TP-Link Pharos CPE605 User Manual

User Guide
For TP-Link Pharos Series Products
CPE210 / CPE220 / CPE510 / CPE520 / CPE605 / CPE610
WBS210 / WBS510
1910012554 REV 3.1.0
March 2019

CONTENTS
About this User Guide ......................................................................................................... 1
Overview ................................................................................................................................. 2
1 Operation Modes ........................................................................................................... 3
1.1 Access Point ................................................................................................................................................ 4
1.2 Client ............................................................................................................................................................... 5
1.3 Repeater (Range Extender) .................................................................................................................... 6
1.4 Bridge ............................................................................................................................................................. 7
1.5 AP Router ...................................................................................................................................................... 7
1.6 AP Client Router (WISP Client) .............................................................................................................. 8
2 Quick Start ....................................................................................................................... 9
2.1 Check the System Requirements ......................................................................................................10
2.2 Log In to the Device ................................................................................................................................10
2.3 Set Up the Wireless Network ...............................................................................................................11
Access Point .................................................................................................................................................. 12
Client ............................................................................................................................................................... 16
Repeater (Range Extender) ...................................................................................................................... 19
Bridge ............................................................................................................................................................... 23
AP Router ........................................................................................................................................................ 27
AP Client Router (WISP Client) ................................................................................................................ 32
3 Monitor the Network ..................................................................................................38
3.1 View the Device Information ................................................................................................................39
3.2 View the Wireless Settings ...................................................................................................................39
3.3 View Wireless Signal Quality................................................................................................................40
3.4 View Radio Status ....................................................................................................................................41
3.5 View the LAN Settings ............................................................................................................................43
3.6 View the WAN Settings ..........................................................................................................................43

3.7 Monitor Throughput ................................................................................................................................44
3.8 Monitor Stations .......................................................................................................................................44
3.9 Monitor Interfaces ...................................................................................................................................45
3.10 Monitor ARP Table ...................................................................................................................................46
3.11 Monitor Routes .........................................................................................................................................46
3.12 Monitor DHCP Clients .............................................................................................................................47
3.13 Monitor Dynamic WAN ...........................................................................................................................47
4 Configure the Network .............................................................................................. 49
4.1 Configure WAN Parameters .................................................................................................................50
4.2 Configure LAN Parameters ..................................................................................................................57
Access Point/Client/Repeater/Bridge Mode ..................................................................................... 57
AP Router/AP Client Router Mode ......................................................................................................... 60
4.3 Configure Management VLAN ............................................................................................................62
4.4 Configure the Forwarding Feature ....................................................................................................62
4.5 Configure the Security Feature ..........................................................................................................66
4.6 Configure Access Control ....................................................................................................................69
4.7 Configure Static Routing .......................................................................................................................70
4.8 Configure Bandwidth Control ..............................................................................................................71
4.9 Configure IP & MAC Binding .................................................................................................................73
5 Configure the Wireless Parameters ..................................................................... 75
5.1 Configure Basic Wireless Parameters .............................................................................................76
5.2 Configure Wireless Client Parameters ............................................................................................78
5.3 Configure Wireless AP Parameters ...................................................................................................82
5.4 Configure Multi-SSID ..............................................................................................................................88
5.5 Configure Wireless MAC Filtering .....................................................................................................90
5.6 Configure Advanced Wireless Parameters ....................................................................................91
6 Manage the Device ..................................................................................................... 94
6.1 Manage System Logs .............................................................................................................................95

6.2 Specify the Miscellaneous Parameters ...........................................................................................96
6.3 Configure Ping Watch Dog ...................................................................................................................97
