Appendix A Importing Certificates
Removing a Certificate in Internet Explorer
This section shows you how to remove a public key certificate in Internet Explorer 7 on Windows XP.
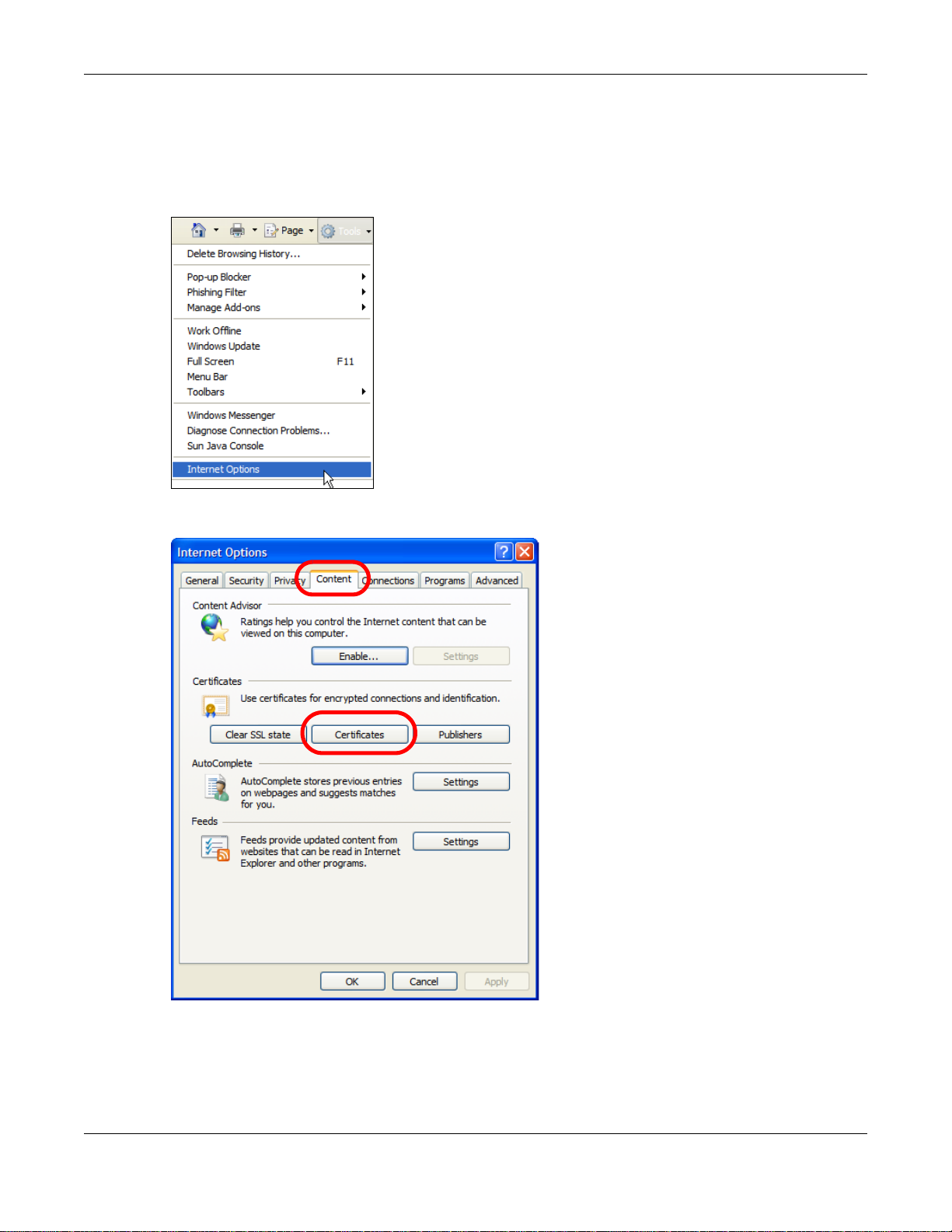
1 Open Internet Explorer and click Tools > Internet Options.
2 In the Internet Options dialog box, click Content > Certificates.
NWA5000 / WAC6000 Series User’s Guide
201
Appendix A Importing Certificates
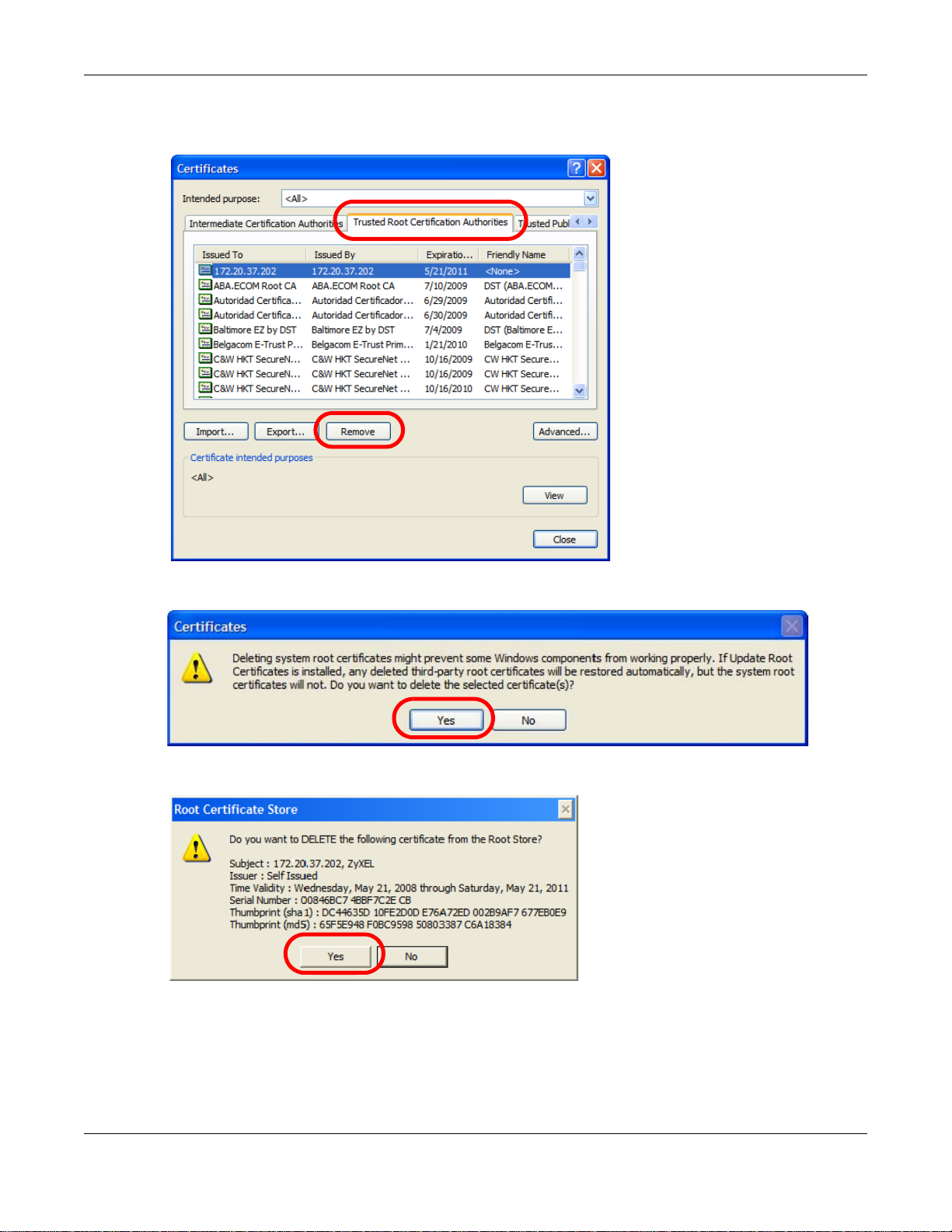
3 In the Certificates dialog box, click the Trusted Root Certificates Authorities tab, select the
certificate that you want to delete, and then click Remove.
