Page 1

ZyWALL 2WG
Security Appliance
Support Notes
Version 4.03
Sep. 2007
Page 2

ZyWALL 2WG Support Notes
INDEX
Application Notes......................................................................................................9
Mobility Internet Access........................................................................................9
Utilize 3G and Wireless for the Internet Access......................................10
Seamless Incorporation into your network..........................................................18
Using Transparent (Bridge Mode) Firewall ............................................18
Internet Connection...................................................................................24
DHCP server/client/relay...........................................................................25
Using NAT/Multi-NAT ..............................................................................26
Optimize network performance & availability....................................................35
Using Bandwidth Management ................................................................35
Secure Connections across the Internet...............................................................43
Site-to-Site VPN (Intranet) Scenario........................................................43
Configure ZyWALLs with Static WAN IP Address.............................43
Configure ZyWALL with Dynamic WAN IP Address.........................44
Configure ZyWALL behind NAT Router ............................................46
Mapping multiple Network policy to same gateway policy................48
Using Certificate for Device Authentication........................................53
Using Self-signed Certificates .....................................................54
Online Enroll Certificates............................................................57
Offline Enroll Certificates............................................................66
Using Pre-Shared Key for Device Authentication...............................99
Using VPN routing between branches...............................................100
NAT over IPSec on ZyNOS...............................................................110
Never lost your VPN connection (IPSec High Availability)..............119
Access control and security VPN connection (Security policy
enforcement IPSec)............................................................................123
How to configure access control rule over VPN .......................123
How to configure Web filtering rule over VPN – Content Filter128
ZyWALL vs 3rd Party VPN Gateway....................................................130
SonicWALL with ZyWALL VPN Tunneling.............................130
NetScreen with ZyWALL VPN Tunneling................................139
Check Point with ZyWALL VPN Tunneling ............................151
FortiNet with ZyWALL VPN Tunneling ...................................185
Remote Access VPN Scenario .................................................................198
Using xAuth for User Authentication................................................198
ZyXEL VPN Client to ZyWALL Tunneling......................................200
Content Filter Application..................................................................................209
All contents copyright (c) 2006 ZyXEL Communications Corporation.
2
Page 3

ZyWALL 2WG Support Notes
To filter non-work related and unproductive web surfing to mitigate
spyware and phishing threats.................................................................209
Centralized Management...................................................................................216
Using Vantage CNM for Management...................................................216
FAQ ...........................................................................................................................221
A. Product FAQ .................................................................................................221
A01. What is the ZyWALL Internet Access Sharing Router? .............221
A02. Will the ZyWALL work with my Internet connection?...............222
A03. What do I need to use the ZyWALL?............................................222
A04. What is PPPoE? ..............................................................................222
A05. Does the ZyWALL support PPPoE?..............................................222
A06. How do I know I am using PPPoE? ..............................................222
A07. Why does my Internet Service Provider use PPPoE?..................222
A08. How can I configure the ZyWALL? ..............................................223
A09. What can we do with ZyWALL? ...................................................223
A10. Does ZyWALL support dynamic IP addressing?.........................223
A11. What is the difference between the internal IP and the real IP
from my ISP?............................................................................................223
A12. How does e-mail work through the ZyWALL?............................223
A13. Is it possible to access a server running behind NAT from the
outside Internet? If possible, how?.........................................................223
A14. What DHCP capability does the ZyWALL support?...................224
A15. How do I used the reset button, more over what field of
parameter will be reset by reset button?
................................................224
A16. What network interface does the new ZyWALL series support?224
A17. How does the ZyWALL support TFTP?.......................................224
A18. Can the ZyWALL support TFTP over WAN?..............................224
A19. How can I upload data to outside Internet over the one-way
cable?.........................................................................................................224
A20. My ZyWALL can not get an IP address from the ISP to connect
to the Internet, what can I do?................................................................225
A21. What is BOOTP/DHCP?................................................................225
A22. What is DDNS?................................................................................225
A23. When do I need DDNS service?.....................................................226
A24. What DDNS servers does the ZyWALL support?........................226
A25. What is DDNS wildcard? ...............................................................226
A26. Does the ZyWALL support DDNS wildcard?...............................226
A27. Can the ZyWALL NAT handle IPSec packets sent by the VPN
All contents copyright (c) 2006 ZyXEL Communications Corporation.
3
Page 4

ZyWALL 2WG Support Notes
gateway behind ZyWALL? .....................................................................226
A28. How do I setup my ZyWALL for routing IPSec packets over
NAT? .........................................................................................................227
A29. What is STP (Spanning Tree Protocol) /RSTP (Rapid STP)?.....227
A30. What is the flow ZyWALL handles inbound and outgoing
traffic?.......................................................................................................227
B. Firewall FAQ.................................................................................................227
B01. What is a network firewall?...........................................................228
B02. What makes ZyWALL secure?......................................................228
B03. What are the basic types of firewalls?...........................................228
B04. What kind of firewall is the ZyWALL?........................................229
B05. Why do you need a firewall when your router has packet
filtering and NAT built-in?.....................................................................229
B06. What is Denials of Service (DoS)attack?.......................................229
B07. What is Ping of Death attack?........................................................230
B08. What is Teardrop attack?...............................................................230
B09. What is SYN Flood attack?............................................................230
B10. What is LAND attack?....................................................................230
B11. What is Brute-force attack?...........................................................230
B12. What is IP Spoofing attack?...........................................................231
B13. What are the default ACL firewall rules in ZyWALL?..............231
B14. Why does traffic redirect/static/policy route be blocked by
ZyWALL?.................................................................................................231
B15. How can I protect against IP spoofing attacks?...........................233
C. Security Service licenses FAQ ......................................................................234
C01. What is iCard? ................................................................................234
C02. Where can I buy the iCard and how much does it cost?.............234
C03. How many kinds of iCard does ZyXEL provide?........................234
C04. Is each type of iCard device specific?............................................234
C05. What are the available security service licenses which require
additional purchase and license activation in ZyNOS v4.00?..............234
C06. What kind of iCard should I buy?.................................................235
C07. If I violate the mappings described above, for example, using a
silver iCard for ZyWALL 35 or ZyWALL 70, what will happen?
.......235
C08. Can I try the Content Filtering service for free? How long is the
free trial period of Content Filtering service?
.......................................235
D. Security Service Activation and UpdateFAQ................................................235
D01. Why do I have to register?.............................................................235
All contents copyright (c) 2006 ZyXEL Communications Corporation.
4
Page 5

ZyWALL 2WG Support Notes
D02. In addition to registration, what can I do with myZyXEL.com?235
D03. Is there anything changed on myZyXEL.com because of the
launch of ZyNOS v4.00? Which ZyWALL models can be registered
via myZyXEL.com?.................................................................................236
D04. What’s the difference between new registration flow and
previous registration? What’s the advantage of new registration flow
over the previous registration flow?.......................................................236
D05. If I were new to myZyXEL.com, what are the required fields
when I register my ZyWALL device on myZyXEL.com?....................237
D06. When using the new registration flow of myZyXEL.com for
ZyNOS v4.0, do I have to create a new account if I were already a
registered user on myZyXEL.com?........................................................237
D07. What is mySecurityZone? ..............................................................237
D08. What is Update Server?..................................................................237
D09. Who maintains mySecurityZone & Update Server? ...................238
D10. What’s the URL for these service portals? ...................................238
E. Content Filter FAQ........................................................................................238
E01. What's the operation between ZyXEL appliance and BlueCoat
data center?..............................................................................................238
E02. How many entries can the cache of Web Site Auto Categorization
keep at most?............................................................................................238
E03. Can I specify the time out value of the query response from
BlueCoat data center? .............................................................................238
E04. Can I decide whether to forward or drop the HTTP response if
the query to BlueCoat data center is timed out?...................................239
E05. How to register for BlueCoat service?...........................................239
E06. Why can't I make registration successfully?................................239
E07. What services can I get with Trial Registration? .........................239
E08. What types of content filter does ZyWALL provide?..................239
E09. What are the primary features of ZyXEL Content Filtering?....239
E10. Who needs ZyXEL Content Filtering? Is ZyXEL Content
Filtering for small companies or for large corporations? ....................240
E11. Can I have different policies in effect for different times of the
day or week?
.............................................................................................240
E12. How many policies can I create?....................................................240
E13. Can I create my own categories?...................................................240
E14. Can I override (block or allow) certain URLs regardless of the
rating?.......................................................................................................240
All contents copyright (c) 2006 ZyXEL Communications Corporation.
5
Page 6

ZyWALL 2WG Support Notes
E15. How many URL keywords does ZyWALL support?....................240
E16. How do I keep database of Content Filtering service updated?.241
E17. What is BlueCoat Filter list?..........................................................241
E18. How many ratings does the BlueCoat database contain?............241
E19. How often does BlueCoat update the database? ..........................241
E20. How do I locate sites to block?.......................................................241
E21. Do humans review the ratings?......................................................242
E22. How can I do if I find a WEB site is mis-categorized?.................242
E23. How many and what categories do you provide?.........................242
E24. How does the ZyXEL content filtering handle dynamically
generated sites?........................................................................................244
E25. Does BlueCoat have more than one data center? Is the BlueCoat
Web Filter geographically load balanced? ............................................244
E26. Who can generate and view reports on BlueCoat WEB site?.....244
E27. How can I get Content Filtering report?.......................................244
E28. Can I change the password for BlueCoat service?.......................244
E29. Which User Name & Password should I input for Content
Filtering report?.......................................................................................245
E30. My device can't get connected to Http://myZyXEL.com, so I
can't get into Registration page. What should I check?.......................245
F. IPSec FAQ......................................................................................................245
F01. How to count my VPN tunnels on ZyWALL?...............................245
F02. What is VPN?...................................................................................246
F03. Why do I need VPN?.......................................................................246
F04. What are most common VPN protocols? ......................................247
F05. What is PPTP?.................................................................................247
F06. What is L2TP?.................................................................................247
F07. What is IPSec?.................................................................................247
F08. What is SA?......................................................................................248
F09. What is Pre-Shared Key?................................................................248
F10. What is Phase 1 ID for?..................................................................248
F11. What are Local ID and Peer ID?....................................................249
F12. Is my ZyWALL ready for IPSec VPN?..........................................249
F13. How do I configure ZyWALL VPN?..............................................249
F14. What VPN protocols are supported by ZyWALL? ......................250
F15. What types of encryption does ZyWALL VPN support?.............250
F16. What types of authentication does ZyWALL VPN support?......250
F17. I am planning my ZyWALL-to-ZyWALL VPN configuration.
All contents copyright (c) 2006 ZyXEL Communications Corporation.
6
Page 7

ZyWALL 2WG Support Notes
What do I need to know?.........................................................................250
F18. Does ZyWALL support dynamic secure gateway IP?..................251
F19. What VPN gateway that has been tested with ZyWALL
successfully?..............................................................................................251
F20. What VPN software that has been tested with ZyWALL
successfully?..............................................................................................251
F21. Will ZyXEL support Secure Remote Management?....................252
F22. Does ZyWALL VPN support NetBIOS broadcast?......................252
F23. Is the host behind NAT allowed to use IPSec?..............................252
F24. How do I configure ZyWALL with NAT for internal servers? ...252
F25. I am planning my ZyWALL behind a NAT router. What do I
need to know?...........................................................................................252
F26. Where can I configure Phase 1 ID in ZyWALL?..........................253
F27. How can I keep a tunnel alive?.......................................................253
F28. Single, Range, Subnet, which types of IP address does ZyWALL
support in VPN/IPSec?............................................................................254
F29. Does ZyWALL support IPSec pass-through?...............................254
F30. Can ZyWALL behave as a NAT router supporting IPSec pass
through and an IPSec gateway simultaneously?...................................254
G. PKI FAQ ........................................................................................................254
G01. Basic Cryptography concept..........................................................254
G02. What is PKI?...................................................................................255
G03. What are the security services PKI provides?..............................255
G04. What are the main elements of a PKI?.........................................255
G05. What is a Certification Authority?................................................256
G06. What is a digital certificate?..........................................................256
G07. What are public and private keys, and what is their
relationship?.............................................................................................256
G08. What are Certificate Policies (CPs)?.............................................256
G09. How does a PKI ensure data confidentiality?..............................257
G10. What is a digital signature?...........................................................257
G11. How does a digital signature work? ..............................................257
G12. Does ZyXEL provide CA service?.................................................259
G13. What if customers don't have access to CA service, but would
like to use PKI function?.........................................................................259
G14. How can I have Self-signed certificate for ZyXEL appliance?...259
G15. Can I create self-signed certificates in addition to the default
one?............................................................................................................259
All contents copyright (c) 2006 ZyXEL Communications Corporation.
7
Page 8