6.4 Configure Dynamic DNS ........................................................................................................................98
6.5 Configure Web Server............................................................................................................................99
6.6 Configure SNMP Agent ....................................................................................................................... 100
6.7 Configure SSH Server ......................................................................................................................... 102
6.8 Configure RSSI LED Thresholds ...................................................................................................... 102
7 Configure the System ............................................................................................. 104
7.1 Configure Device Information .......................................................................................................... 105
7.2 Configure Location Information ...................................................................................................... 105
7.3 Configure User Account ..................................................................................................................... 105
7.4 Configure Time Settings .................................................................................................................... 106
7.5 Update Firmware ................................................................................................................................... 108
7.6 Configure Other Settings ................................................................................................................... 109
8 Use the System Tools ............................................................................................. 110
8.1 Configure Ping ....................................................................................................................................... 111
8.2 Configure Traceroute .......................................................................................................................... 111
8.3 Test Speed .............................................................................................................................................. 112
8.4 Survey ....................................................................................................................................................... 113
8.5 Analyze Spectrum ................................................................................................................................. 115

About this User Guide
This User Guide contains information for setup and management of TP-Link Pharos series
products. Please read this guide carefully before operation.
When using this guide, please notice that features of the product may vary slightly depending on
the model and software version you have, and on your location, language, and internet service
provider. All screenshots, images, parameters and descriptions documented in this guide are used
for demonstration only.
Some models featured in this guide may be unavailable in your country or region. For local sales
information, visit
The information in this document is subject to change without notice. Every effort has been made
in the preparation of this document to ensure the accuracy of the contents, but all statements,
information, and recommendations in this document do not constitute the warranty of any kind,
express or implied. Users must take full responsibility for their application of any products.
http://www.tp-link.com
.
Convention
Unless otherwise noted, the introduction in this guide takes CPE510 as an example.
More Info
The latest software, management app and utility can be found at Download Center at
https://www.tp-link.com/support
The Quick Installation Guide can be found where you find this guide or inside the package of the
product.
Specifications can be found on the product page at
.
https://www.tp-link.com
.
Our Technical Support contact information can be found at the Contact Technical Support page at
https://www.tp-link.com/support
To ask questions, find answers, and communicate with TP-Link users or engineers, please visit
https://community.tp-link.com
.
to join TP-Link Community.
1

Overview
is TP-Link's next generation outdoor product series dedicated to long-distance
outdoor wireless networking solutions.
is a powerful Web-based operating system, which is integrated into all Pharos series
products.
New features of Pharos series products are listed as follows:
• Provides User-friendly UI design.
• TP-Link Pharos MAXtream (Time-Division-Multiple-Access) technology improves product
performance in throughput, capacity and latency, which are ideal for point-to-multipoint
applications.
• Supports multiple operation modes: Access Point, Client, Repeater (Range Extender), Bridge, AP
Router and AP Client Router (WISP Client).
• Provides system-level optimization for long-distance wireless transmission.
• Supports selectable bandwidth of 5/10/20/40MHz.
• Supports easy antenna alignment with Wireless Signal Indicators on Web interface.
• Provides Throughput Monitor, Spectrum Analyzer, Speed Test and Ping tools.
• Supports discovery and management via Pharos Control application.
2

1
The Pharos series products support six operation modes to satisfy user’s diversified
network requirements. This chapter introduces typical usage scenarios of different
modes, including:
1.1 Access Point
1.2 Client
1.3 Repeater (Range Extender)
1.4 Bridge
1.5 AP Router
1.6 AP Client Router (WISP Client)
Operation Modes
3
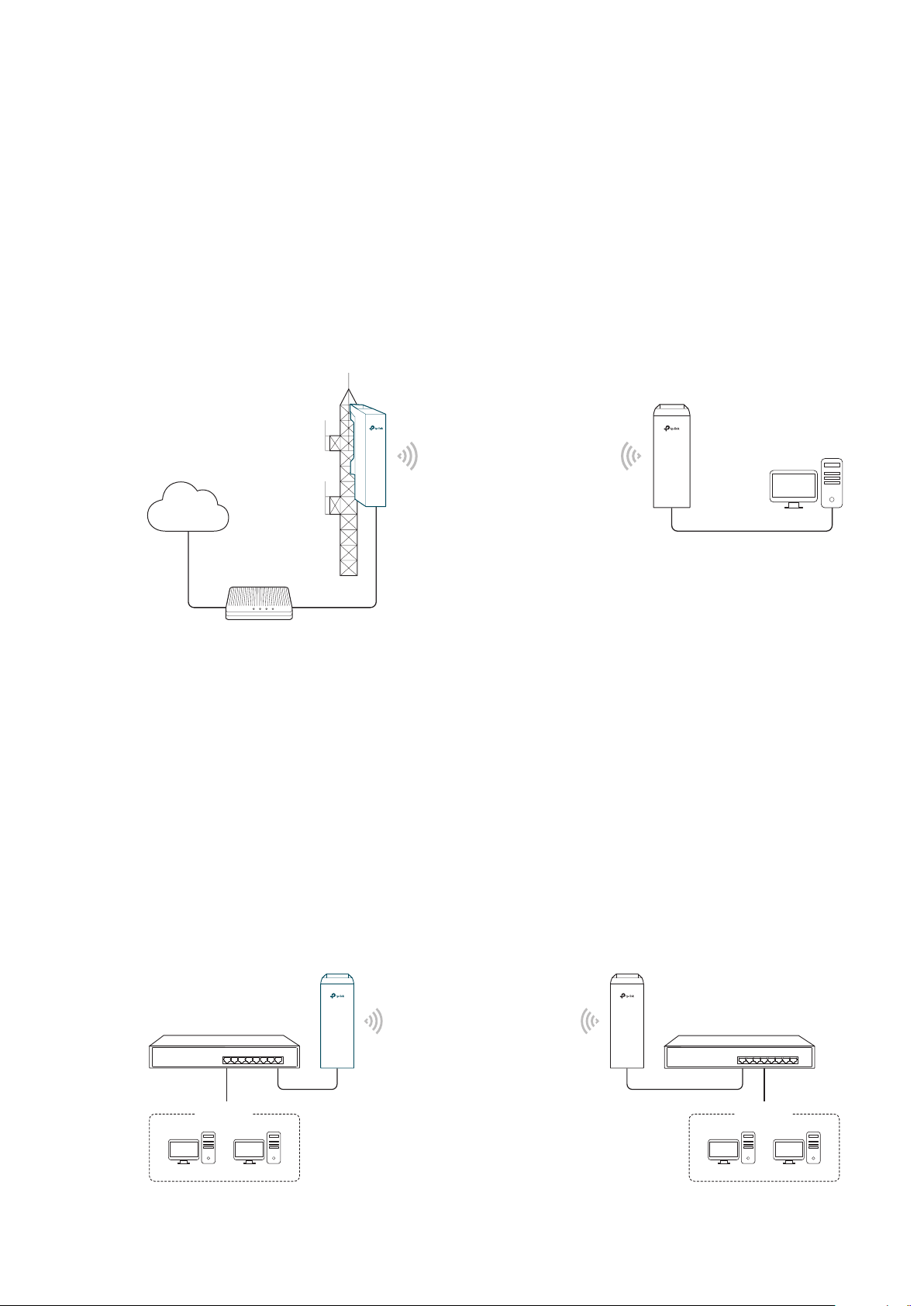
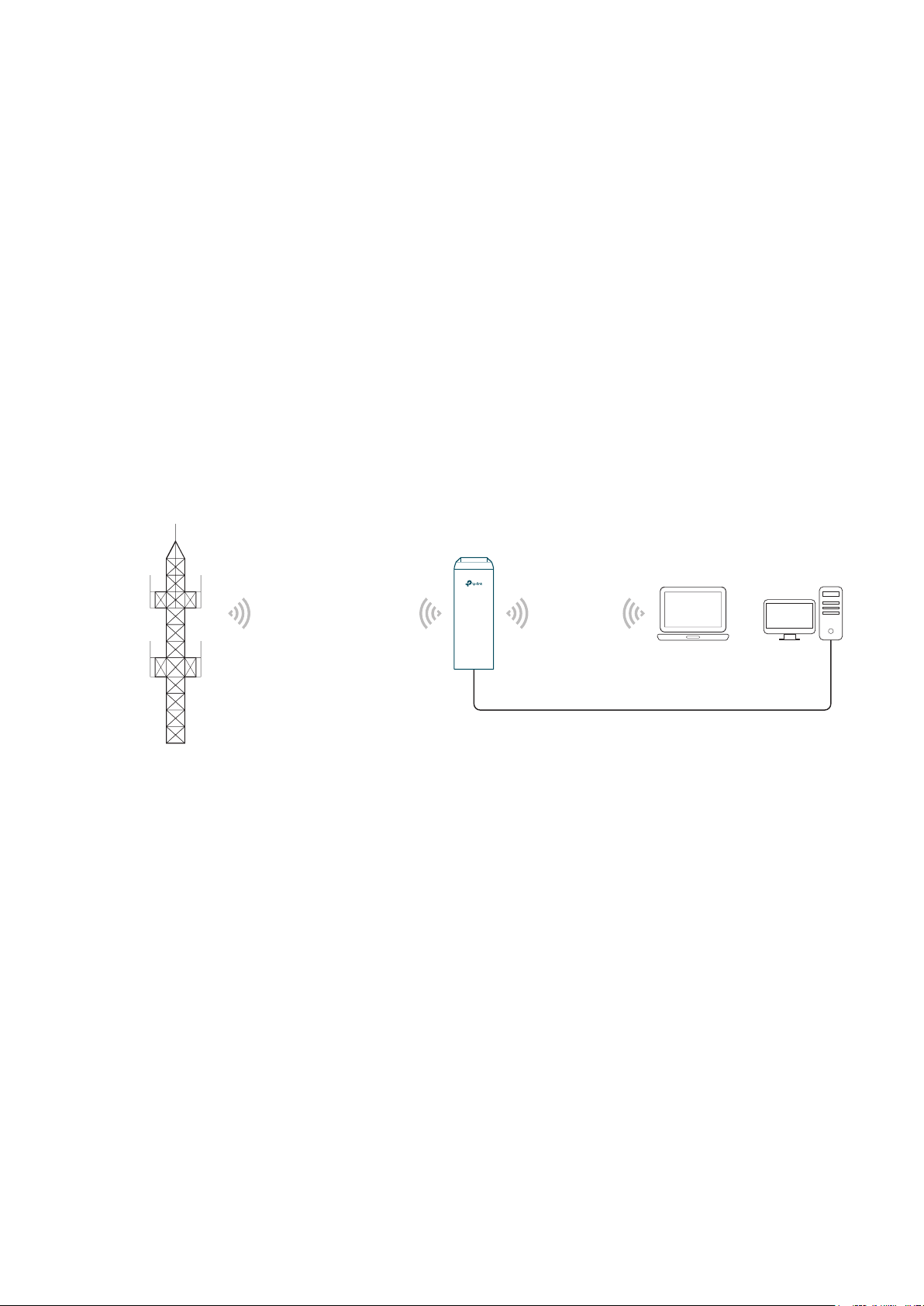
1.1 Access Point
In AP mode, the device acts as a central hub and provides wireless access point for
wireless clients, thus the AP mode is applicable to the following three scenarios.
Meanwhile, Multi-SSID function can be enabled in this mode, providing up to four wireless
networks with different SSIDs and passwords.
Scenario 1
Access Point
LAN: 192.168.7.2
Internet
Router
LAN: 192.168.7.1
AP Client Router
LAN: 192.168.0.254
WAN: Dynamic IP
Network requirements: Establish the network coverage in the remote areas without long-
distance cabling.
The device in the network: In the adjacent town covered by wired network, ISP (Internet
Service Provider) can put up a device in AP mode to access the internet and transform
wired signal into wireless one. In the remote area, users can put up a device in AP Client
Router mode to access the wireless network.
Advantages: Transmit data wirelessly across a long distance and reduce the cabling cost.
Scenario 2
Access Point Client
LAN: 192.168.0.254 LAN: 192.168.0.2
Switch
Oce Oce
4
Switch
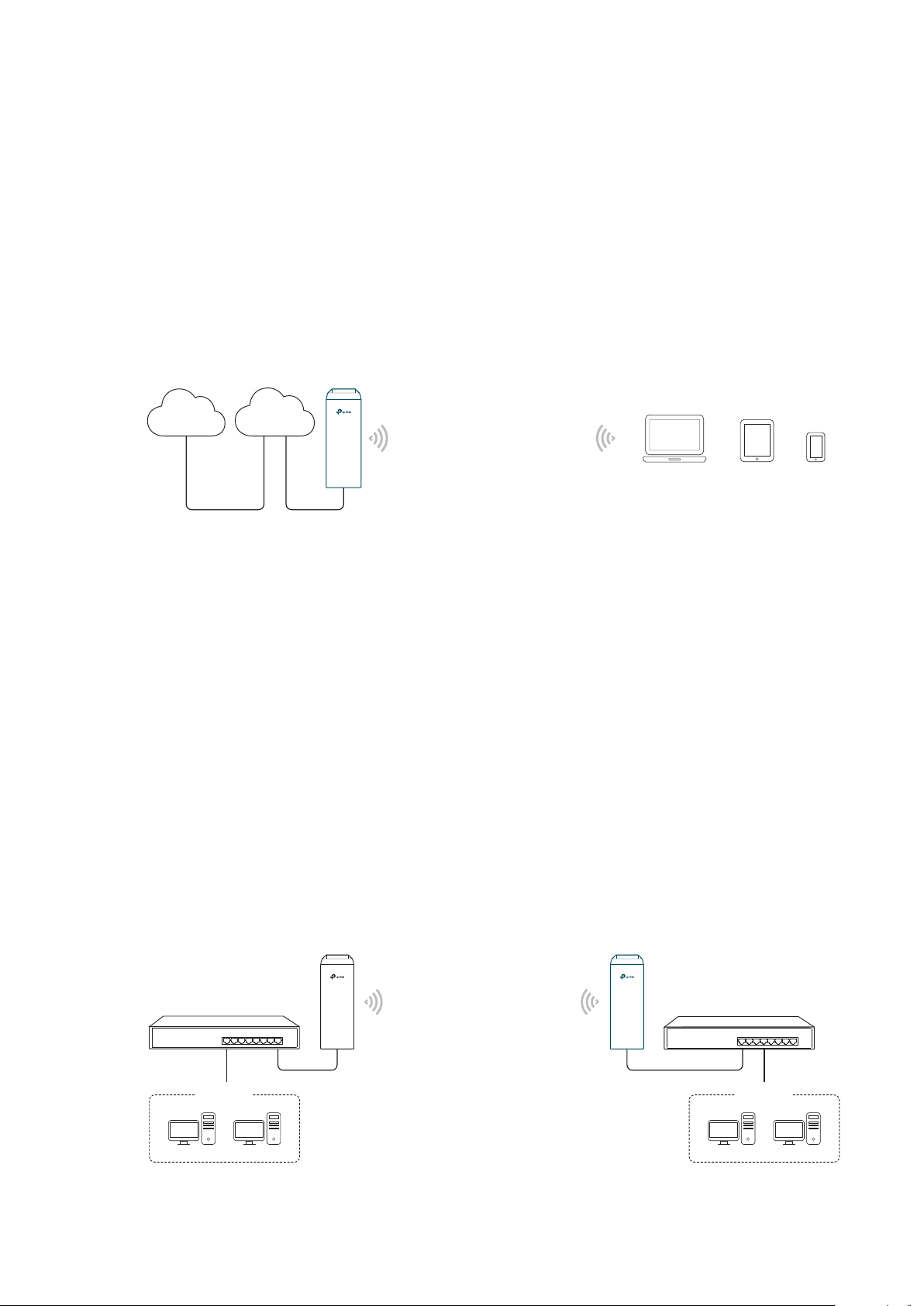
Network requirements: Combine two separate office networks into one.
The device in the network: The device in AP mode connects to one office network
and creates a wireless network. The device in Client mode connects to the other office
network and the wireless network.
Advantages: Establish a point-to-point WLAN across a long distance to achieve the
connectivity between two networks and avoid the cabling trouble.
Scenario 3
Internet
Network requirements: Establish wireless network coverage in the campus, community,
industrial park or public place to provide wireless access for users.
The device in the network: With the access to campus wired network or other wired local
area networks, the device in AP mode provides the wireless access for wireless clients,
such as smart phones, laptops and tablets to connect to the network.
Advantages: Enrich the access ways of local area network and extend the network
coverage.
1.2 Client
Wired Local
Area Network
Access Point
Laptop/Tablet/Smartphone
For the device in Client mode, the most common usage scenario is point-to-point
networking. The device is used to transform wireless signal into wired one.
Access Point
LAN: 192.168.0.254
Switch
Oce Oce
5
Client
LAN: 192.168.0.2
Switch
Network requirements: Help the wired devices to connect to the wireless network.
The device in the network: In Client mode, the device actually serves as a wireless adapter
to receive the wireless signal from root AP or Station. In this case, wired devices can
access the wireless network by connecting to the device in Client mode.
