Us robotics Courier I-modem Getting Started Guide

Courier™ I-modem®
Getting Started Guide
Final Draft
Based on part number 1.024.1153-00
ã1997 U.S. Robotics
8100 N. McCormick Blvd.
Skokie, IL 60076-2999 USA

The material contained in this manual is for information purposes only and is subject to change without notice.
No part of this document may be reproduced, transmitted, transcribed, or stored in a retrieval system in any form or by any means, mechanical, magnetic, electronic, optical, chemical, or otherwise without the written permission of U.S. Robotics.
U.S. Robotics, the U.S. Robotics logo, V.Everything, and Adaptive Speed Leveling are registered trademarks and Courier and x2 are trademarks of U.S. Robotics. Microsoft, MS-DOS, Windows, and Windows NT are registered trademarks of Microsoft Corporation. AppleTalk and Macintosh are trademarks of Apple Computer, Inc.
Any trademarks, trade names, service marks, or service names owned or registered by any other company and used in this manual are the property of their respective companies.
U.S. Robotics assumes no responsibility for errors or omissions in this manual. Nor does U.S. Robotics make any commitment to update the information contained herein.
ã1997 U.S. Robotics
8100 N. McCormick Blvd.
Skokie, IL 60076-2999 USA

Read this First
Installing Your Courier I-modem
To install your |
Go to |
|
|
Internal modem |
Chapter 4, page 1 |
|
|
External modem into a PC |
Chapter 5, page 1 |
|
|
External modem to a Macintosh |
Chapter 5, page 1 |
|
|
Configuring Your Courier I-modem
To configure your Courier for |
Go to |
|
|
Windows 95® |
Chapter 8, page 1 |
|
|
Macintosh® |
Chapter 9, page 1 |
|
|
Other operating systems |
Chapter 10, page 1 |
|
|
Using LEDs, Jumpers, and DIP Switches
To do this |
Go to |
|
|
Locate jumpers |
Chapter 12, page 5 |
|
|
Modify jumper settings (internal Courier) |
Chapter 12, page 5 |
|
|
Locate DIP switches on the internal Courier |
Chapter 12, page 3 |
|
|
Modify DIP switch settings on the internal Courier |
Chapter 12, page 3 |
|
|
Locate DIP switches on the external Courier |
Chapter 12, page 1 |
|
|
Modify DIP switch settings on the external Courier |
Chapter 12, page 1 |
|
|
Understand the LEDs |
Chapter 13, page 1 |
|
|

