Zyxel XS1920-12 operation manual

Quick Start Guide
XS1920 Series
10 GbE Web-managed Switches
Version 4.30
Edition 1, 01/2016
User’s Guide
Default Login Details
LAN IP Address http://192.168.1.1
User Name admin
Password 1234
www.zyxel.com
Copyright © 2016 ZyXEL Communications Corporation

IMPORTANT!
READ CAREFULLY BEFORE USE.
KEEP THIS GUIDE FOR FUTURE REFERENCE.
This is a User’s Guide for a series of products. Not all products support all firmware features.
Screenshots and graphics in this book may differ slightly from your product due to differences in
your product firmware or your computer operating system. Every effort has been made to ensure
that the information in this manual is accurate.
Related Documentation
•Quick Start Guide
The Quick Start Guide shows how to connect the Switch and access the Web Configurator.
• Web Configurator Online Help
Click the help icon in any screen for help in configuring that screen and supplementary
information.
•More Information
Go to support.zyxel.com to find other information on the Switch.
XS1920 Series User’s Guide
2

Contents Overview
Contents Overview
User’s Guide .......................................................................................................................................18
Getting to Know Your Switch ...................................................................................................................19
Hardware Installation and Connection ....................................................................................................23
Hardware Panels .....................................................................................................................................26
Technical Reference ..........................................................................................................................32
The Web Configurator .............................................................................................................................33
Initial Setup Example ..............................................................................................................................41
Tutorials ..................................................................................................................................................45
Status and ZON ....................................................................................................................................... 54
Basic Setting ..........................................................................................................................................63
VLAN ....................................................................................................................................................... 92
Static MAC Forward Setup .................................................................................................................... 114
Static Multicast Forward Setup .............................................................................................................. 116
Filtering ................................................................................................................................................. 119
Spanning Tree Protocol .........................................................................................................................121
Bandwidth Control .................................................................................................................................142
Broadcast Storm Control .......................................................................................................................144
Mirroring ................................................................................................................................................146
Link Aggregation ...................................................................................................................................148
Port Authentication ................................................................................................................................155
Port Security ..........................................................................................................................................163
Time Range ...........................................................................................................................................167
Classifier ...............................................................................................................................................169
Policy Rule ............................................................................................................................................178
Queuing Method ....................................................................................................................................182
Multicast ................................................................................................................................................186
AAA .......................................................................................................................................................210
IP Source Guard ...................................................................................................................................220
Loop Guard ...........................................................................................................................................253
Layer 2 Protocol Tunneling ................................................................................................................... 257
PPPoE ................................................................................................................................................... 261
Error Disable .........................................................................................................................................270
MAC Pinning .........................................................................................................................................276
Private VLAN .........................................................................................................................................278
Green Ethernet ......................................................................................................................................282
Link Layer Discovery Protocol (LLDP) ..................................................................................................284
Static Route ...........................................................................................................................................308
XS1920 Series User’s Guide
3

Contents Overview
Differentiated Services .......................................................................................................................... 313
DHCP ....................................................................................................................................................317
ARP Setup ............................................................................................................................................329
Maintenance ..........................................................................................................................................334
Access Control ......................................................................................................................................343
Diagnostic .............................................................................................................................................360
System Log ...........................................................................................................................................363
Syslog Setup .........................................................................................................................................364
Cluster Management ............................................................................................................................. 367
MAC Table .............................................................................................................................................373
IP Table .................................................................................................................................................376
ARP Table .............................................................................................................................................378
Routing Table ........................................................................................................................................380
Path MTU Table .................................................................................................................................... 381
Configure Clone ....................................................................................................................................382
IPv6 Neighbor Table ..............................................................................................................................385
Troubleshooting .................................................................................................................................... 387
XS1920 Series User’s Guide
4

Table of Contents
Table of Contents
Contents Overview...............................................................................................................................3
Table of Contents .................................................................................................................................5
Part I: User’s Guide .........................................................................................18
Chapter 1
Getting to Know Your Switch.............................................................................................................19
1.1 Introduction .......................................................................................................................................19
1.1.1 Backbone Application .............................................................................................................. 19
1.1.2 Bridging Example ....................................................................................................................20
1.1.3 High Performance Switching Example ....................................................................................20
1.1.4 IEEE 802.1Q VLAN Application Examples ..............................................................................21
1.2 Ways to Manage the Switch ..............................................................................................................22
1.3 Good Habits for Managing the Switch ...............................................................................................22
Chapter 2
Hardware Installation and Connection.............................................................................................23
2.1 Installation Scenarios ........................................................................................................................23
2.2 Desktop Installation Procedure ........................................................................................................23
2.3 Rack Mounting .................................................................................................................................23
2.3.1 Rack-mounted Installation Requirements ................................................................................23
2.3.2 Attaching the Mounting Brackets to the Switch .......................................................................24
2.3.3 Mounting the Switch on a Rack ...............................................................................................24
Chapter 3
Hardware Panels.................................................................................................................................26
3.1 Front Panel ........................................................................................................................................26
3.1.1 Gigabit Ethernet Ports ............................................................................................................26
3.1.2 SFP/SFP+ Slots ......................................................................................................................27
3.2 Rear Panel ........................................................................................................................................29
3.2.1 Power Connector .....................................................................................................................29
3.3 LEDs ...............................................................................................................................................30
3.4 Reset to Factory Defaults ..................................................................................................................30
Part II: Technical Reference............................................................................32
XS1920 Series User’s Guide
5

Table of Contents
Chapter 4
The Web Configurator........................................................................................................................33
4.1 Overview ...........................................................................................................................................33
4.2 System Login ................................................................................................................................. 33
4.3 The Status Screen ........................................................................................................................34
4.3.1 Change Your Password ........................................................................................................38
4.4 Saving Your Configuration ................................................................................................................ 38
4.5 Switch Lockout ................................................................................................................................39
4.6 Resetting the Switch ......................................................................................................................39
4.7 Logging Out of the Web Configurator .............................................................................................. 39
4.8 Help ..................................................................................................................................................39
Chapter 5
Initial Setup Example..........................................................................................................................41
5.1 Overview ...........................................................................................................................................41
5.1.1 Creating a VLAN ...................................................................................................................... 41
5.1.2 Setting Port VID .......................................................................................................................42
5.2 Configuring Switch Management IP Address ....................................................................................43
Chapter 6
Tutorials...............................................................................................................................................45
6.1 Overview ...........................................................................................................................................45
6.2 How to Use DHCP Snooping on the Switch ......................................................................................45
6.3 How to Use DHCP Relay on the Switch ............................................................................................49
6.3.1 DHCP Relay Tutorial Introduction ............................................................................................ 49
6.3.2 Creating a VLAN ...................................................................................................................... 49
6.3.3 Configuring DHCP Relay .........................................................................................................52
6.3.4 Troubleshooting ....................................................................................................................... 53
Chapter 7
Status and ZON...................................................................................................................................54
7.1 Overview ...........................................................................................................................................54
7.1.1 What You Can Do ....................................................................................................................54
7.2 Status ................................................................................................................................................54
7.3 ZyXEL One Network (ZON) Utility ....................................................................................................56
7.4 ZON Neighbor Management ............................................................................................................57
7.5 Port Status .......................................................................................................................................58
7.5.1 Port Details .........................................................................................................................60
Chapter 8
Basic Setting ......................................................................................................................................63
8.1 Overview ...........................................................................................................................................63
8.1.1 What You Can Do ....................................................................................................................63
XS1920 Series User’s Guide
6