4 In the Certificates confirmation, click Yes.
5 In the Root Certificate Store dialog box, click Yes.
6 The next time you go to the web site that issued the public key certificate you just removed, a
certification error appears.
NWA5000 / WAC6000 Series User’s Guide
202
Firefox
Appendix A Importing Certificates
The following example uses Mozilla Firefox 2 on Windows XP Professional; however, the screens can
also apply to Firefox 2 on all platforms.
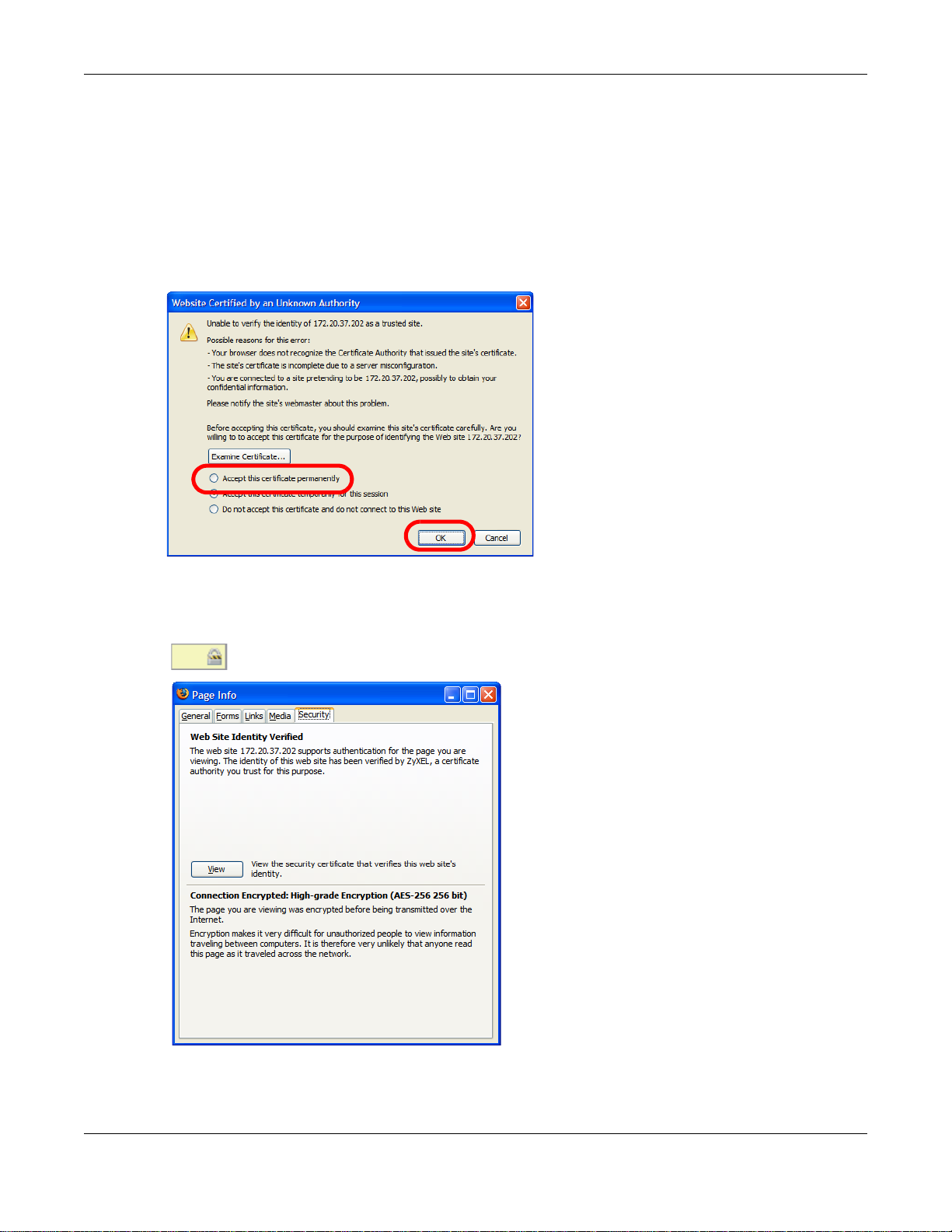
1 If your device’s Web Configurator is set to use SSL certification, then the first time you browse to it
you are presented with a certification error.
