
ZQ511/ZQ521
Mobile Printers
User Guide
P1106523-04EN

ZEBRA and the stylized Zebra head are trademarks of Zebra Technologies Corporation, registered in
many jurisdictions worldwide. All other trademarks are the property of their respective owners.
© 2021 Zebra Technologies Corporation and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved.
Information in this document is subject to change without notice. The software described in this document
is furnished under a license agreement or nondisclosure agreement. The software may be used or copied
only in accordance with the terms of those agreements.
For further information regarding legal and proprietary statements, please go to:
SOFTWARE:www.zebra.com/linkoslegal
COPYRIGHTS:www.zebra.com/copyright
WARRANTY:www.zebra.com/warranty
END USER LICENSE AGREEMENT: www.zebra.com/eula
Terms of Use
Proprietary Statement
This manual contains proprietary information of Zebra Technologies Corporation and its subsidiaries
(“Zebra Technologies”). It is intended solely for the information and use of parties operating and
maintaining the equipment described herein. Such proprietary information may not be used, reproduced,
or disclosed to any other parties for any other purpose without the express, written permission of Zebra
Technologies.
Product Improvements
Continuous improvement of products is a policy of Zebra Technologies. All specifications and designs are
subject to change without notice.
Liability Disclaimer
Zebra Technologies takes steps to ensure that its published Engineering specifications and manuals are
correct; however, errors do occur. Zebra Technologies reserves the right to correct any such errors and
disclaims liability resulting therefrom.
Limitation of Liability
In no event shall Zebra Technologies or anyone else involved in the creation, production, or delivery of the
accompanying product (including hardware and software) be liable for any damages whatsoever
(including, without limitation, consequential damages including loss of business profits, business
interruption, or loss of business information) arising out of the use of, the results of use of, or inability to
use such product, even if Zebra Technologies has been advised of the possibility of such damages. Some
jurisdictions do not allow the exclusion or limitation of incidental or consequential damages, so the above
limitation or exclusion may not apply to you.
“Made for iPod”, “Made for iPhone”, and “Made for iPad” mean that an electronic accessory has been
designed to connect specifically to iPod, iPhone, or iPad, respectively, and has been certified by the
developer to meet Apple performance standards. Apple is not responsible for the operation of this device
or its compliance with safety and regulatory standards. Please note that the use of this accessory with
iPod, iPhone, or iPad may affect wireless performance.
Bluetooth® is a registered trademark of the Bluetooth SIG.
© 1996–2009, QNX Software Systems GmbH & Co. KG. All rights reserved. Published under license by
QNX Software Systems Co.
2

Certified by:
54
IP
65
IP
MIL - STD
810
Publication Date
July 8, 2021
3

Contents
About This Document ........................................................................................................................ 8
Introduction ...................................................................................................................... 8
Configurations.................................................................................................................. 8
Related Documents and Software ................................................................................... 8
Service Information .......................................................................................................... 8
Feedback ......................................................................................................................... 9
Printer Overview ............................................................................................................................... 10
Unpacking and Inspection............................................................................................. 11
Reporting Damage......................................................................................................... 11
Technology.................................................................................................................... 12
PowerPrecision+ (PP+) Battery.............................................................................. 12
Printing Technology ....................................................................................................... 12
Product Information QR Code........................................................................................ 13
Made for iPhone (MFi) ................................................................................................... 13
Near Field Communication (NFC).................................................................................. 13
Thermal Shutdown ................................................................................................. 13
Radio-Frequency Identification (RFID)........................................................................... 14
Printer Features ............................................................................................................. 15
Using the Printer............................................................................................................................... 17
Preparing the Battery for Use......................................................................................... 17
Installing/Removing Battery & Battery Tape Insulator ............................................ 17
Removing the Battery....................................................................................... 17
Removing the Battery Tape Insulator............................................................... 18
Battery Safety ......................................................................................................... 19
Charging the Battery............................................................................................... 21
AC Power Adapter ........................................................................................... 21
Vehicle Cradle ........................................................................................................ 22
Battery Eliminator/Battery Eliminator Vehicle Cradle ............................................. 22
4

Contents
4-Bay Power Station............................................................................................... 22
1-Slot Battery Charger (with US Type-A Line Cord)............................................... 23
Use Case: Home Office/Small Business.......................................................... 23
3-Slot Battery Charger/Dual 3-Slot Battery Charger (w/ US Type-A Line Cord) .... 25
Use Case: Settlement Room............................................................................ 25
Vehicle Adapter ...................................................................................................... 25
Use Case: Vehicle............................................................................................ 25
Loading Media ........................................................................................................ 26
Operator Controls........................................................................................................... 28
Printer Status Icons....................................................................................................... 29
Buttons.......................................................................................................................... 30
Power Up Sequences............................................................................................. 30
Run Time Sequences without LED Flashes ........................................................... 30
LEDs....................................................................................................................... 30
Alerts ...................................................................................................................... 31
Power Saving Features.................................................................................................. 31
Sleep Mode ............................................................................................................ 31
Adaptive Print Performance.................................................................................... 32
Draft Mode.............................................................................................................. 32
Verify That the Printer is Working .................................................................................. 32
Printing a Configuration Report .............................................................................. 32
Connecting the Printer ................................................................................................... 33
Cable Communication ............................................................................................ 33
Zebra Setup Utilities....................................................................................................... 34
Zebra Android Printer Setup Utility (for Link-OS Printers) ...................................... 35
Wireless Communications with Bluetooth..................................................................... 36
Bluetooth Networking Overview ............................................................................. 36
Bluetooth (BT) Security Modes ...................................................................................... 37
Bluetooth Minimum Security Modes ....................................................................... 38
WLAN Overview............................................................................................................. 39
Setting Up the Software ................................................................................................. 39
Designing Labels............................................................................................................ 40
Using Pre-Printed Receipt Media ........................................................................... 41
Black Mark Dimensions (Receipt Media)................................................................ 41
Label Areas ............................................................................................................ 41
Label Design Examples.......................................................................................... 42
Keep-Out Areas...................................................................................................... 43
Near Field Communication (NFC).................................................................................. 43
NFC Use Cases...................................................................................................... 44
Passive............................................................................................................. 44
Wearing the Printer ....................................................................................................... 45
Swivel Belt Clip....................................................................................................... 45
5

Contents
Shoulder Strap........................................................................................................ 46
Soft Case................................................................................................................ 46
Exoskeleton ............................................................................................................ 47
Preventive Maintenance................................................................................................ 48
Extending Battery Life ............................................................................................ 48
General Cleaning Instructions ................................................................................ 48
................................................................................................................................ 49
Troubleshooting ............................................................................................................................... 51
Front Control Panel........................................................................................................ 51
Printer Status Indicators................................................................................................. 51
Troubleshooting Topics................................................................................................. 52
No power ................................................................................................................ 52
Media does not feed ............................................................................................... 53
Poor or faded print.................................................................................................. 53
Partial or missing print ............................................................................................ 53
Garbled print........................................................................................................... 53
No print ................................................................................................................... 53
Reduced battery charge life.................................................................................... 53
flashing ................................................................................................................... 53
or flashing ............................................................................................................... 53
Communication error .............................................................................................. 54
Label binding .......................................................................................................... 54
Blank LCD screen................................................................................................... 54
No NFC Connectivity .............................................................................................. 54
Troubleshooting Tests.................................................................................................... 54
Printing a Configuration Report .............................................................................. 54
Communications Diagnostics ................................................................................. 55
Contacting Technical Support........................................................................................ 56
Specifications ................................................................................................................................... 57
Printing Specifications.................................................................................................... 57
Memory and Communications Specifications ................................................................ 57
Label Specifications ....................................................................................................... 58
CPCL Font and Bar Code Specifications and Commands............................................. 59
ZPL Font and Bar Code Specifications and Commands................................................ 60
Communication Port....................................................................................................... 61
USB ........................................................................................................................ 61
Physical, Environmental and Electrical Specifications................................................... 61
Accessories................................................................................................................... 64
6

Contents
Miscellaneous ................................................................................................................................... 65
Serial Number and PCC Number Locations .................................................................. 65
Cables............................................................................................................................ 66
USB Cables ............................................................................................................ 66
Media Supplies.............................................................................................................. 68
Maintenance Supplies.................................................................................................... 68
Battery Disposal............................................................................................................ 69
Product Disposal............................................................................................................ 69
Alert Messages ............................................................................................................. 70
7

About This Document
Introduction
This guide provides information about using the ZQ511 and ZQ521 mobile printers and accessories.
Configurations
This guide covers the following configurations:
Configuration
ZQ511 LINK-OS 802.11ac/BT 4.1 Dual Color LCD 512 MB
ZQ521 LINK-OS 802.11ac/BT 4.1 Dual Color LCD 512 MB
Operating
System
Related Documents and Software
The following documents provide more information about the ZQ500 Series mobile printers.
• ZQ511/ZQ521 Quick Start Guide
For the latest version of this guide and all guides, go to www.zebra.com/support
Service Information
If you have a problem with your equipment, contact Zebra Global Customer Support for your region.
Contact information is available at www.zebra.com/support
When contacting support, please have the following information available:
• Serial number of the unit
• Model number or product name
• Software/firmware type or version number
Radios Display Memory
.
.
Zebra responds to calls by email, telephone or fax within the time limits set forth in support agreements.
8

About This Document
If your problem cannot be solved by Zebra Customer Support, you may need to return your equipment for
servicing and will be given specific directions. Zebra is not responsible for any damages incurred during
shipment if the approved shipping container is not used. Shipping the units improperly can possibly void
the warranty.
If you purchased your Zebra business product from a Zebra business partner, contact that business
partner for support.
9

Printer Overview
This user guide provides the information to operate the Zebra ZQ511 and ZQ521 printers. The printers use
some of the latest technologies such as an 802.11ac/Bluetooth 4.1 dual radio, a smart battery with
PowerPrecision+ functionality, Near Field Communication (NFC), a color LCD display and Made for
iPhone
as an iPhone or iPad to authenticate and connect over Bluetooth.
These printers use CPCL and ZPL programming languages to configure the printers and print properties,
label design, and communications. See the Zebra Programming Guide at
www.zebra.com/manuals
Software Resources and Utilities:
• ZebraNet Bridge Enterprise
• Zebra Setup Utility: single printer configuration, quick setup
®
(MFi). MFi printers provide Apple co-processor (MFi) support which allows an Apple device such
for more information.
TM
: printer configuration, fleet management
• Zebra Mobile Setup Utility: Android-based setup tool
• ZebraDesigner Pro v2: label design
• Zebra Designer Drivers: Windows
• OPOS Driver: Windows driver
• Multiplatform SDK
• Zebra Downloader
• Printer Profile Manager Enterprise (PPME). Theseutilities can be found on the Zebra website at
www.zebra.com/us/en/support-downloads
®
driver
.
10

Unpacking and Inspection
In case shipping is required, save the carton and all packing material.
1. Open box and make sure it includes the following materials: Printer, Quick Start Guide, Regulatory
Guide, Safety Guide, battery, and belt clip.
Printer Overview
2. Check all exterior surfaces of the product components for damage.
3. Open the media cover (refer to Loading Media on page 26) and inspect the media compartment for
damage.
Reporting Damage
If you discover shipping damage:
• Immediately notify and file a damage report with the shipping company. Zebra Technologies
Corporation is not responsible for any damage incurred during shipment of the printer and will not cover
the repair of this damage under its warranty policy.
• Keep the carton and all packing material for inspection.
• Notify your authorized Zebra reseller.
11
Technology
The printers use several technologies made popular in other mobile printer product lines, as well as newer,
state-of-the-art technologies.
PowerPrecision+ (PP+) Battery
The printers use a 2-cell Li-ion battery pack with integrated intelligence and data storage capability
meeting PowerPrecision+ (PP+) functionality. This intelligent battery has the integrated technology
required to collect the detailed real-time battery metrics needed to maximize useful battery life and ensure
every battery is healthy and able to hold a full charge. In addition, technology inside the batteries tracks
and maintains the metrics required to provide real-time visibility into more meaningful battery statistics,
such as total cycle usage of the battery, whether the battery is old and should be retired or how long a
battery will take to fully charge.
Operating Temperature Charging Temperature Storage Temperature
-20°C to +50°C
(-4°F to 122°F)
IMPORTANT: The printers only function properly with genuine Zebra PP+ battery packs.
The printers also use an extended 4-cell smart battery with higher capacity and stronger security.
Printer Overview
0°C to +40°C
(32°F to 104°F)
-25°C to +60°C
(-13°F to 140°F)
To achieve the best fast charging results, charge batteries at room temperature with the device powered
off. Ideal charging conditions are within temperatures from 5°C to 40°C (41°F to 104°F). The device always
performs battery charging in a safe and intelligent manner. At higher temperatures, the device may for
small periods of time alternately enable and disable battery charging to keep the battery at acceptable
temperatures. Under abnormal temperatures the device will indicate when charging is unable to be
initiated via its LED and a notification that appears on the display.
The smart battery’s health has three states: Good, Replace, and Poor. The battery health factor
determines whether or not the printer can operate and what is communicated to the user via the display.
# of Charge Cycles Health Power-up Message
<300 GOOD None
≥ 300 but <550 REPLACE Battery Diminished Consider Replacing
≥ 550 but <600 REPLACE Warning-Battery Is Past Useful Life
≥ 600 POOR Replace Battery Shutting Down
a. Warning accompanied by one long beep.
b. Warning will flash on and off accompanied by beeping at a rate of once per second. After 30
seconds, the printer will shut down.
NOTE: Power down the printer before removing the battery to minimize the risk of corruption.
a
b
12

