®
Precision Unity Gain
DIFFERENTIAL AMPLIFIER
INA105
FEATURES
● CMR 86dB min OVER TEMPERATURE
● GAIN ERROR: 0.01% max
● NONLINEARITY: 0.001% max
● NO EXTERNAL ADJUSTMENTS
REQUIRED
● EASY TO USE
● COMPLETE SOLUTION
● HIGHLY VERSATILE
● LOW COST
● PLASTIC DIP, TO-99 HERMETIC METAL,
AND SO-8 SOIC PACKAGES
DESCRIPTION
The INA105 is a monolithic Gain = 1 differential
amplifier consisting of a precision op amp and on-chip
metal film resistors. The resistors are laser trimmed
for accurate gain and high common-mode rejection.
Excellent TCR tracking of the resistors maintains
gain accuracy and common-mode rejection over
temperature.
The differential amplifier is the foundation of many
commonly used circuits. The INA105 provides this
precision circuit function without using an expensive
precision resistor network. The INA105 is available in
8-pin plastic DIP, SO-8 surface-mount and TO-99
metal packages.
APPLICATIONS
● DIFFERENTIAL AMPLIFIER
● INSTRUMENTATION AMPLIFIER
BUILDING BLOCK
● UNITY-GAIN INVERTING AMPLIFIER
● GAIN-OF-1/2 AMPLIFIER
● NONINVERTING GAIN-OF-2 AMPLIFIER
● AVERAGE VALUE AMPLIFIER
● ABSOLUTE VALUE AMPLIFIER
● SUMMING AMPLIFIER
● SYNCHRONOUS DEMODULATOR
● CURRENT RECEIVER WITH COMPLIANCE
TO RAILS
● 4mA TO 20mA TRANSMITTER
● VOLTAGE-CONTROLLED CURRENT
SOURCE
● ALL-PASS FILTERS
–In
+In
2
25kΩ 25kΩ
3
25kΩ25kΩ
5
Sense
7
V+
6
Output
4
V–
1
Ref
SBOS145
International Airport Industrial Park • Mailing Address: PO Box 11400, Tucson, AZ 85734 • Street Address: 6730 S. Tucson Blvd., Tucson, AZ 85706 • Tel: (520) 746-1111 • Twx: 910-952-1111
