
ZR138
Mobile Printer
User Guide
P1123853-01EN

ZEBRA and the stylized Zebra head are trademarks of Zebra Technologies Corporation, registered in
many jurisdictions worldwide. All other trademarks are the property of their respective owners.
© 2021 Zebra Technologies Corporation and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved.
Information in this document is subject to change without notice. The software described in this document
is furnished under a license agreement or nondisclosure agreement. The software may be used or copied
only in accordance with the terms of those agreements.
For further information regarding legal and proprietary statements, please go to:
SOFTWARE:zebra.com/linkoslegal
COPYRIGHTS:zebra.com/copyright
WARRANTY:zebra.com/warranty
END USER LICENSE AGREEMENT: zebra.com/eula
Terms of Use
Proprietary Statement
This manual contains proprietary information of Zebra Technologies Corporation and its subsidiaries
(“Zebra Technologies”). It is intended solely for the information and use of parties operating and
maintaining the equipment described herein. Such proprietary information may not be used, reproduced,
or disclosed to any other parties for any other purpose without the express, written permission of Zebra
Technologies.
Product Improvements
Continuous improvement of products is a policy of Zebra Technologies. All specifications and designs are
subject to change without notice.
Liability Disclaimer
Zebra Technologies takes steps to ensure that its published Engineering specifications and manuals are
correct; however, errors do occur. Zebra Technologies reserves the right to correct any such errors and
disclaims liability resulting therefrom.
Limitation of Liability
In no event shall Zebra Technologies or anyone else involved in the creation, production, or delivery of the
accompanying product (including hardware and software) be liable for any damages whatsoever
(including, without limitation, consequential damages including loss of business profits, business
interruption, or loss of business information) arising out of the use of, the results of use of, or inability to
use such product, even if Zebra Technologies has been advised of the possibility of such damages. Some
jurisdictions do not allow the exclusion or limitation of incidental or consequential damages, so the above
limitation or exclusion may not apply to you.
All other brand names, product names, or trademarks belong to their respective holders.
©2019 Zebra Technologies Corporation
Publication Date
June 1, 2021
2

Contents
Printer Overview ................................................................................................................................. 6
Unpacking and Inspection............................................................................................... 7
Reporting Damage........................................................................................................... 7
Battery............................................................................................................................. 8
Printing Technology ........................................................................................................ 9
Product Information QR Code.......................................................................................... 9
Near Field Communication (NFC)................................................................................. 10
Printer Features ............................................................................................................ 11
Using the Printer............................................................................................................................... 12
Preparing the Battery for Use......................................................................................... 12
Installing/Removing Battery & Battery Tape Insulator ............................................ 12
Removing the Battery....................................................................................... 12
Removing the Battery Tape Insulator............................................................... 13
Battery Safety ......................................................................................................... 15
Charging the Battery............................................................................................... 15
AC-to-USB Charger ......................................................................................... 15
1-Slot Battery Charger............................................................................................ 16
Loading Media............................................................................................................... 18
Loading Media Procedure ...................................................................................... 18
Operator Controls........................................................................................................... 19
Printer Status Icons........................................................................................................ 20
Information Screen........................................................................................................ 22
Timed Messages .................................................................................................... 22
User Activity Messages .......................................................................................... 22
Configuration Screen.............................................................................................. 23
Sleep Screen .......................................................................................................... 23
Buttons ................................................................................................................... 24
Verify Printer is Working ......................................................................................... 24
Printing a Configuration Report .............................................................................. 24
Connecting the Printer ................................................................................................... 24
3

Contents
USB Communications ............................................................................................ 25
ZR1 Mobile Configuration Tool ...................................................................................... 25
Wireless Communications with Bluetooth...................................................................... 26
Bluetooth Networking Overview ............................................................................. 26
Bluetooth Security Modes .............................................................................................. 27
Bluetooth Minimum Security Modes ....................................................................... 28
Setting Up the Software ................................................................................................. 29
Designing Labels............................................................................................................ 29
Using Pre-Printed Receipt Media ........................................................................... 30
Black Mark Dimensions (Receipt Media)................................................................ 30
Label Areas ............................................................................................................ 31
Label Design Examples.......................................................................................... 32
Keep-Out Areas...................................................................................................... 33
Using Near Field Communication (NFC)....................................................................... 34
NFC Use Cases...................................................................................................... 34
Passive............................................................................................................. 34
Wearing the Printer ....................................................................................................... 36
Swivel Belt Clip....................................................................................................... 36
Shoulder Strap........................................................................................................ 37
Soft Case................................................................................................................ 38
Preventive Maintenance................................................................................................ 39
Extending Battery Life ............................................................................................ 39
General Cleaning Instructions ................................................................................ 39
Cleaning ................................................................................................................. 40
Troubleshooting ............................................................................................................................... 41
LCD Control Panel Indicators......................................................................................... 41
Troubleshooting Topics.................................................................................................. 41
No power ................................................................................................................ 41
Media does not feed ............................................................................................... 41
Poor or faded print.................................................................................................. 41
Partial or missing print ............................................................................................ 41
Garbled print........................................................................................................... 42
No print ................................................................................................................... 42
Reduced battery charge life.................................................................................... 42
Data icon flashing ................................................................................................... 42
Media Out or Head Open icons flashing................................................................. 42
Communication error .............................................................................................. 42
Label binding .......................................................................................................... 42
Skip Labels ............................................................................................................. 42
Blank LCD screen................................................................................................... 43
4

Contents
No NFC Connectivity .............................................................................................. 43
Troubleshooting Tests.................................................................................................... 43
Printing a Configuration Label ................................................................................ 43
Communications Diagnostics ................................................................................. 43
Contacting Technical Support........................................................................................ 44
Specifications ................................................................................................................................... 46
Printing Specifications.................................................................................................... 46
Memory and Communications Specifications ................................................................ 46
Label Specifications ....................................................................................................... 47
CPCL Font and Bar Code Specifications and Commands............................................ 48
Physical, Environmental and Electrical Specifications.................................................. 49
ZR138 Dimensions........................................................................................................ 50
Accessories................................................................................................................... 51
Miscellaneous ................................................................................................................................... 52
Serial Number and PCC Number Locations .................................................................. 52
USB Cable ..................................................................................................................... 53
Media Supplies.............................................................................................................. 54
Maintenance Supplies.................................................................................................... 54
Battery and Product Disposal......................................................................................... 54
Alert Messages ............................................................................................................. 55
5