ZyWALL 2WG Support Notes
G16. Will Self-signed certificate be erased if I reset to default
configuration file?....................................................................................259
G17. Will certificates stored in ZyXEL appliance be erased if I reset to
default configuration file?.......................................................................259
G18. What can I do prior to reset appliance's configuration?.............259
G19. If I export My Certificates from ZyXEL appliance, save them
locally, and then import them back after resetting the configuration
file, can I reuse the imported My Certificates ?....................................260
H. Wireless FAQ................................................................................................260
H01. What are the capability of wireless feature of ZyWALL? ..........260
H02. What is the coverage range of Wireless in ZyWALL? ................260
H03. What is a Wireless LAN? ...............................................................260
H04. What are the advantages of Wireless LANs?...............................260
H05. What is IEEE 802.11.......................................................................261
H06. What is 802.11b? .............................................................................261
H07. What is 802.11g? .............................................................................261
H08. What is 802.11a? .............................................................................262
H09. What is Wi-Fi? ................................................................................262
H10. What types of devices use the 2.4 GHz Band? .............................262
H11. Can wireless signals pass through walls?......................................262
H12. What are the potential factors that may causes interference
among WLAN products?.........................................................................262
H13. What is SSID (Sever Set ID)? ........................................................263
H14. What is WEP? .................................................................................263
H15. What is a WEP key? .......................................................................263
H16. By turning off the broadcast of SSID, can someone still sniff the
SSID?
.........................................................................................................263
H17. What is 802.1x?...............................................................................264
H18. Can I use WiFi access when I plug a 3G wireless card in the
PCMCIA slot ? .........................................................................................264
All contents copyright (c) 2006 ZyXEL Communications Corporation.
8
Page 9
ZyWALL 2WG Support Notes
Application Notes
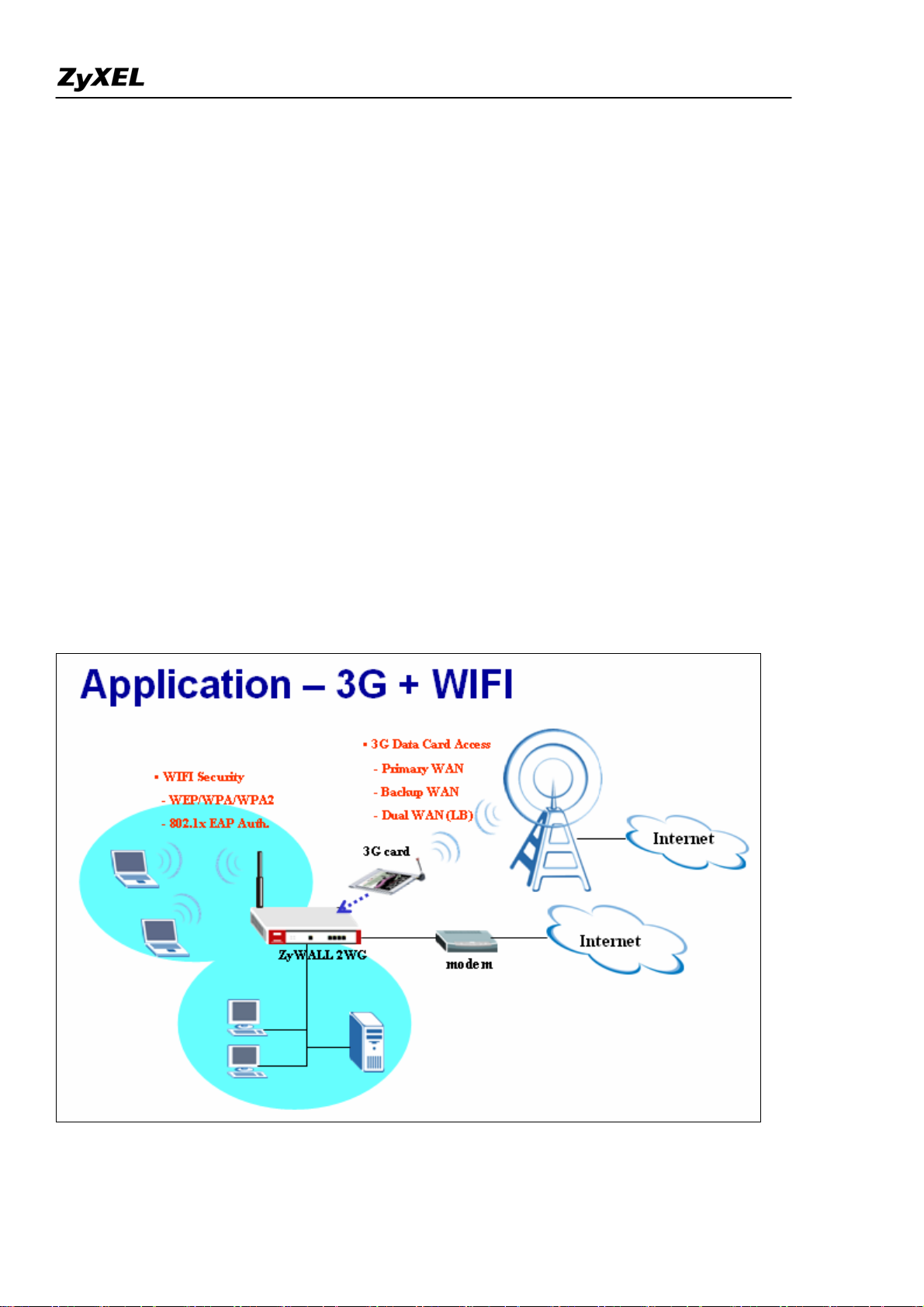
Mobility Internet Access
You may have the experienced a need of Internet access in a location where wired connection is difficult
to deploy, e.g. in countryside or mountain. Or you are just in a public environment without Internet access,
like in a park, on a bus, in a train or metropolitan subway, etc… Or you may temporarily need Internet
access when you are in your exhibition booth and need Internet access for some demonstration. ZyWALL
2WG is especially designed for the mobility Internet access; it is light to carry everywhere and can utilize
a 3G card for dial up to get the Internet access. Besides, you could utilize the embedded wireless card to
provide wireless access for your LAN users.
Not only the mobility, you could also use ZyWALL 2WG as your WAN backup in the small office or
SOHO. You could further choose a certain load balancing mechanism to perform dual WAN access.
In summery, you could utilize the 3G wireless access for your primary WAN, or backup WAN, or work
with your primary WAN(Ethernet or PPP) together as a dual WAN application.
9
All contents copyright (c) 2006 ZyXEL Communications Corporation.
Page 10
ZyWALL 2WG Support Notes
Utilize 3G and Wireless for the Internet Access
Following we will show you how to configure it step-by-step.
Utilize 3G card to get Internet access
1). Plug the 3G card to ZyWALL 2WG's card slot before powering on the ZyWALL 2WG device.
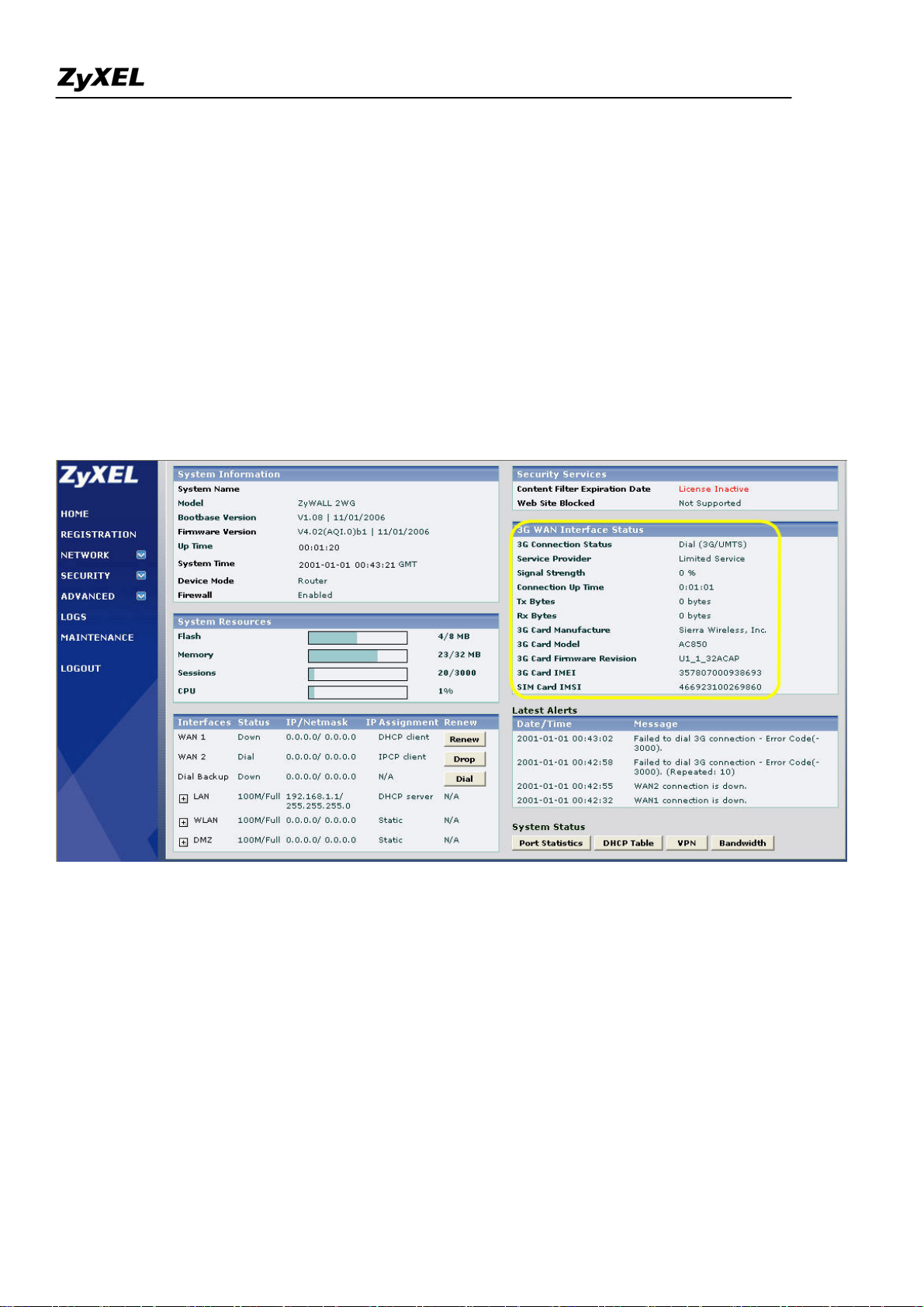
2). Login the GUI. After the system boots up, you can see the 3G card information on the home page. Make
sure there is no "Error" message in "3G Card IMEI" and "SIM Card IMSI" fields. Otherwise, you need to
re-install the 3G card and the SIM card and make sure they are properly installed. Please refer to the quick start
guide if you need to troubleshoot because of an error message.
3) Switch to GUI menu Network > WAN2 tab. Configure the APN, username, password, PIN code, phone
number, the authentication type and other settings you have got from your service provider. Click the Apply
button.
All contents copyright (c) 2006 ZyXEL Communications Corporation.
10
Page 11
ZyWALL 2WG Support Notes
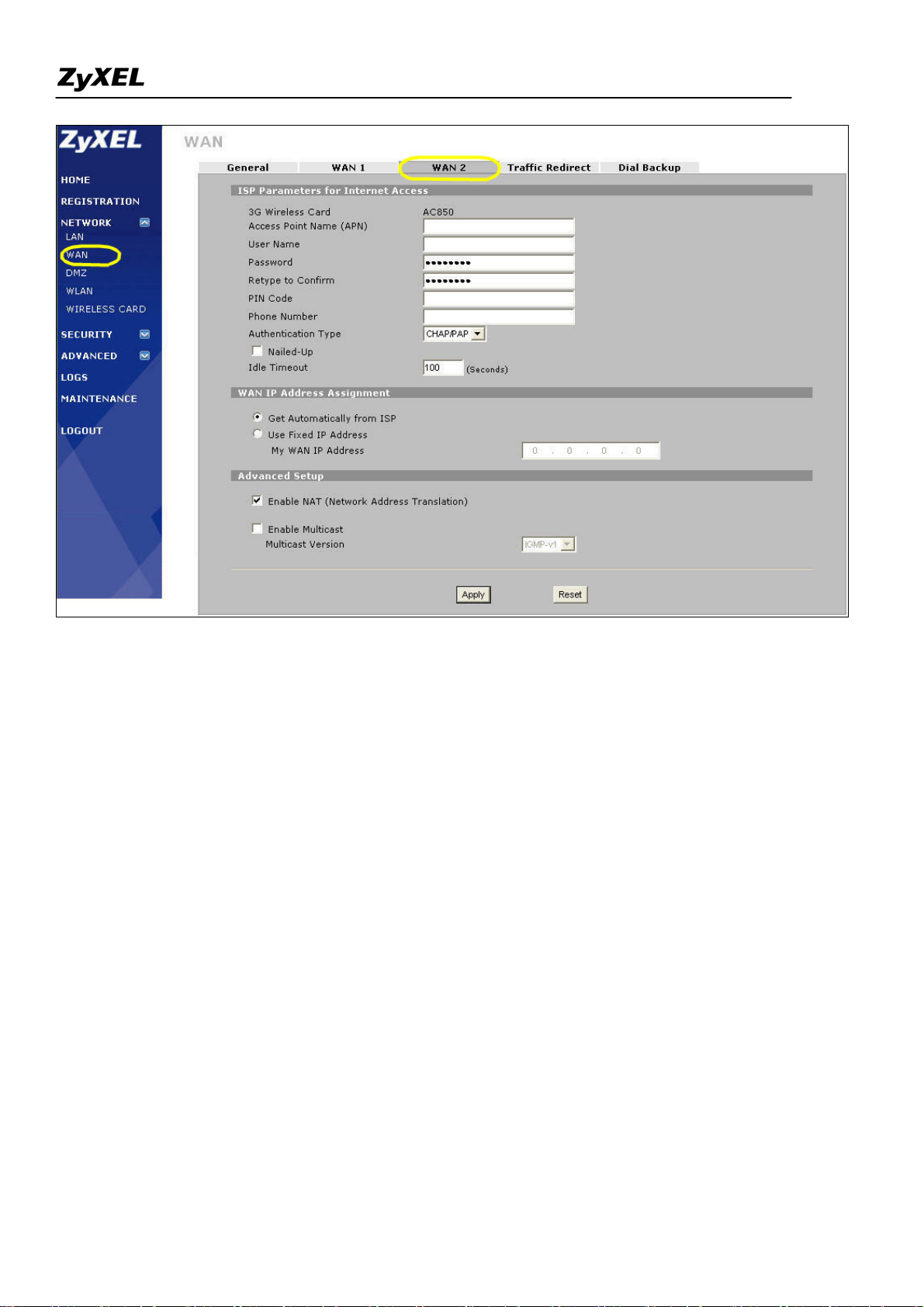
3). Then the 3G wireless card will be dialed up automatically when WAN1 is not available. If you check the
"Nailed-up" option as shown in the figure above, the system will automatically dial up the 3G Internet access
even if WAN1 is available. Then you will see the process in logs as following.
All contents copyright (c) 2006 ZyXEL Communications Corporation.
11
Page 12
ZyWALL 2WG Support Notes
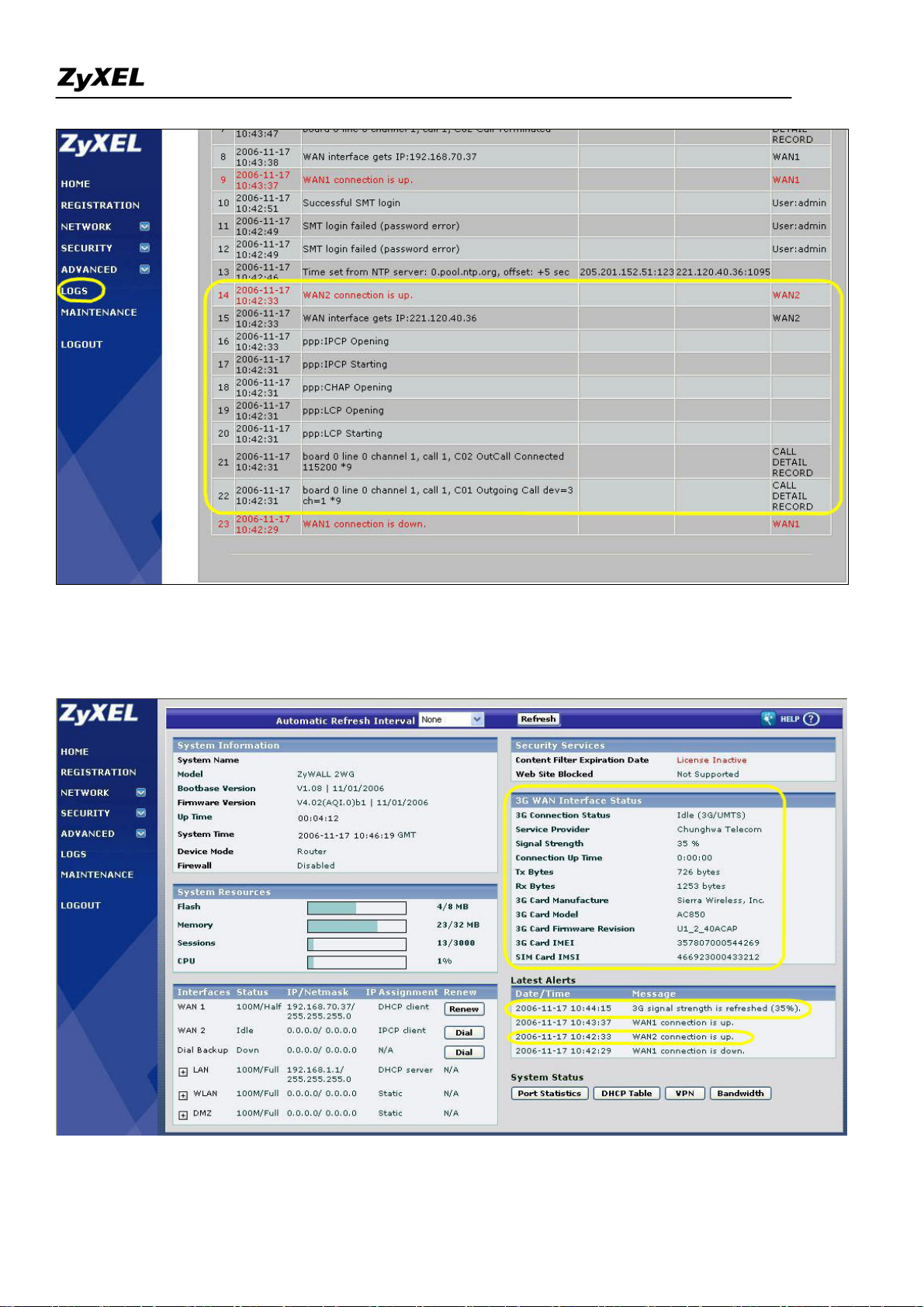
4) If dialed up successfully, you can see the GUI home page as shown below. You will get the "WAN2
connection is up" and "3G card's signal strength" messages in the latest alerts.
All contents copyright (c) 2006 ZyXEL Communications Corporation.
12
Page 13
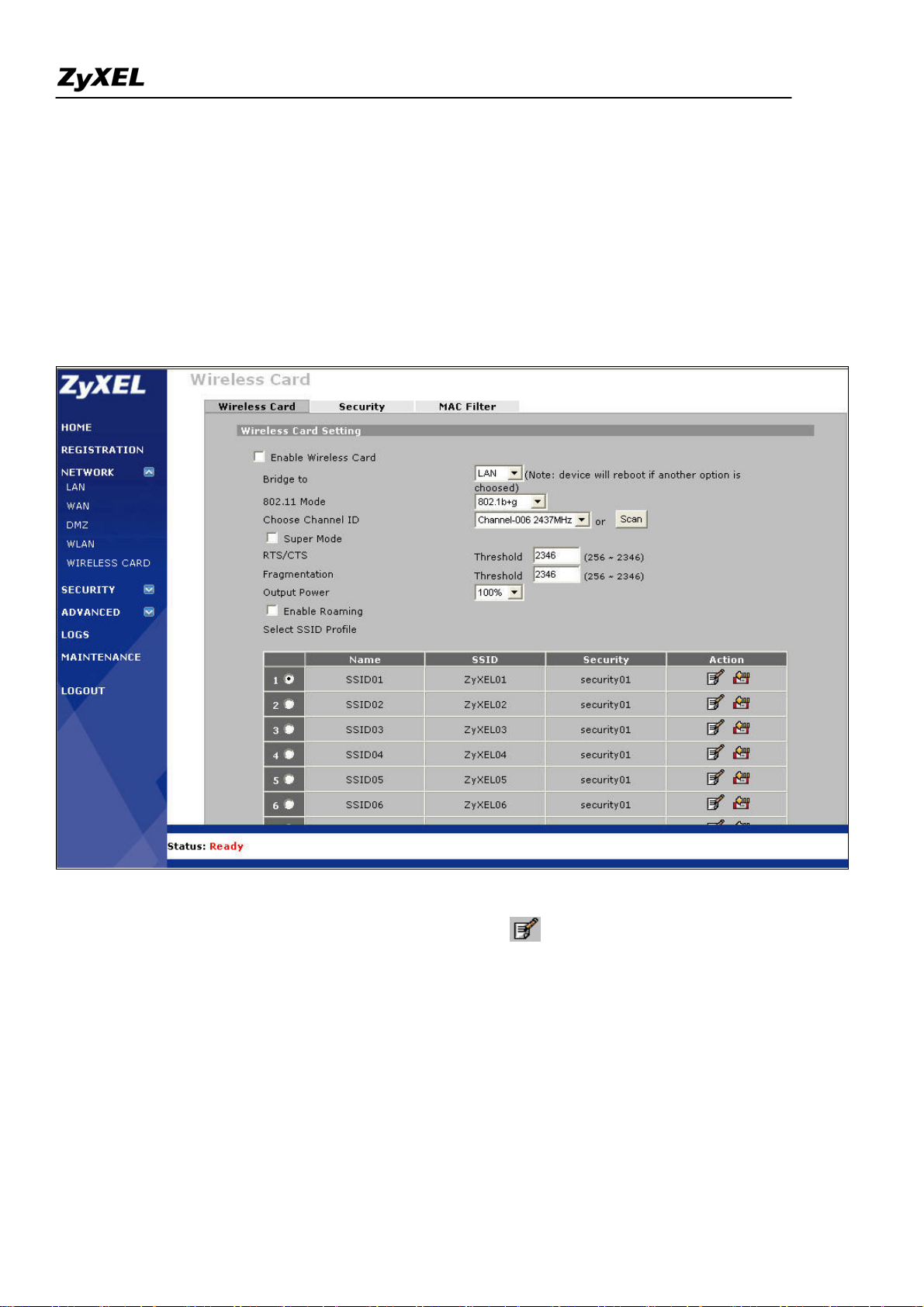
ZyWALL 2WG Support Notes
Utilize the embedded wireless card to provide LAN users access
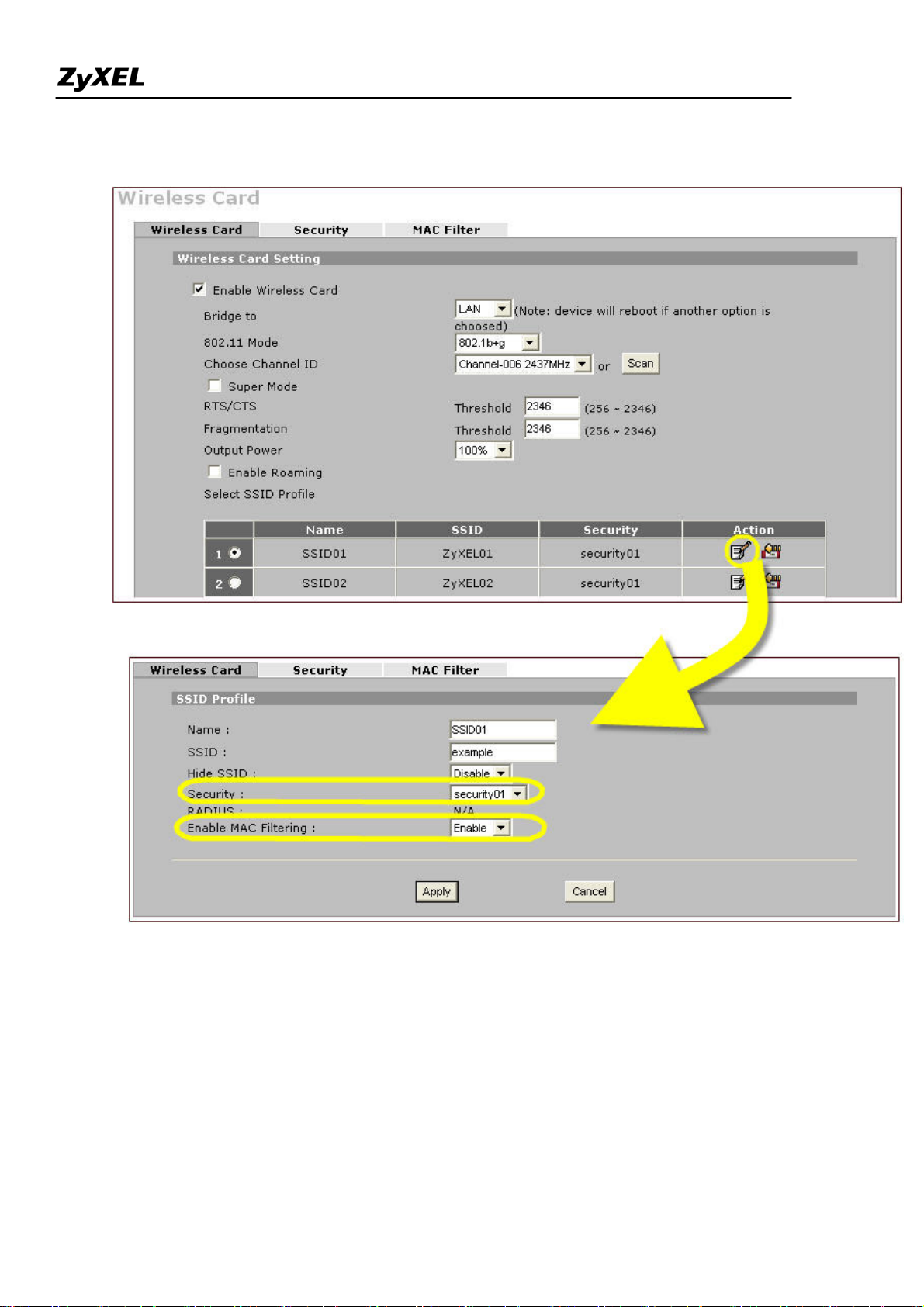
1). Go to GUI menu Network > WIRELESS CARD, enable it and configure the other parameters like 802.11
mode (four modes available: 802.11b only, 802.11g only, 802.11b+g, 802.11a only), channel ID, super mode,
RTS/CTS, fragmentation, output power(four options: 100%, 50%, 25%, 12.5%) and roaming.
ZyWALL 2WG allows you to configure up to 8 SSID profiles. Choose the SSID profile you want to use and
click Apply button.
Note: You can modify the SSID profile by clicking the modify ( ) icon in the figure above: here you can
configure the SSID information and choose the security and the MAC filtering.
All contents copyright (c) 2006 ZyXEL Communications Corporation.
13
Page 14
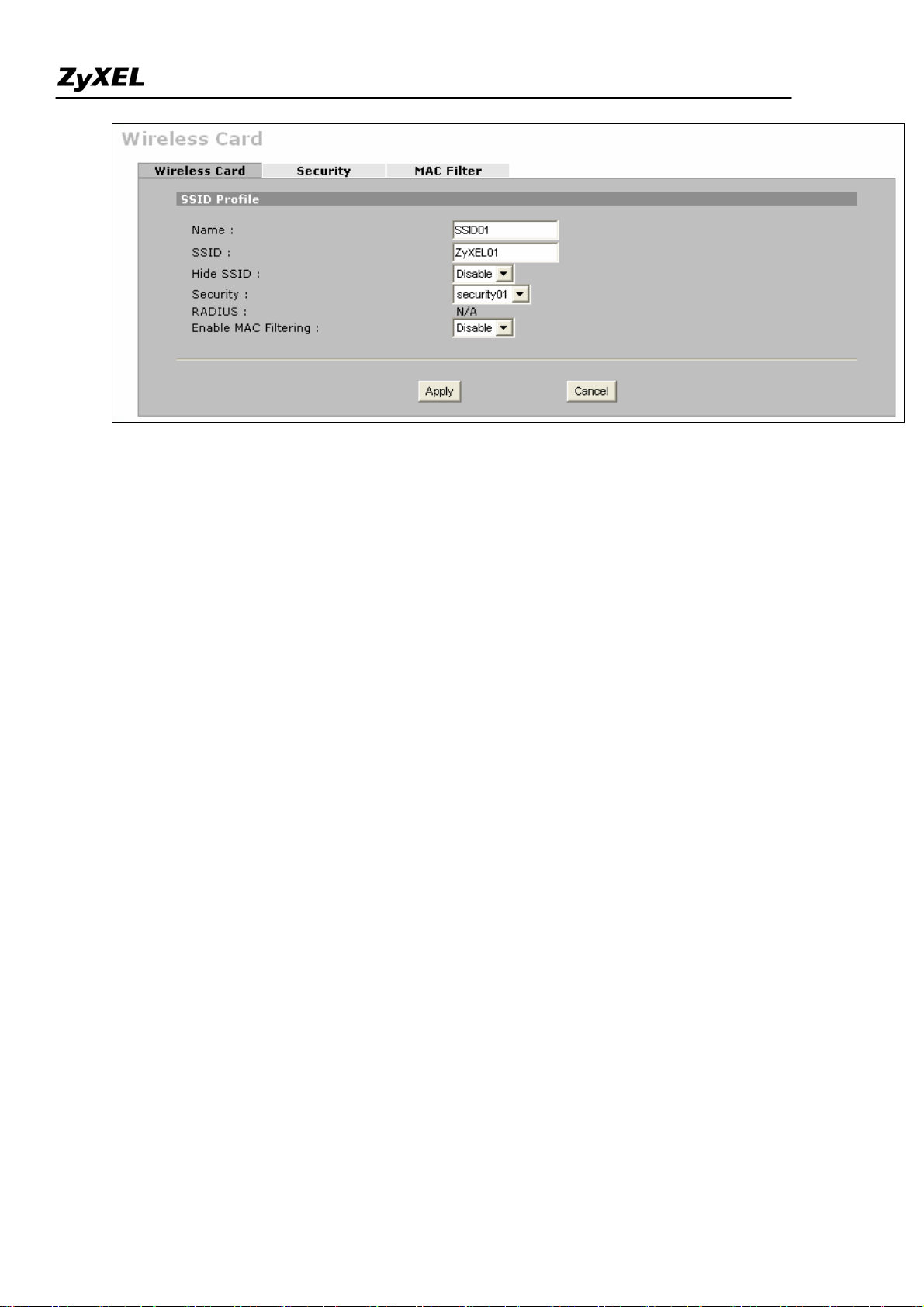
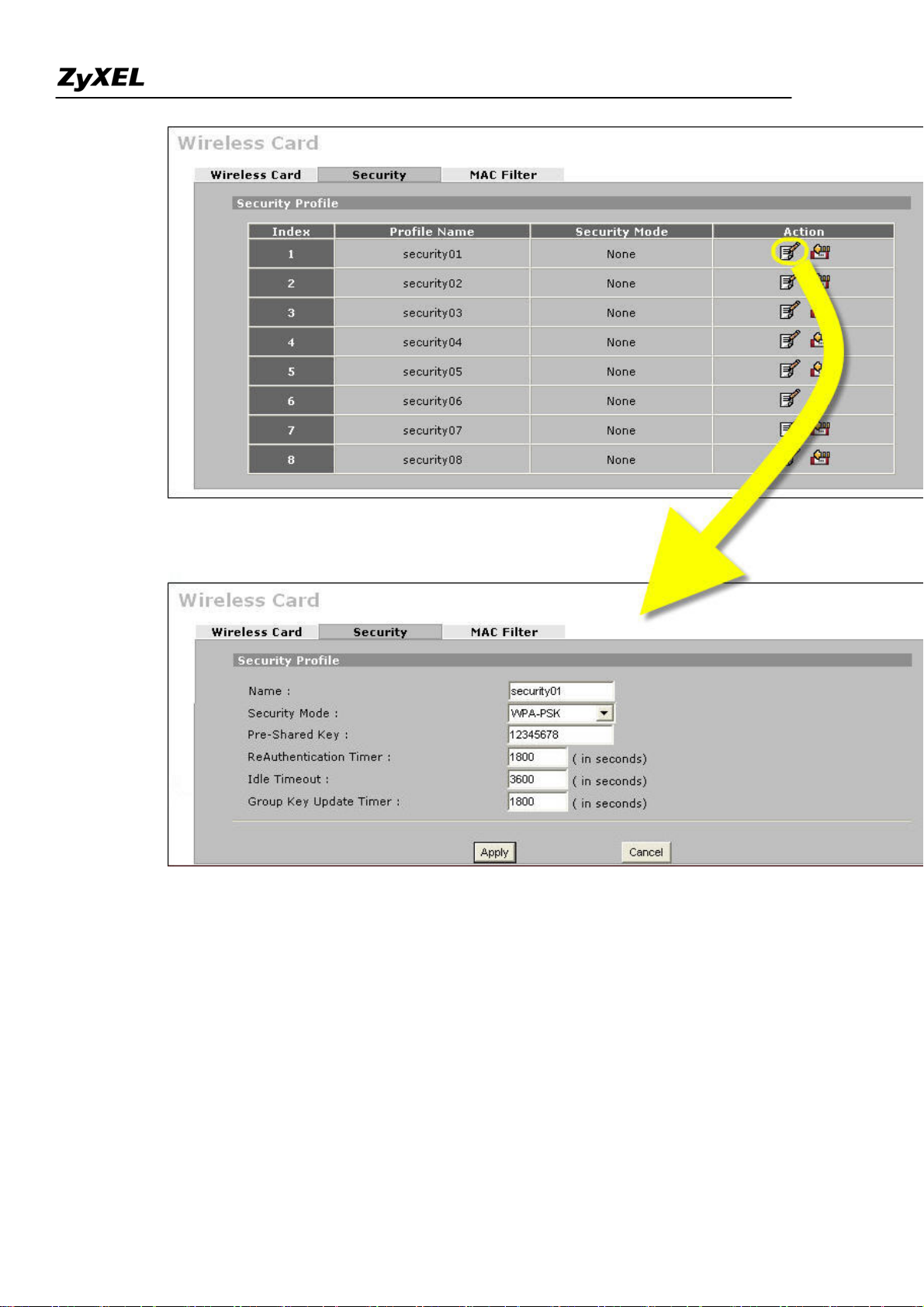
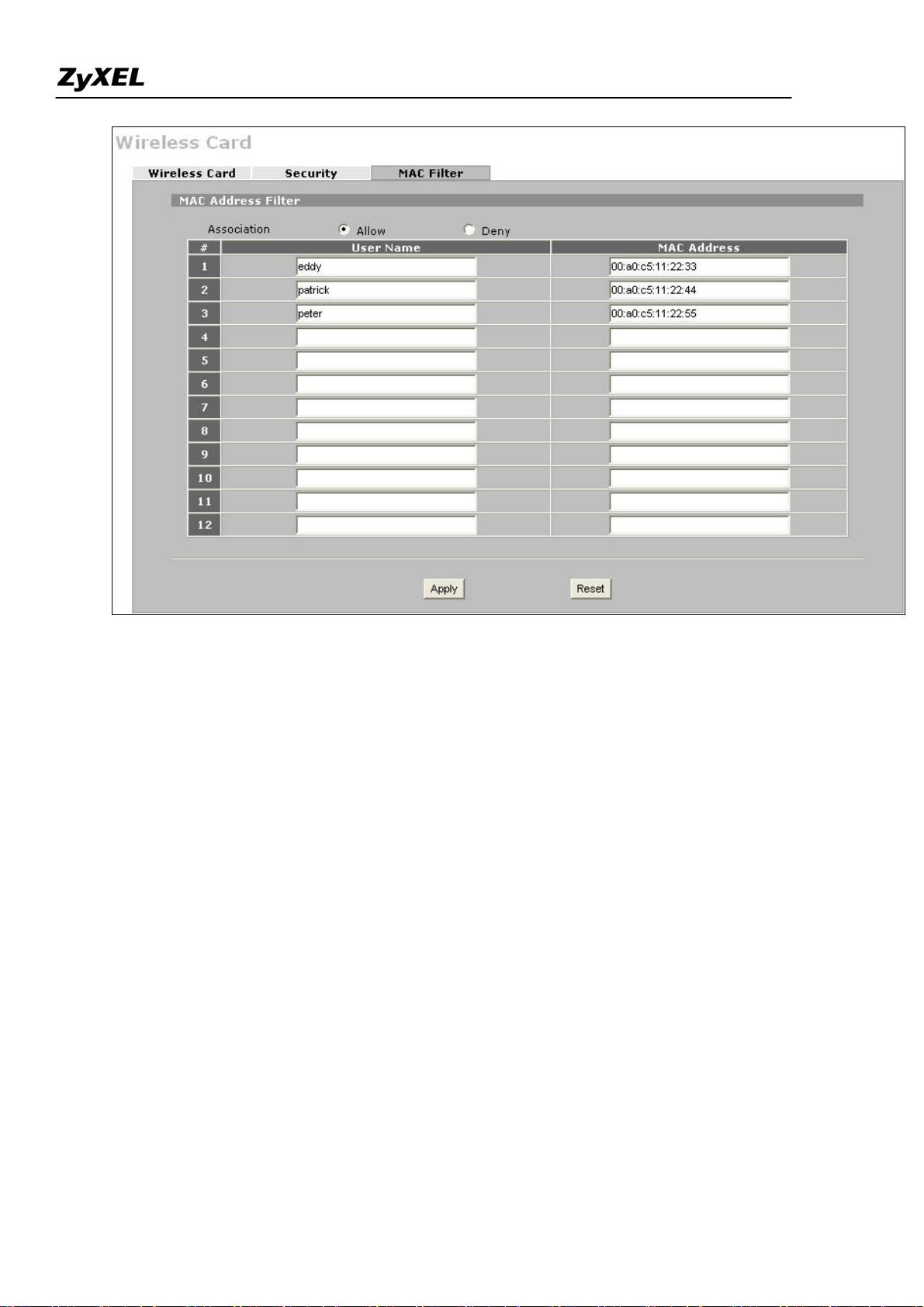
ZyWALL 2WG Support Notes
To configure the security and the MAC filter, go to Wireless Card > Security or Wireless Card > MAC Filter to
further configure it.
For example, we would like to provide the wireless access clients with preset MAC address filtering list.
Furthermore, these clients will also have to pass the security control described below.
a. Wireless security level to "WPA-PSK"with key "12345678".
b. Only allow the PC's with MAC of "00:A0:C5:11:22:33", "00:A0:C5:11:22:44", and
"00:A0:C5:11:22:55" are allowed to associate the wireless network.
All contents copyright (c) 2006 ZyXEL Communications Corporation.
14
Page 15
ZyWALL 2WG Support Notes
All contents copyright (c) 2006 ZyXEL Communications Corporation.
15
Page 16
ZyWALL 2WG Support Notes
All contents copyright (c) 2006 ZyXEL Communications Corporation.
16
Page 17
ZyWALL 2WG Support Notes
After you have configured the Security and MAC filter profiles, you can choose them in the main page
of wireless card setting as shown
All contents copyright (c) 2006 ZyXEL Communications Corporation.
17
Page 18
ZyWALL 2WG Support Notes
Seamless Incorporation into your network
Using Transparent (Bridge Mode) Firewall
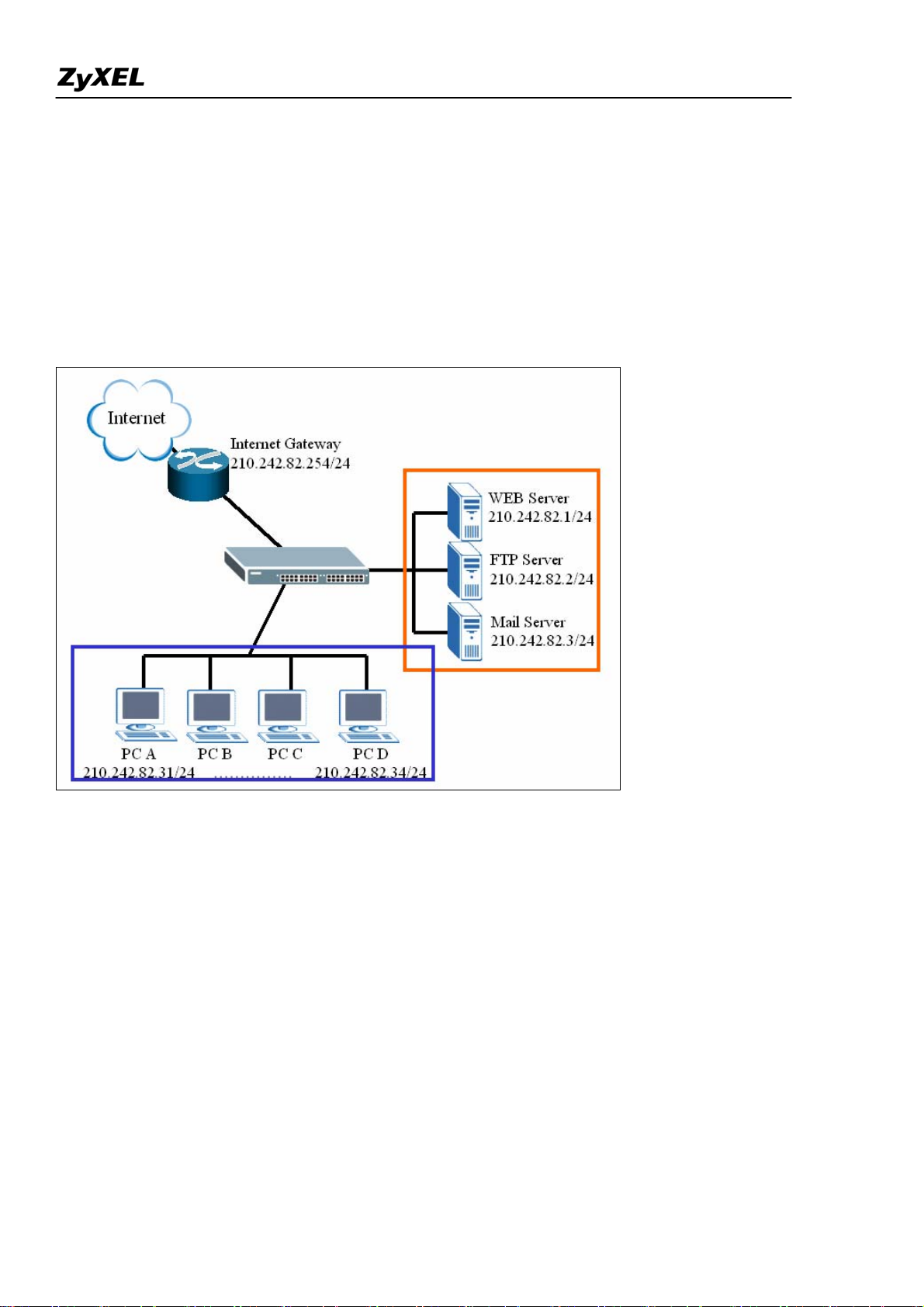
If user wants to insert a firewall into current network, IP setting of hosts and servers may need to change.
Following example illustrates an example of current deployment: servers and other hosts sit in the same IP
segment.
If a router mode firewall is inserted into existing network, user may need to reassign the IP of all servers
and hosts and related setting of applications. However, it may be a huge task to admi nistrators.
All contents copyright (c) 2006 ZyXEL Communications Corporation.
18
Page 19
ZyWALL 2WG Support Notes
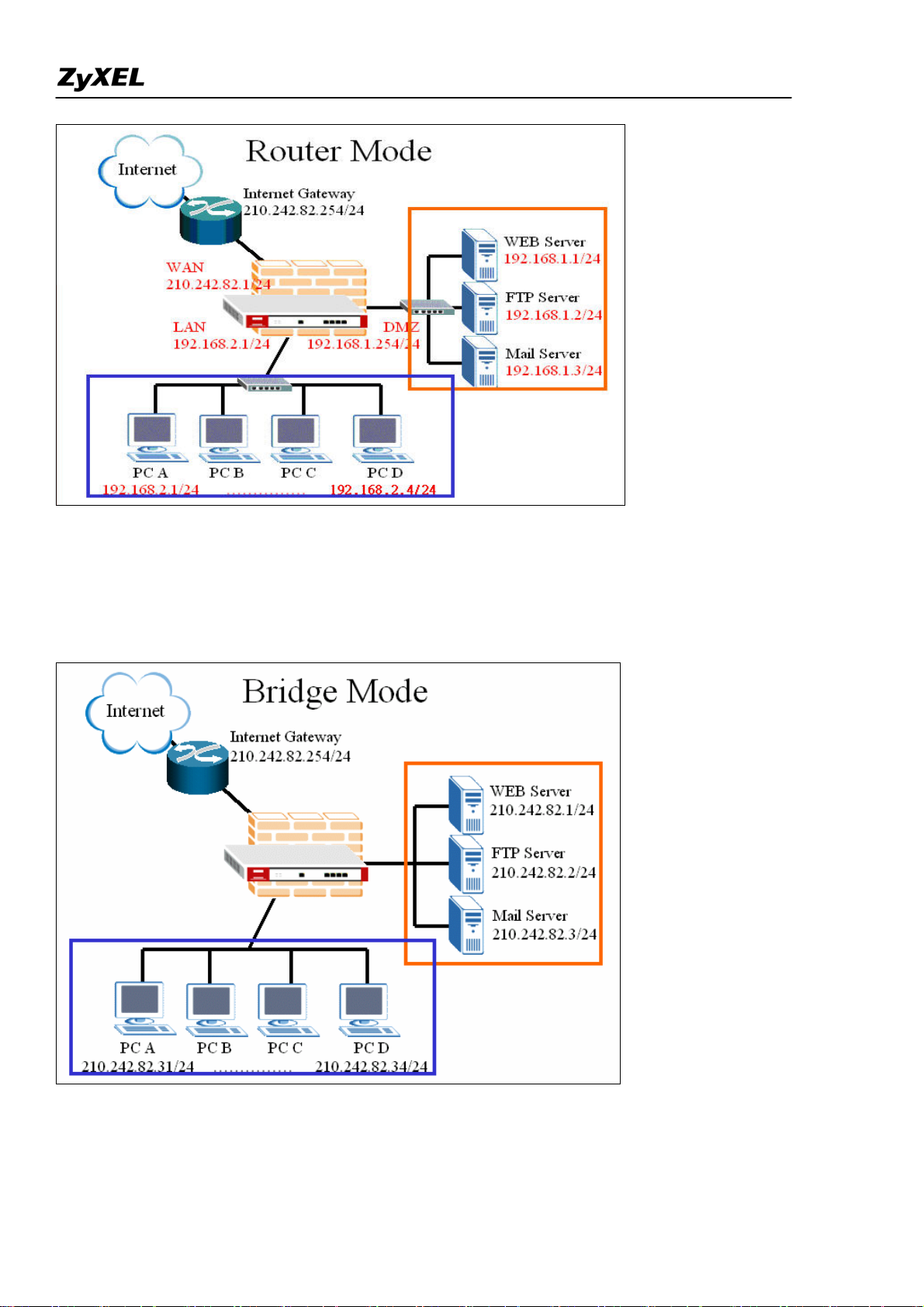
Deploying a transparent mode firewall doesn’t require any changes of settings on the original network
topology. It works as bridge/switch; therefore, all the hosts can communicate with each other as without
firewall in between. At the same time, the transparent firewall can check the packets passing through it
and block attacks and limit unauthorized access through access control right.
In the following section, we will explain how to configure ZyWALL as bridge firewall. Therefore, all
hosts and servers can keep using the same IP as that of current network.
All contents copyright (c) 2006 ZyXEL Communications Corporation.
19
Page 20
ZyWALL 2WG Support Notes
User can configure ZyWALL to act as a router mode firewall or bridge (transparent) firewall. The default
is router mode firewall.
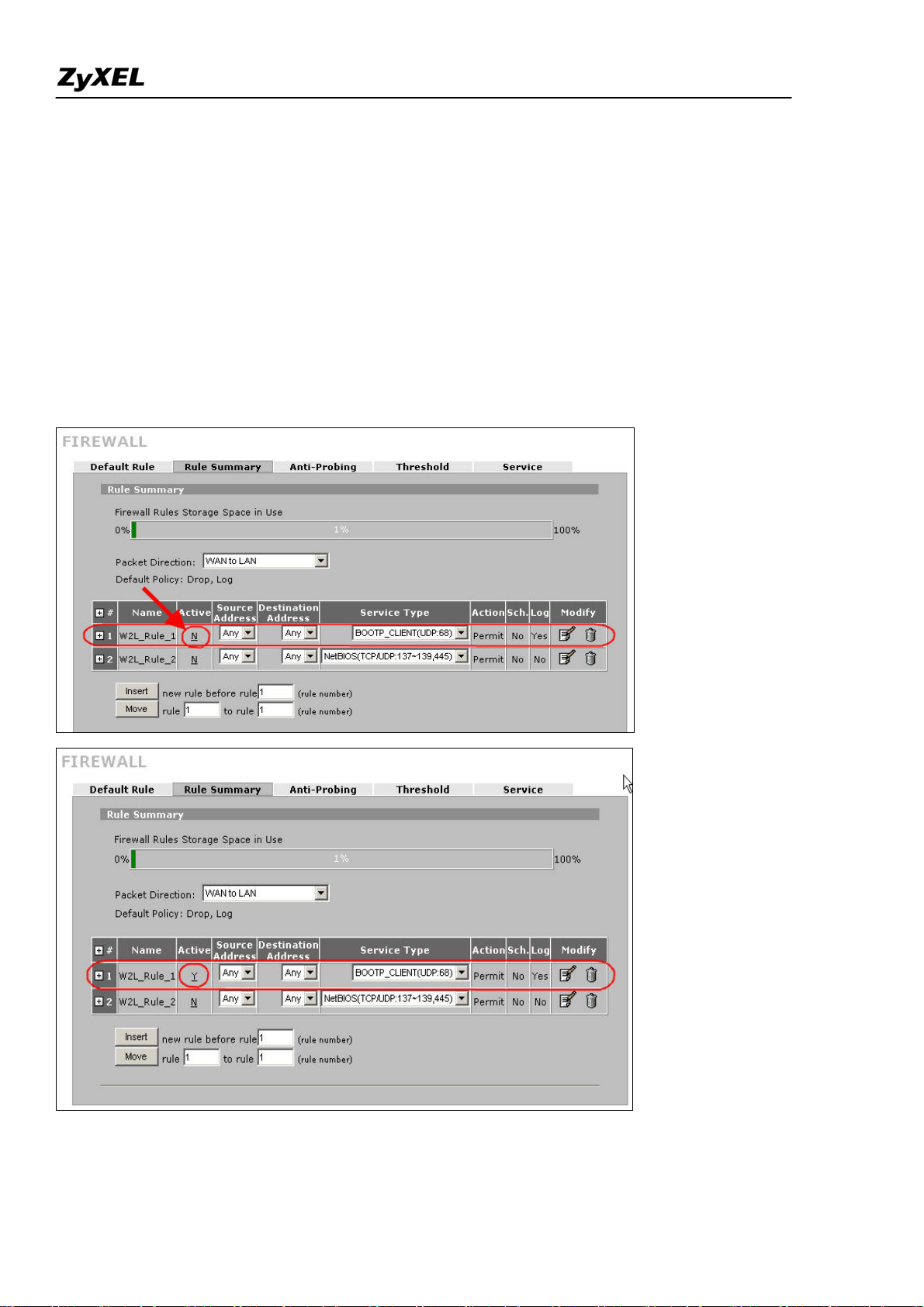
Step1. Before changing ZyWALL to bridge mode, if admin wants to make the ZyWALL’s LAN PC be
able to get DHCP IP address assignment from the DHCP server or the gateway upper than the ZyWALL,
there is one firewall rule needs to be activated.
Go to Firewall >> Rule Summary; choose ‘WAN to LAN’ from ‘Packet Direction’. You will see a rule
to permit the service type, ‘BOOTP_CLIENT(UDP:68)’, to pass firewall. It’s INACTIVE by default.
Admin can activate the rule by clicking the ‘N’ as following picture. Then the rule will be activated right
away.
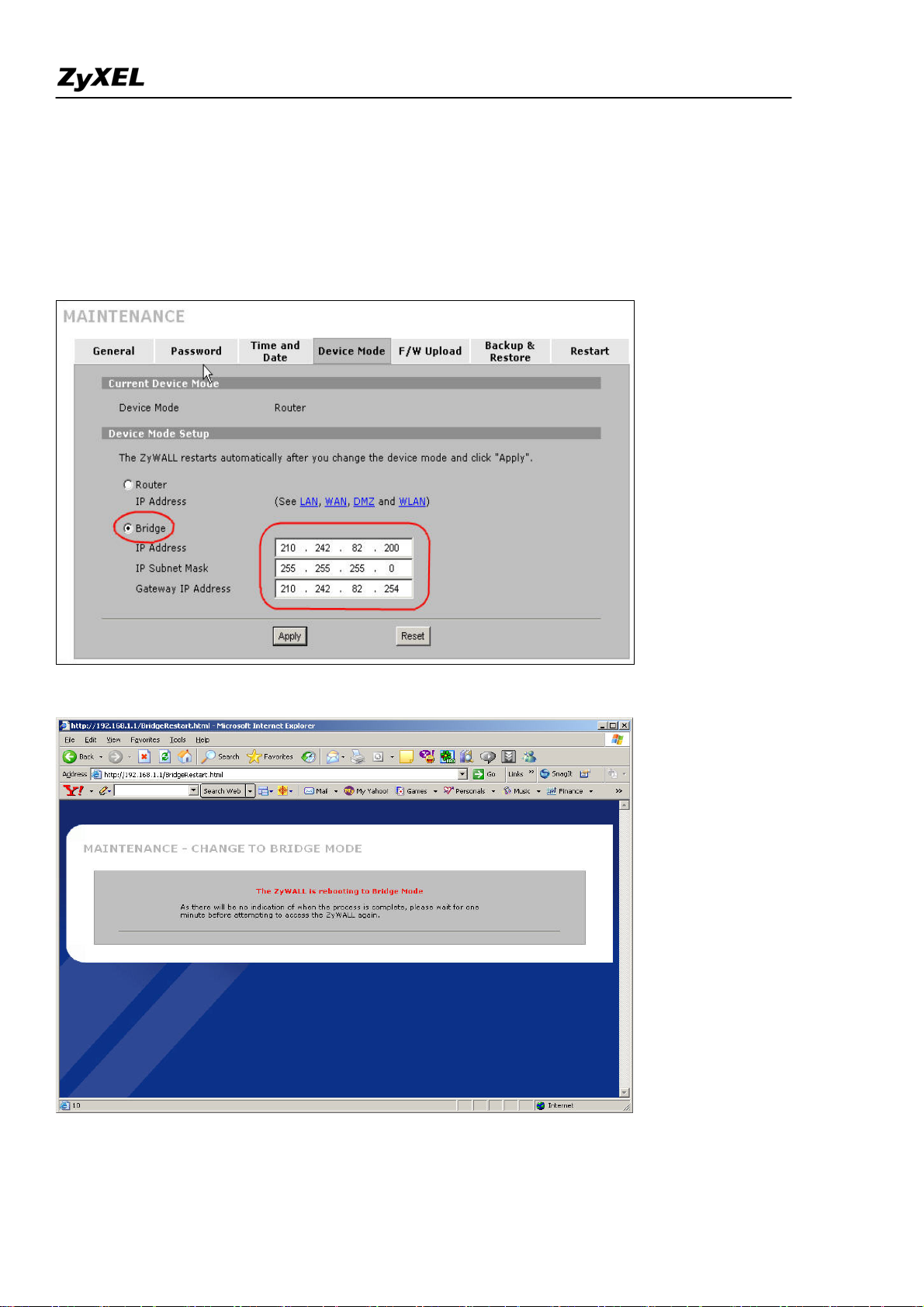
