Page 1

Setup and
Deployment
User’s Guide
For
Infrastructure Mode
DMM000009-03 Copyright 2003, MeshNetworks, Inc. All Rights Reserved
Page 2

Page 3

Setup and Deployment
Foreword
This document describes in detail the confidential and propriet ary technology of MeshNetworks’
™ Architecture. MeshNetworks products and technology are protected by US and
international patent and patent pending technology. This document represents the current
design; the contents are subject to change at any time at the discretion of MeshNetworks, Inc.
, MeshManager, MeshTray, MeshView, and MeshNetworks’ logo are trademarks or
registered trademarks of MeshNetworks, Inc. Microsoft, Windows, Windows 2000, and
Windows PocketPC are registered trademarks of Microsoft Corporation. Sun and Sun Blade
are registered trademarks of Sun Microsystems, Inc. All other product names and services
identified throughout this publication are trademarks or registered trademarks of their respective
companies. No such uses or the use of any trade name is intended to convey endorsement or
other affiliation with this publication. Copyright 2003, MeshNetworks, Inc. All Rights Reserved.
iii
Page 4

MeshNetworks
iv
Page 5

Setup and Deployment
Table of Contents
SECTION 1 - OVERVIEW...........................................................................................................1
Introduction........................................................................................................................1
Documentat io n Overview..................................................................................................1
Acronyms...........................................................................................................................1
Related Documentation ...................................................................................................2
SECTION 2 - DESCRIPTION OF THE SYSTEM............................................................3
Introduction........................................................................................................................3
Subscriber Devices (SDs) .................................................................................................4
Wireless Routers (WRs) ....................................................................................................4
Intelligent Access Points (IAPs) .......................................................................................5
Mobile Internet Switching Controller (MiSC)....................................................................5
Operational View of the System..............................................................................6
Network Architecture.........................................................................................................7
SECTION 3 - SETUP AND DEPLOYMENT................................................................................8
Subscriber Device (SD).....................................................................................................8
Equipment.......................................................................................................................8
Record MAC Address of the WMC6300..........................................................................8
Loading and Verifying Software.......................................................................................8
Testing..........................................................................................................................11
Intelligent Access Point (IAP) .........................................................................................11
Equipment.......................................................................................................................2
Record MAC Address of the IAP.....................................................................................3
IAP Assembly..................................................................................................................3
v
Page 6

MeshNetworks
Deployment.....................................................................................................................5
Initial IAP Configuration...................................................................................................6
Testing............................................................................................................................6
Wireless Router (WR) ........................................................................................................7
Equipment.......................................................................................................................7
Record MAC Address of the MWR6300..........................................................................8
MWR6300 Assembly.......................................................................................................9
Deployment.....................................................................................................................9
Initial Configuration..........................................................................................................9
Testing..........................................................................................................................10
Mobile Internet Switching Controller (MiSC)..................................................................11
Equipment.....................................................................................................................11
Network Setup Description............................................................................................12
MiSC Assembly.............................................................................................................13
Onsite Configuration of Routers....................................................................................14
Network Configuration – Device Manager.....................................................................15
Network Configuration – IAP Configuration Via Web Interface......................................15
Testing..........................................................................................................................22
Default Addresses and Logins.......................................................................................23
SECTION 4 - MAC ADDRESS TABLES..................................................................................25
IAP MAC Addresses ........................................................................................................25
WR MAC Addresses ........................................................................................................25
WMC MAC Addresses......................................................................................................26
SECTION 5 - SITE SELECTION/DEPLOYMENT GUIDELINES...............................................27
General Site Selection Guidelines..................................................................................27
Antenna Guidelines......................................................................................................... 27
vi
Page 7

Setup and Deployment
Lab Checkout...................................................................................................................28
General Deployment Guidelines.....................................................................................28
It is recommended that field deployment follow the same steps as described in
General Site Selection Guidelines..................................................................................28
Antenna Guidelines................................................................Error! Bookmark not defined.
SECTION 6 - CUSTOMER SERVICE INFORMATION.............................................................30
SECTION 7 - WMC INSTALLATION DEBUG PROCEDURES ................................................31
SECTION 8 - LICENSE AND WARRANTY INFORMATION....................................................33
SECTION 9 - FCC REGULATORY INFORMATION.................................................................38
FCC Information...............................................................................................................38
FCC RF Radiation Exposure Statement .........................................................................38
Safety Information for the Products....................................................................40
SECTION 10 - SAFETY CERTIFICATION ...............................................................................40
vii
Page 8

Page 9

Setup and Deployment
Section 1 - Overview
Introduction
The wireless broadband system allows a network operator to deploy a wireless, multihopping ad hoc network. This document describes how to set up, conf ig ure, and deploy a
system to operate in infrastructure mode. Infrastructure mode allows the user’s to have access
to a wired network. For a deployment that does not need access to a wired network, refer to the
Setup and Deployment for Peer-to-Peer Mode” document.
“
The
system are preinstalled with a default configuration for connection to a wired network. Any
configuration items described in this document are for site-specific information.
MeshNetworks recommends that the Network Operator receive setup and deployment training
at MeshNetworks’ facility prior to deploying the
provide the Network Operator assistance with site surveys and deployment.
Note: The
“professional installation” to ensure the installation is performed in accordance with FCC
licensing regulations.
system is designed for easy installation. The infrastructure components of a
network. MeshNetworks may optionally
MWR6300 Wireless Routers and IAP6300 Intelligent Access Points require
Documentation Overview
The Setup and Deployment User’s Guide is arranged in the following sections:
Section 1 - Overview
User’s Guide.
Section 2 – Description of the
Network.
Section 3 - Starter Kit Setup and Deployment
information for the Subscriber Device, Wireless Router, Intelligent Access Point, and the MiSC.
provides an overview of the Starter Kit and t he organization of the
System provides a general overview of a complete
provides installation and configuration
Section 4 - MAC Address Tables
configuration data.
Section 5 – Site Selection Guidelines
Section 6 - The Customer Service Information
need assistance with your
Section 7 - License and Warranty Information
and Warranty for the
Section 8 - FCC Regulatory Information
Starter Kit.
products.
provides three convenient tables to record network
provides deployment and installation suggestions.
provides important warnings and safety information.
Acronyms
HAS Hardware Authentication Server
IAP Intelligent Access Point
Mesh Enabled Architecture
1
section provides contact information if you
contains MeshNetworks’ License Agreement
Page 10

MeshNetworks
MiSC Mobile Internet Switching Controller
SD Subscriber Device (a host device with a WMC6300 installed and operational)
WMC Wireless Modem Card
WR Wireless Router
Related
Setup and Deployment User’s Guide for Peer-to-Peer Mode
WMC6300 Wireless Modem Card User’s Guide for Windows 2000
WMC6300 Wireless Modem Card User’s Guide for Windows XP
MeshView Administration Tool User’s Guide
MeshManager User’s Guide
MeshFlash User’s Guide
Location Analyzer Deployment Tool User’s Guide
Documentation
2
Page 11
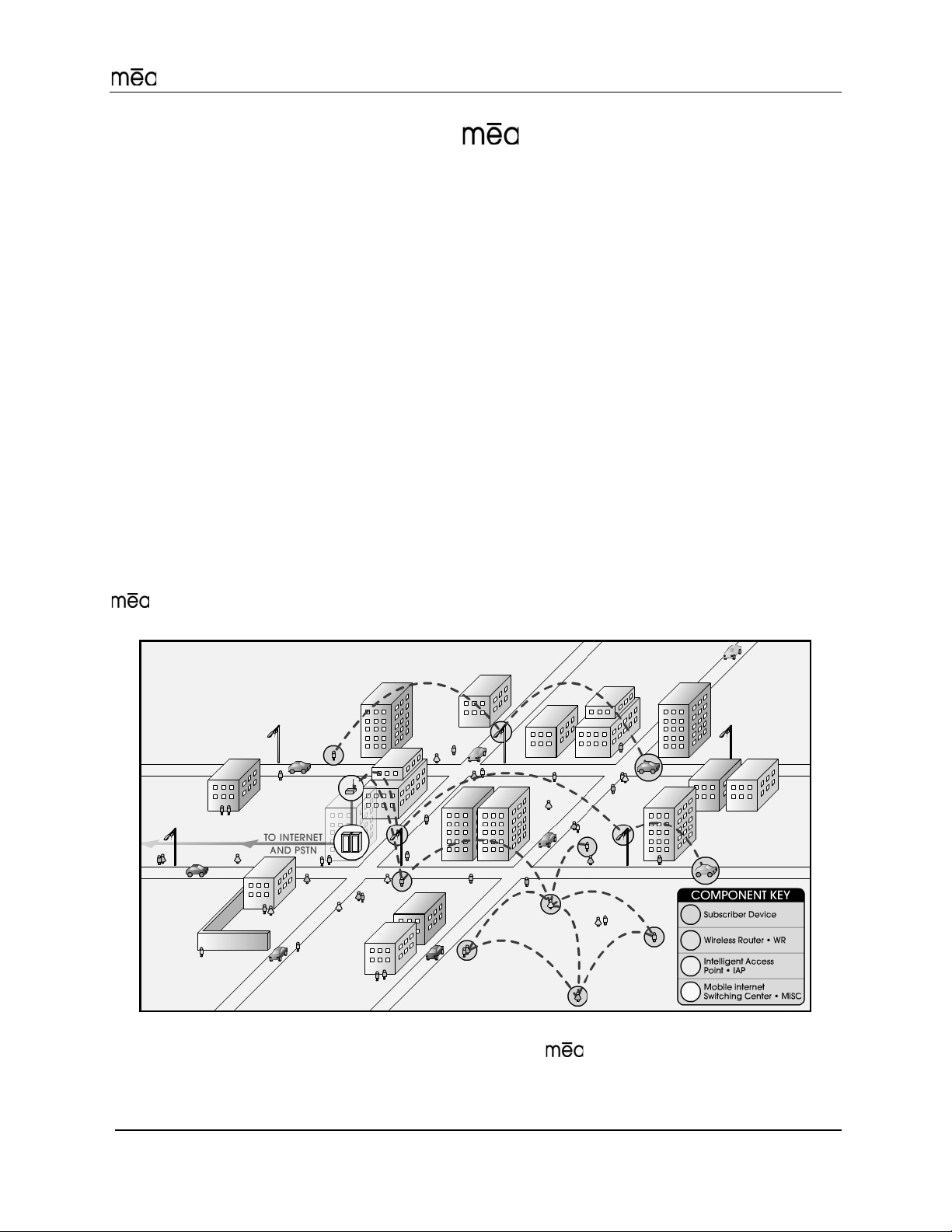
Setup and Deployment
Section 2 - Description of the System
Introduction
MeshNetworks develops Mobile Broadband communications systems with “meshed”
architectures. That is, each node can connect directly, or indirectly (by hopping through other
nodes), with any other node in the network. The peer-to-peer nature of the mesh architecture
combined with data rate control in each subscriber and infrastructure node in the network
insures reliable delivery while providing increased network capacity thr ough g eogr aphic reuse of
the frequency spectrum.
The network comprises four distinct elements:
• Subscriber Devices (SDs)
• Wireless Routers (WRs)
• Intelligent Access Points (IAPs)
• Mobile Internet Switching Controllers (MiSCs)
The overwhelming portion of the value that MeshNetworks provides is in the W ireless Modem
Card (WMC). The WMC is used in Subscriber Devices as well as in the Wireless Router and
Intelligent Access Point (IAP), both of which are types of infrastructure equipment.
MeshNetworks provides a Mobile Internet Switching Controller (MiSC) which is assembled from
industry standard equipment and conforms to industry standards. MeshNetworks also provides
the network applications, which are required for proper operation and value extr action from the
mobile Internet system.
Figure 1. Elements of the
All network elements are designed to support mobile applications. Subscriber Devices can be
either mobile or fixed, while the remaining components are typically fixed. Wireless Routers and
System
3
Page 12