Internet: http://www.burr-brown.com/ • FAXLine: (800) 548-6133 (US/Canada Only) • Cable: BBRCORP • Telex: 066-6491 • FAX: (520) 889-1510 • Immediate Product Info: (800) 548-6132
©
1985 Burr-Brown Corporation PDS-617G Printed in U.S.A. August, 1993
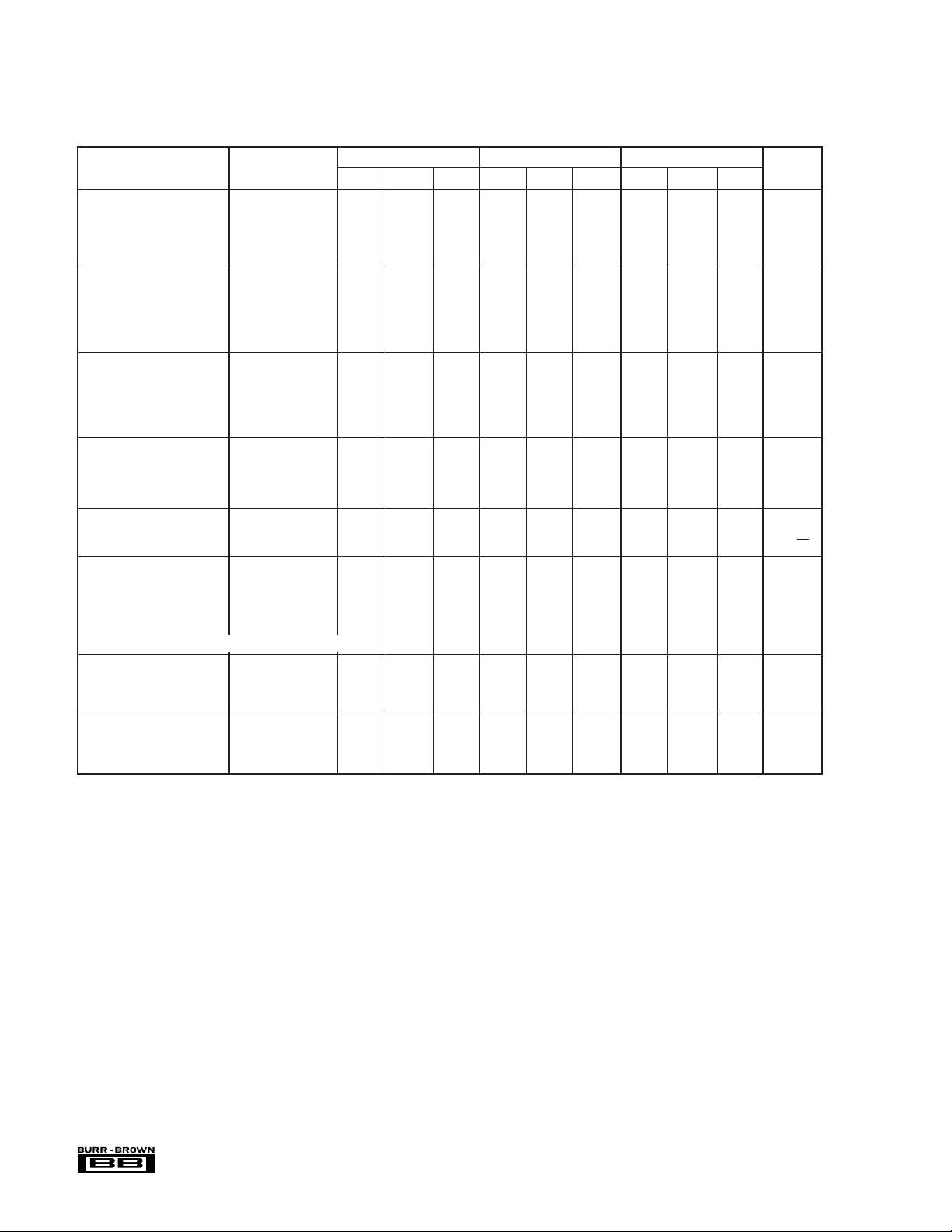
SPECIFICATIONS
ELECTRICAL
At +25°C, VCC = ±15V, unless otherwise noted.
INA105AM INA105BM INA105KP, KU
PARAMETER CONDITIONS MIN TYP MAX MIN TYP MAX MIN TYP MAX UNITS
GAIN
(1)
Initial
Error 0.005 0.01 ✻✻ 0.01 0.025 %
vs Temperature 1 5 ✻✻ ✻✻ppm/°C
Nonlinearity
(2)
OUTPUT
Rated Voltage I
Rated Current V
Impedance 0.01 ✻✻Ω
= +20mA, –5mA 10 12 ✻✻ ✻✻ V
O
= 10V +20, –5 ✻✻ mA
O
Current Limit To Common +40/–10 ✻✻mA
Capacitive Load Stable Operation 1000 ✻✻pF
INPUT
Impedance
Voltage Range
Common-Mode Rejection
OFFSET VOLTAGE RTO
(3)
(4)
(5)
Differential 50 ✻✻kΩ
Common-Mode 50 ✻✻kΩ
Differential ±10 ✻✻ V
Common-Mode ±20 ✻✻ V
TA = T
MIN
to T
(6), (7)
MAX
80 90 86 100 72 ✻ dB
Initial 50 250 ✻✻ ✻500 µV
vs Temperature 5 20 5 10 ✻✻µV/°C
vs Supply ±V
vs Time 20 ✻✻µV/mo
OUTPUT NOISE VOLTAGE RTO
= 6V to 18V 1 25 ✻ 15 ✻✻µV/V
S
(6), (8)
fB = 0.01Hz to 10Hz 2.4 ✻✻µVp-p
f
= 10kHz 60 ✻✻nV/√Hz
O
DYNAMIC RESPONSE
Small Signal Bandwidth –3dB 1 ✻✻MHz
Full Power Bandwidth V
Slew Rate 2 3 ✻✻ ✻✻ V/µs
Settling Time: 0.1% V
0.01% V
0.01% V
= 20Vp-p 30 50 ✻✻ ✻✻ kHz
O
= 10V Step 4 ✻✻µs
O
= 10V Step 5 ✻✻µs
O
= 10V Step, V
CM
= 0V 1.5 ✻✻µs
DIFF
POWER SUPPLY
Rated ±15 ✻✻V
Voltage Range Derated Performance ±5 ±18 ✻✻✻ ✻V
Quiescent Current V
= 0V ±1.5 ±2 ✻✻ ✻✻ mA
O
TEMPERATURE RANGE
Specification –40 +85 ✻✻✻✻°C
Operation –55 +125 ✻✻–40 +85 °C
Storage –65 +150 ✻✻–40 +125 °C
✻ Specification same as for INA105AM.
