
IMACS Product Book

(PAGE INTENTIONALLY LEFT BLANK)

TABLE OF CONTENTS
Section: Title: Page
:
I. IMACS Product Overview
II. Chassis and Common Equipment 14
1. IMACS Chassis and Backplane 14
2. CPU Cards 21
3. Interface Cards 23
4. WAN Cards 27
III. Voice Modules and Applications 31
1. FXS 31
2. FXO 32
3. E&M 34
4. P-Phone 36
5. Voice Channel Bank Application 39
IV. Data Modules and Applications 41
1. HSU 44
2. SRU 47
3. FRAD 50
4. OCU-DP 53
5. BRI 56
6. DSO-DP 60
7. BnR IP Concentrator 61
8. PM-IOR 62
V. Alarm Cards 64

TABLE OF CONTENTS CONTINUED
Section: Title: Page
:
VI. Server Cards 65
1. ADPCM 65
2. ISDN 69
3. Management Channel Concentrator (MCC) 77
4. ACS-FRS 79
5. ATM 85
6. Internet Protocol Router 90
7. Low-Bit Rate Voice Server 94
VII. IMACS System Testing and Diagnostics 98
Zhone Technologies, Inc. IMACS Product Book, Version 4
A
A
I. IMACS Product Overview
IMACS
Zhone Technologies’ Integrated Multiple Access Communications Server (IMACS) is a highly flexible and
intelligent Integrated Access Device (IAD) that enables service providers worldwide to offer a wide variety of
business communication services efficiently and cost-effectively. Services include Plain Old Telephone Services
(POTS), analog private lines, Digital Data Networks (DDN), Frame Relay, Integrated Services Digital Network
(ISDN), Asynchronous Transfer Mode (ATM) based services, high-speed Internet access and integrated routing.
The IMACS supports V.35, V.11/X.21, HDSL, T1, E1, fractional T1, fractional E1 and DS3 network interfaces. For
user connectivity, a variety of interfaces are available to support analog and digital devices.
An integrated Digital Cross Connect is available to consolidate multiple voice, data and T1/E1 services. In addition,
IMACS offers a powerful array of built-in network diagnostic and fault isolation capabilities. These include built-in
Bit Error Rate Testers, test tone and signaling state generation, digital and analog loop-back support and remote
configuration and control. The Server slots on the IMACS platform enable provisioning advanced services such as
voice compression (ADPCM and ACELP), ISDN call handling, Frame Relay switching and concentration, MCC
and ATM adaptation.
Three types of IMACS chassis are available. The IMACS 600, IMACS 800 and IMACS 900 differ in their card
capacity and front or rear card install options. All models support the same range of modular cards, power supplies
and system redundancy options. All IMACS systems can be fully managed either with local craft interface with a
VT100 or PC or through a network management system using SNMP.
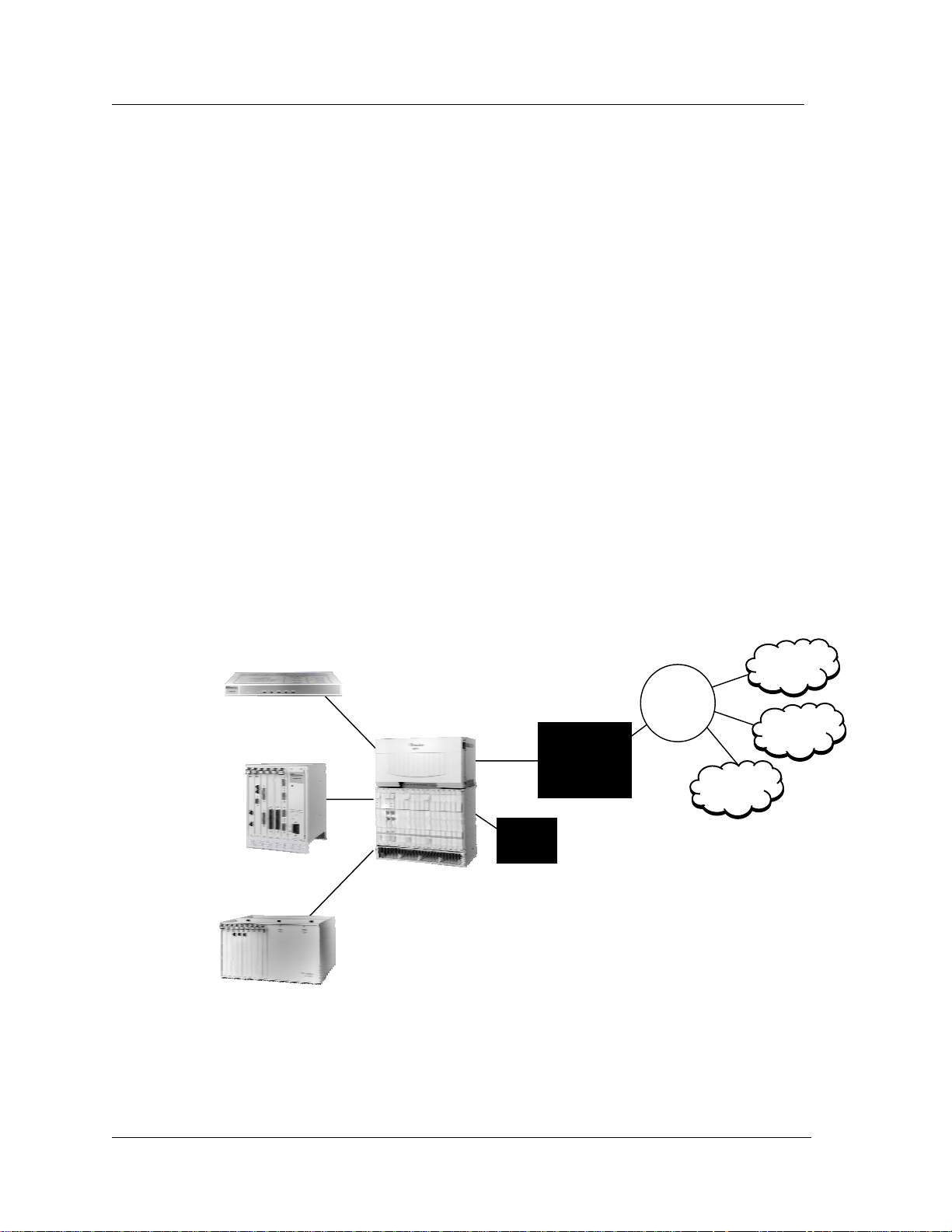
The IMACS is a component of a complete line of managed, integrated access solutions from Zhone Technologies.
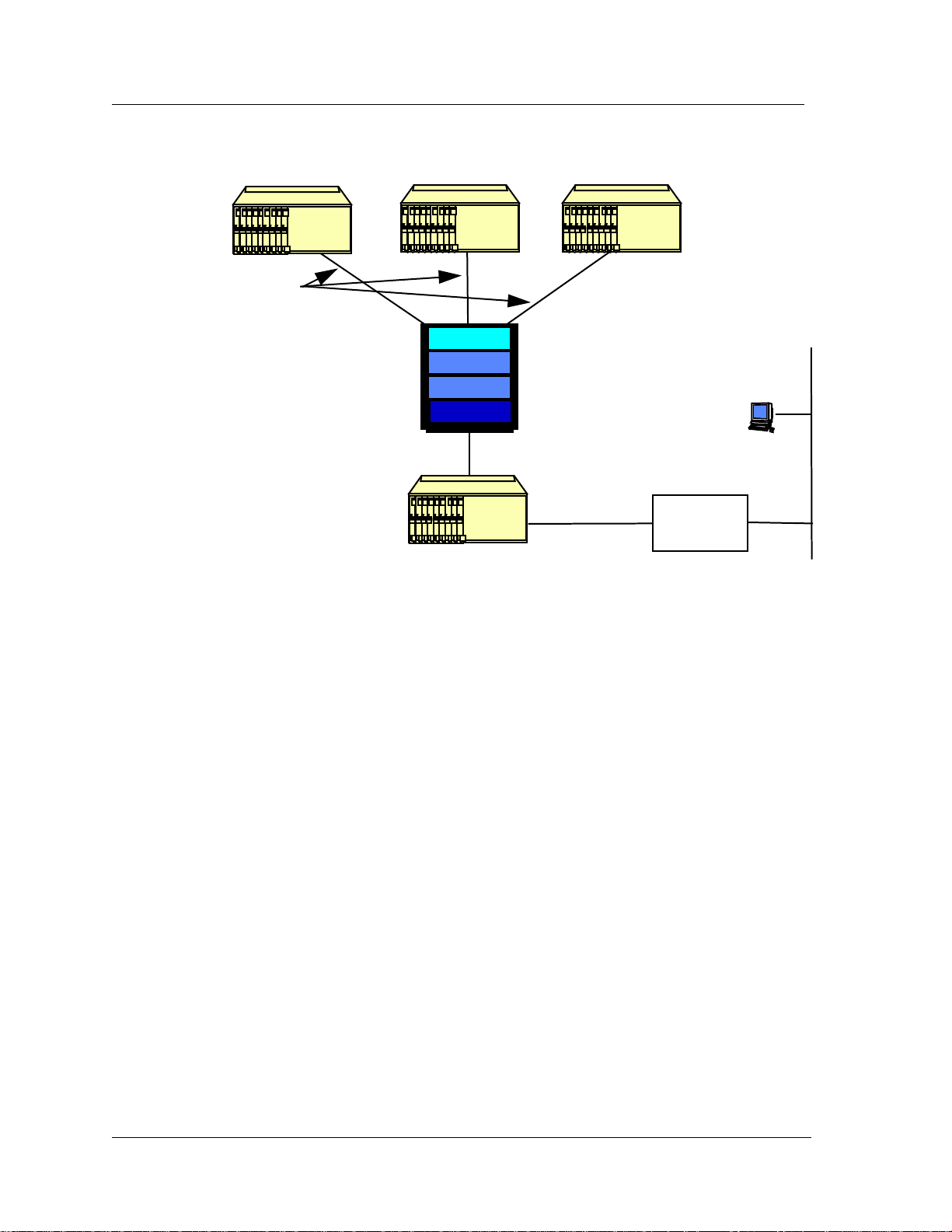
Figure 1 shows how the service provider can deliver a complete suite of fast, efficient and reliable business
communication services to the customers by deploying the Sechtor 300, IMACS, the StreamLine and the Z-Plex 10.
• ISDN
• POTS
• Private Data
• Private Voice
• (PBX)
• Frame Relay
• ATM
• Internet
• Extranet
• Intranet
• Video
Z-Plex 10
StreamLine
IMACS
Secht
3/1/0 DACS
GR303 NS.2
VT/VC Grooming
M13
dd/Drop
Multiplexer
Sonet
Ring
PSTN
Internet
Figure 1 - IMACS Product Family
TM
March 2001 Page 1

Zhone Technologies, Inc. IMACS Product Book, Version 4
IMACS Features and Benefits
Flexibility and Intelligence
Global Standards Compliant—ensures product can be integrated in any international telecommunications network.
Provisioning for extensive array of services and applications—flexibility which enables providers to generate
revenues without replacing existing equipment.
Concurrent support for Circuit, Packet, Frame, and Cell processing—single solution for service providers to use
rather than purchasing and managing multiple boxes and networks.
Cost-effective migration path to emerging access services and technologies - investment protection.
SNMP Manageable—industry-wide accepted standard for network management a Remote software download
capability—time and technical support resources savings.
Modular Architecture
Ease of service and capacity expansion—preserves existing investment and reduces any need to forklift upgrade
from old equipment.
Flexibility of provisioning technologies using multi-bus architecture- analog, digital, packet, frame, cell, etc.—
enables carriers to offer various services and be a “one-stop” provider which generates more revenues.
Interchangeable set of User, WAN, and Server cards determine application set.
Well-designed chassis to fit into a variety of standard racks.
Powerful User Interface and Remote Management Capabilities
Fully configurable through software—loca l ly and remotely—eliminates nee d to send out tec hni cal support
personnel to multiple sites, saving time and money.
Remote software upgrade capability on various cards—eliminates need to purchase new cards.
System Integrity Features
Low power consumption.
Single chassis redundancy of power supply, CPU, network interfaces and converter.
Choice of clock synchronization sources with automatic clock fallback to alternate choice.
Ease of Maintenance and Enhancement
Multiple maintenance ports for WAN, data and voice modules.
Extensive system-wide built-in diagnostics and fault isolation tests.
Continuous alarm monito ring.
Local and remote alarm logging.
Easy access to customer technical support.
Hot swappable cards.
March 2001 Page 2

Zhone Technologies, Inc. IMACS Product Book, Version 4
IMACS Architecture Overview
The IMACS chassis architecture supports three types of buses and five card types. The buses are the:
• User
• WAN
• Server
Communicating through the buses are the following five c ard types:
• CPU
• WAN
• User
• Server
• Interface
Each system has at least one CPU, WAN and one Interface card. These three cards provide common functions for
the shelf. The WAN, User, and Server cards provide the specific voice/data terminal and network interfaces and
processing required by the customer to transfer voice and data traffic from the customer premise to the network.
IMACS architecture has specific card slots, which are tailored to provide either a WAN, User or Server function.
IMACS System Bus Architecture
The IMACS is a multiprocessor-based platform that handles today’s network access needs and provides a migration
path to the wide range of services of the future. A unique multi-bus architecture provides this flexibility by offloading and isolating the Wide Area Network (WAN) link processing tasks from those of inter-processor
communications and channel I/O (input/output) control and signaling. The CPU card employs multiple
communication buses extended through the back plane to the User, Server, WAN and Interface Cards. The CPU
uses these buses to configure hardware on User, Server, WAN, or Interface cards and solicit status. Depending on
the intelligence on the card, the CPU may either read or write to the card’s hardware registers or send and receive
messages using a messaging proto col.
This design approach yields two significant advantages over other access multiplexers. First, the off-loading of
processing tasks across the multi-bus reduces system overhead, thereby improving the effective throughput and
performance. Second, the isolation of functions allows rapid design and development of new network access
compatible WAN functions. As the new functions are introduced, they occupy the Server card slot and do not
impact or disrupt an existing system. For instance, the design of the Frame Relay Server card was performed
utilizing the Server processor bus and is independent of other existing or future IMACS functions. When a Frame
Relay server card is installed, it can perform Frame Relay access concentration on WAN links and fractional
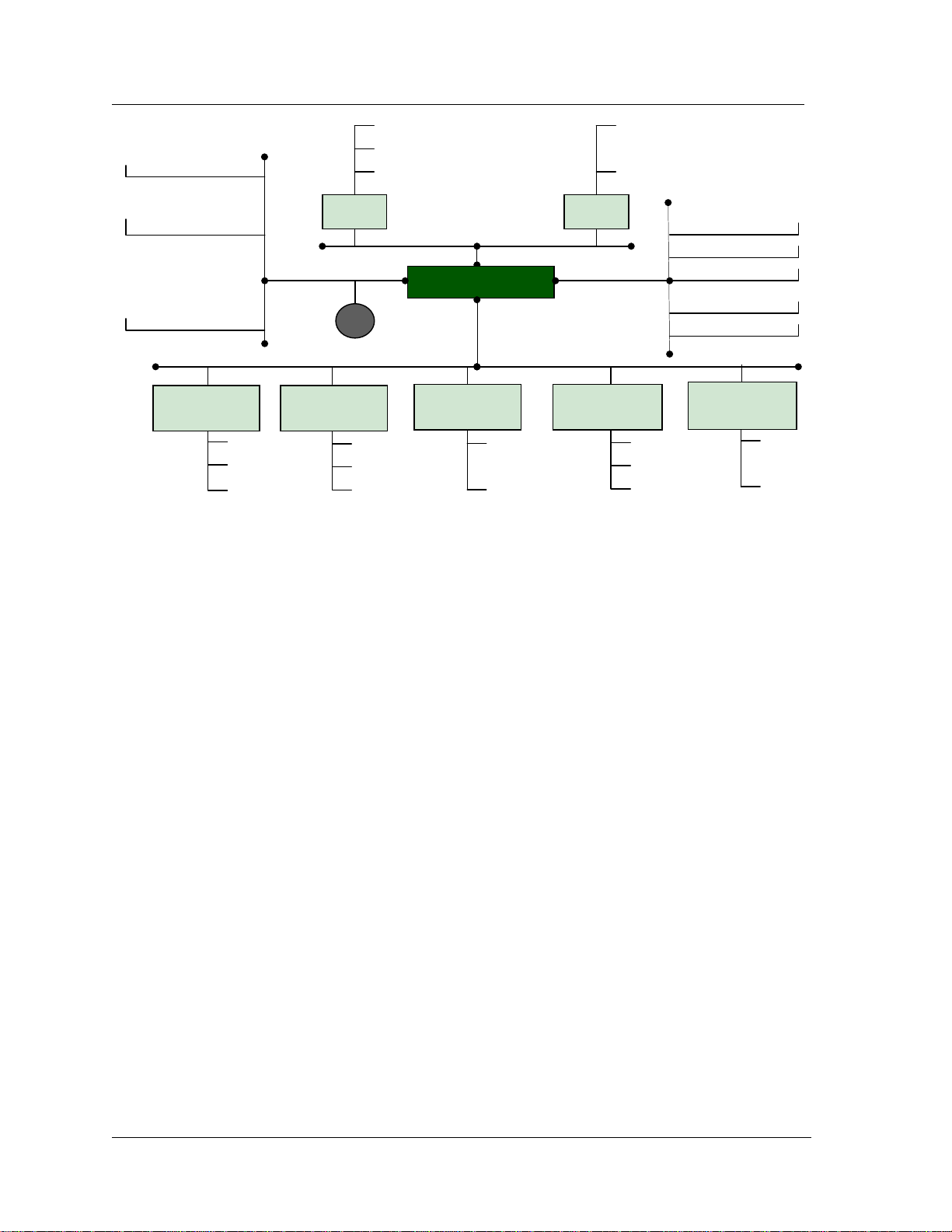
channels assigned to the IMACS. Figure 2 shows a functional block diagram of the IMACS’s multi-bus architecture
and the manner in which functions are isolated.
March 2001 Page 3
Zhone Technologies, Inc. IMACS Product Book, Version 4
NETWORK
MANAGEMENT
AGENT
SNMP
NODE
MANAGEMENT
EXTERNAL ALARMS
MODEM
TELNET
VT100
RITS
T1
C
DSX
CSU
HDSL
WAN CONNECTIVITY
I/O X CONNECT
E1
G.703 CEPT
HDSL
SERVER FUNCTIONS
MANAGEMENT
COMMUNICATION
ISDN PRI
FRAME RELAY
VOICE COMP
ATM
VOICE DATA
LAN
DIGITAL
ACCESS
ISDN
BRI
FXO
FXS
E&M
SUB-RATE
n x 56/64
FRAD
IP/IPX ROUTING
BRIDGING
OCU-DP
DSO-DP
G.703
‘U’ INTERFACE
‘S/T’ INTERFACE
Figure 2 - IMACS Architecture
User Buses
The User buses are essentially a group of four Time Division Multiplexing (TDM) highways, each 2.048 Mbps in
capacity, and named A, B, C, and D. They are utilized by the User cards to format their traffic for further processing
either by Server or WAN cards. User cards are intended to provide physical interfaces to data or voice equipment
that either resides on site or is remotely connected over low speed analog or digital facilities. Server cards may
interface with these buses directly; whereas a cross-connect or bus connect CPU is required to interface the user
buses to WAN cards.
IMACS Voice cards are designed to use the A and B buses only. When there are voice cards installed, the CPU
allocates bandwidth on the A or B buses to these modules first. It then may utilize the remaining A and B bus
bandwidth for any other User cards inserted into the shelf. Most Data Cards can be configured to use all 4 user
buses.
WAN Buses
The WAN buses are a group of eight Time Division Multiplexing (TDM) highways, each 2.048 Mbps in capacity,
and named W1-1, W1-2, W2-1, W2-2, W3-1, W3-2, W4-1 and W4-2, respectively. They are utilized by the WAN
cards to format their traffic for transmission to high-speed digital facilities via the physical connector on the
Interface card. A WAN link is typically a T1, CEPT-E1, DSX-1 or HDSL facility connection. There are four WAN
card slots in an IMACS chassis. Each WAN card slot has 8 leads connected to the Interface card, which can be used
to support a T1/E1 facility. The fourth WAN slot has all the WAN connections from the other 3 slots in addition to
its own. These connections all terminate on the fourth WAN slot to support the WAN redundancy feature. The
WAN in the fourth slot can substitute for one of the other WAN cards by connecting the redundant WAN card to the
facility leads of the failed WAN card.
March 2001 Page 4

Zhone Technologies, Inc. IMACS Product Book, Version 4
Server Buses
The Server buses are all the buses that are accessible by the Server cards. Effectively this is the union of User buses
and WAN bases. This enables the Server cards to provide a data processing function for WAN and User cards. The
Server/Server card typically provides a centralized processing function on data initially entering the system from
User or WAN connections.
A Server/Server card has the same highway interfaces as a CPU card with cross-connect functionality. A Server
card can therefore function as a general cross-connect, or can rely on the cross-connect on the CPU, as needed by
the application. The directions of the highways may be reversed, depending on whether a Server card is interfacing
with User/WAN cards or with another CPU/Server card. For example, when a Server card is interfacing with
User/Wan cards, it will drive the same TDM highways a CPU card normally drives. When interfacing to a CPU
card it will drive the same TDM leads of a highway as a User/WAN card drive. When interfacing to another Server
card, both cards may have to be programmed as to which highway lead to drive on and which to receive on. It may
have to be able to drive and receive on both of the transmit and receive highways on a per time slot basis.
Card Type Summary
The IMACS chassis architecture supports five basic types of cards. They are the Central Processing Unit (CPU)
card, Interface card, Wide Area Network (WAN) card, User card and Server card. Each IMACS system has at least
one CPU and WAN card and one Interface card. These three cards provide common functions for the shelf. The
WAN, User, and Server cards provide the specific data terminal and network interfaces and processing required by
the customer to transfer data from the premise to the network. IMACS architecture has specific card slots, which are
tailored to provide either a WAN, User or Server function.
CPU Card
The CPU is the “brain” of the IMACS and performs most of the configuration, management, and MIB and common
processing for the IMACS. In addition the CPU card provides the interconnection of WAN, User, and Server TDM
buses through a bus connect or cross-connect function. The IMACS can have up to 2 CPU cards, which provide a
redundant control and switching complex. If the primary CPU fails, the standby takes over. A Mini-DACS 1/0
cross-connect for 256 DSOs is available.
Interface Card
The interface card has common hardware, which is managed by the active CPU card. Configuration information
processed on the CPU card is stored in the NVRAM on the interface card. It has interfaces to support a modem,
control terminal, management port, printer, alarm relay, and provides the physical connection to the eight T1/E1
interfaces used by the WAN cards. The card also contains the clock hardware, which provides the entire back plane
timing signals for the PCM buses. One Interface card is required per system.
WAN Card
The WAN cards provide electrical interfaces to high-speed digital facilities, which are connected via the Interface
card. The WAN cards take the voice and data traffic off the TDM bus, which was put there by the User and Server
cards, and transmit the information over a WAN link. A WAN link is typically a T1, CEPT-E1, DSX-1, or HDSL
facility connection. The WAN cards support a 1:N redundancy feature with Cross Connect CPUs only.
March 2001 Page 5

Zhone Technologies, Inc. IMACS Product Book, Version 4
Voice Card
The IMACS supports a wide-variety of cards to support voice channel bank applications. Typically they are a
family of cards each of which provides 8 ports, which translate the analog signal to PCM and translate the signaling
information from the analog interface for transmission over a digital facility. The interfaces supported include FXS,
FXO, E&M, FXS Coin, FXO Coin and P-phone.
Data Card
The IMACS supports multiple types of data cards for transport of Digital Data in 2, 4, 8 or 10 port models. They
include High-speed synchronous V.35, EIA530, RS449, RS422, V.1 data, low speed RS232, V.24 data, DDS traffic
(Digital Data via an OCU-DP or DSO-DP) and ISDN-BRI traffic.
Server Card
The Server cards provide voice and data processing functions for WAN voice and User cards. The Server card
typically provides a centralized processing function on traffic initially entering the system from User or WAN
connections. The function is implemented, as a Server card when processing is needed on the data, following the
termination of the physical interface layer. One example is protocol processing, where information needs to be
extracted from a bit oriented protocol entering from one port, is processed, and sent out another port. The hardware
function of the protocol processing is separated from the hardware required to support the physical interfaces.
Traffic may arrive from time slots over a WAN link, or via an FXS card. An example is the ADPCM voice
compression server card. The compressed voice data can be extracted from selected time slots of T1/E1 WAN links,
and then expanded by ADPCM Server module. This can be accomplished without each WAN card having the
hardware required to compress all its channels. Server cards can also be used to perform a high-speed trunking and
aggregation function for the shelf. In these applications a Server card may have a high-speed cable or optical
interface. An example of a high-speed aggregation function on a Server card is the ATM Server card, which has a
high-speed DS3 interface. Other examples are the Frame Relay module for Frame Relay concentration, ISDN-PRI,
Inverse-muxing, or Low Bit Rate Voice (LBRV).
Redundancy and Load Sharing
IMACS supports load sharing and redundancy of the following critical system modules:
• System Power Supply Unit
• CPU Card
• WAN Card
• ADPCM Voice Compression Card
Power Supply Redundancy
The IMACS Power Supply Units can support load sharing power redundancy and require the installation of two
identical power supplies in the unit. The status of the po wer supplies is repo rted via LEDs that a re visible through
the front panel. Both IMACS power supplies load share in supplying all the power signals on a shelf. This includes
120/240 VAC, 24 VDC and -48VDC (when equipped). The IMACS power supplies are fully equipped with “ORing
Diodes” on all power rails. Therefore, insertion and removal of power supplies are non-intrusive to system
operation. Depending on system configuration, a single power supply can fully support the system. The main
IMACS CPUs are also equipped with power supply monitoring functions. This capability enables the CPU boards
to monitor the instantaneous levels of all voltages in the system. This provides immediate alarming of failed power
supplies by the active CPU card.
March 2001 Page 6

Zhone Technologies, Inc. IMACS Product Book, Version 4
CPU Card Redundancy
The IMACS CPU cards typically support redundant operation when paired with an identical CPU card. The CPUs
communicate with each other once every second. If there is a problem with the standby CPU (i.e., communications
transfer did not take place), an alarm is raised by the active CPU, indicating a problem with the standby CPU. The
active CPU monitoring is achieved via hardwire watchdog timers on the Interface Card. The Interface Card’s
hardware timers are sensing specific control points from the controlling CPU circuit pack. These timers require only
8 seconds to detect and reset to the redundant blinking CPU card.
WAN Card Redundancy
The IMACS Dual WAN cards in conjunction with a Dual WAN card with Relays support a 1-to-N redundancy. For
redundant operation, the redundant WAN card will be located in the last WAN slot which is marked W4 and can be
used in systems with cross connect CPUs to act as a redundant card for up to three Dual WAN cards containing the
same modules. Both ports of the redundant card must be populated with either the DSX/CEPT or CSU module and
must be an exact match to any corresponding WAN Cards with which it is redundant.
All IMACS WAN cards communicate with the active CPU card every half-second. If the WAN card fails to
properly communicate with the active CPU card, the WAN card is declared failed and a switch occurs. These
actions occur within an eight second time frame. The WAN card failures can also occur from craft defined rules.
These rules are based on Carrier Group Alarm (CGA) declaration assignments. A CGA switch will occur 1.5
seconds after a CGA declaration, or forced “OOS” command from the User Interface (UI). The WAN card will
remain in the switched condition for 20 seconds, or until synchronization can be achieved. If synchronization is not
achieved, the WAN switch will return to its original state. If the switch is successful, the active CPU issues an
alarm and the WAN switch continues in a steady state operation.
ADPCM Redundancy
The IMACS Adaptive Differential Pulse Code Modulation (ADPCM) Server card provides 1-to-N redundancy when
used with 2 other identical cards. The ADPCM card has on-board diagnostics that can detect a failure in one second,
and switch in three seconds.
System Synchronization and Clocking
The Interface card includes a Stratum 4 clock circuit, which is capable of running off its own crystal oscillator or
phase locking to a 8 KHz reference clock on t he back plane. Any card plugged into t he back plane that connects to a
network-like facility can be programmed to supply the reference clock input to the Stratum 4 Clock. As an option, a
separate external timing source may be used on a specific interface card.
The IMACS supports a three-tiered hierarchy of system clocking sources that are provisioned under the interface
card menu options. Should the Primary source fail, the system will fall back onto the Secondary source. Should
both Primary and Secondary sources fail, the system will default to its internal Stratum 4 clock. In all cases,
recovery is automatic should the failed clock(s) recover.
Both the Primary and Secondary clocks can be user-programmed to be derived from the following:
• IMACS system’s internal oscillator.
• Any of the WAN interfaces in the system.
• A server card such as the ATM, which can p rovide timing through the DS3 link.
• A user card such as the BRI.
• An external synchroniz ation device (framed T1 and unframed E1) through an 8922 I/F card.
March 2001 Page 7