Printer Overview
This user guide gives you the information that you need to operate the ZR138 Mobile Printer. The
printer uses technologies such as USB charging (Type-C connector),
Bluetooth
devices such as an iPhone or iPad.
This printer uses CPCL and ESC/POS programming languages to configure the printer and print
properties, label design, and communications. Refer to the CPCL Programming Guide and the ESC/POS
Programming guide at zebra.com/manuals
Software Resources and Utilities:
• ZebraNet Bridge Enterprise: printer configuration, fleet management
• ZR1 Mobile Configuration Tool: single printer configuration, quick setup
• ZebraDesigner Pro v2: label design
• Zebra Designer Drivers: Windows driver
• OPOS Driver: Windows driver
5.0, Near Field Communication (NFC) and BT Low Energy (BTLE) to connect with Apple
for more information.
• Multiplatform SDK or ZR138 SDK (CPCL and ESC/POS only)
• Zebra Downloader
• Mobile Label Designer ( 斑马智印)
(Theseutilities can be found on the Zebra website at zebra.com/us/en/support-downloads
.
6

Unpacking and Inspection
In case shipping is required, save the carton and all packing material.
• Check all exterior surfaces for damage.
• Open the media cover (refer to Loading Media on page 18) and inspect the media compartment for
damage.
Printer Overview
1
5
4
1 Quick Start Guide 4 Battery Pack
2 USB Cable 5 AC-to-USB Adapter
3 Printer
2
3
Reporting Damage
If you discover shipping damage:
• Immediately notify and file a damage report with the shipping company. Zebra Technologies
Corporation is not responsible for any damage incurred during shipment of the printer and will not cover
the repair of this damage under its warranty policy.
• Keep the carton and all packing material for inspection.
• Notify your authorized Zebra reseller.
7

Battery
Printer Overview
The printer uses a two-cell Li-Ion battery pack with a charge time of under 3.5 hours using a 7.5W USB
charger while printer power is on. The battery allows the printer to print reliably without recharge for three
work days under the following conditions: 25 stops per day and will power up the device 25 times per day;
up to 500 3x8.5 in. receipts per 8-hour shift with 13% coverage.
Operating Temperature Charging Temperature Storage Temperature
-10°C to 50°C
(14°F to 122°F)
NOTE: Note the following:
- Power down the printer before removing the battery to minimize the risk of corruption.
- The printer will only function properly with genuine Zebra battery packs.
0°C to 40°C
(32°F to 104°F)
-20°C to 60°C
(-4°F to 140°F)
8

Printing Technology
The printer uses the Direct Thermal method to print human readable text, graphics and barcodes. It
incorporates a sophisticated print engine for optimal printing under all operational conditions. Direct
thermal printing uses heat to cause a chemical reaction on specially treated media. This reaction creates a
dark mark wherever a heated element on the printhead comes in contact with the media. Because the
printing elements are arranged very densely at 203 dpi (dots per inch) horizontal and 200 dpi vertical,
highly legible characters and graphic elements may be created a row at a time as the media is advanced
past the printhead. This technology has the advantage of simplicity, as there is no requirement for
consumable supplies such as ink or toner. However, since the media is sensitive to heat, it will gradually
lose legibility over long periods of time, especially if exposed to environments with relatively high
temperatures or in direct sunlight.
Product Information QR Code
The QR code includes human readable text URL, for example zebra.com/zr138-info, which links the user
to printer information and videos on topics such as buying supplies, features overview, loading media,
printing a configuration report, cleaning instructions, and accessory information.
Figure 1 QR Code
Printer Overview
QR Code
9

Printer Overview
Near Field Communication (NFC)
The printer supports a passive NFC tag which complies with the Android Standard Tag format. The NFC
tag is programmed from the factory and supports Bluetooth pairing to enable a tablet, smartphone or
terminal to automatically pair with the printer via a Bluetooth connection (within the bounds of the security
profile being used).
The NFC tag also supports app launching whereby an app developed either by Zebra or a third party
launches on an NFC-enabled smartphone, tablet or terminal. Similarly, the NFC tag enables launching to a
web support page via a tablet, smartphone or terminal. (See Using Near Field Communication (NFC) on
page 34.)
NOTE: Tapping the Zebra Print Touch icon with an NFC-enabled mobile device will provide instant access
to printer-specific information. For more information about NFC and Zebra products, go to zebra.com/nfc
Bluetooth pairing applications via NFC is also possible. Please see Zebra Multi-platform SDK for more
information.
.
10

Printer Features
Figure 2 Overview of Features
Printer Overview
14
13
12
11
10
8
9
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
1 Platen Roller 10 Configure Button
2 Back Side Sensor 11 Power Button
3 Latch Release Lever 12 LCD Display
4 Front Side Sensor 13 Printhead
5 Tear Bar 14 Media Cover
6 Print Touch Icon (NFC) 15 Belt Clip Mounting Hole
7 USB Port 16 Battery
8 Media Feed Button 17 QR Code
9 Strap Posts 18 MAC Address Label
15
16
17
18
11

Using the Printer
Preparing the Battery for Use
Installing/Removing Battery & Battery Tape Insulator
IMPORTANT: Batteries are shipped in sleep mode to preserve their maximum capacity while in storage
prior to initial use. The battery needs an initial charging to wake it up before using for the first time. (See
Charging the Battery on page 15.)
Removing the Battery
1. Depress the release tab on the battery pack and begin to rotate the battery out of the battery
compartment.
12

Using the Printer
Lift the battery pack up and out of the battery well.
2.
Removing the Battery Tape Insulator
CAUTION: The battery can explode, leak or catch fire if improperly charged or exposed to high
temperature. Do not disassemble, crush, puncture, short external contacts or dispose in fire or water.
Charge on a Zebra approved Lithium-Ion charger only.
1. Turn the battery pack over and locate the battery tape over the contacts.
2. Peel off the battery tape to expose the contacts and discard.
Battery Tape
Battery Contacts
13

Installing the Battery
1. Locate the battery compartment on the bottom of the printer.
2. Angle the battery pack and insert it into the battery compartment.
Using the Printer
3. Rotate the battery into the compartment until it locks in place and is sitting flush in the printer.
14

Battery Safety
CAUTION: Avoid accidental short circuiting of any battery. Allowing battery terminals to contact conductive
material creates a short circuit which could cause burns and other injuries or could start a fire.
IMPORTANT: Always refer to the Important Safety Information data sheet shipped with each printer and
the Technical Bulletin shipped with each battery pack. These documents detail procedures to ensure
maximum reliability and safety while using this printer.
IMPORTANT: Always dispose of used batteries properly. Refer to Appendix E for more battery recycling
information.
CAUTION: Use of any charger not approved specifically by Zebra for use with its batteries could cause
damage to the battery pack or the printer and will void the warranty.
CAUTION: Do not incinerate, disassemble, short circuit, or expose to temperatures higher than 65°C
(149°F).
Charging the Battery
CAUTION: Do not place any charger in locations where liquids or metallic objects may be dropped into the
charging bays.
Using the Printer
AC-to-USB Charger
1. Plug the AC-to-USB adapter into the wall outlet and then plug the USB cable into the adapter
2. Rotate the rubber door on the side of the printer to access the USB port.
15

