
Data Manual
2003 PCI Bus Solutions
SCPS053B

IMPORTANT NOTICE
Texas Instruments Incorporated and its subsidiaries (TI) reserve the right to make corrections, modifications,
enhancements, improvements, and other changes to its products and services at any time and to discontinue
any product or service without notice. Customers should obtain the latest relevant information before placing
orders and should verify that such information is current and complete. All products are sold subject to TI’s terms
and conditions of sale supplied at the time of order acknowledgment.
TI warrants performance of its hardware products to the specifications applicable at the time of sale in
accordance with TI’s standard warranty . Testing and other quality control techniques are used to the extent TI
deems necessary to support this warranty . Except where mandated by government requirements, testing of all
parameters of each product is not necessarily performed.
TI assumes no liability for applications assistance or customer product design. Customers are responsible for
their products and applications using TI components. T o minimize the risks associated with customer products
and applications, customers should provide adequate design and operating safeguards.
TI does not warrant or represent that any license, either express or implied, is granted under any TI patent right,
copyright, mask work right, or other TI intellectual property right relating to any combination, machine, or process
in which TI products or services are used. Information published by TI regarding third–party products or services
does not constitute a license from TI to use such products or services or a warranty or endorsement thereof.
Use of such information may require a license from a third party under the patents or other intellectual property
of the third party , or a license from TI under the patents or other intellectual property of TI.
Reproduction of information in TI data books or data sheets is permissible only if reproduction is without
alteration and is accompanied by all associated warranties, conditions, limitations, and notices. Reproduction
of this information with alteration is an unfair and deceptive business practice. TI is not responsible or liable for
such altered documentation.
Resale of TI products or services with statements different from or beyond the parameters stated by TI for that
product or service voids all express and any implied warranties for the associated TI product or service and
is an unfair and deceptive business practice. TI is not responsible or liable for any such statements.
Mailing Address:
Texas Instruments
Post Office Box 655303
Dallas, Texas 75265
Copyright 2003, Texas Instruments Incorporated

Contents
Section Title Page
1 Introduction 1–1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
1.1 Description 1–1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
1.2 Features 1–1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
1.3 Related Documents 1–2. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
1.4 Trademarks 1–2. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
1.5 Ordering Information 1–2. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
2 Terminal Descriptions 2–1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
3 Feature/Protocol Descriptions 3–1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
3.1 Introduction to the PCI2050 3–1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
3.2 PCI Commands 3–2. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
3.3 Configuration Cycles 3–2. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
3.4 Special Cycle Generation 3–4. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
3.5 Secondary Clocks 3–4. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
3.6 Bus Arbitration 3–5. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
3.6.1 Primary Bus Arbitration 3–5. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
3.6.2 Internal Secondary Bus Arbitration 3–5. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
3.6.3 External Secondary Bus Arbitration 3–6. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
3.7 Decode Options 3–6. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
3.8 System Error Handling 3–6. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
3.8.1 Posted Write Parity Error 3–6. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
3.8.2 Posted Write Time-Out 3–6. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
3.8.3 Target Abort on Posted Writes 3–6. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
3.8.4 Master Abort on Posted Writes 3–7. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
3.8.5 Master Delayed Write Time-Out 3–7. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
3.8.6 Master Delayed Read Time-Out 3–7. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
3.8.7 Secondary SERR
3.9 Parity Handling and Parity Error Reporting 3–7. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
3.9.1 Address Parity Error 3–7. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
3.9.2 Data Parity Error 3–7. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
3.10 Master and Target Abort Handling 3–7. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
3.11 Discard Timer 3–7. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
3.12 Delayed Transactions 3–8. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
3.13 Mode Selection 3–8. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
3.14 CompactPCI Hot-Swap Support 3–9. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
3.15 JTAG Support 3–10. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
3.15.1 Test Port Instructions 3–10. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
3.16 GPIO Interface 3–14. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
3–7. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
iii

3.16.1 Secondary Clock Mask 3–14. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
3.16.2 Transaction Forwarding Control 3–14. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
3.17 PCI Power Management 3–15. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
3.17.1 Behavior in Low-Power States 3–15. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4 Bridge Configuration Header 4–1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4.1 Vendor ID Register 4–2. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4.2 Device ID Register 4–2. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4.3 Command Register 4–3. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4.4 Status Register 4–4. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4.5 Revision ID Register 4–5. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4.6 Class Code Register 4–5. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4.7 Cache Line Size Register 4–5. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4.8 Primary Latency Timer Register 4–6. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4.9 Header Type Register 4–6. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4.10 BIST Register 4–6. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4.11 Base Address Register 0 4–7. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4.12 Base Address Register 1 4–7. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4.13 Primary Bus Number Register 4–7. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4.14 Secondary Bus Number Register 4–8. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4.15 Subordinate Bus Number Register 4–8. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4.16 Secondary Bus Latency Timer Register 4–8. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4.17 I/O Base Register 4–9. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4.18 I/O Limit Register 4–9. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4.19 Secondary Status Register 4–10. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4.20 Memory Base Register 4–11. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4.21 Memory Limit Register 4–11. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4.22 Prefetchable Memory Base Register 4–11. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4.23 Prefetchable Memory Limit Register 4–12. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4.24 Prefetchable Base Upper 32 Bits Register 4–12. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4.25 Prefetchable Limit Upper 32 Bits Register 4–13. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4.26 I/O Base Upper 16 Bits Register 4–13. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4.27 I/O Limit Upper 16 Bits Register 4–13. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4.28 Capability Pointer Register 4–14. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4.29 Expansion ROM Base Address Register 4–14. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4.30 Interrupt Line Register 4–14. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4.31 Interrupt Pin Register 4–15. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4.32 Bridge Control Register 4–15. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
5 Extension Registers 5–1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
5.1 Chip Control Register 5–1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
5.2 Extended Diagnostic Register 5–2. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
5.3 Arbiter Control Register 5–3. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
5.4 P_SERR Event Disable Register 5–4. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
5.5 GPIO Output Data Register 5–5. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
5.6 GPIO Output Enable Register 5–5. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
iv

5.7 GPIO Input Data Register 5–6. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
5.8 Secondary Clock Control Register 5–7. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
5.9 P_SERR Status Register 5–8. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
5.10 Power-Management Capability ID Register 5–8. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
5.11 Power-Management Next-Item Pointer Register 5–9. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
5.12 Power-Management Capabilities Register 5–9. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
5.13 Power-Management Control/Status Register 5–10. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
5.14 PMCSR Bridge Support Register 5–11. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
5.15 Data Register 5–11. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
5.16 HS Capability ID Register 5–12. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
5.17 HS Next-Item Pointer Register 5–12. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
5.18 Hot-Swap Control Status Register 5–13. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
6 Electrical Characteristics 6–1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
6.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings Over Operating Temperature Ranges 6–1.
6.2 Recommended Operating Conditions 6–1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
6.3 Recommended Operating Conditions for PCI Interface 6–2. . . . . . . . . . .
6.4 Electrical Characteristics Over Recommended Operating Conditions 6–2
6.5 PCI Clock/Reset Timing Requirements Over Recommended
Ranges of Supply Voltage and Operating Free-Air Temperature 6–2. . .
6.6 PCI Timing Requirements Over Recommended Ranges of
Supply Voltage and Operating Free-Air Temperature 6–3. . . . . . . . . . . .
6.7 Parameter Measurement Information 6–4. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
6.8 PCI Bus Parameter Measurement Information 6–5. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
7 Mechanical Data 7–1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
v

List of Illustrations
Figure Title Page
2–1 PCI2050 GHK Terminal Diagram 2–1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
2–2 PCI2050 ZHK Terminal Diagram 2–1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
2–3 PCI2050 PDV Terminal Diagram 2–2. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
3–1 System Block Diagram 3–1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
3–2 PCI AD31–AD0 During Address Phase of a Type 0 Configuration Cycle 3–2
3–3 PCI AD31–AD0 During Address Phase of a Type 1 Configuration Cycle 3–3
3–4 Bus Hierarchy and Numbering 3–3. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
3–5 Secondary Clock Block Diagram 3–5. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
3–6 Clock Mask Read Timing After Reset 3–14. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
6–1 Load Circuit and Voltage Waveforms 6–4. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
6–2 PCLK Timing Waveform 6–5. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
6–3 RSTIN
6–4 Shared-Signals Timing Waveforms 6–5. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Timing Waveforms 6–5. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
vi

List of Tables
Table Title Page
2–1 208-Terminal PDV Signal Names Sorted by Terminal Number 2–3. . . . . . . .
2–2 209-Terminal GHK/ZHK Signal Names Sorted by Terminal Number 2–5. . .
2–3 Signal Names Sorted Alphabetically 2–7. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
2–4 Primary PCI System Terminals 2–9. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
2–5 Primary PCI Address and Data Terminals 2–9. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
2–6 Primary PCI Interface Control Terminals 2–10. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
2–7 Secondary PCI System Terminals 2–11. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
2–8 Secondary PCI Address and Data Terminals 2–12. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
2–9 Secondary PCI Interface Control Terminals 2–13. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
2–10 Miscellaneous Terminals 2–14. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
2–11 JTAG Interface Terminals 2–14. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
2–12 Power Supply Terminals 2–14. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
3–1 PCI Command Definition 3–2. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
3–2 PCI S_AD31–S_AD16 During the Address Phase of a Type 0
Configuration Cycle 3–4. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
3–3 Configuration via MS0 and MS1 3–9. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
3–4 JTAG Instructions and Op Codes 3–10. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
3–5 Boundary Scan Terminal Order 3–10. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
3–6 Clock Mask Data Format 3–14. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4–1 Bridge Configuration Header 4–1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4–2 Command Register Description 4–3. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4–3 Status Register Description 4–4. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4–4 Secondary Status Register Description 4–10. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4–5 Bridge Control Register Description 4–15. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
5–1 Chip Control Register Description 5–1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
5–2 Extended Diagnostic Register Description 5–2. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
5–3 Arbiter Control Register Description 5–3. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
5–4 P_SERR Event Disable Register Description 5–4. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
5–5 GPIO Output Data Register Description 5–5. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
5–6 GPIO Output Enable Register Description 5–5. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
5–7 GPIO Input Data Register Description 5–6. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
5–8 Secondary Clock Control Register Description 5–7. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
5–9 P_SERR Status Register Description 5–8. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
5–10 Power-Management Capabilities Register Description 5–9. . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
5–11 Power-Management Control/Status Register Description 5–10. . . . . . . . . . . . .
5–12 PMCSR Bridge Support Register Description 5–11. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
5–13 Hot-Swap Control Status Register Description 5–13. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
vii