Table of Contents
8.2 System Information ........................................................................................................................63
8.3 General Setup ...............................................................................................................................66
8.4 Introduction to VLANs ......................................................................................................................67
8.5 Switch Setup Screen ......................................................................................................................68
8.6 IP Setup ...........................................................................................................................................70
8.6.1 IP Status ..................................................................................................................................70
8.6.2 IP Status Detail ........................................................................................................................70
8.6.3 IP Configuration ....................................................................................................................... 72
8.7 Port Setup ........................................................................................................................................ 74
8.8 Interface Setup ................................................................................................................................ 76
8.9 IPv6 ................................................................................................................................................77
8.9.1 IPv6 Interface Status ..............................................................................................................77
8.9.2 IPv6 Configuration ................................................................................................................... 80
8.9.3 IPv6 Global Setup .................................................................................................................... 81
8.9.4 IPv6 Interface Setup ................................................................................................................81
8.9.5 IPv6 Link-Local Address Setup ............................................................................................... 82
8.9.6 IPv6 Global Address Setup ..................................................................................................... 83
8.9.7 IPv6 Neighbor Discovery Setup ...............................................................................................84
8.9.8 IPv6 Router Discovery Setup ..................................................................................................85
8.9.9 IPv6 Prefix Setup .....................................................................................................................86
8.9.10 IPv6 Neighbor Setup ............................................................................................................. 88
8.9.11 DHCPv6 Client Setup ............................................................................................................ 89
8.10 DNS ................................................................................................................................................. 90
Chapter 9
VLAN....................................................................................................................................................92
9.1 Overview ...........................................................................................................................................92
9.1.1 What You Can Do ....................................................................................................................92
9.1.2 What You Need to Know ..........................................................................................................92
9.2 VLAN Status ..................................................................................................................................... 95
9.2.1 VLAN Details ..........................................................................................................................96
9.3 Private VLAN Status ......................................................................................................................97
9.4 VLAN Configuration ..........................................................................................................................98
9.5 Configure a Static VLAN ...............................................................................................................99
9.6 Configure VLAN Port Settings .....................................................................................................100
9.7 Subnet Based VLANs ....................................................................................................................102
9.7.1 Configuring Subnet Based VLAN ........................................................................................ 103
9.8 Protocol Based VLANs ................................................................................................................... 104
9.8.1 Configuring Protocol Based VLAN ...................................................................................... 105
9.9 Voice VLAN .....................................................................................................................................106
9.10 MAC-based VLAN ......................................................................................................................... 108
9.11 Port-based VLAN Setup ...........................................................................................................109
9.11.1 Port-based VLAN Screen .....................................................................................................109
XS1920 Series User’s Guide
7

Table of Contents
9.12 Technical Reference ...................................................................................................................... 112
9.12.1 Create an IP-based VLAN Example .................................................................................... 112
Chapter 10
Static MAC Forward Setup...............................................................................................................114
10.1 Overview ....................................................................................................................................... 114
10.1.1 What You Can Do ................................................................................................................ 114
10.2 Configuring Static MAC Forwarding ......................................................................................... 114
Chapter 11
Static Multicast Forward Setup .......................................................................................................116
11.1 Static Multicast Forward Setup Overview ..................................................................................... 116
11.1.1 What You Can Do ................................................................................................................ 116
11.1.2 What You Need To Know ..................................................................................................... 116
11.2 Configuring Static Multicast Forwarding ........................................................................................ 117
Chapter 12
Filtering..............................................................................................................................................119
12.1 Filtering Overview ......................................................................................................................... 119
12.1.1 What You Can Do ................................................................................................................ 119
12.2 Configure a Filtering Rule ............................................................................................................ 119
Chapter 13
Spanning Tree Protocol....................................................................................................................121
13.1 Spanning Tree Protocol Overview .................................................................................................121
13.1.1 What You Can Do ................................................................................................................121
13.1.2 What You Need to Know ......................................................................................................121
13.2 Spanning Tree Protocol Status Screen .........................................................................................124
13.3 Spanning Tree Configuration .......................................................................................................124
13.4 Configure Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol ...................................................................................125
13.4.1 Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol Status ............................................................................127
13.5 Configure Multiple Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol .....................................................................128
13.5.1 Multiple Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol Status ...............................................................130
13.6 Configure Multiple Spanning Tree Protocol ................................................................................132
13.6.1 Multiple Spanning Tree Port Configuration ..........................................................................135
13.6.2 Multiple Spanning Tree Protocol Status ...........................................................................136
13.7 Technical Reference ......................................................................................................................139
13.7.1 MSTP Network Example .....................................................................................................139
13.7.2 MST Region .........................................................................................................................140
13.7.3 MST Instance ......................................................................................................................140
13.7.4 Common and Internal Spanning Tree (CIST) ......................................................................141
Chapter 14
Bandwidth Control............................................................................................................................142
XS1920 Series User’s Guide
8

Table of Contents
14.1 Overview .......................................................................................................................................142
14.1.1 What You Can Do ................................................................................................................142
14.2 Bandwidth Control Setup .............................................................................................................. 142
Chapter 15
Broadcast Storm Control.................................................................................................................144
15.1 Broadcast Storm Control Overview ..............................................................................................144
15.1.1 What You Can Do ................................................................................................................144
15.2 Broadcast Storm Control Setup .....................................................................................................144
Chapter 16
Mirroring............................................................................................................................................146
16.1 Mirroring Overview ....................................................................................................................... 146
16.1.1 What You Can Do ................................................................................................................146
16.2 Port Mirroring Setup ......................................................................................................................146
Chapter 17
Link Aggregation..............................................................................................................................148
17.1 Link Aggregation Overview .......................................................................................................... 148
17.1.1 What You Can Do ................................................................................................................148
17.1.2 What You Need to Know ......................................................................................................148
17.2 Link Aggregation Status ................................................................................................................149
17.3 Link Aggregation Setting .............................................................................................................150
17.4 Link Aggregation Control Protocol ............................................................................................. 152
17.5 Technical Reference ......................................................................................................................153
17.5.1 Static Trunking Example ...................................................................................................... 153
Chapter 18
Port Authentication ..........................................................................................................................155
18.1 Port Authentication Overview ....................................................................................................... 155
18.1.1 What You Need to Know ......................................................................................................155
18.2 Port Authentication Configuration ................................................................................................. 157
18.3 Activate IEEE 802.1x Security ..................................................................................................157
18.3.1 Guest VLAN ........................................................................................................................158
18.4 Activate MAC Authentication ........................................................................................................160
Chapter 19
Port Security .....................................................................................................................................163
19.1 Port Security Overview .................................................................................................................163
19.1.1 What You Can Do ................................................................................................................163
19.2 Port Security Setup .......................................................................................................................163
19.3 VLAN MAC Address Limit ............................................................................................................165
XS1920 Series User’s Guide
9