Step2. To change the device mode, go to MAINTENANCE >> Device Mode. Select ‘Bridge’ and
All contents copyright (c) 2006 ZyXEL Communications Corporation.
20
Page 21
ZyWALL 2WG Support Notes
assign a management IP for ZyWALL. The Gateway IP Address is used as next-hop of default route.
ZyWALL will restart after applying the change.
(Note: Here we suggest admin to dedicate an IP address to ZyWALL itself at the same subnet as
original one (like 210.242.82.X/24 in this example). In this way, admin doesn’t need to change his
PC’s IP address when he wants to access Internet and ZyWALL’s web GUI at the same time.)
21
All contents copyright (c) 2006 ZyXEL Communications Corporation.
Page 22
ZyWALL 2WG Support Notes
Step3. After rebooting, login ZyWALL’s GUI by accessing ZyWALL’s management IP address.
(Accessing ZyWALL by the PC with a static IP address configured in the same subnet or with an IP from
DHCP server (refer to step1 for the pre-configured firewall rule).
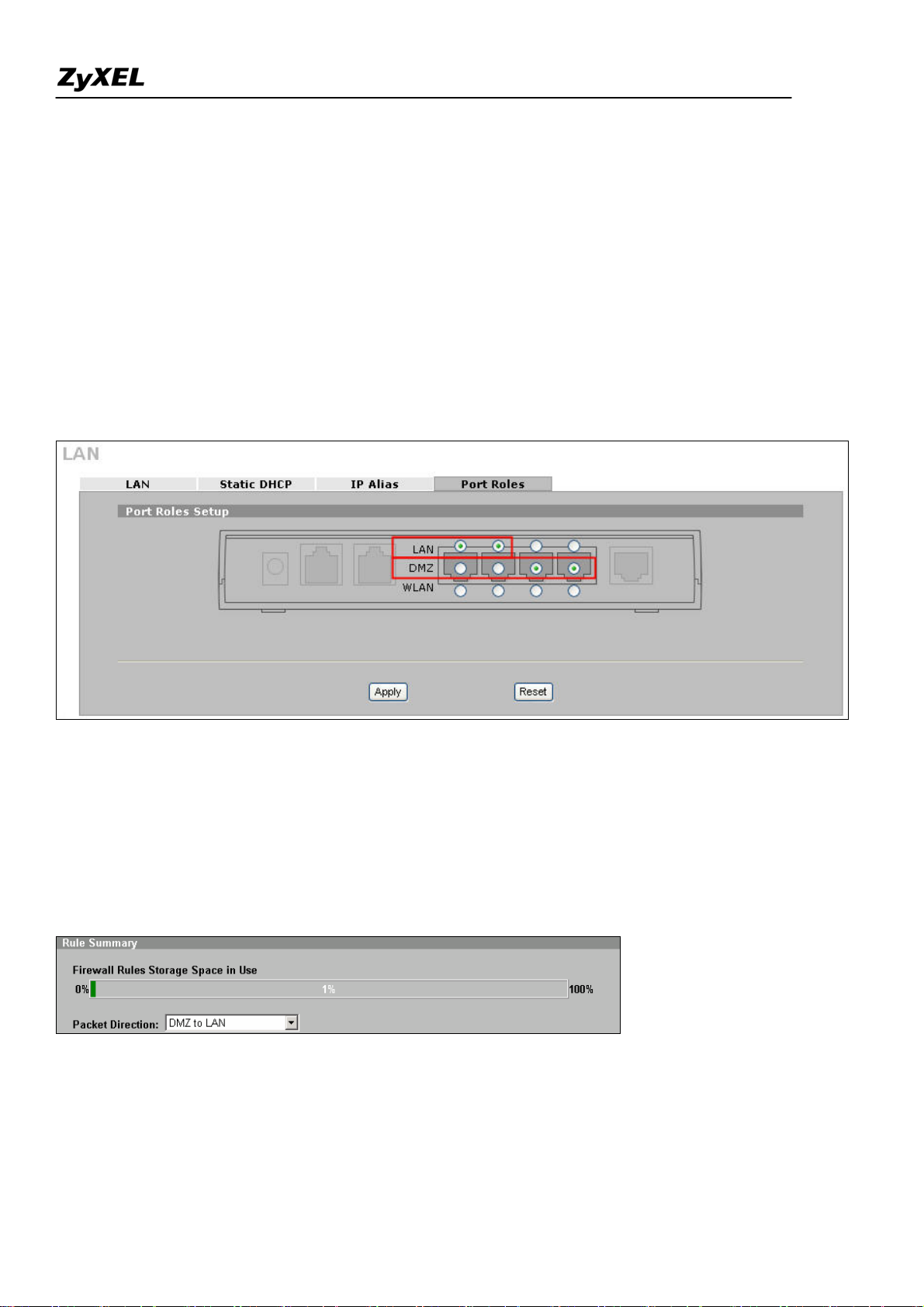
Step4. In this example, since we want to apply a DMZ zone for servers. So for ZyWALL 2 Plus which
the ports of LAN & DMZ can be configured, user can decide the roles of each port.
Go to Network >> LAN (or DMZ or WLAN) >> Port Roles. By default, 4 ports are assigned to LAN.
In this example, we use port 1 & 2 assigned to LAN and Port 3 & 4 assigned to DMZ as following
picture.
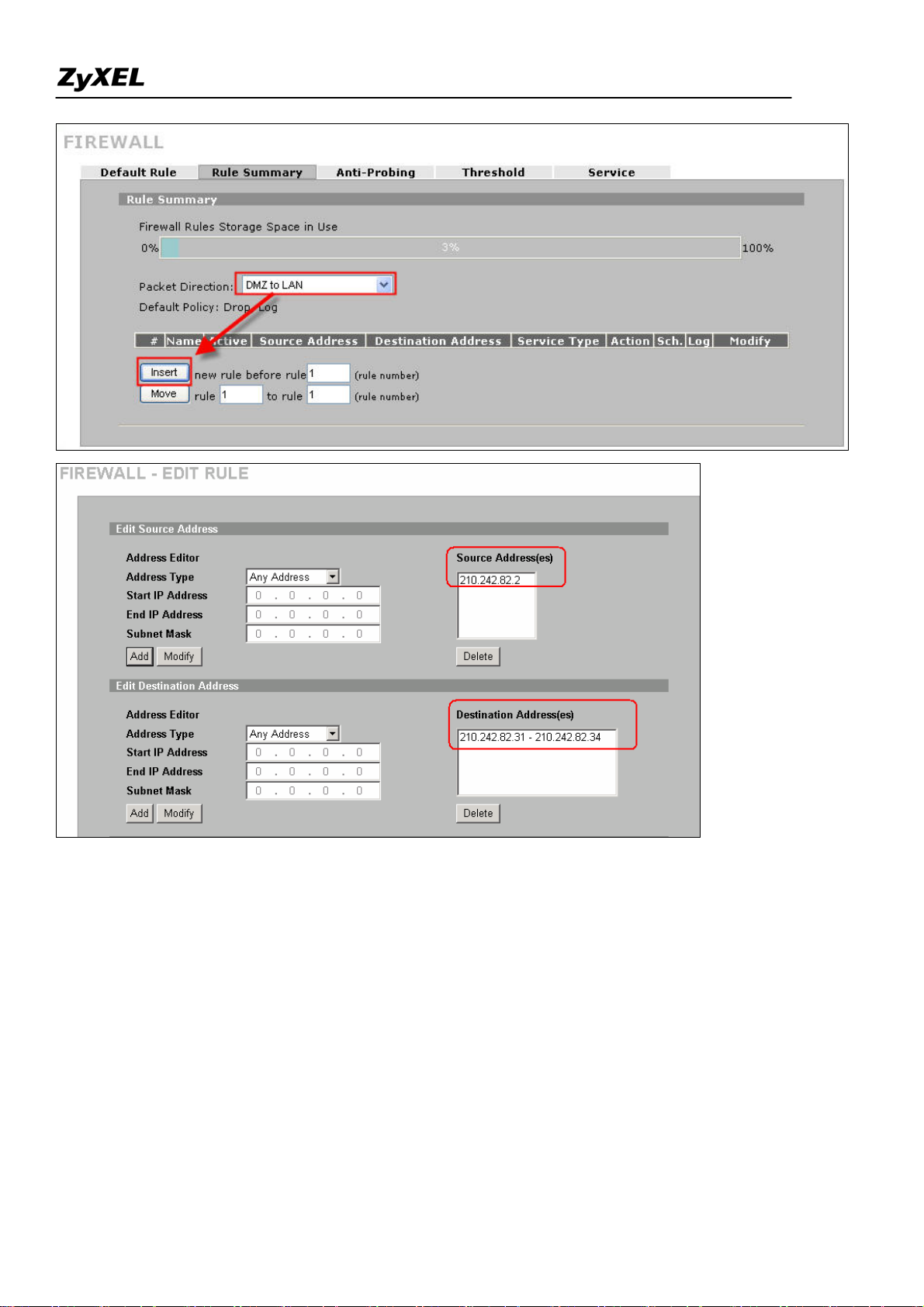
Step5. Furthermore, to configure firewall rule to control the access of your network, go to SECURITY
>> FIREWALL as you do in router mode firewall. For example, user wants to block the access from a
FTP server (210.242.82.2) in DMZ zone to LAN hosts (210.242.82.31~34) (Note that they all sits in the
same IP segment 210.242.82.0/24). Edit the firewall rule via Firewall >> Rule Summary and with
packet direction: DMZ to LAN.
And enter 210.242.82.2 as the source address and 210.242.82.31~34 as destination address. And then
select the service and set the action for ‘Matched Packet’ to
‘BLOCK’.
All contents copyright (c) 2006 ZyXEL Communications Corporation.
22
Page 23
ZyWALL 2WG Support Notes
23
All contents copyright (c) 2006 ZyXEL Communications Corporation.
Page 24
ZyWALL 2WG Support Notes
Internet Connection
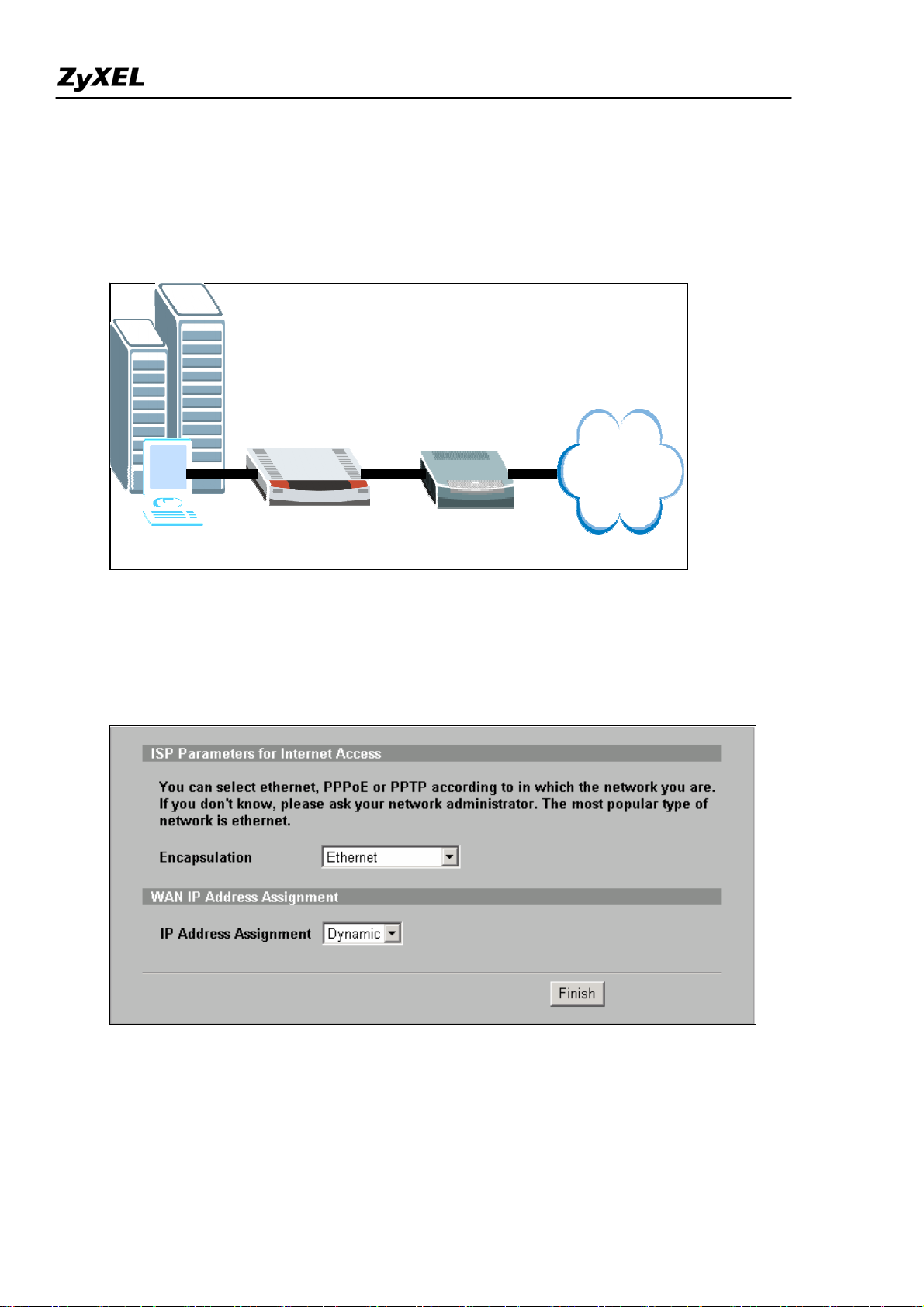
A typical Internet access application of the ZyWALL is shown below. This section guides you how to
configure ZyWALL to gain the Internet access.
ZyWALL
Internet
LAN
WAN
Step1. First of all, Select Home menu and click Internet Access Wizard to configure your WAN
connection. Click “Internet Access” under Home >> Wizards for Internet Access Quick Setup
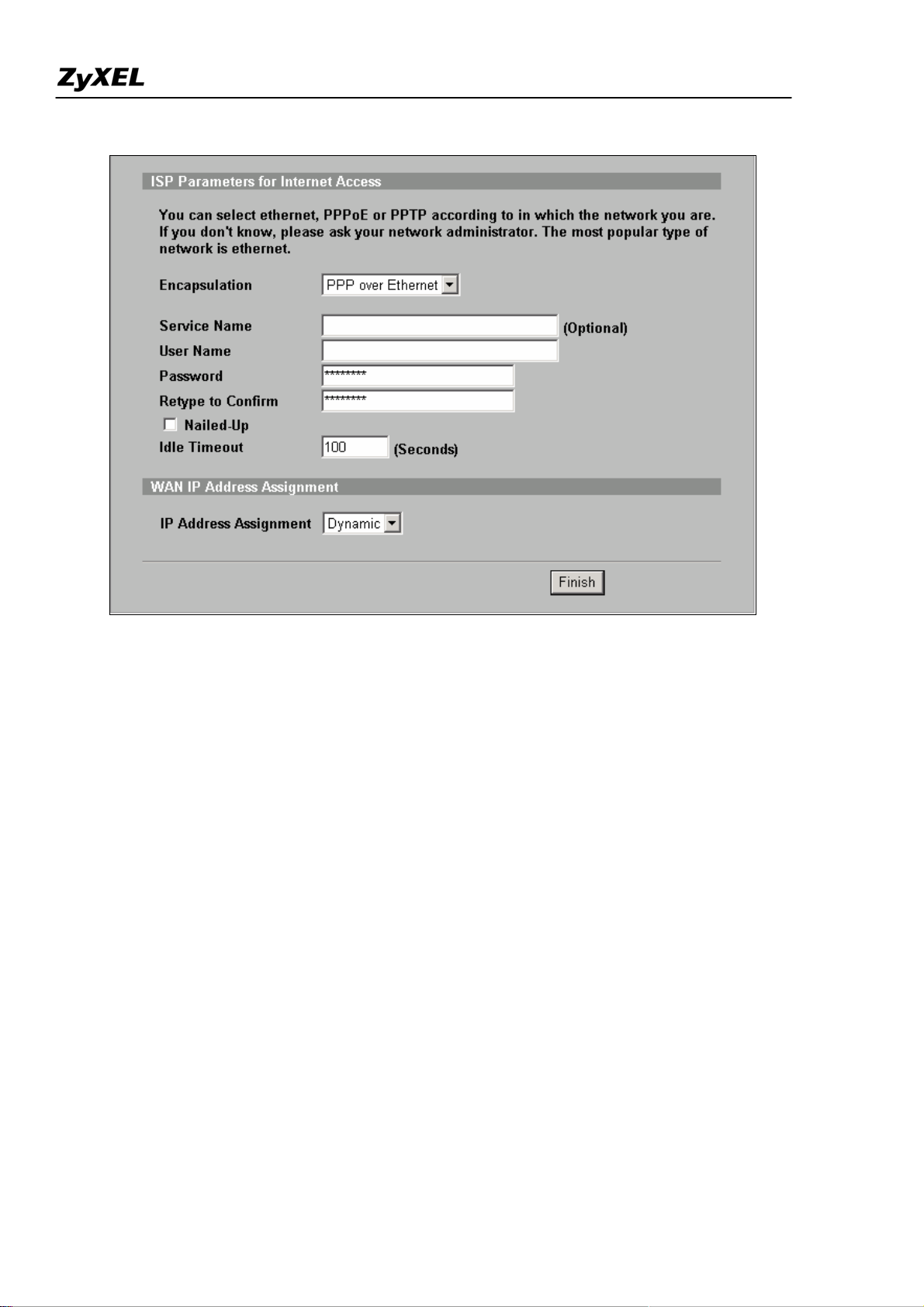
A pop-up window as below will indicate you to enter ISP Parameters for Internet Access .
There are three kinds of encapsulation which are supported by ZyWALL: Ethernet, PPPoE & PPTP.
Select the correct encapsulation type from the drop-down menu. The wizards will requests related
information needed. These fields vary depending on what you select in the Encapsulation field. Fill them
in with the information exactly as given by the ISP or network administrator.
All contents copyright (c) 2006 ZyXEL Communications Corporation.
24
Page 25
ZyWALL 2WG Support Notes
Following picture is an example while PPPoE is selected.
Once the required information is correctly configured, click on the “Finish” button to apply the setting
and then you have finished configuring Internet Access on WAN link.
DHCP server/client/relay
ZyWALL supports
(1) DHCP client on the WAN port
User can choose either a static IP or a dynamic IP address for WAN port. When choosing dynamic IP,
ZyWALL will get a DHCP IP address from ISP or upper layer DHCP server.
(2) DHCP server/relay/none on the LAN ports
ZyWALL supports DHCP server for LAN ports, but also
1. When choosing DHCP setting as ‘None’, the LAN will NOT assign IP address to the
associated hosts. Client PCs need to configure IP address manually.
All contents copyright (c) 2006 ZyXEL Communications Corporation.
25
Page 26
ZyWALL 2WG Support Notes
2. When choosing DHCP setting as a ‘Server’, the LAN will automatically assign IP, subnet,
gateway and DNS to the associated clients.
3. When choosing DHCP setting as a ‘Relay’, the LAN will forward the DHCP request to
another DHCP server.
Using NAT/Multi-NAT
• What is Multi-NAT?
• How NAT works
• NAT Mapping Types
• SUA versus Multi-NAT
• Example
Step 1. Applying NAT on WAN Interface
Step 2. Configuring NAT Address Mapping
Step 3. Using Multiple Global IP addresses for clients and servers (One-to-One, Many-to-One,
Server Set mapping types)
• Application -- Non NAT-Friendly Support
• What is Multi-NAT?
NAT (Network Address Translation-NAT RFC 1631) is the translation of an Internet Protocol address used
within one network to a different IP address known within another network. One network is designated the
inside
network and the other is the
outside
. Typically, a company maps its local inside network addresses to one
or more global outside IP addresses and "unmaps" the global IP addresses on incoming packets back into local
IP addresses. The IP addresses for the NAT can be either fixed or dynamically assigned by the ISP. In addition,
you can designate servers, e.g., a web server and a telnet server, on your local network and make them
accessible to the outside world. If you do not define any servers, NAT offers the additional benefit of firewall
protection. In such case, all incoming connections to your network will be filtered out by the ZyWALL, thus
preventing intruders from probing your network.
The SUA feature that the ZyWALL supports previously operates by mapping the private IP addresses to a
global IP address. It is only one subset of the NAT. The ZyWALL supports the most of the features of the NAT
based on RFC 1631, and we call this feature as 'Multi-NAT'. For more information on IP address translation,
please refer to RFC 1631,
The IP Network Address Translator (NAT)
.
26
All contents copyright (c) 2006 ZyXEL Communications Corporation.
Page 27
ZyWALL 2WG Support Notes
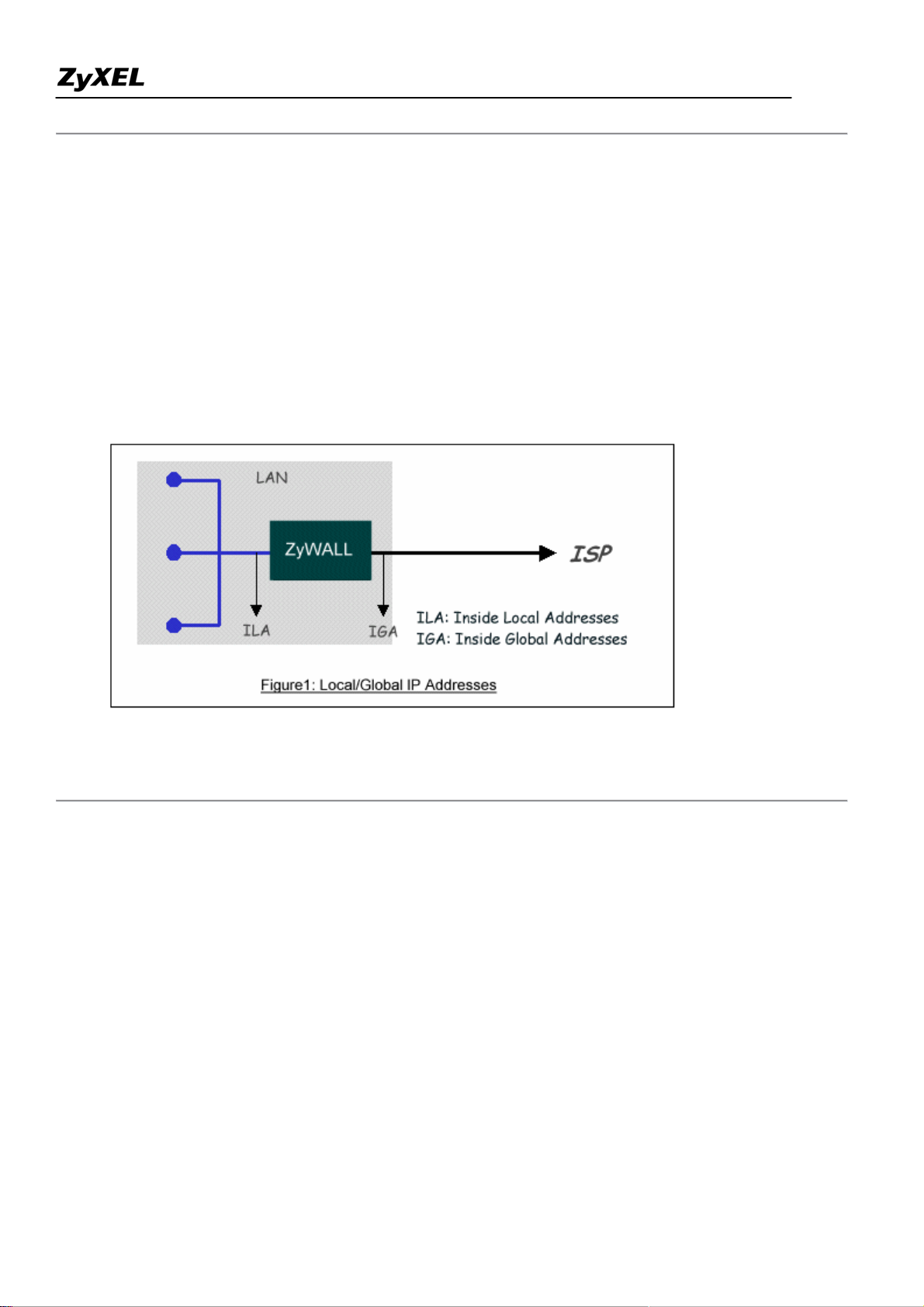
• How NAT works
If we define the local IP addresses as the Internal Local Addresses (ILA) and the global IP addresses as the
Inside Global Address (IGA), see the following figure. The term 'inside' refers to the set of networks that are
subject to translation. NAT operates by mapping the ILA to the IGA required for communication with hosts on
other networks. It replaces the original IP source address (and TCP or UDP source port numbers) and then
forwards each packet to the Internet ISP, thus making them appear as if they had come from the NAT system
itself (e.g., the ZyWALL router). The ZyWALL keeps track of the original addresses and port numbers so
incoming reply packets can have their original values restored.
• NAT Mapping Types
NAT supports five types of IP/port mapping. They are:
1. One to One
In One-to-One mode, the ZyWALL maps one ILA to one IGA.
2. Many to One
In Many-to-One mode, the ZyWALL maps multiple ILA to one IGA. This is equivalent to SUA (i.e., PAT,
port address translation), ZyXEL's Single User Account feature that previous ZyNOS routers supported
(the SUA only option in today's routers).
3. Many to Many Overload
In Many-to-Many Overload mode, the ZyWALL maps the multiple ILA to shared IGA.
4. Many One to One
In Many One to One, the ZyWALL maps each ILA to unique IGA.
All contents copyright (c) 2006 ZyXEL Communications Corporation.
27
Page 28
ZyWALL 2WG Support Notes
5. Server
In Server mode, the ZyWALL maps multiple inside servers to one global IP address. This allows us to
specify multiple servers of different types behind the NAT for outside access. Note, if you want to map
each server to one unique IGA please use the One-to-One mode.
The following table summarizes these types.
NA T Type IP Mapping
One-to-One ILA1<--->IGA1
Many-to-One
(SUA/PAT)
Many-to-Many
Overload
Many One-to-One
Server
ILA1<--->IGA1
ILA2<--->IGA1
...
ILA1<--->IGA1
ILA2<--->IGA2
ILA3<--->IGA1
ILA4<--->IGA2
...
ILA1<--->IGA1
ILA2<--->IGA2
ILA3<--->IGA3
ILA4<--->IGA4
...
Server 1 IP<--->IGA1
Server 2 IP<--->IGA1
• SUA Versus Multi-NAT
SUA (Single User Account), if you get only one public IP address from your ISP, then you should use SUA.
With SUA, PCs on ZyWALL's LAN side can access Internet without further configuration. If you have internal
servers to be accessed by remote users on Internet, you need to go to ADVANCED -> SUA/NAT -> SUA
Server to setup which service, or port numbers, you would like to forward to which Internal server.
Multi-NAT, if you get multiple public IP addresses from your ISP, then you may use Multi-NAT. With
Multi-NAT, you can choose different types of NAT mapping methods to utilize the public IP addresses. You
should define each NAT mapping rules clearly in ADVANCED -> SUA/NAT -> Address Mapping, so that
internal PCs can access Internet and internal servers can be accessed by remote uses on Internet.
28
All contents copyright (c) 2006 ZyXEL Communications Corporation.
Page 29
ZyWALL 2WG Support Notes
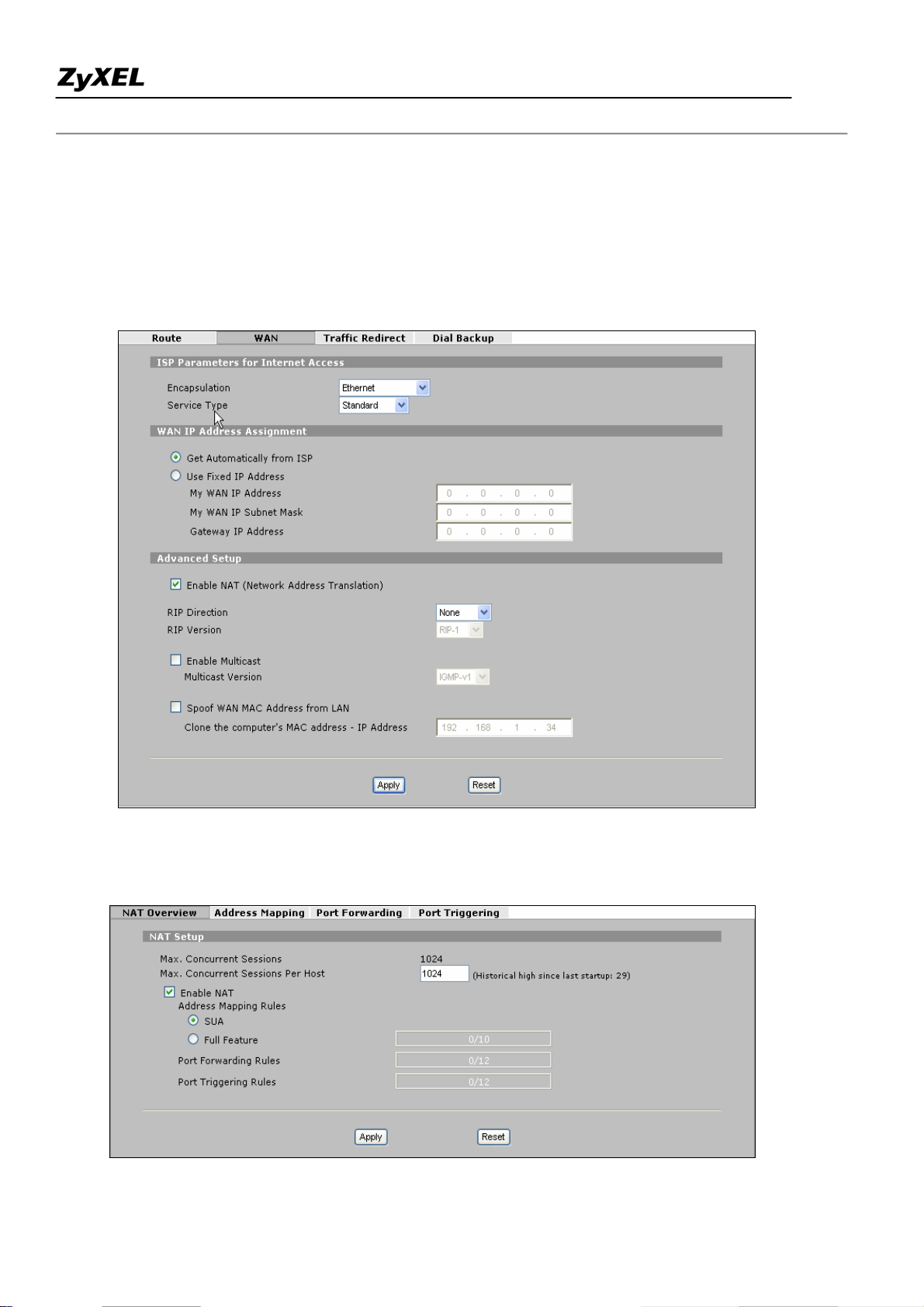
Step 1. Applying NAT in WAN Interface
You can choose the NAT mapping types to either SUA Only or Full Feature in WAN setup.
NETWORK -> WAN
or ADVANCED -> NAT -> NAT Overview
All contents copyright (c) 2006 ZyXEL Communications Corporation.
29
Page 30
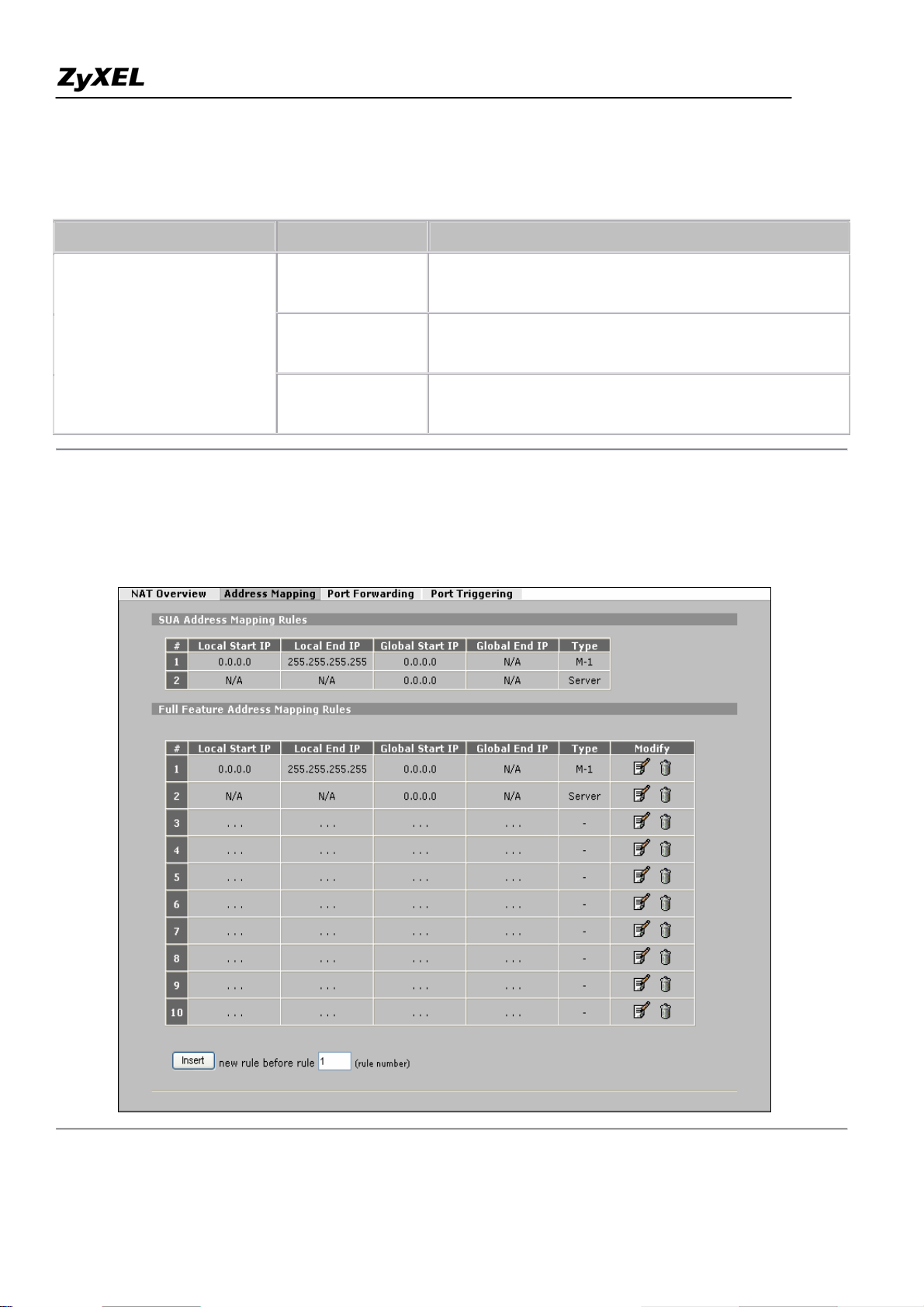
ZyWALL 2WG Support Notes
Key Settings
Field Options Description
Full Feature
Set to 'Full Feature' if there are multiple IP addresses
given by ISP and can assigned to your clients.
Set to 'Routring' if you clients use Internet IP
Network Address Translation
Routing
addresses and thus do not need NAT function.
Set this field to 'SUA Only' if you want all clients
SUA Only
share one IP to Internet.
Step 2. Configuring NAT Address Mapping
To configure NAT, go to ADVANCED -> NAT -> Address Mapping
All contents copyright (c) 2006 ZyXEL Communications Corporation.
30
Page 31

