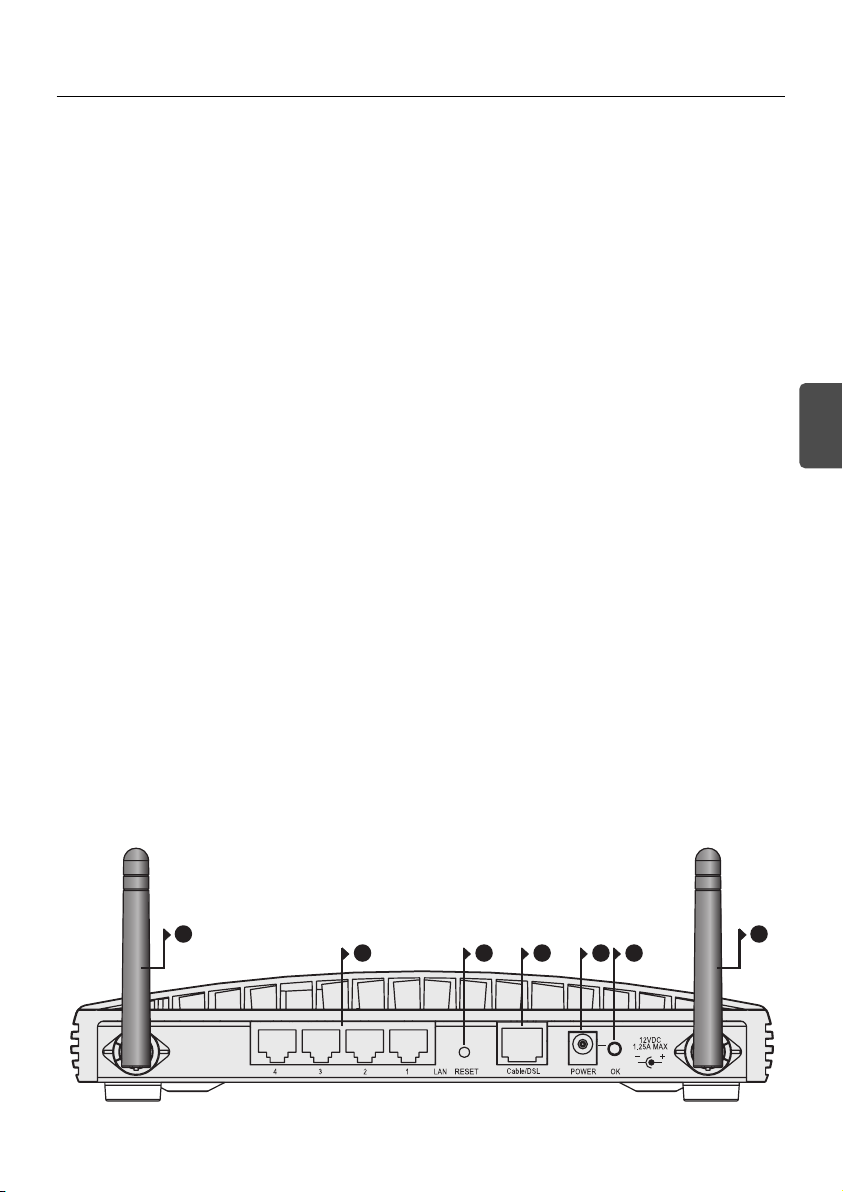
7. Power Adapter Socket
Only use the power adapter supplied with this Router. Do not use any other adapter.
8. Power Adapter OK LED Green
Indicates that the power adapter is supplying power to the Router. If the LED is off, there may be a problem with the power adapter or adapter cable.
9. Ethernet Cable/DSL port
Use the supplied patch cable to connect the Router to the Ethernet port on your cable or DSL modem.
The port will automatically adjust to the correct speed and duplex, and will set itself to MDI or MDIX
depending on the device to which they are connected and the type of cable used.
10. Four 10/100 LAN ports
Using suitable RJ-45 cable, you can connect your Router to a computer, or to any other piece of equipment that has an Ethernet connection (for example, a hub or a switch). The LAN ports will automatically
set themselves to MDI or MDIX depending on the device to which they are connected and the type of
cable used.
11. Reset Button
Press Reset button for 5 seconds then release it. All settings of OfficeConnect Wireless 54 Mbps/108 Mbps
11g Cable/DSL Router will reset to factory default.
GB
OfficeConnect Wireless 54 Mbps/108 Mbps 11g Cable/DSL Router - rear.
6 6
911 7 810
Page 8
Installing Your Router
6
1. INSTALLING YOUR ROUTER
1. Connect the power adapter to the Router and wait for the Alert LED to
stop flashing.
2. Ensure that your modem and computer are both switched on.
3. Insert one end of the supplied Ethernet (RJ-45 Category 5) cable into the
Cable/DSL port on the rear panel of the Router.
4. Insert the other end of the cable into the RJ-45 port on your cable or DSL
modem. Check that the Cable/DSL status LED lights on the Router.
5. Connect the cable or DSL modem to the Internet.
6. Connect your computer to one of the four LAN ports on the Router using
an Ethernet cable. Check that the corresponding LAN status LED on the
Router lights.
To share your Router with more than four users you will need an additional
Hub or Switch. Connect a LAN port of your Router to the Hub or Switch, e.g.
OfficeConnect Dual Speed Switch 8.
Connecting Your Router
Connecting to a Hub or
Switch
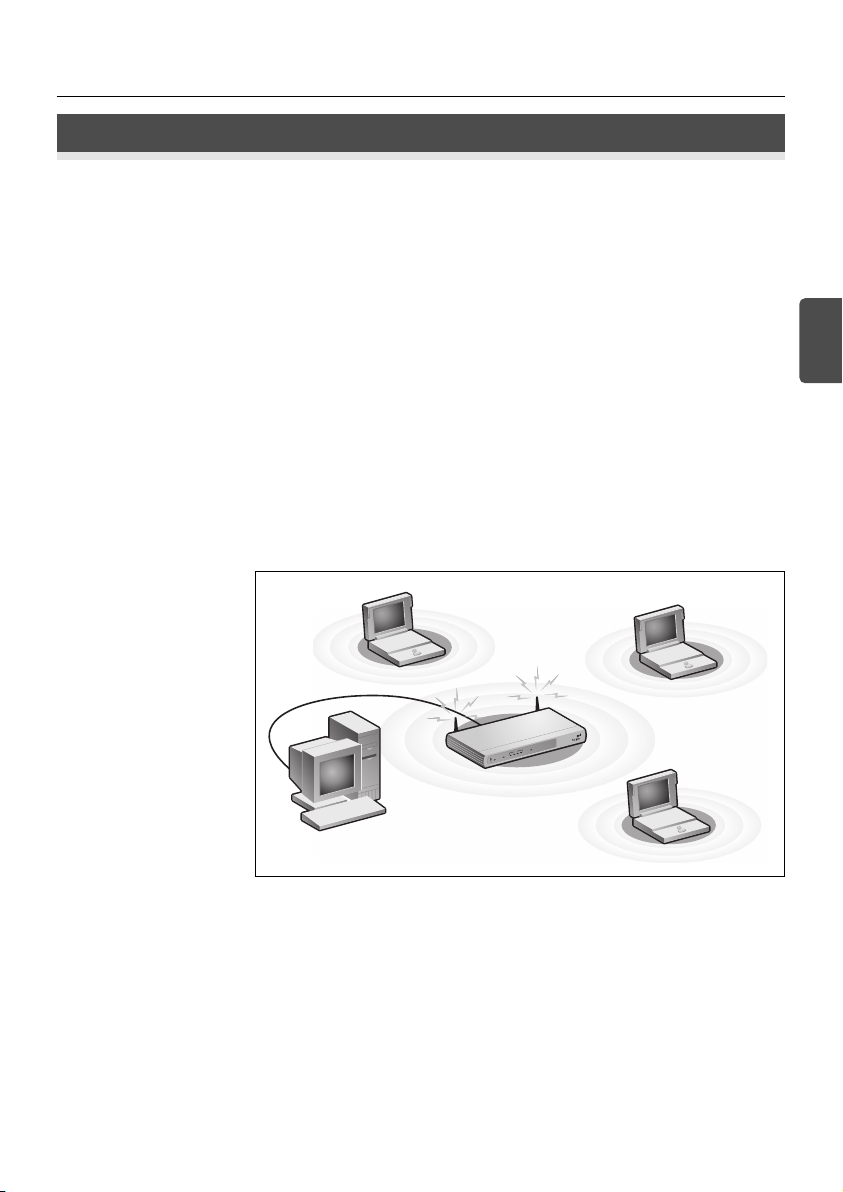
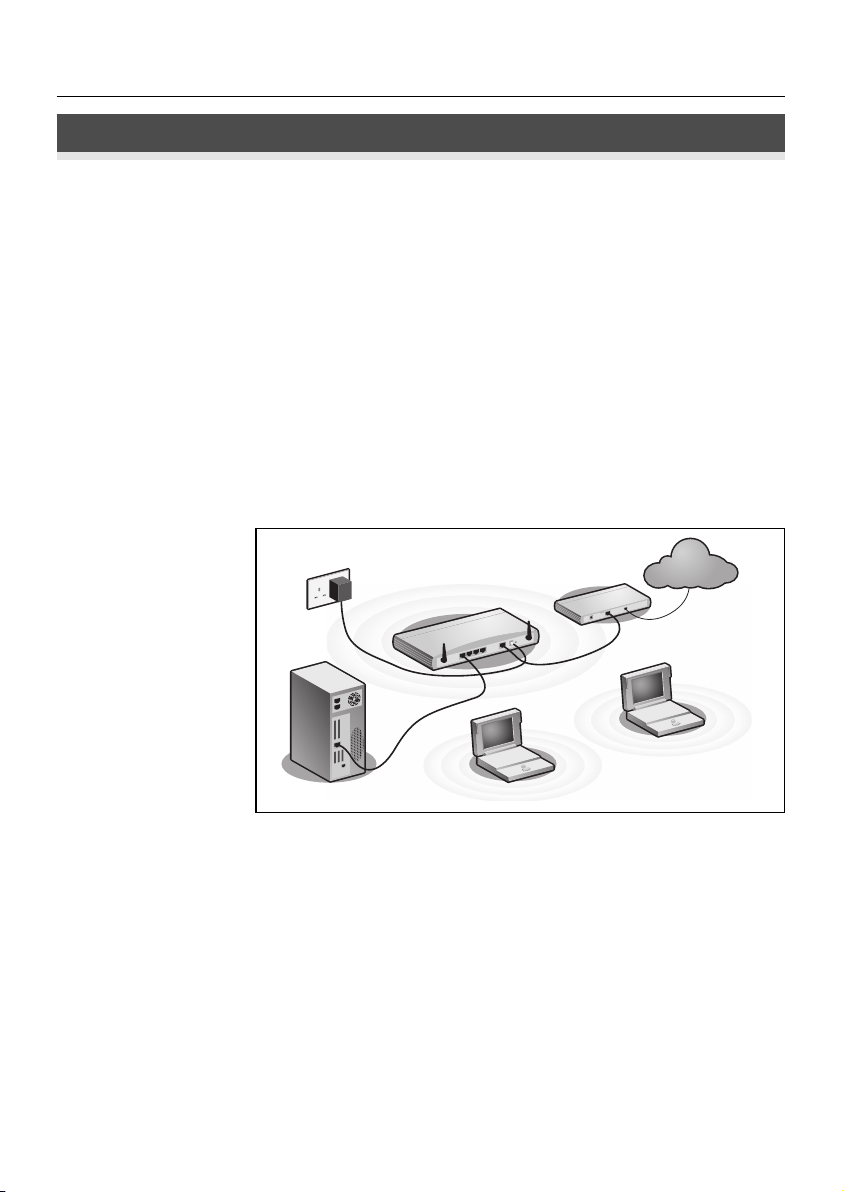
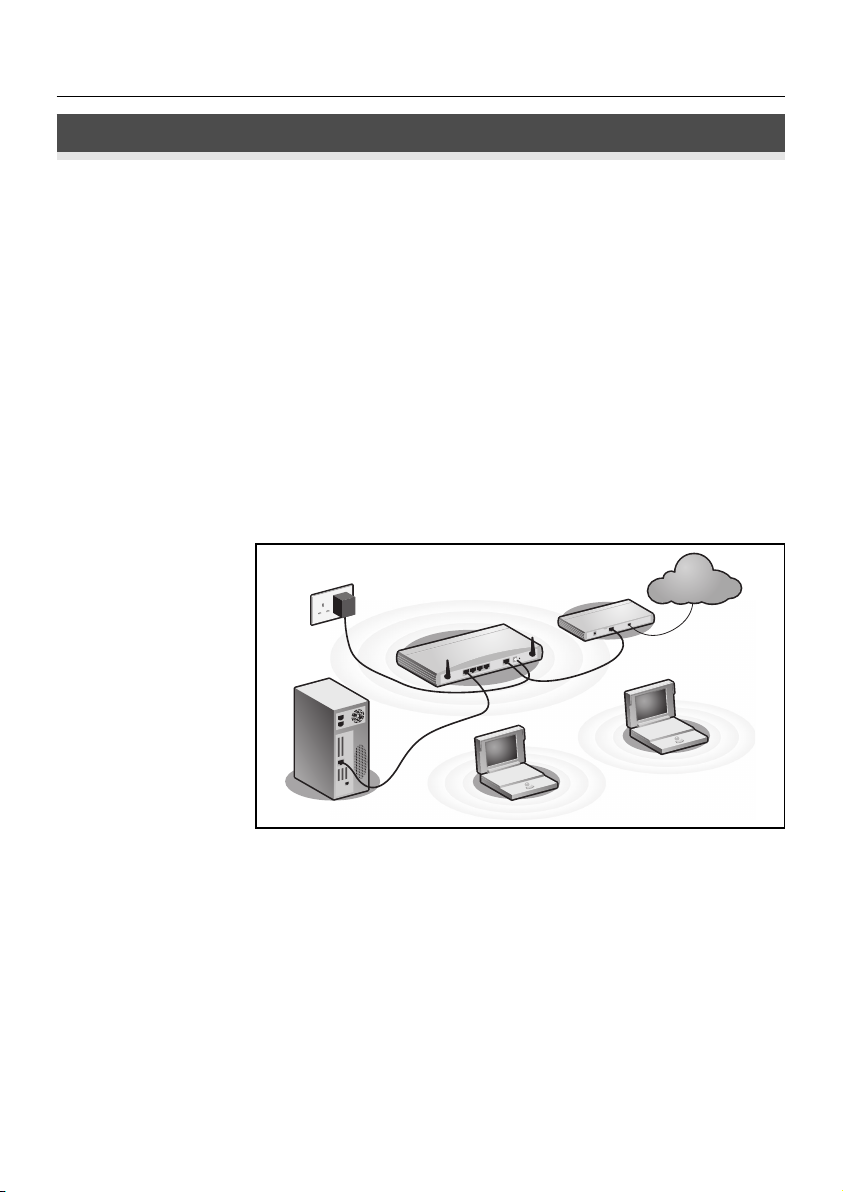
Figure 1. Example Network with OfficeConnect Wireless 54 Mbps/108 Mbps 11g Cable/DSL
Router.
Power
Supply Unit
3Com OfficeConnect Wireless
54Mbps/108Mbps 11g Cable/DSL Router
Your existing
Cable/DSL Modem
t
e
rn
te
In
Wireless
Your PC
Users
Page 9

7
Changing Your Computer's Configuration
2. CHANGING YOUR COMPUTER'S CONFIGURATION
You may need to make some changes to the configuration of your computers
in order to communicate with the Router.
If you have PPPoE or PPTP client software installed on your computer, you will
need to disable it. To do this:
1. From the Windows Start menu, select Settings > Control Panel.
2. Double click on Internet Options.
3. Select the Connections Tab. A screen similar to Figure 2 should be dis-
played.
4. Select the Never Dial a Connection option and click OK.
You may wish to remove the PPPoE client software from your computer to
free resources, as it is not required for use with the Router.
Follow the instructions below for your particular operating system to ensure
that your computers are configured to obtain an IP address automatically.
For computers using Windows XP.
1. From the Windows Start menu, select Control Panel.
2. Click on Network and Internet Connections.
3. Click on the Network Connections icon.
4. Double click on LAN or High Speed Connection icon. A screen titled Local
Area Connection Status will appear.
5. Select Internet Protocol TCP/IP and click on Properties.
6. Ensure that the options Obtain an IP Address automatically, and Obtain DNS
servers automatically are both selected as shown in Figure 4. Click OK.
7. Restart your computer.
For computers using Windows 2000.
1. From the Windows Start Menu, select Settings > Control Panel.
2. Double click on Network and Dial-Up connections.
3. Double click on Local Area Connection.
4. Click on Properties.
5. A screen similar to Figure 3 should be displayed. Select Internet Protocol
TCP/IP and click on Properties.
6. Ensure that the options Obtain an IP Address automatically
, and Obtain DNS
servers automatically are both selected as shown in Figure 4. Click OK.
7. Restart your computer.
GB
Obtaining an IP Address
automatically.
DSL users with PPPoE or
PPTP Client Software.
Figure 3
Figure 2
Page 10

ISP Connection Methods
8
3. ISP CONNECTION METHODS
Before you can configure the Router you need to know the IP information
allocation method used by your ISP. There are four different ways that ISPs
allocate IP information, as described below:
1. Dynamic IP Address (DSL or Cable)
Dynamic IP addressing (or DHCP) automatically assigns the Router IP information. This method is popular with Cable providers. This method is also
used if your modem has a built in DHCP server.
2. PPPoE (DSL only)
If the installation instructions that accompany your modem ask you to
install a PPPoE client on your PC then select this option. Note that when
you install the Router, you will not need to use the PPPoE software on
your PC. To configure the Router you will need to know the following:
Username, Password, and Service Name (if required by your ISP).
3. Static IP Address (DSL or Cable)
The ISP provides the IP addressing information for you to enter manually.
To configure the Router you will need to know the following: IP Address,
Subnet Mask, ISP Router Address, and DNS address (es).
For computers using Windows 95, 98 and ME.
1. From the Windows Start Menu, select Settings > Control Panel.
2. Double click on Network. Select the TCP/IP item for your network card as
shown in Figure 5 and click on Properties.
3. In the TCP/IP dialog, select the IP Address tab, and ensure that Obtain IP
address automatically is selected as shown in Figure 6. Click OK.
4. Restart your computer.
Figure 5
Figure 6
Figure 4
Page 11

9
Running the Setup Wizard
GB
4. PPTP (DSL or Cable)
PPTP is only used by some European providers. If the installation instructions that accompany your modem ask you to setup a dialup connection
using a PPTP VPN tunnel then select this option. Note that when you
install the Router, you will not need to use the dialup VPN on your PC
anymore. To configure the Router you will need to know the following:
Username, Password, Service Name (if required by your ISP), and VPN
Server address (usually your modem).
You will be asked for the IP Allocation Mode when you run the Setup
Wizard.
4. RUNNING THE SETUP WIZARD
1. If you haven’t already done so, restart your computer.
2. Launch your web browser and attempt to contact the Router by typing
the following URL in the location bar: http://192.168.1.1.
If you can access the Login page, then your computer has correctly
received an IP address from the Router.
3. Login using the default password admin. The Wizard will attempt to
launch automatically, but if it fails, select the Wizard tab and click on the
Wizard button.
4. Where possible, the Wizard will recommend settings for most parameters.
However, there are some settings which you must provide. Most of these
will have been provided to you by your ISP when you set the account up.
5. 3Com recommends that you leave the LAN IP address for the router at the
factory set default address of 192.168.1.1. However, if you should choose
to hange it; make a note of the new address:
6. When the DHCP Server Settings page is displayed, make sure that the
Enable the DHCP Server with the following settings option is selected.
When the Wizard has completed, attempt to browse to an Internet web site,
such as www.3com.com. If you can successfully access this site, then your
computer, Router and Cable/DSL modem have been correctly configured.
Refer to the Problem Solving section if you cannot make contact with the
Router or the Internet.
Router's LAN IP Address _______._______._______._______
Connecting to the
Internet
Page 12
Connecting to the Wireless LAN
10
5. CONNECTING TO THE WIRELESS LAN
1. After you have configured the Router via the wired computer, you can
connect to the Router via a wireless computer.
The Router and wireless clients must have both the same SSID and the
same encryption settings. All wireless clients must use Infrastructure mode.
The default wireless settings for the Router are:
2. If you do not have a Wireless LAN you can use the Router’s default settings. Ensure that your wireless clients have the default SSID, channel and
encryption as detailed above.
If you have an existing Wireless LAN, configure the Router to use the
same SSID and and encryption settings to be compatible with your existing wireless network.
3. If your computer has both a wired and wireless NIC installed, you must
ensure that only one NIC is used to communicate with the LAN. To use
the wireless NIC, unplug the Ethernet cable and reboot your computer.
4. Launch your web browser and attempt to browse to an internet web site
such as www.3com.com. If you can successfully access this site, then
your wireless computer, Router and Cable/DSL modem have been successfully configured.
5. 3Com strongly recommends that you enable WPA encryption to improve
the security of your wireless network and you change the SSID to something other than the default. Consult the on line help or the User Guide
for details.
Service Area Name / SSID is 3Com Channel 11 Encryption is off.
Service Area Name/SSID ______________________________
Channel Number ______________________________
Page 13