MeshNetworks
IAPs can be mounted on utility poles, light poles, traffic apparatus, billboards, and buildings.
Their fixed positions allow the Subscriber Device to pinpoint its location within one second.
WRs and IAPs can also be mobile, attached to emergency vehicles, utility vehicles, or fleet
vehicles. It is important to note that the WMC technology within a Subscriber Device is identical
to the WMC technology in Wireless Routers and IAPs.
The
with end user data access rates on the order of DSL or Cable Modem. The chosen metric of
network efficiency for a data centric network is bits per second per Hertz per square kilometer
per dollar (bps/hz/km
coverage area, and cost. One of the most important factors in optimizing this metric is the
choice of network architecture.
system was designed to minimize the cost associated with deploying a mobile Internet
2
/$). This metric balances the user data rates, allocated bandwidth,
Subscriber Devices (SDs)
The MeshNetworks’ Wireless Modem Card (WMC) is
provided as a PCMCIA form factor device. The WMC is
used with an off-the-shelf IP-enabled laptop computer.
These two devices together make up a Subscriber Device
(SD).
The WMC provides access to the fixed infrastructure network
and other networks, such as the Internet, and it can also
function as a Wireless Router and repeater for other SDs.
SDs can therefore be a key part of the network infrastructure. Adding subscribers can
effectively increase the number of Wireless Routers in the network, which increases the number
of alternative paths that subscribers may utilize. This can reduce both the time and cost to
deploy network infrastructure, while also increasing the spectral efficiency and therefore the
capacity of the network. In addition, because SDs can also operate in an ad hoc peer -to-peer
mode, two or more SDs can form a network without the need for any fixed infrastructure.
Wireless Routers (WRs)
The Wireless Router (WR) is a low-cost small-sized wireless device that is prim arily deployed to
seed a geographical area, extending the range between IAPs and subscribers, and to
simultaneously increase the network’s spectral efficiency. Wireless Routers provide a number
of functions in the network, such as:
• Range Extension for Subscriber Devices and IAPs
• Hopping Points for subscriber peer-to-peer
networking
• Automatic Load Balancing
• Route Selection
• Network capacity optimization through small packet
consolidation
• Fixed reference for geo-location services
The Wireless Router's small size and light weight allow it to
be mounted almost anywhere. No towers are required. WR software can be updated via overthe-air downloads.
4
Page 13