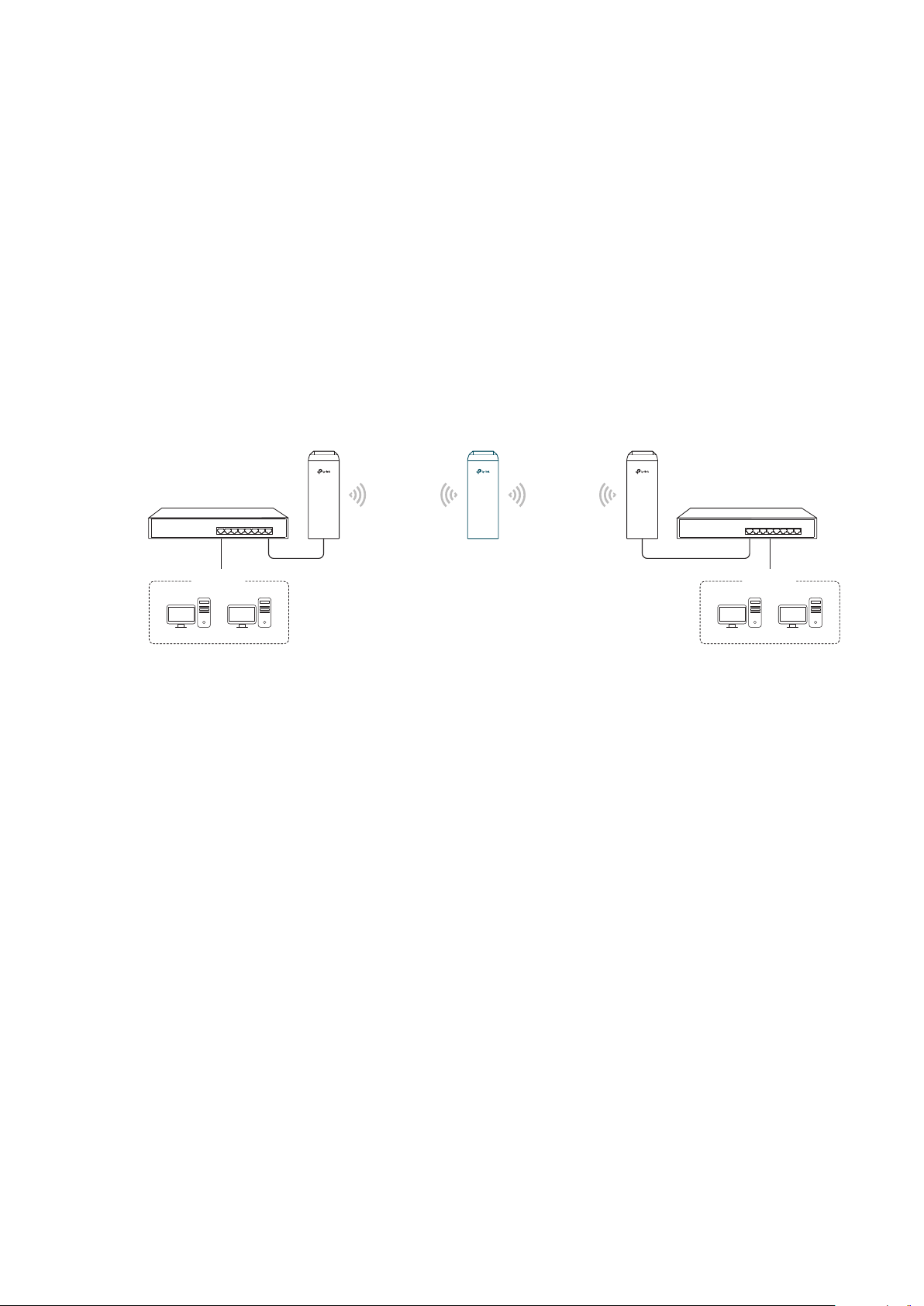
1.3 Repeater (Range Extender)
The device in Repeater mode can extend wireless coverage of an existing wireless
network. The SSID and encryption type of the device should be the same as those of the
root AP.
Access Point Client
LAN: 192.168.0.254
Switch
Oce Oce
SSID: abc
Repeater
LAN: 192.168.0.2 LAN: 192.168.0.3
SSID: abc
Switch
Network requirements: Repeat wireless signal and extend the wireless network coverage.
The device in the network: If you want to combine two networks via wireless connection
but the distance is beyond the networks’ wireless coverage range, you can put one or
more devices in Repeater mode along the path to repeat the wireless signal and extend
the wireless transmission range.
6
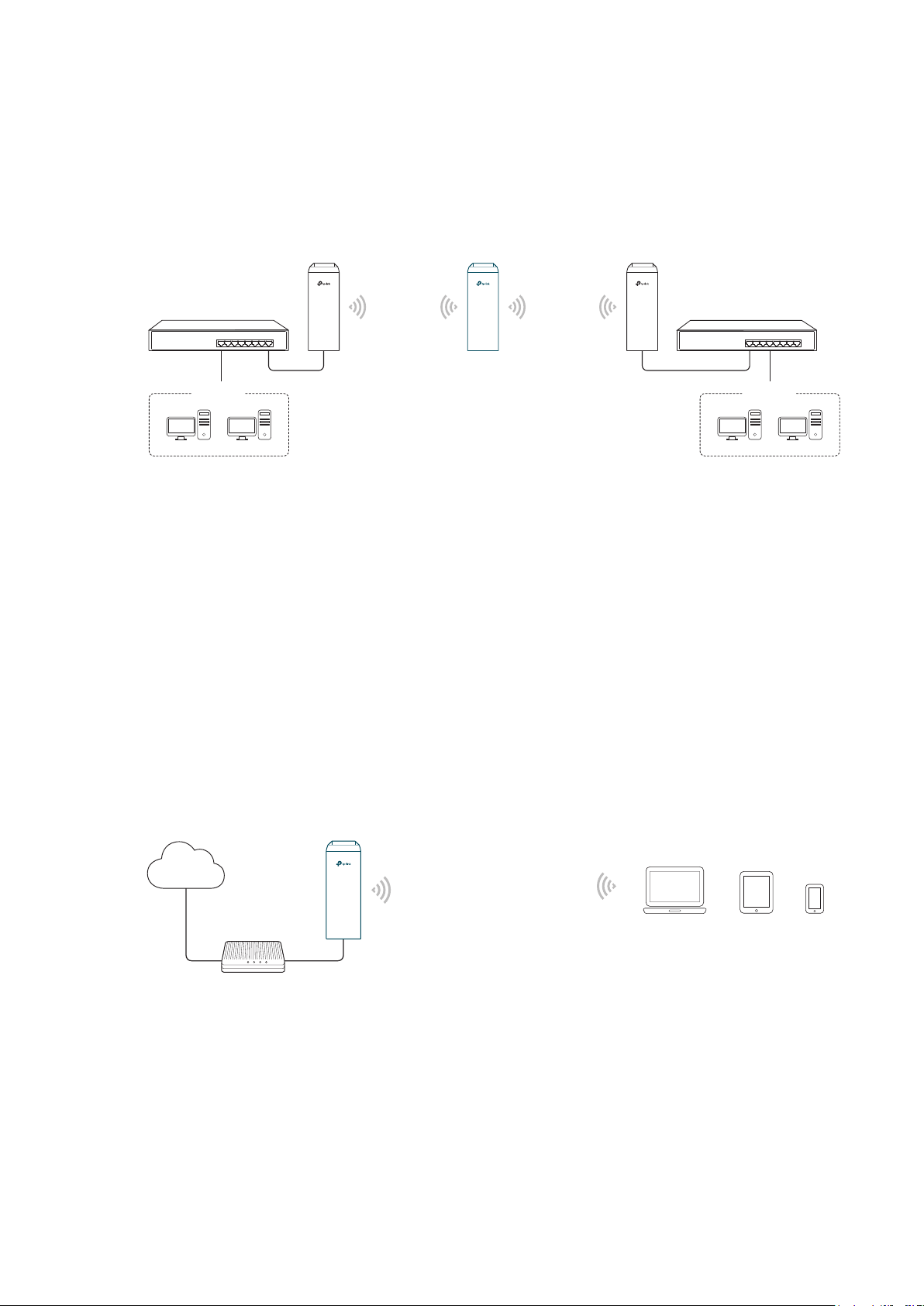
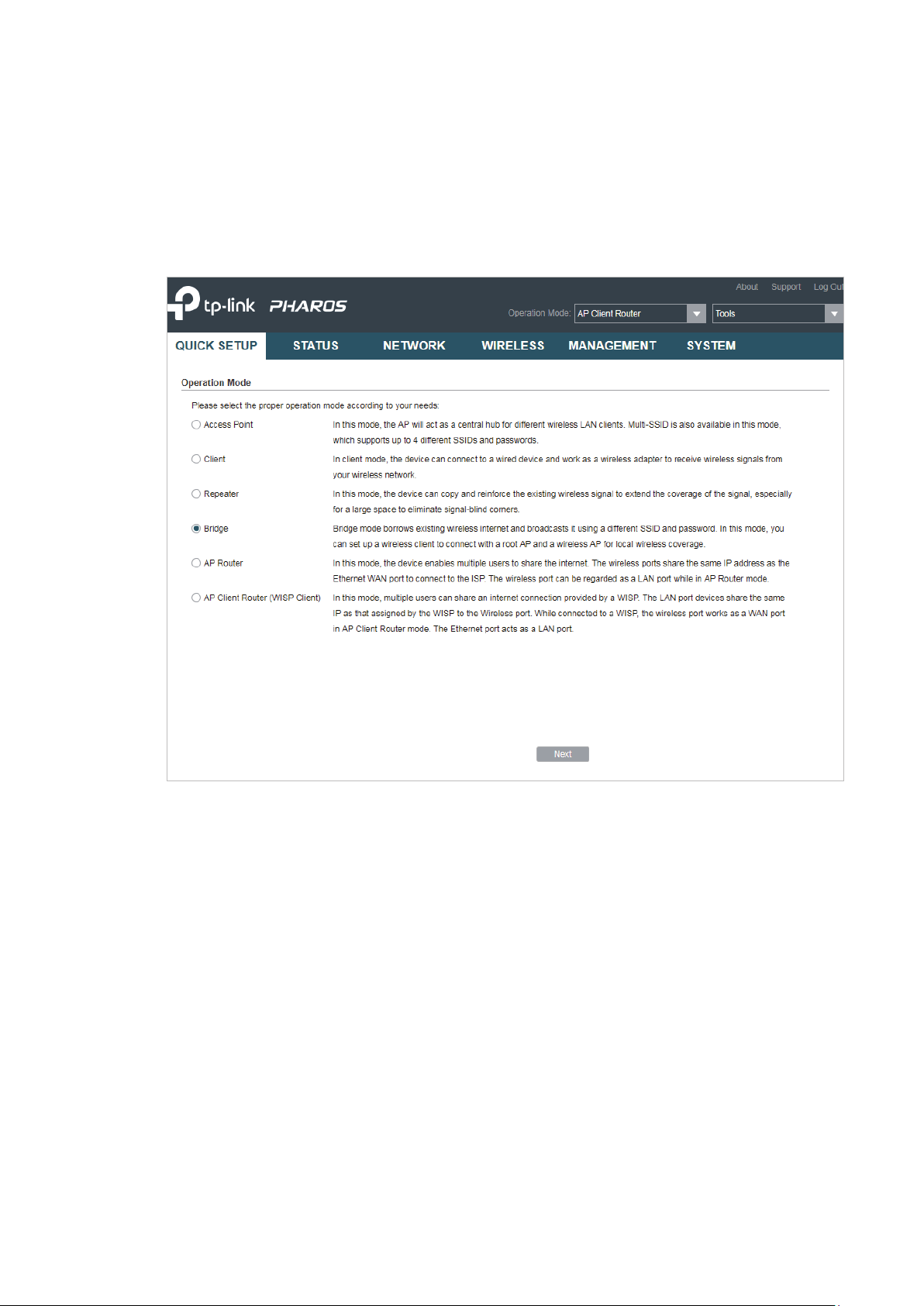
1.4 Bridge
The device in Bridge mode can extend wireless coverage of an existing wireless network.
The SSID and encryption type of the device can be different from those of root AP.
Access Point Client
LAN: 192.168.0.254
Switch
Oce Oce
SSID: abc
Bridge
LAN: 192.168.0.2 LAN: 192.168.0.3
SSID: 123
Switch
Network requirements: Extend the wireless network to eliminate the wireless signal-blind
areas. Users can use different SSID and encryption type from those of the root AP device
to access the network.
The device in the network: Similar to the Repeater mode, the Bridge mode is used to
enhance the exiting wireless signal. However, the difference is that the extended wireless
network has its own SSID and encryption type different from those of root AP.
1.5 AP Router
The device in AP Router mode serves as a normal home wireless router but provides a
wider wireless network range.