1 Introduction
1.1 Description
The Texas Instruments PCI2050 PCI-to-PCI bridge provides a high-performance connection path between two
peripheral component interconnect (PCI) buses. Transactions occur between masters on one PCI bus and targets
on another PCI bus, and the PCI2050 allows bridged transactions to occur concurrently on both buses. The bridge
supports burst-mode transfers to maximize data throughput, and the two bus traffic paths through the bridge act
independently.
The PCI2050 bridge is compliant with the PCI Local Bus Specification, and can be used to overcome the electrical
loading limits of 10 devices per PCI bus and one PCI device per expansion slot by creating hierarchical buses. The
PCI2050 provides two-tier internal arbitration for up to nine secondary bus masters and may be implemented with
an external secondary PCI bus arbiter.
The CompactPCI hot-swap extended PCI capability is provided which makes the PCI2050 an ideal solution for
multifunction CompactPCI cards and for adapting single-function cards to hot-swap compliance.
The PCI2050 bridge is compliant with the PCI-to-PCI Bridge Specification 1.1. The PCI2050 provides compliance
for PCI Power Management 1.0 and 1.1. The PCI2050 has been designed to lead the industry in power conservation.
An advanced CMOS process is used to achieve low system power consumption while operating at PCI clock rates
up to 33 MHz.
The PCI2050I is an industrial version of the PCI2050 that has a larger operating temperature range. All references
to the PCI2050 also apply to the PCI2050I unless otherwise noted.
1.2 Features
The PCI2050 supports the following features:
• Architecture configurable for PCI Bus Power Management Interface Specification
• CompactPCI hot-swap-friendly silicon
• 3.3-V core logic with universal PCI interfaces compatible with 3.3-V and 5-V PCI signaling environments
• Two 32-bit, 33-MHz PCI buses
• Internal two-tier arbitration for up to nine secondary bus masters and supports an external secondary bus
arbiter
• Burst data transfers with pipeline architecture to maximize data throughput in both directions
• Independent read and write buffers for each direction
• Up to three delayed transactions in both directions
• Ten secondary PCI clock outputs
• Predictable latency per PCI Local Bus Specification
• Bus locking propagation
• Secondary bus is driven low during reset
• VGA/palette memory and I/O decoding options
• Advanced submicron, low-power CMOS technology
• 208-terminal QFP or 209-terminal MicroStar BGA package
1–1
1.3 Related Documents
• Advanced Configuration and Power Interface (ACPI) Specification (Revision 1.0)
• IEEE Standard Test Access Port and Boundary-Scan Architecture
• PCI Local Bus Specification (Revision 2.2)
• PCI-to-PCI Bridge Specification (Revision 1.1)
• PCI Bus Power Management Interface Specification (Revision 1.1)
• PICMG CompactPCI Hot-Swap Specification (Revision 1.0)
1.4 Trademarks
CompactPCI is a trademark of PICMG – PCI Industrial Computer Manufacturers Group, Inc.
Intel is a trademark of Intel Corporation.
MicroStar BGA and TI are trademarks of Texas Instruments.
Other trademarks are the property of their respective owners.
1.5 Ordering Information
ORDERING NUMBER VOLTAGE TEMPERATURE PACKAGE
PCI2050PDV 3.3 V , 5-V tolerant I/Os 0 to 70°C 208-terminal QFP
PCI2050IPDV 3.3 V, 5-V tolerant I/Os –40 to 85°C 208-terminal QFP
PCI2050GHK 3.3 V, 5-V tolerant I/Os 0 to 70°C 209-terminal MicroStar BGA
PCI2050IGHK 3.3 V, 5-V tolerant I/Os –40 to 85°C 209-terminal MicroStar BGA
PCI2050ZHK 3.3 V, 5-V tolerant I/Os 0 to 70°C 209-terminal MicroStar BGA
Leadfree
1–2
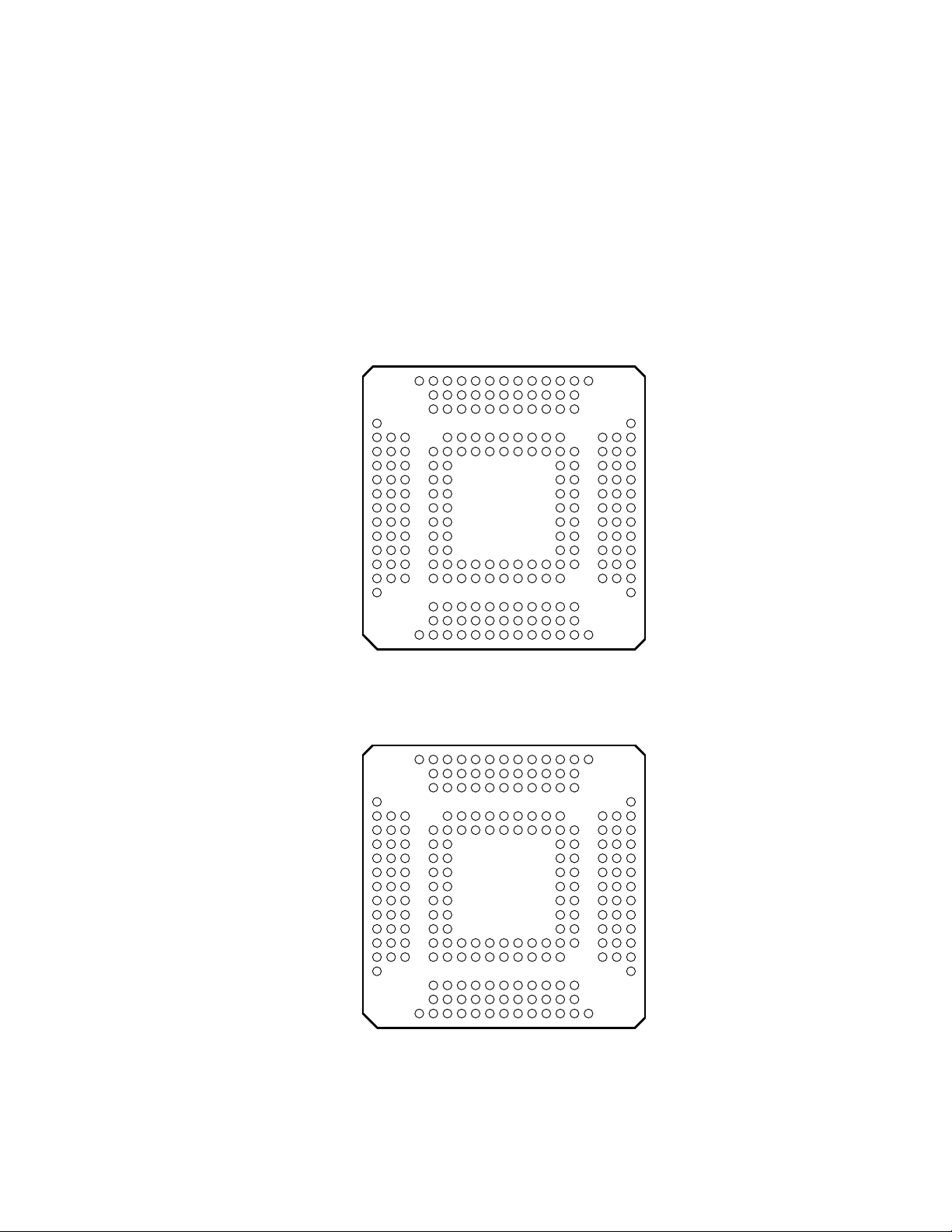
2 Terminal Descriptions
The PCI2050 device is packaged either in a 209-terminal GHK MicroStar BGA a 209-terminal ZHK MicroStar
BGA, or a 208-terminal PDV package. Figure 2–1 is a GHK-package terminal diagram. Figure 2–2 is a
ZHK-package terminal diagram. Figure 2–3 is a PDV-package terminal diagram. T able 2–1 lists terminals on the PDV
packaged device in increasing numerical order, with the signal name and corresponding GHK terminal number for
each. T able 2–2 lists terminals on the GHK packaged device in increasing alphanumerical order , with the signal name
and corresponding PDV terminal number for each. Table 2–3 lists signal names in alphabetical order, with
corresponding terminal numbers for both package types.
W
V
U
T
R
P
N
M
L
K
J
H
G
F
E
D
C
B
A
1
3
2
4
75
6
9
810
12
13141511
16
18
1917
Figure 2–1. PCI2050 GHK T erminal Diagram
W
V
U
T
R
P
N
M
L
K
J
H
G
F
E
D
C
B
A
1
3
2
4
75
6
9
810
12
13141511
16
18
1917
Figure 2–2. PCI2050 ZHK T erminal Diagram
2–1
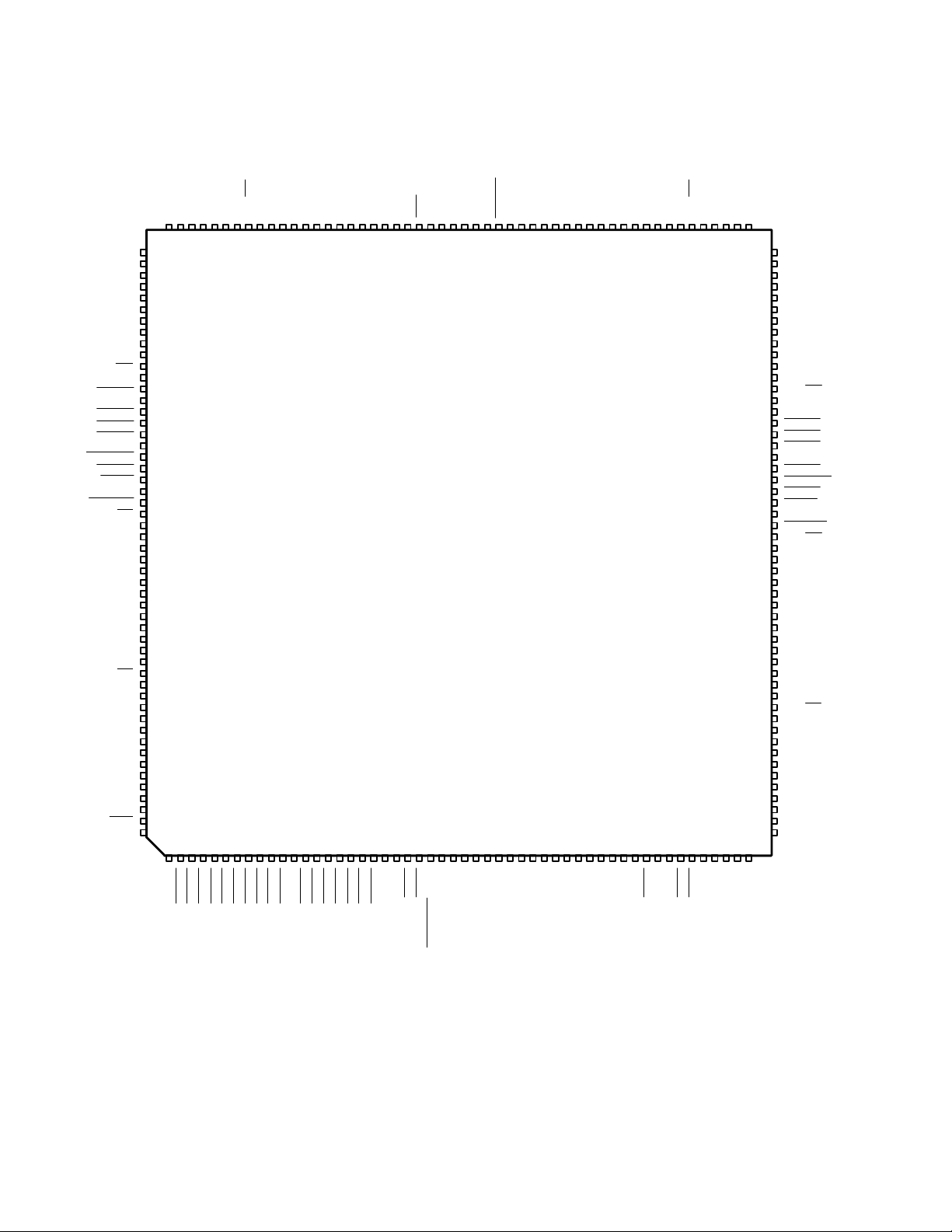
PDV LOW-PROFILE QUAD FLAT PACKAGE
TOP VIEW
V
CC
GND
S_AD11
GND
S_AD12
S_AD13
V
CC
S_AD14
S_AD15
GND
S_C/BE1
S_PAR
S_SERR
V
CC
S_PERR
S_LOCK
S_STOP
GND
S_DEVSEL
S_TRDY
S_IRDY
V
CC
S_FRAME
S_C/BE2
GND
S_AD16
S_AD17
V
CC
S_AD18
S_AD19
GND
S_AD20
S_AD21
V
CC
S_AD22
S_AD23
GND
S_C/BE3
S_AD24
V
CC
S_AD25
S_AD26
GND
S_AD27
S_AD28
V
CC
S_AD29
S_AD30
GND
S_AD31
S_REQ0
V
CC
NC
MSK_IN
HSENUM
126
125
127
CCP
P_V
124
GND
123
P_AD1
P_AD0
122
121
CC
V
120
P_AD2
P_AD3
118
119
GND
117
P_AD4
P_AD5
116
115
CC
V
114
P_AD6
P_AD7
112
113
CCP
GND
148
S_AD7
S_AD6
146
147
V
145
CC
S_AD4
S_AD5
144
143
CC
V
S_M66ENA
S_AD10
S_AD9
S_C/BE0
154
153
152
151
S_AD8
150
149
MS0
155
214365871091211141316151817201922212423262528273029323134333635383740394241444346454847504952
157
158
159
160
161
162
163
164
165
166
167
168
169
170
171
172
173
174
175
176
177
178
179
180
181
182
183
184
185
186
187
188
189
190
191
192
193
194
195
196
197
198
199
200
201
202
203
204
205
206
207
208
GND
156
GND
142
S_AD2
S_AD3
140
141
CC
V
139
S_AD0
S_AD1
138
137
GND
136
S_V
135
TRST
134
TMS
TCK
132
133
PCI2050
CC
V
131
TDO
130
TDI
129
HSLED
128
GND
P_C/BE0
111
110
CC
V
P_AD8
108
109
P_AD9
MS1
107
51 106
CC
V
105
104
103
102
101
100
99
98
97
96
95
94
93
92
91
90
89
88
87
86
85
84
83
82
81
80
79
78
77
76
75
74
73
72
71
70
69
68
67
66
65
64
63
62
61
60
59
58
57
56
55
54
53
GND
V
CC
NC
P_AD10
GND
P_AD11
P_AD12
V
CC
P_AD13
P_AD14
GND
P_AD15
P_C/BE1
V
CC
P_PAR
P_SERR
P_PERR
P_LOCK
GND
P_STOP
P_DEVSEL
P_TRDY
P_IRDY
V
CC
P_FRAME
P_C/BE2
GND
P_AD16
P_AD17
V
CC
P_AD18
P_AD19
GND
P_AD20
P_AD21
V
CC
P_AD22
P_AD23
GND
P_IDSEL
P_C/BE3
P_AD24
V
CC
P_AD25
P_AD26
GND
P_AD27
P_AD28
V
CC
P_AD29
GND
V
CC
2–2
CC
V
S_REQ1
S_REQ2
S_REQ3
S_REQ4
S_REQ6
S_REQ5
CC
V
GPIO2
S_RST
S_CFN
HSSWITCH/GPIO3
GPIO0
GPIO1
GND
S_CLKOUT0
S_CLKOUT1
S_GNT0
S_REQ7
S_REQ8
GND
S_GNT1
S_GNT2
S_GNT5
S_GNT3
S_GNT4
S_GNT8
S_GNT6
S_GNT7
GND
S_CLK
Figure 2–3. PCI2050 PDV Terminal Diagram
CC
V
S_CLKOUT2
S_CLKOUT4
S_CLKOUT3
GND
S_CLKOUT6
S_CLKOUT5
S_CLKOUT7
CC
V
S_CLKOUT8
S_CLKOUT9
P_RST
BPCCE
P_CLK
P_GNT
GND
P_REQ
V
P_AD30
P_AD31
CC
GND
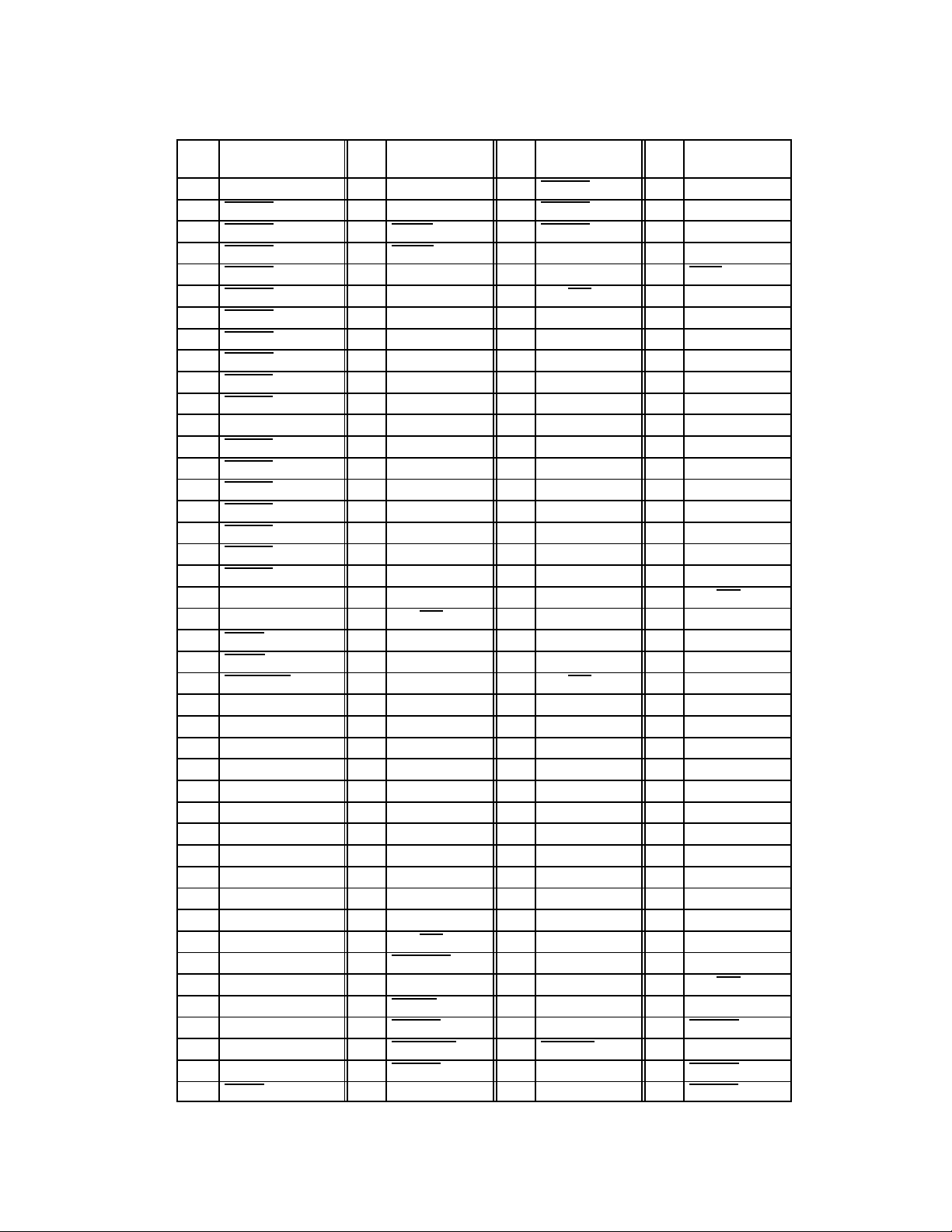
Table 2–1. 208-Terminal PDV Signal Names Sorted by Terminal Number
PDV
NO.
SIGNAL NAME
1 V
CC
2 S_REQ1 45 P_CLK 88 P_PERR 131 V
3 S_REQ2 46 P_GNT 89 P_SERR 132 TMS
4 S_REQ3 47 P_REQ 90 P_PAR 133 TCK
5 S_REQ4 48 GND 91 V
6 S_REQ5 49 P_AD31 92 P_C/BE1 135 S_V
7 S_REQ6 50 P_AD30 93 P_AD15 136 GND
8 S_REQ7 51 V
9 S_REQ8 52 GND 95 P_AD14 138 S_AD1
10 S_GNT0 53 V
11 S_GNT1 54 GND 97 V
12 GND 55 P_AD29 98 P_AD12 141 S_AD3
13 S_GNT2 56 V
14 S_GNT3 57 P_AD28 100 GND 143 S_AD4
15 S_GNT4 58 P_AD27 101 P_AD10 144 S_AD5
16 S_GNT5 59 GND 102 NC 145 V
17 S_GNT6 60 P_AD26 103 V
18 S_GNT7 61 P_AD25 104 GND 147 S_AD7
19 S_GNT8 62 V
20 GND 63 P_AD24 106 MS1 149 S_C/BE0
21 S_CLK 64 P_C/BE3 107 P_AD9 150 S_AD8
22 S_RST 65 P_IDSEL 108 V
23 S_CFN 66 GND 109 P_AD8 152 S_AD9
24 HSSWITCH/GPIO3 67 P_AD23 110 P_C/BE0 153 S_M66ENA
25 GPIO2 68 P_AD22 111 GND 154 S_AD10
26 V
CC
27 GPIO1 70 P_AD21 113 P_AD6 156 GND
28 GPIO0 71 P_AD20 114 V
29 S_CLKOUT0 72 GND 115 P_AD5 158 GND
30 S_CLKOUT1 73 P_AD19 116 P_AD4 159 S_AD11
31 GND 74 P_AD18 117 GND 160 GND
32 S_CLKOUT2 75 V
33 S_CLKOUT3 76 P_AD17 119 P_AD2 162 S_AD13
34 V
CC
35 S_CLKOUT4 78 GND 121 P_AD1 164 S_AD14
36 S_CLKOUT5 79 P_C/BE2 122 P_AD0 165 S_AD15
37 GND 80 P_FRAME 123 GND 166 GND
38 S_CLKOUT6 81 V
39 S_CLKOUT7 82 P_IRDY 125 NC 168 S_PAR
40 V
CC
41 S_CLKOUT8 84 P_DEVSEL 127 HSENUM 170 V
42 S_CLKOUT9 85 P_STOP 128 HSLED 171 S_PERR
43 P_RST 86 GND 129 TDI 172 S_LOCK
PDV
SIGNAL NAME
NO.
44 BPCCE 87 P_LOCK 130 TDO
CC
CC
CC
CC
69 V
CC
CC
77 P_AD16 120 V
CC
83 P_TRDY 126 MSK_IN 169 S_SERR
PDV
SIGNAL NAME
NO.
CC
94 GND 137 S_AD0
96 P_AD13 139 V
CC
99 P_AD11 142 GND
CC
105 V
CC
CC
112 P_AD7 155 MS0
CC
118 P_AD3 161 S_AD12
CC
124 P_V
CCP
PDV
SIGNAL NAME
NO.
CC
134 TRST
CCP
CC
140 S_AD2
CC
146 S_AD6
148 GND
151 V
CC
157 V
CC
163 V
CC
167 S_C/BE1
CC
2–3
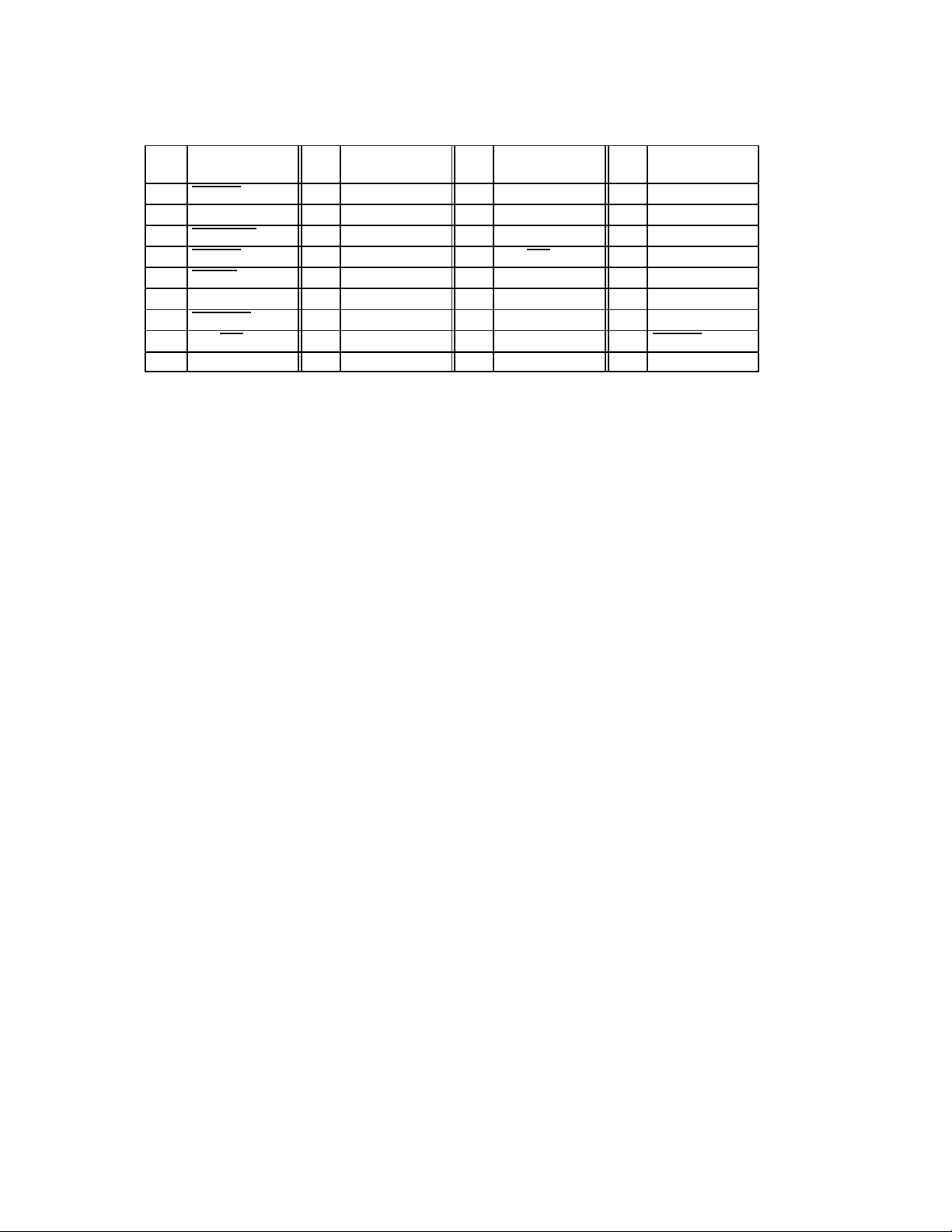
Table 2–1. 208-Terminal PDV Signal Names Sorted by Terminal Number (Continued)
PDV
SIGNAL NAME
NO.
173 S_STOP 182 S_AD16 191 S_AD22 200 S_AD27
174 GND 183 S_AD17 192 S_AD23 201 S_AD28
175 S_DEVSEL 184 V
176 S_TRDY 185 S_AD18 194 S_C/BE3 203 S_AD29
177 S_IRDY 186 S_AD19 195 S_AD24 204 S_AD30
178 V
CC
179 S_FRAME 188 S_AD20 197 S_AD25 206 S_AD31
180 S_C/BE2 189 S_AD21 198 S_AD26 207 S_REQ0
181 GND 190 V
PDV
SIGNAL NAME
NO.
CC
187 GND 196 V
CC
PDV
NO.
193 GND 202 V
199 GND 208 V
SIGNAL NAME
CC
PDV
SIGNAL NAME
NO.
CC
205 GND
CC
2–4
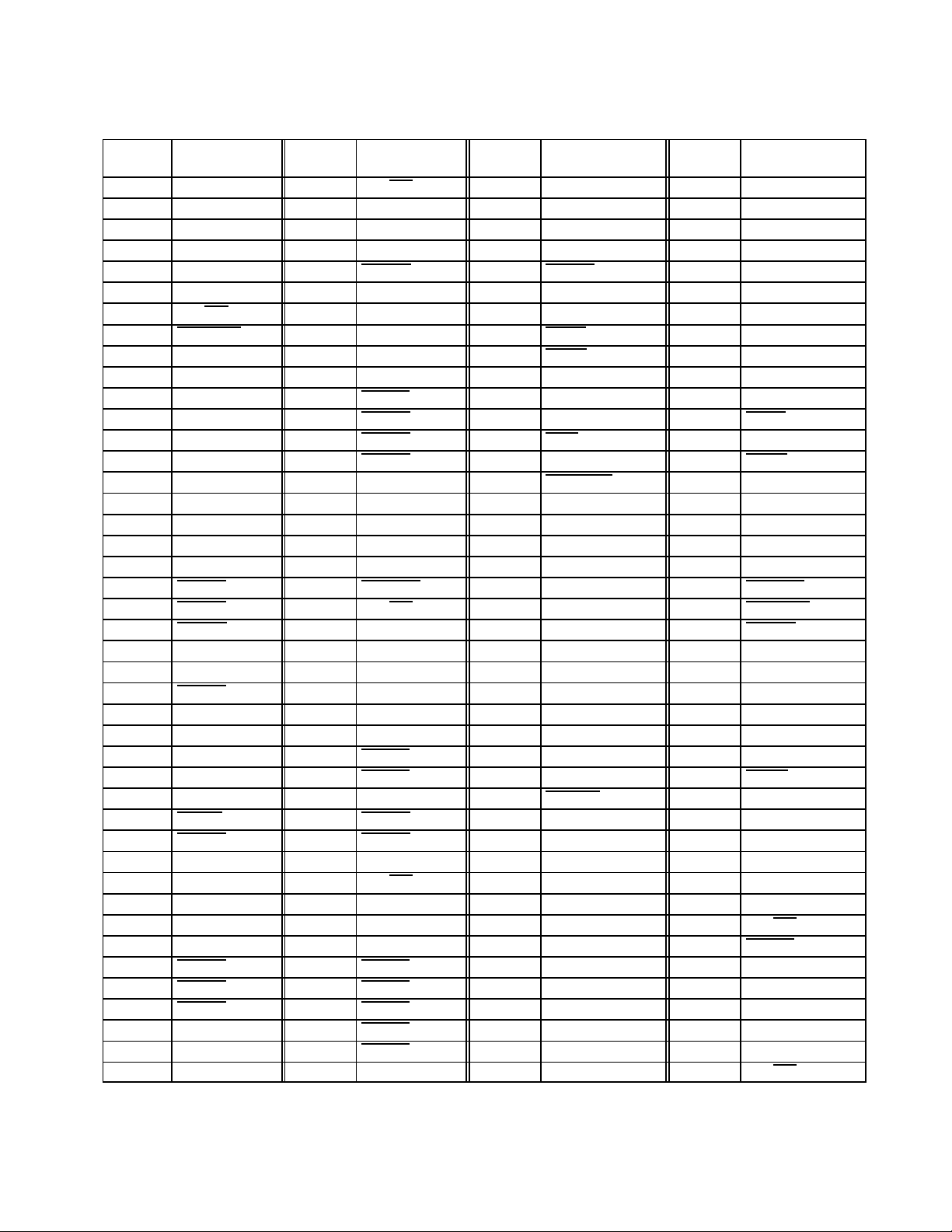
Table 2–2. 209-Terminal GHK/ZHK Signal Names Sorted by Terminal Number
GHK/ZHK
NO.
A4 V
A5 S_AD29 E9 S_AD21 H17 S_AD2 N1 S_CLKOUT7
A6 GND E10 S_AD17 H18 V
A7 S_AD24 E11 V
A8 V
A9 S_AD18 E13 S_AD15 J2 GND N6 S_CLKOUT9
A10 S_C/BE2 E14 S_AD11 J3 S_CLK N14 V
A11 S_DEVSEL E17 MS0 J5 S_RST N15 P_AD6
A12 GND E18 S_M66ENA J6 S_CFN N17 P_AD4
A13 V
A14 GND F1 S_GNT0 J15 S_AD0 N19 P_AD3
A15 S_AD13 F2 S_REQ7 J17 S_V
A16 V
B5 GND F5 S_REQ2 J19 TCK P3 P_GNT
B6 S_AD27 F6 S_AD30 K1 HSSWITCH/GPIO3 P5 P_AD30
B7 V
B8 S_AD22 F8 GND K3 V
B9 S_AD19 F9 S_AD20 K5 GPIO1 P8 P_AD24
B10 GND F10 V
B11 S_TRDY F11 S_FRAME K14 TMS P10 P_FRAME
B12 S_STOP F12 S_C/BE1 K15 V
B13 S_SERR F13 GND K17 TDO P12 P_SERR
B14 S_AD14 F14 S_AD9 K18 TDI P13 GND
B15 S_AD12 F15 S_AD10 K19 HSLED P14 GND
C5 S_REQ0 F17 S_AD8 L1 S_CLKOUT0 P15 P_AD9
C6 V
C7 S_AD25 F19 S_AD7 L3 GND P18 P_AD7
C8 S_AD23 G1 S_GNT3 L5 S_CLKOUT3 P19 V
C9 GND G2 S_GNT2 L6 S_CLKOUT2 R1 P_REQ
C10 S_AD16 G3 GND L14 HSENUM R2 P_AD31
C11 S_IRDY G5 S_REQ8 L15 MSK_IN R3 V
C12 S_LOCK G6 S_REQ3 L17 NC R6 P_AD29
C13 S_PAR G14 S_AD6 L18 P_V
C14 V
C15 GND G17 V
D1 V
D19 GND G19 S_AD4 M3 S_CLKOUT5 R11 P_STOP
E1 S_REQ5 H1 S_GNT7 M5 S_CLKOUT6 R12 P_PAR
E2 S_REQ4 H2 S_GNT6 M6 GND R13 V
E3 S_REQ1 H3 S_GNT5 M14 P_AD5 R14 NC
E5
E6 S_AD31 H6 S_GNT1 M17 V
E7 S_AD28 H14 S_AD3 M18 P_AD1 R19 P_C/BE0
†
Terminal E5 is used as a key to indicate the location of the A1 corner. It is a no-connect terminal.
SIGNAL NAME
CC
CC
CC
CC
CC
CC
CC
CC
†
NC H5 S_GNT4 M15 P_AD2 R17 MS1
GHK/ZHK
NO.
E8 S_C/BE3 H15 GND M19 P_AD0
E12 S_PERR J1 S_GNT8 N5 P_CLK
E19 V
F3 S_REQ6 J18 TRST P2 BPCCE
F7 S_AD26 K2 GPIO2 P6 GND
F18 GND L2 S_CLKOUT1 P17 GND
G15 S_C/BE0 L19 GND R8 P_AD23
G18 S_AD5 M2 S_CLKOUT4 R10 P_C/BE2
SIGNAL NAME
CC
CC
CC
CC
GHK/ZHK
NO.
H19 S_AD1 N3 S_CLKOUT8
J14 GND N18 GND
K6 GPIO0 P9 V
M1 V
SIGNAL NAME
CC
CCP
CC
CC
CCP
CC
CC
GHK/ZHK
NO.
N2 V
P1 P_RST
P7 V
P11 P_DEVSEL
R7 P_AD25
R9 P_AD18
R18 P_AD8
SIGNAL NAME
CC
CC
CC
CC
CC
CC
CC
2–5
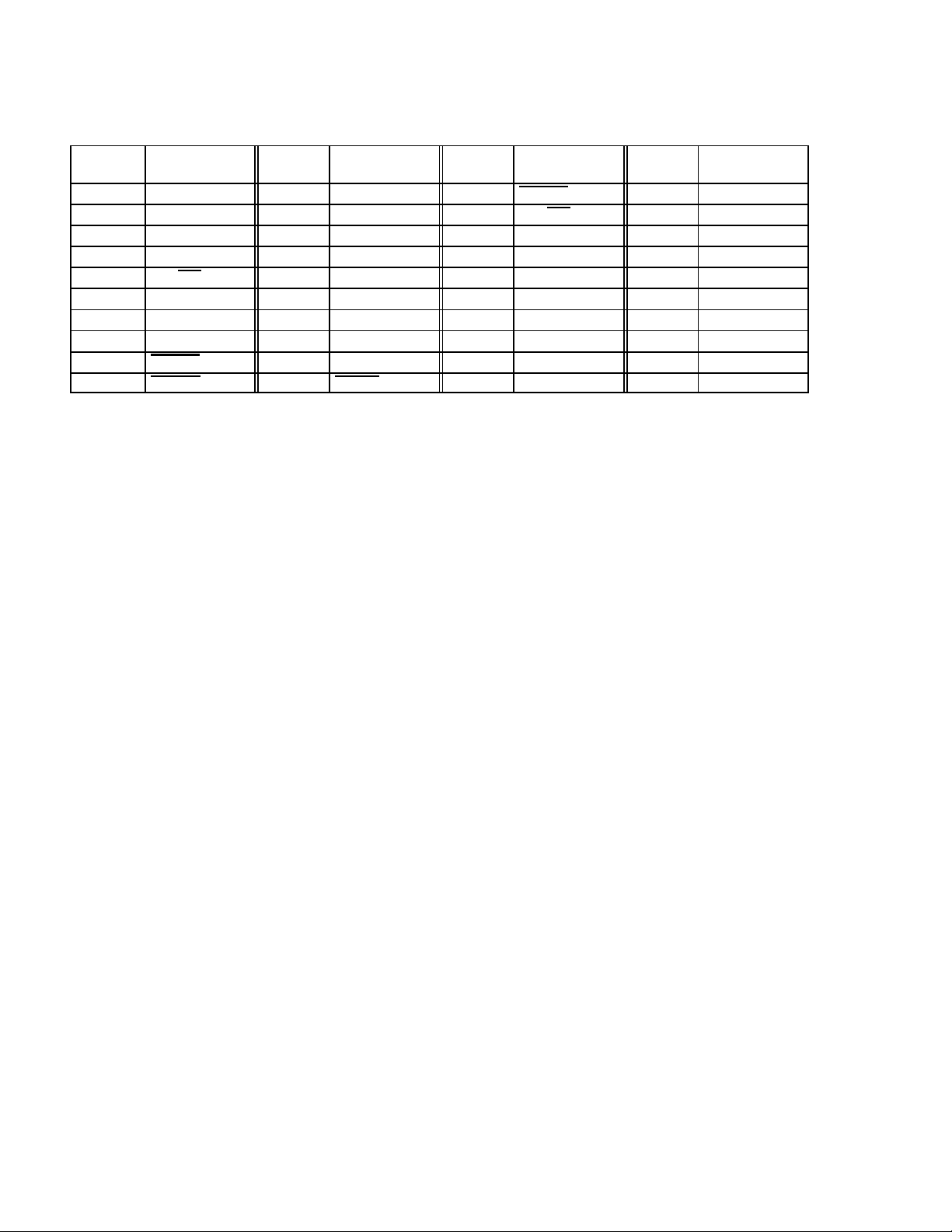
Table 2–2. 209-Terminal GHK/ZHK Signal Names Sorted by Terminal Number (Continued)
GHK/ZHK
NO.
T1 GND U13 P_AD15 V12 P_LOCK W10 P_AD17
T19 V
U5 GND U15 V
U6 GND V5 P_AD28 V15 P_AD10 W13 V
U7 P_C/BE3 V6 P_AD26 W4 V
U8 P_AD22 V7 P_IDSEL W5 P_AD27 W15 P_AD11
U9 P_AD19 V8 V
U10 GND V9 GND W7 GND
U11 P_TRDY V10 P_AD16 W8 P_AD21
U12 P_PERR V11 P_IRDY W9 P_AD20
SIGNAL NAME
CC
GHK/ZHK
NO.
U14 P_AD12 V13 P_C/BE1 W11 V
SIGNAL NAME
CC
CC
GHK/ZHK
NO.
V14 P_AD13 W12 GND
W6 V
SIGNAL NAME
CC
CC
GHK/ZHK
NO.
W14 P_AD14
W16 GND
SIGNAL NAME
CC
CC
2–6
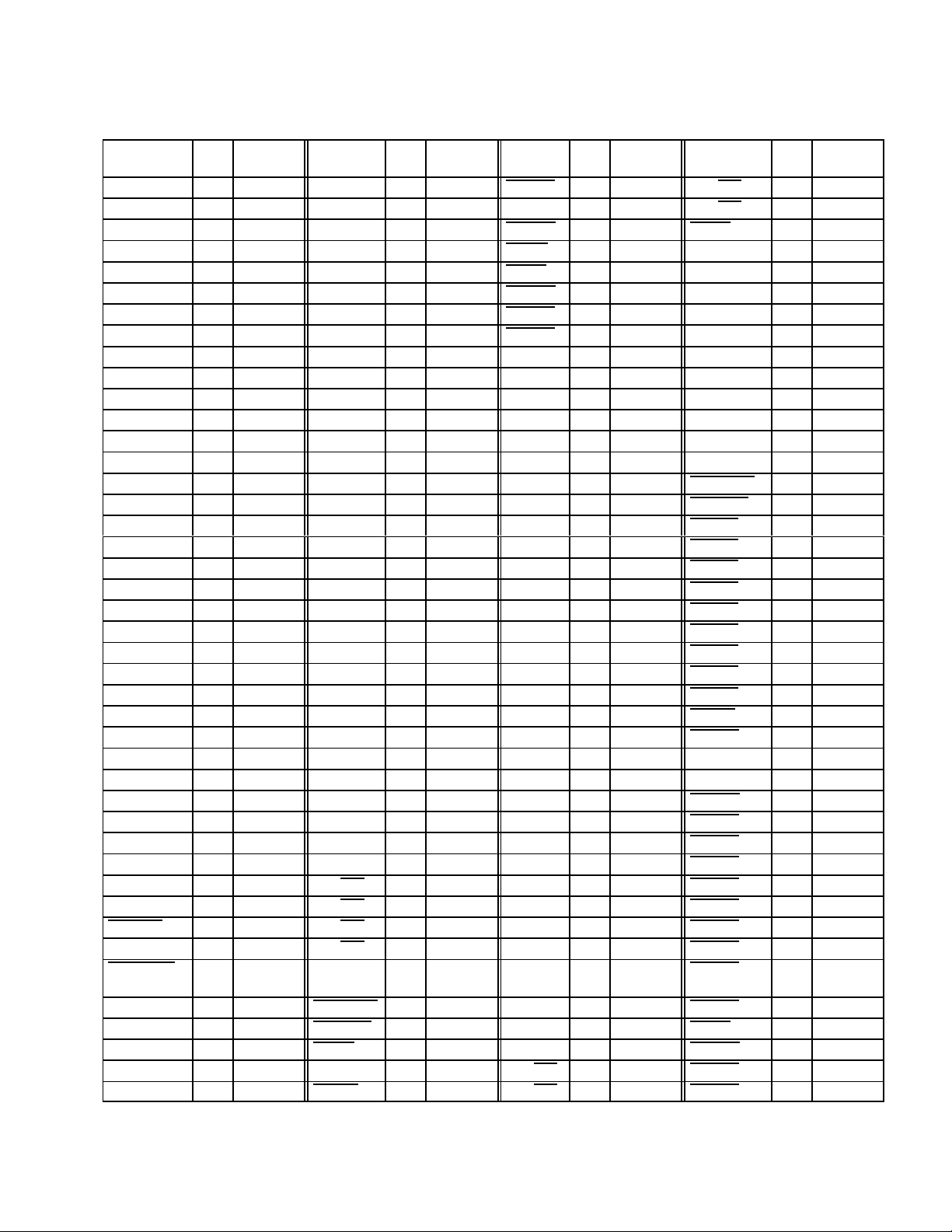
Table 2–3. Signal Names Sorted Alphabetically
SIGNAL
NAME
BPCCE 44 P2 NC 125 L17 P_LOCK 87 V12 S_C/BE2 180 A10
GND 12 G3 P_AD0 122 M19 P_PAR 90 R12 S_C/BE3 194 E8
GND 20 J2 P_AD1 121 M18 P_PERR 88 U12 S_CFN 23 J6
GND 31 L3 P_AD2 119 M15 P_REQ 47 R1 S_CLK 21 J3
GND 37 M6 P_AD3 118 N19 P_RST 43 P1 S_CLKOUT0 29 L1
GND 48 P6 P_AD4 116 N17 P_SERR 89 P12 S_CLKOUT1 30 L2
GND 52 T1 P_AD5 115 M14 P_STOP 85 R11 S_CLKOUT2 32 L6
GND 54 U5 P_AD6 113 N15 P_TRDY 83 U11 S_CLKOUT3 33 L5
GND 59 U6 P_AD7 112 P18 P_V
GND 66 W7 P_AD8 109 R18 S_AD0 137 J15 S_CLKOUT5 36 M3
GND 72 V9 P_AD9 107 P15 S_AD1 138 H19 S_CLKOUT6 38 M5
GND 78 U10 P_AD10 101 V15 S_AD2 140 H17 S_CLKOUT7 39 N1
GND 86 W12 P_AD11 99 W15 S_AD3 141 H14 S_CLKOUT8 41 N3
GND 94 P13 P_AD12 98 U14 S_AD4 143 G19 S_CLKOUT9 42 N6
GND 100 P14 P_AD13 96 V14 S_AD5 144 G18 S_DEVSEL 175 A11
GND 104 W16 P_AD14 95 W14 S_AD6 146 G14 S_FRAME 179 F11
GND 111 P17 P_AD15 93 U13 S_AD7 147 F19 S_GNT0 10 F1
GND 117 N18 P_AD16 77 V10 S_AD8 150 F17 S_GNT1 11 H6
GND 123 L19 P_AD17 76 W10 S_AD9 152 F14 S_GNT2 13 G2
GND 136 J14 P_AD18 74 R9 S_AD10 154 F15 S_GNT3 14 G1
GND 142 H15 P_AD19 73 U9 S_AD11 159 E14 S_GNT4 15 H5
GND 148 F18 P_AD20 71 W9 S_AD12 161 B15 S_GNT5 16 H3
GND 156 D19 P_AD21 70 W8 S_AD13 162 A15 S_GNT6 17 H2
GND 158 C15 P_AD22 68 U8 S_AD14 164 B14 S_GNT7 18 H1
GND 160 F13 P_AD23 67 R8 S_AD15 165 E13 S_GNT8 19 J1
GND 166 A14 P_AD24 63 P8 S_AD16 182 C10 S_IRDY 177 C11
GND 174 A12 P_AD25 61 R7 S_AD17 183 E10 S_LOCK 172 C12
GND 181 B10 P_AD26 60 V6 S_AD18 185 A9 S_M66ENA 153 E18
GND 187 C9 P_AD27 58 W5 S_AD19 186 B9 S_PAR 168 C13
GND 193 F8 P_AD28 57 V5 S_AD20 188 F9 S_PERR 171 E12
GND 199 A6 P_AD29 55 R6 S_AD21 189 E9 S_REQ0 207 C5
GND 205 B5 P_AD30 50 P5 S_AD22 191 B8 S_REQ1 2 E3
GPIO0 28 K6 P_AD31 49 R2 S_AD23 192 C8 S_REQ2 3 F5
GPIO1 27 K5 P_C/BE0 110 R19 S_AD24 195 A7 S_REQ3 4 G6
GPIO2 25 K2 P_C/BE1 92 V13 S_AD25 197 C7 S_REQ4 5 E2
HSENUM 127 L14 P_C/BE2 79 R10 S_AD26 198 F7 S_REQ5 6 E1
HSLED 128 K19 P_C/BE3 64 U7 S_AD27 200 B6 S_REQ6 7 F3
HSSWITCH/
GPIO3
MS0 155 E17 P_DEVSEL 84 P11 S_AD29 203 A5 S_REQ8 9 G5
MS1 106 R17 P_FRAME 80 P10 S_AD30 204 F6 S_RST 22 J5
MSK_IN 126 L15 P_GNT 46 P3 S_AD31 206 E6 S_SERR 169 B13
NC N/A E5 P_IDSEL 65 V7 S_C/BE0 149 G15 S_STOP 173 B12
NC 102 R14 P_IRDY 82 V11 S_C/BE1 167 F12 S_TRDY 176 B11
PDV
GHK/ZHK
NO.
24 K1 P_CLK 45 N5 S_AD28 201 E7 S_REQ7 8 F2
NO.
SIGNAL
NAME
PDV
NO.
GHK/ZHK
NO.
SIGNAL
NAME
CCP
PDV
GHK/ZHK
NO.
124 L18 S_CLKOUT4 35 M2
NO.
SIGNAL
NAME
PDV
NO.
GHK/ZHK
NO.
2–7
Table 2–3. Signal Names Sorted Alphabetically (Continued)
SIGNAL
NAME
S_V
CCP
TCK 133 J19 V
TDI 129 K18 V
TDO 130 K17 V
TMS 132 K14 V
TRST 134 J18 V
V
CC
V
CC
V
CC
V
CC
PDV
GHK/ZHK
NO.
135 J17 V
1 D1 V
26 K3 V
34 M1 V
40 N2 V
NO.
SIGNAL
NAME
CC
CC
CC
CC
CC
CC
CC
CC
CC
CC
PDV
GHK/ZHK
NO.
51 R3 V
53 W4 V
56 P7 V
62 W6 V
69 V8 V
75 P9 V
81 W11 V
91 W13 V
97 R13 V
103 U15 V
NO.
SIGNAL
NAME
CC
CC
CC
CC
CC
CC
CC
CC
CC
CC
PDV
GHK/ZHK
NO.
105 T19 V
108 N14 V
114 P19 V
120 M17 V
131 K15 V
139 H18 V
145 G17 V
151 E19
202 C6
208 A4
NO.
SIGNAL
NAME
CC
CC
CC
CC
CC
CC
CC
PDV
GHK/ZHK
NO.
157 A16
163 C14
170 A13
178 E11
184 F10
190 A8
196 B7
NO.
2–8
The terminals are grouped in tables by functionality, such as PCI system function and power-supply function (see
Table 2–4 through Table 2–12). The terminal numbers are listed for convenient reference.
Table 2–4. Primary PCI System Terminals
TERMINAL
PDV
NAME
P_CLK 45 N5 I
P_RST
GHK/ZHK
NO.
43 P1 I
NO.
I/O DESCRIPTION
Primary PCI bus clock. P_CLK provides timing for all transactions on the primary PCI bus. All primary PCI
signals are sampled at rising edge of P_CLK.
PCI reset. When the primary PCI bus reset is asserted, P_RST causes the bridge to put all output buffers
in a high-impedance state and reset all internal registers. When asserted, the device is completely
nonfunctional. During P_RST, the secondary interface is driven low. After P_RST is deasserted, the
bridge is in its default state.
Table 2–5. Primary PCI Address and Data Terminals
TERMINAL
NAME
P_AD31
P_AD30
P_AD29
P_AD28
P_AD27
P_AD26
P_AD25
P_AD24
P_AD23
P_AD22
P_AD21
P_AD20
P_AD19
P_AD18
P_AD17
P_AD16
P_AD15
P_AD14
P_AD13
P_AD12
P_AD11
P_AD10
P_AD9
P_AD8
P_AD7
P_AD6
P_AD5
P_AD4
P_AD3
P_AD2
P_AD1
P_AD0
P_C/BE3
P_C/BE2
P_C/BE1
P_C/BE0
PDV
NO.
49
50
55
57
58
60
61
63
67
68
70
71
73
74
76
77
93
95
96
98
99
101
107
109
112
113
115
116
118
119
121
122
64
79
92
110
GHK/ZHK
NO.
R2
P5
R6
V5
W5
V6
R7
P8
R8
U8
W8
W9
U9
R9
W10
V10
U13
W14
V14
U14
W15
V15
P15
R18
P18
N15
M14
N17
N19
M15
M18
M19
U7
R10
V13
R19
I/O DESCRIPTION
Primary address/data bus. These signals make up the multiplexed PCI address and data bus on the
primary interface. During the address phase of a primary bus PCI cycle, P_AD31–P_AD0 contain a
I/O
32-bit address or other destination information. During the data phase, P_AD31–P_AD0 contain data.
Primary bus commands and byte enables. These signals are multiplexed on the same PCI terminals.
During the address phase of a primary bus PCI cycle, P_C/BE3
During the data phase, this 4-bit bus is used as byte enables. The byte enables determine which byte
I/O
paths of the full 32-bit data bus carry meaningful data. P_C/BE0 applies to byte 0 (P_AD7–P_AD0),
P_C/BE1
P_C/BE3
applies to byte 1 (P_AD15–P_AD8), P_C/BE2 applies to byte 2 (P_AD23–P_AD16), and
applies to byte 3 (P_AD31–P_AD24).
–P_C/BE0 define the bus command.
2–9
Table 2–6. Primary PCI Interface Control Terminals
TERMINAL
PDV
NAME
P_DEVSEL 84 P11 I/O
P_FRAME
P_GNT
P_IDSEL 65 V7 I
P_IRDY 82 V11 I/O
P_LOCK 87 V12 I/O
P_PAR 90 R12 I/O
P_PERR
P_REQ 47 R1 O
P_SERR 89 P12 O
P_STOP 85 R11 I/O
P_TRDY 83 U11 I/O
GHK/ZHK
NO.
80 P10 I/O
46 P3 I
88 U12 I/O
NO.
I/O DESCRIPTION
Primary device select. The bridge asserts P_DEVSEL to claim a PCI cycle as the target device. As
a PCI master on the primary bus, the bridge monitors P_DEVSEL
responds before time-out occurs, then the bridge terminates the cycle with a master abort.
Primary cycle frame. P_FRAME is driven by the master of a primary bus cycle. P_FRAME is asserted
to indicate that a bus transaction is beginning, and data transfers continue while this signal is
asserted. When P_FRAME is deasserted, the primary bus transaction is in the final data phase.
Primary bus grant to bridge. P_GNT is driven by the primary PCI bus arbiter to grant the bridge
access to the primary PCI bus after the current data transaction has completed. P_GNT
not follow a primary bus request, depending on the primary bus arbitration algorithm.
Primary initialization device select. P_IDSEL selects the bridge during configuration space
accesses. P_IDSEL can be connected to one of the upper 24 PCI address lines on the primary PCI
bus.
Note: There is no IDSEL signal interfacing the secondary PCI bus; thus, the entire configuration
space of the bridge can only be accessed from the primary bus.
Primary initiator ready. P_IRDY indicates ability of the primary bus master to complete the current
data phase of the transaction. A data phase is completed on a rising edge of P_CLK where both
P_IRDY and P_TRDY are asserted. Until P_IRDY and P_TRDY are both sampled asserted, wait
states are inserted.
Primary PCI bus lock. P_LOCK is used to lock the primary bus and gain exclusive access as a bus
master.
Primary parity. In all primary bus read and write cycles, the bridge calculates even parity across the
P_AD and P_C/BE
indicator with a one-P_CLK delay. As a target during PCI read cycles, the calculated parity is
compared to the parity indicator of the master; a miscompare can result in a parity error assertion
(P_PERR
Primary parity error indicator. P_PERR is driven by a primary bus PCI device to indicate that
calculated parity does not match P_PAR when P_PERR
register (PCI offset 04h, see Section 4.3).
Primary PCI bus request. Asserted by the bridge to request access to the primary PCI bus as a
master.
Primary system error. Output pulsed from the bridge when enabled through the command register
(PCI offset 04h, see Section 4.3) indicating a system error has occurred. The bridge needs not be
the target of the primary PCI cycle to assert this signal. When bit 6 is enabled in the bridge control
register (PCI offset 3Eh, see Section 4.32), this signal also pulses, indicating that a system error has
occurred on one of the subordinate buses downstream from the bridge.
Primary cycle stop signal. This signal is driven by a PCI target to request that the master stop the
current primary bus transaction. This signal is used for target disconnects and is commonly asserted
by target devices which do not support burst data transfers.
Primary target ready. P_TRDY indicates the ability of the primary bus target to complete the current
data phase of the transaction. A data phase is completed upon a rising edge of P_CLK where both
P_IRDY and P_TRDY are asserted. Until both P_IRDY and P_TRDY are asserted, wait states are
inserted.
).
buses. As a bus master during PCI write cycles, the bridge outputs this parity
until a target responds. If no target
may or may
is enabled through bit 6 of the command
2–10
TERMINAL
PDV
NAME
S_CLKOUT9
S_CLKOUT8
S_CLKOUT7
S_CLKOUT6
S_CLKOUT5
S_CLKOUT4
S_CLKOUT3
S_CLKOUT2
S_CLKOUT1
S_CLKOUT0
S_CLK
S_CFN 23 J6 I
S_RST 22 J5 O
GHK/ZHK
NO.
42
41
39
38
36
35
33
32
30
29
21 J3 I Secondary PCI bus clock input. This input synchronizes the PCI2050 to the secondary bus clocks.
NO.
N6
N3
N1
M5
M3
M2
L5
L6
L2
L1
Table 2–7. Secondary PCI System Terminals
I/O DESCRIPTION
Secondary PCI bus clocks. Provide timing for all transactions on the secondary PCI bus. Each
secondary bus device samples all secondary PCI signals at the rising edge of its corresponding
O
S_CLKOUT input.
Secondary external arbiter enable. When this signal is high, the secondary external arbiter is
enabled. When the external arbiter is enabled, the PCI2050 S_REQ0
a secondary bus grant input to the bridge and S_GNT0
request to the external arbiter on the secondary bus.
Secondary PCI reset. S_RST is a logical OR of P_RST and the state of the secondary bus reset
bit (bit 6) of the bridge control register (PCI offset 3Eh, see Section 4.32). S_RST
with respect to the state of the secondary interface CLK signal.
is reconfigured as a secondary bus master
terminal is reconfigured as
is asynchronous
2–11
NAME
TERMINAL
PDV
NO.
GHK/ZHK
NO.
Table 2–8. Secondary PCI Address and Data Terminals
I/O DESCRIPTION
S_AD31
S_AD30
S_AD29
S_AD28
S_AD27
S_AD26
S_AD25
S_AD24
S_AD23
S_AD22
S_AD21
S_AD20
S_AD19
S_AD18
S_AD17
S_AD16
S_AD15
S_AD14
S_AD13
S_AD12
S_AD11
S_AD10
S_AD9
S_AD8
S_AD7
S_AD6
S_AD5
S_AD4
S_AD3
S_AD2
S_AD1
S_AD0
S_C/BE3
S_C/BE2
S_C/BE1
S_C/BE0
S_DEVSEL 175 A11 I/O
S_FRAME 179 F11 I/O
S_GNT8
S_GNT7
S_GNT6
S_GNT5
S_GNT4
S_GNT3
S_GNT2
S_GNT1
S_GNT0
206
204
203
201
200
198
197
195
192
191
189
188
186
185
183
182
165
164
162
161
159
154
152
150
147
146
144
143
141
140
138
137
194
180
167
149
19
18
17
16
15
14
13
11
10
E6
F6
A5
E7
B6
F7
C7
A7
C8
B8
E9
F9
B9
A9
E10
C10
E13
B14
A15
B15
E14
F15
F14
F17
F19
G14
G18
G19
H14
H17
H19
J15
E8
A10
F12
G15
J1
H1
H2
H3
H5
G1
G2
H6
F1
I/O
I/O
Secondary address/data bus. These signals make up the multiplexed PCI address and data bus
on the secondary interface. During the address phase of a secondary bus PCI cycle,
S_AD31–S_AD0 contain a 32-bit address or other destination information. During the data phase,
S_AD31–S_AD0 contain data.
Secondary bus commands and byte enables. These signals are multiplexed on the same PCI
terminals. During the address phase of a secondary bus PCI cycle, S_C/BE3
bus command. During the data phase, this 4-bit bus is used as byte enables. The byte enables
determine which byte paths of the full 32-bit data bus carry meaningful data. S_C/BE0 applies to
byte 0 (S_AD7–S_AD0), S_C/BE1
2 (S_AD23–S_AD16), and S_C/BE3
Secondary device select. The bridge asserts S_DEVSEL to claim a PCI cycle as the target device.
As a PCI master on the secondary bus, the bridge monitors S_DEVSEL
If no target responds before time-out occurs, then the bridge terminates the cycle with a master
abort.
Secondary cycle frame. S_FRAME is driven by the master of a secondary bus cycle. S_FRAME
is asserted to indicate that a bus transaction is beginning and data transfers continue while
S_FRAME
data phase.
Secondary bus grant to the bridge. The bridge provides internal arbitration and these signals are
used to grant potential secondary PCI bus masters access to the bus. Ten potential masters
(including the bridge) can be located on the secondary PCI bus.
O
When the internal arbiter is disabled, S_GNT0
request signal for the bridge.
is asserted. When S_FRAME is deasserted, the secondary bus transaction is in the final
applies to byte 1 (S_AD15–S_AD8), S_C/BE2 applies to byte
applies to byte 3 (S_AD31–S_AD24).
is reconfigured as an external secondary bus
–S_C/BE0 define the
until a target responds.
2–12
Table 2–9. Secondary PCI Interface Control Terminals
TERMINAL
PDV
NAME
S_IRDY 177 C11 I/O
S_LOCK 172 C12 I/O
S_PAR 168 C13 I/O
S_PERR
S_REQ8
S_REQ7
S_REQ6
S_REQ5
S_REQ4
S_REQ3
S_REQ2
S_REQ1
S_REQ0
S_SERR
S_STOP 173 B12 I/O
S_TRDY 176 B11 I/O
GHK/ZHK
NO.
171 E12 I/O
9
8
7
6
5
4
3
2
207
169 B13 I
NO.
G5
F2
F3
E1
E2
G6
F5
E3
C5
I/O DESCRIPTION
Secondary initiator ready. S_IRDY indicates the ability of the secondary bus master to complete the
current data phase of the transaction. A data phase is completed on a rising edge of S_CLK where both
and S_TRDY are asserted; until S_IRDY and S_TRDY are asserted, wait states are inserted.
S_IRDY
Secondary PCI bus lock. S_LOCK is used to lock the secondary bus and gain exclusive access as a
master.
Secondary parity. In all secondary bus read and write cycles, the bridge calculates even parity across
the S_AD and S_C/BE
indicator with a one-S_CLK delay . As a target during PCI read cycles, the calculated parity is compared
to the master parity indicator. A miscompare can result in a parity error assertion (S_PERR
Secondary parity error indicator. S_PERR is driven by a secondary bus PCI device to indicate that
calculated parity does not match S_PAR when enabled through the command register (PCI offset 04h,
see Section 4.3).
Secondary PCI bus request signals. The bridge provides internal arbitration, and these signals are used
as inputs from secondary PCI bus masters requesting the bus. Ten potential masters (including the
bridge) can be located on the secondary PCI bus.
I
When the internal arbiter is disabled, the S_REQ0
grant for the bridge.
Secondary system error. S_SERR is passed through the primary interface by the bridge if enabled
through the bridge control register (PCI offset 3Eh, see Section 4.32). S_SERR
the bridge.
Secondary cycle stop signal. S_STOP is driven by a PCI target to request that the master stop the
current secondary bus transaction. S_STOP
by target devices that do not support burst data transfers.
Secondary target ready. S_TRDY indicates the ability of the secondary bus target to complete the
current data phase of the transaction. A data phase is completed on a rising edge of S_CLK where both
S_IRDY and S_TRDY are asserted; until S_IRDY and S_TRDY are asserted, wait states are inserted.
buses. As a master during PCI write cycles, the bridge outputs this parity
signal is reconfigured as an external secondary bus
is never asserted by
is used for target disconnects and is commonly asserted
).
2–13