Contents
Chapter 1 Introduction............................................................................................. |
1-1 |
How to Use this Guide ............................................................................................... |
1-1 |
Contacting U.S. Robotics........................................................................................... |
1-1 |
I-modem Features...................................................................................................... |
1-2 |
Dial Security to Control Access to Your System ..................................................... |
1-2 |
Testing................................................................................................................... |
1-2 |
Flash ROM Upgradability ..................................................................................... |
1-2 |
Plug and Play Support for Windows 95.................................................................. |
1-2 |
Remote Configuration and Diagnostics.................................................................. |
1-2 |
Terminal Adapter Features .................................................................................... |
1-3 |
Integral V.Everything Modem Features ................................................................. |
1-4 |
Chapter 2 The I-modem and ISDN .......................................................................... |
2-1 |
Overview.................................................................................................................... |
2-1 |
Internal I-modem .................................................................................................... |
2-1 |
External I-modem ................................................................................................... |
2-1 |
External I-modem for Macintosh ............................................................................ |
2-1 |
What is ISDN? ........................................................................................................... |
2-2 |
Benefits of ISDN ..................................................................................................... |
2-2 |
The ISDN Basic Rate Interface ............................................................................... |
2-2 |
How Does the I-modem Fit In? ................................................................................... |
2-4 |
U-Interface with Integrated NT-1............................................................................ |
2-5 |
S/T Interface........................................................................................................... |
2-5 |
Setting Up Your I-modem for ISDN ........................................................................... |
2-6 |
How the I-modem Calls a Variety of Devices.............................................................. |
2-6 |
Internet Access (TurboPPP).................................................................................... |
2-6 |
Universal Connect .................................................................................................. |
2-7 |
V.110 Connections.................................................................................................. |
2-7 |
Modem and Fax Calls............................................................................................. |
2-7 |
Clear-Channel Synchronous Connections ............................................................... |
2-7 |
Chapter 3 Ordering ISDN Service ........................................................................... |
3-1 |
Overview................................................................................................................... |
3-1 |
The U.S. Robotics I-team ....................................................................................... |
3-1 |
Requesting ISDN Service .......................................................................................... |
3-2 |
Chapter 4 Installing Your Internal I-modem ......................................................... |
4-1 |
Requirements ............................................................................................................. |
4-1 |
Configuration Manager Requirements ........................................................................ |
4-1 |
Package Contents ....................................................................................................... |
4-2 |
Important! .................................................................................................................. |
4-3 |
Installing Your Internal I-modem ............................................................................... |
4-4 |
Step One: Configuring with Jumpers ...................................................................... |
4-4 |
Step Two : Configuring with DIP Switches.............................................................. |
4-6 |
Step Three: Inserting the Modem ............................................................................ |
4-8 |
Step Four: Connecting the Cables ........................................................................ |
4-10 |
Testing the Installation ............................................................................................. |
4-11 |
Chapter 5 Installing Your External I-modem......................................................... |
5-1 |
What You Need .......................................................................................................... |
5-1 |
Package Contents ....................................................................................................... |
5-1 |
Installing Your External I-modem .............................................................................. |
5-2 |
Step One: Connecting the Serial Cable................................................................... |
5-3 |
Step Two: Connecting the ISDN Cable ................................................................... |
5-4 |
Chapter 6 Using the Configuration Manager .......................................................... |
6-1 |
Overview.................................................................................................................... |
6-1 |
Configuration Manager .......................................................................................... |
6-1 |
Configuring the I-modem........................................................................................ |
6-1 |
What You Should Know............................................................................................. |
6-1 |
Directory Numbers ................................................................................................. |
6-1 |
Service Profile Identifiers ....................................................................................... |
6-2 |
Terminal Endpoint Identifier .................................................................................. |
6-2 |
Installing the Configuration Manager ......................................................................... |
6-2 |
Configuring the I-modem ........................................................................................... |
6-3 |
Testing ....................................................................................................................... |
6-8 |
Special Considerations for AT&T 5ESS Custom ........................................................ |
6-8 |
If You Have No SPIDS and Only One DN ............................................................... |
6-9 |
If You Have One SPID and One DN...................................................................... |
6-10 |
Chapter 7 Configuring With AT Commands........................................................... |
7-1 |
Overview.................................................................................................................... |
7-1 |
Configuring the I-modem........................................................................................ |
7-1 |
What You Should Know............................................................................................. |
7-1 |
Directory Numbers ................................................................................................. |
7-1 |
Service Profile Identifiers ....................................................................................... |
7-1 |
Terminal Endpoint Identifier .................................................................................. |
7-1 |
Preparing to Send AT Commands .............................................................................. |
7-2 |
Configuring and Testing Your I-modem ..................................................................... |
7-3 |
Step One: Configuring the I-modem........................................................................ |
7-3 |
Step Two: Checking the Configuration.................................................................... |
7-6 |
Step Three: Saving the Configuration ..................................................................... |
7-6 |
Step Four: Testing the Configuration...................................................................... |
7-7 |
Special Considerations for AT&T 5ESS Custom ........................................................ |
7-8 |
If You Have No SPIDs and Only One DN................................................................ |
7-9 |
If You Have One SPID and One DN...................................................................... |
7-10 |
Chapter 8 Configuring Your Courier For Windows 95.......................................... |
8-1 |
Overview.................................................................................................................... |
8-1 |
What You Need .......................................................................................................... |
8-1 |
Configuring Your Courier With Plug and Play ........................................................... |
8-1 |
Files Needed By Your I-modem .................................................................................. |
8-3 |
Installing the Latest I-modem Software ...................................................................... |
8-4 |
Accessing Your Internet Service Provider................................................................... |
8-4 |
Step One: Determine if Dial-Up Networking is Installed......................................... |
8-4 |
Step Two: Installing Dial-Up TCP/IP Support ........................................................ |
8-7 |
Step Three: Setting Up a Connection to Your ISP ................................................... |
8-8 |
Step Four: Customizing the TCP/IP Settings......................................................... |
8-11 |
Chapter 9 Configuring Your I-modem For Macintosh........................................... |
9-1 |
Handshaking Cable .................................................................................................... |
9-1 |