Setup and Deployment
Intelligent Access Points (IAPs)
The Intelligent Access Point (IAP) is a lo w-cost small device that
acts as the transition point from the wireless network to the wired
core network and from there, through media gateways, out to the
Internet. Each IAP offers up to 6 Mbps burst data rate to
subscribers. IAPs support the 10/100 base-T Ethernet interface.
Other interfaces are supported through commercially available
media translation devices. If additional network capacity is
required, more IAPs can be easily deployed - without t he need for
extensive RF or site planning. IAPs provide functions such as:
• Local mobility management of SDs
• Fixed reference for geo-location services
• Hopping points for subscriber peer-to-peer networking
• Transition point from the wireless to the wired portions of
the network
• Route Selection
The IAP’s small size and light weight allow it to be mounted anywhere power and network
connectivity are available. No towers are required. IAP software can be updated via over-thewire downloads.
Mobile Internet Switching Controller (MiSC)
The Mobile Internet Switching Cont roller (MiSC) pr ovides
connectivity between the IAPs and wired world, and
hosts the network’s management and provisioning
functions. The MiSC is composed of off-the-shelf
hardware components, such as LAN routers and
application servers. MiSC software consists of both offthe-shelf and MeshNetworks’ proprietary software,
MeshManager. The MeshManager software provides
functions for the network such as:
• Subscriber Provisioning, Management, and
Authentication
• Configuration and Fault Management
• Network Monitoring and Reporting
5
Page 14
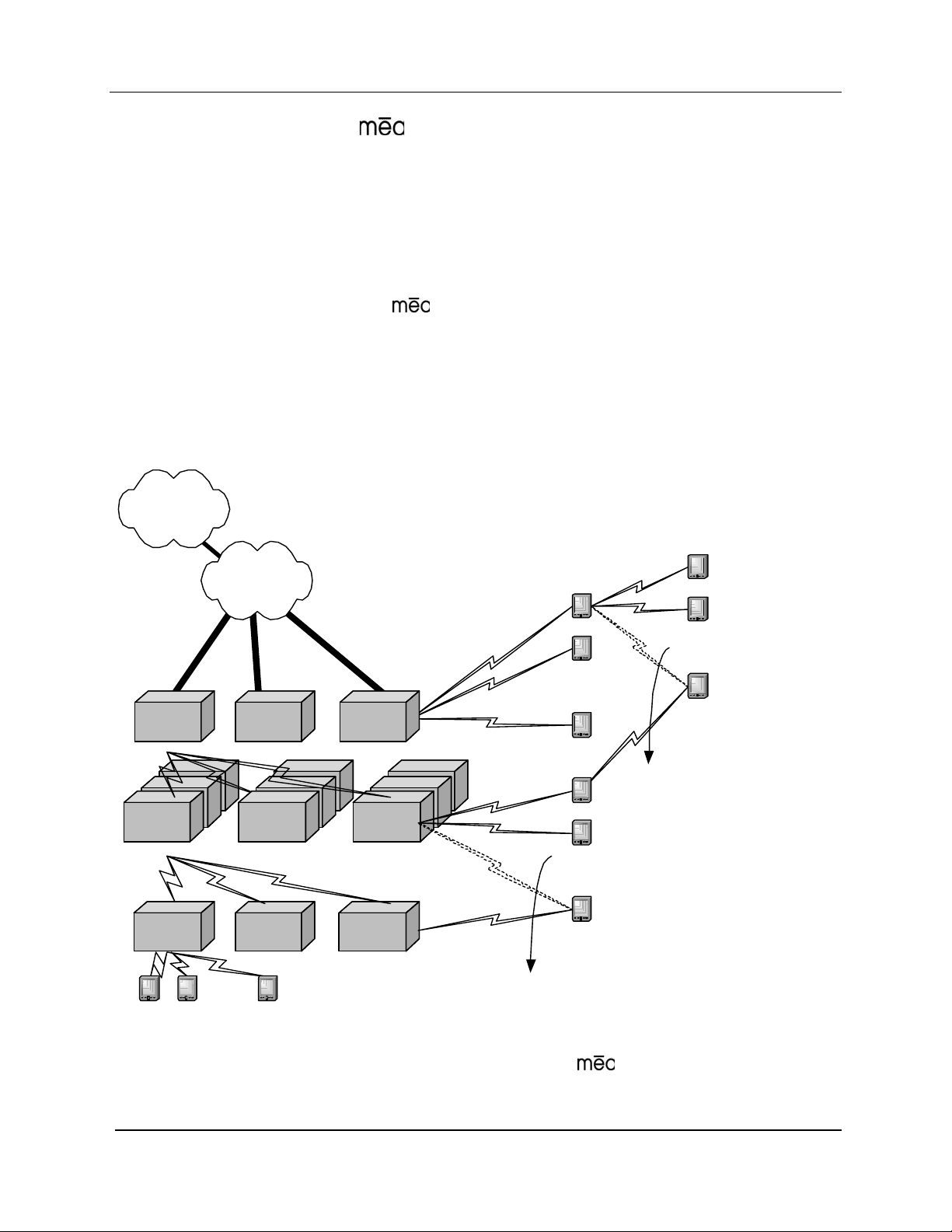
MeshNetworks
Operational View of the System
Figure 2 shows the different ways in which a subscriber can reach an IAP. It can connect
directly, or hop through any number or combination of WRs and SDs. Additionally, if the
subscriber wishes to execute a peer-to-peer application such as a f ile transfer, the subscriber
can communicate directly, or through any combination of SDs, WRs, and IAPs.
The ability to use ad hoc routing to forward traffic improves the scalability of the mobile wireless
Internet. In particular, the ability for the user to accomplish a peer-to-peer application without
the use of infrastructure has tremendous advantages. A significant problem in every mobile
wireless network is backhaul. The
applications through SDs and WRs without ever reaching an IAP or the wired Internet. This
reduces the amount of backhaul required by enabling the SDs to accomplish the backhaul
whenever the opportunity arises. This results in lower deployment costs, reduced backhaul,
and lower operating expenditures. The service provider can provide the same level of service
with less equipment by empowering the SDs with ad hoc networking capability.
architecture provides the ability to route traffic from
Global
Internet
MiSC
T
1
T
IAP 1 IAP 2 IAP N
1
T
1
. . .
. . .
. . .
WR 2
. . .
WR k1WR 1
Router Mesh
WR 1 WR 2 WR k2
. . .
MiSC
IAP
WR
SD
Mobile Interne t Sw itching Control le r
Intellige nt Access Point
Wireless Router
Subscriber Device
SD 1
SD 1
SD 2
. . .
SD 1
SD 2
SD 3
Handoff
SD 1
SD 2
. . .
SD 2
. . .
. . .
SD 2SD 1 SD 4
Handoff
Figure 2. Operational View of the
6
System
Page 15
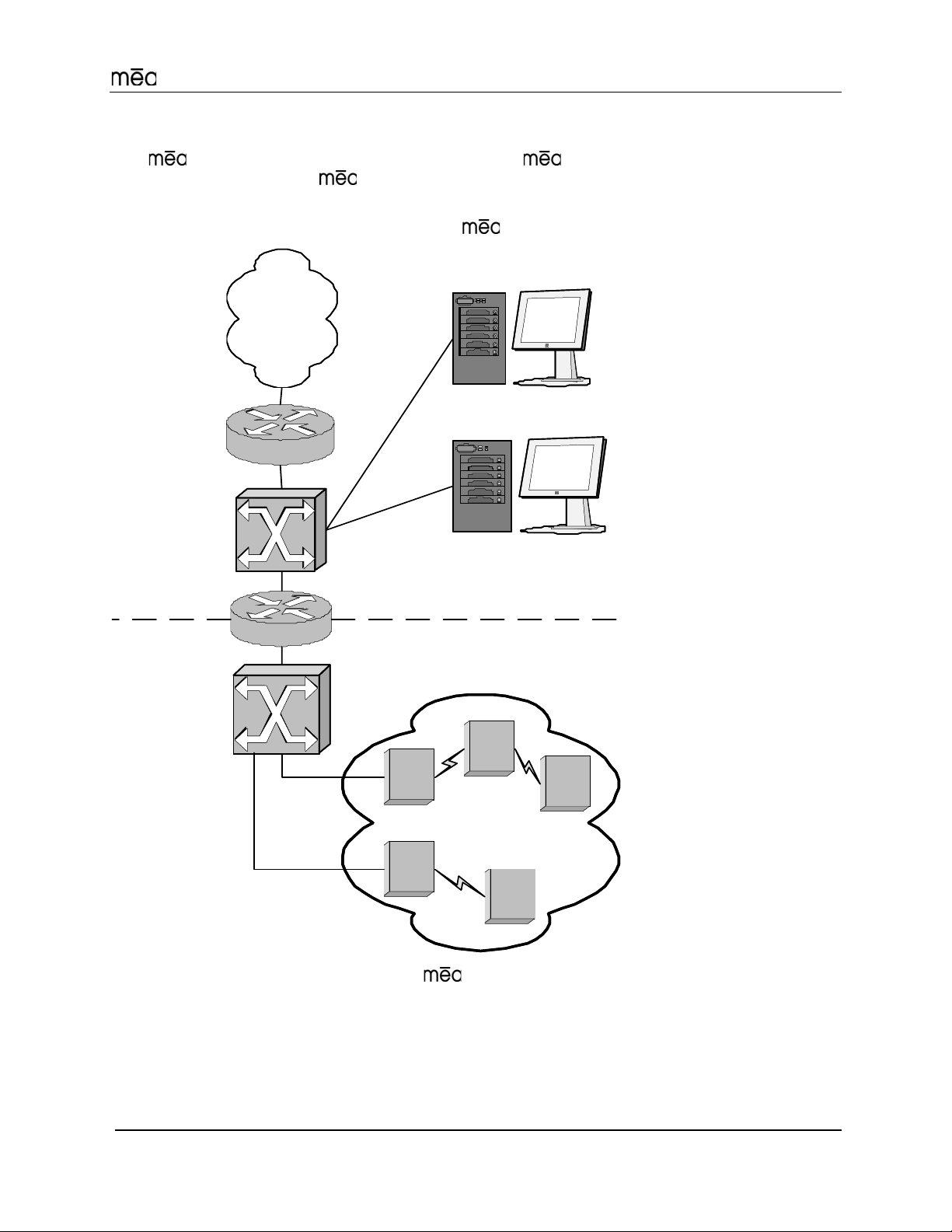
Setup and Deployment
Network Architecture
The network utilizes two subnets, one for the wireless elements and one for the
server elements. All of the
connected together by the core router, and the edge router provides Internet connectivity.
wireless elements must be in a single subnet. The subnets are
Figure 3 shows the logical network layout of a
Internet
edge router
server
switch
server subnet
wireless
subnet
core router
network.
other servers
`
MeshManage r
server
wireless
switch
Figure 3.
IAP1
. . .
IAPn
WR
SD
ma
wireless
dom ain
SD
Network Architecture
7
Page 16
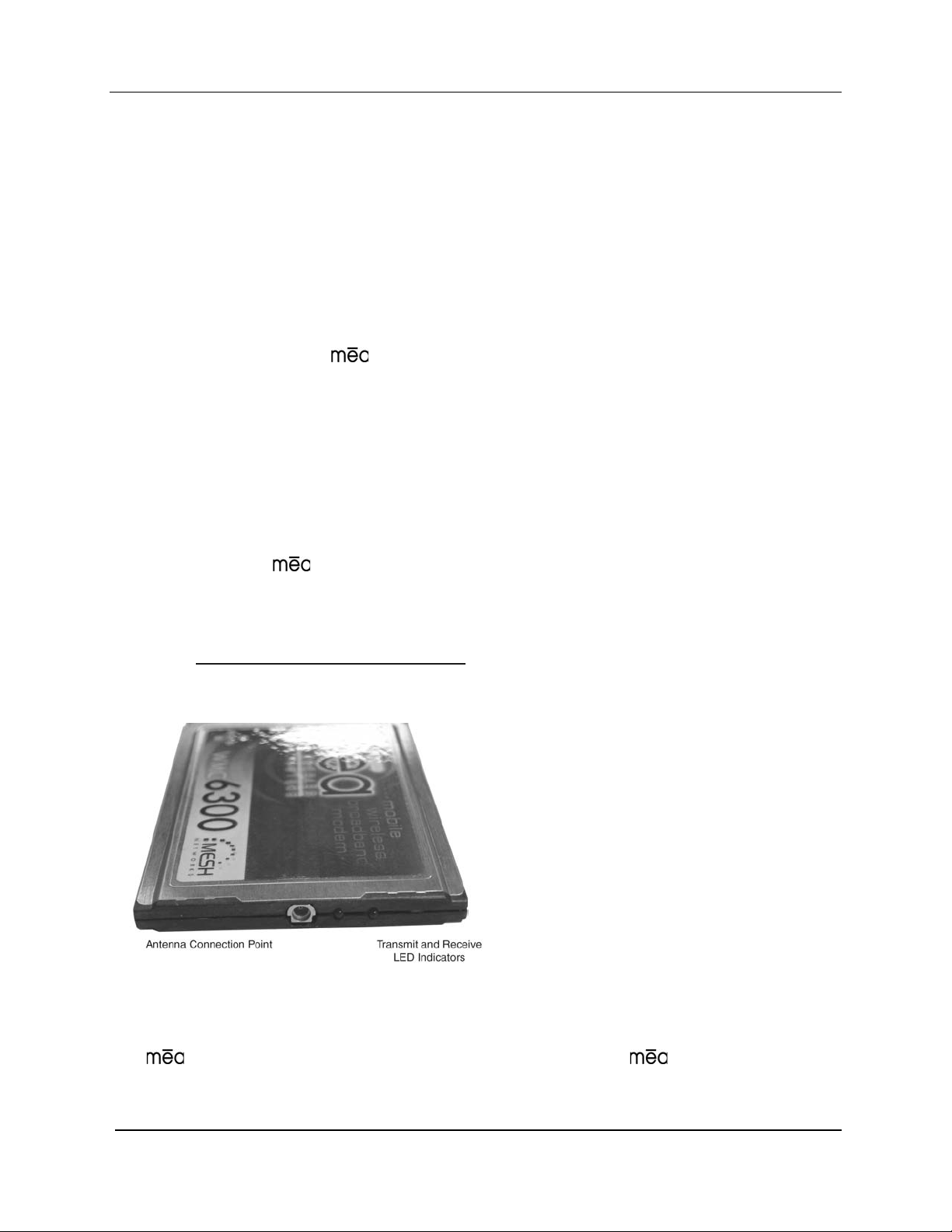
MeshNetworks
Section 3 - Setup and Deployment
Subscriber Device (SD)
A Subscriber Device consists of both a Wireless Modem Card (W MC6300) and an End User
provided host device such as a notebook computer. The WMC6300 is designed for insertion
into an industry-standard Type II PCMCIA card slot located in a Host device. The WMC6300
has an antenna port to connect the external antenna and two LED Indicators. The Red LED is
the transmit indicator and the Green LED is the receive indicator as shown in Figure 4.
Equipment
The following list defines the hardware components required to setup the WMC6300:
• WMC6300 Wireless Modem Card
• Antenna with a MMCX connector
• WMC6300 Software and Documentation CD for Windows 2000™ and Windows XP™
Equipment that must be supplied by the End User includes the following:
• Notebook PCs running the Microsoft Windows 2000 or Windows XP Operating System
Optional Equipment
• Re fe r to th e
data sheets for a list of optional equipment
Record MAC Address of the WMC6300
The transceiver MAC address is recorded on the back of the WMC6300 cards. Record this
number in Section 4 - MAC Address Tables
the device.
Figure 4. WMC6300 Antenna Port and LED Indicators
, as it will be required later to configure and test
Loading and Verifying Software
The W MC6300 Software and Documentation CD contains the drivers and MeshTray
software for use on the End User’s equipment. Please review the instructions for each
operating system as there is a different sequence of events depending on the operating system.
8
Page 17

Setup and Deployment
Detailed instructions can be found in the WMC6300 User’s Guide for each operating system.
In addition, the
software to load the MeshView Administration Tool. MeshView may be installed as an option on
a subscriber device to assist the Network Operator with network deployment. Refer to the
MeshView Administration Tool User’s Guide for additional information on this application.
Administration Software and Documentation CD includes installation
Installing the WMC6300 Software for Windows 2000
The WMC6300 Wireless Modem Card User’s Guide for Windows 2000 provides complete
step-by-step instructions for use during the installation and configuration of the WMC6300. The
following is an abbreviated version of the installation process.
Note: Please install the
Complete the following procedure to install the WMC6300 software and drivers:
1. Insert the
2. The
Note: If the installation program does not start automatically, open the Windows Start
menu, click on Run, and then type d:setup.exe (where d is the letter of the CD-ROM
drive) and click the “OK” button.
3. Click th e “Next” button to continue the software installation process.
4. Follow the onscreen prompts to complete the installation process.
Software and Documentation CD into the computer’s CD-ROM drive.
Setup program will be displayed.
Software before you insert the WMC6300 card.
5. Insert the antenna into the WMC6300 card.
6. Insert theWMC6300 card into the PCMCIA slot of the host computer.
If MeshView is desired, insert the
the Windows Start menu, click on Run, and then type d:setupmv.exe (where d is the letter of
the CD-ROM drive) and click the “OK” button. Follow onscreen prompts to complete the
installation process.
Administration Software and Documentation CD, open
Installing the WMC6300 Software for Windows XP
The W MC6300 Wireless Modem Card User’s Guide for Windows XP provides complete
step-by-step instructions for use during the installation and configuration of the WMC6300. The
following is an abbreviated version of the installation process.
Note: Please install the
Complete the following procedure to install the WMC6300 software and drivers:
1. Insert the antenna into the WMC6300 card.
2. Insert the WMC6300 card into the comp uter.
3. Click th e “Cancel” button for the 2 “Found New Hardware” windows.
4. Click th e “Close” button for the “Found New Hardware information” window.
5. Insert the WMC6300 Software and Documentation CD into the computer’s CD-ROM
drive.
Software after you insert the WMC6300 card. .
9
Page 18