Table of Contents
Chapter 20
Time Range .......................................................................................................................................167
20.1 About Time Range ........................................................................................................................167
20.2 Time Range Setup ........................................................................................................................ 167
Chapter 21
Classifier............................................................................................................................................169
21.1 Overview .......................................................................................................................................169
21.1.1 What You Can Do ................................................................................................................169
21.1.2 What You Need to Know ......................................................................................................169
21.2 Classifier Status ............................................................................................................................169
21.3 Classifier Configuration .................................................................................................................170
21.3.1 Viewing and Editing Classifier Configuration .......................................................................174
21.3.2 Classifier Global Setting ......................................................................................................175
21.4 Classifier Example ........................................................................................................................176
Chapter 22
Policy Rule ........................................................................................................................................178
22.1 Policy Rules Overview .................................................................................................................178
22.1.1 What You Can Do ................................................................................................................178
22.2 Configuring Policy Rules ...............................................................................................................178
Chapter 23
Queuing Method ...............................................................................................................................182
23.1 Queuing Method Overview ............................................................................................................ 182
23.1.1 What You Can Do ................................................................................................................182
23.1.2 What You Need to Know ......................................................................................................182
23.2 Configuring Queuing .....................................................................................................................183
Chapter 24
Multicast ............................................................................................................................................186
24.1 Multicast Overview ........................................................................................................................ 186
24.1.1 What You Can Do ................................................................................................................186
24.1.2 What You Need to Know ......................................................................................................186
24.2 Multicast Setup ..............................................................................................................................190
24.3 IPv4 Multicast Status ....................................................................................................................190
24.3.1 IGMP Snooping .................................................................................................................. 191
24.3.2 IGMP Snooping VLAN ........................................................................................................193
24.3.3 IGMP Filtering Profile .........................................................................................................195
24.4 IPv6 Multicast Status .....................................................................................................................196
24.4.1 MLD Snooping-proxy ...........................................................................................................197
24.4.2 MLD Snooping-proxy VLAN ................................................................................................197
24.4.3 MLD Snooping-proxy VLAN Port Role Setting ....................................................................199
XS1920 Series User’s Guide
10

Table of Contents
24.4.4 MLD Snooping-proxy Filtering .............................................................................................200
24.4.5 MLD Snooping-proxy Filtering Profile ..................................................................................202
24.5 General MVR Configuration ......................................................................................................... 203
24.5.1 MVR Group Configuration ..................................................................................................205
24.5.2 MVR Configuration Example ...............................................................................................207
Chapter 25
AAA....................................................................................................................................................210
25.1 AAA Overview ...............................................................................................................................210
25.1.1 What You Can Do ................................................................................................................210
25.1.2 What You Need to Know ......................................................................................................210
25.2 AAA Screens ................................................................................................................................. 211
25.3 RADIUS Server Setup ............................................................................................................... 211
25.4 TACACS+ Server Setup ............................................................................................................213
25.5 AAA Setup ....................................................................................................................................215
25.6 Technical Reference ......................................................................................................................217
25.6.1 Vendor Specific Attribute .....................................................................................................217
25.6.2 Supported RADIUS Attributes .............................................................................................218
25.6.3 Attributes Used for Authentication .......................................................................................219
Chapter 26
IP Source Guard................................................................................................................................220
26.1 IP Source Guard Overview ..........................................................................................................220
26.1.1 What You Can Do ................................................................................................................220
26.1.2 What You Need to Know ......................................................................................................221
26.2 IP Source Guard Screen ...............................................................................................................221
26.3 IPv4 Source Guard Setup ............................................................................................................ 222
26.4 IPv4 Source Guard Static Binding ................................................................................................223
26.5 DHCP Snooping ........................................................................................................................... 225
26.5.1 DHCP Snooping Configure .................................................................................................228
26.5.2 DHCP Snooping Port Configure .........................................................................................230
26.5.3 DHCP Snooping VLAN Configure ......................................................................................231
26.5.4 DHCP Snooping VLAN Port Configure ................................................................................232
26.6 ARP Inspection Status .................................................................................................................234
26.6.1 ARP Inspection VLAN Status ..............................................................................................235
26.6.2 ARP Inspection Log Status ..................................................................................................235
26.6.3 ARP Inspection Configure ...................................................................................................236
26.6.4 ARP Inspection Port Configure ............................................................................................238
26.6.5 ARP Inspection VLAN Configure .........................................................................................239
26.7 IPv6 Source Guard Overview .......................................................................................................240
26.8 IPv6 Source Binding Status ........................................................................................................... 241
26.9 IPv6 Static Binding Setup .............................................................................................................242
26.10 IPv6 Source Guard Policy Setup ................................................................................................243
XS1920 Series User’s Guide
11

Table of Contents
26.11 IPv6 Source Guard Port Setup ................................................................................................... 244
26.12 IPv6 Snooping Policy Setup .......................................................................................................245
26.13 IPv6 Snooping VLAN Setup .......................................................................................................247
26.14 IPv6 DHCP Trust Setup .............................................................................................................247
26.15 Technical Reference ....................................................................................................................249
26.15.1 DHCP Snooping Overview ................................................................................................249
26.15.2 ARP Inspection Overview ..................................................................................................250
Chapter 27
Loop Guard .......................................................................................................................................253
27.1 Loop Guard Overview ..................................................................................................................253
27.1.1 What You Can Do ................................................................................................................253
27.1.2 What You Need to Know ......................................................................................................253
27.2 Loop Guard Setup .........................................................................................................................255
Chapter 28
Layer 2 Protocol Tunneling.............................................................................................................. 257
28.1 Layer 2 Protocol Tunneling Overview ..........................................................................................257
28.1.1 What You Can Do ................................................................................................................257
28.1.2 What You Need to Know ......................................................................................................257
28.2 Configuring Layer 2 Protocol Tunneling ........................................................................................258
Chapter 29
PPPoE................................................................................................................................................261
29.1 PPPoE Intermediate Agent Overview ...........................................................................................261
29.1.1 What You Can Do ................................................................................................................261
29.1.2 What You Need to Know ......................................................................................................261
29.2 The PPPoE Screen .......................................................................................................................264
29.3 PPPoE Intermediate Agent ..........................................................................................................264
29.3.1 PPPoE IA Per-Port .............................................................................................................265
29.3.2 PPPoE IA Per-Port Per-VLAN ............................................................................................267
29.3.3 PPPoE IA for VLAN ............................................................................................................268
Chapter 30
Error Disable.....................................................................................................................................270
30.1 Error Disable Overview .................................................................................................................270
30.2 The Error Disable Screens Overview ............................................................................................270
30.3 Error-Disable Status .....................................................................................................................270
30.4 CPU Protection Configuration ......................................................................................................272
30.5 Error-Disable Detect Configuration ..............................................................................................273
30.6 Error-Disable Recovery Configuration .........................................................................................274
Chapter 31
MAC Pinning .....................................................................................................................................276
XS1920 Series User’s Guide
12