Internet
Modem
Network requirements: Establish the wireless network coverage in the campus,
community, industrial park or other public places and so on.
The device in the network: The device in AP Router mode connects to root ADSL/Cable
AP Router
Laptop/Tablet/Smartphone
7
Modem for internet access. Meanwhile, it creates a wireless network for the wireless
clients to connect to the internet.
Note:
In this mode, the device cannot be managed directly through the port connected to ADSL/Cable
Modem. To manage the device, you can connect the management host to the device wirelessly or
via the other LAN port.
1.6 AP Client Router (WISP Client)
In AP Client Router mode, the device access the internet provided by WISP (Wireless
Internet Service Provider) through wireless connection. For the downstream clients, the
device serves as a normal home wireless router. It can provide wired connection and
wireless connection simultaneously.
AP Client Router
WISP
LAN: 192.168.0.254
WAN: Dynamic IP
WISP’s network
User Network
Network requirements: Get internet service from WISP.
The device in the network: The device in Client Router Mode connects to WISP wirelessly
for internet service. It provides both wired access and wireless access for the clients.
8

2
This chapter introduces how to quickly build a wireless network in different operation
modes. Follow the steps below:
2.1 Check the System Requirements
2.2 Log In to the Device
2.3 Set Up the Wireless Network
Quick Start
9
2.1 Check the System Requirements
Operating System:
Microsoft Windows XP, Windows Vista, Windows 7, Windows 8, Windows 10, Linux, or
Mac OS X.
Web Browser
Google Chrome, Safari, Firefox, and Apple Safari. IE browsers are not recommended.
2.2 Log In to the Device
Before configuring the device, you need to access the PharOS configuration interface.
Follow the steps below:
1. Connect your PC to the device.
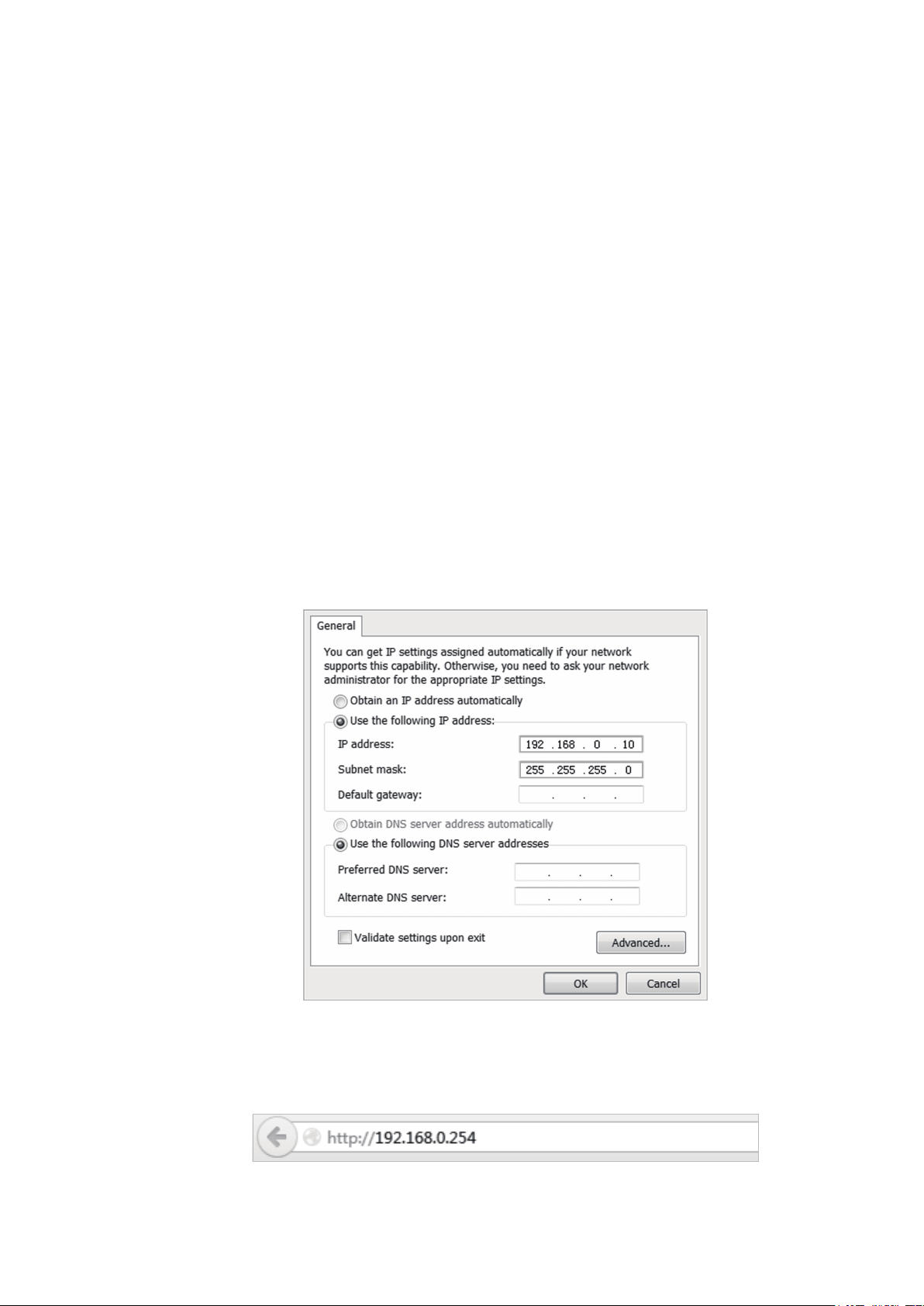
2. Set the IP address of your PC as static IP address on 192.168.0.X subnet (X ranges from
2 to 253, e.g.192.168.0.10).
3. Launch a web browser on and enter the management IP address of the device
(192.168.0.254 by default) in the address bar to load the login page of the PharOS
configuration interface.
10
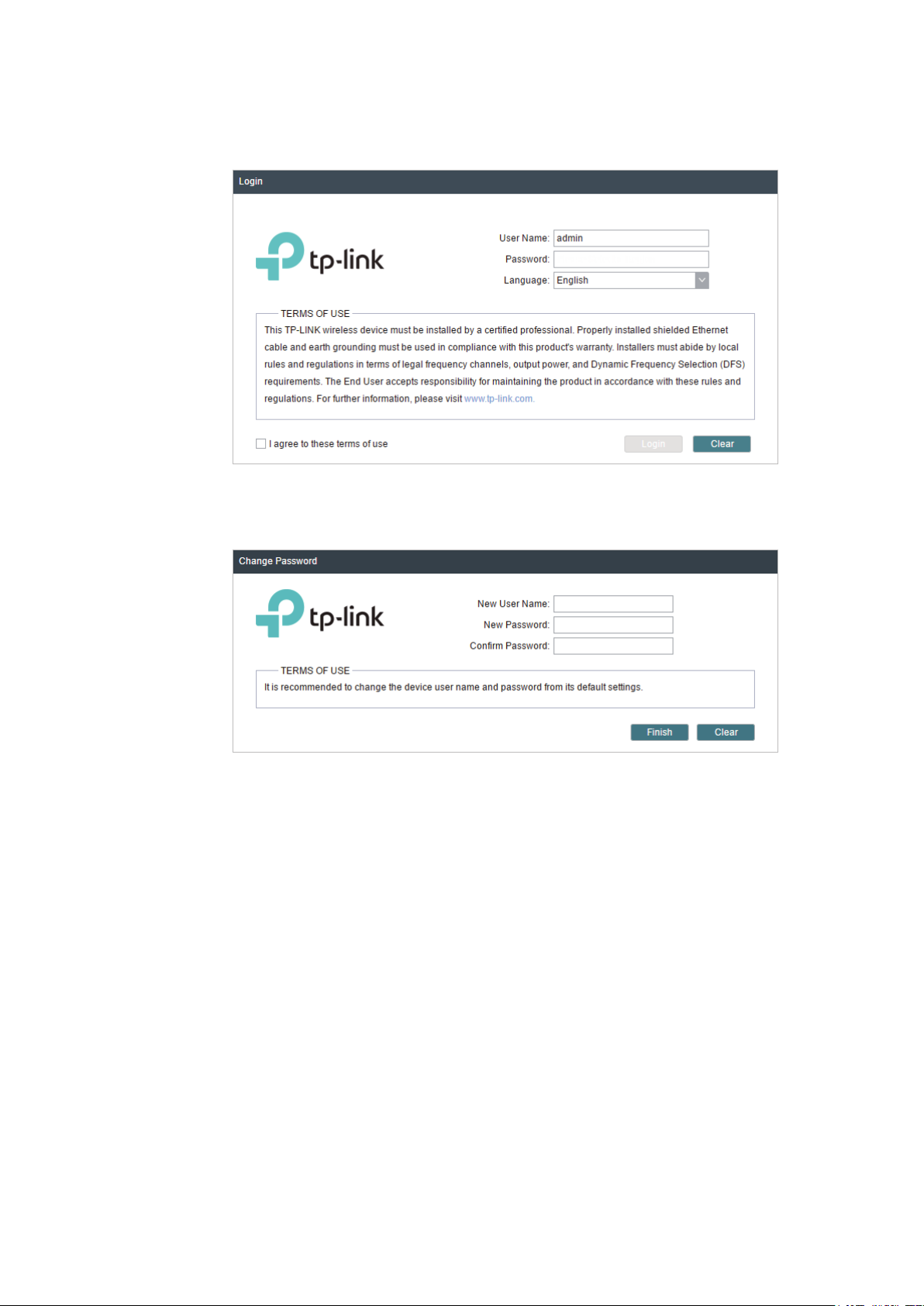
4. Use admin for both of
User Name
and
Password
. Select the appropriate language from
the Language drop-down list. Read and agree the terms of use, then click
5. Create a new username and password for network security. Click
PharOS.
Login
Finish
to log in to the
.
2.3 Set Up the Wireless Network
You can use the Quick Setup wizard to quickly configure your device step by step. Choose
the suitable operation mode according to your network environment and follow the step-
by-step instructions.