2 Select Accept this certificate permanently and click OK.
3 The certificate is stored and you can now connect securely to the Web Configurator. A sealed
padlock appears in the address bar, which you can click to open the Page Info > Security window
to view the web page’s security information.
NWA5000 / WAC6000 Series User’s Guide
203
Appendix A Importing Certificates
Installing a Stand-Alone Certificate File in Firefox
Rather than browsing to a ZyXEL Web Configurator and installing a public key certificate when
prompted, you can install a stand-alone certificate file if one has been issued to you.
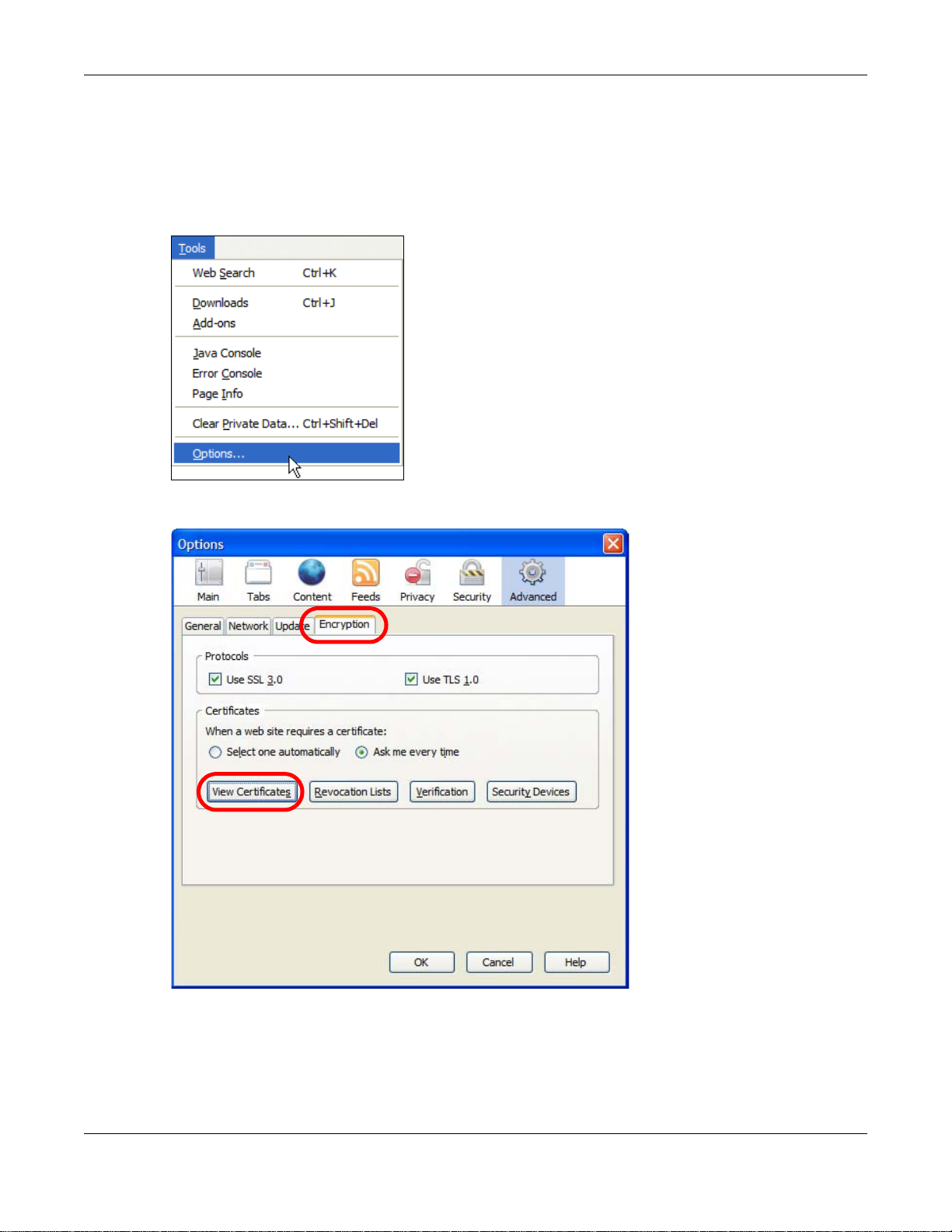
1 Open Firefox and click Tools > Options.
2 In the Options dialog box, click Advanced > Encryption > View Certificates.
NWA5000 / WAC6000 Series User’s Guide
204
Appendix A Importing Certificates
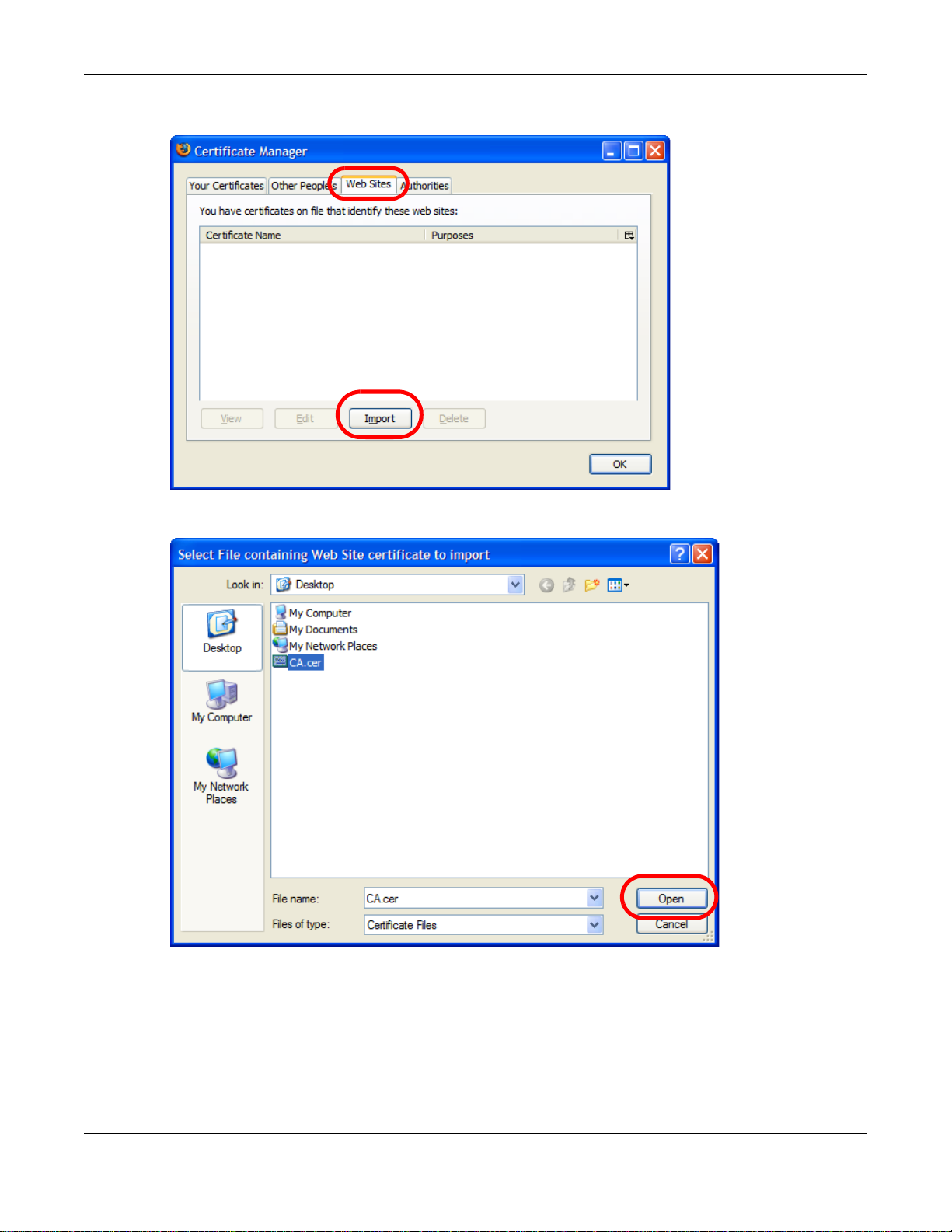
3 In the Certificate Manager dialog box, click Web Sites > Import.
4 Use the Select File dialog box to locate the certificate and then click Open.
5 The next time you visit the web site, click the padlock in the address bar to open the Page Info >
Security window to see the web page’s security information.
Removing a Certificate in Firefox
This section shows you how to remove a public key certificate in Firefox 2.
