Page 1

6238-I2 Wi-Fi Router with VoIP
User’s Guide
Document Part Number: 6238-A2-ZB20-20
February 2007
Page 2

Zhone Technologies
@Zhone Way
7001 Oakport Street
Oakland, CA 94621
USA
510.777.7000
www.zhone.com
info@zhone.com
COPYRIGHT 2007 Zhone Technologies, Inc. All rights reserved.
This publication is protected by copyright law. No part of this publication may be copied, distributed,
displayed, modified, transmitted, stored in a retrieval system, or translated without express written
permission from Zhone Technologies, Inc.
Acculink, ADSL/R, Bitstorm, Comsphere, DSL the Easy Way, ETC, Etherloop, FrameSaver,
GranDSLAM, GrandVIEW, Hotwire, the Hotwire logo, iMarc, Jetstream, MVL, NextEDGE, Net to Net
Technologies, OpenLane, Paradyne, the Paradyne logo, Performance Wizard, ReachDSL, StormPort,
TruePut are registered trademarks of Zhone Technologies, Inc.
BAN, Connect to Success, GigMux, Hotwire Connected, JetFusion, JetVision, MALC, MicroBurst,
PacketSurfer, Quick Channel, Raptor, Reverse Gateway, SLMS, Spectrum Manager, StormTracker, ZEdge, Zhone, ZMS, and the Zhone logo are trademarks of Zhone Technologies, Inc.
All other products names or service marks mentioned herein are the trademarks, trade names and service
names of their respective owners.
Zhone Technologies makes no representation or warranties with respect to the contents hereof and
specifically disclaims any implied warranties of merchantability, noninfringement, or fitness for a
particular purpose. Further, Zhone Technologies reserves the right to revise this publication and to make
changes from time to time in the contents hereof without obligation of Zhone Technologies to notify any
person of such revision or changes.
2 6238 Wi-Fi Router with VOIP User’s Guide 6238-A2-ZB20-10
Page 3
Table of Contents
General Information........................ ... .... .... ... .... ... .... .... ... .... ... ................................5
Package Contents .................................................................................................. 5
Safety Instructions—Please Read ......................................................................... 5
Front Panel View .................................................................................................. 6
Indication .............................................................................................................. 6
Back Panel View................................................................................................... 8
Installing the Router...............................................................................................9
Connect the ADSL Line to a POTS Splitter (Optional)........................................ 9
Connect the ADSL Line to the Router.................................................................. 9
Connect the PC to the Router................................................................................ 9
Connect a Printer or Server to the Router ........................................................... 10
Connect the Telephone to the Router..................................................................10
Connect the Router to a Phone Jack....................................................................10
Connect the Power Adapter ................................................................................ 10
Installation Diagram.............................................................................................11
Mounting the Router ........................................................................................... 12
USB Driver Installation........................................................................................13
Configuring Your Computer ...............................................................................16
Windows 2000 .................................................................................................... 16
Windows XP ....................................................................................................... 17
Log in to the Router..............................................................................................18
Device Info.............................................................................................................19
Summary............................................................................................................. 19
WAN...................................................................................................................20
Statistics .............................................................................................................. 20
Route...................................................................................................................23
ARP..................................................................................................................... 23
DHCP.................................................................................................................. 25
Quick Setup................ .... .... ... .... ... .... ... .... .... ... .... ... .... .... ... .... ... .... .... ... .... ... .... ... .... .25
Advanced Setup..................... .... ... .... ... .... ... .... .... ... .... ... .... .... ... .... .... ... .... ... .... ... .... .30
WAN...................................................................................................................30
Local Area Network (LAN) Setup...................................................................... 34
Ethernet Mode..................................................................................................... 35
NAT .................................................................................................................... 35
Firewall ............................................................................................................... 38
Quality of Service ............................................................................................... 43
Routing................................................................................................................ 47
DNS .................................................................................................................... 49
ADSL .................................................................................................................. 50
Port Mapping ...................................................................................................... 52
Wireless..................................................................................................................53
Basic.................................................................................................................... 53
Security ............................................................................................................... 54
MAC Filter.......................................................................................................... 55
Wireless Bridge...................................................................................................56
6238-A2-ZB20-10 6238 Wi-Fi Router with VOIP User’s Guide 3
Page 4

Advanced ............................................................................................................ 56
Quality of Service ............................................................................................... 58
Station Info ......................................................................................................... 60
Voice.......................................................................................................................61
SIP Basic............................................................................................................. 61
SIP Advanced ..................................................................................................... 62
Dial Plan ............................................................................................................. 65
Phonebook .......................................................................................................... 66
SIP Provision ...................................................................................................... 67
Call Features ....................................................................................................... 68
Diagnostics.............................................................................................................69
Management..........................................................................................................70
Settings................................................................................................................ 70
System Log ......................................................................................................... 72
SNMP.................................................................................................................. 73
TR-069 Client ..................................................................................................... 74
Internet Time....................................................................................................... 74
Access Control .................................................................................................... 75
Update Software.................................................................................................. 78
Reboot Router ..................................................................................................... 79
4 6238 Wi-Fi Router with VOIP User’s Guide 6238-A2-ZB20-10
Page 5
General Information
The 6238 Wi-Fi Router with VOIP is a 3-in-1 router having the functions of a
standard
ADSL router, plus voice capabilities and wireless accessibility, all in one box. These
three features add convenience and provide increased functions to one router.
Package Contents
Included in the package is one of each of the following:
• Wi-Fi Router
• AC power adapter
• USB cable
• RJ11 telephone cable
• RJ45 Ethernet cable
• Quick Installation Instructions
• CD containing USB drivers and user’s guide
Safety Instructions—Please Read
• Place your router on a flat surface close to the cables in a location with
sufficient ventilation.
• To prevent overheating, do not obstruct the ventilation openings of this
equipment.
• Plug this equipment into a surge protector to reduce the risk of damage from
power surges and lightning strikes.
• Operate this equipment only from an electrical outlet with the correct power
source as indicated on the adapter.
• Unplug equipment first before cleaning. A damp cloth can be used to clean
the equipment. Do not use liquid / aerosol cleaners or magnetic / static
cleaning devices.
• Do not open the cover of this equipment. Opening the cover will void any
warranties on the equipment.
6238-A2-ZB20-10 6238 Wi-Fi Router with VOIP User’s Guide 5
Page 6

Front Panel View
LED Mode
Solid The router is on.
Power
ADSL / LINK
ADSL / ACT
LAN 1-4
USB Device
No light
Solid ADSL is connected.
No light ADSL is not connected. ALARM LED will be red.
Blinking Router is connected to ADSL.
Solid ADSL is connected; no traffic.
No light ADSL is not connected.
Blinking Presence of ADSL traffic.
Solid Router is connected to LAN.
No light
Blinking Presence of LAN traffic.
Solid Connection established using USB.
Flashing The router is sending or receiving data using USB.
Indication
The router is not on.
Check if the AC power adapter is connected to the
router and plugged in.
No connection to LAN. Check if LAN cable is
connected to router.
Solid Connection established using USB.
USB Host
Wi-Fi
6 6238 Wi-Fi Router with VOIP User’s Guide 6238-A2-ZB20-10
Flashing The router is sending or receiving data using USB.
Solid Wireless is enabled.
No light Wireless is disabled.
Page 7

LED Mode
Blinking Presence of wireless traffic.
Solid Line2 is off-hook.
Phone2
No light Line2 is on-hook.
Indication
Phone1
LINE
Solid Line1 is off-hook.
No light Line1 is on-hook.
Solid Line is off-hook.
No light Line is on-hook.
6238-A2-ZB20-10 6238 Wi-Fi Router with VOIP User’s Guide 7
Page 8
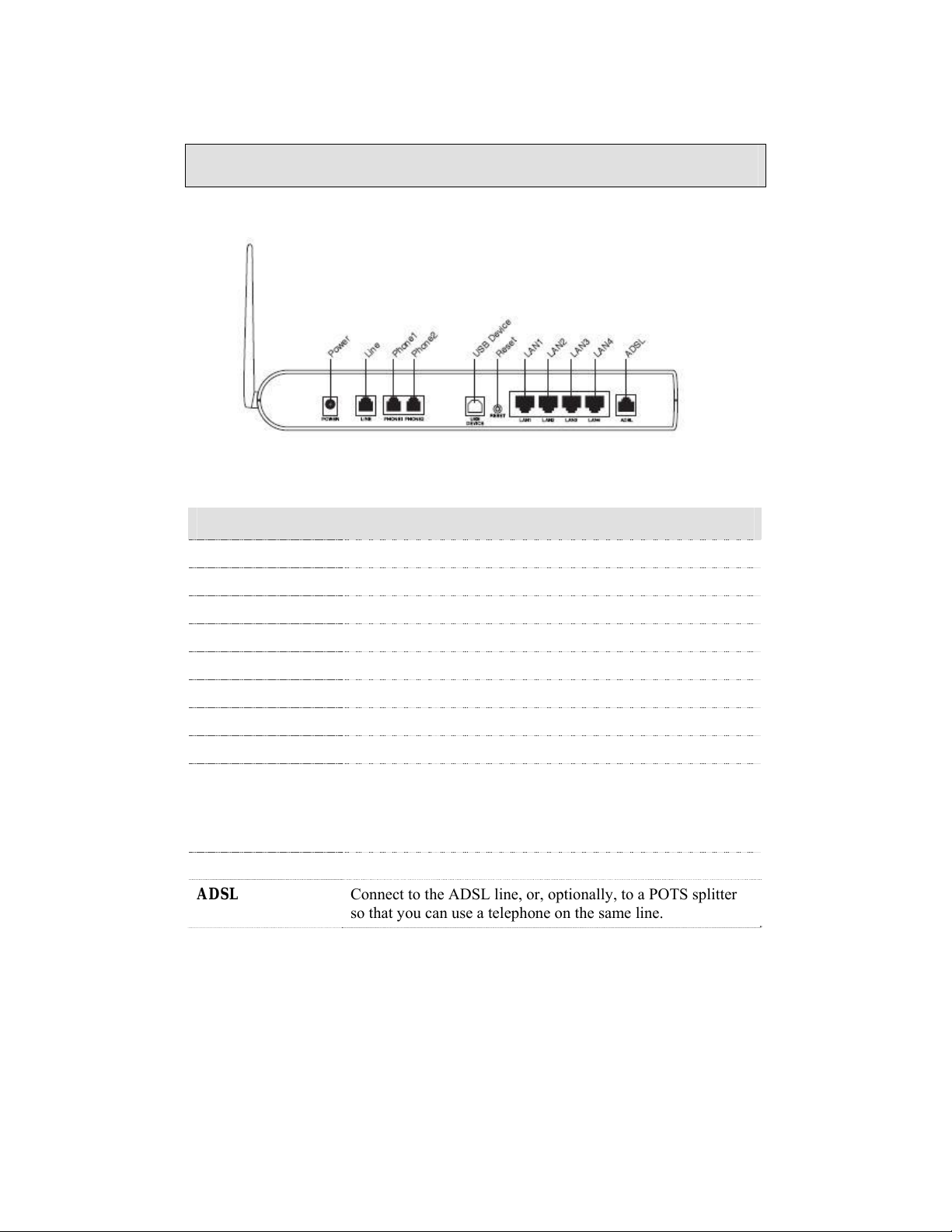
Back Panel View
Port Description
On / Off Press to turn the router on and off.
DC 15V 1.2A
LINE
Phone1
Phone2
Console
USB Host
USB Device
Reset
LAN 1–4
Connects to the AC adapter.
Connects to the wall outlet using an RJ11 cable.
Connects to a telephone using an RJ11 cable.
Connects to a second telephone using another RJ11 cable.
For use by service personnel only.
Connects to a printer or server using the USB cable provided.
Optional: Use only if not using any of the LAN lines.
Short reset (system reboot) — Push and hold the reset button
for 4 seconds.
Long reset (return to default settings) — Push the reset button
for more than 4 seconds and then release.
Connect to PCs using RJ45 cables.
ADSL
8 6238 Wi-Fi Router with VOIP User’s Guide 6238-A2-ZB20-10
Connect to the ADSL line, or, optionally, to a POTS splitter
so that you can use a telephone on the same line.
Page 9
Installing the Router
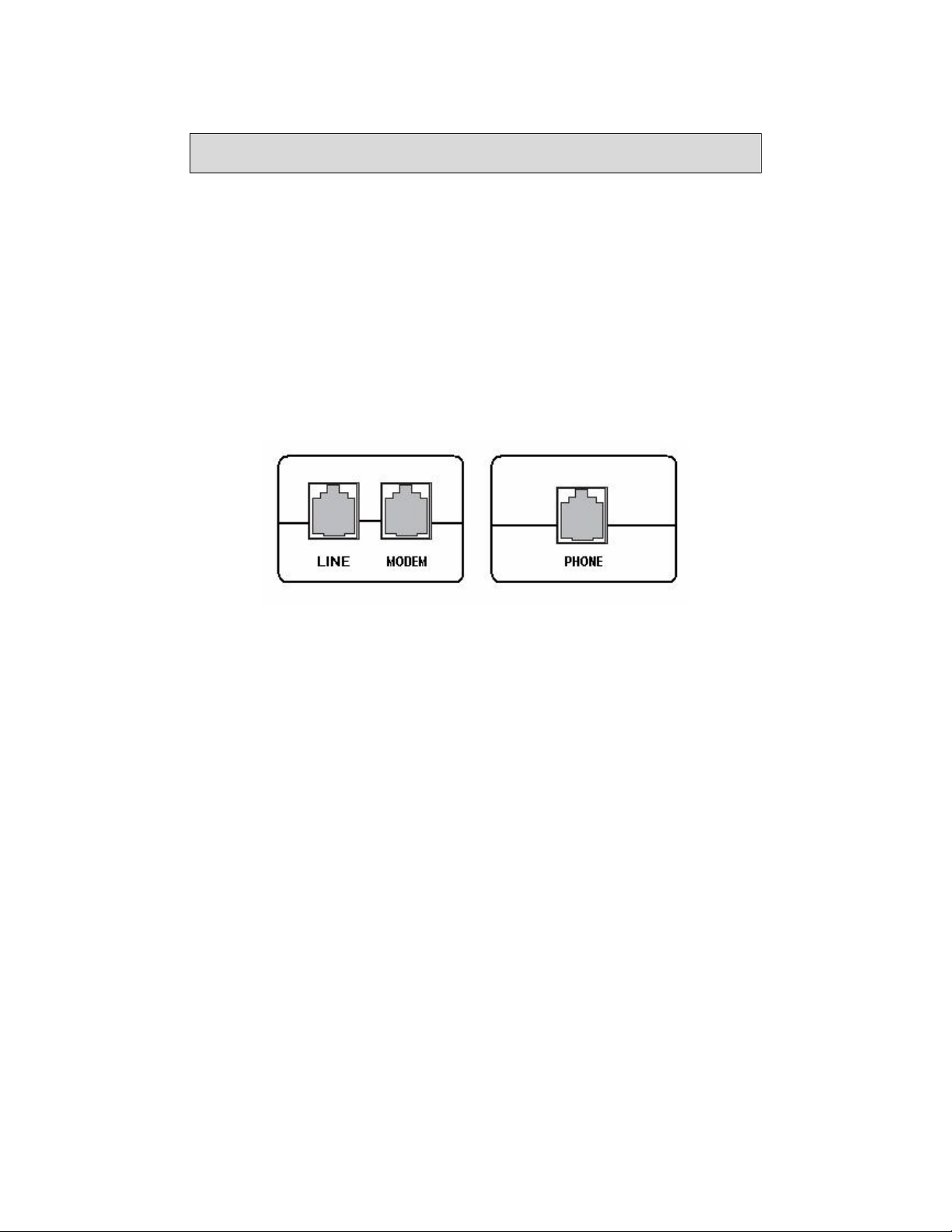
Connect the ADSL Line to a POTS Splitter (Optional)
Follow this procedure if you connect a telephone to the ADSL line using a POTS
splitter.
• Connect an RJ11 cable between the wall phone jack and the LINE port of the
splitter (see diagram below).
• Attach another RJ11 phone wire to the MODEM port of the splitter and the
ADSL port on the rear panel of the router.
• Attach the PHONE port of the splitter to the telephone using a third RJ11
phone wire.
Connect the ADSL Line to the Router
Follow this procedure if you will not connect a telephone to the ADSL line using a
POTS splitter.
• Connect an RJ11 cable between the wall phone jack and the ADSL port of the
router.
Connect the PC to the Router
By Ethernet—
To use the Ethernet connection, connect the Ethernet cable from the computer
directly to the router.
• Connect one end of the Ethernet cable to the port(s) labeled LAN 1-4 on the back
of the router and attach the other end to the Ethernet port of your computer. Do
not use the USB Device port of the router.
• If your LAN has more than one computer, you can attach one end of an Ethernet
cable to a hub or a switch and the other to the Ethernet port (labeled LAN) on the
router. Note that either a crossover or straight-through Ethernet cable can be used.
The router automatically recognizes the type of connection that is required.
6238-A2-ZB20-10 6238 Wi-Fi Router with VOIP User’s Guide 9
Page 10

