Page 1

Administrator and Provisioning Manual
VSP600
VSP601
DECT SIP Cordless Base Station and Handset
Rev. 3 05/14
Page 2

VSP600/VSP601 Administrator and Provisioning Manual
Congratulations on your purchase of this VTech product. Before using this VTech
product, please read Important Safety Information on page 92 of this manual. Please
horoughly read this manual for all the feature operation s and troubleshooting
t
information necessary to install and operate your new VTech product. You can also
visit our website at businessphones.vtech.com or call 1 (888) 370-2006.
Model number: VSP600/VSP601
Type: DECT SIP-cordless base station and handset
Serial number: ________________________________
Purchase date: ________________________________
Place of purchase: _____________________________
Both the model and serial numbers of your VTech product can be found on th e
bottom of the base station and inside the battery compartment of the handset.
Save your sales receipt and original packaging in case it is necessary to return your
product for warranty service.
2
Page 3

VSP600/VSP601 Administrator and Provisioning Manual
Table of contents
Introduction.................................................................................................. 5
Audience ................................................................................................... 5
Related documents ..................................................................................... 5
About the base station................................................................................. 5
Network Requirements.................................................................................... 7
Configuring the Base Station ........................................................................... 8
Using the WebUI............................................................................................ 9
Saving Your Settings..................................................................................10
WebUI: Status..............................................................................................11
System Status...........................................................................................11
Handset Status..........................................................................................12
WebUI: System ............................................................................................13
SIP Account Management ...........................................................................13
Dial Plan...................................................................................................15
Call Settings .............................................................................................22
Preferences...............................................................................................24
Signaling Settings......................................................................................25
Handset Settings .......................................................................................26
Account Assignments..............................................................................26
Handset Name .......................................................................................27
WebUI: Network...........................................................................................28
Basic Network Settings...............................................................................28
Advanced Network Settings.........................................................................29
WebUI: Contacts...........................................................................................31
Base Directory...........................................................................................31
Directory Import/Export ..........................................................................34
Blacklist ...................................................................................................35
Blacklist Import/Export............................................................................37
WebUI: Servicing..........................................................................................38
Time and Date ..........................................................................................38
Firmware Upgrade .....................................................................................41
Provisioning..............................................................................................43
Security ...................................................................................................47
Certificates ...............................................................................................50
System Logs.............................................................................................51
Provisioning Using Configuration Files ..............................................................53
Resynchronization—Configuration File Checking .............................................53
The Provisioning Process.............................................................................53
Base Station Restart ..................................................................................54
Configuration File Types..............................................................................55
Data Files.................................................................................................55
Configuration File Guide..............................................................................56
Guidelines for the MAC-Specific Configuration File.......................................56
Securing Configuration Files with AES Encryption ........................................56
Troubleshooting............................................................................................58
Specifications...............................................................................................59
Appendix A: Configuration File Settings ............................................................60
“sip_account” Module: SIP Account Settings..................................................60
General Configuration File Settings ...........................................................60
MAC-Specific Configuration File Settings ....................................................69
3 Table of contents
Page 4

VSP600/VSP601 Administrator and Provisioning Manual
“network” Module: Net
General Configuration File Settings ...........................................................71
MAC-Specific Configuration File Settings ....................................................73
“provisioning” Module: Provisioning Settings..................................................75
“time_date” Module: Time and Date Settings.................................................79
“log” Module: Log Settings..........................................................................83
“web” Module: Web Settings .......................................................................84
“user_pref” Module: User Preference Settings................................................85
“call_settings” Module: Call Settings.............................................................86
“file” Module: Imported File Settings ............................................................88
General Configuration File Settings ...........................................................88
MAC-Specific Configuration File Settings ....................................................89
“profile” Module: Password Settings .............................................................90
General Configuration File Settings ...........................................................90
MAC-Specific Configuration File Settings ....................................................90
Maintenance.................................................................................................91
Important Safety Information.........................................................................92
Safety Information.....................................................................................92
Industry Canada...........................................................................................93
FCC part 15..................................................................................................94
GPL License Information ................................................................................95
work Settings ............................................................71
4 Table of contents
Page 5

VSP600/VSP601 Administrator and Provisioning Manual
Introduction
This administrator and provisioning guide contains detailed instru ctions for
configuring the VSP600 DECT SIP cordless base station and VSP601 cordless
handset. Please read this guide before attempting to configure the devices.
Audience
This guide is written for installers and system administrators. It assumes that you
are familiar with networks and VoIP, both in theory and in practice. This guide also
assumes that you have ordered your IP PBX equipment or service and selected which
PBX features you want to implement. This guide references specific IP PBX
equipment or services only for features or settings that have been designed for a
specific service. Please consult your equipment or service provider for recommended
switches, routers, and firewall and NAT traversal settings, and so on.
As the VSP600 base station becomes certified for IP PBX equipment or services,
VTech may make interop guides available for those specific services. The interop
guides will recommend second-party devices and settings, along with base-stationspecific configurations for optimal performance with those services.
Related documents
The VSP600 DECT SIP Cordless Base Station Quick Start Guide contains a quick
reference guide to the base station and handset external features and brief
instructions on connecting the base station to a working IP PBX system and
registering a handset.
The VSP600/VSP601 User Guide contains a quick reference guide, full installation
instructions, instructions for making and receiving calls, and a guide to all userconfigurable settings.
The documents are available from our website at businessphones.vtech.com.
About the base station
The VTech VSP600 base station is designed to work with popular SIP telephone (IP
PBX) equipment and services. Once you have ordered and configured your SIP
equipment or service, the base station and DECT cordless handsets enable you to
make and receive calls as you would with any other business phone.
The VSP600 base station features include:
Registration of up to 6 DECT cordless handsets
Up to 6 SIP account registrations
Up to 4 active SIP sessions (per account)
Power over Ethernet
Handset locator
DECT cordless handset features include:
Backlit display
Speakerphone, hold, intercom and mute capability
Corded headset jack
3-way conferencing
200-entry call history
5 Introduction
Page 6

VSP600/VSP601 Administrator and Provisioning Manual
You can configure the base station using a browser-based interface called the
WebUI, or an automatic provisioning process (see Provisioning Using Configuration
Files on pag
is connected to the same Local Area Network. The WebUI resides on the base
that
station and may get updated with firmware updates.
e 53). The WebUI enables you to configure the base station using a PC
6 Introduction
Page 7

VSP600/VSP601 Administrator and Provisioning Manual
Network Requirements
A switched network topology is recommended for your LAN (using standard 10/100
Ethernet switches that carry traffic at a nominal rate of 100 Mbit/s).
The office LAN infrastructure should use Cat.-5/Cat.-5e cable.
The base station requires a wired connection to the LAN. However, wireless
connections to other devices (such as laptops) in your office will not impede
performance.
A Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) server is recommended and must be
on the same subnet as the base station so that an IP address can be auto-assigned.
In most cases, your network router will have a DHCP server. By default, the base
station has DHCP enabled for automatic IP address assignment.
NOTE: Some DHCP servers have default settings that limit the number of network IP
addresses assigned to devices on the network. You should log in to your server to
confirm that the IP range is sufficient.
If no DHCP server is present, you can assign a static IP to the base station. You can
assign a static IP address using the WebUI. See Basic Network Settings on page 28.
do not have a DHCP server or do not manually assign a static IP, you will not
If you
be able to access the WebUI and/or enable automatic time updates from an NTP
server.
A DNS server is recommended to resolve the path to the Internet and to a server for
firmware and configuration updates. If necessary, the system administrator can also
download upgrade files and use the WebUI to update the base station firmware
and/or configuration settings manually.
7 Network Requirements
Page 8

VSP600/VSP601 Administrator and Provisioning Manual
Configuring the Base Station
You can configure the base station using one of two methods:
The Web User Interface, or WebUI, which you access using your Internet
browser. See Using the WebUI on page 9. The browser-based interface is easy
to navigate
WebUI has every setting required for configuring the base station and
handsets. You can enter service provider account settings on the WebUI, assign
accounts to handsets, and set up provisioning, which will allow you to
automatically and remotely update the base station after initial configuration.
Provisioning using configuration files. Working with configuration files allows
you to configure the base station at regular intervals. There are several
methods available to enable the base station to locate and upload a
configuration file. For example, you can enable the base station, when it starts
up or reboots, to check for the presence of a configuration file on a provisioning
server. If the configuration file is new or has been modified in any way, the
base station automatically downloads the file and applies the new settings. For
more information, see Provisioning Using Configuration Files on page 53.
and best-suited to configuring a wide variety of settings. The
Most o
handset menus allow users to customize the screen appearance, sounds, and
manage calls. For more information, see the VSP600/VSP601 User Guide.
f the settings accessible on the handset are most useful for end users. The
8 Configuring the Base Station
Page 9

VSP600/VSP601 Administrator and Provisioning Manual
Using the WebUI
The Web User Interface (WebUI) resides on the base station. You can access it using
an Internet browser. After you log in to the WebUI, you can configure the base
station and handsets on the following pages:
System
o SIP Account Management
o Call settings
o User Preferences
o Signaling Settings
o Handset Settings
Network
o Basic Network Settings
o Advanced Network Settings
Contacts
o Base Directory
o Blacklist
Servicing
o Reboot
o Time and Date
o Firmware Upgrade
o Provisioning
o Security
o Certificates
o System Logs
The WebUI also has a System Status page, where you can view network status and
general information about the base station and handsets. Some of the information on
the status page is also available on the Status menu available on the handset.
To access the WebUI:
1. Ensure that your computer is connected to the same network as the base station.
2. Find the IP address of the base station:
a. On a handset, press MENU.
b. Press to highlight Status, and then press SELECT.
c. With Network highlighted, press SELECT.
The Network status screen appears.
d. On the Network status screen, note the IP Address.
Network
IP Address:
10.88.51.133
DHCP:
Enabled
BACK OK
9 Using the WebUI
Page 10

VSP600/VSP601 Administrator and Provisioning Manual
3. On your computer, open an Internet browser. (Depending on your browser, some
of the pages presented here may look different and have different controls.
Ensure that you are running the latest update of your preferred browser.)
4. Type the IP address in the browser address bar and press ENTER on your
computer keyboard.
The browser displays a window asking for your user name and password.
5. For the user name, enter admin. For the password, enter the default password,
admin. You can change the password later on the Servicing > Security page.
6. Click OK.
The WebUI appears.
Click topics from the navigation bar along the top of the WebUI, and then click links
to individual pages along the left. You view and chan ge settings in two different
types of fields: drop-down lists and entry fields into which you type information. For
your security, the WebUI times out after 10 minutes, so if it is idle for that time, you
must log in again.
The remaining procedures in this section assume that you are already l ogged into
the WebUI.
NOTE: The settings tables in this section contain settings that appear in the WebUI
along with links to their equivalent settings in the configuration file template. You
can use the configuration file template to create custom configuration files.
Configuration files can be hosted on a provisioning server and used for automatically
configuring base stations. For more information, see Provisioning Using Configuration
Files on pag
e 53.
Saving Your Settings
Each WebUI settings page has a button. Click to save any changes
you have made on the page. During a configuration session, click
move on to the next WebUI page.
before you
10 Using the WebUI
Page 11

VSP600/VSP601 Administrator and Provisioning Manual
WebUI: Status
On the Status pages, you can view network status and general information about
the base station and handsets. Some of the information on the Status pages is also
available on the Status menu available on the handset.
System Status
The system status page shows:
General information about the base station, includin g model, MAC address,
and software version
Account Status information about the current SIP account registration
Network information regarding the base station’s network address and
network connection.
11 WebUI: Status
Page 12

VSP600/VSP601 Administrator and Provisioning Manual
Handset Status
The handset status page shows the name and registration status of cordless
handsets. The page lists the maximum of six handsets, even if fewer handsets are
registered. If you have not given the handsets unique names, the default name of
“HANDSET” appears.
12 WebUI: Status
Page 13

VSP600/VSP601 Administrator and Provisioning Manual
WebUI: System
SIP Account Management
On the SIP Account Management pages, you can enter the account settings for each
line you have ordered from your service provider. Each line has its own Account
settings page.
The SIP account settings are also available as parameters in the configuration file.
See “sip_account” Module: SIP A
ccount Settings on page 60.
General Account Settings
Click the link for each setting to see the matching configuration file parameter in
Appendix A: Configuration File Settings. Default values and
Setting Description
Enable Account Enable or disable the SIP account. Select to enable.
Display Name The display name identifies the SIP account throughout
the WebUI and on the handset Line menu. The display
name is also the text portion of the caller ID that is
displayed for outgoing calls using account x.
13 WebUI: System
ranges are listed there.
Page 14