NOTES: (1) Connected as difference amplifier (see Figure 4). (2) Nonlinearity is the maximum peak deviation from the best-fit straight line as a percent of full-scale peak-
to-peak output. (3) 25kΩ resistors are ratio matched but have ±20% absolute value. (4) Maximum input voltage without protection is 10V more than either ±15V supply
(±25V). Limit I
circuit has a gain of 2 for the operational amplifier’s offset voltage and noise voltage. (7) Includes effects of amplifier’s input bias and offset currents. (8) Includes effects
to 1mA. (5) With zero source impedance (see “Maintaining CMR” section). (6) Referred to output in unity-gain difference configuration. Note that this
IN
of amplifier’s input current noise and thermal noise contribution of resistor network.
1 ✻✻V/V
0.0002 0.001 ✻✻ ✻✻ %
The information provided herein is believed to be reliable; however, BURR-BROWN assumes no responsibility for inaccuracies or omissions. BURR-BROWN assumes
no responsibility for the use of this information, and all use of such information shall be entirely at the user’s own risk. Prices and specifications are subject to change
without notice. No patent rights or licenses to any of the circuits described herein are implied or granted to any third party. BURR-BROWN does not authorize or warrant
any BURR-BROWN product for use in life support devices and/or systems.
®
INA105
2
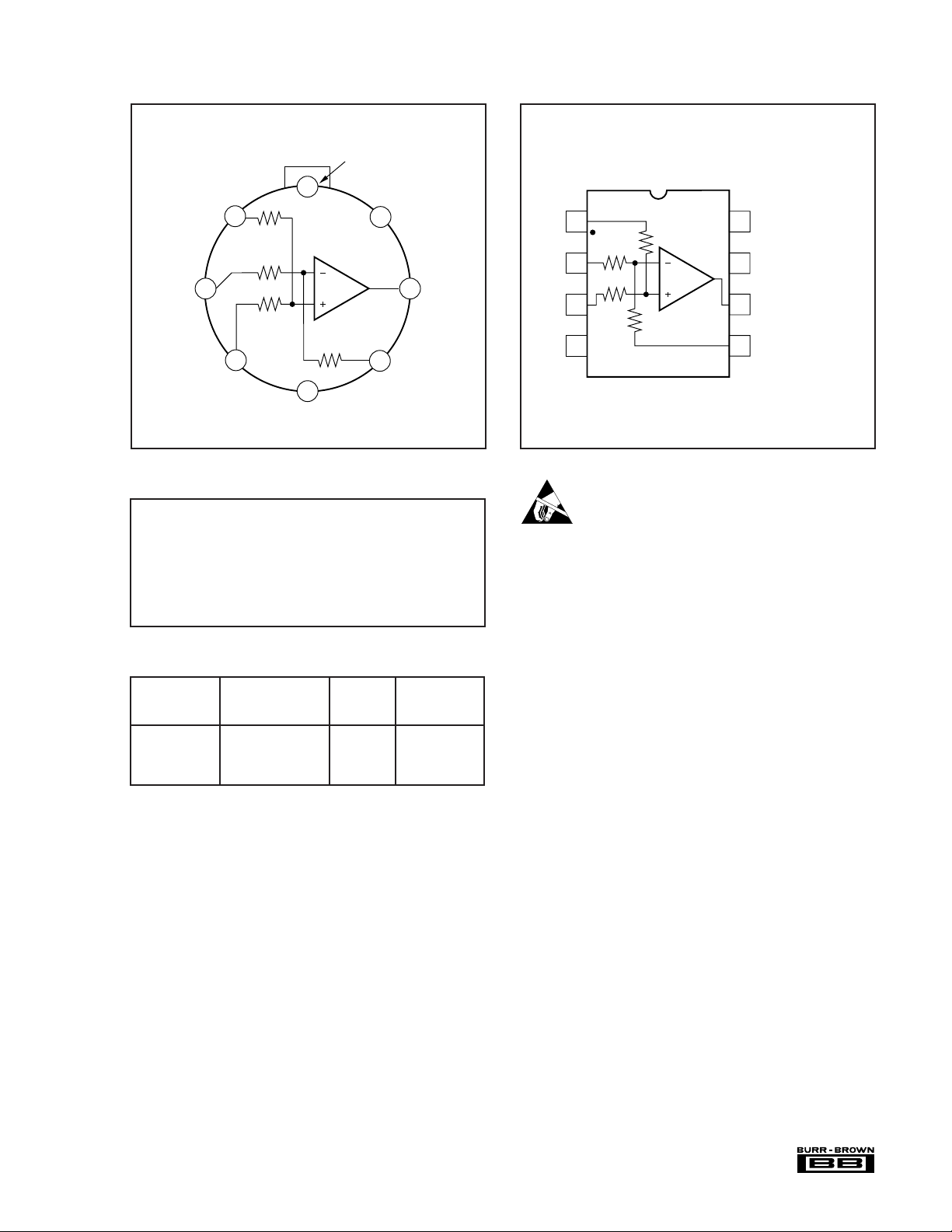
PIN CONFIGURATIONS
y
Top View TO-99
Ref
–In
Case internall
Tab
1
3
+In
connected to V–. Make no connection.
8
4
V–
No Internal
Connection
7
5
Sense
V+
62
Output
INA105AM
INA105BM
ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATINGS
Supply ................................................................................................±18V