NWA5000 / WAC6000 Series User’s Guide
205
Appendix A Importing Certificates
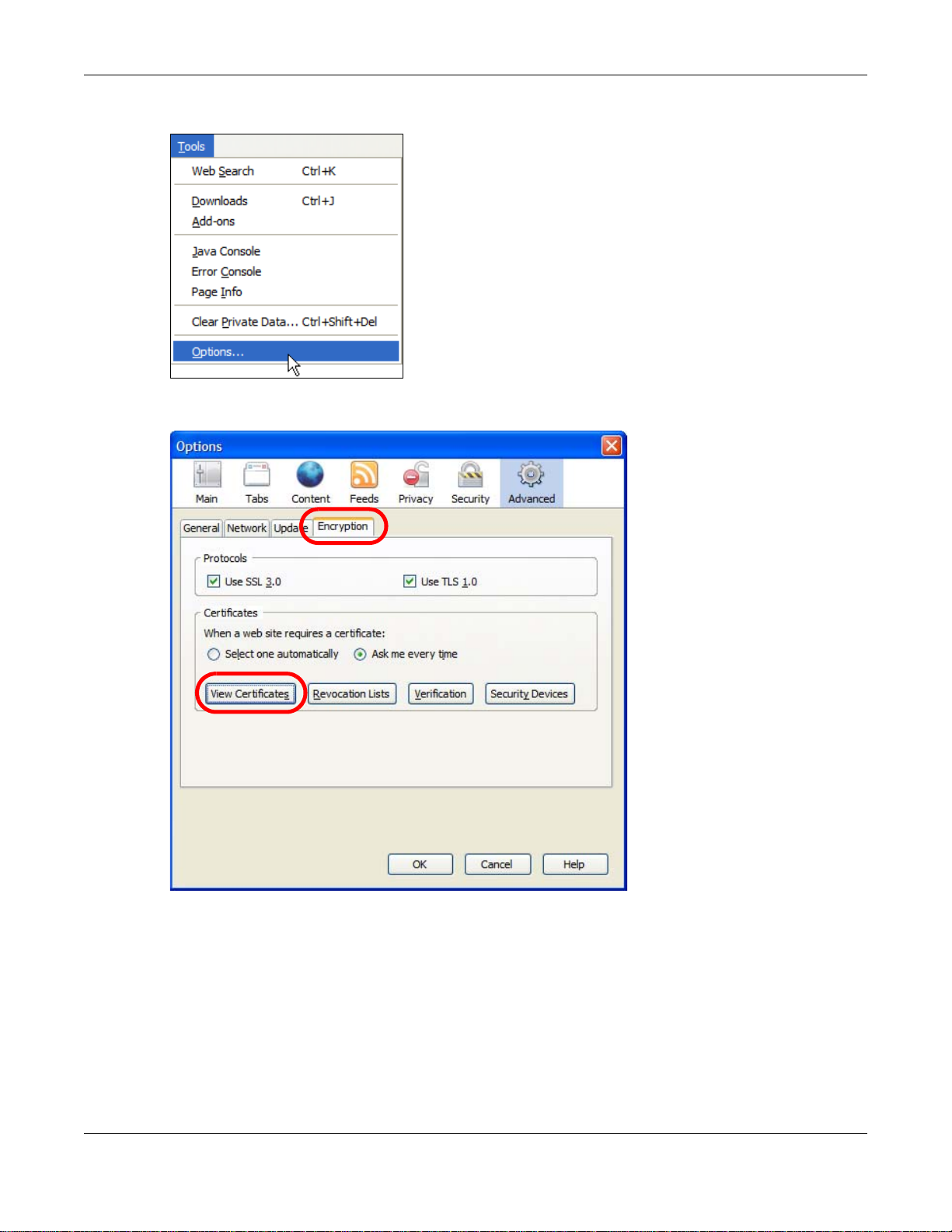
1 Open Firefox and click Tools > Options.
2 In the Options dialog box, click Advanced > Encryption > View Certificates.
NWA5000 / WAC6000 Series User’s Guide
206
Appendix A Importing Certificates
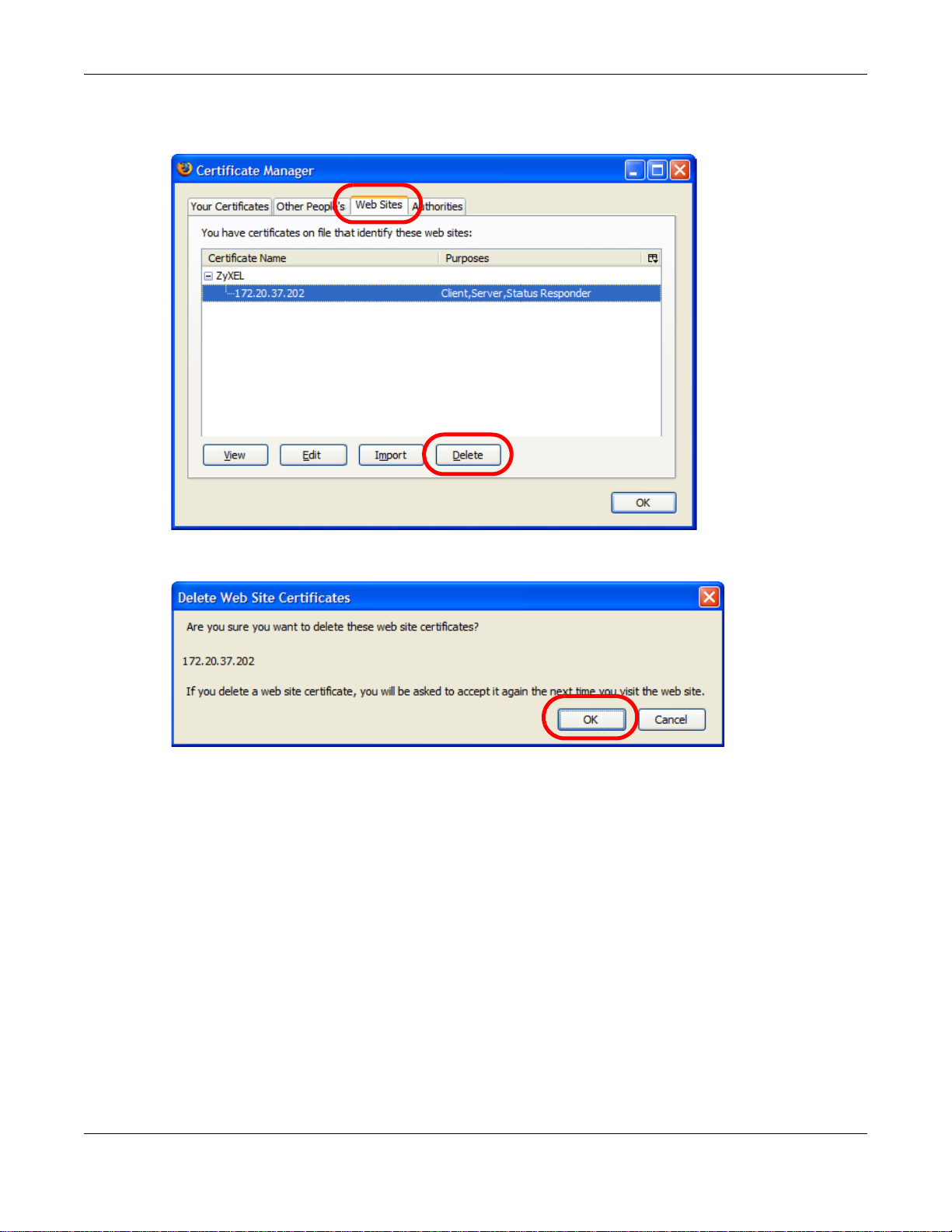
3 In the Certificate Manager dialog box, select the Web Sites tab, select the certificate that you
want to remove, and then click Delete.
4 In the Delete Web Site Certificates dialog box, click OK.
5 The next time you go to the web site that issued the public key certificate you just removed, a
certification error appears.
NWA5000 / WAC6000 Series User’s Guide
207

Overview
APPENDIX B
IPv6
IPv6 (Internet Protocol version 6), is designed to enhance IP address size and features. The
increase in IPv6 address size to 128 bits (from the 32-bit IPv4 address) allows up to 3.4 x 10
addresses.
IPv6 Addressing
The 128-bit IPv6 address is written as eight 16-bit hexadecimal blocks separated by colons (:). This
is an example IPv6 address 2001:0db8:1a2b:0015:0000:0000:1a2f:0000.
IPv6 addresses can be abbreviated in two ways:
• Leading zeros in a block can be omitted. So 2001:0db8:1a2b:0015:0000:0000:1a2f:0000 can
be written as 2001:db8:1a2b:15:0:0:1a2f:0.
• Any number of consecutive blocks of zeros can be replaced by a double colon. A double colon can
only appear once in an IPv6 address. So 2001:0db8:0000:0000:1a2f:0000:0000:0015 can be
written as 2001:0db8::1a2f:0000:0000:0015, 2001:0db8:0000:0000:1a2f::0015,
2001:db8::1a2f:0:0:15 or 2001:db8:0:0:1a2f::15.
Prefix and Prefix Length
Similar to an IPv4 subnet mask, IPv6 uses an address prefix to represent the network address. An
IPv6 prefix length specifies how many most significant bits (start from the left) in the address
compose the network address. The prefix length is written as “/x” where x is a number. For
example,
38
IP
2001:db8:1a2b:15::1a2f:0/32
means that the first 32 bits (2001:db8) is the subnet prefix.