VSP600/VSP601 Administrator and Provisioning Manual
User identifier
Authentication name If authentication is enabled on the server, enter the
Authentication password If authentication is enabled on t he server, e nter the
Dial Plan Enter the dial plan, with dialing strings separated by a |
Inter Digit Timeout (secs) Sets how long the handset waits after any “P” (pause) in
Maximum Number of Calls Select the maximum number of concurrent active calls
Feature Synchronization Enables the base station to synchronize with Broadworks
Enter the User identifier supplied by your service provider.
The User ID, also known as the Account ID, is a SIP URI
field used for SIP regis tratio n. It i s also used a s pa rt of the
caller ID displayed for outgoing calls.
authentication name (or authentication ID) for
authentication with the server.
authentication password for a uthe nticatio n with t he ser ver.
symbol. See Dial Plan on pa g e 15.
the dial string or in the dial plan.
allowed for that account.
Application Server. Changes to features such as DND, Call
Forward All, Call Forward No Answer, and Call Forward
Busy on the server side will also update the settings on
the handset menu and WebUI. Similarly, changes using
the handset or WebUI will update the settings on the
server.
DTMF method Select the default DTMF transmission method. You may
need to adjust this if call quality problems are triggering
unwanted DTMF tones or you have problems sending
DTMF tones in general.
Unregister after reboot Enables the base station to unregister the account(s) after
rebooting—before the account(s) register agai n as the base
station starts up.
14 WebUI: System
Page 15

VSP600/VSP601 Administrator and Provisioning Manual
Dial Plan
The dial plan consists of a series of dialing rules, or strings, that determine whether
what the user has dialed is valid and when the handset should dial the number.
Dialing rules must consist of the elements defined in the table below.
Element Description
x Any dial pad key from 0 to 9, including # and *.
[0-9] Any two n u m b e r s s e p a r a t e d b y a h y phen, where the second number is greater
than the first. All numbers within the range or valid, excluding # and *.
x+ An unlimited series of digits.
, This represents the playing of a secondary dial tone after the user enters
the digit(s) specified or dials an external call prefix before the comma. For
instance, “9,xxxxxxx” means the secondary dial tone is played after the
user dials 9 until any new digit is entered. “9,3xxxxxx” means that only
when the digit 3 is hit would the secondary dial tone stop playing.
PX This represents a pause of a defined time; X is the pause duration in
seconds. For instance, “P3” would represent pause duration of 3 seconds.
When “P” only is used, the pause time is the same as the Inter Digit
Timeout (see SIP Account Management on page 13).
(0:9) This is a substitution rule where the first number is replaced by the second.
For example, “(4:723)xxxx” would replace “46789” with “723-6789”. If the
substituted number (the first number) is empty, the second number is
added to the number dialed. For example, in “(:1)xxxxxxxxxx”, the digit 1
is appended to any 10-digit number dialed.
|
A sample dial plan appears below.
This separator is used to indicate the start of a new pattern. Can be used to
add multiple dialing rules to one pattern edit box.
15 WebUI: System
Page 16

VSP600/VSP601 Administrator and Provisioning Manual
SIP Server Settings
Setting Description
Server address Enter the IP address or domain name for the SIP server.
Server port Enter the port number that the SIP server will use.
Registration Settings
Setting Description
Server address Enter the IP address or domain name for the registrar server.
Server port Enter the port number that the registrar server will use.
Expiration Enter the desired registration expiry time in seconds.
Registration Freq (secs) Enter the desired registration retry frequency in seconds. If
registration using the Primary Outbound Proxy fails, the
Registration Freq setting determines the number of seconds
before a registration attempt is made using the Backup
Outbound Proxy.
Outbound Proxy Settings
Setting Description
Server address Enter the IP address or domain name for the proxy server.
Server port Enter the port number that the proxy server will use.
16 WebUI: System
Page 17

VSP600/VSP601 Administrator and Provisioning Manual
Backup Outbound Proxy Settings
Setting Description
Server address Enter the IP address or domain name for the backup proxy server.
Server port Enter the port number that the backup proxy server will use.
Audio Settings
Setting Description
Codec priority 1 Select the codec to be used first during a call.
Codec priority 2 Select the codec to be used second during a call if the previous
codec fails.
Codec priority 3 Select the codec to be used third during a call if previous codecs
fail.
Codec priority 4 Select the codec to be used fourth during a call if previous codecs
fail.
Codec priority 5 Select the codec to be used fifth during a call if previous codecs
fail.
Enable voice
encryption (SRTP)
Select to enable secure RTP for voice packets.
17 WebUI: System
Page 18

VSP600/VSP601 Administrator and Provisioning Manual
Quality of Service
Setting Description
DSCP (voice) Enter the Differentiated Services Code Point (DSCP) v a lue from the
Quality of Service setting on your router or switch.
DSCP (signalling) Enter the Differentiated Services Code Point (DSCP) value from the
Quality of Service setting on your router or switch.
Signaling Settings
Setting Description
Local SIP port Enter the local SIP port.
Transport Select the SIP transport protocol:
TCP (Transmission Control Protocol) is the most reliable protocol
and includes error checking and delivery validation.
UDP (User Datagram Protocol) is generally less prone to
latency, but SIP data may be subject to network congestion.
TLS (Transport Layer Security)—the VSP600 supports secured
SIP signalling via TLS. Optional server authentication is
supported via user-uploaded certificates. TLS certificates are
uploaded using the configuration file. See “file” Module:
Imported File Settings o
provider.
n page 88 and consult your service
18 WebUI: System
Page 19

VSP600/VSP601 Administrator and Provisioning Manual
Feature Access Codes Settings
If your IP PBX service provider uses feature access codes, then enter the applicable
codes here.
Setting Description
Voicemail Enter the voicemail access code. The code is dialed when the user
selects an account from the handset’s Message menu.
DND ON Enter the Do Not Disturb ON access code.
DND OFF Enter the Do Not Disturb OFF access code.
Call Forward All ON Enter the Call Forward All ON access code.
Call Forward All OFF Enter the Call Forward All OFF access code.
Call Forward No Answer ON Enter the Call Forward No Answer ON access code.
Call Forward No Answer OFF Enter the Call Forward No Answer OFF access code.
Call Forward Busy ON Enter the Call Forward Busy ON access code.
Call Forward Busy OFF Enter the Call Forward Busy OFF access code.
Anonymous Call Reject ON Enter the Anonymous Call Reject ON access code.
Anonymous Call Reject OFF Enter the Anonymous Call Reject OFF access code.
Anonymous Call ON Enter the Anonymous Call ON access code.
Anonymous Call OFF Enter the Anonymous Call OFF acces s code.
19 WebUI: System
Page 20

VSP600/VSP601 Administrator and Provisioning Manual
Voicemail Settings
Setting Description
Enable MWI Subscription When enabled, the account subscribes to the “message
summary” event package. The account may use the User
ID or the service provider’s “Mailbox ID”.
Mailbox ID Enter the URI for the mailbox ID. The base station uses this
URI for the MWI subscription. If left blank, the User ID is
used for the MWI subscription.
Expiration (secs) Enter the MWI subscription expiry time (in seconds) for
account x.
Ignore unsolicited MWI When selected, unsolicited MWI notifications—notifications
in addition to, or instead of SUBSCRIBE and NOTIFY
methods—are ignored for account x.
Disable this setting if:
MWI service does not involve a subscription to a
voicemail server. That is, the server supports unsolicited
MWI notifications.
you want the handset LCD to indicate new messages
when the base station receives unsolicited MWI
notifications.
20 WebUI: System
Page 21

VSP600/VSP601 Administrator and Provisioning Manual
NAT Traversal
Setting Description
Enable STUN Enables or disables STUN (Simple Traversal of UDP through
NATs) for account x. The Enable STUN setting allows the
base station to identify its publicly addressable information
behind a NAT via communicating with a STUN server.
Server address Enter the STUN server IP address or domain name.
Server port Enter the STUN server port.
Enable UDP Keep-Alive Enables or disables UDP keep-alives. Keep-alive packets are
used to maintain connections established through NAT.
Keep-alive interval (secs) E nter the interval (in seconds) for sending UDP keep-alives.
Music On Hold Settings
Setting Description
Enable Local MoH Enables or disables a hold-reminder tone that the user
hears when a far-end caller puts the call on hold.
Session Timer
Setting Description
Enable Session Timer Enables or disables the SIP session timer. The session timer
allows a periodic refreshing of a SIP session using the RE -
INVITE message.
Minimum value (secs) Sets the session timer minimum value (in seconds) for
account x.
Maximum value (secs) Sets the session timer maximum value (in seconds) for
account x.
21 WebUI: System
Page 22

VSP600/VSP601 Administrator and Provisioning Manual
Call Settings
You can configure call settings for each account. Call Settings include Do Not Disturb
and Call Forward settings.
The call settings are also available as parameters in the configuration file. See
“call_settings” Module: Call Settings on page 86.
General Call Settings
Setting Description
Anonymous Call Reject Enables or disables rejecting calls indicated as “Anonymous.”
Enable Anonymous Call Enables or disables outgoing anonymous calls. When enabled,
the caller name and number are indicated as “Anonymous.”
Do Not Disturb
Setting Description
Enable Do Not Disturb Turns Do Not Disturb on or off. When DND is on, incoming
calls on that account are rejected.
22 WebUI: System
Page 23

VSP600/VSP601 Administrator and Provisioning Manual
Call Forward
Setting Description
Enable Call Forward Always Enables or disables call forwarding for all incoming
calls on that account. Select to enable.
Target Number Enter a number to which all incoming calls will be
forwarded.
Enable Call Forward Busy Enables or disables forwarding incoming calls to the
target number if the number of active calls has
reached the maximum number of calls configured for
account x.
Target Number Enter a number to which incoming calls will be
forwarded when Call Forward Busy is enabled.
Enable Call Forward No Answer Enables or disables call forwarding for unanswered
calls on that line.
Target Number Enter a number to which unanswered calls will be
forwarded.
Delay Select the number of rings before unanswered calls
are forwarded.
23 WebUI: System
Page 24
VSP600/VSP601 Administrator and Provisioning Manual
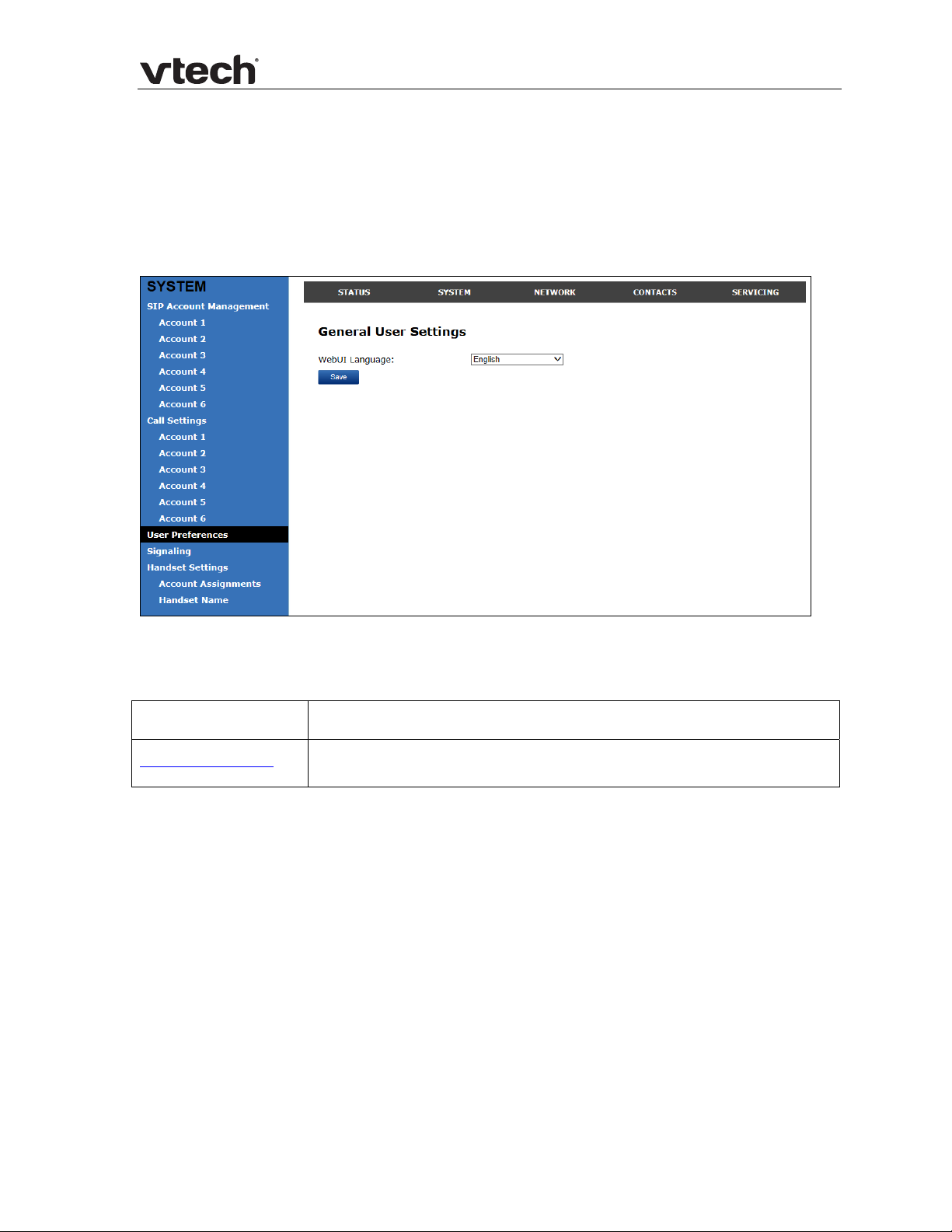
User Preferences
On the User Preferences page, you can set the language that appears on the WebUI.
The Preferences page is also available to users when they log on to the WebUI.
The user preference settings are also available as parameters in the configuration
file. See “user_pref” Module: User Preference Settings on page 85.
General User Settings
Click the link for each setting to see the matching configuration file parameter in
Appendix A: Configuration File Settings. Default values and
Setting Description
WebUI Language Sets the language that appears on the WebUI.
ranges are listed there.
24 WebUI: System
Page 25