Table of Contents
31.1 MAC Pinning Overview ................................................................................................................ 276
31.2 MAC Pinning Configuration ...........................................................................................................276
Chapter 32
Private VLAN.....................................................................................................................................278
32.1 Private VLAN Overview ................................................................................................................278
32.1.1 Configuration ....................................................................................................................... 280
Chapter 33
Green Ethernet..................................................................................................................................282
33.1 Green Ethernet Overview .............................................................................................................282
33.2 Configuring Green Ethernet .......................................................................................................... 282
Chapter 34
Link Layer Discovery Protocol (LLDP)...........................................................................................284
34.1 LLDP Overview .............................................................................................................................284
34.2 LLDP-MED Overview .................................................................................................................... 285
34.3 LLDP Screens ............................................................................................................................... 286
34.4 LLDP Local Status ........................................................................................................................287
34.4.1 LLDP Local Port Status Detail ............................................................................................288
34.5 LLDP Remote Status ....................................................................................................................291
34.5.1 LLDP Remote Port Status Detail ........................................................................................292
34.6 LLDP Configuration ...................................................................................................................... 298
34.6.1 LLDP Configuration Basic TLV Setting ...............................................................................300
34.6.2 LLDP Configuraion Basic Org-specific TLV Setting ............................................................301
34.7 LLDP-MED Configuration .............................................................................................................302
34.8 LLDP-MED Network Policy .........................................................................................................303
34.9 LLDP-MED Location ...................................................................................................................304
Chapter 35
Static Route.......................................................................................................................................308
35.1 Static Route Overview ..................................................................................................................308
35.1.1 What You Can Do ................................................................................................................308
35.2 Static Routing ................................................................................................................................308
35.3 IPv4 Static Route ........................................................................................................................309
35.4 IPv6 Static Route ......................................................................................................................... 311
Chapter 36
Differentiated Services.....................................................................................................................313
36.1 Differentiated Services Overview .................................................................................................313
36.1.1 What You Can Do ................................................................................................................313
36.1.2 What You Need to Know ......................................................................................................313
36.2 Activating DiffServ ........................................................................................................................314
XS1920 Series User’s Guide
13

Table of Contents
36.3 DSCP-to-IEEE 802.1p Priority Settings ......................................................................................315
36.3.1 Configuring DSCP Settings .................................................................................................316
Chapter 37
DHCP..................................................................................................................................................317
37.1 DHCP Overview ............................................................................................................................317
37.1.1 What You Can Do ................................................................................................................317
37.1.2 What You Need to Know ......................................................................................................317
37.2 DHCP Configuration ......................................................................................................................318
37.3 DHCPv4 Status ............................................................................................................................319
37.4 DHCPv4 Relay .............................................................................................................................319
37.4.1 DHCPv4 Relay Agent Information .......................................................................................319
37.4.2 DHCPv4 Option 82 Profile ...................................................................................................320
37.4.3 Configuring DHCPv4 Global Relay ......................................................................................322
37.4.4 DHCPv4 Global Relay Port Configure ................................................................................ 323
37.4.5 Global DHCP Relay Configuration Example .......................................................................324
37.5 Configuring DHCPv4 VLAN Settings .........................................................................................324
37.5.1 DHCPv4 VLAN Port Configure ...........................................................................................325
37.5.2 Example: DHCP Relay for Two VLANs ...............................................................................326
37.6 DHCPv6 Relay ..............................................................................................................................327
Chapter 38
ARP Setup .........................................................................................................................................329
38.1 ARP Overview ..............................................................................................................................329
38.1.1 How ARP Works ..................................................................................................................329
38.1.2 ARP Learning Mode ............................................................................................................329
38.2 ARP Setup ....................................................................................................................................331
38.2.1 ARP Learning ..................................................................................................................... 331
38.2.2 Static ARP ...........................................................................................................................332
Chapter 39
Maintenance...................................................................................................................................... 334
39.1 Overview .......................................................................................................................................334
39.2 The Maintenance Screen .............................................................................................................334
39.2.1 Erase Running-Configuration .............................................................................................335
39.2.2 Save Configuration ..............................................................................................................335
39.2.3 Reboot System .................................................................................................................... 336
39.2.4 Firmware Upgrade ..............................................................................................................336
39.2.5 Restore a Configuration File .............................................................................................338
39.2.6 Backup a Configuration File .............................................................................................338
39.2.7 Tech-Support ......................................................................................................................339
39.3 Technical Reference ......................................................................................................................340
39.3.1 FTP Command Line ............................................................................................................340
XS1920 Series User’s Guide
14

Table of Contents
39.3.2 Filename Conventions ........................................................................................................341
39.3.3 FTP Command Line Procedure ........................................................................................... 341
39.3.4 GUI-based FTP Clients ........................................................................................................342
39.3.5 FTP Restrictions .................................................................................................................342
Chapter 40
Access Control .................................................................................................................................343
40.1 Access Control Overview .............................................................................................................343
40.1.1 What You Can Do ................................................................................................................343
40.2 The Access Control Main Screen ..................................................................................................343
40.3 Configuring SNMP .....................................................................................................................344
40.3.1 Configuring SNMP Trap Group .........................................................................................345
40.3.2 Enabling/Disabling Sending of SNMP Traps on a Port .......................................................346
40.3.3 Configuring SNMP User ................................................................................................... 347
40.4 Setting Up Login Accounts ...........................................................................................................348
40.5 Service Port Access Control ......................................................................................................350
40.6 Remote Management ..............................................................................................................351
40.7 Technical Reference ......................................................................................................................352
40.7.1 About SNMP .......................................................................................................................352
40.7.2 Introduction to HTTPS .........................................................................................................355
Chapter 41
Diagnostic .........................................................................................................................................360
41.1 Overview .......................................................................................................................................360
41.2 Diagnostic ....................................................................................................................................360
Chapter 42
System Log .......................................................................................................................................363
42.1 Overview .......................................................................................................................................363
42.2 System Log ...................................................................................................................................363
Chapter 43
Syslog Setup..................................................................................................................................... 364
43.1 Syslog Overview ...........................................................................................................................364
43.1.1 What You Can Do ................................................................................................................364
43.2 Syslog Setup .................................................................................................................................364
Chapter 44
Cluster Management ........................................................................................................................367
44.1 Cluster Management Overview .....................................................................................................367
44.1.1 What You Can Do ................................................................................................................368
44.2 Cluster Management Status ..........................................................................................................368
44.3 Clustering Management Configuration ........................................................................................369
XS1920 Series User’s Guide
15