By USB—
Or, you can use the supplied USB cable to connect your computer directly to the
router.
• Connect one end of the USB cable to the USB port (labeled USB Device) on the
back of the router and connect the other end to a free USB port on your PC. Do
not use the LAN ports of the router.
• The Found New Hardware Wizard will open on your PC. See USB Driver
Installation below.
Connect a Printer or Server to the Router
If you have a printer or server that you wish to connect to the router, attach the printer
or server to the port labeled USB Host using the USB cable that comes with the
device.
Connect the Telephone to the Router
There are two ports on the back of your router labeled Phone 1 and Phone 2 for you
to connect up to two telephones to. Use RJ11 cables to connect the telephone(s) to the
router.
Connect the Router to a Phone Jack
• Before connecting the power adapter, connect the router directly to a phone jack
using an RJ11 cable.
• Connect one end of an RJ11 cable to the port labeled Line on the back of the
router and the other end to a wall phone jack.
Connect the Power Adapter
• Complete the process by connecting the AC power adapter to the POWER
connector on the back of the device and plug the adapter into a wall outlet or
power strip.
• Then turn on and boot up your PC and any LAN devices, such as hubs or
switches, and any computers connected to them.
10 6238 Wi-Fi Router with VOIP User’s Guide 6238-A2-ZB20-10
Page 11
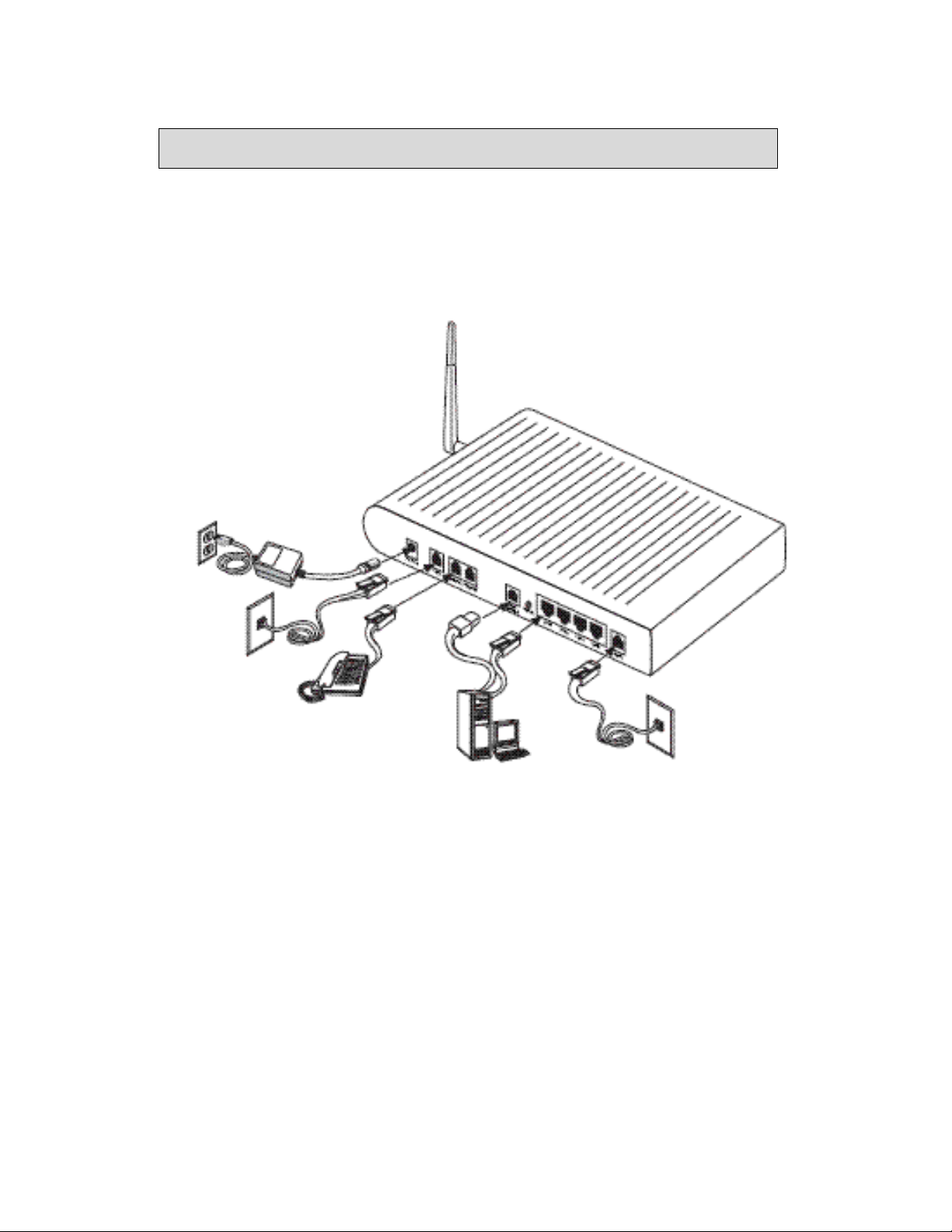
Installation Diagram
6238-A2-ZB20-10 6238 Wi-Fi Router with VOIP User’s Guide 11
Page 12
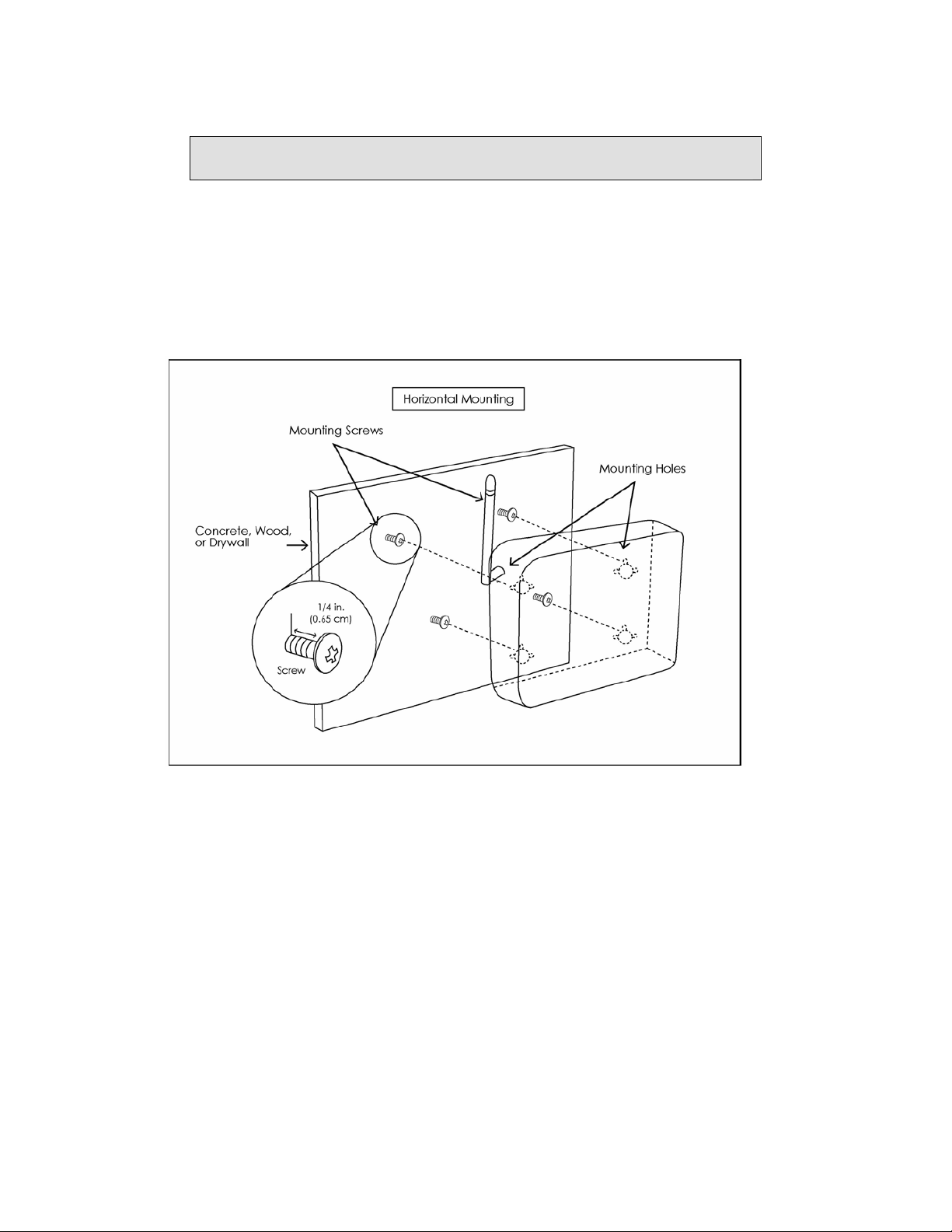
Mounting the Router
The router can be mounted on the wall with screws. Mounting can be done on wall
material including concrete, wood, or drywall. Select an appropriate location free
from obstructions or any possible interference. Make sure the cables can be easily
attached to
the router without strain. The illustration below shows how to mount the router
horizontally
on a wall.
12 6238 Wi-Fi Router with VOIP User’s Guide 6238-A2-ZB20-10
Page 13
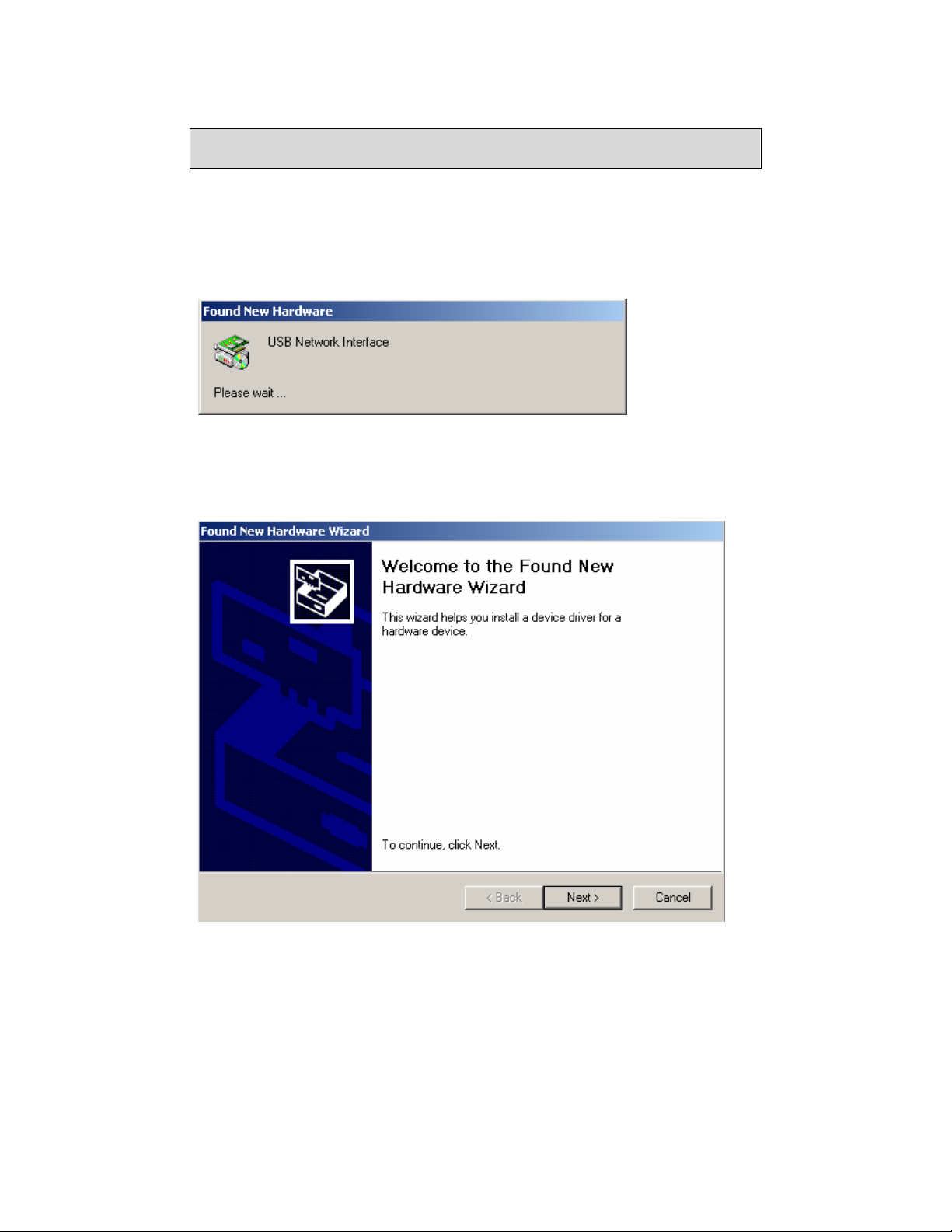
USB Driver Installation
The following instructions will guide you through the installation of the USB driver.
The procedure is not required if you use the LAN ports of the router instead of the
USB Device
port.
1. When you attach the USB cable to the router for the first time and turn on the
device, Windows will detect new hardware and the Found New Hardware
Wizard will appear.
6238-A2-ZB20-10 6238 Wi-Fi Router with VOIP User’s Guide 13
Page 14
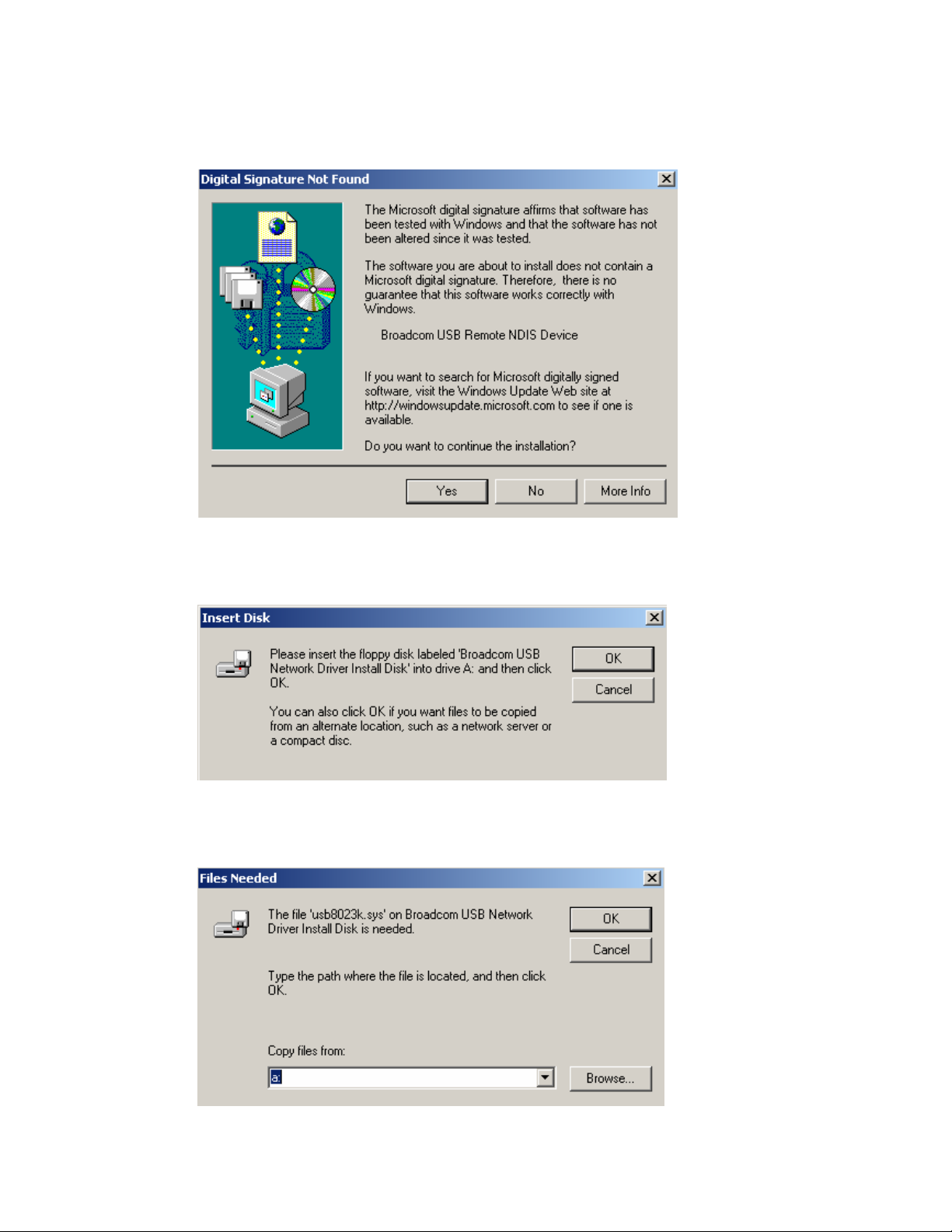
2. The Found New Hardware Wizard will appear shortly after, showing that a
USB driver is needed. Click on Next to continue with the installation.
3. The Digital Signature Not Found window appears. Click on Yes to continue
with the installation.
4. The Insert Disk window prompts you to insert the disk (or CD) containing
the USB driver. Click on OK after inserting the disk (or CD).
14 6238 Wi-Fi Router with VOIP User’s Guide 6238-A2-ZB20-10
Page 15
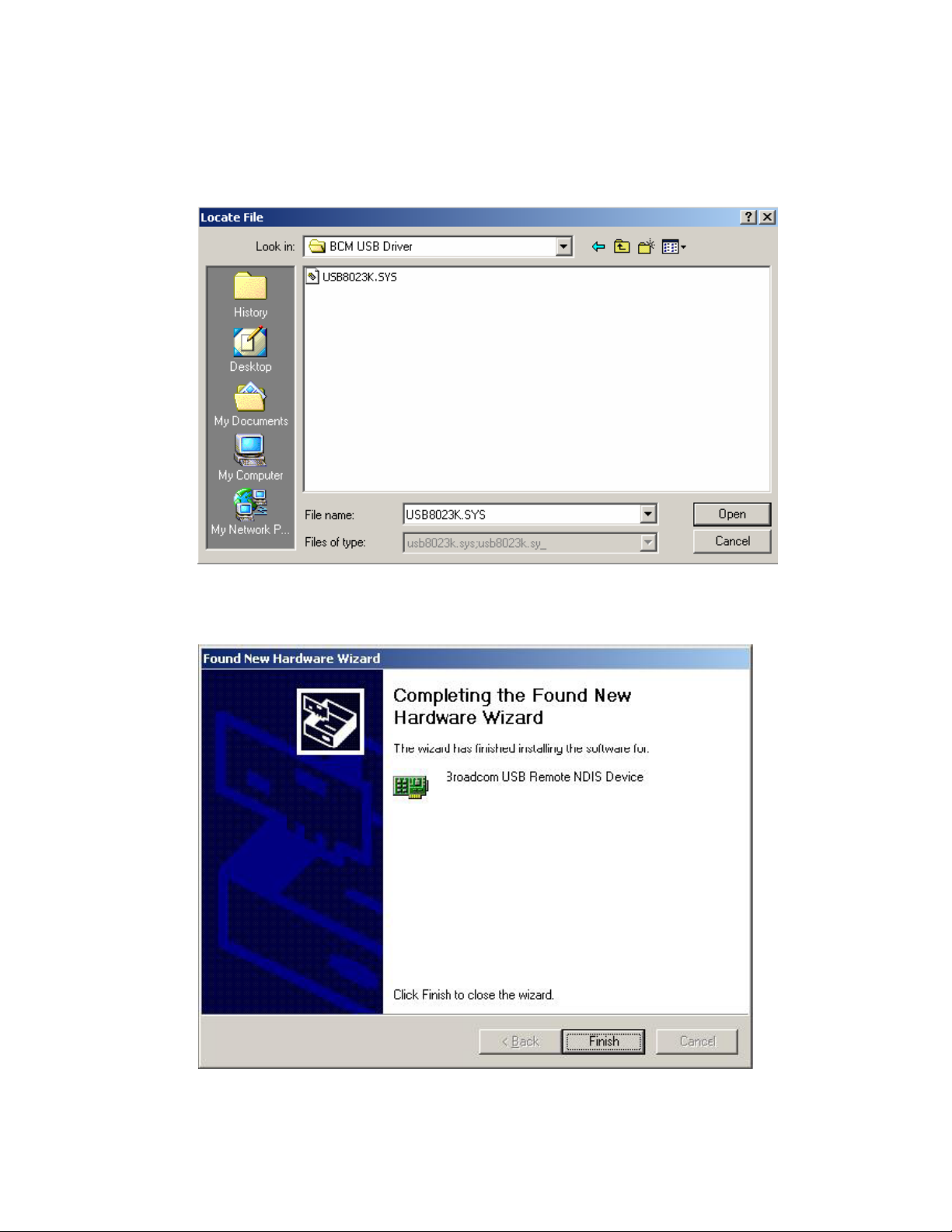
5. After clicking OK at the previous window, you will be asked to browse for
the location of the disk (or CD) that the USB driver is on. Then click on OK
to continue to the next step.
6. When you select the location of the disk (or CD), the required file
USB8023K.SYS is displayed in the filename window of this screen. Click on
Open to continue with the installation process.
6238-A2-ZB20-10 6238 Wi-Fi Router with VOIP User’s Guide 15
Page 16