VSP600/VSP601 Administrator and Provisioning Manual
Signaling Settings
The signalling settings are also available as parameters in the configu ration file. See
“network” Module: Network Settings on page 71.
Af
ter entering information on this page, click
Voice
Click the link for each setting to see the matching configuration file parameter in
Appendix A: Configuration File Settings. Default values and
to save it.
ranges are listed there.
Setting Description
Min Local RTP port Enter the lower limit of the Real-time Transport Protocol
(RTP) port range. RTP ports specify the minimum and
maximum port values that the base station will use for RTP
packets.
Max Local RTP port Enter the upper limit of the RTP port range.
NAT Traversal
The NAT Traversal settings are communicated to the VoIP server so that the base
station is reachable when connected to the Internet behind NAT.
Setting Description
Enable IP Masquerading Select to enable NAT traversal and IP masquerading.
Public IP address Enter the external IP address of your router. This setting
identifies the router’s public address to the VoIP server.
25 WebUI: System
Page 26

VSP600/VSP601 Administrator and Provisioning Manual
Public SIP port
Min Public RTP port Enter the lower limit of the public RTP port range.
Max Public RTP port Enter the upper limit of the public RTP port range.
Enter the router port number being used for SIP. This
setting identifies the router’s port to the VoIP server.
Handset Settings
The Handset Settings allow you to configure account assignments and names for the
cordless handsets that are registered to the base station. For more information on
registering cordless handsets, see the VSP600/VSP601 User Guide.
Account Assignments
The Account Assignments table lists the maximum of six handsets, even if there a
fewer handsets registered. The registration status of currently registered handsets
does not affect what is listed on this table.
The table always displays the maximum six accounts, even if there are fewer SIP
accounts enabled.
If you have not entered any unique handset names yet, then the default name of
“HANDSET” appears.
On the Account Assignments table, you can select which accounts will be available
for both incoming and outgoing calls on each handset.
The handset will first attempt to use the account you select under Default when
going off-hook.
26 WebUI: System
Page 27

VSP600/VSP601 Administrator and Provisioning Manual
Handset Name
On the Handset Name page, you can enter a name for each Handset. The Handset
Name will be used throughout the WebUI and will appear on the handset Idle screen.
The Handset Name is limited to a maximum of 12 characters.
The default name is “HANDSET”. Blank name fields are n ot allowed. If you click
when any fields are empty, an error message appears.
27 WebUI: System
Page 28

VSP600/VSP601 Administrator and Provisioning Manual
WebUI: Network
You can set up the base station for your network configuration on the Network
settings page. Your service provider may require you to configure your network to be
compatible with its service, and the base station settings must match the network
settings.
The network settings are also available as parameters in the configuration file. See
“network” Module: Network Settings on page 71.
ter entering information on this page, click
Af
to save it.
Basic Network Settings
NOTE: If you disable DHCP on this page, you must configure static IP settings for
the base station. You must be familiar with TCP/IP principles and protocols to
configure static IP settings.
Basic Network Settings
Click the link for each setting to see the matching configuration file parameter in
Appendix A: Configuration File Settings. Default values and
Setting Description
ranges are listed there.
Enable DHCP DHCP is selected (enabled) by default, which means the base station
will get its IP address, Subnet Mask, Gateway, and DNS Server(s)
from the network. When DHCP is disabled, you must enter a static IP
address for the base station, as well as addresses for the Subnet
Mask, Gateway, and DNS Server(s).
IP Address If DHCP is disabled, enter a static IP address for the base station.
Subnet Mask Enter the subnet mask.
Gateway Enter the address of the default gateway (in this case, your
router).
Primary DNS
Secondary DNS
28 WebUI: Network
If DHCP is disabled or you don’t wish to use the DHCP-assigned
DNS server (or one specified by your service provider), enter
addresses for the primary and secondary DNS servers.
Page 29

VSP600/VSP601 Administrator and Provisioning Manual
Advanced Network Settings
VLAN
You can organize your network and optimize VoIP performance by creating a virtual
LAN for base stations and related devices.
Click the link for each setting to see the matching configuration file parameter in
Appendix A: Configuration File Settings. Default values and
Setting Description
Enable LAN Port VLAN Enable if the base station is part of a VLAN on your network.
Select to enable.
VID Enter the VLAN ID (vlan 5, for example).
Priority Select the VLAN priority that matches the Quality of Service
(QOS) settings that you have set for that VLAN ID. Outbound
SIP packets will be marked and sent according to their priority. 7
is the highest priority. NOTE: Configuring QOS settings for your
router or switch is a subject outside the scope of this document.
LLDP-MED
Setting Description
Enable LLDP-MED Enables or disables Link Layer Discovery Protocol for Media
Endpoint Devices (LLDP-MED). LLDP-MED is a standards-based
discovery protocol supported on some network switches. It is
required for auto-configuration with VLAN settings.
ranges are listed there.
Packet Interval (secs) Sets the LLDP-MED packet interval (in seconds).
29 WebUI: Network
Page 30

VSP600/VSP601 Administrator and Provisioning Manual
802.1x
Setting Description
Enable 802.1x Enables or disables the 802.1x authentication protocol. This
protocol allows the base station to attach itself to network
equipment that requires device authentication via 802.1x.
Identity Enter the 802.1x EAPOL identity.
MD5 Password Enter the 802.1x EAPOL MD5 password.
30 WebUI: Network
Page 31

VSP600/VSP601 Administrator and Provisioning Manual
WebUI: Contacts
Base Directory
On the Base Directory page, you can manage directory entries that will be availab le
on all handsets. You can sort, edit, delete, and add contact information for up to 200
entries. In order to back up your contacts or import another directory file, the page
also enables you to export and import the base directory.
The Base Directory lists entries on up to 10 pages, with 20 entries per page. Click
, , , or a page number to view the desired page of entries.
NOTE: Each handset also has its own directory. You can add entries to the handset
directory using the handset. For more information, see the VSP600/VSP601 User
Guide.
31 WebUI: Contacts
Page 32

VSP600/VSP601 Administrator and Provisioning Manual
The following table describes the buttons available on the Local Directory page.
Click To…
Sort the list by last name.
Edit information for an entry
View the next page of entries.
View the last page of entries.
View the first page of entries.
Delete selected entries from the directory. Click Select All
to select every entry on the page you are viewing.
Add a new directory entry.
Delete all Directory entries.
Import a directory file.
Export the directory.
32 WebUI: Contacts
Page 33

VSP600/VSP601 Administrator and Provisioning Manual
To add a new directory entry:
1. Click
The Create Base Directory Entry page appears.
2. Enter the required information as described in the followin g table.
Create Local Directory Entry
Setting Description Range Default
First Name
Last Name
.
Enter the appropriate names in these fields.
The maximum length of the first name and
last name fields is 15 characters.
n/a Blank
Ringer Tone Sets a unique ringer tone for calls from this
directory entry.
Account Sets the account used when you dial this
directory entry.
Home Number
Work Number
Mobile Number
Enter the appropriate names and numbers
in these fields.
Auto, Tone
1–10
Default
Account,
Account 1–6
n/a Blank
Tone 1
Default
Account
33 WebUI: Contacts
Page 34
VSP600/VSP601 Administrator and Provisioning Manual
Directory Import/Export
The best way to create a directory file for import is to first export the directory from
the base station. After exporting the file, open it in an .xml edit or and add or modify
entries.
Importing a directory file adds the imported directory entries to existing entries.
Therefore, it is possible to have duplicate entries after importing a directory file. If
you are importing a “complete” directory file with the aim of replacing the entire
current directory, use Select All and
importing the file.
NOTE: Using the configuration file, you can set whether an imported directory file
adds to or replaces existing entries. See “file” Module: Imported File Settings on
page 88.
rectory files are .xml files that have the following tags:
Di
Local Directory WebUI field Directory file XML tag
First Name <DIR_ENTRY_NAME_FIRST>
to clear the directory before
Last Name <DIR_ENTRY_NAME_LAST>
Home Number <DIR_ENTRY_NUMBER_HOME>
Work Number <DIR_ENTRY_NUMBER_WORK>
Mobile Number <DIR_ENTRY_NUMBER_MOBILE>
Account <DIR_ENTRY_LINE_NUMBER>
Call Block (not on WebUI) <DIR_ENTRY_BLOCK>
Ringer Tone <DIR_ENTRY_RINGER>
34 WebUI: Contacts
Page 35

VSP600/VSP601 Administrator and Provisioning Manual
Blacklist
On the Blacklist page, you can manage local blacklist entries. The base station
rejects calls from numbers that match blacklist entries. You can sort, edit, delete,
and add up to 200 blacklist entries. In order to back up your blacklist entries or
import another blacklist file, the page also enables you t o export and import the
blacklist.
The blacklist lists entries on up to 10 pages, with 20 entries per page. Click
, , or a page number to view the desired page of entries.
NOTE: You can also use the handset menu to manage blacklist entries. For more
information, see the VSP600/VSP601 User Guide.
,
35 WebUI: Contacts
Page 36

VSP600/VSP601 Administrator and Provisioning Manual
The following table describes the buttons available on the Blacklist page.
Click To…
Sort the list by last name.
Edit information for an entry
View the next page of entries.
View the last page of entries.
View the first page of entries.
Delete selected entries. Click Select All to select every
entry on the page you are viewing.
Add a new entry.
Delete all entries.
Import a blacklist file.
Export the blacklist.
To add a new blacklist entry:
1. Click
The Create Blacklist Entry page appears.
.
2. Enter the required information as described in the followin g table.
36 WebUI: Contacts
Page 37

VSP600/VSP601 Administrator and Provisioning Manual
Create Blacklist Entry
Setting Description Range Default
First Name
Last Name
Account Sets the account used when you dial
Home Number
Work Number
Mobile Number
Enter the appropriate names in
these fields. The maximum length of
the first name and last name fields
is 15 characters.
this directory entry.
Enter the appropriate names and
numbers in these fields.
n/a Blank
Default
Account,
Account 1–6
n/a Blank
Account 1
Blacklist Import/Export
The best way to create a blacklist file for import is to first export the blacklist from
the base station. After exporting the file, open it in an .xml edit or and add or modify
entries.
Importing a blacklist file adds the imported blacklist entries to existing entries.
Therefore, it is possible to have duplicate entries after importing a blacklist file. If
you are importing a “complete” blacklist file wi th the aim of replacing the entire
current blacklist, use Select All and
importing the file.
to clear the blacklist before
NOTE: Using the configuration file, you can set whether an imported blacklist file
adds to or replaces existing entries. See “file” Module: Imported File Settings on
page 88.
list files are .xml files that have the following tags:
Black
Blacklist WebUI field Blacklist file XML tag
First Name <BLACKLIST_ENTRY_NAME_FIRST>
Last Name <BLACKLIST_ENTRY_NAME_LAST>
Home Number <BLACKLIST_ENTRY_NUMBER_HOME>
Work Number <BLACKLIST_ENTRY_NUMBER_WORK>
Mobile Number <BLACKLIST_ENTRY_NUMBER_MOBILE>
Account <BLACKLIST_ENTRY_LINE_NUMBER>
37 WebUI: Contacts
Page 38

VSP600/VSP601 Administrator and Provisioning Manual
WebUI: Servicing
Time and Date
On the Time and Date page, you can manually set the time and date, and the time
and date formats. You can also set the system time to follow a Network Time
Protocol (NTP) Server (recommended) or you can set the time and date manually.
The time and date settings are also available as parameters in the configuration file.
See “time_date” Module: Time and
Date Settings on page 79.
38 WebUI: Servicing
Page 39