Printing Technology
The printers use the Direct Thermal method to print human readable text, graphics, and barcodes. It
incorporates a sophisticated print engine for optimal printing under all operational conditions. Direct
thermal printing uses heat to cause a chemical reaction on specially treated media. This reaction creates a
dark mark wherever a heated element on the printhead comes in contact with the media. Since the printing
elements are arranged very densely at 203 d.p.i. (dots per inch) horizontal and 200 d.p.i. vertical, highly
legible characters and graphic elements may be created a row at a time as the media is advanced past the
printhead. This technology has the advantage of simplicity, as there is no requirement for consumable
supplies such as ink or toner. However, since the media is sensitive to heat, it will gradually lose legibility
over long periods of time, especially if exposed to environments with relatively high temperatures or in
direct sunlight.
Product Information QR Code
The QR barcode includes human readable text URL, for example www.zebra.com/ZQ511-info, which links
the user to printer information and videos on topics such as buying supplies, features overview, loading
media, printing a configuration report, cleaning instructions, and accessory information.
Figure 1 QR Code (ZQ511 Shown)
Printer Overview
Made for iPhone (MFi)
The printers support communication with Apple devices running iOS 10 or later over a standalone
Bluetooth 4.1 radio and the BT4.1 radio included with the 802.11ac (dual) radio.
13

Printer Overview
Near Field Communication (NFC)
The printers support a passive NFC tag which complies with the Android Standard Tag format since
Android devices are the most common found on the market today. The NFC tag is programmed from the
factory and supports Bluetooth pairing to enable a tablet, smartphone or mobile computer to automatically
pair with the printer via a Bluetooth connection (within the bounds of the security profile being used).
The NFC tag also supports app launching whereby an app developed either by Zebra or a third party will
launch on a NFC-enabled smartphone, tablet or mobile computer. Similarly, the NFC tag enables
launching to a web support page via a tablet, smartphone or mobile computer.
Thermal Shutdown
The printers have a thermal shutdown feature whereby the printer hardware will detect a printhead
over-temperature condition at 65°C (149°F). The printer automatically stops printing until the printhead
cools down to 60°C (140°F). Printing then recommences without a loss of label data or without any
degradation of print quality.
Radio-Frequency Identification (RFID)
The printers are equipped with an RFID encoder/reader, which is integrated into the printer’s printhead
assembly. The printers encode (write) information on ultra-thin UHF RFID transponders that are
embedded in “smart” labels, tickets, and tags. The printers encode the information; verify proper encoding;
and print bar codes, graphics, and/or text on the label’s surface. The printers use Zebra’s extensive set of
RFID commands running under ZPL programming language.
The RFID transponder is sometimes called the RFID tag or an inlay. The transponder is usually made of
an antenna that is bonded to an integrated circuit (IC) chip. The IC chip contains the RF circuit, coders,
decoders, and memory. If you hold an RFID label up to the light, you can see the transponder’s antenna,
and you can feel a bump in the label where the IC chip is located. The printers can encode and verify EPC
(Electronic Product Code) Generation 2 Class 1 UHF passive RFID tags, in addition to printing human
readable text and conventional 1-D and 2-D barcode information on Zebra supplied RFID thermal transfer
media. EPC is a product numbering standard that can be used to identify a variety of items by using RFID
technology. EPC Generation 2 tags offer advantages over other tag types. The tag identification (TID)
memory in a Generation 2 tag includes the chip manufacturer and model number information, which can
be used to identify which optional features are present on the tag. These optional features include those
for data content and security.
Gen 2 tags typically have a 96-bit EPC identifier, which is different from the 64-bit identifiers common in
early EPC tags. The 96-bit EPC code links to an online database, providing a secure way of sharing
product-specific information along the supply chain. Gen 2 tags also support much larger data structures.
The size of user memory available (if any) varies by the model and manufacturer of the tag.
Encoding and printing of an RFID label usually are completed on the first try, but some failures may occur.
If you experience consistent encoding failures, it may signal a problem with the RFID tags, your label
formats, or with the transponder placement. If an RFID tag cannot be encoded, “VOID” will be printed on
the label. The printer then attempts to read/encode “n” labels before the next format is attempted, where
“n” is specified by the ZPL programming language “^RS” command. Acceptable values of “n” are 1 to 10
and the default is 3. After printing the defined number of voided RFID labels, the printer default is No
Action (Label format causing the error is dropped).
While the user doesn’t have control of where on the label the VOID is printed, they can control the length of
the image. The start of the VOID image is always at the program position (or F0 if a backward program
position). More information on the “^RS” command may be found in the RFID Programming Guide 3
available on www.zebra.com/manuals
.
14

Printer Overview
RFID is an optional feature and is a factory-installed option only.
NOTE: Refer to www.zebra.com/warranty
Printer Features
Figure 2 Overview of Features (ZQ511 Shown).
10
4
1
9
for complete information on product warranties.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
1 Tear bar (Not present in Linerless. Scraper
present instead.)
2 Platen roller 7 DC input
3 Black bar sensor 8 USB port
4 Media support disks 9 Gap sensor
5 Printhead 10 Media cover
NOTE: Scanning the QR code with a mobile device will provide printer-specific information at
www.zebra.com/ZQ511-info
NOTE: Tapping the Zebra Print Touch ™ icon with a Near Field Communication (NFC) enabled mobile
device will provide instant access to printer-specific information. For more information about NFC and
Zebra products, go to http://www.zebra.com/nfc
Please see Zebra Multi-platform SDK for more information.
and www.zebra.com/ZQ521-info.
6 Latch release button
. Bluetooth pairing applications via NFC is also possible.
15
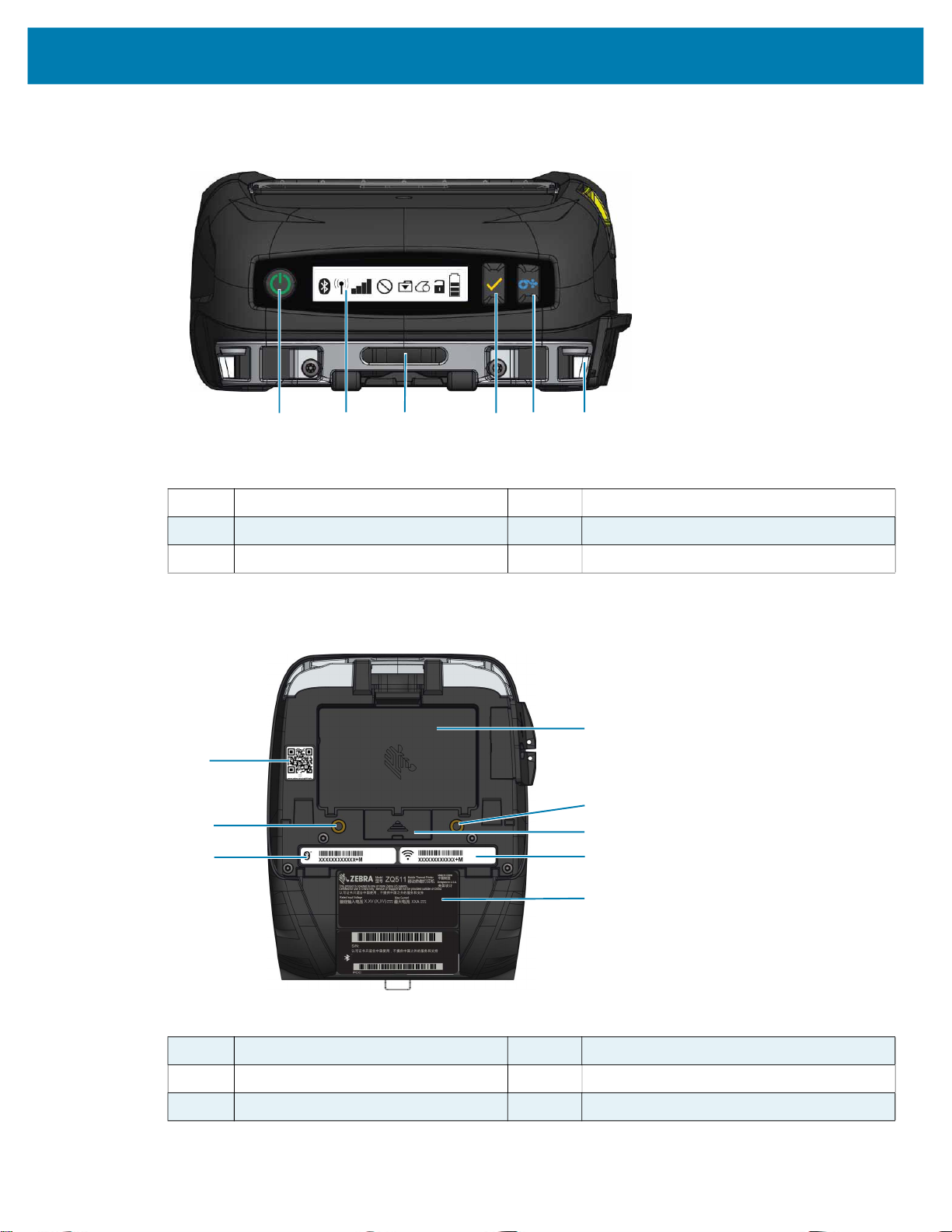
Figure 3 Printer Front Features
Printer Overview
11
11 Power button 14 Select button
12 Control panel 15 Paper feed button
13 Belt clip opening 16 Strap post
Figure 4 Printer Bottom Features
22
18
20
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
17 Battery 20 MAC address/Bluetooth ID
18 Mounting points 21 Serial labels
19 Docking contacts cover 22 QR code
16

Using the Printer
Preparing the Battery for Use
Installing/Removing Battery and Battery Tape Insulator
IMPORTANT: Batteries are shipped in sleep mode to preserve their maximum capacity while in storage
prior to initial use. The battery needs an initial charging to wake it up before using for the first time. (See
Charging the Battery on page 21.)
Removing the Battery
1. If a belt clip is present on the bottom of the printer, rotate it such that it provides clearance for the
battery.
2. Depress the latch on the battery pack (Figure 5).
Figure 5 Battery Latch
17

Using the Printer
Rotate the battery pack forward and lift it up and out of the battery well (Figure 6).
3.
Figure 6 Removing Battery
Removing the Battery Tape Insulator
CAUTION: The battery can explode, leak or catch fire if improperly charged or exposed to high
temperature. Do not disassemble, crush, puncture, short external contacts or dispose of in fire or water.
Charge on a Zebra approved Lithium-Ion charger only.
1. Pull up on the tape insulator tab located on the bottom of the battery pack.
2. Peel back the tape insulator and remove it from the top of the battery pack. Discard upon removal.
Figure 7 Removing Battery Tape Insulator
18

Battery Safety
CAUTION: Avoid accidental short circuiting of any battery. Allowing battery terminals to contact conductive
material will create a short circuit which could cause burns and other injuries or could start a fire.
IMPORTANT: Always refer to the Important Safety Information data sheet shipped with each printer and
the Technical Bulletin shipped with each battery pack. These documents detail procedures to ensure
maximum reliability and safety while using this printer.
IMPORTANT: Always dispose of used batteries properly. Refer to Product Disposal on page 69 for more
battery recycling information.
CAUTION: Use of any charger not approved specifically by Zebra for use with its batteries could cause
damage to the battery pack or the printer and will void the warranty.
CAUTION: Do not incinerate, disassemble, short circuit, or expose to temperatures higher than 65°C
(149°F).
Using the Printer
19

Installing the Battery
1. Locate the battery compartment on the bottom of the printer (Figure 8).
2. Swivel the belt clip (if present) to access the battery compartment.
Figure 8 Battery Compartment
3. Insert the battery into the printer as shown. (It is not possible to insert the pack in the incorrect
orientation.)
Using the Printer
Figure 9 Battery Insertion
4. Rotate the battery into the compartment until it locks in place and is sitting flush in the printer.
Figure 10 Battery Installed
20

