ZyXEL Prestige 153X User Manual Supplement

Prestige 153X
WAN Access Router
User's Guide Supplement
ZyXEL
TOTAL INTERNET ACCESS SOLUTION
Prestige 153X Supplement
NNeeww FFeeaattuurreess:
The Prestige 153X now supports Frame Relay! You may have up to 6 simultaneous frame relay connections
i.e., 3 PVCs on WAN port 1or 2. Each PVC has its own encapsulation type, DLCI (Data Link Connection
Identifier), CIR (Committed Information Rate) and EIR (Excess Information Rate). When frame relay is not
used, the WAN port can also be configured to run PPP over HDLC on a leased-sync line. The Connection
Type must be set to
used). Each of these ports can be configured as either the network side or the user side of the UNI interface.
The options for the Connection Type field are shown in the following table. UNI (User Network Interface)
defines the connection between user equipment and the Frame Relay network.
Leased-Sync
Network
User
None
Connection
Type
to configure Frame Relay (so only P153X WAN ports 1 and/or 2 may be
Frame relay is configured as the network side of the UNI interface.
Frame relay is configured as the user side of the UNI interface.
Runs PPP over HDLC without frame relay on a leased-sync line.
:
1.1 What is Frame Relay?
This is some background information on frame relay. Please skip ahead if you wish to begin configuring your