VSP600/VSP601 Administrator and Provisioning Manual
Network Time Settings
Click the link for each setting to see the matching configuration file parameter in
Appendix A: Configuration File Settings. Default values and
Setting Description
Enable Network Time Enables or disables getting time and date information for the
base station from the Internet.
NTP Server If Enable Network Time is selected, enter the URL of your
preferred time server.
Use DHCP (Option 42) If Enable Network Time is selected, select to use DHCP to
locate the time server. Option 42 specifies the NTP server
available to the base station. When enabled, the base station
obtains the time in the following priority: 1. Option 42 2. NTP
Server 3. Manual time.
Time Zone and Daylight Savings Time Settings
ranges are listed there.
Setting Description
Time Zone Select your time zone from the list.
Automatically adjust
clock for Daylight
Savings
User-defined DST Select to set your own start and end dates and offset for
DST Start: Month
DST Start: Week
DST Start: Day
DST Start: Hour
DST End: Month
DST End: Week
DST End: Day
Select to adjust the clock for daylight savings time according
to the NTP server and time zone setting. To disable daylight
savings adjustment, disable both this setting and Userdefined Daylight Savings Time.
Daylight Savings time. To disable daylight savings
adjustment, disable both this setting and Automatically
adjust clock for Daylight Savings.
If User-defined DST
for daylight savings: Month, week, day, and hour.
If User-defined DST
daylight savings: Month, week, day, and hour.
is enabled, set the start date and time
is enabled, set the end date and time for
DST End: Hour
39 WebUI: Servicing
Page 40

VSP600/VSP601 Administrator and Provisioning Manual
Daylight Savings Offset
Use DHCP
(Option 2/100/101)
Manual Time Settings
If Enable Network Time
Time Settings to set the current time.
Setting Description
Date Select the current year, month, and day.
Time Sets the current hour, minute, and second.
Click to start the base station using the manual time settings.
If User-defined DST is enabled, this specifies the daylight
savings adjustment (in minutes) to be applied when the
current time is between Daylight Savings Start and Daylight
Savings End.
If Enable Network Time
determine the time zone offset. Options 2, 100 and 101
determine time zone information.
is disabled or if the time server is not available, use M anual
is selected, select to use DHCP to
40 WebUI: Servicing
Page 41

VSP600/VSP601 Administrator and Provisioning Manual
Firmware Upgrade
You can update the base station with new firmware using the following methods:
Retrieving a firmware update file from a remote host computer and accessed
via a URL. This central location may be arranged by you, an authorized VESA
dealer, or your SIP service provider. Enter the URL under Firmware Server
Settings.
Using a file located on your computer or local network. No connection to the
Internet is required. Consult your dealer for access to firmware update files.
Click Manual Upgrade to view the page where you can manually upgrade the
base station firmware.
The firmware upgrade settings are also available as parameters in the configuration
file. See “provisioning” Module: Provisioning Settings on page 75.
Firmware Server Settings
Click the link for each setting to see the matching configuration file parameter in
Appendix A: Configuration File Settings. Default values and
Setting Description
Firmware URL The URL where the firmware update file resides. This
should be a full path, including the filename of t he
firmware file.
Server authentication name Authentication username for the firmware server
Server authentication password Authentication password for the firmware server
To update the firmware immediately:
1. Click
NOTE: You can also configure the base station to check for firmware updates at
regular intervals. See the Provisioning page.
.
ranges are listed there.
41 WebUI: Servicing
Page 42

VSP600/VSP601 Administrator and Provisioning Manual
Manual Firmware Update and Upload
On the Manual Firmware Update Settings page, you can upgrade the base station
firmware using a file located on your computer or local network.
To update the firmware using a file on your computer or local network:
1. On the Manual Firmware Update page, click
the firmware update file.
2. Click
The base station will update its firmware and restart.
.
to locate and open
42 WebUI: Servicing
Page 43

VSP600/VSP601 Administrator and Provisioning Manual
Provisioning
Provisioning refers to the process of acquiring and applying new settings for the base
station using configuration files retrieved from a remote computer. After a base
station is deployed, subsequent provisioning can update the base station with new
settings; for example, if your service provider releases new features. See also
Provisioning Using Configuration Files on page 53.
th automatic provisioning, you enable the base station to get its settings
Wi
automatically—the process occurs in the background as part of routine system
operation.
With manual provisioning, you update the base station settings (configuration and/or
firmware) yourself via Provisioning > Import Configuration and/or Firmware
Upgrade > Manual Upgrade.
On the Provisioning page, you can enter settings that will enable the base station
to receive automatic configuration and firmware updates. The Provisioning page also
allows you to manually update base station configuration from a locally stored
configuration file using an Import function. You can also export the base station
configuration—either to back it up or to apply it to anoth er base station—to a file on
your computer.
The provisioning process functions according to the Resynchronization settings and
Provisioning Server Settings. The base station checks for the provisioning URL
from the following sources in the order listed below:
1. PnP—Plug and Play Subscribe and Notify protocol
2. DHCP Options
3. Preconfigured URL
If one of these sources is disabled, not available, or has not been configured, the
base station proceeds to the next source until reaching the end of the list.
The provisioning settings are also available as parameters in the configuration file.
“provisioning” Module: Provisioning Settings on page 75.
See
43 WebUI: Servicing
Page 44

VSP600/VSP601 Administrator and Provisioning Manual
Provisioning Settings
Setting Description
Provisioning server URL of the provisioning file(s). The format of the URL must
be RFC 1738 compliant, as follows:
“<schema>://<user>:<password>@
<host>:<port>/<url-path>”
“<user>:<password>@” may be empty.
“<port>” can be omitted if you do not need to specify the
port number.
Server authentication
name
Server authentication
password
Plug-and-Play Settings
Setting Description
Enable PnP Subscribe Select to enable the base station to search for the
DHCP Settings
Use DHCP Options
Enables the base station to use DHCP options to locate and
User name for access to the provisioning server
Password for access to the provisioning server
provisioning URL via a SUBSCRIBE message to a multicast
address (224.0.1.75). The base station expects the server
to reply with a NOTIFY that includes the provisioning URL.
The process times out after five attempts.
retrieve the configuration file. When selected, the base station
automatically attempts to get a provisioning server address,
and then the configuration file. If DHCP options do not locate a
configuration file, then the server provisioning string is
checked.
NOTE: Ensure that DHCP is also enabled on the Network
> Basic settings page.
DHCP Option Priority 1 If DHCP is enabled, sets the DHCP Option priority. Select
the highest priority option.
DHCP Option Priority 2 If DHCP is enabled, sets the DHCP Option priority. Select
the second highest priority option.
DHCP Option Priority 3 If DHCP is enabled, sets the DHCP Option priority. Select
the third highest priority option.
44 WebUI: Servicing
Page 45

VSP600/VSP601 Administrator and Provisioning Manual
Vendor Class ID (DHCP 60)
User Class Info (DHCP 77) DHCP Option 77 is available to send vendor-specific
DHCP Option 60 is available to send vendor-specific
information to the DHCP Server.
information to the DHCP Server.
Resynchronization
Setting Description
Mode Sets which files the base station checks for at regular intervals. It
can check for configuration files, firmware update files (from the
URL entered on the Firmware Server Settings page), or both.
NOTE: When checking for both config and firmware files, the
firmware URL can be within the config file. This firmware URL takes
take precedence over the URL on the Firmware Server Settings
page. It will also update the URL on the Firmware Server Settings
page. This allows you to change the firmware URL automatically.
Bootup Check Sets the base station to check the provisioning URL for new
configuration and/or firmware files upon bootup. The update is
applied as part of the reboot process.
Interval Sets an interval, in minutes, for checking for updates.
Use encryption Enables an AES-encrypted configuration file to be decrypted before
being applied to the base station. Select if the configurat ion file
has been secured using AES encryption. See Securing
onfiguration Files with AES Encryption on page 56.
C
45 WebUI: Servicing
Page 46

VSP600/VSP601 Administrator and Provisioning Manual
Passphrase
Import Configuration
You can configure the base station by importing a configuration file from your
computer or your local network. For more information about configuration file types
and configuration file formatting, see Provisioning Using Conf iguration Files on page
53.
o import a configuration file:
T
1. Click
2. Click
The base station will update its configuration.
Manually importing a configuration file differs from the auto-provisioning process in that:
The base station does not check whether the file has been loaded before. The
The base station will restart immediately after importing the configuration file,
If the configuration file has been secured using AES encryption,
enter the 16-bit key. See Securing Configuration Files with AES
yption on page 56.
Encr
to locate and open the configuration file.
.
configuration file is processed whether or not it is different from the current
version.
without waiting for one minute of activity.
Export Configuration
You can export all the settings you have configured on the WebUI and save them as
a configuration file on your computer. You can then use this conf iguration file as a
backup, or use it to update other base stations.
NOTE: The exported configuration file will contain the following passwords in plain
text:
SIP account authentication password
EAPOL password
Firmware server password
Provisioning server password
Encryption passphrase
Please ensure that you save the exported configuration file in a secure location.
To export the configuration file:
1. Click
The format of the exported file is <model name>_<mac address>.cfg. For
example, VSP600_0011A0OCF489.cfg.
Exporting a configuration file generates two header lines i n the configuration file.
These header lines provide the model number and software version in the following
format:
#Model Number = xxxxxxx
#SW Version = xxxxxxx
.
46 WebUI: Servicing
Page 47

VSP600/VSP601 Administrator and Provisioning Manual
You can use the exported file as a general configuration file, and duplicate the
settings across multiple units. However, ensure th at you edit the file to remove any
MAC-specific SIP account settings before applying the general configuration file to
other units.
Reset Configuration
You can reset the base station to its default settings.
To reset the base station to its default configuration:
1. Under Reset Configuration, click
2. When the confirmation box appears, click OK.
.
Security
On the Security page you can reset the admin password, reset the user password,
and enter web server settings.
The security settings are also available as parameters in the configuration file. See
47 WebUI: Servicing
Page 48

VSP600/VSP601 Administrator and Provisioning Manual
“web” Module: Web Settings on page 84.
Administrator Password
You can set the administrator password on the WebUI or by using provisioning. For
more information on using provisioning to set the administrator password, see
“profile” Module: Password Settings on page 90.
ange the admin password:
To ch
1. Enter the old password (for a new base station, the default password is admin).
2. Enter and re-enter a new password. The password is case sensitive and can
consist of both numbers and letters.
3. Click
.
48 WebUI: Servicing
Page 49

VSP600/VSP601 Administrator and Provisioning Manual
User Password
You can set the user password on the WebUI or by using provisioning. For more
information on using provisioning to set th e user password, see “profile” Module:
Password
To ch
1. Enter the old password (for a new base station, the default password is user).
2. Enter and re-enter a new password. The password is case sensitive and can
consist of both numbers and letters.
Settings on page 90.
ange the User password:
3. Click
Web Server
Setting Description
HTTP Server port Port used by the HTTP server.
Enable Secure Browsing Sets the server to use the HTTPS protocol.
HTTPS Server port Port used by the HTTPS server.
To configure Web Server Settings:
1. Enter the HTTP Server port number. The default setting is 80.
2. Enable or Disable Secure Browsing. When enabled, the HTTPS protocol is used,
and you must select the HTTPS server port in the next step.
3. Enter the HTTPS server port number. The default setting is 443.
.
49 WebUI: Servicing
Page 50

VSP600/VSP601 Administrator and Provisioning Manual
Certificates
You can upload an optional web server certificate to the base station to establish a
secure connection between base station and server. If a certificate is not available,
the base station’s self-signed certificate will be used durin g the connection
transaction.
A web server certificate can also be uploaded using provisioning. For more
information, see “file” Module: Imported File Sett in g s on page 88.
To upload a web server certificate:
1. On the Server Certificate page, click
2. Locate the certificate file and click Open.
3. On the Server Certificate page, click
.
.
50 WebUI: Servicing
Page 51

VSP600/VSP601 Administrator and Provisioning Manual
System Logs
On the Syslog page, you can enter settings related to system logging activities. It
supports the following logging modes:
Syslog server
Volatile file
Under Network Trace, you can capture network traffic related to the base station’s
activity and save the capture as a .pcap file. The file can be used for diagnostic and
troubleshooting purposes.
Under Download Log, you can save the system log to a file.
The Syslog settings are also available as parameters in the configuration file. See
“log” Module: Log Settings on page 83.
Syslog
Setting Description
Enable Syslog Enable log output to syslog server.
Server address Syslog server IP address.
Port Syslog server port.
Log Level Sets the log level. The higher the level, the larger the debug output.
5—ALL
4—DEBUG
3—INFO
2—WARNING
1—ERROR
0—CRITICAL
51 WebUI: Servicing
Page 52