MeshNetworks
6. The Setup program will be displayed.
Note: If the installation program does not start automatically, open the Windows Start
menu, click on Run, and then type d:setup.exe (where d is the letter of the CD-ROM
drive) and click the OK button.
7. Click th e “Next” button to continue the software installation process.
8. Follow the onscreen prompts to complete the software installation process.
9. Eject the WMC6300 card. Wait 10 seconds and reinsert the WMC6300 card.
10. For the 2 Found New Hardware windows, ensure the Install Software Automatically
button is selected, click on the Next button, and follow the onscreen prompts.
Installing the MeshView Administration Tool
Complete the following procedure to install MeshView:
1. Insert the
2. Click the W indows “Start” menu. Click on “Run” and enter d:setupmv.exe in the
textbox (Note: d is the letter of the CD-ROM drive). Click the “OK” button to continue the
installation process.
3. Follow onscreen prompts to complete the installation process.
Administration Software and Documentation CD into the CD-ROM drive.
DNS Server Configuration
The DNS server IP address is automatically supplied to the Subscriber Device upon
successfully connecting to the Network. If there are problems with resolving web URLs, the
DNS address can also be manually configured. The Network Operator must supply the DNS IP
address for the Internet connection.
Instructions to setup a Windows 2000 Host:
1. St art/Settings/Network and Dial-up Connections/Local Area Connection
(choose the Local Area Connection Corresponding to the Wireless Modem Card)
2. Click on the “Properties” button.
3. Highlight Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) in the Components window.
4. Click on the “Properties” button.
5. Click on the “Advanced” button.
6. Click on the DNS tab
7. Click on the DNS “Add” button.
8. Ent er the “DNS Server IP Address” provided by the network administrator and then click
the “Add” button.
9. Click the “OK” button to close the Advanced TCP/IP Settings windows.
10. Click the “OK” button to close the Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) Properties windows.
11. Click the “OK” button to close the Local Area Connection Properties windows.
12. Click the “Close” button to close the Local Area Connection Status window.
This configuration should remain in the Windows 2000 host.
10
Page 19

Setup and Deployment
Instructions to setup a Windows XP host:
4. Click on Start/Contr ol Panel/Network and Dial-up Connections/Local Area Connection
5. Right click on the Local Area Connection Corresponding to the Wireless Modem Card
and select “Properties” from the pop up menu.
6. Highlight Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) in the Components window.
7. Click on the “Properties” button.
8. Click on the “Advanced” button.
9. Click on the DNS tab
10. Click on the DNS “Add” button.
11. Enter the “DNS Server IP Address” provided by the network administrator and then click
the “Add” button.
12. Click the “OK” button to close the Advanced TCP/IP Settings windows.
13. Click the “OK” button to close the Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) Properties windows.
14. Click the “OK” button to close the Local Area Connection Properties windows.
15. Click the “Close” button to close the Local Area Connection Status window.
This configuration should remain in the Windows XP host.
Testing
When the WMC6300 is inserted, you may receive an audible indicator t hat the device has been
recognized. (If there is a problem with the drivers, Windows will prompt you for a new device
installation.)
Using MeshTray, configure the WMC6300 for peer-to-peer mode. Click on the Windows “Start”
button and select “Run” from the popup menu. Enter t he command “ipconfig“ in the textbox
and click on the “OK” button to check your IP address. If an IP address in the range of 10.x.y.2
is displayed, the transceiver is working properly. Change the WMC6300 back to Infrastructure
mode.
Intelligent Access Point (IAP)
The IAP is an infrastructure device that is positioned at a fixed location such as a building
rooftop. The IAP6300 requires professional installation to ensure that the installation is
performed in accordance with FCC licensing regulations.
The principle function of the IAP is to provide the Subscriber Devices in the coverage area of
the IAP access to wired services. The IAP also provides a fixed location reference for GeoLocation (optional feature), provides wireless routing for units in the IAPs coverage area, and is
the principal network management interface to associated Wireless Routers and Subscriber
Devices.
The
pole or a flat surface. For a
be provided. The RJ-45 weatherproof plug can be terminated in the field, allowing custom
IAP provides a mounting point for a mounting bracket that can be attached to either a
deployment, a permanent AC power source for each IAP must
11
Page 20

MeshNetworks
lengths to be assembled quickly on site.
Equipment
The following list defines the standard hardware components for the IAP:
• IAP Box with N-type Female Antenna Connector
• 120V A/C Power Cable with a NEMA 5-15 plug
• Antenna with N-type Male Antenna Connector
• Weatherproof RJ-45 Connector
• Mounting Bracket
The Network Operator must supply the following:
• Mounting Location
• 120V A/C Power Source
• Ethernet connection between the IAP and the MiSC
• Hand tools for bracket installation (??)
Optional Equipment
Typical optional equipment includes the following:
• Net-to-Net boxes for T1 deployment
• Power Cords terminating in PE cell connector
Approved Antennas Options
Manufacturer
Maxrad Z1578 8 dBi Onmi
Maxrad Z1576 4 dBi Onmi
Hyperlink HG2409MU 8 dBi Onmi
Hyperlink HG2407U 7.5 dBi Onmi
Refer to the IAP data sheet for a complete list of options.
Part Number
Gain Type
2
Page 21

Setup and Deployment
Antenna Connector
Record MAC Address of the IAP
The transceiver MAC address is recorded on a label located on the antenna side of the IAP as
shown in Figure 5. Record this number in Section 4 - MAC Address Tables
required later to configure and test the device.
, because it will be
Figure 5 IAP6300 Identification Label
IAP Assembly
The Figure 6 shows the external connection points on an IAP6300 box.
Test Port
(Not Shown)
Power Out (3-pin)Power In (4-pin)
RJ45 (Data) Port
Figure 6. IAP6300 Connection Points
3
Page 22

MeshNetworks
Figure 7 Mounting Bracket Assembly
Figure 8. Bracket Attached to the IAP6300
4
Page 23

Setup and Deployment
Assemble the IAP using the following procedure:
1. If desired, mount the IAP6300 box using the enclosed bracket. Refer to Figure 8.
2. Place the bracket at the desired position on the pole The bracket can accommodate
pole diameters between 1-3.5 inches. The bolts supplied with the bracket will
accommodate pole diameters of 2.75 – 3.5 inches. If needed, obtain a ¼-20 hex bolt of
an appropriate length for pole diameters between 1-2.75 inches (stainless steel bolts are
recommended).
3. Adjust the position of the box so that the antenna will be in a vertical position. Tighten
the pivot and angle locking bolts on the shaft of the bracket as shown in Figure 9
4. Insert the antenna into the N-type Connector on the top of the box, and rotate to close.
5. Insert the IAP Power Plug into the 4-pin connector.
6. Install the weatherproof connector on the Ethernet cable as described at:
http://www.siemon.com/installation_instructions/pdf/IMAXIndustrialUTPPlug.pdf
7. Insert the Ethernet Cable into the RJ-45 port and tighten the connector to ensure a
weatherproof seal.
8. If used, insert the Media Converter Power Cable into the 3-pin connector.
9. The Test Port is unused during deployment
Deployment
6 x 32 x 3/4
Angle Locking Bolt
1/4 x 1 inch Pivot Bolt
(Requres 7/16 Wrench)
Figure 9. Bracket Adjustment Bolts
The IAP may be mounted on a pole having a diameter of 1-3.5 inches, utilizing the provided
bracket. The antenna must have a separation distance of at least 2 m eters from the body of all
persons and must not be co-located or operating in conjunction with any other antenna or
transmitter. Users and installers must be provided with antenna installation and transmitter
operating conditions to satisfy RF exposure compliance.
5
Page 24

MeshNetworks
When deploying the IAP, the antenna should be a minimum of 30 inches from any nearby metal
poles to avoid distortion of the RF pattern.
The IAP must have an Ethernet connection to the MiSC. If the distance between the IAP and
the MiSC is greater than 100 meters, the Network Operator may utilize a T1 with the optional
Net-to-Net boxes. The IAP has a 5V, 3-pin, power out connection on the side of the box to
power the Net-to-Net boxes. Other media converters may be used at the network operator’s
discretion.
The installation location must provide AC power to the IAP.
It is the responsibility of the Network Operator to ensure that the installation complies with any
local building codes and permits.
Initial IAP Configuration
Prior to attempting configuration of the IAP, the IAP m ust be powered on and have connectivity
to the MiSC.
Geo-location is an optional configuration item t hat is entered into an infrastructure device via the
Device Manager tool, located on the MeshManager server (refer to the MeshManager User’s
Guide). MeshNetworks recommends that a DGPS receiver be used to obtain accurate GPS
coordinates, and that the longitude, latitude, and altitude values have 5 digits following the
decimal point.
Testing
Once there is an Ethernet connection to the MiSC, verify the health of the IAP with the following
procedure:
1. Apply power to the IAP.
2. Obtain the transceiver MAC address that was recorded in Section 4 - MAC Address
Tables. The address will be in the format 00-05-12-0A-xx-yy.
3. From MeshManager, display devices using the MAC address.
4. Select the appropriate IAP in the device tree, and then ping the device (right click and
select ping).
A response to the ping commands verifies that both the transceiver and SBC are
communicating.
6
Page 25

Setup and Deployment
Wireless Router (WR)
The MWR6300 (Wireless Router) is an infrastructure device positioned in a fixed location, such
as on a pole, wall, or rooftop. The MWR6300 requires professional installation to ensur e the
installation is performed in accordance with FCC licensing regulations.
The Wireless Routers provides range extension, a means to route around obstructions, and a
fixed location reference for use in Geo-Location (an optional feature).
The
diameter of 1-3.5 inches . For a
must be provided.
MWR6300s comes with a mounting bracket that can be attached to a pole with a
deployment, a permanent AC power source for each WR
Equipment
The following list defines the hardware components needed to setup a WR:
• WR Box with N-type Antenna Connector
• 120V A/C Power Cable with a NEMA 5-15 plug
• Antenna with N-type Male Antenna Connector
• Mounting Bracket
The Network Operator must supply the following:
• Mounting Location
• 120V A/C Power Source
• Hand tools for bracket installation
Optional Configurations:
• Power Cable to connect to a Fisher-Pierce 7570B photoelectric cell
Approved Antennas Options:
Manufacturer
Maxrad Z1578 8 dBi Onmi
Maxrad Z1576 4 dBi Onmi
Hyperlink HG2409MU 8 dBi Onmi
Hyperlink HG2407U 7.5 dBi Onmi
Refer to the WR data sheet for a complete list of options.
Part Number
Gain Type
7
Page 26

MeshNetworks
Record MAC Address of the MWR6300
The transceiver MAC address is recorded on the label located on the antenna side of the
MWR6300 as shown in Figure 10.
Record this number in Section 4 - MAC Address Tables
configure and test the device.
Figure 10. MWR6300 Identification Label
, because it will be required later to
8
Page 27