11
Problem Solving
GB
PROBLEM SOLVING
If you are experiencing difficulties with your installation, try the following:
• Ensure all networking equipment is switched on. The Router should be
showing a green Power LED. If it is not, check the power adapter connection. Do not use any power adapter with your Router other than the one
supplied.
• Ensure the Cable/DSL Modem is connected. The Router should be dis-
playing a green or yellow Cable/DSL Status LED. If no LED is displayed,
check that your modem is switched on and that it is connected to the
Cable/DSL port with an Ethernet cable.
• Ensure that the computer is connected to the Router. The Router
should be displaying a green or yellow LAN Status LED. If it is not, check
that the computer is connected to one of the Router's LAN ports with an
Ethernet cable.
• Ensure that you do not have a web proxy enabled on your computer.
Go to the Control Panel and click on Internet Options. Select the
Connections tab and click on the LAN Settings button at the bottom. Make
sure that the Use Proxy Server option is unchecked.
• If you are unable to access the Router's Web interface. Launch a web
browser and enter http://192.168.1.1. If you chose a different IP address,
use that instead. Ensure that you include the http:// prefix.
• If the Power LED or Power Adapter OK LED are not lit refer to the
table.
Power Adapter Power LED Problem and Action
OK LED
On On All functioning correctly.
On Off The internal power supply has failed. Contact 3Com
Technical Support for a replacement Router.
Off Off The power adapter or power adapter connection is
faulty. Check your power adapter connections. If
there is still no power, contact 3Com Technical
Support and ask for a replacement power adapter.
Page 14

• Some Cable providers authenticate to the user’s computer MAC address. If
this is required, go to Internet Settings and select Clone the MAC Address.
This will copy the MAC address of your computer onto the Internet port
of the Router.
• Some Cable providers authenticate to the user’s Host Name. If this is
required, go to Internet Settings and enter the host name of your computer into the Host Name field.
• If you have an existing DSL line and have PPPoE or PPTP client software
installed on your computer, you will need to disable it. See section 2.
• If your DSL line uses PPPoE or PPTP, go to Internet Settings and ensure
that the correct IP Allocation mode is selected. Check that your Username
and Password are correct.
• Some DSL providers require the use of a PPPoE Service Name. If this is
required, go to Internet Settings and enter the PPPoE Service Name in the
field provided. If it is not required, you must leave it blank.
If you are unable to access the wireless LAN:
• Ensure that the wireless client is set to infrastructure mode.
• If you have a wired and wireless NIC in the same computer, ensure that
the wired NIC is disabled. See section 5 for details.
• Ensure that the Service Area Name (SSID) is the same for the wireless
client and the Router.
• Ensure that the Router WLAN LED is on. If not, go to the Wireless Settings
menu and enable Wireless Networking.
• Ensure that encryption settings are the same for the wireless client and
the Router. If there are problems, turn wireless encryption off in the client
and the Router until you have established a wireless connection.
Problem Solving
12
Cable Internet
Connections
DSL Internet
Connections
Wireless Configuration
Page 15

13
Introducción
INTRODUCCIÓN
Este manual le guiará a lo largo de los pasos básicos para instalar y configurar
su OfficeConnect Wireless 54 Mbps/108 Mbps 11g Cable/DSL Router y
establecer una conexión a Internet desde sus PCs. A lo largo de esta guía,
nos referiremos al OfficeConnect Wireless 54 Mbps/108 Mbps 11g Cable/DSL
Router simplemente como el router.
• Un OfficeConnect Wireless 54 Mbps/108 Mbps 11g Cable/DSL Router
• Un adaptador de alimentación para usar con el router
• Cuatro pies de goma
• Un cable Ethernet
• Un CD-ROM con la Guía de instalación rápida y la Guía de usuario
• Esta Guía de instalación
• Una hoja de información de soporte y seguridad
• Un folleto de garantía
• Hoja de notas de versiones
• Hoja de gama de producto
Antes de empezar, debe asegurarse de lo siguiente:
• Ya dispone de una conexión a Internet de banda ancha mediante cable o
DSL con un módem adecuado y esta conexión funciona correctamente. El
módem debe disponer de un puerto Ethernet para poder conectarse a su
router.
• Tiene un PC con una conexión Ethernet disponible y adecuadamente configurado para su comunicación con Internet. Su PC debe poder conectarse
a Internet mediante el módem y ha de disponer de un navegador web
instalado.
• No hay ningún otro dispositivo de servidor DHCP en su red local responsable de la asignación de direcciones IP a sus PCs y a otros dispositivos
conectados a la red. Su router se encargará en adelante de realizar esta
función por defecto.
Si una o varias de estas condiciones no se cumple, consulte la guía de usuario
del router facilitada en el CD-ROM que se adjunta y que incluye una información completa al respecto.
Acerca de esta guía:
Su caja contiene los
siguientes componentes:
Requisitos del sistema
E
Page 16
Dimensiones y estándares
14
DIMENSIONES Y ESTÁNDARES
Funcionales: ISO 8802/3, IEEE802.3, IEEE802.11b, 802.11g
Seguridad: UL60950, CSA22.2 #60950, IEC 60950, EN 60950
EMC: EN 55022 Clase B, EN55024, CISPR 22, FCC Parte 15 Clase B*
ICES-003 Clase B, ETSI EN 301 489-17
Radio: CFR 47 FCC Parte 15.207, 15.209, 15.247 and 15.249.
ETS 300 328 (sistemas de transmisión de banda ancha ISM de
2,4 GHz), RSS-210
Condiciones
ambientales: EN 60068 (IEC 68)
*
Consulte la sección de 'Avisos reglamentarios' en la hoja de información de soporte y seguridad
ADVERTENCIA: Antes de empezar, por favor lea atentamente la sección 'Información importante de seguridad' en la hoja de información
de soporte y seguridad.
WARNING: Please read the 'Important Safety Information' section in
the Support and Safety Information sheet before you start.
VORSICHT: Bitte lesen Sie den Abschnitt ,Wichtige
Sicherheitsinformationen' sorgfältig durch, bevor Sie das Gerät einschalten.
Use los cuatro pies de goma auto-adhesivos para impedir que su router resbale por la superficie de su mesa o cuando vaya a apilarlo con otras unidades
OfficeConnect de superficie plana. Sólo tiene que pegar los pies de goma en
las zonas marcadas en cada esquina en la parte inferior de su router.
Estándares
Información de
seguridad
Dimensiones
Uso de los pies de goma
Requisito de
alimentación: 7VA, 23.9
BTU/hr
Temperatura de
funcionamiento: de 0 a
40ºC (de 32 a 105ºF)
Humedad: de 0 a 90%
(sin condensación)
41.5 mm
(1.6 in.)
224.8 mm
(8.8 in.)
OfficeConnect Wireless 54 Mbps/108 Mbps
11g Cable/DSL Router 592 g(1.3lb)
Page 17
15
Ubicación de su router
UBICACIÓN DE SU ROUTER
• La unidad se sitúa en una posición central respecto de los PCs inalámbricos que se conectarán al router. Una ubicación adecuada podría ser encima de una estantería alta o de un mueble similar, para optimizar las
conexiones inalámbricas de los PCs, tanto en el plano horizontal como
vertical, permitiendo así una cobertura total.
• Para poder cumplir con las normativas de exposición a radiaciones del
FCC, el router debe estar situado a una distancia mínima de 20 cm (8 pulgadas) de cualquier persona (para una información detallada, consulte la
Guía de usuario).
• El router no está expuesto directamente a la luz del sol y está alejado de
cualquier fuente de calor.
• El cableado está alejado de cables eléctricos, lámparas fluorescentes y
fuentes de ruido eléctrico tales como radios, transmisores y amplificadores
de banda ancha.
• El agua o la humedad no puede penetrar en la carcasa de la unidad.
• El flujo de aire alrededor de la unidad, y a través de las pequeñas aberturas en el panel lateral de la unidad, no está restringido. Le recomendamos que deje un espacio libre mínimo de 25 mm (1 pulgada).
E
Page 18
Acerca de su router
16
ACERCA DE SU ROUTER
1. LED de alerta Naranja
Indica una serie de condiciones distintas, tal como se indica a continuación.
Apagado - El router funciona con normalidad.
Parpadeo rápido - Indica uno de los casos siguientes:
• El router acaba de iniciarse y está realizando una rutina de comprobación interna, o
• El administrador ha lanzado el comando Resetear valores por defecto de fábrica, o
• El software del sistema se está actualizando
En cada uno de estos casos, espere hasta que el router haya completado la operación en curso y que el
LED de alerta esté apagado.
Parpadeo lento - El router ha completado el proceso de Resetear valores por defecto de fábrica, y está
esperando que usted resetee la unidad. Para ello, apague el router, espere 10 segundos y, a continuación,
enciéndalo de nuevo. El router iniciará entonces la secuencia de inicio y reanudará su funcionamiento normal.
Encendido durante 2 segundos y a continuación se apaga - El router ha detectado e impedido el ataque
de un hacker a su red desde Internet.
Continuamente encendido - Se ha detectado un fallo en su router durante el proceso de arranque.
Consulte la Guía principal de usuario.
2. LED de alimentación Verde
Indica que el router está encendido.
3. LED de estado de LAN inalámbrica (WLAN) Amarillo
Si el LED está encendido, significa que la conectividad inalámbrica está habilitada. Si el LED está parpadeando,
indica que se están transmitiendo o recibiendo datos. Si el LED está apagado, significa que la LAN inalámbrica
ha sido inhabilitada en el router, o que hay un problema. Consulte la sección de 'Resolución de problemas'.
4. Cuatro LEDs de estado de LAN Verde (enlace de 100 Mbps) / Amarillo (enlace de 10 Mbps)
Si el LED está encendido, el enlace entre el puerto y el siguiente equipo de red es correcto. Si el LED está
parpadeando, el enlace es correcto y se están transmitiendo o recibiendo datos. Si el LED está apagado,
OfficeConnect Wireless 54 Mbps/108 Mbps 11g Cable/DSL Router – frontal.
1
2
3
5 4
Page 19
17
Acerca de su router
no hay ningún dispositivo conectado, o el dispositivo conectado está apagado, o bien hay un problema
con la conexión (consulte la sección de 'Resolución de problemas'). El puerto ajustará automáticamente la
velocidad y el modo dúplex correctos.
5. LED de estado de cable/DSL Verde (enlace de 100 Mbps) / Amarillo (enlace de 10 Mbps)
Si el LED está encendido, el enlace entre el router y el módem de cable o DSL es correcto. Si el LED está
parpadeando, el enlace es correcto y se están transmitiendo o recibiendo datos. Si el LED está apagado,
no hay ningún dispositivo conectado, o el módem está apagado, o bien hay un problema (consulte la sección de 'Resolución de problemas').
6. Antena inalámbrica
En el momento de su instalación, la antena de este producto debe colocarse en forma de 'V'.
PRECAUCIÓN: No fuerce la antena más allá de sus topes mecánicos. Si sigue girando la antena, podría
causar daños.
7. Toma de adaptador de alimentación
Utilice únicamente el adaptador de alimentación suministrado con este router. No use ningún otro adaptador.
8. LED de adaptador de alimentación conectado Verde
Indica que el adaptador de alimentación está suministrando alimentación eléctrica al router. Si el LED está
apagado, puede haber un problema con el adaptador de alimentación o con el cable del adaptador.
9. Puerto Ethernet de cable/DSL
Use el cable suministrado para conectar el router al puerto Ethernet en su módem de cable o DSL. El puerto
ajustará automáticamente la velocidad y el modo dúplex correctos, y se auto-configurará automáticamente
como MDI o MDIX en función del dispositivo al que esté conectado y del tipo de cable utilizado.
10. Cuatro puertos de LAN 10/100
Si utiliza cable RJ-45 adecuado, podrá conectar su router a un PC o a cualquier otro equipo que disponga
de una conexión Ethernet (por ejemplo, un hub o un switch). Los puertos de LAN se auto-configurarán
automáticamente como MDI o MDIX en función del dispositivo al que estén conectados y del tipo de
cable utilizado.
11. Botón de reset
Pulse el botón de reset durante 5 segundos y a continuación suéltelo. Todos los ajustes del OfficeConnect
Wireless 54 Mbps/108 Mbps 11g Cable/DSL Router se reiniciarán a sus valores por defecto de fábrica.
E
OfficeConnect Wireless 54 Mbps/108 Mbps 11g Cable/DSL Router – trasera.
6 6
911 7 810
Page 20
Instalación de su router
18
1. INSTALACIÓN DE SU ROUTER
1. Conecte el adaptador de alimentación al router y espere a que el LED de
alerta deje de parpadear.
2. Compruebe que tanto su módem como su PC están encendidos.
3. Inserte uno de los extremos del cable Ethernet suministrado (RJ-45
Categoría 5) en el puerto de Cable/DSL, en el panel trasero del router.
4. Inserte el otro extremo del cable en el puerto RJ-45 en su módem de cable
o DSL. Compruebe que el LED de estado de Cable/DSL se enciende en el
router.
5. Conecte el módem de cable o DSL a Internet.
6. Conecte su PC a uno de los cuatro puertos de LAN en el router usando un
cable Ethernet. Compruebe que se enciende el correspondiente LED de
estado de LAN en el router.
Para poder compartir su router entre más de cuatro usuarios, necesitará un
hub o un switch adicional. Conecte un puerto de LAN de su router al hub o
switch, como por ejemplo el OfficeConnect Dual Speed Switch 8.
Conexión de su router
Conexión a un hub o a
un switch
Figura 1. Ejemplo de red con el OfficeConnect Wireless 54 Mbps/108 Mbps 11g Cable/DSL
Router.
Unidad de fuente
de alimentación
3Com OfficeConnect Wireless
54 Mbps/108 Mbps 11g Cable/DSL Router
Su módem de
cable/DSL existente
Internet
Usuarios inalámbricos
Su PC
Page 21

19
Cambio de configuración de su PC
2. CAMBIO DE CONFIGURACIÓN DE SU PC
Es posible que tenga que realizar algunos cambios de configuración en sus
PCs para poder comunicar con el router.
Si tiene instalado en su PC software de cliente PPPoE o PPTP, deberá desactivarlo. Para ello, sigua los pasos siguientes:
1. En el menú Inicio de Windows, seleccione Configuración > Panel de control.
2. Haga doble clic en Opciones de Internet.
3. Seleccione la pestaña Conexiones. Se abrirá una ventana similar a la Figura 2.
4. Seleccione la opción No marcar nunca una conexión, y haga clic en
Aceptar. Puede que quiera quitar el software de cliente PPPoE de su PC para
liberar recursos, dado que no se requiere para su uso con el router.
Siga las instrucciones indicadas a continuación para su sistema operativo particular, para asegurarse de que sus PCs están configurados para obtener una
dirección IP automáticamente.
Para PCs con Windows XP.
1. En el menú Inicio de Windows, seleccione Configuración > Panel de control.
2. Haga clic en el icono de Conexiones de red.
3. Haga doble clic en el icono que encontrará bajo LAN o Internet de alta
velocidad. Se abrirá una ventana denominada Estado de conexiones de
área local.
4. Seleccione Protocolo de Internet (TCP/IP) y haga clic en Propiedades.
5. Compruebe que tanto la opción Obtener una dirección IP automáticamente
como la opción Obtener la dirección del servidor DNS automáticamente están
seleccionadas, tal como se muestra en la Figura 4. Haga clic en Aceptar.
6. Reinicie su PC.
Para PCs con Windows 2000.
1. En el menú Inicio de Windows, seleccione Configuración > Panel de control.
2. Haga doble clic en Conexiones de red y acceso telefónico.
3. Haga doble clic en Conexión de área local.
4. Haga clic en Propiedades.
5. Debería abrirse una ventana similar a la Figura 3. Seleccione Protocolo de
Internet (TCP/IP) y haga clic en Propiedades.
6. Compruebe que tanto la opción Obtener una dirección IP automáticamente
como la opción Obtener la dirección del servidor DNS automáticamente están
seleccionadas, tal como se muestra en la Figura 4
. Haga clic en Aceptar.
7. Reinicie su PC.
Usuarios DSL con
software de cliente
PPPoE o PPTP
Obtención de una
dirección IP de forma
automática
E
Figura 3
Figura 2
Page 22

Métodos de conexión a ISP
20
Para PCs con Windows 95, 98 y ME.
1. En el menú Inicio de Windows, seleccione Configuración > Panel de control.
2. Haga doble clic en Red. Seleccione el componente TCP/IP para su tarjeta
de red, tal como se muestra en la Figura 5, y haga clic en Propiedades.
3. En la ventana de Propiedades de TCP/IP, seleccione la pestaña Dirección IP y
compruebe que la opción Obtener una dirección IP automáticamente está
seleccionada, tal como se muestra en la Figura 6. Haga clic en Aceptar.
4. Reinicie su PC.
Figura 5
Figura 6
Figura 4
3. MÉTODOS DE CONEXIÓN A ISP
Antes de poder configurar el router, necesita conocer el método de asignación
de la información IP usado por su ISP. Existen cuatro formas diferentes con las
que los ISPs asignan la información IP, tal como se describe a continuación:
1. Dirección IP dinámica (DSL o Cable)
El direccionamiento IP dinámico (o DHCP) asigna automáticamente la
información IP del router. Este método es común entre los proveedores de
cable. Este método también se usa si su módem dispone de un servidor
DHCP integrado.
2. PPPoE (sólo DSL)
Seleccione esta opción si en las instrucciones de instalación de su módem
se le solicita instalar un cliente PPPoE en su PC. Tenga en cuenta que al
instalar el router no necesitará usar el software PPPoE en su PC. Para configurar el router, necesitará conocer lo siguiente: Nombre de usuario,
Contraseña y Nombre de servicio (si así lo requiere su ISP).
3. Dirección IP estática (DSL o Cable)
El ISP proporciona la información de direccionamiento IP que tiene que
introducir manualmente. Para configurar el router, necesitará conocer lo
siguiente: Dirección IP, Máscara de subred, Dirección de router del ISP y
dirección(iones) de DNS.
Page 23

21
Cómo usar el asistente de configuración
4. PPTP (DSL o Cable)
Sólo algunos proveedores europeos usan PPTP. Seleccione esta opción si en
las instrucciones de instalación de su módem se le solicita configurar una
conexión de acceso telefónico usando un túnel VPN PPTP. Tenga en cuenta
que al instalar el router ya no tendrá que usar más la VPN de acceso telefónico
en su PC. Para configurar el router, necesitará conocer lo siguiente: Nombre de
usuario, Contraseña, Nombre de servicio (si así lo requiere su ISP) y dirección
del Servidor VPN (normalmente, su módem).
Cuando utilice el Asistente de configuración, se le solicitará el Modo de asignación IP.
4. CÓMO USAR EL ASISTENTE DE CONFIGURACIÓN
1. Si todavía no lo ha hecho, reinicie su PC.
2. Abra su navegador web e intente conectar con el router escribiendo la
siguienteURL en la barra de direcciones: http://192.168.1.1.
Si puede acceder a la página de Login, significa que su PC ha recibido correctamente una dirección IP del router.
3. Conéctese usando la contraseña por defecto admin. El asistente intentará
lanzarse automáticamente pero, si no lo consigue, seleccione la pestaña
Asistente y haga clic en el botón Asistente.
4. Cuando sea posible, el asistente recomendará ajustes para la mayoría de
los parámetros. Sin embargo, hay algunos ajustes que deberá establecer
usted mismo. En la mayoría de los casos, su ISP se los habrá facilitado
cuando su cuenta fue dada de alta.
5. 3Com le recomienda que no modifique la dirección IP de LAN del router
establecida por defecto en fábrica: 192.168.1.1. Sin embargo, si elige
cambiarla, apunte la nueva dirección:
6. Cuando aparezca en pantalla la página de configuración del servidor
DHCP, asegúrese de que la opción Activar el servidor DHCP con los ajustes
siguientes esté seleccionada.
Una vez completado el asistente de configuración, intente acceder a una
página web de Internet, como por ejemplo www.3com.com. Si consigue
acceder con éxito a esta página, esto significa que tanto su PC como su
router y su módem de Cable/DSL han sido configurados correctamente.
Consulte la sección de ‘Resolución de problemas’ si no consigue contactar
con el router o acceder a Internet.
E
Dirección IP de LAN del router _______._______._______._______
Conexión a Internet
Page 24
Conexión a la LAN inalámbrica
22
5. CONEXIÓN A LA LAN INALÁMBRICA
1. Después de haber configurado el router a través del PC cableado, puede
conectarse al router desde un PC inalámbrico.
Tanto el router como los clientes inalámbricos deben tener el mismo SSID y
los mismos ajustes de encriptación. Todos los clientes inalámbricos deben
usar el modo Infraestructura.
Los ajustes inalámbricos por defecto del router son:
2. Si no dispone de una LAN inalámbrica, puede usar la configuración por defecto del router. Asegúrese que sus clientes inalámbricos usan el SSID, el canal y
la encriptación por defecto, conforme a los datos indicados anteriormente.
Si dispone de una LAN inalámbrica existente, configure el router para usar
el mismo SSID y la misma configuración de encriptación, de forma que sea
compatible con su red inalámbrica existente.
3. Si tiene instalado en su PC una NIC de cable y otra inalámbrica, debe asegurarse que sólo se usa una NIC para comunicar con la LAN. Para usar la
NIC inalámbrica, desconecte el cable Ethernet y reinicie su PC.
4. Abra su navegador web e intente acceder a una página web, como por
ejemplo www.3com.com. Si consigue acceder con éxito a esta página,
esto significa que tanto su PC inalámbrico como su router y su módem de
cable/DSL han sido configurados correctamente.
5. 3Com le recomienda encarecidamente que active la encriptación WPA
para mejorar la seguridad de su red inalámbrica, y que cambie el SSID a
un valor distinto del valor por defecto. Para una información detallada,
consulte la ayuda on-line o la Guía de usuario.
El SSID / nombre de área Canal 11 La encriptación
de servicio es 3Com está desactivada
SSID / nombre de área de servicio ______________________________
Número de canal ______________________________
Page 25