Charging the Battery
CAUTION: Do not place any charger in locations where liquids or metallic objects may be dropped into the
charging bays.
AC Power Adapter
Figure 11 AC Power Adapter Charging
AC Power Cord
(varies with
geographic location)
Using the Printer
AC Adapter
DC Input
1. Open the protective cover on the printer to expose the DC input charger jack.
2. Connect the appropriate AC power cord for your location to the adapter and then plug the power cord
into an AC receptacle.
3. Plug the barrel plug from the AC adapter into the charger jack on the printer.
4. The printer powers up and begins charging. The printer can be left on or turned off at this point.
Charging continues in either state.
IMPORTANT: While it is possible to charge the battery when using the printer, charge times will increase
under this condition.
21

Vehicle Cradle
The Vehicle Cradle provides a means to mount a printer in a vehicle while at the same time providing
charging power to the battery. The Vehicle Cradle features USB connectivity to allow the user to connect a
laptop or tablet to the cradle.
Figure 12 Vehicle Cradle
Using the Printer
Docking
Contacts
Docking the Printer Removing the Printer
Battery Eliminator/Battery Eliminator Vehicle Cradle
The Battery Eliminator Vehicle Cradle enables the user to mount a ZQ511 or ZQ521 printer in a vehicle
without the use of a battery.
4-Bay Power Station
The 4-Bay Power Station allows a total of four printers to be docked and charged. The Power Station
provides battery charging power while still maintaining all of the printer’s functionality.
NOTE: For detailed information on accessories, refer to the ZQ500 Series VC User Guide, the ZQ500
Series 4-Bay Power Station User Guide, the Battery Eliminator User Guide, and the Battery Eliminator
Cradle User Guide at www.zebra.com/manuals
Before docking the printer on either the Vehicle Cradle or the 4-Bay Power Station, you must remove the
docking contacts cover located on the bottom of the printer. To remove the cover, first remove the battery,
and then use a small screwdriver or coin to detach the cover and expose the docking contacts.
.
22

Figure 13 4-Bay Power Station
2
1
1-Slot Battery Charger
Use Case: Home Office/Small Business
Using the Printer
The 1-Slot Battery Charger provides the user with a single, spare battery charging solution. Similar to the
3-Slot Battery Charger, the single charger charges a 2-cell battery from empty to fully charged in less than
four hours and a 4-cell battery from empty to fully charged in less than six hours.
Figure 14 1-Slot Battery Charger
LED Indicator
23

Charging Status Indicators
Both the 3-slot and 1-slot battery chargers use an LED indicator located next to each slot to indicate the
charge state in either green, red, or amber as detailed below.
Using the Printer
Mode
Charge Fault Fast Blinking Red
Charging (Healthy)
Charge Done (Healthy) Solid Green
Charging (Unhealthy) Solid Red
Charging Done (Unhealthy) Solid Red
Best Battery (Charging) Alternates between solid and bright bursts of
Best Battery (Charge Done) Alternates between solid and bright bursts of
Charging Indication Description
Solid Amber
amber
green
24

Using the Printer
3-Slot Battery Charger/Dual 3-Slot Battery Charger
Use Case: Settlement Room
The 3-Slot Battery Charger is a charging system for use with the 2-cell lithium-ion batteries used in the
printers. The 3-slot charger is capable of charging three 2-cell batteries simultaneously from empty to full in
less than four hours and 4-cell batteries from empty to fully charged in less than six hours. It can either be
used as a standalone charger or mounted on a 5-slot shared cradle.
Figure 15 3-Slot Battery Charger
Vehicle Adapter
Use Case: Vehicle
The printers, along with accompanying Zebra TC51/TC56 mobile computers, can be charged in the vehicle
though the use of a Vehicle Adapter. The Vehicle Adapter uses either an open-ended connection or
cigarette lighter adapter, along with a power supply.
Figure 16 Vehicle Adapters
Cigarette Lighter
Adapter
Power Supply
DC
Connector
Open-ended
Connector
Power Supply
25

Loading Media
The printers are designed to print either continuous (receipt) media or label stock.
1. Press the media cover button on the side of the printer. The media cover opens automatically.
Figure 17 Media Cover Button
Using the Printer
2. Rotate the media cover back completely, exposing the media compartment and adjustable media
supports.
Figure 18 Opening the Media Cover
Media Supports
26

Using the Printer
Pull the media supports apart as shown in Figure 19. When you move one support, both supports will
3.
move.
4. Insert the roll of media between the supports in the orientation shown, and let the supports secure the
media in place. The media roll should be able to spin freely on the supports.
Figure 19 Loading Media
5. Close the media cover until it clicks into place and the media advances.
Figure 20 Closing the Media Cover
NOTE: Refer to the Zebra Programming Guide for information about adjusting the media feed length via a
Set/Get/Do (SGD) command.
27

Operator Controls
The printers feature a control panel with buttons for the Power On/Off and Media Feed functions, as well
as a display for providing information regarding printer functions. The menu displays a single row of icons
used to indicate printer status. The LCD also displays acknowledged alerts and unacknowledged alerts.
Acknowledged alerts have a single response option which requires the user to press the Select button,
whereas unacknowledged alerts do not require a response.
Figure 21 Control Panel
Using the Printer
1
3
1 Printer Status Icons - Indicates the status of several printer functions.
2 Select Button - Press to select a menu choice on the LCD.
3 Power Button - Press to turn unit on. Press again to turn unit off.
4 Paper Feed Button - Press to advance the media one blank label or a software determined
length of journal media.
2
4
28

Printer Status Icons
DC
Using the Printer
Icon
Description Icon
Description
Bluetooth Media
WiFi Connection Cover Open
WiFi Signal Strength Battery
Error Battery Eliminator
Data Power Save Mode
Draft Mode
When the printer is in Power Save Mode and is not in a media out condition, the Power Save icon displays.
When the printer is in Power Save Mode and also in a media out condition, the blinking Media Out icon
displays instead of the Power Save icon. This is because the printer is not running when there is a media
out condition. If the printer is in both Power Save Mode and Draft Mode, the Power Save icon displays.
When the printer is in Draft Mode due to a user setting, the Draft Mode icon will be displayed. However,
when the printer is in Draft Mode and in a media out condition, the blinking Media Out icon will be
displayed.
For more detailed information on the printer status icons, see Printer Status Indicators on page 51
29

Buttons
The user has the ability to use the three button interface on the printers with the following Power Up and
Run Time sequences.
Power Up Sequences
Sequence # Function Keys
1
2 Print configuration report then
3 Initiate forced download Hold down the Select and Feed buttons while
4 Turn the printer on or off or to
NOTE: A forced download is when the printer is powered up in a mode where it is running only the code
that allows for firmware downloads to happen.
Using the Printer
Print configuration report Hold down Feed button while pressing the Power
button.
Hold down Select button while pressing the Power
network report
enter Sleep Mode
button.
pressing the Power button.
Power Button
Run Time Sequences without LED Flashes
Sequence # Function Keys
1 Two-key and ZPL Config Hold down Feed button and Select button for 3
2 Repeated Feed Events Feed button
3 Wake (if in Sleep Mode) Power button or Select button
LEDs
The printers feature a tri-colored LED ring located around the Power button which indicates the state of the
battery during charging process.
Icon Behavior State of Battery
Power On/Charged Battery
Power On/Battery Eliminator Plugged In
Battery Charging (Amber LED Ring)
Sleep Mode and Charging (Blinking Amber LED Ring)
(( ))
seconds.
(( ))
Sleep Mode (Blinking Green LED Ring)
Battery Fault (Red LED Ring)
30

Alerts
BATTERY LOW
Using the Printer
The control panel displays various alerts to the user in the form of Acknowledged Alerts, Unacknowledged
Alerts, and Error Alerts. An Acknowledged Alert displays over the printer status icons and requires user
input to be cleared, i.e. press the Select button to clear such an alert.
Figure 22 Control Panel
LED indicating
battery fault
An Unacknowledged Alert also displays over the printer status icons, but in this case it does not require
user input to be cleared. The alert will automatically be cleared after being displayed for five seconds.
Error Alerts also appear over the printer status icons and require no user input via the front panel to be
cleared, but they do require the user clearing the error condition by other means. The Error Alert will
remain on the display until the error condition is cleared.
Power Saving Features
The printers have a few key features designed to extend the life of the battery. These features are
described below.
Sleep Mode
The Sleep Mode feature is a way the printer conserves battery life whereby the printer will automatically go
into a “sleep” state after two minutes of inactivity. When the printer is in this state there will be no content
displayed on the LCD in addition to no backlight. The printer will indicate Sleep Mode by a slow blinking
green LED ring around the Power Button (see LEDs on page 30).
• If the Power Button is pressed for less than three seconds (<3), then the printer will enter Sleep Mode.
• If the Power Button is pressed for more than three seconds (>3), then the printer will power down
completely.
Acknowledged Alert
In order to “wake up” the printer, the user must press the Power or Select <icon> buttons for less than
three seconds, or the printer will wake up on its own when communication is initiated via Bluetooth.
The printers will also wake from Sleep Mode when communication is initiated via WLAN. If the Power
Button is pressed for more than three seconds, the printer will wake up and shut down completely.
To enable or disable Sleep Mode, send the power.sleep.enable command to the printer using Zebra Setup
Utilities (ZSU) and set it to either
printer will enter Sleep Mode, send the power.sleep.timeout (in seconds) to the printer using the ZSU.
"on" or "off". (The default setting is “on”.) To set the time after which the
31
Adaptive Print Performance
The printers use PSPT PrintSmart Gen 2 technology which adapts to your print conditions such that print
quality is not sacrificed. When the printer sees environmental conditions such as state of charge, battery
health, cold temperature extremes, or high density printing, the printer will adjust print performance to
preserve battery function and allow printing to continue. This may affect the speed and sound of printing
but not the print quality.
Draft Mode
Using the Printer
The user can configure the printer to print in Draft Mode via SGD command
(default is “off”), which optimizes the printer for text-only printing. While in Draft Mode, print speed
increases from the maximum of 4 inches per second (ips) at the printer’s highest speed setting to a
maximum of 5 ips with a 22% reduction in optical density. When a printer is in this user setting, a Draft
Mode icon will be displayed. If the printer is in both Power Save mode and Draft Mode, the Power Save
icon will display. If the printer is in Draft Mode during a media out condition, the blinking Media Out icon will
be displayed.
NOTE: For an explanation and a list of all SGD commands, please refer to the Zebra Programming Guide
at: http://www.zebra.com/us/en/support-downloads.html
NOTE: For detailed information on sending SGD commands to the printer using Zebra Setup Utilities,
please refer to the Wireless Configuration for 802.11n and Bluetooth Radios for Link-OS Mobile Printers
at: http://www.zebra.com/us/en/support-downloads.html
NOTE: Draft Mode printing is optimized for printing receipts comprised of text only with no reverse image,
black fill or barcodes present. Draft Mode is designed to operate at temperatures between ambient and the
maximum thermal range of the printer.
Verify That the Printer is Working
Before you connect the printer to your computer or portable data terminal, make sure that the printer is in
proper working order. You can do this by printing a configuration report using the “two key” method. If you
can’t get this report to print, refer to Troubleshooting Tests on page 54.
media.draft_mode
Printing a Configuration Report
1. Turn the printer off. Load the media compartment with journal media (media with no black bars or gaps
on the back)
2. Press and hold the Feed Button.
3. Press and release the Power button and keep the Feed button pressed. When printing starts, release
the Feed button. The unit will print a line of interlocking “x” characters to ensure all elements of the
printhead are working, print out the version of software loaded in the printer and then print the report.
The report indicates model, serial number, baud rate, and more detailed information on the printer’s
configuration and parameter settings. (See the Troubleshooting Section for sample printouts and a further
discussion on how to use the configuration report as a diagnostic tool.)
32
Connecting the Printer
The printer must establish communications with a host terminal which sends the data to be printed.
Communications occur in four basic ways:
• The printers can communicate by cable via either RS-232C or USB 2.0 protocols. Windows drivers that
support printing via Serial, USB and the network are included in the Zebra Designer Driver which can
be downloaded from www.zebra.com/drivers
• By means of a wireless LAN (Local Area Network) per 802.11 specifications. (Optional)
• By means of the Ethernet when docked on the Ethernet cradle.
• By means of a Bluetooth short range radio frequency link.
• WinMobile
• These printers are compatible with iOS devices, therefore printing via Bluetooth to an Apple
possible.
®
, Blackberry®, and Android® devices use standard Bluetooth protocol.
Using the Printer
.
®
device is
Cable Communication
CAUTION: The printer should be turned off before connecting or disconnecting a communication cable.
The standard cable connection for the printers is USB. The USB port provides 500mA to the A/B port when
in host mode and can connect a printer to a PC via a Type A plug to Micro B plug. The cable has a plastic
twist lock cap that provides strain relief and locks the cable into the printer housing (see below). Visit
www.zebra.com/accessories
Figure 23 Twist Lock. Rotate in a clockwise direction to lock cable in place.
Twist Lock in a clockwise
direction to lock cable in place.
for part numbers.
33