Connect the USB cable to the printer.
3.
IMPORTANT: Batteries that have reached partial charge capacity may be used. However, it is
recommended that you allow the batteries to reach a full charge to maintain maximum battery life.
1-Slot Battery Charger
The 1-Slot Battery Charger allows one battery to be charged at a time and features an LED that displays
solid red when charging and solid green when the battery is fully charged.
Using the Printer
1. Plug the USB cable into the port on the back of the charger.
2. Plug the other end of the cable into the AC-to-USB adapter and plug the adapter into the wall outlet.
16

Using the Printer
Angle the battery pack and insert it into the battery compartment. Rotate the battery into the
3.
compartment until it locks in place and sits flush in the charger.
The LED on the charger will display solid red when charging and solid green to indicate the battery is fully
charged.
LED
17

Loading Media
The printer is designed to print either continuous (receipt) media or label stock.
Loading Media Procedure
1. Slide the latch release forward to unlock the media cover. Lift and rotate the media cover to open.
Using the Printer
2. Insert the roll of media (in the orientation shown) in the media compartment. The media roll should be
able to spin freely inside the media compartment.
3. Close the media cover until it clicks into place and the media will advance as shown.
18

Using the Printer
NOTE: Refer to the Programming Guide for information on changing the setting to adjust the media feed
length via a Set Get Do (SGD).
Operator Controls
The printer features a three-button user interface for menu navigation (Figure 3). The printer also features
an OLED display which remains lit while the printer is powered on.
xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx xxxxxxxxxx
Figure 3 Control Panel
1
2
3
4
1 OLED Display - Indicates the status of several printer functions.
2 Power Button - Press to turn unit on. Press again to turn unit off.
3 Configure Button - Press to select a menu choice on the LCD
4 Paper Feed Button - Press to advance the media one blank
label or a software determined length of journal media.
19

Printer Status Icons
The LCD control panel allows the user to view content in one of four modes:
• Operation Screen Mode.
• Information Screen Mode.
• Configuration Screen Mode.
• Sleep Screen Mode.
The default mode, which the user sees upon powering up the printer, is Operation Screen mode. This
mode is the display shown when the printer is idle, printing and/or receiving data and has no need to
convey information beyond icons shown on the display. The LCD can display up to five (5) status icons,
including Status, Media, Data, Bluetooth and Battery.
Table 1
Icon Description
Indicates printer is fully operational.
Using the Printer
Indicates there is a condition the user should be aware of but the printer is still
functional.
Indicates there is something wrong with the printer that prevents some basic
functionality from being used.
Indicates media is loaded and ready to print.
Indicates no media is loaded in the printer.
Indicates media cover is unlatched.
Indicates printer is not receiving data.
Indicates printer is receiving data.
20

Using the Printer
Table 1
Icon Description
Connected to Bluetooth. (No icon means Bluetooth is disconnected.)
Indicates battery charge status.
Indicates battery level while charging.
Indicates printer is getting power from USB.
Indicates battery charge error.
21

Information Screen
打印 就绪
系列
ZR138
机
系列
ZR138
㕪㓨
The Information Screen displays when text is used to convey information to the user. The display is split
into two viewing areas: The top portion will display the same icons previously described on the Operation
Screen; the bottom portion will display text messages. There are two types of messages that can be
displayed on the Information Screen as described below.
Timed Messages
These messages will appear for a specific period of time, and then be removed. For example, after
powering up the printer and the printer is ready to print, the message PRINTER READY will appear for 30
seconds.
Using the Printer
PRINTER READY Message
User Activity Messages
These messages require that the user performs a needed action. For example, when the printer is out of
media, a MEDIA OUT message displays until new media is loaded in the printer.
MEDIA OUT Message
22

The following User Activity Messages are supported by the printer:
DOWNLOAD FW HEAD UNDERTEMP
DOWNLOAD FAILED BATTERY TOO LOW
PAIRING SUCCESS MEDIA OUT
HEAD OVERTEMP HEAD OPEN
When the Information Screen is used to display text messages, it replaces the Operation Screen. When
the text message has been acknowledged, the printer will return to the Operation Screen.
Configuration Screen
The Configuration Screen is used to change printer parameters or initiate printing a configuration label.
Specifically, the user will be able to change the following parameters.
Using the Printer
NO PRINTING CHARGE ERROR
BATTERY LOW PRINTER READY
• Darkness: Increase or decrease the darkness by pressing Media Feed.
• Power Up: Select either Feed On or Feed Off by pressing Media Feed.
• Head Close: Select either Head Open or Head Close by pressing Media Feed.
• Power Sleep Mode: Select either Enable or Disable by pressing Media Feed.
• Print: Print a configuration report by pressing Media Feed.
• MAC Address: Select either Display On or Display Off by pressing Media Feed.
• Media Type: Select either Journal, Front Black Mark, Back Black Mark, or Label by pressing
Media Feed.
• Exit Configuration: Exit the Configuration Screen and return to the Operation Screen by pressing
Media Feed.
Sleep Screen
The Sleep Screen is displayed within 10 seconds when there is no activity. In this state, the screen
displays either the Zebra logo moving across the screen from left to right or the battery charge icon if the
printer is charging.
Sleep Mode
Sleep Mode While Charging
23

Buttons
The user has the ability to use the printer’s multi-button interface to run the following power-up and runtime
sequences.
Table 2 Power-Up Sequences
Sequence # Function Keys
1 Configuration Report Hold down Media Feed while pressing and
2 Forced Download Hold down Configuration and Media Feed while
3 Turn Printer On or Off Press Power.
Verify Printer is Working
Before you connect the printer to your computer or portable data terminal, make sure that the printer is in
proper working order. You can do this by printing a configuration label using the “two key” method. If you
can’t get the label to print, refer to “Troubleshooting Topics”.
Using the Printer
releasing Power.
pressing Power.
Printing a Configuration Report
1. Turn the printer off. Load the media compartment with journal media (media with no black bars or gaps
on the back).
2. Press and hold Media Feed.
3. Press and release Power and keep Media Feed pressed. When printing starts, release Media
Feed. The unit will print a line of interlocking “x” characters to ensure all elements of the printhead are
working, print out the version of software loaded in the printer and then print the report.
The report indicates model, serial number, baud rate, and more detailed information on the printer’s
configuration and parameter settings. See Troubleshooting for sample printouts and a further
discussion on how to use the configuration label as a diagnostic tool.
You can also print a configuration report by turning the printer on, pressing Configure multiple times
until you get to the SETTINGS-PRINT screen, and then pressing Media Feed.
Connecting the Printer
The printer must establish communications with a host terminal, which sends the data to be printed.
Communications occur in two basic ways:
• Via a cable using USB 2.0 protocols. Windows drivers that support printing via USB are included in the
Zebra Designer Driver which can be downloaded from zebra.com/drivers
• By means of a Bluetooth short range radio frequency link.
.
24