Table 2–10. Miscellaneous Terminals
TERMINAL
PDV
NAME
BPCCE 44 P2 I
GPIO3/HSSWITCH
GPIO2
GPIO1
GPIO0
HSENUM 127 L14 O Hot-swap ENUM
HSLED 128 K19 O Hot-swap LED output
MS0
MS1
NC
S_M66ENA 153 E18 O
GHK/ZHK
NO.
24
25
27
28
155 E17 I Mode select 0
106 R17 I Mode select 1
102
125
NO.
K1
K2
K5
K6
R14
L17
I/O DESCRIPTION
Bus/power clock control management terminal. When signal BPCCE is tied high and when
the PCI2050 is placed in the D3 power state, it enables the PCI2050 to place the secondary
bus in the B2 power state. The PCI2050 disables the secondary clocks and drives them to
0. When tied low, placing the PCI2050 in the D3 power state has no effect on the secondary
bus clocks.
General-purpose I/O terminals
GPIO3 is HSSWITCH
I
HSSWITCH
NC These terminals have no function on the PCI2050.
Secondary bus 66-MHz enable terminal. This terminal is always driven low to indicate that
the secondary bus speed is 33 MHz.
provides the status of the ejector handle switch to the cPCI logic.
in cPCI mode.
Table 2–11. JTAG Interface Terminals
TERMINAL
PDV
NAME
TCK 133 J19 I JTAG boundary-scan clock. TCK is the clock controlling the JTAG logic.
TDI 129 K18 I
TDO 130 K17 O
TMS 132 K14 I JTAG test mode select. TMS causes state transitions in the test access port controller.
TRST 134 J18 I
NO.
GHK/ZHK
NO.
I/O DESCRIPTION
JTAG serial data in. TDI is the serial input through which JTAG instructions and test data enter the JT AG
interface. The new data on TDI is sampled on the rising edge of TCK.
JTAG serial data out. TDO is the serial output through which test instructions and data from the test logic
leave the PCI2050.
JTAG T AP reset. When TRST is asserted low , the TAP controller is asynchronously forced to enter a reset
state and initialize the test logic.
Table 2–12. Power Supply Terminals
TERMINAL
NAME PDV NO. GHK/ZHK NO.
2–14
GND
V
P_V
S_V
12, 20, 31, 37, 48, 52, 54,
59, 66, 72, 78, 86, 94, 100,
104, 111, 117, 123, 136,
142, 148, 156, 158, 160,
166, 174, 181, 187, 193,
199, 205
1, 26, 34, 40, 51, 53, 56, 62,
69, 75, 81, 91, 97, 103, 105,
CC
CCP
CCP
108, 114, 120, 131, 139,
145, 151, 157, 163, 170,
178, 184, 190, 196, 202,
208
124 L18
135 J17
A6, A12, A14, B5, B10, C9,
C15, D19, F8, F13, F18,
G3, H15, J2, J14, L3, L19,
M6, N18, P6, P13, P14,
P17, T1, U5, U6, U10, V9,
W7, W12, W16
A4, A8, A13, A16, B7, C6,
C14, D1, E11, E19, F10,
G17, H18, K3, K15, M1,
M17, N2, N14, P7, P9, P19,
R3, R13, T19, U15, V8, W4,
W6, W11, W13
DESCRIPTION
Device ground terminals
Power-supply terminal for core logic (3.3 V)
Primary bus-signaling environment supply. P_V
protection circuitry on primary bus I/O signals.
Secondary bus-signaling environment supply. S_V
protection circuitry on secondary bus I/O signals.
is used in
CCP
CCP
is used in