VSP600/VSP601 Administrator and Provisioning Manual
The logging levels are:
CRITICAL: Operating conditions to be reported or corrected immediately (for
example, an internal component failure or file system error).
ERROR: Non-urgent failures—unexpected conditions that won't cause the
device to malfunction.
WARNING: An indication that an error or critical condition can occur if action is
not taken.
INFO: Normal operational messages.
DEBUG: Developer messages for troubleshooting/debugging purposes.
Network Trace
To perform a network trace:
1. Start a network trace by clicking
2. Stop the network trace by clicking
3. Save the trace by clicking
the capture.pcap file.
Download Log
To download the system log:
1. Click
2. After your browser prompts you to save the system.log file, save the file in the
desired location.
.
. The button changes to .
.
. Your browser should prompt you to save
52 WebUI: Servicing
Page 53

VSP600/VSP601 Administrator and Provisioning Manual
Provisioning Using Configuration Files
Provisioning using configuration files allows you to place a configuration file on a
provisioning server, where the base station can retrieve the file and update it s
configuration automatically.
Configuration files have the extension .cfg and contain parameters that define
various base station settings. To edit a configuration file, open it with a text editor
such as Notepad.
The parameters (or settings) within configuration files are grouped into modules.
Most of the modules group their settings in the same way that settings are grouped
on the WebUI. For example, the “time_date” module contains the same settings that
are on the Time and Date WebUI page.
Using the WebUI, you can also import a configuration file and apply the conf iguration
file settings to the base station. For more information, see Provisioning on page 43.
Resynchronization—Configuration File Checking
You can select a number of options to set when the base station checks for new
configuration files. This process of checking for configuration files is called
Resynchronization. Resynchronization options are available on the WebUI
Provisioning page, but you can also include them in a configuration file.
The resynchronization options are:
Mode—sets the base station to check for a configuration file only, a firmware
update file only, or both types of file.
Never—configuration file checking is disabled
Bootup—the base station checks for new configuration files when it boots up.
Any updates are applied during the boot-up process.
Remote check-sync—enables you to start a resynchronization remotely using
your hosted server’s web portal. The Remote check-sync settings are available
only in the configuration file, not the WebUI.
Repeatedly, at a defined interval from 60 to 65535 minutes (45 days).
The Provisioning Process
The base station’s automatic provisioning process is as follows:
1. Check for new or updated configuration files. The base station maintains a list of
the last loaded provisioning files. The base station compares its current
configuration against the files it finds on the provisioning server.
If provisioning has been triggered by the resync timer expiring or by remote
check-sync, the base station checks for updated files after one minute of
inactivity.
2. Download the configuration files.
If any file on the provisioning server has changed, the base station treats it as a
new file and downloads it.
53 Provisioning Using Configuration Files
Page 54

VSP600/VSP601 Administrator and Provisioning Manual
If the provisioning URL specifies a path only with no filename, then by default the
base station fetches the following two files:
General file: <model>.cfg.
MAC-specific file: <model>_<MAC Address>.cfg.
The <model> variable is the VTech product model: VSP600, for example.
If the provisioning URL specifies both a path and filename, then the base station
fetches only the configuration file specified.
3. The base station restarts after one minute of inactivity.
During provisioning, the base station reads the configuration file and validates each
module and setting. The base station considers a setting valid if it is:
a valid data type
formatted as a valid setting
within a valid data range
part of a module that passes an integrity check. That is, the module’s setting s
are consistent and logical. For example, in the “n etwork” module, if DHCP is
disabled, but no static IP address is specified, the module will fail the integrity
check and none of the settings will apply.
Invalid modules or invalid settings are skipped and logged as ERRORs in the system
log, but will not interrupt the provisioning process. The system log will include the
module parameters that have not been applied. A recognized module w ith
unrecognized settings will cause all other settings in that module to be skipped.
A successful configuration or firmware update is reported as an INFO message in the
system log.
Appendix A: Configuration File Settings on page 60 for the options and value
See
ranges avai
lable for each configuration file setting.
Base Station Restart
If the base station needs to restart after an auto-update, the restart happens only
after the base station has been idle for one minute.
To prevent users from delaying the update process (auto-updates cannot begin until
the base station has been idle for one minute), or to avoid base station restarts that
might interfere with incoming calls:
set the resynchronization interval to a suit able period
upload any new configuration file(s) to your provisioning serv er after work
hours so that the base station will download the file(s) when there is little or no
call activity.
When you update the base station by importing a configuration file using the WebUI,
the base station restarts immediately after applying the new settings, regardless of
whether the base station is idle.
54 Provisioning Using Configuration F iles
Page 55

VSP600/VSP601 Administrator and Provisioning Manual
Configuration File Types
The base station is able to retrieve and download two types of configuration file.
Depending on your requirements, you may want to make both types of configuration
file available on your provisioning server.
The two configuration file types are a general configuration file and a MAC-specific
configuration file. The types differ in name on ly. The formatting of the files’ content
is identical.
The general configuration file contains settings that are required by all base stations
in the system.
The MAC-specific configuration file is a file that only a single base station can
retrieve. The MAC-specific configuration file n a me contains a base station’s MAC
address and can only be retrieved by the base station with a matching MAC address.
The filename formats for both files are:
General file: <model>.cfg
MAC-specific file: <model>_<MAC Address>.cfg
The <model> variable is the VTech product model; for example, VSP600. For more
information about the MAC-specific configuration file, see Guidelines for the MACSpecif
ic Configuration File on page 56.
the provisioning URL specifies a path only with no filename, then by default the
If
base station will fetch both files.
However, if the provisioning URL specifies both a path and filen ame, then the base
station will only fetch the single configur ation file specified.
Both the general and MAC-specific files can contain any of th e available configuration
settings. A setting can appear in the general configuration file or the unit
configuration file, or both files, or neither file. If a setting appears in both files, the
setting that is read last is the one that applies.
When the base station fetches both a general and a MAC-specific configuration file,
the general file is processed first. You can configure a setting for most of your base
stations in the general file, and then overwrite that setting for just a few base
stations using the MAC-specific file.
Data Files
The configuration file can also include links to data files for product customization.
Allowed data types include the following:
Directory (contacts, blacklist) in xml format
Certificates (server and provisioning) in pem format
Links to data files are in the configuration file’s “file” module. This is where you enter
any URLs to the data files you require.
None of the data files are exported when you export a configuration file from the
base station. However, you can export a Directory or Blacklist .xml file using the
WebUI. After modifying the .xml file, you can use the configur ation file “file” module
to have the base station import the new file. For a complete list of data file
parameters, see “file” Module: Imported File Settings on page 88.
55 Provisioning Using Configuration F iles
Page 56

VSP600/VSP601 Administrator and Provisioning Manual
Configuration File Guide
All configuration settings are initially stored in a configuration template file. Copy,
rename, and edit the template file to create a general configurat ion file and the MACspecific configuration files you will need. You can store th e general configuration file
and the MAC-specific files on your provisioning server.
Do not modify the header line that includes the model and firmware version.
To save yourself time and effort, consider which settings will be common to all ( or
the majority of) base stations. Such settings might include Call settings, language,
and NAT settings. You can then edit those settings in the configur ation template and
save it as the general configuration file. The remaining settings will make up the
MAC-specific configuration file, which you will h a ve to copy and edit for each base
station.
Guidelines for the MAC-Specific Configuration File
The base station downloads the MAC-specific configuration file after the Main
configuration file. You must create a MAC-specific configuration file for each base
station in your system. The file name must contain the base station’s MAC address,
which is printed on a label on the bottom of the base station. For ex ample, a VTech
VSP600 base station with the MAC address of 00:11:A0:10:6F:2D would download
the VSP600_0011A0106F2D.cfg file.
NOTE: When renaming a MAC-specific configuration file, ensure the filename is all
upper case.
The MAC-specific configuration file contains settings intended exclusively for that
base station. Such settings will include SIP account settings such as display na me,
user ID, and authentication ID.
Securing Configuration Files with AES Encryption
You can encrypt your configuration files to prevent unauthorized users modifying the
configuration files. The base station firmware decrypts files using the AES 256
algorithm. After encrypting a file and placing it on your provisioning server, you can
enable the base station to decrypt the file after fetching it from the server.
The procedures in this section use OpenSSL for file encryption. The illustration
provided shows OpenSSL for Windows.
To decrypt a configuration file, you will need a 16-character AES key that you specified
when you encrypted the file. The key (or passphrase) is limited to 16 characters and
supports special characters ~^`%!&-_+=|.@*:;,?()[]{}<>/\# as well as spaces.
NOTE: The encryption of configuration files is supported only for the auto
provisioning process. Encrypt files only if you intend to store them on a provisioning
server. Do not encrypt files that you intend to manually import to the base station.
You cannot enable decryption for manually imported configuration files.
56 Provisioning Using Configuration F iles
Page 57

VSP600/VSP601 Administrator and Provisioning Manual
To encrypt a configuration file:
1. (Optional) Place your configuration file in t he same folder as the openssl
executable file. If the configuration file is not in the same folder as the openssl
executable file, you can enter a relative pathname for the [infile] in the next step.
2. On the openssl command line, type:
enc -aes-256-cbc -pass pass:[passphrase123456] -in [infile] -out [outfile] -nosalt -p
Elements in brackets are examples—do not enter the brackets. Enter a 16-character
passphrase and the unencrypted configuration file filename (the “infile”) and a name
for the encrypted file (“outfile”) that will result.
To enable configuration file decryption:
1. On the WebUI, click Servicing > Provisioning.
2. On the Provisioning page under Resynchronization, select Use Encryption for
configuration file.
3. Enter the 16-character passphrase that you created when you encrypted the
configuration file.
4. Click Save.
NOTE: You must ensure that configuration files are encrypted when enabling AES
Encryption. Decrypting an unencrypted file will result in a garbage file that is not
processed. This will also be logged as an error in the system log.
57 Provisioning Using Configuration F iles
Page 58

VSP600/VSP601 Administrator and Provisioning Manual
Troubleshooting
If you have difficulty with your base station, please try the suggestions below. For
customer service, visit our website at
1 (888) 370-2006.
The DECT handset doesn’t register. “Registration failed” appears on the
screen.
Ensure the handset is fully charged and in the charger.
Ensure the handset is not already registered to another base station. If it has
been registered to another base station, deregister it.
My caller ID isn’t working.
Caller ID is a subscription service. You must subscribe to this service from your
telephone service provider for this feature to work on your telephone.
The caller must be calling from an area that supports caller ID.
Both your and your caller’s telephone service providers must use caller ID
compatible equipment.
The manual firmware upgrade or configuration update isn’t working.
Before using the WebUI, ensure you have the latest version of your web
browser installed. Some menus and controls in older browsers may operate
differently than described in this manual.
Ensure you have specified the correct path to the firmware and configuration
files on the SERVICING > Firmware Upgrade > Auto Upgrade page and
the SERVICING > Provisioning page.
businessphones.vtech.com or call
Provisioning: “Use DHCP Option” is enabled, but the base station is not
getting a provisioning URL from the DHCP Server.
Ensure that DHCP is enabled in Network settings.
58 Troubleshooting
Page 59

VSP600/VSP601 Administrator and Provisioning Manual
Specifications
RF frequency band: 1921.536–1928.448 MHz
Channels: 5
Operating temperature: 32–122 °F (0–50 °C)
Power requirements: Base: 5.0 Vdc @ 800 mA
Handset charger: 6.0 Vdc @ 300 mA
Handset: 2.4 V 550/750 mAh, Ni-MH battery pack
Power over Ethernet: IEEE 802.3at supported, class 3
Ethernet port: 10/100 Mbps RJ-45 port
59 Specifications
Page 60

VSP600/VSP601 Administrator and Provisioning Manual
Appendix A: Configuration File Settings
This section lists the available options for all the settings within the configuration file.
Most settings in the configuration file have an equivalent in the WebUI (see the
settings tables in Using the WebUI on page 9). However, the options you must enter
hen editing the configuration file have a different syntax and format.
w
The settings are divided into modules. Each module loosely corresponds to a page on
the WebUI. You may wish to reorganize the modules within the configuration file
itself. The configuration file settings can be listed in any order, and the configuration
file will still be valid.
“sip_account” Module: SIP Account Settings
The SIP Account settings enable you to configure SIP accounts for the base station.
You can add up to six accounts for each base station. Each account requires you to
configure the same group of SIP account settings. The SIP account settings for each
account are identified by the account number, from 1 to 6 for the VSP600 base
station, for example.
For example, for account 1 you would set:
sip_account.1.sip_account_enable = 1
sip_account.1.display_name = 1001
sip_account.1.user_id = 2325551001
and so on.
For account 2, you would set:
sip_account.2.sip_account_enable = 1
sip_account.2.display_name = 1002
sip_account.2.user_id = 2325551002
and so on.
The SIP account settings follow the format: sip_account.x.[element], where x is an
account number ranging from 1 to 6 for the VSP600 base station.
All these settings are exported when you manually export the configuration from the
base station.
General Configuration File Settings
Setting:
Description: Sets the dial plan for account x. See Dial Plan on pag e 15.
Values: Text string Default: Blank
sip_account.x.dial_plan
60 Appendix A: Configuration File Settings
Page 61