USB Communications
LAN
CAUTION: The printer should be turned off before connecting or disconnecting a communication cable.
The standard cable connection for the printers is a USB 2.0 communication and charging cable. One end
of the cable has a USB Type-A connector while the other end is USB Type-C
The small Type C connector on the USB cable plugs into the printer. The connector is not keyed and
therefore can be plugged in in either direction. However, do not try to force the cable if it does not plug in.
The Type A end of the cable must be plugged into any USB 2.0 host port. The printers utilize the USB
cable to charge the printer (see AC-to-USB Charger on page 15) and for communications between the
printer and computer.
Figure 4 USB Cable Communication with PC
Using the Printer
.
USB drivers are included in the Zebra Designer Driver which can be downloaded from the Zebra website.
ZR1 Mobile Configuration Tool
Before you start to configure your printer for use, you will need some basic information which will enable
you to establish the network configuration for your printer. The ZR1 Mobile Configuration Tool provides a
quick and easy way to configure your printer for a variety of purposes, including setting it up to use the
international Bluetooth communications standard.
Once ZR1 Mobile Configuration Tool has been downloaded to your computer, attach the USB cable to the
printer and computer as shown in Figure 4. Go to zebra.com/us/en/support-downloads.html
the tool.
to download
25

Using the Printer
Wireless Communications with Bluetooth
Bluetooth is a worldwide standard for the exchange of data between two devices via radio frequencies.
This form of point-to-point communication does not require access points or other infrastructure. Bluetooth
radios are relatively low powered to help prevent interference with other devices running at similar radio
frequencies. This limits the range of a Bluetooth device to about 10 meters (32 feet). The default for the
printers is Class 2. Both the printer and the device it communicates with must follow the Bluetooth
standard.
Bluetooth Networking Overview
Each Bluetooth enabled printer is identified by a unique Bluetooth Device Address (BDADDR). This
address resembles a MAC address whereby the first three bytes are vendor, and the last three bytes are
device (e.g. 00:22:58:3C:B8:CB). This address is labeled on the back of the printer via a barcode for ease
of pairing (Figure 5 on page 28). In order to exchange data, two Bluetooth enabled devices must establish
a connection. Bluetooth software is always running in the background, ready to respond to connection
requests. One device (known as the client) must request/initiate a connection with another. The second
device (the server) then accepts or rejects the connection. A Bluetooth enabled printer will normally act as
a peripheral creating a miniature network with the terminal sometimes referred to as a “piconet”. Discovery
identifies Bluetooth devices that are available for pairing whereby the central device broadcasts a
discovery request and devices respond. If a device is not discoverable, the central cannot pair unless in
knows the BDADDR or has previously paired with the device. If both devices support Bluetooth 2.1 or
higher they will use Security Level 4 Secure Simple Pairing (SSP), a mandatory security architecture that
features two (2) association models: Passkey Entry (default 0000) and Just Works (no user confirmation).
26

Bluetooth Security Modes
Security Mode 1 Security Mode 2 Security Mode 3
For Bluetooth Low Energy only. If a BT >/= 2.1 device is pairing
Simple Secure Pairing: a new security architecture introduced supported in BT >= 2.1. Service-level
enforced, similar to mode 2. Mandatory when both devices are BT >= 2.1. There are four association
models currently supported by mode 4. Security requirements for services must be classified as one of
the following: authenticated link key required, unauthenticated link key required, or no security required.
SSP improves security through the addition of ECDH public key cryptography for protection against
passive eavesdropping. For BT Classic only.
Using the Printer
Unsupported.
with a BT </= 2.0 device, it falls
back to BT 2.0 compatibility
mode and behaves the same as
BT 2.0. If both devices are BT
>/= 2.1, Secure Simple Pairing
must be used according to the
BT spec. For BT Classic only.
Security Mode 4: Simple Secure Pairing
Passkey Entry Just Works
Need to input PIN code when connecting to the
printer (default PIN is 0000). PIN can be updated
via bluetooth.bluetooth_pin SGD.
The SSP mode is usually negotiated automatically based on the capabilities of both the central and
peripheral. Lower security modes can be disabled via the
bluetooth.minimum_security_mode SGD sets the lowest security level at which the printer will establish a
Bluetooth connection. The printer will always connect at a higher security level if requested by the central
device. To change the security mode and security settings in the printers, use ZR1 Mobile Configuration
Tool.
Designed for situation where one (or both) of the
pairing devices has neither a display nor keyboard
for entering digits (e.g. Bluetooth headset). It
performs authentication step 1 in the same manner
as numeric comparison, but the user cannot verify
that both values match, so MITM
(man-in-the-middle) protection is not provided.
This is the only model in SSP that does not provide
authenticated link keys.
bluetooth.minimum_security_mode SGD. The
27