ZyWALL 2WG Support Notes
Step 3. Using Multiple Global IP addresses for clients and servers (One-to-One, Many-to-One, Server Set
mapping types)
In this case we have 3 IGAs (IGA1, IGA2 and IGA3) from the ISP. We have two very busy internal FTP
servers and also an internal general server for the web and mail. In this case, we want to assign the 3 IGAs by
the following way using 4 NAT rules.
Rule 1 (One-to-One type) to map the FTP Server 1 with ILA1 (192.168.1.10) to IGA1 (200.1.1.1).
Rule 2 (One-to-One type) to map the FTP Server 2 with ILA2 (192.168.1.11) to IGA2 (200.1.1.2).
Rule 3 (Many-to-One type) to map the other clients to IGA3 (200.1.1.3).
Rule 4 (Server type) to map a web server and mail server with ILA3 (192.168.1.20) to IGA3. Type
Server allows us to specify multiple servers, of different types, to other machines behind NAT on
the LAN.
Rule 1 Setup: Select One-to-One type to map the FTP Server 1 with ILA1 (192.168.1.10) to IGA1 (200.1.1.1).
All contents copyright (c) 2006 ZyXEL Communications Corporation.
31
Page 32

ZyWALL 2WG Support Notes
Rule 2 Setup: Selecting One-to -One type to map the FTP Server 2 with ILA2 (192.168.1.11) to IGA2
(200.1.1.2).
Rule 3 Setup: Select Many-to-One type to map the other clients to IGA3.
Rule 4 Setup: Select Server type to map our web server and mail server with ILA3 (192.168.1.20) to IGA3.
When we have configured all four rules in the rule summary page.
All contents copyright (c) 2006 ZyXEL Communications Corporation.
32
Page 33

ZyWALL 2WG Support Notes
Now we configure all other incoming traffic to go to our web server and mail server in "Port Mapping" page,
Please note that if you turn on ZyWALL's firewall function, then you should add a firewall rule from WAN to
LAN to forward the incoming connections. If you would like to only allow traffic going to the internal server,
you should specify server's private IP address in the field of the destination IP address.
All contents copyright (c) 2006 ZyXEL Communications Corporation.
33
Page 34

ZyWALL 2WG Support Notes
Application for Non NAT Friendly Support
Some servers providing Internet applications such as some mIRC servers do not allow users to login using the
same IP address. In this case it is better to use Many One-to-One or One-to-One NAT mapping types, thus each
user login to the server is using a unique global IP address. The following figure illustrates this.
One rule configured for using Many One-to-One mapping type is shown below.
All contents copyright (c) 2006 ZyXEL Communications Corporation.
34
Page 35