7. The last window lets you know that the driver installation is complete. Click
on Finish to close the wizard.
Configuring Your Computer
Prior to accessing the router through the LAN or the USB port, your PC’s IP address
must be set to 192.168.1.x, where x is any number between 2 and 254. The Subnet
Mask must be set to 255.255.255.0.
The router’s default IP address is 192.168.1.1.
Below are the procedures for configuring your computer. Follow the instructions for
the operating system that you are using.
Windows 2000
1. In the Windows taskbar, click on the Start button and point to Settings,
Control Panel, and Network and Dial-up Connections (in that order).
2. Click on Local Area Connection. When you have the Local Area Connection
Status window open, click on Properties.
3. Listed in the window are the installed network components. If the list
includes Internet Protocol (TCP/IP), then the protocol has already been
enabled, and you can skip to Step 10.
4. If Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) does not appear as an installed component, then
click on Install.
5. In the Select Network Component Type window, click on protocol and then
the Add button.
6. Select Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) from the list and then click on OK.
7. If prompted to restart your computer with the new settings, click OK.
8. After your computer restarts, click on the Network and Dial-up Connections
icon again, and right click on the Local Area Connection icon and then select
Properties.
9. In the Local Area Connection Properties dialog box, select Internet Protocol
(TCP/IP) and then click on Properties.
10. In the Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) Properties dialog box, click in the radio
button labeled Use the following IP address and type 192.168.1.x (where x
is any number between 2 and 254) and 255.255.255.0 in the IP address field
and Subnet Mask field.
16 6238 Wi-Fi Router with VOIP User’s Guide 6238-A2-ZB20-10
Page 17