Using the Printer
Bluetooth Minimum Security Modes
Set Get Do BT Version of Central Device (>2.1)
bluetooth.minimum_security_mode=1 Just Works
bluetooth.minimum_security_mode=2 Passkey Entry
bluetooth.minimum_security_mode=3 Unsupported
bluetooth.minimum_security_mode=4 Secure Simple Pairing
bluetooth.bluetooth_PIN Passkey Entry (default 0000)
IMPORTANT: bluetooth.minimum_security_mode sets the lowest security level at which the printer will
establish a Bluetooth connection. The printer will always connect at a higher security level if requested by
the master device.
The printers also feature bonding for Bluetooth. The printer caches pairing info so devices stay paired
through power cycles and disconnects. This eliminates the need to repair on every connection
establishment.
The bluetooth.bonding SGD is always on but this SGD is not supported.
NOTE: For detailed information on Bluetooth, please refer to the Bluetooth Wireless User Guide at:
zebra.com/us/en/support-downloads.html
In addition, the printers support a “scan and pair” function via a handheld device and the MAC address
label on the bottom of the printer (see Figure 5). The printer also features passive NFC technology. Using
the “Print Touch” feature located on the top of the printer, end-users can automatically pair with a handheld
device that supports NFC technology. The NFC tag has the printer’s BDADDR encoded in a URL on the
tag. Simply touching the NFC handheld device to the “Print Touch” icon on the printer will connect and pair
the handheld device to the printer.
Figure 5 BT Communications
MAC Address Label
28
Setting Up the Software
Safe Printing Zone
1.59 mm
1.59 mm
(0.06 in.)
1.25 mm
(0.05 in)
1.25 mm
(0.05 in.)
“H”
Max Label Height = “H” = 2.5 mm
Bottom edge of
die-cut label
Top edge of
die-cut label
CPCL Label
Height
Media Feed Direction
Safe Printing Zone
Media Feed Direction
)
The printer uses Zebra’s CPCL Programming language which were designed for mobile printing
applications. CPCL is fully described in the CPCL Programming Guide available on-line at
zebra.com/us/en/support-downloads.html
based label creation program which uses a graphical interface to create and edit labels in either language.
Designing Labels
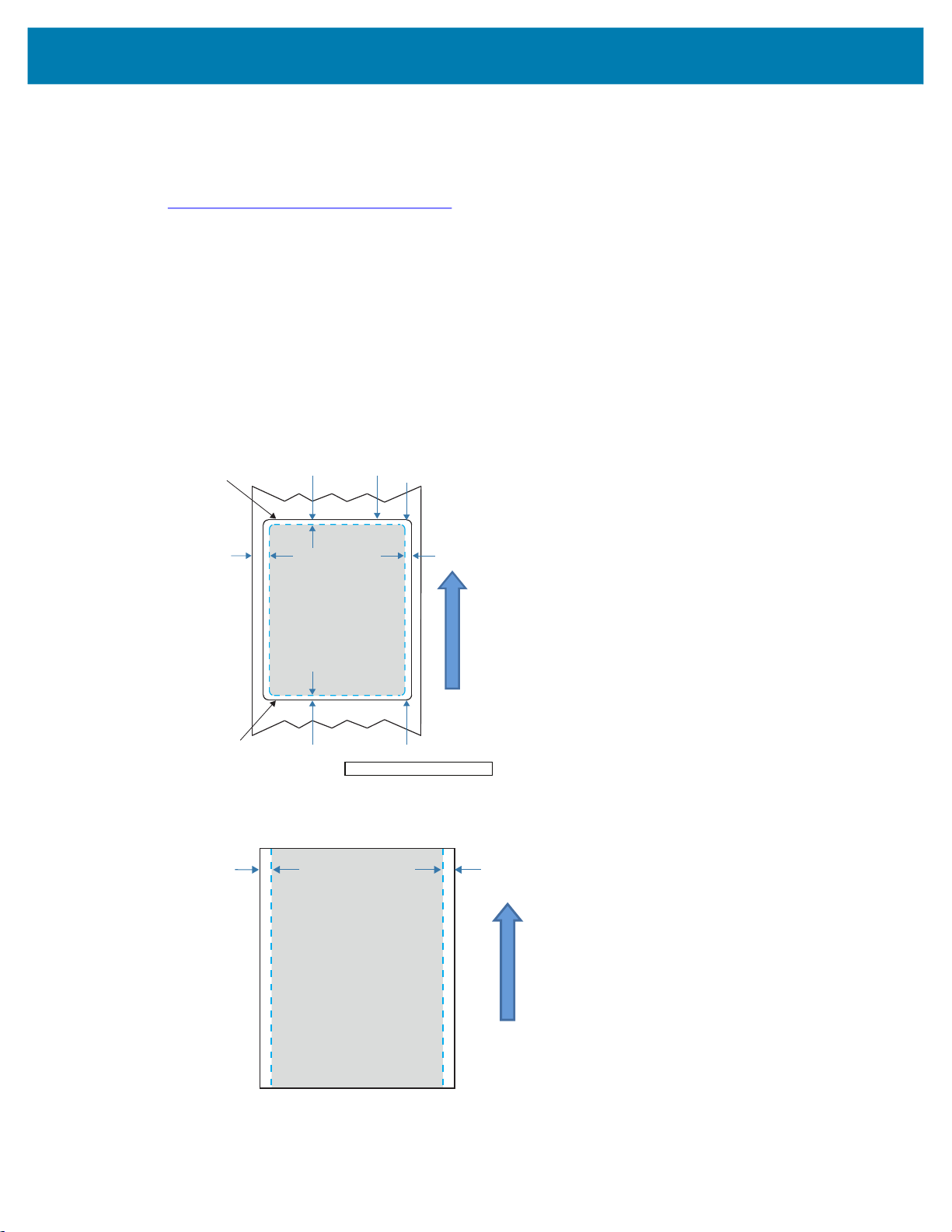
The following examples provide guidelines for designing labels for the printers, specifically for Gap Media,
Black Bar Media and Journal Media. The illustrations for each media type define recommended
tolerances, keep-out zones and safe printing zones designed to avoid any vertical registration issues
during printing. Dimensions are determined based on product registration capabilities and
Zebra-recommended media tolerances.
Figure 6 Gap Media
Using the Printer
. You can also use ZebraDesigner Pro v2, Zebra’s Windows
Figure 7 Journal Media
1.59 mm
(0.06 in.)
1.59 mm
(0.06 in.
29

Figure 8 Black Bar Label Media
Safe Printing Zone
1.59 mm1.59 mm
(0.06 in.)
(0.05 in.)
1.25 mm
(0.06 in.)
“H”
Max Label Height = “H” = 2.5 mm
CPCL Label
Height
Media Feed Direction
Safe Printing Zone
Black Bar
Black Bar
Using the Printer
Using Pre-Printed Receipt Media
The printer supports alignment of pre-printed receipts by using the out of paper sensor located near the
printhead.
Black Mark Dimensions (Receipt Media)
The reflective media black marks (or black bar/marks) should extend past the centerline of the roll on the
front side of the paper.
• Minimum mark width: 15 mm (0.59 in.) perpendicular to the edge of the media, and centered within the
width of the roll.
• Mark length: 4.8 - 6.0 mm (0.19 - 0.24 in.) parallel to the edge of the media.
30

Label Areas
Keep
dark color
pre-printed
graphics,
barcodes,
and text
out of the
path
of the
bar sensor.
15 mm
(0.59 in.)
The media/black bar sensor detects the dark, pre-printed bar on the media, so a path in the center of the
paper must be kept free of dark, pre-printed graphics.
NOTE: Dark, pre-printed graphics refer to any symbols, barcodes, text and/or colored areas that have
been applied to the receipt paper rolls before they have ever been used in the printer.
Figure 9 Label Areas
Using the Printer
31

Label Design Examples
ACME COLLEGE
PARKING
VIOLATION
PARKING
VIOLATION
ACME COLLEGE
ACME RECEIPT
Quality FIRST
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
ACME RECEIPT
Quality FIRST
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
This section shows examples of labels with and without problems.
Figure 10 Label Design Examples
Problem Label Designs Good Label Designs
Using the Printer
The dark colors, pre-printed text, and
graphics are in the path of the black bar
at the bottom of the receipt.
The center path to the black bar is free of
dark colors, pre-printed text,
and graphics.
NOTE: Complete information on using pre-printed receipt paper can be found in the FORM command in
the CPCL Programming Guide at zebra.com/manuals.
32