VSP600/VSP601 Administrator and Provisioning Manual
Setting:
sip_account.x.inter_digit_timeout
Description: Sets the inter-digit timeout (in seconds) for account x. The inter-
digit timeout sets how long the device waits after the last digit is
entered before dialing the number.
Values: 1–10 Default: 3
Setting:
sip_account.x.maximum_call_number
Description: Sets the maximum number of concurrent active calls allowed for
that account.
Values: 1–4 Default: 4
Setting:
sip_account.x.dtmf_transport_method
Description: Sets the transport method for DTMF signalling for account x.
Values: auto, rfc2833, inband,
Default: auto
info
Setting:
sip_account.x.unregister_after_reboot_enable
Description: Enables or disables the device to unregister account x after
rebooting.
Values: 0 (disabled), 1 (enabled) Default: 0
Setting:
sip_account.x.primary_sip_server_address
Description: Sets the SIP server IP address for account x.
Values: Text string Default: Blank
Setting:
sip_account.x.primary_sip_server_port
Description: Sets the SIP server port for account x.
Values: 1–65535 Default: 5060
61 Appendix A: Configuration File Settings
Page 62

VSP600/VSP601 Administrator and Provisioning Manual
Setting:
sip_account.x.primary_registration_server_address
Description: Sets the registration server IP address for account x.
Values: Text string Default: Blank
Setting:
sip_account.x.primary_registration_server_port
Description: Sets the registration server port for account x.
Values: 1–65535 Default: 5060
Setting:
sip_account.x.primary_registration_expires
Description: Sets the expiration time (in seconds) of the current registration for
account x.
Values: 0–65535 Default: 3600
Setting:
sip_account.x.registration_retry_time
Description: Sets the retry frequency (in seconds) of the current registration for
account x.
Values: 1–1800 Default: 10
Setting:
sip_account.x.primary_outbound_proxy_server_address
Description: Sets the outbound proxy server IP address for account x.
Values: Text string Default: Blank
Setting:
sip_account.x.primary_outbound_proxy_server_port
Description: Sets the outbound proxy server port for account x.
Values: 1–65535 Default: 5060
62 Appendix A: Configuration File Settings
Page 63

VSP600/VSP601 Administrator and Provisioning Manual
Setting:
sip_account.x.backup_outbound_proxy_server_address
Description: Sets the backup outbound proxy server IP address for account x.
Values: Text string Default: Blank
Setting:
sip_account.x.backup_outbound_proxy_server_port
Description: Sets the backup outbound proxy server port for account x.
Values: 1–65535 Default: 5060
Setting:
sip_account.x.codec_priority.1
Description: Sets the highest-priority codec for account x.
Values: g711u, g711a, g729,
Default: g711u
g726, g722
Setting:
sip_account.x.codec_priority.2
Description: Sets the second highest-priority codec for account x.
Values: none, g711u, g711a,
Default: g711a
g729, g726, g722
Setting:
sip_account.x.codec_priority.3
Description: Sets the third highest-priority codec for account x.
Values: none, g711u, g711a,
Default: g729
g729, g726, g722
Setting:
sip_account.x.codec_priority.4
Description: Sets the fourth highest-priority codec for account x.
Values: none, g711u, g711a,
Default: g726
g729, g726, g722
63 Appendix A: Configuration File Settings
Page 64

VSP600/VSP601 Administrator and Provisioning Manual
Setting:
Description: Sets the fifth highest-priority codec for account x.
Values: none, g711u, g711a,
Setting:
Description: Enables or disables SRTP voice encryption for account x.
Values: 0 (disabled), 1 (enabled) Default: 0
Setting:
Description: Sets the Voice Quality of Service Layer 3 – DSCP for account x.
Values: 0–63 Default: 46
sip_account.x.codec_priority.5
Default: g722
g729, g726, g722
sip_account.x.voice_encryption_enable
sip_account.x.dscp
Setting:
Description: Sets the Signalling Quality of Service Layer 3 – DSCP for account x.
Values: 0–63 Default: 26
Setting:
Description: Sets the Local SIP port for account x.
Values: 1–65535 Default: Account 1: 5060
sip_account.x.sip_dscp
sip_account.x.local_sip_port
Account 2: 5070
Account 3: 5080
Account 4: 5090
Account 5: 5100
Account 6: 5200
64 Appendix A: Configuration File Settings
Page 65

VSP600/VSP601 Administrator and Provisioning Manual
Setting:
sip_account.x.transport_mode
Description: Sets the Signalling Transport Mode for account x.
Values: udp, tcp, tls Default: udp
Setting:
sip_account.x.access_code_retrieve_voicemail
Description: Sets the voicemail retrieval feature access code for account x.
Values: Text string Default: Blank
Setting:
sip_account.x.access_code_dnd_on
Description: Sets the do not disturb (DND) ON feature access code for account x.
Values: Text string Default: Blank
Setting:
sip_account.x.access_code_dnd_off
Description: Sets the do not disturb (DND) OFF feature access code for account x.
Values: Text string Default: Blank
Setting:
sip_account.x.access_code_cfa_on
Description: Sets the Call Forward All ON feature access code for account x.
Values: Text string Default: Blank
Setting:
sip_account.x.access_code_cfa_off
Description: Sets the Call Forward All OFF feature access code for account x.
Values: Text string Default: Blank
65 Appendix A: Configuration File Settings
Page 66

VSP600/VSP601 Administrator and Provisioning Manual
Setting:
sip_account.x.access_code_cfna_on
Description: Sets the Call Forward No Answer ON feature access code for account x.
Values: Text string Default: Blank
Setting:
sip_account.x.access_code_cfna_off
Description: Sets the Call Forward No Answer OFF feature access code for
account x.
Values: Text string Default: Blank
Setting:
sip_account.x.access_code_cfb_on
Description: Sets the Call Forward Busy ON feature access code for account x.
Values: Text string Default: Blank
Setting:
sip_account.x.access_code_cfb_off
Description: Sets the Call Forward Busy OFF feature access code for account x.
Values: Text string Default: Blank
Setting:
sip_account.x.access_code_anonymous_call_block_on
Description: Sets the Anonymous Call Block ON feature access code for account x.
Values: Text string Default: Blank
Setting:
sip_account.x.access_code_anonymous_call_block_off
Description: Sets the Anonymous Call Block OFF feature access code for account x.
Values: Text string Default: Blank
66 Appendix A: Configuration File Settings
Page 67

VSP600/VSP601 Administrator and Provisioning Manual
Setting:
Description: Sets the Anonymous Outgoing Call ON feature access code for
Values: Text string Default: Blank
Setting:
Description: Sets the Anonymous Outgoing Call OFF feature access code for
Values: Text string Default: Blank
Setting:
Description: Enables or disables message waiting indicator subscription for
sip_account.x.access_code_outgoing_call_anonymous_on
account x.
sip_account.x.access_code_outgoing_call_anonymous_off
account x.
sip_account.x.mwi_enable
account x. Enable if SUBSCRIBE and NOTIFY methods are used for
MWI.
Values: 0 (disabled), 1 (enabled) Default: 0
Setting:
Description: Sets the MWI subscription expiry time (in seconds) for account x.
Values: 0–65535 Default: 3600
Setting:
Description: Enables or disables ignoring of unsolicited MWI notifications—
Values: 0 (disabled), 1 (enabled) Default: 0
sip_account.x.mwi_subscription_expires
sip_account.x.mwi_ignore_unsolicited
notifications in addition to, or instead of SUBSCRIBE and NOTIFY
methods—for account x. Disable if MWI service is configured on the
voicemail server and does not involve a subscription to a voicemail
server.
67 Appendix A: Configuration File Settings
Page 68

VSP600/VSP601 Administrator and Provisioning Manual
Setting:
sip_account.x.nat_traversal_stun_enable
Description: Enables or disables STUN (Sim ple Traversal of UDP through NATs) for
account x. STUN enables clients, each behind a firewall, to establish
calls via a service provider hosted outside of either local network.
Values: 0 (disabled), 1 (enabled) Default: 0
Setting:
sip_account.x.nat_traversal_stun_server_address
Description: Sets the STUN server IP address.
Values: Text string Default: Blank
Setting:
sip_account.x.nat_traversal_stun_server_port
Description: Sets the STUN server port.
Values: 1–65535 Default: 3478
Setting:
sip_account.x.nat_traversal_udp_keep_alive_enable
Description: Enables or disables UDP keep-alives. Keep-alive packets are used to
maintain connections established through NAT.
Values: 0 (disabled), 1 (enabled) Default: 0
Setting:
sip_account.x.nat_traversal_udp_keep_alive_interval
Description: Sets the interval (in seconds) for sending UDP keep-aliv es.
Values: 0–65535 Default: 30
Setting:
sip_account.x.music_on_hold_enable
Description: Enables or disables a hold-reminder tone that a far-end caller hears
when put on hold during a call on account x.
Values: 0 (disabled), 1 (enabled) Default: 1
68 Appendix A: Configuration File Settings
Page 69

VSP600/VSP601 Administrator and Provisioning Manual
Setting:
Description: Enables or disables the SIP session timer.
Values: 0 (disabled), 1 (enabled) Default: 0
Setting:
Description: Sets the session timer minimum value (in seconds) for account x.
Values: 90–65535 Default: 90
Setting:
Description: Sets the session timer maximum value (in seconds) for account x.
Values: 0–65535 Default: 1800
sip_account.x.sip_session_timer_enable
sip_account.x.sip_session_timer_min
sip_account.x.sip_session_timer_max
Setting:
Description: Enables or disables accepting only a trusted TLS certificate for
Values: 0 (disabled), 1 (enabled) Default: 0
Setting:
Description: Enables or disables accepting the first TLS certificate for all
Values: 0 (disabled), 1 (enabled) Default: 0
sip_account.x.check_trusted_certificate
account x.
sip_account.x.use_first_trusted_certificate_for_all
accounts.
MAC-Specific Configuration File Settings
Setting:
Description: Enables account x to be used by the device. Specific to the MAC
Values: 0 (disabled), 1 (enabled) Default: 0
sip_account.x.sip_account_enable
configuration file.
69 Appendix A: Configuration File Settings
Page 70

VSP600/VSP601 Administrator and Provisioning Manual
Setting:
Description: Sets the account name displayed on the device LCD. This could be
Values: Text string Default: Blank
Setting:
Description: Sets the account ID for account x. Depending on your service
Values: Text string (SIP URI) Default: Blank
Setting:
Description: Sets the authentication name for account x. Depending on your
sip_account.x.display_name
the user’s name or another descriptor. Specific to the MAC
configuration file.
sip_account.x.user_id
provider’s specifications, this could be an extension number. Specific
to the MAC configuration file.
sip_account.x.authentication_name
service provider’s specifications, this could be identical to the user
ID. Specific to the MAC configuration file.
Values: Text string Default: Blank
Setting:
Description: Sets the authentication password for account x. Specific to the MAC
Values: Text string Default: Blank
Setting:
Description: Enables or disables feature synchronization for account x. When
Values: 0 (disabled), 1 (enabled) Default: 0
sip_account.x.authentication_password
configuration file.
sip_account.x.feature_sync_enable
enabled, features configured on the service provider’s web portal will
automatically be updated on the device’s WebUI. Specific to the MAC
configuration file.
70 Appendix A: Configuration File Settings
Page 71

VSP600/VSP601 Administrator and Provisioning Manual
Setting:
Description: Sets the MWI URI that will be used for MWI subscription. If this
Values: Text string (SIP URI) Default: Blank
sip_account.x.mwi_uri
setting is left blank, the base station uses the account x user ID for
MWI subscription.
“network” Module: Network Settings
The network settings follow the format: network.[element].
General Configuration File Settings
Setting:
Description: Sets the Local RTP port range start.
Values: 1–65535 Default: 18000
Setting:
network.rtp.port_start
network.rtp.port_end
Description: Sets the Local RTP port range end.
Values: 1–65535 Default: 19000
Setting:
Description: Enables or disables the WAN VLAN.
Values: 0 (disabled), 1 (enabled) Default: 0
Setting:
Description: Sets the WAN VLAN ID.
Values: 0–4095 Default: 0
network.vlan.wan.enable
network.vlan.wan.id
71 Appendix A: Configuration File Settings
Page 72