23
Resolución de problemas
RESOLUCIÓN DE PROBLEMAS
Si experimenta dificultades con su instalación, compruebe lo siguiente:
• Compruebe que todos los equipos de red están encendidos. El LED de
alimentación del router debería estar encendido y de color verde. Si no
fuera el caso, verifique la conexión del adaptador de alimentación. Use sólo
el adaptador de alimentación suministrado con el router.
• Compruebe que el módem de cable/DSL está conectado. El LED de
estado de cable/DSL del router debería estar encendido y de color verde o
amarillo. Si no fuera el caso, verifique que su módem está encendido y que
está conectado al puerto de cable/DSL con un cable Ethernet.
• Compruebe que el PC está conectado al router. El LED de estado de
LAN del router debería estar encendido y de color verde o amarillo. Si no
fuera el caso, verifique que el PC está conectado a uno de los puertos de
LAN del router con un cable Ethernet.
• Compruebe que no está activado ningún servidor proxy en su PC.
Vaya al Panel de control y haga clic en Opciones de Internet. Seleccione la
pestaña Conexiones y haga clic en el botón Configuración de LAN en la
parte inferior. Compruebe que la casilla Usar servidor proxy no esté seleccionada.
• Si no puede acceder a la interfaz web del router. Abra un navegador
web y escriba http://192.168.1.1 en la barra de direcciones. Si ha elegido
una dirección IP distinta, use ésta en su lugar. Asegúrese de incluir el prefijo
http://.
• Si el LED de alimentación o el LED de adaptador de alimentación
conectado no están encendidos, consulte la tabla.
E
LED de
adaptador de
alimentación LED de
conectado alimentación Problema y acción
Encendido Encendido Todo está funcionando correctamente.
Encendido Apagado La fuente de alimentación interna no funciona.
Contacte con el Soporte Técnico de 3Com para que
le proporcionen un router de sustitución.
Apagado Apagado El adaptador de alimentación, o la conexión del
adaptador de alimentación, es defectuoso.
Compruebe las conexiones de su adaptador de alimentación. Si sigue sin tener alimentación, contacte
con el Soporte Técnico de 3Com y pida que le proporcionen un adaptador de alimentación de sustitución.
Page 26

Resolución de problemas
24
• Algunos proveedores de cable autentican la dirección MAC del PC del
usuario. Si este es su caso, vaya a Configuración de Internet y seleccione
Clonar la dirección MAC. Esto permitirá copiar la dirección MAC de su PC
en el puerto Internet del router.
• Algunos proveedores de cable autentican el nombre de host del usuario.
Si este es su caso, vaya a Configuración de Internet e introduzca el nombre de host de su PC en el campo Nombre de host.
• Si dispone de una línea DSL existente y tiene instalado en su PC un software de cliente PPPoE o PPTP, deberá desactivarlo. Consulte la sección 2.
• Si su línea DSL usa PPPoE o PPTP, vaya a Configuración de Internet y
asegúrese de que el Modo de asignación IP correcto está seleccionado.
Compruebe que su Nombre de usuario y su Contraseña son correctos.
• Algunos proveedores de DSL requieren el uso de un Nombre de Servicio
PPPoE. Si se le requiere, vaya a Configuración de Internet e introduzca el
Nombre de Servicio PPPoE en el campo correspondiente. Si no se le
requiere, deberá dejar este campo en blanco.
Si no consigue acceder a la LAN inalámbrica:
• Compruebe que el cliente inalámbrico está configurado en modo
infraestructura.
• Si su PC dispone de una NIC de cable y una inalámbrica, asegúrese de que
la NIC de cable está desactivada. Para más información, consulte la sección 5.
• Compruebe que el Nombre de Área de Servicio (SSID) es el mismo para el
cliente inalámbrico y el router.
• Compruebe que el LED de WLAN del router está encendido. Si no fuera el
caso, vaya al menú Configuración de Internet y habilite el Networking
Inalámbrico.
• Compruebe que los ajustes de encriptación son los mismos para el cliente
inalámbrico y el router. Si hay algún problema, desactive la encriptación
inalámbrica en el cliente y en el router hasta que haya establecido una
conexión inalámbrica.
Conexiones a Internet
de cable
Conexiones a
Internet DSL
Configuración
inalámbrica
Page 27

25
Introduction
INTRODUCTION
Ce guide décrit l’installation et la configuration du routeur OfficeConnect
Wireless 54 Mbps/108 Mbps 11g Cable/DSL Router, jusqu’à sa connexion aux
ordinateurs et à Internet. Dans l’ensemble du document, le routeur
‘OfficeConnect Wireless 54 Mbps/108 Mbps 11g Cable/DSL Router sera simplement dénommé « routeur ».
• Un routeur OfficeConnect Wireless 54 Mbps/108 Mbps 11g Cable/DSL Router
• Un adaptateur secteur spécifique
• Quatre pieds caoutchouc
• Un câble Ethernet
• Un CD-ROM contenant le Guide de mise en route et le Guide de l’utilisateur
• Le présent Guide d’installation
• Une fiche d’information Support et sécurité
• Une carte de Garantie
• Une note de version
• Une brochure OfficeConnect
Avant de commencer, vérifiez que :
• vous disposez d’une connexion Internet haut débit par câble ou DSL ainsi
que du modem correspondant et cette connexion fonctionne correctement.
Le modem doit être muni d’un port Ethernet pour la connexion au routeur.
• vous disposez d’un ordinateur doté d’une connexion Ethernet et configuré
pour Internet. Cet ordinateur doit pouvoir se connecter à Internet par l’intermédiaire du modem et être équipé d’un navigateur.
• il n’existe sur le réseau local aucun autre serveur DHCP chargé d’affecter
des adresses IP à vos ordinateurs et aux périphériques connectés au
réseau. Par défaut, votre routeur prend en charge cette fonction.
Si l’une de ces conditions n’est pas remplie, reportez-vous au Guide de l’utilisateur
sur CD-ROM pour plus d’informations.
Composition
du produit :
Configuration minimum
F
Page 28

Dimensions et Normes
26
DIMENSIONS ET NORMES
Fonctionnement : ISO 8802/3, IEEE802.3, IEEE802.11b, 802.11g
Sécurité : UL60950, CSA22.2 #60950, IEC 60950, EN 60950
EMC : EN 55022 Class B, EN55024, CISPR 22, FCC Part 15 Class B*
ICES-003 Class B, ETSI EN 301 489-17
Radio : CFR 47 FCC Part 15.207, 15.209, 15.247 et 15.249.
ETS 300 328 (systèmes de transmission ISM 2,4 GHz), RSS-210
Environnement : EN 60068 (IEC 68)
* Voir les avertissements réglementaires de la fiche d’information Support et sécurité.
AVERTISSEMENT: Avant de commencer, lisez attentivement la section
« Consignes de sécurité » de la fiche d’information Support et sécurité.
WARNING: Please read the ‘Important Safety Information’ section in
the Support and Safety Information sheet before you start.
VORSICHT: Bitte lesen Sie den Abschnitt ‘Wichtige
Sicherheitsinformationen’ sorgfältig durch, bevor Sie das Gerät
einschalten.
Utilisez les quatre pieds caoutchouc autocollants pour éviter à votre routeur
de glisser sur les surfaces planes ou pour l’empiler avec des unités
OfficeConnect à couvercle plat. Collez ces pieds exclusivement aux endroits
indiqués, à chaque angle, sous l’appareil.
Normes
Dimensions
Utilisation des pieds
caoutchouc
Consignes de sécurité
Alimentation :
7 VA, 23,9 BTU/h
Température en
fonctionnement :
0 - 40ºC
Humidité : 0 - 90%
(sans condensation)
41.5 mm
(1.6 in.)
224.8 mm
(8.8 in.)
OfficeConnect Wireless 54 Mbps/108 Mbps
11g Cable/DSL Router 592 g(1.3lb)
Page 29

27
Placement de votre routeur
F
PLACEMENT DE VOTRE ROUTEUR
En installant votre routeur, assurez-vous que :
• le routeur est placé au milieu des ordinateurs sans fil qui lui seront connectés. Pour une couverture idéale, choisissez de préférence le haut d’une
étagère ou d’un meuble, c’est-à-dire l’endroit d’où les connexions seront
les plus directes possibles, tant horizontalement que verticalement.
• le routeur, conformément à la législation portant sur l’exposition aux
ondes radio, est placé à au moins 20 cm des utilisateurs (reportez-vous au
Guide de l’utilisateur pour plus d’informations).
• le routeur n’est pas exposé directement aux rayons du soleil ou à une
source de chaleur.
• les câbles sont éloignés des lignes électriques, des éclairages fluorescents
et autres sources d’interférences électriques (postes de radio, émetteurs et
amplificateurs à large bande, par exemple).
• l’eau ou l’humidité ne peuvent en aucun cas pénétrer à l’intérieur du boîtier.
• l’air peut circuler librement autour de l’appareil et des ouïes situées sur ses
côtés. Nous recommandons un dégagement minimum de 25 mm autour
de l’appareil.
Page 30

Présentation de votre routeur
28
PRÉSENTATION DE VOTRE ROUTEUR
1. LED Alert Orange
Indique l’état du routeur :
Eteinte – Le routeur fonctionne normalement.
Clignotement rapide – Indique que :
• le routeur vient d’être mis sous tension et effectue sa routine de test, ou
• l’administrateur a réinitialisé le routeur à ses paramètres par défaut, ou
• le logiciel système est en cours de mise à niveau.
Dans tous les cas, attendez que le routeur ait achevé l’opération en cours et que la LED Alert s’éteigne.
Clignotement lent – Le routeur a achevé sa réinitialisation. Eteignez-le et attendez 10 secondes avant de
le rallumer. Il reprend alors sa routine de démarrage normale.
Allumée 2 secondes, puis éteinte – Le routeur a détecté une tentative de piratage de votre réseau à partir
d’Internet et l’a repoussée.
Allumée en continu – Un problème erreur a été détecté sur le routeur au cours du démarrage. Reportezvous au Guide de l’utilisateur.
2. LED Power Verte
Indique que le routeur est sous tension.
3. LED WLAN (état du LAN sans fil) Jaune
Si la LED est allumée, le réseau sans fil est actif ; clignotante, des données sont en cours de transmission ;
éteinte, le réseau sans fil a été désactivé au niveau du routeur ou la connexion pose problème (voir le
chapitre ‘Résolution des problèmes’).
4. Quatre LED LAN Status Vertes (liaison 100 Mbps) / Jaunes (liaison 10 Mbps)
Si la LED est allumée, la liaison entre le port et l’équipement réseau qui lui est directement connecté est
correcte ; clignotante, la liaison est active et des données sont en cours de transmission ; éteinte, la liaison n’est pas établie, aucun équipement n’est connecté, l’équipement connecté est hors tension ou la
connexion pose problème (voir le chapitre ‘Résolution des problèmes’). Le port s’adapte automatiquement
à la vitesse et au mode de Duplex appropriés.
OfficeConnect Wireless 54 Mbps/108 Mbps 11g Cable/DSL Router – avant.
1
2
3
5 4
Page 31

29
Présentation de votre routeur
F
5. LED Cable/DSL LED Verte (liaison 100 Mbps) / Jaune (liaison 10 Mbps)
Si la LED est allumée, la liaison entre le routeur et le modem câble/DSL est établie ; clignotante, la liaison
est active et des données sont en cours de transmission ; éteinte, la liaison n’est pas établie, le modem
est éteint ou la connexion pose problème (voir le chapitre ‘Résolution des problèmes’).
6. Antenne sans fil
L’antenne de ce produit doit être déployée en ‘V’ lors de l’installation initiale.
ATTENTION : Ne forcez pas sur l’antenne, vous risquez de l’endommager irrémédiablement.
7. Prise de l’adaptateur secteur
Utilisez exclusivement l’adaptateur secteur fourni avec votre commutateur. N’utilisez en aucun cas un
autre adaptateur.
8. LED OK (adaptateur secteur) Verte
Indique que l’adaptateur secteur alimente le routeur. Si la LED est éteinte, il peut y avoir problème avec
l’adaptateur secteur ou son câble.
9. Port Ethernet Cable/DSL
Utilisez le câble fourni pour connecter le routeur au port Ethernet de votre modem câble ou DSL. Le port
ajuste automatiquement la vitesse et le mode de Duplex utilisés et active le mode MDI ou MDIX en fonction de l’équipement qui lui est connecté et du type de câble employé.
10. Quatre ports LAN 10/100
Par un câble RJ-45 approprié, vous pouvez relier votre routeur à un ordinateur, ou à tout autre
équipement muni d’une connexion Ethernet (concentrateur ou commutateur, par exemple). Les ports LAN
activent automatiquement le mode MDI ou MDIX en fonction de l’équipement auquel ils sont connectés
et du type de câble employé.
11. Bouton Reset
Appuyez sur le bouton Reset pendant 5 secondes et relâchez-le. Tous les paramètres du routeur
OfficeConnect Wireless 54 Mbps/108 Mbps 11g Cable/DSL Router sont réinitialisés à leur valeur par
défaut en sortie d’usine.
OfficeConnect Wireless 54 Mbps/108 Mbps 11g Cable/DSL Router – arrière.
6 6
911 7 810
Page 32

Installation de votre routeur
30
1. INSTALLATION DE VOTRE ROUTEUR
1. Branchez l’adaptateur secteur sur le routeur et attendez que la LED Alert
arrête de clignoter.
2. Vérifiez que votre modem et votre ordinateur sont tous deux allumés.
3. Branchez le câble Ethernet (RJ-45, Catégorie 5) fourni dans le port
Cable/DSL, à l’arrière du routeur.
4. Branchez l’autre extrémité de ce câble dans le port RJ-45 de votre modem
câble/DSL. Vérifiez la LED Cable/DSL à l’avant du routeur.
5. Connectez le modem Câble ou DSL à Internet.
6. Connectez votre ordinateur à l’un des quatre ports LAN du routeur à
l’aide d’un câble Ethernet. Vérifiez que la LED LAN Status correspondante
s’allume à l’avant du routeur.
Le partage du routeur entre plus de quatre utilisateurs suppose que vous disposiez d’un concentrateur ou d’un commutateur supplémentaire. Connectez
l’un des ports LAN du routeur à cet équipement (OfficeConnect Dual Speed
Switch 8 Plus, par exemple).
Connexion
Connexion à un
concentrateur ou un
commutateur
Figure 1. Exemple de réseau avec routeur OfficeConnect Wireless 54 Mbps/108 Mbps 11g
Cable/DSL Router.
Alimentation
3Com OfficeConnect Wireless
54 Mbps/108 Mbps 11g Cable/DSL Router
Votre modem
câble/DSL
Internet
Utilisateurs sans fil
Votre PC
Page 33

31
Modification de la configuration de l’ordinateur
F
2. MODIFICATION DE LA CONFIGURATION DE L’ORDINATEUR
Pour permettre à vos ordinateurs de communiquer avec le routeur, vous
devrez peut-être modifier leur configuration.
Si un client PPPoE ou PPTP a été installé sur votre ordinateur, vous devez le
désactiver. Pour ce faire :
1. Dans le menu Démarrer de Windows, sélectionnez Paramètres > Panneau
de configuration.
2. Double-cliquez sur Options Internet.
3. Cliquez sur l’onglet Connexions. Un écran similaire à celui illustré par la
Figure 2 s’affiche.
4. Sélectionnez l’option Ne jamais établir de connexion et cliquez sur OK.
Dans la mesure où il n’est pas utilisé par le routeur, vous pouvez désinstaller
le logiciel client PPPoE de votre ordinateur pour libérer des ressources.
Suivez les instructions correspondant à votre système d’exploitation pour
configurer vos ordinateurs de manière à obtenir automatiquement une adresse IP.
Pour les ordinateurs sous Windows XP.
1. Dans le menu Démarrer de Windows, sélectionnez Panneau de configuration.
2. Cliquez sur Connexions réseau.
3. Cliquez sur l’icône Connexion au réseau local.
4. Double-cliquez sur l’icône Connexion LAN ou haut débit. La fenêtre Etat
de Connexion au réseau local s’affiche à l’écran.
5. Cliquez sur le bouton Propriétés, sélectionnez Protocole Internet (TCP/IP)
et cliquez sur Propriétés.
6. Vérifiez que les cases Obtenir une adresse IP automatiquement et Obtenir
les adresses des serveurs DNS automatiquement sont toutes deux cochées
(voir Figure 4). Cliquez sur OK.
7. Redémarrez votre ordinateur.
Pour les ordinateurs sous Windows 2000.
1. Dans le menu Démarrer de Windows, sélectionnez Paramètres > Panneau
de configuration.
2. Double-cliquez sur Connexions réseau et accès à distance.
3. Double-cliquez sur Connexion au réseau local.
4. Cliquez sur Propriétés.
5. Un écran similaire à celui à celui illustré par la Figure 3 s’affiche.
Sélectionnez Protocole Internet (TCP/IP) et cliquez sur Propriétés.
6. Vérifiez que les cases Obtenir une adresse IP automatiquement et Obtenir
les adresses des serveurs DNS automatiquement sont toutes deux cochées,
(voir Figure 4). Cliquez sur OK.
7. Redémarrez votre ordinateur.
Obtention automatique
d’une adresse IP
Utilisateurs DSL avec
client PPPoE ou PPTP
Figure 3
Figure 2
Page 34

Connexion au fournisseur d’accès Internet
32
Pour les ordinateurs sous Windows 95, 98 et ME.
1. Dans le menu Démarrer de Windows, sélectionnez Paramètres > Panneau
de configuration.
2. Double-cliquez sur l’icône Réseau. Sélectionnez Protocole Internet (TCP/IP)
pour votre carte réseau, comme illustré par la Figure 5 et cliquez sur
Propriétés.
3. Dans la boîte de dialogue TCP/IP, sélectionnez l’onglet Adresse IP et
assurez-vous que la case Obtenir automatiquement une adresse IP est
cochée, comme illustré par la Figure 6. Cliquez sur OK.
4. Redémarrez votre ordinateur.
3. CONNEXION AU FOURNISSEUR D’ACCÈS INTERNET
Pour configurer votre routeur, vous devez savoir quelle méthode d’affectation
des adresses IP votre fournisseur d’accès utilise. Quatre méthodes différentes
sont utilisées :
1. Adressage IP dynamique (DSL ou câble)
L’adressage dynamique (ou DHCP) affecte automatiquement les informations
IP au routeur. Cette méthode est courante chez les câblo-opérateurs. Elle
est également employée lorsque le modem intègre un serveur DHCP.
2. PPPoE (DSL uniquement)
Si les instructions d’installation de votre modem vous demandent d’installer
un client PPPoE sur votre PC, choisissez cette option. Remarquez qu’avec votre
routeur, vous n’utilisez plus le logiciel PPPoE de votre PC. Pour configurer votre
routeur, vous devez disposer des informations suivantes : nom d’utilisateur,
mot de passe et nom de service (s’il est imposé par votre FAI).
3. Adresse IP statique (DSL ou câble)
Votre fournisseur d’accès vous communique les informations d’adressage
IP que vous saisissez manuellement. Pour configurer le routeur, vous devez
disposer des informations suivantes : adresse IP, masque de sous-réseau IP,
adresse du routeur du FAI et adresse(s) DNS.
Figure 5
Figure 6
Figure 4
Page 35