Keep-Out Areas
15 mm
(0.59 in.)
*
*
*
*
At times, incomplete printing of text and/or graphics appear because minimum margins are not provided
during label design. The recommended minimum margins, or “keep out areas” are shown in Figure 11.
Figure 11 Keep Out Areas
Using the Printer
*
NOTE: The length of each “continuous” receipt is determined by the data sent to the printer.
*
33

Using the Printer
http://www.zebra.com/nfc
Using Near Field Communication (NFC)
Near Field Communication (NFC) allows wireless communication and data exchange between digital
devices such as this printer and a smartphone by using electromagnetic radio fields, while technologies
such as Bluetooth use radio transmissions instead.
NFC is a sub-class of Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) technology that is designed for use by
devices within close proximity to each other. NFC technology allows devices to establish communication
by touching or bringing them into close proximity, usually no more than 7.62 cm (3 in.).
The printer contains a passive NFC device which contains information that other devices can read but
does not read any information itself.
An active device, such as a smartphone, can read the information on the printer’s NFC tag, but the tag
itself does nothing except transmit the info to authorized devices.
Active devices can read information and send data. An active NFC device, such as a smartphone, would
not only be able to collect information from NFC tags, but it would also be able to exchange information
with other compatible phones or devices. An active device could even alter the information on the NFC tag
if authorized to make such changes. To ensure security, NFC often establishes a secure channel and uses
encryption when sending sensitive information.
Figure 12 NFC Pairing
NFC Use Cases
Passive
• Bluetooth Pairing – used to cause a tablet, smart phone or terminal to automatically pair with the printer
via a Bluetooth connection, within the bounds of the security profile being used. This shall contain the
BT address and serial number of the printer.
• App launching – used to cause an app, developed either by Zebra or a third party, to be executed on a
smartphone, tablet or terminal.
34

Using the Printer
• Web site launching – used to cause a smart phone, tablet or terminal to display a web site developed by
Zebra or a third party developer.
Tapping the Zebra Print Touch icon with an NFC-enabled smartphone will provide instant access to
printer-specific information. For more information about NFC and Zebra produncts, go to zebra.com/nfc
Bluetooth pairing applications via NFC is also possible. Please see Zebra Multi-platform SDK for more
information.
.
35

Wearing the Printer
Swivel Belt Clip
The printer has a plastic swivel belt clip included as an accessory.
1. Remove the battery pack and insert the ball on the back of the belt clip in the socket on the bottom of
the printer.
Using the Printer
Belt Clip
2. Swivel the belt clip horizontally to clear the opening to the battery compartment.
3. Reinstall the battery pack and swivel the belt clip vertically.
36

Shoulder Strap
A shoulder strap accessory is also offered to provide another option for comfortably carrying the ZR138
printer. The shoulder strap attaches to the two strap posts on the front of the printer via rugged swivel snap
hooks. The strap is easily adjustable up to 142.2 cm (56 in.) from end to end.
1. Clip each shoulder strap snap hook to its corresponding strap post on the front of the printer.
Using the Printer
Swivel Snap Hook
2. Hang the shoulder strap over one shoulder so the printer hangs securely in a vertical position.
37

Soft Case
The printers have an environmental Soft Case option that helps protect the printer, while also allowing the
user to carry it from their belt. The paper path is left open to maintain printing capability and the controls
are visible and accessible while in the case. D-Ring connectors allow for attachment to the shoulder strap
option.
1. Lift the top flap of the soft case which is secured with Velcro.
2. Insert the printer in the case with the bottom of the printer facing forward as shown.
Using the Printer
3. Turn the case around to access the LCD display and user controls which are visible through the plastic
window. Lift the bottom half of the window to access the paper path.
Window to Access Paper Path
38

Preventive Maintenance
Extending Battery Life
• Never expose the battery to direct sunlight or temperatures over 40°C (104°F) when charging.
• Always use a Zebra charger designed specifically for Lithium-Ion batteries. Any other kind of charger
may damage the battery.
• Use the correct media for your printing requirements. An authorized Zebra re-seller can help you
determine the optimum media for your application.
• Consider using a pre-printed label if you print the same text or graphic on every label.
• Choose the correct print darkness, and print speed for your media.
• Use software handshaking (XON/XOFF) whenever possible.
• Remove the battery if the printer won’t be used for a day or more and you’re not performing a
maintenance charge.
• Consider purchasing an extra battery.
• Remember that any rechargeable battery will lose its ability to maintain a charge over time. It can only
be recharged a finite number of times before it must be replaced. Always dispose of batteries properly.
See Battery and Product Disposal on page 54 for more information on battery disposal.
Using the Printer
General Cleaning Instructions
CAUTION: Avoid possible personal injury or damage to the printer. Never insert any pointed or sharp
objects into the printer. Always turn off the printer before performing any cleaning procedures. Use care
when working near the tear bars as the edges are very sharp.
CAUTION—HOT SURFACE: The printhead can get very hot after prolonged printing. Allow it to cool off
before attempting any cleaning procedures.
IMPORTANT: Only use a Zebra cleaning pen (not supplied with the printer) or a cotton swab with 90%
medical grade alcohol for cleaning the printhead.
CAUTION: Use only cleaning agents specified in the following tables. Zebra Technologies Corporation will
not be responsible for damage caused by any other cleaning materials used on this printer.
39

Cleaning
Using the Printer
Area Method Interval
Printhead Use a Zebra cleaning pen
(p/n 105950-035), a Zebra preventative
maintenance kit (p/n 47362), or a clean
swab dipped in 99.7% isopropyl alcohol.
After every five rolls of media (or more
often, if needed). When using
linerless type media, cleaning is
required after every roll of media.
Platen Surface Rotate the platen roller and clean it
thoroughly with a fiber-free swab, or lint
free, clean, damp cloth lightly moistened
with 99.7% isopropyl alcohol (Figure 13).
Tear Bar Clean thoroughly with 99.7% isopropyl
alcohol and a cotton swab (Figure 13).
Printer Exterior Water-dampened cloth or 99.7%
isopropyl alcohol wipe.
Printer Interior Gently brush out printer. Ensure the
sensor windows are free of dust (Figure
13).
Figure 13 Cleaning Areas
After every five rolls of media (or more
often, if needed).
As needed.
As needed.
As needed.
Platen
40
Printer Interior
Printhead
Tear Bar

