Page 1

What is an electrocardiogram?
An electrocardiogram—often abbreviated, as EKG or ECG—is a test
that measures the electrical activity of the heartbeat. With each beat,
an electrical impulse (or “wave”) travels through the heart. This wave
causes the muscle to squeeze and pump blood from the heart.
Why is it done?
An ECG gives two major kinds of information. First, by measuring time
intervals on the ECG, a doctor can determine how long the electrical
wave takes to pass through the heart. Finding out how long the wave
takes to travel from one part of the heart to the next shows if the
electrical activity is normal or slow, fast or irregular. Second, by
measuring the amount of electrical activity passing through the heart
muscle, a cardiologist may be able to find out if parts of the heart are
too large or are overworked.
CARDIOPERFECT ECG PATIENT INFORMATION
How is it done?
Several sensors called electrodes will pick up the electrical activity in the
heart. You will be asked to lie down, and technicians will put several
patches (electr
odes) on the chest, arms and legs. Usually the electr
odes
are soft and don’
t cause any discomfor
t when they ar
e put on or taken of
f
by the technician. The electr
odes are connected to wires called leads,
which are connected to the ECG machine. The electrical activity of the
heart is then recorded on a moving strip of paper in the ECG machine.
During the ECG r
ecor
ding, you should lie quietly for 10-20 seconds,
because the electr
ocardiograph will detect any muscle or body movement.
Does it hurt?
No. Ther
e is no pain or risk associated with having an electr
ocar
diogram.
Is it harmful?
No. The machine only r
ecords the ECG.
Condition Causes Actions
Lead-off information is displayed on the screen.
OR
O
ne or more leads prints as a square wave:
• Electrode contact may be poor.
• A lead may be loose.
• A lead is disconnected from patient.
• Reattach the lead.
• Replace the electrode.
• Verify that the electrode area has been properly
p
repared: shaved, cleaned with alcohol or acetone,
allowed to dry.
• Verify that electrodes have been properly stored
a
nd handled.
Wandering baseline (an upward and
downward fluctuation of the waveforms):
• Electrodes that are dirty, corroded, loose, or
positioned on a bony area.
• Insufficient or dried electrode gel.
• Oily skin or body lotions.
• Rising and falling of chest during rapid or
apprehensive breathing.
• Patient moved.
• Clean skin with alcohol or acetone.
• Reposition or replace electrodes.
• Help patient relax.
• If wandering baseline persists, turn the
baseline filter on.
• Ask patient to remain still and relaxed.
Muscle tremor interference (random, irregular
voltage superimposed on the waveforms). May
resemble or coincide with AC interference:
• Patient is uncomfortable, tense, nervous.
• Patient is cold and shivering.
• Exam bed is too narrow or short to
comfortably support arms and legs.
• Arm or leg electrode straps are too tight.
• Help patient get comfortable.
• Check all electrode contacts.
• If interference persists, turn the muscle-tremor
filter on. If interference still persists, the problem
is probably electrical in nature. See the following
suggestions for reducing AC interference.
AC interference (even-peaked, regular voltage
superimposed on the waveforms).
May resemble or coincide with muscle tremor
interfer
ence:
• Electrodes that are dirty, corroded, loose, or
positioned on a bony area.
•
Insuf
ficient or dried electr
ode gel.
• Patient or technician touching an electrode
during recording.
• Patient touching any metal parts of an exam
table or bed.
• Broken lead wire, patient cable, or power cord.
•
Electrical devices in the immediate area,
lighting, concealed wiring in walls or floors.
• Improperly grounded electrical outlet.
•
Incorr
ect AC filter fr
equency setting or
AC filter is turned off.
• Verify that the patient is not touching any metal.
• Verify that the AC power cable is not touching the
patient lead cable.
• Verify that the proper AC filter is selected.
• If interference still persists, the noise may be caused
by other equipment in the room or by poorly grounded
power lines. T
r
y moving to another r
oom.