Using the Printer
Figure 24 Cable Communication with PC
USB Communications
Cable to PC
LAN
The small 5-pin connector on the USB cable plugs into the printer, and the connectors are keyed to ensure
correct alignment. Do not try to force the cable if it does not plug in as this could damage the pins.
The other end of the cable plugs into the USB port on a computer as shown in Figure 24. The printers are
configured with the USB Open HCI interface allowing them to communicate with Windows
USB drivers are included in the Zebra Designer Driver which can be downloaded from the Zebra website.
Zebra Setup Utilities
Before you start to configure your printer for use on a Local Area Network (LAN), you will need some basic
information which will enable you to establish the network configuration for your printer. Zebra Setup
Utilities (ZSU) provides a quick and easy way to configure your printers for a variety of purposes, including
setting them up for wireless communications either on a Local Area Network (LAN) or using the
international Bluetooth ™ communications standard.
Once ZSU has been downloaded to your computer, attach the USB cable to the printer and computer as
shown in Figure 24. Refer to Wireless Configuration Guide to follow the steps necessary for setting up and
configuring your printer via ZSU.
Go to https://www.zebra.com/us/en/support-downloads.html
Configuration Guide.
®
based devices.
to download ZSU and the Wireless
34

Using the Printer
Zebra Android Printer Setup Utility (for Link-OS Printers)
The printers can also be configured using the Zebra Android Printer Setup Utility. This utility can be
downloaded from Google Play to an Android device such as a smartphone or the TC51 or TC56 mobile
handheld computers. The Android mobile device can be paired with the printer via Bluetooth or a USB
cable and users can quickly navigate the app to perform the following tasks.
Figure 25 Setup Utility Main Screen
Shows currently connected printer
Displays current printer status
= all clear
= error present
Quick access to Wizards, Printer Actions
and Files
35

Using the Printer
Wireless Communications with Bluetooth
Bluetooth is a worldwide standard for the exchange of data between two devices via radio frequencies.
This form of point-to-point communication does not require access points or other infrastructure. Bluetooth
radios are relatively low powered to help prevent interference with other devices running at similar radio
frequencies. This limits the range of a Bluetooth device to about 10 meters (32 feet). The default for the
printers is Class 2, but the range can be set to Class 1 via a
power. Both the printer and the device it communicates with must follow the Bluetooth standard.
Bluetooth Networking Overview
• Each Bluetooth enabled printer is identified by a unique Bluetooth Device Address (BDADDR). This
address resembles a MAC address whereby the first three bytes are vendor, and the last three bytes
are device (e.g. 00:22:58:3C:B8:CB).
• This address is labeled on the back of the printer via a barcode for ease of pairing. (For the dual radio,
the MAC address label only represents WiFi MAC address.) (Figure 26 on page 39.) In order to
exchange data, two Bluetooth enabled devices must establish a connection.
• Bluetooth software is always running in the background, ready to respond to connection requests. One
device (known as the client) must request/initiate a connection with another. The second device (the
server) then accepts or rejects the connection.
SGD (bluetooth.power_class) to increase
• A Bluetooth enabled printer will normally act as a peripheral creating a miniature network with the
terminal sometimes referred to as a “piconet”. Discovery identifies Bluetooth devices that are available
for pairing whereby the central device broadcasts a discovery request and devices respond. If a device
is not discoverable, the central cannot pair unless in knows the BDADDR or has previously paired with
the device.
• If both devices support Bluetooth 2.1 or higher they will use Security Level 4 Secure Simple Pairing
(SSP), a mandatory security architecture that features two association models: Numeric Comparison
and Just Works (no user confirmation).
36

Bluetooth (BT) Security Modes
Security Mode 1 Security Mode 2 Security Mode 3
If a BT device greater than or
equal to 2.1 is pairing with a BT
device less than or equal to 2.1,
it falls back to BT 2.0
compatibility mode and behaves
the same as BT 2.0. If both BT
devices are greater than or equal
to 2.1, Secure Simple Pairing
must be used according to the
BT spec.
Security Mode 4: Simple Secure Pairing
Simple Secure Pairing:
• A new security architecture introduced supported in BT >= 2.1.
• Service-level enforced, similar to mode 2.
Using the Printer
If a BT device greater than or
equal to 2.1 is pairing with a BT
device less than or equal to 2.0,
it falls back to BT 2.0
compatibility mode and behaves
the same as BT 2.0. If both BT
devices are greater than or equal
to 2.1, Secure Simple Pairing
must be used according to the
BT spec.
Same as Security Mode 2.
• Mandatory when both devices are BT >= 2.1.
• There are four association models currently supported by mode 4.
• Security requirements for services must be classified as one of the following: authenticated link key
required, unauthenticated link key required, or no security required. SSP improves security through
the addition of ECDH public key cryptography for protection against passive eavesdropping and
man-in-the-middle (MITM) attacks during pairing.
Numeric Comparison Just Works
• Designed for situation where both devices are
capable of displaying a six-digit number and
allowing user to enter “yes” or “no” response.
• During pairing, user enters “yes” if number
displayed on both devices matches to complete
pairing. Differs from the use of PINs in legacy
(BT<=2.0) pairing because the number
displayed for comparison is not used for
subsequent link key generation, so even if it is
viewed or captured by an attacker, it could not
be used to determine the resulting link or
encryption key.
• Designed for situation where one (or both) of
the pairing devices has neither a display nor
keyboard for entering digits (e.g. Bluetooth
headset). It performs authentication step 1 in
the same manner as a numeric comparison,
but the user cannot verify that both values
match, so MITM (man-in-the-middle) protection
is not provided. This is the only model in SSP
that does not provide authenticated link keys.
Each mode, except for Just Works, has Man-In-The-Middle (MITM) protection, meaning no third device
can view the data being passed between the two devices involved. The SSP mode is usually negotiated
automatically based on the capabilities of both the central and peripheral. Lower security modes can be
disabled via the
SGD sets the lowest security level at which the printer will establish a Bluetooth connection. The printer will
always connect at a higher security level if requested by the central device. To change the security mode
and security settings in the printers, use Zebra Setup Utilities.
bluetooth.minimum_security_mode SGD. The bluetooth.minimum_security_mode
37

Using the Printer
Bluetooth Minimum Security Modes
bluetooth.minimum_security_mode=1 Secure Simple Pairing
bluetooth.minimum_security_mode=2 Secure Simple Pairing
bluetooth.minimum_security_mode=3 Secure Simple Pairing
bluetooth.minimum_security_mode=4 Secure Simple Pairing
bluetooth.bluetooth_PIN Not Used
IMPORTANT: bluetooth.minimum_security_mode sets the lowest security level at which the printer will
establish a Bluetooth connection. The printer will always connect at a higher security level if requested by
the central device.
The printers also feature bonding for Bluetooth. The printer caches pairing info so devices stay paired
through power cycles and disconnects. This eliminates the need to repair on every connection
establishment.
BT Version of central Device (>2.1)
Just Works/Numeric Comparison
Just Works/Numeric Comparison
Numeric Comparison
Numeric Comparison
The
bluetooth.bonding SGD is on by default.
NOTE: For detailed information on Bluetooth, please refer to the ZQ500 Series product page at:
http://www.zebra.com/us/en/support-downloads.html
All Link-OS firmware versions prior to version 6.0
In all versions of Link-OS firmware prior to version 6.0, if bluetooth.discoverable is set to “on”, the
printer enters General Discoverable mode. It responds to discovery requests at any time, and is
connectable and pairable. If set to “off”, the printer is not discoverable, but it is still connectable and
pairable. The default was “on”.
Link-OS firmware version 6.0
If bluetooth.discoverable is set to “on”, the behavior is the same as pre-6.0 firmware. The printer
enters General Discoverable mode and is connectable and pairable. If set to “off”, the printer is not
discoverable, is still connectable and pairable. The default was changed to “off”. A new feature was added
to all printers called “Limited Pairing Mode” that turns on a limited discoverability and pairing window to
users who have physical access to the printer. If the user holds the feed key for 5 seconds, the printer
enters limited pairing mode for 2 minutes.
Link-OS firmware versions 6.1 and later
If bluetooth.minimum_security_mode is set to “1”, unconditionally enable pairing, regardless of the
bluetooth.discoverable mode setting. If bluetooth.minimum_security_mode is set to a value other
than 1, pairing is not allowed if discoverable is set to “off” and the printer is not in limited pairing mode.
NOTE: Discoverability does not apply to Bluetooth LE. For Zebra printers that support Bluetooth LE, the
bluetooth.discoverable setting affects pairing exact
38