Setup and Deployment
MWR6300 Assembly
Figure 11 shows the external; connection points on a MWR6300 box.
Test Port
Figure 11. MWR6300 External Connection Points
Assemble the WR using the following procedure:
1. If desired, mount the WR box using the enclosed bracket. Refer to the procedure in the
IAP assembly section of this document.
2. Insert the Antenna into the N-type Connector on the top of the box, and rotate to close.
3. Insert the Power Plug into the 4-pin Connector.
4. The transceiver MAC address is recorded on the back of the WR. Record this number in
Section 4 - MAC Address Tables
5. The Test Port is unused during deployment.
, as it will be required to configure and test the device.
Deployment
The MWR6300 can be mounted on a pole by using the provided bracket.
When deploying the MWR6300, the antenna should be a minimum of 30 inches from any
nearby metal poles to avoid distortion of the RF pattern. The antenna must have a separation
distance of at least 2 meters from the body of all persons and must not be co-located or
operating in conjunction with any other antenna or transmitter. Users and installers must be
provided with antenna installation and transmitter operating conditions to satisfy RF exposure
compliance.
Typically, wireless routers are distributed within a network to extend range and guarantee
coverage. A rule of thumb is to deploy 3-4 hop networks to optimize range, latency, and
throughput.
The MWR6300 installation location must provide AC power for the device.
It is the responsibility of the Network Operator to ensure that the installation complies with any
local building codes and permits.
Initial Configuration
The optional configuration process for Geo-Location is the same as the IAP.
9
Page 28

MeshNetworks
Testing
Verify the operation of the MWR6300 using the following procedure:
1. Apply power to the MWR6300.
2. Obtain the transceiver MAC address that was recorded in Section 4 - MAC Address
Tables. The address will be in the format 00-05-12-0A-xx-yy.
3. From MeshManager, display devices using the MAC address.
4. Select the appropriate WR in the device tree, and then ping the device (right click and
select ping).
A response to the ping command verifies that the transceiver is communicating.
10
Page 29

Setup and Deployment
Mobile Internet Switching Controller (MiSC)
The MiSC provides routing, switching, and management functions for the wireless network, and
the connection to the wired world.
Equipment
The following list defines the standard components needed for the MiSC:
• SMC 24 Port Switch
• Cisco 1720 – Edge Router
• Cisco 1720 – Core Router
• MeshManager Server (Server, Monitor, Keyboard, Mouse), pre-installed with the
MeshManager software
• 5 Ethernet Cables
The Network Operator must supply the following:
• Physical location and AC power for the routers, switch, and server(s)
• Ethernet connection(s) from the switch to the IAP(s)
• Ethernet connection to Internet or to Network Operator’s private network (Custom IP
network configuration may be required depending on Network Operator’s network
configuration)
• Public address for Edge Router, DNS resolver address
• PC running Windows 2000 with an Ethernet Port for MiSC Configuration and
MeshView
• Optional Equipment:
• Geo Server
• T1 Network Extenders
Refer to the MiSC data sheet for a complete list of options.
11
Page 30

MeshNetworks
Network Setup Description
The basic MiSC hardware configuration is shown in Figure 12.
Figure 12. Basic MiSC Configuration
The following describes the parameters for setting up the network:
• All
• currently uses the non-routable 10.x.x.x (8 bit) subnet as defined in RFC 1918.
• The IAPs, WRs, and SDs will use DHCP to obtain an IP address, the default
configuration returns a 10.x.x.x address.
• All MeshNetworks devices have a default gateway of 10.0.0.1
• The Network Operator provides the address of the DNS server. The Subscriber
Devices must be manually configured to access the DNS server in order to resolve web
URLs. (See WMC6300 User’s Guide for instructions on this.)
wireless devices must be within the same subnet.
12
Page 31

Setup and Deployment
MiSC Assembly
The MiSC hardware consists of commercial off-the-shelf components. The components are
pre-configured with a basic configuration that requires minimal site-specific changes.
The SMC switch arrives configured as two virtual LANs. The upper row of Ethernet ports is for
the server subnet; the lower row of ports is for the wireless subnet.
Unpack the SMC switch and mount as desired (either in a rack or on a table top). Connect t he
switch to a power source.
Unpack the Cisco router labeled “EdgeRTR” and connect to a po wer source. Plug interface
labeled “10BT Ethernet” into the Internet or the Network Operator’s private network. (The
network operator supplies this cable; it will be an Ethernet cable for connecting to a hub or
switch, or an Ethernet crossover cable if connecting to another router.) Plug interface labeled
“10/100 Ethernet” into the SMC switch on port 1.
Unpack the Cisco router labeled “CoreRTR” and connect to a power source. Plug interface
labeled “10BT Ethernet” into the SMC switch on port 12. Plug the interface labeled “10/100
Ethernet” into the SMC switch on port 24.
Unpack the Sun Blade/MeshManager server and monitor and connect to a power source. Plug
the network interface into any of the ports 2-11 on the SMC Switch.
Connect Network Operator supplied computer running Windows 2000. Plug the network
interface into any of the ports 2-11 on the SMC Switch.
Connect the IAPs to any of the ports 13-23 on the SMC switch.
13
Page 32

MeshNetworks
Onsite Configuration of Routers
EdgeRTR Configuration
The EdgeRTR must have on-site configuration done if there is a desire to connect to the
Internet. Prior to performing the following steps, obtain the IP address, netmask, and default
gateway for the public interface from the Internet Service Provider. These are shown as
ip.ip.ip.ip, nm.nm.nm.nm, and gw.gw.gw.gw, respectively, in the instructions below. Also,
obtain the IP address of the EdgeRTR, it will be in the form of 172.a.0.1.
Telnet into the EdgeRTR from a computer connected to the server subnet. Use the address
172.a.0.1 to connect to the EdgeRTR.
Update the public IP information using the commands below
Password:g0ld1
EdgeRTR>enable
Password:g0ld11
EdgeRTR#configure terminal
Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z.
EdgeRTR(config)#interface Ethernet0
EdgeRTR(config-if)#ip address
ip.ip.ip.ip mm.nm.nm.nm
EdgeRTR(config-if)#exit
EdgeRTR(config)#no ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0
EdgeRTR(config)#ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0
EdgeRTR(config)#exit
EdgeRTR#copy running-config startup-config
Destination filename [startup-config]? <return>
Building configuration...
!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!![OK]
EdgeRTR#exit
gw.gw.gw.gw
EdgeRTR TEST
Use a computer connected to the switch (in either the server or wireless subnet) to ping to the
ISP gateway IP. Next, test access to the Internet using a web browser. If this fails troubleshoot
and retry.
14
Page 33

Setup and Deployment
Network Configuration – Device Manager
“Device Manager” is a utility located on the MeshManager server. It is used to configure and
monitor the deployed network. Refer to the MeshManager User’s Guide for detailed instr uctions
on how to use the Device Manager.
Mea systems are delivered with the initial configuration of IAPs, WRs, and SDs in the
MeshManager system. This allows for easy testing of the system as units are tested on site.
There are two basic tests to verify correct operation the system. The first test is to perform ping
tests to each device and the second test is to verify access the Internet.
Network Configuration – IAP Configuration Via Web Interface
A second method of performing various network configuration functions for an IAP may be
accomplished using a standard web browser. Connect a host PC to the switch in the MiSC.
Using a standard Internet Browser such as Microsoft’s Internet Explorer or Netscape, enter the
IP Address corresponding to the IAP to be configured as shown in Figure 13. If you do not
know the IP address of the IAP then contact the system administrator. Optionally, if the network
has been configured with a DHCP Server and a DNS Server, you may use the Device System
Name. Since all IAPs ship with the same default Device System Name, it is recommended that
you install and configure the IAPs one at a time.
Figure 13. MEA Device Administ r ation Connection
A Log On window for the Configuration Utility will be displayed in the browser, as shown in
Figure 14. Before the Configuration Utility is displayed, the user must complete the simple
logon procedure before proceeding. When the Log On is complete, the Configuration Utility will
be displayed. The default login is “admin’ and the password is “admin”. The password can be
changed, as described further in this document.
15
Page 34

MeshNetworks
Figure 14. MEA Device Administ r ation Logon Window
At the completion of the logon, the Home Tab screen will be displayed as shown in Figure 15.
Home Tab
Figure 15. MEA Device Administ ration Home Tab
The Device Information window provides data on:
Wireless Interface Status (up or down)
System Firmware Version (software running on the SBC in the IAP)
Ethernet MAC Address (address of the SBC)
Wireless MAC Address (address of the transceiver)
Also located on the Home Tab are Device Management options for
Change Administration Password
Update Device Firmware
Restore Factory Defaults
16
Page 35

Setup and Deployment
Reset the Device
The Device Management options are detailed below.
Home Tab – Change Admin Password
From the Home tab, the user can select the “Change Admin Password” to change the
administrator password of the device.
WARNING – If the password is lost, the password can only be reset at the factory. Do not
forget to record the information in an appropriate location for future use.
1. To change the password, select “Change Admin Password”.
2. “Enter the new password” will be displayed on the Change Password window as shown
in Figure 16. Enter the new password in the “Ne w Password” textbox.
3. Enter the new password again
Figure 16. MEA Device Administ r ation Enter New Password Window
4. Click on the “Submit” button. The browser will display a message that confirms the
password change as shown in Figure 17.
in the “New Passwo rd (ag ain) ” textbox.
Figure 17. MEA Device Administ r ation Password Changed W indow
Home Tab – Update Device Firmware
From the Home Tab, select “Update Device Firmware” to load a new version of the firmware
into the IAP.
. A New Device Firmware window will be displayed as shown in Figure 18
17
Page 36

MeshNetworks
Figure 18. MEA Device Administration Update Device Firmware Window
1. Click on the “Browse” button to navigate to the correct location of the firmware “bin” file,
or specify the path and file name of the firmware “bin” file to be uploaded to the device.
If the “Browse” button is selected, the “Choose file” window is displayed. Selecting the
filename starting with “m-krc” will overwrite any custom configurations which have been applied
to the AP. Selecting the filename starting with “m-r” will retain any custom configurations.
Locate and select the desired firmware “bin” file to be uploaded to the device. Then click on
the “OK” button
The path and file name of the firmware “bin” file will be displayed in the Update Device
Firmware window as shown in Figure 19. Click on the “Upload” button to continue the process
or select “Cancel” to terminate the Firmware Update procedure
Figure 19. MEA Device Administ r ation Updat e Device Firmware Window (2)
2. If the “Upload” button is selected, an upload confirmation message is displayed as
shown in Figure 20 to confirm that you want to continue the Firmware Update procedure.
18
Page 37

Setup and Deployment
Click on the “OK” button to continue or select “Cancel” to terminate the Firmware
Update procedure.
Figure 20. MEA Device Administ r ation Updat e Conf irmation Window
3. If the “OK” button is selected, the new Firmware is loaded into the device. The Firmware
Update window will then be displayed to indicate that the selected file was successfully
uploaded and to recommend that you reboot the device.
4. As the Firmware is being uploaded, a status page is displayed as shown in Figure 21.
Figure 21. MEA Device Administration Update Device Status Window
5. At the completion of the update, the IAP’s SBC must be reset for the update to take
effect. Select t he “Home” tab and then click on the “Reset Device” button as described
in the procedure located on page 21. The device will reset and return to the “Home” tab.
Note: Do not to close the browser until the process is complete.
19
Page 38