Zhone Technologies, Inc. IMACS Product Book, Version 4
The system will switch to the backup clock source upon detection of one of the following conditions in the currently
active source:
• CGA Red Alarm.
• CGA Yellow Alarm.
• Out-Of-Service (OOS) condition.
• Clock source is placed in loop back mode.
• Clock source is placed in standby mode.
IMACS System Management
When the IMACS’ active CPU runs the IP protocol stack, it provides SNMP and Telnet support for management of
local and remote IMACS units as well as provides for routing of IP datagrams to other IMACS systems. The Telnet
protocol is a remote terminal protocol that allows any PC or workstation equipped with a TELNET client application
to establish terminal sessions with an IMACS.
The Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) is a widely adopted industry standard method of providing
common network management control. A typical SNMP mana gement architecture i nvolves a Manager, such as
Zhone Technologies’ Element Management System (EMS) product and an SNMP Agent, which is responsible for
providing device management data to the manager. Agents come in two forms: Embedded and Proxy. Embedded
agents run directly on the device being managed, while Proxy agents require an intermediate system to translate
from a proprietary messaging format. The IMACS uses Embedded SNMP agents to report management information
to the manager.
SNMP is a protocol standard that specifies how management data should be transported between an Agent and a
Manager. SNMP MIBs (Management Information Base) specifies what comprises the management data. There are
multiple MIBs that address many types of computer and telecommunications equipment. Some of these are defined
as standards and are referred to by their RFC (Request For Comment) number. Other MIBs are specific to the
device being managed and are referred to as Enterprise MIBs. The IMACS supports the following standard and
enterprise MIBs:
• MIB-II (RFC 1213)
• DS1 MIB (RFC 1406)
• Alarm MIB (Traps to RFC 1215)
• Cross Connect MIB
• Frame Relay MIB RFC1604
• Frame Relay DTE MIB - RFC 1315
• MCC MIB
• ATM Forum UNI3.0 MIB
• DS3 MIB (RFC 1495)
• AToM MIB (RFC 1595)
Standard MIBs are written to provide management data on a wide number of devices, and in some cases not all of
the parameters of a MIB are appropriate for the device being managed. Therefore extensions or omissions may be
required in any standards based MIB.
The IMACS offers several methods of transporting the SNMP and Telnet traffic from remote sites to the Network
Management.
These methods include transport via:
• PPP or SLIP.
• FDL for T1 ESF mode or E1 National Bit 4.
• B7R Encoded Time Slots 24 (T1) or 31 (E1).
• Nx64 HDLC or FR available on CPU5.
• Frame Relay Management PVC.
• ATM Management P VC.
March 2001 Page 8
Zhone Technologies, Inc. IMACS Product Book, Version 4
IMACS Management Via PPP or SLIP
IMACS alarms are reported either to a local device or via an internal 2400 bps modem in a proprietary ASCII
format to a central site. Additionally, the IMACS can be optioned to use TCP/IP and encode alarms as standard
SNMP traps. One method of transmitting TCP/IP management information and SNMP traps is to activate the Serial
Line Internet Protocol (SLIP) on the DB-9 port set at 9.6 Kbps. requires that a routed network exists and has full
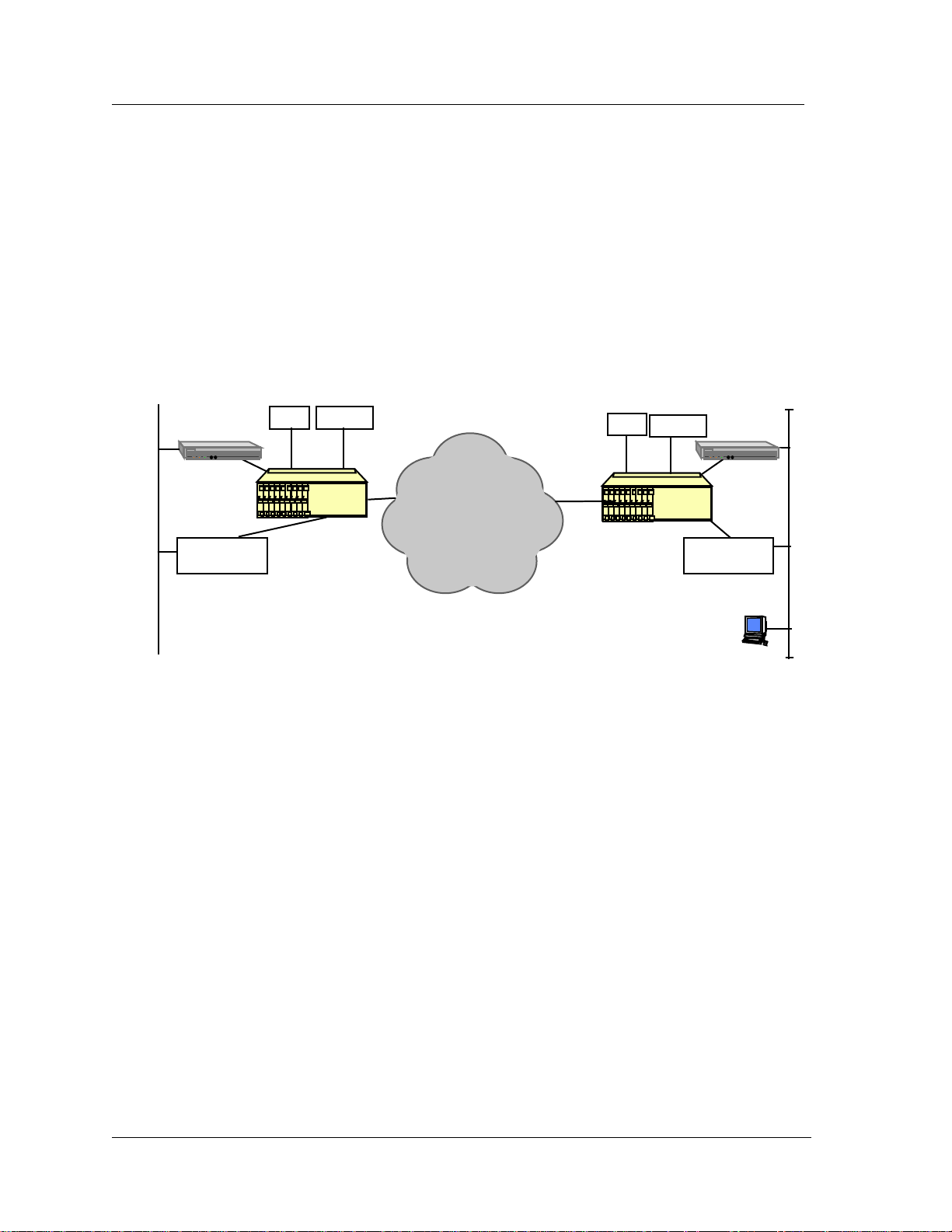
connectivity back to the location where the SNMP-based NMS resides. Figure 4 illustrates how terminal servers are
used to provide connectivity from the IMACS’ serial interface to the router-based network. A typical NMS scenario
is described below:
Remote Site 1
Remote Site 2
Router
PBX CODEC
IMACS
Frame Relay
PBX CODEC
Router
IMACS
Network
Terminal
Server
Terminal
Server
NMS
Figure 3 - IMACS Connectivity to Terminal Servers
1. An alarm occurs in the IMACS on the left side of the diagram and an SNMP trap is sent out the serial port on
the interface card.
2. A serial port of a Terminal Server that is configured for SLIP or PPP accepts the SNMP trap and forwards it
over the Ethernet LAN.
3. The IP destination is the NMS; where it is picked up by the router for delivery to the NMS.
4. T he router forwards the trap and other traffic destined for remote LANs, via its Frame Relay WAN connection.
The router i s connecte d through t he IMACS to a Fr ame Relay network. T he Frame Relay Network delivers the
SNMP trap to the Operations Center on the right side of the diagram.
5. At the Operations Center, the IMACS, acting as a DSU/CSU, delivers traffic to the router.
6. The router places the SNMP trap onto the appropriate LAN where the NMS resides.
7. The NMS acknowledges and processes the trap. At this point an operator, noticing this new alarm, could initiate
a TELNET session back to the originating IMACS or could browse the MIBs from the NMS.
March 2001 Page 9
Zhone Technologies, Inc. IMACS Product Book, Version 4
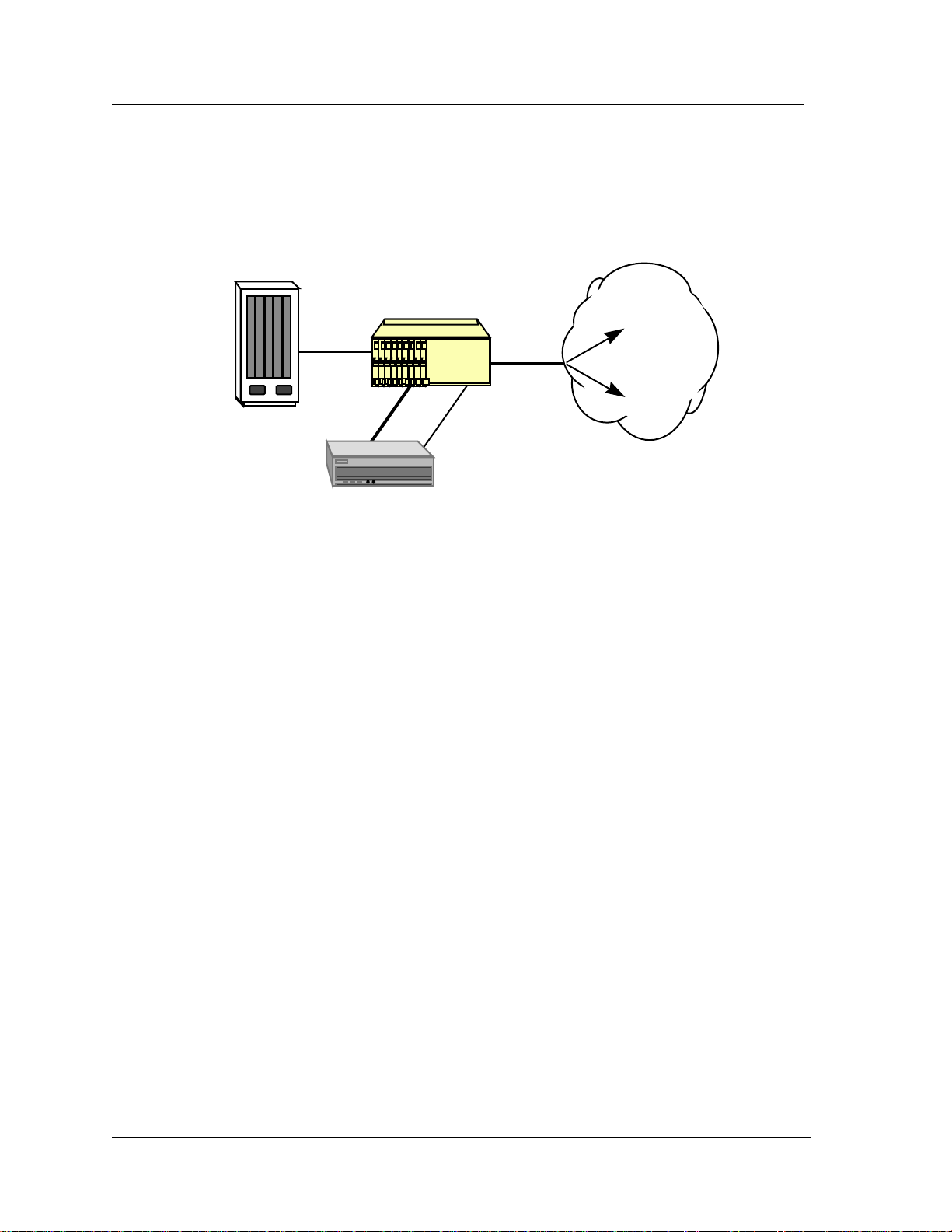
As shown in Figure 4 the IMACS supports multiple methods of communicating SNMP messages and Telnet
terminal sessions between an end node and the network management station. The addition of PPP support allows
the IMACS to connect to routers or terminal servers to establish a connectivity path to the network management
station. The utilization of PPP is similar to that of SLIP.
PSTN
T1/E1
Frame
Relay
PBX
PPP
Router
Figure 4 - SNMP Messages and Telnet Sessions on IMACS
IMACS Management Using FDL/SA4
Another method of transporting IP datagrams is via the Facility Data Link (FDL) on a T1 link using the Extended
Super Frame (ESF) format. The FDL channel is a 4 Kbps channel available on the DS1 frame in the ESF overhead.
The SA4 bits in the frame alignment word of the E1 constitute the equivalent for E1. This method requires that a
DACS II is used in the central office, and is provisioned to extract the FDL / SA4 stream from the T1 /E1 and map it
into a DS0 channel. DS0 channels from each remote node are then transported to an IMACS equipped with a B7R
or MCC card so that IP datagrams can be extracted.
The use of the 4 Kbps FDL to carry management information across the network is illustrated in Figure 6. The
remote IMACS at the top of the figure are terminated in a DACS II. The remote IMACS transport the TCP/IP
management information across the FDL. The DACS II transforms the FDL channel into a DS0 channel using its
proprietary B7R encoding scheme. These DS0s, carrying management information are combined with other DS0s
carrying user information and arrive at the IMACS as shown in the bottom of the figure.
March 2001 Page 10
Zhone Technologies, Inc. IMACS Product Book, Version 4
IMACSIMACSIMACS
FDL over ESF
DACS
Each FDL is mapped
to a separate DS0
T1
IMACS
Concentrator Node
38.4 kbps SLIP
Terminal
Server
NMS
Figure 5 - IMACS Management Using FDL
The management DS0s are connected internally to the B7R card with a limit of eight management DS0s per card.
The output of the B7R card is RS-232 at up to 38.4 Kbps using SLIP. This output is fed into a terminal server or a
router and transported to a NMS. Alternatively, the SLIP Async stream can be connected directly into a locally
attached NMS if a port is available. Furthermore, the MCC server card supports up to 128 remote connections.
IMACS Management Using B7R encoded DS0 (TS 24 for T1 and TS 31 for E1)
A third method is to carry IP traffic in a DS1’s time slot 24 or E1’s time slot 31. This method requires that each
time slot 24/31 from multiple remote nodes are groomed in the network into a single T1, and are transported to an
IMACS equipped with a B7R or MCC card so that IP data can be extracted.
A B7R card or a MCC card is used in the IMACS at the central site to accept and decode SNMP network
management information from up to eight remote IMACS (via separate DS0s) (128 for MCC). The IMACS at the
remote sites can place SNMP traps and other IP traffic in a B7R encoded DS0 (time slot 24/31). A B7R card is not
required at the remote sites. At the central site a B7R/MCC card is required only if the B7R / DS0 transport
mechanism is utilized.
The TCP/IP option must be available to support the B7R function. If the SNMP traps and associated TELNET
sessions are carried in a B7R encoded DS-0 from the originating IMACS (instead of within the FDL), a DACS II is
not required. In this case the NMS data from the originating IMACS is formatted by the remote IMACS’s CPU in
the same B7R format as would have been generated by the DACS II if the FDL scheme was used. In either case, a
B7R or MCC card is required at the NMS concentrator site. The B7R card is a User card, therefore up to eight B7R
cards may reside in an IMACS node, supporting eight DS0s each, for a total of 64 remote sites per IMACS. The
MCC card is a server card, supporting up to 128 remote IMACS nodes. A total of 3 MCC cards are supported per
concentrator node.
March 2001 Page 11

Zhone Technologies, Inc. IMACS Product Book, Version 4
To manage the IMACS containing the B7R card, a separate SLIP/PPP connection from the DB9 on the interface
card is required. The local IMACS cannot route its own SNMP information to an internal B7R card. For example,
if a network has eight remote nodes, two SLIP connections are required at the central site - one for the eight remote
IMACS and one for the local IMACS.
The Management Channel Concentrator (MCC) card allows management of the local system as well as 128 remote
IMACS nodes. The remote systems may either be communicating using B7R on TS 24 (T1) or B4R on TS31 (E1)
directly, via a cross-connect or be using FDL (T1) /SA4 (E1) with a DACS version 6.2 or equivalent. In addition,
the MCC card has also four ports configurable with for a variable number of nx64 kbit DS0s. These can be used to
forward already concentrated IP traffic down to a second MCC card.
Any SNMP manager can receive the SNMP trap and respond by initiating a TELNET session with the originating
IMACS for diagnostics and control. Note that the local and remote reporting feature of the IMACS is disabled if the
TCP/IP network management feature is active. The IMACS supports sending traps up to three SNMP trap servers,
allowing alarms to be sent to multiple network management stations.
However, once the cards are installed and the chassis populated, these identifiers are no longer visible.
March 2001 Page 12

Zhone Technologies, Inc. IMACS Product Book, Version 4
a) E & M card with 2713 Hz Loop back – Module# 811760:
This feature will provide digital loop back (both audio and signaling) when activated by a 2713 Hz tone of specified
level and duration. The requirements are provided by BellCore PUB 42004. When a validated tone is detected the
channel should disconnect the user and provide loop back of signals (audio and signaling) received from the
network. The loop back must be performed without inserting any gain or loss in the path. After tone activation, the
channel shall remain in the loop back mode unless deactivated for a period of 20 minutes (+/- 1 minute) after which
the channel shall automatically revert to the idle (non loop back) mode.
b) (Optional) P-Phone Line card with 8 ports (PPS Module# 812160 and PPO Module#
813160):
The purpose of this feature is to provide an 8-port P-Phone Line card in the Streamline for Host 1.2. The P-Phone
line card is used by Nortel to support transport of P-Phone service. There are two applications of the line card, one
at the Office end (P-Phone Office – PPO), and one at the Station end (P-Phone Station – PPS). Hence, PPO and
PPS are two user cards designed to support connectivity between a Nortel SL-100 PBX or DMS-100 based Centrex
PBX and Nortel M5000 series Electronic Business Sets (P-Phones). The P-Phone is an electronic telephone set
capable of supporting premium Meridian Digital Centrex (MDC) features offered by the local DMS switch. The
data channel allows out-of-band signaling between the P-Phone and the DMS switch. This data channel allows the
user to activate MDC features, such as conference calling by simply pushing keys on the P-Phone set, and for the
DMS to deliver information, such as caller identification, to the P-Phone display. This P-Phone line card encodes the
received out-of-band signaling tones, transports them across the carrier and decodes the digital representation back
to out-of-band tones at the other end. Hence, this line card simply repeats the signaling end-to-end.
The market for P-Phones is by definition limited to Nortel switches and PBXs: DMS100 (Class 5 switch), DMS500
(Combination of Class 5 and a Tandem switch), DMS10 (Lower capacity switch for rural areas) and SL100 (Large
Enterprise PBX).
P-Phones supported include: M5000 series business sets, models M5009, M5112, M5209, M5212 and M5312.
March 2001 Page 13
Zhone Technologies, Inc. IMACS Product Book, Version 4
II. IMACS Chassis and Common Equipment
1. IMACS Chassis and Back Plane
The IMACS is available in three chassis models to meet various space/capacity requirements. They are the IMACS
600 Universal Enclosure, the IMACS 800 Universal Enclosure and the IMACS 900 Universal Enclosure.
IMACS 800 Universal Enclosure
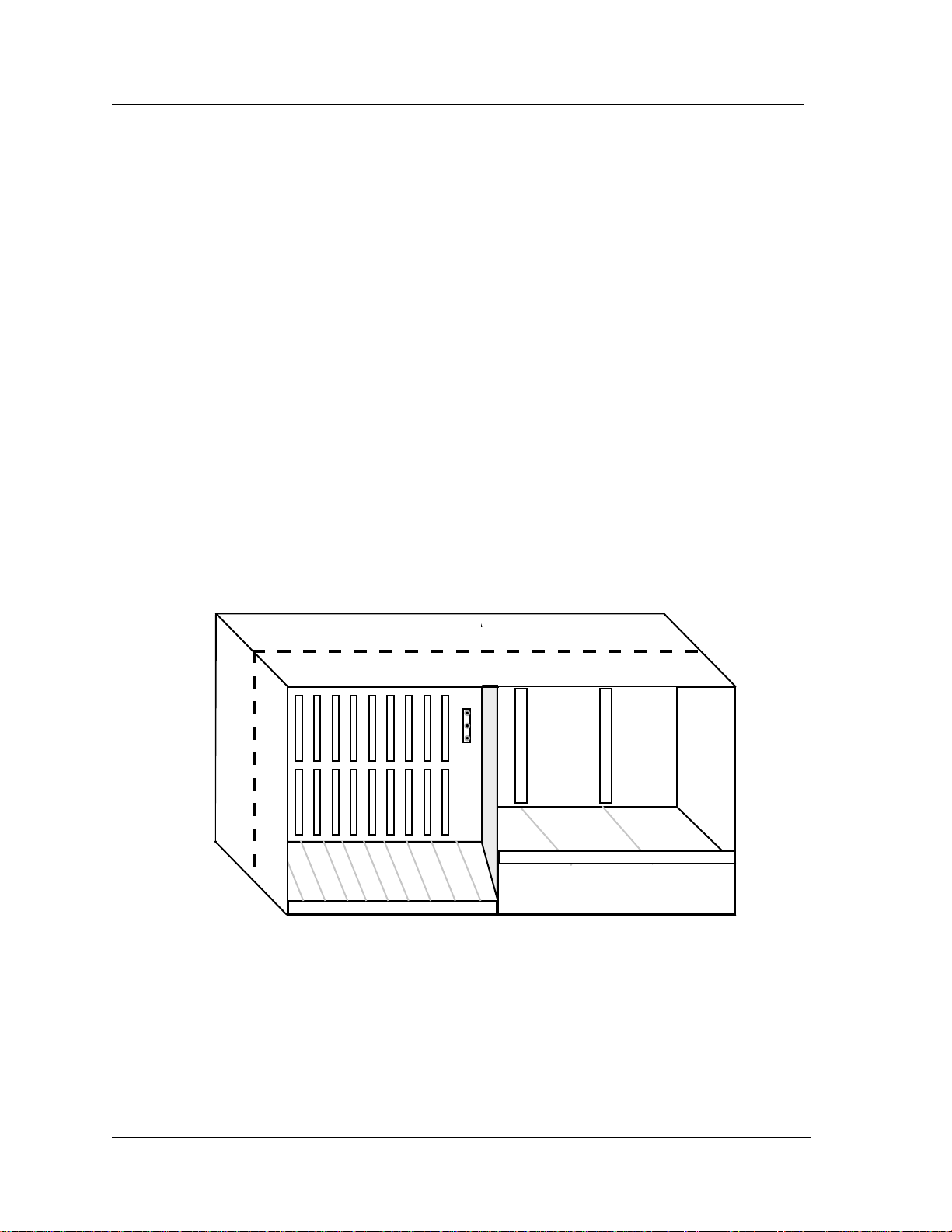
The IMACS 800 Universal Enclosure provides card slots on both the front and back of the unit for both front and
rear loading. These are sometimes referred to as the “Network” and “User” sides respectively. There are nine card
slots that are accessible from the front and an additional nine that are accessible from the back. Card slots are
intended to accommodate specific card types and are keyed so that only those card types may be inserted in those
slots. A CPU card may be inserted in either Slot C1 or C2. Two CPUs can be installed in Slots C1 and C2
simultaneously to provide CPU redundancy. All IMACS Universal Enclosure models are NEBS (TR63) approved.
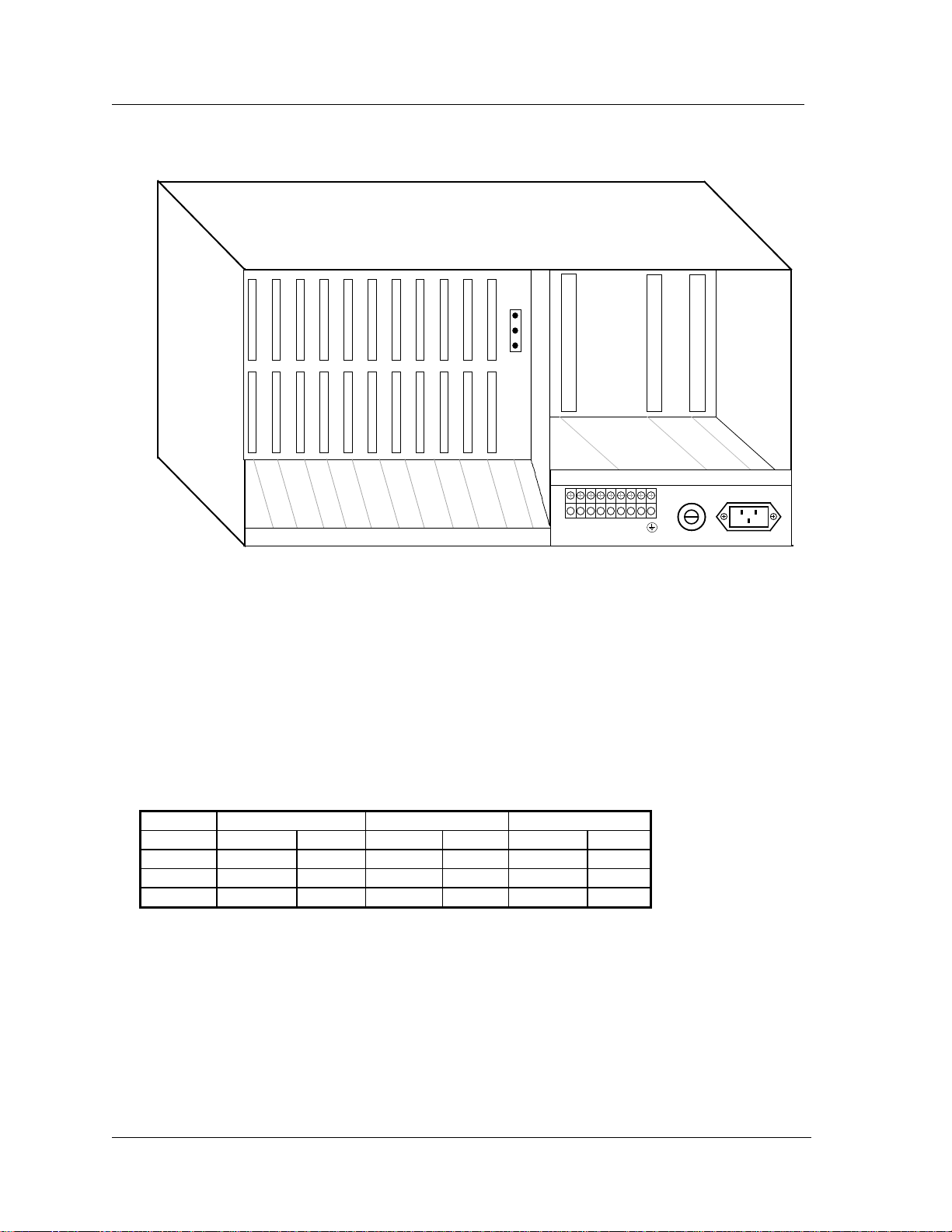
The nine front card slots are allocated and shown in Figure 7 as follows:
Slot Number Card Types Supported
C1 and C2 CPU cards
P1, P2 and P3 Server cards
W1, W2, W3 and W4 WAN cards
JP1
1
2
EUR/US
3
F1 F2
C1 C2 P1 P2 P3 W1 W2 W3 W4
Figure 6 - IMACS 800 Universal Enclosure—Front View
March 2001 Page 14
Zhone Technologies, Inc. IMACS Product Book, Version 4
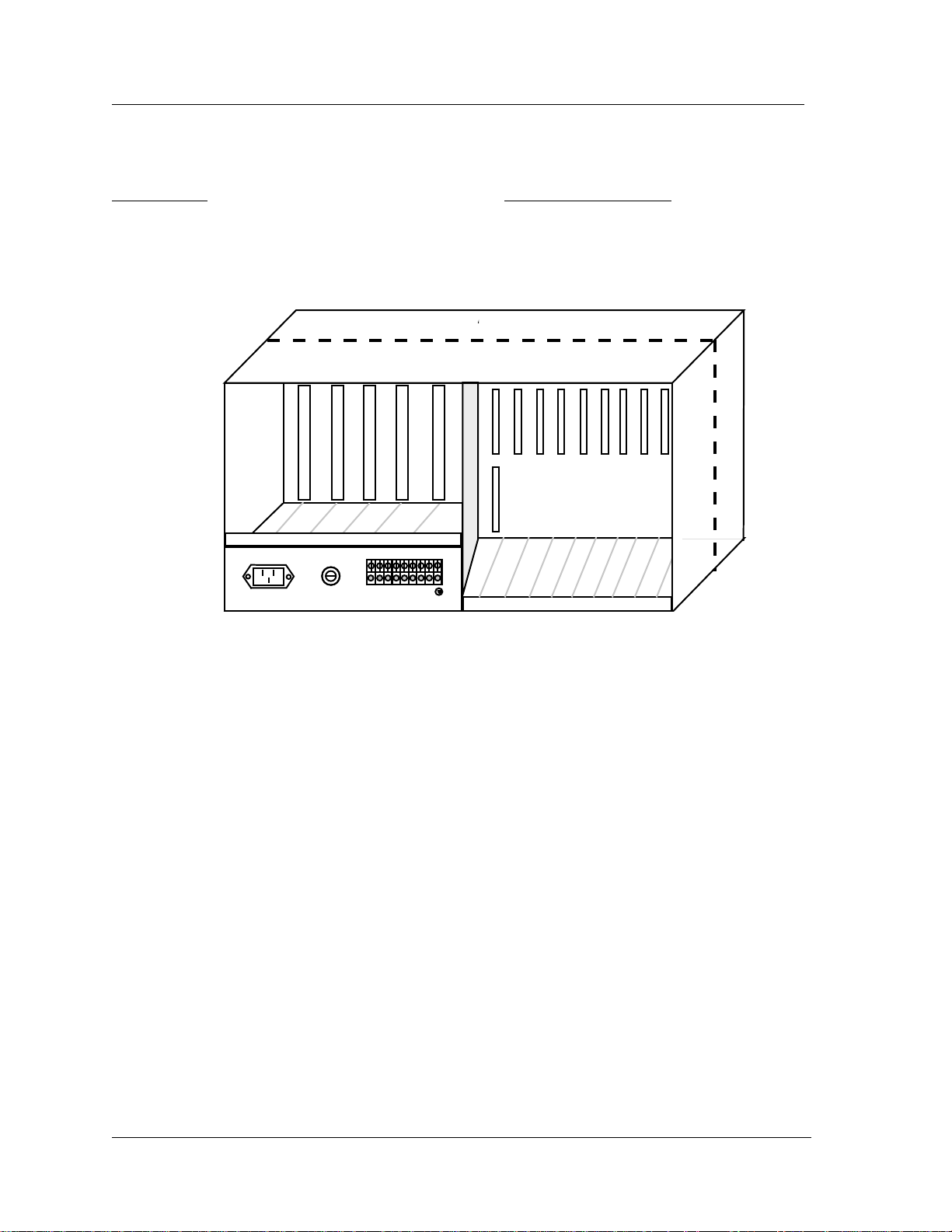
The nine back c ard slots are designated as IF and U 1 through U8 respectively and are allo cated and shown in Figure
7 as follows:
Slot Number Card Types Supported
IF Interface card
U1 through U8 Voice, Data and External Alarm cards
R1 R2 R3 R4 R5
AC
R
+++-- -C
VNVBV
G
R
O
A
M
IF U2U1 U3 U4 U5 U6 U7 U8
Figure 7 - IMACS 800 Universal Enclosure—Rear View
In addition to the card slots described above, the IMACS 800 chassis accommodates a power supply and ringing
generator system. The power and ringing system can consist of up to two power supplies, two 120/240VAC-to48VDC Converters, and up to three ringing generators. Five ringing generators can be supported in a system if there
are no 120/240VAC-to-48VDC Converters installed. The maximum power consumption of an IMACS is 125
Watts. Power supplies are inserted into either of the two power slot positions (F1 and F2) from the front of the
chassis.
The IMACS 800, 900 and 600 models support load sharing power redundancy. To achieve redundancy, the
installation of two identical power supplies is required. The power supply status is reported via LEDs that are
visible through the front panel. Alarm messages are generated when one of the two power supplies malfunctions or
fails.
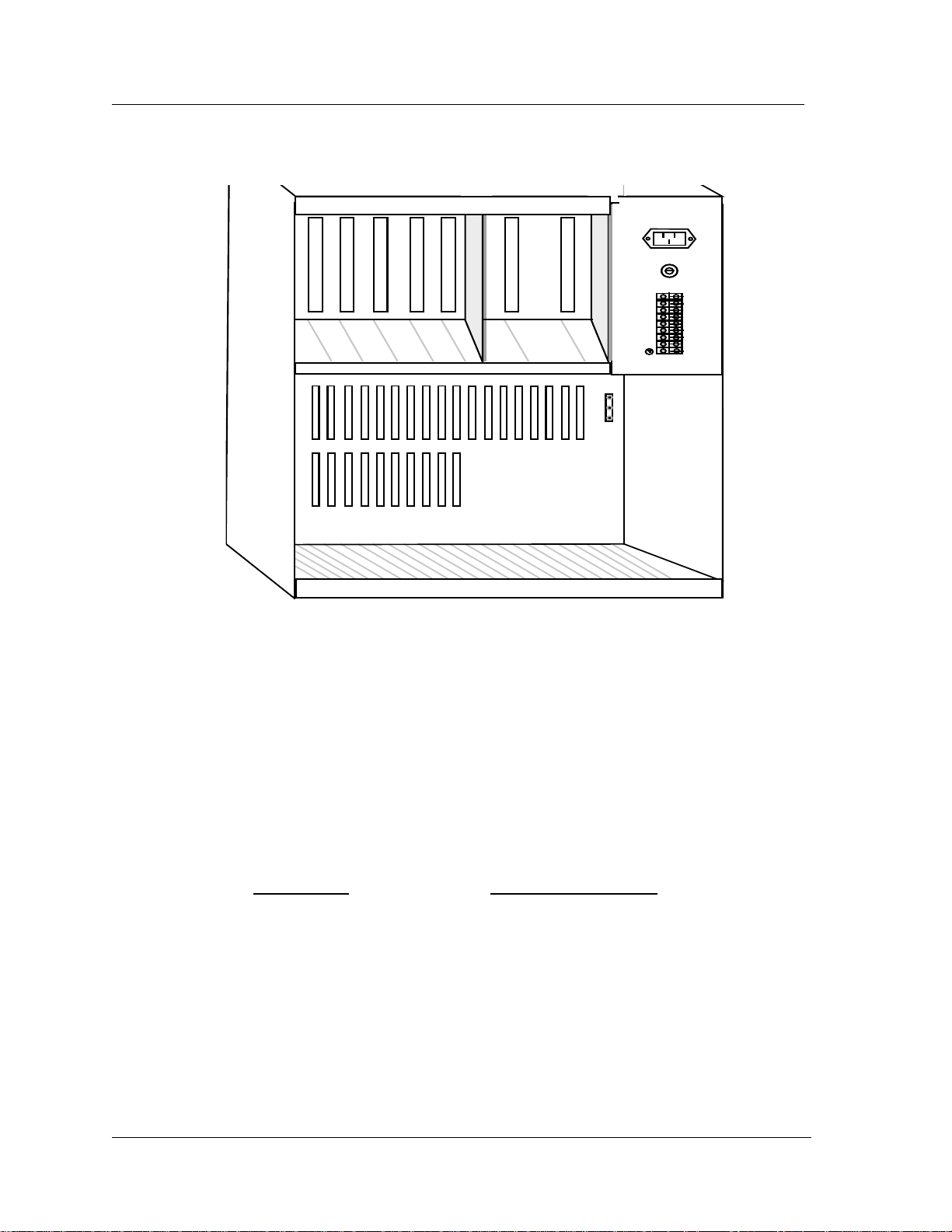
IMACS 900 Universal Enclosure
The IMACS 900 Universal Enclosure has the same capacity as and provides the same module slots in a frontloading only “repackaged” version of the IMACS 800 chassis.
There are nine slots that are referred to as the “Network” cards and an additional nine (9) that are “User” cards
respectively. CPU card installation and slot allocation is the same as the IMACS 800. The nine network card slots
are allocated the same as the IMACS 800 and are shown in Figure 9. The nine user card slots are designated as IF
and U1 through U8 respectively and are the same as the IMACS 800.
March 2001 Page 15
Zhone Technologies, Inc. IMACS Product Book, Version 4
R1 R2 R3 R4 R5 F1 F2
JP1
1
S
U
/
2
R
U
E
3
C1 C2 P1 P2 P3 W 1 W2 W3 W4 IF U1 U2 U3 U4 U5 U6 U7 U8
RGR
V
N
V
A
V
B
COM
AC
+
-
+
+
-
Figure 8 - IMACS 900 Universal Enclosure
In addition to the card slots described above, the IMACS 900 chassis supports the same power supply and ringing
generator system as the IMACS 800. Power supply loading is done the same way as the IMACS 800.
IMACS 600 Front Load Enclosure
The IMACS 600 Universal Enclosure provides card slots only on the front of the unit as shown in Figure 10.
This chassis is ideally suited for wall mount installations. In contrast to the IMACS 800 and 900 Enclosures (where
User, CPU, WAN, and Server Cards were installed in the dedicated card slots), the IMACS 600 chassis allows user
cards to be installed in any unused Server card or WAN card slo t .
Slot Number Card Types Supported
C1 and C2 CPU card
P1-P4 Any Server or User card
W1-W4 Any WAN or User card
IF Interface card
March 2001 Page 16
Zhone Technologies, Inc. IMACS Product Book, Version 4
A
/
JP1
1
S
U
2
R
U
E
3
S1 S2 R1
C1 C2 P1 P2 P3 P4 W1 W2 W3 W4 IF
R
+-- -++
G
VNV
R
C
O
V
B
M
Figure 9 - IMACS 600 Universal Enclosure
In addition to the card slots described above, the IMACS 600 Universal Enclosure accommodates two power
supplies or one AC Power Supply, one AC-DC converter, and one ringing generator.
Physical and Environmental Characteristics
The IMACS Universal Enclosure dimensions are shown in Table 1.
Table 1--IMACS Dimensions
Chassis Height Width Depth
Model in. cm in cm in cm
600 9.120 23.16 17.042 43.29 9.131 23.19
800 9.120 23.16 17.042 43.29 15.300 38.86
900 15.375 39.05 16.918 42.97 9.105 23.13
The IMACS 600/800/900 can be mounted on:
• EIA 19” (482 mm) standard open rack
• Enclosed Cabinet or a WECO 23” (584 mm) standard open rack
• Enclosed Cabinet (by using adapter ears)
• Wall-mounted (with 4 screws)
• Desktop
March 2001 Page 17
Zhone Technologies, Inc. IMACS Product Book, Version 4
All the IMACS units are convection-cooled and require some minimum clearances for optimum operation.
Clearance requirements also account for distance required for removal and insertion of cards from/into the
chassis. The minimum clearances are shown in Table 2.
Table 2—IMACS Minimum Clearances
Front 15” (38 cm) 15” (38 cm) 15” (38 cm)
Back 0” (0 cm) 15” (38 cm) 0” (0 cm)
Top 2” (5 cm) 2” (5 cm) 2” (5 cm)
Bottom 2” (5 cm) 2” (5 cm) 2” (5 cm)
In all cases, the unit must be installed in an environment that meets the following specifications:
AC power (120VAC): 90 VAC to 135 VAC
AC power (120/240 VAC): 175 VAC to 264 VAC
DC power (-48 VDC): -42 VDC to -60 VDC OR-39VDC TO -60VDC
DC power (24 VDC): 20 to 32 VDC OR -18VDC TO 36 VDC
Power consumption: 125 Watts
Operating temperature: 0oC to 50oC (41oF to 121oF)
Storage temperature: -20oC to 80oC (-4 oF to 176oF)
Operating Rel. Humidity: 5% to 85%
The IMACS Universal Enclosures conform to the following regulatory standards shown in Table 3.
Table 3—IMACS Compliance With Regulatory Standards
ANSI 310-D Racks, Panels, and Associated Equipment
UL 459 Telephone Equipment
Bellcore GR-63-CORE Network Equipment-Building System (NEBS), Level 3
Bellcore GR-1089-CORE, Issue 1 Electrical compatibility and electrical safety generic criteria
Bellcore TR-NWT-000295 Issue 2 Isolated Ground Planes: Definition and Application to
CE EN 500 81-1 Electromagnetic compatibility generic emission standard
CE EN 500 82-1 Electromagnetic compatibility generic immunity standard
CE EN 60 950/A2 Safety of information technology equipment including
UL 1459 UL Standard for Safety of Telephone Equipment
CSA C22.2, No. 950, DOC CS03 Safety of information technology equipment including
FCC Part 68 – Subpart B Requirements for Connection of Terminal Equipment
IEC 297-1 Racks, Panels, and Associated Equipment
FCC Part 15 Subpart B
Power Supplies
The IMACS has six power supplies and two ring generators, which can be installed or configured depending on the
application. Power supply models 8901, 8902 and 8907 provide +/-5VDC and +/-12VDC. As shown in table 4, the
main difference between these models is the input voltage.
600 800 900
Requirements: Physical Protections
for network tele communications equipment
Telephone Central Offices
Part 1 Residential, commercial and light industry
Part 1 Residential, commercial and light industry
electrical business equipment
electrical business equipment
Systems and Protective Apparatus to the Telephone Network
March 2001 Page 18
Zhone Technologies, Inc. IMACS Product Book, Version 4
Models 8903, 8905 and 8908 power supplies provide -48 VDC talk battery voltage from an AC input voltage. As
shown in table 4, the difference between models 8903 and 8905 is the input voltage range. Model 8905 has a much
wider input voltage range. Allowing it to operate from any AC line voltage, where as model 8903 has a limited
range. Model 8908 can only be used with the 900 chassis. It also has the benefit of a wide input voltage range but
with the addition of providing 300 watts of talk battery power.
Table 4—Power Supply Specificatio ns
Model 8901 AC Power Supply 120/240 AC
Input Voltage Self-detecting, 90VAC to 135 VAC at 60HZ
175 VAC to 264 VAC at 50 Hz
Input Frequency 47 to 63 Hz
Inrush Surge Current Max. 12 amp peak at 264 VAC cold start
Output Power 55W Continuous
Maximum Number per system 2
Redundancy Optional
Ventilation Convection cooled
Protection Unit is fused and protected from short circuits and over-
voltage
Approvals UL 1459, EN 60950, CSA-C22.2 No.950, CE Mark
Model 8902 DC Power Supply 48 VDC
Input Voltage -39 to -60 VDC
Inrush Surge Current Maximum 12 amp at 60VDC
Output Power 5 5 Watts Continuous
Maximum Number per system 2
Redundancy Optional
Ventilation Convection cooled
Protection
Unit is fused protected from short circuits and overage
Unit is diode protected from reversed polarity
Approvals UL 1459, EN60950, CSA-C22.2 No.950, CE Mark
Model 8907 DC Power Supply 24 VDC,
Input Voltage 18 to 36 VDC
Inrush Surge Current Maximum 12 amp at 36 VDC
Output Power: 55 Watts Continuous
Maximum Number per system 2
Redundancy Optional
Ventilation Convection cooled
Protection
Unit is fuse protected from short circuits and over-voltage
Unit is diode protected from reverse polarity
Approvals UL 1459, EN60950, CSA-C22.2 No.950, CE Mark
Model 8903 Power Supply 120 VAC
Input Voltage 90VAC to 132 VAC
Input Frequency 60 Hz
Inrush Surge Current Max. 20amp peak at 132 VAC cold start
Output Voltage -48.0 VDC
Maximum Number per system 2
Redundancy Optional
Ventilation Convection cooled
Protection Unit is fused and protected from short circuits and over-
voltage
Approvals UL 1459, UL 1950, CSA-C22.2 No.950
March 2001 Page 19
Zhone Technologies, Inc. IMACS Product Book, Version 4
Model 8905 Power Supply, 120/240 VAC
Input Voltage 90 Vrms to 260 Vrms
Input Frequency 50/60 Hz
Output Power 100W max
Output Voltage -48.0 VDC
Output Current 2 amp
Maximum Number per system 2
Redundancy Optional
Ventilation Convection cooled
Approvals UL 1459, UL 1950, CSA-C22.2 No.950, CE Mark
Model 8908 Power Supply, 105/240 VAC
Input Voltage 90 Vrms to 260 Vrms
Input Frequency 50/60 Hz
Output Power 300 W max
Output Voltage -48.0 VDC
Output Current 6.25 amp
Maximum Number per system 2
Redundancy Optional
Ventilation Forced Air, (120mm Fan)
Approvals UL 1459, UL 1950, CSA-C22.2 No.950
Ring Generator
Ring generators are required to supply ringing current whenever there are Foreign Exchange Station (FXS) Cards
operating in the unit or if there is one or more Foreign Exchange Office (FXO) ports that are used in Manual Ring
Down (MRD) mode.
• The current ring generator model is: Model 890620
Model 890620,the internal ring generators, will support up to 24 simultaneously ringing phones. Additional ringers
can be added depending on the chassis and application, (see table 5). The exact number of simultaneously ringing
subscriber lines supported is a function of the Bell Ringer Equivalency Number (REN) of the attached devices and
the loop impedance. The user may attach an external ring generator to the IMACS terminal block location marked
RGR.
The model 890620 is an enhanced version of the current 8906 ring generator. This model has improved operating
efficiency and inrush current limiting.
Table —Ring Generator Specifications
Model 890620 Ringing Generator
Input Voltage 42 to 57 VDC, linear = 0.84 max.
Efficiency 57% at 48 V and 1 kOhm load
Protection 5 A slow blow fuse, primary current limiting
Noise Less than 32dBrnc
Output Voltage 100 VDC rms default – adjustable from 60 to 105 Vrms
Output Current 160 mA RMS continuous, 230 mA RMS cadence
Output Frequency 20 Hz +/- 1 Hz
Operational Modes Strap selectable: Master or Slave
Maximum Number per system IMACS 600
IMACS 800
IMACS 900
Redundancy There is no provision for Maste r Ringer redundancy, however
1
1 Master, 3 slaves (DC operation)
2 slaves (AC operation)
1 Master, 1 slave
the slave units provide fail-over protection
March 2001 Page 20