Input Voltage Range ............................................................................ ±V
Operating Temperature Range: M .................................. –55°C to +125°C
P, U................................ –40°C to +85°C
Storage Temperature Range: M ..................................... –65°C to +150°C
P, U ................................. –40°C to +125°C
Lead Temperature (soldering, 10s) M, P ....................................... +300°C
Wave Soldering (3s, max) U .......................................................... +260°C
Output Short Circuit to Common.............................................. Continuous
S
PACKAGE/ORDERING INFORMATION
PACKAGE
DRAWING TEMPERATURE
PRODUCT PACKAGE NUMBER
INA105AM TO-99 Metal 001 –40°C to +85°C
INA105BM TO-99 Metal 001 –40°C to +85°C
INA105KP 8-Pin Plastic DIP 006 –40°C to +85°C
INA105KU 8-Pin SOIC 182 –40°C to +85°C
NOTE: (1) For detailed drawing and dimension table, please see end of data
sheet, or Appendix C of Burr-Brown IC Data Book.
(1)
RANGE
Top View DIP/SOIC
1
Ref
–In
+In
V–
NOTE: (1) Performance grade identifier box for small outline surface mount.
Blank indicates K grade. Part is marked INA105U.
(1)
2
3
4
No Internal Connection
8
V+
7
Output
6
Sense
5
ELECTROSTATIC
DISCHARGE SENSITIVITY
This integrated circuit can be damaged by ESD. Burr-Brown
recommends that all integrated circuits be handled with
appropriate precautions. Failure to observe proper handling
and installation procedures can cause damage.
ESD damage can range from subtle performance degradation
to complete device failure. Precision integrated circuits may
be more susceptible to damage because very small parametric
changes could cause the device not to meet its published
specifications.