11. Click on OK twice to save your changes and then close the Control Panel.
Windows XP
1. In the Windows taskbar, click on the Start button and point to Settings and
then click Network Connections.
2. In the Network Connections window, right click on the Local Area
Connection icon and click on properties.
3. Listed in the Local Area Connection window are the installed network
components. Make sure the box for Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) is checked and
then click on Properties.
4. In the Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) Properties dialog box, click in the radio
button labeled Use the following IP address and type 192.168.1.x (where x
is any number between 2 and 254) and 255.255.255.0 in the IP address field
and Subnet Mask field.
5. Click on OK twice to save your changes and then close the Control Panel.
6238-A2-ZB20-10 6238 Wi-Fi Router with VOIP User’s Guide 17
Page 18
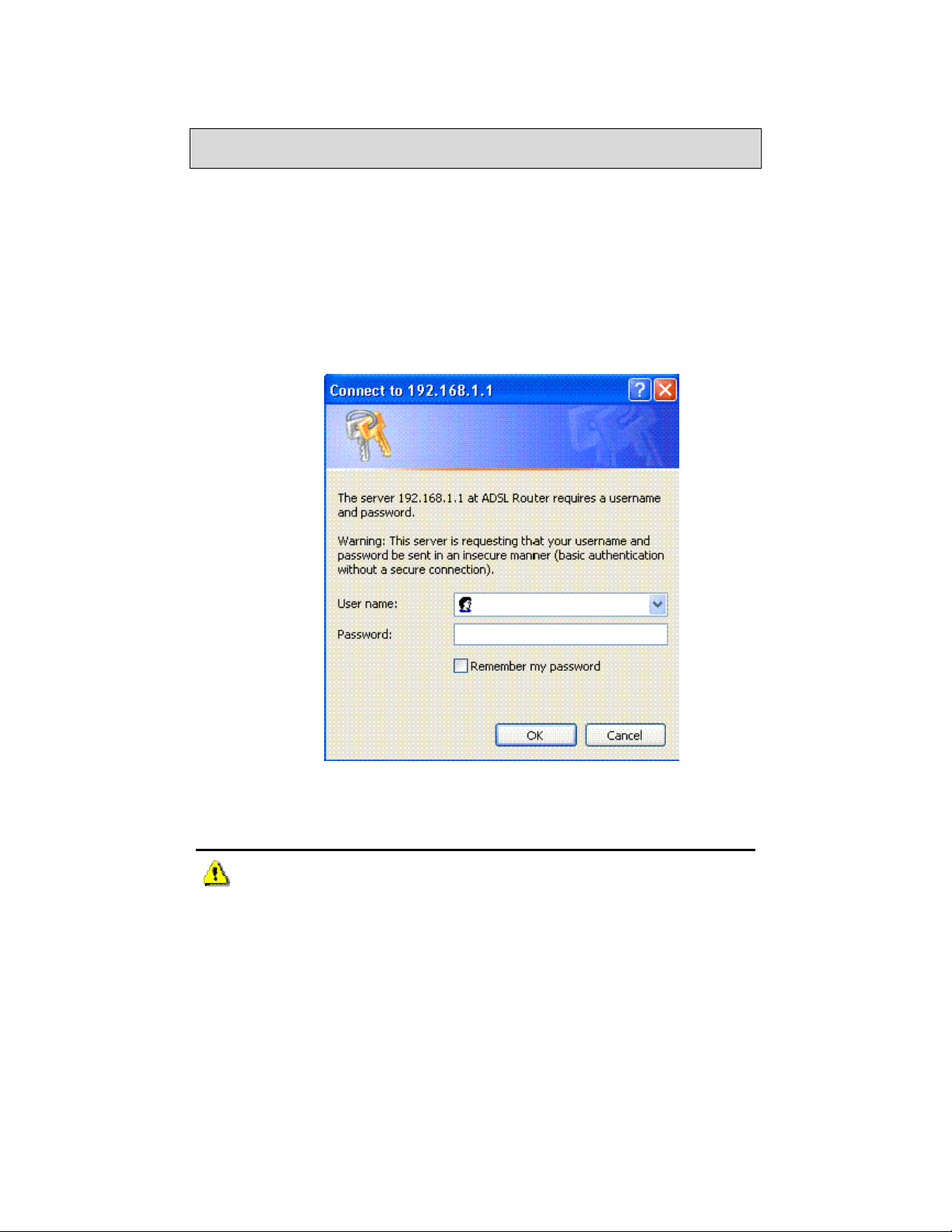
Log in to the Router
This section explains how to log in to your router.
1. Launch your web browser.
2. Enter the URL http://192.168.1.1 in the Address field of your browser
and press Enter.
A login screen like the one below appears.
3. Enter your user name and password, and then click on OK to display the
user interface.
NOTE: There are two default user name and password combinations. The
user / user name and password combination can display device status, but cannot
change or save configurations. The admin / admin co m bination can perform all
functions. Passwords can be changed at any time. Some procedures in this manual
require the admin login.
____________________________________________________
18 6238 Wi-Fi Router with VOIP User’s Guide 6238-A2-ZB20-10
Page 19
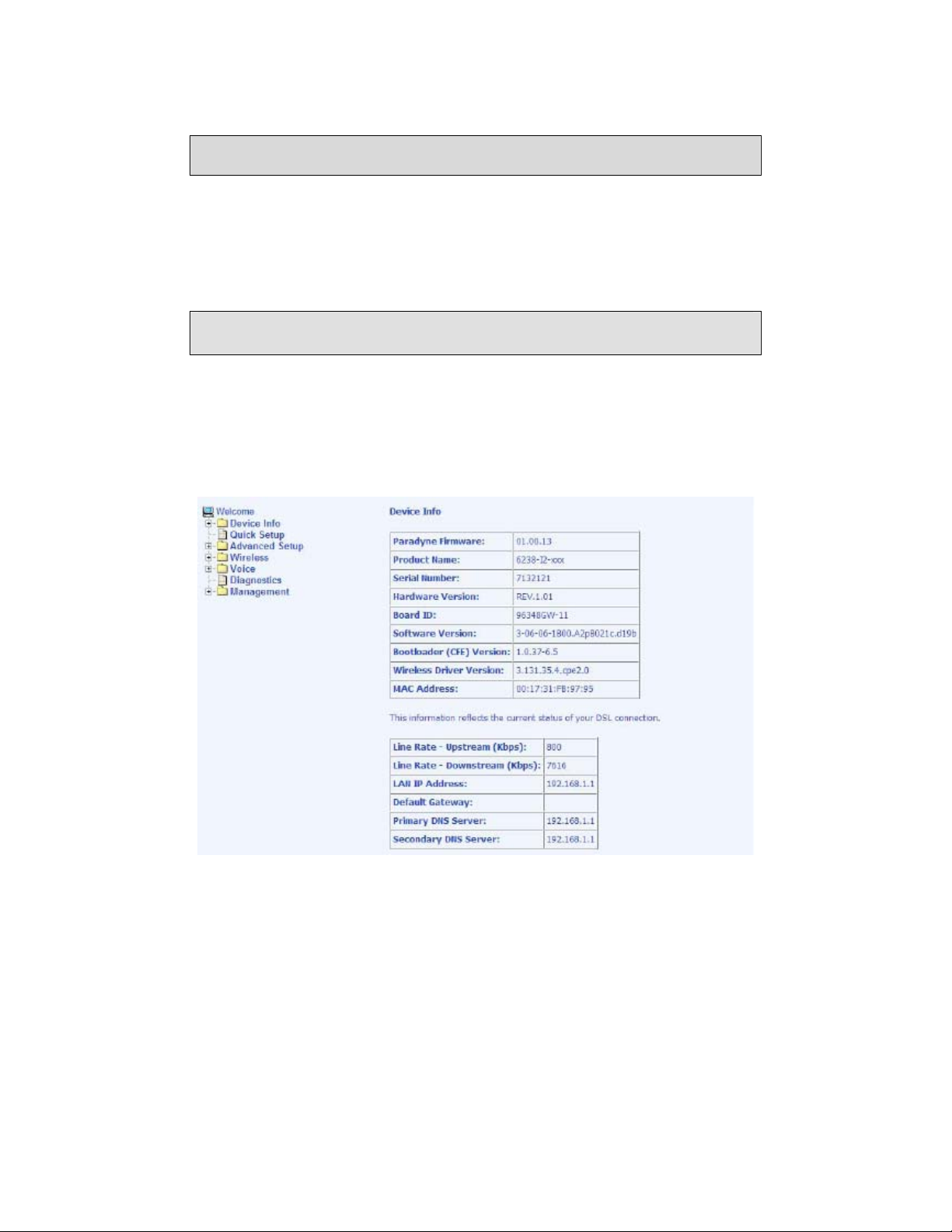
Device Info
This section describes the system information that can be accessed using the menu
items
under Device Info.
Summary
Access the general information of the router by clicking on Summary under Device
Info. The display shows details of the router such as software version, wireless driver
version, and LAN IP address. It also displays the current status of your DSL