Zhone Technologies, Inc. IMACS Product Book, Version 4
Ventilation Convection cooled
Approval UL 1459, CSA-C22.2, No. 950
March 2001 Page 21

Zhone Technologies, Inc. IMACS Product Book, Version 4
2. CPU Cards
The CPU card has two micro-controllers, which perfo rms most of the configuration, management, and common
processing for the IMACS. The CPU card provides the interconnecti on of WAN/User/Ser ver TDM buses through a
bus connect or cross-connect function. The CPU can have flash memory which is used to store configuration
information and facilitates new firmware uploads. The IMACS can have up to 2 CPU cards, which provide
redundant control and switching capabilities. If the primary CPU fails, the standby takes over.
There are two microprocessors on the CPU card. The primary micro-controller on the CPU card does the
configuration and maintenance functio ns for the IMACS. It is connected thro ugh an internal bus to a ll the
Server/WAN/User cards and the Interface card. It controls the modem, database, serial terminal interfaces, and
Stratum 4 clock configuration contained on the Interface card. The CPU is responsible for configuring the hardware
residing on the cross-connect module (CCM), and configuring hardware on WAN/User cards. It is responsible for
downloading configurations onto intelligent cards thro ugh the appropriate configuration interface. Finally, it
accesses each WAN card to process FDL messages. The CPU provides control functionality, however it is the
Interface card that stores the system configuration information.
The second micro-controller handles standard signaling processing for voice app l ications. It manages b oth the
digital (bit-robbed) and the analog (48V) signaling capabilities of the IMACS. It has enough throughput and
interfaces to handle the 62 voice channels routed through the A and B buses. The CPU receives signaling from each
analog voice port and in turn processes the data and generates the appropriate signaling bits over the signaling
highway to the WAN cards. The WAN cards then embed the signaling bits into the T1/E1 data stream. It also
processes the signaling from the T1/E1 link to the User cards. The CPU can also customize the format of the
signaling bits. This is an important feature when interfacing with a variety of central office switches and PBXs.
Additionally, the CPU card has an interface to the IMACS’ time slot switching matrix. The switching matrix may
either be a Bus connect (BCON) or Cross Connect (XCON). In the Bus connect configuration, the User bus ports
can be connected to WAN bus ports but not the Server bus. When Cross-connect is used, all the TDM buses are
brought up to t he switching matrix, which is able to cross-connect time slots between the incoming and outgoing
buses.
CPU cards can only be installed in the CPU slots. The shelf can be equipped with two CPUs, which form an
active/standby pair. Watchdog timer circuitry on the Interface card helps monitor the active CPU and will activate
the standby CPU if the active CPU fails. The active and standby CPUs communicate directly and the active can
switch to standby by sending a single message. Additionally, a user can manually switch from the active to standby
CPU by initiating a command from the VT-100 console. It is the CPU card, which initializes the system upon
power-up and runs a self-test on all cards plugged into the system. After the initialization procedure, the CPU card
continuously polls all cards in the system to determine their operating status. Table 7 provides detailed
specifications on the five CPU models.
March 2001 Page 22
Zhone Technologies, Inc. IMACS Product Book, Version 4
Table 7—Operational Modes
Model Mode Cross Connect Drop and Insert Terminate
880060 Bus-connect No Yes Yes
880460 Enhanced bus-
connect
880160, 880260,
880360
LED Indicators
Code Storage
Models 880060, 880160, 880460 256K EPROM
Model 880260 512K EPROM
Model 880360 Configurable with maximum 8MB DRAM and 4MB Flash memory
Maximu m number of WA N links
Model 880060 Up to 2 WAN links
Model 880160, 880260, 880360 Up to 8 WAN links
Model 880460 Up to 4 WAN links. WANs in slot W1 supports voice only operate in
Support for CPU redundancy
Model 880060 No
Model 880160, 880260, 880360,
880460
Support for WAN link redundancy
Model 880060 No
Model 880460 1:1—A WAN card in slot W2 provides backup for an identically
Model 880160, 880260, 880360 1:N—A single model 8014 WAN card in slot W4 provides backup for
Support for Server Cards
Model 880060, 880460 No
Model 880160 Only ADPCM Server card
Model 880260, 880360 Support for all server cards
Standards Conformance
Bellcore GR-63-CORE Network Equipment-Building System (NEBS) Requirements: Physical
CE EN 500 81-1 Electromagnetic compatibility generic emission standard Part 1
CE EN 500 82-1 Electromagnetic compatibility generic immunity standard Part 1
CE EN 60 950/A2 Safety of information technology equipment including electrical
UL 1950 UL Standard for Safety of Information Technology Equipment
CSA C22.2, No. 950 Safety of information technology equipment including electrical
Cross-connect Yes Yes Yes
No Yes Yes
Green for normal operation. Amber for card fault or test mode (amber
on new cards).
either Terminate or Drop and Insert mode. WANs in slot W3 operate
in Terminate mode only and only terminate certain data ports.
Yes
configured WAN card in slot W1. A WAN card in slot W4 provides
backup for an identically configured WAN card in slot W3.
identically configured 8010 WANs in slots W1 through W3.
Protections
Residential, commercial and light industry
Residential, commercial and light industry
business equipment
business equipment
March 2001 Page 23

Zhone Technologies, Inc. IMACS Product Book, Version 4
3. Interface Cards
The Interface card has common hardware, which is managed by the active CPU card. One Interface card is required
per system residing in Slot IF on the IMACS chassis. It provides the physical interface to support a modem, control
terminal, printer, alarm relay, and provides the connection up to 8 T1/E1 interfaces used by the WAN cards. The
card also contains the clock hardware, which provides the entire back plane timing signals for the TDM buses. The
Interface card also contains the configuration database of the IMACS, time of day clock function and watchdog
timer.
The database resides in non-volatile SRAM, which enables it to retain its information even when the card is
unplugged or the IMACS is p owered down. The IMACS has software configurable settings for both the primary
and secondary system-timing clocks. If the primary clock fails, the system will automatically switch to the operator
defined secondary clock source. The interface card contains the Stratum 4 clock hardware for providing internal
timing. Other timing options include: timing off the WAN card; timing off an installed ATM server card and timing
off an installed 826070 or 826171 BRI card. It also has an option for external timing from external synchronization
clocks (892260 IF card).
The Interface card may have a Modem port that is used to connect an ITU V.22 internal dial modem to a standard
telephone line. This port may be used either to log into the unit from a remote VT100 terminal or to send system
alarms to a remote device. The modem port presents an RJ11 female connector.
The node port on the Interface card provides the form-C contact closure and the physical interface so that the Alarm
Cut-Off (ACO) alarm may activate an external alarm system. The node port presents an RJ48 female connector
with an RS485 electrical interface.
The Control Terminal port is used to connect a VT100 or compatible terminal to the IMACS system for node
management and control purposes. The Control Terminal port presents an RJ48 female connector with an RS232
DCE electrical interface. The port is set to VT100 mode for asynchronous operation at 9600 bps with 8 data bits, 1
stop bit, and no parity. Also, the port supports an automatic log out feature after 15 minutes of inactivity.
The Computer Port connects a local device for printing alarms or can be configured to support SLIP for transport of
SNMP management information or database configuration information. IMACS Release 5.x provides support of
asynchronous PPP and SLIP. The computer port presents a DB9 male connector with an RS232 electrical interface.
The Interface card also stores ISDN Call profiles and signaling translation tables. All configuration information is
stored on the Interface card NVRAM for non-volatile storage of system configuration. A copy of the system
configuration is stored on the Interface card can be downloaded to the Flash memory on the CPU card. There are
eight Interface card Models:
1. 892060 Eight port T1/E1 Interface Card, 2400bps modem
2. 892160 Eight port T1/E1 Interface Card, no modem
3. 892260 Eight port T1/E1 Interface Card, no modem, with external sync input
4. 892360 Eight port T1/E1 Interface Card, 2400bps modem
5. 892460 Eight port T1/E1 Interface Card, no modem (required for CPU 8803)
6. 892560 Two port T1/E1 Interface Card, no modem or DB9 port
7. 892660 Two port T1/E1 Interface Card, 2400bps modem
8. 892760 Two port E1 Interface Card, no modem
The 8920 Interface Card supports eight T1 or E1 WAN links, via a 50-pin Amphenol connector. The card has a DB9 serial port for network management and two RJ48 jacks: one for an RS 485 node port and one for an RS-232 VT100 control terminal port. There is a RJ-11 modem port as well. It supports eight T1 or E1 WAN links. The
March 2001 Page 24

Zhone Technologies, Inc. IMACS Product Book, Version 4
892160 Interface Card is the same as the 892060 Interface card with the exception of the modem and can be used
with the 880060, 880160 and 880460 CPU cards.
The 892260 Interface Card is similar to the 892460 except there is an external synchronization option, no node port
and the DB-9 serial port is a DTE-male type. The external synchronization option is for support of up to 8 T1
Framed or E1 Unframed signals and this card can be used with the 880260 and 880360 CPU cards.
The 892360 Interface Card supports eight T1 or E1 WAN links, via a 50-pin AMP connector. The card has 128KB
of NVRAM, a DB9 serial port for network management and three RJ48 jacks that connect to the modem, nodal port
and VT-100 control terminal port.
The 892460 Interface Card supports the same functionality as the 892360 Interface card except that it has no internal
modem port. It requires an 880360 CPU and 5.X.Y CPU firmware.
The 892560 Interface card supports one or two T1 or E1 WAN links via 2 RJ-48 jacks and includes a single RJ-48
jack for a VT100 control terminal. Additionally, two sets of Bantam jacks are available for monitoring each WAN.
This interface card does not
The 892660 Interface card supports one or two T1 or E1 WAN links via 2 RJ-48 jacks. The 892660 includes a
single RJ-48 jack for a VT100 control terminal, an RJ11 port for an internal 2400 bps, and a DB9 port.
Additionally, two sets of Bantam jacks are available for monitoring each WAN. This interface card does not support
WAN redundancy.
The 892760 Interface card supports two E1 WAN links via 2 BNC connectors. The 892760 includes a single RJ-48
jack for a VT100 control terminal, an RS 485 Node Port and a DB9 port. Table 8 provides a detailed list of the
Interface Cards’ specifications.
support WAN redundancy.
March 2001 Page 25
Zhone Technologies, Inc. IMACS Product Book, Version 4
Table 8—Interface Card Specifications
Model 892xxx Interface Cards Configuration Storage CPU Host Firmware compatible
Models 892060, 892160, 892560,
892660 and 892760
Models 892260, 892261, 892360
and 892460
Interfaces
Model T1/E1
Links
Computer Port
(DB-9)
32KB NVRAM 3.x.y
128KB NVRAM 4.x.y, 5.x.y
Control
Terminal
Node Port Internal
Modem
External Sync
Interface
Port
892060 8 T1/E1 YES YES YES YES NO
892160 8 T1/E1 YES YES YES NO NO
892260 8 T1/E1 YES YES YES NO YES
892261 8 T1/E1 YES YES YES NO YES
892360 8 T1/E1 YES YES YES YES NO
892460 8 T1/E1 YES YES YES NO NO
892560 2 T1 NO YES YES NO NO
892660 2 T1 YES YES NO YES NO
892760 2 E1 YES YES YES NO NO
WAN Ports
Electrical Interface G.703 or DSX-1
Model Connector Type
892060, 892160, 892260, 892261, 892360 and 892460 One Female 50-pin RJ-27X Telco connector
892560 and 892660 Two Female RJ-48 connector
892760 Two Pair Female BNC connector
All Models prior to Rev CO DB9F DCE (requires 1201 cable)
All Models from Rev CO DB9M DTE (requires 1202 cable)
Electrical Interface RS-232, ITU-T V.28
Function Connects to local Element Management System
Code Set 8 bit characters plus one start and one stop bit with no parity
Max Speed 19.2Kbps (PPP) or 9.6Kbps (SLIP)
March 2001 Page 26

Zhone Technologies, Inc. IMACS Product Book, Version 4
Table 8—Interface Card Specifications (continued)
Control Terminal Interface Port
Connector RJ-48F, 8 pin, EIA 561
Electrical Interface DCE RS232, ITU-T V.28
Function Connect local VT100-compatible Control Terminal (local craft interface on the
892260)
Speed Maximum 9,600 bps asynchronous
Code Set 8 bit characters plus one start and one stop bit with no parity
Node Port
Connector RJ-48F, 8-pin
Electrical Interface Dry contact
Alarm Output Passive current loop, one normally open loop and one normally closed loop
Function Alarm management between co-located IMACS nodes and external alarm
management systems and panels
Modem Port
Connector Female 6-pin RJ-11c socket
Electrical Interface 600 ohm 2-wire balanced
Protection HV zener, 0.25A fuses on Tip and Ring
Function Con nect internal modem to PSTN for access to remote operato r and remote EMS
Modem Specifications
Compatibility ITU-T V.22 bis
Modulation 16 point QAM
Line interface 2-wire balanced 600 ohm
Ringer Equivalence 0.2 A
Approval FCC Part 68
Equalization Recei ve automatic adaptive, transmit fixed co mpromise
Transmit Level -9.5 dBm
Receiver Sensitivity On to OFF threshold -4.5dBm, OFF to ON threshold -48 dBm
Dialing Mode DTMF Tone
Speed Supported 2,400 bps asynchronous
Code Set 8 bit characters plus one start and one stop bit with no parity
Adapters
Model 1106 with 2 BNC
connectors
Model 1121 with 2 RJ48 sockets Supports 2 T1 or E1 circuits on twisted pair cable plus bantam jacks for test
Model 1181 with 8 RJ48 sockets Supports 8 T1 or E1 circuits on twisted pair cable
Model 1184 with 16 BNC sockets Supports 8 E1 circuits (suitable for IMACS 800)
Standards Conformance
Models 892060, 892360, 892660 only
network management system
Model 892060, 892360, 892660 only
Supports 1 E1 circuit on 75 ohm coaxial cable (RG59)
ITU-T V.28 Electrical characteristics for unbalanced double-current interchange circuits
ITU-T G.703 Physical/Electrical Characteristics of Hierarchical Digital I/F
ITU-T V.22 bis 2400 bits per second Duplex Modem Using the Frequency Division
Technique
EIA 56 8-Position Non-Synchronous Interface between DTE and DCE Employing
Serial Data Interchange
March 2001 Page 27

Zhone Technologies, Inc. IMACS Product Book, Version 4
Table 8—Interface Card Specifications (continued)
EIA RS232-C Interface between DTE and DCE Employing Serial Binary Data
Bellcore GR-63-CORE Network Equipment-Building System (NEBS) Requirements: Physical Protections
CE EN 500 81-1 Electromagnetic compatibility generic emission standard Part 1 Residential,
commercial and light industry
CE EN 500 82-1 Electromagnetic compatibility generic immunity standard Part 1 Residential,
commercial and light industry
CEN EN 60 950/A2 Safety of information technology equipment including electrical business
equipment
FCC Part 68
DOC CS03
UL 1459 UL Standard for Safety of Telephone Equipment
UL 1950 UL Standard for Safety of Information Technology Equipment
CSA C22.2, No. 950 Safety of information technology equipment including electrical business
Requirements for Connection of Terminal Equipment Systems and Protective
Apparatus to the Telephone Network
equipment
4. WAN Cards
The WAN cards manage the flow of data through the integrated access system network. It provides the logical and
electrical interface to high-speed digital facilities, which are typically physically connected via the Interface card.
WAN cards take the data off the bus, which was put there by the User and Server cards, and transmit the information
over a WAN link. A WAN link is typically a T1, E1, DSX-1, or HDSL facility connection. This WAN link can be
either user or network link. In combination with the CPU card, the WAN card provides E1 to T1 and T1 to E1
conversion.
The WAN Cards also provide performance statistics. They are stored in memory on the IMACS’ host CPU card and
retrieved upon command. The performance statistics are gathered and displayed in 15-minute intervals and retained
for 24 hours. In the T1 environment, an error is defined as any CRC-6, Controlled Slip, or Out of Frame (OOF)
error for ESF framing, and any Bipolar Violation (BPV), Controlled Slip, or OOF error for the D4 format. In an E1
environment, an error is define d as any CRC-4 error, Controlle d Slip, or OOF error.
In the AT&T mode, two sets of registers (user and network) accumulate performance data for T1 WAN links. It is
possible to view both the user and network registers, but the end user can only clear the user registers. The network
only has access to the network registers, and can only clear those registers. The ANSI and E1 WAN links have only
one set of registers.
For further information regarding performance, and integrated test capabilities such as loop backs, BERT Tests and
Signal Quality please see Section 13, IMACS System Testing and Diagnostics.
Each port on the WAN cards can be individually configured with DSX/CEPT or CSU plug-in modules. Both CSU
and DSX modules are used to connect to T1 facilities operating at 1.544 Mbps. The CEPT module is used for
connection to a 2.048 Mbps E1 facility. All WAN interfaces comply with the appropriate North American and
international standards. Those cards equipped with CSU or DSX/CEPT modules also act as the “near end”
termination points for the Subscriber Loop Carrier (SLC-96) facilities defined in BellCore publication
TR-TSY-000008, Issue 2, August 1987. Each WAN card can operate in dual channel bank, drop and insert, or full
digital cross-connect mode and can perform T1-E1 conversion, including PCM A-Law to µ-Law conversion. When
fully populated with 4 dual WAN cards, the IMACS supports 8 T1 or E1 connections, in any combination of T1
(DSX1 or DSX1 with CSU) , E1 (CEPT) and HDSL interfaces.
The DSX/CEPT and CSU Modules are used to connect to T1 facilities, which operate at 1.544 Mbps. The CEPT
function of the DSX/CEPT module is used internationally for connection to a 2.048 Mbps E1 network. The HDSL
module provides a high-speed digital subscriber line (HDSL) interface.
Each WAN card slot has eight leads connected to the Interface card slot, which can be used to support facility
interfaces. The last WAN slot has all the WAN connections from the other three slots in addition to its own to
support the WAN redundancy feature. The WAN card in the last slot can substitute for one of the other WAN cards.
March 2001 Page 28