WLAN Overview
The printers are optionally equipped with a Dual Radio that uses the industry standard 802.11ac protocols
and Bluetooth 4.1. They will have the FCC ID number on the serial number label on the back of the unit.
• Wireless Network Printers with the Zebra 802.11ac WLAN radio module can be identified by the text
“Wireless Network Printer” on the serial number label on the back of the printer.
• These printers allow communication as a node within a wireless local area network (WLAN). Methods
of establishing communications to the printer will vary with each application.
More information and LAN configuration utilities are included in the ZebraNet Bridge Enterprise™ program
(version 2.8 and later).
Zebra Setup Utilities (ZSU) and Zebra Mobile Setup Utility can also be used to configure WLAN
communications settings. Both ZebraNet Bridge Enterprise and ZSU may be downloaded from the Zebra
Web site.
Figure 26 BT/WLAN Communications
Using the Printer
Setting Up the Software
The printers use Zebra’s CPCL and ZPL Programming languages which were designed for mobile printing
applications. CPCL and ZPL are fully described in the Zebra Programming Guide, CPCL Programming
Guide, and ZPL II Programming Guide available on-line at
https://www.zebra.com/us/en/support-downloads.html
Windows
language.
®
based label creation program which uses a graphical interface to create and edit labels in either
. You can also use ZebraDesigner Pro v2, Zebra’s
39
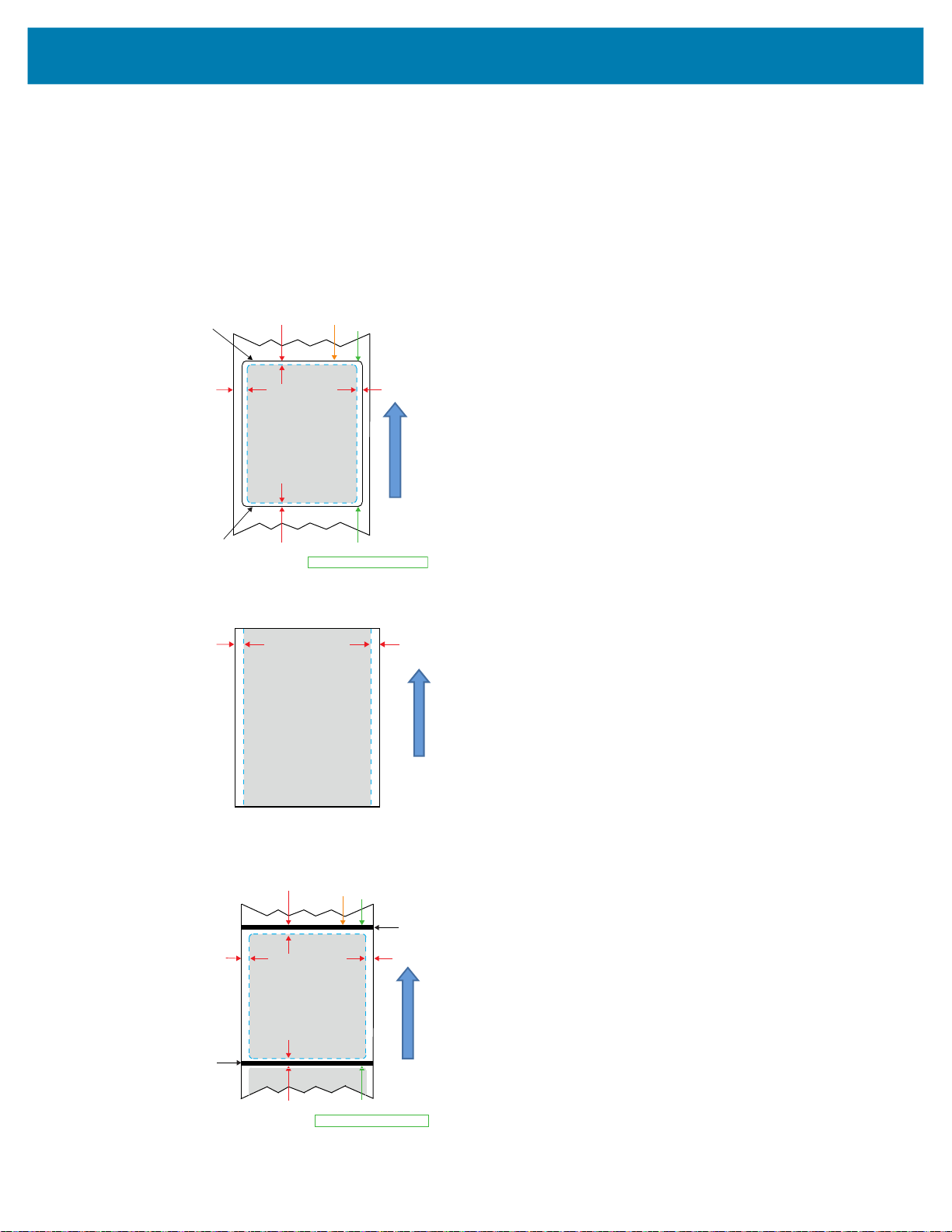
Designing Labels
Safe Printing Zone
1.59 mm
1.59 mm
(0.06 in.)
1.25 mm
(0.05 in)
1.25 mm
(0.05 in.)
“H”
Max Label Height = “H” = 2.5 mm
Bottom edge of
die-cut label
Top edge of
die-cut label
CPCL Label
Height
Media Feed Direction
Safe Printing Zone
Media Feed Direction
)
Safe Printing Zone
1.59 mm1.59 mm
(0.06 in.)
1.25 mm
(0.05 in.)
1.25 mm
(0.06 in.)
“H”
Max Label Height = “H” = 2.5 mm
CPCL Label
Height
Media Feed Direction
Safe Printing Zone
Black Bar
Black Bar
The following examples provide guidelines for designing labels for the printers, specifically for Gap Media,
Black Bar Media and Journal Media. The illustrations for each media type define recommended
tolerances, keep-out zones and safe printing zones designed to avoid any vertical registration issues
during printing. Dimensions are determined based on product registration capabilities and
Zebra-recommended media tolerances.
Figure 27 Gap Media
Using the Printer
Figure 28 Journal Media
1.59 mm
(0.06 in.)
Figure 29 Black Bar Label Media
1.59 mm
(0.06 in.
40
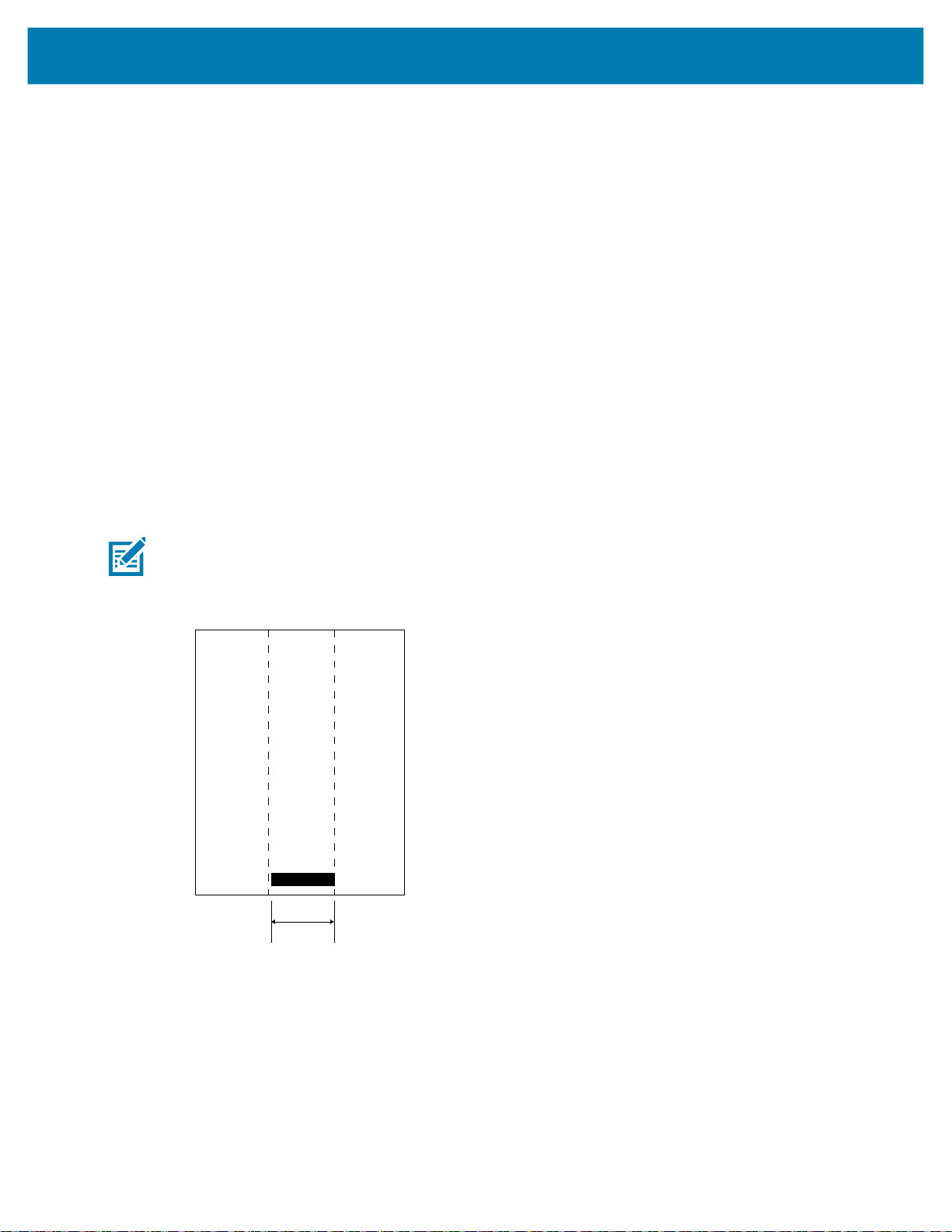
Using the Printer
Keep
dark color
pre-printed
graphics,
barcodes,
and text
out of the
path
of the
bar sensor.
15 mm
(0.59 in.)
Using Pre-Printed Receipt Media
For alignment of pre-printed documents to Top of Form (TOF), the use of a black mark is necessary. The
black bar can be placed on the back of the documents by following the recommendation below.
The black bar can also be placed on the front of the document. The user must change the
media.bar_location setting to "front".
Black Mark Dimensions (Receipt Media)
The reflective media black marks (or black bar/marks) should extend past the centerline of the roll on the
front side of the paper.
• Minimum mark width: 15 mm (0.59 in.) perpendicular to the edge of the media, and centered within the
width of the roll.
• Mark length: 4.8 - 6.0 mm (0.19 - 0.24 in.) parallel to the edge of the media.
Label Areas
The media/black bar sensor detects the dark, pre-printed bar on the media, so a path in the center of the
paper must be kept free of dark, pre-printed graphics.
NOTE: Dark, pre-printed graphics refer to any symbols, barcodes, text and/or colored areas that have
been applied to the receipt paper rolls before they have ever been used in the printer.
Figure 30 Label Areas
41

Label Design Examples
ACME COLLEGE
PARKING
VIOLATION
PARKING
VIOLATION
ACME COLLEGE
ACME RECEIPT
Quality FIRST
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
ACME RECEIPT
Quality FIRST
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
This section shows examples of labels with and without problems with the black mark located in the front of
the document.
Figure 31 Label Design Examples
Problem Label Designs Good Label Designs
Using the Printer
The dark colors, pre-printed text, and
graphics are in the path of the black bar
at the bottom of the receipt.
The center path to the black bar is free of
dark colors, pre-printed text,
and graphics.
NOTE: Complete information on using pre-printed receipt paper can be found in the FORM command in
the CPCL Programming Guide at www.zebra.com/manuals
.
42

Keep-Out Areas
15 mm
(0.59 in.)
*
*
*
*
*
At times, incomplete printing of text and/or graphics appear because minimum margins are not provided
during label design. The recommended minimum margins, or “keep out areas” are shown in Figure 32.
Figure 32 Keep Out Areas
Using the Printer
Receipt Paper with Black Bars
*Maintain a minimum “keep out area”
of 1.59 mm (1/16 in.) from the two outer
edges of the paper roll and from the
black bars.
NOTE: The length of each “continuous” receipt is determined by the data sent to the printer.
Near Field Communication (NFC)
Much like Bluetooth and Wi-Fi technologies, Near Field Communication (NFC) allows wireless
communication and data exchange between digital devices like smartphones. Yet NFC utilizes
electromagnetic radio fields while technologies such as Bluetooth and Wi-Fi focus on radio transmissions
instead.
NFC is a sub-class of Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) technology that is designed for use by
devices within close proximity to each other. NFC technology allows devices to establish communication
by touching or bringing them into close proximity, usually no more than 7.62 centimeters (3 inches).
The printer contains a passive NFC device which contains information that other devices can read but
does not read any information itself
An active device, such as a smartphone, can read the information on the printer’s NFC tag, but the tag
itself does nothing except transmit the info to authorized devices.
Continuous Receipt Paper
(without Black Bars)
*Maintain a minimum “keep out area”
of 1.59 mm (1/16 in.) from the two outer
edges of the paper roll.
Active devices can read information and send data. An active NFC device, like a smartphone, would not
only be able to collect information from NFC tags, but it would also be able to exchange information with
other compatible phones or devices. An active device could even alter the information on the NFC tag if
authorized to make such changes. To ensure security, NFC often establishes a secure channel and uses
encryption when sending sensitive information.
43

Using the Printer
http://www.zebra.com/nfc
Figure 33 NFC Pairing Using Print Touch
NFC Use Cases
TM
Passive
• Bluetooth Pairing – used to cause a tablet, smart phone or terminal to automatically pair with the printer
• App launching – used to cause an app, developed either by Zebra or a third party to be executed on a
• Web site launching – used to cause a smart phone, tablet or terminal to display a web site developed by
Tapping the Zebra Print Touch ™ icon with a Near Field Communication (NFC) enabled smartphone will
provide instant access to printer-specific information. For more information about NFC and Zebra products,
go to http://www.zebra.com/nfc
Multi-platform SDK for more information.
via a Bluetooth connection, within the bounds of the security profile being used. This shall contain the
BT address and serial number of the printer.
smart phone, tablet or terminal.
Zebra or a third party developer.
. Bluetooth pairing applications via NFC is also possible. Please see Zebra
44

Wearing the Printer
Swivel Belt Clip
The printers have a plastic swivel belt clip included as a standard feature. (It should be noted that printers
with extended capacity battery do not come equipped with a belt clip.) To use: hook the clip over your belt,
and ensure that the clip is securely attached to the belt. The belt clip will pivot to allow you to move freely
while wearing the printer. In order to install or remove the plastic Belt Clip, secure it to the cut-out in the
front of the printer (where shown).
Figure 34 Printer with Belt Clip
Using the Printer
Clip Here
Hand Strap
The Hand Strap accessory attaches to the front posts of the printer to provide the user with a convenient
and secure method of carrying the printer. To attach the Hand Strap to the printer:
1. Attach one swivel snap hook to its corresponding post on the front of the printer.
2. Attach the opposite end of the strap to its corresponding post on the front of the printer where shown.
Figure 35 Hand Strap
Strap
Post
Swivel
Snap
Hook
45

Shoulder Strap
A Shoulder Strap accessory is also offered to provide another option for comfortably carrying the ZQ511
and ZQ521 printers. Similar to the Hand Strap, the shoulder strap attaches to the two strap posts on the
front of the printer via rugged swivel snap hooks as shown in Figure 36. The strap is easily adjustable up to
56 inches from end to end.
Figure 36 Shoulder Strap
Using the Printer
Adjustable
Clip
Swivel Snap
Hooks
Soft Case
The printers have an environmental Soft Case option that helps protect the printer, while also allowing the
user to carry it from their belt. The paper path is left open to maintain printing capability and the controls
are visible and accessible while in the case. D-Ring connectors allow for attachment to the shoulder strap
option.
Figure 37 Soft Case
46

Exoskeleton
In order to provide extreme ruggedness for the printers, they come with an optional hard case, or
“Exoskeleton”. This case features a clam shell design whereby the printer is placed securely inside and the
Exoskeleton is clamped shut. The Exoskeleton comes with a shoulder strap for easy portability.
All printer ports are inaccessible while the printer is in the hard case, but the printer control buttons can still
be used (Figure 38). The user will also be able to mount and charge the printer on the Vehicle Cradle and
4-Bay Power Station while in the hard case.
NOTE: Since linerless printers don’t have the reverse tear bar feature which allows media to be torn both
upwards and downwards, it is recommended that linerless printers not be used with the Exoskeleton.
Linerless media can only be torn down and the Exoskeleton is not resistant to the adhesive of the linerless
media.
Figure 38 Exoskeleton
Using the Printer
NOTE: For more information on accessories for the ZQ500 printers, see Accessories on page 64.
47