3 Feature/Protocol Descriptions
The following sections give an overview of the PCI2050 PCI-to-PCI bridge features and functionality. Figure 3–1
shows a simplified block diagram of a typical system implementation using the PCI2050.
CPU
Host Bus
PCI Bus 0
PCI2050
PCI Bus 1
Host
Bridge
Memory
PCI
Device
PCI Bus 2
PCI2050
PCI Option Slot
PCI
Device
PCI
Device
Figure 3–1. System Block Diagram
PCI
Device
PCI Option Card
PCI Option Card
(Option)
3.1 Introduction to the PCI2050
The PCI2050 is a bridge between two PCI buses and is compliant with both the PCI Local Bus Specification and the
PCI-to-PCI Bridge Specification. The bridge supports two 32-bit PCI buses operating at a maximum of 33 MHz. The
primary and secondary buses operate independently in either a 3.3-V or 5-V signaling environment. The core logic
of the bridge, however, is powered at 3.3 V to reduce power consumption.
Host software interacts with the bridge through internal registers. These internal registers provide the standard PCI
status and control for both the primary and secondary buses. Many vendor-specific features that exist in the TI
extension register set are included in the bridge. The PCI configuration header of the bridge is only accessible from
the primary PCI interface.
The bridge provides internal arbitration for the nine possible secondary bus masters, and provides each with a
dedicated active-low request/grant pair (REQ
PCI2050 bridge defaulting to the highest priority tier.
Upon system power up, power-on self-test (POST) software configures the bridge according to the devices that exist
on subordinate buses, and enables performance-enhancing features of the PCI2050. In a typical system, this is the
only communication with the bridge internal register set.
/GNT). The arbiter features a two-tier rotational scheme with the
3–1

3.2 PCI Commands
The bridge responds to PCI bus cycles as a PCI target device based on internal register settings and on the decoding
of each address phase. Table 3–1 lists the valid PCI bus cycles and their encoding on the command/byte enable
(C/BE
) bus during the address phase of a bus cycle.
Table 3–1. PCI Command Definition
C/BE3–C/BE0
0000 Interrupt acknowledge
0001 Special cycle
0010 I/O read
0011 I/O write
0100 Reserved
0101 Reserved
0110 Memory read
0111 Memory write
1000 Reserved
1001 Reserved
1010 Configuration read
1011 Configuration write
1100 Memory read multiple
1101 Dual address cycle
1110 Memory read line
1111 Memory write and invalidate
COMMAND
The bridge never responds as a PCI target to the interrupt acknowledge, special cycle, or reserved commands. The
bridge does, however, initiate special cycles on both interfaces when a type 1 configuration cycle issues the special
cycle request. The remaining PCI commands address either memory , I/O, or configuration space. The bridge accepts
PCI cycles by asserting DEVSEL
as a medium-speed device, i.e., DEVSEL is asserted two clock cycles after the
address phase.
The PCI2050 converts memory write and invalidate commands to memory write commands when forwarding
transactions from either the primary or secondary side of the bridge if the bridge cannot guarantee that an entire cache
line will be delivered.
3.3 Configuration Cycles
PCI Local Bus Specification defines two types of PCI configuration read and write cycles: type 0 and type 1. The
bridge decodes each type differently . T ype 0 configuration cycles are intended for devices on the primary bus, while
type 1 configuration cycles are intended for devices on some hierarchically subordinate bus. The difference between
these two types of cycles is the encoding of the primary PCI (P_AD) bus during the address phase of the cycle.
Figure 3–2 shows the P_AD bus encoding during the address phase of a type 0 configuration cycle. The 6-bit register
number field represents an 8-bit address with the two lower bits masked to 0, indicating a doubleword boundary . This
results in a 256-byte configuration address space per function per device. Individual byte accesses may be selected
within a doubleword by using the P_C/BE
31 11 10 8 721 0
Reserved
Figure 3–2. PCI AD31–AD0 During Address Phase of a Type 0 Configuration Cycle
The bridge claims only type 0 configuration cycles when its P_IDSEL terminal is asserted during the address phase
of the cycle and the PCI function number encoded in the cycle is 0. If the function number is 1 or greater, then the
signals during the data phase of the cycle.
Function
Number
Register
Number
0 0
3–2

bridge does not recognize the configuration command. In this case, the bridge does not assert DEVSEL, and the
configuration transaction results in a master abort. The bridge services valid type 0 configuration read or write cycles
by accessing internal registers from the bridge configuration header (see Table 4–1).
Because type 1 configuration cycles are issued to devices on subordinate buses, the bridge claims type 1 cycles
based on the bus number of the destination bus. The P_AD bus encoding during the address phase of a type 1 cycle
is shown in Figure 3–3. The device number and bus number fields define the destination bus and device for the cycle.
31 24 23 16 15 11 10 8 721 0
Reserved Bus Number
Device
Number
Function
Number
Register
Number
0 1
Figure 3–3. PCI AD31–AD0 During Address Phase of a Type 1 Configuration Cycle
Several bridge configuration registers shown in Table 4–1 are significant when decoding and claiming type 1
configuration cycles. The destination bus number encoded on the P_AD bus is compared to the values programmed
in the bridge configuration registers 18h, 19h, and 1Ah, which are the primary bus number, secondary bus number,
and subordinate bus number registers, respectively. These registers default to 00h and are programmed by host
software to reflect the bus hierarchy in the system (see Figure 3–4 for an example of a system bus hierarchy and how
the PCI2050 bus number registers would be programmed in this case).
PCI Bus 0
PCI2050
Primary Bus 00h
Secondary Bus 01h
Subordinate Bus 02h
PCI Bus 1 PCI Bus 3
PCI2050
Primary Bus 01h
Secondary Bus 02h
Subordinate Bus 02h
PCI Bus 2
Primary Bus 00h
Secondary Bus 03h
Subordinate Bus 03h
PCI2050
Figure 3–4. Bus Hierarchy and Numbering
When the PCI2050 claims a type 1 configuration cycle that has a bus number equal to its secondary bus number,
the PCI2050 converts the type 1 configuration cycle to a type 0 configuration cycle and asserts the proper S_AD line
as the IDSEL (see Table 3–2). All other type 1 transactions that access a bus number greater than the bridge
secondary bus number but less than or equal to its subordinate bus number are forwarded as type 1 configuration
cycles.
3–3

Table 3–2. PCI S_AD31–S_AD16 During the Address
Phase of a Type 0 Configuration Cycle
DEVICE
NUMBER
10h–1Eh 0000 0000 0000 0000 –
3.4 Special Cycle Generation
SECONDARY IDSEL
S_AD31–S_AD16
0h 0000 0000 0000 0001 16
1h 0000 0000 0000 0010 17
2h 0000 0000 0000 0100 18
3h 0000 0000 0000 1000 19
4h 0000 0000 0001 0000 20
5h 0000 0000 0010 0000 21
6h 0000 0000 0100 0000 22
7h 0000 0000 1000 0000 23
8h 0000 0001 0000 0000 24
9h 0000 0010 0000 0000 25
Ah 0000 0100 0000 0000 26
Bh 0000 1000 0000 0000 27
Ch 0001 0000 0000 0000 28
Dh 0010 0000 0000 0000 29
Eh 0100 0000 0000 0000 30
Fh 1000 0000 0000 0000 31
S_AD
ASSERTED
The bridge is designed to generate special cycles on both buses through a type 1 cycle conversion. During a type 1
configuration cycle, if the bus number field matches the bridge secondary bus number, the device number field is 1Fh,
and the function number field is 07h, then the bridge generates a special cycle on the secondary bus with a message
that matches the type 1 configuration cycle data. If the bus number is a subordinate bus and not the secondary , then
the bridge passes the type 1 special cycle request through to the secondary interface along with the proper message.
Special cycles are never passed through the bridge. Type 1 configuration cycles with a special cycle request can
propagate in both directions.
3.5 Secondary Clocks
The PCI2050 provides 10 secondary clock outputs (S_CLKOUT[0:9]). Nine are provided for clocking secondary
devices. The tenth clock should be routed back into the PCI2050 S_CLK input to ensure all secondary bus devices
see the same clock. Figure 3–5 is a block diagram of the secondary clock function.
3–4