11
Access Point
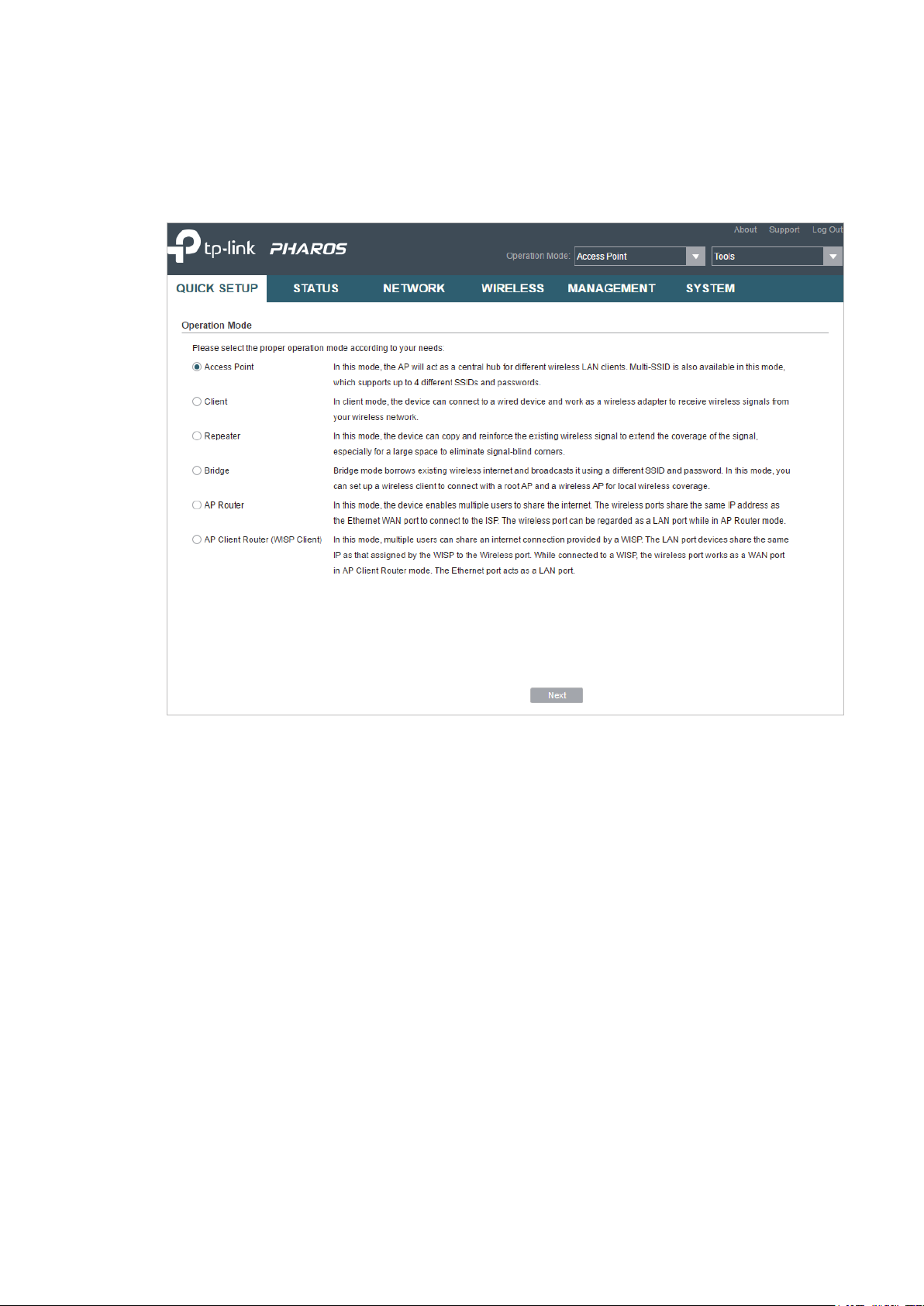
Follow the steps below to configure the device as Access Point mode:
1. Go to the QUICK SETUP page, select
Access Point
and click
Next
.
12
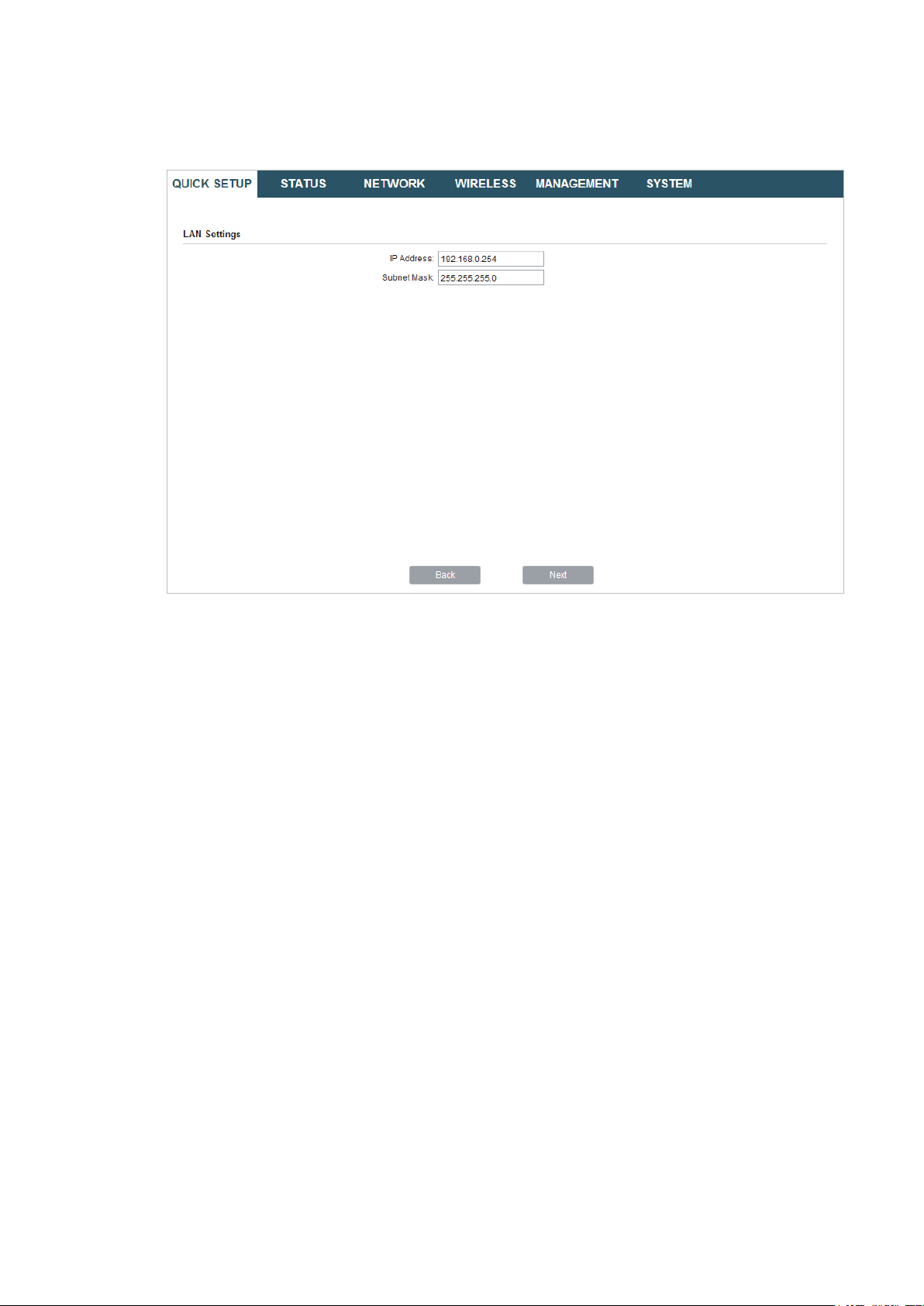
2. In the LAN Settings section, specify the LAN IP address and the Subnet Mask for the
device. Then, click
Next
.
13
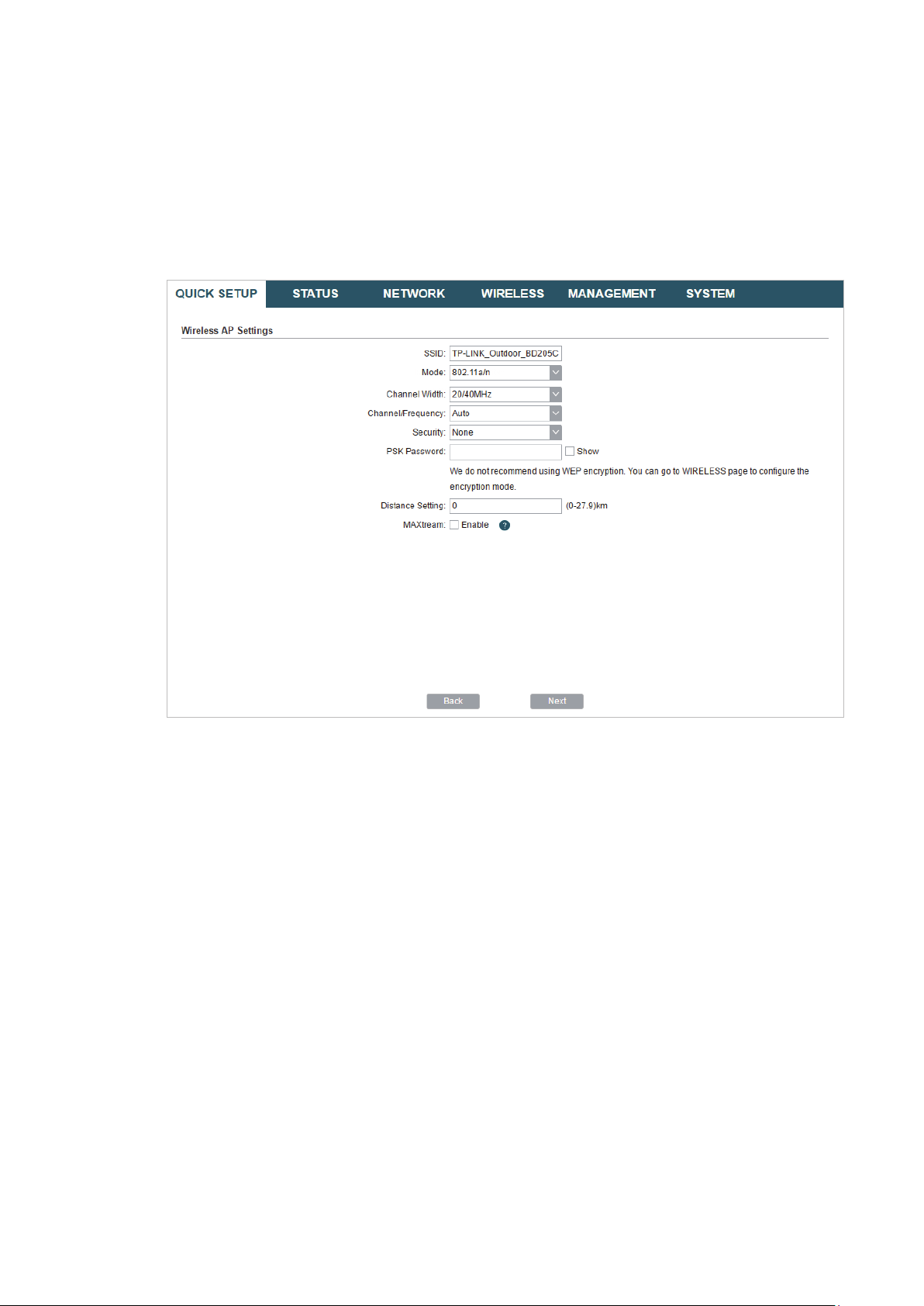
3. In the Wireless AP Settings section, specify the basic wireless parameters to create a
wireless network. Click
Next
.
Tips:
It is recommended to specify
·
You can keep the default settings or specify the parameters according to your need. For details,
·
refer to
5. Configure the Wireless Parameters
Security
as WPA-PSK/WPA2-PSK for the network security.
.