33
Lancement de l’assistant de configuration
F
4. PPTP (DSL ou câble)
PPTP n’est utilisé que par quelques fournisseurs d’accès européens. Si les
installations d’instructions de votre modem vous demandent de configurer
une connexion par accès réseau à distance sur tunnel VPN PPTP, choisissez
cette option. Remarquez qu’avec votre routeur, le VPN d’accès réseau à
distance installé sur votre PC n’est plus utilisé. Pour configurer le routeur,
vous devez disposer des informations suivantes : nom d’utilisateur, mot de
passe et nom de service (s’il est imposé par votre FAI) et adresse du
serveur VPN (en général votre modem).
L’assistant d’installation vous demande le mode d’affectation de l’adresse IP.
4. LANCEMENT DE L’ASSISTANT DE CONFIGURATION
1. Si ce n’est pas déjà fait, redémarrez votre ordinateur.
2. Lancez votre navigateur web et essayez de contactez le routeur en tapant
http://192.168.1.1 dans la barre d’adresse.
Si vous accédez à la page de connexion, votre ordinateur a correctement
reçu une adresse IP en provenance du routeur.
3. Connectez-vous avec le mot de passe par défaut admin. L’assistant tente
de se lancer automatiquement. S’il n’y parvient pas, cliquez sur l’onglet
Assistant puis sur le bouton Assistant.
4. Lorsque c’est possible, l’assistant recommande des valeurs pour chaque
paramètre. Il vous revient cependant de définir certains d’entre eux. La
plupart vous ont été fournis par votre fournisseur d’accès lorsque vous
avez ouvert votre compte.
5. 3Com vous conseille de conserver l’adresse IP du routeur sur le LAN par
défaut (192.168.1.1). Si vous choisissez de la modifier, notez soigneusement la nouvelle adresse :
6. Sur la page Paramètres du serveur DHCP, vérifiez que l’option Activer le
serveur DHCP est sélectionné, avec les paramètres suivants.
Une fois l’assistant terminé, essayez de consulter une page web, par exemple
www.3com.com. Si vous accédez au site, l’ordinateur, le routeur et le
modem câble/DSL sont correctement configurés.
Si vous ne parvenez pas à établir le contact avec le routeur ou Internet,
reportez-vous au chapitre Résolution des problèmes.
Adresse IP du routeur sur le LAN _______._______._______._______
Connexion à Internet
Page 36

Connexion au LAN sans fil
34
5. CONNEXION AU LAN SANS FIL
1. Une fois la configuration par l’ordinateur câblé terminée, connectez-vous
au routeur par un ordinateur sans fil.
Le routeur et les clients sans fil doivent posséder le même SSID et les
mêmes paramètres de chiffrement. Tous les clients sans fil doivent employer le mode Infrastructure.
Par défaut, les paramètres sans fil du routeur sont :
2. Si vous n’avez pas encore de réseau sans fil, ces paramètres par défaut
sont acceptables. Vérifiez que vos clients sans fil sont paramétrés avec les
valeurs de SSID, canal et WEP ci-dessus.
Si vous disposez déjà d’un réseau sans fil, configurez le routeur en fonction des valeurs de SSID et WEP utilisées sur le réseau existant.
3. Si votre ordinateur est équipé d’une carte réseau filaire et d’une carte
réseau sans fil, vérifiez qu’une seule carte est utilisée pour communiquer
avec le LAN. Pour utiliser la carte sans fil, débranchez le câble Ethernet et
redémarrez votre ordinateur.
4. Lancez votre navigateur web et essayez de consulter une page web,
www.3com.com, par exemple. Si vous pouvez accéder à ce site, votre
ordinateur sans fil, le routeur et le modem câble/DSL sont correctement
configurés.
5. 3Com vous conseille fortement d’activer le chiffrement WPA pour renforcer
la sécurité de vos transmissions sans fil et de ne pas conserver le SSID par
défaut. Consultez l’aide en ligne ou le Guide de l’utilisateur pour plus de
détails.
SSID : 3Com Channel 11 Chiffrement désactivé.
SSID ______________________________
Numéro de canal ______________________________
Page 37

35
Résolution des problèmes
F
RÉSOLUTION DES PROBLÈMES
Si vous rencontrez des problèmes lors de l’installation :
• vérifiez que tous les équipements du réseau sont sous tension. La
LED Power du routeur doit être allumée (verte). Dans le cas contraire, vérifiez le branchement de l’adaptateur secteur. Utilisez exclusivement l’adaptateur secteur fourni avec votre routeur.
• vérifiez que le modem câble/DSL est correctement branché. La LED
Cable/DSL doit être allumée (verte ou jaune). Dans le cas contraire, vérifiez
que le modem est sous tension et qu’il est connecté au port Cable/DSL
par un câble Ethernet.
• vérifiez que l’ordinateur est connecté au routeur. La LED LAN Status
du routeur doit être allumée (verte ou jaune). Dans le cas contraire, vérifiez que l’ordinateur est connecté à l’un des ports LAN du routeur par un
câble Ethernet.
• vérifiez qu’aucun proxy n’est activé sur votre ordinateur. Ouvrez le
Panneau de configuration et cliquez sur Options Internet. Cliquez sur l’onglet Connexions puis sur le bouton Paramètres réseau, en bas de la
fenêtre. Assurez-vous que la case Utiliser un serveur Proxy n’est pas
cochée.
• si vous ne parvenez pas à accéder à l’interface web du routeur.
Lancez votre navigateur et tapez http://192.168.1.1 ou l’adresse IP que
vous avez vous-même définie. N’oubliez pas le préfixe http://.
• si la LED Power (en face avant) ou la LED OK (en face arrière) n’est
pas allumée, reportez-vous au tableau.
LED OK LED Power Problème et remède
Allumée Allumée Tout fonctionne correctement.
Allumée Eteinte L’alimentation interne est défectueuse. Contactez le
support technique 3Com et demandez un échange
standard du routeur.
Eteinte Eteinte L’adaptateur est défectueux ou mal branché.
Vérifiez vos branchements. Si le problème persiste,
contactez le support technique 3Com et demandez
un échange standard de l’adaptateur.
Page 38

• Chez certains câblo-opérateurs, l’authentification s’effectue par l’adresse
MAC de l’ordinateur. Dans ce cas, ouvrez le menu Paramètres Internet et
sélectionnez l’option Cloner l’adresse MAC. L’adresse MAC de l’ordinateur
sera copiée sur le port Internet du routeur.
• Pour d’autres, l’authentification dépend du nom d’hôte de l’utilisateur.
Dans ce cas, ouvrez le menu Paramètres Internet et tapez le nom d’hôte
de votre ordinateur dans le champ Nom de l’hôte.
• Si vous disposez d’une ligne DSL et qu’un client PPPoE ou PPTP est déjà
installé sur l’ordinateur, désactivez ce client. Reportez-vous au chapitre 2.
• Si votre ligne DSL emploie PPPoE ou PPTP, ouvrez le menu Paramètres
Internet et vérifiez le mode d’affectation de l’adresse IP retenu, votre nom
d’utilisateur et votre mot de passe.
• Selon le fournisseur, votre ligne DSL peut nécessiter l’utilisation d’un nom
de service PPPoE. Au besoin, ouvrez le menu Paramètres Internet et tapez
le nom de service PPPoE dans le champ correspondant. Autrement, laissez
ce champ vierge.
Si vous ne parvenez pas à accéder au réseau sans fil :
• Vérifiez que le client sans fil est paramétré en mode infrastructure.
• Si l’ordinateur est équipé d’une carte réseau filaire et d’une carte réseau sans
fil, vérifiez que la carte filaire est désactivée. Reportez-vous au chapitre 5.
• Vérifiez que le SSID du client sans fil est identique à celui du routeur.
• Vérifiez que la LED WLAN du routeur est allumé. Dans le cas contraire,
allez dans le menu Paramètres sans fil et activez la case Réseau sans fil.
• Vérifiez que les paramètres de chiffrement du client sans fil sont identiques à ceux du routeur. En cas de problème, désactivez le chiffrement
des transmissions sans fil sur le client et sur le routeur jusqu’à ce que la
connexion sans fil soit établie.
Résolution des problèmes
36
Connexion Internet
par câble
Connexion Internet
par DSL
Configuration sans fil
Page 39

37
Introduzione
INTRODUZIONE
Nel presente manuale sono illustrati i passaggi fondamentali per installare e
configurare il prodotto OfficeConnect Wireless 54 Mbps/108 Mbps 11g
Cable/DSL Router e per stabilire una connessione a Internet con il proprio computer. Nel seguito del manuale il prodotto OfficeConnect Wireless 54 Mbps/
108 Mbps 11g Cable/DSL Router verrà chiamato semplicemente il router.
• Un router OfficeConnect Wireless 54 Mbps/108 Mbps 11g Cable/DSL
• Un adattatore di corrente da utilizzare con il router
• Quattro piedini di gomma
• Un cavo Ethernet
• Un CD-ROM contenente la Guida rapida all’installazione e la Guida dell’utente
• La presente Guida all’installazione
• Una scheda con le informazioni per l’assistenza e la sicurezza
• La scheda di garanzia
• Note di rilascio
• Scheda della gamma di prodotti
Prima di iniziare, accertarsi che le seguenti condizioni siano soddisfatte.
• Si deve disporre di una connessione a Internet a banda larga funzionante
(via cavo o DSL) tramite un modem idoneo. Il modem deve avere una
porta Ethernet per la connessione al router.
• Il computer deve disporre di una connessione Ethernet ed essere correttamente configurato per le comunicazioni su Internet. Sul computer, che
deve essere in grado di connettersi a Internet, è necessario che sia installato un browser Web.
• Sulla rete locale non devono essere presenti altri server DHCP per l’assegnazione degli indirizzi IP a computer e altre periferiche collegate alla rete.
Per impostazione predefinita, è il router a svolgere questa funzione.
Se anche una sola di queste condizioni non è soddisfatta, consultare la Guida dell’utente del router, disponibile sul CD-ROM, per maggiori informazioni.
Informazioni su questo
manuale:
La confezione contiene:
Requisiti di sistema
I
Page 40

Dimensioni e standard
38
DIMENSIONI E STANDARD
Funzionamento: ISO 8802/3, IEEE802.3, IEEE802.11b, 802.11g
Sicurezza: UL60950, CSA22.2 #60950, IEC 60950, EN 60950
Compatibilità EN 55022 Classe B, EN55024, CISPR 22, FCC sezione 15
elettromagnetica: Classe B* ICES-003 Classe B, ETSI EN 301 489-17
Onde radio: CFR 47 FCC sezioni 15.207, 15.209, 15.247 e 15.249.
ETS 300 328 (sistemi di trasmissione a banda larga nella
banda ISM 2,4 GHz), RSS-210
Ambientali: EN 60068, IEC 68
* Fare riferimento alla sezione sulle conformità normative contenuta nella scheda delle
informazioni per l’assistenza e la sicurezza
ATTENZIONE: prima di iniziare, leggere la sezione ‘Informazioni di
sicurezza importanti’ (Important Safety Information) contenuta nella
scheda delle informazioni per l’assistenza e la sicurezza.
WARNING: Please read the ‘Important Safety Information’ section in
the Support and Safety Information sheet before you start.
VORSICHT: Bitte lesen Sie den Abschnitt ‚Wichtige
Sicherheitsinformationen’ sorgfältig durch, bevor Sie das Gerät einschalten.
AVERTISSEMENT: Veuillez lire attentivement la section « Consignes
importantes de sécurité » avant de mettre en route.
Utilizzare i quattro piedini di gomma autoadesivi per impedire che il router si
sposti quando è appoggiato sul piano di lavoro o quando viene impilato
insieme ad altre unità OfficeConnect. Applicare i piedini alle zone contrassegnate, poste ai quattro angoli del fondo del router.
Standard
Dimensioni
Uso dei piedini di
gomma
Informazioni sulla
sicurezza
Requisiti elettrici:
7 VA, 23,9 BTU/ora
224.8 mm
(8.8 in.)
Temperatura di
funzionamento:
da 0º C a 40º C
Umidità (senza
condensazione):
da 0 a 90%
41.5 mm
(1.6 in.)
OfficeConnect Wireless 54 Mbps/108 Mbps
11g Cable/DSL Router 592 g(1.3lb)
Page 41

39
Collocazione del router
I
COLLOCAZIONE DEL ROUTER
Quando si sceglie una posizione per il router, assicurarsi che vengano soddisfatte le condizioni seguenti.
• Collocare l’unità al centro rispetto ai sistemi wireless che si connetteranno
al router. Una collocazione ideale per ottimizzare le comunicazioni wireless
sia in senso orizzontale che verticale e garantire la massima copertura,
potrebbe essere il ripiano alto di una scaffalatura (o mobile simile).
• In conformità alle normative sull’esposizione alle radiazioni FCC, il router
deve essere collocato ad una distanza minima di 20 cm dal personale (per
maggiori informazioni, consultare la Guida dell’utente).
• Evitare l’esposizione alla luce diretta del sole e tenerlo lontano da fonti di
calore.
• Tenere i cavi a debita distanza da fili elettrici, apparecchi a luce fluorescente e fonti di rumore elettrico quali radio, trasmettitori e amplificatori a
banda larga.
• Evitare che acqua e umidità penetrino all’interno dell’unità.
• Non ostruire la circolazione dell’aria attorno all’unità e attraverso le fessure
di ventilazione poste ai lati dell’unità. Si consiglia di lasciare uno spazio di
almeno 25 mm.
Page 42

Informazioni sul router
40
INFORMAZIONI SUL ROUTER
1. Spia Alert Arancione
Indica le varie condizioni descritte di seguito.
Spenta: il router funziona normalmente.
Lampeggio rapido: indica una delle condizioni seguenti:
• Il router è stato appena avviato e sta eseguendo un test di autodiagnostica, oppure
• L’amministratore ha richiamato il comando Reset to Factory Defaults, oppure
• È in corso l’aggiornamento del software del sistema
In ciascuno di questi casi, è necessario attendere che il router abbia completato l’operazione in corso
perché la spia Alert si spenga.
Lampeggio lento: il router ha completato il processo di ripristino delle impostazioni predefinite (comando
Reset to Factory Defaults) ed è in attesa che l’utente esegua il reset dell’unità. A questo scopo, scollegare
l’alimentazione, attendere 10 secondi e quindi ricollegare l’alimentazione. A questo punto il router
rieseguirà la sequenza di avvio e riprenderà la normale attività.
Accesa per 2 secondi, quindi spenta: il router ha identificato e bloccato un attacco alla rete locale da
parte di un hacker.
Sempre accesa: è stato rilevato un problema del router durante il processo di avvio. Fare riferimento alla
Guida dell’utente.
2. Spia Power Verde
Indica che il router è acceso.
3. Spia di stato WLAN (rete wireless) Gialla
Se la spia è accesa, la rete wireless è attiva. Se lampeggia, è in corso la trasmissione o la ricezione dei
dati. Se è spenta, la rete wireless è disattivata nel router o si è verificato un problema. Consultare la
sezione “Risoluzione dei problemi”.
4. Quattro spie di stato della rete Verdi (connessione a 100 Mbps) / Gialle (connessione a 10 Mbps)
Se la spia è accesa, la connessione tra la porta e il dispositivo di rete successivo è funzionante. Se lampeggia,
OfficeConnect Wireless 54 Mbps/108 Mbps 11g Cable/DSL Router - anteriore.
1
2
3
5 4
Page 43

41
Informazioni sul router
I
la connessione è funzionante ed è in corso la trasmissione o la ricezione dei dati. Se la spia è spenta, non vi
sono dispositivi collegati, i dispositivi collegati sono spenti oppure vi sono problemi di connessione (consultare la sezione “Risoluzione dei problemi”). La velocità e la modalità duplex della porta si regolano
automaticamente sul valore più corretto.
5. Spia di stato Cable/DSL Verde (connessione a 100 Mbps) / Gialla (connessione a 10 Mbps)
Se la spia è accesa, la connessione tra router e modem via cavo/DSL è funzionante. Se lampeggia, la connessione è funzionante ed è in corso la trasmissione o la ricezione dei dati. Se è spenta, non vi sono dispositivi collegati, il modem è spento oppure si è verificato un problema (consultare la sezione “Risoluzione
dei problemi”).
6. Antenne wireless
Le antenne del prodotto devono assumere una posizione a “V” alla prima installazione.
ATTENZIONE: non forzare le antenne oltre i rispettivi punti di arresto. Se ruotate oltre questa posizione,
le antenne potrebbero danneggiarsi.
7. Presa dell’adattatore di corrente
Utilizzare solo l’adattatore di corrente fornito con il router. Non utilizzare adattatori di altro tipo.
8. Spia OK dell’adattatore di corrente Verde
Indica che l’adattatore sta erogando corrente al router. Se la spia è spenta, l’adattatore o il cavo dell’adattatore potrebbero avere problemi.
9. Porta Ethernet Cable/DSL
Utilizzare il cavo fornito per collegare il router alla porta Ethernet del modem via cavo/DSL. La velocità e la
modalità duplex della porta si regolano automaticamente. La porta verrà impostata automaticamente su
MDI o MDIX a seconda del dispositivo collegato e del tipo di cavo utilizzato.
10. Quattro porte LAN 10/100
Utilizzando cavi RJ-45 idonei, è possibile collegare il router a un computer o ad altri dispositivi che dispongono di connessione Ethernet (ad esempio, un hub o uno switch). Le porte LAN verranno impostate automaticamente su MDI o MDIX a seconda del dispositivo collegato e del tipo di cavo utilizzato.
11. Pulsante Reset
Premere il pulsante Reset per 5 secondi, quindi rilasciarlo. Tutte le impostazioni del router OfficeConnect
Wireless 54 Mbps/108 Mbps 11g Cable/DSL verranno riportate alle loro condizioni originali.
OfficeConnect Wireless 54 Mbps/108 Mbps 11g Cable/DSL Router - posteriore.
6 6
911 7 810
Page 44

Installazione del router
42
1. INSTALLAZIONE DEL ROUTER
1. Collegare l’adattatore di corrente al router e attendere che la spia Alert
smetta di lampeggiare.
2. Controllare che il modem e il computer siano accesi.
3. Inserire un’estremità del cavo Ethernet in dotazione (RJ-45 livello 5) nella
porta Cable/DSL sul retro del router.
4. Inserire l’altra estremità del cavo nella porta RJ-45 del modem via
cavo/DSL. Controllare che sul router sia accesa la spia di stato Cable/DSL.
5. Connettere il modem via cavo/DSL a Internet.
6. Collegare il computer a una delle quattro porte LAN disponibili sul router
utilizzando un cavo Ethernet. Controllare che sul router sia accesa la
rispettiva spia di stato LAN.
Affinché il router possa essere condiviso tra più di quattro utenti, è necessario
utilizzare un ulteriore hub o switch. Collegare una porta LAN del router all’hub
o allo switch, ad esempio a un’unità OfficeConnect Dual Speed Switch 8.
Connessione del router
Connessione a un hub o
uno switch
Figura 1. Esempio di rete con 3Com OfficeConnect Wireless 54 Mbps/108 Mbps 11g
Cable/DSL Router
Alimentazione
3Com OfficeConnect Wireless
54Mbps/108Mbps 11g Cable/DSL Router
Modem via cavo/DSL
esistente
Internet
Utenti wireless
Computer
Page 45

43
Modifica della configurazione del computer
I
2. MODIFICA DELLA CONFIGURAZIONE DEL COMPUTER
Potrebbe essere necessario apportare alcune modifiche alla configurazione dei
computer per stabilire la comunicazione con il router.
Se si hanno applicazioni client PPPoE o PPTP installate sul computer, potrebbe
essere necessario disattivarle. A questo scopo:
1. Dal menu di avvio di Windows, scegliere Impostazioni > Pannello di controllo.
2. Fare doppio clic su Opzioni Internet.
3. Selezionare la scheda Connessioni. Viene visualizzata una schermata simile
a quella riportata nella Figura 2.
4. Selezionare l’opzione Non utilizzare mai connessioni remote e scegliere OK.
Poiché il client PPPoE non è necessario per utilizzare il router, potrebbe
essere utile rimuoverlo dal computer per liberare risorse.
Attenersi alle istruzioni seguenti per il sistema operativo in uso per fare in modo
che al proprio computer venga assegnato automaticamente un indirizzo IP.
Per computer che utilizzano Windows XP.
1. Dal menu di avvio di Windows, scegliere Pannello di controllo.
2. Fare clic su Rete e connessioni Internet.
3. Fare clic sull’icona Connessioni di rete.
4. Fare doppio clic sull’icona LAN o Internet ad alta velocità. Viene visualizza-
ta la schermata Stato di connessione alla rete locale.
5. Selezionare Protocollo Internet (TCP/IP) e fare clic su Proprietà.
6. Verificare che le opzioni Ottieni automaticamente un indirizzo IP e Ottieni
indirizzo server DNS automaticamente siano entrambe selezionate come
mostrato nella Figura 4. Scegliere OK.
7. Riavviare il computer.
Per computer che utilizzano Windows 2000.
1. Dal menu di avvio di Windows, scegliere Impostazioni > Pannello di controllo.
2. Fare doppio clic su Rete e connessioni remote.
3. Fare doppio clic su Connessione alla rete locale (LAN).
4. Fare clic su Proprietà.
5. Viene visualizzata una schermata simile a quella riportata nella Figura 3.
Selezionare Protocollo Internet (TCP/IP) e fare clic su Proprietà.
6. Verificare che le opzioni Ottieni automaticamente un indirizzo IP e Ottieni
indirizzo server DNS automaticamente
siano entrambe selezionate come
mostrato nella Figura 4. Scegliere OK.
7. Riavviare il computer.
Come ottenere
un indirizzo IP
automaticamente
Utenti DSL con client
PPPoE o PPTP
Figura 3
Figura 2
Page 46