Troubleshooting
LCD Control Panel Indicators
The printer’s display shows several icons which indicate the status of various printer functions. Check the
indicator status, then refer to the corresponding troubleshooting topic to resolve the problem.
Troubleshooting Topics
No power
• Check that battery is installed properly.
• Recharge or replace battery as necessary.
CAUTION: Always dispose of batteries properly. Refer to Battery and Product Disposal on page 54
for more information on proper battery disposal.
Media does not feed
• Be sure media cover is closed and latched.
• Check the media compartment for any binding.
• Ensure label sensor is not blocked.
Poor or faded print
• Clean print head.
• Check quality of media.
Partial or missing print
• Check media alignment.
• Clean print head.
• Ensure media cover is properly closed and latched.
41

Garbled print
• Replace battery.
• Check cable to terminal.
• Establish RF Link and/or restore LAN associativity.
No print
• Replace battery.
• Check cable to terminal.
• Establish RF Link and/or restore LAN associativity.
• Invalid label format or command structure. Place printer in Communications Diagnostic (Hex Dump)
Mode to diagnose problem.
Reduced battery charge life
• If battery is older than one year, short charge life may be due to normal aging.
Troubleshooting
• Check battery health.
• Replace battery.
Data icon flashing
• Flashing Data icon is normal while data is being received.
Media Out or Head Open icons flashing
• Check that media is loaded and that the media cover is closed and securely latched.
Communication error
• Replace cable to terminal.
• Check baud rate.
Label binding
• Open head release latch and media cover.
• Remove and reinstall media.
Skip Labels
• Check media for top of form sensor mark or label gap.
• Check that the maximum print field has not been exceeded on label.
• Ensure bar or gap sensor is not blocked or malfunctioning.
42

Blank LCD screen
• Make sure printer is turned on.
• No application loaded or application corrupted: reload program.
No NFC Connectivity
• Ensure smartphone is positioned 7.62 cm (3 in.) or closer to the Print Touch icon on the top of the
printer.
Troubleshooting Tests
Printing a Configuration Label
To print out a listing of the printer’s current configuration follow these steps:
1. Turn the printer off. Load the media compartment with journal media (media with no black bars printed
on the back).
2. Press and hold Media Feed.
Troubleshooting
3. Press and release Power and keep Media Feed pressed. When printing starts, release Media Feed.
Refer to Figure 14 on page 45 for sample configuration printouts.
Communications Diagnostics
If there is a problem transferring data between the computer and the printer, try putting the printer in the
Communications Diagnostics Mode (also referred to as the “DUMP” mode). The printer will print the ASCII
characters and their text representation (or the period ‘.’, if not a printable character) for any data received
from the host computer.
To enter Communications Diagnostics Mode:
1. Print a configuration label.
2. At the end of the diagnostics report, the printer will print: “Press Media Feed to enter DUMP mode”.
3. Press Media Feed. The printer will print: “Entering DUMP mode”.
NOTE: If Media Feed is not pressed within three seconds, the printer will print “DUMP mode not entered”
and will resume normal operation.
At this point, the printer is in DUMP mode and will print the ASCII hex codes of any data sent to it, and their
text representation (or “.” if not a printable character).
Additionally, a file with a “.dmp” extension containing the ASCII information is created and stored in the
printer’s memory. It can be viewed, “cloned” or deleted using the Net Bridge application. (Refer to the
ZebraNet Bridge Enterprise documentation for more information.)
To terminate the Communications Diagnostics Mode and return the printer to normal operations:
1. Turn the printer OFF.
2. Wait five seconds.
3. Turn the printer ON.
43

Contacting Technical Support
If the printer fails to print the configuration label, or if you encounter problems not covered in the
Troubleshooting section, contact Zebra Technical Support.
You will need to supply the following information:
• Model number (for example, ZR138)
• Unit serial number (Found on the large label on the back of the printer, also found in the configuration
label printout.) See Figure 16 on page 52.
• Product Configuration Code (PCC) (15 digit number found on the label on the back of the unit) See
Figure 16.
Troubleshooting
44

Troubleshooting
Figure 14 ZR138 Configuration Label
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
1 Printhead Test
2 Identifies Printer as a ZR138
3 Printer Serial Number
4 Firmware Version
5 Bluetooth Radio Address
6 Flash and RAM memory installed
7 Resident Human Readable Fonts Installed
8 Files loaded in printer memory (includes pre-scaled or scalable fonts)
45

Specifications
NOTE: Printer specifications are subject to change without notice.
Printing Specifications
Parameter ZR138
Print Width Up to 72 mm (2.83 in.)
Print Speed 45.72 to 50.8 mm (1.8 to 2 in.)/second @ 13% max density
Printhead Burn Line to Tear
Edge Distance
Printhead Life 4064 m (160,000 in.) of paper feed MTBF of output at 13% density at
Print Density 203 dots/in. or better
Front Side: 5.4 mm (0.21 in.) +/- 0.5 mm (0.02 in.)
Reverse tear not available.
23°C
+/- 5 when using virgin media.
Memory and Communications Specifications
Parameter ZR138
Flash Memory 16 MB
RAM Memory 8 MB
Standard Communications USB 2.0
Wireless Communication
Options
a. Memory configuration on your printer may be found by referring to Printing a Configuration Label
on page 43.
a
a
Bluetooth 5.0
46

Label Specifications
Parameter ZR138
Media Width Standard: 80 mm +/- 0.75 mm (3.15 in. +/- 0.02 in.)
Media Length 12.7 mm minimum to 203.2 mm maximum (0.5 to 8 in.)
Black Bar Sensor to Printhead
Burnline Distance
Media Thickness
Max Label Roll Outer
Diameter
Inner Core Diameters 12.7 mm (0.5 in.) standard
Black Mark Location The reflective media black marks should be centered on media roll
Black Mark Dimensions Minimum mark width: 12.7 mm (0.5 in.)
Specifications
*Optional: 76.2 mm +/- 0.65 mm (3 in. +/- 0.025 in.)
*Optional: 58 mm +/- 0.65 mm (2.28 in. +/- 0.025 in.)
*Optional: 50.8 mm +/- 0.65 mm (2 in. +/- 0.025 in.)
16.57 mm (0.65 in.) +/- 1.0/-0.6 mm (0.03/-0.02 in.)
0.058 to 0.1575 mm (2.28 to 6.2 mils)
50 mm (1.97 in.)
Mark length: 2.4 to 11 mm (0.09 to 0.43 in.)
* Optional media requires use of media spacers.
47