Table of Contents
44.4 Technical Reference ......................................................................................................................371
44.4.1 Cluster Member Switch Management ................................................................................ 371
Chapter 45
MAC Table .........................................................................................................................................373
45.1 MAC Table Overview ....................................................................................................................373
45.1.1 What You Can Do ................................................................................................................373
45.1.2 What You Need to Know ......................................................................................................373
45.2 Viewing the MAC Table ................................................................................................................374
Chapter 46
IP Table ..............................................................................................................................................376
46.1 IP Table Overview ........................................................................................................................376
46.2 Viewing the IP Table ......................................................................................................................377
Chapter 47
ARP Table..........................................................................................................................................378
47.1 Overview .......................................................................................................................................378
47.1.1 What You Can Do ................................................................................................................378
47.1.2 What You Need to Know ......................................................................................................378
47.2 Viewing the ARP Table ..................................................................................................................378
Chapter 48
Routing Table....................................................................................................................................380
48.1 Overview .......................................................................................................................................380
48.2 Viewing the Routing Table Status .................................................................................................380
Chapter 49
Path MTU Table................................................................................................................. ................381
49.1 Path MTU Overview .....................................................................................................................381
49.2 Viewing the Path MTU Table .........................................................................................................381
Chapter 50
Configure Clone................................................................................................................................382
50.1 Overview .......................................................................................................................................382
50.2 Configure Clone ...........................................................................................................................382
Chapter 51
IPv6 Neighbor Table..........................................................................................................................385
51.1 IPv6 Neighbor Table Overview .....................................................................................................385
51.2 Viewing the IPv6 Neighbor Table ..................................................................................................385
Chapter 52
Troubleshooting................................................................................................................................387
XS1920 Series User’s Guide
16

Table of Contents
52.1 Power, Hardware Connections, and LEDs ....................................................................................387
52.2 Switch Access and Login ..............................................................................................................388
52.3 Switch Configuration .....................................................................................................................390
Appendix A Customer Support ........................................................................................................391
Appendix B Common Services ........................................................................................................397
Appendix C IPv6 ..............................................................................................................................400
Appendix D Legal Information .........................................................................................................409
Index .................................................................................................................................................414
XS1920 Series User’s Guide
17