Metodi di connessione all’ISP
44
Per computer che utilizzano Windows 95, 98 e ME.
1. Dal menu di avvio di Windows, scegliere Impostazioni > Pannello di controllo.
2. Fare doppio clic su Rete. Selezionare la voce TCP/IP per la scheda di rete in
uso come mostrato nella Figura 5 e fare clic su Proprietà.
3. Nella finestra di dialogo TCP/IP, selezionare la scheda Indirizzo IP e control-
lare che sia selezionata l’opzione Ottieni automaticamente un indirizzo IP
come mostrato nella Figura 6. Scegliere OK.
4. Riavviare il computer.
3. METODI DI CONNESSIONE ALL’ISP
Prima di poter configurare il router, occorre conoscere il metodo di assegnazione degli indirizzi IP utilizzato dal proprio ISP. Esistono quattro modi distinti con cui gli ISP assegnano gli indirizzi IP, come illustrato qui di seguito.
1. Indirizzo IP dinamico (connessioni DSL o via cavo)
Tramite il protocollo DHCP le informazioni IP del router sono assegnate
automaticamente. Questo metodo è molto diffuso tra gli ISP che forniscono connessioni via cavo e viene utilizzato quando il modem dispone
di un server DHCP integrato.
2. PPPoE (solo connessioni DSL)
Selezionare questa opzione se le istruzioni di installazione fornite con il
modem richiedono l’installazione di un client PPPoE sul computer da configurare. Si sottolinea che per installare il router non è necessario utilizzare
un client PPPoE sul computer. Per configurare il router è necessario
conoscere nome utente, password e nome di servizio (se richiesto dall’ISP).
3. Indirizzo IP statico (connessioni DSL o via cavo)
Il provider ISP fornisce informazioni sull’indirizzo IP da immettere manualmente. Per configurare il router è necessario conoscere indirizzo IP, subnet
mask, indirizzo del router presso l’ISP e indirizzi DNS.
Figura 5
Figura 6
Figura 4
Page 47

45
Procedura di installazione guidata (Setup Wizard)
I
4. PPTP (connessioni DSL o via cavo)
Il protocollo PPTP è utilizzato soltanto da alcuni provider europei.
Selezionare questa opzione se le istruzioni di installazione fornite con il
modem richiedono la configurazione di una connessione di accesso remoto tramite un tunnel VPN con protocollo PPTP. Si sottolinea che per installare il router non è necessario utilizzare la rete VPN di accesso remoto sul
computer. Per configurare il router è necessario conoscere nome utente,
password, nome di servizio (se richiesto dall’ISP) e indirizzo del server VPN
(in genere il modem in uso).
Il metodo di assegnazione degli indirizzi IP verrà richiesto durante la procedura di installazione guidata.
4. PROCEDURA DI INSTALLAZIONE GUIDATA (SETUP WIZARD)
1. Se non è già stato fatto, riavviare il computer.
2. Avviare il browser Web e provare a contattare il router digitando l’URL
seguente nella barra degli indirizzi: http://192.168.1.1.
Se viene visualizzata la pagina Login, il computer ha ricevuto corretta-
mente l’indirizzo IP dal router.
3. Eseguire l’accesso utilizzando la password predefinita, admin. La procedu-
ra guidata prova ad avviarsi automaticamente. Nel caso in cui non venga
avviata, selezionare la scheda Wizard e fare clic sul pulsante Wizard.
4. Se possibile, la procedura guidata suggerisce le impostazioni per gran
parte dei parametri. Tuttavia alcune opzioni devono essere impostate dall’utente. In genere queste opzioni sono fornite dal provider ISP quando si
imposta il proprio account.
5. 3Com consiglia di mantenere per il router l’indirizzo IP di rete predefinito,
ovvero 192.168.1.1. Se invece si decide di modificarlo, prendere nota del
nuovo indirizzo:
6. Quando viene visualizzata la pagina DHCP Server Settings, controllare che
sia selezionata l’opzione Enable the DHCP Server with the following settings.
Al termine della procedura guidata, provare ad aprire un sito Web su Internet,
ad esempio www.3com.com. Se si riesce ad accedere al sito, significa che il
computer, il router e il modem via cavo/DSL sono stati configurati correttamente.
Se non si riesce a comunicare con il router o a connettersi a Internet, consultare la sezione Risoluzione dei problemi.
Indirizzo IP di rete del router _______._______._______._______
Connessione a Internet
Page 48

46
Connessione alla rete locale wireless
5. CONNESSIONE ALLA RETE LOCALE WIRELESS
1. Dopo aver configurato il router tramite il computer cablato, è possibile
effettuare la connessione al router dei computer wireless.
Il router e i client wireless devono condividere lo stesso SSID e le stesse
impostazioni per quanto riguarda la cifratura. Tutti i client wireless devono
utilizzare la stessa modalità Infrastructure.
Le impostazioni wireless predefinite per il Router sono le seguenti:
2. Se non si utilizza una rete locale wireless, è possibile utilizzare le
impostazioni predefinite del router. Verificare che i valori di SSID, Channel
ed Encryption siano impostati come indicato in precedenza.
Per rendere compatibile il router con un’eventuale rete locale wireless
preesistente, impostare i medesimi valori per SSID ed Encryption.
3. Se sul computer sono installate schede di rete sia cablate che wireless, è
necessario fare in modo che solo una scheda venga utilizzata per comunicare con la rete locale. Per utilizzare una scheda di rete wireless, disconnettere il cavo Ethernet e riavviare il computer.
4. Avviare il browser Web e provare ad aprire un sito Web su Internet, ad
esempio www.3com.com. Se si riesce ad accedere al sito, significa che il
computer wireless, il router e il modem via cavo/DSL sono stati configurati
correttamente.
5. 3Com consiglia vivamente di abilitare la cifratura WPA per potenziare la
sicurezza della rete wireless e di cambiare l’SSID utilizzando un valore
diverso da quello predefinito. Consultare la Guida in linea o la Guida dell’utente per ulteriori informazioni.
Service Area Name/SSID: 3COM Channel: 11 Encryption: Off
Service Area Name/SSID ______________________________
Channel Number ______________________________
Page 49

47
Risoluzione dei problemi
I
RISOLUZIONE DEI PROBLEMI
In caso di difficoltà durante l’installazione, provare le seguenti soluzioni:
• Controllare che tutti i dispositivi collegati alla rete siano accesi. La
spia Power del router deve essere illuminata (colore verde). In caso contrario, controllare la connessione dell’adattatore di corrente. Non utilizzare
un adattatore di corrente diverso da quello fornito con il router.
• Controllare che il modem via cavo/DSL sia collegato. La spia di stato
Cable/DSL del router deve presentare una luce verde o gialla. Se la spia
non è illuminata, verificare che il modem sia acceso e che sia connesso alla
porta Cable/DSL tramite un cavo Ethernet.
• Controllare che il computer sia connesso al router. La spia di stato
LAN del router deve presentare una luce verde o gialla. In caso contrario,
verificare che il computer sia connesso a una delle porte LAN del router
tramite un cavo Ethernet.
• Controllare di non avere un proxy Web attivo sul proprio computer.
Andare al Pannello di controllo e fare clic su Opzioni Internet. Selezionare
la scheda Connessioni e fare clic sul pulsante Impostazioni LAN in fondo
alla schermata. Controllare che l’opzione Usa server proxy sia deselezionata.
• Se non si riesce ad accedere all’interfaccia Web del router. Avviare il
browser Web e digitare http://192.168.1.1. Se si è scelto un indirizzo IP
diverso, utilizzare quello nuovo. Assicurarsi di includere http:// come prefisso.
• Se la spia Power o la spia OK dell’adattatore di corrente non sono
illuminate, fare riferimento alla tabella.
Spia OK
dell’adattatore
di corrente Spia Power Problema e azione correttiva
On On Tutto funziona correttamente.
On Off Problema dell’alimentatore interno. Contattare
l’Assistenza Tecnica 3Com per richiedere un router
sostitutivo.
Off Off Guasto dell’adattatore di corrente o della relativa
connessione. Verificare le connessioni dell’adattatore. Se il problema persiste, contattare l’Assistenza
Tecnica 3Com e richiedere un adattatore di corrente
sostitutivo.
Page 50

Risoluzione dei problemi
48
• Alcuni provider di connessioni via cavo eseguono l’autenticazione dell’indirizzo MAC dei computer degli utenti. Se è richiesta questa autenticazione,
scegliere Impostazioni Internet e selezionare Duplica indirizzo MAC. In
questo modo l’indirizzo MAC del computer verrà copiato sulla porta
Internet del router.
• Alcuni provider di connessioni via cavo eseguono l’autenticazione del
nome host degli utenti. Se è richiesta questa autenticazione, scegliere
Impostazioni Internet e immettere il nome host del computer in uso nel
campo Nome host.
• Se si dispone di una linea DSL esistente e si hanno client PPPoE o PPTP
installati sul computer, potrebbe essere necessario disattivarli. Fare riferimento alla sezione 2.
• Se la linea DSL in uso si basa sui protocolli PPPoE o PPTP, scegliere
Impostazioni Internet e controllare che sia selezionata la modalità corretta
di assegnazione degli indirizzi IP. Controllare la correttezza di nome utente
e password.
• Alcuni provider di connessioni DSL richiedono l’uso di un nome di servizio
PPPoE. Se è richiesta questa autenticazione, andare a Impostazioni Internet
e immettere il nome di servizio PPPoE nel campo opportuno. Se non è
richiesta, lasciare vuoto il campo.
Se non si riesce ad accedere alla rete wireless:
• Controllare che il client wireless sia in modalità Infrastructure.
• Se si hanno schede di rete cablate e wireless installate sullo stesso computer, assicurarsi che la scheda cablata sia disattivata. Per ulteriori informazioni, fare riferimento alla sezione 5.
• Controllare che il Service Area Name (SSID) sia il medesimo per il client
wireless e il router.
• Controllare che la spia WLAN del router sia accesa. In caso contrario,
andare al menu Wireless Settings e selezionare l’opzione Wireless
Networking.
• Controllare che le impostazioni di cifratura siano le medesime per il client
wireless e il router. In caso di problemi, disattivare la cifratura wireless del
client e del router fino a quando non si è stabilita una connessione wireless.
Connessioni a
Internet via cavo
Connessioni
DSL a Internet
Configurazione wireless
Page 51

49
Einführung
EINFÜHRUNG
Diese Anleitung führt Sie durch die grundlegenden Schritte zur Installation
und Konfiguration des OfficeConnect Wireless 54 Mbps/108 Mbps 11g
Cable/DSL Routers. Außerdem wird hier beschrieben, wie Sie eine Verbindung
Ihrer Computer zum Internet herstellen. In dieser Anleitung wird der
OfficeConnect Wireless 54 Mbps/108 Mbps 11g Cable/DSL Router der
Einfachheit halber nur als Router bezeichnet.
• OfficeConnect Wireless 54 Mbps/108 Mbps 11g Cable/DSL Router
• Netzteil zur Verwendung mit dem Router
• Vier Gummifüße
• Ethernet-Kabel
• CD-ROM auf der sich die Kurzinstallationsanleitung und die
Bedienungsanleitung befindet
• Installationsanleitung
• Informationsblatt zu Support und Sicherheit
• Garantiekarte
• Informationsblatt mit Hinweisen zur Software (Release Notes)
• Informationsblatt Produktpalette
Vor Beginn der Installation müssen Sie erst prüfen, ob Folgendes gewährleistet ist:
• Eine funktionierende Kabel- oder DSL-Breitbandverbindung zum Internet
über ein geeignetes Modem wurde bereits hergestellt. Das Modem muss
über einen Ethernet-Port für den Anschluss an den Router verfügen.
• Ihr Computer verfügt über eine Ethernet-Verbindung und ist bereits richtig
für die Kommunikation mit dem Internet konfiguriert. Der Computer muss
über das Modem eine Verbindung zum Internet herstellen können. Sie
müssen einen Webbrowser installiert haben.
• In Ihrem lokalen Netzwerk gibt es keine weiteren DHCPServerkomponenten, die Ihren Computern und anderen Netzwerkgeräten
IP-Adressen zuweisen. Der Router führt diese Funktion jetzt standardmäßig aus.
Falls mindestens eine dieser Bedingungen nicht erfüllt ist, lesen Sie die ausführliche Bedienungsanleitung des Routers auf der mitgelieferten CD-ROM
für weitere Anweisungen.
Informationen zu
diesem Handbuch:
Lieferumfang:
Systemanforderungen
D
Page 52

Abmessungen und Standards
50
ABMESSUNGEN UND STANDARDS
Funktionalität: ISO 8802/3, IEEE802.3, IEEE802.11b, 802.11g
Sicherheit: UL60950, CSA22.2 #60950, IEC 60950, EN 60950
EMV: EN 55022 Klasse B, EN55024, CISPR 22, FCC Teil 15 Klasse B*
ICES-003 Klasse B, ETSI EN 301 489-17
Funk: CFR 47 FCC Teile 15.207, 15.209, 15.247 und 15.249.
ETS 300 328 (Übertragungssysteme mit einer ISM-Bandbreite
von 2,4 GHz), RSS-210
Umgebungsbedingungen: EN 60068 (IEC 68)
* Lesen Sie den Abschnitt über die gesetzlichen Regelungen im Informationsblatt zu
Support und Sicherheit
WARNING: Please read the ‘Important Safety Information’ section in
the Support and Safety Information sheet before you start.
VORSICHT: Bitte lesen Sie den Abschnitt „Wichtige
Sicherheitsinformationen“ sorgfältig durch, bevor Sie das Gerät in
Betrieb nehmen.
AVERTISSEMENT: Veuillez lire attentivement la section "Consignes
importantes de sécurité" avant de mettre en route.
Verwenden Sie die vier selbstklebenden Gummifüße, um zu verhindern, dass
der Router auf dem Schreibtisch verrutscht oder wenn er auf andere flache
OfficeConnect-Geräte gestellt wird. Kleben Sie die Füße nur auf die
markierten Stellen an den vier Ecken auf der Unterseite des Routers.
Standards
Abmessungen
Verwendung der
Gummifüße
Sicherheitsinformationen
Spannungsversorgung
7 VA, 23,9 BTU/hr
Betriebstemperatur
0 °C bis 40 ºC
41.5 mm
(1.6 in.)
224.8 mm
(8.8 in.)
0 % bis 90 % (nicht
kondensierend)
OfficeConnect Wireless 54 Mbps/108 Mbps
11g Cable/DSL Router 592 g(1.3lb)
Page 53

51
Aufstellen des Routers
D
AUFSTELLEN DES ROUTERS
Beachten Sie beim Aufstellen des Routers folgende Hinweise:
• Das Gerät sollte zentral zwischen den drahtlosen Computern aufgestellt
werden, die mit dem Router verbunden werden sollen. Ein geeigneter
Aufstellort wäre auf einem hohen Regal oder einem ähnlichen
Möbelstück. Dadurch lässt sich eine optimale drahtlose Verbindung zwischen den Computern in horizontaler und vertikaler Richtung erreichen, die
eine vollständige Abdeckung ermöglicht.
• Zur Erfüllung der FCC-Richtlinien zur Strahlungsemission sollte beim
Aufstellort des Router mindestens 20 cm Abstand zu Personen eingehalten werden. (Einzelheiten dazu können Sie dem Benutzerhandbuch entnehmen.)
• Setzen Sie den Router keiner direkten Sonnenbestrahlung aus, und stellen
Sie ihn nicht in die Nähe von Wärmequellen.
• Die Verkabelung darf nicht entlang von Stromleitungen, LeuchtstoffLampen und elektrischen Störquellen wie Radiogeräten, Sendern und
Breitbandverstärkern verlaufen.
• Es dürfen weder Wasser noch Feuchtigkeit in das Gerätegehäuse gelangen.
• Die Luftzirkulation rund um das Gerät und durch die Belüftungsöffnungen
seitlich am Gerät darf nicht behindert werden. Rund um das Gerät sollte
ein Freiraum von mindestens 25 mm eingehalten werden.
Page 54

Erläuterung des Routers
52
ERLÄUTERUNG DES ROUTERS
1. Alert-LED Orange
Anzeige für verschiedene Betriebszustände, siehe nachfolgende Beschreibung.
Aus – Normaler Routerbetrieb.
Blinkt schnell – Anzeige für folgende Betriebszustände:
• Der Router wurde gerade gestartet und durchläuft einen Selbsttest, oder
• Der Administrator hat den Befehl zum Zurücksetzen auf die Standardeinstellungen ausgegeben, oder
• Die Systemsoftware wird gerade aktualisiert
Warten Sie, bis der Router den gerade ausgeführten Vorgang beendet hat und die Alert-LED erlischt.
Blinkt langsam – Der Router hat das Zurücksetzen auf die Standardeinstellungen beendet und wartet
darauf, dass Sie das Gerät zurücksetzen. Trennen Sie dazu die Stromversorgung 10 Sekunden lang. Der
Router ruft dann die Startsequenz auf und nimmt den normalen Betrieb wieder auf.
Leuchtet 2 Sekunden, erlischt dann – Der Router hat einen Hacker erkannt und einen Angriff auf Ihr
Netzwerk über das Internet verhindert.
Leuchtet ständig – Ein Router-Fehler wurde während des Startvorgangs ermittelt. Lesen Sie in der
Bedienungsanleitung nach.
2. Power-LED Grün
Anzeige, dass der Router eingeschaltet ist
3. Wireless LAN (WLAN) Status-LED Gelb
Wenn die LED leuchtet, wurde der drahtlose Netzwerkbetrieb aktiviert. Wenn die LED blinkt, werden
Daten gesendet oder empfangen. Wenn die LED nicht leuchtet, wurde das drahtlose LAN im Router
deaktiviert, oder es ist ein Problem aufgetreten. Lesen Sie dazu den Abschnitt „Problemlösung“.
4. Vier LAN Status-LEDs Grün (100 Mbps Verbindung) / Gelb (10 Mbps Verbindung)
Wenn die LED leuchtet, besteht eine Verbindung zwischen dem Port und dem damit verbundenen
Netzwerkgerät. Wenn die LED blinkt, ist die Verbindung hergestellt, und es werden Daten gesendet oder
empfangen. Wenn die LED nicht leuchtet, ist kein Gerät angeschlossen, das angeschlossene Gerät ausgeschaltet, oder es liegt ein Verbindungsproblem vor. (Lesen Sie dazu den Abschnitt „Problemlösung“.) Der
Port stellt sich automatisch auf die richtige Geschwindigkeit und den entsprechenden Duplexbetrieb ein.
OfficeConnect Wireless 54 Mbps/108 Mbps 11g Cable/DSL Router - Vorder.
1
2
3
5 4
Page 55

53
Erläuterung des Routers
D
5. Kabel/DSL Status-LEDs Grün (100 Mbps Verbindung) / Gelb (10 Mbps Verbindung)
Wenn die LED leuchtet, ist die Verbindung zwischen dem Router und dem Kabel- oder DSL-Modem
hergestellt. Wenn die LED blinkt, ist die Verbindung hergestellt, und es werden Daten gesendet oder
empfangen. Wenn die LED nicht leuchtet, ist kein Gerät angeschlossen, das Modem ausgeschaltet, oder
es ist ein Problem aufgetreten. (Lesen Sie dazu den Abschnitt „Problemlösung“.)
6. Funkantenne
Die Antenne am Gerät sollte bei der Erstinstallation senkrecht nach oben stehen.
ACHTUNG: Klappen Sie die Antenne nur bis zum Anschlag. Sie kann beschädigt werden, wenn sie
gewaltsam weiter ausgeklappt wird.
7. Netzadapterbuchse
Verwenden Sie nur das im Lieferumfang des Routers enthaltene Netzteil. Andere Netzteile dürfen nicht
verwendet werden.
8. OK-LED für Netzteil Grün
Anzeige, dass der Router vom Netzteil mit Strom versorgt wird. Wenn die LED nicht leuchtet, ist ein
Problem mit dem Netzteil oder dem Stromkabel aufgetreten.
9. Kabel/DSL Ethernet-Port
Schließen Sie den Router über das mitgelieferte Patchkabel an den Ethernet-Port am Kabel- oder DSLModem an. Der Port stellt sich automatisch auf die richtige Geschwindigkeit und den entsprechenden
Duplexbetrieb ein. Außerdem stellt er sich je nach dem Gerät, an das er angeschlossen ist, und dem verwendeten Kabeltyp automatisch auf MDI oder MDIX ein.
10. Vier 10/100 LAN-Ports
Mit Hilfe geeigneter RJ45-Kabel können Sie den Router an einen Computer oder ein anderes Gerät
anschließen, das über eine Ethernet-Verbindung verfügt (beispielsweise ein Hub oder ein Switch). Die
LAN-Ports stellen sich je nach dem Gerät, an das sie angeschlossen sind, und dem verwendeten Kabeltyp
automatisch auf MDI oder MDIX ein.
11. Reset-Taste
Die Reset-Taste wird für 5 Sekunden gedrückt und anschließend losgelassen. Alle Einstellungen des
OfficeConnect Wireless 54 Mbps/108 Mbps 11g Cable/DSL Router werden auf die werkseitigen
Standardeinstellungen zurückgesetzt.
OfficeConnect Wireless 54 Mbps/108 Mbps 11g Cable/DSL Router - Rückseite.
6 6
911 7 810
Page 56