System Configuration ................................................................................................. |
9-1 |
Accessing the Internet ................................................................................................ |
9-1 |
Configuring MacTCP ............................................................................................. |
9-2 |
Installing MacPPP Dialer ...................................................................................... |
9-2 |
Configuring ConfigPPP Dialer............................................................................... |
9-3 |
Dialing With ConfigPPP......................................................................................... |
9-3 |
Chapter 10 Configuring Your I-modem for Other Operating Systems ............... |
10-1 |
If You Are Using Windows 3.x................................................................................ |
10-1 |
If You Are Using Windows NT 4.0.......................................................................... |
10-2 |
What You Need .................................................................................................... |
10-2 |
Configuring Your I-modem .................................................................................. |
10-2 |
Installing the Latest I-modem Software ................................................................ |
10-2 |
If You Are Using MS-DOS...................................................................................... |
10-3 |
If You Are Using OS/2 ............................................................................................ |
10-4 |
If You Are Using UNIX, Linux, or AIX .................................................................. |
10-5 |
Chapter 11 Configuring TurboPPP With AT Commands..................................... |
11-1 |
Overview................................................................................................................. |
11-1 |
Point to Point Protocol (PPP) / ML-PPP................................................................... |
11-1 |
Determining TurboPPP Settings .......................................................................... |
11-1 |
Setting PPP/ML-PPP Host and Originate Mode .................................................. |
11-2 |
Making Calls With ML-PPP ................................................................................ |
11-2 |
Dynamic Data Bandwidth Allocation....................................................................... |
11-4 |
Controlling Dynamic Bandwidth Allocation in ML-PPP ...................................... |
11-4 |
Setting When the Second Link Comes Up............................................................. |
11-5 |
Setting When the Second Link Comes Down......................................................... |
11-5 |
Enabling the Tone When the Second Link Comes Up ........................................... |
11-5 |
Using Compression in TurboPPP mode ............................................................... |
11-6 |
Chapter 12 Configuring Your I-modem With DIP Switches and Jumpers........... |
12-1 |
DIP Switches on the External I-modem .................................................................... |
12-1 |
Locating DIP Switches.......................................................................................... |
12-1 |
Default DIP Switches (Model U)........................................................................... |
12-1 |
Default DIP Switches (Model U, V.35).................................................................. |
12-2 |
Default DIP Switches (Model S/T) ........................................................................ |
12-2 |
DIP Switches on the Internal I-modem ..................................................................... |
12-3 |
Locating DIP Switches.......................................................................................... |
12-3 |
Default DIP Switches............................................................................................ |
12-3 |
Using DIP Switches to Configure Your I-modem................................................... |
12-4 |
Jumpers on the Internal I-modem ............................................................................. |
12-4 |
Locating Jumpers ................................................................................................. |
12-4 |
Changing Jumper Settings .................................................................................... |
12-5 |
Setting Jumpers for a Specific COM Port ............................................................. |
12-6 |
Setting Jumpers for a Specific IRQ ....................................................................... |
12-6 |
Chapter 13 Viewing LEDs...................................................................................... |
13-1 |
Chapter 14 Using x2 ............................................................................................... |
14-1 |
Enhanced x2 Features.............................................................................................. |
14-1 |
How to Tell if x2 is Enabled in Your I-modem ........................................................ |
14-2 |
Obtaining x2 ........................................................................................................... |
14-2 |
How x2 Works......................................................................................................... |
14-3 |
Controlling x2 ......................................................................................................... |
14-3 |
x2 Server Mode ................................................................................................... |
14-3 |
x2 Symmetric Mode (Host Mode) ......................................................................... |
14-3 |
Controlling Link Speeds with &N and &U .............................................................. |
14-3 |
Controlling Link Speeds ...................................................................................... |
14-4 |
Limiting the Highest Possible Connect Speed ...................................................... |
14-4 |
Limiting the Lowest Possible Connect Speed........................................................ |
14-5 |
Limiting a Range of Possible Connect Speeds...................................................... |
14-5 |
&N and &U Command Values ............................................................................. |
14-6 |
Troubleshooting x2 Client Connections ................................................................... |
14-7 |
New x2 Result Codes............................................................................................... |
14-8 |
Appendix A Other I-modem Features..................................................................... |
A-1 |
Data Over Voice ....................................................................................................... |
A-1 |
Protocols Supported by Data Over Voice.............................................................. |
A-1 |
Configuring Data Over Voice ............................................................................... |
A-1 |
Period Dial Modifier................................................................................................. |
A-2 |
PCSDL vs. XMODEM ............................................................................................. |
A-2 |
230 kbps DTE Rate Under Windows® ...................................................................... |
A-2 |
Saving Money With Analog Calls............................................................................. |
A-3 |
Appendix B Technical Information......................................................................... |
B-1 |
Technical Specifications ........................................................................................... |
B-1 |
Standards Compatibility ....................................................................................... |
B-1 |
ISDN .................................................................................................................... |
B-1 |
Modulation ........................................................................................................... |
B-2 |
Error Control, Data Compression, Testing, and Dialing....................................... |
B-3 |
Fax ....................................................................................................................... |
B-3 |
Additional Specifications ...................................................................................... |
B-4 |
Ringer Equivalence .............................................................................................. |
B-5 |
Power Consumption ................................................................................................. |
B-5 |
Serial Ports............................................................................................................... |
B-5 |
The EIA-232 Interface.............................................................................................. |
B-6 |
Wiring a DB-25 to DB-9 Cable............................................................................. |
B-7 |
Minimum Requirements ........................................................................................ |
B-7 |
For Macintosh Computers ........................................................................................ |
B-8 |
Serial Ports (Macintosh modem) ........................................................................... |
B-9 |
Appendix C The Serial Port .................................................................................... |
C-1 |
Choosing a Serial Cable ............................................................................................ |
C-1 |
Macintosh ................................................................................................................. |
C-2 |
Appendix D Warranty............................................................................................. |
D-1 |
U.S. Robotics Access Corp. Limited Warranty ........................................................... |
D-1 |
Terms of the Limited Warranty .............................................................................. |
D-1 |
What Is NOT Covered By the Limited Warranty ....................................................... |
D-3 |
How To Access Your Warranty Services.................................................................... |
D-4 |
Notices ...................................................................................................................... |
D-7 |
FCC Registration .................................................................................................. |
D-7 |
IC (Industry Canada)............................................................................................. |
D-8 |
UL Listed Accessory .............................................................................................. |
D-9 |