Specifications
CPCL Font and Bar Code Specifications and Commands
Item Available Options
Standard Fonts FONTA.CPF - ESC/POS default font, 12x24 bitmap;
FONTB.CPF - ESC/POS default font, 9x17 bitmap;
FONTC.CPF - ESC/POS default font, 9x24 bitmap;
GBUNSG16.CPF - SimSun, Simplified Chinese 16x16 bitmap;
GBUNSG24.CPF - SimSun, Simplified Chinese 24x24 bitmap.
Available Optional Fonts SWIS721.CSF - CPCL scalable font;
DEJAVU12.CPF - Pre-Scaled font;
DEJAVU14.CPF - Pre-Scaled font;
DEJAVU16.CPF - Pre-Scaled font;
DEJAVU20.CPF - Pre-Scaled font;
MUTOS16.CPF - Utah, Vietnamese, 16x16 bitmap;
CTUNMK24.CPF - M Kai, Traditional Chinese, 24x24 bitmap;
NSMTTC16.CPF - New Sans MT, Traditional Chinese, 16x16 bitmap.
Linear Bar Codes Codabar (CODABAR, CODABAR 16); UCC/EAN 128 (UCCEAN128)
Code 39 (39, 39C, F39, F39C); Code 93 (93); Code 128 (128);
EAN 8, 13, 2 and 5 digit extensions (EAN8, EAN82, EAN85, EAN13,
EAN132, and EAN135); EAN-8 Composite (EAN8)
EAN-13 Composite (EAN13); Plessey (PLESSEY); lnterleaved 2 of 5
(I2OF5); MSI (MSI, MSI10, MSI1110); FIM/POSTNET (FIM); TLC39
(TLC39); UCC Composite A/B/C (128(Auto)); UPCA, 2 and 5 digit
extensions (UPCA2 and UPCA5); UPCA Composite (UPCA)
UPCE, 2 and 5 digit extensions (UPCE2 and UPCE5);
UPCE Composite (UPCE)
2-D Bar Codes Aztec (AZTEC)
MaxiCode (MAXICODE)
PDF 417 (PDF-417)
QR Code (QR)
RSS-14 (RSS-Subtype 1)
RSS-14 Truncated (RSS-Subtype 2)
RSS-14 Stacked (RSS-Subtype 3)
RSS-14 Stacked Omnidirectional (RSS-Subtype 4)
RSS Limited (RSS-Subtype 5)
RSS Expanded (RSS-Subtype 6)
Rotation Angles 0°, 90°, 180°, and 270°
48

Specifications
Physical, Environmental and Electrical Specifications
Parameter ZR138
Weight w/ battery Less than 390 g (0.85 lb.)
Temperature Operating: -5°C to 50 °C (23°F to 122°F)
Storage: -20°C to 60°C (-4°F to 140°F)
Charging: 0°C to 40°C (32°F to 104°F)
Relative Humidity Operating/Storage: 10% to 90% non-condensing
Battery 2-cell Lithium-Ion Battery; 7.2VDC (nominal); 2500 mAh (rated capacity);
2600 mAh (nominal capacity).
Intrusion Protection (IP)
Rating
IP54 (without soft case)
49

ZR138 Dimensions
系列
ZR138
Figure 15 Printer Dimensions
Specifications
Height
Height - 58.8mm (2.31 in.)
Width - 114.5 mm (4.5 in.)
Length - 129.5 mm (5.09 in.)
Width
Length
50

Accessories
For a complete list of printer accessories, go to zebra.com/manuals, search for the Mobile Printer
Accessories guide, and go to the ZR138 product page in the guide. Or scan the following QR code with a
mobile device to access the guide.
Figure 16 Accessories Guide
Specifications
51

Miscellaneous
Serial Number and PCC Number Locations
Figure 16 ZR138 (Bottom View)
1
2
1 Serial # Barcode
2 PCC Barcode
IMPORTANT: Due to compliance and customs restraints, an integrator may not be able to ship a printer
purchased in one country to another country based on the limitations imposed by regional SKUs. The
country code identified in the printer SKU determines the area of the world in which the printer can be
used.
52

USB Cable
Figure 17 USB A-to-C Cable
Miscellaneous
4
1
A1, B1,A12, B12
A4, B4, A9, B9
B1
B12
A6
A7
A12
A1
Type-C Plug Wire Type-A Plug
Pin # Signal Name Wire # Signal Name Pin # Signal Name
A1,B1,A12,B12
A4,B4,A9,B9
GND 1 GND_PWrt1 4 GND
VBUS 2 PWR_VBUS1 1 VBUS
A5
B5
A6
A7
CC
VCONN
Dp1 3 UTP_Dp 3 D+
Dn1 4 UTP_Dn 2 D-
Shield Braid Shield Shell Shield
See Note 1
Notes:
1. Pin A5 (CC) of the USB Type-C plug shall be connected to VBUS through resistor Rp (56 k Ω +/- 5%).
2. Contacts B6 and B7 should not be present in the USB Type-C plug.
3. All VBUS pins shall be connected together within the USB Type-C plug. Bypass capacitors are not
required for the VBUS pins in this cable.
4. All ground return pins shall be connected together within the USB Tupe-C plug.
5. Shield and GND grounds shall be connected within the USB Type-C and USB 2.0 Standard-A plugs on
both ends of the cable assembly.
6. All USB Type-C plug pins that are not listed in this table shall be open (not connected).
53

Media Supplies
To ensure maximum printer life and consistent print quality and performance for your individual application,
it is recommended that only media produced by Zebra be used.
Advantages include:
• Consistent quality and reliability of media products.
• Large range of stocked and standard formats.
• In-house custom format design service.
• Large production capacity which services the needs of many large and small media consumers
including major retail chains world wide.
• Media products that meet or exceed industry standards.
Miscellaneous
NOTE: For more information go the Zebra website (www.zebra.com
Maintenance Supplies
In addition to using quality media provided by Zebra, it is recommended that the printer be cleaned as
prescribed in the maintenance section. The following item is available for this purpose:
• Cleaning Pen (12 pack): p/n 105950-035
Battery and Product Disposal
The majority of this printer’s components are recyclable. Do not dispose of any printer components in
unsorted municipal waste. Please dispose of the battery according to your local regulations, and recycle
the other printer components according to your local standards.
For more information, please see our web site at: zebra.com/environment.
IMPORTANT: When the battery is depleted, insulate the terminals with tape before disposal.
) and select the Products tab.
54

Alert Messages
The printer displays the following alert messages on the Information Screen to inform the user of various
performance conditions that might occur.
Download Firmware User Activity Download FW
Download Failed User Activity Download Failed
Head Over Temp User Activity Head Overtemp
Head Under Temp User Activity Head Undertemp
Battery Too Low User Activity Battery Too Low
Media Out User Activity Media Out
Head Open User Activity Head Open
Charge Error User Activity Charge Error
Battery Missing User Activity No Printing
Battery Low User Activity Battery Low
Miscellaneous
Message Type English Phrase
Printer Ready Timed - 30 seconds Printer Ready
55

www.zebra.com
 Loading...
Loading...