PART I
User’s Guide
18

1.1 Introduction
This chapter introduces the main features and applications of the Switch. The XS1920 Series
consist of the following models at the time of writing:
• XS1920-12
The Switch is a 10G Ethernet web-managed switch with layer-2, layer-3, and layer-4 features.
With its built-in web configurator, including the ZyXEL One Network (ZON) Neighbor Management
feature (Section 7.3 on page 56), viewing, managing and configuring the Switch and its
neighboring devices is easy. The Switch can also be managed via third-party SNMP management.
ZyXEL One Network (ZON) Utility is a tool that lets set up and maintain network devices in a simple
and efficient way. You can download the ZON Utility at www.zyxel.com and install it on a computer.
For more information on the ZON Utility see Section 7.3 on page 56.
CHAPTER 1
Getting to Know Your Switch
The following table describes the port features of the 10G Switch. 100Mbps connections are not
guaranteed.
Table 1 Port Features
SWITCH MODEL PORT FEATURES
XS1920-12 • 12 10 Gbps Ethernet ports
• 2 1G/10G SFP+fiber ports
The next section shows a few examples of using the Switch in various network environments.
1.1.1 Backbone Application
The Switch is an ideal solution for small networks where rapid growth can be expected in the near
future. The Switch can be used standalone for a group of heavy traffic users. You can connect
computers and servers directly to the Switch’s port or connect other switches to the Switch.
In this example, all computers can share high-speed applications on the server. To expand the
network, simply add more networking devices such as switches, routers, computers, print servers
etc.
XS1920 Series User’s Guide
19
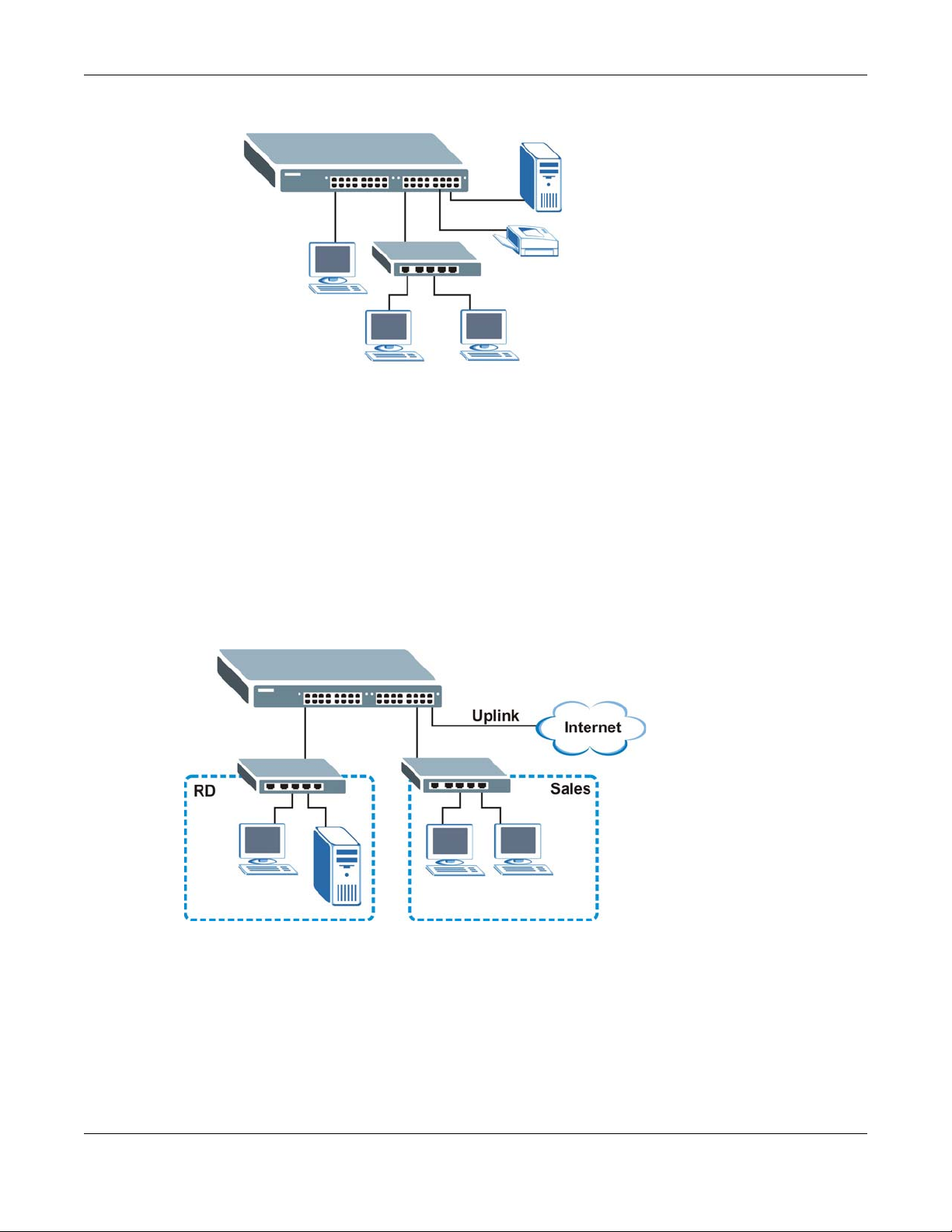
Figure 1 Backbone Application
1.1.2 Bridging Example
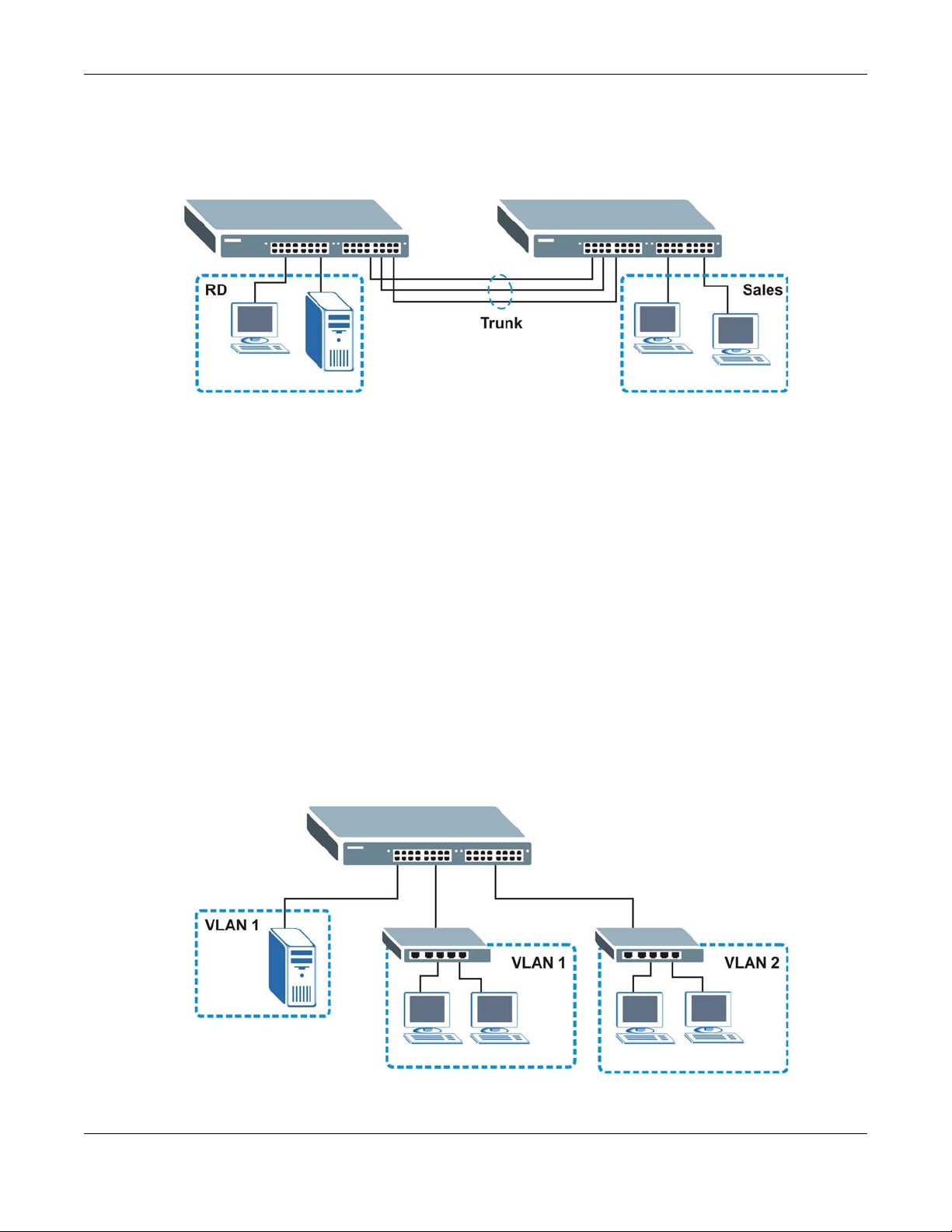
In this example, the Switch connects different company departments (RD and Sales) to the
corporate backbone. It can alleviate bandwidth contention and eliminate server and network
bottlenecks. All users that need high bandwidth can connect to high-speed department servers via
the Switch. You can provide a super-fast uplink connection by using a Gigabit Ethernet/mini-GBIC
port on the Switch.
Chapter 1 Getting to Know Your Switch
Moreover, the Switch eases supervision and maintenance by allowing network managers to
centralize multiple servers at a single location.
Figure 2 Bridging Application
1.1.3 High Performance Switching Example
The Switch is ideal for connecting two networks that need high bandwidth. In the following
example, use trunking to connect these two networks.
Switching to higher-speed LANs such as ATM (Asynchronous Transmission Mode) is not feasible for
most people due to the expense of replacing all existing Ethernet cables and adapter cards,
restructuring your network and complex maintenance. The Switch can provide the same bandwidth
XS1920 Series User’s Guide
20
Chapter 1 Getting to Know Your Switch
as ATM at much lower cost while still being able to use existing adapters and switches. Moreover,
the current LAN structure can be retained as all ports can freely communicate with each other.
Figure 3 High Performance Switched Workgroup Application
1.1.4 IEEE 802.1Q VLAN Application Examples
A VLAN (Virtual Local Area Network) allows a physical network to be partitioned into multiple logical
networks. Stations on a logical network belong to one group. A station can belong to more than one
group. With VLAN, a station cannot directly talk to or hear from stations that are not in the same
group(s) unless such traffic first goes through a router.
For more information on VLANs, refer to Chapter 9 on page 92.
1.1.4.1 Tag-based VLAN Example
Ports in the same VLAN group share the same frame broadcast domain thus increase network
performance through reduced broadcast traffic. VLAN groups can be modified at any time by
adding, moving or changing ports without any re-cabling.
Shared resources such as a server can be used by all ports in the same VLAN as the server. In the
following figure only ports that need access to the server need to be part of VLAN 1. Ports can
belong to other VLAN groups too.
Figure 4 Shared Server Using VLAN Example
XS1920 Series User’s Guide
21

Chapter 1 Getting to Know Your Switch
1.2 Ways to Manage the Switch
Use any of the following methods to manage the Switch.
• Web Configurator. This is recommended for everyday management of the Switch using a
(supported) web browser. See Chapter 4 on page 33.
• FTP. Use FTP for firmware upgrades and configuration backup/restore. See Section 39.3.1 on
page 340.
• SNMP. The Switch can be monitored by an SNMP manager. See Section 40.5 on page 350.
• Cluster Management. Cluster Management allows you to manage multiple switches through one
switch, called the cluster manager. See Chapter 44 on page 367.
1.3 Good Habits for Managing the Switch
Do the following things regularly to make the Switch more secure and to manage the Switch more
effectively.
• Change the password. Use a password that’s not easy to guess and that consists of different
types of characters, such as numbers and letters.
• Write down the password and put it in a safe place.
• Back up the configuration (and make sure you know how to restore it). Restoring an earlier
working configuration may be useful if the device becomes unstable or even crashes. If you
forget your password, you will have to reset the Switch to its factory default settings. If you
backed up an earlier configuration file, you would not have to totally re-configure the Sw itch. Y ou
could simply restore your last configuration. See Section 3.4 on page 30 for how to reset the
Switch.
XS1920 Series User’s Guide
22