Chapter 1
Introduction
How to Use this Guide
Use this Getting Started Guide to obtain the information you need to get your Courier™ I-modem® modem installed, configured, and running correctly.
For more information about advanced commands, view the I-modem Command Reference, which is on the Connections CD-ROM.
If you understand how ISDN works, you can skip directly to Chapter 3,
Ordering ISDN.
Contacting U.S. Robotics
Please contact U.S. Robotics if you have any questions.
To do this |
Contact |
|
|
Contact U.S. Robotics Technical Support |
1.800.231.8770 |
|
|
Use the Fax-on-Demand service |
1.800.762.6163 |
|
|
Download updated I-modem x2 code from |
847.982.5092 (analog) |
the U.S. Robotics Bulletin Board System |
847.734.8612 (V.120 ISDN) |
|
|
|
|
Download updated I-modem code |
http://totalservice.usr.com |
|
|
Visit the U.S. Robotics web site |
http://www.usr.com |
|
|
Visit U.S. Robotics on Compuserve |
GO USROBOTICS |
|
|
Visit U.S. Robotics on America Online |
Keyword: USROBOTICS |
|
|
Introduction |
1-1 |

I-modem Features
Dial Security to Control Access to Your System
The Courier’s Dial Security feature allows you to control access at a modem-to-modem level instead of using software that runs on the host computer. With Dial Security, you can prevent unauthorized access to a system through the use of password prompting and dial-back.
Testing
ITU-T V.54 loopback testing is available. The Courier can perform analog, digital, and remote digital loopback tests to determine if there are problems with the phone line, the remote device, or your Courier’s transmitter or receiver.
Flash ROM Upgradability
Courier modems are software-upgradable using XMODEM file transfers and U.S. Robotics Software Download (SDL) application, allowing you quick, easy access to updates of your Courier’s technology. The latest upgrades can be obtained on the U.S. Robotics web site or Bulletin Board System.
Plug and Play Support for Windows 95
The software for the external and internal Courier has been developed to support Plug and Play (as defined by the Plug and Play External and Internal COM Device Specification, Version 1.00). When you connect your Courier to a computer that uses a Plug and Play operating system, the computer automatically detects and configure itself to the support your Courier.
Remote Configuration and Diagnostics
You can remotely configure and test your Courier. If you are a network administrator supporting remote users, this feature can save you time and money.
Terminal Adapter Features
ISDN Terminal Adapter
The I-modem is an ISDN terminal adapter; it enables your computer to
1-2 |
Courier I-modem Getting Started Guide |

communicate on the ISDN at speeds of up to 64 kbps.
Optional Built-in NT-1
The I-modems with Integrated NT-1 contain an on-board NT-1, sparing you the expense and extra cabling associated with an external NT-1.
Optional Analog Device Jack
The I-modem with Integrated NT-1 and Analog Device Jack allows you to plug in an analog telephone, fax machine, or modem, allowing analog devices to communicate over an ISDN B-channel. This applies to external units only.
TurboPPP
TurboPPP is U.S. Robotics’ unique combination of asynchronous- to-synchronous PPP conversion, compression, multilink PPP (ML-PPP). You can use TurboPPP to access the Internet or remote local-area networks (LANs) at speeds of up to 128 kbps before compression and up to 512 kbps with compression.
Rate Adaptation
The I-modem’s support of the V.120 and V.110 protocols allows it to map slower-speed asynchronous data to the 64-kbps B-channel. The I-modem’s rate adaptation capability spans the range of 300 to 57600 bps.
Central Office Switch Compatibility
Works with AT&T 5ESS and Northern Telecom DMS-100 switches that run either their custom protocols or National ISDN-1, as well as with other manufacturer’s switches that use National ISDN-1 or National ISDN-2 call control signaling (ITU-T Q.931/I.451 call control signaling).
Introduction |
1-3 |