Preventive Maintenance
Extending Battery Life
• Never expose the battery to direct sunlight or temperatures over 40°C (104°F) when charging.
• Always use a Zebra charger designed specifically for Lithium-Ion batteries. Use of any other kind of
charger may damage the battery.
• Use the correct media for your printing requirements. An authorized Zebra re-seller can help you
determine the optimum media for your application.
• If you print the same text or graphic on every label, consider using a pre-printed label.
• Choose the correct print darkness, and print speed for your media.
• Use software handshaking (XON/XOFF) whenever possible.
• Remove the battery if the printer won’t be used for a day or more and you’re not performing a
maintenance charge.
• Consider purchasing an extra battery.
• Remember that any rechargeable battery will lose its ability to maintain a charge over time. It can only
be recharged a finite number of times before it must be replaced. Always dispose of batteries properly.
See Product Disposal on page 69 for more information on battery disposal.
Using the Printer
General Cleaning Instructions
CAUTION: Avoid possible personal injury or damage to the printer. Never insert any pointed or sharp
objects into the printer. Always turn off the printer before performing any cleaning procedures. Use care
when working near the tear bars as the edges are very sharp.
CAUTION—HOT SURFACE: The printhead can get very hot after prolonged printing. Allow it to cool off
before attempting any cleaning procedures.
IMPORTANT: Only use a Zebra cleaning pen (not supplied with the printer) or a cotton swab with 90%
medical grade alcohol for cleaning the printhead.
CAUTION: Use only cleaning agents specified in the following tables. Zebra Technologies Corporation will
not be responsible for damage caused by any other cleaning materials used on this printer.
48

Using the Printer
Area Method Interval
Printhead Use a Zebra cleaning pen to swab the
thin gray line on the printhead, cleaning
the print elements from the center to the
outside edges of the printhead.
After every five rolls of media (or more
often, if needed). When using
linerless type media, cleaning is
required after every roll of media.
Platen Surface
(Linered)
Platen Surface
(Linerless)
Scraper (Linerless
Units Only)
Tear Bar Clean thoroughly with 90% medical
Printer Exterior Water-dampened cloth or 90% medical
Printer Interior Gently brush out printer. Ensure the Bar
Interior of units with
Linerless Platens
Rotate the platen roller and clean it
thoroughly with a fiber-free swab, or lint
free, clean, damp cloth lightly moistened
with medical grade alcohol (90% pure or
better). (Figure 39)
Rotate platen roller and clean with a
fiber-free swab and 1 part liquid soap
(Palmolive or Dawn) and 25 parts water.
Use pure water to clean after soap/water
mixture. (Figure 40)
Use adhesive side of media to clean
scraper on linerless units. (Figure 40)
grade alcohol and a cotton swab. (Figure
39)
grade alcohol wipe.
Sensor and Gap Sensor windows are
free of dust. (Figure 39)
Clean thoroughly with 90% medical
grade alcohol and a fiber-free swab.
(See Figure 40 for specific target areas
for interior cleaning.)
After every five rolls of media (or more
often, if needed)
Clean platen only if there is an issue
during printing, such as media not
releasing from the platen. (*See Note
below.)
After every five rolls of media (or more
often, if needed).
As needed
As needed
As needed
After every five rolls of media (or more
often, if needed).
NOTE: This is an emergency procedure only to remove foreign contaminates (oils, dirt) from the platen
that can damage the printhead or other printer components. This procedure will shorten or even exhaust
the linerless platen’s useable life. If the linerless media continues to bind after cleaning and feeding 1 to 2
meters (3 to 5 feet) of media, replace the platen.
49

Using the Printer
Figure 39 Cleaning Locations (Linered Printer)
Black Bar
Sensor
Platen Roller
Tear Bar
Printhead
Gap Sensor
Tear Bar
Figure 40 Cleaning Locations (Linerless Printer)
Elements
Media
Support
Printer
Frame
Platen Roller
Platen Holder
Media Support Disk
Media Support
Printhead
Elements
50
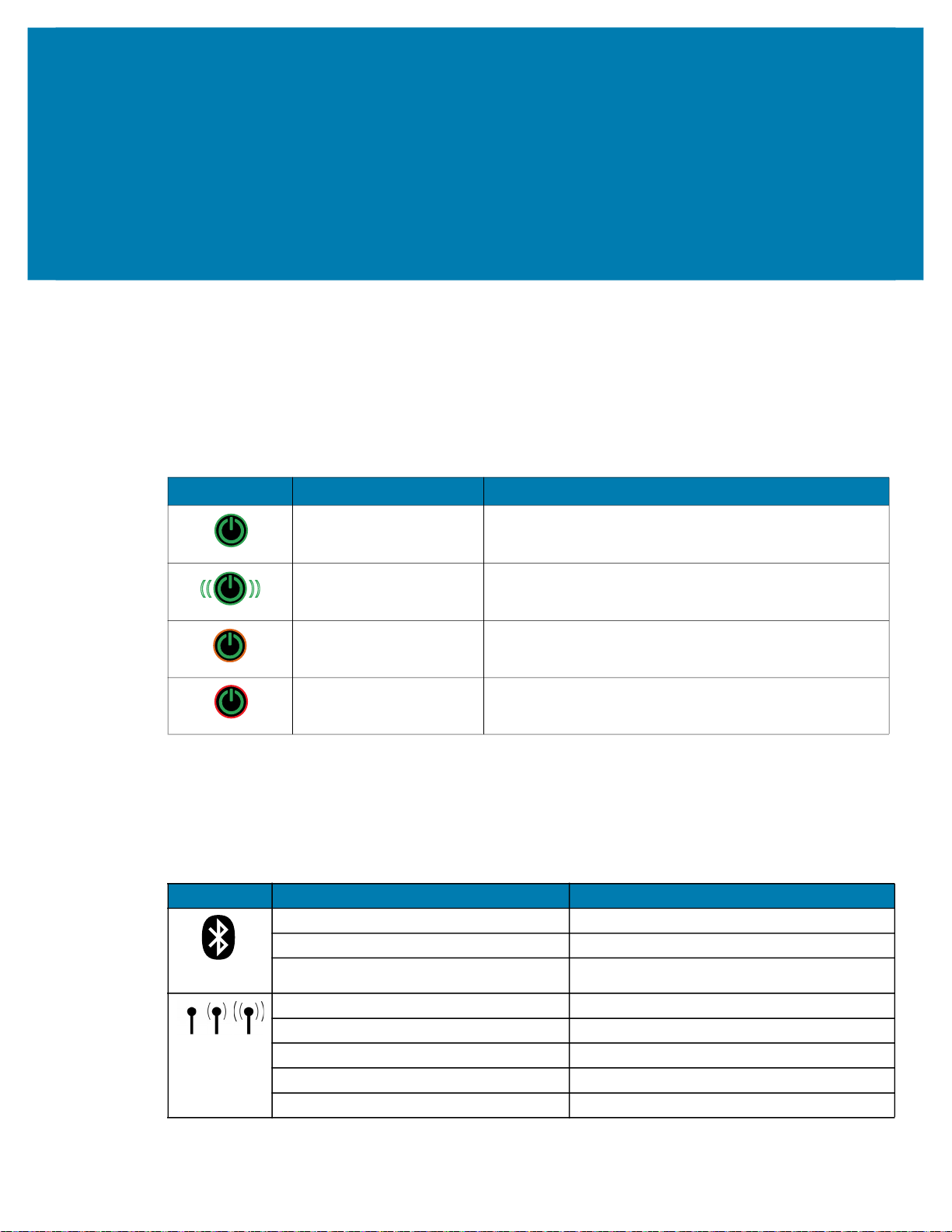
Troubleshooting
(( ))
Front Control Panel
If the printer is not functioning properly, refer to the table below to determine the state of the LED indicator
ring located around the Power button.
LED Indicator LED State Indication
Solid Green Charged Battery; Battery Eliminator in Use
Blinking Green Sleep Mode
Solid Amber Battery Charging
Solid Red Battery Fault
Printer Status Indicators
The printer’s control panel displays multiple icons which indicate the status of various printer functions.
Check the indicator status and then refer to the Troubleshooting topic referenced on the following pages to
resolve the problem.
Icon Status Indication
On Bluetooth link established
Grayed Out Inactive
Blinking Receiving printer data
Not Present No WLAN radio detected
Antenna Blinking Looking for AP
Antenna Blinking/1 Parenthesis Solid WLAN Associated/Attempting Authentication
Antenna and 2 Parentheses Solid WLAN Associated and Authenticated
Antenna and 2 Parentheses Blinking Receiving Data
51

Troubleshooting
DC
Icon Status Indication
4 Bars 802.11 Signal Strength >75%
3 Bars 802.11 Signal Strength </=75%
2 Bars 802.11 Signal Strength </= 50% but >25%
1 Bar 802.11 Signal Strength </= 25%
0 Bars No network detected
On Bluetooth link established
Grayed Out Inactive
Blinking Data processing in progress
Steady No data being received
Blinking Out of media
Steady Media present
Blinking Media cover open
4 Bars >80% charged
3 Bars 60%-80% charged
2 Bars 40%-60% charged
1 Bar 20%-40% charged
0 Bars Low Battery
On Battery Eliminator present
On
(Media Out icon Off)
On
(Media Out icon Off)
Troubleshooting Topics
No power
(Replaces Battery icons)
Printer in Segmentation Mode
Printer in Draft Mode
• Check that the battery is installed properly.
• Recharge or replace the battery as necessary.
• If using the battery eliminator to power the printer, ensure that it is connected properly to an active (ON)
source.
52

CAUTION: Always dispose of batteries properly. Refer to Battery Disposal on page 69 for more
information on proper battery disposal.
Media does not feed
• Be sure the media cover is closed and latched.
• Check the spindle holding media for any binding.
• Ensure that the label sensor is not blocked.
Poor or faded print
• Clean the printhead.
• Check the quality of media.
Partial or missing print
• Check the media alignment.
• Clean the print head.
Troubleshooting
• Ensure that the media cover is properly closed and latched.
Garbled print
• Replace the battery.
• Check the cable to the terminal.
• Establish RF Link and/or restore LAN association.
No print
• Replace the battery.
• Check the cable to the terminal.
• Establish an RF Link and/or restore LAN association.
• Check for an invalid label format or command structure. Place the printer in Communications
Diagnostic (Hex Dump) Mode to diagnose the problem.
Reduced battery charge life
• If the battery is more than 1 year old, short charge life may be due to normal aging.
• Check the battery health.
• Replace the battery.
Data icon flashing
• No action is needed. A flashing Data icon is normal while data is being received.
53