Link-local Address
A link-local address uniquely identifies a device on the local network (the LAN). It is similar to a
“private IP address” in IPv4. You can have the same link-local address on multiple interfaces on a
device. A link-local unicast address has a predefined prefix of fe80::/10. The link-local unicast
address format is as follows.
Table 85 Link-local Unicast Address Format
1111 1110 10 0 Interface ID
10 bits 54 bits 64 bits
NWA5000 / WAC6000 Series User’s Guide
208
Global Address
A global address uniquely identifies a device on the Internet. It is similar to a “public IP address” in
IPv4. A global unicast address starts with a 2 or 3.
Unspecified Address
An unspecified address (0:0:0:0:0:0:0:0 or ::) is used as the source address when a device does
not have its own address. It is similar to “0.0.0.0” in IPv4.
Loopback Address
A loopback address (0:0:0:0:0:0:0:1 or ::1) allows a host to send packets to itself. It is similar to
“127.0.0.1” in IPv4.
Multicast Address
In IPv6, multicast addresses provide the same functionality as IPv4 broadcast addresses.
Broadcasting is not supported in IPv6. A multicast address allows a host to send packets to all hosts
in a multicast group.
Appendix B IPv6
Multicast scope allows you to determine the size of the multicast group. A multicast address has a
predefined prefix of ff00::/8. The following table describes some of the predefined multicast
addresses.
Table 86 Predefined Multicast Address
MULTICAST ADDRESS DESCRIPTION
FF01:0:0:0:0:0:0:1 All hosts on a local node.
FF01:0:0:0:0:0:0:2 All routers on a local node.
FF02:0:0:0:0:0:0:1 All hosts on a local connected link.
FF02:0:0:0:0:0:0:2 All routers on a local connected link.
FF05:0:0:0:0:0:0:2 All routers on a local site.
FF05:0:0:0:0:0:1:3 All DHCP severs on a local site.
The following table describes the multicast addresses which are reserved and can not be assigned
to a multicast group.
Table 87 Reserved Multicast Address
MULTICAST ADDRESS
FF00:0:0:0:0:0:0:0
FF01:0:0:0:0:0:0:0
FF02:0:0:0:0:0:0:0
FF03:0:0:0:0:0:0:0
FF04:0:0:0:0:0:0:0
FF05:0:0:0:0:0:0:0
FF06:0:0:0:0:0:0:0
FF07:0:0:0:0:0:0:0
FF08:0:0:0:0:0:0:0
FF09:0:0:0:0:0:0:0
NWA5000 / WAC6000 Series User’s Guide
209
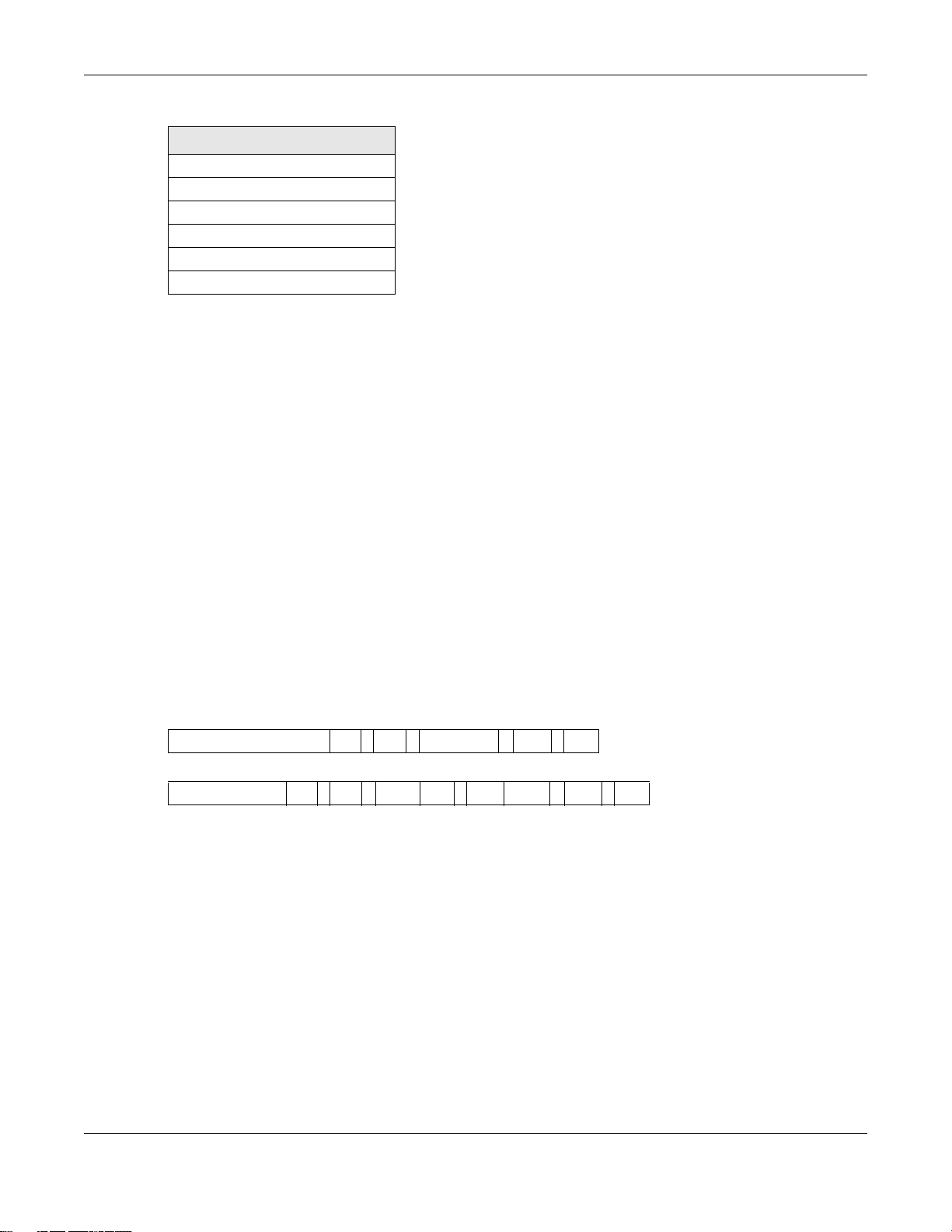
Table 87 Reserved Multicast Address (continued)
MULTICAST ADDRESS
FF0A:0:0:0:0:0:0:0
FF0B:0:0:0:0:0:0:0
FF0C:0:0:0:0:0:0:0
FF0D:0:0:0:0:0:0:0
FF0E:0:0:0:0:0:0:0
FF0F:0:0:0:0:0:0:0
Subnet Masking
Both an IPv6 address and IPv6 subnet mask compose of 128-bit binary digits, which are divided
into eight 16-bit blocks and written in hexadecimal notation. Hexadecimal uses four bits for each
character (1 ~ 10, A ~ F). Each block’s 16 bits are then represented by four hexadecimal
characters. For example, FFFF:FFFF:FFFF:FFFF:FC00:0000:0000:0000.