Link Diagnostics
After each call, you can display a Link Diagnostics screen (ATI6) containing information about the last call, including the number of data characters transferred, line statistics, the call's rate, and the reason the call was disconnected.
Switched-56 Support
The I-modem can communicate to remote devices connected via Switched-56 circuits.
V.120 and V.110 Connections
V.120 and V.110 are standards for passing asynchronous data over ISDN B-channels, which are inherently synchronous. To make a connection using V.120 or V.110, devices at both ends of the connection must support V.120 or V.110.
Modem and Fax Calls
The I-modem emulates an analog fax/modem, allowing you to connect to remote analog modems and fax machines using 3.1 kHz audio format.
Voice Calls
If your I-modem has an Analog Device port, you can connect a standard, analog telephone and use the phone over your ISDN line. Be aware that the internal I-modem cannot provide ringing voltage through the Analog Device port, so equipment that autoanswers, such as a fax or answering machine, will not work correctly.
Integral V.Everything Modem Features
Supports Analog Fax/Modem Calls
The I-modem always makes and receives calls over ISDN. Since there is no guarantee that the device at the other end of the line is ISDN-capable, the I-modem can communicate with non-ISDN devices, such as analog modems and Group III fax.
1-4 |
Courier I-modem Getting Started Guide |

x2 56-kbps Connectivity
If you have enabled x2, your Courier can connect at speeds up to 56 kbps. While line conditions may not always allow for 56 kbps
connections, the new Courier software allows you to achieve the fastest analog speeds available.
Adaptive Speed Leveling to Adjust to Line Conditions
Adaptive Speed Leveling® (ASL) allows your Courier to monitor line conditions while connected, and fall back to the next lower speed if conditions are poor. Couriers also detect improved line conditions and shift upward to the next higher speed. The transmit and receive channels adapt independently, each detecting and adjusting to line conditions.
Calls to and from Modems and Fax Machines
When used with fax-capable communications software, your Courier auto-detects and responds to calls from modems and Group III fax machines using EIA-standard Class 1 or 2.0 fax software.
Data Compression¾V.42 bis/MNP5
Data compression enables throughput of up to 230.4 kbps on analog connections. I-modems connecting under V.42 or HST error control use V.42bis compression. I-modems connecting under MNP error control use MNP Level 5 compression. Typically, files can be compressed from 2:1 to 4:1.
Error Control¾V.42/MNP
Data integrity is ensured when the I-modem connects with remote devices that use the V.42 (LAPM), HST, or MNP error control protocols. Error control is available on analog calls at 1200 bps and above.
V.Everything
The Courier provides full support of the x2, V.34 standard, V.Fast Class, V.32 terbo, and many other modulation schemes, spanning the range of speeds between 300 bps and 56 kbps.
Introduction |
1-5 |

1-6 |
Courier I-modem Getting Started Guide |

Chapter 2
The I-modem and ISDN
The Courier I-modem with ISDN/V.Everything is an Integrated Services Digital Network (ISDN) terminal adapter that can perform all the functions of a Courier V.Everything fax/modem.
Overview
The I-modem is capable of exchanging data over the ISDN at speeds of up to 128 kbps with ISDN devices or up to 56 kbps with analog devices, before compression.
Internal I-modem
There are two versions of the internal I-modem:
∙The ISDN U-Interface with an analog device jack (Model U)
∙The ISDN S/T-Interface (Model S/T)
External I-modem
There are two versions of the external I-modem:
∙The ISDN U-Interface with an analog device jack (Model U)
∙The ISDN S/T-Interface (Model S/T)
External I-modem for Macintosh
There is one version of the I-modem for Macintosh. The Courier I-modem for Macintosh is the same as Model U (ISDN U-Interface with Analog Device Jack).
The I-modem and ISDN |
2-1 |
What is ISDN?
Integrated Services Digital Network is an application of digital technology that provides end-to-end digital service over the public communications network. ISDN was designed to integrate the transmissions from a variety of devices, (computers, telephones, and fax machines) into one digital network.
Because ISDN was designed for transmitting digital information, it has many advantages over the analog telephone network. Digital transmission is more accurate and reliable, and that helps increase transmission speeds to up to 64 kbps per channel.
Benefits of ISDN
The benefits of ISDN include:
∙Increased bandwidth
∙Fewer errors during data transfer
∙Quicker call setups and teardowns.
The ISDN Basic Rate Interface
Physical Appearance
The I-modem communicates over an ISDN Basic Rate Interface (BRI) line. You must order a BRI line from your local telephone company before you can use your I-modem. Chapter 2, Ordering ISDN Service, explains how to order ISDN and which services to request.
BRI works over the same wiring that is in place for your analog telephone lines. The difference is in the equipment you attach and the signaling used.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
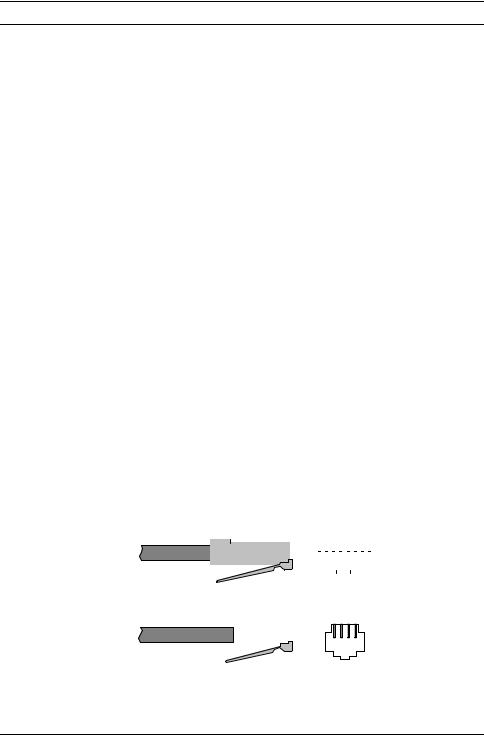
RJ45 Connector |
RJ45 Jack |
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
RJ11 Connector |
RJ11 Jack |
Figure 2.4 RJ45 and RJ11 Connectors and Jacks.
2-2 |
Courier I-modem Getting Started Guide |
At your site, the BRI line takes the form of an RJ45 or RJ11 wall jack, which in ISDN is called the U interface. RJ45 connectors have eight pins and RJ11s have four or six pins. At the U-interface, you can plug an RJ11 connector into an RJ45 jack, and your line will work correctly.
The telephone company adds a line termination device at their end of the BRI that adapts the line for ISDN.
B-channels and D-channels
Though BRI signals are transmitted over an ordinary pair of wires, BRI typically contains three channels. The channels are created by complex signaling techniques.
BRI is composed of two 64-kbps B-channels and one 16-kbps D-channel:
This |
Does this |
|
|
B-channels |
Carries (or “Bears”) data or voice traffic |
|
|
D-channel |
Sets up and tears down calls |
|
|
Logical View
D-channel (16 Kbps)
B-channel (64 Kbps)
B-channel (64 Kbps)
Physical View
RJ45 Connector
Figure 2.5 ISDN BRI—Three Logical Channels Over One Pair of
Wires.
The I-modem and ISDN |
2-3 |