Prestige for Frame Relay right away.
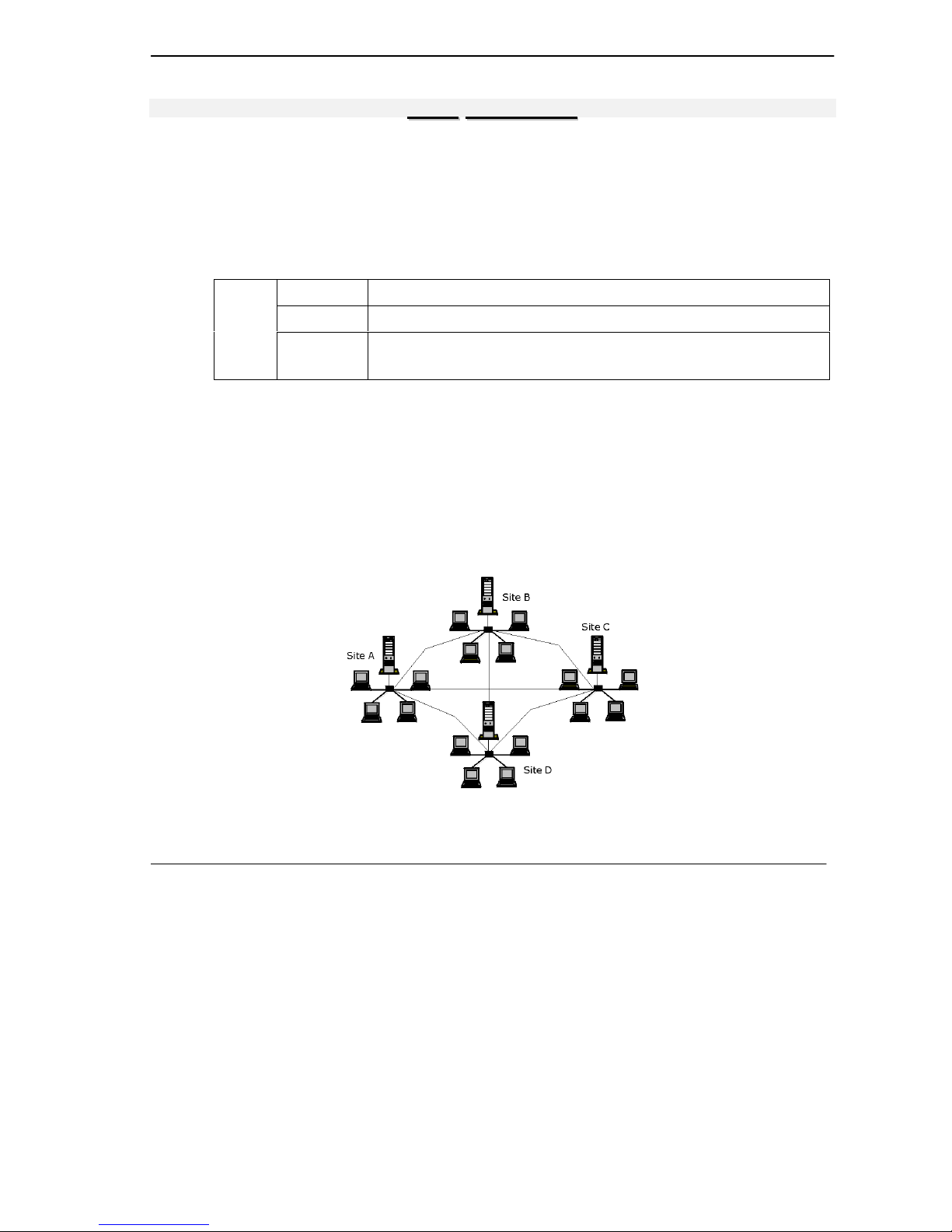
Frame relay is a form of packet-switching technology that routes frames of information from source to
destination over a switching network owned by a carrier. Suppose a corporate network has 4 sites, site A, site
B, site C and site D (as shown in the next figure) and you need to interconnect these sites with both data links
and voice lines. As data traffic is relatively continuous throughout the day one solution (though inefficient)
would be to set up dedicated leased lines connecting each office as shown in Figure 1.
Figure 1 Dedicated Leased Lines – Multiple Sites
User's Guide Supplement
1
Prestige 153X Supplement
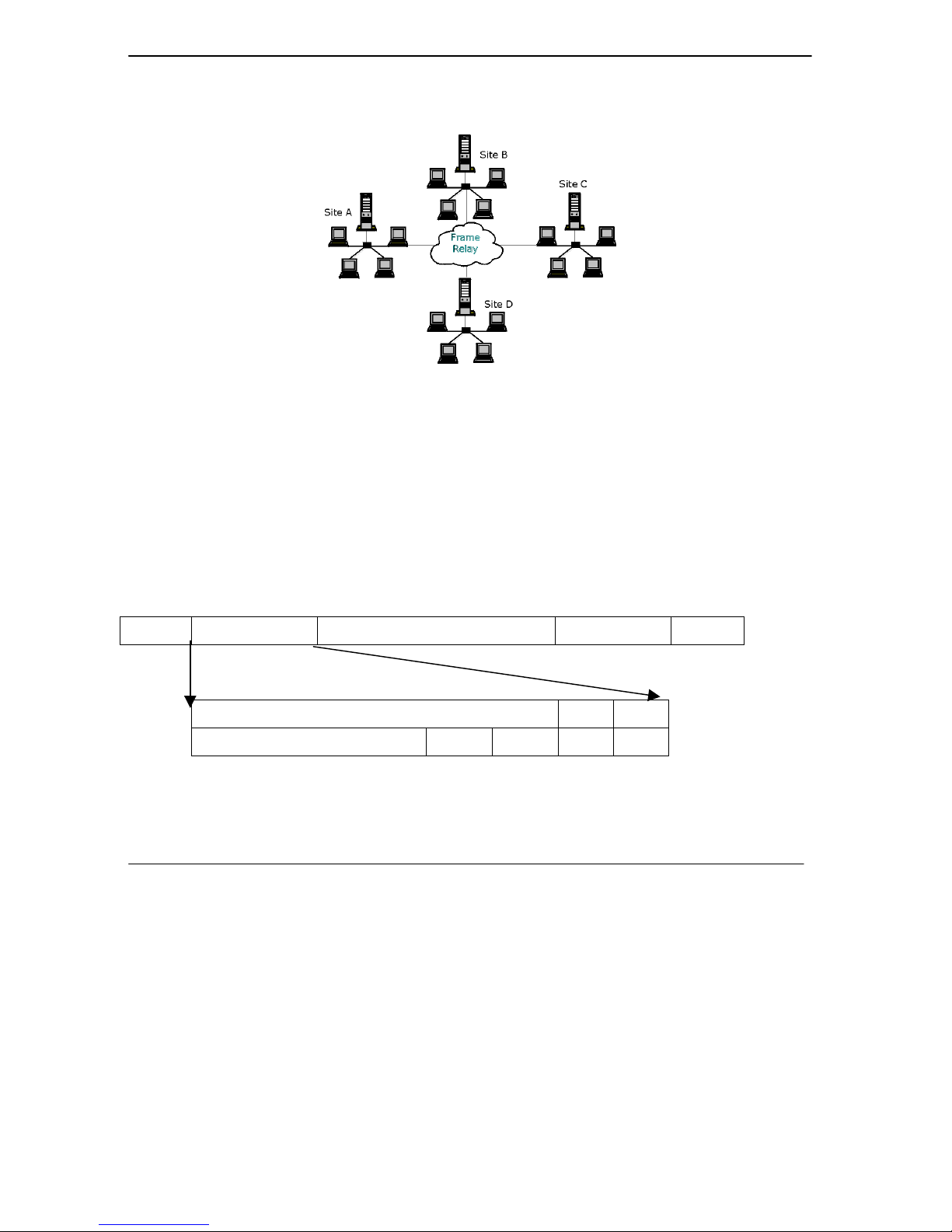
The frame relay solution would be to rent short dedicated leased lines to the carriers frame relay access point
and then the carrier programs virtual circuits into the network between your sites.
Figure 2 Frame Relay Solution
Frames are “relayed” through switches in the network, creating basically a virtual private network (VPN)
between linked sites. This logical point-to-point circuit between customer sites is called a VC (virtual circuit)
of which there are two types. Permanent VCs (PVCs) have constant end points and need to be set up in