LEAD QUALITY PROBLEMS
4341 State Str
eet Road, PO Box 220, Skaneateles Falls, NY 13153-0220 USA
(p) 800.535.6663 (f) 315.685.2174 www.welchallyn.com
© 2007 W
elch Allyn REF 101910 Mat. Number: 708550, Ver: B
CARDIOPERFECT
RESTING ECG
QUICK START GUIDE
MC3817 CardioPerfect ECG QSG 7/23/07 4:49 PM Page 1
Page 2
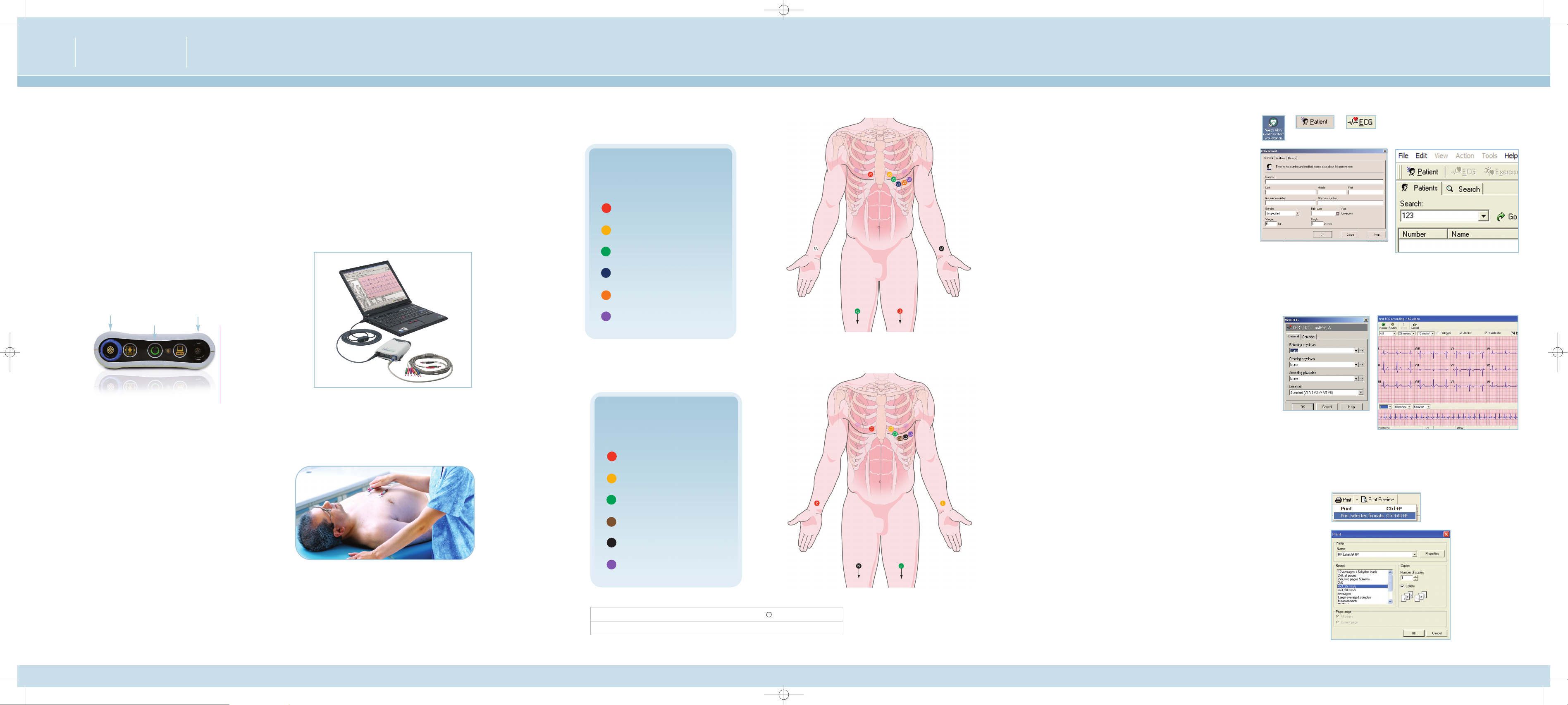
1 Install Software and USB Drivers
2 Connect your Recorder
• Connect the PC interface cable (ProLink) to a USB port on your computer.