PCI2050
S_CLK
S_CLKOUT9
S_CLKOUT8
S_CLKOUT2
S_CLKOUT1
S_CLKOUT0
PCI
Device
PCI
Device
PCI
Device
PCI
Device
Figure 3–5. Secondary Clock Block Diagram
3.6 Bus Arbitration
The PCI2050 implements bus request (P_REQ) and bus grant (P_GNT) terminals for primary PCI bus arbitration.
Nine secondary bus requests and nine secondary bus grants are provided on the secondary of the PCI2050. Ten
potential initiators, including the bridge, can be located on the secondary bus. The PCI2050 provides a two-tier
arbitration scheme on the secondary bus for priority bus-master handling.
The two-tier arbitration scheme improves performance in systems in which master devices do not all require the same
bandwidth. Any master that requires frequent use of the bus can be programmed to be in the higher priority tier.
3.6.1 Primary Bus Arbitration
The PCI2050, acting as an initiator on the primary bus, asserts P_REQ when forwarding transactions upstream to
the primary bus. If a target disconnect, a target retry , or a target abort is received in response to a transaction initiated
on the primary bus by the PCI2050, then the device deasserts P_REQ
When the primary bus arbiter asserts P_GNT
in response to a P_REQ from the PCI2050, the device initiates a
for two PCI clock cycles.
transaction on the primary bus during the next PCI clock cycle after the primary bus is sampled idle.
When P_REQ
parking the P_AD31–P_AD0 bus, the C/BE3
is not asserted and the primary bus arbiter asserts P_GNT to the PCI2050, the device responds by
–C/BE0 bus, and primary parity (P_P AR) by driving them to valid logic
levels. If the PCI2050 is parking the primary bus and wants to initiate a transaction on the bus, then it can start the
transaction on the next PCI clock by asserting the primary cycle frame (P_FRAME
P_GNT
is deasserted, then the bridge must rearbitrate for the bus to initiate a transaction.
) while P_GNT is still asserted. If
3.6.2 Internal Secondary Bus Arbitration
S_CFN controls the state of the secondary internal arbiter. The internal arbiter can be enabled by pulling S_CFN low
or disabled by pulling S_CFN
high. The PCI2050 provides nine secondary bus request terminals and nine secondary
3–5

bus grant terminals. Including the bridge, there are a total of ten potential secondary bus masters. These request and
grant signals are connected to the internal arbiter. When an external arbiter is implemented, S_REQ8
S_GNT8
–S_GNT1 are placed in a high-impedance mode.
–S_REQ1 and
3.6.3 External Secondary Bus Arbitration
An external secondary bus arbiter can be used instead of the PCI2050 internal bus arbiter. When using an external
arbiter, the PCI2050 internal arbiter should be disabled by pulling S_CFN
high.
When an external secondary bus arbiter is used, the PCI2050 internally reconfigures the S_REQ0
signals so that S_REQ0 becomes the secondary bus grant for the bridge and S_GNT0 becomes the secondary bus
request for the bridge. This is done because S_REQ0
the bridge, and S_GNT0
When an external arbiter is used, all unused secondary bus grant outputs (S_GNT8
impedance mode. Any unused secondary bus request inputs (S_REQ8
the inputs from oscillating.
is an output and can thus provide the request output from the bridge.
is an input and can thus be used to provide the grant input to
–S_GNT1) are placed in a high
–S_REQ1) should be pulled high to prevent
and S_GNT0
3.7 Decode Options
The PCI2050 supports positive decoding on the primary interface and negative decoding on the secondary interface.
Positive decoding is a method of address decoding in which a device responds only to accesses within an assigned
address range. Negative decoding is a method of address decoding in which a device responds only to accesses
outside of an assigned address range.
3.8 System Error Handling
The PCI2050 can be configured to signal a system error (SERR) for a variety of conditions. The P_SERR event
disable register (offset 64h, see Section 5.4) and the P_SERR status register (offset 6Ah, see Section 5.9) provide
control and status bits for each condition for which the bridge can signal SERR
reporting for both downstream and upstream transactions.
By default, the PCI2050 will not signal SERR
command register (offset 04h, see Section 4.3), then the bridge signals SERR
P_SERR event disable register occur and that condition is enabled. By default, all error conditions are enabled in the
P_SERR event disable register . When the bridge signals SERR
see Section 4.19) is set.
. If the PCI2050 is configured to signal SERR by setting bit 8 in the
, bit 14 in the secondary status register (offset 1Eh,
. These individual bits enable SERR
if any of the error conditions in the
3.8.1 Posted Write Parity Error
If bit 1 in the P_SERR event disable register (offset 64h, see Section 5.4) is 0, then parity errors on the target bus
during a posted write are passed to the initiating bus as a SERR
(offset 6Ah, see Section 5.9) is set. The status bit is cleared by writing a 1.
. When this occurs, bit 1 of the P_SERR status register
3.8.2 Posted Write Time-Out
If bit 2 in the P_SERR event disable register (offset 64h, see Section 5.4) is 0 and the retry timer expires while
attempting to complete a posted write, then the PCI2050 signals SERR
of the P_SERR status register (offset 6Ah, see Section 5.9) is set. The status bit is cleared by writing a 1.
on the initiating bus. When this occurs, bit 2
3.8.3 Target Abort on Posted Writes
If bit 3 in the P_SERR event disable register (of fset 64h, see Section 5.4) is 0 and the bridge receives a target abort
during a posted write transaction, then the PCI2050 signals SERR
the P_SERR status register (offset 6Ah, see Section 5.9) is set. The status bit is cleared by writing a 1.
3–6
on the initiating bus. When this occurs, bit 3 of

3.8.4 Master Abort on Posted Writes
If bit 4 in the P_SERR event disable register (PCI offset 64h, see Section 5.4) is 0 and a posted write transaction
results in a master abort, then the PCI2050 signals SERR
status register (PCI offset 6Ah, see Section 5.9) is set. The status bit is cleared by writing a 1.
on the initiating bus. When this occurs, bit 4 of the P_SERR
3.8.5 Master Delayed Write Time-Out
If bit 5 in the P_SERR event disable register (PCI offset 64h, see Section 5.4) is 0 and the retry timer expires while
attempting to complete a delayed write, then the PCI2050 signals SERR
of the P_SERR status register (PCI offset 6Ah, see Section 5.9) is set. The status bit is cleared by writing a 1.
on the initiating bus. When this occurs, bit 5
3.8.6 Master Delayed Read Time-Out
If bit 6 in the P_SERR event disable register (offset 64h, see Section 5.4) is 0 and the retry timer expires while
attempting to complete a delayed read, then the PCI2050 signals SERR
of the P_SERR status register (offset 6Ah, see Section 5.9) is set. The status bit is cleared by writing a 1.
on the initiating bus. When this occurs, bit 6
3.8.7 Secondary SERR
The PCI2050 passes SERR from the secondary bus to the primary bus if it is enabled for SERR response, that is,
if bit 8 in the command register (PCI offset 04h, see Section 4.3) is set, and if bit 1 in the bridge control register (PCI
offset 3Eh, see Section 4.32) is set.
3.9 Parity Handling and Parity Error Reporting
When forwarding transactions, the PCI2050 attempts to pass the data parity condition from one interface to the other
unchanged, whenever possible, to allow the master and target devices to handle the error condition.
3.9.1 Address Parity Error
If the parity error response bit (bit 6) in the command register (PCI offset 04h, see Section 4.3) is set, then the PCI2050
signals SERR
on address parity errors and target abort transactions.
3.9.2 Data Parity Error
If the parity error response bit (bit 6) in the command register (PCI offset 04h, see Section 4.3) is set, then the PCI2050
signals PERR
register (PCI offset 06h, see Section 4.4) is set.
If the bridge is configured to respond to parity errors via bit 6 in the command register (PCI offset 04h, see Section 4.3),
then bit 8 (data parity error detected) in the status register (PCI offset 06h, see Section 4.4) is set when the bridge
detects bad parity . The data parity error detected bit is also set when the bridge, as a bus master, asserts PERR
detects PERR
when it receives bad data. When the bridge detects bad parity , bit 15 (detected parity error) in the status
or
.
3.10 Master and Target Abort Handling
If the PCI2050 receives a target abort during a write burst, then it signals target abort back on the initiator bus. If it
receives a target abort during a read burst, then it provides all of the valid data on the initiator bus and disconnects.
T arget aborts for posted and nonposted transactions are reported as specified in the PCI-to-PCI Bridge Specification.
Master aborts for posted and nonposted transactions are reported as specified in the PCI-to-PCI Bridge Specification.
If a transaction is attempted on the primary bus after a secondary reset is asserted, then the PCI2050 follows bit 5
(master abort mode) in the bridge control register (PCI offset 3Eh, see Section 4.32) for reporting errors.
3.11 Discard Timer
The PCI2050 is free to discard the data or status of a delayed transaction that was completed with a delayed
transaction termination when a bus master has not repeated the request within 2
10
or 215 PCI clocks (approximately
3–7

30 µs and 993 µs, respectively). The PCI Local Bus Specification recommends that a bridge wait 215 PCI clocks
before discarding the transaction data or status.
The PCI2050 implements a discard timer for use in delayed transactions. After a delayed transaction is completed
on the destination bus, the bridge may discard it under two conditions. The first condition occurs when a read
transaction is made to a region of memory that is inside a defined prefetchable memory region, or when the command
is a memory read line or a memory read multiple, implying that the memory region is prefetchable. The other condition
occurs when the master originating the transaction (either a read or a write, prefetchable or nonprefetchable) has not
retried the transaction within 2
timer. When the discard timer expires, the bridge is required to discard the data. The PCI2050 default value for the
discard timer is 2
(offset 3Eh, see Section 4.32). For more information on the discard timer , see error conditions in the PCI Local Bus
Specification.
15
clocks; however, this value can be set to 210 clocks by setting bit 9 in the bridge control register
10
or 215 clocks. The number of clocks is tracked by a timer referred to as the discard
3.12 Delayed Transactions
The bridge supports delayed transactions as defined in PCI Local Bus Specification. A target must be able to complete
the initial data phase in 16 PCI clocks or less from the assertion of the cycle frame (FRAME
phases must complete in eight PCI clocks or less. A delayed transaction consists of three phases:
• An initiator device issues a request.
• The target completes the request on the destination bus and signals the completion to the initiator.
• The initiator completes the request on the originating bus.
If the bridge is the target of a PCI transaction and it must access a slow device to write or read the requested data,
and the transaction takes longer than 16 clocks, then the bridge must latch the address, the command, and the byte
enables, and then issue a retry to the initiator. The initiator must end the transaction without any transfer of data and
is required to retry the transaction later using the same address, command, and byte enables. This is the first phase
of the delayed transaction.
), and subsequent data
During the second phase, if the transaction is a read cycle, the bridge fetches the requested data on the destination
bus, stores it internally, and obtains the completion status, thus completing the transaction on the destination bus.
If it is a write transaction, then the bridge writes the data and obtains the completion status, thus completing the
transaction on the destination bus. The bridge stores the completion status until the master on the initiating bus retries
the initial request.
During the third phase, the initiator rearbitrates for the bus. When the bridge sees the initiator retry the transaction,
it compares the second request to the first request. If the address, command, and byte enables match the values
latched in the first request, then the completion status (and data if the request was a read) is transferred to the initiator.
At this point, the delayed transaction is complete. If the second request from the initiator does not match the first
request exactly, then the bridge issues another retry to the initiator.
The PCI supports up to three delayed transactions in each direction at any given time.
3.13 Mode Selection
Table 3–3 shows the mode selection via MS0 (PDV terminal 155, GHK/ZHK terminal E17) and MS1 (PDV terminal
106, GHK/ZHK terminal R17).
3–8

Table 3–3. Configuration via MS0 and MS1
MS0
0 0 CompactPCI hot-swap friendly
0 1 CompactPCI hot-swap disabled
1 X Intel compatible
MS1 MODE
PCI Bus Power Management Interface Specification Revision 1.1
HSSWITCH/GPIO(3) functions as HSSWITCH
PCI Bus Power Management Interface Specification Revision 1.1
HSSWITCH/GPIO(3) functions as GPIO(3)
No cPCI hot swap
PCI Bus Power Management Interface Specification Revision 1.0
3.14 CompactPCI Hot-Swap Support
The PCI2050 is hot-swap friendly silicon that supports all of the hot-swap capable features, contains support for
software control, and integrates circuitry required by the PICMG CompactPCI Hot-Swap Specification. To be
hot-swap capable, the PCI2050 supports the following:
• Compliance with PCI Local Bus Specification
• Tolerance of V
• Asynchronous reset
• Tolerance of precharge voltage
• I/O buffers that meet modified V/I requirements
• Limited I/O terminal voltage at precharge voltage
from early power
CC
• Hot-swap control and status programming via extended PCI capabilities linked list
• Hot-swap terminals: HS_ENUM
, HS_SWITCH, and HS_LED
cPCI hot-swap defines a process for installing and removing PCI boards without adversely affecting a running system.
The PCI2050 provides this functionality such that it can be implemented on a board that can be removed and inserted
in a hot-swap system.
The PCI2050 provides three terminals to support hot-swap when configured to be in hot-swap mode: HS_ENUM
(output), HS_SWITCH (input), and HS_LED (output). The HS_ENUM output indicates to the system that an insertion
event occurred or that a removal event is about to occur. The HS_SWITCH
input indicates the state of a board ejector
handle, and the HS_LED output lights a blue LED to signal insertion- and removal-ready status.
3–9

3.15 JTAG Support
The PCI2050 implements a JTAG test port based on IEEE Standard 1149.1, IEEE Standard Test Access Port and
Boundary-Scan Architecture. The JTAG test port consists of the following:
• A 5-wire test access port
• A test access port controller
• An instruction register
• A bypass register
• A boundary-scan register
3.15.1 Test Port Instructions
The PCI2050 supports the following JTAG instructions:
• EXTEST, BYPASS, and SAMPLE
• HIGHZ and CLAMP
• Private (various private instructions used by TI for test purposes)
Table 3–4 lists and describes the different test port instructions, and gives the op code of each one. The information
in Table 3–5 is for implementation of boundary scan interface signals to permit in-circuit testing.
Table 3–4. JTAG Instructions and Op Codes
INSTRUCTION OP CODE DESCRIPTION
EXTEST 00000 External test: drives terminals from the boundary scan register
SAMPLE 00001 Sample I/O terminals
CLAMP 00100 Drives terminals from the boundary scan register and selects the bypass register for shifts
HIGHZ 00101 Puts all outputs and I/O terminals except for the TDO terminal in a high-impedance state
BYPASS 11111 Selects the bypass register for shifts
BOUNDARY SCAN
REGISTER NO.
0 137 J15 S_AD0 19 Bidirectional
1 138 H19 S_AD1 19 Bidirectional
2 140 H17 S_AD2 19 Bidirectional
3 141 H14 S_AD3 19 Bidirectional
4 143 G19 S_AD4 19 Bidirectional
5 144 G18 S_AD5 19 Bidirectional
6 146 G14 S_AD6 19 Bidirectional
7 147 F19 S_AD7 19 Bidirectional
8 149 G15 S_C/BE0 19 Bidirectional
9 150 F17 S_AD8 19 Bidirectional
10 152 F14 S_AD9 19 Bidirectional
11 153 E18 S_M66ENA 19 Bidirectional
12 154 F15 S_AD10 19 Bidirectional
13 155 E17 MS0 – Input
14 158 C15 S_AD11 19 Bidirectional
15 161 B15 S_AD12 19 Bidirectional
16 162 A15 S_AD13 19 Bidirectional
17 164 B14 S_AD14 19 Bidirectional
18 165 E13 S_AD15 19 Bidirectional
19 – – – – Control
PDV TERMINAL
NUMBER
Table 3–5. Boundary Scan Terminal Order
GHK/ZHK TERMINAL
NUMBER
TERMINAL NAME
GROUP DISABLE
REGISTER
BOUNDARY-SCAN
CELL TYPE
3–10

Table 3–5. Boundary Scan Terminal Order (continued)
BOUNDARY SCAN
REGISTER NO.
20 167 F12 S_C/BE1 19 Bidirectional
21 168 C13 S_PAR 19 Bidirectional
22 169 B13 S_SERR – Input
23 171 E13 S_PERR 26 Bidirectional
24 172 C12 S_LOCK 26 Bidirectional
25 173 B12 S_STOP 26 Bidirectional
26 – – – – Control
27 175 A11 S_DEVSEL 26 Bidirectional
28 176 B11 S_TRDY 26 Bidirectional
29 177 C11 S_IRDY 26 Bidirectional
30 179 F11 S_FRAME 26 Bidirectional
31 180 A10 S_C/BE2 48 Bidirectional
32 182 C10 S_AD16 48 Bidirectional
33 183 E10 S_AD17 48 Bidirectional
34 185 A9 S_AD18 48 Bidirectional
35 186 B9 S_AD19 48 Bidirectional
36 188 F9 S_AD20 48 Bidirectional
37 189 E9 S_AD21 48 Bidirectional
38 191 B8 S_AD22 48 Bidirectional
39 192 C8 S_AD23 48 Bidirectional
40 194 E8 S_C/BE3 48 Bidirectional
41 195 A7 S_AD24 48 Bidirectional
42 197 C7 S_AD25 48 Bidirectional
43 198 F7 S_AD26 48 Bidirectional
44 200 B6 S_AD27 48 Bidirectional
45 201 E7 S_AD28 48 Bidirectional
46 203 A5 S_AD29 48 Bidirectional
47 204 F6 S_AD30 48 Bidirectional
48 – – – – Control
49 206 E6 S_AD31 48 Bidirectional
50 207 C5 S_REQ0 – Input
51 2 E3 S_REQ1 – Input
52 3 F5 S_REQ2 – Input
53 4 G6 S_REQ3 – Input
54 5 E2 S_REQ4 – Input
55 6 E1 S_REQ5 – Input
56 7 F3 S_REQ6 – Input
57 8 F2 S_REQ7 – Input
58 9 G5 S_REQ8 – Input
59 10 F1 S_GNT0 61 Output
60 11 H6 S_GNT1 61 Output
61 – – – – Control
PDV TERMINAL
NUMBER
GHK/ZHK TERMINAL
NUMBER
TERMINAL NAME
GROUP DISABLE
REGISTER
BOUNDARY-SCAN
CELL TYPE
3–11

Table 3–5. Boundary Scan Terminal Order (continued)
BOUNDARY SCAN
REGISTER NO.
62 13 G2 S_GNT2 61 Output
63 14 G1 S_GNT3 61 Output
64 15 H5 S_GNT4 61 Output
65 16 H3 S_GNT5 61 Output
66 17 H2 S_GNT6 61 Output
67 18 H1 S_GNT7 61 Output
68 19 J1 S_GNT8 61 Output
69 21 J3 S_CLK – Input
70 22 J5 S_RST 78 Output
71 23 J6 S_CFN – Input
72 24 K1 GPIO3 78 Bidirectional
73 25 K2 GPIO2 78 Bidirectional
74 27 K5 GPIO1 78 Bidirectional
75 28 K6 GPIO0 78 Bidirectional
76 29 L1 S_CLKOUT0 – Output
77 30 L2 S_CLKOUT1 – Output
78 – – – – Output
79 32 L6 S_CLKOUT2 – Output
80 33 L5 S_CLKOUT3 – Output
81 35 M2 S_CLKOUT4 – Output
82 36 M3 S_CLKOUT5 – Output
83 38 M5 S_CLKOUT6 – Output
84 39 N1 S_CLKOUT7 – Output
85 41 N3 S_CLKOUT8 – Output
86 42 N6 S_CLKOUT9 – Output
87 43 P1 P_RST – Input
88 44 P2 BPCCE – Input
89 45 N5 P_CLK – Input
90 46 P3 P_GNT – Input
91 47 R1 P_REQ 92 Output
92 – – – – Control
93 49 R2 P_AD31 111 Bidirectional
94 50 P5 P_AD30 111 Bidirectional
95 55 R6 P_AD29 111 Bidirectional
96 57 V5 P_AD28 111 Bidirectional
97 58 W5 P_AD27 111 Bidirectional
98 60 V6 P_AD26 111 Bidirectional
99 61 R7 P_AD25 111 Bidirectional
100 63 W6 P_AD24 111 Bidirectional
101 64 U7 P_C/BE3 111 Bidirectional
102 65 V7 P_IDSEL – Input
103 67 R8 P_AD23 111 Bidirectional
104 68 U8 P_AD22 111 Bidirectional
PDV TERMINAL
NUMBER
GHK/ZHK TERMINAL
NUMBER
TERMINAL NAME
GROUP DISABLE
REGISTER
BOUNDARY-SCAN
CELL TYPE
3–12

Table 3–5. Boundary Scan Terminal Order (continued)
BOUNDARY SCAN
REGISTER NO.
105 70 W8 P_AD21 111 Bidirectional
106 71 W9 P_AD20 111 Bidirectional
107 73 U9 P_AD19 111 Bidirectional
108 74 R9 P_AD18 111 Bidirectional
109 76 W10 P_AD17 111 Bidirectional
110 77 V10 P_AD16 111 Bidirectional
111 – – – – Control
112 79 R10 P_C/BE2 111 Bidirectional
113 80 P10 P_FRAME 118 Bidirectional
114 82 V11 P_IRDY 118 Bidirectional
115 83 U11 P_TRDY 118 Bidirectional
116 84 P11 P_DEVSEL 118 Bidirectional
117 85 R11 P_STOP 118 Bidirectional
118 – – – – Control
119 87 V12 P_LOCK 118 Input
120 88 U12 P_PERR 118 Bidirectional
121 89 P12 P_SERR 142 Output
122 90 R12 P_PAR 142 Bidirectional
123 92 V13 P_C/BE1 142 Bidirectional
124 93 U13 P_AD15 142 Bidirectional
125 95 W14 P_AD14 142 Bidirectional
126 96 V14 P_AD13 142 Bidirectional
127 98 U14 P_AD12 142 Bidirectional
128 99 W15 P_AD11 142 Bidirectional
129 101 V15 P_AD10 142 Bidirectional
130 106 R17 MS1 – Input
131 107 P15 P_AD9 142 Bidirectional
132 109 R18 P_AD8 142 Bidirectional
133 110 R19 P_C/BE0 142 Bidirectional
134 112 P18 P_AD7 142 Bidirectional
135 113 N15 P_AD6 142 Bidirectional
136 115 M14 P_AD5 142 Bidirectional
137 116 N17 P_AD4 142 Bidirectional
138 118 N19 P_AD3 142 Bidirectional
139 119 M15 P_AD2 142 Bidirectional
140 121 M18 P_AD1 142 Bidirectional
141 122 M19 P_AD0 142 Bidirectional
142 – – – – –
143 126 L15 MSK_IN – Input
144 – – – – Control
145 127 L14 HS_ENUM 144 Output
146 128 K19 HS_LED 144 Output
PDV TERMINAL
NUMBER
GHK/ZHK
TERMINAL NUMBER
TERMINAL NAME
GROUP DISABLE
REGISTER
BOUNDARY-SCAN
CELL TYPE
3–13

3.16 GPIO Interface
The PCI2050 implements a four-terminal general-purpose I/O interface. Besides functioning as a general-purpose
I/O interface, the GPIO terminals can be used to read in the secondary clock mask and to stop the bridge from
accepting I/O and memory transactions.
3.16.1 Secondary Clock Mask
The PCI2050 uses GPIO0, GPIO2, and MSK_IN to shift in the secondary clock mask from an external shift register.
A secondary clock mask timing diagram is shown in Figure 3–6. Table 3–6 lists the format for clock mask data.
MSK_IN
GPIO2
GPIO0
P_RST
S_RST
Bit 15
Bit 14 Bit 13 Bit 12 Bit 11 Bit 10 Bit 9 Bit 8 Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0
Figure 3–6. Clock Mask Read Timing After Reset
Table 3–6. Clock Mask Data Format
BIT CLOCK
[0:1] S_CLKOUT0
[2:3] S_CLKOUT1
[4:5] S_CLKOUT2
[6:7] S_CLKOUT3
8 S_CLKOUT4
9 S_CLKOUT5
10 S_CLKOUT6
11 S_CLKOUT7
12 S_CLKOUT8
13 S_CLKOUT9 (PCI2050 S_CLK input)
[14:15] Reserved
3.16.2 Transaction Forwarding Control
The PCI 2050 will stop forwarding I/O and memory transactions if bit 5 of the chip control register (offset 40h, see
Section 5.1) is set to 1 and GPIO3 is driven high. The bridge will complete all queued posted writes and delayed
requests, but delayed completions will not be returned until GPIO3 is driven low and transaction forwarding is
resumed. The bridge will continue to accept configuration cycles in this mode. This feature is not available when in
CompactPCI hot-swap mode because GPIO3 is used as the HS_SWITCH
3–14
input in this mode.