14
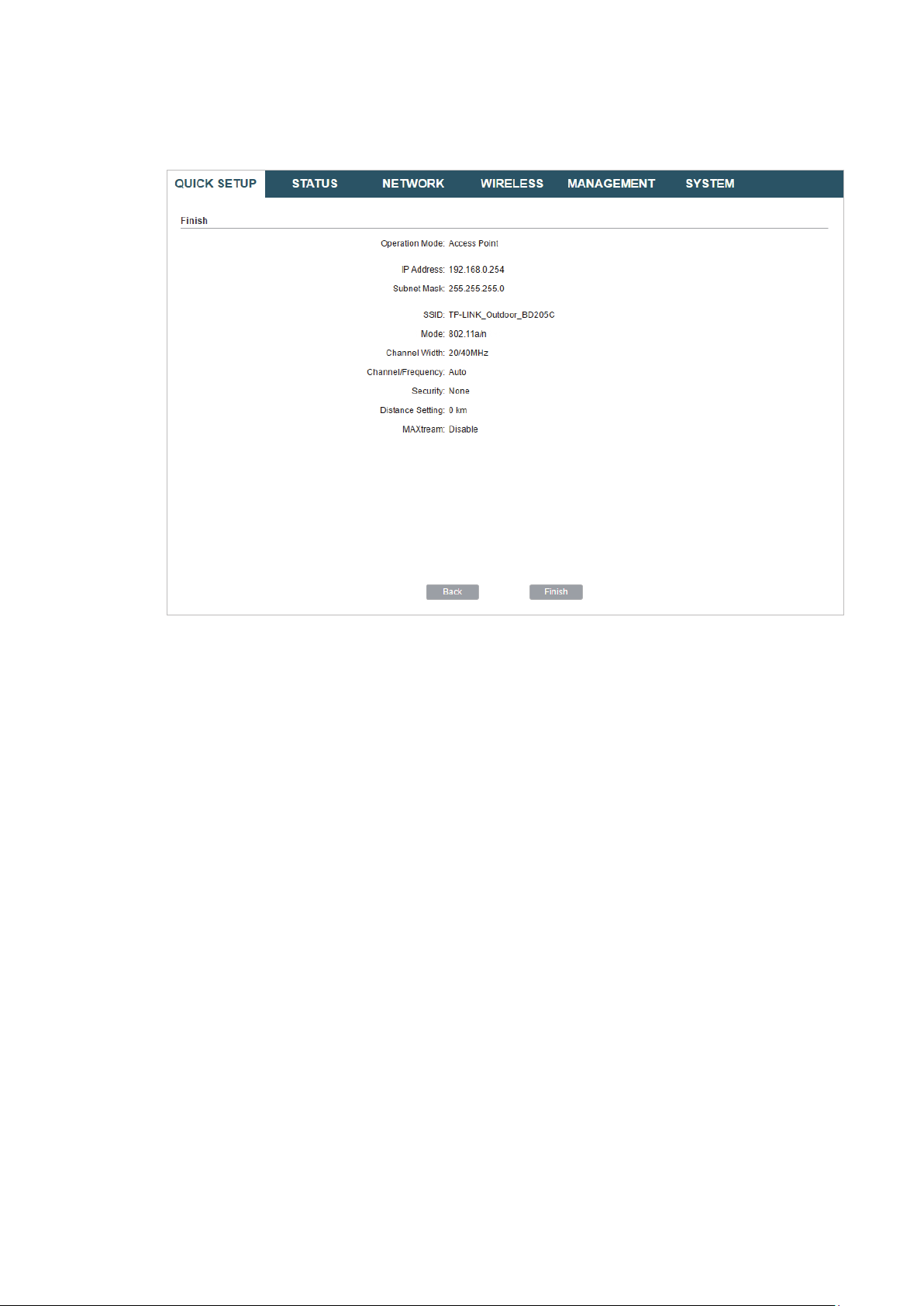
4. In the Finish section, review the configurations and click
setup.
Finish
to complete the quick
5. Connect the device according to your network topology and use it normally.
15
Client
Follow the steps below to configure the device as Client mode:
1. Go to the QUICK SETUP page, select
Client
and click
Next
.
16
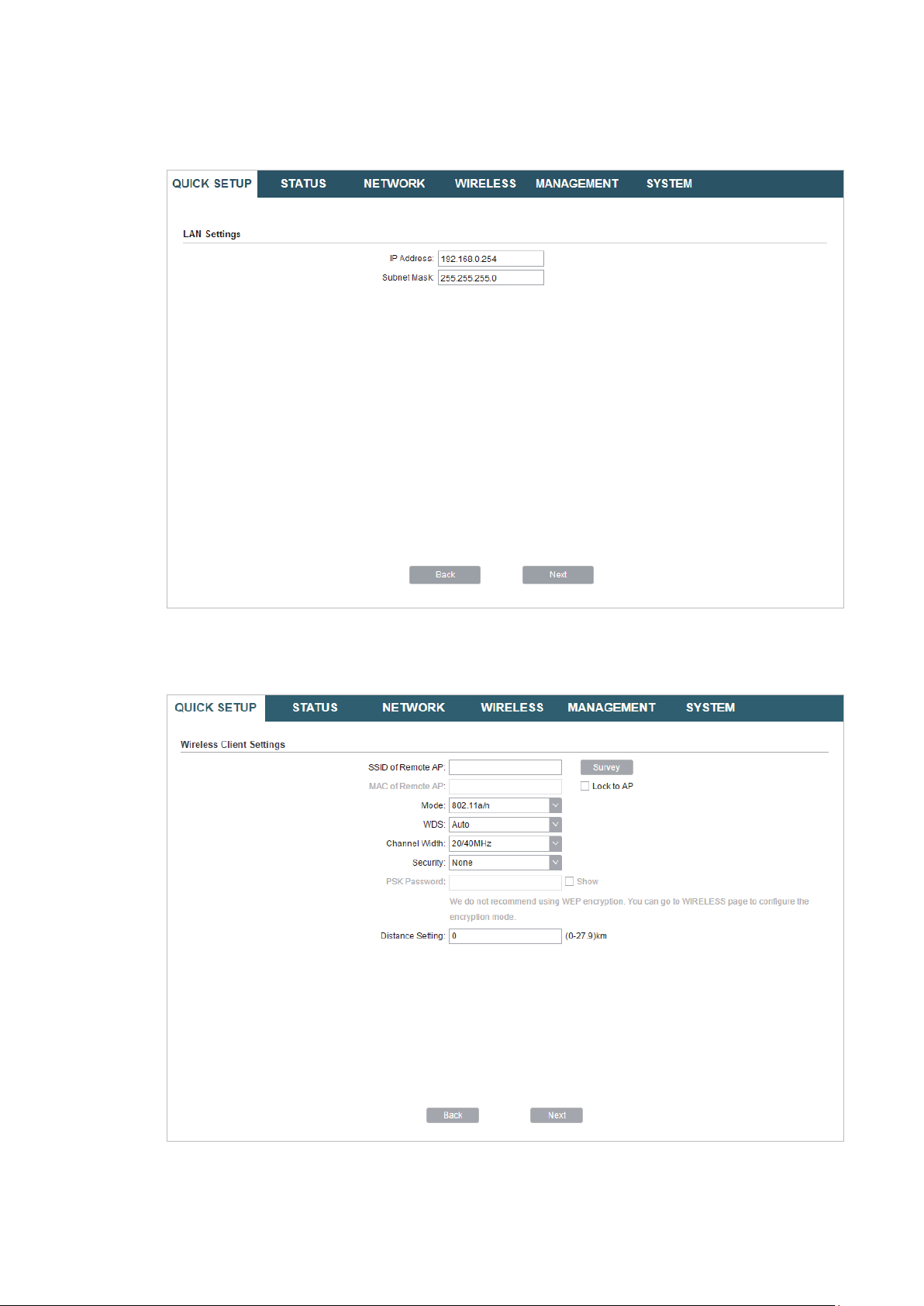
2. In the LAN Settings section, specify the LAN IP Address and the Subnet Mask for the
device. Then, click
Next
.
3. In the Wireless Client Settings section, click
network.
Survey
to search for the upstream wireless
4. Select the desired wireless network and click
17
Connect
.
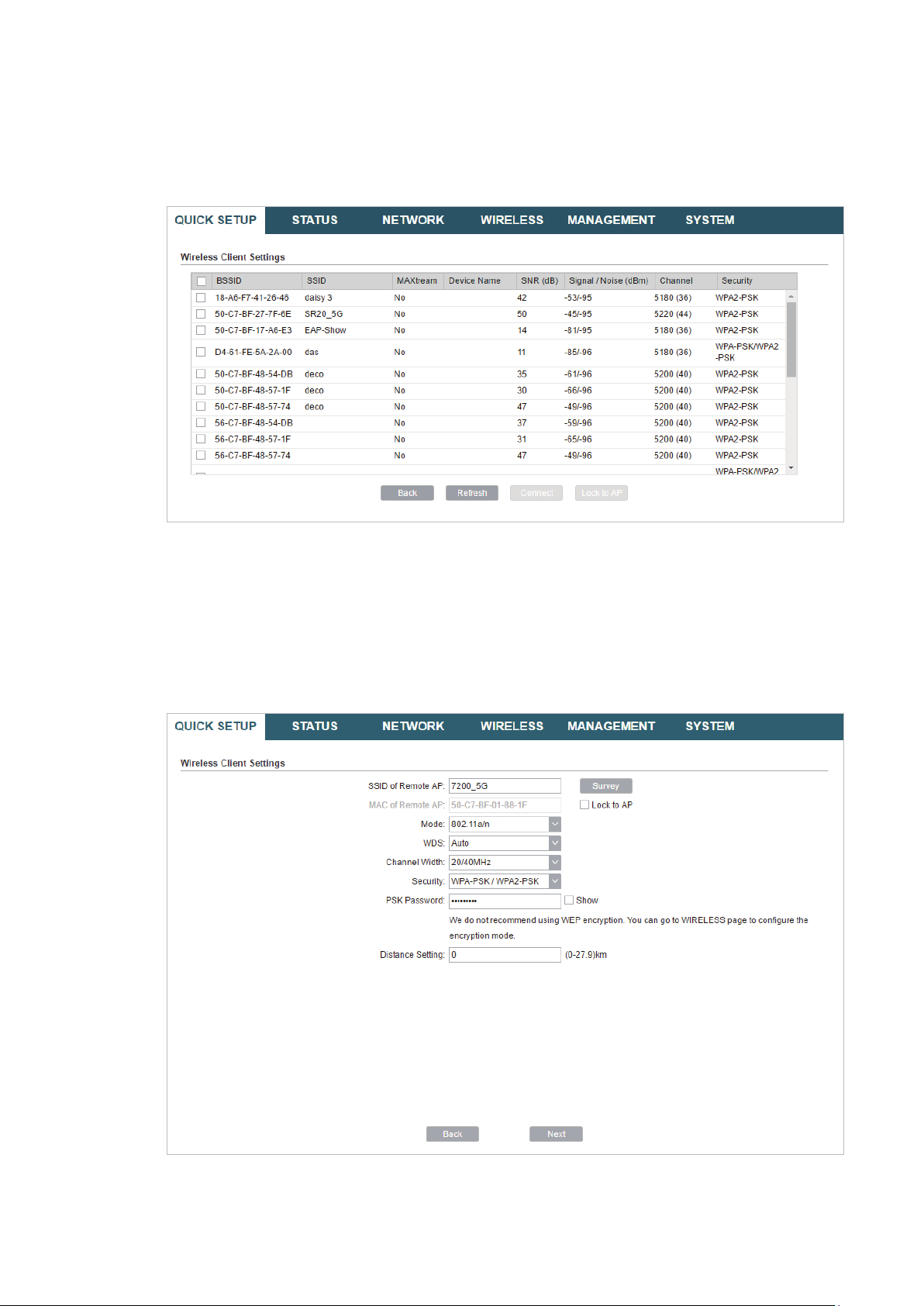
Tips:
There may be two or more networks with the same SSID in the AP list. Click
the SSID and AP simultaneously, which can make the device connect to the specific AP next
time.