Zhone Technologies, Inc. IMACS Product Book, Version 4
There are four highways dedicated to the WAN slot, which are used to carry TDM data and signaling. Each WAN
slot is connected to the Interface card through the back plane.
The IMACS supports six models of WAN cards:
1. 800060 Single T1/E1 WAN card
2. 801060 Dual T1/E1 WAN Card
3. 801460 Dual T1/E1 WAN Card with Relays
4. 801160 Dual E1 HDSL WAN Card
5. 801560 Dual T1 WAN card with ESF loop back
6. 802060 PairGain HDSL T1 WAN Card
The 800060 Single T1/E1 Link Card is the basic WAN Card. It has a single port for DSX/CEPT or CSU modules.
The 801060 Dual T1/E1 WAN card has two ports for either DSX/CEPT or CSU operation or a combination of the
two. Both ports of this card must be populated with either the DSX/CEPT or CSU module.
The 801460 Dual T1/E1 Link Card with Relays can be used in systems with Cross Connect CPUs to act as a
redundant card (1:N redundancy) for up to three standard WAN cards. Both ports of this card must be populated
with either the DSX/CEPT or CSU module and must be an exact match to any WAN Cards with which it is
redundant.
The 801560 WAN card with ESF Loop back is able to detect ESF data link codewords for line and payload activate
and deactivate commands and the universal loop back deactivate command. A minimum reception of 10 continuous
command patterns by each channel is required to trigger the loop back detection process, and the performing of the
command. Since all 8 channels (4 WAN cards) are processed by one processor on the CPU card, simultaneous
detection on more than one channel requires more than 10 repetitions.
The 802060 Pair Gain HDSL WAN is a dual WAN card designed to support the North American (T1) market using
the PairGain HDSL OEM module (HOM). This also supports 4:1 redundancy as well as user configurable HRU
functionality relative to HDSL timing. The IMACS can support up to four (4) 802060 WAN cards simultaneously
and can be configured, monitored and tested through the IMACS craft interface and/or through the SNMP MIB
interface. This design supports two PairGain HDSL modules per card for either IMACS to IMACS configurations
as well as IMACS to PairGain NTU configurations.
There must be one primary and one subordinate in the circuit. The unit designated as the primary can be accessed to
change system parameters and view HDSL system performance history and current status. The subordinate
provides HDSL system performance history and current status. The subordinate unit receives configuration
parameters from the master unit at the other end of the loop. These configuration parameters include: Timeout for
loop back, DS1 line code option (e.g. B8ZS/AMI), DS1 framing format (e.g. SF/ESF). The 802060 HDSL WAN
module is supported by IMACS HOST 5.1 (or greater).
For connection to T1/E1 facilities, a DSX/CEPT or CSU Plug-in module is required per WAN port. The available
modules are:
• 811 T1-DSX/E1-CEPT Plug-in Module (transmission range is 655 ft.)
• 812 T1-CSU Plug-in Module (transmission range is 3000 to 6000 ft)
• 82030 2*1168Kbps E1 HDSL Module (compliant with ETSI ETR-152)
• 82100 Dual T1 HDSL Module
These plug-in modules are mounted on the WAN cards for operation. The 811 T1-DSX/CEPT plug-in module
supports either DSX or CEPT modes. Jumper / shorting pin settings on the module specify DSX or CEPT
operation. The 812 CSU plug-in module is required for T1 Channel Service Unit (CSU) operation. It can be
operated in D4, ESF, SLC96 or SLCD4 mode.
The 801160 Dual E1-HDSL WAN Card has two ports that are equipped with E1-HDSL modules from ADTRAN.
The HDSL modules provide 2.048 Mbps E1 transmission over 2 copper pairs. It provides transport of data at an E1
rate over copper cable without mid-span repeaters or conditioning. For connection to copper loops, one HDSL
module is required per WAN port.
Each module may be configured as primary or subordinate.
March 2001 Page 29

Zhone Technologies, Inc. IMACS Product Book, Version 4
The 802060 Dual T1 HDSL WAN Card has two ports that that are equipped with 82100 T1 HDSL modules. The
HDSL modules provide 1.544 Mbps T1 transmission over 2 copper pairs. Both modules have to be installed for
proper operation and do not support redundancy. Table 9 depicts the various T1/E1 WAN card specifications. In
addition to the specifications listed in Table 9 (below) the 802060 card is in conformance with ITU-T Q.421 and
ITU-T Q.422. The transmission range is software selectable for the following: 0, 133, 266, 399, 533 or 655 ft. (up
to 200 meters), and CSU (allowing connections to the equipment side of a co-located external CSU over a short
distance, four-wire cable). Software selectable line build out (LBO) settings are also available for all of the
aforementioned transmission ranges.
Table 9—WAN Card Hardware Specifications
Model Number of Ports Number of
Cards
800060 1 1 to 4 Through 892xxx I/ F
801060,
801460
801560 2 1 to 4 Through 892xxx I/ F
802060 2 1 to 4 Through 892xxx I/ F
801160 2 1 to 4 Through 892xxx I/ F
T1 Signal Format
Electrical Interface
Frame Format D4, ESF, Subscriber Loop Carrier (SLC) 96, SLCD4
Line Coding AMI or B8ZS
Signaling AT&T 43801, 62411, ITU-T, Q.421, Q.422 using Robbed-bit method
Error Detection CRC-6, Controlled Slip, Bipolar Violation, Out of Frame
Alarm Indication BellCore TR-TSY-000191
SLIP Limit 126 bits or 138 bits
Bit Rate and Tolerance 1.544Kbps +32PPM. Jitter complies with ANSI T1.403
E1 Signal Format
Electrical Interface
Coding HDB3
Framing ITU-T G.704 Timeslots consist of 8 bits. Frame consists of 32 time slots,
Signaling CAS, CCS In Timeslot 16 if required.
Error Detection CRC-4, Controlled Slip, Out of Frame
Alarm Indication ITU-T G.732
Performance and Test Options
Loop backs Line, local, channel, loop back generation and detection
T1 FDL in accordance with AT&T 54016 or ANSI T1.403 (8015 only)
E1 National Bit Supporting (G.704)
Standards Conformance
AT&T TR43801 Digital Channel Bank Requirements & Objectives
AT&T TR54016 Requirements for Interfacing Digital Terminal Equipment to Service
AT&T TR62411 Accunet T1.5 Service, Description and Interface Specifications
AT&T TR41449 ISDN Primary Rate Interface Specification
BellCore TR-TSY-000008 Digital Interface Between the SLC 96 Digital Loop
BellCore TR-TSY-000191 Alarm Indication Signal, Requirements and Objectives
2 1 to 4 Through 892xxx I/F
ANSI T1.102/T1.403, DSX-1, balanced 100 Ω
G.703 balanced 120 Ω or unbalanced 75 Ω
Multi-frame consists of 16 frames
CAS Signaling protocols: AT&T 43801, 62411, ITU-T Q.421 (2)
Employing the Extended Superframe Format
Physical Interface Electrical Interface
811 (T1-DSX/E1-CEPT)
card
card
card
card
card
812 (T1-CSU) - 1 per port
811 (T1-DSX/E1-CEPT)
812 (T1-CSU) - 1 per port
811 (T1-DSX/E1-CEPT)
812 (T1-CSU) - 1 per port
82100 is used to provide 1 T1
HDSL interface
82030 provides 2*1168Kbps E1
HDSL module. Required for each
port.
March 2001 Page 30

Zhone Technologies, Inc. IMACS Product Book, Version 4
Table 9—WAN Card Hardware Specifications (continued)
ANSI T1.101
ANSI T1.107
ANSI T1.403 ISDN, Network-to-Customer Installation -DS1 Metallic I/F
ANSI T1.408 ISDN Primary Rate
FCC Part 68
ITU-T G.703 Physical/Electrical Characteristics of Hierarchical Digital I/F
ITU-T G.704 Synchronous Frame Structure Used at Primary and Secondary Hierarchical
ITU-T G.735 Characteristics Of Primary PCM Multiplexed Equipment Operating at 2048
ITU-T G.732 Characteristics of Primary PCM Multiplexed Equipment Operating at 2048
ITU-T G.736 Characteristics of A Synchronous Digital Multiplex Equipment at 2048 Kbps
ITU-T G.823 The Control of Jitter and Wander Within Digital Networks Which Are Based
ITU-T G.824 The Control of Jitter and Wander Within Digital Networks Which Are Based
Bellcore GR-63-CORE Issue 1 Network Equipment-Building System (NEBS) Requirements: Physical
Bellcore GR-1089 ESD Sec 2, EMC Sec 3,
CE EN 500 81-1 Electromagnetic compatibility generic emission standard Part 1 Residential,
CE EN 500 82-1 Electromagnetic compatibility generic immunity standard Part 1 Residential,
CE EN 550-22 EMI Level B
CE EN 60 950/A2 Safety of information technology equipment including electrical business
UL 1950 UL Standard for Safety of Information Technology Equipment
ETSI ETR 152 High Bit Rate Digital Subscriber Line Transmission
CSA C22.2, No. 950 Safety of information technology equipment including electrical business
Synchronization Interface Standards for Digital Networks
Digital Hierarchy - Formats Specifications
Requirements for Connection of Terminal Equipment Systems and Protective
Apparatus to the Telephone Network
Levels
Kbps and Offering Synchronous Digital Access At 384 Kbps and/or 64 Kbps
Kbps
on the 2048 Kbps Hierarchy
on the 1544 Kbps Hierarchy
Protections
commercial and light industry
commercial and light industry
equipment
equipment
March 2001 Page 31

Zhone Technologies, Inc. IMACS Product Book, Version 4
III. IMACS Voice Modules and Applications
1. Foreign Exchange Station (FXS) Card
The IMACS supports one Foreign Exchange Station (FXS) card, the 812960 FXS Card, which provides eight 2-wire
analog ports with a terminating impedance of 600 ohms.
FXS cards can be installed in any IMACS chassis User Slot, and will (in most cases) require a ring generator. AC
powered systems will also require a –48 VDC converter. FXS cards encode the incoming analog voice signals into
64 Kbps PCM format before transmission onto the network. Each FXS card provides a single 50-pin female
amphenol connector (RJ27X).
All port parameters are software configurable on a port-by-port basis. The Mode setting specifies whether the port
is to be used fo r standard For eign Exchange Station, Foreign Exchange Software Defined Network (“wink”), Private
Line Automatic Ringdown (PLAR), or Dial Pulse Origination applications. For example in the case of a PLAR
circuit, the port can be programmed to provide Ringback Tone towards the caller. The Type setting specifies Loop
Start, Loop Start with Forward Disconnect, Ground Start, Ground Start Immediate and Ground Start Automatic
operation. If the PLAR mode is selected, then the two options supported under Type are “D3” and “D4” which meet
the pre-1988 and post-1988 specifications for PLAR circuits. The PCM Coding options supported include µ-Law ,
A-Law and inverted A-Law, and the user may also select the Trunk Conditioning mode (busy or idle) that should be
applied towards the attached equipment should the WAN facility that the port is connected to fails. In addition, both
the Transmit (Tx) and Receive (Rx) TLP levels can be set in increments of 0.1 dB. The Tx TLP range is from -10.0
dB to +5.0 dB. The Rx TLP range is from -10.0 dB to +2.0 dB.
The user may also specify, on a port-by-port basis, whether to use North American ANSI standard ABCD signaling
(which is the default) or ITU ( CCITT) ABCD si gnaling by turning the signaling conversion setting “on” or “off”.
The trans-hybrid balance may be specified as one of eight values as well as for a customized user-specified
terminating impedance. At the present time, all eight values are identical and are set for a terminating impedance of
600+2.15µF in the case of a Model 8129 FXS card.
Software-initiated testing and diagnostics supported on FXS cards include the setting of both analog and digital loop
back towards the network and the generation of a Digital MilliWatt (DMW) signal on a port-by-port basis. A robust
set of Test functions allow the user to monitor and set the state of the analog Tip and Ring leads of any FXS port and
to set and monitor the state of the ABCD signaling bits of the digitized voice signal. In cross-connect systems, the
Test functionality also includes the ability to generate test tones (300Hz, 1 kHz, 3 kHz and “quiet”) and transmit
those toward either the user side or the network side of the system. FXS cards can use the voice-compression
features of the ADPCM and LBRV Server cards. Table 10 provides all the relevant FXS cards specifications.
Table 10—FXS Specifications
Model 8129 2-wire Analog FXS Voice Card
Physical Characteristics
Model 812960 8 ports
Physical Interface 1 female 50-pin Telco connector
Dimensions of Card 8 x 0.94 x 7.48 inches (HWD)
Weight of Card 1 lb or .4 k
Power Consumption of Card 3.12 W
Signaling Modes Software configurable on a per port basis: foreign exchange station
(FXS), FXS defined network (Megacom), Private Line Automatic
Ringdown (PLAR), Dial Pulse Originating (DPO)
Signaling Types Loop Start, Ground Start, Loop Start with Forward Disconnect, Feature
Group D (for high-speed modem services), Bill On Answer, D3, D4,
DPO and Single Party, Universal Grade Voice
Specification Short Loop Long Loop
Loop Resistance
Termination Impedance 600 + 2.16 uF
VF Transmission
Min 300 Ω, Max 700 Ω Min 300 Ω, Max 1800 Ω
March 2001 Page 32

Zhone Technologies, Inc. IMACS Product Book, Version 4
Characteristics
Nominal Transmit TLP Software configurable, -10.0dB to +5.0dB, steps of 0.1dB
Nominal Receive TLP Software configurable, -10.0dB to +2.0dB, steps of 0.1dB
2-Wire Return Loss >28 dB Echo, >20 dB singing (against 600 ohm, in series with 2.16 uF
with additional 25 ohm resistor between tip and ring)
PCM Coding
Transhybrid Loss
Standards Conformance
AT&T TR43801
Bel1Core TR-NWT 000057
BellCore GR-63-CORE
ITU-T G.712
ITU-T Q.552
FCC Part 68 Requirements for Connection of Terminal Equipment Systems and
FCC Part 15 Subpart 15
UL 1459 UL Standard for Safety, Telephone Equipment
Software configur able, A-Law, A-Law inverted , u-Law
Echo: 20dB, SRL-LO: 12dB, SRL-HI: 12 dB
Digital Channel Bank Requirements and Objectives - November 1982;
Functional Criteria for Digital Loop Carrier System - January 1993
Network Equipment-Building System (NEBS) Requirements: Physical
Protection
(11/96) - Transmission Performance Characteristics of Pulse Code
Modulation (replaces G.712, G.713, G.714 and G.715)
Transmission Characteristics of 2 -wire analog interface of a Digital
Exchange
Protective Apparatus to the Telephone Network
2. Foreign Exchange Office (FXO) Card
The IMACS supports only one variant of Foreign Exchange Office (FXO) card:
• 813960/813970 FXO Card provides eight 2-wire analog ports with terminating impedance of 600 ohms.
FXO cards can be installed in any of the User Slots of the IMACS chassis. FXO cards encode the incoming analog
voice signals into 64 Kbps PCM format before transmission onto the network. A Ringing Generator is required if
one or more FXO ports in a system are programmed to operate in Manual Ringdown (MRD) mode. In addition, a
physical jumper must be set on the FXO card for each port programmed for MRD operation. Each FXO card
provides a single 50-pin female AMPHENOL connector (RJ27X).
All port parameters are software configurable on a port-by-port basis. The Mode setting specifies whether the port
is to be used for standard Foreign Exchange Office, Foreign Exchange So ftware Defined Network, Dial Pulse
Terminate, or Manual Ring Down (MRD). As described above, the MRD mode also requires the setting of physical
jumpers. The Signal setting specifies Loop Start, Loop Start with Forward Disconnect, Ground Start, R2, and
Immediate R2 operation. In “fxodn” and “dpt” modes, the user may also specify the wink duration time and wink
delay from 0.1 seconds to 9.9 seconds in 0.1-second increments. The PCM Coding options supported include “µ-
Law”, “A-Law” and inverted A-Law. The user may select the Trunk Conditioning mode (“busy” or “idl e”) that
should be applied towards the attached equipment should the WAN facility that the port is connected to fail. In
addition, both the Transmit (Tx) and Receive (Rx) TLP levels can be set in increments of 0.1 dB. The Tx TLP range
is from -10.0 dB to +5.0 dB. The Rx TLP range is from -10.0 dB to +2.0 dB.
The user may also specify, on a port-by-port basis, whether to use North American ANSI standard ABCD signaling
(which is the default) or ITU ( CCITT) ABCD si gnaling by turning the signaling conversion setting “on” or “off.”
The trans-hybrid balance may be sp ecified as one of eight values (known as “set1” through “set8”) as well as for a
customized user-specified terminating impedance (“user”). All eight values are identical and are set for a
terminating impedance of 600Ω ± 2.15µF in the case of the Model 813960 FXO cards.
Software-initiated testing and diag nost ics suppor t ed on FXO cards include the setting of both
analog and digital loop backs towards the net work and generating a Digital MilliWatt signal on a
port-by-port basis. A robust set of Test functions allow the user to monitor and set t he state of
March 2001 Page 33

Zhone Technologies, Inc. IMACS Product Book, Version 4
the analog Tip and Ring leads of any FXO por t . It also sets and monitors the state of the
digitized voice signal’s ABCD signaling bits in cross-connect system s, the Test functionality also
includes the ability to generate test tones ( 300Hz, 1 kHz, 3 kHz and “quiet”) and transmit those
toward either the user side or the network side of t he system .
specifications.
Table 11 reviews the FXO Card
Table 11—FXO Specifications
Model 813960 2-wire Analog FXO
Voice Card
Physical Characteristics
Model 813960 8 ports
Physical Interface 1 female 50-pin Telco connector
Dimensions of Card 8 x 0.94 x 7.48 inches (HWD)
Weight of Card 1 lb or .4 k
Power Consumption of 813960
Card
Models 813960 Signaling Mode Software configurable on a per port basis: Foreign Exchange
Models 813960 Signaling Type Loop Start, Ground Start, Loop Start Forward Disconnect, Loop
Termination Impedance 600 ohms
VF Transmission Characteristics
Nominal Transmit TLP Software configurable, -10.0dB to +5.0dB, steps of 0.1dB
Nominal Receive TLP Software configurable, -10.0dB to +2.0dB, steps of 0.1dB
2-Wire Return Loss >28 dB Echo, >20 dB singing (against 600 ohm, in series with
PCM Coding
Transhybrid Loss
Standards Conformance
AT&T TR43801
Bell CoreTR-NWT-000057
BellCore Protections GR-63 CORE
ITU-T G.712
ITU-T Q552
ITU-T Q.553
FCC Part 68 Requirements for Connection of Terminal Equipment Systems and
FCC Part 15 Subpart B
UL 1459 Standard for Safety, Telephone Equipment
3.03 W
Office (FXO), FXO Defined Network, Manual Ringdown and
Dial Pulse Terminating (DPT)
Start R2, Ground Start Automatic, Loop Start E&M, MRD, DPT,
R2, Immediate R2, Dial Pulse E&M, Caller ID
2.16 uF with additional 25 ohm resistor between tip and ring
Software configur able, A-Law, A-Law inverted , u-Law
Echo: 22dB, SRL-LO: 14dB, SRL-HI: 20 dB
Digital Channel Bank Requirements and Objectives – November
Functional Criteria for Digital Loop Carrier System – January
1993
Network Equipment-Building System (NEBS) Requirements:
Physical Protection
(11/96) – Transmission Performance Characteristics of Pulse Code
Modulation (replaces G.712, G.713, G.714 and G.715)
Transmission Characteristics of 2 –wire analog interface of a Digital
Exchange
Transmission Characteristics of 4 –wire anal og
Exchange
Protective Apparatus to the Telephone Network
interface of a Digital
March 2001 Page 34

Zhone Technologies, Inc. IMACS Product Book, Version 4
3. E&M Card
The IMACS supports three variants of E&M cards:
• 810860 E&M Card supports eight 2-wire E&M or Transmission Only (TO) ports
• 811760 E&M Card support eight 4-wire E&M or Transmission Only (TO) ports and 2713 Hz loop back support
• 811960 E&M Card supports eight 4-wire E&M or Transmission Only (TO) ports
The 811960 E&M card offers an extended Transmit TLP range (-17.5 to +14.5dB) to better support dedicated 4wire modem applications. This may be required in situations when specific types of modems being connected to the
ports cannot, or will not, change their output power levels. Modems can only be connected with the E&M when
placed in TO mode.
E&M cards can be installed in any of the User Slots of the IMACS chassis. E&M cards encode the incoming analog
voice signals into 64 Kbps PCM format before transmission onto the network. Each E&M card provides a single
50-pin female AMPHENOL connector (RJ27X). All three cards support E&M signaling types I, II, IV and V.
Most port parameters are software configurable on a port-by-port basis including the Mode of each port (“E&M”,
“E&MR2” or “TO”). The PCM Coding to be used is either u-Law, A-Law or A-inv (for inverted A-Law). The
Trunk Conditioning (busy or idle) is configured on the e quipment in case the WAN facility that the port is conne c t ed
to fails.
The user may also specify, on a port-by-port basis, whether to use North American ANSI standard default, ABCD
signaling, or ITU (CCITT) ABCD signaling by turning the signaling conversi on setting “on” or “off”.
Software-initiated testing and diagnostics supported on E&M cards include the setting of both analog and digital
loop backs towards the network and the generation of a Digital MilliWatt signal on a port-by-port basis. A robust
set of test functions allow the user to monitor and set the state of the analog E & M leads of any port and to set and
monitor the state of the ABCD signaling bits of the digitized voice signal. In cross-connect systems, the Test
functionality also includes the ability to generate test tones (300Hz, 1 kHz, 3 kHz and “quiet”) and transmit those
toward either the user side or the network side of the system.
The 811760 E&M with 2713 Hz Loop back will provide digital loop back (both PCM voice and signaling) when
activated by a 2713 Hz tone of specified level and duration. This complies with requirements as per Bellcore PUB
42004.
When a validated tone is detected the channel disconnects the transmit path from the user and provides loop back of
signals (PCM voice and signaling) received from the network. The loop back is performed at “equal level”, i.e.
without inserting any gain or loss in the path. In addition, a “make busy” signal is being applied towards the user.
Table 12 reviews the E&M card specifications.
Table 12—E&M Analog Voice Card Specifications
Models 810860 2-wire
Models 811760 and 811960 4-wire
E&M Analog Voice Card
Physical Characteristics
Model 810860 and 811960 8 ports
Physical Interface 1 female 50-pin Telco connector
Dimensions of Card 8 x 0.94 x 7.48 inches (HWD)
Weight of Card 1 lb or .4 k (Model 811960)
Power Consumption of Card 3.5 W (Model 811960)
Signaling Mode
2-wire (810860)
4-wire (811960)
Signaling Types Types I, II, V are switch configurable by card. Supports Normal
Software configurable on a per port basis: E&M, Transmit Only,
Symmetrical R2 signaling, E&MR2, Modified R2 (r2mod)
March 2001 Page 35

Zhone Technologies, Inc. IMACS Product Book, Version 4
(toward user) and Tandem (toward CO)
E&M Sensor Characteristics 2-wire (810860) and 4-wire (811960), Impedance > 15K ohms,
Sensitivity > 2.5 mA
Nominal Transmit TLP Software configurable, -16.5dB to +7.3dB, steps of 0.1dB (2-wire); -
17.5 dB +14.5dB, steps of 0.1 dB (4-wire)
Nominal Receive TLP Software configurable, -16.3dB to +7.5dB, steps of 0.1dB (2-wire); -
16.3dB +7.5dB steps of 0.1dB
Termination Impedance 600 Ohms with 2.16 uF capacitor in series (2-wire); 600 Ohms (4-wire)
Delay Specification
Absolute Group Delay
(dependent on codec)
Peak to Average Ratio (PAR) 94 to 97 (2-wire and 4-wire)
Standards Conformance
AT&T TR43801
Bell CoreTR-NWT-000057
BellCore GR-63 CORE
ITU-T G.712
ITU-T Q.552
ITU-T Q.553
FCC Part 68 Requirements for Connection of Terminal Equipment Systems and
FCC Part 15 Subpart B
UL 1459 Standard for Safety, Telephone Equipment
UL 1950 UL Standard for Safety of Information Technology Equipment
CE EN 500 81-1 Electromagnetic compatibility generic emission standard Part 1
CE EN 500 82-1 Electromagnetic compatibility generic immunity standard Part 1
CE EN 60 950/A2 Safety of information technology equipment including electrical
<600 us (2-wire and 4-wire)
Digital Channel Bank Requirements and Objectives – November 1982
Functional Criteria for Digital Loop Carrier System – January 1993
Network Equipment-Building System (NEBS) Requirements: Physical
Protection
(11/96) – Transmission Performance Characteristics of Pulse Code
Modulation (replaces G.712, G.713, G.714 and G.715)
Transmission Characteristics of 2 –wire analog interface of a Digital
Exchange
Transmission Characteristics of 4 –wire analog interface of a Digital
Exchange
Protective Apparatus to the Telephone Network
Residential, commercial and light industry
Residential, commercial and light industry
business equipment
March 2001 Page 36

Zhone Technologies, Inc. IMACS Product Book, Version 4
P-Phone Station and Office Line Ca rds
The P-Phone Line Cards support transport of Nortel Electronic Business Service (EBS) or P-Phone service. Nortel’s
EBS is provide d through the use of an Elect ronic Business Set (also EBS) capable of supporting premium Meridian
Digital Centrex (MDC) features offered by the local DMS SuperNode switch. A data channel allows out-of-band
signaling between the EBS and the DMS SuperNode switch. This data channel allows the user to activate MDC
features, such as conference calling, by simply pushing special keys on the EBS, and for the DMS SuperNode to
deliver information, such as calling number identification, to the EBS display.
P-Phone is a very popular service among large corporations who have chosen Nortel Centrex vs. a PBX. This
service is very popular in metropolitan areas; as more companies move away from purchasing their own PBXs, PPhone will be even more popular among the corporate DMS customers. In addition, as more and more CLECs enter
traditional RBOC bases, they will need to be able to provide P-Phone services.
Figure 10A shows a general application drawing where an IMACS system is used at both the CO end and at the
customer remote end. As shown, there are two applications of the Line Card, one at the office end, also known as PPhone Office (PPO), and one at the station end referred to as P-Phone Station (PPS).
Figure 10 - Universal IMACS P-Phone Application
P-Phone #1
:
Line 1
IMACS with
PPO Line Card
T1
E1
Network
T1
E1
IMACS with
PPS Line Card
:
:
:
:
:
:
:
P-Phone #N
Nortel CO Switch
Two types of P-Phone line cards are used in pair gain carrier systems such as DLCs and the IMACS system. One
type, referred to as a passive line card, encodes the received out-of-band signaling tones, transports them across the
carrier and decodes the digital representation back to out-of-band tones at the other end. In other words, the passive
line card simply repeats the signaling end-to-end. The second type, referred to as an active line card, terminates the
messages received at the 2-wire port and either responds as appropriate to the local terminal device or forwards the
message over the digital carrier.
The above figure shows just one working circuit. In reality, the Line Card will be able to support eight (8) working
circuits. The most common application for P-Phone would have more than one circuit going to a customer location.
Very rarely would there be just one circuit terminating at one customer. The P-Phone line cards support the
following Nortel PBXs, switches and Me ridian business phone sets:
• DMS100 (Class 5 switch)
• DMS500 (Combinations of Class 5 and a tandem switch)
• DMS10 (Lower capacity switch for rural areas)
• SL100 (Large enterprise PBX; same as DMS100)
• M5000 series business sets
Table 12A reviews the PPO and PPS line card specifications.
March 2001 Page 37

Zhone Technologies, Inc. IMACS Product Book, Version 4
Table 12A—PPO and PPS Line Card Specificat ions
Models 812160 and 813160 Eight Channel Line
Card
Physical Characteristics
Model 812160 and 813160 8 channels
Software provisionable options Level control and A-Law/Mu law
Transport length Over 3,000 feet of copper cable at 2W VF ports
Out of band signal ing 8 kHz tone, ASK, half duplex
Voice Transmission
Status Indicators
Subscriber and Central Office
Interface—Transmit Channel
Levels received from 2W port -2 dBm to +1 dBm
Level adjustment -3 to +2dB in 0.1 dB increments
Attenuation distortion (relative to 1 kHz) -0.5 to +1.0 db, 400 Hz to 2800 Hz
Idle channel noise
7-bit voice encoding scheme. LSb used t o carry signaling.
Loop current, presence or absence at the local end; loss of
sealing current, far end
≤ 23 dBrnC
March 2001 Page 38

Zhone Technologies, Inc. IMACS Product Book, Version 4
Table 12A—PPO and PPS Line Card Specificat ions (continued)
Subscriber and Central Office
Interface—Receive Channel
Level generated to 2W port with 0dB loss
0 dBm ± 0.5 Db
Level adjustment -3 to +2 dB in 0.1 dB increments
Attenuation distortion (relative to 1 kHz) -0.5 to +1.0 db, 400 Hz to 2800 Hz
Idle channel noise
2W Port Characteristics
≤ 23 dBrnC
Maximum connected copper loop 3000 feet, 26 gauge, non-loaded pair
Impedance 900 ohms
Return Loss, voiceband into 900Ω + 2.16 µF
Return loss, single frequency into 900Ω + 2.16 µF
Sealing Current Source
> 18 dB ERL, > 0 dB SRL LO, HI
> 25.6 dB @ 8 kHz
Minimum voltage at NI (display set) 15.8 V into a 38 ma sink through 3000 ft
Minimum voltage at NI ( non-display set) 14.5 V into a 17 mA sink thr ough 3000 ft
Loop length 0 to 3000 feet
Polarity Ring lead must be negative relative to tip lead
Sealing Current Sink
<960 ohms DC resistance
8 kHz Signaling Specifications
Signaling method ASK half duplex, carrier only present during transmission of
information or acknowledgment
Signaling rate 1 kb/s, half duplex
Received 8kHz signal levels at 2W port .200 to 1.5 V peak to peak
Standards Conformance
BellCore GR 1089-CORE, Section 2 ESD Protection
BellCore GR 1089 section 3 and EN 500
Radiated Emissions
81-1, Level B
BellCore GR 1089 CORE, Section 3 Conducted Emissions
BellCore GR 1089 CORE, Section 3 Immunity
FCC Part 68 Requirements for Connection of Terminal Equipment Systems
and Protective Apparatus to the Telephone Network
FCC Part 15 Subpart B
UL 1459 Standard for Safety, Telephone Equipment
UL 1950 UL Standard for Safety of Information Technology Equipment
CE EN 500 81-1 Electromagnetic compatibility generic emission standard Part 1
Residential, commercial and light industry
CE EN 500 82-1 Electromagnetic compatibility generic immunity standard Part 1
Residential, commercial and light industry
CE EN 60 950/A2 Safety of information technology equipment including electrical
business equipment
March 2001 Page 39