ZyWALL 2WG Support Notes
Optimize network performance & availability
Using Bandwidth Management
Why Bandwidth Management (BWM)?
Nowadays, we have many different traffic types for Internet applications. Some traffic may consume high
bandwidth, such as FTP (File Transfer Protocol), if you are downloading or uploading files with large size.
Some other traffic may not require high bandwidth, but they require stable supply of bandwidth, such as
VoIP traffic. The VoIP quality would not be good, if all of the outgoing bandwidth is occupied via FTP.
Additionally, chances are that you would like to grant higher bandwidth for some body special that is
using specific IP address in your network. All of these are reasons why we need bandwidth management.
All contents copyright (c) 2006 ZyXEL Communications Corporation.
35
Page 36

ZyWALL 2WG Support Notes
How Bandwidth Management in ZyWALL?
ZyWALL achieves BWM by classifying packets, and control when to send out the classified packets.
Bandwidth Management of ZyXEL appliances operates on the IP layer. The major step to configure
BWM is defining filter rules by fields of IP header or TCP/UDP port number. Then specify the volume of
bandwidth you want to allocate to the filtered traffic. There are two types of BWM in ZyXEL
implementations, Full and Lite versions.
Full version: Users can define how they want to classify traffic on each interface. In this version,
child-class can borrow bandwidth from parent-class if necessary by Bandwidth Borrowing. For classes
that need more bandwidth even after bandwidth borrowing, users can also apply Maximize Bandwidth
Usage from the interface.
Using BWM
All contents copyright (c) 2006 ZyXEL Communications Corporation.
36
Page 37

ZyWALL 2WG Support Notes
Go to ADVANCED->BW MGMT->Summary, activate bandwidth management on the interface you
would like to manage. We enable the BWM function on WAN interface in this example.
Enter the total speed for this interface that you want to allocate using bandwidth management. This
appears as the bandwidth budget of the interface’s root class.
Select how you want the bandwidth to be allocated. Priority-Based means bandwidth is allocated via
priority, so the traffic with highest priority would be served first, then the second priority is served
secondly and so on. If Fairness-Based is chosen, then the bandwidth is allocated by ratio. Which means if
A class needs 300 kbps, B class needs 600 kbps, then the ratio of A and B's actual bandwidth is 1:2. So if
we get 450 kbps in total, then A would get 150 kbps, B would get 300 kbps.
Key Settings:
Active
Speed
Scheduler
Maximize
Bandwidth
Usage
Go to ADVANCED->BW MGMT->Class Setup, select the interface on which you would like to setup
Check the box to enable BWM on the interface. Note that if you would like to manage
traffic from WAN to LAN, you should apply BWM on LAN interface.
Enter the total speed to manage on this interface. This value is the budget of the class
tree's root.
Choose the principle to allocate bandwidth on this interface. Priority-Based allocates
bandwidth via priority. Fairness-Based allocates bandwidth by ratio.
Check this box if you would like to give residuary bandwidth from Interface to the
classes who need more bandwidth than configured amount. Do not select this if you
want to reserve bandwidth for traffic that does not match a bandwidth class or you want
to limit the bandwidth of each class at the configured value. (Please note that to meat the
second condition, you should also disable bandwidth borrowing on the class.)
the Class tree.
Click the radio button besides the Root Class, then press 'Add Sub-Class'
All contents copyright (c) 2006 ZyXEL Communications Corporation.
37
Page 38

ZyWALL 2WG Support Notes
Key Settings:
Class Name
Bandwidth
Budget
Priority
Bandwidth
Borrowing
Enable
Bandwidth
Filter
Destination IP
Address
Give this class a name, for example, 'App'
Configure the speed you would like to allocate to this class
Enter a number between 0 and 7 to set the priority of this class. The higher the number,
the higher the priority. The default setting is 3.
Check this box if you would like to let this class to borrow bandwidth from it's parents
when the required bandwidth is higher than the configured amount. Do not check this if
you want to limit the bandwidth of this class at the configured value.(Please note that
you should also disable Maximize Bandwidth Usage on the interface to meat the
condition.)
Check this to specify the traffic types via IP addresses/Port numbers.
Enter the IP address of destination that meats this class.
Destination
Subnet Mask
Destination
Port
Enter the destination subnet mask.
Enter the destination port number of the traffic.
All contents copyright (c) 2006 ZyXEL Communications Corporation.
38
Page 39

ZyWALL 2WG Support Notes
Source IP
Enter the IP address of source that meats this class. Note that for traffic from 'LAN to
WAN', since BWM is before NAT, you should use the IP address before NAT
Address
processing.
Source Subnet
Enter the destination subnet mask.
Mask
Source Port
Protocol ID
Enter the source port number of the traffic.
Enter the protocol number for the traffic. 1 for ICMP, 6 for TCP or 17 for UDP
After configuration BWM, you can check current bandwidth of the configured traffic in
ADVANCED->BWM MGMT->Monitor. The values in the column of Current usage (kbps) would
display the actually number.
Scenario - Limit bandwidth usage, but when there is residual bandwidth, we hope it can be shared fairly
among several active traffic.
Description
FTP Client A can get 400kbps FTP traffic and FTP Client B can get 800 kbps FTP traffic and IPTV user
can retrieve 800 kbps UDP streaming.
LAN Interface: Fairness-based, Speed = 2048kbps
Class 1: Budget = 400kbps, Dest. IP = FTP Client A’s IP, Service = FTP, Priority = 3, enable Borrow
Class 2: Budget = 800kbps, Dest. IP = FTP Client B’s IP, Service = FTP, Priority = 3, enable Borrow
Class 3: Budget = 800kbps, Dest IP = IPTV Client’s IP, Protocol = UDP.
All contents copyright (c) 2006 ZyXEL Communications Corporation.
39
Page 40

ZyWALL 2WG Support Notes
Step1.
Activate Bandwidth Management on the interface on which you want to control. In this example, it is
LAN. Assign 2048Kbps to LAN interface.
Step2. Go to “Class Setup” and select LAN from the drop-down list of Interface. Click on Root Class and
then click on “Add Sub-Class” to create and add a new class under root.
We add a service and allocate 400kbps for FTP and destined to FTP Client A. Select the Service as FTP
from drop-down list. Input Client A’s IP address as Destination IP Address.
All contents copyright (c) 2006 ZyXEL Communications Corporation.
40
Page 41

ZyWALL 2WG Support Notes
Step3. Add another service and allocate 800kbps for FTP and destined to FTP Client B. Select the Service
as FTP from drop-down list. Input Client B’s IP address as Destination IP Address.
All contents copyright (c) 2006 ZyXEL Communications Corporation.
41
Page 42
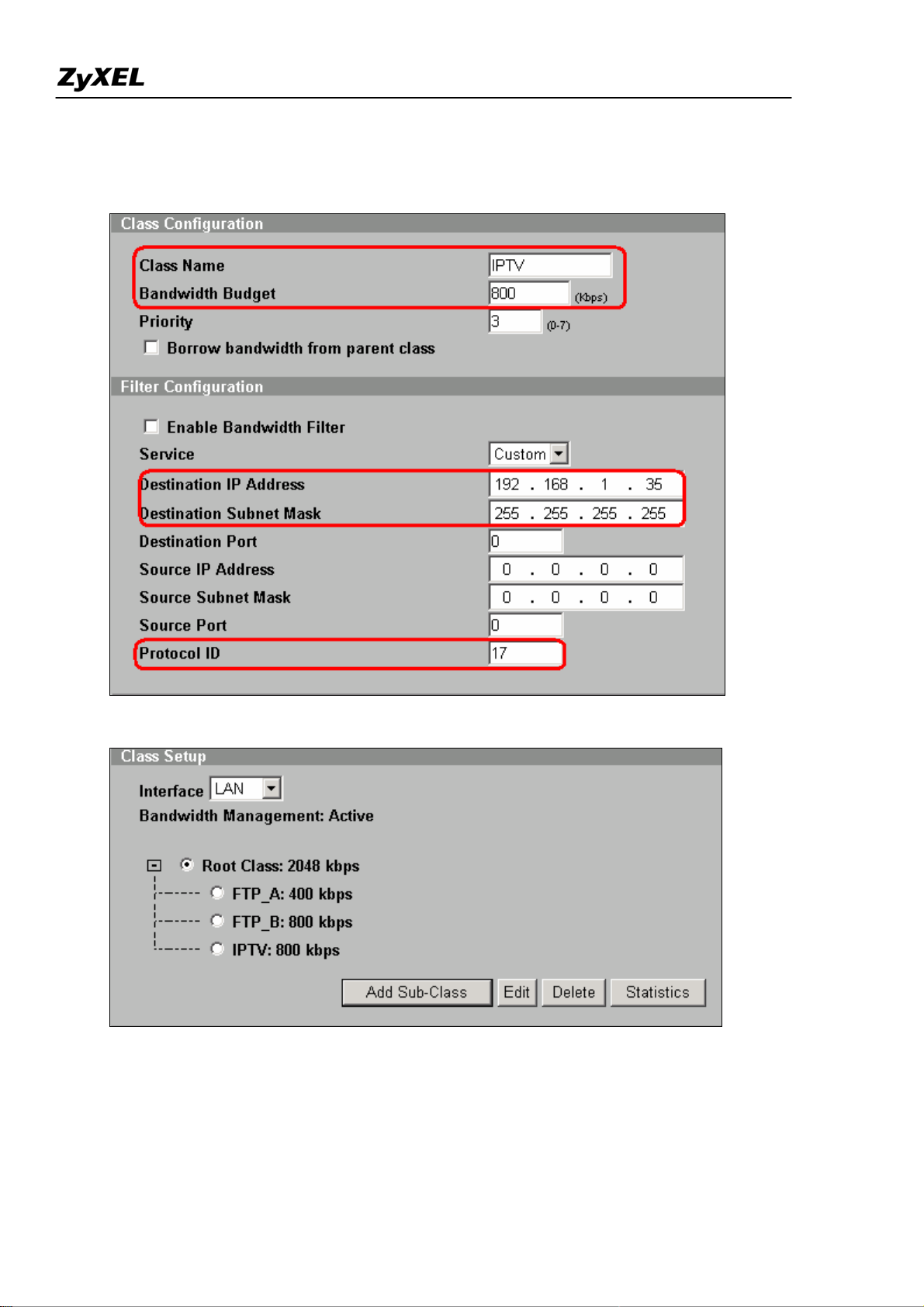
ZyWALL 2WG Support Notes
Step4. Add another service and allocate 800kbps for IPTV user and destined to Media traffic to IPTV user.
Select the Service as Custom from drop-down list and set Protocol IP as 17 (UDP). Input IPTV user’s IP
address as Destination IP Address.
Step 5. Three classes are created for FTP Client A, B & IPTV user as below:
All contents copyright (c) 2006 ZyXEL Communications Corporation.
42
Page 43
ZyWALL 2WG Support Notes
Secure Connections across the Internet
Site-to-Site VPN (Intranet) Scenario
A site-to-site VPN protects the network resources on your protected networks from unauthorized use by
users on an unprotected network, such as the public Internet. Site-to-site VPN connects offices in different
locations with encryption technology.
Configure ZyWALLs with Static WAN IP Address
This section describes an example configuration ZyWALL with static WAN IP address.
If ZyWALL is used as Internet gateway and public IP address is assigned on ZyWALL’s WAN interface.
ZyWALL uses this public WAN IP address for terminating the VPN tunnels from remote VPN gateways.
In following example, local VPN gateway (ZyWALL) uses a static public IP address.
All contents copyright (c) 2006 ZyXEL Communications Corporation.
43
Page 44

ZyWALL 2WG Support Notes
1) Configure the static Public IP address to WAN interface through Network-> WAN-> WAN IP Address
Assignment
2) Enter the WAN IP address as My Address in Gateway Policy
3) On peer VPN gateway, use the same IP address as Remote Gateway Address in Gateway Policy
On Local VPN gateway, select IP as the Local IP Type and enter the public WAN IP address as the
content of identify. One remote VPN peer, select IP as the Peer ID Type and enter the same IP address as
the content of identify.
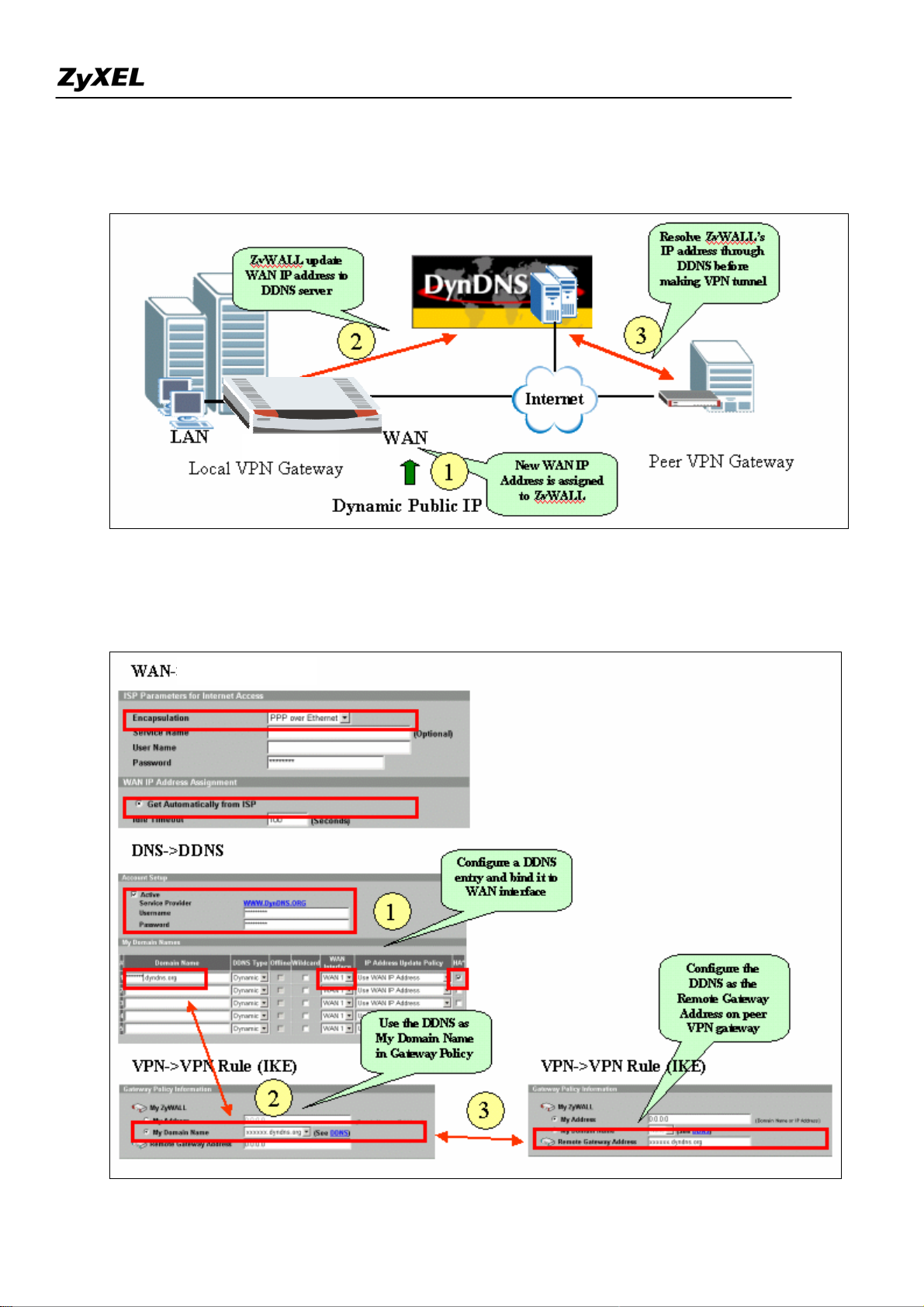
Configure ZyWALL with Dynamic WAN IP Address
This section describes an example configuration ZyWALL with dynamic WAN IP address.
If ZyWALL uses PPPoE or Ethernet/DHCP for its Internet connection, WAN IP address is dynamically
assigned by ISP. Since ZyWALL has no idea about its WAN IP address before it is assigned, it is
difficult/impossible to use WAN IP Address for My Address in Gateway Policy.
To overcome this problem, Dynamic DNS can be used to resolving the VPN gateway. When new IP
All contents copyright (c) 2006 ZyXEL Communications Corporation.
44
Page 45
ZyWALL 2WG Support Notes
address is assigned to ZyWALL’s WAN interface, ZyWALL will updates the related record in DDNS
server. Therefore the peer VPN gateway can resolve ZyWALL’s IP address to make a VPN tunnel.
In following example, local VPN gateway (ZyWALL) uses a dynamic WAN IP address (PPPoE with
dynamic IP assignment).
All contents copyright (c) 2006 ZyXEL Communications Corporation.
45
Page 46
ZyWALL 2WG Support Notes
4) Configure the DDNS entry under DNS-> DDNS and bind it to a WAN interface.
5) Under Gateway Policy menu, select the DDNS entry from drop-down list and use it as My Domain
Name.
6) Configure the DDNS entry in Remote Gateway Address on peer VPN gateway.
7) Both DNS and E-mail can be used as the Local ID & Peer ID for authentication.
Note: If Hi-Available (HA) for incoming VPN HA is necessary, enable the HA option while configure the
DDNS entry under DNS-> DDNS ZyWALL will update its DDNS entry with another WAN interface
when the specified WAN interface is not available. Therefore, the next coming VPN connection will go
through second WAN interface.
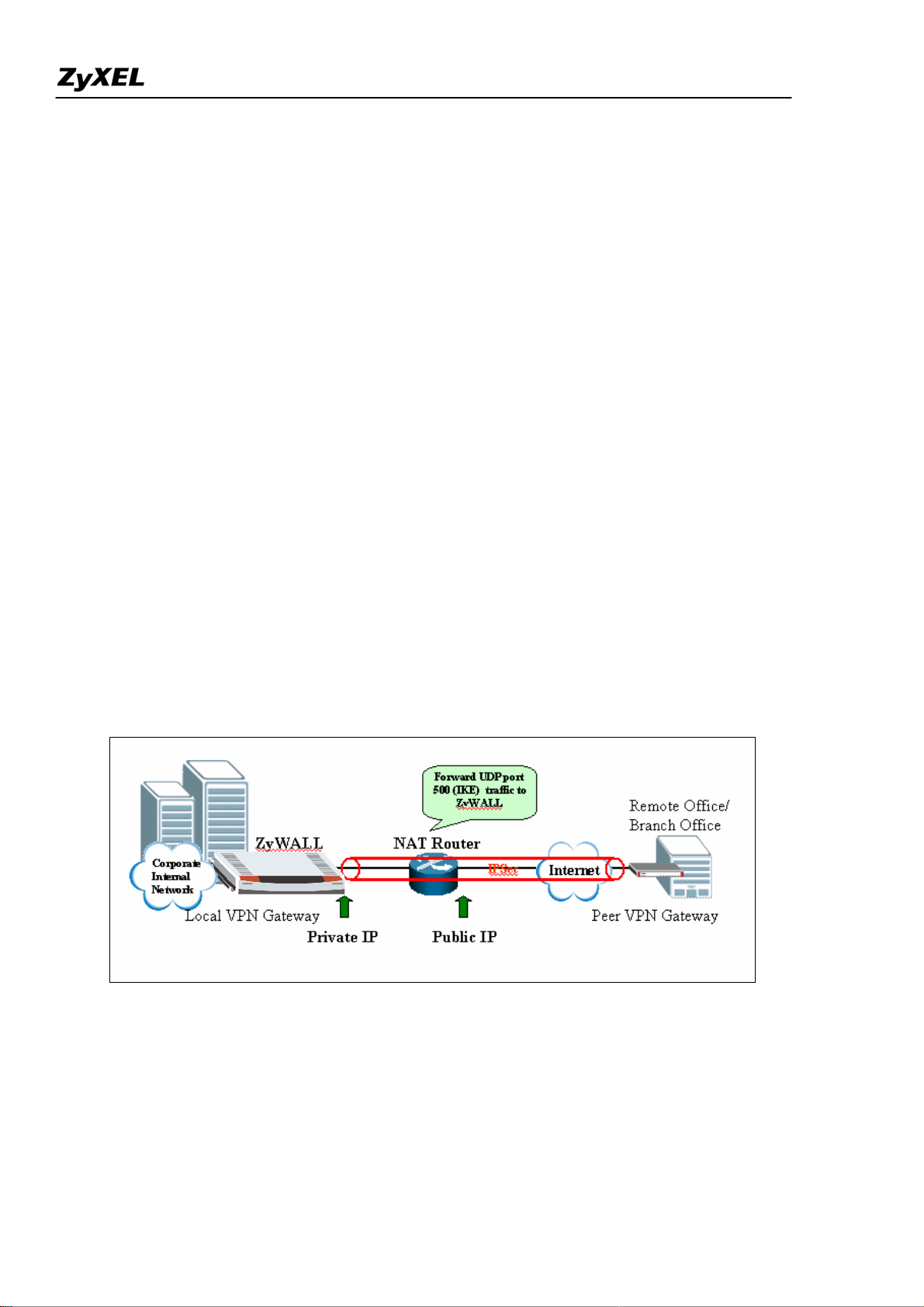
Configure ZyWALL behind NAT Router
This section describes an example configuration ZyWALL behind NAT Router (Internet Gateway).
NAT routers sit on the border between private and public (Internet) networks, converting private
addresses in each IP packet into legally registered public ones. NAT is commonly supported by Internet
access routers that sit at the network edge. However, IPSec is NAT-sensitive protocol which means
modification on IPSec traffic may cause failure of VPN connection.
By far the easiest way to combine IPSec and NAT is to completely avoid these problems by locating
IPSec endpoints in public address space. This can be accomplished in two ways:
1) Perform NAT on a device located behind IPSec gateway
2) Use an IPSec gateway for both IPSec (VPN) and NAT (Internet Access).
However, in some situation, it is inevitable to locate IPSec gateway in public IP address and it must be
All contents copyright (c) 2006 ZyXEL Communications Corporation.
46
Page 47
ZyWALL 2WG Support Notes
placed behind the NAT router. For example, the NAT router has a different interface (e.g. leased line,
ISDN) which are not supported by IPSec gateway. This example gives some guideline for configuring
ZyWALL behind NAT router.
1) UDP 500 (IKE) must be forwarded to ZyWALL to accept incoming VPN connection from peer VPN
gateway or client.
2) If Firewall is running on the same NAT router, make sure a firewall rule is configured to allow
IKE/IPSec (AH/ESP) traffic to pass-through.
Configuration on Peer VPN gatewayConfiguration on Loca l ZyWALL
WAN->WAN1 or WAN2
VPN->VPN Rule (IKE) on ZyWALL
4
3
VPN->VPN Rule (IKE) on ZyWALL
VPN->VPN Rule (IKE) on ZyWALL
5
6
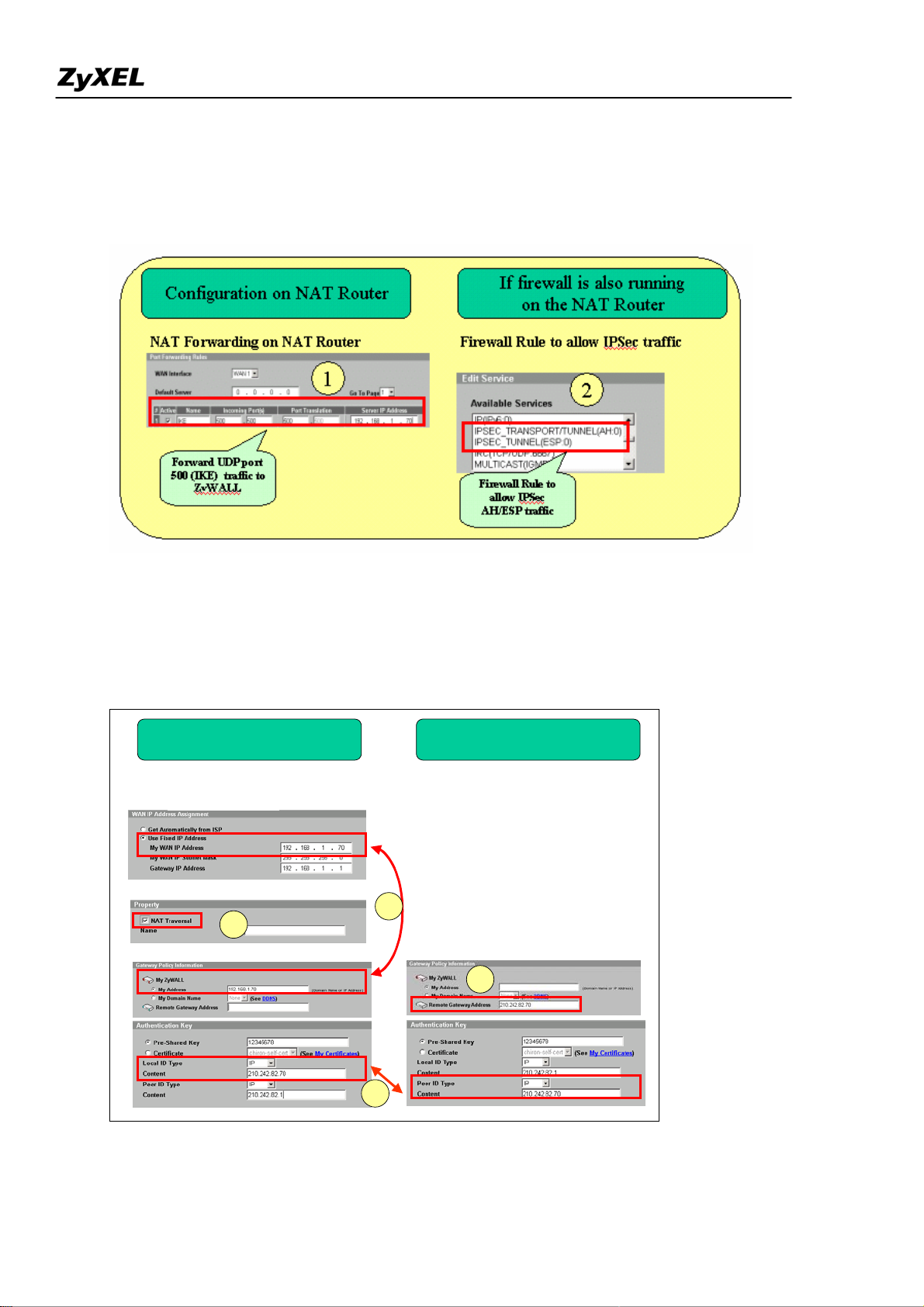
3) On ZyWALL, enable “NAT T raversal” no matter if the front NAT router supports NAT Traversal
(IPSec pass-through) or not. With this option enabled, ZyWALL can detect if it is placed behind NAT
All contents copyright (c) 2006 ZyXEL Communications Corporation.
47
Page 48