VSP600/VSP601 Administrator and Provisioning Manual
Setting:
network.vlan.wan.priority
Description: Sets the WAN port priority.
Values: 0–7 Default: 0
Setting:
network.lldp_med.enable
Description: Enables or disables LLDP-MED.
Values: 0 (disabled), 1 (enabled) Default: 0
Setting:
network.lldp_med.interval
Description: Sets the LLDP-MED packet interval (in seconds).
Values: 1–30 Default: 30
Setting:
network.eapol.enable
Description: Enables or disables 802.1x EAPOL.
Values: 0 (disabled), 1 (enabled) Default: 0
Setting:
network.eapol.identity
Description: Sets the 802.1x EAPOL identity.
Values: Text string Default: Blank
Setting:
network.eapol.password
Description: Sets the 802.1x EAPOL MD5 password.
Values: Text string Default: Blank
72 Appendix A: Configuration File Settings
Page 73

VSP600/VSP601 Administrator and Provisioning Manual
Setting:
Description: Sets the vendor ID for DHCP option 60.
Values: Text string Default: Vtech Vesa VSP600
Setting:
Description: Sets the user class for DHCP option 77.
Values: Text string Default: Vtech Vesa VSP600
network.vendor_class_id
network.user_class
MAC-Specific Configuration File Settings
Setting:
Description: Enables or disables IP masquerading.
Values: 0 (disabled), 1 (enabled) Default: 0
network.nat.masquerading_enable
Setting:
Description: Sets the public IP address.
Values: Text string (IPv4) Default: Blank
Setting:
Description: Sets the public SIP port.
Values: 1–65535 Default: 5060
Setting:
Description: Sets the public RTP port range start.
Values: 1–65535 Default: 18000
network.nat.public_ip_addr
network.nat.public_sip_port
network.nat.public_rtp_port_start
73 Appendix A: Configuration File Settings
Page 74

VSP600/VSP601 Administrator and Provisioning Manual
Setting:
network.nat.public_rtp_port_end
Description: Sets the public RTP port range end.
Values: 1–65535 Default: 19000
Setting:
network.ip.dhcp_enable
Description: Indicates whether DHCP is enabled.
Values: 0 (disabled), 1 (enabled) Default: 1
Setting:
network.ip.static_ip_addr
Description: Sets a static IP address for the network.
Values: Text string (IPv4) Default: Blank
Setting:
network.ip.subnet_mask
Description: Sets the subnet mask for the network.
Values: Text string (IPv4) Default: Blank
Setting:
network.ip.gateway_addr
Description: Sets the Gateway IP address.
Values: Text string (IPv4) Default: Blank
Setting:
network.ip.dns1
Description: Sets the primary DNS server IP address.
Values: Text string (IPv4) Default: Blank
74 Appendix A: Configuration File Settings
Page 75

VSP600/VSP601 Administrator and Provisioning Manual
Setting:
Description: Sets the secondary DNS server IP address.
Values: Text string (IPv4) Default: Blank
network.ip.dns2
“provisioning” Module: Provisioning Settings
The provisioning settings follow the format: provisionin g .[element].
All these settings are exported when you manually export the configuration from the
base station.
All the provisioning settings are included in the general configuration file.
Setting:
Description: Sets the URL for the server hosting the firmware file.
Values: Text string Default: Blank
Setting:
provisioning.firmware_url
provisioning.fw_server_username
Description: Sets the authentication name for the server hosting the firmware file.
Values: Text string Default: Blank
Setting:
Description: Sets the authentication password for the server hosting the firmware
Values: Text string Default: Blank
Setting:
Description: Sets the provisioning server IP address.
Values: Text string Default: Blank
provisioning.fw_server_password
file.
provisioning.server_address
75 Appendix A: Configuration File Settings
Page 76

VSP600/VSP601 Administrator and Provisioning Manual
Setting:
provisioning.server_username
Description: Sets the authentication name for the provisioning server.
Values: Text string Default: Blank
Setting:
provisioning.server_password
Description: Sets the authentication password for the provisioning server.
Values: Text string Default: Blank
Setting:
provisioning.dhcp_option_enable
Description: Enables or disables using DHCP options for locating the configuration
and firmware files.
Values: 0 (disabled), 1 (enabled) Default: 1
Setting:
provisioning.dhcp_option_priority_1
Description: Sets the first priority DHCP option for the provisionin g/firmware file
check.
Values: 66, 159, 160 Default: 66
Setting:
provisioning.dhcp_option_priority_2
Description: Sets the second priority DHCP option for the provisioning/firmware file
check.
Values: 66, 159, 160 Default: 159
Setting:
provisioning.dhcp_option_priority_3
Description: Sets the third priority DHCP option for the provisioning/firmware file
check.
Values: 66, 159, 160 Default: 160
76 Appendix A: Configuration File Settings
Page 77

VSP600/VSP601 Administrator and Provisioning Manual
Setting:
Description: Sets the mode of the device’s provisioning/firmware file check. This
Values: config_only,
Setting:
Description: Enables or disables bootup check for configuration and firmware files.
Values: 0 (disabled), 1 (enabled) Default: 1
Setting:
Description: Sets the interval (in minutes) between checks for new firmware
provisioning.resync_mode
determines which files the device retrieves when the resync process
begins.
Default: config_and_firmware
firmware_only,
config_and_firmware
provisioning.bootup_check_enable
provisioning.resync_time
and/or configuration file
Values: 0–65535 Default: 0 (OFF)
Setting:
Description: Enables or disables remotely triggering the device to check for new
Values: 0 (disabled), 1 (enabled) Default: 1
Setting:
Description: Enables or disables encryption check for the configuration file(s).
Values: 0 (disabled), 1 (enabled) Default: 0
provisioning.remote_check_sync_enable
firmware and/or configuration files. The file checking is triggered
remotely via a SIP Notify message from the server containing the
check-sync event.
provisioning.crypto_enable
Enable if you have encrypted the configuration file(s) using AES
encryption.
77 Appendix A: Configuration File Settings
Page 78

VSP600/VSP601 Administrator and Provisioning Manual
Setting:
Description: Sets the AES encryption passphrase for decrypting the configuration
Values: Text string Default: Blank
Setting:
Description: Enables or disables accepting only a trusted TLS certificate for
Values: 0 (disabled), 1 (enabled) Default: 0
Setting:
Description: Enables or disables the base station checking for the provisioning
Values: 0 (disabled), 1 (enabled) Default: 1
provisioning.crypto_passphrase
file(s). Enter the key that was generated when you encrypted the file.
provisioning.check_trusted_certificate
access to the provisioning server.
provisioning.pnp_enable
URL using the Plug-and-Play Subscribe and Notify protocol.
78 Appendix A: Configuration File Settings
Page 79

VSP600/VSP601 Administrator and Provisioning Manual
“time_date” Module: Time and Date Settings
The time and date settings follow the format: time_date.[elemen t].
All these settings are exported when you manually export the configuration from the
base station.
All the time and date settings are included in the general configu r ation file.
Setting:
Description: Enables or disables NTP server to set time and date.
Values: 0 (disabled), 1 (enabled) Default: 1
Setting:
Description: Sets the URL for the NTP server.
Values: Text string Default: us.pool.ntp.org
Setting:
Description: Enables or disables DHCP option 42 to find the NTP server.
Values: 0 (disabled), 1 (enabled) Default: 0
time_date.ntp_server
time_date.ntp_server_addr
time_date.ntp_dhcp_option
Setting:
Description: Sets the local timezone.
Values: Pacific/Pago_Pago, Pacific/Honolulu,
79 Appendix A: Configuration File Settings
time_date.selected_timezone
Default: America/New_York
America/Adak, America/Anchorage,
America/Vancouver, America/Tijuana,
America/Los_Angeles,
America/Edmonton,
America/Chihuahua, America/Denver,
America/Phoenix, America/Winnipeg,
Pacific/Easter, America/Mexico_City,
America/Chicago, America/Nassau,
America/Montreal,
America/Grand_Turk,
America/Havana, America/New_York,
America/Caracas, America/Halifax,
America/Santiago, America/Asuncion,
Atlantic/Bermuda, Atlantic/Stanley,
Page 80

VSP600/VSP601 Administrator and Provisioning Manual
America/Port_of_Spain,
America/St_Johns, America/Godthab,
America/Argentina/Buenos_Aires,
America/Fortaleza,
America/Sao_Paulo,
America/Noronha, Atlantic/Azores,
GMT, America/Danmarkshavn,
Atlantic/Faroe, Europe/Dublin,
Europe/Lisbon, Atlantic/Canary,
Europe/London, Africa/Casablanca,
Europe/Tirane, Europe/Vienna,
Europe/Brussels, Europe/Zagreb,
Europe/Prague, Europe/Copenhagen,
Europe/Paris, Europe/Berlin,
Europe/Budapest, Europe/Rome,
Europe/Luxembourg, Europe/Skopje,
Europe/Amsterdam, Africa/Windhoek,
Europe/Tallinn, Europe/Helsinki,
Asia/Gaza, Europe/Athens,
Asia/Jerusalem, Asia/Amman,
Europe/Riga, Asia/Beirut,
Europe/Chisinau, Europe/Kaliningrad,
Europe/Bucharest, Asia/Damascus,
Europe/Istanbul, Europe/Kiev,
Africa/Djibouti, Asia/Baghdad,
Europe/Moscow, Asia/Tehran,
Asia/Yerevan, Asia/Baku, Asia/Tbilisi,
Asia/Aqtau, Europe/Samara,
Asia/Aqtobe, Asia/Bishkek,
Asia/Karachi, Asia/Yekaterinburg,
Asia/Kolkata, Asia/Almaty,
Asia/Novosibirsk, Asia/Krasnoyarsk,
Asia/Bangkok, Asia/Shanghai,
Asia/Singapore, Australia/Perth,
Asia/Seoul, Asia/Tokyo,
Australia/Adelaide, Australia/Darwin,
Australia/Sydney, Australia/Brisbane,
Australia/Hobart, Asia/Vladivostok,
Australia/Lord_Howe, Pacific/Noumea,
Pacific/Auckland, Pacific/Chatham,
Pacific/Tongatapu
Setting:
Description: Sets the device to automatically adjust clock for daylight savings.
Values: 0 (disabled), 1 (enabled) Default: 1
80 Appendix A: Configuration File Settings
time_date.daylight_saving_auto_adjust
Page 81

VSP600/VSP601 Administrator and Provisioning Manual
Setting:
time_date.daylight_saving_user_defined
Description: Enables or disables manual daylight savings configuration.
Values: 0 (disabled), 1 (enabled) Default: 0
Setting:
time_date.daylight_saving_start_month
Description: Sets the month that daylight savings time starts.
Values: January–December Default: March
Setting:
time_date.daylight_saving_start_week
Description: Sets the week that daylight savings time starts.
Values: 1–5 Default: 2
Setting:
time_date.daylight_saving_start_day
Description: Sets the day that daylight savings time starts.
Values: Sunday, Monday, Tuesday,
Default: Sunday
Wednesday, Thursday,
Friday, Saturday
Setting:
time_date.daylight_saving_start_hour
Description: Sets the hour that daylight savings time starts.
Values: 00:00–23:00 Default: 02:00
Setting:
time_date.daylight_saving_end_month
Description: Sets the month that daylight savings time ends.
Values: January–December Default: November
81 Appendix A: Configuration File Settings
Page 82

VSP600/VSP601 Administrator and Provisioning Manual
Setting:
time_date.daylight_saving_end_week
Description: Sets the week that daylight savings time ends.
Values: 1–5 Default: 1
Setting:
time_date.daylight_saving_end_day
Description: Sets the day that daylight savings time ends.
Values: Sunday, Monday, Tuesday,
Default: Sunday
Wednesday, Thursday,
Friday, Saturday
Setting:
time_date.daylight_saving_end_hour
Description: Sets the hour that daylight savings time ends.
Values: 00:00–23:00 Default: 02:00
Setting:
time_date.daylight_saving_amount
Description: Sets the daylight savings time offset in minutes.
Values: 0–255 Default: 60
Setting:
time_date.timezone_dhcp_option
Description: Enables or disables DHCP option 2/100/101 for determining time zone
information.
Values: 0 (disabled), 1 (enabled) Default: 0
Setting:
time_date.ntp_server_update_interval
Description: Sets the delay between NTP server updates, in seconds.
Values: 0–4294967295 Default: 1000
82 Appendix A: Configuration File Settings
Page 83