Zhone Technologies, Inc. IMACS Product Book, Version 4
Voice Channel Bank Application
This is the simplest IMACS application, which can be used by a service provider. The IMACS is used in this
configuration when one or more digital T1/E1 trunks are needed to interface with analog PBXs or key systems at the
customer premises . In the US, the break-even point for bringing in a T1 trunk as opposed to multiple analog lines is
typically 6 analog lines. As a result, there is a huge market for cost-effective voi ce channel bank such as t he IMACS.
A single IMACS can be used to provision up to 62 analog POTS lines (FXS, FXO, E&M) on digital Central Office
switches as shown in Figure 11.
Figure 11—IMACS As A Voice Channel Bank
Local Digital Switch
POTS/
CLASS
IMACS
Max 8 T1/E1
D
S
X
P
A
• 62 POTS/CLASS Lines
N
E
L
Customer Premise
The IMACS can also be deployed in applications, which do just the reverse of voice channel banks. This is most
likely to be found in wireless local loop applications in which the wireless service provider may use a state-of-theart wireless local loop. The output of the wireless base station is normally a T1/E1. However, the existing PSTN
may still have analog switches. The IMACS is used to convert from robbed-bit signaling/CAS to analog trunks
(FXO).
The voice channel bank platform can be upgraded to provide an array of additional services just by adding
application modules to the chassis. It comes with a built-in suite of testing and diagnostics tools, which significantly
enhance the service and support capabilities.
Central Office
TR-008 Application
BellCore’s TR-008 standard describes the requirements necessary for a Local Digital Switch (LDS) to connect to a
remote terminal (RT) across a T1 (1.544Mbps) digital interface. The standard allows supporting from one to four
T1s per RT without facility Automatic Protection Switching (APS), and two to five T1s with facility APS.
The LDS can interface the RT in Mode I (no concentration), Mode II (2:1 concentration), and Mode III (24 specialservice circuits on 24 DS1 time-slots). TR-008 supports traditional POTS, CLASS, and Coin services but does not
support ISDN BRI. If the service provider deploys a channel bank at the customer premise that does not provide
TR-008 capability then it needs a 1/0 DCS with TR-008 capability at the central office to integrate with the LDS.
The IMACS also supports TR-008 switch integration. The IMACS with TR-008 operation can connect directly to
the LDS, eliminating the need for the 1/0 DCS as shown in Figure 12a.
March 2001 Page 40

Zhone Technologies, Inc. IMACS Product Book, Version 4
Local Digital Switch
POTS/
CLASS
IMACS
2 x T1/E1
D
S
X
P
A
• 48 TR008 Lines
• MODE 1 (Shelves A&B)
N
E
L
Customer Premise
Central Office
Figure 12a - IMACS Using TR-008
IMACS TR-008 feature can support 48 lines on 2 T1 links. IMACS is an ideal vehicle to provide integrated POTS
services for line sizes of 48 and under. IMACS supports Mode I, Shelf A&B of TR-008 specification. The IMACS
supports extensive testing and diagnostics capabilities, which minimizes troubleshooting and allows for high service
levels.
T1-E1 Conversion
The Digital Access and Cross-connect System (DACS) capabilities and the signaling and companding conversion
features of the IMACS can be used to provide gateway functionality between a DS1 transport network and an E1
transport network. See Figure 12b for an illustration of this capability.
W1-1
W2-1
DS1
Transport
Network
W3-1
W4-1
IMACS
W1-2
W2-2
W3-2
W4-2
E1
Transport
Network
Figure 12b - IMACS Using T1/E1 Conversion
Depending on the application, the signaling conversion can be set by the user to ITU-to-ANSI; ANSI-to-ITU or
None. Similarly, the companding can be set by the user to A-Law-to-µ-Law, µ-Law-to-A-Law or none. As shown
in the figure above, each WAN card must be configured with one port for DSX1 and one for CEPT. A crossconnection circuit must be made for each DS1 to E1 DSO re-assignment. Time Slots 0 and 16 cannot be used on the
E1 link. Time slot 0 is used for timing and time slot 16 is used for Channel Associated Signaling (CAS). TS16 is
available in data-only applications.
March 2001 Page 41

Zhone Technologies, Inc. IMACS Product Book, Version 4
IMACS Data Modules and Applications
The IMACS supports multiple user cards for transport of digital data. A list of all cards/model types that can be
used in the chassis is provided in Table 13.
Table 13—Data Card Types
Type of Card Description
820260 HSU Card Supports two RS530/V.35 or RS-449 data ports via DB25 female connectors. It can
also support RS232 data through the use of the appropriate Personality module.
Supports 56K, 64K and Nx56/64K data applications.
820360 HSU Card Supports two V.11/X.21 data ports which connects to RS530 or X.21 CPE devices via
DB25 female connectors. The ports may be configured as user ports, or can be used as
externally clocked network interface ports. Supports 56K, 64K and Nx56/64K data
applications.
821260 HSU Card Supports two V.35 synchronous data ports via two DB25 female connectors. Supports
56K, 64K and Nx56/64K data applications.
821360 HSU Card Provides two miniature DB26 female connectors. Each port can be configured to
support RS530 or V.35 devices. Interface selection is made on a port-by-port basis.
The 8213 supports V.25bis dialing commands (an in-band dialing protocol) and RS366 dialing through the use of separate DB15 pin RS-366 port connectors on the rear
of the card. Supports 56K, 64K and Nx56/64K data applications.
821460 HSU Card Supports two V.35 synchronous data ports via two DB25 female connectors. The
ports can be configured as user ports, or be used as externally clocked network
interface ports. Supports 56K, 64K and Nx56/64K data applications.
821560 HSU Card Provides four miniature DB26 female connectors. Each port can be configured to
support RS530 or V.35 devices. Interface selection is made on a port-by-port basis.
Supports 56K, 64K and Nx56/64K data applications. Can also support RS232 data at
56Kbps thr ough the use of the 1253xx Personality Module and 1240 cable layer. The
821570 HSU card has improved clock jitter performance.
821660 HSU Card Provides four miniature DB26 female connectors. Each port can be configured to
support RS530 or V.35 devices. Interface selection is made on a port-by-port basis.
Supports 56K, 64K and Nx56/64K data applications. Can also support RS232 data at
56Kbps thr ough the use of the 1253xx Personality Module and 1240 cable layer.
Supports tail circuits greater than 24 timeslots. V.35 interface compatible with
international standards, and individually selectable transmit/receive clock inversion
options.
March 2001 Page 42

Zhone Technologies, Inc. IMACS Product Book, Version 4
Table 13—Data Card Types (co nt inued)
822060 SRU Card Provides 10 port RS-232C/V.24 interfaces. Supports synchronous and/or
asynchronous data ports from 300 bps to 38.4 Kbps.. Supports DS0-A, DS0-B,
V.14 and X.50 Division 3 sub-rate multiplexing format. SRU card ports can also
be multiplexed with voice traffic on an ADPCM engine (up to 19.2 Kbps data
circuit in 24 Kbps ADPCM channel). The 822061 SRU card provides equivalent
functionality as the 822060 except the Idle Pattern has been changed.
822160 SRU Card Functionality equivalent to 822060 SRU card. When used with 822060, increases
the SRU port density per IMACS system beyond the current limit of 60.
822460 SRU Card The 822460 SRU has 4 DB-26 female connectors. Supports synchronous and/or
asynchronous data ports from 300 bps to 38.4 Kbps. Supports DS0-A, DS0-B,
V.14 and X.50 Division 3 sub-rate multiplexing formats. SRU card ports can also
be multiplexed with voice traffic on an ADPCM engine (up to 19.2 Kbps data
circuit in 24 Kbps ADPCM channel).
822560 SRU Card Supports 10 RS-232E synchronous and/or asynchronous data ports from 300 bps to
38.4 Kbps. Supports DS0-A, DS0-B, V.14 and X.50 Division 3 sub-rate
multiplexing formats by hardware instead of software. The configuration is
controlled via local terminal or remote NMS. The SRU offers lower delay and
increasing throughput. SRU card ports can also be multiplexe d with voice traffic on
an ADPCM engine (up to 19.2 Kbps data circuit in 24 Kbps ADPCM channel).
Supports CSU, DSU and OCU loop backs.
822860 BnR
Concentrator Card
823160 FRAD Card Frame Relay Assembler/Disassembler provides encapsulation for HDLC/SDLC or
824160 and 822460
OCU-DP Cards
BRI Card
OCU-DP Card 8249 The 8249 is a 2 port OCU-DP card that provides interfaces for provisioning of
Provides concentration for time slots containing diagnostics from remote IMACS
units. Multiplexes up to 8 ports of Bit-7-Redundant (B7R) or B4R formatted data
channels from up to 8 different DS0s onto a single, asynchronous channel at up to
38.4 Kbps. Data on the aggregate channel is in SLIP format and the interface is
RS-232.
Async ports up to 38.4 Kbps. Transparent/Sync up to 38.4 Kbps. This card
concentrate up to 8 non-frame inputs into 2 data streams at 56Kbps or 64Kbps.
Total of 10 ports may be assigned to input (FRAD) or output (concentrator) ports
based on configuration guidelines. Access to this card is via on-card RS-232 or
through DS0-B over T1.
The 824160 (5 port) and 822460 (10 port) allows provisioning of DDS services or
consolidation of DSU traffic as DS0-A or DS0-B. Interfaces directly to DSU at
speeds up to and including 64 Kbps. Does not support BCH error correction,
performance monitoring or operation in CSU mode (used only for back-to-back
OCU-DP ports). Emulates an 8247 for existing system compatibility. Each port
may be connected to a DSU/CSU operating at 64, 56, Switched 56, 19.2, 9.6, 4.8 or
2.4 Kbps. DSUs can be local to several thousand feet distant to IMACS based on
speed and wire gauge.
DDS services or consolidation of DSU traffic. Supports DS0-A or DS0-B sub-rate,
56K, 64K and Switched 56Kbps DDS. Supports BCH error correction,
performance monitoring or operation in CSU mode. Secondary channel operation
can be enabled if desired. Optional error correction for inter-IMACS circuits.
March 2001 Page 43

Zhone Technologies, Inc. IMACS Product Book, Version 4
825460 DSO-DP Card Provides 4 ports of DS0-DP or G.703 64K. For G.703, clock can be selected to be
co- directional or contra-directional.
826070 BRI Card This BRI-U card provides 8 ports of 2-wire 2B1Q interface via a single RJ27X (F),
50-pin amphenol connector. Adheres to 2B+D format. Supports external timing.
Can be used to support NTUs for dedicated operation or for connections to BRI-U
interface devices. Commonly used for BRI Terminal extension.
826170 BRI Card This BRI-U card provides 8 ports of 2-wire 2B1Q interface via a single RJ27X (F),
50-pin amphenol connector. Adheres to 2B+D format. Supports external timing.
Can be used to support NTUs for dedicated operation or for connections to BRI-U
interface devices. Commonly used for BRI Terminal extension. Provides sealing
(or wetting) current, 7.5mA or 15mA.
826171 BRI Card This BRI-U card provides 8 ports of 2-wire 2B1Q interface via a single RJ27X (F),
50-pin amphenol connector. Adheres to 2B+D format. Supports external timing.
Can be used to support NTUs for dedicated operation or for connections to BRI-U
interface devices. Commonly used for BRI Terminal extension. Provides sealing
(or wetting) current, 7.5mA or 15mA. No “DC signature” feature support.
826270 BRI Card This BRI-S/T card provides 8 ports of 4-wire interfaces via a single RJ27X (F), 50-
pin amphenol connector. Adheres to 2B+D format. Supports external timing.
Provides TE, NT1 and NT2 emulation. Commonly used to provide remote
extension of four wire BRI CPE devices from an ISDN PBX. Requires external
power connection (-48V DC) if more than 3 cards installed in IMACS chassis
unless 891330 and 8908 are used (special cable required).
826361 BRI Card Supports 8 ports of 2-wire 2B1Q via a single RJ27X connector. Supports LULT
and LUNT. Supports Bi-directional B1, B2 and D channel. Network clock for bit
timing to LULT and EOC as per TR000397 using 3 DS0 TDM methods. Support
Interim Performance Monitoring as per TR-000397 and TR-000829. Provides
sealing current. No “DC Signature”.
826461 BRI Card Supports 8 ports of 2-wire 2B1Q via a single RJ27X connector. Supports LULT
and LUNT. Supports Bi-directional B1, B2 and D channel. Network clock for bit
timing to LULT and EOC as per TR000397 using 3 DS0 TDM methods. Support
Interim Performance Monitoring as per TR-000397 and TR-000829. Provides “DC
Signature” but no sealing current.
826462 BRI Card Supports 8 ports of 2-wire 2B1Q via a single RJ27X connector. Supports LU, LT,
LULT and LUNT and network management of NTUs (2560 and 2561). Supports
Bi-directional B1, B2 and D channel. Network clock for bit timing to LULT and
EOC as per TR000397 using 3 DS0 TDM methods. Support Interim Performance
Monitoring as per TR-000397 and TR-000829.
828060 PM-IOR Card Inter Office Router card is based on Lucent Technologies PortMaster product line.
Connects 10BaseT Ethernet LAN to T1/E1 WAN. Uses PPP or Frame Relay and
IP (TCP/IP and IPX) to route up to 1.2 Mbps through WAN. Can assign Nx56/64
Kbps DS0s. Configure router through RJ-45 conso le port. Supports SNMP
network management.
March 2001 Page 44

Zhone Technologies, Inc. IMACS Product Book, Version 4
HSU Card
The HSU card allows the connection of high-speed data terminal equipment (DTE) and data communications
equipment (DCE) to WAN links, server cards (FRS) or another HSU card. The HSU card also provides low or middensity connectivity for local, synchronous peripherals such as, LAN Bridge/Routers and legacy SNA/SDLC
devices. Additionally, these high-speed data cards provide broadcast functionality for point to multi-point
operations suitable for applications such as video-conferencing. When used in conjunction with an 8840 PRI Server
Card, the HSU card can be used to provide switched data application functionality. All HSU cards can be installed
in any of the User Slots in an IMACS chassis.
Each port on a HSU can be independently configured to operate at speeds of Nx56 or Nx64 Kbps, where N equals 1
to 24 in T1 mode or 1 to 31 in E1 mode. In addition to the data rate, each synchronous port’s Transmit Clock can be
programmed for Internal or External modes and both the Clock and Data Polarity may be inve rted through software.
The External Transmit Clock mode and the Inverted Clock Polarity mode may be useful in ensuring that both the
Transmit Clock and the Transmit Data are in sync when they reach the HSU port. This should occur when the HSU
port and the attached device are connected over a long cable. The Data Polarity may be inverted to ensure the
density for Nx64 Kbps data circuits supporting HDLC-based protocols that are connected to non-B8ZS T1 facilities.
The “Clear To Send” control lead may always be set to high, low or local mode. In local mode, the CTS signal
reflects the state of the Request To Send (RTS) signal that is received from the attached DTE device. In that mode,
the delay between RTS and CTS is software set-able, with options of 0, 30, 60 or 100 milliseconds. Additionally, if
the HSU port is programmed to operate at Nx56 Kbps, then RTS will be transmitted end-to-end and presented as
RLSD at the far end of the circuit.
Software-initiated diagnostics support the setting of local loop backs towards either the network or the attached DTE
equipment. Additionally, a remote loop back function allows the HSU card to generate three DDS-compatible
latching loop back codes for the far-end OCU, CSU and DSU equipment. Similarly, the HSU data port may be
programmed to detect and respond to both latching and non-latching DDS-format OCU, CSU and DSU loop back
codes initiated from the remote end of the circuit. A time-out option authorizes the HSU port to automatically
release the loop back after ten minutes. This feature applies to an HSU port that is running at 56 Kbps or for super rate circuits if the loop back code is transmitted in the first super-rate’s DSO. The card can also generate and
recognize two industry standard in-band loop-up and loop-down codes that act on the entire super-rate circuit.
Those are the ITU (CCITT) V.54 code and the ANSI Fractional T1 code.
Additionally, the integral Bit Error Rate Tester (BERT) can be used to generate test patterns and route those towards
the WAN facility. These test patterns can then be used to verify synchronization and measure circuit quality. For
further information regarding Performance Monitoring and Diagnostic Capabilities, see Section 13, IMACS System
Testing and Diagnostics.
Applications
There are several business applications the IMACS equipped with an HSU card supports.
LAN to LAN
LAN to WAN to LAN
Work Station to Computer
Computer to Computer
Compressed Video
CAD/CAM
Call Center
IMACS and HSU Application Example
A major Health Maintenance Organization has numerous locations, which have a Central main hospital facility and
smaller satellite facilities. The HMO cannot afford to fully staff each main and satellite site with specialists. As
patients enter the satellite facilities, video and audio sessions can be established with the specialists at the Main
March 2001 Page 45

Zhone Technologies, Inc. IMACS Product Book, Version 4
y
y
y
hospital. Although the satellite sites are not equipped with Intensive Care Units, emergencie s can be admitted and
support solicited from the Main hospital personnel as shown in Figure 13.
Remote
Medical
Facilit
Video Codec
Remote
Medical
Facilit
Video Codec
IMACS
FT1
1 WAN
Card
1 WAN
IMACS
FT1
FT1
IMACS
Video Codec
Multichannel
Conferencing Unit
Figure 13 - Point to MultiPoint One-Way Video and Audio Using HSUs
Main
Medical
Facilit
March 2001 Page 46

Zhone Technologies, Inc. IMACS Product Book, Version 4
Table 14 describes the various high-speed data cards.
Table 14—820260, 820360, 821260, 821360, 821460, 821560, 821570 and 821660 High-speed Data Cards
Model Number Number of
Data Ports
Model 820260
Model 820360
Model 821260
Model 821360
Model 821460
Model 821560
Model 821570 (improved
clock jitter performance)
2 2 female 25-pin DB25 D-connectors ITU-T V.35, RS232,
2 DB25 female connectors ITU-T V.11, RS 530
2 2 female 25-pin DB25 D-connectors ITU-T V.35 (True V.35)
2 2 female 26-pin DB26 D-connectors
2 2 female 25-pin DB26 D-connectors ITU -T V.35 (True V.35),
4 4 female 26-pin DB26 D-connectors RS530, RS-232, V.35 devices
Physical Interfaces Electrical Interfaces
RS530/RS449
ITU-T V.35, V.25bis, RS366,
2 DB15 female connectors
RS530
(V25 bis and/or RS-366 dialing
when used with 8840 PRI Card)
Model 821660 4 female DB26 connectors RS530, RS-232 and True V.35 devices
Nx56K and Nx64K where N=1 to 31 (up to 1984 Kbps)-Software Configurable
by port
Data Format Synchronous
Data Protocol Transparent
Transmit Clock per
Internal or external (software configurable)
Port
Clock Polarity per Port Normal or inverted (software configurable)
Data Polarity per Port Normal or inverted (software configurable)
Dial Capability
Number of Dialing
Model 8213 only when used with 8840 PRI Server Card
2
Ports
Dialing Electrical
EIA RS-366, ITU-T V.25 bis
Interface
Dialing Physical
2 female 15-pin D-connectors
Interface
Performance Statistics
Errored Seconds, Unavailable Second, Severely Errored Second, Burst Errored
Second, Loss of Packet Seconds, Loss of Frame Count
Standards
Conformance
ITU-T V.35 Data Transmission of 48 kbps Using 60-108 kHz Group Band Circuits
ITU-T V.11 (10/96) Electrical characteristics for balanced double-current interchange circuits operating at
data signaling rates up to 10 Mbps
ITU-T v.24 (10/96) - List of definitions for interchange circuits between data terminal equipment
(DTE) and data circuit-terminating equipment (DCE)
ITU-T V.28 Electrical characteristics for unbalanced double-current interchange circuits
ITU-T G.704 (7/95) Synchronous frame structures used at 1544, 6312, 2048, 8488 and 44 736 Kbps
hierarchical levels
ITU-T V.25bis (Model 8213 only) (10/96) - Automatic answering equipment and general procedures for
automatic calling equipment on the general switched telephone network including
procedures for disabling of echo control devices for both manually and automatically
EIA RS-422 Electrical characteristics of balanced voltage digital interface circuits
EIA RS-449 General purpose 37 position and 9 position interface for DTE and DCE equipment
employing serial binary data interchanges
March 2001 Page 47

Zhone Technologies, Inc. IMACS Product Book, Version 4
EIA RS-530 High-speed 25 Position Interface for Data Terminal Equipment, Including Alternative 25
Position Connector.
EIA RS-366 Interface Between Data Terminal Equipment and Automatic Calling Equipment for Data
Communication
FCC Part 15 Subpart B
UL 1950 UL Standard for Safety of Information Technology Equipment
CE EN 500 81-1 Electromagnetic compatibility generic emission standard Part 1 Residential,
commercial and light industry
CE EN 500 82-1 Electromagnetic compatibility generic immunity standard Part 1 Residential,
commercial and light industry
CE EN 60 950/A2 Safety of information technology equipment including electrical business
equipment
BellCore GR-63-CORE
2. SRU Card
The 822060/822161 SRU Card allows synchronous or asynchronous connections of up to ten RS-232, low-speed
and medium-speed (300 bps to 38.4 kbps) data terminals to the integrated access system. Since an SRU port does
not require a complete 64Kbps time slot, the Sub-Rate card allows the multiplexing of a number of devices into a
single, subdivided time slot on a WAN card. SRU card ports can also be multiplexed with voice traffic on an
ADPCM engine. The 822060 accesses user buses A & B, and the 822161 SRU accesses user buses C & D. The
822061 SRU has equivalent functions as the 822060 with the exception of Idle Pattern changes. The 822460 SRU
has 4 RS-422 ports that support synchronous and/or asynchronous connections from 300 bps to 38.4 Kbps. The
Low Delay SRU provides 10 RS-232E ports that support synchronous and/or asynchronous V.14 operations. The
sub-rate multiplexing is performed by hardware instead of software.
Network Equipment-Building System (NEBS) Requirements: Physical Protection
Each RS-232 port can be independently programmed for synchronous (including HDLC) or asynchronous operation.
Synchronous operation is available at speeds of 2.4 Kbps up to 38.4 Kbps while for asynchronous the range is 300
bps up to 38.4 Kbps. Each synchronous port can receive timing from either the DTE device or the system clock. If
the DTE supplies the transmit clocking, it must be synchronized with the system clocking source. For each
asynchronous data port, the stop bits, data bits and parity are user configurable. The SRU incorporates a built-in
V.14 Async-to-sync converter to avoid over-sampling and consequently saves bandwidth. Asynchronous data
circuits are converted to synchronous mode by the SRU card prior to multiplexing onto a WAN aggregate.
Sub-rate data ports are multiplexed into industry standard DSO formats. The user may specify the format of the
DSO that the data port is assigned to. The choices are: DSO-A which allows only one data port to be mapped into
the DSO and DSO-B which allows multiple data ports from multiple SRU cards in the system to be mapped into the
same DSO time slot. If the DSO-B format is selected, then the user can specify the type of DSO-B format required
(b-5, b-10 and b-20) and the sub-rate position that the data port will occupy within the DSO-B frame.
In b-5 mode, the DSO is divided into five sub-rate positions, each of which are occupied by a data port operating at
9.6 Kbps, 4.8 Kbps, or 2.4 Kbps. Additionally, one or two 19.2 Kbps circuits are supported in b-5 mode. Each
would occupy two of the five sub-rate positions. Add itionally, data circuits running at 28.8 Kbps or 38.4 Kb ps are
supported in b-5 mode and will occupy three or four of the five available sub-rate positions. In b-10 mode, the DSO
is divided into ten sub-rate positions, each of which are occupied by a data port operation at 4.8 Kbps or 2.4 Kbps.
In b-20 mode, the DSO is divided into 20 sub-rate positions, each of which are occupied by a data port operating at
2.4 Kbps.
In the application shown in Figure 14, the IMACS with the SRU card (on the right hand side) can either send each
sub-rate on a separate DS0 (DSO-A format) or groom multiple sub-rate channels into a single DS0 (one of the DSOB formats).
March 2001 Page 48

Zhone Technologies, Inc. IMACS Product Book, Version 4
S
Local
DTE
V.35
CSU/DSU
OCU-DP
IMAC
T1 carrier
Network
IMA C S w / SR U
Figure 14 - IMACS With SRU Card Application
The SRU card also supports X.50 division 3, an ITU (CCITT) standard for sub-rate multiplexing. The
maximum bandwidth of the SRU card is 115.2Kbps. The SRU card provides the ability for software
configurable delay optimization. If delay optimization is used on all 10 ports, the maximum bandwidth
available will be 76.8Kbps. Software-initiated diagnostics supported on the SRU card is the same as on the
HSU card. Table 15 describes the SRU card specifications.
-
March 2001 Page 49

Zhone Technologies, Inc. IMACS Product Book, Version 4
Table 15—SRU Card Specifications
Model Number # of data ports Physical Interfaces Electrical Interfaces
822060 SRU Card 10 10 female 8-pin RJ-48 RS-232C, V.24
822061 SRU Card 10 10 female 8-pin RJ-48 RS-232C, V.24
822160 SRU Card 10 10 female 8-pin RJ-48 RS-232C, V.24
822460 SRU Card 4 4 female 26 pin DB-26 RS-422
822560 SRU Card 10 10 female 8-pin RJ-48 RS-232E
Operational Interface DCE—full duplex
Interface Settings Asynchronous, synchronous, V.14
Sub-rate Framing Format X.50, V.14, DSO-A, DSO-B with 5, 10 or 20 divisions per DSO
Sub-rate Ti me slot number 1 through 20 dependi ng on sub-rate framing format
Synchronous Data
Format Transparent
Transmit Clocking Software configurable per port; internal or external
Speeds 2.4; 4.8; 9.6; 14.4; 19.2; 28.8 and 38.4 Kbps
Asynchronous Data
Format V.14 or proprietary
Stop Bits Software configurable per port; 1 or 2
Data Bits Software configurable per port; 5, 6, 7 or 8
Parity Software configurable per port; none, odd, even, space or mark
Speeds 2.4; 4.8; 9.6; 14.4; 19.2; 28.8 and 38.4 Kbps
Signaling
DSR Tied to DTR
CTS Software configurable per port; on, off (tied to RTS)
CTS delay Software configurable per port; immediate, 30, 60 or 100 ms
RLSD Software configurable per port; permanently on, follows remote RTS (drop
Standards Compatibility
AT&T TR54075 Sub-rate Data Multiplexing - A Service of DATAPHONE Digital Service
ITU-T V.24 Definitions for Interchange Circuits Between DTE and CE
ITU-T V.28 Electrical characteristics for unbalanced double-current interchange
ITU-T X.50 Division 3 Fundamental Parameters of a Multiplexing Scheme for the International
ITU-T V.14 Transmission of Start-Stop Characters over Synchronous Bearer Channels
EIA RS232 Interface between DTE and DCE employing serial binary data interchange
FCC Part 15 Subpart B
UL 1950 UL Standard for Safety of Information Technology Equipment
CE EN 500 81-1 Electromagnetic compatibility generic emission standard Part 1 Residential,
CE EN 500 82-1 Electromagnetic compatibility generic immunity standard Part 1
CE EN 60 950/A2 Safety of information technology equipment including electrical business
on receipt of IDL or CGA RED)
Network Equipment-Building System (NEBS) Requirements: Physical
Protection
Interface Between Synchronous Data Networks (note: does not support
600bps data
(using Async to synch converters)
commercial and light industry
Residential, commercial and light industry
equipment
March 2001 Page 50

Zhone Technologies, Inc. IMACS Product Book, Version 4
3. FRAD Card
The 823160 Frame Relay Assembler/Disassembler (FRAD) user card provides eight ports for transport of low speed
data across Frame Relay Networks. The FRAD can encapsulate HDLC protocols (such as SDLC). Each port can be
independently configured for asynchronous, transparent synchronous data or HDLC.
When taking data from the on-board RS-232 port, the FRAD card supports speeds of 2.4, 4.8, 9.6, 14.4, 19.2, 28.8
and 38.4 Kbps, independently configured on a per port basis. The aggregate Frame Relay encapsulated traffic
coming out of the WAN card can be configured to transmit at 56Kbps or 64 Kbps.
When processing HDLC data, the flags and the CRC are re move d before assembling the frames. For asynchronous
data, start and stop bits are removed before the frames are assembled. Other data is treated as a transparent data
stream and all bits will be encapsulated into transmitted frames. The FRAD card supports proprietary subaddressing over a PVC. This sub-addressing is transparent to the Frame Relay Transport Network, and allows
multiple ports on a single FRAD to share the same PVC, resulting in lower costs.
The FRAD card also maintains performance statistics detailing the number of frames transmitted, number of frames
received, number of octets transmitted, number of octets received, number of frames dropped before being received
during a 15 minute interval and a status field describing the conditional that caused the dropped packets (DTE port
down, loop back in progress or port in standby). All these performance statistics are gather for 24 hours, in 1-hour
intervals. The FRAD card also provides test frame generators for additional diagnostics.
In the application represented by the Figure 16 , the router on the left (at a remote office) is connected to the IMACS
via the FRAD card at 9.6Kbps, along with other voice traffic from a PBX. The router traffic is mapped onto a DS0
on the T1 link to the Central Office where it is separated by a DACS and directed towards a Frame Relay network
and switched/routed to the destination router at the headquarters. See Figure 15 for an illustration of the FRAD
Card’s capabilities and Table 16 for the FRAD Card’s specifications.
March 2001 Page 51

Zhone Technologies, Inc. IMACS Product Book, Version 4
PBX
IMACS w/ FRAD
Router
Figure 15 - IMACS FRAD Card Application
PSTN
DACS
Frame
Relay
March 2001 Page 52