ZyWALL 2WG Support Notes
when peer VPN entity also support NAT Traversal function. If yes, the IPSec traffic will be
encapsulated in UDP packet to avoid traversal problem on NAT routers.
4) Under VPN->Gateway Policy-> Gateway Policy Information configure the private IP address as
“My Address” on local ZyWALL gateway (behind NAT router).
5) On peer VPN gateway, use the public WAN IP address of NAT Router as the “Remote Gateway
Address” of Gateway Policy rule.
The ID must be consistent no matter if IP/DNS/EMAIL is used. So long as if the ID Type and content are
consistent on both VP entities.
Mapping multiple Network policy to same gateway policy
This section describes an example configuration to map multiple (different) network policies to same
gateway policy which is built between two VPN gateways. Different network policies allow user in one
network to access multiple destination networks which are not in the continuous range. The other feature
of this application is to limit some users to access some specific destination and prevent others from
accessing the same network.
In following example, the owner of PC1 belongs to financial department and needs to connect to the
financial department (Dept.1) for business sensitive application. PC2 belongs to other group (Dept.2) and
need to access Dept.2 .
Traffic (PC1 <– > Dept1)
Dept. 1
Dept. 2
GW1
IPSec
IPSec Tunnel 1
Tunnel
IPSec
IPSec Tunnel 2
Tunnel
IKE Tunnel
Traffic (PC2 <–> Dept2)
IPSec
IPSec Tunnel 1IPSec Tunnel
Tunnel
IPSec
IPSec Tunnel 2
Tunnel
PC 1
GW2
PC 2
Dept. 1
Dept. 2
Internet
PC1
PC 1
PC2
PC 2
GW1
VPN tunnel 1
VPN tunnel 2
GW2
All contents copyright (c) 2006 ZyXEL Communications Corporation.
48
Page 49

ZyWALL 2WG Support Notes
The configuration goal is to achieve following two:
1) Setup VPN rule to allow PC1 to access Dept.1 through the tunnel between GW1 & GW2
2) Setup VPN rule to allow PC2 to access Dept.2 through the tunnel between GW1 & GW2
PC1 PC2 GW2 GW1 Dept.1 Dept.2
192.168.35.101 192.168.35.102
WAN
210.242.82.35
WAN
192.168.71.0/24 192.168.72.0/24
210.242.82.70
The following will illustrate how to configure on the GW1:
1) Login ZyWALL and click at “VPN”
3) Click on the icon to add a new “gateway policy” of the VPN tunnel
4) Enable “NAT Traversal” and configure the WAN IP as the “My Address” of My ZyWALL and
5) Under Authentication Key, “Pre-Shared Key” or “Certificate” can be used as authentication method.
For detailed usage of “Pre-Shared Key” and “Certificate”, please refer to XXX. In this example,
“Pre-Shared Key” is used and the string “12345678” is used as example.
All contents copyright (c) 2006 ZyXEL Communications Corporation.
49
Page 50

ZyWALL 2WG Support Notes
6) Extended Authentication (xAuth) can be enabled or not depending on your application. For detailed
info, you can refer to XXX.
7) Under “IKE Proposal”, select the Encryption and Authentication Algorithm. Note the configuration
must be consist on both ZyWALLs (GW1 & GW2)
8) Click on “Apply” to save profile
9) The IKE rule will be configured as below:
All contents copyright (c) 2006 ZyXEL Communications Corporation.
50
Page 51

ZyWALL 2WG Support Notes
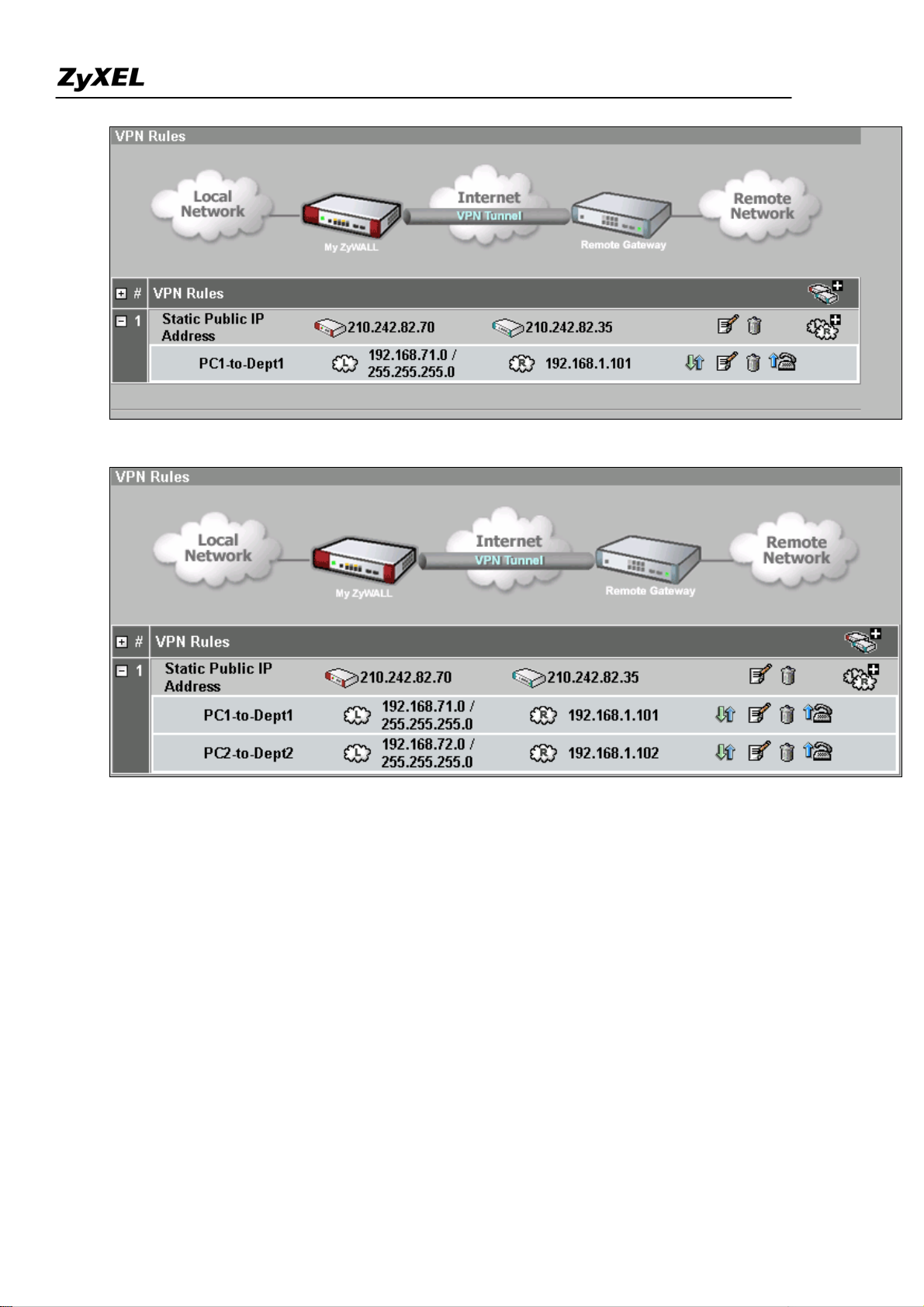
10) Click on the icon to add a new “Network Policy” over the configured Gateway Policy.
11) Activate the profile and name this policy as “PC1-to-Dept1” in this example. Enable “Nailed-Up”
option if you need the functionality that will automatically re-initiate a tunnel to a configured peer in
the event of SA Lifetime expires, failure on the link.
12) This network policy “PC1-to-Dept1” will be mapped to Gateway Policy, “Static Public IP Address”
by default. If you need to change to other pre-defined Gateway Policy, you can select from the
drop-down list.
13) Under “Local Network”, choose “Subnet” and input “192.168.71.0” and “255.255.255.0” for Dept1 in
this example.
All contents copyright (c) 2006 ZyXEL Communications Corporation.
51
Page 52

ZyWALL 2WG Support Notes
14) Under “Remote Network”, choose “Single” and input “192.168.1.101” for PC1 in this example.
15) Under “IPSec Proposal”, select the Encryption and Authentication Algorithm. Note the configuration
must be consist on both ZyWALLs (GW1 & GW2)
16) Click on “Apply” to save profile
17) The new Network Policy, PC1-to-Dept1 is added to the Gateway Policy.
All contents copyright (c) 2006 ZyXEL Communications Corporation.
52
Page 53
ZyWALL 2WG Support Notes
18) Follow the same procedures as step 10~16 to add 2nd Network Policy, PC2-to-Dept2.
Finish
Using Certificate for Device Authentication
IKE must authenticate the identities of the systems using the Diffie-Hellman algorithm. This process is
known as primary authentication. IKE can use two primary authentication methods:
1) Digital Signatures
2) Pre-shared keys
Digital signature and public-key encryption are both based on asymmetric key encryption and require a
mechanism for distributing public keys. This is usually done using security certificates and a Public Key
Infrastructure (PKI).
If certificate (Digital Signatures) is used for authentication, there are five available types of identity: IP,
All contents copyright (c) 2006 ZyXEL Communications Corporation.
53
Page 54

ZyWALL 2WG Support Notes
DNS, E-mail, Subject Name and Any.
Depending how certificates are generated, it can be classified into three methods:
1) Using Self-signed Certificates (both entities must be ZyXEL IPSec gateway)
2) Online Enroll Certificates
3) Offline Enroll Certificates
This example displays how to use PKI feature in VPN function of ZyXEL appliance. Through PKI
function, users can achieve party identification when doing VPN/IPSec negotiation.
Using Self-signed Certificates
For customers who don't have CA service support in their environment but would like to use PKI feature,
ZyWALL provides self-signed certificates to achieve this. As the name indicates, a self-signed certificate
is a certificate signed by the device (ZyWALL) itself.
ZyWALL has the feature to sign itself a so-called self-signed certificate which can be imported to other
ZyWALL for authentication. This feature allows users to use certificate without CA. The certificate must
be exchanged and imported into Trusted Remote Hosts before making a VPN connection.
All contents copyright (c) 2006 ZyXEL Communications Corporation.
54
Page 55

ZyWALL 2WG Support Notes
The factory default self-signed certificates are the same on all ZyWALL models. It is not secure to use the
default self-signed certificate. To make the self-signed certificate unique for this device, you should
replace the factory default certificate by pressing the Apply button in the following page at the first time
you login to ZyWALL.
If you reset ZyWALL to default configuration file, the original self-signed certificate is also erased, and a
new self-signed certificate should be created at the first boot up time.
To use self-signed certificate, go to ZyWALL CERTIFICATES->My Certificates and export ZyWALL’s
certificate.
1) Press “Export” to save the ZyWALL self-signed certificate to local computer in Binary X.509 format.
All contents copyright (c) 2006 ZyXEL Communications Corporation.
55
Page 56

ZyWALL 2WG Support Notes
2) Or mark the certificate in PEM (Base-64) Encoded Format and then copy to a test editor (e.g.
Notepad) and then save to you local computer in PEM (Base-64) Encoded Format.
Then import the certificate to the other ZyWALL VPN gateway. Go to the other ZyWALL and click
“Import” button under CERTIFICATES->Trusted Remote Hosts
Select the certificate from local computer.
All contents copyright (c) 2006 ZyXEL Communications Corporation.
56
Page 57

ZyWALL 2WG Support Notes
When you configure VPN rule with certificate, select Certificate under VPN-> Gateway Policy. Select My
Certificate from the drop-down list. When (My) certificate is selected, ZyWALL will show what is the Local ID
Type and Content in my certificate. You must configure the same setting on peer ZyWALL and vise versal.
For example, on Local ZyWALL, the Local ID Type is E-mail and content is
00A0C5012345@auto.gen.cert.
Therefore, configure Peer ID Type and content on peer ZyWALL.
Online Enroll Certificates
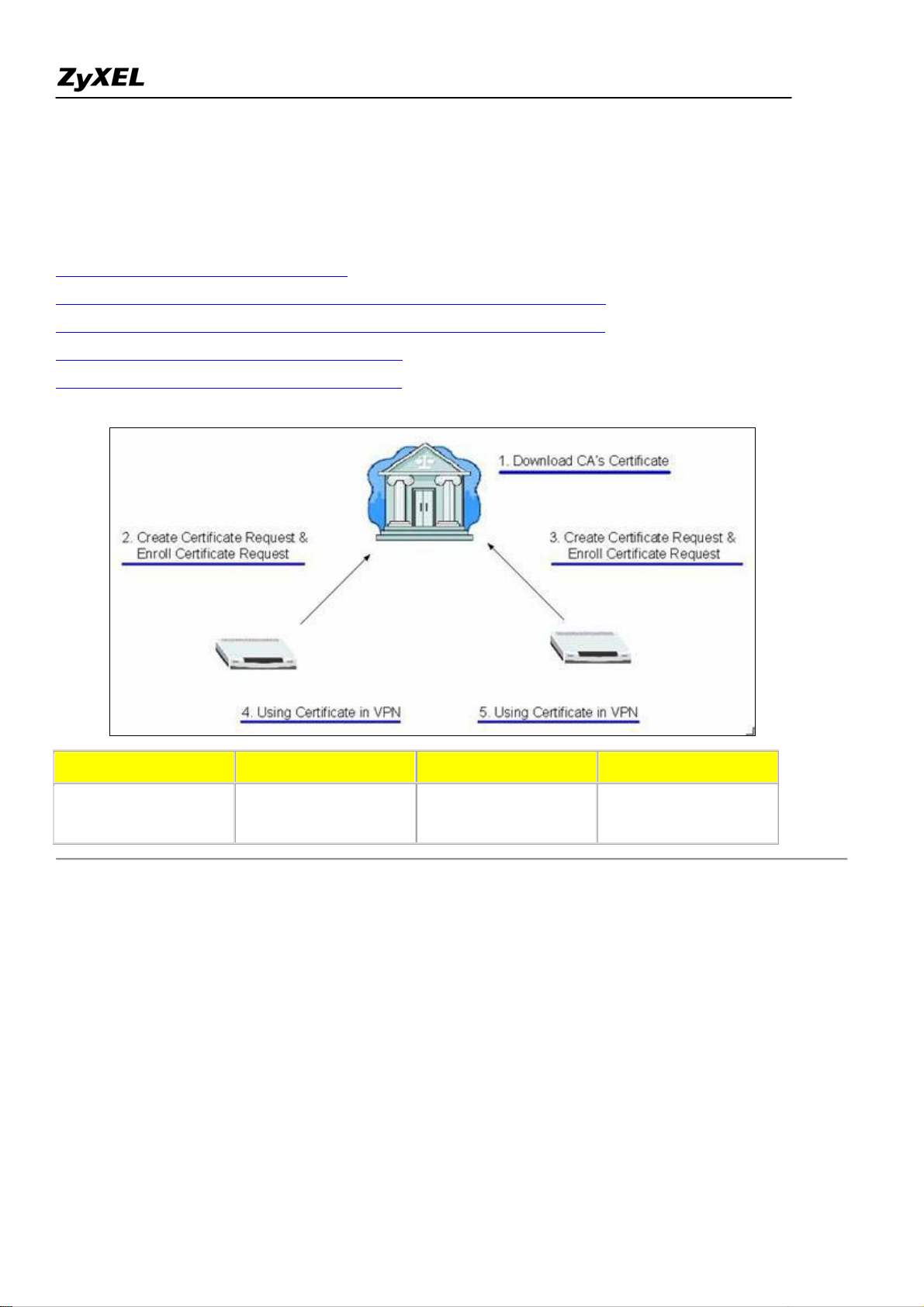
This example displays how to use PKI feature in VPN function of ZyXEL appliance. Through PKI function,
users can achieve party identification when doing VPN/IPSec negotiation. With online enrollment, ZyWALL
firstly create certification request locally, then send certification request to trusted CA (Certificate Authority)
All contents copyright (c) 2006 ZyXEL Communications Corporation.
57
Page 58
ZyWALL 2WG Support Notes
servers, and finally get a certificate for further usage. ZyWALL supports both SCEP and CMP protocols as
methods of online enrollment. Both SCEP and CMP online enrollment protocols provide secure mechanisms to
transmit ZyWALL's certification request securely over Internet. In this example, we adopt SCEP protocol to
enroll certificates.
Step 1. Download CA server's Certificate
Step 2. Create certificate request and enroll certificate request on ZyWALL A
Step 3. Create certificate request and enroll certificate request on ZyWALL B
Step 4. Using Certificate in VPN on ZyWALL A
Step 5. Using Certificate in VPN on ZyWALL B
LAN 1 ZyW ALL A ZyWALL B LAN 2
10.1.133.0/24
LAN: 10.1.133.1
WAN: 192.168.1.35
Step 1. Download CA server's Certificate
LAN: 192.168.2.1
192.168.2.0/24
WAN: 192.168.1.36
The most critical part for online certification request would be we need to send the certification request over
Internet, which is an insecure environment. To prevent certification request from being modified or
eavesdropped, we need to download CA server's certificate in the first step. When ZyWALL delivers the
certification requests, the public key in CA server's certificate will be used to protect the data.
You may need to access CA server's WEB interface or contact the administrator to get CA's certificate. Then
you can go to SECURITY->CERTIFICATES->Trusted CAs to import the downloaded certificate.
All contents copyright (c) 2006 ZyXEL Communications Corporation.
58
Page 59

ZyWALL 2WG Support Notes
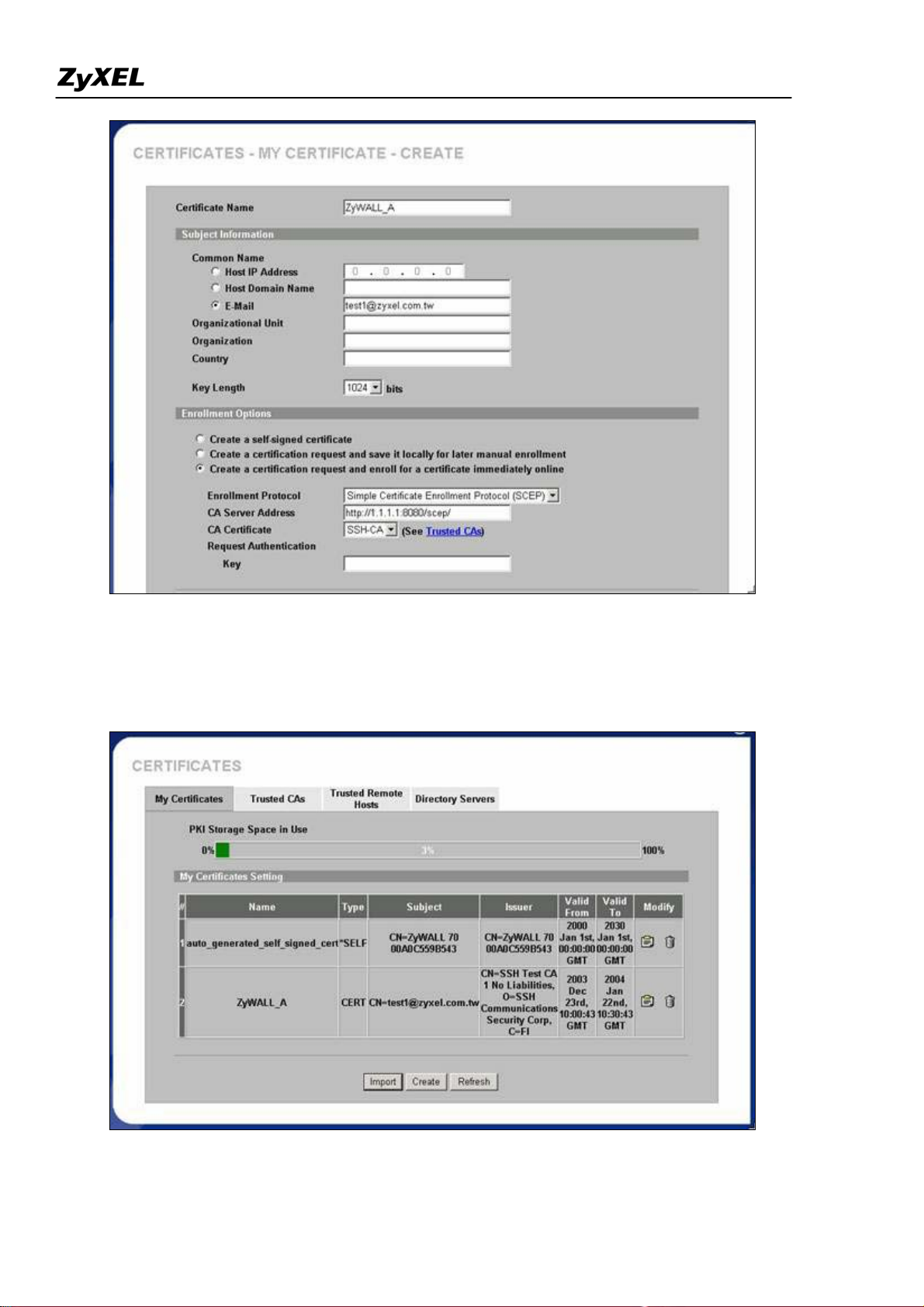
Step 2. Create certificate request and enroll certificate request on ZyWALL A
Input a name, for this Certificate so you can identify this Certificate later.
1.
2.
In Subject Information, give this certificate a Common Name by either Host IP Address, Host Domain
Name or E-Mail address. Organizational Unit, Organization, Country are optional fields, you are free to
either enter them or not.
3.
Finally, specify the key length.
4. Select Create a certification request and enroll for a certificate immediately online.
5. Specify the Enrollment Protocol to Simple Certificate Enrollment Protocol (SCEP).
6.
In the "CA Server's Address" field, input the URL to access CA server, for example,
http://1.1.1.1:8080/scep/
7. Choose the previously downloaded CA server's certificate from the drop down list.
8.
Input user name and password if necessary.
9.
Then click Apply.
All contents copyright (c) 2006 ZyXEL Communications Corporation.
59
Page 60
ZyWALL 2WG Support Notes
After pressing the Apply button, ZyWALL would create the certification request and send it to the CA server
for enrollment. It may take one minutes to complete the whole process. After CA server agrees to issue the
corresponding certificate, you will find a newly enrolled certificate in My Certificates.
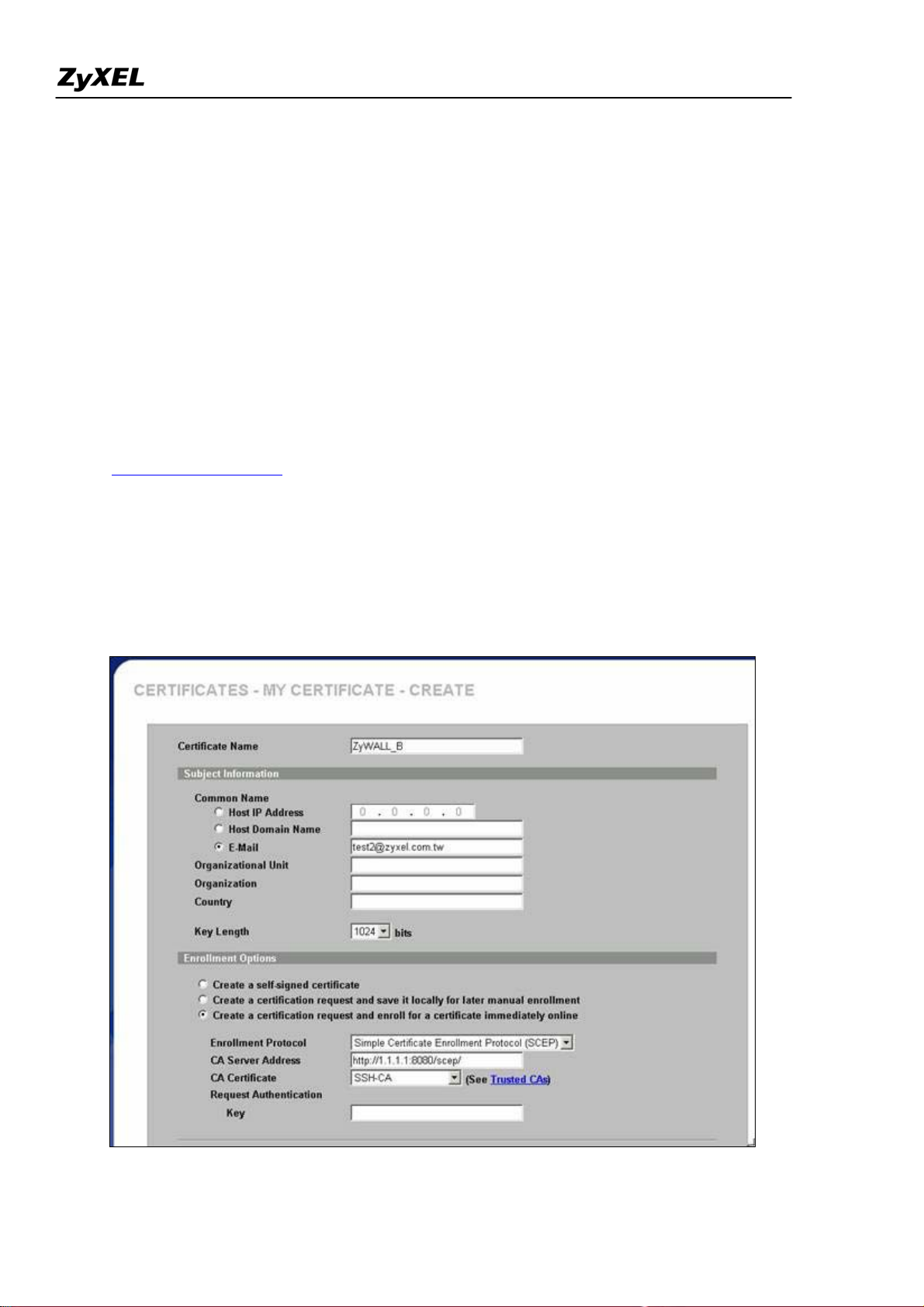
Step 3. Create certificate request and enroll certificate request on ZyWALL B
All contents copyright (c) 2006 ZyXEL Communications Corporation.
60
Page 61
ZyWALL 2WG Support Notes
1. Input a name, for this Certificate so you can identify this Certificate later.
2.
In Subject Information, give this certificate a Common Name by either Host IP Address, Host Domain
Name or E-Mail address. Organizational Unit, Organization, Country are optional fields, you are free to
either enter them or not.
3.
Finally, specify the key length.
Select Create a certification request and enroll for a certificate immediately online.
4.
5.
Specify the Enrollment Protocol to Simple Certificate Enrollment Protocol (SCEP).
6.
In the "CA Server's Address" field, input the URL to access CA server, for example,
http://1.1.1.1:8080/scep/
7.
Choose the previously downloaded CA server's certificate from the drop down list.
8.
Input user name and password if necessary.
9. Then click Apply.
All contents copyright (c) 2006 ZyXEL Communications Corporation.
61
Page 62
ZyWALL 2WG Support Notes
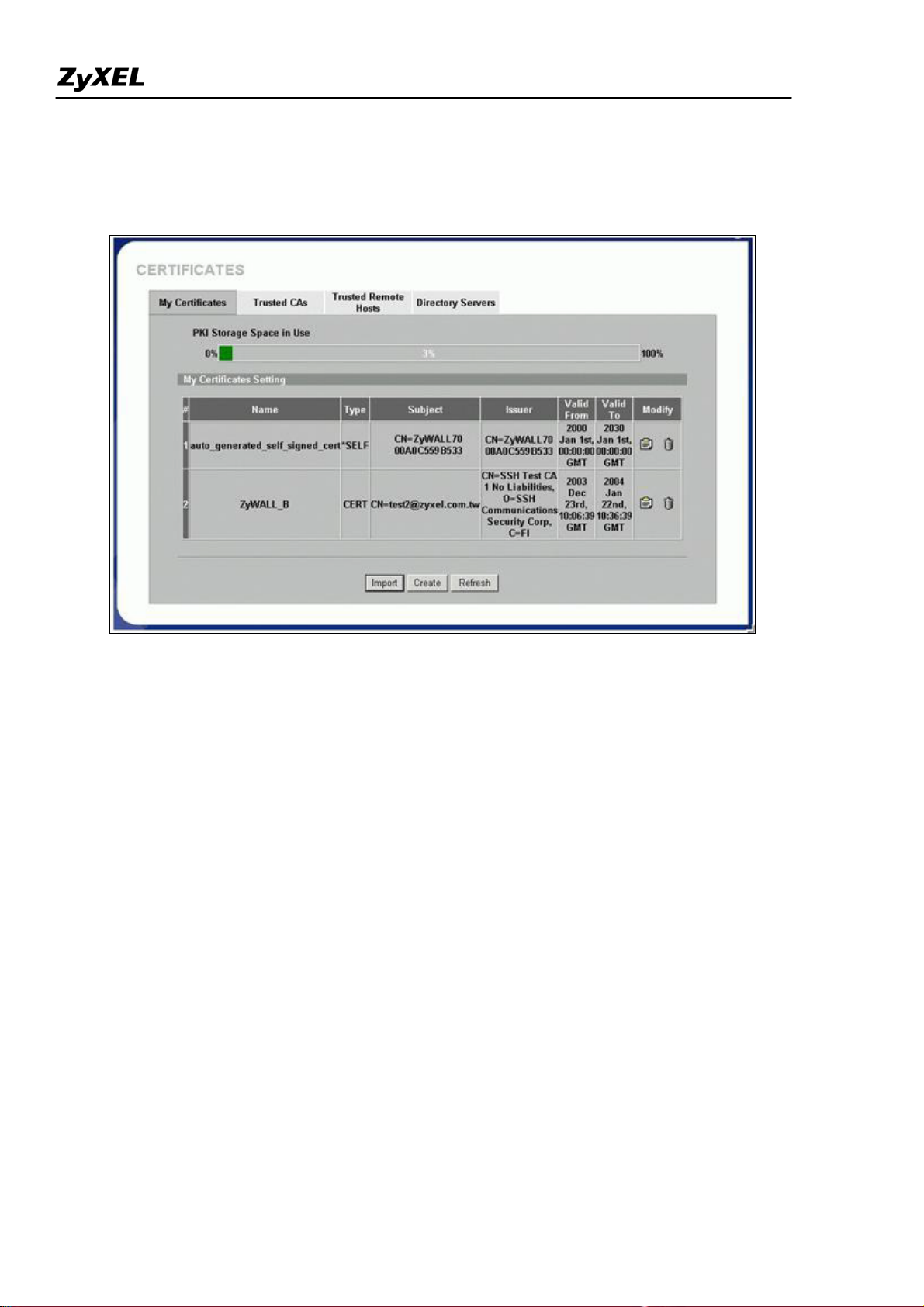
After pressing the Apply button, ZyWALL would create the certification request and send it to the CA server
for enrollment. After CA server agrees to issue the corresponding certificate, ZyWALL will receive it
automatically, and you will find a newly enrolled certificate in My Certificates.
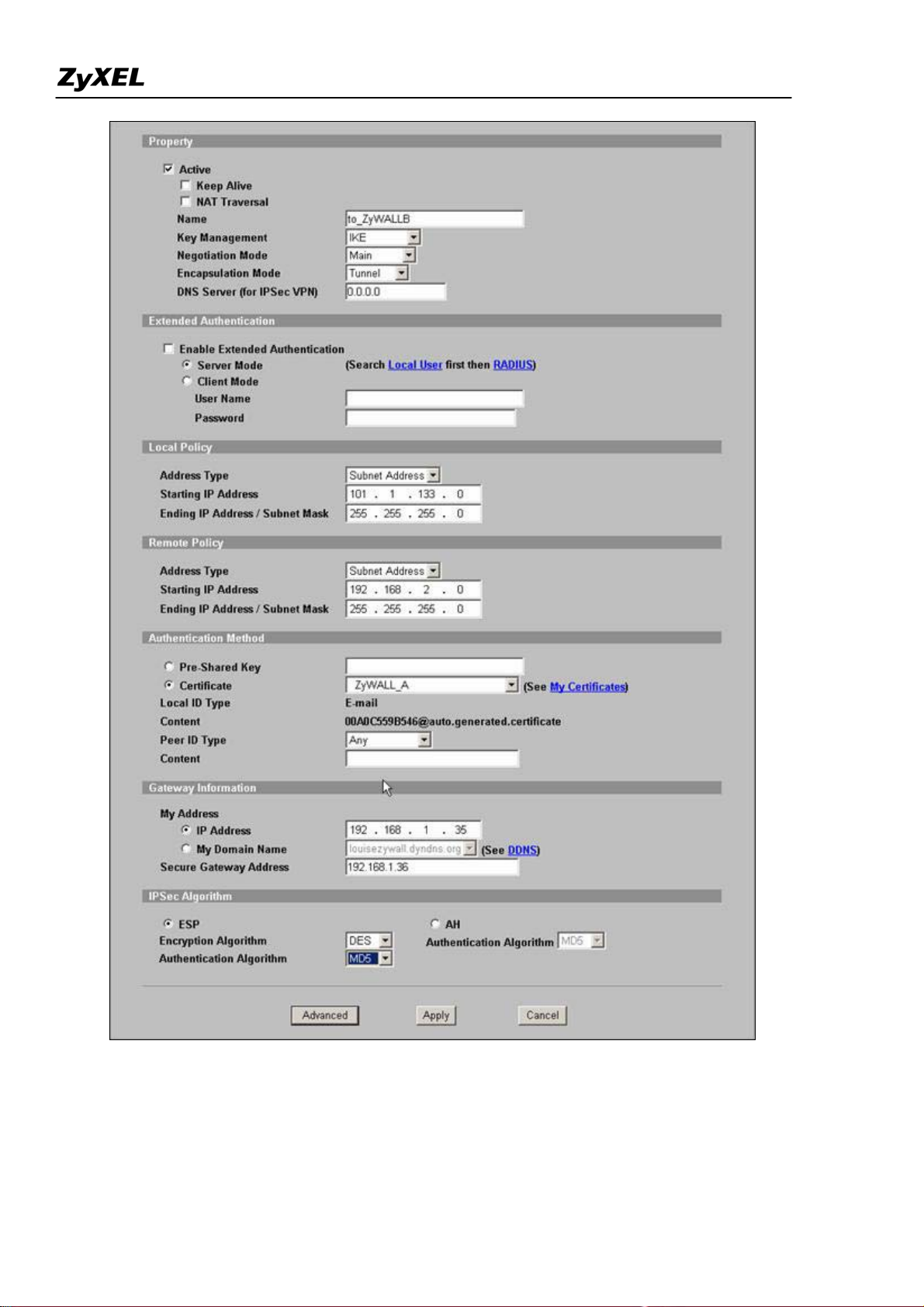
Step 4. Using Certifica e in VPN on ZyWALL A
t
1. Activate the rule
2. Give this VPN rule a name "toZyWALL_B"
3. Select Key Management to "IKE"
4. Select Negotiation Mode to "Main"
5. Edit Local: Address Type="Subnet Address", Starting IP Address="10.1.33.0", End IP Address/Subnet
Mask="255.255.255.0"
6. Edit Remote: Address Type="Subnet Address", Starting IP Address="192.168.2.0", End IP Address/Subnet
Mask="255.255.255.0"
7. Authentication Key, Select Certificate, and choose certificate you enrolled for this device from drop down list.
8. Fill in My IP address= "192.168.1.35"
9. Peer ID type= "ANY"
10. Secure Gateway Address= "192.168.1.36"
11. Encapsulation Mode="Tunnel"
12. Leave other options as default.
All contents copyright (c) 2006 ZyXEL Communications Corporation.
62
Page 63
ZyWALL 2WG Support Notes
13. You can check detailed settings by clicking Advanced button.
All contents copyright (c) 2006 ZyXEL Communications Corporation.
63
Page 64