3.17 PCI Power Management
The PCI Power Management Specification establishes the infrastructure required to let the operating system control
the power of PCI functions. This is done by defining a standard PCI interface and operations to manage the power
of PCI functions on the bus. The PCI bus and the PCI functions can be assigned one of four software visible power
management states, which result in varying levels of power savings.
The four power management states of PCI functions are D0—fully on state, D1 and D2—intermediate states, and
D3—off state. Similarly , bus power states of the PCI bus are B0–B3. The bus power states B0 –B3 are derived from
the device power state of the originating PCI2050 device.
For the operating system to manage the device power states on the PCI bus, the PCI function supports four power
management operations:
• Capabilities reporting
• Power status reporting
• Setting the power state
• System wake-up
The operating system identifies the capabilities of the PCI function by traversing the new capabilities list. The
presence of the new capabilities list is indicated by a bit in the status register (offset 06h, see Section 4.4) which
provides access to the capabilities list.
3.17.1 Behavior in Low-Power States
The PCI2050 supports D0, D1, D2, and D3
power states when in TI mode. The PCI2050 only supports D0 and
hot
D3 power states when in Intel mode. The PCI2050 is fully functional only in D0 state. In the lower power states, the
bridge does not accept any memory or I/O transactions. These transactions are aborted by the master. The bridge
accepts type 0 configuration cycles in all power states except D3
. The bridge also accepts type 1 configuration
cold
cycles but does not pass these cycles to the secondary bus in any of the lower power states. Type 1 configuration
writes are discarded and reads return all 1s. All error reporting is done in the low power states. When in D2 and D3
hot
states, the bridge turns off all secondary clocks for further power savings.
When going from D3
to D0, an internal reset is generated. This reset initializes all PCI configuration registers to
hot
their default values. The TI specific registers (40h – FFh) are not reset. Power management registers also are not
reset.
3–15

4 Bridge Configuration Header
The PCI2050 bridge is a single-function PCI device. The configuration header is in compliance with the PCI-to-PCI
Bridge Specification 1.1. T able 4–1 shows the PCI configuration header, which includes the predefined portion of the
bridge configuration space. The PCI configuration offset is shown in the right column under the OFFSET heading.
Table 4–1. Bridge Configuration Header
REGISTER NAME OFFSET
Device ID Vendor ID 00h
Status Command 04h
Class code Revision ID 08h
BIST Header type Primary latency timer Cache line size 0Ch
Base address 0 10h
Base address 1 14h
Secondary bus latency timer Subordinate bus number Secondary bus number Primary bus number 18h
Secondary status I/O limit I/O base 1Ch
Memory limit Memory base 20h
Prefetchable memory limit Prefetchable memory base 24h
Prefetchable base upper 32 bits 28h
Prefetchable limit upper 32 bits 2Ch
I/O limit upper 16 bits I/O base upper 16 bits 30h
Reserved Capability pointer 34h
Expansion ROM base address 38h
Bridge control Interrupt pin Interrupt line 3Ch
Arbiter control Extended diagnostic Chip control 40h
Reserved 44h–60h
GPIO input data GPIO output enable GPIO output data P_SERR event disable 64h
Reserved P_SERR status Secondary clock control 68h
Reserved 6Ch–D8h
Power management capabilities PM next item pointer PM capability ID DCh
Data PMCSR bridge support Power management control/status E0h
Reserved Hot swap control status HS next item pointer HS capability ID E4h
Reserved E8h–FFh
4–1

4.1 Vendor ID Register
This 16-bit value is allocated by the PCI Special Interest Group (SIG) and identifies TI as the manufacturer of this
device. The vendor ID assigned to TI is 104Ch.
Bit 15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Name Vendor ID
Type R R R R R R R R R R R R R R R R
Default 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 1 1 0 0
Register: Vendor ID
Type: Read-only
Offset: 00h
Default: 104Ch
4.2 Device ID Register
This 16-bit value is allocated by the vendor and identifies the PCI device. The device ID for the PCI2050 is AC28h.
Bit 15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Name Device ID
Type R R R R R R R R R R R R R R R R
Default 1 0 1 0 1 1 0 0 0 0 1 0 1 0 0 0
Register: Device ID
Type: Read-only
Offset: 02h
Default: AC28h
4–2

4.3 Command Register
The command register provides control over the bridge interface to the primary PCI bus. VGA palette snooping is
enabled through this register, and all other bits adhere to the definitions in the PCI Local Bus Specification. Table 4–2
describes the bit functions in the command register.
Bit 15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Name Command
Type R R R R R R R/W R/W R R/W R/W R R R/W R/W R/W
Default 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
Register: Command
Type: Read-only, Read/Write
Offset: 04h
Default: 0000h
Table 4–2. Command Register Description
BIT TYPE FUNCTION
15–10 R Reserved
9 R/W Fast back-to-back enable. This bit defaults to 0.
8 R/W
7 R
6 R/W
5 R/W
4 R Memory write and invalidate enable. In a PCI-to-PCI bridge, bit 4 must be read-only and return 0 when read.
3 R
2 R/W
1 R/W
0 R/W
System error (SERR) enable. Bit 8 controls the enable for the SERR driver on the primary interface.
0 = Disable SERR
1 = Enable the SERR
Wait cycle control. Bit 7 controls address/data stepping by the bridge on both interfaces. The bridge does not support
address/data stepping and this bit is hardwired to 0.
Parity error response enable. Bit 6 controls the bridge response to parity errors.
0 = Parity error response disabled (default)
1 = Parity error response enabled
VGA palette snoop enable. When set, the bridge passes I/O writes on the primary PCI bus with addresses 3C6h, 3C8h,
and 3C9h inclusive of ISA aliases (that is, only bits AD9–AD0 are included in the decode).
Special cycle enable. A PCI-to-PCI bridge cannot respond as a target to special cycle transactions, so bit 3 is defined as
read-only and must return 0 when read.
Bus master enable. Bit 2 controls the ability of the bridge to initiate a cycle on the primary PCI bus. When bit 2 is 0, the bridge
does not respond to any memory or I/O transactions on the secondary interface since they cannot be forwarded to the
primary PCI bus.
0 = Bus master capability disabled (default)
1 = Bus master capability enabled
Memory space enable. Bit 1 controls the bridge response to memory accesses for both prefetchable and nonprefetchable
memory spaces on the primary PCI bus. Only when bit 1 is set will the bridge forward memory accesses to the secondary
bus from a primary bus initiator.
0 = Memory space disabled (default)
1 = Memory space enabled
I/O space enable. Bit 0 controls the bridge response to I/O accesses on the primary interface. Only when bit 0 is set will
the bridge forward I/O accesses to the secondary bus from a primary bus initiator.
0 = I/O space disabled (default)
1 = I/O space enabled
driver on primary interface (default)
driver on primary interface
4–3

4.4 Status Register
The status register provides device information to the host system. Bits in this register are cleared by writing a 1 to
the respective bit; writing a 0 to a bit location has no effect. Table 4–3 describes the status register.
Bit 15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Name Status
Type R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R R R/W R R R R R R R R
Default 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 1 0 0 1 0 0 0 0
Register: Status
Type: Read-only, Read/Write
Offset: 06h
Default: 0290h
Table 4–3. Status Register Description
BIT TYPE FUNCTION
15 R/W Detected parity error. Bit 15 is set when a parity error is detected.
Signaled system error (SERR). Bit 14 is set if SERR is enabled in the command register (offset 04h, see Section 4.3,
14 R/W
13 R/W
12 R/W
11 R/W
10–9 R
8 R/W
7 R
6 R
5 R 66-MHz capable. The PCI2050 operates at a maximum P_CLK frequency of 33 MHz; therefore, bit 5 is hardwired to 0.
4 R
3–0 R Reserved. Bits 3–0 return 0s when read.
Command Register) and the bridge signals a system error (SERR). See Section 3.8, System Error Handling.
0 = No SERR signaled (default)
1 = Signals SERR
Received master abort. Bit 13 is set when a cycle initiated by the bridge on the primary bus has been terminated by a master
abort.
0 = No master abort received (default)
1 = Master abort received
Received target abort. Bit 12 is set when a cycle initiated by the bridge on the primary bus has been terminated by a target
abort.
0 = No target abort received (default)
1 = Target abort received
Signaled target abort. Bit 11 is set by the bridge when it terminates a transaction on the primary bus with a target abort.
0 = No target abort signaled by the bridge (default)
1 = T arget abort signaled by the bridge
DEVSEL timing. These read-only bits encode the timing of P_DEVSEL and are hardwired 01b, indicating that the bridge
asserts this signal at a medium speed.
Data parity error detected. Bit 8 is encoded as:
0 = The conditions for setting this bit have not been met. No parity error detected. (default)
1 = A data parity error occurred and the following conditions were met:
a. P_PERR
b. The bridge was the bus master during the data parity error.
c. The parity error response bit (bit 6) was set in the command register (offset 04h, see Section 4.3).
Fast back-to-back capable. The bridge supports fast back-to-back transactions as a target; therefore, bit 7 is hardwired to
1.
User-definable feature (UDF) support. The PCI2050 does not support the user-definable features; therefore, bit 6 is
hardwired to 0.
Capabilities list. Bit 4 is read-only and is hardwired to 1, indicating that capabilities additional to standard PCI are
implemented. The linked list of PCI power management capabilities is implemented by this function.
was asserted by any PCI device including the bridge.
4–4

4.5 Revision ID Register
The revision ID register indicates the silicon revision of the PCI2050.
Bit 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Name Revision ID
Type R R R R R R R R
Default 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
Register: Revision ID
Type: Read-only
Offset: 08h
Default: 00h (reflects the current revision of the silicon)
4.6 Class Code Register
This register categorizes the PCI2050 as a PCI-to-PCI bridge device (0604h) with a 00h programming interface.
Bit 23 22 21 20 19 18 17 16 15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Name Class code
Base class Sub class Programming interface
Type R R R R R R R R R R R R R R R R R R R R R R R R
Default 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
Register: Class code
Type: Read-only
Offset: 09h
Default: 06 0400h
4.7 Cache Line Size Register
The cache line size register is programmed by host software to indicate the system cache line size needed by the
bridge for memory read line, memory read multiple, and memory write and invalidate transactions. The PCI2050
supports cache line sizes up to and including 16 doublewords for memory write and invalidate. If the cache line size
is larger than 16 doublewords, the command is converted to a memory write command.
Bit 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Name Cache line size
Type R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W
Default 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
Register: Cache line size
Type: Read/Write
Offset: 0Ch
Default: 00h
4–5

4.8 Primary Latency Timer Register
The latency timer register specifies the latency timer for the bridge in units of PCI clock cycles. When the bridge is
a primary PCI bus initiator and asserts P_FRAME
before the bridge transaction has terminated, then the bridge terminates the transaction when its P_GNT
, the latency timer begins counting from 0. If the latency timer expires
is
deasserted.
Bit 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Name Latency timer
Type R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W
Default 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
Register: Latency timer
Type: Read/Write
Offset: 0Dh
Default: 00h
4.9 Header Type Register
The header type register is read-only and returns 01h when read, indicating that the PCI2050 configuration space
adheres to the PCI-to-PCI bridge configuration. Only the layout for bytes 10h–3Fh of configuration space is
considered.
Bit 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Name Header type
Type R R R R R R R R
Default 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1
Register: Header type
Type: Read-only
Offset: 0Eh
Default: 01h
4.10 BIST Register
The PCI2050 does not support built-in self test (BIST). The BIST register is read-only and returns the value 00h when
read.
Bit 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Name BIST
Type R R R R R R R R
Default 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
Register: BIST
Type: Read-only
Offset: 0Fh
Default: 00h
4–6

4.11 Base Address Register 0
The bridge requires no additional resources. Base address register 0 is read-only and returns 0s when read.
Bit 31 30 29 28 27 26 25 24 23 22 21 20 19 18 17 16
Name Base address register 0
Type R R R R R R R R R R R R R R R R
Default 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
Bit 15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Name Base address register 0
Type R R R R R R R R R R R R R R R R
Default 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
Register: Base address register 0
Type: Read-only
Offset: 10h
Default: 0000 0000h
4.12 Base Address Register 1
The bridge requires no additional resources. Base address register 1 is read-only and returns 0s when read.
Bit 31 30 29 28 27 26 25 24 23 22 21 20 19 18 17 16
Name Base address register 1
Type R R R R R R R R R R R R R R R R
Default 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
Bit 15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Name Base address register 1
Type R R R R R R R R R R R R R R R R
Default 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
Register: Base address register 1
Type: Read-only
Offset: 14h
Default: 0000 0000h
4.13 Primary Bus Number Register
The primary bus number register indicates the primary bus number to which the bridge is connected. The bridge uses
this register, in conjunction with the secondary bus number and subordinate bus number registers, to determine when
to forward PCI configuration cycles to the secondary buses.
Bit 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Name Primary bus number
Type R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W
Default 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
Register: Primary bus number
Type: Read/Write
Offset: 18h
Default: 00h
4–7

4.14 Secondary Bus Number Register
The secondary bus number register indicates the secondary bus number to which the bridge is connected. The
PCI2050 uses this register, in conjunction with the primary bus number and subordinate bus number registers, to
determine when to forward PCI configuration cycles to the secondary buses. Configuration cycles directed to the
secondary bus are converted to type 0 configuration cycles.
Bit 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Name Secondary bus number
Type R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W
Default 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
Register: Secondary bus number
Type: Read/Write
Offset: 19h
Default: 00h
4.15 Subordinate Bus Number Register
The subordinate bus number register indicates the bus number of the highest numbered bus beyond the primary bus
existing behind the bridge. The PCI2050 uses this register, in conjunction with the primary bus number and secondary
bus number registers, to determine when to forward PCI configuration cycles to the subordinate buses. Configuration
cycles directed to a subordinate bus (not the secondary bus) remain type 1 cycles as the cycle crosses the bridge.
Bit 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Name Subordinate bus number
Type R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W
Default 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
Register: Subordinate bus number
Type: Read/write
Offset: 1Ah
Default: 00h
4.16 Secondary Bus Latency Timer Register
The secondary bus latency timer specifies the latency time for the bridge in units of PCI clock cycles. When the bridge
is a secondary PCI bus initiator and asserts S_FRAME
expires before the bridge transaction has terminated, then the bridge terminates the transaction when its S_GNT
deasserted. The PCI-to-PCI bridge S_GNT
is an internal signal and is removed when another secondary bus master
arbitrates for the bus.
Bit 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Name Secondary bus latency timer
Type R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W
Default 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
Register: Secondary bus latency timer
Type: Read/Write
Offset: 1Bh
Default: 00h
, the latency timer begins counting from 0. If the latency timer
is
4–8

4.17 I/O Base Register
The I/O base register is used in decoding I/O addresses to pass through the bridge. The bridge supports 32-bit I/O
addressing; thus, bits 3–0 are read-only and default to 0001b. The upper four bits are writable and correspond to
address bits AD15–AD12. The lower 12 address bits of the I/O base address are considered 0. Thus, the bottom of
the defined I/O address range is aligned on a 4K-byte boundary. The upper 16 address bits of the 32-bit I/O base
address corresponds to the contents of the I/O base upper 16 bits register (offset 30h, see Section 4.26).
Bit 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Name I/O base
Type R/W R/W R/W R/W R R R R
Default 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1
Register: I/O base
Type: Read-only, Read/Write
Offset: 1Ch
Default: 01h
4.18 I/O Limit Register
The I/O limit register is used in decoding I/O addresses to pass through the bridge. The bridge supports 32-bit I/O
addressing; thus, bits 3–0 are read-only and default to 0001b. The upper four bits are writable and correspond to
address bits AD15–AD12. The lower 12 address bits of the I/O limit address are considered FFFh. Thus, the top of
the defined I/O address range is aligned on a 4K-byte boundary. The upper 16 address bits of the 32-bit I/O limit
address corresponds to the contents of the I/O limit upper 16 bits register (offset 32h, see Section 4.27).
Bit 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Name I/O limit
Type R/W R/W R/W R/W R R R R
Default 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1
Register: I/O limit
Type: Read-only, Read/Write
Offset: 1Dh
Default: 01h
4–9

4.19 Secondary Status Register
The secondary status register is similar in function to the status register (offset 06h, see Section 4.4); however, its
bits reflect status conditions of the secondary interface. Bits in this register are cleared by writing a 1 to the respective
bit.
Bit 15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Name Secondary status
Type R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R R R/W R R R R R R R R
Default 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
Register: Secondary status
Type: Read-only, Read/Write
Offset: 1Eh
Default: 0280h
Table 4–4. Secondary Status Register Description
BIT TYPE FUNCTION
Detected parity error. Bit 15 is set when a parity error is detected on the secondary interface.
15 R/W
14 R/W
13 R/W
12 R/W
11 R/W
10–9 R
8 R/W
7 R Fast back-to-back capable. Bit 7 is hardwired to 1.
6 R User-definable feature (UDF) support. Bit 6 is hardwired to 0.
5 R 66-MHz capable. Bit 5 is hardwired to 0.
4–0 R Reserved. Bits 4–0 return 0s when read.
0 = No parity error detected on the secondary bus (default)
1 = Parity error detected on the secondary bus
Received system error. Bit 14 is set when the secondary interface detects S_SERR asserted. Note that the bridge never
asserts S_SERR
0 = No S_SERR
1 = S_SERR
Received master abort. Bit 13 is set when a cycle initiated by the bridge on the secondary bus has been terminated by a
master abort.
0 = No master abort received (default)
1 = Bridge master aborted the cycle
Received target abort. Bit 12 is set when a cycle initiated by the bridge on the secondary bus has been terminated by a target
abort.
0 = No target abort received (default)
1 = Bridge received a target abort
Signaled target abort. Bit 1 1 is set by the bridge when it terminates a transaction on the secondary bus with a target abort.
0 = No target abort signaled (default)
1 = Bridge signaled a target abort
DEVSEL timing. These read-only bits encode the timing of S_DEVSEL and are hardwired to 01b, indicating that the bridge
asserts this signal at a medium speed.
Data parity error detected.
0 = The conditions for setting this bit have not been met
1 = A data parity error occurred and the following conditions were met:
a. S_PERR
b. The bridge was the bus master during the data parity error.
c. The parity error response bit (bit 1) was set in the bridge control register (offset 3Eh, see Section 4.32).
.
detected on the secondary bus (default)
detected on the secondary bus
was asserted by any PCI device including the bridge.
4–10

4.20 Memory Base Register
The memory base register defines the base address of a memory-mapped I/O address range used by the bridge to
determine when to forward memory transactions from one interface to the other. The upper 12 bits of this register
are read/write and correspond to the address bits AD31–AD20. The lower 20 address bits are considered 0s; thus,
the address range is aligned to a 1M-byte boundary. The bottom four bits are read-only and return 0s when read.
Bit 15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Name Memory base
Type R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R R R R
Default 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
Register: Memory base
Type: Read-only, Read/Write
Offset: 20h
Default: 0000h
4.21 Memory Limit Register
The memory limit register defines the upper-limit address of a memory-mapped I/O address range used to determine
when to forward memory transactions from one interface to the other. The upper 12 bits of this register are read/write
and correspond to the address bits AD31–AD20. The lower 20 address bits are considered 1s; thus, the address
range is aligned to a 1M-byte boundary. The bottom four bits are read-only and return 0s when read.
Bit 15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Name Memory limit
Type R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R R R R
Default 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
Register: Memory limit
Type: Read-only, Read/Write
Offset: 22h
Default: 0000h
4.22 Prefetchable Memory Base Register
The prefetchable memory base register defines the base address of a prefetchable memory address range used by
the bridge to determine when to forward memory transactions from one interface to the other. The upper 12 bits of
this register are read/write and correspond to the address bits AD31–AD20. The lower 20 address bits are considered
0; thus, the address range is aligned to a 1M-byte boundary. The bottom four bits are read-only and return 0s
when read.
Bit 15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Name Prefetchable memory base
Type R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R R R R
Default 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
Register: Prefetchable memory base
Type: Read-only, Read/Write
Offset: 24h
Default: 0000h
4–11

