Page 1

Quick Reference Guide
Combined Wind Sensors
WMS301 & WMS302
– Combined wind speed & direction
measurements
– Suitable for low power applications
DESCRIPTION
WMS301 and WMS302 are compact sized wind sensors with the
wind speed and direction sensors integrated into one unit. The
sensor electronics is located inside a watertight compartment
providing full protection against water, dust, pollutants, and
electromagnetic interference.
The cup wheel shape, dimensions, and material have been
carefully designed to achieve maximum quality of measurement.
The conical cups have been tested to give linear response
between wind speed and angular velocity of the cup wheel. The
polyamide plastic reinforced with carbon fiber guarantees a rigid
structure even at the highest wind speeds.
The anemometer ball bearing assembly is composed of a wheel
shaft, a pair of low friction ball bearings, and a shaft fixed
magnet. A reed relay with electronics located in the body of the
sensor converts the cup wheel rotation to pulses. Therefore,
when properly supplied the sensor can be read practically with
any data logger, either by counting the number of pulses within a
fixed time period or measuring the time between successive
transients. Averaging of transient intervals should be used, since
two pulses with non-symmetric positioning are generated during
one revolution.
The balanced wind vane is integrated in the housing, underneath
the cup wheel. The circular tail is located far enough from the
body and the cup wheel to avoid turbulences due to these
structures. The vane assembly is of PA reinforced with glass
fiber providing durable and lightweight structure with fast
response and low inertia.
The angular position of the vane is detected using an axial