Lock to AP
to select
5. In the Wireless Client Settings section, specify the wireless parameters to connect to
the specified wireless network. Click
Next
.
Note:
Make sure that
Other parameters set in this page and those of the upstream wireless network should be
compatible with each other. For details, refer to
Security
and
PSK Password
are the same as the upstream wireless network’s.
5. Configure the Wireless Parameters
.
18
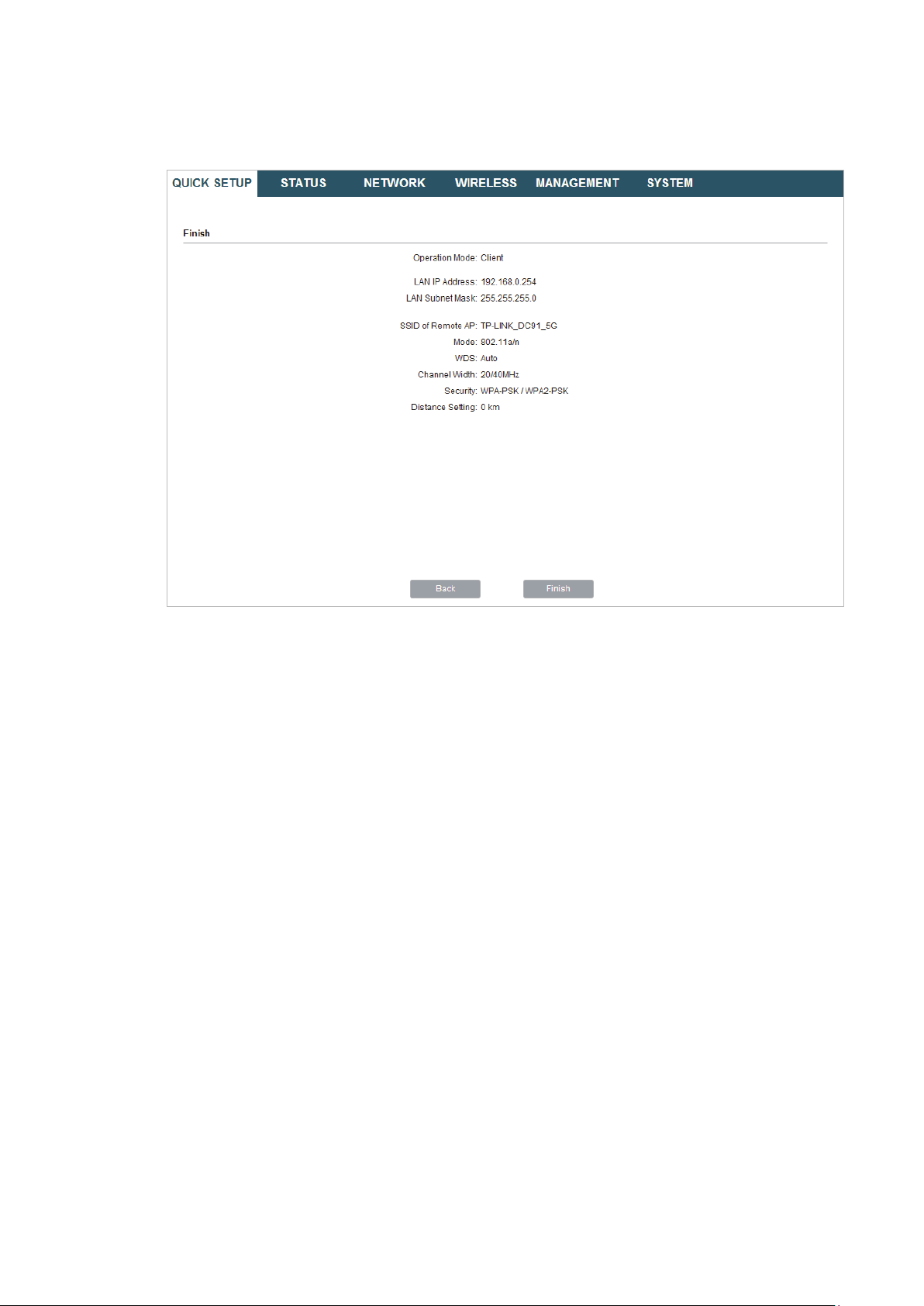
6. In the Finish section, review the configurations and click
setup.
Finish
to complete the quick
7. Connect the device according to your network topology and use it normally.
Repeater (Range Extender)
Follow the steps below to configure the device as Repeater (Range Extender) mode:
19
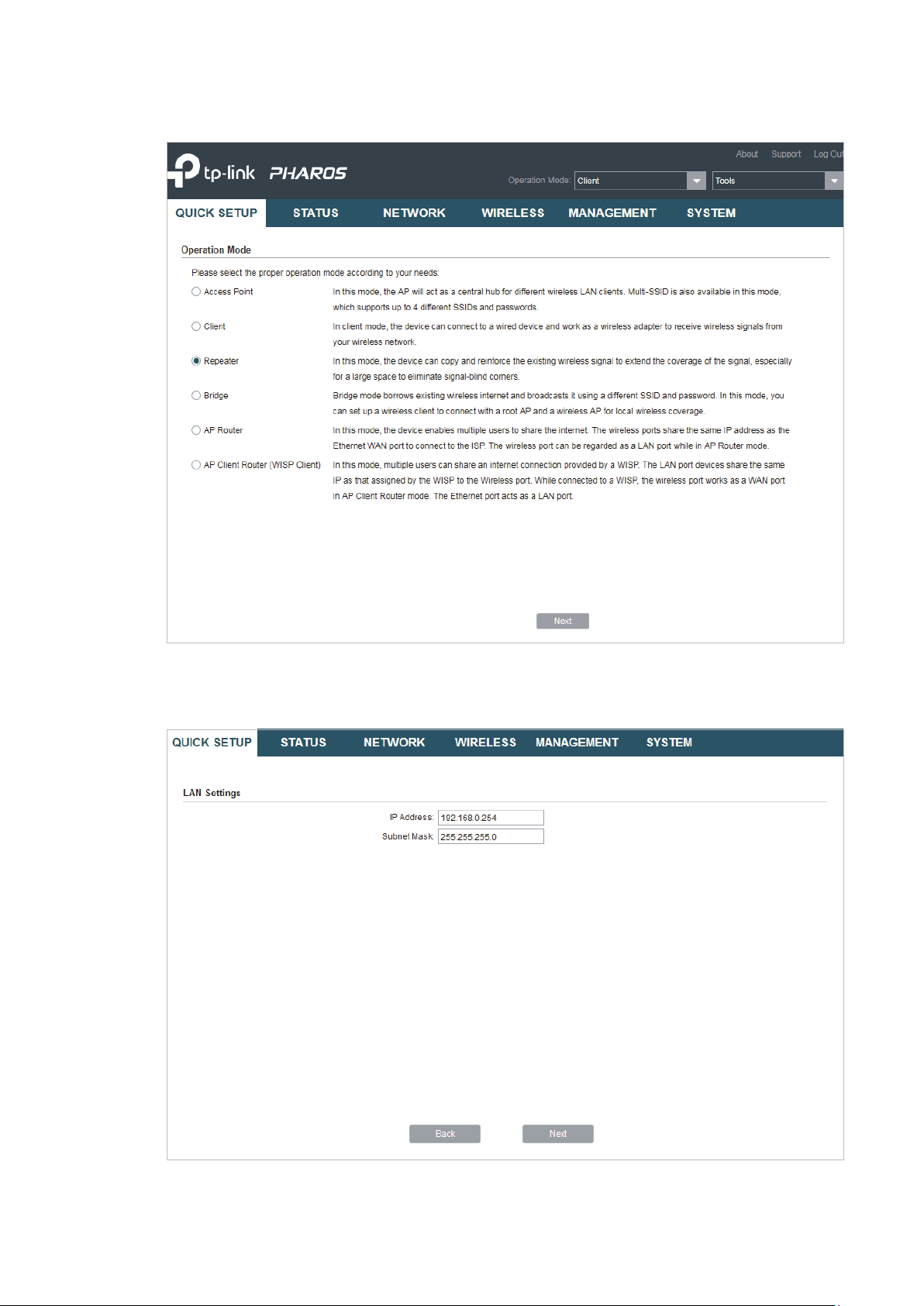
1. Go to the QUICK SETUP page, select
Repeater
and click
Next
.
2. In the LAN Settings section, specify the LAN IP address and the Subnet Mask for the
device. Then, click
Next
.
20
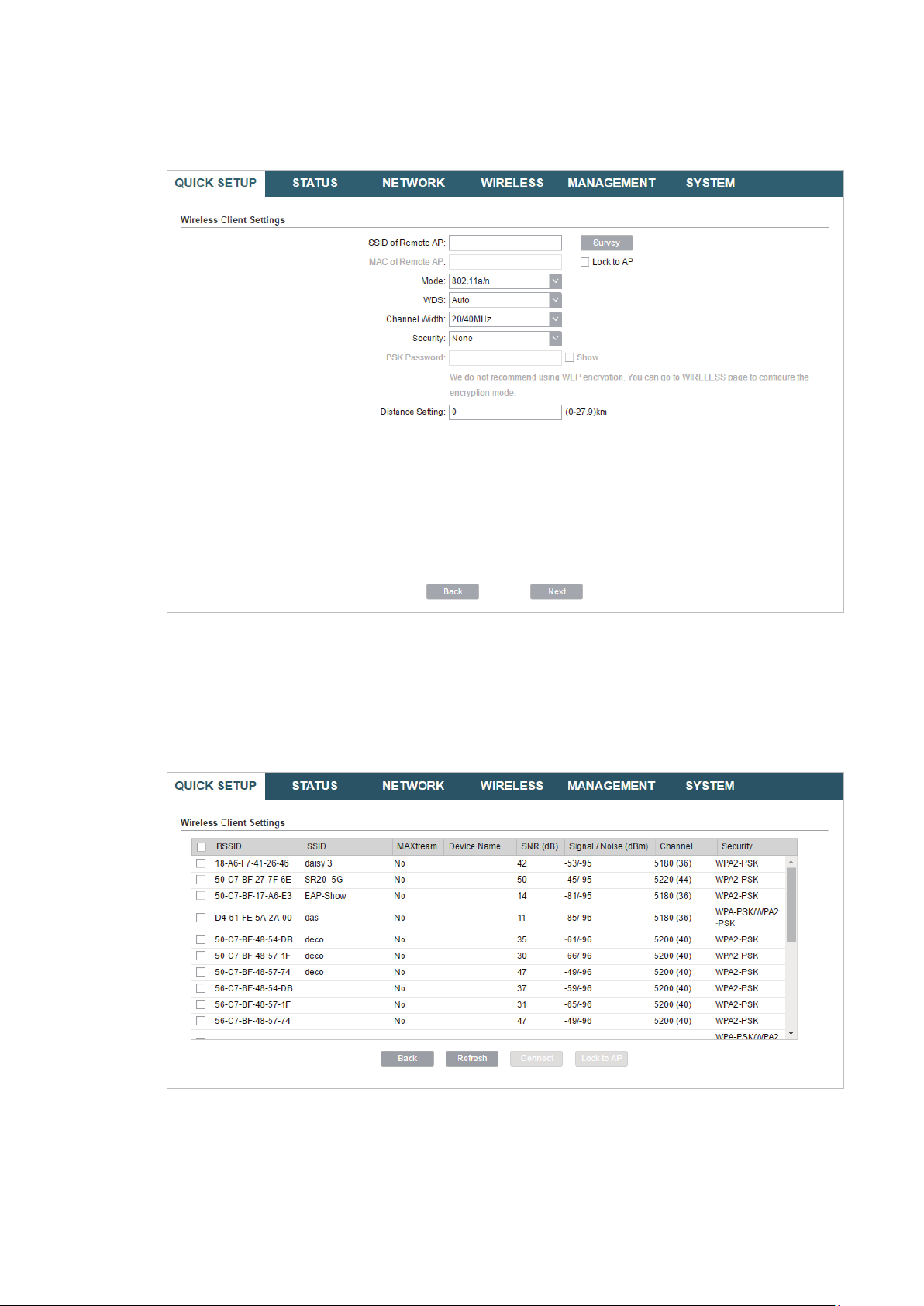
3. In the Wireless Client Settings section, click
network.