Interface ID
In IPv6, an interface ID is a 64-bit identifier. It identifies a physical interface (for example, an
Ethernet port) or a virtual interface (for example, the management IP address for a VLAN). One
interface should have a unique interface ID.
Appendix B IPv6
EUI-64
The EUI-64 (Extended Unique Identifier) defined by the IEEE (Institute of Electrical and Electronics
Engineers) is an interface ID format designed to adapt with IPv6. It is derived from the 48-bit (6byte) Ethernet MAC address as shown next. EUI-64 inserts the hex digits fffe between the third and
fourth bytes of the MAC address and complements the seventh bit of the first byte of the MAC
address. See the following example.
Table 88
MAC 00 : 13 : 49 : 12 : 34 : 56
Table 89
EUI-64 02 : 13 : 49 : FF : FE : 12 : 34 : 56
Stateless Autoconfiguration
With stateless autoconfiguration in IPv6, addresses can be uniquely and automatically generated.
Unlike DHCPv6 (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol version six) which is used in IPv6 stateful
autoconfiguration, the owner and status of addresses don’t need to be maintained by a DHCP
server. Every IPv6 device is able to generate its own and unique IP address automatically when
IPv6 is initiated on its interface. It combines the prefix and the interface ID (generated from its own
Ethernet MAC address, see Interface ID and EUI-64) to form a complete IPv6 address.
When IPv6 is enabled on a device, its interface automatically generates a link-local address
(beginning with fe80).
When the interface is connected to a network with a router and the NWA/WAC is set to
automatically obtain an IPv6 network prefix from the router for the interface, it generates
NWA5000 / WAC6000 Series User’s Guide
210
1
another
address which combines its interface ID and global and subnet information advertised from the
T1
T2
Renew
Rebind
Rebind
to S1
Renew
to S1
Renew
to S1
Renew
to S1
Renew
to S1
Renew
to S1
to S2
to S2
router. This is a routable global IP address.
DHCPv6
The Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol for IPv6 (DHCPv6, RFC 3315) is a server-client protocol
that allows a DHCP server to assign and pass IPv6 network addresses, prefixes and other
configuration information to DHCP clients. DHCPv6 servers and clients exchange DHCP messages
using UDP.
Each DHCP client and server has a unique DHCP Unique IDentifier (DUID), which is used for
identification when they are exchanging DHCPv6 messages. The DUID is generated from the MAC
address, time, vendor assigned ID and/or the vendor's private enterprise number registered with
the IANA. It should not change over time even after you reboot the device.
Identity Association
An Identity Association (IA) is a collection of addresses assigned to a DHCP client, through which
the server and client can manage a set of related IP addresses. Each IA must be associated with
exactly one interface. The DHCP client uses the IA assigned to an interface to obtain configuration
from a DHCP server for that interface. Each IA consists of a unique IAID and associated IP
information.
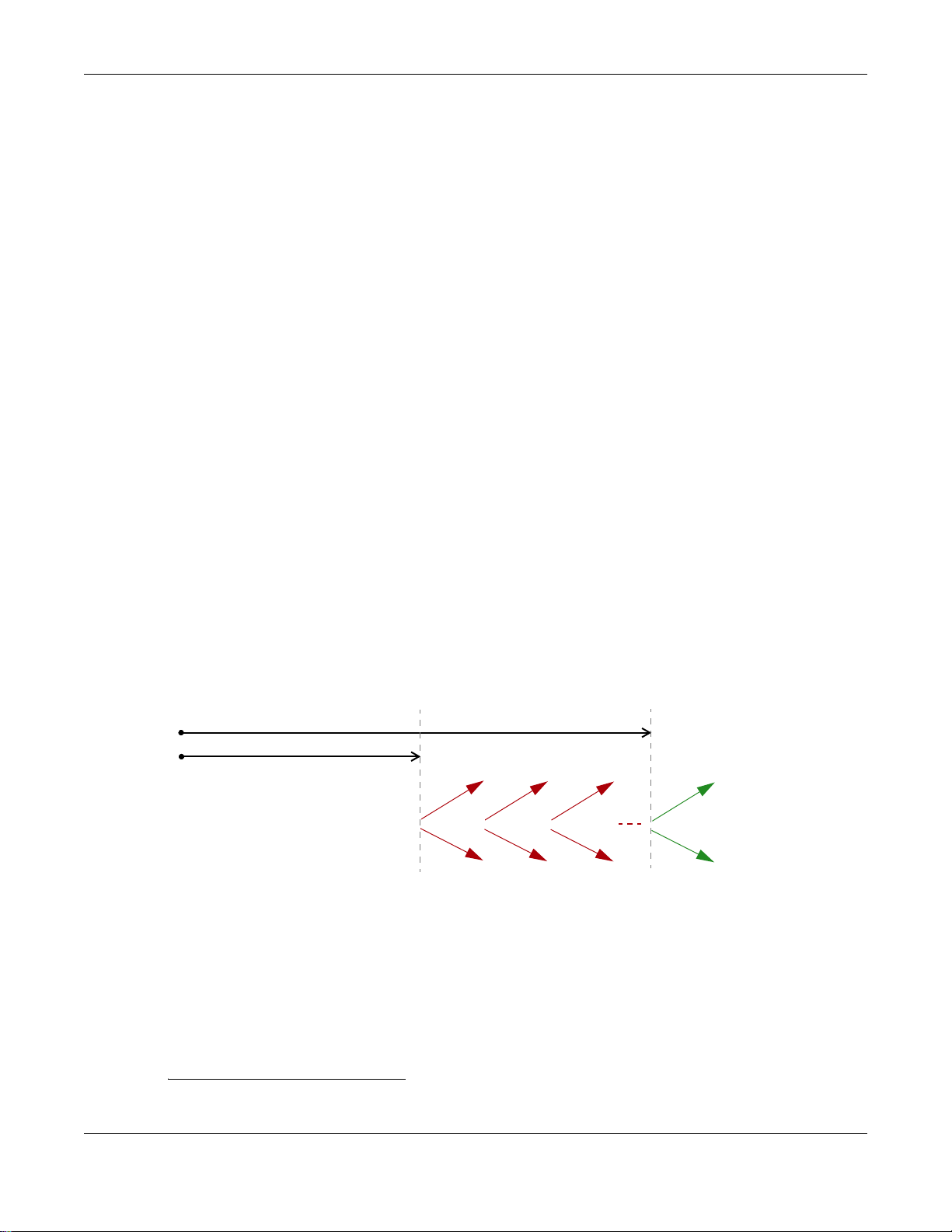
The IA type is the type of address in the IA. Each IA holds one type of address. IA_NA means an
identity association for non-temporary addresses and IA_TA is an identity association for temporary
addresses. An IA_NA option contains the T1 and T2 fields, but an IA_TA option does not. The
DHCPv6 server uses T1 and T2 to control the time at which the client contacts with the server to
extend the lifetimes on any addresses in the IA_NA before the lifetimes expire. After T1, the client
sends the server (S1) (from which the addresses in the IA_NA were obtained) a Renew message. If
the time T2 is reached and the server does not respond, the client sends a Rebind message to any
available server (S2). For an IA_TA, the client may send a Renew or Rebind message at the client's
discretion.
Appendix B IPv6
DHCP Relay Agent
A DHCP relay agent is on the same network as the DHCP clients and helps forward messages