symmetric rotating potentiometer. The potentiometer features
low starting and running torque, linear arc-to-resistance transfer
ratio, and long operation life.
WMS301 is equipped with a one-wiper-type potentiometer with
an open cap of only 5 degrees. With constant voltage applied to
the potentiometer, the output voltage is directly proportional to
the azimuth angle. WMS302 has a two-wiper-type potentiometer
to overcome the cap discontinuity. However, a more complex
voltage-to-direction conversion process is needed.
0009-020
Figure 1 Connectors of WMS301 and WMS302
INSTALLATION
After a proper place for wind measurement has been selected,
the WMS301 sensor can be mounted to the mast as follows:
Fit the cable through the mounting piece and connect the
1.
cable to the sensor.
Fasten the mounting piece to the sensor with the plastic
2.
collar.
Place the sensor onto the mast.
3.
Connect the ohmmeter between +Vref and the DIR pin
4.
(WMS301) or between +Vref and DIR1 pin (WMS302).
Keep the vane pointed to the north and turn the base until
5.
resistance reaches its minimum value. Fasten the
mounting screw.
After initial installation, the sensor can be removed and
remounted to its place with the plastic collar without realigning,
except after potentiometer replacement.
– Fast response
– Excellent linearity
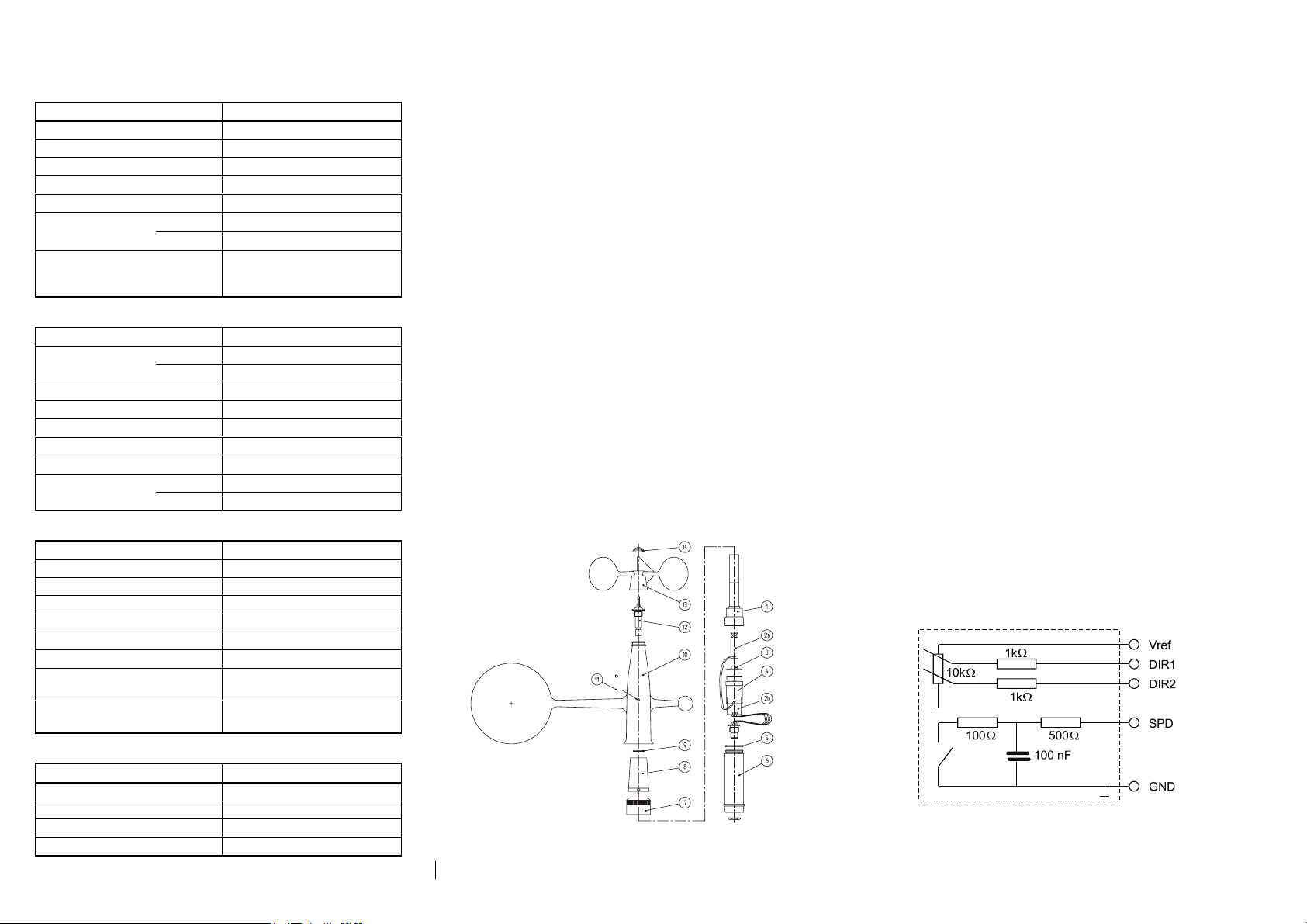
INITIAL CHECK
After having unpacked the sensor, please check for any signs of
shipping damage. Test that the vane and cup wheel rotate
without friction. Before installation, use an ohmmeter to check
the proper operation of SPEED output and DIR output(s) while
rotating the cup wheel/vane slowly. 10 kΩ/360º and
10 kΩ/180° potentiometers are used with WMS301 and
WMS302, respectively. Refer to Figure 4.