connection.
6238-A2-ZB20-10 6238 Wi-Fi Router with VOIP User’s Guide 19
Page 20
WAN
Access the WAN status report from the router by clicking on “WAN” under
“Device Info”. The first time you do this, there is no information to view,
since a WAN connection has not been set up yet. After completing the
configurations for a WAN connection, you can return to this screen to view
the information on your WAN status.
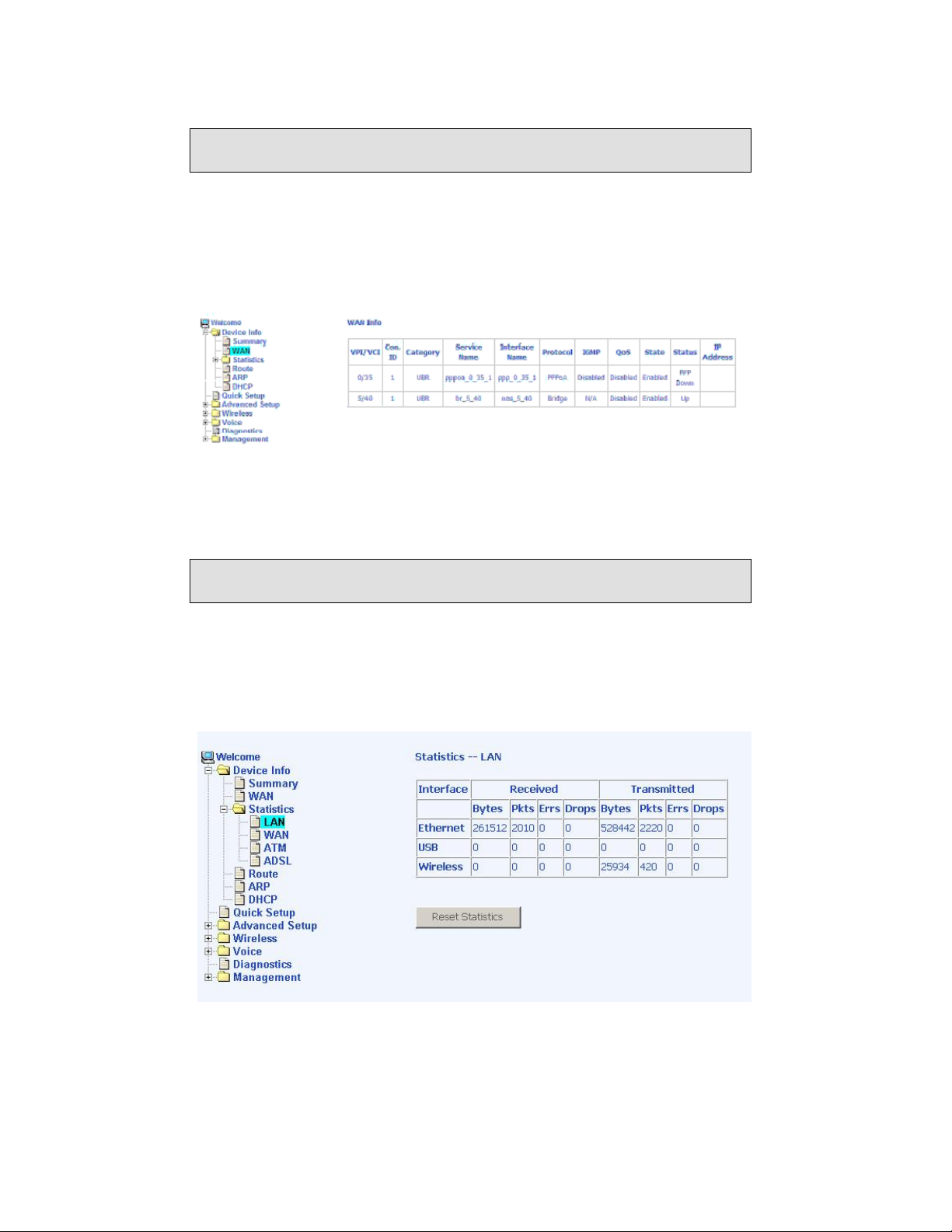
Statistics
LAN Statistics
Access the LAN statistics from the router by clicking on the “LAN” item
under “Statistics”
WAN Statistics
20 6238 Wi-Fi Router with VOIP User’s Guide 6238-A2-ZB20-10
Page 21
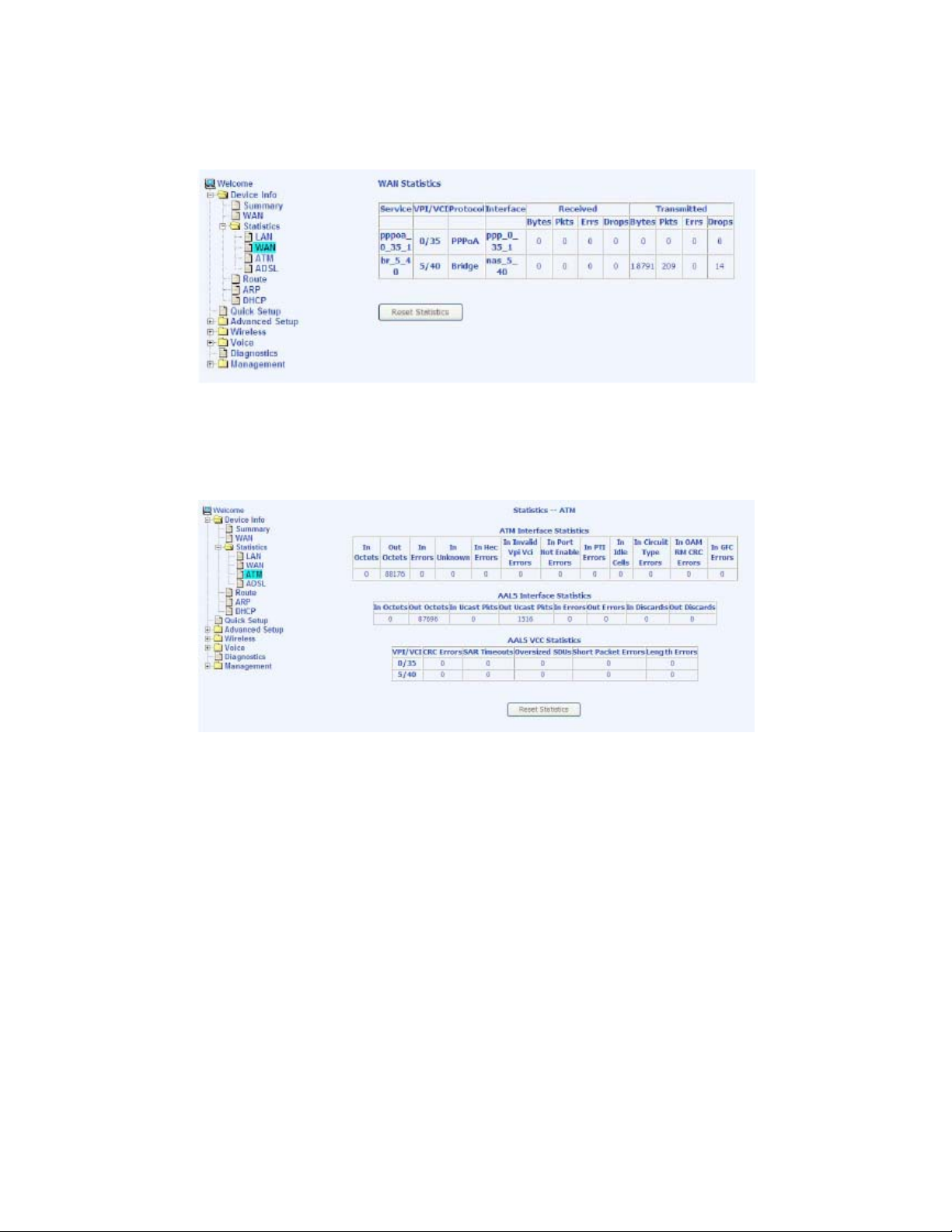
Access the WAN statistics from the router by clicking on the WAN item
under Statistics.
ATM Statistics
Access ATM statistics from the router by clicking on the ATM item under Statistics.
6238-A2-ZB20-10 6238 Wi-Fi Router with VOIP User’s Guide 21
Page 22
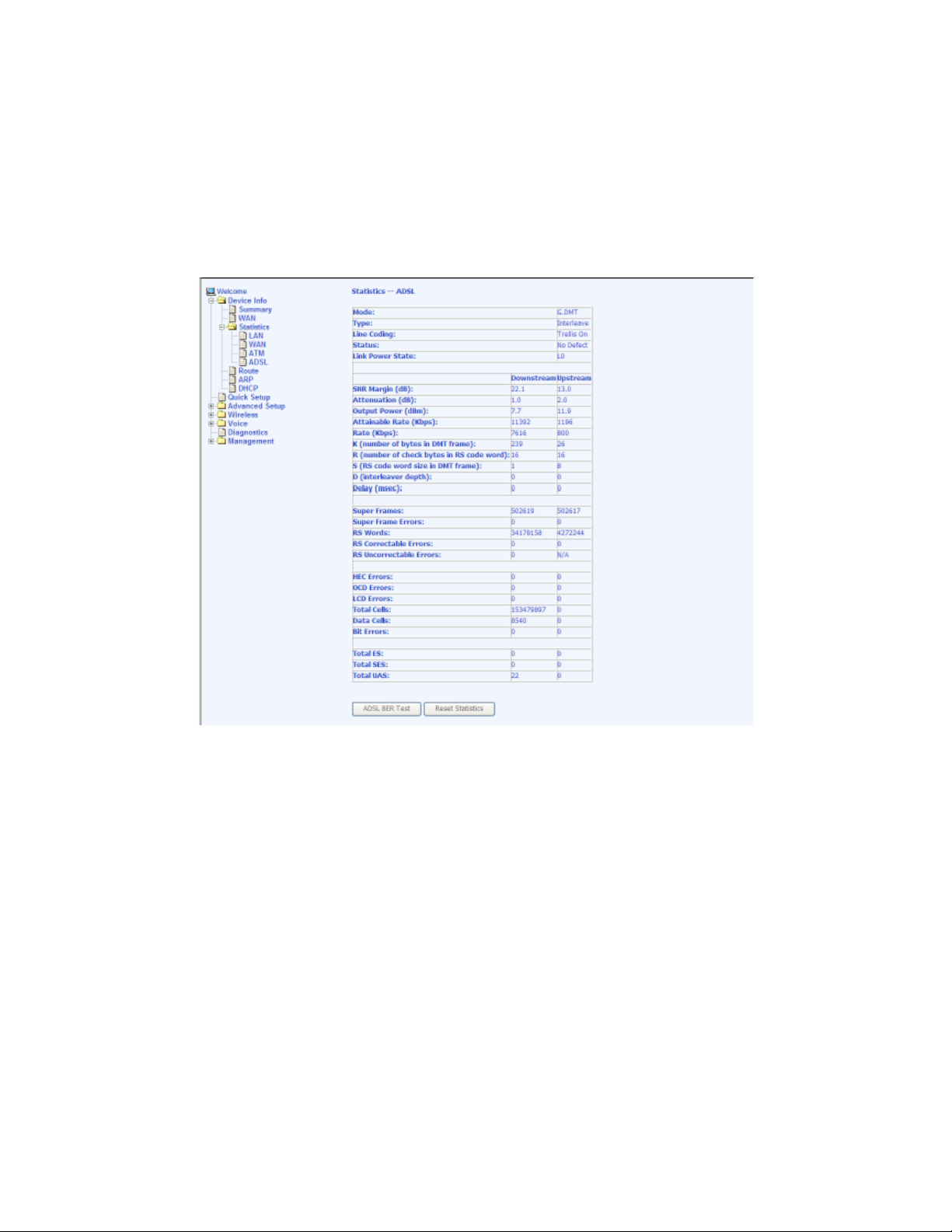
ADSL Statistics
You can view ADSL statistics by clicking on the ADSL item under
Statistics. Information contained in this screen is useful for troubleshooting
and diagnostics of connection problems.
ADSL BER Test
A Bit Error Rate Test (BER Test) is a test that reflects the ratio of bits in error to
the total number transmitted.
If you click on the ADSL BER Test button at the bottom of the ADSL Statistics
screen, the following popup screen will appear allowing you to set the tested time and
to begin the test.
22 6238 Wi-Fi Router with VOIP User’s Guide 6238-A2-ZB20-10
Page 23
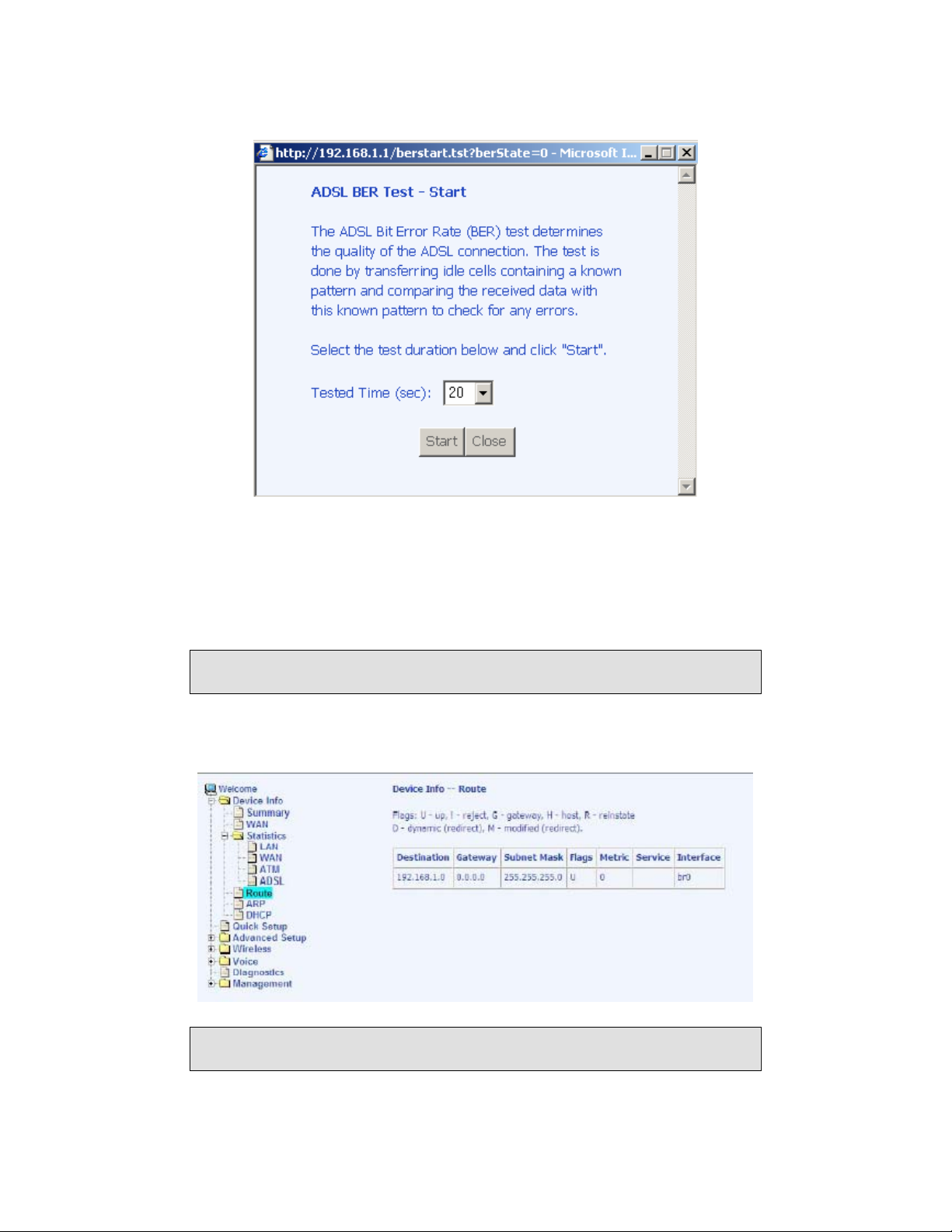
Route
Access the routing status report from the router by clicking on the Route item
under Device Info.
ARP
6238-A2-ZB20-10 6238 Wi-Fi Router with VOIP User’s Guide 23
Page 24
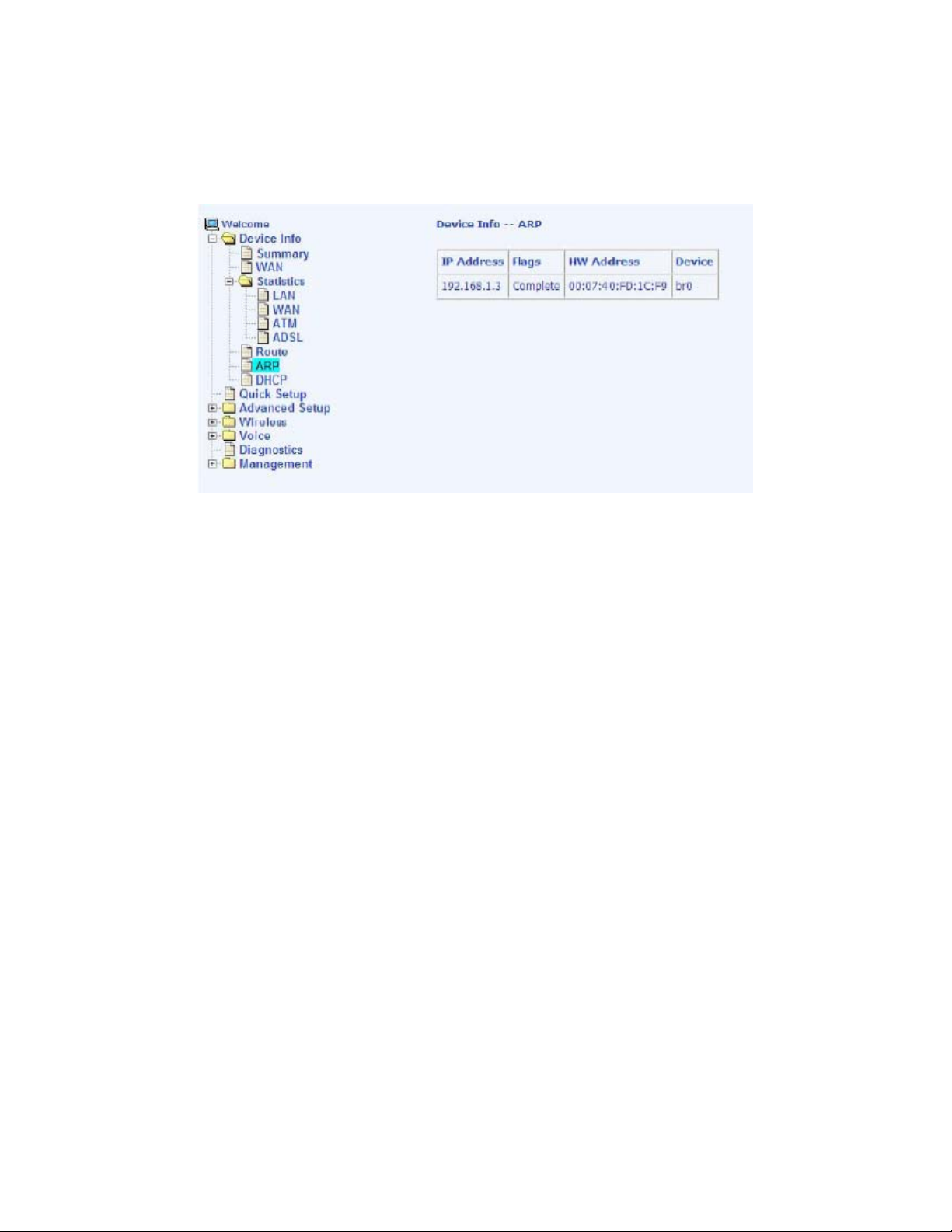
Access the ARP status report from the router by clicking on the ARP item
under Device Info. ARP (Address Resolution Protocol) maps the IP address
to the physical address, labeled HW Address (the MAC address) and helps to
identify computers on the LAN.
24 6238 Wi-Fi Router with VOIP User’s Guide 6238-A2-ZB20-10
Page 25