Installation des Routers
54
1. INSTALLATION DES ROUTERS
1. Schließen Sie das Netzteil an den Router an, und warten Sie, bis die Alert-
LED zu blinken aufhört.
2. Achten Sie darauf, dass Modem und Computer eingeschaltet sind.
3. Schließen Sie ein Ende des mitgelieferten Ethernet-Kabels (RJ-45 Kategorie
5) an den Kabel-/DSL-Port an der Rückseite des Routers an.
4. Schließen Sie das andere Ende des Kabels an den RJ-45-Port am Kabeloder DSL-Modem an. Prüfen Sie, ob die Kabel/DSL Status-LED am Router
leuchtet.
5. Schließen Sie das Kabel- oder DSL-Modem an das Internet an.
6. Schließen Sie den Computer mit einem Ethernet-Kabel an einen der vier
LAN-Ports am Router an. Prüfen Sie, ob die entsprechende LAN Status-LED
am Router leuchtet.
Damit der Router von mehr als vier Anwendern gemeinsam genutzt werden
kann, benötigen Sie einen zusätzlichen Hub oder Switch. Verbinden Sie einen
LAN-Port des Routers mit dem Hub oder Switch, beispielsweise dem
OfficeConnect Dual Speed Switch 8.
Anschließen des Routers
Anschließen an einen
Hub oder Switch
Abbildung 1. Beispielnetzwerk mit OfficeConnect Wireless 54 Mbps/108 Mbps 11g
Cable/DSL Router.
Netzteil
3Com OfficeConnect Wireless
54Mbps/108Mbps 11g Cable/DSL Router
Vorhandenes
Kabel-/DSL-Modem
Internet
Drahtlose Anwender
PC
Page 57

55
Ändern der Computerkonfiguration
2. ÄNDERN DER COMPUTERKONFIGURATION
Um mit dem Router kommunizieren zu können, müssen Sie eventuell einige
Änderungen an der Konfiguration des Computers vornehmen.
Wenn Sie auf Ihrem Computer eine PPPoE- oder PPTP Client-Software installiert
haben, müssen Sie diese deaktivieren. Gehen Sie dazu folgendermaßen vor:
1. Wählen Sie unter Windows im Menü Start die Optionen Einstellungen >
Systemsteuerung.
2. Doppelklicken Sie auf Internetoptionen.
3. Wählen Sie die Registerkarte Verbindungen. Ein Bildschirm ähnlich
Abbildung 2 wird angezeigt.
4. Wählen Sie die Option Keine Verbindung wählen, und klicken Sie auf OK.
Sie können die PPPoE Client-Software vom Computer löschen, um
Ressourcen freizugeben, da Sie diese für den Router nicht benötigen.
Computer mit Windows XP.
1. Wählen Sie unter Windows im Menü Start die Option Systemsteuerung.
2. Klicken Sie auf Netzwerk- und Internetverbindungen.
3. Klicken Sie auf das Symbol Netzwerkverbindungen.
4. Doppelklicken Sie auf das Symbol LAN oder
Hochgeschwindigkeitsverbindung. Ein Bildschirm mit der Bezeichnung
LAN-Verbindungsstatus wird angezeigt.
5. Wählen Sie Internetprotokoll TCP/IP, und klicken Sie auf Eigenschaften.
6. Vergewissern Sie sich, dass die Optionen IP-Adresse automatisch beziehen
und DNS Server automatisch beziehen ausgewählt sind (siehe Abbildung
4). Klicken Sie auf OK.
7. Starten Sie den Computer neu.
Computer mit Windows 2000.
1. Wählen Sie unter Windows im Menü Start die Optionen Einstellungen >
Systemsteuerung.
2. Doppelklicken Sie auf Netzwerk- und DFÜ-Verbindungen.
3. Doppelklicken Sie auf LAN-Verbindung.
4. Klicken Sie auf Eigenschaften.
5. Ein Bildschirm ähnlich Abbildung 3 wird angezeigt. Wählen Sie
Internetprotokoll TCP/IP, und klicken Sie auf Eigenschaften.
6. Vergewissern Sie sich, dass die Optionen
IP-Adresse automatisch beziehen
und DNS Server automatisch beziehen ausgewählt sind (siehe Abbildung
4). Klicken Sie auf OK.
7. Restart your computer.
D
Automatisches Beziehen
einer IP-Adresse
DSL-Anwender mit
PPPoE- oder PPTP
Client-Software
Abbildung 3
Abbildung 2
Page 58

Computer mit Windows 95, 98 und ME.
1. Wählen Sie unter Windows im Menü Start die Optionen Einstellungen >
Systemsteuerung.
2. Doppelklicken Sie auf Netzwerk. Wählen Sie das TCP/IP-Objekt für Ihre
Netzwerkkarte (siehe Abbildung 5), und klicken Sie auf Eigenschaften.
3. Wählen Sie im Dialogfeld TCP/IP die Registerkarte IP-Adresse, und
vergewissern Sie sich, dass IP-Adresse automatisch beziehen ausgewählt
ist (siehe Abbildung 6). Klicken Sie auf OK.
4. Starten Sie den Computer neu.
ISP-Verbindungsmethoden
56
Abbildung 5
Abbildung 6
Abbildung 4
3. ISP-VERBINDUNGSMETHODEN
Bevor Sie den Router konfigurieren können, müssen Sie wissen, welche
Zuweisungsmethode für die IP-Informationen Ihr Internet Service Provider verwendet. Für die Zuweisung von IP-Informationen haben ISPs vier verschiedene
Möglichkeiten, die nachfolgend beschrieben sind:
1. Dynamische IP-Adresse (DSL oder Kabel)
Die dynamische IP-Adressierung (oder DHCP) weist automatisch dem Router
IP-Informationen zu. Dies ist die gängige Methode bei Kabel-Providern. Sie
findet außerdem Anwendung, wenn das Modem über einen integrierten
DHCP-Server verfügt.
2. PPPoE (nur DSL)
Wenn Sie in den Installationsanweisungen, die mit dem Modem geliefert
werden, aufgefordert werden, einen PPPoE-Client auf dem PC zu installieren,
wählen Sie diese Option. Beachten Sie, dass Sie nach der Installation des
Routers keine PPPoE-Software auf dem PC benötigen. Für die Konfiguration
des Routers benötigen Sie folgende Informationen: Benutzername, Kennwort
und Name des Dienstes (falls vom ISP angefordert)
3. Statische IP-Adresse (DSL oder Kabel)
Der ISP liefert Ihnen IP-Adressinformationen, die Sie manuell eingeben müssen.
Für die Konfiguration des Routers benötigen Sie folgende Informationen: IPAdresse, Subnetzmaske, ISP Router-Adresse und DNS-Adresse(n)
Page 59

57
Ausführen des Setup-Assistenten
D
4. PPTP (DSL oder Kabel)
PPTP wird nur von einigen europäischen Providern verwendet. Wenn Sie in
den Installationsanweisungen, die mit dem Modem geliefert werden,
aufgefordert werden, über einen PPTP VPN-Tunnel eine DFÜ-Verbindung
einzurichten, wählen Sie diese Option. Beachten Sie, dass Sie nach der
Installation des Routers keine DFÜ-VPN auf dem PC benötigen. Für die
Konfiguration des Routers benötigen Sie folgende Informationen:
Benutzername, Kennwort, Name des Dienstes (falls von Ihrem ISP angefordert) und VPN-Serveradresse (üblicherweise Ihr Modem).
Sie werden nach dem IP-Zuweisungsmodus gefragt, wenn Sie den SetupAssistenten ausführen.
4. AUSFÜHREN DES SETUP-ASSISTENTEN
1. Falls noch nicht geschehen, müssen Sie den Computer jetzt neu starten.
2. Starten Sie den Webbrowser, und versuchen Sie, Verbindung zum Router
aufzunehmen. Geben Sie dazu folgende URL in der Adresszeile ein:
http://192.168.1.1. Wenn Sie auf die Anmeldeseite zugreifen können,
hat der Computer die richtige IP-Adresse vom Router empfangen.
3. Melden Sie sich mit dem Standard-Kennwort admin an. Der Assistent
sollte automatisch gestartet werden. Falls nicht, wählen Sie die
Registerkarte Assistent, und klicken Sie auf die Schaltfläche Assistent.
4. Soweit möglich, empfiehlt der Assistent für die meisten Parameter die
geeigneten Einstellungen. Einige Einstellungen müssen jedoch von Ihnen
angegeben werden. Die meisten dieser Einstellungen erhalten Sie beim
Einrichten des Benutzerkontos von Ihrem ISP.
5. 3Com empfiehlt Ihnen, die standardmäßig gesetzte LAN IP-Adresse für
den Router (192.168.1.1) beizubehalten. Sollten Sie diese jedoch ändern
wollen, notieren Sie sich die neue Adresse:
6. Wenn die Seite „DHCP Server Einstellungen“ angezeigt wird, vergewissern
Sie sich, dass die Option DHCP Server mit folgenden Einstellungen
aktivieren gewählt ist.
Wenn der Assistent beendet wurde, versuchen Sie, eine Internet-Website
aufzurufen, beispielsweise www.3com.de. Wenn Sie auf diese Site zugreifen
können, sind der Computer, Router und das Kabel-/DSL-Modem richtig konfiguriert.
Falls Sie keine Verbindung zum Router oder dem Internet herstellen können,
lesen Sie dazu den Abschnitt „Problemlösung“.
LAN IP-Adresse des Routers _______._______._______._______
Internetverbindung
Page 60

Verbindung zum drahtlosen LAN
58
5. VERBINDUNG ZUM DRAHTLOSEN LAN
1. Nachdem Sie den Router über den drahtgebundenen Computer konfiguriert
haben, können Sie über einen drahtlosen Computer eine Verbindung zum
Router herstellen.
Der Router und die drahtlosen Clients müssen über die gleiche SSID und
die gleichen Verschlüsselungs-Einstellungen verfügen. Alle drahtlosen
Clients müssen im Infrastrukturmodus ausgeführt werden.
Standardmäßige Einstellungen für drahtlosen Routerbetrieb:
2. Wenn Sie kein drahtloses LAN haben, können Sie die Standardeinstellungen
des Routers verwenden. Achten Sie darauf, dass für die drahtlosen Clients die
standardmäßigen Werte für SSID, Kanal und Verschlüsselung (siehe oben)
eingestellt wurden.
Wenn Sie über ein drahtloses LAN verfügen, konfigurieren Sie den Router
so, dass er die gleichen SSID- und Verschlüsselungs-Einstellungen verwendet und mit dem bestehenden drahtlosen Netzwerk kompatibel ist.
3. Wenn in Ihrem Computer eine drahtgebundene und eine drahtlose
Netzwerkkarte installiert sind, müssen Sie sicherstellen, dass die
Kommunikation mit dem LAN lediglich über eine dieser Netzwerkkarten
erfolgt. Zur Verwendung der drahtlosen Netzwerkkarte stecken Sie das
Ethernet-Kabel ab und starten anschließend den Computer neu.
4. Starten Sie den Webbrowser, und versuchen Sie, eine Internet-Website
aufzurufen, beispielsweise www.3com.de. Wenn Sie auf diese Site
zugreifen können, sind der drahtlose Computer, Router und das Kabel/DSL-Modem richtig konfiguriert.
5. 3Com empfiehlt Ihnen dringend, die WPA-Verschlüsselung zu aktivieren.
Dadurch erhöht sich die Sicherheit des drahtlosen Netzwerks, und Sie können die standardmäßige SSID ändern. Einzelheiten hierzu finden Sie in der
Online-Hilfe oder in der Bedienungsanleitung.
Dienstbereichsname / SSID: 3Com Kanal 11 Verschlüsselung
deaktiviert
Dienstbereichsname/SSID ______________________________
Kanalnummer ______________________________
Page 61

59
Problemlösung
D
PROBLEMLÖSUNG
Sollten Sie Probleme mit Ihrer Installation haben, versuchen Sie Folgendes:
• Vergewissern Sie sich, dass alle Netzwerkgeräte eingeschaltet sind.
Am Router sollte die grüne Power-LED leuchten. Falls nicht, prüfen Sie, ob
das Netzteil richtig angeschlossen ist. Verwenden Sie beim Router nur das
mitgelieferten Netzteil.
• Vergewissern Sie sich, dass das Kabel-/DSL-Modem angeschlossen
ist. Am Router sollte die Kabel/DSL Status-LED grün oder gelb leuchten.
Wenn keine LED leuchtet, prüfen Sie, ob das Modem eingeschaltet und
über ein Ethernet-Kabel an den Kabel/DSL-Port angeschlossen ist.
• Vergewissern Sie sich, dass der Computer an den Router
angeschlossen ist. Am Router sollte eine grüne oder gelbe LAN Status-LED
leuchten. Falls nicht, prüfen Sie, ob der Computer mit Hilfe eines EthernetKabels an einen der LAN-Ports des Routers angeschlossen ist.
• Vergewissern Sie sich, dass auf Ihrem Computer kein Web-Proxy
aktiviert ist. Öffnen Sie die Systemsteuerung, und klicken Sie auf
Internetoptionen. Wählen Sie die Registerkarte Verbindungen, und klicken
Sie unten auf die Schaltfläche LAN-Einstellungen. Vergewissern Sie sich,
dass die Option Proxyserver für LAN verwenden deaktiviert ist.
• Sie können nicht auf die Weboberfläche des Routers zugreifen.
Starten Sie einen Webbrowser, und geben Sie http://192.168.1.1 ein.
Wenn Sie eine andere IP-Adresse eingestellt haben, verwenden Sie diese
stattdessen. Vergessen Sie dabei nicht das Präfix http://
• Wenn die Power-LED oder die OK-LED des Netzteils nicht leuchtet,
sehen Sie in der Tabelle.
Netzteil
OK-LED Power-LED Problem und Maßnahme
Ein Ein Es funktioniert alles korrekt.
Ein Aus Die interne Stromversorgung ist ausgefallen. Fordern
Sie vom Technischen Support von 3Com einen
Ersatz-Router an.
Aus Aus Das Netzteil oder das Kabel des Netzteils ist fehler-
haft. Prüfen Sie die Verbindung des Netzteils. Wenn
die Stromversorgung weiterhin nicht hergestellt
wird, fordern Sie vom Technischen Support von
3Com ein Ersatznetzteil an.
Page 62

60
Problemlösung
• Einige Kabel-Provider führen die Authentifizierung anhand der MACAdresse des Anwendercomputers aus. Falls dies notwendig ist, rufen Sie
unter Internet Einstellungen die Option MAC-Adresse klonen auf. Die
MAC-Adresse Ihres Computers wird dann auf den Internet-Port des
Routers kopiert.
• Einige Kabel-Provider führen die Authentifizierung anhand des HostNamens des Anwenders aus. Falls erforderlich, gehen Sie zu Internet-
Einstellungen, und geben Sie den Host-Namen Ihres Computers im Feld
Host Name ein.
• Wenn Sie bereits einen DSL-Anschluss besitzen und auf Ihrem Computer
PPPoE oder PPTP Client-Software installiert haben, müssen Sie diese deaktivieren. Siehe Abschnitt 2.
• Wenn Ihr DSL-Anschluss PPPoE oder PPTP verwendet, gehen Sie zu
Internet-Einstellungen, und vergewissern Sie sich, dass der richtige IPZuordnungmodus gewählt wurde. Prüfen Sie, ob Ihr Benutzername und
Kennwort stimmen.
• Einige DSL-Provider verlangen die Verwendung eines PPPoE-Dienstnamens.
Falls erforderlich, gehen Sie zu Internet-Einstellungen, und geben Sie den
PPPoE-Dienstnamen im entsprechenden Feld ein. Falls nicht, müssen Sie
dieses Feld leer lassen.
Sie können nicht auf das drahtlose LAN zugreifen:
• Vergewissern Sie sich, dass der drahtlose Client in den Infrastrukturmodus
gesetzt wurde.
• Wenn in einem Computer drahtgebundene und drahtlose Netzwerkkarten
installiert sind, muss die drahtgebundene Netzwerkkarte deaktiviert werden. Einzelheiten dazu finden Sie in Abschnitt 5.
• Vergewissern Sie sich, dass der Dienstbereichsname (SSID) vom drahtlosen
Client und vom Router gleich ist.
• Vergewissern Sie sich, dass die WLAN-LED am Router leuchtet. Falls nicht,
aktivieren Sie im Menü für die drahtlosen Einstellungen den drahtlosen
Netzwerkbetrieb.
• Vergewissern Sie sich, dass die Verschlüsselungs-Einstellungen vom drahtlosen Client und vom Router gleich sind. Bei Problemen deaktivieren Sie
die Verschlüsselung im Client und Router, bis Sie eine drahtlose
Verbindung herstellen konnten.
Kabel-
Internetverbindungen
DSL-
Internetverbindungen
Drahtlose Konfiguration
Page 63

61
Introduktion
INTRODUKTION
Den här guiden tar dig igenom de grundläggande stegen för att installera
och konfigurera din OfficeConnect Wireless 54 Mbps/108 Mbps 11g
Cable/DSL Router, och skapa en förbindelse från din dator till internet. Längre
fram i denna guide benämns OfficeConnect Wireless 54 Mbps/108 Mbps 11g
Cable/DSL Router som Router.
• En OfficeConnect Wireless 54 Mbps/108 Mbps 11g Cable/DSL Router
• En strömadapter för användning med Routern
• Fyra gummifötter
• En Ethernet kabel
• En CD-skiva med installations guide och användarguide
• Ett support och säkerhets informationsblad
• En garanti sedel
• Release Note Sheet
• Product Range Sheet
Innan du startar kontrollera följande:
• Du har redan en kabel, DSL (kabalmodem) anslutning till internet med
fungerande modem, och att denna anslutning fungerar tillfredställande.
Modemet måste ha en ethernet port för anslutning mot din Router.
• Du har en dator med Ethernet anslutning tillgänlig som är konfigurerad
för kommunikation med internet. Din dator måste kunna få kontakt med
internet via modemet för din nuvarande anslutning och ha en Webläsare
installerad.
• Att det inte är andra DHCP servrar installerade på ditt lokala nätverk som
tilldelar IP addresser till datorer eller andra nätverksenheter. Din Router
kommer efter installetion att göra detta enligt grundinställningar.
Om någon av dessa krav inte uppfylls, se Router User Guide på CD-Skivan tillhandahållen med Routern.
Om denna Guide;
Paketet innehåller:
System krav:
S
Page 64

Dimensioner och standarder
62
DIMENSIONER OCH STANDARDER
Funktion: ISO 8802/3, IEEE802.3, IEEE802.11b, 802.11g
Säkerhet: UL60950, CSA22.2 #60950, IEC 60950, EN 60950
EMC: EN 55022 Class B, EN55024, CISPR 22, FCC Part 15 Class B*
ICES-003 Class B, ETSI EN 301 489-17
Radio: CFR 47 FCC Part 15.207, 15.209, 15.247 and 15.249.
ETS 300 328 (2.4 GHz ISM band wide band transmission
systems), RSS-210
Miljö: EN 60068 (IEC 68
* Se sektionen Regulator Notices i Support and Safety Information bladet
VARNING : Läs ‘Important Safety Information’ section i Support and
Safety Information sheet innan du startar.
WARNING: Please read the ‘Important Safety Information’ section in
the Support and Safety Information sheet before you start.
VORSICHT: Bitte lesen Sie den Abschnitt ‘Wichtige
Sicherheitsinformationen’ sorgfältig durch, bevor Sie das Gerät
einschalten.
Använd gummifötterna så undviker du att din Router åker omkring på bordet
eller när du ställer flera enheter på varandra. Gummfötterna är självhäftande
och sätts enkelt fast i varje hörn på din Router.
Standards
Dimensions
Använd gummifötterna
Säkerhetsinformation
7VA, 23.9 BTU/hr power
requirement
0 to 40ºC
arbetstemperatur
0 to 90% (icke
kondenserande)
luftfuktighet
41.5 mm
(1.6 in.)
224.8 mm
(8.8 in.)
OfficeConnect Wireless 54 Mbps/108 Mbps
11g Cable/DSL Router 592 g(1.3lb)
Page 65

63
Placering av Routern
S
PLACERING AV ROUTERN
När du placerar din Router tänk på följande:
• Placera enheten centralt i mellan det område och datorer där du önskar
trådlös täckning. En bra placering kan vara ovanpå ett högt skåp eller
annan möbel.
• För att möta kravet på FCC exponering av strålning skall routern inte placeras närmare än 20 cm från en människa.
• Undvik direkt solljus eller närhet till andra värmekällor.
• Undvik närhet till starka kraft och radiokällor, som kraftledningar,
radiosändare etc.
• Vatten eller andra vätskor får inte komma i kontakt med enheten.
• Tillse att det finns möjlighet för circulation av luft runt enheten och
genom luftinsläppen på sidorna. Vi rekommenderar att det dinns utrymme
minst 25 mm runt hela enheten.
Page 66