0009-021
Figure 2 Mounting of WMS Sensors to the Mast
Page 2
TECHNICAL DATA
Anemometer
Property Description / Value
Sensor / Transducer type Dual Reed switch
Measuring range 0.5 ... 60 m/s
Starting threshold < 0.4 m/s
Distance constant 2 m
Transducer output 1 Hz ~ 0.7 m/s
Accuracy
Transfer function, where
U = wind speed [m/s]
F = output frequency [Hz]
Vane
Sensor / Transducer type Potentiometer
Measuring range WMS302 0 ... 360°
Starting threshold < 1.0 m/s
Damping ratio 0.3
Overshoot Ratio 0.4
Delay Distance 0.6 m
Accuracy
Transducer output WMS302 Vref/180 ~ 1°
Common
Supply voltage 3 ... 15 VDC
Electrical connections 5-pin male with 12 mm threads
Operating temperature - 40 ... + 55 °C
Storage temperature - 60 ... + 65 °C
Dimensions 265 (h) × 360 (w) mm
Weight 360 g
Body material AlMgSi, gray anodized
Cup material
Vane material PA, reinforced with glass fiber,
(≤ 10 m/s) ± 0.3 m/s
(> 10 m/s)
WMS301 0 ... 355°
WMS301 Vref/360 = 1°
error < 2 %
U = - 0.24 + F × 0.699
better than ± 3°
PA, reinforced with carbon
fiber; black
white
MAINTENANCE
It is recommended to check the ball bearings of the anemometer
and the vane every year. If the cup wheel or the vane is not
rotating smoothly or creates detectable noise, the bearings must
be replaced (refer to Figure 3).
Anemometer bearings:
Loosen the hubnut (14) with fingers or a 10 mm tool and
1.
remove the cup wheel (13).
Remove the ball bearing assembly (12) by unscrewing it
2.
counterclockwise (with a 10 mm tool).
Insert a new bearing assembly (12). Tighten gently.
3.
Fasten the cup wheel to the sensor. Tighten gently.
4.
Vane bearings:
Proceed as described in steps 1 and 2 above.
1.
Open the lock screw (11) of the assembly (10) and
2.
remove the screw.
Remove the Seeger-ring (9) (with narrow point pliers).
3.
Remove the bearing assembly (8).
4.
Replace the bearings inside the housing with new ones.
5.
Assemble the sensor in the reverse work order.
6.
Due to normal wear, it may become necessary to renew the
direction potentiometer or the anemometer electronics assembly.
Remove the sensor housing parts as described in steps
1.
1 to 6 above.
Open the body (1 + 6) by unscrewing it clockwise.
2.
To replace the potentiometer, proceed as follows:
3.
Pull the potentiometer PCB (2b) out from the sleeve (4).
3-1.
Unsolder the potentiometer wires from the PCB.
3-2.
Solder new potentiometer wires to the PCB.
3-3.
Push the PCB (2b) into the plastic sleeve (4) by pressing
3-4.
the sleeve sides. Note the guide holes.
To replace the reed-switch PCB, proceed as follows:
4.
Pull out the retainer (3) and the reed-switch PCB (2b).
4-1.
Unsolder the old wires and solder new ones for the PCB.
4-2.
Push the PCB into the tube of the casing (1).
4-3.
Fit the flat wire to the groove at the casing wall and
4-4.
insert the retainer. Make sure that the flat wire is tightly
against the casing wall.
Insert the potentiometer assembly into the upper part
5.
tubing.
Screw the body parts (1) and (6) together. Tighten
6.
carefully.
Ensure the mast adapter sleeve (7) is on the base part (6).
7.
Place the bearing housing (8) to the casing and secure
8.
with a Seeger-ring (9).
Place the vane assembly (10) onto the body. The lock
9.
screw hollow at the casing must be seen through the lock
screw hole of the vane body.
Fasten the assembly with a lock screw (11). Tighten
10.
gently.
Screw the bearing housing (12) into the casing (1).
11.
Tighten gently.
Fasten the cup wheel to the sensor shaft.
12.
A pull up resistor (10 kΩ, e.g.) is needed at SPD output to
supply the anemometer electronics. It is recommended to use a
Schmitt-trigger input with the SPD signal.
Spare Parts
Spare Part Order Code
Cup wheel assembly WA45233
Anemometer bearing assembly WA45232
Vane assembly WA35234
Set of bearings 25160WA
www.vaisala.com Ref. M010030en-C
Figure 3 WMS Sensor Assembly
0009-022
0009-023
Figure 4 WMS302 Principal Circuit Diagram (DIR2 Is Not in
Use with WMS301)
 Loading...
Loading...