DHCP
Access the DHCP Leases screen by clicking DHCP under Statistics. This
shows the computers, identified by the hostname and MAC address that have
acquired IP addresses by the DHCP server with the time that the lease for the
IP address is up.
Quick Setup
This section explains how to quickly configure the router for the single
purpose of connecting to the Internet. To use any additional functions of the
router, continue to the Advanced Setup section.
To enable the auto-connect process, click on the box labeled DSL Autoconnect. This is a process that automatically detects the first usable PVC and
automatically detects PPPoE, PPPoA, and Bridge Protocol (with DHCP
Server available). To continue, click on the Next button.
6238-A2-ZB20-10 6238 Wi-Fi Router with VOIP User’s Guide 25
Page 26

If you uncheck the DSL Auto-connect box, the resulting screen is seen below.
Enter the VPI / VCI as indicated by your ISP and enable Quality of Service to
enable the function. To continue, click on Next.
26 6238 Wi-Fi Router with VOIP User’s Guide 6238-A2-ZB20-10
Page 27

Next is the Connection Type screen, where you select the type of network
protocol and encapsulation mode over the ATM PVC that your ISP has
instructed you to use. The following is a PPPoA example. Click on Next to
continue.
Enter the PPP username and password as given by your ISP. Then decide if
you will be using any features such as dial on demand, PPP IP extension,
keep alive. Then click on Next.
6238-A2-ZB20-10 6238 Wi-Fi Router with VOIP User’s Guide 27
Page 28

The next step is to configure the Network Address Translation (NAT)
settings. Enable the necessary services and then click on Next to continue.
You can configure the DSL Router IP address and Subnet Mask for the LAN
interface to correspond to your LAN’s IP Subnet. If you want the DHCP server
to automatically assign IP addresses, then enable the DHCP server and enter the
range of IP addresses that the DHCP server can assign to your computers.
Disable the DHCP server if you would like to manually assign IP addresses.
Click on Next to continue.
28 6238 Wi-Fi Router with VOIP User’s Guide 6238-A2-ZB20-10
Page 29

The next screen allows you to enable or disable the wireless function. If you
enable wireless, then enter the wireless network name (SSID). The default
SSID (wireless) is already entered. Click on Next to continue.
After all of the WAN configurations have been made, the WAN Setup
Summary screen displays all WAN settings that you have made. Verify that
the settings are correct before clicking on the Save/Reboot button. Clicking
on Save/Reboot will save your settings and restart your router.
6238-A2-ZB20-10 6238 Wi-Fi Router with VOIP User’s Guide 29
Page 30

Advanced Setup
This section of the setup is an advanced version of the quick setup. If you
want to make
specific configurations to your router such as firewall, port mapping, quality
of service, or DNS, consider going through this advanced setup for a more
comprehensive configuration.
WAN
Configure the WAN settings as provided by your ISP. The following screen
shows the PPPoA connection that was established in the previous Quick
Setup example.
Click on the Add button if you want to add a new connection for the WAN
interface.
The ATM PVC Configuration screen is seen below. The ATM PVC
Configuration
screen allows you to configure an ATM PVC (identified by VPI and VCI)
and select
a service category.
30 6238 Wi-Fi Router with VOIP User’s Guide 6238-A2-ZB20-10
Page 31

Find out the following values from your ISP before you change them.
• VPI: Virtual Path Identifier. The valid range is 0 to 255.
• VCI: Virtual Channel Identifier. The valid range is 32 to 65535.
• Service Category: Five classes of traffic are listed:
o UBR Without PCR (Unspecified Bit Rate without Peak Cell Rate)—
UBR service is suitable for applications that can tolerate variable delays
and some cell losses. Applications suitable for UBR service include
text/data/image transfer, messaging, distribution, and retrieval and also
for remote terminal applications such as telecommuting.
o UBR With PCR (Unspecified Bit Rate with Peak Cell Rate)
o CBR (Constant Bit Rate)— Used by applications that require a fixed data
rate that is continuously available during the connection time. It is
commonly used for uncompressed audio and video information such as
videoconferencing, interactive audio (telephony), audio / video
distribution (e.g. television, distance learning, and pay-per-view), and
audio / video retrieval (e.g. video-on-demand and audio library).
o Non Realtime VBR (Non-Real-time Variable Bit Rate)— Can be used
for data transfers that have critical response-time requirements such as
airline reservations, banking transactions, and process monitoring.
o Realtime VBR (Real-time Variable Bit Rate)— Used by time-sensitive
applications such as real-time video. Rt-VBR service allows the network
more flexibility than CBR.
To enable the Quality of Service function, it must be enabled on the previous screen
in order for the traffic classification rule that you specify (later in the Quality of
Service Screen under Advanced Setup) to be activated. Once a PVC is setup with
QoS, two more PVC queues will be used up for this function meaning 3 PVC queues
will be used. Note there is a total of 8 PVC queues available for this unit.
6238-A2-ZB20-10 6238 Wi-Fi Router with VOIP User’s Guide 31
Page 32

The next screen shows the below types of network protocols and encapsulation
modes:
• PPP over ATM (PPPoA)
• PPP over Ethernet (PPPoE)
• MAC Encapsulation Routing (MER)
• IP over ATM (IpoA)
• Bridging
Select the mode that your ISP has instructed you to use and click on Next.
Since this example uses a PPPoA connection, the next screen requires you to enter a
PPP username and password. After filling in the page and making any selections your
ISP has instructed you to, click on Next to continue.
32 6238 Wi-Fi Router with VOIP User’s Guide 6238-A2-ZB20-10
Page 33

When the settings are complete, the next screen shows a WAN Setup –
Summary screen displaying the WAN configurations made. Click on Save to
save the settings.
After the settings are saved, the WAN Setup screen displays the WAN
settings that you made, with the option to Add or Remove any of the
connections that you have made. When satisfied with the settings click on the
Finish button.
6238-A2-ZB20-10 6238 Wi-Fi Router with VOIP User’s Guide 33
Page 34

After selecting the Finish button, the DSL Router Reboot screen appears.
The router reboots to save the changes made.
Local Area Network (LAN) Setup
You can configure the DSL Router IP address and Subnet Mask for the LAN
interface to correspond to your LAN’s IP Subnet. If you want the DHCP
server to automatically assign IP addresses, then enable the DHCP server and
enter the range of IP addresses that the DHCP server can assign to your
computers. Disable the DHCP server if you prefer to manually assign IP
addresses. Click on Next to continue. The Save button only saves the LAN
configuration data, but does not apply the configurations. Select the
Save/Reboot button to save the LAN configuration data and reboot the router
and apply the new configurations.
34 6238 Wi-Fi Router with VOIP User’s Guide 6238-A2-ZB20-10
Page 35

Ethernet Mode
The Ethernet speed of each of the 4 LAN ports can be configured here. Speed
settings include: auto, 100 full, 100 half, 10 full, and 10 half. You can also
view the status of each port’s settings, whether it is connected or not and the
speed at which it is connected.
NAT
If you enable NAT (Network Address Translation), you can configure the
Virtual Server, Port Triggering, and DMZ Host.
Virtual Servers
A virtual server allows you to direct incoming traffic from the WAN side to a
specific IP address on the LAN side. Click on Add to configure a virtual
server.
6238-A2-ZB20-10 6238 Wi-Fi Router with VOIP User’s Guide 35
Page 36

Select the virtual server from the drop-down list and complete the server IP
address, then click on the Save/Apply button.
Port Triggering
Click on the Add button to add Port Triggering to your Internet application.
The following screen appears when you click on Add allowing you to select
the application that you want to set the port settings for. After a selection has
been made, click on the Save/Apply button.
36 6238 Wi-Fi Router with VOIP User’s Guide 6238-A2-ZB20-10
Page 37

The following screen appears after you save your selections. You will be able
to add or remove selections made, by clicking on the Add and Remove
buttons.
6238-A2-ZB20-10 6238 Wi-Fi Router with VOIP User’s Guide 37
Page 38

DMZ Host
You can define the IP address of the DMZ Host on this screen. Enter the IP
address and click on Save/Apply.
Firewall
IP Filtering—Outgoing
The outgoing filter blocks the LAN traffic from entering the WAN side.
Click on the Add button to create filters.
The following screen appears when you click on Add. Input the filter name,
source information (from the LAN side), and destination information (from
the WAN side). Then click on Save/Apply.
38 6238 Wi-Fi Router with VOIP User’s Guide 6238-A2-ZB20-10
Page 39

The following screen appears when you Save/Apply the IP filter. The screen
lists the IP filters that were added from the previous screen. To change your
settings, click on the Add or Remove buttons.
IP Filtering—Incoming
Incoming IP filter filters the WAN traffic to the LAN side. Click on the Add
button to add incoming filter settings.
6238-A2-ZB20-10 6238 Wi-Fi Router with VOIP User’s Guide 39
Page 40

Enter a filter name, information about the source address (from the WAN
side), and information about the destination address (to the LAN side). Select
the protocol and WAN interface, then click on Save/Apply to add the setting.
You can view and delete the incoming filter settings from this screen.
MAC Filtering
MAC filtering can forward or block traffic by MAC address. You can change
the policy or add settings to the MAC filtering table using the MAC Filtering
Setup screen.
40 6238 Wi-Fi Router with VOIP User’s Guide 6238-A2-ZB20-10
Page 41

If you click on Change Policy, a confirmation dialog allows you to verify your
change.
If you click on the Add button, then the following window allows you to
create a MAC filter.
If you want to add a setting to the MAC filtering table, enter the Source and
Destination MAC address, and select protocol type, frame direction, and
WAN interface. Then click on Save/Apply to save it.
After you save the settings, a screen showing the settings will appear. On this
screen you will be able to view and delete MAC filtering rules.
6238-A2-ZB20-10 6238 Wi-Fi Router with VOIP User’s Guide 41
Page 42

Parental Control
In a home setting, parents can also restrict the day of the week certain
computers can access the router. Click on Add to set up the restrictions.
To set up a restricted user, enter the user name, the MAC address, and select
the days to restrict. You can also enter the start and end of the blocking time.
When completed, click on Save/Apply.
42 6238 Wi-Fi Router with VOIP User’s Guide 6238-A2-ZB20-10
Page 43

Quality of Service
You can configure the Quality of Service to apply different priorities to
traffic on the router. Click on Add to configure network traffic classes.
After you click on the Add button, the following screen appears allowing you
to set up Quality of Service and Differentiated Services configurations by
defining traffic classification rules.
NOTE: The following screen is the default screen where Enable
Differentiated Service Configuration item has not been enabled. If the
checkbox is checked, the screen looks slightly different as shown in the next
screenshot after this one.
6238-A2-ZB20-10 6238 Wi-Fi Router with VOIP User’s Guide 43
Page 44

• Traffic Class Name— The name that you assign this class of traffic for
which you are configuring quality of service.
• Enable Differentiated Service Configuration— allows you to enable
the differentiated service if this checkbox is checked. Note: If this function is
enabled, you will only need to assign ATM transmit priority (next item).
• Assign ATM Transmit Priority— Select from low, medium, or high priority
level for transmitting ATM packets.
• Mark IP Precedence— Used to mark a packet to notify the network in
regard to the importance of the packet. IP precedence values range from 0-7
with 6 and 7 reserved and should not be used. The precedence values have
the following meanings—
o (0) – Routine
o (1) – Priority
o (2) – Immediate
o (3) – Flash
o (4) – Flash Override
o (5) – Critical
o (6) – Internetwork Control
o (7) – Network Control
44 6238 Wi-Fi Router with VOIP User’s Guide 6238-A2-ZB20-10
Page 45

• Mark IP Type of Service— Select from the following choices:
o Normal Service
o Minimize Cost
o Maximize Reliability
o Maximize Throughput
o Minimize Delay
• Mark 802.1p if 802.1q is enabled on WAN— (See Connection
Type screen located under WAN under the Advanced group.) The
values range from 0-7.
NOTE:
Enter the following conditions either for SET-1 or for SET-2.
SET-1
• Physical LAN Port— Select the physical port—Ethernet LAN 1-4,
USB, or wireless.
• Protocol— Select from the following protocols—TCP/UDP, TCP,
UDP, or ICMP.
• Source IP Address— The IP address for the computer which
packets are coming from.
• Source Subnet Mask— The subnet mask for the source of the
packets being sent.
6238-A2-ZB20-10 6238 Wi-Fi Router with VOIP User’s Guide 45
Page 46

• UDP / TCP Source Port (port or port:port)— If TCP or UDP was
selected, then enter the port number.
• Destination IP Address— The IP address of the computer where the
packets will be sent.
• Destination Subnet Mask— The subnet mask for the destination of
the packets.
• UDP / TCP Destination Port (port or port:port)— If TCP or UDP
was selected, then enter the port number.
SET-2
• 802.1p Priority— If 802.1q was enabled on WAN, then select a
value between 0-7.
The following screen shows the configuration fields available when the
Enable Differentiated Service Configuration checkbox is checked.
46 6238 Wi-Fi Router with VOIP User’s Guide 6238-A2-ZB20-10
Page 47