Required Components
BRI-line signals must be translated into signals your computer can understand. Several devices must be in place to perform the translation.
This |
Is a device |
|
|
|
|
TE2 |
That does not have built-in ISDN capability. |
|
(Terminal Equipment 2) |
TE2s require Terminal Adapters (TAs), |
|
such as the I-modem, to communicate over |
||
|
||
|
the ISDN. Example: Computer. |
|
|
|
|
TA |
That translates between non-ISDN signaling |
|
(Terminal Adapter) |
that TE2s provide (such as EIA-232) and the |
|
S/T-interface signaling that the NT-1 |
||
|
||
|
understands. |
|
|
|
|
NT-1 |
That ranslates between the short-distance |
|
(Network Termination |
signaling used at the S/T-interface and the |
|
longer-distance signaling used at the |
||
[Unit] -1 |
||
U-interface. NT-1s also convert from the |
||
|
||
|
two wires used for the phone line to the six |
|
|
or eight wires needed for the S/T bus. |
|
|
|
How Does the I-modem Fit In?
The I-modem needs an NT-1 device to work with ISDN. If you currently use an NT-1 device, you can use the S/T-interface I-modem.
This version of I-modem |
Allows the I-modem to connect |
|
|
U-Interface Integrated NT-1 |
Directly to the U-interface |
|
|
S/T-Interface |
To an external NT-1 device (you must |
|
have an NT-1 device) |
|
|
2-4 |
Courier I-modem Getting Started Guide |
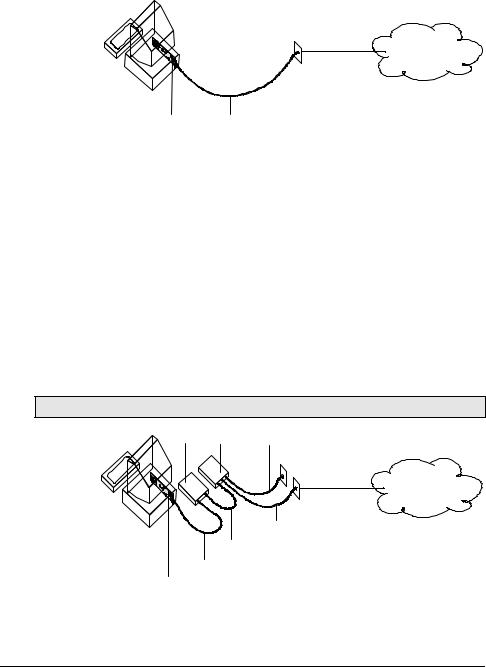
U-Interface with Integrated NT-1
Figure 1–5 illustrates how the I-modems with Integrated NT-1 connect your computer to the ISDN.
ISDN
BRI Line
I-modem U
Figure 2.6 A Typical Installation of the I-modem
Once you’ve subscribed to ISDN service (see Chapter 2, Ordering ISDN Service, for much more detail), your local telephone company will install a BRI line at your site.
You install the I-modem in your computer and connect a cable between the I-modem and the phone jack. Then run the I-modem Configuration Manager or send commands to change a few settings. Before long, you’ll be making calls on the ISDN.
S/T Interface
Figure 2.6 illustrates how the I-modem S/T connects your computer to the ISDN.
Note: Some NT-1s contain an integrated power supply.
Power
NT-1 Supply AC Power
ISDN
BRI
U
U + Power
S/T
I-modem
Figure 2.7 A Typical Installation of the I-modem S/T.
The I-modem and ISDN |
2-5 |