• Connect the other end to the black connector on the recorder.
• Connect the patient cable to the blue connector on the recorder.
3 Pr
epar
e Y
our Patient
The quality of an ECG is dependent on the preparation and the resistance
between the skin and the electr
ode. To ensure a good quality ECG and
minimize the skin/electrode resistance, remember the following points:
• Ensure that the patient is warm and relaxed.
• Shave electrode area before cleaning.
• Thoroughly clean the area with alcohol.
• Let dry prior to applying electr
odes.
4 Connect Electrodes
5 Create a New Patient
• O
pen the CardioPerfect Workstation Software.
• Select Patient.
• F
ill in Patient Card.
• Click on the ECG Icon.
• To select a patient from the database:
1. In the Search box, type parts of the patient
name or number.
2. Click the Go button.
3. Click on the patient for whom you want to
record the test.
7 Review Data and Print Report
• Y
ou can choose from multiple ECG r
eport templates.
• If automatic printing is checked in the ECG Print settings,
the report will print now.
• If you did not select Automatic printing in the Settings,
click on the down ar
r
ow next to the Print icon and choose
“Print Selected For
mats” to initiate printing.
• If you just want to print one type of report, click on the
Print icon, and select the desir
ed report page.
This Quick Start Guide is intended for use with CardioPerfect Workstation
v
ersion 1.6.0 or higher. For complete directions for use and warnings, please
consult your user manual located on the software CD.
AHA Electrode Placement
R
A and LA electrodes should be placed on
the wrists.
RL and LL electrodes should be placed a
few inches above the ankle.
V1
Fourth intercostal space at
the right border of the sternum
V2 Fourth intercostal space at
the left bor
der of the sternum
V3
Midway between locations
V2 and V4
V4 At the mid-clavicular line in
the fifth intercostal space
V5 At the anterior axillary line on
the same horizontal level as V4
V6 At the mid-axillary line on the
same horizontal level as V4 and V5
6 Record a Test
Select physician names and lead configuration, and click OK.
Auto ECG
• Click the Record button to start a 12-lead resting ECG.
Rhythm/Manual ECG
• Click the Rhythm button to start a recording of up to 300 seconds.
• Click Event button to mark areas of interest.
• Click the Rhythm button a second time to stop the rhythm recording.
• Click the Cancel button to cancel.
Note: The pretrigger option helps catch events by already saving
5 seconds of traces befor
e you star
t the r
ecording.The notch filter
r
emoves noise that is caused by AC power interfer
ence.
C
ARDIOPERFECT
™
PC-BASED ECG
QUICK START GUIDE
Patient Cable Connection
PC Interface Connection
On/Off Switch
AAMI
IEC
V1
l
C1
l
V2
l
C2
l
V3
l
C3
l
V4
l
C4
l
V5
l
C5
l
V6
l
C6
l
RA
ll
R
l
LA
l
L
l
RL
l
N
l
LL
l
F
l
IEC Electrode Placement
R and L electr
odes should be placed on
the wrists.
N and LF electrodes should be placed a
few inches above the ankle.
C1
Four
th inter
costal space at
the right bor
der of the ster
num
C2 Fourth intercostal space at
the left border of the sternum
C3
Midway between locations
C2 and C4
C4 At the mid-clavicular line in
the fifth intercostal space
C5 At the anterior axillary line on
the same horizontal level as C4
C6 At the mid-axillary line on the
same horizontal level as C4 and C5
MC3817 CardioPerfect ECG QSG 7/23/07 4:50 PM Page 4
 Loading...
Loading...