ZyWALL 2WG Support Notes
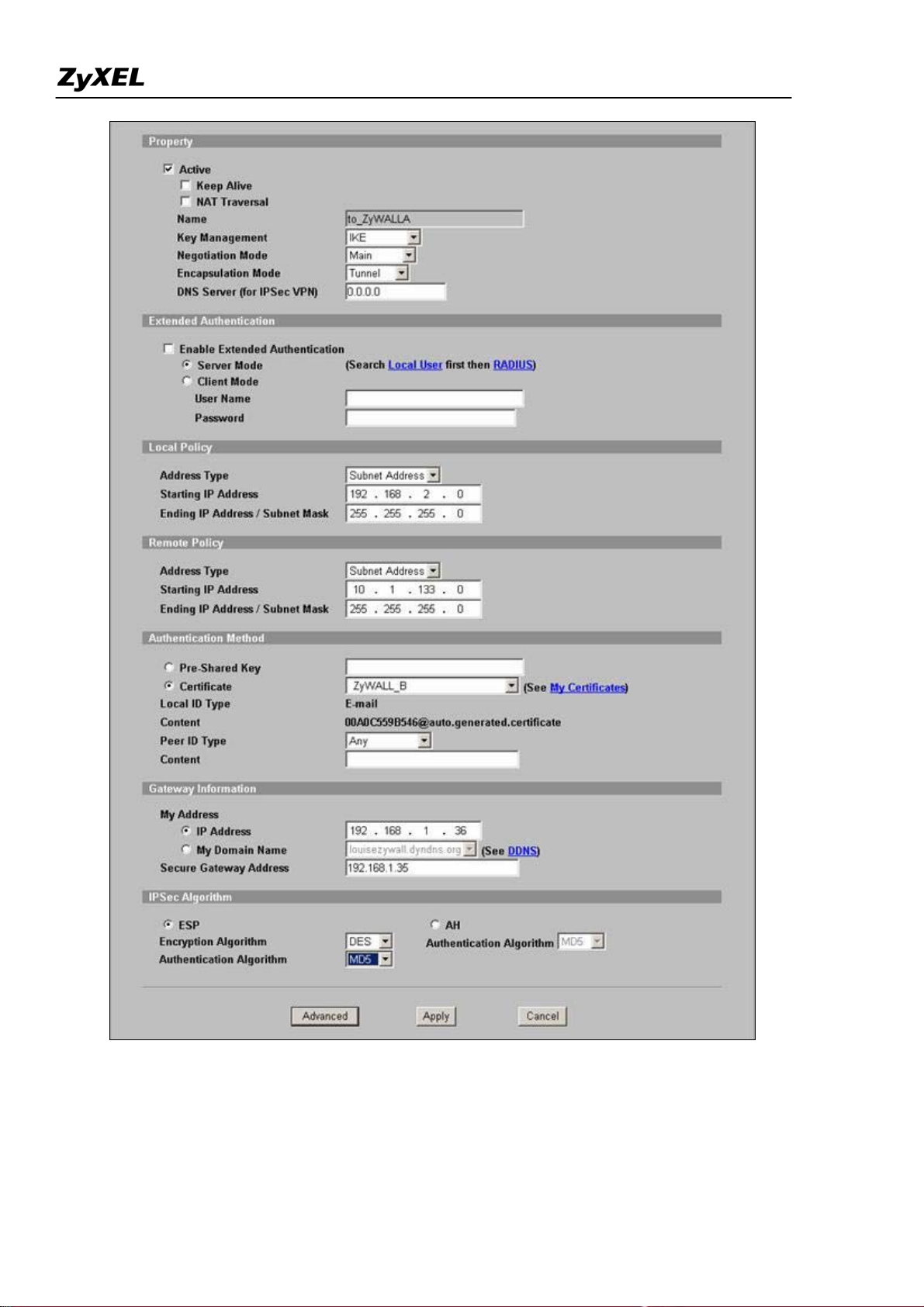
Step 5. Using Certifica e in VPN on ZyWALL B
t
1. Activate the rule
2. Give this VPN rule a name "toZyWALL_A"
3. Select Key Management to "IKE"
4. Select Negotiation Mode to "Main"
5. Edit Local: Address Type="Subnet Address", Starting IP Address="192.168.2.0", End IP Address/Subnet
Mask="255.255.255.0"
6. Edit Remote: Address Type="Subnet Address", Starting IP Address="10.1.33.0", End IP Address/Subnet
Mask="255.255.255.0"
7. Authentication Key, Select Certificate, and choose certificate you enrolled for this device from drop down list.
8. Fill in My IP address= "192.168.1.36"
9. Peer ID type= "ANY".
10. Secure Gateway Address= "192.168.1.35"
11. Encapsulation Mode="Tunnel"
12. Leave other options as default.
All contents copyright (c) 2006 ZyXEL Communications Corporation.
64
Page 65
ZyWALL 2WG Support Notes
13. You can check detailed settings by clicking Advanced button.
All contents copyright (c) 2006 ZyXEL Communications Corporation.
65
Page 66

ZyWALL 2WG Support Notes
Offline Enroll Certificates
In this guide, we describe how ZyWALL devices, both ZyWALL A and ZyWALL B as IPSec/VPN tunnel
end points, authenticate each other through PKI. We use CA (Certificate Authority) service provided by
Windows 2000 server in this example. The whole procedure includes
Step 1. Create certificate request on ZyWALL A.
Step 2. Enroll the certificate request to Windows 2000.
Step 3. Create certificate request on ZyWALL B.
Step 4. Enroll the certificate request to Windows 2000.
Step 5. Setup VPN rule on ZyWALL A
Step 6. Setup VPN rule on ZyWALL B.
All contents copyright (c) 2006 ZyXEL Communications Corporation.
66
Page 67

ZyWALL 2WG Support Notes
LAN 1 ZyW ALL A ZyWALL B LAN 2
LAN: 10.1.133.1
LAN: 192.168.2.1
10.1.133.0/24
WAN: 192.168.1.35
WAN: 192.168.1.36
tStep 1. Create Certificate Reques on ZyWALL A
1. Go to VPN->My Certificates -> Click Create button.
192.168.2.0/24
All contents copyright (c) 2006 ZyXEL Communications Corporation.
67
Page 68

ZyWALL 2WG Support Notes
2. Input a name, for this Certificate so you can identify this Certificate later. In Subject Information, give this
certificate a Common Name by either Host IP Address, Host Domain Name or E-Mail address. Organizational
Unit, Organization, Country are optional fields, you are free to either enter them or not. Finally, specify the key
length and select Create a certification request and save it locally for later manual enrollment.
3. Wait for 1-2 minutes until "Request Generation Successful" displays. During this period, ZyWALL is
working on creation of private, public key pair, and certificate request.
4. After creating certificate request, ZyWALL would return Successful Message.
All contents copyright (c) 2006 ZyXEL Communications Corporation.
68
Page 69

ZyWALL 2WG Support Notes
5. In My Certificates tab, you can get a new entry in grey color. This is the Certificate Request you just created.
Click Details to export the request.
Step 2. Enroll Certificate Request
1. Copy the content of Certificate in PEM Encoded Format, by selecting all of the content, then right click your
mouse, and select Copy. Keep your copy in clipboard for later paste.
69
All contents copyright (c) 2006 ZyXEL Communications Corporation.
Page 70

ZyWALL 2WG Support Notes
In this support note, we utilize certificate enrollment service from Microsoft Windows 2000 CA server. The
enrollment procedure of your CA server may be different, you may need to check your CA service provider for
details. For how to setup Windows 2000 CA server, users may refer to http://www.microsoft.com.
2. Issue the URL to access the CA server, type in User Name/Password/Domain fields.
All contents copyright (c) 2006 ZyXEL Communications Corporation.
70
Page 71

ZyWALL 2WG Support Notes
3, Select Request a Certificate, then press Next> button.
All contents copyright (c) 2006 ZyXEL Communications Corporation.
71
Page 72

ZyWALL 2WG Support Notes
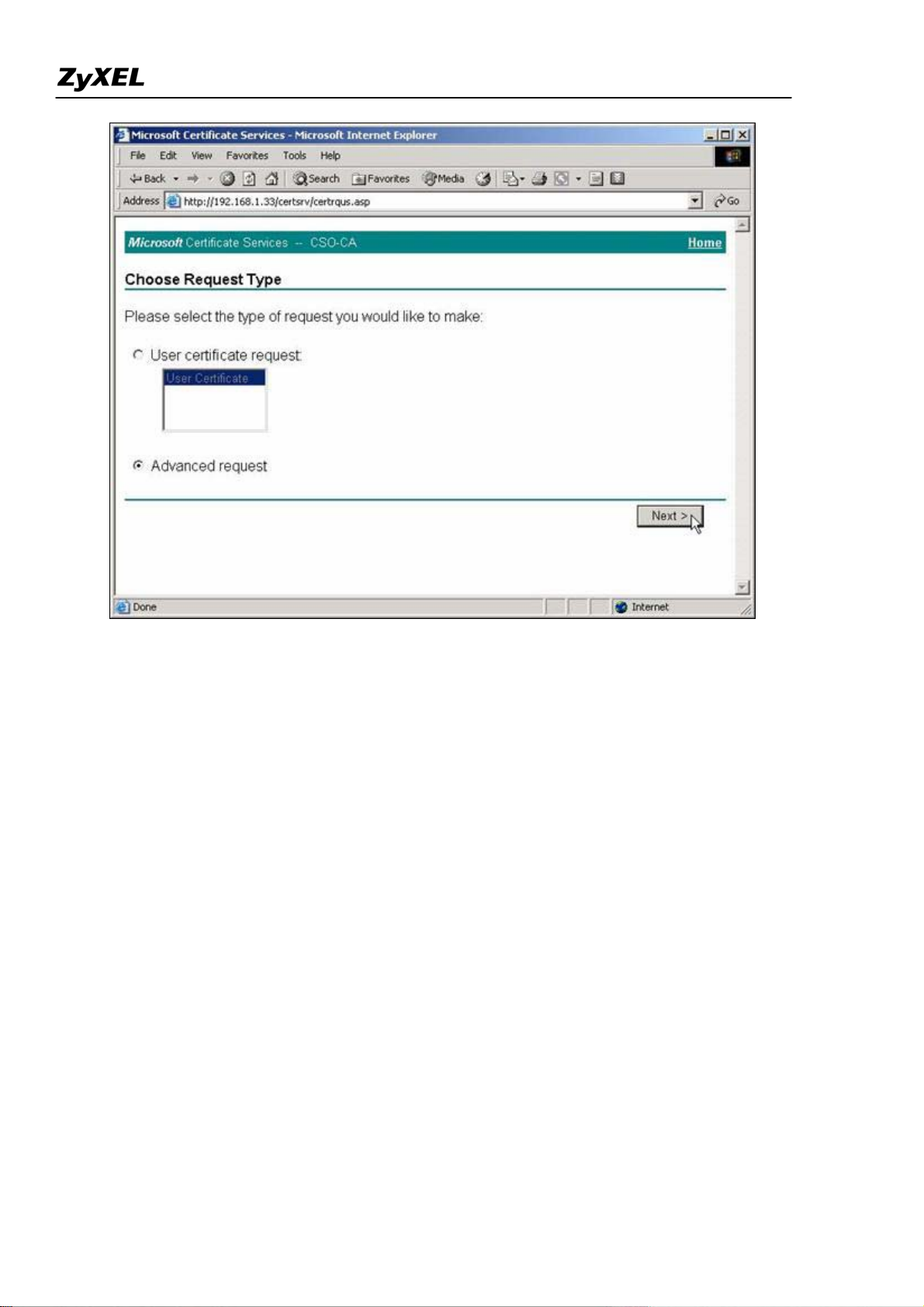
4. Choose Advanced request, the press Next> button.
All contents copyright (c) 2006 ZyXEL Communications Corporation.
72
Page 73
ZyWALL 2WG Support Notes
5. Choose "Submit a certificate request using a base64...", then press Next> button.
All contents copyright (c) 2006 ZyXEL Communications Corporation.
73
Page 74
ZyWALL 2WG Support Notes
6. Right click your mouse, then paste the certificate request you get in
step 2.1.
All contents copyright (c) 2006 ZyXEL Communications Corporation.
74
Page 75