The above highlighted items are available to configure only when Enable
Differentiated Service Configuration checkbox is checked. The configuration fields
include the following:
• Assign Differentiated Services Code Point (DSCP) Mark— different markers
representing differentiated grades of service placed on various packet streams to
be recognized by the router for router purposes
•
Source MAC Address— the MAC address of the computer where packets are
coming from
• Source MAC Mask— the mask selected to mask the MAC of the source of the
packets being sent
•
Destination MAC Address— the MAC address of the computer where the packets
will be sent to
• Destination MAC Mask— the mask selected to mask the MAC of the packet’s
destination
Routing
Default Gateway
You can enable automatic assigned default gateway on the Routing – Default
Gateway screen. By default, the box is checked for the automatically assigned default
gateway to be enabled. Click on the Save/Apply button to enable or disable this
feature.
If you deselect the Enable Automatic Assigned Default Gateway option, you will be
asked to manually enter the default gateway IP address and select the appropriate user
interface that you will be using. Click on Save/Apply to continue.
6238-A2-ZB20-10 6238 Wi-Fi Router with VOIP User’s Guide 47
Page 48

Static Route
The Static Route screen can be used to add a routing table (a maximum of 32 entries
can be configured). Click on Next to add.
Enter the route information and then save and apply your configurations.
48 6238 Wi-Fi Router with VOIP User’s Guide 6238-A2-ZB20-10
Page 49

RIP
If RIP is enabled, the router operation can be configured as active or passive.
DNS
DNS Server
Use the DNS Server screen to enable automatic assignment of a DNS or to specify a
primary and secondary DNS.
If you uncheck the Enable Automatic Assigned DNS checkbox, two additional entry
fields—primary and secondary DNS server—will appear as seen below.
6238-A2-ZB20-10 6238 Wi-Fi Router with VOIP User’s Guide 49
Page 50

Dynamic DNS
Access Dynamic DNS located under DNS. Dynamic DNS (Domain Name Service) is
a system that allows more than one IP address to be assigned to one domain name.
The following Add dynamic DDNS screen allows you to set up your DDNS server.
Select the Dynamic DNS provider from the list—DynDNS.org or TZO. Enter the
hostname and the ADSL interface and the username / password provided by the DNS
server site. Note that you will need to register first at DynDNS.org.
ADSL
The DSL settings screen contains three sections—modulation, phone line, and
capability—that should be specified by your ISP.
Consult with your ISP to select the correct settings for each. Then click on
Save/Apply if you are finished or click on Advanced Settings if you want to
configure more advanced settings.
50 6238 Wi-Fi Router with VOIP User’s Guide 6238-A2-ZB20-10
Page 51

DSL Advanced Settings
The test mode can be selected from the DSL Advanced Settings screen.
Test modes include normal, reverb, medley, no retrain, and L3.
Tone Settings
The frequency band of ADSL is split up into 256 separate tones, each spaced
4.3125 kHz apart. With each tone carrying separate data, the technique operates as if
256 separate modems were running in parallel. The tone range is from 0 to 31 for
upstream and from 32 to 255 for downstream. Do not change these settings unless so
directed by your ISP.
6238-A2-ZB20-10 6238 Wi-Fi Router with VOIP User’s Guide 51
Page 52

Port Mapping
Port mapping is a feature that allows you to open ports to allow certain Internet
applications on the WAN side to pass through the firewall and enter your LAN. To
use this feature, mapping groups need to be created.
Click on the Add button as displayed below.
After clicking on the Add button, the following configuration screen appears,
allowing you to enter the groups and the interfaces they are associated with.
52 6238 Wi-Fi Router with VOIP User’s Guide 6238-A2-ZB20-10
Page 53

Wireless
This section allows you to configure wireless settings on your router.
Basic
The Wireless – Basic screen lets you enable or disable the wireless function. The
default setting for wireless is enabled. You can also hide the access point so others
cannot see your ID on the network.
6238-A2-ZB20-10 6238 Wi-Fi Router with VOIP User’s Guide 53
Page 54

Security
The next screen is the Wireless – Security screen, which allows you to select the
network authentication method and to enable or disable WEP encryption. Note that
depending on the network authentication that is selected, the screen will change
accordingly so that additional fields can be configured for the specific authentication
method.
Network authentication methods include the following:
• Open— Anyone can access the network. The default is a disabled WEP
encryption setting.
• Shared— WEP encryption is enabled and encryption key strength of 64-bit
or 128-bit needs to be selected. Click on Set Encryption Keys to manually
set the network encryption keys. Up to 4 different keys can be set and you
can come back to select which one to use at anytime.
• 802.1X— Requires mutual authentication between a client station and the
router by including a RADIUS-based authentication server. Information
about the RADIUS server such as its IP address, port and key must be
entered. WEP encryption is also enabled and the encryption strength must
also be selected.
• WPA (Wi-Fi Protected Access)— Usually used for the larger enterprise
environment, WPA uses a RADIUS server and TKIP (Temporal Key
Integrity Protocol) encryption (instead of WEP encryption, which is
54 6238 Wi-Fi Router with VOIP User’s Guide 6238-A2-ZB20-10
Page 55

disabled). TKIP uses 128-bit dynamic session keys (per user, per session, and
per packet keys).
• WPA-PSK (Wi-Fi Protected Access – Pre-Shared Key)—WPA for home
and SOHO environments, also using the same strong TKIP encryption, perpacket key construction, and key management that WPA provides in the
enterprise environment. The main difference is that the password is entered
manually. A group re-key interval time is also required.
• WPA2 (Wi-Fi Protected Access 2)— Second generation of WPA, which
uses AES (Advanced Encryption Standard) instead of TKIP as its encryption
method. Network re-auth interval is the time in which another key needs to be
dynamically issued.
• WPA2-PSK (Wi-Fi Protected Access 2 – Pre-Shared Key)— Suitable for
home and SOHO environments, it also uses AES encryption and requires you
to enter a password and a re-key interval time.
• Mixed WPA2 / WPA— During transitional times for upgrades in the
enterprise environment, this mixed authentication method allows upgraded
users and users not yet upgraded to access the network via the router.
RADIUS server information must be entered for WPA and a as well as a
group re-key interval time. Both TKIP and AES are used.
• Mixed WPA2 / WPA-PSK—useful during transitional times for upgrades in
the home or SOHO environment, a pre-shared key must be entered along
with the group re-key interval time. Both TKIP and AES are also used.
MAC Filter
The MAC filter screen allows you to manage MAC address filters. Add the MAC
addresses that you want to manage and then select the mode that you want to use to
manage them. You can disable this feature or you can allow or deny access to the
MAC addresses that you add to the list.
The following screen allows you to add a MAC address to the filter. When
completed, click on the Save/Apply button.
6238-A2-ZB20-10 6238 Wi-Fi Router with VOIP User’s Guide 55
Page 56

Wireless Bridge
In this next screen you can select the mode, either acce ss poi nt or wireless bridge that
you want the router to be in. In the screen below, Bridge Restrict is enabled, therefore
you see the Remote Bridges MAC Address fields. If Bridge Restrict is disabled, then
there is nothing left to do afterwards. Click on Save/Apply to continue.
Advanced
Advanced features of the wireless LAN interface can be configured in this section.
Settings can be configured for the following:
• AP Isolation— If you select enable, then each of your wireless clients will
not be able to communicate with each other.
• Band— A default setting at 2.4GHz – 802.11g
• Channel— 802.11b and 802.11g use channels to limit interference from
other devices. If you are experiencing interference with another 2.4Ghz
device such as a baby monitor, security alarm, or cordless phone, then change
the channel on your router.
• Auto Channel Timer—this value cannot be changed.
56 6238 Wi-Fi Router with VOIP User’s Guide 6238-A2-ZB20-10
Page 57

• 54g™ Rate—data rate speed up to 54 MBps which results in faster wireless
network access and file transfer. 54g also provides a strong wireless
connection as well as quick and safe delivery to its destination.
• Multicast Rate— The rate at which a message is sent to a specified group of
recipients.
• Basic Rate— The set of data transfer rates that all the stations will be capable
of using to receive frames from a wireless medium.
• Fragmentation Threshold— Used to fragment packets which help improve
performance in the presence of radio frequency (RF) interference.
• RTS Threshold (Request to Send Threshold)— Determines the packet size
of a transmission through the use of the router to help control traffic flow.
• DTIM Interval— Sets the Wake-up interval for clients in power-saving
mode.
• Beacon Inter v al— A packet of information that is sent from a connected
device to all other devices where it announces its availability and readiness.
A beacon interval is a period of time (sent with the beacon) before sending
the beacon again. The beacon interval may be adjusted in milliseconds (ms).
• Maximum Associated Clients—the maximum number of users that can
access your router via wireless connection
.
• Xpress Technology— A technology that utilizes standards based on
framebursting to achieve higher throughput. With Xpress Technology
enabled, aggregate throughput (the sum of the individual throughput speeds
of each client on the network) can improve by up to 25% in 802.11g only
networks and up to 75% in mixed networks comprised of 802.11g and
802.11b equipment.
• 54g Mode—
54g is a Broadcom Wi-Fi technology.
o 54g Auto: is used for compatibility with 802.11b/g.
o
54g Performance: improves the performance, but only works with
clients that support 54g wireless mode.
o
54g LRS: In some cases, older 802.11b clients may not be
compatible with 54g wireless. 54g-LRS (Limited Rate Support)
allows these clients to be compatible with the newer 54g technology.
Switching to this mode can solve problems that sometimes occur
with these clients. If there is no driver update available for these
clients, switching to 54g-LRS mode may fix the problem. Please
note that switching to 54g-LRS mode may decrease 54g
performance. It is not recommended to use this mode unless there is a
very specific reason to do so. This mode exists only to solve unique
problems that may occur with some 802.11b client adapters and is
NOT necessary for interoperability of 54g and 802.11b standards.
• 54g Protection— The 802.11g standards provide a protection method so
802.11g and 802.11b devices can co-exist in the same network. Do not
disable 54g Protection if there is a possibility that a 802.11b device may need
to use your wireless network. In Auto Mode, the wireless device will use
RTS/CTS (Request to Send / Clear to Send) to improve 802.11g performance
6238-A2-ZB20-10 6238 Wi-Fi Router with VOIP User’s Guide 57
Page 58

in mixed 802.11g/802.11b networks. Turn protection off to maximize
802.11g throughput under most conditions.
• WMM (Wi-Fi Multimedia)—feature that improves the experience for
audio, video and voice applications over a Wi-Fi network.
Quality of Service
WMM (Wi-Fi Multimedia)—feature that improves your experience for audio, video
and voice applications over a Wi-Fi network.
If you enable WMM, then you will need to configure the network traffic classes by
clicking on the Add Qos Entry button.
58 6238 Wi-Fi Router with VOIP User’s Guide 6238-A2-ZB20-10
Page 59

The following screen allows you to set up your wireless traffic quality of service rule.
To set up your traffic rule, start by giving a name to the traffic class. Then set up the
conditions that must be satisfied for the rule to take effect.
Also, assign a wireless transmit priority from the selection of 0-7. The following are
the different priority levels to choose from.
0 – WMM Best Effort (default)
1 – WMM Background
2 – WMM Background
3 – WMM Best Effort
4 – Video Priority
5 - Video Priority
6 – Voice Priority
7 - Voice Priority
To specify the traffic class rules, enter the information for the following fields:
• Protocol—select from these protocols:
— TCP/UDP
— TCP
— UDP
— ICMP
• Source IP Address
• Source Subnet Mask
• UDP / TCP Source Port (port or port:port)
• Destination IP Address
• Destination Subnet Mask
• UDP / TCP Destination Port (port or port:port)
6238-A2-ZB20-10 6238 Wi-Fi Router with VOIP User’s Guide 59
Page 60

Station Info
This screen shows computers or other devices accessing your router through its
wireless connection.
60 6238 Wi-Fi Router with VOIP User’s Guide 6238-A2-ZB20-10
Page 61

Voice
This section explains the configuration of the voice function of your router.
Configurations include basic and advanced SIP setup, phonebook, and call history.
SIP Basic
Following is the screen for SIP configuration.
• Interface Name— Select the name of the interface that you are using.
• SIP Mode— Includes peer-to-peer or proxy mode.
• SIP Proxy— Enter 0.0.0.0 if no proxy server is being used or enter the IP
address that was issued by the VoIP service provider when you signed up.
• SIP Proxy Port— This number is optional or if you obtained one from the
VoIP service provider, enter it here.
• SIP Registrar— Enter 0.0.0.0 if no proxy server is being used or enter the IP
address that was issued by the VoIP service provider when you signed up.
• SIP Registrar Port— This number is optional.
• SIP Domain Name— Enter the domain name of the SIP server if you are
using one.
• SIP Outbound Proxy— Provided by your service provider.
6238-A2-ZB20-10 6238 Wi-Fi Router with VOIP User’s Guide 61
Page 62

• SIP Outbound Proxy Port— Provided by your service provider.
• STUN Server— (optional-enter only if you are using this service) – IP
address of the STUN server, a protocol for assisting devices behind a NAT
firewall or router with their packet routing.
• STUN Server Port— (optional-used with the STUN server) - UDP port
3478 is the port that the STUN server is contacted on.
• User 1 ID— this is the phone number (integers only).
• User 1 ID Name— the name that appears on caller ID when you call out
(characters such as "<>%\^[]`+$,='#&@.: are not accepted).
• User 1 Authentication Name— the user name provided by your service
provider. Characters such as "<>%\^[]`+$,='#&@.: are not accepted.
• User 1 ID Password—the password for the User 1 ID. Characters such as
"<>%\^[]`+$,='#&@.: are not accepted.
• User 2 ID / ID Name / Authentication Name / ID Password— enter info
only if you have a second telephone line using the same integer /or character
format for the User 1 info.
• SIP Local Port— 5060 is the typical SIP port number, but it depends on
your service provider.
• RTP Start Port— This is a starting parameter, usually a number in the
10000s, for Real-Time Transport Protocol.
SIP Advanced
This screen allows you to configure how to send and receive voice activity.
62 6238 Wi-Fi Router with VOIP User’s Guide 6238-A2-ZB20-10
Page 63