MeshNetworks
Home Tab – Restore Factory Defaults
From the Home Tab, the user can select “Restore Factory Defaults” t o restore the firmware to
Factory Default settings. By selecting the “Restore Factory Defaults” button, the IAP setting
will be returned to the default configuration. The user will receive a caution message before
proceeding with the restore process as shownbe in Figure 22.
Figure 22. MEA Device Administration Restore Factory Defaults Window
6. Click on the “Apply” button to continue the restore process or select the “Cancel” button
to terminate the process with out changing the device settings.
7. If the “Apply” button is selected, a confirmation message is displayed as shown in
Figure 23 to confirm that you want to continue the Restore Factory Settings procedure.
Figure 23. Restore Factory Defaults Confirmation Message
8. Click on the “OK” button to continue or select “Cancel” to terminate the procedure.
If the “OK” button is selected, the setting will be restored and the device will reset automatically.
Upon completion of the process, the browser will return automatically to the “Home” tab.
Home Tab – Reset Device
From the Home tab, the user can select the “Reset the Device” button to reset the device and
reinitialize the IAP. The configuration settings are preserved during the initialization process.
The user will receive a caution message before proceeding with the reset.
1. Select the “Reset the Device” button to initiate the reset process on the IAP.
2. The Reset the Device window is displayed as shown in Figure 24. Select the “Reset”
button to continue the process.
The Reset the Device window displays a message that describes the process and the time to
completion as shown in Figure 25. The device will reset automatically upon completion of the
update process and then return to the “Home” tab to display status information.
20
Page 39

Setup and Deployment
Figure 24. MEA Device Adm inistration Device Reset Window
Figure 25. MEA Device Administration Device Reset Window (2)
System Settings Tab
The System Settings Tab is shown in Figure 26
21
Page 40

MeshNetworks
Figure 26. MEA Device Administration System Settings Tab
Associations Tab
The Associations Tab is an information only window as is shown in Figure 27
Figure 27. MEA Device Administration Associations Tab
This window displays all devices currently associated with an IAP. There will always be at least
2 entries: one for the IAP’s SBC and one for the IAP’s transceiver.
Testing
Basic MiSC Tests
To verify the basic connectivity of the MiSC, conduct the following from the MeshManager
server using the Device Manager application:
22
Page 41

Setup and Deployment
• Ping an IAP
• Ping the NAT Router
• Ping the Edge Router
Wireless System Tests
From Device Manager, complete the following to verify correct operation of the system:
1. Ping the SBC of the deployed IAPs
• From the Device Manager drop down menu, select Preferences/Use SBC Address
• For each IAP in the device tree, right click and select Ping Device
2. Ping the transceiver of the deployed IAPs
• From the Device Manager drop down menu, select Preferences/Use Transceiver
Address
• For each IAP in the device tree, right click and select Ping Device
3. Ping the transceiver of the deployed WRs
• From the Device Manager drop down menu, select Preferences/Use Transceiver
Address
• For each WR in the device tree, right click and select Ping Device
4. Ping the transceiver of each Subscriber Devices
• From the Device Manager drop down menu, select Preferences/Use Transceiver
Address
• For each SD in the device tree, right click and select Ping Device
Internet Test
If the system has been configured to access the Internet, complete one of the two
following tests to verify correct network setup:
1. From a provisioned SD, start the web browser and enter a URL such as
http://www.MeshNetworks.com
2. From a SD, open a DOS/cmd window and ping an URL, e.g., ping
www.meshnetworks.com.
Default Addresses and Logins
The following are the default values for the system components. These may be updated during
installation.
Device Description Default
.
Core Router login password
Core Router enable password
Core Router IP address on Sever
g0ld1
g0ld11
172.31.0.2
23
Page 42

MeshNetworks
Device Description Default
Core Router
Edge Router login password
Edge Router enable password
Edge Router IP address on Server
Sun Blade root password
Sun Blade node name
Sun Blade
Sun Blade
Sun Blade Secondary IP address for IAP rdate server
Sun Blade Secondary IP address for IAP HAS server
Sun Blade
Sun Blade Server subnet DHCP range
Sun Blade Wireless subnet DHCP range
IAP Default Gateway
Wireless subnet IP address for Core
Router
IP address for next-level hierarchical DNS
server
IP address if Mesh VPN support is
provided
Secondary IP address for IAP syslog
server
10.0.0.1
g0ld1
g0ld11
172.31.0.1
g0ld11
MeshManager
(none)
172.31.0.20
192.168.50.20
192.168.50.20
172.18.0.50
172.31.1.1 to 172.31.1.254
10.2.0.1 to 10 .2 .0.254
10.0.0.1
IAP IP address for rdate server
IAP IP address for HAS server
IAP IP address for syslog server
Subscriber
Device
Subscriber
Device
Default Gateway
DNS Server
192.168.50.20
192.168.50.20
172.18.0.50
10.0.0.1
192.168.50.20
24
Page 43

Setup and Deployment
Section 4 - MAC Address Tables
IAP MAC Addresses
IAP MAC Address
00-05-12-0A-xx-yy
WR MAC Addresses
WR MAC Address
00-05-12-0A-xx-yy
25
Page 44

MeshNetworks
WMC MAC Addresses
WMC MAC Address
00-05-12-0A-xx-yy
26
Page 45

Setup and Deployment
Section 5 - Site Selection/Deployment Guidelines
General Site Selection Guidelines
The IAP location(s) should be selected first since they have the additional requirement of routing
information back to the MiSC. This may be done via an Ethernet cable if the IAP and MiSC are
located within 100 meters (the max length permitted for standard Ethernet) of each other. If the
distance is greater than 100 meters, a mechanism for extending the Ethernet connection will be
required, e.g., using fiber or T1. (MeshNetworks recommends T1 backhaul equipment from
Net-to-Net Technologies.)
Once the IAPs have been placed, then the location of the WRs can be determined. Optimally,
the devices should be distributed such that a SD has no more than 3 hops to an IAP.
AC power must be available for both IAPs and WRs.
Lastly, any local building/structure codes must be adhered to, as well as proper permits for
placing devices on structures that are not owned by the Network Operator (e.g., light poles).
MeshNetworks has developed the “Location Analyzer” tool to assist in the placement of
infrastructure. This tool runs on a Windows 2000 SD. The tool collects and analyzes data,
ultimately resulting in a deployment quality indication. Refer to the Location Analyzer
documentation for information on configuring and using this tool.
Antenna Guidelines
The location of fixed infrastructure antennas must address proper antenna orientation, selection
of elevation pattern for the specific locale, the avoidance of pattern distortion, and t he impact of
obscuration and non-line-of-sight paths.
Polarization - Most of the antennas used in deployment will be vertically polarized. To maximize
line-of-sight signal reception, both the tr ansmitting and receiving antennas should be vertically
oriented to avoid signal loss due to polarization mismatch. T his applies t o mobile and stationary
antennas. For example, placing a magnetically mounted vehicle antenna on a curved portion of
the vehicle roof so that its axis is not vertical risks a measure of signal loss at range, dependent
upon the specific elevation pattern details, as discussed above.
Local obstructions - Antennas should be mounted either above or below the plane of
obstructions as shown in Figure 28.
Obstruction
Antenna
Antenna
Obstruction
Figure 28. Antenna Mounting
Low gain “rubber duck” antennas that are mounted directly to Mesh transceivers are designed
27
Page 46

MeshNetworks
for transmitting and receiving vertically polarized radiation. Hence, care must be taken to insure
close-to-vertical orientation of these antennas to avoid subst ant ial signal loss due to polarization
mismatch. Additionally, attenuation sustained by use of these antennas inside vehicles can be
as high as 10 dB. Typically, losses are in the 4 to 7 dB range if the antenna is above the “metal
can” of the vehicle so that radiation and reception occur at window level.
Lab Checkout
Prior to deploying any equipment in the field, it is recommended to test the equipment in a lab
environment to ensure the equipment is functioning.
Step 1 - Verify MiSC
Set up the MiSC as discussed in the MiSC Assembly section. Attach a Windows computer to
the SMC switch. Verify that the following can be pinged: edge router, core router,
MeshManager. Refer to the Default Addresses and Logins section for the addresses.
Step 2 – Verify IAPs.
Using an Ethernet cable, attach the IAPs, one at a time, to the SMC switch. Using either the
MAC or ETH address on the IAP box for reference, use MeshManager to verify that the IAP
can be reached, and that it is obtaining an address from the DHCP server. Next, start an SD in
infrastructure mode, and ensure that it also receives an IP address from the DHCP server.
This verifies that both the SBC and the transceiver in the IAP are functioning.
Step 3 – Verify WRs
Connect an IAP as described in Step 2. Power up the WRs one at a time. Using the MAC
address on the WR box for reference, verify that the MeshManager console can reach each
WR, and that an appropriate IP address is displayed.
Step 4 – Verify PCMCIA cards
Connect an IAP as described in Step 2, Load a host computer with the WMC6300 drivers as
described in section ??. Insert a WMC6300 card into the host device. Start MeshTray. Verify
that the status tab displays a valid IP address. Eject the WMC6300 card utilizing the “Unplug
or Eject Hardware” icon. Insert another WMC6300 card and repeat the MeshTray test.
General Deployment Guidelines
It is recommended that field deployment follow the same steps as
described in General Site Selection Guidelines
The IAP location(s) should be selected first since they have the additional requirement of routing
information back to the MiSC. This may be done via an Ethernet cable if the IAP and MiSC are
located within 100 meters (the max length permitted for standard Ethernet) of each other. If the
distance is greater than 100 meters, a mechanism for extending the Ethernet connection will be
required, e.g., using fiber or T1. (MeshNetworks recommends T1 backhaul equipment from
Net-to-Net Technologies.)
Once the IAPs have been placed, then the location of the WRs can be determined. Optimally,
the devices should be distributed such that a SD has no more than 3 hops to an IAP.
AC power must be available for both IAPs and WRs.
Lastly, any local building/structure codes must be adhered to, as well as proper permits for
placing devices on structures that are not owned by the Network Operator (e.g., light poles).
28
Page 47