Setting Up Your I-modem for ISDN
You can get your ISDN service working by following these five easy steps:
Step One: Subscribe to ISDN service.
Step Two: Your local telephone company will install a BRI line at your site.
Step Three: Install the I-modem in your computer.
Step Four: Purchase and install an NT-1 (if necessary) and connect the cables.
Step Five: Run the I-modem Configuration Manager and change a few settings.
How the I-modem Calls a Variety of Devices
When you use the I-modem, all your calls go over one or both ISDN B-channels. However, you can set the I-modem to make different kinds of calls over the B-channel:
Internet Access (TurboPPP)
TurboPPP makes the most of your ISDN line in a way that’s transparent to your computer and the networking applications running on it. You can use TurboPPP to access the Internet or remote local-area networks (LANs) at speeds of up to 128 Kbps before compression and up to 512 Kbps with compression.
TurboPPP is U.S. Robotics’ unique combination of asynchronous-to-synchronous PPP conversion, compression, multilink PPP (MP-PPP), and PPP/MP-PPP spoofing.
Asynchronous-to-Synchronous PPP Conversion
Most Internet service providers that allow ISDN connections expect your data to arrive in synchronous Point-to-Point Protocol (PPP) format. Most computers, however, can’t deliver synchronous PPP through their serial ports.
To solve this problem, the I-modem has the ability to convert asynchronous PPP data to synchronous PPP. This capability allows you to use networking software that is intended for asynchronous PPP connections (such as Windows 95 Dial-Up Networking or NetManage Chameleon) to access the Internet or remote LANs.
2-6 |
Courier I-modem Getting Started Guide |

Compression
The I-modem supports the leading de-facto standards for compression over ISDN: Stac LZS, Microsoft, and Ascend.
Multilink PPP (MP-PPP)
Multilink PPP support enables the I-modem to use both of the available B-channels simultaneously. The I-modem uses PPP/MP-PPP spoofing to mediate between applications running on your computer, which may not be aware of MP-PPP, and host computers that support MP-PPP. In effect, the I-modem tricks both ends of the connection, keeping them happy communicating the way they’re accustomed, while maximizing throughput.
Universal Connect
When the I-modem is set to Universal Connect, it autosenses V.120, V.110, or analog fax/modem connections. Use Universal Connect when calling ISDN or analog Bulletin Board Systems (BBSs), for example. For details, see Chapter 11, Handshaking, Error Control, Data Compression, and Throughput, in the I-modem Command Reference manual.
V.110 Connections
V.120 and V.110 are standards for passing asynchronous data over ISDN B-channels, which are inherently synchronous. To make a connection using V.120 or V.110, the device at the other end of the connection must also support V.120 or V.110. A typical application of V.120 is for BBSs.
Modem and Fax Calls
The I-modem emulates an analog fax/modem, allowing you to connect to remote analog modems and fax machines.
Clear-Channel Synchronous Connections
When you set the I-modem to make clear-channel synchronous connections, it sets up a 64 Kbps connection with a remote device, enabling you to exchange any kind of synchronous data. Common applications of clear-channel synchronous are videoconferencing and remote access to minior mainframe computers.
The I-modem and ISDN |
2-7 |

2-8 |
Courier I-modem Getting Started Guide |

Chapter 3
Ordering ISDN Service
This chapter gives you and your local telephone company all the information needed to set up the lines correctly.
Overview
To order ISDN service, contact your local telephone company, give them information about your I-modem, and record information that they give you, such as your new ISDN telephone numbers, called SPIDs.
If you decide that you would like assistance with the ordering process, call the U. S. Robotics I-team at (888) USR-ISDN.
The U.S. Robotics I-team
The I-team is a subset of U.S. Robotics’ Customer Support department that provides assistance with the ISDN ordering and configuring process. The I-team determines the availability and pricing of ISDN service in your area, installation costs, lead time for installation, and will coordinate the configuration of the telephone company’s equipment so your I-modem will work properly.
Ordering ISDN Service |
3-1 |