4.23 Prefetchable Memory Limit Register
The prefetchable memory limit register defines the upper-limit address of a prefetchable memory address range used
to determine when to forward memory transactions from one interface to the other. The upper 12 bits of this register
are read/write and correspond to the address bits AD31–AD20. The lower 20 address bits are considered 1s; thus,
the address range is aligned to a 1M-byte boundary. The bottom four bits are read-only and return 0s when read.
Bit 15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Name Prefetchable memory limit
Type R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R R R R
Default 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
Register: Prefetchable memory limit
Type: Read-only, Read/Write
Offset: 26h
Default: 0000h
4.24 Prefetchable Base Upper 32 Bits Register
The prefetchable base upper 32 bits register, plus the prefetchable memory base register, defines the base address
of the 64-bit prefetchable memory address range used by the bridge to determine when to forward memory
transactions from one interface to the other. The prefetchable base upper 32 bits register should be programmed to
all zeros when 32-bit addressing is being used.
Bit 31 30 29 28 27 26 25 24 23 22 21 20 19 18 17 16
Name Prefetchable base upper 32 bits
Type R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W
Default 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
Bit 15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Name Prefetchable base upper 32 bits
Type R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W
Default 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
4–12
Register: Prefetchable base upper 32 bits
Type: Read/Write
Offset: 28h
Default: 0000 0000h

4.25 Prefetchable Limit Upper 32 Bits Register
The prefetchable limit upper 32 bits register plus the prefetchable memory limit register defines the base address of
the 64-bit prefetchable memory address range used by the bridge to determine when to forward memory transactions
from one interface to the other. The prefetchable limit upper 32 bits register should be programmed to all zeros when
32-bit addressing is being used.
Bit 31 30 29 28 27 26 25 24 23 22 21 20 19 18 17 16
Name Prefetchable limit upper 32 bits
Type R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W
Default 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
Bit 15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Name Prefetchable limit upper 32 bits
Type R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W
Default 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
Register: Prefetchable limit upper 32 bits
Type: Read/Write
Offset: 2Ch
Default: 0000 0000h
4.26 I/O Base Upper 16 Bits Register
The I/O base upper 16 bits register specifies the upper 16 bits corresponding to AD31–AD16 of the 32-bit address
that specifies the base of the I/O range to forward from the primary PCI bus to the secondary PCI bus.
Bit 15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Name I/O base upper 16 bits
Type R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W
Default 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
Register: I/O base upper 16 bits
Type: Read/Write
Offset: 30h
Default: 0000h
4.27 I/O Limit Upper 16 Bits Register
The I/O limit upper 16 bits register specifies the upper 16 bits corresponding to AD31–AD16 of the 32-bit address
that specifies the upper limit of the I/O range to forward from the primary PCI bus to the secondary PCI bus.
Bit 15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Name I/O limit upper 16 bits
Type R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W
Default 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
Register: I/O limit upper 16 bits
Type: Read/Write
Offset: 32h
Default: 0000h
4–13

4.28 Capability Pointer Register
The capability pointer register provides the pointer to the PCI configuration header where the PCI power management
register block resides. The capability pointer provides access to the first item in the linked list of capabilities. The
capability pointer register is read-only and returns DCh when read, indicating the power management registers are
located at PCI header offset DCh.
Bit 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Name Capability pointer register
Type R R R R R R R R
Default 1 1 0 1 1 1 0 0
Register: Capability pointer
Type: Read-only
Offset: 34h
Default: DCh
4.29 Expansion ROM Base Address Register
The PCI2050 does not implement the expansion ROM remapping feature. The expansion ROM base address
register returns all 0s when read.
Bit 31 30 29 28 27 26 25 24 23 22 21 20 19 18 17 16
Name Expansion ROM base address
Type R R R R R R R R R R R R R R R R
Default 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
Bit 15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Name Expansion ROM base address
Type R R R R R R R R R R R R R R R R
Default 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
Register: Expansion ROM base address
Type: Read-only
Offset: 38h
Default: 0000 0000h
4.30 Interrupt Line Register
The interrupt line register is read/write and is used to communicate interrupt line routing information. Since the bridge
does not implement an interrupt signal terminal, this register defaults to 00h.
Bit 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Name Interrupt line
Type R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W
Default 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
Register: Interrupt line
Type: Read/Write
Offset: 3Ch
Default: 00h
4–14

4.31 Interrupt Pin Register
The bridge default state does not implement any interrupt terminals. Reads from bits 7–0 of this register return 0s.
Bit 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Name Interrupt pin
Type R R R R R R R R
Default 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
Register: Interrupt pin
Type: Read-only
Offset: 3Dh
Default: 00h
4.32 Bridge Control Register
The bridge control register provides many of the same controls for the secondary interface that are provided by the
command register for the primary interface. Some bits affect the operation of both interfaces.
Bit 15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Name Bridge control
Type R R R R R/W R/W R/W R/W R R/W R/W R R/W R/W R/W R/W
Default 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
Register: Bridge control
Type: Read-only, Read/Write
Offset: 3Eh
Default: 0000h
Table 4–5. Bridge Control Register Description
BIT TYPE FUNCTION
15–12 R Reserved. Bits 15–12 return 0s when read.
Discard timer SERR enable.
11 R/W
10 R/W
9 R/W
8 R/W
7 R
6 R/W
0 = SERR
1 = SERR
Discard timer status. Once set, this bit must be cleared by writing 1 to this bit.
0 = No discard timer error (default)
1 = Discard timer error. Either primary or secondary discard timer expired and a delayed transaction was discarded from
Secondary discard timer. Selects the number of PCI clocks that the bridge will wait for a master on the secondary interface
to repeat a delayed transaction request.
0 = Secondary discard timer counts 215 PCI clock cycles (default)
1 = Secondary discard timer counts 210 PCI clock cycles
Primary discard timer. Selects the number of PCI clocks that the bridge will wait for a master on the primary interface to
repeat a delayed transaction request.
0 = Primary discard timer counts 215 PCI clock cycles (default)
1 = Primary discard timer counts 210 PCI clock cycles
Fast back-to-back capable. The bridge never generates fast back-to-back transactions to different secondary devices. Bit
7 returns 0 when read.
Secondary bus reset. When bit 6 is set, the secondary reset signal (S_RST) is asserted. S_RST is deasserted by resetting
this bit. Bit 6 is encoded as:
0 = Do not force the assertion of S_RST (default).
1 = Force the assertion of S_RST
signaling disabled for primary discard time-outs (default)
signaling enabled for primary discard time-outs
the queue in the bridge.
.
4–15

Table 4–5. Bridge Control Register Description (continued)
BIT TYPE FUNCTION
Master abort mode. Bit 5 controls how the bridge responds to a master abort that occurs on either interface when the bridge
is the master. If this bit is set, the posted write transaction has completed on the requesting interface, and SERR
(bit 8) of the command register (offset 04h, see Section 4.3) is 1, then P_SERR
5 R/W
4 R Reserved. Returns 0 when read. Writes have no effect.
3 R/W
2 R/W
1 R/W
0 R/W
If the transaction has not completed, then a target abort is signaled. If the bit is cleared, then all 1s are returned on reads
and write data is accepted and discarded when a transaction that crosses the bridge is terminated with master abort. The
default state of bit 5 after a reset is 0.
0 = Do not report master aborts (return FFFF FFFFh on reads and discard data on writes) (default).
1 = Report master aborts by signaling target abort if possible, or if SERR
asserting SERR
VGA enable. When bit 3 is set, the bridge positively decodes and forwards VGA-compatible memory addresses in the video
frame buffer range 000A 0000h–000BFFFFh, I/O addresses in the range 03B0h–03BBh, and 03C0–03DFh from the
primary to the secondary interface, independent of the I/O and memory address ranges. When this bit is set, the bridge
blocks forwarding of these addresses from the secondary to the primary. Reset clears this bit. Bit 3 is encoded as:
0 = Do not forward VGA-compatible memory and I/O addresses from the primary to the secondary interface
(default).
1 = Forward VGA-compatible memory and I/O addresses from the primary to the secondary, independent of the I/O
and memory address ranges and independent of the ISA enable bit.
ISA enable. When bit 2 is set, the bridge blocks the forwarding of ISA I/O transactions from the primary to the secondary,
addressing the last 768 bytes in each 1K-byte block. This applies only to the addresses (defined by the I/O window registers)
that are located in the first 64K bytes of PCI I/O address space. From the secondary to the primary, I/O transactions are
forwarded if they address the last 768 bytes in each 1K-byte block in the address range specified in the I/O window registers.
Bit 2 is encoded as:
0 = Forward all I/O addresses in the address range defined by the I/O base and I/O limit registers (default).
1 = Block forwarding of ISA I/O addresses in the address range defined by the I/O base and I/O limit registers when
these I/O addresses are in the first 64K bytes of PCI I/O address space and address the top 768 bytes of each
1K-byte block.
SERR enable. Bit 1 controls the forwarding of secondary interface SERR assertions to the primary interface. Only when
this bit is set will the bridge forward S_SERR
bit 8 of the command register (offset 04h, see Section 4.3) must be set.
0 = SERR disabled (default)
1 = SERR
Parity error response enable. Bit 0 controls the bridge response to parity errors on the secondary interface. When this bit
is set, the bridge asserts S_PERR
0 = Ignore address and parity errors on the secondary interface (default).
1 = Enable parity error reporting and detection on the secondary interface.
enabled
.
to the primary bus signal P_SERR. For the primary interface to assert SERR,
to report parity errors on the secondary interface.
is asserted when a master abort occurs.
enable
is enabled via bit 1 of this register, by
4–16

5 Extension Registers
The TI extension registers are those registers that lie outside the standard PCI-to-PCI bridge device configuration
space (i.e., registers 40h–FFh in PCI configuration space in the PCI2050). These registers can be accessed through
configuration reads and writes. The TI extension registers add flexibility and performance benefits to the standard
PCI-to-PCI bridge. Mapping of the extension registers is contained in Table 4–1.
5.1 Chip Control Register
The chip control register contains read/write and read-only bits and has a default value of 00h. This register is used
to control the functionality of certain PCI transactions.
Bit 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Name Chip control
Type R R R/W R/W R R R/W R
Default 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
Register: Chip control
Type: Read/Write, Read-only
Offset: 40h
Default: 00h
Table 5–1. Chip Control Register Description
BIT TYPE FUNCTION
7–6 R Reserved. Bits 7–6 return 0s when read.
Transaction forwarding control for I/O and memory cycles.
5 R/W
4 R/W
3–2 R Reserved. Bits 3 and 2 return 0s when read.
1 R/W
0 R Reserved. Bit 0 returns 0 when read.
0 = Transaction forwarding controlled by bits 0 and 1 of the command register (offset 04h, see Section 4.3) (default).
1 = Transaction forwarding will be disabled if GPIO3 is driven high.
Memory read prefetch. When set, bit 4 enables the memory read prefetch.
0 = Upstream memory reads are disabled (default).
1 = Upstream memory reads are enabled
Memory write and memory write and invalidate disconnect control.
0 = Disconnects on queue full or 4-KB boundaries (default)
1 = Disconnects on queue full, 4-KB boundaries and cacheline boundaries.
5–1

5.2 Extended Diagnostic Register
The extended diagnostic register is read or write and has a default value of 00h. Bit 0 of this register is used to reset
both the PCI2050 and the secondary bus.
Bit 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Name Extended diagnostic
Type R R R R R R R W
Default 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
Register: Extended diagnostic
Type: Read-only, Write-only
Offset: 41h
Default: 00h
Table 5–2. Extended Diagnostic Register Description
BIT TYPE FUNCTION
7–1 R Reserved. Bits 7–1 return 0s when read.
0 W
Writing a 1 to this bit causes the PCI2050 to set bit 6 of the bridge control register (offset 3Eh, see Section 4.32) and then
internally reset the PCI2050. Bit 6 of the bridge control register will not be reset by the internal reset. Bit 0 is self-clearing.
5–2

5.3 Arbiter Control Register
The arbiter control register is used for the bridge internal arbiter. The arbitration scheme used is a two-tier rotational
arbitration. The PCI2050 bridge is the only secondary bus initiator that defaults to the higher priority arbitration tier.
Bit 15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Name Arbiter control
Type R R R R R R R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W
Default 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
Register: Arbiter control
Type: Read-only, Read/Write
Offset: 42h
Default: 0200h
Table 5–3. Arbiter Control Register Description
BIT TYPE FUNCTION
15–10 R Reserved. Bits 15–10 return 0s when read.
Bridge tier select. This bit determines in which tier the PCI2250 bridge is placed in the two-tier arbitration scheme.
9 R/W
8 R/W
7 R/W
6 R/W
5 R/W
4 R/W
3 R/W
2 R/W
1 R/W
0 R/W
0 = Low priority tier
1 = High priority tier (default)
GNT8 tier select. This bit determines in which tier the S_GNT8 is placed in the arbitration scheme. This bit is encoded as:
0 = Low priority tier (default)
1 = High priority tier
GNT7 tier select. This bit determines in which tier the S_GNT7 is placed in the arbitration scheme. This bit is encoded as:
0 = Low priority tier (default)
1 = High priority tier
GNT6 tier select. This bit determines in which tier the S_GNT6 is placed in the arbitration scheme. This bit is encoded as:
0 = Low priority tier (default)
1 = High priority tier
GNT5 tier select. This bit determines in which tier the S_GNT5 is placed in the arbitration scheme. This bit is encoded as:
0 = Low priority tier (default)
1 = High priority tier
GNT4 tier select. This bit determines in which tier the S_GNT4 is placed in the arbitration scheme. This bit is encoded as:
0 = Low priority tier (default)
1 = High priority tier
GNT3 tier select. This bit determines in which tier the S_GNT3 is placed in the arbitration scheme. This bit is encoded as:
0 = Low priority tier (default)
1 = High priority tier
GNT2 tier select. This bit determines in which tier the S_GNT2 is placed in the arbitration scheme. This bit is encoded as:
0 = Low priority tier (default)
1 = High priority tier
GNT1 tier select. This bit determines in which tier the S_GNT1 is placed in the arbitration scheme. This bit is encoded as:
0 = Low priority tier (default)
1 = High priority tier
GNT0 tier select. This bit determines in which tier the S_GNT0 is placed in the arbitration scheme. This bit is encoded as:
0 = Low priority tier (default)
1 = High priority tier
5–3

5.4 P_SERR Event Disable Register
The P_SERR event disable register is used to enable/disable the SERR event on the primary interface. All events
are enabled by default.
Bit 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Name P_SERR event disable
Type R R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R
Default 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
Register: P_SERR event disable
Type: Read-only, Read/Write
Offset: 64h
Default: 00h
Table 5–4. P_SERR Event Disable Register Description
BIT TYPE FUNCTION
7 R Reserved. Bit 7 returns 0 when read.
Master delayed read time-out.
6 R/W
5 R/W
4 R/W
3 R/W
2 R/W
1 R/W
0 R Reserved. Bit 0 returns 0 when read.
0 = P_SERR
1 = P_SERR
Master delayed write time-out.
0 = P_SERR
1 = P_SERR
Master abort on posted write transactions. When set, bit 4 enables P_SERR reporting on master aborts on posted write
transactions.
0 = Master aborts on posted writes enabled (default)
1 = Master aborts on posted writes disabled
Target abort on posted writes. When set, bit 3 enables P_SERR reporting on target aborts on posted write transactions.
0 = T arget aborts on posted writes enabled (default).
1 = Target aborts on posted writes disabled.
Master posted write time-out.
0 = P_SERR
1 = P_SERR
Posted write parity error.
0 = P_SERR
1 = P_SERR
signaled on a master time-out after 224 retries on a delayed read (default).
is not signaled on a master time-out.
signaled on a master time-out after 224 retries on a delayed write (default).
is not signaled on a master time-out.
signaled on a master time-out after 224 retries on a posted write (default).
is not signaled on a master time-out.
signaled on a posted write parity error (default).
is not signaled on a posted write parity error.
5–4

5.5 GPIO Output Data Register
The GPIO output data register controls the data driven on the GPIO terminals configured as outputs. If both an
output-high bit and an output-low bit are set for the same GPIO terminal, the output-low bit takes precedence. The
output data bits have no effect on a GPIO terminal that is programmed as an input.
Bit 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Name GPIO output data
Type R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W
Default 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
Register: GPIO output data
Type: Read/Write
Offset: 65h
Default: 00h
Table 5–5. GPIO Output Data Register Description
BIT TYPE FUNCTION
7 R/W GPIO3 output high. Writing a 1 to this bit causes the GPIO signal to be driven high. Writing a 0 has no ef fect.
6 R/W GPIO2 output high. Writing a 1 to this bit causes the GPIO signal to be driven high. Writing a 0 has no ef fect.
5 R/W GPIO1 output high. Writing a 1 to this bit causes the GPIO signal to be driven high. Writing a 0 has no ef fect.
4 R/W GPIO0 output high. Writing a 1 to this bit causes the GPIO signal to be driven high. Writing a 0 has no ef fect.
3 R/W GPIO3 output low. Writing a 1 to this bit causes the GPIO signal to be driven low. Writing a 0 has no ef fect.
2 R/W GPIO2 output low. Writing a 1 to this bit causes the GPIO signal to be driven low. Writing a 0 has no ef fect.
1 R/W GPIO1 output low. Writing a 1 to this bit causes the GPIO signal to be driven low. Writing a 0 has no ef fect.
0 R/W GPIO0 output low. Writing a 1 to this bit causes the GPIO signal to be driven low. Writing a 0 has no ef fect.
5.6 GPIO Output Enable Register
The GPIO output enable register controls the direction of the GPIO signal. By default all GPIO terminals are inputs.
If both an output-enable bit and an input-enable bit are set for the same GPIO terminal, the input-enable bit takes
precedence.
Bit 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Name GPIO output enable
Type R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W
Default 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
Register: GPIO output enable
Type: Read/Write
Offset: 66h
Default: 00h
Table 5–6. GPIO Output Enable Register Description
BIT TYPE FUNCTION
7 R/W GPIO3 output enable. Writing a 1 to this bit causes the GPIO signal to be configured as an output. W riting a 0 has no effect.
6 R/W GPIO2 output enable. Writing a 1 to this bit causes the GPIO signal to be configured as an output. W riting a 0 has no effect.
5 R/W GPIO1 output enable. Writing a 1 to this bit causes the GPIO signal to be configured as an output. W riting a 0 has no effect.
4 R/W GPIO0 output enable. Writing a 1 to this bit causes the GPIO signal to be configured as an output. W riting a 0 has no effect.
3 R/W GPIO3 input enable. Writing a 1 to this bit causes the GPIO signal to be configured as an input. Writing a 0 has no ef fect.
2 R/W GPIO3 input enable. Writing a 1 to this bit causes the GPIO signal to be configured as an input. Writing a 0 has no ef fect.
1 R/W GPIO3 input enable. Writing a 1 to this bit causes the GPIO signal to be configured as an input. Writing a 0 has no ef fect.
0 R/W GPIO3 input enable. Writing a 1 to this bit causes the GPIO signal to be configured as an input. Writing a 0 has no ef fect.
5–5

5.7 GPIO Input Data Register
The GPIO input data register returns the current state of the GPIO terminals when read.
Bit 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Name GPIO input data
Type R R R R R R R R
Default X X X X 0 0 0 0
Register: GPIO input data
Type: Read-only
Offset: 67h
Default: X0h
Table 5–7. GPIO Input Data Register Description
BIT TYPE FUNCTION
7–4 R GPIO3–GPIO0 input data. These four bits return the current state of the GPIO terminals.
3–0 R Reserved. Bits 3–0 return 0s when read.
5–6

5.8 Secondary Clock Control Register
The secondary clock control register is used to control the secondary clock outputs.
Bit 15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Name Secondary clock control
Type R R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W
Default 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
Register: Secondary clock control
Type: Read-only, Read/Write
Offset: 68h
Default: 0000h
Table 5–8. Secondary Clock Control Register Description
BIT TYPE FUNCTION
15–14 R Reserved. These bits return 0 when read.
S_CLKOUT9 disable.
13 R/W
12 R/W
11 R/W
10 R/W
9 R/W
8 R/W
7–6 R/W
5–4 R/W
3–2 R/W
1–0 R/W
0 = S_CLKOUT9 enabled (default).
1 = S_CLKOUT9 disabled and driven high.
S_CLKOUT8 disable.
0 = S_CLKOUT8 enabled (Default).
1 = S_CLKOUT8 disabled and driven high.
S_CLKOUT7 disable.
0 = S_CLKOUT7 enabled (default).
1 = S_CLKOUT7 disabled and driven high.
S_CLKOUT6 disable.
0 = S_CLKOUT6 enabled (default).
1 = S_CLKOUT6 disabled and driven high.
S_CLKOUT5 disable.
0 = S_CLKOUT5 enabled (default).
1 = S_CLKOUT5 disabled and driven high.
S_CLKOUT4 disable.
0 = S_CLKOUT4 enabled (default).
1 = S_CLKOUT4 disabled and driven high.
S_CLKOUT3 disable.
00, 01, 10 = S_CLKOUT3 enabled (00 is the default).
11 = S_CLKOUT3 disabled and driven high.
S_CLKOUT2 disable.
00, 01, 10 = S_CLKOUT2 enabled (00 is the default).
11 = S_CLKOUT2 disabled and driven high.
S_CLKOUT1 disable.
00, 01, 10 = S_CLKOUT1 enabled (00 is the default).
11 = S_CLKOUT1 disabled and driven high.
S_CLKOUT0 disable.
00, 01, 10 = S_CLKOUT0 enabled (00 is the default).
11 = S_CLKOUT0 disabled and driven high.
5–7