Setup and Deployment
MeshNetworks has developed the “Location Analyzer” tool to assist in the placement of
infrastructure. This tool runs on a Windows 2000 SD. The tool collects and analyzes data,
ultimately resulting in a deployment quality indication. Refer to the Location Analyzer
documentation for information on configuring and using this tool.
Antenna Guidelines
The location of fixed infrastructure antennas must address proper antenna orientation, selection
of elevation pattern for the specific locale, the avoidance of pattern distortion, and t he impact of
obscuration and non-line-of-sight paths.
Polarization - Most of the antennas used in deployment will be vertically polarized. To maximize
line-of-sight signal reception, both the tr ansmitting and receiving antennas should be vertically
oriented to avoid signal loss due to polarization mismatch. T his applies t o mobile and stationary
antennas. For example, placing a magnetically mounted vehicle antenna on a curved portion of
the vehicle roof so that its axis is not vertical risks a measure of signal loss at range, dependent
upon the specific elevation pattern details, as discussed above.
Local obstructions - Antennas should be mounted either above or below the plane of
obstructions as shown in Figure 28.
Figure 28. Antenna Mounting
Low gain “rubber duck” antennas that are mounted directly to Mesh transceivers are designed
for transmitting and receiving vertically polarized radiation. Hence, care must be taken to insure
close-to-vertical orientation of these antennas to avoid subst ant ial signal loss due to polarization
mismatch. Additionally, attenuation sustained by use of these antennas inside vehicles can be
as high as 10 dB. Typically, losses are in the 4 to 7 dB range if the antenna is above the “metal
can” of the vehicle so that radiation and reception occur at window level.
Lab Checkout. IAPs should be deployed first and verified as functional. Next the WRs should
be deployed in a “near to far” pattern; in other words, WRs that are 1 hop from an IAP should
be deployed first, followed by WRs that are 2 hops from an IAP, etc. This allows the
functionality of each WR to be determined at the time of installation, thus eliminating any extra
truck rolls to trouble-shoot a WR.
29
Page 48

MeshNetworks
Section 6 - Customer Service Informa tion
For information about solving difficulties in deploying your System, please see the
Frequently Asked Questions in the support page at
If you have read this document, reviewed the FAQ, and made every effort to resolve installation
or operation issues yourself and still require help, please contact MeshNetworks Customer
Support using the following contact information:
MeshNetworks, Inc.
Attention: Customer Support
PO Box 948133
Maitland, Florida 32794-8133
Hours of Operation
Monday through Friday 8:00 AM – 5:00 PM (Eastern Standard Time)
Technical Support: (800) 311 – 3365 (USA)
(407) 659 – 5300
e-mail measupport@meshnetworks.com
http://www.meshnetworks.com/.
30
Page 49

Setup and Deployment
Section 7 - WMC Installation Debug Procedures
<add in document from Glen>
Due to the multi-function driver which is installed as part of the WMC6300 software, there are
occasionally some problems encountered during the installation. The following is a set of
procedures for correcting problem installations.
31
Page 50

MeshNetworks
32
Page 51

Setup and Deployment
Section 8 - License and Warranty Information
MeshNetworks, Inc.
End User License Agreement
IMPORTANT NOTICE TO END USERS: This End User License Agreement (this
“Agreement
available for use with the MeshNetworks Equipment (either an individual person or a single
legal entity, who will be referred to in this Agreement as “You
”) is a legal agreement between the licensee of the Licensed Software being made
”) and MeshNetworks. Inc.
1 DEFINITIONS. In this Agreement, “Li ce n se d Software
machine-readable, interpreted, compiled or other form, furnished to You for use with the
MeshNetworks Equipment, whether owned or licensed by MeshNetworks, and including without
limitation, (i) computer programs residing on any medium and all materials or contained in any
download supplied by MeshNetworks in connection with the Licensed Software, (ii) related user
manuals and explanatory written materials or files (“Documentation
modified versions, updates, additions, and copies of the Licensed Software, if any, provided to
You by MeshNetworks, either directly or indirectly (collectively, “Updates
Equipment” means the equipment on which the Licensed Software is intended to operate.
“Source
obtained the Licensed Software. “MeshNetworks
Road, Suite 250, Maitland, FL 32751. “Support Services
2 LICENSE. As long as You comply with the terms of this Agreement, MeshNetworks grants
You a personal, non-exclusive, non-transferable (except as provided in Section 11) license to
use the Licensed Software (in object code form only) for Your own use in the operation on the
MeshNetworks Equipment. The license granted hereunder is perpetual.
3 SOFTWARE TITLE. MeshNetworks is not selling You the Licensed Software. Title to the
Licensed Software, including all translations, compilations, derivative works and copies remain
with MeshNetworks or its licensors, as the case may be.
4 INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY AND CONFIDENTIALITY. You acknowledge that the
Licensed Software and Documentation contain copyrighted material, trade secrets and other
material that is proprietary to MeshNetworks, and that except as expressly provided in this
Agreement, MeshNetworks retains all rights, title and interests in and to the Licensed Software
and all proprietary rights in it. You further acknowledge that unauthorized use of such material
may cause serious and irreparable loss or damage to MeshNetworks and its licensors, and
therefore you agree that in the event of a breach of this Agreement MeshNetworks will be
entitled to injunctive relief to restrain such breach, in addition to monetary damages and its
reasonable attorneys’ fees, charges and costs in enforcing the Agreement. You will keep the
Licensed Software, any backup copy of the Licensed Software and the Documentation strictly
confidential and will not disclose or provide them (or any information relating to them) to any
other person or entity. You will also take all reasonable steps to safeguard the Licensed
Software to ensure that unauthorized personnel do not have access to the Licensed Software,
and You will notify MeshNetworks of any unauthorized use of the Licensed Software. Except as
expressly stated herein, this Agreement does not grant You any intellectual property rights in
the Licensed Software and all rights not expressly granted herein are reserved by
MeshNetworks.
” means the party from whom you purchased the MeshNetworks Equipment and
” means MeshNetworks, Inc., 485 N. Keller
” means the computer programs, in
”); and (b) upgrades,
”). The “MeshNetworks
” has the meaning set forth in Section 7.
33
Page 52

MeshNetworks
5 RESTRICTIONS. You will not:
5.1 Use t he Licensed Software in conjunction with any other equipment or for any purpose
other than for the operation and monitoring of the MeshNetworks Equipment and for your
internal business purposes in accordance with the operating instructions MeshNetworks
or the Source may provide to you from time to time;
5.2 Decom pile, r e verse engineer, disassemble, translate or reduce the Licensed Software to a
human-perceivable form;
5.3 Modif y, adapt, or translate or create derivative works based upon the Licensed Software
in whole or in part;
5.4 Lease, rent, sublicense, share, lend, distribute, disclose, network, or pledge the Licensed
Software to or for the benefit of any third party;
5.5 Use t he Licensed Software in a client-server environment, electr onically transmit the
Licensed Software from one computer to another or over a network or otherwise allow a
third party to remotely access or use the Licensed Software;
5.6 Transfer any of your rights in the Licensed Software or the Documentation to another
party;
5.7 Use t he Licensed Software for any unlawful or harmful purpose;
5.8 Make copies of the Licensed Software, other than a reasonable number of copies of the
Licensed Software for back-up or archival purposes and such other copies as are
necessary for You to use the Licensed Software as described in the Documentation;
5.9 Rem ove or alt er any trademark, copyright, confidentiality or ot her proprietar y rig ht notice
in the Licensed Software or Documentation or any copy made by You; or
5.10 Circumvent any access control mechanism that effectively controls access to the Licensed
Software for any purpose.
6 LIMITED WARRANTY.
6.1 Software Warranty
substantially in compliance with the Documentation for a period of ninety (90) days after
delivery to You. Any supplements or Updates to the Licensed Software provided to You
after the expiration of ninety (90) days limited warranty period are not covered by any
warranty or condition, express or implied. In the event of a breach of the foregoing
warranty, You must notify the Source within such 90-day period. In the event that you
notify the Source of a breach of the foregoing warranty within such 90-day period, the
Source will, at the Source’s option, either (i) use commercially reasonable efforts to
correct any substantial non-conformity, (ii) replace the non-conforming item of Licensed
Software, or (iii) return the fee paid by You for such item of Licensed Software. The
foregoing will be entire liability of MeshNetworks and the Source and your sole and
exclusive remedy for a breach under the foregoing limited warranty. Neither the Source,
nor MeshNetworks will have no liability under this warranty to the extent that (a) the
Licensed Software has been misused or exposed to environmental or operating conditions
beyond those specified by MeshNetworks, (b) the Licensed Software has been damaged,
altered by accident, neglect, misuse or other abuse, (c) the claimed defect has been
caused, in whole or in part, by a person or persons other than MeshNetworks, by other
products or software not provided by MeshNetworks, or by circumstances not under
MeshNetworks' control, or (d) You fail to incorporate all error fix releases that
MeshNetworks or the Source has provided. In the event the Source fails to perform its
. MeshNetworks warrants that the Licensed Software will operate
34
Page 53

Setup and Deployment
responsibilities as described in this Section 6.1 within a reasonable period of time,
MeshNetworks or one of its independent contractors will perform such obligations. The
warranty period, but not the scope of obligations described above, may be extended by a
written agreement between You and the Source.
6.2 DISCLAIMER OF PERFORMANCE WARRANTIES
SECTION 6.1 ABOVE, THE LICENSED SOFTWARE IS LICENSED TO YOU “AS IS.”
MESHNETWORKS DOES NOT REPRESENT OR WARRANT , AND EXPRESSLY
DISCLAIMS ANY REPRESENTATION OR WARRANTY, THAT:
6.2.a THE OPERATION OF THE LICENSED SOFTWARE WILL BE UNINTERRUPTED OR
ERROR FREE; AND
6.2.b THE FUNCTIONS OR FEATURES OF THE LICENSED SOFTWARE WILL MEET
YOUR REQUIREMENTS, OR THAT THE LICENSED SOFTWARE WILL OPERATE IN
THE HARDWARE AND SOFTWARE COMBINATIONS SELECTED BY YOU. YOU
ASSUME ALL RESPONSIBILITY FOR THE SELECTION OF PRODUCTS AND THE
LICENSED SOFTWARE TO ACHIEVE YOUR INTENDED RESULTS, AND FOR YOUR
USE OF AND RESULTS OBTAINED FROM THE LICENSED SOFTWARE.
6.3 DISCLAIMER OF IMPLIED WARRANTIES
ABOVE, THE LICENSED SOFTWARE IS LICENSED TO YOU “AS IS.”
MESHNETWORKS EXPRESSLY DISCLAIMS, TO THE MAXIMUM EXTENT
PERMITTED BY APPLICABLE LAW, ANY AND ALL REPRESENTATIONS AND
WARRANTIES, EXPRESS, IMPLIED, OR STATUTORY, INCLUDING
REPRESENTATIONS OR WARRANTIES OF NON-INFRINGEMENT OF ANY THIRD
PARTY INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY RIGHTS, OWNERSHIP, MERCHANTABILITY,
FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE, QUIET ENJOYMENT, SYSTEM
INTEGRATION, AND DATA ACCURACY. MESHNETW ORKS’ EXPRESS WARRANTY
WILL NOT BE ENLARGED, DIMINISHED OR AFFECTED BY, AND NO OBLIGATION
OR LIABILITY WILL ARISE OUT OF, THE RENDERING OF TECHNICAL OR OTHER
ADVICE OR SERVICE BY MESHNETWORKS OR THE SOURCE IN CONNECTI ON
WITH THE LICENSED SOFTWARE.
. EXCEPT AS SET FORTH IN SECTION 6.1
. EXCEPT AS SET FORTH IN
6.4 NO CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES
PARTY BE LIABLE FOR ANY SPECIAL, INCIDENTAL OR CONSEQUENTIAL
DAMAGES ARISING IN ANY WAY OUT OF THIS AGREEMENT OR THE USE OF THE
LICENSED SOFTWARE AND DOCUMENTATION HOWEVER CAUSED (WHETHER
ARISING UNDER A THEORY OF CONTRACT, TORT (INCLUDI NG NEGLIGENCE), OR
OTHERWISE), INCLUDING, WITHOUT LIMITATION, DAMAGES FOR LOST PROFITS,
LOSS OF DATA, OR COSTS OF PROCUREMENT OF SUBSTITUTE GOODS OR
SERVICES. THE LIMITATIONS ON LIABILITY SET FORTH IN THIS SECTION WILL
APPLY NOTWITHSTANDING THE FAILURE OF ESSENTIAL PURPOSE OF ANY OF
THE LIMITED REMEDIES SET FORTH IN SECTION 6.1 ABOVE.
6.5 LIMITATION OF LIABILITY
SOURCE AND MESHNETWORKS’ LICENSORS ARISING OUT OF OR RELATING TO
THIS AGREEMENT WILL NOT EXCEED THE LICENSE FEES AND PURCHASE PRICE
RECEIVED BY THE SOURCE FROM YOU IN THE TWELVE (12) MONTHS PRIOR TO
THE EVENT GIVING RISE TO THE LIABILITY.
7 SUPPORT SERVICES. The Source may provide You with support services related to the
Licensed Software (“Support Services”). Use of Support Services is governed by the Source’s
policies and programs or in other materials from the Source. Any Updates or other
. THE TOTAL LIABILITY OF MESHNETWORKS, THE
. UNDER NO CIRCUMSTANCES WILL EITHER
35
Page 54