Requesting ISDN Service
1 Call your local telephone company and request Bellcore Capability Package S (listed in Bellcore SR-3840).
If your telephone company does not recognize Bellcore capability packages, request the following items:
∙ISDN BRI service.
∙Number of channels: 2B+D, with no packet-mode data on the D- channel.
∙Call type support:
This channel |
Supports |
|
|
Data B-channel |
Circuit-Switched Voice and Data |
|
(CSV/D) |
|
|
Analog Device B-channel |
Circuit-Switched Voice and Data |
|
(CSV/D) |
|
|
∙Dynamic TEI assignment.
∙Multipoint bus configuration.
∙No features or special services such as CACH EKTS, call forwarding, or hunt groups.
∙Terminal Type A.
∙RJ45 jack (RJ11 is acceptable).
2 Specify your preferred long-distance provider.
3 Ask the telephone company which type of central-office switch your ISDN line will terminate and which protocol the switch uses. Record the switch type and protocol here:
ü |
Switch |
Protocol |
|
|
|
r |
AT&T 5ESS |
Custom |
|
|
|
r |
AT&T 5ESS |
National ISDN-1 |
|
|
|
r |
Northern Telecom DMS-100 |
Custom (PVC 0 or 1) |
|
|
|
r |
Northern Telecom DMS-100 |
National ISDN-1 (PVC 2) |
|
|
|
r |
Siemens EWSD |
National ISDN-1 |
|
|
|
r |
Other |
National ISDN-1 |
|
|
|
3-2 |
Courier I-modem Getting Started Guide |
4 Obtain the following information from your local telephone company:
∙1 SPID (Service Profile Identifier) per B-channel.
∙1 DN (Directory Number) per B-channel.
∙Call types supported on each B-channel.
∙If the switch does not auto-assign TEIs (most do), then you need one fixed TEI per B-channel.
For this Record the number here
SPID 1
SPID 2
DN 1
DN 2
5 If you have an internal I-modem, continue with Chapter 4, Installing the Internal I-modem.
If you have an external I-modem, continue with Chapter 5, Installing the External I-modem.
Ordering ISDN Service |
3-3 |

3-4 |
Courier I-modem Getting Started Guide |

Chapter 4
Installing Your
Internal I-modem
This chapter explains how to:
∙Configure with jumpers
∙Configure with DIP switches
∙Insert the internal I-modem
∙Connect cables to the internal I-modem
Important: Review Chapter 2, The I-modem and ISDN, and Chapter 3, Ordering ISDN Service, before installing the I-modem.
Requirements
You need the following to install your I-modem:
∙IBM-compatible computer with a free interface card slot
∙An ISDN Basic Rate Interface line
∙Communications software
∙An NT-1 and Power Supply (I-modem S/T only)
Note: An NT-1 is a device that terminates the ISDN line and translates between the U-interface signaling from the telephone company and the S/T-interface signaling needed by ISDN terminal devices, such as the I-modem S/T. Only I-modem S/T’s require an external NT-1.
Configuration Manager Requirements
You need the following to run the U.S. Robotics I-modem Configuration Manager software:
∙386SX, or better, CPU.
∙8 MB, or more, RAM.
∙DOS 5.0 or higher and Windows 3.1, or higher.
Installing the Internal I-modem |
4-1 |

Package Contents
Your I-modem package contains the following items:
∙The I-modem
∙Telephone cable
∙Quick Reference card
∙Customer Support card
∙This Getting Started manual
∙I-modem Configuration Manager diskette.
∙The Connections CD-ROM, which contains:
–I-modem Command Reference Guide
–RapidComm communications software and manuals
–Stampede Remote Office Gold software and manuals
–Special offers
–Updated I-modem INF file
4-2 |
Courier I-modem Getting Started Guide |

Important!
The I-modem emulates a serial interface card with a 16550 UART. Like serial interface cards, it must be assigned a unique communications (COM) port number and a unique interrupt request (IRQ) number.
If you are using a computer with a Plug and Play compliant BIOS and operating system and you set the I-modem’s jumpers to Plug and Play (the default), your computer’s operating system will take care of the COM and IRQ settings for you.
Setting the COM port and IRQ yourself requires a detailed knowledge of the settings of the other adapter cards in your computer. If other adapter cards are set to use the same COM port or IRQ, conflicts may occur that could result in data loss or lockups.
First, determine whether your computer has a Plug and Play ISA bus. Check your computer’s documentation to be sure. Keep these points about Plug and Play in mind:
∙Your computer’s operating system must support Plug and Play (examples of those that do: OS/2 Warp, Windows 95, Windows NT), or your computer’s manufacturer must supply you with Plug and Play software.
∙Your computer’s Basic Input/Output System (BIOS) must support Plug and Play.
Installing the Internal I-modem |
4-3 |
 Loading...
Loading...