Zhone Technologies, Inc. IMACS Product Book, Version 4
Table 16—FRAD Card Specifications
Model 823160 FRAD Card
Number of Ports 10
Speeds 2.4; 4.8; 9.6; 14.4; 19.2; 28.8 and 38.4 Kbps
Physical Interface 10 Female 8-pin RJ-48
Electrical Interface RS232, ITU-T V.28
Data Format Synchronous and asynchronous
Data Protocol Async or HDLC (SDLC); transparent
DLCI 16 to 991
LMI ANSI, CCITT, LMI (Gang of Four)
Maximum Frame Size 5 to 512 bytes
Frame Relay Aggregate Rate 56 or 64 kbps
Time Slot Number for WAN 1 through 31 on an WAN (T1/E1) link
Diagnostics
HDLC Test Pattern Active or inactive
Loop Back To DT E, to network or remote
Synchronous Data
Format Transparent
Transmit Clocking Software configurable per port; internal or external
Asynchronous Data
Format V.14 or proprietary
Stop Bits Software configurable per port; 1 or 2
Data Bits Software configurable per port; 5, 6, 7 or 8
Parity Software configurable per port; none, odd, even, space or mark
Speeds 2.4; 4.8; 9.6; 14.4; 19.2; 28.8 and 38.4 Kbps
Standards Compatibility
BellCore GR-63-CORE Network Equipment-Building System (NEBS) Requirements:
AT&T TR54075 Sub-rate Data Multiplexing - A Service of DATAPHONE Digital
FCC Part 15 Subpart B
ITU-T V.28 Electrical characteristics for unbalanced double current
UL 1950 UL Standard for Safety of Information Technology Equipment
CE EN 500 81-1 Electromagnetic compatibility generic emission standard Part 1
CE EN 500 82-1 Electromagnetic compatibility generic immunity standard Part 1
CE EN 60 950/A2 Safety of information technology equipment including electrical
Physical Protection
Service
interchange currents
Residential, commercial and light industry
Residential, commercial and light industry
business equipment
March 2001 Page 53

Zhone Technologies, Inc. IMACS Product Book, Version 4
4. OCU-DP Card
The OCU-DP (Office Channel Unit - Data Port) is used to interface directly to DSU/CSUs (Data Service Units
Channels Service Units) supporting data traffic up to and including 64Kbps. A four-wire circuit can connect the
OCU-DP card to a DSU/CSU that can be located up to four miles away. In switched 56 Kbps mode, users can
access the network on an as-needed basis by dial-up commands. The system unit must be equipped to provide -48
VDC power to fully support the functionality of the OCU-DP card.
OCU-DP Card Models
The IMACS supports three cards for support of external CSU/DSUs:
• 8249 OCU-DP 2 Port Card
• 824160 OCU-DP 5 Port Card
• 824660 OCU-DP 10 Port Card
The 8249 OCU-DP card supports two ports while the 824160 and 824660 are five and ten port cards, respectively.
All OCU-DP cards support RJ48 female connectors.
Each OCU-DP port can be independently programmed to operate at 2.4, 4.8, 9.6, 19.2, 56 and 64 Kbps in either
DSO-A, (one channel per DS0) or DS0-B format, which allows multiple data ports from multiple OCU-DP cards in
the system to be mapped into the same DS0 time slot. If the DS0-B format is selected, the user then specifies the
type of DS0-B format required (b-5, b-10 or b-20) and the sub-rate position that the data port occupied by the data
port within the DS0-B frame.
In switched-56K mode, an OCU-DP port provides a connection for an external Switched-56K DSU/CSU that will
perform all call set-up and dialing functions. The OCU-DP card converts the call set-up commands into standard
signaling and sends the signaling over the WAN facility.
All OCU-DP cards support a low speed secondary channel that is established in the 8
slot to which the OCU-DP port is assigned. The secondary channel can be used for testing and maintenance of the
main circuit or for the transmission of other, independent, low speed data. The specification table shows the
secondary channel rates associated with the standard primary port rates of the OCU-DP card.
The 8249 OCU-DP card also supports two methods of error correction. The first is known as “Majority Vote” and
applies to the lower data rates, specifically, 2.4, 4.8 and 9.6 Kbps. The other is known as the BCH (BoseChaudhuri-Hocquenghem) method and applies to data rates of 19.2 Kbps and 56 Kbps. In the case of a 19.2 Kbps
circuit, the error correction information is placed in the same DS0 that the circuit occupies. In the case of a 56 Kbps
circuit, the error correction information is placed in a following, adjacent DS0 time slot on the WAN aggregate.
On all OCU-DP car ds, performance statistics are collected by the system and are available through the user
interface. Performance statistics include Errored Seconds (any second with an error), Severely Errored Seconds
(any second with an error rate exceeding 10E-3) and Consecutive Severely Errored Seconds (CSES). They are
displayed in one-hour intervals for up to 24 hours. CSES are counted by the system once ten consecutive Severely
Errored Seconds are logged. The counter stops when the system logs ten consecutive non-Severely Errored
Seconds. An OCU-DP port on the 8249 card may be programmed for OCU mode or CSU mode. OCU mode is the
most common and is used whenever the OCU-DP port attaches to a CSU/DSU over a four-wire circuit. CSU mode
allows the card to be connected directly to the digital network.
Software initiated diagnostics supported by the OCU-DP card include the setting of six different loop backs. Three
of these act on the OCU-DP card itself and are known as local loop backs and the other three generate loop back
patterns to remote devices and are known as remote loop backs. Among local loop backs, there are three types:
th
bit position of the DS0 time
• Loop backs of the 4-wire analog interface of the OCU-DP port towards the attached CSU
• Loop backs of the 4-wire OCU-DP interface towards the network
• Loop backs towards the network at the point where the OCU-DP card interfaces with the system bus
March 2001 Page 54

Zhone Technologies, Inc. IMACS Product Book, Version 4
All three remote loop backs are latching loop backs. These latching loop backs are:
• Loop back of the analog interface of the remote OCU-DP device back towards the network
• Loop back of the 4-wire interface of the remote CSU device back towards the network
• Loop backs of the 4-wire interface of the local CSU device towards the network.
An OCU-DP port may be programmed to detect and respond to both latching and non-latching (i.e., alternating)
DDS-format OCU loop back codes that are initiated from the remote end of the circuit. A time-out option
authorizes the OCU-DP port to automatically release the loop back after ten minutes.
March 2001 Page 55

Zhone Technologies, Inc. IMACS Product Book, Version 4
Table 17 depicts the OCU-DP card’s specifications. For further information regarding Performance Monitoring and
Diagnostic Capabilities, see Chapter 13, IMACS System Testing and Diagnostics.
Table 17—OCU-DP Specifications
Model Number Number of Ports Physical Interfaces
Model 8249 2 Female 8-pin RJ-48
Model 824160 5 Female 8-pin RJ-48
Model 824660 10 Female 8-pin RJ-48
Data Format Synchronous—binary, serial
Data Encoding Bipolar, return to 0, AMI
Line Interface 4-wire
Speeds 2.4; 4.8; 9.6; 14.4; 19.2, 56 and 64 Kbps
Sub-rate Framing Formatting DS0-A, DS0-B with 5, 10 or 20 divisions per DS0
Error Correction Majority vote for speeds 9.6kbps or less; BCH for 19.2, 456 and 64kbps (8249
model only)
Secondary port As described in AT&T 62310, 62411 Addendum and TA (pass through only) TSY
000077 and TA TSY000083, a separate lower speed data circuit, which may be
used for testing and maintenance. Modes are on or off.
Distances
Supported
Primary Secondary Line Loss Limit 19 Ga. 22 Ga. 24 Ga. 26 Ga.
Rate Rate Rate dB (KF) (KF) (KF) (KF)
2400 --- 2400 34 133.0 90.7 71.5 56.8
2400 133 3200 34 114.3 79.1 61.9 48.7
4800 --- 4800 34 97.6 65.8 51.1 40.2
4800 267 6400 34 86.3 57.5 44.8 35.1
9600 --- 9600 34 74.2 48.3 37.1 28.4
9600 533 12800 34 67.5 42.9 32.8 25.2
19200 --- 19200 34 60.0 36.9 27.6 21.0
19200 1067 25600 34 57.0 33.9 25.1 19.9
56000 --- 56000 43 60.7 35.0 24.5 17.6
56000 2667 72000 43 57.6 33.3 23.1 16.5
64000 --- 72000 43 57.6 33.3 23.1 16.5
Primary Port Rate Secondary Port Rate
56 kbps 2,666 bps
19.2 kbps 1,066 bps
9.6 kbps 533 bps
4.8 kbps 266 bps
2.4 kbps 133 bps
Operational Modes Software configurable per line ocu or csu
Standards Compliance
AT&T TR62411 Accunet T1.5 Service Description
TA-TSY-000077 Digital Channel Banks- Requirements for Data port Channel Unit Functions, Issue
TA-TSY-000083 Generic Requirements for the Digital Data System (DDS) Network Office Channel
BellCore Pub 62310 DSO Digital Local Channel Description Interface Speci ficati on (August 1993)
CCITT T1.107-1988 Digital Hierarchy- Format Specifications 1988
ANSI T1.107b-1990 Digital Hierarchy- Supplement to Format Specifications (Synchronous Digital Data
3, April 1986
Unit, Issue 2, April 1986
Format), June 1991
March 2001 Page 56

Zhone Technologies, Inc. IMACS Product Book, Version 4
5. BRI Card
The 826xxx line of BRI Cards offers industry standard ISDN BRI “U” or “S/T” Interfaces. Each BRI Card supports
eight BRI “U” Interfaces for long line circuit provisioning, or “S/T” Interface for local provisioning. The BRI
Interface provides two bearer and one data channel over two wires (1 pair). The S/T interface provides the same
functionality over 4-wires (2 pair). In addition to this, each BRI “U” Interface supports 256x Zhone Technologies
NTUs or Adtran 64/1218 NTUs, providing remote NTU management. With the 826361 and 826461 cards available
with host release 5.1.X or above, full NTU management and ISDN switch signaling are supported.
The Basic Rate Interface “U” Interface card offers connectivity to sites located up to 18,000 feet from the integrated
access system. This distance is influenced by factors such as wire gauge, bridge tap and loading patterns as
described in ANSI T1.601-1992 specifications. The BRI cards are equipped with eight “U” interfaces that can carry
one BRI, 2B+D channel. This will give users either two 64 Kbps or one 128 Kbps bearer channels per interface.
The “U” Interface is also provides optional sealing current for maintaining wire pair performance. When used with
IMACS WAN and Server Card options, the BRI card supports two transmission protocols (BRITE for the
826361/826461 models and Zhone Technologies proprietary protocol for 826070/826171 models), facilitating
leased line or IDSL (2B1Q) provisioning, BRI to PRI operation and BRI (data) to Frame Relay/ATM Operation.
Either protocol allows the IMACS to extend the reach of an ISDN PBX hundred of miles away from the location of
the PBX switch as shown in Figure 16. All services are passed to the remote location with no restrictions, enabling
the end user or agent to use all PBX functionality as if they were locally attached to the switch. Management of this
solution is transparent to the PBX programmer. All remote extensions are treated as if they are local connections.
No special programming or management is necessary. For example, if there was an ISDN switch located in San
Francisco, ISDN capabilities could be transparently transported across the network to a remote call center or other
customer in San Ramon. There is no technical limit once connected to the network; service could be as far away as
New York.
ISD N Te r mina l E xten s io n
San Francisco
NT1
T1
“U”
IMA C S w ith
BRITE card
Central Office
ISD N Switch
NT1
“U”
18k ft IS DN
Service Limit
ISD N Se rv ice A re a E x t e n s io n
NT1
“U”
IMACS with
BRITE card
T1
San
Ramon
CO
Figure 16 - IMACS BRI Terminal Extension Application
March 2001 Page 57

Zhone Technologies, Inc. IMACS Product Book, Version 4
The two transmission protocol supports switched connectivity to ISDN capable switches and D channel signaling on
either a full DS0 or multiplexed 4:1 on a single DS0. The ability to multiplex 4 channels onto one DS0 allows for
more efficient provisioning. The 826361 and 826461 cards only support 3 DS0s at this time.
Another application of the BRI card is for leased line, or IDSL (ISDN Digital Subscriber Loop) as shown in Figure
18. This allows for a DDS type circuit, with 2 * 64 kbps bearer channels over a single wire pair. The leased circuit
can be any standard 2B1Q (U interface) NTU device that supports “nailed-up” (1 or 2B channels) connections and
no D channel signaling for the 826070, 826171, and 826270 cards. The 826361 and 826461 cards support a
standard non-direct OS/NE communication scheme or multipoint eoc (mp-eoc). The mp-eoc is used for sending
operations messages between the ISDN switch and NE line units.
The requirements are specified in TR-829. The performance monitoring portion of this specification will not be
implemented. For the 3-DS0 TDM, the overhead bits are transported between the LUNT and LULT as described in
TR-397, and for the 4:1 TDM, this is done in a proprietary format. This allows continued customer deployment of
D4 equipment as shown in Figure 17.
Leased Line or IDSL (2B1Q)
DTE
2B1Q
NTU
IMACS
T1/E1 carrier
Network
IMACS
2B1Q
NTU
DTE
Figure 17 - IMACS BRI Card In A Leased Line or IDSL Application
Central O ffice
T1
T1
D4 Channel Bank
IS D N
Switch
NT1
NT1
IM A C S w it h
BRITE card
IM A C S w it h
BRITE card
Figure 18 - Use of Legacy D4 Equipment Application
BRI Card Models
In both cases , leased line and BRITE, B channels carrying voice traffic on the BRI card can be compressed t hrough
the ADPCM card to extend the user’s Servers. The only limitation on BRI traffic is that NTUs or NT1s must be
located less than 18,000 feet from the system unit.
March 2001 Page 58

Zhone Technologies, Inc. IMACS Product Book, Version 4
The 826070 BRI “U” Card has software configurable mode operation of LT and NT. It supports up to eight leased
or BRI terminal extension applications. The 826070 does not support sealing current generation or termination.
The 826171 BRI “U” Card has all of the functionality of the 826070, however, switching between the LT and NT
modes must be performed by making a menu selection and changing jumper connections on the card. Also, the
826171, unlike the 826070 the card supports a user configurable sealing current of 7.5mA or 15.0mA.
The 826270 BRI “ST” Card is designed to support “S/T” 4-wire interface applications. This card provides TE, NT1
and NT2 emulation and is commonly used to provide remote extension of four-wire BRI CPE devices from an ISDN
PBX.
This section outlines the applicable features in TR-NWT-000397. The LULT has the same master DSL transceiver
as the LT in the ISDN switch. However, the LULT differs from the LT in several respects that deal with the DSL
overhead and options for supporting multiplexing. The following list notes some of the key distinctions of the
LULT from the LT.
Features of an LT like line unit (LULT):
• The LULT “functional backplane” interface is the IMACS backplane, not a switch.
• The LULT supports 3-DS0 TDM (BRITE) for multiplexing ISDN Basic Access over a carrier system. This
implies appropriate processing and transport of the DSL overhead information.
• The LULT acts as a multipoint eoc intermediate slave node.
• The LULT has the option of disabling standard processing of the eoc to permit carrier transport of non-ISDN
applications.
• The LULT supports generic segmented performance monitoring processing.
Features of an NT like line unit (LUNT):
This section outlines the applicable features in TR-NWT-000397. The LUNT has the same master DSL transceiver
as an NT1. However, the LUNT differs from an NT1 in several respects.
• The LUNT “functional backplane” interface is the IMACS backplane, not a T interface.
• The LUNT supports 3-DS0 TDM for multiplexing ISDN Basic Access over a carrier system. This implies
appropriate processing and transport of the DSL overhead information.
• The LUNT acts as a multipoint eoc intermediate slave node.
• The LUNT has the option of disabling standard processing of the eoc to permit carrier transport of non-ISDN
applications.
• The LUNT only passes through NT1 power status bits or NT1-in-test-mode bits.
• The LUNT originates nib and aib, as well as pass on any nib values received from the customer direction and
originated by a downstream line unit.
• The LUNT supports generic segmented performance monitoring processing.
• The LUNT does not require the ANSI T1.601-1992 NT1 dc termination. It provides a simple dc resistive
signature for metallic testing purposes.
The 826x70 series of IMACS BRI cards are also designed to support external timing part of the standard
functionality. All IMACS BRI cards support extensive built in diagnostics and tests. Loop backs can be generated
on a per channel basis; with choice of loop back generation mode and loop back codes. Built in BERT tests include
off, mark, space, and 1:1, 1:7, p_1, p_0, p_1:1, p_1:7.
In addition to all of the software configurable options on the BRI card itself, the BRI card has the ability to remotely
manage up to eight NTUs. The NTU’s DTE interface type, data rate and asynchronous baud rate are a few options
that are configurable through the IMACS BRI card interface. This further enhances network manageability by
accessing all ISDN equipment from a single platform.
March 2001 Page 59

Zhone Technologies, Inc. IMACS Product Book, Version 4
Table 18 describes the BRI card specifications.
Table 18—BRI Card Specifications
Models 826070, 826171, 826270, 826361 and 826461 Basic
Rate ISDN Cards
Physical Characteristics
Number of ports 8
Capacity per port Two B (64 kbps each) and one D (16 kbps)
Physical Interface
Electrical Interface
Model 826070, 826171, 826361 and 826461 2-wire, U-interface per ANSI T1.601
Model 826270 4-wire, S/T interface per ANSI T1.602/ITU
826070 and 826171 Transmission
Range
Wire Gauge 22 AWG (.644 mm)
Distance 26,000 ft (7.9 km) 22,000 ft, (6.7 km) 18,000 ft (5.5 km)
826270 Transmission Range Distance
NT p-p Max 1500m
NT s-b Max. 1500m
NT e-b Max. 1500m. 35 m between devices
Code Alternate Mark Inversion (AMI)
Rate 192 Kbps +/- 100ppm
Timing External and internal (software configurable)
Remote NTU Configuration Options
(for 256x Zhone Technologies and
Adtran NTUs
DTE Interface Type V.36 or V.24
Procedural Characteristics
Data Protocol Transparent up to 64kbps or 128 kbps
Channel collision arbitration (Model 8262 only) As per I.430 (D channel bit echo)
Sealing Current
Amperage Jumper set-able 7.5mA or 15mA (requires -48VDC power
Control Soft set-able options for start time, duration, repeat time
Multidrop Capability (Model 8262 only) Max 2
Phantom Power
Wattage Limited to 90 mA per port.
Software Configurable Options
Models 826070 and 826171 U termination Network (nt) or User (lt)
Model 826270 S/T termination TE, NT point-to-Point, NT short-bus, NT extended
Termination Mode for 826070 and
826171
Termination Mode for 826270 Lease, Proprietary Interworking
23 UK SWG
Remote NTU not applicable for the 8263 and 8264.
(Model 8261 only)
(Model 8262 manual settings)
bus
Lease, Proprietary, Interworking, NTU-1
channel
Female 50-pin RJ-27X Telco connector
1.430
24 AWG (.511 mm)
25 UK SWG
26 AWG (.405 mm)
27 US SW
March 2001 Page 60

Zhone Technologies, Inc. IMACS Product Book, Version 4
Table 18—BRI Card Specifications (continued)
B-Channel Mode None, B1, B2, B1+B2, or 128 kbps
D-subchannel None, 1, 2, 3 or 4 (used for BRITE mode)
Sealing Current Off or On per port (Models 826361 and 826171 only)
Design Standards for Models 826070 and 826171
ANSI T1.601 ISDN Basic Access Interface for Use on Metallic Loops for
ANSI T1.602 ISDN Signaling Specification for Application at the User-
ITU-T I.430 ISDN, Basic User-network Interface - Layer 1 specification
TR-NWT-000397 ISDN Basic Access Transport System Requirements
GR-000303 Integrated Digital Loop Carrier System Generic Requirements,
Design Standards for Model 826270
ANSI T1.605 ISDN Basic Access Interface for S and T Reference Layer 1
ITU-T I.430 ISDN, Basic User-network Interface, Layer 1 specification
TR-NWT-000397 ISDN Basic Access Transport System Requirements
GR-000303 Integrated Digital Loop Carrier System Generic Requirements,
Application on the Network Side of the NT (layer 1
Specification) 8261, 8263
Network Interface – Layer 2 Specification
Objectives and Interface
Specification
Objectives and Interface
The following is a summary of the general requirements of the LULT and LUNT as described in the TR-NWT-
000397.
Function LULT LUNT Notes
DSL master transceiver (2-wire U interface) Yes ANSI T1.601.1992 & TR-393
DSL slave transceiver (2-wire U interface) Yes ANSI T1.601.1992 & TR-393
Sealing current so urce Yes
Sealing current termination
DC Test Signature Yes Yes ANSI T1.601-1992
Metallic Test Access Yes TR-476
Loop backs Yes Yes
6. DSO-DP
The 825460 DSO Data Port/G.703 Data Unit (DSO-DP/G.703) is a plug-in user card for the system. The DSODP/G.703 provides a 64 Kbps interface to a DSO of a T1/E1 network. The card supports four (4) ports which
provide a 64 Kbps interface to a DSO on a T1 or E1 WAN link. Each DSO-DP/G.703 card can be installed in any
User Slot and provides four (4) DB15 female connectors.
The DSO-DP/G.703 card can be programmed to operate in either DSO-DP mode or in G.703 mode. In G.703 mode,
the card supports either co-directional or contra-directional operation and this option can be set on a port-by-port
basis. In DS0-DP mode, in addition to Transmit Data and Receive Data, the card can be programmed to either
provide a 64 Kbps bit clock and an 8 kHz byte clock to the attached device or to receive those two clocks from the
attached device.
In G.703 Co-Directional mode, the Transmit Data and Receive Data leads are supported. The clock information and
the data make up a composite signal and the clock must be derived from the data stream. In G.703 ContraDirectional mode, the port provides separate Transmit and Receive Clocks to the attached device. Both clocks are
64 Kbps clocks with embedded 8 kHz Bipolar Violations (BPVs) to mark the byte boundaries.
March 2001 Page 61

Zhone Technologies, Inc. IMACS Product Book, Version 4
Software-initiated diagnostics supported on the DS0-DP/G.703 card include the setting of local loop backs towards
either the network or the attached DTE equipment. In addition, a remote loop back function allows the DS0DP/G.703 card to generate four DDS-compatible latching loop back codes for the far-end OCU, CSU, DSU or DS0DP equipment respectively. A time-out option authorizes the DS0-DP/G.703 port to automatically release the loop
back after ten minutes.
7. BnR IP Concentrator Card
The 822860 BnR IP Concentrator card provides a means of concentrating network management data from up to 8
remote IMACS onto a single asynchronous SLIP link for connection to a NMS. Essentially the 822860 takes IP
management data from the 8 B7R-formatted DSOs and concentrates it onto a single, asynchronous SLIP line which
can then be connected to an asynchronous terminal server for connection to a LAN-based NMS.
Management information from remote IMACS systems can be directed to the IMACS containing the 822860 over
the Facilities Data Link (FDL) or an ESF T1 link as shown in Figure 19. FDL is a 4 Kbps channel normally used to
manage the T1 link. When the FDL is used to carry IMACS management data it is no longer able to carry T1
management data as well.
IMACS
4Kbps
IMACS
IMACS
FDL
NMS
DACS
IMACS
IMACS
IMACS
IMACS
IMACS
T1
Up to 8 DS0s
IMACS
38.4Kbps
Terminal Server
Figure 19 - IMACS Using the 822860 For Network Management
March 2001 Page 62

Zhone Technologies, Inc. IMACS Product Book, Version 4
The remote IMACS systems must be configured with the TCP/IP CPU software option. Remote IMACS units send
management information in IP packets over the FDL to an intervening AT&T DACS II. The DACS II can be
configured to convert the IP management information fr om the FDL channel into a full DS0 using a link level
protocol calle d Bit-4 Redundant (B4R). Even though the management information is only 4 Kbps it will occupy the
full 64 Kbps DS0. The resulting 8 DS0s are then routed over T1 link(s) to the IMACS that contains the 822860.
Physically the 822860 is the same card as the 822060 SRU card. Both have ten RJ-48 interface ports, but on the
822860 the first eight are physically disabled and, effectively, replaced by eight “internal” ports used for the DS0s.
The ninth RJ-48 port is available for maintenance and the tenth RJ-48 port is used for the aggregate SLIP line to the
terminal server. Table 19 details the BnR IP concentrator card specifications.
Table 19—B7R IP Concentrator Card Specifications
822860 External Ports
Number 2
Port 9 Available for maintenance and diagnostics (9.6kbps)
Port 10 Asynchronous SLIP port for aggregated NMS data (9.6, 19.2, 28.2 and 38.4 kbps
Physical Interface Female 8-pin RJ-48
Electrical Interface RS232, ITU-T V.28
Procedural Interface DCE—Full Duplex
IP Address Software configurable on port 10
Subnet Mask Software configurable on port 10
Options (port 10)
Data Bits Software configurable per port; 5, 6, 7 or 8
Stop Bits Software configurable per port; 1 or 2
Parity Software configurable per port; none, odd, even, space or mark
Internal Ports
Number 8
Protocol DS0 using Bit-7 Redundant (B7R or B4R) protocol
Data Rate Preset to 4 kbps
IP Address Of the corresponding remote IMACS
Subnet Mask Software configurable (same for all 8 internal ports)
Standards Compatibility
EIA RS232 Interface between DTE and DCE employing serial binary data interchange
ITU-T V.28
Electrical characteristics for unbalanced double-current interchange circuits
7. PortMaster Integrated Office Router (PM-IOR)
Introduction:
The Zhone Technologies Integrated Office Router (IOR) integrates Internet/LAN connectivity within the IMACS
and StreamLine product solutions. From a single customer premises device, the IOR card, in conjunction with other
voice and data cards, will allow service providers to bundle voice, data, ISDN, and Internet services.
The IOR is a collaborative effort on the part of Lucent Technologies and Zhone Technologies. The hardware design
is built from the Lucent model OR-HS, (Office Router, High-speed), and the Zhone Technologies model 821460
dual port V.35. The model number of the IOR is 828060. The IOR is a single blade device in the form factor of the
Zhone Technologies modules provides a fully featured IP (IPX) router card that operates in both Zhone
Technologies IMACS and StreamLine chassis. The versions for the host software supporting the IOR are the
StreamLine 1.1 and IMACS 3.8/5.1.
The IOR is fully standards compliant. The card provides secure Internet access, firewall packet filtering, LAN-toLAN connectivity, and management of the communications network.
March 2001 Page 63

Zhone Technologies, Inc. IMACS Product Book, Version 4
y
X
V
To
PSTN
To
Frame
Rela
oice
Ethernet
IMACS
Channelized
T1
Repeater/Switch
Figure 20 -
Bundled Voice and Internet Services
Technical Specifications:
Product Compatibility IMACS 600, 800 or 900 Chassis Releases 3.8 or 5.1
Routing Protocols Routing Information Protocol (RIP), OSPF, Lucent Technologies ComOS,
UDP, ICMP
LAN Protocols TCP/IP, IPX
WAN Protocols Point to Point (PPP), Frame Relay (up to 14 PVCs supported, Inverse ARP
Data Rates From 56 Kbps to 1.544 (T1) or 2.048 Mbps (E1)
Hardware Interfaces 1 Ethernet 10BaseT LAN, 1 – Asynchronous serial (115.2 Kbps), 1 NxDS0
Frame Relay or PPP WAN, 1 RJ-45 Console Port
Server Connectivity Frame Relay or WAN Servers, PPP, Connection to WAN or ATM server
Configuration and Management SNMP, Telnet, Out-of-band console re mot e management, Flash Upgrade
capability
March 2001 Page 64

Zhone Technologies, Inc. IMACS Product Book, Version 4
V. Alarm Cards
The Model 840 xxx Alarm Cards provide the capability to input external alarm signals to the IMACS and to output
alarm signals from the IMACS to an external device. Depending on the model, from 3 to 28 alarms may be input
and from 4 to 14 alarms can be output.
The alarm input sensors are current loop detectors, with an operating range of 4 to 20 mA detection. Input sensors
can be selected as active (they both supply and detect current and, therefore, can not be isolated and provide surge
protection only) or passive (current sense only, completely isolated passive current detectors). When selected as
passive sensors, the current source is provided externally and the sensors are Opto-isolated from the source of the
alarm. If the sensors are configured as active, they can provide current source for the loop as well as current
detectors, not isolated from the external loop. Depending on the model, power for active sensors can originate from
network battery (usually +48 VDC) or system voltage (+12 VDC).
Input alarm conditions are reported on the Active Alarm screens, and may be logged and/or reported in the same
manner as other IMACS alarms. Alarm reporting can be in the form of an ASCII string or an SNMP trap,
depending on the network configuration and host software o ptions installed.
Alarm signals are output via dual-pole, double throw relay switches. Depending on the model, these relays may be
of Form A (normally open), Form B (normally closed), Form C (switched) or a combination of Form A, B and C
contacts. All alarm outputs are relay-isolated. Power for these circuits must be provided externally.
The alarm contacts are connected to the external alarm equipment through on or more (depending on model) 50-pin
Amphenol connectors located on the front panel of the Alarm Card.
The Alarm card model 840160 provides 4 input sensors and 4 output Form C closures. It can use either +48VDC or
+12VDC to power the input sensors. If +12VDC is used, care must be exercised not to ground the circuit. The
840160 card model also has a -12VDC strapping option that allows it to be used in either European (CE Mark)
systems or in US systems.
The Alarm card model 840260 provides 3 input sensors and 3 output Form C closures, one of which can only be
used to signal power failure of the unit. It can use either +48VDC or +12VDC to power the input sensors. If
+12VDC is used, care must be exercised not to ground the circuit. The 840260 card model also has a -12VDC
strapping option that allows it to be used in either European (CE Mark) systems or in US systems.
The Alarm card model 840360 provides 28 input sensors and 14 output closures (4 Form A, 2 Form B and 8 Form
C). It can use either +48VDC or +12VDC to power the input sensors. If +12VDC is used, care must be exercised
not to ground the circuit. The sensors are grouped into two groups of 14 each for the purpose of selecting current
source, either from the network battery or the system. Within each group, an alarm sensor can be independently
configured for active or passive operation. The 8403 also has a -12VDC strapping option that allows it to be used in
either European (CE Mark) systems or in U.S. systems. Additionally, it also includes a buzzer to provide an audible
alarm. The buzzer can be sounded locally. This capability allows a remote site to transmit an audible alarm. The
840360 also provides a single FXS phone interface that provides a “Voice Order Wire” capability from a remote site
and the voice channel can be transported being via a time slot to a central site. This connection is Loop Start only,
with the “ring” signal being indicated through the buzzer, and is presented via an RJ-11 jack located on the front
panel of the Alarm card. The buzzer and the phone must both be configured to use the same time slot, but only one
of the functions can operate at any time.
March 2001 Page 65