MeshNetworks
supplemental software code provided to You as part of the Support Services are considered
part of the Licensed Software and subject to the terms and conditions of this Agreement. You
acknowledge and agree that MeshNetworks and its licensors, contractors, resellers and
distributors may use technical information You provide to them as part of the Support Services
for its business purposes, including for product support and development.
8 INDEMNIFICATION. MeshNetworks will defend, indemnify and hold You harmless from any
liability arising from any third party claim or proceeding against You to the extent that such claim
or proceeding is based on an assertion that the Licensed Software infringes any issued United
States patent or any trade secret or copyright of any third party; provided
notify MeshNetworks promptly in writing of any such claim or proceeding and give
MeshNetworks full and complete authority, information and assistance to defend such claim or
proceeding at the expense of MeshNetworks; and further
sole control of the selection of counsel and the defense of any such claim or proceeding and all
negotiations for its compromise or settlement. Should the Licensed Software become, or in
MeshNetworks’ opinion be likely to become, the subject of a claim of infringement,
MeshNetworks will have the right, at MeshNetworks’ option and expense, (i) to procure for You
the right to continue using the Licensed Software, or (ii) to replace or modify the Licensed
Software with a non-infringing version of substantially equivalent function and performance.
9 LIMITATION. MeshNetworks will have no liability to You hereunder for any infringement
based upon (i) the combination of the Licensed Software with other products not provided by
MeshNetworks; (ii) the use of other than a current, unaltered version of the Licensed Software;
(iii) the use of any derivative works, modification or improvement of the Licensed Software not
created by MeshNetworks; (iv) any use of the Licensed Software in the practice of a process not
specified by MeshNetworks. Section 8 and 9 state the sole, exclusive and entire liability of
MeshNetworks, and the sole, exclusive and entire remedy with respect to any claim of
intellectual property infringement by the Licensed Software.
provided that You give MeshNetworks
, however, that You
10 TERMINATION. If You breach any provision of this Agreement, then MeshNetworks may, in
addition to any other remedies it may have under law, terminate any license granted hereunder
effective immediately without liability after ten (10) days written notice to You, and You will
promptly cease all use of the Licensed Software and will return to MeshNetworks all copies of
the Licensed Software. In such event, at the request of MeshNetworks you will certify in writing
that the original and all copies of the Licensed Software has been destroyed or returned to
MeshNetworks.
11 ASSIGNMENT AND MESHNETWORKS EQUIPMENT TRANSFER. You may not
sublicense or assign this Agreement or any interest or right granted herein without
MeshNetworks’ prior written consent. The Licensed Software is designed and configured for the
sole purpose of operating with the MeshNetworks Equipment, and accordingly this Agreement
will be automatically assigned on the sale or transfer of the MeshNetworks Equipment with
which the Licensed Software operates to the person or entity who takes title to such
MeshNetworks Equipment; provided
obligations and restrictions set forth in this Agreement.
12 GOVERNMENT LICENSEE. The MeshNetworks Equipment and Licensed Software and
accompanying documentation were developed at private expense and no part of them is in the
public domain. The Licensed Software is “Restricted Computer Software” and “Commercial
Computer Software” and if You are acquiring the Licensed Software for the United States
Government, then it is acquiring only “restricted rights” in the Licensed Software and its
Documentation, all as defined in the applicable provisions of the Department of Defense Federal
Acquisition Regulation Supplement and the Federal Acquisition Regulations. Such unit will
, however, that such assignee or transferee abides by the
36
Page 55

Setup and Deployment
include a “restricted rights legend” on the MeshNetworks Equipment and Licensed Software as
may be necessary to insure the limitation of rights acquired by the government.
Notwithstanding the foregoing, this Agreement will not become effective with respect to the
United States Government without MeshNetworks’ prior written approval.
13 EXPORT CONTROLS. This Agreement is subject to the laws, regulations, orders, and
decrees of the United States that may be imposed from time to time restricting the import/export
of the Products to/from the United States. You will not export or re-export the Licensed
Software, or any part of the Licensed Software, directly or indirectly, prohibited by or in violation
of the laws, rules or regulations of the United States or any applicable jurisdiction. Nor will You
export or re-export the Licensed Software, or any part of the Licensed Software, directly or
indirectly without first obtaining the required permission to do so from the applicable
governmental agencies.
14 COMPLIANCE WITH LICENSES. You agree that upon request from MeshNetwork or the
Source, You will within fifteen (15) days fully document and certify in writing that use of any and
all Licensed Software at the time of the request is in conformity with this Agreement or some
other valid license from MeshNetworks.
15 MISCELLANEOUS. This Agreement is governed by the laws of the state of Florida, United
States of America. The state or federal courts located in or having jurisdiction over Orlando,
Florida, United States of America will have exclusive jurisdiction over all maters pertaining to
this Agreement. If any term or condition of this Agreement is or will become invalid or
unenforceable, then such part will be ineffective to the extent of such invalidity only, without
affecting this Agreement’s remaining provisions. Those rights and obligation, which by their
nature are intended to survive the expiration or termination of this Agreement, will survive. The
remedies at law of either party in the event of default or impending default by the other party in
the performance of any terms of this Agreement will not be adequate, and such terms may be
specifically enforced by a decree for specific performance, injunction or other appropriate
equitable relief. The failure of MeshNetworks to enforce at any time any provision of this
Agreement will in no way be construed to be a present or future waiver of such provision, nor
will it affect MeshNetworks ability to enforce any provisions of this Agreement. This Agreement
is the entire agreement between the parties with respect to the subject matter set forth herein
and supersedes all prior oral written agreements between the parties with respect thereto and
may only be amended in writing by the parties.
37
Page 56

MeshNetworks
Section 9 - FCC Regulatory Information
FCC Information
This device complies with Part 15 of the FCC Rules. Operation is subject to the following two
conditions: (1) this device may not cause harmful interference, and (2) t his device must accept
any interference received; including interference that may cause undesired operation.
The IAP6300 (Intelligent Access Point) is an infrastr ucture device that is positioned at a fixed
location such as a building rooftop. The IAP6300 requires professional installation to ensure
that the installation is performed in accordance with FCC licensing regulations.
The MWR6300 (Wireless Router) is an infrastructure device positioned in a fixed location, such
as on a pole, wall, or rooftop. The MWR6300 requires professional installation to ensur e the
installation is performed in accordance with FCC licensing regulations.
Federal Communications Commission (FCC) Statement:
This Equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a Class A digital device,
pursuant to Part 15 of the FCC rules. These limits are designed to provide reasonable
protection against harmful interference in a commercial installation. This equipment generates,
uses and can radiate radio frequency energy and, if not installed and used in accordance with
the instructions, may cause harmful interference to radio comm unications. However, there is no
guarantee that interference will not occur in a particular installation. If this equipment does
cause harmful interference to radio or television reception, which can be determined by turning
the equipment off and on, the user is encouraged to try to correct the interference by one or
more of the following measures:
• Reorient or relocate the receiving antenna.
• Increase the separation between the equipment and receiver.
• Connect the equipment into an outlet on a circuit different from that to which the
receiver is connected.
• Consult the dealer or an experienced radio/TV technician for help.
Any changes or modifications not expressly approved by MeshNetworks could void the user’s
authority to operate the equipment.
FCC RF Radiation Exposure Statement
1. CAUTION: This equipment complies with FCC RF radiation exposure limits set forth for
an uncontrolled environment. This equipment should be installed and operated with a
minimum distance of 2 meters between the antenna and your body.
2. This Transmitter must not be co-located or operating in conjunction with any other
antenna or transmitter.
38
Page 57

Setup and Deployment
39
Page 58

MeshNetworks
Safety Information for the Products
The Federal Communications Commission (FCC) with its action in ET Docket 96-8 has adopted
a safety standard for human exposure to radio frequency (RF) electr omagnetic energy emitted
by FCC certified equipment. MeshNetworks’
environmental limits found in OET-65 and ANSI C95.1, 1991. Proper operation of this radio
according to the instructions found in this manual and the hardware and software guides on the
CD will result in user exposure that is substantially below the FCC recommended limits.
• Do not touch or move the antenna(s) while the unit is transmitting or receiving.
• Do not hold any component containing a radio such that the antenna is very close to or
touching any exposed parts of the body, especially the face or eyes, while transmitting.
• Do not operate a portable transmitter near unshielded blasting caps or in an explosive
environment unless it is a type especially qualified for such use.
• Do not operate the radio or attempt to transmit data unless the antenna is connected;
otherwise, the radio may be damaged.
• Antenna use:
• In order to comply with FCC RF exposure limits, dipole antennas should be located
at a minimum distance of 2 meters or more from the body of all persons.
products meet the uncontrolled
Section 10 - Safety Certification
XXXXXX (6 digit control # assigned by Follow Up Services, upon completion of the
listing report)
Conforms to UL STD ANSI/UL 60950 3
Certified to CAN/CSA C22.2 NO. 60950-00
Equipment shall be suitable for use in Air pressure: 86kPa to106kPa.
rd
Edition
40
 Loading...
Loading...