VSP600/VSP601 Administrator and Provisioning Manual
“log” Module: Log Settings
The log settings control system logging activities. The following loggin g modes are
supported:
Serial/Console
Syslog server
Volatile file
The log settings follow the format: log.element.
All the log settings are included in the general configuration file.
Setting:
Description: Enables or disables log output to syslog server.
Values: 0 (disabled), 1 (enabled) Default: 0
Setting:
Description: Sets the syslog server IP address.
Values: Text string (IPv4) Default: Blank
Setting:
Description: Sets the syslog server port.
Values: 1–65535 Default: 514
log.syslog_enable
log.syslog_server_address
log.syslog_server_port
Setting:
Description: Sets the log level. The higher the level, the larger the debug output.
Values: 0–5 Default: 2
83 Appendix A: Configuration File Settings
log.syslog_level
5—all
4—debug
3—info
2—warning
1—error
0—critical
Page 84

VSP600/VSP601 Administrator and Provisioning Manual
“web” Module: Web Settings
The web settings control the web server IP, port, and security settings.
The web settings follow the format: web.element.
All the web settings are included in the general configuration file.
Setting:
Description: Sets the http port when http is enabled.
Values: 1–65535 Default: 80
Setting:
Description: Sets server to use the https protocol.
Values: 0 (disabled), 1 (enabled) Default: 0
Setting:
Description: Sets the https port when https is enabled.
Values: 1–65535 Default: 443
web.http_port
web.https_enable
web.https_port
84 Appendix A: Configuration File Settings
Page 85

VSP600/VSP601 Administrator and Provisioning Manual
“user_pref” Module: User Preference Settings
The user settings are accessible to the user. These settings are useful for initial
setup. You may wish to remove these settings from auto-provisioning update files so
that users do have their own settings overwritten.
The user preference settings follow the format: user_pref.element.
The user preference setting is included in the general configuration file.
Setting:
Description: Sets the language that appears on the WebUI.
Values: en, fr, es Default: en
user_pref.web_language
85 Appendix A: Configuration File Settings
Page 86

VSP600/VSP601 Administrator and Provisioning Manual
“call_settings” Module: Call Settings
The call settings configure data related to a user’s call preferences. The data is
stored internally at /mnt/flash/CallSettings.xml.
All the call settings (except one) follow the format: call_settings.account.x.[element]
where x is an account number ranging from 1 to 6.
All the call settings are included in the MAC-specif ic configuration file.
Setting:
Description: Enables or disables anonymous call blocking.
Values: 0 (disabled), 1 (enabled) Default: 0
Setting:
Description: Enables or disables outgoing anonymous calls.
Values: 0 (disabled), 1 (enabled) Default: 0
Setting:
Description: Enables or disables Do Not Disturb for account x.
Values: 0 (disabled), 1 (enabled) Default: 0
call_settings.account.x.block_anonymous_enable
call_settings.account.x.outgoing_anonymous_enable
call_settings.account.x.dnd_enable
Setting:
Description: Enables or disables Call Forward Always for account x.
Values: 0 (disabled), 1 (enabled) Default: 0
Setting:
Description: Sets the Call Forward Always target number for account x.
Values: Text string Default: Blank
86 Appendix A: Configuration File Settings
call_settings.account.x.call_fwd_always_enable
call_settings.account.x.call_fwd_always_target
Page 87

VSP600/VSP601 Administrator and Provisioning Manual
Setting:
Description: Enables or disables Call Forward Busy for account x.
Values: 0 (disabled), 1 (enabled) Default: 0
Setting:
Description: Sets the Call Forward Busy target number for account x.
Values: Text string Default: Blank
Setting:
Description: Enables or disables Call Forward No Answer for account x.
Values: 0 (disabled), 1 (enabled) Default: 0
call_settings.account.x.call_fwd_busy_enable
call_settings.account.x.call_fwd_busy_target
call_settings.account.x.cfna_enable
Setting:
Description: Sets the Call Forward No Answer target number for account x.
Values: Text string Default: Blank
Setting:
Description: Sets the Call Forward No Answer delay (in number of rings) for
Values: 1–10 Default: 6
call_settings.account.x.cfna_target
call_settings.account.x.cfna_delay
account x.
87 Appendix A: Configuration File Settings
Page 88

VSP600/VSP601 Administrator and Provisioning Manual
“file” Module: Imported File Settings
The “file” parameters enable the provisioning file to import additional configuration
files of various types, including:
Contact lists
Security certificates
The following certificates are supported:
Per-account TLS certificate (you can choose to use the Account 1 certificate for
all accounts)
Web server (the base station has a default self-signed web server certificate)
Provisioning
Languages
File parameter values are URLs that direct the base station to the location of th e file
to be imported.
None of these settings are exported when you manually export the configuration
from the base station.
General Configuration File Settings
Setting:
Description: URI of HTTPS server certificate to be imported, .e.g.
Values: Text string Default: Blank
Setting:
Description: URI of provisioning certificate to be imported, e.g.
Values: Text string Default: Blank
Setting:
Description: URI of SIPS (TLS transport) certificate to be imported for account x,
Values: Text string Default: Blank
file.https_user.certificate
<protocol>://<user>:<password>@<host>:<port>/<url-path>
file.provisioning.trusted.certificate
<protocol>://<user>:<password>@<host>:<port>/<url-path>
file.sips.trusted.certificate.x
e.g. <protocol>://<user>:<password>@<host>:<port>/<url-path>
88 Appendix A: Configuration File Settings
Page 89

VSP600/VSP601 Administrator and Provisioning Manual
MAC-Specific Configuration File Settings
Setting:
Description: URL of contact directory to be imported. Entries in the imported file
Values: Text string Default: Blank
Setting:
Description: URL of contact directory to be imported. Entries in the imported file
Values: Text string Default: Blank
Setting:
Description: URL of contact blacklist to be imported. Entries in the imported file will
Values: Text string Default: Blank
file.contact.directory.append
will be added to existing directory entries.
file.contact.directory.overwrite
will replace all existing directory entries.
file.contact.blacklist.append
be added to existing blacklist entries.
Setting:
Description: URL of contact blacklist to be imported. Entries in the imported file will
Values: Text string Default: Blank
file.contact.blacklist.overwrite
replace all existing directory entries.
89 Appendix A: Configuration File Settings
Page 90

VSP600/VSP601 Administrator and Provisioning Manual
“profile” Module: Password Settings
The password settings allow you to set the default administrator and user passwords
in the configuration file. The administrator passw ord is usually included in the
general configuration file, while the user password is usually included in the MACspecific configuration file. The passwords can also be set using the WebUI. Be aware
that scheduled provisioning configuration file updates may reset these passwords.
General Configuration File Settings
Setting:
Description: Sets the administrator password, used for accessing the admin menus
Values: Text string Default: admin
profile.admin.password
on the base station and the WebUI.
MAC-Specific Configuration File Settings
Setting:
Description: Sets the user password, used for accessing the voicemail and settings
Values: Text string Default: user
profile.user.password
on the base station and the WebUI.
90 Appendix A: Configuration File Settings
Page 91

VSP600/VSP601 Administrator and Provisioning Manual
Maintenance
Taking care of your products
Your base station and handsets contain sophisticated electronic parts, so you
must treat them with care.
Avoid rough treatment.
Place the handset down gently.
Save the original packing materials to protect your base station and handsets if
you ever need to ship them.
Avoid water
You can damage your base station and handsets if they get wet. Do not use the
handset in the rain, or handle it with wet hands. Do not install the base station
near a sink, bathtub or shower.
Electrical storms
Electrical storms can sometimes cause power surges harmful to electronic
equipment. For your own safety, take caution when using electric appliances
during storms.
Cleaning your products
Your products have a durable plastic casing that should retain its luster for
many years. Clean it only with a soft clot h slightly dampened with water or a
mild soap.
Do not use excess water or cleaning solvents of any kind.
Remember that electrical appliances can cause serious injury if used when you are
wet or standing in water. If the base station should fall into water, DO NOT
RETRIEVE IT UNTIL YOU UNPLUG THE POWER CORD AND NETWORK CABLE FROM
THE WALL, then pull the unit out by the unplugged cords.
91 Maintenance
Page 92

VSP600/VSP601 Administrator and Provisioning Manual
Important Safety Information
This symbol is to alert you to important operating or servicing
instructions that may appear in this user’s manual. Always follow basic
safety precautions when using this product to reduce the risk of injury,
fire, or electric shock.
Safety Information
Read and understand all instructions in the user’s manual. Observe all
markings on the product.
Avoid using a telephone during a thunderstorm. There may be a slight chance
of electric shock from lightning.
Do not use the device to report a gas leak in the vicinity of the leak. Under
certain circumstances, a spark may be created when the adapter is plugged
into the power outlet, or when the handset is replaced in its cradle. This is a
common event associated with the closing of any electrical circuit. The user
should not plug the device into a power outlet, and should not put a charged
handset into the cradle, if the device is located in an env ironment containing
concentrations of flammable or flame-supporting gases, unless there is
adequate ventilation. A spark in such an environment could create a fire or
explosion. Such environments might include: medical use of oxygen without
adequate ventilation; industrial gases (cleanin g solvents; gasoline vapors;
etc.); a leak of natural gas; etc.
Do not use this product near water, or when you are wet. For example, do not
use it in a wet basement or shower, or next to a swimming pool, bathtub,
kitchen sink, or laundry tub. Do not use liquids or aerosol sprays for cleaning.
If the product comes in contact with any liquid, unplug any line or power cord
immediately. Do not plug the product back in until it has dried thoroughly.
Install this product in a protected location where no one can trip over any line
or power cords. Protect cords from damage or abrasion.
If this product does not operate normally, see the Troubleshooting section in
your product’s manual. If you cannot solve the problem, or if the product is
damaged, refer to the Limited warranty. Do not open this product except as
directed in your user’s manual. Opening the product or reassembling it
incorrectly may expose you to hazardous voltages or other risks.
This power adapter is intended to be correctly oriented in a vertical or floor
mount position. The prongs are not designed to hold the plug in place if it is
plugged into a ceiling, an under-the-table or cabinet outlet.
Caution: Use only the power adapter provided with this product. To
obtain a replacement, visit our website at
businessphones.vtech.com or call 1 (888) 370-2006.
SAVE THESE INSTRUCTIONS
92 Important Safety Information
Page 93

VSP600/VSP601 Administrator and Provisioning Manual
Industry Canada
Operation is subject to the following two conditions: (1) this device may not cause
harmful interference, and (2) this device must accept any interf erence, including
interference that may cause undesired operation.
The term “IC:” before the certification/registration number only signifies that the
Industry Canada technical specifications were met.
This product meets the applicable Industry Canada technical specifications.
93 Industry Canada
Page 94

VSP600/VSP601 Administrator and Provisioning Manual
FCC part 15
This device complies with Part 15 of the FCC rules. Operation is subject to the
following two conditions: (1) This device may not cause harmful interference, and
(2) this device must accept any interference received, inclu ding interference that
may cause undesired operation.
This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a Class A
digital device, pursuant to Part 15 of the FCC Rules. These limits are designed to
provide reasonable protection against harmful interference when the equipment is
operated in a commercial environment. This equipment generates, uses, and can
radiate radio frequency energy and, if not installed and used in accordance with the
instruction manual, may cause harmful interference to radio communications.
Operation of this equipment in a residential area is likely to cause harmful
interference in which case the user will be required to correct the interference at the
user’s expense.
Privacy of communications may not be ensured when using this phone.
This Class A digital apparatus complies with Canadian ICES-003.
Cet appareil numérique de la classe A est conforme à la norme NMB-003 du Canada.
94 FCC part 15
Page 95

VSP600/VSP601 Administrator and Provisioning Manual
GPL License Information
Portions of the software associated with this product are open source, and fall within
the scope of the GNU General Public License (GPL). Accordingly, those portions of
code are available to the public, consistent with the requirements of the GPL, in
either source code format or object code format, depending upon the nature of the
code at issue. If you would like to exercise your right to receive the available code,
please send a cashier’s check, payable to VTech Communications, Inc., in the
amount of $15.00 (U.S.$) to:
VTech Communications, Inc.,
9590 SW Gemini Drive, Suite 120
Beaverton OR 97008
ATTN: Information Technology Group—VSP600 GPL code request, along with a
written request for the available code. If your request does not fully comply with the
foregoing requirements, VTech reserves the right to reject your request. Further, by
requesting and receiving the available code, you release VTech, its affiliates, and its
and their officers, directors, employees, and representatives (“VTech Parties”) from
any liability or responsibility relating to such code, and you acknowledge that the
VTech Parties make no representations with respect to the origin, accuracy, usability,
or usefulness of such code, and the VTech Parties have no responsibility to you
whatsoever concerning the code, including without limitation any responsibility to
provide explanation, support, upgrade, or any communication whatsoever. Your
review or use of the available code is at your sole risk and responsibility.
95 GPL License Information
 Loading...
Loading...