Zhone Technologies, Inc. IMACS Product Book, Version 4
Table 20—Alarm Card Specifications
Model 840160, 840260, 840360
Physical Interface Female 50-pin RJ-27x Telco connector
Electrical Interface 4 to 20 mA Active Current Loop
Alarm Input Modes Active/passive (jumper selectable per port)
Alarm Input Trigger External circuit opening/closing (software selectable per port)
Alarm Input Power Requirements Network batter (+48V DC) or system voltage (+12V DC). Needed
only in Active Mode
Alarm Input Power Sour ce through
jumper selection
Alarm Output Modes Active/standby (software selectable per port)
Alarm Output Trigger Major alarm/minor alarm/any alarm (software selectable per port)
Alarm Output Power Source Supplied by external device
Alarm Output Action Open/close
I/O Ports 840160 840260 840360
User-defined Input 4 3 28
User-defined Output 4 Form C 4 Form C 4 Form A, 2 Form B, 8 Form C
Automatic on power fail 0 1 1 Form C only
Model 8403 Buzzer
Type Piezo buzzer
Tones 3kHz internally generated or user supplied via the network
Modes Local or remote (software selectable)
Model 840360 Telephone Port
Physical Interface RJ11F
Type FXS Loop Start
Loop Resistance 2400 Ohm
Loop Current 18 mA to 32 mA
Termination Impedance 600 Ohm
Nominal Transmit TLP -10.0 dB to + 5.0 dB in steps of 0.1 dB
Nominal Receive TLP -10.0 dB to +2.0 dB in steps of 0.1 dB
PCM Coding µ-Law only
Standards Compatibility
UL 1950 UL standard for safety of information technology equipment
CEN 60 950/A2 Safety of information technology equipment including electrical
CEN 50082-1 Electromagnetic compatibility generic immunity standard part 1
Selection applies to all ports in 840160 and 840260. Selection
applies to a group of 14 sensors in 840360.
business equipment
for commercial, residential and light industry.
VI. Server Cards
1. ADPCM Voice Compression Server
The 887160 ADPCM (Adaptive Differential Pulse Code Modulation) server card is designed to compress digital and
analog voice traffic for transmission over wide area network links. The level of compression for an individual
channel is software configurable at 24Kbps, 32Kbps or 40Kbps. This card requires a matching card at the other end
to decompress the voice channels to normal 64 Kbps operation. A single ADPCM card is capable of compressing
64 channels of voice simultaneously. Since the ADPCM card is a server card, these 64 channels can be originated
from a variety of interfaces, including FXS, FXO, E&M, SRU, BRI, and T1/E1. In a 3.x platform, up to two
ADPCM server cards can be supported per IMACS system for a total of 128 compressed voice channels. In a 5.x
platform, 3 ADPCM cards could be used to carry a total of 192 voice channels.
March 2001 Page 66

Zhone Technologies, Inc. IMACS Product Book, Version 4
The sum of the compression rates for the engine pair must equal 64Kbps. A 32Kbps circuit can only be paired with
a 32Kbps circuit. A 40Kbps circuit can only be paired with a 24Kbps circuit and vice-versa. The ADPCM server
card can also pair a low speed asynchronous data transmission (19.2Kbps or less) from an SRU port with a 40kbps
engine. This data path will occupy a 24Kbps engine. Group II FAX is supported in 32Kbps channels and Group III
FAX is supported in 40Kbps channels.
Modem support up to 4.8Kbps, and V.32bis to 9.6Kbps is supported in 32Kbps channels. Modem speeds up to
12Kbps, and V.32bis speeds up to 14.4Kbps is supported in 40Kbps channels. Modem data is not supported in
24Kbps channels.
The ADPCM card supports Transition Signaling as defined by ANSI T1.302-1989 with the exception of the Alarm
bits. ANSI T1.302 specifies signaling at the 32Kbps compression rate. The ADPCM card uses this scheme for
24Kbps and 40Kbps although it is not included in the standard.
The ADPCM card can be used in a variety of applications to reduce the number of transmission lines for efficient
transport of voice traffic. It can be used in:
• PBX-to-PBX trunk appl ication
• Automatic Call Distribution application
• Efficient wireless base station/hub application
PBX-to-PBX Trunk Application
Figure 21a shows the IMACS with an ADPCM server is used to co mpr ess two T1 or E1 PBX-to-PBX trunks i nt o a
single trunk. The voice from each PBX is connected via a digital T1 or E1 connection to the IMACS. The vo ice
channels are routed to the ADPCM server, where each voice channel is compressed to 32 Kbps. The compressed
voice is routed to the outbound T1/E1 link to the other IMACS unit, where it is decompressed and placed back into
two T1 or E1 trunks to the remote PBX. PBX-to-PBX trunk lines can be compressed 2:1 to reduce leased line
charges. The application is also valid for analog PBXs and key systems.
T1/E1
T1/E1 carrier
IMACS IMACS
Network
PBX
T1/E1
PBX
Figure 21a - IMACS Using ADPCM for PBX to PBX Application
March 2001 Page 67

Zhone Technologies, Inc. IMACS Product Book, Version 4
Automatic Call Distribution Application
The ADPCM server can be used to reduce leased line charges in automatic call distribution or remote call center
applications by increasing the number of voice circuits supported on a single T1 or E1.
The application shown in Figure 21b illustrates an ISDN-based automatic call distribution system. The IMACS is
used to provision BRI remotely via BRITE (BRI Terminal Extension). With the IMACS, ten BRI circuits can be
extended to remote locations over a single T1 line, and 13 over a single E1 line. The IMACS is able to do this by
placing the 2B+D signal into 2.25 time slots (1 for each B, and .25 (16Kbps) for the D channel).
The ADPCM server is used to increase the number of BRI circuits supported per T1 or E1 by compressing the B
channels in voice only applications. This means that a 2B+D channel can be transported in 1.25 time slots (.5 for
each B, and .25 for the D channel). Hence, 19 BRI circuits (38 voice channels) are transported over a single T1 and
24 BRI circuits are transported (48 voice channels) over a single E1.
ISDN or Automatic
Call Distribution Switch
BRI-U BRI-U
IMACS
IMACS
Voice is compressed
T1/E1
Backbone
network
2:1 for efficient
Voice Provisioning
IMACS
BRI-U
NT1
BRI-ST
ISDN Terminals
Agent Positions
Figure 21b - IMACS In An ISDN-based ACD System
. . . . . .
IMACS
BRI-ST
ISDN Terminals
Agent Positions
March 2001 Page 68

Zhone Technologies, Inc. IMACS Product Book, Version 4
Wireless Base Station Application
In the application shown in Figure 22, the IMACS is used as a channel bank at each of the remote Base Stations. In
each of the stations, the IMACS is connected via T1/E1 or Analog voice ports to the radio transmission equipment.
The voice circuits that are destined for the switching center are sent to the ADPCM voice compression server at each
base station. This compressed voice traffic is then groomed with other Base Station data traffic and transmitted over
Fractional T1/E1 lines. An IMACS is used at a central location to groom the Fractional T1/E1 lines into two T1s or
E1s. These two lines are connected to the Switching Center where an IMACS with two ADPCM servers is used to
decompress the voice circuits and send them to the switch via four T1s or E1s.
ADPCM Engines at Base Station/Hub/MSO
Main Switching Office
(MSO)
IMACS
T1/E1
MSO
Switch
Base Stations
1
2
3
4
5
6
V.35
E1/T1
Radio
Equip.
IMACS
V.24
Alarms
Aux.
Equip
6 Fractional T1/E1s
E&M/FXS
Maint.
Phone
Base Station/Hub
IMACS
V.35
E1/T1
Alarms
V.24
Radio
Equip.
Equip
Aux.
Cellular
Packet Data
E&M/FXS
Maint.
Phone
Cellular
Packet Data
Data
Figure 22 - IMACS In A Wir e le ss Base Station Application
Base Station to MSO voice traffic can be compressed to efficiently backhaul traffic, which reduces line charges. An
alternative to this application would be to transport the voice from the Base Station to the Hub uncompressed over
the Fractional T1s and E1s and then perform the voice compression function in the IMACS at the hub. Table 21
describes the ADPCM Server card specifications.
March 2001 Page 69

Zhone Technologies, Inc. IMACS Product Book, Version 4
Table 21—ADPCM Server Card Specifications
Input Voice Channels Can originate from any 2-wire or 4-wire voice card or from a DSO on a WAN
(El/T1 or HDSL) interface. µ-Law & A-Law 64Kbps PCM compatible on a per
channel basis
Input Sub-rate Data SRU data traffic at 19.2Kbps or less can be carried on a 24Kbps sub-channel
Input BRI traffic B channel voice traffic can be compressed at any of the configurable rates
Modem Data Support Transcoder rate: 24, 32 or 40 Kbps; Modem Data: none, up to 4.8Kbps, V.32
to 9.6Kbps, up to 12Kbps and V.32 bis to 14.4Kbps
Fax Support Transcoder rate for fax: 24, 32 or 40 Kbps; none, Group II and Group III fax
Voice Quality As measured by Mean Opinion Score (MOS) analysis, a subjective
evaluation with a range of 0 (poor quality) to 5 (good quality). Toll
quality voice is accorded a MOS of 4.0 24Kbps transcoder rate MOS is
3.6-3.8; 32Kbps transcoder rate MOS is 4.0-4.3 and 40Kbps transcoder
rate MOS is 4.0-4.3
Echo Cancellation No n pr o vided—typically not required
Signaling Transmitted in-band utilizing CAS transitional signaling, as per ANSI
T1.302—1986 for 32Kbps and modified for use with 24Kbps and
40Kbps. Note Robbed Bit Signaling Alarm Transmission, as specified
in ANSI T1.302a-1989 is not supported
Maximum Card Count 3 (with 3.x CPU-2 active with 1 redundant or 3 active, 5.x CPU 3active)
Transcoder Operation Compliant to G.761 Alarm Indication and Fault Handling
Standards Compliance ANSI T1.3021989, ANSI T1.302a 1992, ANSI T1.3031989, CE EN
500- 81-1, CE EN 500-82-1, CE EN 60950/A2, ITU-T G.721, ITU-T
G.723, ITU-T G.726 12/90
2. ISDN Primary Rate Interface (PRI) Server
The PRI Server Card provides flexible access and routing of PRI-based ISDN services. The ISDN PRI Server can
be used for enabling applications such as Video Conferencing, Video Broadcast, ISDN Grooming, and Fractional
PRI provisioning. The PRI Server card supports B channel bandwidth of 56K, 64K, 384K, 1536K and Multi-Rate
speeds where available. Multi-Rate speeds allow the PRI server card to select calls in increments of 64Kbps. In
areas where Multi-Rate is not supported by the local ISDN switch, an Inverse Mux (IMUX) Server Card should be
used to aggregate individual 64Kbps calls.
The PRI card can be utilized with the 8213 Switched HSU Card for RS-366 and V.25bis bandwidth on demand
dialing. Additionally, regular HSU cards can be used for DTR dialing. The PRI server card supports both the
Network and User side protocols associated with ISDN PRI services and therefore the IMACS can be used to both
originate and terminate ISDN calls.
The following components make up the BRI/PRI solution:
• One 881160 Multi-Server Card
• One 65100 BRI/PRI Service Translation Software Package
• Optional WAN Interfaces with associated Line Interface Modules
• Optional ISDN ‘U’ and “S/T” Interfaces
March 2001 Page 70

Zhone Technologies, Inc. IMACS Product Book, Version 4
Three ISDN PRI Server Cards are supported:
• 8840A ISDN PRI Server Card with 1 D Channel
• 8840B ISDN PRI Server Card with 2 D Channels
• 8840C ISDN PRI Server Card with 8 D Channels
The cards provide flexible access to PRI-based ISDN services such as Switched 384, Switched T1, and Switched
56/64. The PRI Server Card (PRI card) provides both local D channel origination and termination and D channel
consolidation. The PRI Server card is available in three different software versions based on the number of D
channels (1, 2, or 8) to be supported. It offers a perfect alternative to standalone ISDN access devices when other
“non-ISDN” voice and data services must be consolidated in addition to ISDN services.
The 8840B and 8840C ISDN cards can be simultaneously connected to several network and user side ISDN PRI
facilities. The ISDN PRI card provides D channel support of both the network side protocol and the user side
protocol. Typically, the IMACS with an ISDN PRI card, supplies the network side protocol on a D channel
connected to a PBX, and provides the user side protocol on the D channel connected to a carrier switch.
The 8840C ISDN PRI server card, which supports eight (8) D-channels can be configured to route calls from a PBX,
multiple PBXs, and DTE devices to multiple ISDN service providers. The 8840x ISDN PRI Server does not support
BRI-to-PRI translation. This application is supported by the 65100 ISDN BRI-PRI translation software running on
an 8811xx ACS card.
NFAS (Non-Facility Associated Signaling)
All ISDN PRI cards can be configured to support NFAS (Non-Facility Associated Signaling). The IMACS limit for
NFAS is 191B+D in T1 environments (8 times 24 minus 1 D channel) and 239 B+D in E1 environments (8 times 30
time slots minus 1 D channel).
A basic ISDN PRI facility is a T1 link that consists of 23 B channels and 1 D channel (23B+D), or an E1 link that
consists of 30 B channels and 1 D channel (30B+D). Note that one time slot on any E1 link is reserved for framing
and maintenance use, and is neither a B channel nor a D channel. The D channel provides signaling for all of the
(23 or 30) B channels on the facility carrying that D channel.
However, many ISDN applications have relatively low call rates (i.e., the D channel is not very busy), but need
more than 23 (or 30) B channels to carry user (bearer) traffic. In these cases, a D channel can be set up to perform
signaling not only for the B channels on its own facility, but also for B channels on other facilities (i.e., other T1/E1
WAN links). When a D channel is so provisioned, it is considered to be performing non-facility associated
signaling (NFAS). The IMACS is limited to 8 WAN links. Thus the IMACS limit for NFAS is 191B+D in T1
environments (8 times 24 minus 1 D channel) and 239B+D in E1 environments (8 times 30 minus 1).
Although IMACS supports NFAS, it can only be implemented within private networks or in public networks where
the service provider supports it. Within EC and EFTA countries NFAS is considered an EC-MOU2 supplementary
service, which is still at the discussion stage and therefore is not supported by any of the European Service
Providers.
Remote Login
In addition to carrying ISDN signaling information, the D channel can also be used to log into a remote system unit
to check card status, and perform necessary system maintenance. This unique application does not require B
channel allocation. The ISDN call is placed on the D channel to the ISDN network and routed to the D channel of
the remote unit. Coordination with the ISDN facility provider is necessary to obtain the number for the remote
system unit.
March 2001 Page 71

Zhone Technologies, Inc. IMACS Product Book, Version 4
Applications
The ISDN PRI Server card can be used in a variety of applications:
• Fractional ISDN PRI provisioning
• Video conferencing
• Integrated ISDN access with SINA
• Video Broadcast
• Router with redund ant trunk routing via I S DN
• Router adding incremental bandwidth
• PRI to FXS
Fractional PRI Provisioning
An IMACS equipped with a 8840C PRI Server card is used to groom multiple fractional PRI circuits into one or
more PRI circuits for backhaul to an ISDN switch. Perhaps a customer may not need the entire bandwidth delivered
by a PRI circuit. The optimal alternative would be to purchase a fractional PRI service delivered over a regular T1
or E1 circuit. When a service provider has multiple fractional PRI customers, the service provider can deploy the
IMACS to groom the multiple fractional PRI circuits into one fully utilized PRI T1/E1 circuit, which is back hauled
to the switch. This concentration of PRI circuits reduced back haul costs for the service provider, and conserves
T1/E1 ports and D-channels on the ISDN switch itself.
Figure 23 shows that three customers are subscribing to ISDN services. Each customer is using a fractional PRI
service. Each customer could be directly connected to the ISDN switch, which would consume three fractional
T1/E1 circuits, and three D channels. Instead, the 3 fractional ISDN circuits are connected to a PRI Server equipped
IMACS. The PRI server grooms the B channels in the three fractional ISDN circuits into one circuit. It also grooms
the three D-channel circuits into a single D channel that is routed to the switch. The IMACS benefits in this
application include saving on back haul costs, switch port costs and switch system resources.
Customer 1
10B+D
ISDN
Switch
Customer 2
7B+D
Customer 3
5B+D
IMACS
23B+D on T1
30B+D on E1
Figure 23—Fractional PRI Provisioning Using IMACS
ISDN Video Conferencing and Video Broadcast
The IMACS is used to connect video-conferencing equipment to an ISDN PRI line. In Figure 24, a video CODEC
is sharing a PRI line with an ISDN PBX. The IMACS is simultaneously routing calls on a call by call basis to either
the PBX, the CODEC, or out to the network. The video-conferencing equipment can be connected via an RS-449
connection with an RS-366 dialer or directly to the IMACS via an ISDN PRI interface. A connection to the
IMACS via the RS-449/RS-366 combination would require the use of a switched HSU card in the IMACS.
March 2001 Page 72

Zhone Technologies, Inc. IMACS Product Book, Version 4
PRI
IMACS
PRI
ISDN
Provider
PBX
CODEC
Figure 24—Video Conferencing System and PBX Sharing A PRI Line
By grooming the PBX and CODEC PRI circuits onto a single, outbound PRI facility, the IMACS utilizes Dynamic
Bandwidth Allocation (DBA). The PBX would seize B-channels on a call-by-call basis, utilizing one B-channel for
every call. The Video Codec would request a pre-determined number of B-channels. For example, if a 384K call
was required, the Video CODEC requests a single 384K circuit, which would consume six of the B-channels. If the
ISDN service supports 384K calls, or Multi-Rate services, and the bandwidth is available, the ISDN server card will
connect the Video CODEC to proper time slots. If the bandwidth is not available, the IMACS rejects the call. If
384K-bonded service is not supported by the ISDN service, the IMACS must be equipped with an Inverse
Multiplexer (IMUX) server card. The IMUX server card is capable of bonding or aggregating multiple 64K circuits
into a single larger capacity circuit.
Inbound calls would be handled in a similar manner. All inbound calls would be screened by the IMACS’ PRI
Server card. Calls destined for the PBX would be routed to the PBX, and calls destined for the Video Conference
Unit would be routed there. If the video Codec was in use, the IMACS will inform the ISDN service that the unit
was in a busy condition.
A unique feature of the PRI Server card is its ability to combine multiple ISDN circuits to form a Video Broadcast.
This feature is very useful for distance learning applications where a central site broadcasts video to multiple remote
locations. In this application, an IMACS equipped with a PRI server card takes a video source and makes a twoway connection with the first remote IMACS video-conference site as shown in Figure 25. Once that connection is
established, the host IMACS calls up to a total of 32 additional remote video-conference sites and distributes the
same outbound video feed to all of those sites. These additional sites are in a view-only mode and do not distribute
video back to the central site. The loss of one or more of the remote sites will not affect the broadcast to the other
sites. This application can be upgraded to allow two-way audio to each of the sites though the use of analog voice
cards.
March 2001 Page 73

Zhone Technologies, Inc. IMACS Product Book, Version 4
T1/E1
Video
IMACS
T1/E1
Backbone
network
IMACS
IMACS
Video
Video
IMACS
Video
Figure 25—IMACS in Video Broadcast Applications
Integrated ISDN Access with SINA
The IMACS is used to support both ISDN and non-ISDN services over the same T1/E1 circuit. This multiplexing of
leased line and ISDN services is commonly referred to as Static Integrated Network Access (SINA).
As shown in Figure 26, several non-ISDN applications are used including analog voice and data applications, low
speed SNA data, and non-ISDN PBXs. Several ISDN based applic ations are being used including videoconferencing, dial routers, and an ISDN PBX. The non-ISDN circuits are groomed onto the T1/E1 circuit for
delivery to the network. ISDN applications are sent to the PRI Server card for concentration and are switched onto
the same T1/E1 circuit in time slots appropriate for switched ISDN calls. Within the network, these circuits are
groomed via a cross-connect to the appropriate services.
Phone
PBX
PBX
Router
March 2001 Page 74
IMACS
Video
PRI
SINA
Non-ISDN
Services
ISDN
Services

Zhone Technologies, Inc. IMACS Product Book, Version 4
Figure 26—IMACS Using SINA for ISDN and Leased Line Traffic
Data Backup and Bandwidth on Demand
The IMACS with a PRI server is used to back up data networks in the event of a circuit outage. In the example
shown in Figure 27, an IMACS is used to connect a router to a leased line circuit. The PBX is using the IMACS
equipped with a PRI server card to connect to the PRI circuit. In normal operation, both the voice traffic and the
data traffic simply pass through the IMACS. In the event that the leased line circuit is dropped the router will sense
the loss of data and attempt to dial bandwidth via its second line. This second port can be configured on the IMACS
to accept dial commands using the V.25bis, or to dial a pre-determined number when the IMACS senses DTR.
When the router senses that a failure has occurred, it will request bandwidth from the IMACS. If the PRI does not
have enough bandwidth to satisfy the route r’s request, the IMACS reje cts the call. The router will then request
another call with smaller bandwidth requirements and will monitor the original leased line for presence of data.
When the router detects that the leased line is back in operation, it will switch its transmission path back to its
original state, and drop the ISDN connection.
This configuration is utilized to provide bandwidth-on-demand during peak utilization times such as nightly
backups. With this application, the PBX utilizes the PRI bandwidth on a call-by-call basis during the day, and the
router utilizes the leased line. At a pre-determined time-of-day, the router would request all or the majority of the
PRI bandwidth. The router utilizes both the leased circuit and the ISDN circuit for a set period of time. For
example, the PRI line would be used during the day to carry the voice calls, at night the PRI line would be used to
increase the bandwidth available for the nightly computer systems backup. The router routes packets over both the
leased line and the PRI line until the backup was complete. At that time, it would disconnect the PRI call.
PBX
PRI
Router
IMACS
V.25bis/DTR
Dialing
T1/E1
PRI
T1/E1
Backbone
network
ISDN
Network
T1/E1
PRI
IMACS
PBX
V.25bis/DTR
Dialing
Router
Figure 27—IMACS Using A PRI Server Card For Data Backup
March 2001 Page 75

Zhone Technologies, Inc. IMACS Product Book, Version 4
PRI to FXS Termination
The IMACS is used to connect calls to an analog modem rack as shown in Figure 28. This application is usually
used to terminate a mix of ISDN originated calls and analog modem originated calls to the same destination. This is
common in remote access applications where there is a need to support both existing analog modem applications and
new digital ISDN connections over the same network facility. End users can migrate as needed from analog
modems to ISDN, sharing the same facility, and maximizing utilization of network bandwidth. The IMACS
receives all calls, examines the called number and routes the analog modem calls to the FXS hunt group. ISDN data
calls are routed directly to the ISDN remote access server. This application only works for inbound calls since the
modems in the rack cannot be used to dial out through the IMACS over ISDN.
March 2001 Page 76

Zhone Technologies, Inc. IMACS Product Book, Version 4
ISDN
Network
PRI
Modem Rack
FXS
IMACS
Mail
Server
LAN
ISDN Remote
Access Server
Modem
PSTN
PRI
Figure 28—PRI to FXS Termination
Routing Capabilities
Call Routing
An IMACS system can be simultaneously connected to several Network and User side ISDN PRI facilities and to a
user’s data terminal equipment such as a video codec or LAN router. DTE is usually connected to the system’s
HSU cards.
Any call originating from a HSU port (with the exception of the Switched HSU card), must be associated with a call
profile. The call profile specifies which D channel is to carry the call. Any device attached to an HSU port that is
able to receive incoming calls is assigned a unique number that allows the system to route the incoming call to it.
Optionally, a shared hunt group phone number can be assigned to the same HSU port.
When an incoming call is received by the system, it first scans all of the primary HSU or FXS phone numbers to
attempt a match. If no match is found, the system then sea rches the list of hunt gr oup numbers to find a match. If a
match is not found, the system will begin searching the D channel routing tables, for routing of the call to a PRI line.
If no matches are found, the call is rejected.
Local Routing
From an IMACS perspective, devices such as video codecs or PBXs that are directly attached to the system (i.e. do
not pass through a carrier network to connect to the system) a re considered “local” devices. All HSU port s are local
devices. Any PRI device, such as a PBX, that is connected to an IMACS D channel configured for “Network” side
is a local device. Local routing is defined as call routing between any two devices. Calls can be locally routed from
a PRI to a PRI (for example, from a local PBX to another local PBX), or from an HSU to a PRI. HSU to HSU call
routing is not supported.
Incoming calls are routed based on the called phone number, not on call profiles. Because the IMACS system does
not provide billing information, users may want to prohibit local routing of D-channels. For example, a carrier may
require that all calls ar e routed through the CO based switch for billing purposes. T o provide for this, local routing
can be disabled.
If local routing is disabled, any call coming into the system on a network side (i.e. local) D channel will be routed
only to a user side D channel based on the called number. Even if the called number matches, such a call will never
be routed to an HSU port or a network side D channel when local routing is disabled. When local routing is
enabled, then any call coming in on a D channel will be routed to the first matching phone number, regardless of
whether or not the match is for a local device.
March 2001 Page 77

Zhone Technologies, Inc. IMACS Product Book, Version 4
Bi-directional Default Routing
Bi-directional Default Routing is provided for automatic routing when a node is configured with two Primary Rate
D channels as shown in Figure 29. In two channel systems, the user does not have to configure any routing
information, as all calls received on one D channel are automatically routed to the second D channel. The user only
needs to enter routing information for those calls destined to a local HSU or FXS ports.
HSU/FXS
ISDN
Switch
D ch 1
IMACS
D ch 2
PBX
Default
Figure 29—Bi-Directional Default Routing
Alternate Routing
Alternate ro uting is provided for calls to take an alternat e path in the event of a congested or failed primar y tr unk.
When there are more than two Primary Rate D channels, phone numbers can be assigned to more than one D
channel. Calls placed or routed through the PRI server will now have an alternate route if no bandwidth is available
on the first specified path. Alternate routing will also take place in the event of a failure of the first Primary Rate
circuit. In the example shown in Figure 30, the call from D1 is usually routed to D2, as the D channel numbering is
more specific. However, if the D2 trunk become congested or go out of service, the call will be routed to D3.
ISDN
Switch
415-6xxx
Dial 415 - 6xxx
IMACS
D1
PBX
D2
D3
ISDN
Switch
415-xxxx
Figure 30—Alternate Routing
March 2001 Page 78

Zhone Technologies, Inc. IMACS Product Book, Version 4
DPNSS Trunk Routing
Digital Private Network Signaling System #1 (DPNSS) is the predominant Common Channel Signaling scheme
used in the United Kingdom for private inter PABX communications. DPNSS Trunk Routing provides low delay
for multi DPNSS channel provisioning off a single E1 DPNSS aggregate. This is achieved by mapping the B
channels to dedicated time slots rather than to hunt groups, which in turn pr ovides efficient D channel grooming and
subsequent billing.
3. Management Channel Concentrator (MCC) Server
The Management Communications Concentrator (MCC) provides management connectivity to remote IMACS
systems. It can concentrate the TCP/IP management traffic from up to 131 remote IMACS networks onto either a
single, local 10 BASE-T Ethernet port, or encapsulate the information as per RFC1490 on to a Frame Relay link.
There can be up to 3 MCC server cards in an IMACS chassis in non-redundant operation. The following hardware
and firmware must be included in an IMACS to add MCC Server operation:
• 880360- CPU Control Card with 8 T1/E1 Cross Connect (redundant-capable)
• 892260/892360/892460 - 8 T1/E1 Interface card w/ 128K NVRAM.
• 881360 - Advanced Communication Server (ACS) with 131 logical ports
• 60511 - Host Firmware version 5.0.x
• 63110 - MCC Server firmware
The following protocols are supported by the MCC:
• Ethernet Media Access Control Protocol (MAC)
• Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) (RFC 1122)
• Internet Protocol, version 4. (IP) (RFC 791, RFC950, RFC 1122)
• Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP) RFC 792
• User Datagram Protocol (UDP) RFC 768
• Routing Information Protocol (RIP) (RFC1812)
• Frame Relay (RFC1490)
The MCC provides routing between the bxr formatted ports and Ethernet, allowing IP management data of remote
IMACS’ to be terminated onto a local area network. The MCC can route between any of its interfaces depending on
its configuration. In addition to the B7R protocol used for T1, and B4R used for E1, a full DS0 is also provided on
all ports. B7R and full DS0 cannot be combined unless configured in groups of 64.
The MCC offers far more interfaces and functionality than the BnR, thus replacing it and the terminal server
required to bring the IP traffic to a LAN. The MCC can be configured to use unnumbered or numbered interfaces.
If unnumbered interfaces are used, MCC is accessed through the global E t hernet address regardless of what interface
is used. If numbered interfaces are used, each interface has a local IP add ress. When unnumbered interfaces are
selected, the IP address entered on the port is the IP address of the remote device. Similarly, when numbered
interfaces are used, the IP address entered for any given numbered port is the IP address of the local port itself.
Unnumbered interfaces help conserving IP addr esses as only one address is used per interface. This addressing
method may not be compatible with HP Openview.
The MCC routes IP datagrams between all of its interfaces, based on each datagram’s IP destination address.
Datagrams are directed (or routed) to the interface carrying the sub-net to which the datagram belongs or is being
transported to, according to the content of the routing table. The routing table may be supplied with dynamic routes
from the Routing Information Protocol (RIP) when enabled. If no match is found in the routing table, a default route
can be designated to direct all unresolved datagrams to a specific interface.
Initial configuration of the MCC can made through the local VT100 port. When a working interface is established
to the CPU hosting the MCC, subsequent configurations can be done remotely via SNMP/TELNET. All
March 2001 Page 79

Zhone Technologies, Inc. IMACS Product Book, Version 4
w
w
configurable port parameters are permanently stored in NVRAM and downloaded to the card during startup.
Statistics are available on a per port and protocol basis.
IP-based management information from IMACS clients is typically provided to the MCC by a Digital Access and
Cross-connect System (DACS) as Bit Seven Redundant (B7R) or Bit Four Redundant (B4R) DS0 channels on a T1
or E1 link. The MCC routes IP packets among the 131 available WAN interfaces, the local host CPU and Ethernet.
Each interface represents a separate network or subnet as specified by the IP address and Netmask combination.
Three of the 131 are high-speed interfaces that can either be configured as Nx64 kbps (N=1 to 24 for T1 or 1 to 31
for E1). Those interfaces can independently be configured for the Frame Relay protocol or for transparent HDLC.
The 128 lower-speed WAN interfaces can be configured in groups of 64, to either be in BnR mode.
Figure 31 shows FDL channels from the remote IMACS a, b, c, and fed into a DACS II for translation into multiple
B7R encoded DS0 channels. IMACS I, connected to the DACS II, routes IP datagrams to IMACS II thr ough the
alternative high-speed interfaces. IMACS II in turn routes datagrams to the Local Ethernet to the NMS.
Remote IMACS using FDL
DA CS
IMACS
IMACS
1 Nx64 Kbps T1/E1
IMACS
IMACS
2 Nx64 Kbps T1/E1
Nx 64Kbps T1/E1
B7R formatted DS0's from DACS II
/MCC
IMACS
/MCC
NMS
Figure 31—MCC In A Multilevel Concentration Application
March 2001 Page 80