• Preferred Codec— Select the voice encoder that you prefer. This does not
guarantee that this encoder will be used, but will be taken into consideration
when deciding which voice encoder to use. Each voice encoder varies by the
amount of compression on the voice.
• Packetisation Time (in milliseconds)— This is how often a packet should
be sent. This can increase or decrease the time duration between each packet
sent.
z VAD State (Voice Activity Detection)— Enabling this will control voice
information to be sent based on voice activity, which can reduce voice traffic.
z ECAN State— Echo Cancelle r — Enabling this feature will cancel out any
echo in the call.
• DTMF Relay State— Select between voice band and RFC 2833. RFC 2833
describes how to carry out DTMF signaling, other tone signals, and telephony
events in RTP packets.
• Fax Mode— Select between none or voice band data.
o None: Fax data is being processed as audio using an audio codec. If
the codec is not suitable for fax signal, then fax transmission will fail.
o Voice Band Data: Fax data is being sent processed as audio using an
audio codec, and if the codec is not suitable for fax signal, IAD will
automatically change to a suitable codec for fax transmission.
• SIP Re-register Timer (in seconds)— The amount of time before
registration is required again.
z Session Expire Timer (in seconds)— When a connected call session will be
dropped if the keep alive facility is down.
• Signaling / Voice TOS— Type of service for signaling and voice. A
signaling transmission is used for building a voice connection. Voice TOS is
used for voice transmission. Each call has two parts—first part involves the
signaling transmission when a call is made or received. The second part is
when the call is connected, it transfers voice in voice transmission.
• Inter / Critical Digit Timer (in seconds) — Inter-digit timer (IDT) is used as
timeout check between each digit dialed, while the critical digit timer (CDT)
is used for "almost completed" dialing to wait for more digits. Essentially,
CDT is the time that the device waits after the digits are dialed before it dials
the numbers.
z Do Not Disturb— This call-filtering feature prevents incoming calls from
coming through. Callers will hear a busy signal when you have the Do Not
Disturb featured enabled.
z Answer Only— This call-filtering feature disables the ability to make
outgoing calls. You can only accept incoming calls after you turn on this
feature.
z Pass “#” as Dialing Digit –if this is disabled, dial “#” to terminate the
dialing. When enabled, dial the “*” to terminate the dialing and then IP
dialing will be disabled.
• Prefix for Switch VOIP to PSTN— One of the ways that a phone number
can be dialed using PSTN (and not VoIP). It is the number prefix that you
must enter in order to switch from using VOIP to your regular phone (public
switched telephone network).
6238-A2-ZB20-10 6238 Wi-Fi Router with VOIP User’s Guide 63
Page 64

• PSTN Route Rule— For incoming calls using PSTN, this is the line (line 1
or line 2) that the call is received through. You can select auto so that it
automatically selects an open line.
• Route PSTN to VoIP— For incoming PSTN calls you can select whether or
not you want to route the call to use VoIP.
• Route VoIP to PSTN— For incoming VoIP calls you can select whether or
not you want to route the call to a PSTN line and which VoIP line you want
to be able to route to the PSTN line.
Note: There are 2 VoIP lines and only 1 PSTN line, therefore onl y o ne
of the VoIP lines can have the option of being routed to a PSTN line. The
options here are to select which VoIP line (line 1 or 2) will have the service
of being routed to a PSTN line.
• Locale Selection— The location of the router.
• Remote Server for SIP Log Messages— If you enable the remote server,
then fill out the following two fields: Log IP Address and Log Port.
• Log IP Address— The IP address of the remote server for SIP log message.
• Log Port— The port number of the remote server.
Phone1 & Phone2 Default Connections
Factory default configuration set the Default Connect to PSTN to Disabled and
assigned Phone1 and Phone2 to connect to the VoIP network as shown below:
When the Default Connect to PSTN is enabled for either Phone1 or Phone2 or
Both, as shown below:
64 6238 Wi-Fi Router with VOIP User’s Guide 6238-A2-ZB20-10
Page 65

Phone1 and/or Phone2 will generate or receive calls to the PSTN via the Line port on
this unit. The user can then select the desired Prefix for switching from PSTN to
VoIP network on a per outgoing call basis.
Dial Plan
The dial plan allows you to create rules for processing the numbers you dial.
• Prefix— The prefix numbers that determine the type of call when you dial a
string of numbers. This must be at least 1 digit.
6238-A2-ZB20-10 6238 Wi-Fi Router with VOIP User’s Guide 65
Page 66

• Min. Accept Digits— The minimum number of digits that must be dialed to
be accepted as a correct number. This includes the prefix.
• Max. Accept Digits— The maximum number of digits that can be dialed to
be a valid phone number. This includes the prefix.
• Delete Digits— The number of digits at the beginning of the dialed number
that will be taken off. For example, if you dial the number 88-0930-123-456
and have a rule with prefix 88 and set the number of digits to be deleted as 2,
then it will dial the number without the 88 prefix at the beginning and insert
the 2 in its place.
• Insert Digits— The digits that will be inserted at the beginning of the dial-
string after the specified digits are first deleted.
• Type— There are 3 types of dial plans: PSTN, VoIP, and block. You can
create dial plans for PSTN and VoIP numbers in addition to dial plans that
you want to block. For example, if you want to block a phone number with a
certain prefix, you need only to enter the prefix and the Min. and Max.
Accept Digits and select Block under the Type column.
Phonebook
The phonebook allows you to filter calls from specified IP addresses. Enter the IP
addresses in the Call ID field and then decide whether you want to allow or deny
those enabled callers. You can also organize the calls by ring group (default, family,
friend, and colleague).
66 6238 Wi-Fi Router with VOIP User’s Guide 6238-A2-ZB20-10
Page 67

SIP Provision
This page allows you to set up a provision configuration for downloading SIP settings
from a server. All SIP related settings will use the values from the downloading
provision file. The following steps will allow you to set up this feature.
1. To enable this feature, click on the Enabled clickbox.
2. Select a Provision Method. The default provision method for downloading
the configurations is by TFTP.
3. Enter the provision server address and file name obtained from your VoIP
service provider.
4. After all the fields are completed, click on the Save Config button.
5. Lastly, click on the Stop SIP client button and then when the button changes
to Start SIP client, click on it to finish.
6238-A2-ZB20-10 6238 Wi-Fi Router with VOIP User’s Guide 67
Page 68

Call Features
NOTE: Reference Only—This is not a section in the router’s user interface.
This is a reference of the feature codes for different call features such as call
waiting, call forwarding, etc.
Call Feature Function Dial String
Call Waiting If call waiting is enabled on a
line and you hear the call
waiting tone during a call,
press flash to answer the
second call. The first call is
automatically placed on hold.
To switch between calls,
press flash again.
Call Waiting Once Allows you to enable or
disable call waiting during
one call only.
Call Forward Number Enables you to set the
dialstring of the designated
phone number for which
calls will be forwarded to
Call Forward No Answer Enables you to forward
incoming calls to another
number when you do not
answer within 18 seconds
Call Forward Busy Enables you to immediately
forward incoming calls to the
designated number if the
phone is off-hook. Previous
settings for Call Forward
Busy or No Answer are not
modified.
Call Forward All Enables you to forward ALL
incoming calls (whether it is
no answer or busy) to the
designated phone number
Call Return Enables you to place a call to
the last known incoming
caller (answered or not)
Redial Enables you to redial the last
outgoing number
Call Pick Up Enables you to pick up on a
second incoming call while
• To Disable, dial *60
• To Enable, dial *61
• NOTE: Call forward
feature settings (Busy or All)
takes priority over the call
waiting feature.
• Call waiting feature is
ignored on new incoming
calls if there is already a call
on hold or in conference.
• To Disable the call waiting
feature one time, dial *62
• To Enable the call waiting
feature one time, dial *63
• To set the dialstring ONLY,
dial *74 and the phone
number for which calls
should be forwarded to
• To Enable, dial *71
• To Enable, dial *72
• To Enable, dial *73
• To dial the number, dial
*69
• To redial the last number
dialed, dial *68
• To answer another ringing
phone, dial *99. For
68 6238 Wi-Fi Router with VOIP User’s Guide 6238-A2-ZB20-10
Page 69

you are already on the line example, line 1 is ringing,
you can off-hook line 2, and
dial *99 to answer the
incoming call
Speed Dial Enables you to speed dial any
number that is entered in the
Phonebook section of the
Voice Page
• To speed dial, dial *00 -
*09
Diagnostics
The diagnostics screen allows you to run diagnostic tests to check your DSL
connection. The results show test results of three connections:
• Connection to your local network
• Connection to your DSL service provider
• Connection to your Internet service provider
There are two buttons at the bottom of the screen—Test and Test with OAM F4—
which allow you to retest if necessary.
6238-A2-ZB20-10 6238 Wi-Fi Router with VOIP User’s Guide 69
Page 70

Management
The Management section gives you access to certain setups for the purpose of
maintaining the system, including backing up the configurations, viewing system log,
maintaining access control, and updating software.
Settings
Backup Settings
To save a copy of the configurations that you have made on your router, click on the
Backup Settings button.
The following pop-up screen appears with a prompt to open or save the file to your
computer.
70 6238 Wi-Fi Router with VOIP User’s Guide 6238-A2-ZB20-10
Page 71

Restore User Settings
To load a previously saved configuration file onto your router, click on Browse to
find the file on your computer and click on Update Settings.
The router restores settings and reboot to activate the restored settings.
Restore Default
Restore Default deletes all current settings and restore the router to factory default
settings. Click on the Restore Default Settings button.
Click on OK when the pop-up window appears confirming that you want to restore
factory default settings to your router.
6238-A2-ZB20-10 6238 Wi-Fi Router with VOIP User’s Guide 71
Page 72

The router restores the default settings and reboot.
System Log
The System Log dialog allows you to view the System Log and configure the System
Log options. To view the System Log, click on the View System Log button.
Below is a view of the System Log.
72 6238 Wi-Fi Router with VOIP User’s Guide 6238-A2-ZB20-10
Page 73

Configure System Log
If the log is enabled, the system will log selected events including Emergency, Alert,
Critical, Error, Warning, Notice, Informational, and Debugging. All events above or
equal to the selected log level will be logged and displayed.
If the selected mode is Remote or Both, events will be sent to the specified IP
address and UDP port of a remote system log server. If the selected mode is Local or
Both, events will be recorded in the local memory. Select the desired values and click
on the Save/Apply button to configure the system log options.
SNMP
SNMP (Simple Network Management Protocol) provides a means to monitor status
and performance as well as set configuration parameters. It enables a management
station to configure, monitor and receive trap messages from network devices.
6238-A2-ZB20-10 6238 Wi-Fi Router with VOIP User’s Guide 73
Page 74

TR-069 Client
The router includes a TR-069 client which is a WAN management protocol. All the
values are already filled in. If you wish to enable this protocol, then select enable.
You must click on the Save/Reboot button for the change to take place.
Internet Time
The Time Settings screen allows you to automatically synchronize your time with a
timeserver on the Internet.
If you choose to automatically synchronize with Internet time servers, then click on
the box and the following fields appear.
Select from the list of NTP (Network Time Protocol) time servers. Then select the
time zone that you are in and click on Save/Apply to save and complete your time
settings.
74 6238 Wi-Fi Router with VOIP User’s Guide 6238-A2-ZB20-10
Page 75

Access Control
You can enable or disable some services of your router by LAN or WAN. If no WAN
connection is defined, then only the LAN side can be configured.
Services
Services that can be enabled include FTP, HTTP, ICMP, SNMP, SSH, TELNET, and
TFTP. Click on Apply when finished.
6238-A2-ZB20-10 6238 Wi-Fi Router with VOIP User’s Guide 75
Page 76

IP Addresses
Any access to the router can be controlled when Access Control Mode is enabled.
The IP addresses of allowed hosts can be added in the IP Address page under Access
Control.
On the Access Control – IP Address page, enter the IP addresses of the allowed
hosts by clicking the Add button.
The IP Address entry page will be displayed as below:
Add the IP address of the allowed host into the entry box.
Provide the proper subnet mask to specify the range of hosts within the IP address
subnet that are allowed to control this unit.
Click the Save/Apply button after the entry.
Note: It is recommended that the IP address and its associated subnet mask must be
added into this IP address list before the Access Control Mode is enabled. This
address list is used for both LAN and WAN control access to the unit.
76 6238 Wi-Fi Router with VOIP User’s Guide 6238-A2-ZB20-10
Page 77

More IP addresses can be added by repeating the above procedures.
6238-A2-ZB20-10 6238 Wi-Fi Router with VOIP User’s Guide 77
Page 78

Passwords
Access the Passwords screen under the Access Control section to change a
password. Select an account and enter the current password and the new password.
Then click on the Save/Apply button.
Update Software
If your ISP releases new software for this router, follow these steps to perform an
upgrade.
1. Obtain an updated software image file from your ISP.
2. Enter the path to the image file location or click on the Browse button to locate
the image file.
3. Click on the Update Software button once to upload the new image file.
78 6238 Wi-Fi Router with VOIP User’s Guide 6238-A2-ZB20-10
Page 79

Reboot Router
Select Reboot Router under Access Control to reboot the router using the web
interface. The router saves the current configuration and reboots itself using the new
configuration.
6238-A2-ZB20-10 6238 Wi-Fi Router with VOIP User’s Guide 79
 Loading...
Loading...