CHAPTER 2
Hardware Installation and Connection
2.1 Installation Scenarios
This chapter shows you how to install and connect the Switch.
The Switch can be placed on a desktop or rack-mounted on a standard EIA rack. Use the rubber
feet in a desktop installation and the brackets in a rack-mounted installation.
Note: For proper ventilation, allow at least 4 inches (10 cm) of clearance at the front and
3.4 inches (8 cm) at the back of the Switch. This is especially important for
enclosed rack installations.
2.2 Desktop Installation Procedure
1 Make sure the Switch is clean and dry.
2 Set the Switch on a smooth, level surface strong enough to support the weight of the Switch and
the connected cables. Make sure there is a power outlet nearby.
3 Make sure there is enough clearance around the Switch to allow air circulation and the attachment
of cables and the power cord.
2.3 Rack Mounting
The Switch can be mounted on an EIA standard size, 19-inch rack or in a wiring closet with other
equipment. Follow the steps below to mount your Switch on a standard EIA rack using a rackmounting kit.
2.3.1 Rack-mounted Installation Requirements
• Two mounting brackets.
• Eight M3 flat head screws and a #2 Philips screwdriver.
• Four M5 flat head screws and a #2 Philips screwdriver.
Failure to use the proper screws may damage the unit.
2.3.1.1 Precautions
• Make sure the rack will safely support the combined weight of all the equipment it contains.
XS1920 Series User’s Guide
23

Chapter 2 Hardware Installation and Connection
• Make sure the position of the Switch does not make the rack unstable or top-heavy. Take all
necessary precautions to anchor the rack securely before installing the unit.
2.3.2 Attaching the Mounting Brackets to the Switch
1 Position a mounting bracket on one side of the Switch, lining up the four screw holes on the br acket
with the screw holes on the side of the Switch.
Figure 5 Attaching the Mounting Brackets
2 Using a #2 Philips screwdriver, install the M3 flat head screws through the mounting bracket holes
into the Switch.
3 Repeat steps 1 and 2 to install the second mounting bracket on the other side of the Switch.
4 You may now mount the Switch on a rack. Proceed to the next section.
2.3.3 Mounting the Switch on a Rack
1 Position a mounting bracket (that is already attached to the Switch) on one side of the rack, lining
up the two screw holes on the bracket with the screw holes on the side of the rack.
XS1920 Series User’s Guide
24
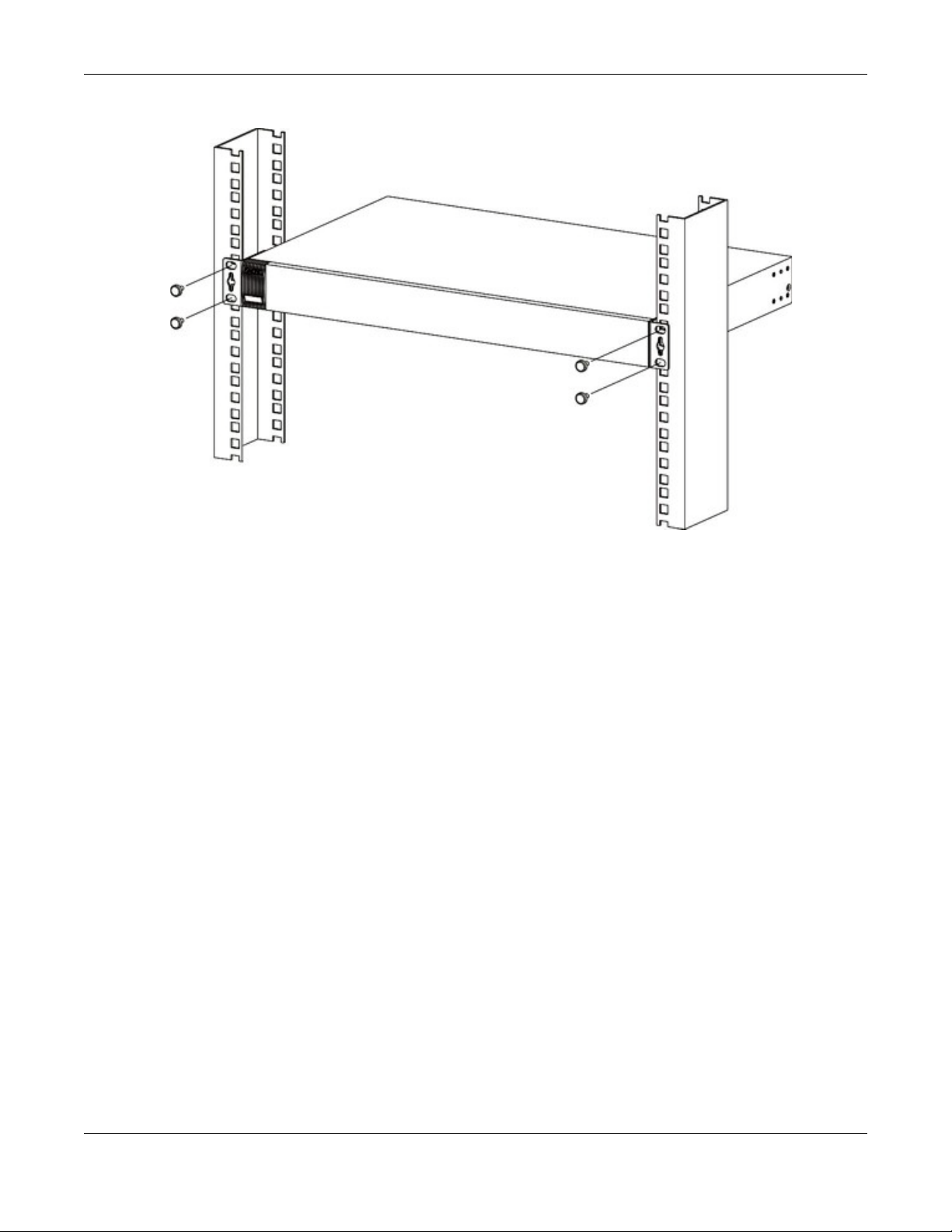
Chapter 2 Hardware Installation and Connection
Figure 6 Mounting the Switch on a Rack
2 Using a #2 Philips screwdriver, install the M5 flat head screws through the mounting bracket holes
into the rack.
3 Repeat steps 1 and 2 to attach the second mounting bracket on the other side of the rack.
XS1920 Series User’s Guide
25