ZyWALL 2WG Support Notes
7. Click "Download CA certification path"
8. A file download would pop out, press Save button, and choose the local folder you would like to store the
certification path.
All contents copyright (c) 2006 ZyXEL Communications Corporation.
75
Page 76
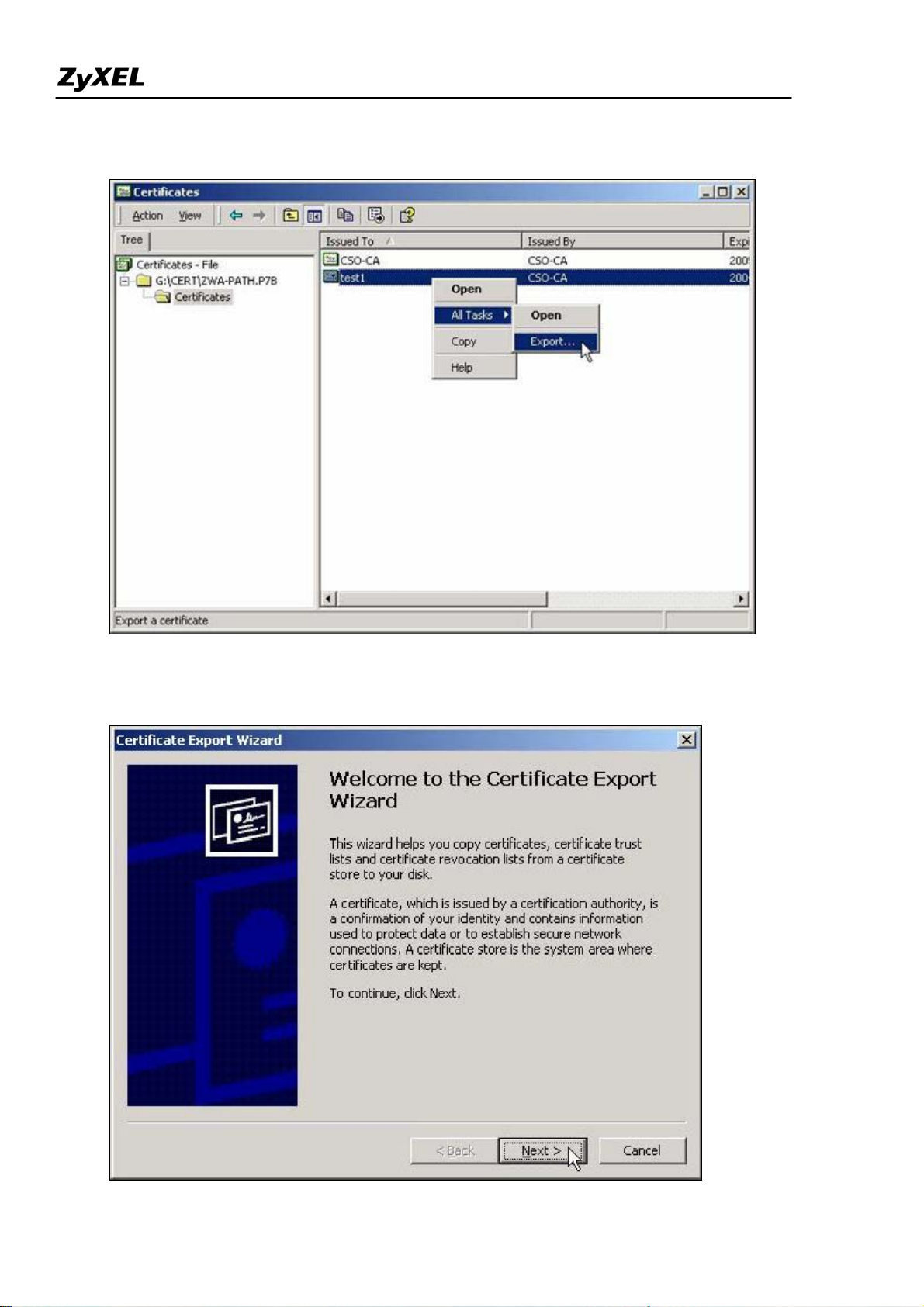
ZyWALL 2WG Support Notes
9. Double click the saved file, Select Certificates, right click the Certificate, choose All Tasks-> Export...
10. Certificate Export Wizard would be popped up, then press Next>.
All contents copyright (c) 2006 ZyXEL Communications Corporation.
76
Page 77
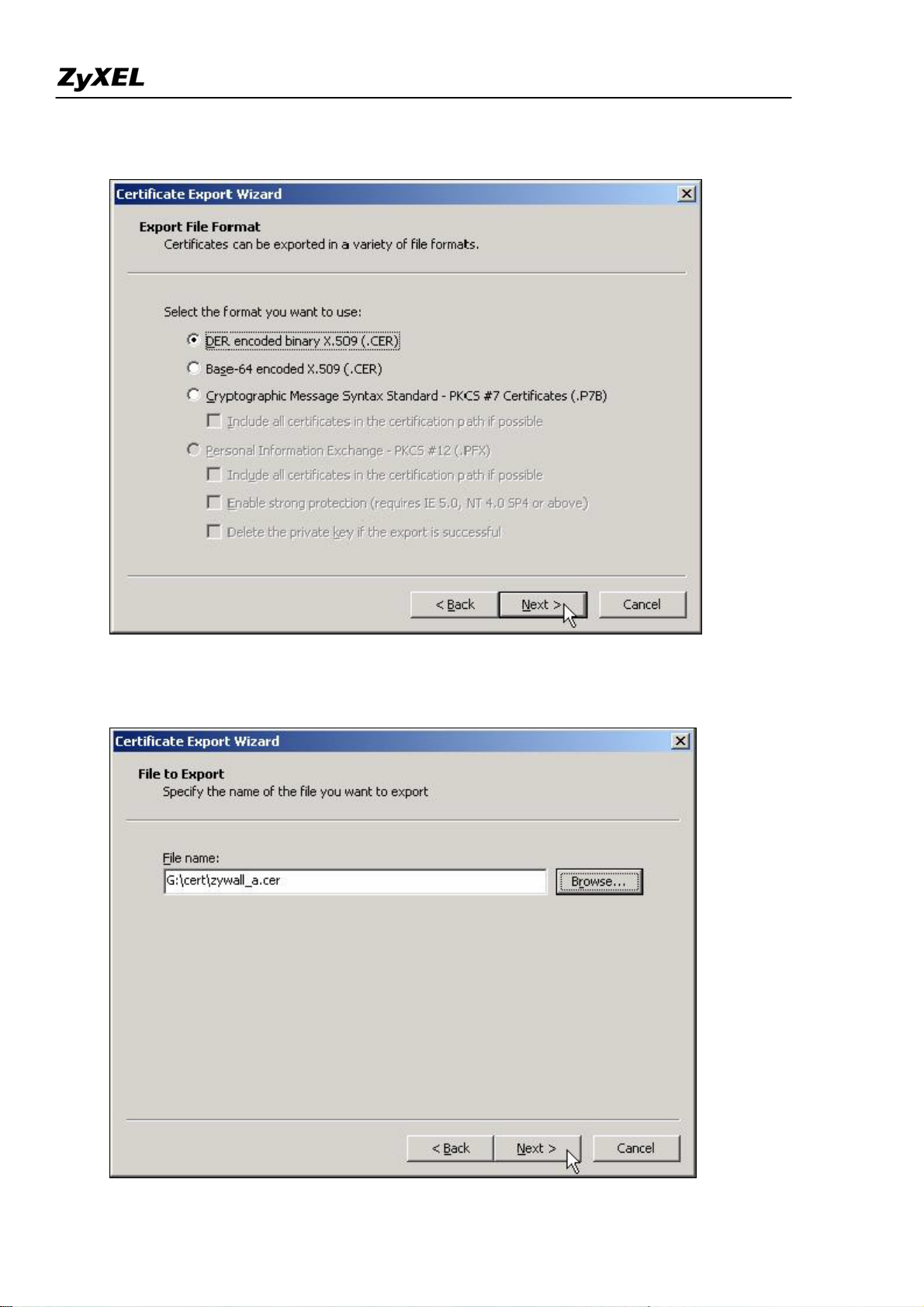
ZyWALL 2WG Support Notes
11. Choose DER encoded binary X.509(.CER), then press Nxet>,
12. Specify the path to store your exported Certificate.
All contents copyright (c) 2006 ZyXEL Communications Corporation.
77
Page 78
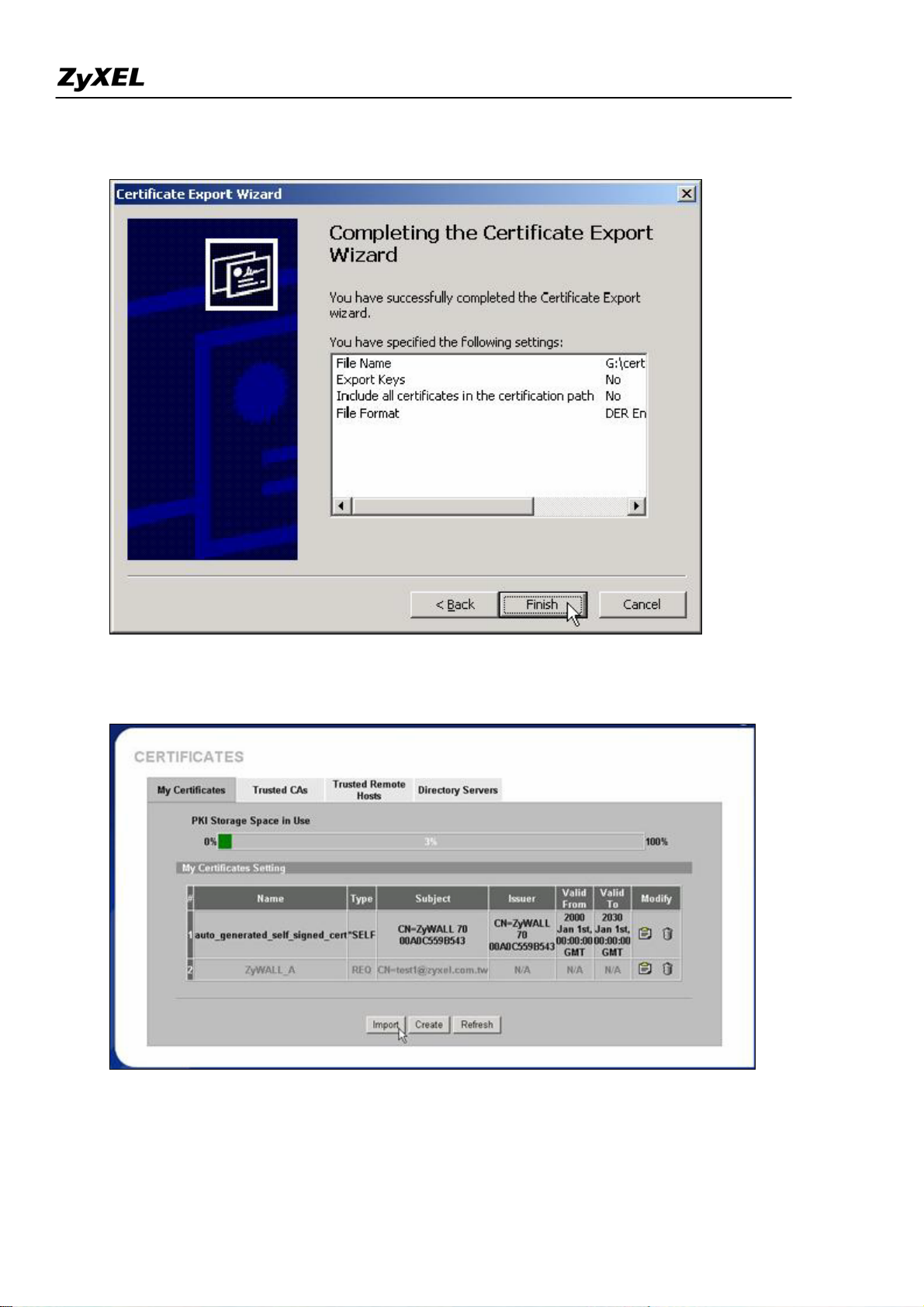
ZyWALL 2WG Support Notes
13. Click Finish.
14. Go to ZyWALL WEB GUI -> VPN -> My Certificates -> click Import button.
15. Click Browse... button to find the location you stored ZyWALL's certificate then press Apply button.
All contents copyright (c) 2006 ZyXEL Communications Corporation.
78
Page 79
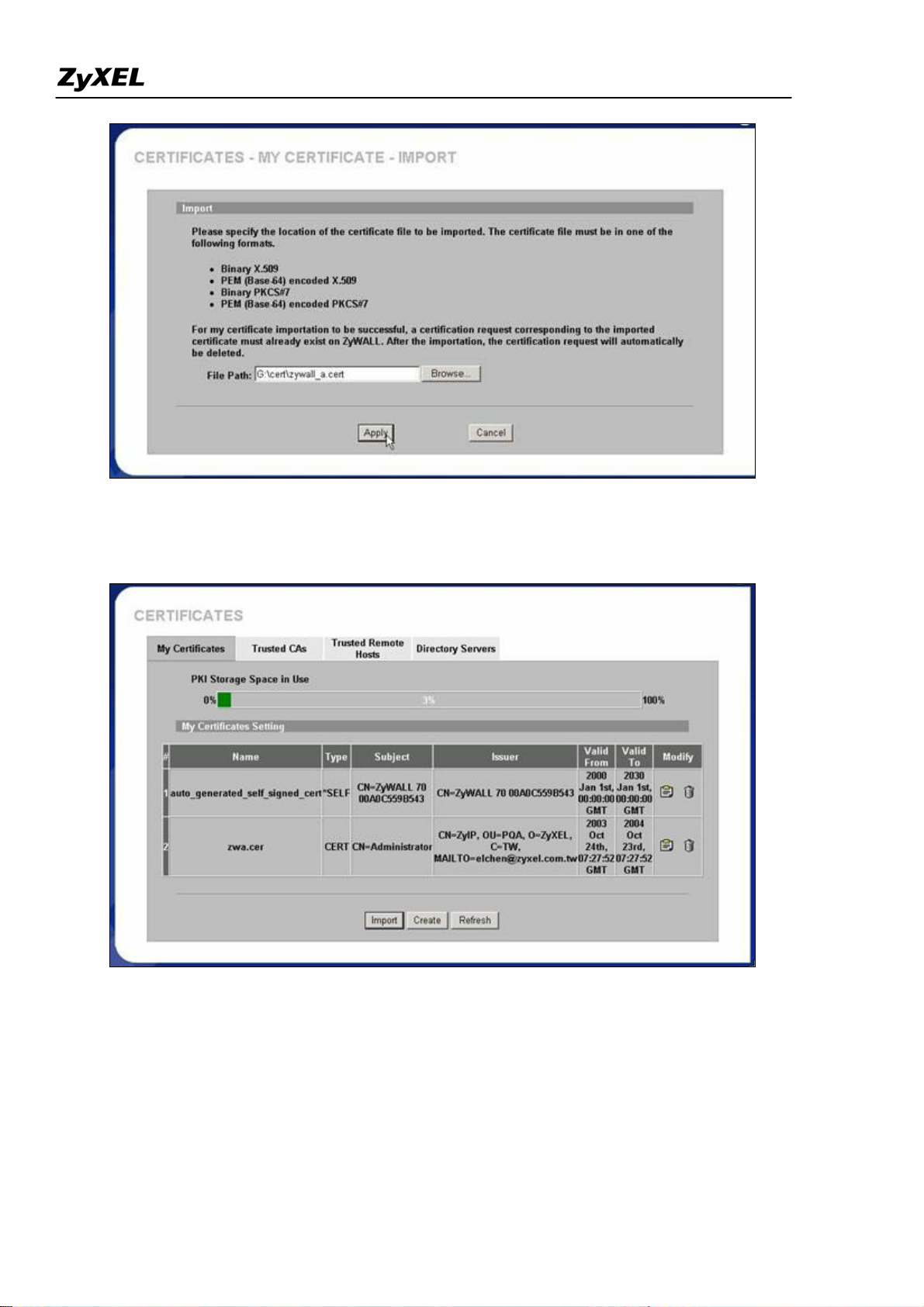
ZyWALL 2WG Support Notes
16. After a while, if you see the gray entry turns to a black one, then it means the import of ZyWALL's
certificate is successful.
17. Repeat the same procedure from 9 to 13, to export CA's certificate. Note that you may get more than one
CA server's certificate, it's not necessary to export all of the CA server's certificates, you can double click
ZyWALL's certificate, such as zywall_a.cert.cert in this example, and select Certification Path to view the
nearest CA server's name, and then - export that CA server's certificate.
Import the saved CA server's certificate. Click Browse... button, and then select the location.
All contents copyright (c) 2006 ZyXEL Communications Corporation.
79
Page 80

ZyWALL 2WG Support Notes
After import CA's certificate, you will get this display.
tStep 3. Create Certificate Reques on ZyWALL_B
1. Go to VPN->My Certificates -> Click Create button.
All contents copyright (c) 2006 ZyXEL Communications Corporation.
80
Page 81

ZyWALL 2WG Support Notes
2. Input a name, for this Certificate so you can identify this Certificate later. In Subject Information, give this
certificate a Common Name by either Host IP Address, Host Domain Name or E-Mail address. Organizational
Unit, Organization, Country are optional fields, you are free to either enter them or not. Finally, specify the key
length and select Create a certification request and save it locally for later manual enrollment.
All contents copyright (c) 2006 ZyXEL Communications Corporation.
81
Page 82

ZyWALL 2WG Support Notes
3. Wait for 1-2 minutes until "Request Generation Successful" displays. During this period, ZyWALL is
working on creation of private, public key pair, and certificate request.
4. After creating certificate request, ZyWALL would return Successful Message.
5. In My Certificates tab, you can get a new entry in grey color. This is the Certificate Request you just created.
Click Details to export the request.
All contents copyright (c) 2006 ZyXEL Communications Corporation.
82
Page 83

ZyWALL 2WG Support Notes
Step 4. Enroll Certificate Request on ZyWALLB
1. Copy the content of Certificate in PEM Encoded Format, by selecting all of the content, then right click your
mouse, and select Copy. Keep your copy in clipboard for later paste.
In this support note, we utilize certificate enrollment service from Microsoft Windows 2000 CA server. The
enrollment procedure of your CA server may be different, you may need to check your CA service provider for
details. For how to setup Windows 2000 CA server, users may refer to http://www.microsoft.com.
2. Issue the URL to access the CA server, type in User Name/Password/Domain fields.
83
All contents copyright (c) 2006 ZyXEL Communications Corporation.
Page 84

ZyWALL 2WG Support Notes
3, Select Request a Certificate, then press Next> button.
All contents copyright (c) 2006 ZyXEL Communications Corporation.
84
Page 85

ZyWALL 2WG Support Notes
4. Choose Advanced request, the press Next> button.
All contents copyright (c) 2006 ZyXEL Communications Corporation.
85
Page 86

ZyWALL 2WG Support Notes
5. Choose "Submit a certificate request using a base64...", then press Next> button.
All contents copyright (c) 2006 ZyXEL Communications Corporation.
86
Page 87

ZyWALL 2WG Support Notes
6. Right click your mouse, then paste the certificate request you get in step 4.1.
All contents copyright (c) 2006 ZyXEL Communications Corporation.
87
Page 88

ZyWALL 2WG Support Notes
7. Click "Download CA certification path"
8. A file download would pop out, press Save button, and choose the local folder you would like to store the
certification path.
All contents copyright (c) 2006 ZyXEL Communications Corporation.
88
Page 89

ZyWALL 2WG Support Notes
9. Double click the saved file, Select Certificates, right click the Certificate, choose All Tasks-> Export...
10. Certificate Export Wizard would be popped up, then press Next>.
All contents copyright (c) 2006 ZyXEL Communications Corporation.
89
Page 90
ZyWALL 2WG Support Notes
11. Choose DER encoded binary X.509(.CER), then press Nxet>,
All contents copyright (c) 2006 ZyXEL Communications Corporation.
90
Page 91

ZyWALL 2WG Support Notes
12. Specify the path to store your exported Certificate.
All contents copyright (c) 2006 ZyXEL Communications Corporation.
91
Page 92
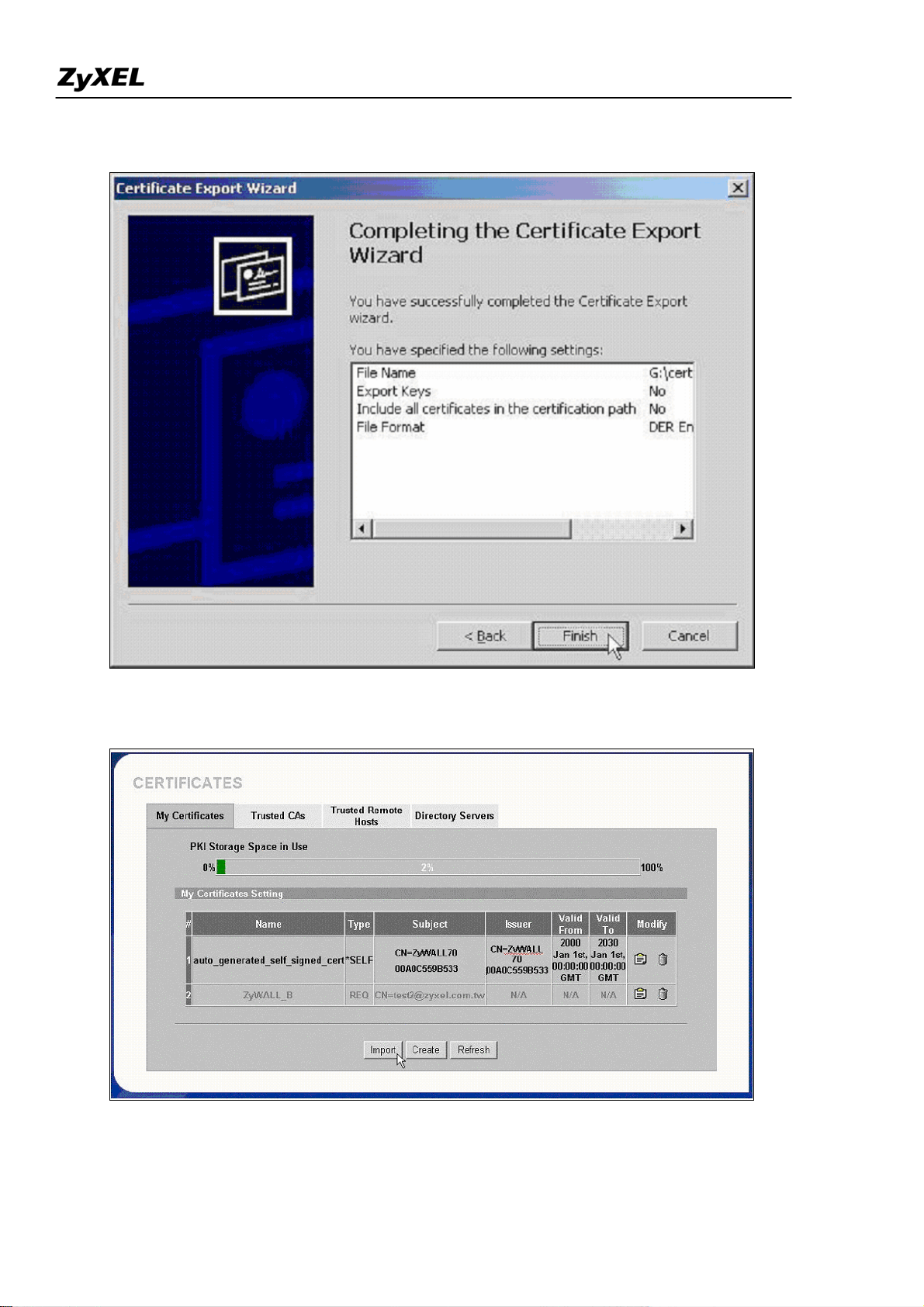
ZyWALL 2WG Support Notes
13. Click Finish.
14. Go to ZyWALL WEB GUI -> VPN -> My Certificates -> click Import button.
15. Click Browse... button to find the location you stored ZyWALL's certificate then press Apply button.
All contents copyright (c) 2006 ZyXEL Communications Corporation.
92
Page 93
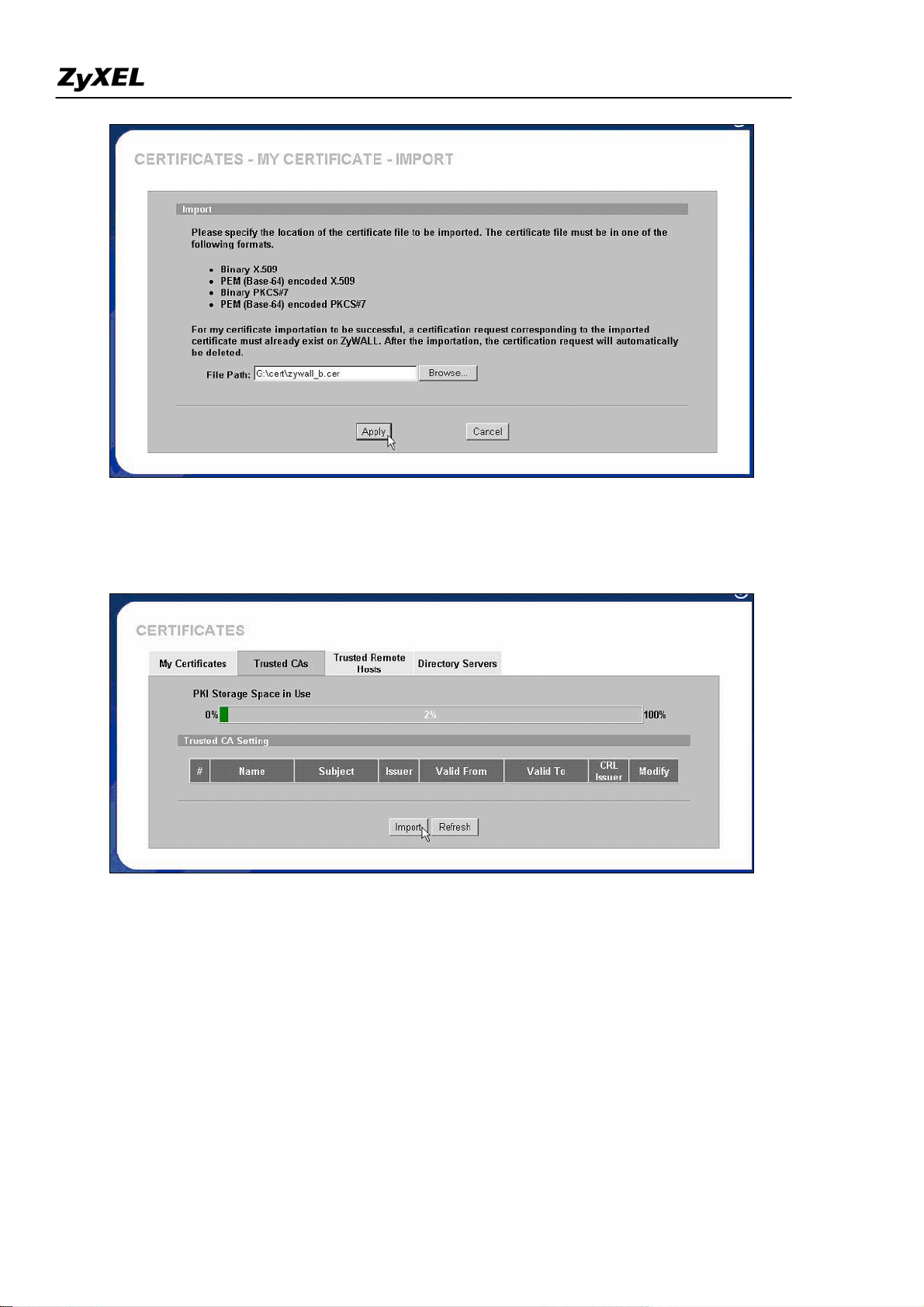
ZyWALL 2WG Support Notes
16. After a while, if you see the gray entry turns to a black one, then it means the import of ZyWALL's
certificate is successful.
17. Repeat the same procedure from 9 to 13, to export CA's certificate. Note that you may get more than one
CA server's certificate, it's not necessary to export all of the CA server's certificates, you can double click
ZyWALL's certificate, such as zywall_a.cert.cert in this example, and select Certification Path to view the
nearest CA server's name, and then - export that CA server's certificate.
Import the saved CA server's certificate. Click Browse... button, and then select the location.
All contents copyright (c) 2006 ZyXEL Communications Corporation.
93
Page 94

ZyWALL 2WG Support Notes
18. After import CA's certificate, you will get this display.
Step 5. Using Certifica e in VPN on ZyWALL A
t
1. Activate the rule
2. Give this VPN rule a name "toZyWALL_B"
3. Select Key Management to "IKE"
4. Select Negotiation Mode to "Main"
5. Edit Local: Address Type="Subnet Address", Starting IP Address="10.1.33.0", End IP Address/Subnet
Mask="255.255.255.0"
6. Edit Remote: Address Type="Subnet Address", Starting IP Address="192.168.2.0", End IP Address/Subnet
Mask="255.255.255.0"
7. Authentication Key, Select Certificate, and choose certificate you enrolled for this device from drop down list.
8. Fill in My IP address= "192.168.1.35"
94
All contents copyright (c) 2006 ZyXEL Communications Corporation.
Page 95

ZyWALL 2WG Support Notes
9. Peer ID type= "ANY".
10. Secure Gateway Address= "192.168.1.36"
11. Encapsulation Mode="Tunnel"
12. Leave other options as default.
All contents copyright (c) 2006 ZyXEL Communications Corporation.
95
Page 96

ZyWALL 2WG Support Notes
13. You can check detailed settings by clicking Advanced button.
All contents copyright (c) 2006 ZyXEL Communications Corporation.
96
Page 97

ZyWALL 2WG Support Notes
Step 6. Using Certificate in VPN on ZyWALL B
1. Activate the rule
2. Give this VPN rule a name "toZyWALL_A"
3. Select Key Management to "IKE"
4. Select Negotiation Mode to "Main"
5. Edit Local: Address Type="Subnet Address", Starting IP Address="192.168.2.0", End IP Address/Subnet
Mask="255.255.255.0"
6. Edit Remote: Address Type="Subnet Address", Starting IP Address="10.1.33.0", End IP Address/Subnet
Mask="255.255.255.0"
7. Authentication Key, Select Certificate, and choose certificate you enrolled for this device from drop down list.
8. Fill in My IP address= "192.168.1.36"
9. Peer ID type= "ANY".
10. Secure Gateway Address= "192.168.1.35"
11. Encapsulation Mode="Tunnel"
12. Leave other options as default.
All contents copyright (c) 2006 ZyXEL Communications Corporation.
97
Page 98

ZyWALL 2WG Support Notes
13. You can check detailed settings by clicking Advanced button.
All contents copyright (c) 2006 ZyXEL Communications Corporation.
98
Page 99

ZyWALL 2WG Support Notes
Using Pre-Shared Key for Device Authentication
The IKE protocol also provides primary authentication - verifying the identity of the remote system
before negotiating the encryption algorithm and keys. Two kinds of authentication methods are supported
on ZyWALL: pre-shared key & certificate.
If pre-shared key is used, a shared, symmetric key must be manually exchanged and configured on the
two entities. Three types of identity are available: IP, DNS and E-mail.
Here are some rules to follow in Authentication Key:
3) Pre-shared key must be configured identically on both entities
4) The Local ID Type & Content of Local ZyWALL must be the same as that of Peer ID Type &
Content of peer VPN gateway.
5) When IP is selected as ID Type, the Content must be in the format of X.X.X.X (e.g. 210.242.82.70)
6) When DNS/E-mail are selected as ID Type, the same string must be configured on both entities.
All contents copyright (c) 2006 ZyXEL Communications Corporation.
99
Page 100

ZyWALL 2WG Support Notes
Configuration on Peer VPN gatewayConfiguration on Local ZyWALL
Pre-Shared Key must be identical on both entities
Local ID Type & Content on Local ZyWALL must be identical as
Peer ID Type & Content on Peer VPN gateway
Peer ID Type & Content on Local ZyWALL on Local ZyWALL must be identical as
Local ID Type & Content on Peer VPN gateway
Note:
1) If “ID T ype” is mis-configured on Local/Remote IPSec Gateway, the ZyWALL will show
[NOTFY:ERR_ID_INFO] error message in related IKE log.
2) If “Pre-shared Key” or ID “Content” are mis-configured on Local/Remote IPSec Gateway,
ZyWALL will show [NOTFY:ERR_ID_INFO] error message in related IKE log.
Using VPN routing between branches
Setup VPN in Branch Office A
1.
2. Setup VPN in Branch Office B
3.
Setup VPN in Headquarter
This page guides us how to setup VPN routing between branch offices through headquarter. So that whenever
branch office A wants to talk to branch office B, headquarter plays as a VPN relay. Users can gain benefit
from such application when the scale of branch offices is very large, because no additional VPN tunnels
between branch offices are needed. In this support note, we skip the detailed configuration steps for Internet
access and presume that you are familiar with basic ZyNOS VPN configuration.
All contents copyright (c) 2006 ZyXEL Communications Corporation.
100
 Loading...
Loading...