Om din Router
64
OM DIN ROUTER
1. Alarm DIOD Orange
Indikerar ett antal olika saker beskrivet nedan.
AV – Routern fungerar normalt.
Snabbt blinkande – Indikerar något av följande:
• Routern har just startat upp och genomgår självtest rutinen, eller
• Administratören har genomfört återställning till fabriksinsällningar (Reset to Factory Defaults), eller
• Systemets mjukvara är i process att uppgraderas
I alla ovan fall, vänta tills åtgärden är avslutat och alarm DIODEN släcks.
Långsamt blinkande – Routern har slutfört återställning till fabriksinställning, och väntar på att du skall
starta om enheten. För att göra detta dra ur strömkabeln och vänta 10 secunder och sätt den tillbaka.
Routern kommer då att genomgå start upp sekvensen och återgå till normal drift.
På I 2 sekunder och sen släckt – Routern har identifierat och skyddat dig mot en hacker attack från internet.
Ständigt lysande – Ett fel har upptäckts hos din Router under uppstarten. Se användarmanualen (main
User Guide).
2. Ström DIOD Grön
Indikerar att Routern får ström.
3. Trådlöst LAN (WLAN) Status DIOD Gul
Om denna DIOD lyser indikerar det att det trådlösa nätverket är aktivt. Om DIODEN blinkar, skickas eller
tas data emot. Om DIODEN är släckt är det trådlösa nätverket avstängt, eller att något problem har uppstått. Se problem lösningsdelen I denna guide.
4. Fyra LAN Status DIODER Grön (100Mbps länk) / Gul (10Mbps länk)
Om DIODEN lyser, är länken mellan porten och nästa nätverksenhet OK. Om DIODEN blinkar, är länken
OK och data skickas eller tas emot. Om DIODEN är släckt, är ingenting anslutet, den anslutna enheten är
avstängd, eller så är det ett problem (se problem lösnings delen i denna guide). Porten kommer
automatskt att justera rätt hastighet och duplex.
OfficeConnect Wireless 54 Mbps/108 Mbps 11g Cable/DSL Router - fram.
1
2
3
5 4
Page 67

65
Om din Router
S
5. Cable/DSL Status DIOD Grön (100Mbps länk) / Gul (10Mbps länk)
Om DIODEN lyser är länken mellan Routern och ditt kabel/DSL modem OK. Om DIODEN blinkar är länken
OK och data skickas eller tas emot. Om DIODEN är släckt är ingenting anslutet, modemet är avstängt eller
det är ett problem (se problem lösnings delen i denna guide).
6. Trådlös Antenn
Antennen på denna produkt skall vara placerad I en ‘V’ position när produkten installeras.
VARNING: Pressa inte antennen längre än dom mekaniska stop som den har. Om den pressas längre kan
antennen skadas.
7. Strömadapter enheten
Använd enbart den strömadapter som följer med denna router. Använd ingen annan typ av strömadapter.
8. Strömadaptern OK dioden lyser Grön
Indikerar att strömadaptern genererar ström till Routern . Om dioden inte lyser, kan det innebära att det
är något fel på strömadaptern eller kabeln till strömadaptern.
9. Ethernet Kabel/DSL porten
Använd den bifogade nätverkskabeln för att ansluta Routern till Ethernet porten på ditt kabel eller DSL
modem. Porten kommer automatiskt justera sig till den korrekta hastigheten och full duplex, och kommer
själv ställa in MDI eller MDIX beroende på vilken enhet den är ansluten till och vilken typ av kabel som
används.
10. Fyra 10/100 LAN portar
Använd lämplig RJ-45 kabel, du kan ansluta din Router till en dator, eller till någon annan enhet som har
en Ethernet anslutning (till exempel, en hub eller en switch). LAN portarna kommer automatiskt ställa in
sig på MDI eller MDIX beroende den enhet den är kopplad till och den kabel som används.
11. Reset Knappen
Tryck in Reset knappen i 5 sekunder. Alla inställningar för OfficeConnect Wireless 54 Mbps/108 Mbps 11g
Cable/DSL Router kommer återställas till defaultvärden från fabrik.
OfficeConnect Wireless 54 Mbps/108 Mbps 11g Cable/DSL Router - baksida.
6 6
911 7 810
Page 68

Installera din Router
66
1. INSTALLERA DIN ROUTER
1. Anslut strömadaptern till Routern och vänta tills ”Alert” dioden slutat
blinka.
2. Försäkra dig om att både ditt modem och dator är påslagna.
3. Sätt in ena änden av nätverkskabeln Ethernet (RJ-45 Kategori 5) kabeln i
Kabel/DSL porten på baksidan av Routern.
4. Sätt in andra änden av kabeln i RJ-45 porten på ditt kabel eller DSL
modem. Kontrollera att Kabel/DSL lampan lyser på Routern.
5. Anslut ditt modem till Internet.
6. Anslut din dator till en av de fyra LAN portarna på Routern med en
nätverkskabel. Kontrollera att lampan LAN lyser på din Router.
För att dela din Router med mer än fyra användare så behöver du en Hub
eller Switch. Anslut via LAN porten på din Router till Hubben eller Switchen,
ex. 3Coms OfficeConnect Dual Speed Switch 8.
Anslut din Router
Anslutning via en Hub
eller Switch
Bild 1. Exenpel på Nätverk med OfficeConnect Wireless 54 Mbps/108 Mbps 11g Kabel/DSL
Router.
Strömförsörjningsenhet
Din PC
3Com OfficeConnect Wireless
54Mbps/108Mbps 11g Kabel/DSL Router
Ditt befintliga
Kabel/DSL Modem
Internet
Trådlösa användare
Page 69

67
Konfigurera om din dator
S
2. KONFIGURERA OM DIN DATOR
Du kan behöva göra vissa förändringar I din dators inställningar för att den
skall kommunicera med routern på ett korrekt sätt.
Om du har PPPoE eller PPTP klient programvara installerat på din dator, så
behöver du avinstallera den enligt följande:
1. Från Windows Start meny, välj Inställningar > KontrollPanelen.
2. Dubbel klicka på Internet alternativ.
3. Välj anslutnings fliken. Ett fönster liknande Bild 2 skall visa sig.
4. Välj alternativet Anslut ej genom en uppringd anslutning och klicka på
OK. Du kanske vill ta bort PPPoE klient programvaran från din dator för att
frigöra utrymme, då den inte behövs för funktionen av routern.
Följ instruktionerna nedan för just ditt operativ system för att säkerställa att
din dator erhåller en IP address automatiskt.
För datorer som använder Windows XP.
1. Klicka på Windows Start meny, välj Kontrollpanelen.
2. Klicka på Nätverk och Internet anslutningar.
3. Klicka på Nätverksanslutningar.
4. Dubbelklicka på knappen LAN eller Höghastighets uppkoppling. Ett fön-
ster kommer visa sig med benämningen Lokal Nätverksanslutning.
5. Välj Internet Protocol TCP/IP och klicka på tillbehör.
6. Försäkra dig om funktionen tilldela en IP Address automatiskt, och tilldela
DNS serverar automatiskt båda är valda som på Bild 4. Klicka OK.
7. Restart your computer.
För datorer som använder Windows 2000.
1. Från Windows Start Meny, välj Inställningar > Kontrollpanelen.
2. Dubble klicka på Nätverk och Uppringda förbindelser.
3. Dubble klicka på Lokal Nätverks Anslutning.
4. Klicka på Tillbehör.
5. En sida liknande Bild 3 ska visa sig be displayed. Välj Internet Protokoll
TCP/IP och klicka på tillbehör.
6. Försäkra dig om funktionen tilldela en IP Address automatiskt
, och tilldela
DNS serverar automatiskt båda är valda som på Bild 4. Klicka OK.
7. Starta om din dator.
Automatisk tilldelning
av IP adress
DSL användare med
PPPoE eller PPTP Klient
programvara
Bild 3
Bild 2
Page 70

Uppkopplingsmetoder från din Internetleverantörer
68
För datorer med Windows 95, 98 och ME.
1. Från Windows Start Meny, välj inställningar > kontrollpanelen.
2. Dubbel klicka på Nätverk. Välj TCP/IP enhet för ditt nätverkskort som
bilden 5 visar och klicka på tillbehör.
3. I TCP/IP rutan, välj IP Address knappen, och försäkra dig att erhåll IP
address automatiskt är vald som bild 6 visar. Klicka OK.
4. Starta om din dator.
3. UPPKOPPLINGSMETODER FRÅN DIN INTERNETLEVERANTÖRER
Innan du kan konfigurera din Router, så behöver du veta vilken IP adress
information och tilldelning som används av din Internetleverantör. Det finns
fyra olika sätt som din Internetleverantör kan använda sig, alla fyra finns
beskrivna här nedan.
1. Dynamisk IP Address (DSL eller Kabel)
Dynamisk IP addressering (eller DHCP) bestämms automatiskt från
Routerns IP information. Detta är vanligt från leverantörer som använder
kabeluppkoppling mot Internet. Denna metod används också ifall ditt
modem har inbyggd DHCP server.
2. PPPoE (DSL enbart)
Om installations instruktionerna som följer med ditt modem frågar dig om
att installera en PPPoE klient på din PC välj då detta alternativ. Notera att
när du installerar Routern, så behöver du inte använda PPPoE mjukvara på
din PC. För att konfigurera Routern behöver du veta följande:
Användarnamn, lösenord, och Service Namn ( enbart om det begärs av
din Internetleverantör).
3. Statisk IP Address (DSL eller kabel)
Din Internetleverantör tillhandahåller IP address information som du lägger
in manuellt. För att konfigurera Routern behöver du veta följande : IP
Address, Subnät Mask, ISP Router Address, och DNS address (es).
Bild 5
Bild 6
Bild 4
Page 71

69
Köra (The Setup Wizard)
S
4. PPTP (DSL eller Kabel)
PPTP används enbart av ett fåtal Europeiska Internetleverantörer. Om
installations instruktionerna som följer med ditt modem frågar om en
uppringd förbindelse med hjälp av en PPTP VPN tunnel välj detta alternativ. Notera att när du installerar Routern, så behöver du ingen uppringd
VPN på din PC längre. För att konfigurera Routern behöver du veta följande: Användarnamn, Lösenord, Service Namn (ifall det krävs av din
Internetleverantör), och VPN Server address (vanligtvis ditt modem).
Du kommer bli tillfrågad om IP tilldelnings sätt när du kör installations
genomgången.
4. KÖRA (THE SETUP WIZARD)
1. Om du inte redan gjort det, starta om din dator.
2. Starta upp din webläsare och försök att kontakta Routern genom att skri-
va in följande följande IP adress i adressfältet: http://192.168.1.1.
Om du kan komma åt Login sidan, så har din dator fått korrekt IP address
från Routern.
3. Logga in genom att använda default lösenordet admin. ”The Wizard”
kommer försöka starta automatiskt, men ifall det falerar, välj ”the Wizard”
tangenten och klicka på ”the Wizard” knappen.
4. Där det är möjligt, kommer “the Wizard” rekommendera inställningar för
de flesta parametrar. Men, det är några inställningar som du måste
tillföra. De flesta kommer du att ha fått från din bredbandsleverantör när
du skaffade din bredbandsanslutning.
5. 3Com rekommenderar att du låter LAN IP addressen för routern behålla
de förinställda adressvärdet på 192.168.1.1. Men, ifall du skulle välja att
ändra dom; gör en notering om den nya adressen:
6. När DHCP Server Inställnings sidan visas, var säker på att förbereda DHCP
Servern med följande inställningar.
När “the Wizard” är färdig, forsök att öppna en web sida, såsom
www.3com.se. Om du kan nå denna sida, så har din dator, Router och
Kabel/DSL modem blivit korrekt inkopplade.
Titta under problemlösnings delen i denna guide, om du inte får kontakt med
Routern eller Internet.
Routern's LAN IP Address _______._______._______._______
Anslutning mot Internet
Page 72

Anslutning mot trådlöst LAN
70
5. ANSLUTNING MOT TRÅDLÖST LAN
1. Efter att du har konfigurerat Routern via den trådbundna datorn, så kan
du nu ansluta Routern via en trådlös dator. Routern och dom trådlösa
klienterna måste båda ha SSID och samma krypterings inställningar. Alla
trådlösa klienter måste använda infrastruktur nät. Defaultvärde för de
trådlösa inställningarn till Routern är:
2. Om du inte har ett trådlöst LAN kan du använda Routern’s default inställningar. Försäkra att din trådlösa klient har default SSID, kanal och kryptering beskrivet som ovan.
Om du har ett existerande trådlöst LAN, konfigurera Routern att använda
samma SSID och krypterings inställninagr för att bli kompatibelt med ditt
existerande trådlösa nätverk.
3. Om din dator har både trådbunden och trådlös nätverksanslutning
installerad, så måste du försäkra dig om att enbart en nätverksanslutning
används för att kommunicera med ditt LAN. För att koppla upp den
trådlösa anslutningen, ta ur nätverkskabeln och starta om din dator.
4. Starta din webläsare och prova att koppla upp dig mot en web sida ex
www.3com.se. Om sidan visas korrekt, så fungerar din trådlösa dator,
Router och Kabel/DSL modem som det ska.
5. 3Com rekommenderar att du skapar en WPA kryptering för att öka säkerheten I ditt trådlösa nätverk. Och ändra ditt SSID till något annat än
default värdet. Kontrollera med Online hjälpen eller användarguiden för
detaljer.
Service Area Name / SSID is 3Com Channel 11 Encryption is off.
Service Area Name/SSID ______________________________
Channel Number ______________________________
Page 73

71
Problemlösning
S
PROBLEMLÖSNING
Om du har problem med din installation, prova att felsöka enligt nedan.
• Försäkra dig om att alla nätverksenheter är påslagna. Routern skall
ha en grönt lysande lampa. Om inte kontrollera strömförsörjningen,
använd enbart den strömadapter som medföljer produkten.
• Försäkra dig om att ditt DSL/kabel modem är anslutet korrekt.
Routern skall visa ett grönt eller gult ljus. Om ingen diod lyser kontrollera
att modemet är påslaget och att det är anslutet mot kabel/DSL porten på
routern med en nätverkskabel.
• Försäkra dig om att datorn är ansluten till routern. Routern skall lysa
med grönt eller gult sken, om ingen diod lyser kontrollera att datorn är
ansluten till någon av Roterns LAN portar med en nätverkskabel.
• Försäkra dig om att du inte har en Proxyserver inställning på din
dator. Gå till kontrollpanelen och klicka på Internet inställningar, välj
fliken anslutningar och klicka på LAN inställningar, se till att fältet för
Proxy server är omarkerat.
• Om du ej får anslutning till roterns web gränssnitt. Öppna upp en
websida och skriv in följande http://192.168.1.1. Om du väljer en annan IP
adress , använd den istället. Försäkra dig då om att skriva in prefixet
http://.
• Om strömförsörjningslampan och strömadapterns OK lampa ej
lyser, se upplysningar.
Ström adapter Ström
OK LED lampan Problem och lösningsförslag
På På Allt fungerar korrekt.
På Av Den interna strömförsörjningen fungerar inte.
Kontakta 3Com´s Tekniska Support för utbyte till en
ny enhet.
Av Av Strömadaptern eller strömadapterkabeln är trasig.
Kontrollera din strömadapter och tillhörande kabel.
Om enheten fortfarande ej fungerar, kontakta
3Com´s tekniska support och be om byte till en ny
fungerande strömadapter.
Page 74

• Vissa bredbandsleverantörer autentiserar användarens dator genom MAC
adressen, om detta begärs gå till Internet inställningarna och välj kopiera
MAC adressen, detta gör att MAC adressen kopieras från din dator till
Internet porten på routern.
• Vissa bredbandsleverantörer autentiserar användaren genom datorns
anvädarnamn. Om detta begärs. Gå till Internet inställningarna och skriv
in din dators användarnamn under fältet som är markerat Host Name eller
datorns anvädarnamn.
• Om du har en befintlig DSL förbindelse och har en PPPoE eller PPTP klient
mjukvara installerad på din dator, så behöver du koppla ur den (Under
avsnitt 2).
• Om din DSL förbindelse använder PPPoE eller PPTP. Gå till Internet inställningar och försäkra dig om att inställningarna för IP adresser är korrekt
ifyllda i enlighet med din bredbandsleverantörs anvisningar, kontrollera
också att korrekt användarnamn och lösenord är ifyllt.
• Vissa Bredbandsleverantörer kräver ett PPPoE Service namn. Om detta
begärs, gå till Internet inställningarna och skriv in PPPoE om du har tillgång till det. Om det inte begärs lämna rutan tom.
Om du har problem att ansluta mot det trådlösa nätverket
• Försäkra att den trådlösa enheten är satt i ”infrastructure mode”.
• Om du har både en trådlös och en trådbunden nätverksanslutning till
samma dator, försäkra dig om att den trådbundna enheten är urkopplad
(Se kapitel 5 för detaljer).
• Försäkra dig om att Service Area Name (SSID) är samma som för den
trådlösa enheten som för routern.
• Försäkra att Routerns WLAN LED är påslagen. Om inte, gå till menyn för
trådlösa inställningar och Wireless Networking.
• Försäkra att krypterings inställningarna är samma för den trådlösa enheten
och Routern. Om det är problem, stäng av den trådlösa krypteringen i både
den trådlösa enheten och routern tills dess en trådlös anslutning skapats.
Problemlösning
72
Internetanslutning via
fastighetsnät/kabel
DSL Internet
Anslutningar
Trådlös konfiguration
Page 75

73
Introdução
INTRODUÇÃO
Ele irá conduzi-lo nas etapas básicas necessárias para instalar e configurar o
Roteador OfficeConnect Wireless para Cabo/DSL (Digital Subscriber Line –
Linha Digital do Assinante) 54 Mbps/108 Mbps (megabits por segundo) 11g e
criar uma conexão entre os seus computadores e a Internet. Em todo o texto,
o Roteador OfficeConnect Wireless para Cabo/DSL 54 Mbps/108 Mbps 11g
será designado simplesmente como roteador.
• Um Roteador OfficeConnect Wireless para Cabo/DSL 54 Mbps/108 Mbps 11g
• Um adaptador de alimentação para ser utilizado com o roteador
• Quatro pés de borracha
• Um cabo Ethernet
• Um CD-ROM com o Guia de Instalação Rápida e o Guia do Usuário
• Este Guia de Instalação
• Um folheto com informações sobre suporte e segurança
• Um folheto com informações sobre garantia
• Um folheto com informações sobre a versão do produto
• Um folheto com informações sobre a linha de produtos
Antes de iniciar, você precisará certificar-se do seguinte:
• Você já possui uma conexão de banda larga à Internet por cabo ou DSL,
com um modem adequado, e essa conexão está funcionando corretamente. É necessário que o modem tenha uma porta Ethernet para
conexão com o roteador.
• Você tem um computador com uma conexão Ethernet disponível, já configurado corretamente para comunicação com a Internet. É necessário que
o seu computador possa conectar-se à Internet através do modem e nele
haja instalado um navegador de Internet.
• Na rede local não há outros dispositivos de servidor DHCP (Protocolo de
Configuração Dinâmica do Servidor) que sejam responsáveis pela alocação
de endereços de IP (protocolo de Internet) aos computadores e a outros
dispositivos conectados à rede. A partir de agora, o roteador passará a ser
o padrão para o desempenho dessa função.
Caso não esteja sendo cumprida uma ou mais dessas condições, obtenha
orientação adicional no Guia do Usuário do Roteador (mais abrangente), que
é fornecido no CD-ROM que acompanha o produto.
Sobre este guia:
Este pacote contém:
Requisitos do sistema
P
Page 76

Dimensões e padrões
74
DIMENSÕES E PADRÕES
Funcionais: ISO 8802/3, IEEE802.3, IEEE802.11b, 802.11g
Segurança: UL60950, CSA22.2 nº 60950, IEC 60950, EN 60950
EMC: EN 55022 Classe B, EN55024, CISPR 22, FCC Parte 15 Classe B*
(compatibilidade ICES-003 Classe B, ETSI EN 301 489-17
eletromagnética)
Rádio: CFR 47 FCC Partes 15.207, 15.209, 15.247 e 15.249.
ETS 300 328 (sistemas de transmissão de banda larga com
banda ISM – Industrial, Médica e Científica de 2,4 GHz),
RSS-210
Ambiental: EN 60068 (IEC 68)
* Consulte a seção “Observações sobre regulamentação” no folheto com informações
sobre suporte e segurança
AVISO: Antes de iniciar, leia a seção “Informações importantes sobre
segurança” no folheto com informações sobre suporte e segurança.
WARNING: Please read the ‘Important Safety Information’ section in
the Support and Safety Information sheet before you start.
VORSICHT: Bitte lesen Sie den Abschnitt ‘Wichtige
Sicherheitsinformationen’ sorgfältig durch, bevor Sie das Gerät
einschalten.
AVERTISSEMENT: Veuillez lire attentivement la section "Consignes
importantes de sécurité" avant de mettre en route.
Utilize os quatro pés de borracha auto-adesivos para impedir que o roteador
fique se mexendo quando estiver sobre a mesa ou colocado sobre outras
unidades OfficeConnect com face superior plana. Basta fixar os pés nas áreas
indicadas em cada um dos cantos da face inferior do roteador.
Padrões
Dimensões
Como utilizar os pés de
borracha
Informações sobre
segurança
Requisitos de energia:
7VA, 23,9 BTU/h
224.8 mm
(8.8 in.)
Temperatura de
operação: de 0 a 40 ºC
(de 32 a 105 ºF)
Umidade: de 5 a 90%
(não condensante)
41.5 mm
(1.6 in.)
OfficeConnect Wireless 54 Mbps/108 Mbps
11g Cable/DSL Router 592 g(1.3lb)
Page 77