Zhone Technologies, Inc. IMACS Product Book, Version 4
4. ACS-FRS Advanced Communication Server - Frame Relay Server
The 881160 FRS card concentrates multiple N x 56K or N x 64K frame relay data streams onto one or more
Nx56/64K links of the IMACS. In addition to frame relay concentration, the card encapsulates data for Nx56/64K
HDLC or SDLC data streams. RED frames can be discarded rather than forwarded to the FRS end-point screen.
The ACS-FRS uses flag sharing, meaning that the closing flag of one frame will be the opening flag of the following
frame.
The frame relay server software (v1.8) runs on the card, which provides up to 68 logical ports. Up to 128 permanent
virtual circuits (PVCs) can be configured on a single card. The aggregate speeds of all ports associated with each
FRS cannot exceed 8 Mbps.
The FRS has a maximum of 68 ports. When all four “C” ports are used to interface to other cards such as the HSU,
64 ports are left to interface to the external cross-connect.
The FRS card also maintains detailed performance statistics both on a per port and a per PVC level.
Frame Relay Server Specifications
There can be up to three Frame Relay server cards in an IMACS chassis in non-redundant operation. The Frame
Relay Server performance figure of 4000 Frames/Second was obtained using 64 byte frames. The following
hardware and firmware must be included in an IMACS to add Frame Relay Server operation:
• 880360- CPU Control Card with 8 T1/E1 Cross Connect (redundant-capable)
• 892360/892460 - 8 T1/E1 Interface card w/ 128K NVRAM
• 881160 - Advanced Communication Server (ACS) with 68 logical Frame Relay ports
• 60500 - Host Firmware version 5.0.0 or above
• 62180 - ACS Frame Relay Server firmware
Table 22—Frame Relay Server Specifications
Input/Output Ports 68 logical ports (maximum)
Input Traffic Ports T 1, E1, fT1, fE1, V.35, RS422, EIA530, OCU-DP, FRAD
Output Traffic ports T1 , E1, fT1, fE1, V.35, RS422, EIA530, OCU-DP, FRAD
Output Port types/Input UNI DCE, UNI DTE, NNI, Nx64K/56K FRAD
Maximum Frame Size 4K Bytes
Traffic Bandwidth 8 Mbps, Full Duplex
Performance 4,000 Frames per second (maximum)
Number of PVCs 128
System Capacity Maximum 3 per IMACS
Management RFC1315, DTE MIB, Frame Relay Service MIB, SNMP Alarm Traps per RFC 1215
Connectivity Craft Interface, SNMP or TELNET
LMI Options Q.933 Annex A, ANSI T1.617 Annex D, LMI (Gang of 4), None
Information Rates CIR = 0 to 2048 Kbps, Bc = 0 to 2048 Kb, Be = 0 to 2048 Kb
Congestion Handli ng FECN, BECN
Circuit Priorities 4 (Version 2.0 or above)
March 2001 Page 81

Zhone Technologies, Inc. IMACS Product Book, Version 4
Frame Relay Access and Concentration Server
This section highlights the capabilities of the IMACS Frame Relay server card as a cost-effective, efficient, and
intelligent high-speed Frame Relay Assembly and Disassembly (FRAD) device and access concentrator in a Frame
Relay network. This enables the service provider to deliver Frame Relay and Internet services with a high degree of
quality in an economical fashion. The following is a list of the Zhone Technologies Frame Relay server card key
benefits:
Highly efficient assembly, disassembly and concentration of Frame Relay traffic allows for significant Frame Relay
switch port savings.
High Frame Relay port density offers significant hardware savings when compared to typical backbone switches
making it suitable for deployment at the customer premises. Bringing the frame relay network features closer to the
end-user and CO reduces backhaul charges due to efficient use of the frame relay backbone switch port.
100% compliance with industry Frame Relay standards enables ready interoperability in multi-vendor networks.
Support for existing UNI (User to Network Interface) and NNI (Network to Network Interface) standards implies
that the frame relay server easily integrates into existing, standards-compliant frame relay infrastructure of the
service provider.
- Manageability via SNMP and TELNET eliminates need for separate network management package and
offers compre hensive diagnostics for both physical and logical networ k.
- Complete Support for physical layer diagnostics. In addition, it provides network access for a wide range of
devices ranging from high-speed data interfaces (HSU), DDS interfaces (OCU-DP, DS0-DP), IDSL interfaces
(BRI), and sub-rate data (FRAD).
- Comprehensive, standards-based congestion management techniques.
Standards based congestion management ensure interoperability with existing infrastructure and enables the service
provider to offer better, more cost-effective Frame Relay services to its subscribers.
The Frame Relay Server can be deployed in the following application scenarios to provide a very cost-efficient and
high-quality Frame Relay access to the end-users:
• Frame relay switch port savings
• Frame relay and Internet service provisioning
• IDSL service provisioning
• Grooming and concentration in cellular networks
• Central Offic e FRAD
• Frame relay concentration at hub sites
Frame Relay Switch Port Savings
Figure 32 shows an IMACS equipped with one or more Frame Relay server cards that is utilized at the service
provider’s Central Office to efficiently concentrate multiple lower speed Frame Relay circuits into a consolidated
Frame Relay stream into the backbone Frame Relay switch. This results in significant savings in port occupancy on
the Frame Relay switch. It is amplified by the fact that these channelized ports on the backbone switches are much
more expensive than their unchannnelized counterpart s.
The presence of 68 highly-integrated channelized Frame Relay ports combined with the statistical multiplexing
advantages of Frame Relay facilitate the savings by reducing the backbone switch port occupancy by over 2.5 times
(67 DS0 circuits instead of 2 4 DS0 circuits on a single channelized T1 trunk). I n a typical case this reduces circuit
cost per DS0 by 20%.
March 2001 Page 82

Zhone Technologies, Inc. IMACS Product Book, Version 4
Without Frame Relay Server:
Channelized Frame Relay
DACS
With Frame Relay Server:
circuits with sm aller CIRs
Frame Relay
Network
DACS
Channelized Frame Relay
circuits with smaller C IR s
Concentrated Frame
Relay Stream on T1/E1
IMACS
Frame Relay
Network
Figure 32—IMACS Using Frame Relay Server Cards
Frame Relay and Internet Service Provisioning
The inherent flexibility of the IMACS platform and the versatility of the Frame Relay server are brought into
synergy to provide significant savings to both the service provider and user. An IMACS is used as a CLE
(Customer Located Equipment) to provide a wide-variety of voice and data services to a multi-tenant premise. The
service provider can now add Internet services and native Frame Relay services by simply installing a Frame Relay
server in the existing IMACS as shown in Figure 33. There is no significant addition of new hardware or replacing
of existing platform or complicated provisioning schemes. The Frame Relay Server also provides a PVC backup
feature, which the service provider can offer as a premium, uninterrupted service to a customer in case the primary
link fails.
The cost benefits are realized by the service provider as a result of:
• The high density of logical Nx56/64K ports on the Frame relay server enables very efficient grooming and
concentration of Nx56/64K Frame Relay connections to the service provider access links.
• Savings in capital expenditure due to minimal hardware upgrades and ease of provisioning. In addition, the
remote management capabilities of the IMACS and Frame Relay server improve the quality of service delivered
thereby lowering costs.
March 2001 Page 83

Zhone Technologies, Inc. IMACS Product Book, Version 4
Multi-tenant Premises
X.25 PAD
Nx56/64
PBX/Key
System
Mainframe
Router
Nx56/64 or T1/E1
IMACS
DS1/E1
Backup Link
DACS
Service Provider
Central Office
PSTN
Frame Relay
Network
Figure 33—Frame Relay and Internet Services Using IMACS’ FRAD Server
IDSL Service Provisioning
An IMACS with a Frame Relay server can be used for efficient ISDN DSL (IDSL) provisioning for Internet access
at speeds up to 128K. Each IMACS BRI card provides up to eight IDSL ports over single twisted pair wire. There
can be up to seven such BRI cards in an IMACS800/900. This arrangement cost-effectively replaces external DDS
CSU/DSU equipment and offers higher bandwidth.
Each Frame Relay server supports up to 35 NTUs at 128K over 1 T1 (with 3:1 concentration) or 1 E1 (with 2.5:1
concentration), thereby taking advantage of frame relay’s statistical multiplexing capabilities. Up to 64 DS0s are
channelized through the Frame Relay Server ports and are co ncentrated onto a single port conne cted to the network.
Three concentrator ports bring in additional NXDS0s channels to be concentrated onto the single outgoing port as
shown in Figure 34.
March 2001 Page 84

Zhone Technologies, Inc. IMACS Product Book, Version 4
2B1Q
NTU
Router
Ethernet
Router
Ethernet
Router
Ethernet
64/128Kbps
Frame Relay
2B1Q
NTU
64/128Kbps
Frame Relay
2B1Q
NTU
BRI Cards provide 2B1Q IDSL termination
FRS provides IDSL concent ration
IMACS
64/128Kbps
Frame Relay
• Support data rates up to 128 kbps over single twisted
pair over 5Km
• DDS CSU / DSU replacement with BRI-NTU scenarios
T1/E1
Frame Relay
Network
.
Figure 34—IDSL Service Provisioning
Grooming and Concentration in Cellular Networks
Figure 35 shows how a remote cell site uses an IMACS, trademarked “CellDAX” for all cellular environments, to
transport cellular voice and data traffic to the Mobile Switch Center (MSC). At the MSC, a DCS directs the CDPD
traffic (typically, a single DS0) from each of the 96 cell sites to the IMACS at same MCS. Because CDPD uses
HDLC framing the traffic from the 96 DS0s can be encapsulated by the two Frame Relay server cards located in the
IMACS. Each Frame Relay server can take in 64 DS0s directly into ports. Typically the CDPD traffic is bursty and
often less than one full DS0 and so can be groomed and concentrated by the Frame Relay server down to 48 or 24
DS0s depending upon the level of concentration needed. This results in a net savings of two or three T1/E1 spans
across the regional MSCs respectively. The MD-IS (Mobile Data Intermediate System) then processes the traffic
and routes it to the appropriate destinations.
March 2001 Page 85

Zhone Technologies, Inc. IMACS Product Book, Version 4
Mobile Switch Office
56/64Kbps
CellDAX
DS1
Mobile
Base Station
Cell
Site
# 96
T1
4 Channelized
DS1s = 96 DS0s
IMACS
T1
2 Frame Relay DS1s
IMACS
Frame Switch
MDIS
Figure 35—Cellular Network Frame Relay Application
Frame Relay Concentration at Hub Sites
In the application shown in Figure 36, a corporatio n, which serves a wide geographical area thr ough multiple branch
offices, is able to utilize the Frame Relay server’s ability to consolidate and multiplex multiple NX56/64K circuits
into a single high-speed facility. This significantly reduces its access charges from its service provider for its
corporate Frame Relay network. Typical examples include banks, health care providers, technology parks, etc.
The branch offices typically subscribe to a Frame Relay service with a Committed Information Rate (CIR) of
56/64K. At the Head Office/Data Center the traffic is typically from a “farm” of front-end processors, routers and
servers. Without an IMACS+FRS at the Head Office/Data Center, multiple circuits would occupy multiple ports in
the service provider’s switch and would be tariffed for lower individual speeds. With an IMACS+FRS, the multiple
lower speed circuits are consolidated and groomed into a single/few high-speed (Nx64K) circuit. Since the marginal
access charge of Frame Relay is lower at higher speeds, due to economies of scale, this could reduce costs.
March 2001 Page 86

Zhone Technologies, Inc. IMACS Product Book, Version 4
BRANCH OFFICES
HEAD OFFICE DATA CENTER
FEP
Data Proc
Application
IMACS
T1 Frame
Relay
Frame Relay
Network
56/64K
56/64K
56/64K
Router
FEP
FRAD
FRAD
Figure 36—Fram e Relay Concentration at Corporate Headquarter s
5. ATM SERVER CARD
Although ATM is being touted as an ubiquitous technology for all business communications services, the reality is
that it is playing a significant role so far only in backbone campus network for LAN applications for local transport.
This section highlights the benefits of the various applications of the IMACS 882060 ATM Server card and
demonstrates how it can effectively and efficiently to deploy various services. The ATM Server Card provides the
ability to provision legacy voice, data, and video services over an ATM backbone via a DS3, multi-mode and singlemode.
The ATM Server card includes support for efficient, standards-based ATM adaptation of a multitude of legacy
traffic types. Examples include analog key systems, routers, video codecs and PBXs. Legacy traffic is directed from
T1, E1, data and voice interfaces to the ATM Server, which then provide ATM adaptation and encapsulation. By
providing direct, integrated connectivity to the ATM network, the IMACS eliminates the need to run parallel
networks for ATM and TDM traffic. The ATM Server Card is based on standards adopted by the ATM Forum and
the ITU. These standards allow the IMACS ATM Server to inter-operate with a wide variety of ATM switches and
to adapt multiple traffic types for aggregation and transmission across an ATM network. Some of the well-known
switches include those from FORE, Lucent, NORTEL, GDC, ADC Kentrox.
Since the ATM Server Card fits in any IMACS server slot, service providers can deploy the IMACS in non-ATM
access networks today, and easily migrate to ATM based access by simply adding an ATM Server Card. The ATM
Server Card, combined with the wide range of interfaces on the IMACS, provides the most flexible platform for
service provisioning in the market today.
The following is a list of the ATM server card key benefits:
• Standards-based ATM adaptation for voice, video, and data. This feature enables the IMACS to adapt the
traffic from a wide variety of legacy interfaces to ATM. Therefore there is no need to upgrade or replace
existing equipment while migrating to ATM solutions. This results in significant savings in capital expenditure.
• Interoperable with deployed ATM switching equipment such as ADC Kentrox, Fore Systems, Lucent, etc. This
is a key selling point of the ATM server. Because of its interoperability with already deployed ATM switching
March 2001 Page 87

Zhone Technologies, Inc. IMACS Product Book, Version 4
equipment, it can be easily added with minimal costs when the MIS manager wants to collapse parallel ATM
and TDM networks into a single ATM network. When an ATM network is installed, typically there is excess
bandwidth and port capacity that behooves such a merger of networks. For instance, when an ATM switch is
deployed each line card will have multiple ATM ports out of which only one or two may be used for data
traffic. The IMACS w/ ATM server can be connected to the unused port(s) t hereby consolidat ing other legacy
traffic on to the ATM network. This results in significant cost savings for the customer since there is only one
as opposed to two networks to be managed.
• Provides DSO granularity for virtual circuit input. By providing DS0 granularity, the ATM server is able to
direct individual lower speed voice and data circuits to unique destinations thro ugh out the ATM network. This
is accomplished without “burning up” multiple physical ports on the ATM switches, which are expensive. The
ATM server’s highly efficient and cost-effective aggregation of lower speed CBR and VBR virtual circuits
makes this possible.
• Supports constant and variable bit rate adaptation. By supporting constant and variable bit rate services, the
ATM server tailors the adaptation to best suit application requirements for quality of service (QoS). E.g.,
typically voice and video appli cations require constant guarante ed bandwidth and stringent delay constraint and
are modeled as CBR traffic. Data, compressed voice and compressed video are amenable to variations in
bandwidth and delay requirements and are modeled as VBR traffic.
• Manageability via SNMP and TELNET. SNMP and TELNET manageability eliminates need for a separate
IMACS network management package. The IMACS and its components can be managed from the same
existing network management device that manages the AT M backbone and other device s .
The ATM server is deployed in the following application scenarios to provide a very cost-efficient and high-quality
ATM service to the end-users:
• Interactive Distance Learning/Tele-Medicine
• Legacy Adaptation to ATM
• Analog PBXs/Key Systems
• Digital PBXs
• Nx56K/64K Data terminal equipment
• Video Codecs
• Transparent LAN Extension
Legacy Adaptation to ATM
The addition of the ATM Server card further extends the capabilities of the IMACS as a truly integrated access
platform by efficiently provisioning a multitude of legacy services for transportation over an ATM network as
shown in Figure 37.
There are still many legacy services (PBXs, key systems, video codecs etc.) which need a parallel TDM network to
operate since they are not “ATM-ready.” Two parallel networks drive up the cost of installation, operation and
maintenance. Since businesses have very significant capital investment in these legacy systems and processes they
cannot justifiably be fork lifted and replaced by equivalent “ATM-ready” equipment. Furthermore, when a new
ATM campus network is deployed, typically there is excess bandwidth and port capacity that is under utilized.
What needs to be added is a cost-effective product for adaptation of all these legacy services to ATM. This would
enable connecting a multitude of “non-ATM ready” equipment to the ATM network.
March 2001 Page 88

Zhone Technologies, Inc. IMACS Product Book, Version 4
ATM
DS3/OC3c/STM1
Network
IMACS
ATM Edge Switch
Router
Figure 37—Migrating Legacy Networks to ATM
Interactive Distance Learning/Tele-Medicine
The IMACS’ integrated multi-service capabilities supports interactive distance learning applications where the
central site and the major educational centers are connected t hrough an ATM network and the remote sites are
accessed via leased T1/E1 lines.
The video stream (TDM traffic) from the central site is adapted to ATM by the ATM server and multi-cast to the
sites on the ATM network as shown in Figure 38. The ATM servers located at the Major University locations
convert the video from ATM to TDM traffic and pass it on to remote sites over leased T1/E1. The IMACS’ ISDN
PRI server is utilized in conjunction to connect the remote sites to the video-conferencing network over T1/E1
leased lines. The entire network is managed from a central network management system.
The same network structure is deployed effectively in a Tele Medicine application in which doctors from central
medical centers can exchange patient information, X-rays etc. with remote hospitals and provide remote diagnosis.
March 2001 Page 89

Zhone Technologies, Inc. IMACS Product Book, Version 4
RS36
V.2
Video Conf
System
Network Management System
DS3 ATM
IMACS
Major University
OC3c/STM1
DS3 ATM
IMACS
T1/E1 Leased Line
IMACS
RS36
Video Conf
V.2
Remote Campus
System
PRI PRI
Central Site
OC3c/STM1
T1/E1 Leased Line
Video Conf
MCU
IMACS
RS36
V.2
Video Conf
System
Remote Campus
DS3 ATM
Major University
IMACS
Figure 38—Interactive Distance Learning Application
ATM Server Specifications
Up to three ATM server cards can be functional in an IMACS in a non-redundant configuration. The ATM Server
card performance figure of 4000 Frames/Second was obtained using 64 byte frames. Table 23 depicts the ATM
Server card specifications. The following hardware and firmware must be included in an IMACS to add ATM
Server operation:
RS36
V.2
Video Conf
System
• 880360- CPU Control Card with 8 T1/E1 Cross Connect (redundant-capable)
• 892360/892460 - 8 T1/E1 Interface card w/ 128K NVRAM
• 882060- ATM Server card with 1 DS3 ATM UNI port
• 60511 - Host Firmware version 5.1.1
March 2001 Page 90

Zhone Technologies, Inc. IMACS Product Book, Version 4
Table 23—ATM Server Card Specifications
ATM I/F 1 DS3 Private UNI 3.1
Framing Cbit, M23 for DS3
Cell Delineation HCS (+ PLCP for DS3)
Clocking Line (+PLCP for DS3)
VPI Support One configurable VPI bit
VCI Support 33 - 1023 (configurable) values
Idle Cell Idle or Unassigned
TX_RX Scrambling ON/OFF
Traffic Types CBR, VBR
AALs AAL1, AAL3/4, AAL5
Number of PVCs 68 VBR, 96 CBR (with multi-user support)
Performance 4,000 FPS @ 64bits/frame
System Capacity Maximum 3 per IMACS (1 active)
Management DS3 MIB, UNI3.1 ILMI MIB, ATM MIB
Connectivity SNMP or TELNET; Access via up to seven (7) Management
PVCs
Standards ATM Forum UNI3.0, ITU-T I.363, ITU-T G.709,
BellCore TR-NWT-000253, ATM Forum Circuit-Emulation
Services over DS1/E1, ATM Forum Service Interoperability
March 2001 Page 91

Zhone Technologies, Inc. IMACS Product Book, Version 4
6. Internet Protocol Router
Internet Protocol Router: 883060 (10Base2) and 883160 (10BaseT)
Introduction:
IPR is an IP router server card that runs on the ACS hardware. It therefore must be inserted in one of the P slots of
the Zhone Technologies IMACS concentrator. IPR uses 68360 communication controller and has 4 MB of DRAM.
To use the IPR card, one must use host version 5.0. The IPR has 4 interfaces: 1 Ethernet 10Base-T or 10Base-2
LAN interface and 3 Frame Relay WAN interfaces (ports). Ethernet interface supports 10Mbits/sec and 3 Frame
Relay interfaces together support 2 * T1/E1 access speed. IPR card has no Munich ports. Frame Relay ports can be
connected thr ough HSU or WAN car ds. IPR is an IP router. This means t hat IPR forwards (routes) packets based on
IP destination address, as opposed to FRS, that forwards packets based on a Frame Relay data link (dlci) address.
IPR routes IP datagrams (packets) between Ethernet and Frame Relay PVCs. Frame Relay PVCs can be associated
with any of the 3 Frame Relay ports. (use of Ethernet is not mandatory, IPR can easily route just between Frame
Relay PVCs). The maximum number of PVCs supported is 128. IPR also has provisions to automatically forward
IP packets to and from the host (CPU) IP node of the IMACS box that IPR resides in. It automatically takes care of
all the IP fragmentation to and from the host (CPU) IP node.
In addition to routing, IPR v2.0 is capable to bridge packets between Ethernet and Frame Relay bridge PVCs, and
between Frame Relay bridge PVCs. IPR will forward packets matching an entry in the MAC addresses table,
configured manually by the user. LAN broadcasts are being forwarded to all bridge PVCs. Because no spanning
tree or learning algorithm is supported and to avoid loops, there should be no more than one physical connection
between the same nodes. The maximum number of MAC addresses supported is 9. The maximum number of
bridge PVCs supported is 9. Bridging function is enabled on host version 5.1.
IPR(s) can also be (optionally) connected to FRS server card (on the same IMACS), giving the customer an option
of concentrating Ethernet traffic in addition to other ports of concentration on the FRS card (this is called an
EtherFrad mode). This connection is possible from IPR port C1 only and is subject to bus allocation conflicts due to
hardware limitation of the ACS card.
Maximu m Byte Size:
The maximum number of bytes that an IPR can handle in a single packet is 1528 bytes (this is regardless whether a
packet arrives from Ethernet or Frame Relay interface).
SNMP Support:
IPR has SNMP support for MIB 2, as well as SNMP support for Zhone Technologies Private MIB. IPR has a
testing/debuggi ng “on-the-fly” support, which includes displaying Routing table, displaying and clearing ARP table,
displaying and clearing IP statistics, displaying and clearing PVC statistics in 15 minutes intervals for the last 96
intervals, displaying and clearing frame relay port statistics in 15 minutes intervals for the last 96 intervals,
displaying and clearing LMI statistics, displaying and clearing Ethernet statistics.
Standards Support:
• IPR uses a standard encapsulation of IP over Frame Relay (RFC 1490).
• IPR supports RIP (Routing Information Protocol, RFC 1058) for dynamically discovering IP routes from the
adjacent IP routers on Frame Relay or Ethernet. IPR also supports static routes.
• IPR supports a DCE side of the Inverse ARP Protocol (RFC 1293).
• IPR can use different LMI encapsulations: ANSI, CCITT or LMI (Gang of Four). Each Frame Relay Port can
be configured as either U-DTE, U-DCE, or NNI type.
• IPR supports Motorola LAPD packet forwarding protocol.
March 2001 Page 92

Zhone Technologies, Inc. IMACS Product Book, Version 4
Uses of IPR:
• IPR can be use d for connecting IP LANs together through Frame Relay network.
• IPR card can be used as a gateway to the Internet through Frame Relay network.
• IPR card can be used for connecting IP nodes on Ethernet to the IP nodes on Frame Relay network.
Application:
IPR-3
Frame Relay
PVC between
IPR-3 and IPR-2
IPR-2
Ethernet
LAN 2
Frame Relay
PVC between
IPR-1 and IPR-2
Ethernet
LAN 1
Frame Relay
PVC between
IPR-1 and IPR-3
Note: Frame Relay PVCs can be associated with the same or with different Frame Relay ports.
Routing Server
IPR-1
Frame Relay
Network
Ethernet
LAN 3
The IP Routing Server enables the IMACS to act as a gateway router to the Internet via bundled service deployment
or in private Intranet network deployment. Specifically, the primary market for the IP Routing Server is Internet
access via bundled service arrangements (integrated access). The bundled service marketplace is simply the
provisioning of multiple services over a single T1 or E1 to a customer. Typical bundled service arrangements
include local voice service, long distance service and a data service. Internet access is one of the possible data
services. The potential market for this technology is quite extensive. There are over 6.5 million small businesses in
the US, and about 1.3 million of these have 6 to 20 phone lines. These businesses are prime candidates for bundled
service arrangements.
The IMACS platform is unique in that it possesses many of the qualities listed below in a flexible form factor. The
addition of layer-3 (IP) data services to the product portfolio will further distance Zhone Technologies from the
competition. As equipment and technologies mature, there is a constant requirement to consolidate communications
equipment for many reasons, including:
• Lower capital costs
• Integrated mana gement
• Ease of use and installation
• Remote connection efficiency
March 2001 Page 93

Zhone Technologies, Inc. IMACS Product Book, Version 4
y
Bundled Service Deployment
The IP Routing Server is targeted at performing boundary routing functions for access to Internet or Intranet based
services. The standard application for an IMACS in this environment is in bundled service arrangements where the
IMACS is utilized to integrate voice circuits and an Ethernet-based Internet port at the customer location as shown
in Figure 39. The carrier would typically switch the voice circuits to the PSTN via a DACS, while the frame relaybased data connection from the Ethernet port would be connected to a Frame Relay network for transmission to the
Internet. An external firewall can be used for providing and maintaining security when connected to the Internet.
DACS
PBX/Key
System
T1/E1
DACS
IMACS
Router
IP Network
PSTN
Frame Rela
Network
Figure 39 – IP Routing Server For Internet or Intranet Based Services
Private Intranet Deployment
A secondary market for the IP Routing Server is private Intranet access. In the application shown in Figure 40, the
IMACS on the left is connected to a private WAN. It has a single connection to a centralized router, which provides
full IP routing functionality. The IMACS on the right has two T1 connections, one to each of the two remote
IMACS, and one connection to the router. Normally, there would be two connections to the router. However, in
this application, the IMACS on the right includes a Frame Relay Server card, which switches both frame relay
streams into the router.
March 2001 Page 94

Zhone Technologies, Inc. IMACS Product Book, Version 4
PBX/Key
System
IMACS
T1/E1
PBX/Key
System
T1/E1
IMACS
IP Network
T1/E1
IP Network
IMACS
IP Network
PBX/Key
System
Figure 40—Private Intranet Deployment Using IP Routing Server Card
IP Routing Server Specifications
Up to three IP Routing server cards can be functional in an IMACS in a non-redundant configuration. The processor
performance figure of 3500 packets/second was obtained using 64 byte packets. Table 24 describes the IP Routing
Server card specifications. The following hardware and firmware must be included in an IMACS to add IP Server
operation:
• 880360 - CPU Control Card with 8 T1/E1 Cross Connect (redundant-capable)
• 892360/892460 - 8 T1/E1 Interface card w/ 128K NVRAM
• 883060 - Advanced Communications Server (ACS) with 10Base2 card
• 883160 - ACS with 10BaseT card
• 60511 - Host Firmware version 5.1.x
• 67200 - IP Routing Server firmware
March 2001 Page 95

Zhone Technologies, Inc. IMACS Product Book, Version 4
Table 24—IP Routing Server Card Specifications
Input/Output 4 maximum (1 10-BaseT Ethernet, 3 Frame Relay Wide-Area Network)
LAN Traffic I/O 10BaseT, 10Base2
Frame Relay Traffic I/O T1, E1, fT1, fE1, V.35, RS422, EIA530
Frame Relay Port types UNI DCE, UNI DTE, NNI
MTU 1500 bytes
Traffic Bandwidth 4Mbps Full Duplex
Total Buffer Space 4 Mb DRAM
Performance 3500 Packets Per Second
No of PVCs 128
Routing Table 512 entries (up to 128 static entries)
ARP Table 100 entries (LRU)
Card Capacity Maximum 3 per IMACS
Management RFC 1315 DTE MIB, Frame Relay Service MIB, SNMP Alarm Traps per
RFC 1215
Connectivity SNMP or TELNET
LMI Options Q.933 Annex A, ANSI T1.617 Annex D, LMI (Gang of 4), None
Information Rates CIR = 0 to 2048 Kb/s, Bc = 0 to 2048 Kb, Be = 0 to 2048 Kb
Congestion Handli ng FECN, BECN
DCE Parameters N392, T391, N393 all configurable
DTE Parameters N392, T391, N393, N391 all configurable
IP subnet Topologies Point-to-point, hub-and-spoke, fully/ partially meshed subnets, and
unnumbered IP interfaces.
7. Low-Bit Rate Voice Server
The LBRV (Low Bit Rate Voice) Server card allows for the compression of 64Kbps digital voice channels into
8Kbps (plus overhead) digital sub-channels, and subsequently for the sub-channels to be multiplexed over one, two
or three composite transmission paths over Wide Area Network (WAN) links. The LBRV Server can accept voice
inputs from either ana log voice ports (such as FXS, FXO, E&M) or from T1/E1 WAN links through the IMACS.
Each LBRV / ACELP (G.729) voice compression server card supports up to three composite transmission paths at
speeds of 64k, 128k or 192k, by using one, two or three WAN time slots, respectively. The composite transmission
paths use HDLC protocol as the transport mechanism. Users assign voice channels to one, two or three transmission
paths based o n t he need to route those channels through the network. The composite t ransmission paths can be
routed directly to WAN cards or to the Frame Relay Server. When routed to a Frame Relay Server (FRS), the FRS
provides a FRAD function for the compressed voice frames. No Frame Relay sub-addressing is supported, so all
voice channels within each composite transmission paths from the ACELP will be treated as a single PVC.
There are two models of the LBRV server cards: 830060 (8 port) and 831060 (16 port) capacities. A single IMACS
chassis we can support up to 3 LBRV cards for compression of a maximum of 48 voice ports.
The LBRV card performs DTMF recognition and re-construction. This means the integrity of DTMF does not
suffer from the compression/decompression processes. The LBRV card does not support MF signaling between
switches. The following is a list of the Zhone Technologies LBRV key benefits:
• Simple topologies including Point-to-Point, Star and Mesh LBRV performs a compression and transport
function. It does NOT perform voice switching and cal l routing.
• High density of channe l s and high volume of traffic.
• LBRV solution is competitive with high volumes of traffic. There should be many (24+) voice channels in one
location.
• High reliability in mission-critical installations.
March 2001 Page 96
 Loading...
Loading...