This chapter describes the front panel and rear panel of the Switch and shows you how to make the
100Mbps/1Gbps/10Gbps
Ethernet/SFP(+)
Uplink Ports/Slots
Ethernet Ports
hardware connections.
3.1 Front Panel
The following figures show the front panel of the Switch. See Section 3.3 on page 30 for information
on the LEDs. The reset button is also located here as circled below. See Section 3.4 on page 30 for
more information on using that.
Figure 7 Front Panel: XS1920-12
CHAPTER 3
Hardware Panels
The following table describes the ports.
Table 2 Panel Connections
CONNECTOR DESCRIPTION
Ports 1-10 These are 100Mbps/1Gbps/10Gbps RJ-45 Ethernet ports.
Connect these ports to a computer, a hub, an Ethernet switch or router.
Ports 11-12
Ethernet
Ports 11-12 Fiber These are SFP / SFP+ uplink Slots Use SFP transceivers in these slots for fiber-optic to
These are 100Mbps/1Gbps/10Gbps RJ-45 combo uplink ports. The fiber port connection
takes priority if the corresponding Ethernet uplink port is also connected.
Connect these ports to high-bandwidth backbone network Ethernet switches using 100/
1000/10G Base-T cables.
backbone Ethernet switches.
3.1.1 Gigabit Ethernet Ports
Ports 1-10 on the Switch are 100Mbps/1Gbps/10Gbps auto-negotiating, auto-crossover Ethernet
ports with full duplex support.
An auto-negotiating port can detect and adjust to the optimum Ethernet speed of the connected
device. Auto-1000M / Full-Duplex supports Ethernet and fiber connections at 100Mbps or
XS1920 Series User’s Guide
26

Chapter 3 Hardware Panels
1000Mbps (1Gbps) full-duplex mode. Auto-10G / Full-Duplex supports Ethernet connections at
100Mbps, 1000Mbps or 10Gbps full-duplex mode and 10Gbps only for fiber connections.
When auto-negotiation is turned on, an Ethernet port negotiates with the peer automatically to
determine the connection speed. If the peer Ethernet port does not support auto-negotiation or
turns off this feature, the Switch determines the connection speed by detecting the signal on the
cable. When the Switch’s auto-negotiation is turned off, an Ethernet port uses the pre-configured
speed when making a connection, thus requiring you to make sure that the settings of the peer
Ethernet port are the same in order to connect.
An auto-crossover (auto-MDI/MDI-X) port automatically works with a str aight -through or crossov er
Ethernet cable.
Ports 11 and 12 are Ethernet ports paired with Ports 11 and 12 SGP/SFP+ (fiber) slots. The Switch
uses one of either the Ethernet or fiber connection with the fiber connection having priority if the
corresponding Ethernet port is also connected. This means that if Port 11 fiber slot and Port 11
Ethernet port are connected at the same time, then Ethernet port 11 will be disabled. Ethernet and
fiber ports 12 work the same way.
3.1.1.1 Default Ethernet Negotiation Settings
The factory default negotiation settings for the Ethernet ports on the Switch are:
• Speed: Auto
•Duplex: Full
• Flow control: Off
• Link Aggregation: Disabled
3.1.2 SFP/SFP+ Slots
Fiber ports 11 and 12 are slots for Small Form-Factor Pluggable (Plus) modules, such as an SFP or
SFP+ transceivers. SFP+ is an enhanced version of SFP and supports data rates of 10 Gbps. A
transceiver is a single unit that houses a transmitter and a receiver. Use a transceiver to connect a
fiber-optic cable to the Switch. The Switch does not come with transceivers. You must use
transceivers that comply with the Small Form-Factor Pluggable (SFP) Transceiver MultiSource
Agreement (MSA). See the SFF committee’s INF-8074i specification Rev 1.0 for details.
You can change transceivers while the Switch is operating. You can use different transceivers to
connect to Ethernet switches with different types of fiber-optic connectors.
• Type: SFP/SFP+ connection interface
• Connection speed: 1 or 10 Gigabit per second (Gbps)
3.1.2.1 Transceiver Installation
Use the following steps to install a mini-GBIC transceiver (SFP+ module).
1 Insert the transceiver into the slot with the exposed section of PCB board facing down.
2 Press the transceiver firmly until it clicks into place.
XS1920 Series User’s Guide
27

Chapter 3 Hardware Panels
3 The Switch automatically detects the installed transceiver. Check the LEDs to verify that it is
functioning properly.
4 Close the transceiver’s latch (latch styles vary).
5 Connect the fiber optic cables to the transceiver.
Figure 8 Transceiver Installation Example
Figure 9 Connecting the Fiber Optic Cables
3.1.2.2 Transceiver Removal
Use the following steps to remove a mini-GBIC transceiver (SFP+ module).
1 Remove the fiber optic cables from the transceiver.
2 Open the transceiver’s latch (latch styles vary).
3 Pull the transceiver out of the slot.
Figure 10 Removing the Fiber Optic Cables
Figure 11 Opening the Transceiver’s Latch Example
Figure 12 Transceiver Removal Example
XS1920 Series User’s Guide
28

3.2 Rear Panel
The following figures show the rear panel of the Switch.
Figure 13 Rear panel: XS1920-12
3.2.1 Power Connector
Note: Make sure you are using the correct power source as shown on the panel.
T o connect power to the Switch, insert the female end of the power cord to the AC power receptacle
on the rear panel. Connect the other end of the supplied power cord to a power outlet. Make sure
that no objects obstruct the airflow of the fans (located on the side of the unit).
Chapter 3 Hardware Panels
XS1920 Series User’s Guide
29
3.3 LEDs
After you connect the power to the Switch, view the LEDs to ensure proper functioning of the
Switch and as an aid in troubleshooting.
Table 3 LED Descriptions
LED COLOR STATUS DESCRIPTION
PWR Green On The system is turned on.
SYS Green On The system is on and functioning properly.
ALM Red On A hardware failure, such as high temperature, wrong voltage
LOCATOR Blue Blinking Shows the actual location of the Switch between several
100M/1G/10G Ethernet Ports 100Mbps connections are not recommended as some legacy 100Mbps
LNK/ACT (Left)
LNK/ACT
(Right)
SFP / SFP+ Slots
11-12
SFP/SFP+ LNK/
ACT (Left)
11-12
SFP/SFP+ LNK/
ACT (Right)
Chapter 3 Hardware Panels
Off The system is off or has failed.
Blinking The system is rebooting and performing self-diagnostic
tests.
Off The power is off or the system is not ready/malfunctioning.
or abnormal fan speed is detected.
Off The system is functioning normally.
devices in a rack.
devices may have interoperability issues when connected to the combo
ports. The LED displays green for successfully connected 100Mbps
devices that do not have interoperability issues.
Green Blinking The port is transmitting/receiving to/from a 100 Mbps or a
1000 Mbps (1 Gbps) Ethernet network.
On The link to a 100 Mbps or a 1000 Mbps Ethernet network is
up.
Off The link to an Ethernet network is down.
Blue Blinking The port is transmitting/receiving to/from a 10 Gbps
Ethernet network.
On The link to a 10 Gbps Ethernet network is up.
Off The link to an Ethernet network is down.
Green On The uplink port is linking at 1000 Mbps.
Blinking The port is transmitting/receiving data 1000 Mbps.
Off There is no link or the uplink port is shut down.
Blue On The uplink port is linking at 10 Gbps.
Blinking The port is transmitting/receiving data 10 Gbps.
Off There is no link or the uplink port is shut down.
3.4 Reset to Factory Defaults
If you forget your password or cannot access the Web Configurator, you will need to use the Reset
button on the device to reload the factory-default configuration file. This means that you will lose all
configurations that you had previously and the default Switch IP address, user name and password
will be reset to 192.168.1.1, admin and 1234 respectively.
XS1920 Series User’s Guide
30
 Loading...
Loading...