75
Localização do roteador
P
LOCALIZAÇÃO DO ROTEADOR
Ao definir a localização do roteador, verifique os seguintes pontos:
• A unidade deve estar localizada num ponto central em relação aos computadores sem fio que ficarão conectados ao roteador. Seria adequado
posicioná-la sobre uma estante alta ou sobre um móvel semelhante, a fim
de otimizar as conexões sem fio entre a unidade e computadores que
estejam nas direções horizontal e vertical, permitindo que haja cobertura
em toda a área.
• A fim de cumprir as normas da FCC (Comissão Federal de Comunicações
– EUA) sobre exposição à radiação, o roteador deve ficar localizado numa
posição na qual se mantenha uma distância mínima de 20 cm (8 polegadas) em relação a qualquer pessoa (mais detalhes no Guia do Usuário).
• Ele não deve ficar diretamente sob a luz solar, nem próximo a fontes de calor.
• Os cabos devem ficar longe da rede elétrica, dos aparelhos de luz fluorescente e de fontes de ruído produzido eletronicamente, tais como rádios,
transmissores e amplificadores de banda larga.
• Não se pode permitir a entrada de água ou de umidade no gabinete da
unidade.
• Não há restrições quanto ao fluxo de ar em torno da unidade e através
das aberturas laterais do gabinete. Recomendamos que se permita um
espaço livre mínimo de 25 mm (1 polegada).
Page 78

Sobre o roteador
76
SOBRE O ROTEADOR
1. LED de alerta Laranja
Indica diversas situações diferentes, descritas a seguir.
Desligado – O roteador está funcionando normalmente.
Piscando rápido – Indica uma das seguintes situações:
• O roteador acabou de ser ligado e está executando uma rotina de autoteste, ou
• O administrador ativou o comando Restaurar padrões de fábrica, ou
• O software de sistema está em processo de atualização
Em qualquer dessas situações, aguarde até que o roteador tenha completado a operação que estiver real-
izando no momento e que o LED de alerta esteja desligado.
Piscando lentamente – O roteador completou o processo de restauração dos padrões de fábrica, e aguar-
da que você reinicie a unidade. Para isso, desligue a energia, aguarde durante 10 segundos e em seguida
volte a ligar a energia. O roteador realizará a seqüência de inicialização e voltará a funcionar normalmente.
Ligado durante dois segundos, desligando em seguida – O roteador detectou e impediu o ataque de um
hacker através da Internet contra a sua rede.
Permanentemente ligado – Foi detectado um defeito no roteador durante o processo de inicialização.
Consulte o Guia do Usuário.
2. LED de energia Verde
Indica que o roteador está ligado.
3. LED do status da LAN (rede local) sem fio (Wireless LAN – WLAN) Amarelo
O LED ligado indica que a rede sem fio está ativada. Quando o LED pisca, está havendo transmissão ou
recebimento de dados. Quando o LED está desligado, é porque a Wireless LAN foi desativada no
roteador, ou está havendo algum problema. Consulte a seção “Resolução de problemas”.
4. Quatro LEDs do status da LAN Verde (ligação de 100 Mbps)/Amarelo (ligação de 10 Mbps)
Quando o LED está ligado, a ligação entre a porta e o próximo componente do equipamento de rede
está funcionando bem. Quando o LED pisca, a ligação está funcionando bem e está havendo transmissão
ou recebimento de dados. Quando o LED está desligado, não está havendo nenhuma conexão, o dispositivo conectado está desligado ou está havendo algum problema com a conexão (consulte a seção
Roteador OfficeConnect Wireless para Cabo/DSL 54 Mbps/108 Mbps 11g – frontal.
1
2
3
5 4
Page 79

77
Sobre o roteador
P
“Resolução de Problemas”). A porta irá ajustar-se automaticamente à velocidade e ao duplex corretos.
5. LED do status do cabo/DSL Verde (ligação de 100 Mbps)/Amarelo (ligação de 10 Mbps)
Quando o LED está ligado, a ligação entre o roteador e o modem a cabo ou DSL está funcionando bem.
Quando o LED pisca, a ligação está funcionando bem e está havendo transmissão ou recebimento de
dados. Quando o LED está desligado, não está havendo nenhuma conexão, o modem está desligado ou
está havendo algum problema (consulte a seção “Resolução de problemas”).
6. Antenas sem fio
Ao serem instaladas pela primeira vez, as antenas do produto devem ser colocadas numa posição em
forma de “V”.
CUIDADO: Não force as antenas além de seus limites mecânicos de giro. Se girar as antenas mais do que
isso, você poderá danificá-las.
7. Tomada do adaptador de alimentação
Utilize apenas o adaptador de alimentação fornecido juntamente com este roteador. Não utilize nenhum
outro adaptador.
8. LED do adaptador de alimentação Verde
Indica que o adaptador de alimentação está fornecendo energia para o roteador. Se o LED está desligado,
pode estar havendo um problema com o adaptador de alimentação ou com o cabo do adaptador.
9. Porta do cabo/DSL Ethernet
Para conectar o roteador à porta Ethernet do modem a cabo ou DSL, utilize o cabo direto (“patch cable”)
fornecido com o produto. A porta irá ajustar-se automaticamente à velocidade e ao duplex corretos, e irá
configurar-se para MDI (Interface Dependente do Meio) ou MDIX (outra versão da MDI) conforme o dispositivo ao qual esteja conectada e o tipo de cabo utilizado.
10. Quatro portas LAN 10/100
Com a utilização do cabo RJ-45 correto, você poderá conectar o roteador a um computador ou a qualquer
outro componente de equipamento que tenha uma conexão Ethernet (por exemplo, um hub ou um
switch). As portas LAN irão configurar-se automaticamente à MDI ou à MDIX conforme o dispositivos ao
qual estejam conectadas e o tipo de cabo utilizado.
11. Botão Reiniciar
Pressione o botão Reiniciar por cinco segundos e solte-o. Todas as configurações do Roteador OfficeConnect
Wireless para Cabo/DSL 54 Mbps/108 Mbps 11g serão restauradas para o padrão de fábrica.
Roteador OfficeConnect Wireless para Cabo/DSL 54 Mbps/108 Mbps 11g – traseira.
6 6
911 7 810
Page 80

Instalação do roteador
78
1. INSTALAÇÃO DO ROTEADOR
1. Conecte o adaptador de alimentação ao roteador e aguarde até que o
LED de alerta pare de piscar.
2. Verifique se o modem e o computador estão ligados.
3. Insira uma das extremidades do cabo Ethernet (RJ-45 Categoria 5), que é
fornecido com o produto, na porta Cabo/DSL no painel traseiro do
roteador.
4. Insira a outra extremidade do cabo na porta RJ-45 do modem a cabo ou
DSL. Verifique se o LED de status do cabo/DSL se acende no roteador.
5. Conecte o modem a cabo ou DSL à Internet.
6. Conecte o computador a uma das quatro portas LAN do roteador com a
utilização de um cabo Ethernet. Verifique se o correspondente LED de status da LAN se acende no roteador.
Para compartilhar o roteador com mais de quatro usuários, será necessário
um hub ou um switch a mais. Conecte uma das portas LAN do roteador ao
hub ou ao switch (por exemplo, o OfficeConnect Dual Speed Switch 8).
Conexão do roteador
Conexão a um hub ou a
um switch
Figura 1. Exemplo de rede com Roteador OfficeConnect Wireless para Cabo/DSL 54 Mbps/
108 Mbps 11g.
Power
Supply Unit
3Com OfficeConnect Wireless
54Mbps/108Mbps 11g Cable/DSL Router
Your existing
Cable/DSL Modem
Internet
Wireless
Your PC
Users
Page 81

79
Alteração da configuração do computador
P
2. ALTERAÇÃO DA CONFIGURAÇÃO DO COMPUTADOR
Pode ser necessário realizar algumas alterações na configuração dos seus
computadores a fim de fazê-los entrar em comunicação com o roteador.
Se houver um software cliente PPPoE (Protocolo Ponto a Ponto sobre
Ethernet) ou PPTP (Protocolo de Encapsulamento Ponto a Ponto) instalado no
seu computador, será necessário desativá-lo. Siga o procedimento seguinte:
1. A partir do menu Iniciar do Windows, selecione Configurações > Painel de
controle.
2. Clique duas vezes em Opções da Internet.
3. Selecione a guia Conexões. Será exibida uma caixa semelhante à da Figura 2.
4. Selecione a opção Nunca discar uma conexão e clique em OK.
Pode ser que você queira remover do computador o software cliente PPPoE,
para liberar recursos, uma vez que não é necessário utilizá-lo com o roteador.
Siga as instruções abaixo para que o sistema operacional que você utiliza
verifique se os seus computadores estão configurados para obter automaticamente um endereço de IP.
Para computadores que utilizam o Windows XP:
1. No menu Iniciar do Windows, selecione Painel de controle.
2. Clique em Conexões de rede e Internet.
3. Clique no ícone Conexões de rede.
4. Clique duas vezes no ícone Rede local ou Internet de alta velocidade.
Aparece uma caixa denominada Status de conexão local.
5. Selecione Protocolo TCP/IP e clique em Propriedades.
6. Verifique se as opções Obter um endereço IP automaticamente e Obter o
endereço dos servidores DNS automaticamente estão selecionadas con-
forme se vê na Figura 4. Clique em OK.
7. Reinicie o computador.
Para computadores que utilizam o Windows 2000:
1. No menu Iniciar do Windows, selecione Configurações > Painel de controle.
2. Clique duas vezes em Conexões de rede e dial-up.
3. Clique duas vezes em Conexão local.
4. Clique em Propriedades.
5. Será exibida uma caixa semelhante à da Figura 3. Selecione Protocolo
TCP/IP e clique em Propriedades.
6. Verifique se as opções Obter um endereço IP automaticamente e Obter o
endereço dos servidores DNS automaticamente estão selecionadas con-
forme se vê na Figura 4. Clique em OK.
7. Reinicie o computador.
Obtenção automática
de um endereço de IP
Usuários de DSL com
software cliente PPPoE
ou PPTP
Figura 3
Figura 2
Page 82

Métodos de conexão ISP
80
Para computadores que utilizam Windows 95, 98 ou ME:
1. No menu Iniciar do Windows, selecione Configurações > Painel de controle.
2. Clique duas vezes em Rede. Selecione o item TCP/IP para a placa de rede,
conforme se vê na Figura 5, e clique em Propriedades.
3. Na caixa de diálogo TCP/IP, selecione a guia Endereço IP e verifique se a
opção Obter um endereço IP automaticamente está selecionada, con-
forme se vê na Figura 6. Clique em OK.
4. Reinicie o computador.
3. MÉTODOS DE CONEXÃO ISP
Antes de configurar o roteador, é necessário conhecer o método de alocação
de informações de IP utilizado pelo seu provedor de acesso à Internet (ISP).
Existem quatro formas diferentes utilizadas pelos ISPs para alocação de informações de IP, descritas a seguir.
1. Endereço dinâmico de IP (DSL ou cabo)
O endereçamento dinâmico de IP (ou DHCP) atribui automaticamente
informações de IP ao roteador. Esse método é muito utilizado entre os
provedores de Internet a cabo. E também é utilizado quando o modem
tem um servidor DHCP embutido.
2. PPPoE (apenas DSL)
Selecione essa opção caso as instruções de instalação que acompanham o
seu modem indiquem que você deve instalar um cliente PPPoE no seu PC.
Observe que, ao instalar o roteador, não será necessário utilizar o software
PPPoE no PC. Para configurar o roteador é necessário saber o seguinte:
nome do usuário, senha e nome do serviço (se for exigido pelo seu ISP).
3. Endereço estático de IP (DSL ou cabo)
O ISP fornece as informações de endereçamento de IP para que você as
insira manualmente. Para configurar o roteador é necessário saber o
seguinte: endereço de IP, máscara de sub-rede, endereço do roteador do
ISP e endereço(s) DNS (Sistema de Nome de Domínio).
Figura 5
Figura 6
Figura 4
Page 83

81
Execução do Assistente de configuração
P
4. PPTP (DSL ou cabo)
O PPTP é utilizado apenas por alguns provedores europeus. Selecione essa
opção caso as instruções de instalação que acompanham o seu modem
indiquem que você deve configurar uma conexão de dial-up com a utilização de um túnel PPTP de VPN (Rede Virtual Privada). Observe que, ao
instalar o roteador, não será mais necessário utilizar a VPN de dial-up no
PC. Para configurar o roteador é necessário saber o seguinte: nome do
usuário, senha, nome do serviço (se for exigido pelo seu ISP) e endereço
do servidor VPN (normalmente é o seu modem).
Quando executar o Assistente de configuração, você receberá uma solicitação para informar o Modo de alocação IP.
4. EXECUÇÃO DO ASSISTENTE DE CONFIGURAÇÃO
1. Caso ainda não o tenha feito, reinicie o computador.
2. Abra o navegador de Internet e tente entrar em contato com o roteador
digitando a seguinte URL na barra de endereços: http://192.168.1.1.
Se você consegue acessar a página de Login, é porque o computador
recebeu corretamente um endereço IP a partir do roteador.
3. Execute o login utilizando a senha padrão admin. O Assistente tentará
abrir automaticamente, mas, se ele não o fizer, selecione a guia Assistente
e clique no botão Assistente.
4. Sempre que for possível, o Assistente irá recomendar configurações para a
maioria dos parâmetros. Porém, será necessário que você forneça algumas
configurações. A maioria delas já foi fornecida pelo seu ISP quando você
configurou a conta.
5. A 3Com recomenda que você deixe o endereço IP de LAN para o roteador
no endereço padrão de fábrica: 192.168.1.1. Porém, caso prefira alterá-lo,
anote aqui o novo endereço:
6. Quando for exibida a página de Configurações do Servidor DHCP, veri-
fique se está selecionada a opção Habilitar o servidor DHCP com as
seguintes configurações.
Quando o Assistente houver terminado, tente navegar até um site da
Internet, como por exemplo www.3com.com.br. Se você conseguiu acessar
esse site, é porque o computador, o roteador e o modem a Cabo/DSL foram
configurados corretamente.
Caso não consiga entrar em contato com o roteador ou a Internet, consulte a
seção “Resolução de problemas”.
Endereço IP de LAN do roteador _______._______._______._______
Conexão à Internet
Page 84

Conexão à Wireless LAN (sem fio)
82
5. CONEXÃO À WIRELESS LAN (SEM FIO)
1. Depois de ter configurado o roteador através do computador com fio,
você poderá conectar-se ao roteador através de um computador sem fio.
Será necessário que o roteador e os clientes sem fio tenham o mesmo
SSID (Identificador de Conjunto de Serviços) e as mesmas configurações
de criptografia. Será necessário que todos os clientes sem fio utilizem o
modo Infra-estrutura.
O padrão de configurações sem fio para o roteador é:
2. Caso não possua uma Wireless LAN, você pode utilizar os padrões de
configuração do roteador. Verifique se os seus clientes sem fio têm o SSID,
o canal e a criptografia padronizados conforme as referências precedentes.
Caso possua uma Wireless LAN já em funcionamento, configure o roteador
de forma que ele utilize as mesmas configurações de SSID e criptografia
para ficar compatível com a sua rede sem fio já existente.
3. Caso o computador tenha placas de rede com e sem fio instaladas, será
necessário verificar se está sendo utilizada apenas uma placa de rede para
comunicação com a LAN. Para utilizar a placa de rede sem fio, tire da
tomada o cabo Ethernet e reinicialize o computador.
4. Abra o navegador de Internet e tente navegar até um site da Internet,
como por exemplo www.3com.com.br. Se você conseguiu acessar esse
site, é porque o computador sem fio, o roteador e o modem a Cabo/DSL
foram configurados corretamente.
5. A 3Com recomenda enfaticamente que você ative a criptografia WPA
(Acesso Protegido Wi-Fi) para aumentar a segurança da sua rede sem fio e
que o SSID seja alterado para um código diferente do padrão. Maiores
detalhes na ajuda on-line ou no Guia do Usuário.
Nome da área de serviço/SSID ______________________________
Número do canal ______________________________
Nome da área de Canal 11 Criptografia
serviço/SSID: 3Com desativada
Page 85

83
Resolução de problemas
P
RESOLUÇÃO DE PROBLEMAS
Se tiver dificuldades na instalação, tente adotar os seguintes procedimentos:
• Certifique-se de que todos os equipamentos de rede estejam ligados.
A luz verde do LED de energia do roteador deve estar acesa. Caso negativo, verifique a conexão do adaptador de alimentação. Não utilize no
roteador nenhum outro adaptador de alimentação, e sim apenas o que foi
fornecido juntamente com o produto.
• Verifique se o modem a cabo/DSL está conectado. A luz verde ou
amarela do LED de status do cabo/DSL do roteador deve estar acesa. Caso
nenhum dos LEDs esteja aceso, verifique se o modem está ligado e se está
conectado à porta de cabo/DSL com um cabo Ethernet.
• Verifique se o computador está conectado ao roteador. A luz verde
ou amarela do LED de status da LAN do roteador deve estar acesa. Caso
negativo, verifique se o computador está conectado a uma das portas
LAN do roteador com um cabo Ethernet.
• Verifique se no computador não há um proxy de Internet habilitado.
Abra o Painel de controle e clique em Opções da Internet. Selecione a
guia Conexões e clique no botão Configurações da LAN, na parte inferior.
Certifique-se de que a opção Usar um servidor proxy para a rede local
esteja desativada.
• Caso não consiga acessar a interface do roteador na Internet: Abra
o navegador de Internet e digite http://192.168.1.1. Caso tenha preferido
um outro endereço de IP, utilize-o. Não deixe de incluir o prefixo http://.
• Caso o LED de energia ou o LED do adaptador de alimentação não
estejam acesos, consulte a tabela.
LED do
adaptador de LED de
alimentação energia Problema e procedimento a ser adotado
Ligado Ligado Tudo está funcionando corretamente.
Ligado Desligado A fonte de alimentação interna não está funcionando.
Procure o suporte técnico da 3Com para realizar a
substituição do roteador.
Desligado Desligado Há defeito no adaptador de alimentação ou na
conexão do adaptador de alimentação. Verifique as
conexões do adaptador de alimentação. Caso ainda
assim não haja energia, procure o suporte técnico
da 3Com e solicite a substituição do adaptador de
alimentação.
Page 86

• Alguns provedores de Internet a cabo fazem a autenticação pelo endereço
de MAC (Controle de Acesso Médio) do computador do usuário. Caso
isso seja necessário, abra Configurações da Internet e selecione Clonar o
endereço de MAC. Assim você copiará o endereço de MAC do computador para a porta de Internet do roteador.
• Alguns provedores de Internet a cabo fazem a autenticação pelo nome do
servidor do usuário. Caso isso seja necessário, abra Configurações da Internet
e digite o nome do servidor do computador no campo Nome do servidor.
• Se houver uma linha DSL já existente e um software cliente PPPoE ou PPTP
instalado no seu computador, será necessário desativá-lo. Veja a seção 2.
• Caso a linha DSL utilize o PPPoE ou o PPTP, abra Configurações de Internet
e verifique se está selecionado o Modo de alocação IP correto. Verifique se
o seu Nome de usuário e a sua Senha estão corretos.
• Alguns provedores DSL exigem a utilização de um nome de serviço PPPoE.
Caso isso seja necessário, abra Configurações de Internet e digite o nome
de serviço PPPoE no campo indicado para isso. Caso não seja necessário,
deixe o campo em branco.
Caso não esteja conseguindo acessar a Wireless LAN:
• Verifique se o cliente sem fio está configurado no modo Infra-estrutura.
• Caso tenha placas de rede com e sem fio no mesmo computador, certifique-se de que a placa de rede com fio esteja desativada. Mais detalhes
na seção 5.
• Verifique se o Nome da área de serviço (SSID) é o mesmo para o cliente
sem fio e o roteador.
• Verifique se o LED da WLAN do roteador está aceso. Caso negativo, abra
o menu Configurações sem fio e ative a Rede sem fio.
Resolução de problemas
84
Conexões de
Internet a cabo
Conexões de
Internet DSL
Configuração sem fio
Page 87

Page 88

3Com Corporation. 350 Campus Drive, Marlborough, MA. USA 01752-3064
Copyright © 2006 3Com Corporation. All rights reserved. 3Com, the 3Com logo, and
OfficeConnect are registered trademarks of 3Com Corporation. Microsoft, MS-DOS and
Windows are registered trademarks of Micorsoft Corporation.
All other company and product names may be trademarks of their respective companies.
 Loading...
Loading...