between the DHCP server and clients. When a client cannot use its link-local address and a wellknown multicast address to locate a DHCP server on its network, it then needs a DHCP relay agent
to send a message to a DHCP server that is not attached to the same network.
The DHCP relay agent can add the remote identification (remote-ID) option and the interface-ID
option to the Relay-Forward DHCPv6 messages. The remote-ID option carries a user-defined string,
1. In IPv6, all network interfaces can be associated with several addresses.
NWA5000 / WAC6000 Series User’s Guide
211

such as the system name. The interface-ID option provides slot number, port information and the
VLAN ID to the DHCPv6 server. The remote-ID option (if any) is stripped from the Relay-Reply
messages before the relay agent sends the packets to the clients. The DHCP server copies the
interface-ID option from the Relay-Forward message into the Relay-Reply message and sends it to
the relay agent. The interface-ID should not change even after the relay agent restarts.
Prefix Delegation
Prefix delegation enables an IPv6 router to use the IPv6 prefix (network address) received from the
ISP (or a connected uplink router) for its LAN. The NWA/WAC uses the received IPv6 prefix (for
example, 2001:db2::/48) to generate its LAN IP address. Through sending Router Advertisements
(RAs) regularly by multicast, the NWA/WAC passes the IPv6 prefix information to its LAN hosts. The
hosts then can use the prefix to generate their IPv6 addresses.
ICMPv6
Internet Control Message Protocol for IPv6 (ICMPv6 or ICMP for IPv6) is defined in RFC 4443.
ICMPv6 has a preceding Next Header value of 58, which is different from the value used to identify
ICMP for IPv4. ICMPv6 is an integral part of IPv6. IPv6 nodes use ICMPv6 to report errors
encountered in packet processing and perform other diagnostic functions, such as "ping".
Appendix B IPv6
Neighbor Discovery Protocol (NDP)
The Neighbor Discovery Protocol (NDP) is a protocol used to discover other IPv6 devices and track
neighbor’s reachability in a network. An IPv6 device uses the following ICMPv6 messages types:
• Neighbor solicitation: A request from a host to determine a neighbor’s link-layer address (MAC
address) and detect if the neighbor is still reachable. A neighbor being “reachable” means it
responds to a neighbor solicitation message (from the host) with a neighbor advertisement
message.
• Neighbor advertisement: A response from a node to announce its link-layer address.
• Router solicitation: A request from a host to locate a router that can act as the default router and
forward packets.
• Router advertisement: A response to a router solicitation or a periodical multicast advertisement
from a router to advertise its presence and other parameters.
IPv6 Cache
An IPv6 host is required to have a neighbor cache, destination cache, prefix list and default router
list. The NWA/WAC maintains and updates its IPv6 caches constantly using the information from
response messages. In IPv6, the NWA/WAC configures a link-local address automatically, and then
sends a neighbor solicitation message to check if the address is unique. If there is an address to be
resolved or verified, the NWA/WAC also sends out a neighbor solicitation message. When the NWA/
WAC receives a neighbor advertisement in response, it stores the neighbor’s link-layer address in
the neighbor cache. When the NWA/WAC uses a router solicitation message to query for a router
and receives a router advertisement message, it adds the router’s information to the neighbor
cache, prefix list and destination cache. The NWA/WAC creates an entry in the default router list
cache if the router can be used as a default router.
When the NWA/WAC needs to send a packet, it first consults the destination cache to determine the
next hop. If there is no matching entry in the destination cache, the NWA/WAC uses the prefix list
NWA5000 / WAC6000 Series User’s Guide
212
 Loading...
Loading...