advance while switched VCs (SVCs) are set up on the fly as needed. The Prestige supports PVCs only.
1.1.1 Frame relay frame format
The frame format for frame relay is as follows.
Bytes
1 2-4 0-4,000 2 1
Flag Link Info Data FCS Flag
Upper DLCI (6 bits) C/R EA 0
Lower DLCI (4 bits) FECN BECN DE EA 1
Figure 3 Frame Relay Format
Each frame is described as follows:
2
User's Guide Supplement
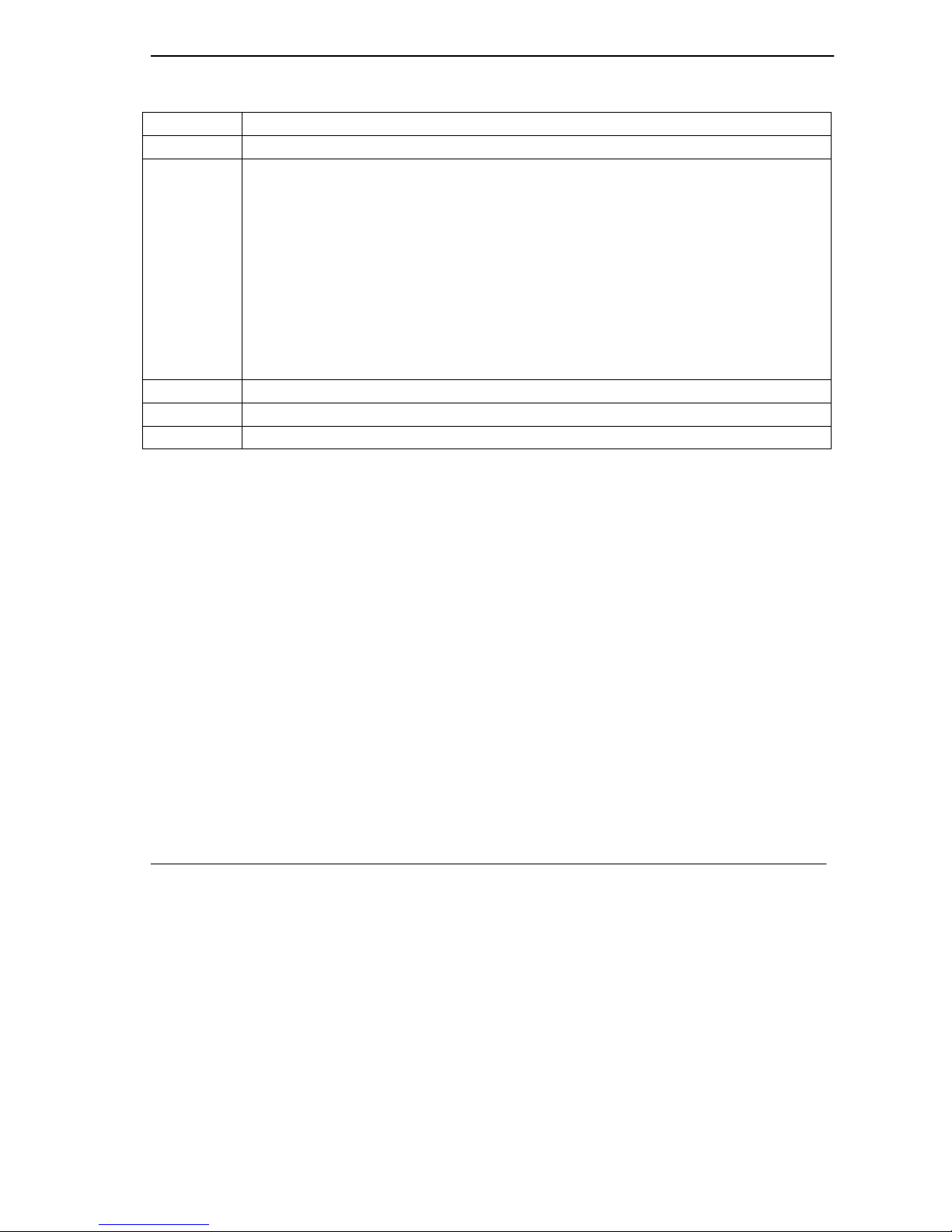
Table 1 Frame Relay Format
Frame Description
FLAG
LINK INFO
DLCI DLCI (data link connection identifier)
FECN FECN (forward explicit congestion notification)
BECN
DATA
FCS FCS (FRAME CHECK SEQUENCE)
FLAG
The flag field holds the “Start of frame” marker.
This field holds the logical connection address and control fields as described here:
identifies the logical connections.
C/R
Command/Response bit related to congestion control.
EA EA (extended address)
more than 10 bits.
congestion.
BECN (backward explicit congestion notification)
congestion.
DE
DE (discard eligibility)
congested.
Control information or encapsulated data goes in this field.
This flag field holds the “End of frame” marker.
is used to extend the header field to support DLCI addresses of
indicates whether frames can be discarded if the network is
is a checksum used for error detection.
1.1.2 Connection setup
Prestige 153X Supplement
warns receivers about network
warns senders about network
The carrier gives you a specific DLCI (Data Link Connection Identifier) for each PVC which is a path
number of a portion of the PVC (the DLCI changes for each hop through the network), not the address of the
destination. It is a logical identifier with local significance only.
A management protocol called LMI (Local Management Interface) provides information about the status of
PVC-to-network access devices. It defines management frames for monitoring the integrity of a link and
whether a link is active or not.
The frame-relay network manages congestion by setting bits in frames that warn end devices that there is
congestion on the network. A bit called FECN (forward explicit congestion notification) is set to notify a
receiving system of congestion and a bit called BECN (backward explicit congestion notification) is set to
notify sending devices of congestion. In the latter case, the sending device will temporarily slow down or
stop transmissions.
1.1.3 Standards
The two main groups that create recommendations and standards in the telecommunications field are ITU – T
(International Telecommunication Union – Telecommunications Standardization Sector) and ANSI
(American National Standards Institute). Standards vary slightly for both organizations, so please select the
User's Guide Supplement
3
 Loading...
Loading...