Troubleshooting
Media or Cover Open icons flashing
• Check to see if media is loaded and that the media cover is closed and securely latched.
Communication error
• Check the cable to computer or laptop, and if necessary, replace the cable.
Label binding
• Open the head release latch and media cover.
• Remove and reinstall the media.
Blank LCD screen
• Make sure the printer is turned on.
• Check to see if application is loaded or corrupted: If so, reload the program.
• Check the LED ring around the Power button to see if it is blinking green indicating the printer is in
sleep mode. Press Power or Select buttons to “wake up” the printer.
No NFC Connectivity
• Ensure that your smartphone is positioned 3 inches (7.62 cm) or closer to the Print Touch icon on the
side of the printer.
Troubleshooting Tests
Printing a Configuration Report
To print out a listing of the printer’s current configuration follow these steps:
1. Turn the printer off. Load the media compartment with journal media (media with no black bars printed
on the back).
2. Press and hold the Feed button.
3. While pressing the Feed button, press and release the Power button.
4. When printing starts, release the Feed button.
Refer to Figure 41 on page 55 for sample configuration reports.
54
Troubleshooting
XXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXX
Zebra Technologies
ZQ521R
Serial Number:
XXRBJ192300731
PCC:
ZQ52-BUW0300-00
Name:
XXRBJ192300731
Program:
OS: 7.0.0
PLD: 21 Rev. 1
PSPT: 10 Rev. 16
PMCU: Rev. 10
Firmware: V91.21.02ZP46528
Checksum: 91CB
Universal Serial Bus:
2.0 Full Speed Device
Vendor ID No: 0x0A5F
Product ID No: 0x016F
Manufacturer String: Zebra Tec
hnologies
Product String: ZTC ZQ521R-203
dpi CPCL
ID string: off
Bluetooth:
iOS: supported
Version: 6.0.1
Date: 12/05/2018
Baud: 115200
Device: Printer
Mode: Slave
Friendly Name: XXRBJ192300731
Minimum Security Mode: 3
Discoverable: off
Bluetooth Spec: 3.0/4.0
Enabled: on
Address: 48:A4:93:OF:44:C5
48A4930F44C5
Wireless:
Radio: 802.11 a/b/g/n/ac
Region: usa/canada
Country: usa/canada
Enabled: on
MAC Address: 48:a4:93:0f:44:c4
IP Address: 0.0.0.0
Netmask: 255.255.255.0
Gateway: 0.0.0.0
Operating Mode: infrastructure
International Mode: off
Preamble Length: long
Security: none
Stored ESSID:
Associated: no
DHCP: on
DHCP CID type: 1
DHCP CID: 48a4930f44c4
Power Save: on
Active Network Information:
Active Network: Unknown
IP Address: 0.0.0.0
Netmask:
255.255.255.0
Gateway: 0.0.0.0
TCP Port: 6101
Alternate TCP Port: 9100
TCP JSON Config Port: 9200
UDP Port: 6101
Remote Server:
TCP: on
UDP: on
LPD: on
DHCP: on
BOOTP: on
FTP: on
HTTP: on
SMTP: on
POP3: on
SNMP: on
MIRROR: off
UDP Discovery: on
Weblink:
DHCP CID type: 1
DHCP CID: 48a4930f44c4
Product support website:
http://zebra.com/zq510-info
Peripherals:
LCD: Installed
Power Management:
In-activity Timeout:36000 Secs
Low-battery Timeout:0 Secs
Remote (DTR) pwr-off:Disabled
Voltage :7.83
Low-bat Warning :8 %
Low-bat Shut-down :2 %
Power On Cycles :23
Battery Health :good
Battery Cycle Count:NA
Memory:
Flash :67108864 Bytes
RAM :8372224 Bytes
Label:
Width :832 dots, 104 mm
Height:65535 dots, 8191 mm
Sensors: (Adj)
Black Bar [DAC:120,Thr:70,Cur:1
]
Gap [DAC:130,Thr:50,Cur:96]
Temperature :26C (63)
Voltage :7.6V (255)
Resident Fonts:
Font Sizes Chars
--------- ----- -----
0 0- 6 20-FF
1 0 20-80
2 0- 1 20-59
4 0- 7 20-FF
5 0- 3 20-FF
6 0 20-44
7 0- 1 20-FF
File Directory:
File Size
--------------- ------- E:TT0003M_.TTF 169188
64360448 Bytes Free
Command Language:
CCL Key ‘!’[21]
ZPL Configuration Information:
Rewind.........Print Mode
Mark...........Media Type
10.0.............Darkness
+00.......Tear Off Adjust
2030.........Label Length
104mm.........Print Width
7Eh........Control Prefix
5Eh.........Format Prefix
2Ch.............Delimiter
00...........Top Position
No Motion..Media Power Up
Feed....Media Head Closed
00............Left Margin
832..........Dots per row
End ZPL Configuration
Print-head test: OK
End of report
Press FEED key to
enter DUMP mode
Figure 41 ZQ521 configuration report Example
Communications Diagnostics
If there is a problem transferring data between the computer and the printer, try putting the printer in the
Communications Diagnostics Mode (also referred to as the “DUMP” mode). The printer will print the ASCII
characters and their text representation (or the period ‘.’, if not a printable character) for any data received
from the host computer.
To enter Communications Diagnostics Mode:
1. Print a configuration report as described above.
2. At the end of the diagnostics report, the printer will print: “Press FEED key to enter DUMP mode”.
3. Press the FEED key. The printer will print: “Entering DUMP mode”.
NOTE: If the FEED key is not pressed within 3 seconds, the printer will print “DUMP mode not entered”
and will resume normal operation.
At this point, the printer is in DUMP mode and will print the ASCII hex codes of any data sent to it, and their
text representation (or “.” if not a printable character).
Additionally, a file with a “.dmp” extension containing the ASCII information will be created and stored in
the printer’s memory. It can be viewed, “cloned” or deleted using the Net Bridge application. (Refer to the
ZebraNet Bridge Enterprise documentation for more information.)
55

To terminate the Communications Diagnostics Mode and return the printer to normal operations:
1. Turn the printer OFF.
2. Wait 5 seconds.
3. Turn the printer ON.
Contacting Technical Support
If the printer fails to print the configuration report, or you encounter problems not covered in the
Troubleshooting Guide, contact Zebra Technical Support. To contact product support in your region, go to:
https://www.zebra.com/contact
You will need to supply the following information:
• Model number (e.g. ZQ511 and ZQ521)
• Unit serial number (Found on the large label on the back of the printer, also found in the configuration
report printout.)
• Product Configuration Code (PCC) (15 digit number found on the label on the back of the unit)
Troubleshooting
56

Specifications
NOTE: Printer specifications are subject to change without notice.
Printing Specifications
Parameter ZQ521 ZQ511
Print Width Up to 104 mm (4.09 in.) Up to 72 mm (2.83in.)
Print Speed Up to 127 mm (5 in.)/second @ 12% max density Same
76.2 mm (3 in.)/second @ 16% max density
(linerless)
Printhead Burn Line to
Tear Edge Distance
Printhead Life 600K inches of paper feed MTBF of output at 18%
Print Density 203 dots/in. or better Same
Front Side: 4.8 mm (0.18 in.) +/- 0.5 mm (0.02 in.) Same
Reverse Side (Linered): 6.2 mm (0.24 in.) +/- 0.5 mm
(0.02 in.)
density at 20°C when using virgin media.
Same
Memory and Communications Specifications
Parameter ZQ511 and ZQ521 Printers
Flash Memory 512 MB
RAM Memory 512 MB
Standard
Communications
Wireless
Communication
Options
a. Memory configuration on your printer may be found by referring to the Printing a Configuration Report
on page 54
USB (Micro AB on the go)
1. Standalone Bluetooth Classic and BLE Radio
2. 802.11AC/BT/BLE Combo Radio
a
a
57

Label Specifications
Parameter ZQ521 ZQ511
Media Width 51 mm (2.0 in.) to
Media Length 12.5 mm
Black Bar Sensor to
Printhead Burnline
Distance
Media Thickness
(except Tag)
Max Tag Thickness 2.3 to 5.5 mils
Max Label Roll Outer
Diameter
Inner Core
Diameters**
Black Mark Location The reflective media black marks
Black Mark
Dimensions
Specifications
35 mm (1.37 in.) to
113 mm (4.45 in.) +1 mm
(0.5) minimum
15.87 mm (0.62 in.) +/-
0.635 mm (0.025 in.)
2.1 to 6.5 mils (0.053 to 0.1651 mm) Linerless: 2.1 to 6.5 mils (0.053 to
(0.05842 to 0.1397 mm)
57 mm (2.24 in.) 51 mm (2.0 in.)
19 mm (0.75 in.) standard
12.5 mm (0.5 in.) optional*
should be centered on media roll
Minimum mark width: 12,7 mm (0.5
in.) perpendicular to inside edge of
media, centered within the width of
the roll.
Mark length: 2.4-11 mm (0.09 to
0.43 in.) parallel to inside edge of
media.)
80 mm (3.15 in.) +1 mm
Same
Same
0.1651 mm)
Linered: 2.3 to 6.5 mils (0.05842to
0.1651 mm)
Same
Same
Same
Same
NOTE: Customers who want to use the 12.5 mm (0.5 in.) core size will be required to uninstall the media
disks and install new media support disks.
58

Specifications
CPCL Font and Bar Code Specifications and Commands
Item Available Options
Standard Fonts 25 bit-mapped fonts; 1 scalable font (CG Trimvirate Bold Condensed*)
*Contains UFST from Agfa Monotype Corporation Downloadable
optional bit-mapped and scalable fonts via Net Bridge software.
International Character Sets Chinese 16 x 16 (traditional)
Chinese 16 x 16 (simplified)
Chinese 24 x 24 (simplified)
Japanese 16 x 16
Japanese 24 x 24
Linear Bar Codes Aztec (AZTEC)
Codabar (CODABAR, CODABAR 16)
UCC/EAN 128 (UCCEAN128)
Code 39 (39, 39C, F39, F39C)
Code 93 (93)
Code 128 (128)
EAN 8, 13, 2 and 5 digit extensions (EAN8, EAN82, EAN85, EAN13,
EAN132, and EAN135)
EAN-8 Composite (EAN8)
EAN-13 Composite (EAN13)
Plessey (PLESSEY)
lnterleaved 2 of 5 (I2OF5)
MSI (MSI, MSI10, MSI1110)
FIM/POSTNET (FIM)
TLC39 (TLC39)
UCC Composite A/B/C (128(Auto))
UPCA, 2 and 5 digit extensions (UPCA2 and UPCA5)
UPCA Composite (UPCA)
UPCE, 2 and 5 digit extensions (UPCE2 and UPCE5)
UPCE Composite (UPCE)
MaxiCode (MAXICODE)
PDF 417 (PDF-417)
Datamatrix (using ZPL emulation) (DATAMATRIX)
QR Code (QR)
2-D Bar Codes RSS-14 (RSS-Subtype 1)
RSS-14 Truncated (RSS-Subtype 2)
RSS-14 Stacked (RSS-Subtype 3)
RSS-14 Stacked Omnidirectional (RSS-Subtype 4)
RSS Limited (RSS-Subtype 5)
RSS Expanded (RSS-Subtype 6)
Rotation Angles 0°, 90°, 180°, and 270°
59

Specifications
ZPL Font and Bar Code Specifications and Commands
Item Available Options
Standard Fonts 15 bit-mapped fonts; 1 scalable font (CG Trimvirate Bold Condensed)
Downloadable optional bit-mapped and scalable fonts via Net Bridge
software.
International Font Options Zebra offers font kits covering multiple languages including Simplified
and Traditional Chinese, Japanese, Korean, Hebrew/Arabic, and
others.
Linear Bar Codes
2-D Bar Codes
Rotation Angles 0°, 90°, 180°, and 270°
Barcode (CPCL Command)
Aztec (^B0)
Codabar (^BK)
Codablock (^BB)
Code 11 (^B1)
Code 39 (^B3)
Code 49 (B4)
Code 93 (^BA)
Code 128 (^BC)
DataMatrix (^BX)
EAN-8 (^B8)
EAN-13 (^BE)
GS1 DataBar Omnidirectional (^BR)
Industrial 2 of 5 (^BI)
lnterleaved 2 of 5 (^B2)
ISBT-128 (^BC)
LOGMARS (^BL)
Micro-PDF417 (^BF)
MSI (^BM)
PDF-417 (^B7)
Planet Code (^B5)
Plessey (^BP)
Postnet (^BZ)
Standard 2 of 5 (^BJ)
TLC39 (^BT)
UPC/EAN extensions (^BS)
UPC-A (^BU)
UPC-E (^B9)
Maxi Code (^BD)
QR Code (^BQ)
60
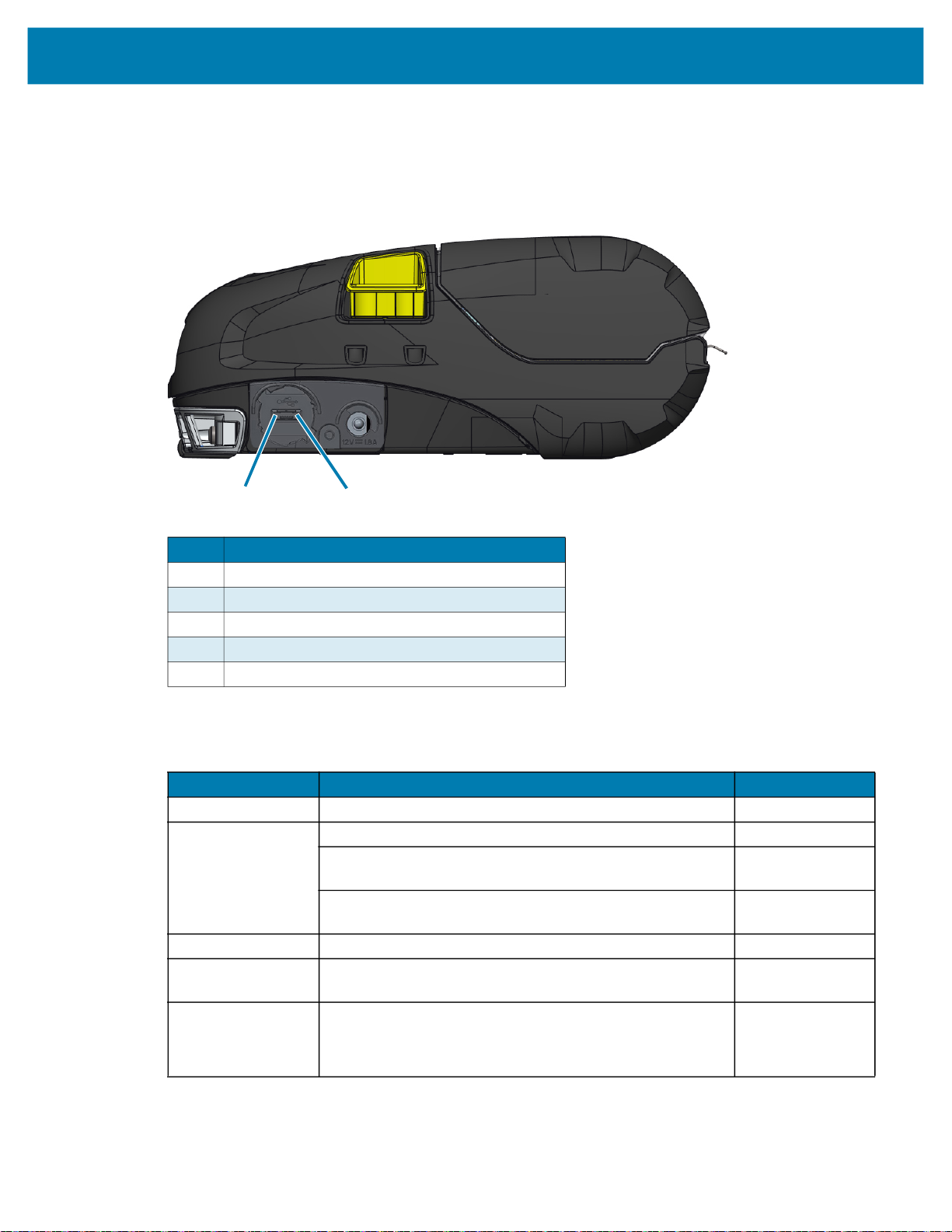
Communication Port
USB
Figure 40 USB Port
Specifications
Pin 5
Pin # Signal Name
1 VBUS
2 DM(-)
3 DP(+)
4 ID
5 GND
Pin 1
Physical, Environmental and Electrical Specifications
Parameter ZQ521 ZQ511
Weight w/ battery 1.6 lbs. (0.75 kg) 1.35 lbs. (0.61 kg)
Temperature Operating: -20°C to 55°C (-4°F to 131°F) Same
Storage: -30°C to 66°C
(-22°F to 150.8°F)
Charging: 0°C to 40°C
(32°F to 104°F)
Relative Humidity Operating/Storage: 10% to 90% non-condensing Same
Battery Smart Battery (2 or 4 cell) Lithium-Ion, 7.4VDC (nominal);
2.45AHr min.
Intrusion
Protection (IP)
Rating
IP54 (without soft case)
IP65 (with hard case)
Same
Same
Same
Same
61