Survey
to search for the upstream wireless
4. Select the desired wireless network and click
Connect
.
Tips:
There may be two or more networks with the same SSID in the AP list. Click
the SSID and AP simultaneously, which can make the device connect to the specific AP next
time.
Lock to AP
to select
5. In the Wireless Client Settings section, specify the wireless parameters to connect to
the specified wireless network. Click
Next
21
.

Note:
Make sure that
Other parameters set in this page and those of the upstream wireless network should be
compatible with each other. For details, refer to
Security
and
PSK Password
are the same as the upstream wireless network’s.
5. Configure the Wireless Parameters
.
6. In the Finish section, review the configurations and click
setup.
Finish
to complete the quick
22
7. Connect the device according to your network topology and use it normally.
Bridge
Follow the steps below to configure the device as Bridge mode:
1. Go to the QUICK SETUP page, select
Bridge
and click
Next
.
23
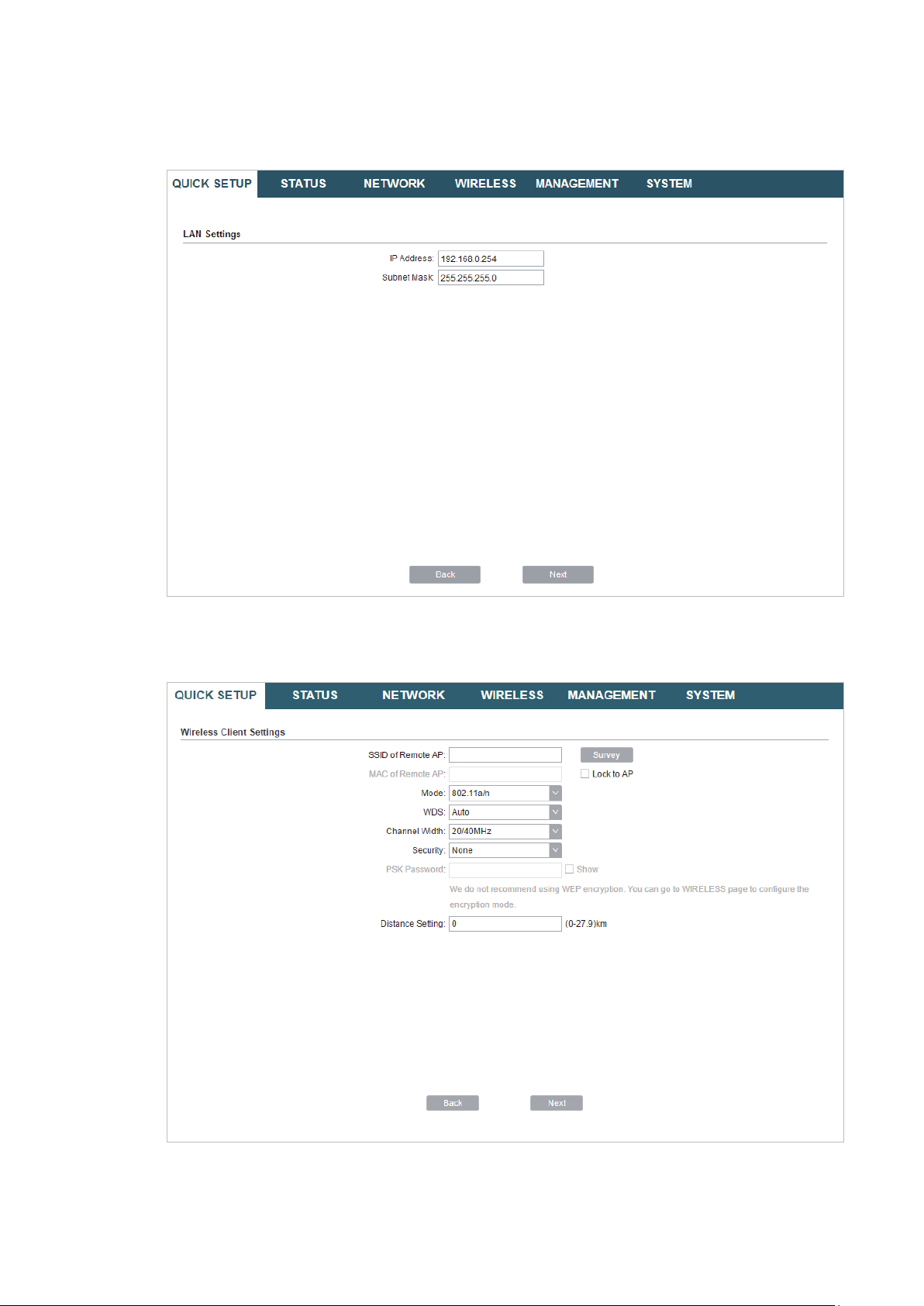
2. In the LAN Settings section, specify the LAN IP address and the Subnet Mask for the
device. Then, click
Next
.
3. In the Wireless Client Settings section, click
network.
Survey
to search for the upstream wireless
4. Select the desired wireless network and click
24
Connect
.
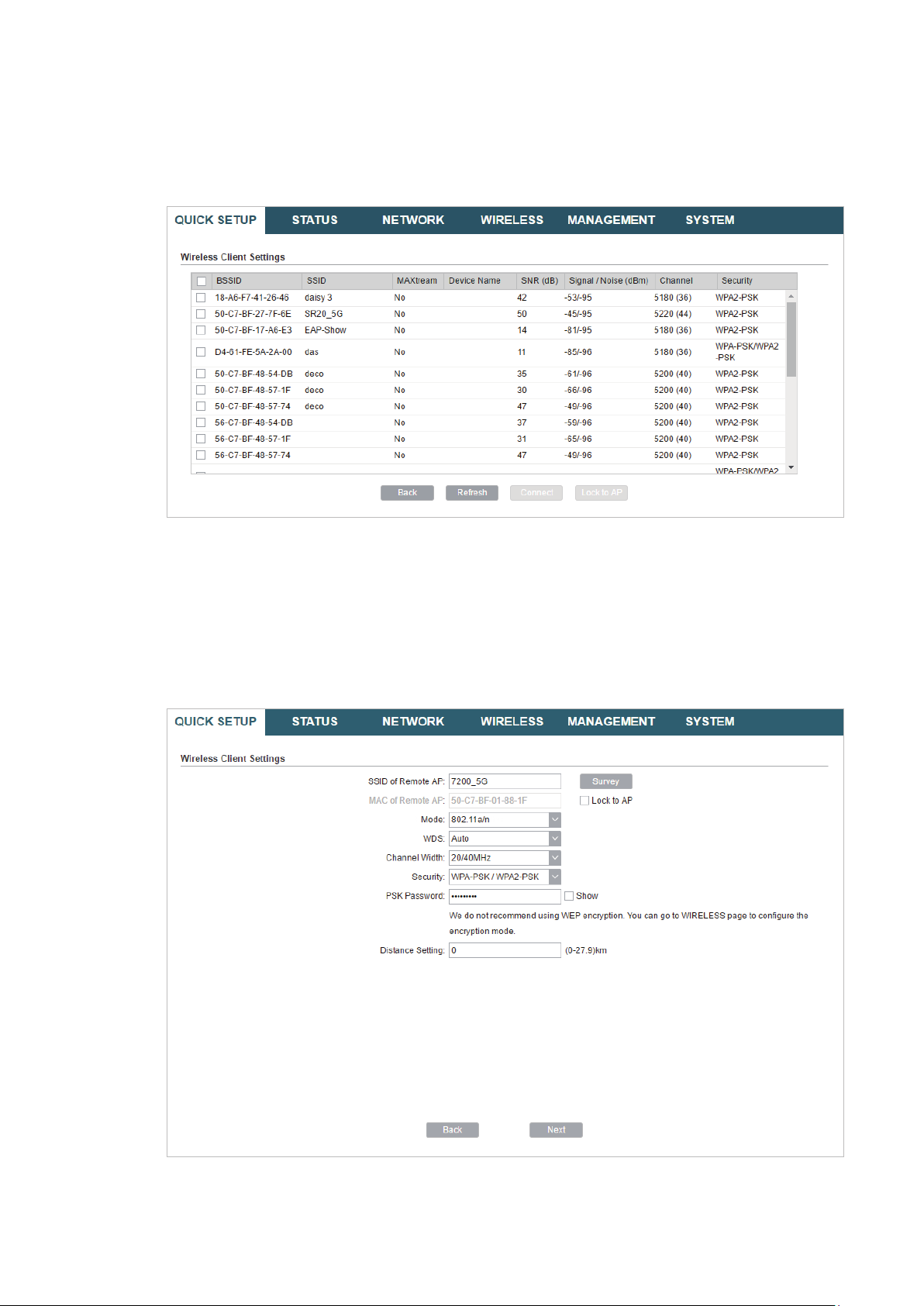
Tips:
There may be two or more networks with the same SSID in the AP list. Click
the SSID and AP simultaneously, which can make the device connect to the specific AP next
time.
Lock to AP
to select
5. In the Wireless Client Settings section, specify the wireless parameters to connect to
the specified wireless network. Click
Next
.
Note:
Make sure that the
Other parameters set in this page and those of the upstream wireless network should be
compatible with each other. For details, refer to
Security
and
PSK Password
are the same as the upstream wireless network’s.
5. Configure the Wireless Parameters
.
25

6. In the Wireless AP Settings section, specify the parameters to create a new wireless
network for the downstream clients. Click
Next
.
7. In the Finish section, review the configurations and click
setup.
Finish
to complete the quick
8. Connect the device according to your network topology and use it normally.
26
 Loading...
Loading...