5.9 P_SERR Status Register
The P_SERR status register indicates what caused a SERR event on the primary interface.
Bit 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Name P_SERR status
Type R R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R
Default 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
Register: P_SERR status
Type: Read-only Read/Write
Offset: 6Ah
Default: 00h
Table 5–9. P_SERR Status Register Description
BIT TYPE FUNCTION
7 R Reserved. Bit 7 returns 0 when read.
6 R/W
5 R/W
4 R/W
3 R/W Target abort on posted writes. A 1 indicates that P_SERR was signaled because of a target abort on a posted write.
2 R/W
1 R/W Posted write parity error. A 1 indicates that P_SERR was signaled because of parity error on a posted write.
0 R Reserved. Bit 0 returns 0 when read.
Master delayed read time-out. A 1 indicates that P_SERR was signaled because of a master time-out after 224 retries on
a delayed read.
Master delayed write time-out. A 1 indicates that P_SERR was signaled because of a master time-out after 224 retries on
a delayed write.
Master abort on posted write transactions. A 1 indicates that P_SERR was signaled because of a master abort on a posted
write.
Master posted write time-out. A 1 indicates that P_SERR was signaled because of a master time-out after 224 retries on
a posted write.
5.10 Power-Management Capability ID Register
The power-management capability ID register identifies the linked list item as the register for PCI power management.
The power-management capability ID register returns 01h when read, which is the unique ID assigned by the PCI
SIG for the PCI location of the capabilities pointer and the value.
Bit 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Name Power-management capability ID
Type R R R R R R R R
Default 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1
Register: Power-management capability ID
Type: Read-only
Offset: DCh
Default: 01h
5–8

5.11 Power-Management Next-Item Pointer Register
The power-management next-item pointer register is used to indicate the next item in the linked list of PCI
power-management capabilities. The next-item pointer returns E4h in CompactPCI mode, indicating that the
PCI2050 supports more than one extended capability, but in all other modes returns 00h, indicating that only one
extended capability is provided.
Bit 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Name Power-management next-item pointer
Type R R R R R R R R
Default 1 1 1 0 0 1 0 0
Register: Power-management next-item pointer
Type: Read-only
Offset: DDh
Default: E4h cPCI mode
00h All other modes
5.12 Power-Management Capabilities Register
The power management capabilities register contains information on the capabilities of the PCI2050 functions related
to power management. The PCI2050 function supports D0, D1, D2, and D3 power states when MS1 is low. The
PCI2050 does not support any power states when MS1 is high.
Bit 15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Name Power-management capabilities
Type R R R R R R R R R R R R R R R R
Default 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0
Register: Power-management capabilities
Type: Read-only
Offset: DEh
Default: 0602h or 0001h
Table 5–10. Power-Management Capabilities Register Description
BIT TYPE FUNCTION
PME support. This five-bit field indicates the power states that the device supports asserting PME. A 0 for any of these bits
15–11 R
10 R
9 R
8–6 R Reserved. Bits 8–6 return 0s when read.
5 R
4 R Auxiliary power source. This bit returns a 0 when read because the PCI2050 does not support PME signaling.
3 R PMECLK. This bit returns a 0 when read because the PME signaling is not supported.
2–0 R
indicates that the PCI2050 cannot assert PME
read, indicating that PME
D2 support. This bit returns 1 when MS0 is 0, indicating that the bridge function supports the D2 device power state. This
bit returns 0 when MS0 is 1, indicating that the bridge function does not support the D2 device power state.
D1 support. This bit returns 1 when MS0 is 0, indicating that the bridge function supports the D1 device power state. This
bit returns 0 when MS0 is 1, indicating that the bridge function does not support the D1 device power state.
Device specific initialization. This bit returns 0 when read, indicating that the bridge function does not require special
initialization (beyond the standard PCI configuration header) before the generic class device driver is able to use it.
Version. This three-bit register returns the PCI Bus Power Management Interface Specification revision.
001 = Revision 1.0, MS0 = 1
010 = Revision 1.1, MS0 = 0
is not supported.
from that power state. For the PCI2050, these five bits return 00000b when
5–9

5.13 Power-Management Control/Status Register
The power-management control/status register determines and changes the current power state of the PCI2050. The
contents of this register are not affected by the internally generated reset caused by the transition from D3
state.
Bit 15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Name Power-management control/status
Type R R R R R R R R R R R R R R R/W R/W
Default 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
Register: Power-management control/status
Type: Read-only, Read/Write
Offset: E0h
Default: 0000h
Table 5–11. Power-Management Control/Status Register
BIT TYPE FUNCTION
15 R PME status. This bit returns a 0 when read because the PCI2050 does not support PME.
14–13 R
12–9 R
8 R PME enable. This bit returns a 0 when read because the PCI2050 does not support PME signaling.
7–2 R Reserved. Bits 7–2 return 0s when read.
1–0 R/W
Data scale. This 2-bit read-only field indicates the scaling factor to be used when interpreting the value of the data
register. These bits return only 00b, because the data register is not implemented.
Data select. This 4-bit field is used to select which data is to be reported through the data register and data-scale
field. These bits return only 0000b, because the data register is not implemented.
Power state. This 2-bit field is used both to determine the current power state of a function and to set the function
into a new power state. The definition of this is given below:
00 – D0
01 – D1
10 – D2
11 – D3
hot
hot
to D0
5–10

5.14 PMCSR Bridge Support Register
The PMCSR bridge support register is required for all PCI bridges and supports PCI-bridge-specific functionality.
Bit 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Name PMCSR bridge support
Type R R R R R R R R
Default X X 0 0 0 0 0 0
Register: PMCSR bridge support
Type: Read-only
Offset: E2h
Default: X0h
Table 5–12. PMCSR Bridge Support Register Description
BIT TYPE FUNCTION
Bus power control enable. This bit returns the value of the MS1/BCC input.
7 R
6 R
5–0 R Reserved.
0 = Bus power/ clock control disabled.
1 = Bus power/clock control enabled.
B2/B3 support for D3
are stopped when the device is placed in D3
states.
Note: If the primary clock is stopped, then the secondary clocks will stop because the primary clock is used to
generate the secondary clocks.
. This bit returns the value of MS1/BCC input. When this bit is 1, the secondary clocks
hot
. When this bit is 0, the secondary clocks remain on in all device
hot
5.15 Data Register
The data register is an optional, 8-bit read-only register that provides a mechanism for the function to report
state-dependent operating data such as power consumed or heat dissipation. The PCI2050 does not implement the
data register.
Bit 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Name Data
Type R R R R R R R R
Default 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
Register: Data
Type: Read-only
Offset: E3h
Default: 00h
5–11

5.16 HS Capability ID Register
The HS capability ID register identifies the linked list item as the register for cPCI hot-swap capabilities. The register
returns 06h when read, which is the unique ID assigned by the PICMG for PCI location of the capabilities pointer and
the value. In Intel-compatible mode, this register is read-only and defaults to 00h.
Bit 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Name HS capability ID
Type R R R R R R R R
Default 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 0
Register: HS capability ID
Type: Read-only
Offset: E4h
Default: 06h TI mode
00h Intel-compatible mode
5.17 HS Next-Item Pointer Register
The HS next-item pointer register is used to indicate the next item in the linked list of cPCI hot swap capabilities.
Because this is the last extended capability that the PCI2050 supports, the next-item pointer returns all 0s.
Bit 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Name HS next-item pointer
Type R R R R R R R R
Default 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
Register: HS next-item pointer
Type: Read-only
Offset: E5h
Default: 00h
5–12

5.18 Hot-Swap Control Status Register
The hot-swap control status register contains control and status information for cPCI hot swap resources.
Bit 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Name Hot swap control status
Type R R R R R/W R R/W R
Default 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
Register: Hot-swap control status
Type: Read-only, Read/Write
Offset: E6h
Default: 00h
Table 5–13. Hot-Swap Control Status Register Description
BIT TYPE FUNCTION
ENUM insertion status. When set, the ENUM output is driven by the PCI2050. This bit defaults to 0, and will be set after
7 R
6 R
5–4 R Reserved. Bits 5 and 4 return 0s when read.
3 R/W
2 R Reserved. Bit 2 returns 0 when read.
1 R/W
0 R Reserved. Bit 0 returns 0 when read.
a PCI reset occurs, the pre-load of serial ROM is complete, the ejector handle is closed, and bit 6 is 0. Thus, this bit is set
following an insertion when the board implementing the PCI2050 is ready for configuration. This bit cannot be set under
software control.
ENUM extraction status. When set, the ENUM output is driven by the PCI2050. This bit defaults to 0, and is set when the
ejector handle is opened and bit 7 is 0. Thus, this bit is set when the board implementing the PCI2050 is about to be removed.
This bit cannot be set under software control.
LED ON/OFF . This bit defaults to 0, and controls the external LED indicator (HSLED) under normal conditions. However,
for a duration following a PCI_RST
is interpreted, a 1 causes HSLED high and a 0 causes HSLED low.
Following PCI_RST
conditions are met, the HSLED is under software control via this bit.
ENUM interrupt mask. This bit allows the HSENUM output to be masked by software. Bits 6 and 7 are set independently
from this bit.
0 = Enable HSENUM output
1 = Mask HSENUM
, the HSLED output is driven high by the PCI2050 until the ejector handle is closed. When these
output
, the HSLED output is driven high by the PCI2050 and this bit is ignored. When this bit
5–13

6 Electrical Characteristics
†
†
§
6.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings Over Operating Temperature Ranges
†
Supply voltage range: VCC –0.5 V to 3.6 V. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
S_V
P_V
Input voltage range, V
Output voltage range, V
Input clamp current, I
Output clamp current, I
: PCI –0.5 V to 6.5 V. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
I
O
(VI < 0 or VI > VCC) (see Note 1) ±20 mA. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
IK
OK
Storage temperature range, T
Virtual junction temperature, T
†
Stresses beyond those listed under absolute maximum ratings may cause permanent damage to the device. These are stress ratings only, and
functional operation of the device at these or any other conditions beyond those indicated under recommended operating conditions is not implied.
Exposure to absolute-maximum-rated conditions for extended periods may affect device reliability.
NOTES: 1. Applies for external input and bidirectional buffers. VI > VCC does not apply to fail-safe terminals.
2. Applies to external output and bidirectional buffers. VO > VCC does not apply to fail-safe terminals.
–0.5 V to 6 V. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
CCP
–0.5 V to 6 V. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
CCP
: PCI –0.5 V to VCC + 0.5 V. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
(VO < 0 or VO > VCC) (see Note 2) ±20 mA. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
–65°C to 150°C. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
stg
150°C. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
J
6.2 Recommended Operating Conditions (see Note 3)
OPERATION MIN NOM MAX UNIT
V
CC
P_V
S_V
V
IH
V
IL
V
I
V
O
t
t
T
A
¶
T
J
NOTE 3: Unused or floating pins (input or I/O) must be held high or low.
†
Applies for external input and bidirectional buffers without hysteresis
§
Applies for external output buffers
¶
These junction temperatures reflect simulation conditions. The customer is responsible for verifying junction temperature.
Supply voltage (core) Commercial 3.3 V 3 3.3 3.6 V
PCI primary bus I/O clamping rail voltage Commercial
CCP
PCI secondary bus I/O clamping rail voltage Commercial
CCP
High-level input voltage
Low-level input voltage
Input voltage PCI 0 V
Output voltage
Input transition time (tr and tf) PCI
Operating ambient temperature range
Virtual junction temperature
PCI
PCI
PCI2050
PCI2050I
3.3 V 3 3.3 3.6
5 V 4.75 5 5.25
3.3 V 3 3.3 3.6
5 V 4.75 5 5.25
3.3 V 0.5 V
5 V 2 V
3.3 V 0 0.3 V
5 V 0
3.3 V 0 V
5 V
3.3 V 0 25 70
3.3 V –40 25 85
5 V 0 25 115 °C
CCP
0 V
1 4 ns
V
CCP
CCP
CCP
0.8
CCP
CC
CC
°
°C
V
V
V
V
V
V
6–1

6.3 Recommended Operating Conditions for PCI Interface
†
‡
‡
OH
g e e ou u o age
IH
g
†
µ
OPERATION MIN NOM MAX UNIT
V
CC
P_V
S_V
V
I
V
O
V
IH
V
IL
†
Applies to external output buffers
‡
Applies to external input and bidirectional buffers without hysteresis
Core voltage Commercial 3.3 V 3 3.3 3.6 V
PCI supply voltage Commercial
CCP
PCI supply voltage Commercial
CCP
Input voltage
Output voltage
High-level input voltage
Low-level input voltage
CMOS compatible
CMOS compatible
3.3 V 3 3.3 3.6
5 V 4.75 5 5.25
3.3 V 3 3.3 3.6
5 V 4.75 5 5.25
3.3 V 0 V
5 V
3.3 V 0 V
5 V
3.3 V 0.5 V
5 V 2
3.3 V 0.3 V
5 V
0 V
0 V
CCP
6.4 Electrical Characteristics Over Recommended Operating Conditions
PARAMETER TERMINALS OPERATION TEST CONDITIONS MIN MAX UNIT
3.3 V
V
High-level output voltage
OH
TTL 5 V IOH = –1.4 mA 2.4
Low-level output voltage
V
OL
I
High-level input current
IH
I
Low-level input current
IL
I
High-impedance output current VO = V
OZ
†
For I/O terminals, the input leakage current includes the off-state output current IOZ.
‡
For TTL signals, IOH = 1.4 mA is the test condition for the industrial-temperature-range PCI2050I.
Input terminals, PCI VI = V
I/O terminals
Input terminals, PCI
I/O terminals
†
5 V
3.3 V
5 V
IOH = –0.5 mA
IOH = –2 mA
IOL = 1.5 mA
IOL = 6 mA
CCP
VI = V
CCP
VI = GND
or GND ±10 µA
CCP
0.9 V
2.4
CC
0.1 V
0.55
–10
CCP
CCP
CCP
CCP
CCP
10
10
–1
0.8
CC
V
V
V
V
V
V
V
V
µA
µA
6.5 PCI Clock/Reset Timing Requirements Over Recommended Ranges of Supply
Voltage and Operating Free-Air Temperature (see Figure 6–2 and Figure 6–3)
t
c
t
wH
t
wL
∆v/∆t Slew rate, PCLK tr, t
t
w
t
su
NOTE 4: The setup and hold times for the secondary are identical to those for the primary; however, the times are relative to the secondary PCI
6–2
ALTERNATE
SYMBOL
Cycle time, PCLK t
Pulse duration, PCLK high t
Pulse duration, PCLK low t
Pulse duration, RSTIN t
Setup time, PCLK active at end of RSTIN (see Note 4 ) t
clock.
cyc
high
low
rst
rst-clk
MIN MAX UNIT
30 ∞ ns
11 ns
11 ns
f
1 4 V/ns
1 ms
100 ms

6.6 PCI Timing Requirements Over Recommended Ranges of Supply Voltage and
Operating Free-Air Temperature (see Note 5 and Figure 6–1 and Figure 6–4)
ALTERNATE
SYMBOL
PCLK to shared signal
t
pd
t
en
t
dis
t
su
t
h
NOTES: 5. This data sheet uses the following conventions to describe time (t) intervals. The format is: tA, where subscript A indicates the type
Propagation delay time
Enable time,
high-impedance-to-active delay time from PCLK
Disable time,
active-to-high-impedance delay time from PCLK
Setup time before PCLK valid tsu, See Note 4 7 ns
Hold time after PCLK high th, See Note 4 0 ns
of dynamic parameter being represented. The following are used: tpd = propagation delay time, tsu = setup time, and th = hold time.
6. PCI shared signals are AD31–AD0, C/BE3
valid delay time
PCLK to shared signal
invalid delay time
–C/BE0, FRAME, TRDY, IRDY, STOP, IDSEL, DEVSEL, and PAR.
t
t
t
t
val
inv
on
off
TEST CONDITIONS MIN MAX UNIT
11
CL = 50 pF, See Note 6
2
2 ns
28 ns
ns
6–3

6.7 Parameter Measurement Information
LOAD CIRCUIT PARAMETERS
†
PARAMETER
t
en
t
dis
t
pd
†
C
LOAD
V
LOAD
‡
I
OL
TIMING
t
PZH
t
PZL
t
PHZ
t
PLZ
includes the typical load-circuit distributed capacitance.
– V
OL
C
LOAD
(pF)
50
50 8 –8
50 8
= 50 Ω, where VOL = 0.6 V, IOL = 8 mA
I
OL
(mA)
8
I
OH
(mA)
–8
–8
V
LOAD
(V)
1.5
0
3
‡
From Output
Under Test
Test
Point
C
LOAD
LOAD CIRCUIT
I
OL
I
OH
V
LOAD
Timing
Input
(see Note A )
Data
Input
(see Note A)
Out-of-Phase
90% V
10% V
Input
In-Phase
Output
Output
50% V
CC
t
su
CC
50% V
50% V
CC
CC
50% V
50% V
CC
t
r
VOLTAGE WAVEFORMS
SETUP AND HOLD TIMES
INPUT RISE AND FALL TIMES
t
pd
t
pd
t
50% V
50% V
CC
CC
h
t
f
CC
CC
t
pd
50% V
t
pd
50% V
V
0 V
V
0 V
CC
CC
V
0 V
V
V
V
V
CC
OH
CC
OL
OH
CC
OL
High-Level
Input
Low-Level
Input
Output
Control
(low-level
enabling)
Waveform 1
(see Note B)
Waveform 2
(see Note B)
50% V
50% V
VOLTAGE WAVEFORMS
PULSE DURATION
50% V
t
PZL
t
PZH
t
PLZ
50% V
t
PHZ
50% V
t
CC
V
CC
50% V
50% V
50% V
CC
VOL+ 0.3 V
VOH– 0.3 V
CC
CC
0 V
V
0 V
CC
V
CC
0 V
V
CC
≈ 50% V
V
OL
V
OH
≈ 50% V
0 V
CC
CC
CC
w
CC
CC
CC
VOLTAGE WAVEFORMS
PROPAGATION DELAY TIMES
NOTES: A. Phase relationships between waveforms were chosen arbitrarily. All input pulses are supplied by pulse generators having the
following characteristics: PRR = 1 MHz, ZO = 50 Ω, tr ≤ 6 ns, tf ≤ 6 ns.
B. Waveform 1 is for an output with internal conditions such that the output is low except when disabled by the output control.
Waveform 2 is for an output with internal conditions such that the output is high except when disabled by the output control.
C. For t
PLZ
and t
, VOL and VOH are measured values.
PHZ
ENABLE AND DISABLE TIMES, 3-STATE OUTPUTS
VOLTAGE WAVEFORMS
Figure 6–1. Load Circuit and Voltage Waveforms
6–4

6.8 PCI Bus Parameter Measurement Information
t
wH
t
wL
t
f
t
w
PCLK
RSTIN
0.8 V
t
r
2 V
t
c
Figure 6–2. PCLK Timing Waveform
Figure 6–3. RSTIN Timing Waveforms
2 V min Peak-to-Peak
t
su
PCLK
PCI Output
PCI Input
1.5 V
t
pd
1.5 V
Valid
t
on
Valid
t
su
t
pd
t
off
t
h
Figure 6–4. Shared-Signals Timing Waveforms
6–5

7 Mechanical Data
GHK (S-PBGA-N209) PLASTIC BALL GRID ARRAY
16,10
15,90
SQ
W
V
U
T
R
P
N
M
L
K
J
H
G
F
E
D
C
B
A
14,40 TYP
0,80
0,80
0,95
0,85 1,40 MAX
0,12
0,08
NOTES: A. All linear dimensions are in millimeters.
B. This drawing is subject to change without notice.
C. MicroStar BGA configuration
0,55
0,45
0,08
M
0,45
0,35
1
3
2
4
Seating Plane
0,10
75
6
9
810
12
13141511
16
4145273–2/B 12/98
17
18
19
MicroStar BGA is a trademark of Texas Instruments.
7–1

ZHK (S-PBGA-N257) PLASTIC BALL GRID ARRAY
16,10
0,95
15,90
SQ
A1 Corner
W
V
U
T
R
P
N
M
L
K
J
H
G
F
E
D
C
B
A
1
1,40 MAX0,85
5
2436
14,40 TYP
0,80
7
Bottom View
11 15
128910
141316
17
18
0,80
19
0,55
0,45
NOTES: A. All linear dimensions are in millimeters.
B. This drawing is subject to change without notice.
C. MicroStar BGA configuration.
D. This package is lead-free.
0,08
0,45
0,35
Seating Plane
0,12
4204905/A 01/03
MicroStar is a trademark of Texas Instruments.
7–2

PDV (S-PQFP-G208) PLASTIC QUAD FLATPACK
157
208
156
1
105
52
104
53
0,27
0,17
0,50
0,08
M
0,13 NOM
Gage Plane
25,50 TYP
28,05
SQ
27,95
30,20
SQ
29,80
1,45
1,35
1,60 MAX
NOTES: A. All linear dimensions are in millimeters.
B. This drawing is subject to change without notice.
C. Falls within JEDEC MS-026
0,05 MIN
0,25
0°–ā7°
0,75
0,45
Seating Plane
0,08
4087729/D 11/98
7–3
 Loading...
Loading...