Figure 41 ZQ511 Dimensions
Specifications
Height
Height - 61 mm (2.40 in.)
Width - 120 mm (4.7 in.)
Length - 150 mm (5.9 in.)
Figure 42 ZQ521 Dimensions
Width
Length
Height
Height - 67 mm (2.6 in.)
Width - 155 mm (6.1 in.)
Length - 150 mm (5.9 in.)
62
Width
Length

Specifications
Figure 43 Mounting Hole Dimensions
ZQ511
54.0 mm
(2.12 in.)
NOTE: Use two M4 x 8.0 mm screws in the indicated positions
ZQ521
63

Accessories
For a complete list of printer accessories, go to www.zebra.com/manuals, search for the Mobile Printer
Accessories Guide, and go to the ZQ500 Series product page for a complete list of accessories. Or scan
the following QR code with a mobile device to access the guide.
Figure 44 Accessories Guide QR Code
Specifications
64

Miscellaneous
Serial Number and PCC Number Locations
Figure 45 ZQ511 (Bottom View)
Serial #
Barcode
IMPORTANT: Due to compliance and customs restraints, an integrator may not be able to ship a printer
purchased in one country to another country based on the limitations imposed by regional SKUs. The
country code identified in the printer SKU determines the area of the world in which the printer can be
used.
PCC
Barcode
65
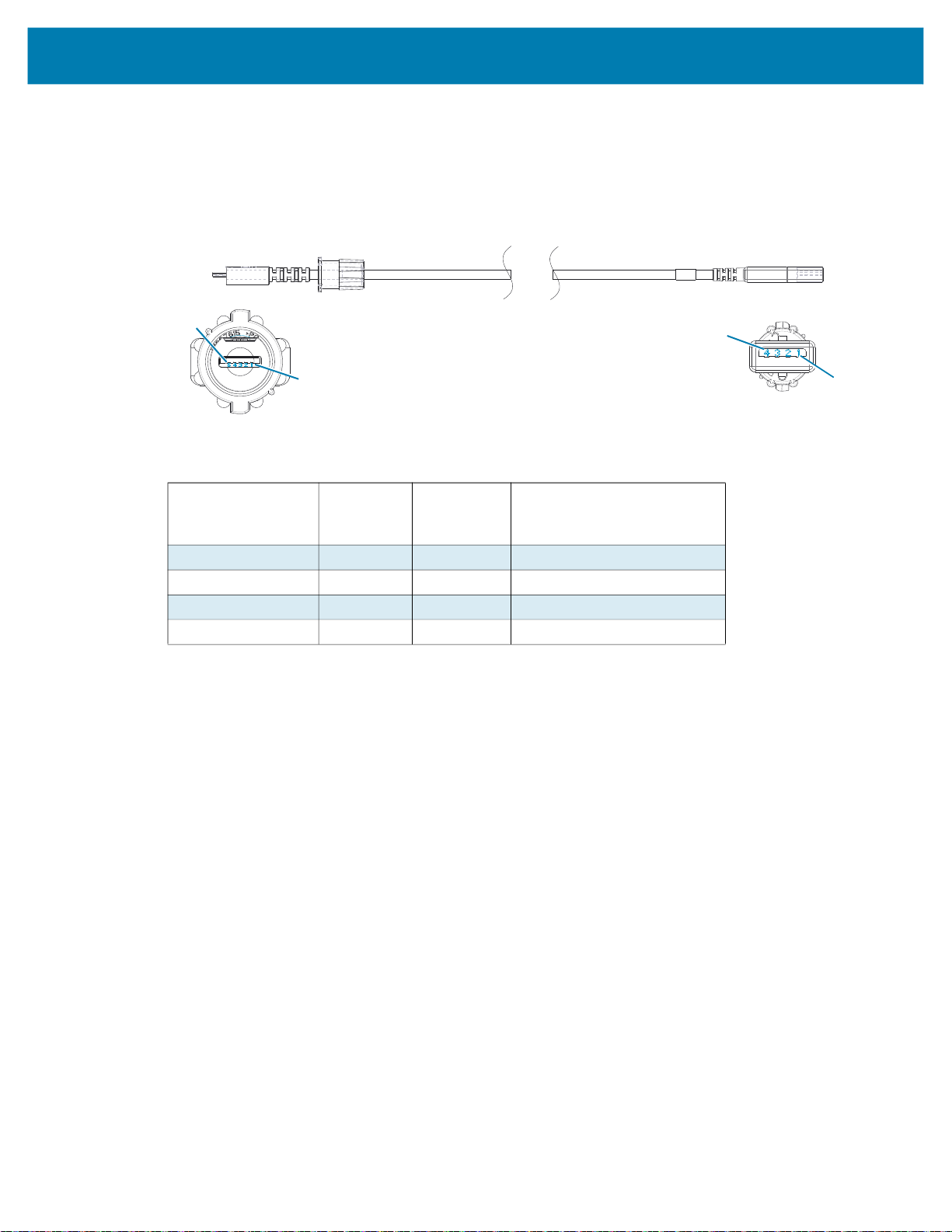
Cables
USB Cables
Miscellaneous
Figure 46 Micro,USB-A to USB-A
Connector B
Pin 5
CONNECTOR B
5 POSITION USB
MICRO TYPE A
PIN 1 VBUS RED PIN 1
PIN 2 USB D- WHITE PIN 2
PIN 3 USB D+ GREEN PIN 3
PIN 5 GROUND BLACK PIN 4
Pin 1
SIGNAL COLOR
Connector A
Pin 4
Pin 1
CONNECTOR A
4 POSITION USB
TYPE A RECEPTACLE
66

Miscellaneous
Figure 47 Micro USB-B to USB-A Plug, 1.8m/3.5m
Connector B
Pin 5
Pin 1
CONNECTOR B
5 POSITION USB
MICRO TYPE B
PIN 1 VBUS RED PIN 1
PIN 2 USB D- WHITE PIN 2
PIN 3 USB D+ GREEN PIN 3
PIN 5 GROUND BLACK PIN 4
NOTE: Visit the Zebra website at: www.zebra.com/accessories
numbers for all Zebra mobile printers.
SIGNAL COLOR
CONNECTOR A
4 POSITION USB
TYPE A PLUG
Connector A
Pin 4
Pin 1
for a listing of interface cables and part
67

Media Supplies
To insure maximum printer life and consistent print quality and performance for your individual application,
it is recommended that only media produced by Zebra be used.
Advantages include:
• Consistent quality and reliability of media products.
• Large range of stocked and standard formats.
• In-house custom format design service.
• Large production capacity which services the needs of many large and small media consumers
including major retail chains world wide.
• Media products that meet or exceed industry standards.
Miscellaneous
NOTE: For more information go the Zebra website (www.zebra.com
Maintenance Supplies
In addition to using quality media provided by Zebra, it is recommended that the printer be cleaned as
prescribed in the maintenance section. The following item is available for this purpose:
• Cleaning Pen (12 pack): p/n 105950-035
Serial and PCC Number Locations for ZQ511 & ZQ521 Printers
) and select the Products tab.
68

Battery Disposal
The EPA certified RBRC® Battery Recycling Seal on the Lithium-Ion (Li-Ion) battery supplied with your
printer indicates Zebra Technologies Corporation is voluntarily participating in an industry program to
collect and recycle these batteries at the end of their useful life, when taken out of service in the United
States or Canada. The RBRC program provides a convenient alternative to placing used Li-Ion batteries
into the trash or the municipal waste stream, which may be illegal in your area.
IMPORTANT: When the battery is depleted, insulate the terminals with tape before disposal.
Please call 1-800-8-BATTERY for information on Li-Ion battery recycling and disposal bans/restrictions in
your area.
Zebra Technologies Corporation’s involvement in this program is part of our commitment to preserving our
environment and conserving our natural resources.
Miscellaneous
Outside North America, please follow local battery recycling guidelines.
Product Disposal
The majority of this printer’s components are recyclable. Do not dispose of any printer components in
unsorted municipal waste. Please dispose of the battery according to your local regulations, and recycle
the other printer components according to your local standards.
For more information, please see our web site at: http://www.zebra.com/environment.
69

Alert Messages
The printers display the following alert messages to inform the user of various fault conditions that might
occur.
HeadOverTemp PRINT HEAD OVERTEMP PRINTING HALTED
HeadMaintenanceNeeded HEAD MAINTEN. NEEDED PRINTING HALTED
BatteryHelathReplace BATTERY DIMINISHED CONSIDER REPLACING
BatteryHealthNearDeath WARNING - BATTERY IS PAST USEFUL LIFE
BatteryHealthShutdown BATTERY DIMINISHED SHUTTING DOWN
BatteryAuthenticationFail BATTERY FAILED REPLACE BATTERY
BatteryOverTemp CHARGING TEMP FAULT MUST BE 0-40°C
BatteryUnderTemp CHARGING TEMP FAULT MUST BE 0-40°C
BatteryChargeFault CHARGING FAULT REPLACE BATTERY
DownloadingFirmware DOWNLOADING FIRMWARE
Miscellaneous
Message Text Line One Text Line Two
BadFirmwareDownload DOWNLOAD FAILED PLEASE REBOOT
WritingFirmwareToFlash FIRMWARE WRITING TO FLASH
Mirroring LOOKING FOR UPDATES PLEASE WAIT...
MirroringApplication RECEIVING FIRMWARE DO NOT POWER OFF!
MirroringCommands MIRRORING COMMANDS
MirroringFeedback SENDING FEEDBACK PLEASE WAIT...
MirrorProcessingFinished MIRROR PROCESSING FINISHED
WlanInvalidChannels WIRELESS ERROR INVALID CHANNEL
WlanInvalidSecurityMode WIRELESS ERROR INVALID SECURITY
PauseRequest PRINTER PAUSED
CancelAll ALL JOBS CLEARED
CancelOne ONE JOB CLEARED
OutOfMemoryStoringGraphic OUT OF MEMORY STORING GRAPHIC
OutOfMemoryStoringFont OUT OF MEMORY STORING FONT
OutOfMemoryStoringFormat OUT OF MEMORY STORING FORMAT
OutOfMemoryStoringBitmap OUT OF MEMORY STORING BITMAP
AckAlertTooManyUsbHostDevices TOO MANY MASS STORAGE DEVICES
AckAlertUnsupportedUsbHostDevice UNSUPPORTED USB HOST DEVICE
AckAlertUnsupportedUsbHost-
Filesystem
UNSUPPORTED USB HOST FILESYSTEM
70

www.zebra.com
 Loading...
Loading...