®
3
INA105
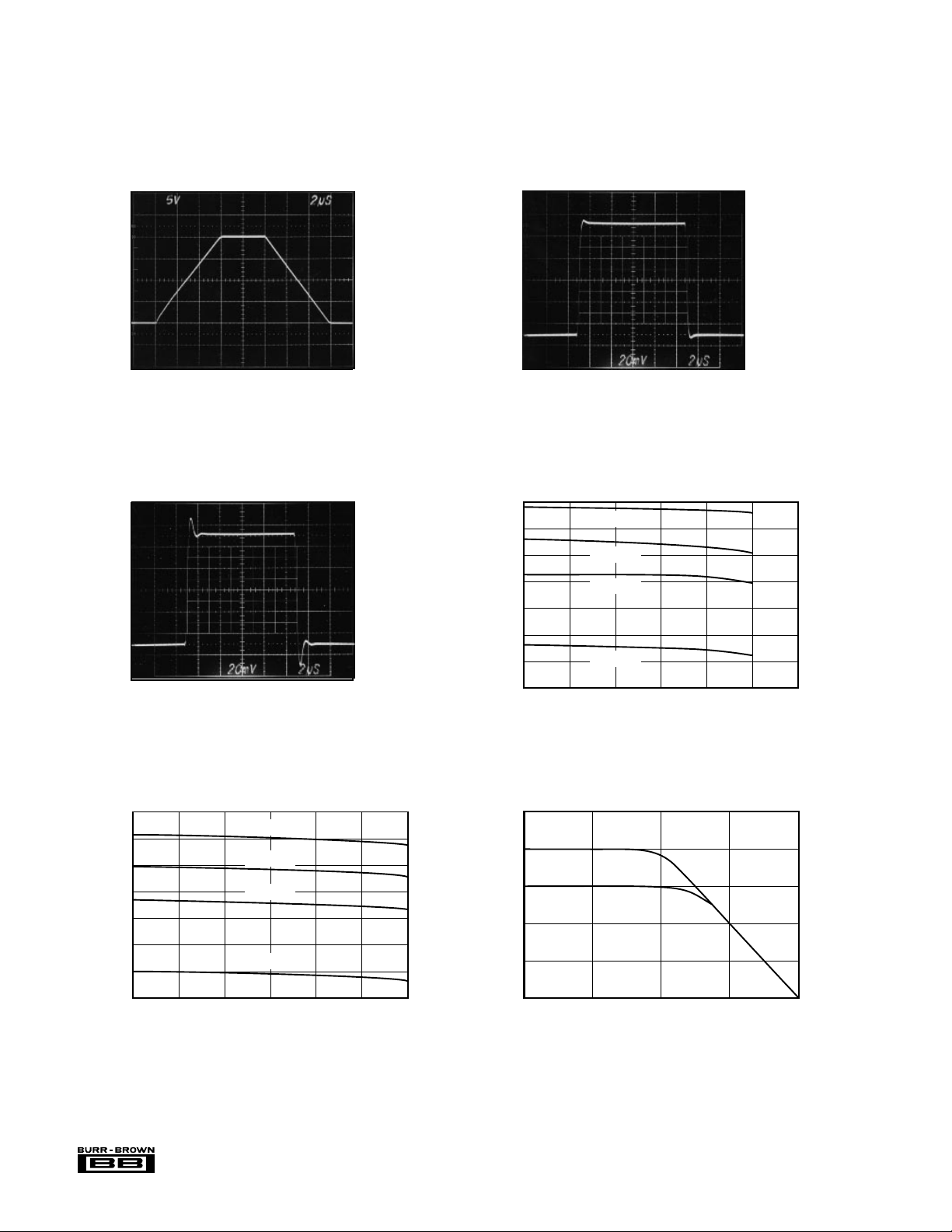
TYPICAL PERFORMANCE CURVES
At TA = 25°C, VS = ±15V, unless otherwise noted.
STEP RESPONSE
–10 to +10
Output Voltage (V)
+50
0
–50
Output Voltage (mV)
SMALL SIGNAL RESPONSE
(No Load)
0 4 8 12 16
(R
+50
0
–50
Output Voltage (mV)
17.5
15
12.5
10
(V)
OUT
7.5
V
5
2.5
0
0
Time (µs)
SMALL SIGNAL RESPONSE
Ω
LOAD
= , C
∞
= 1000pF)
LOAD
0510
Time (µs)
MAXIMUM V
(Positive Swing)
OUT
vs I
OUT
VS = ±18V
VS = ±15V
VS = ±12V
VS = ±5V
6 1218243036
I
(mA)
OUT
–17.5
–15
–12.5
–10
(V)
OUT
–7.5
V
–5
–2.5
110
100
90
CMR (dB)
80
70
60
0510
Time (µs)
MAXIMUM V
(Negative Swing)
OUT
vs I
OUT
VS = ±18V
VS = ±15V
VS = ±12V
VS = ±5V
0
–2 –4 –6 –8 –10 –12
0
–I
(mA)
OUT
CMR vs FREQUENCY
BM
AM, KP, U
10
100 1k 10k 100k
Frequency (Hz)
®
INA105
4
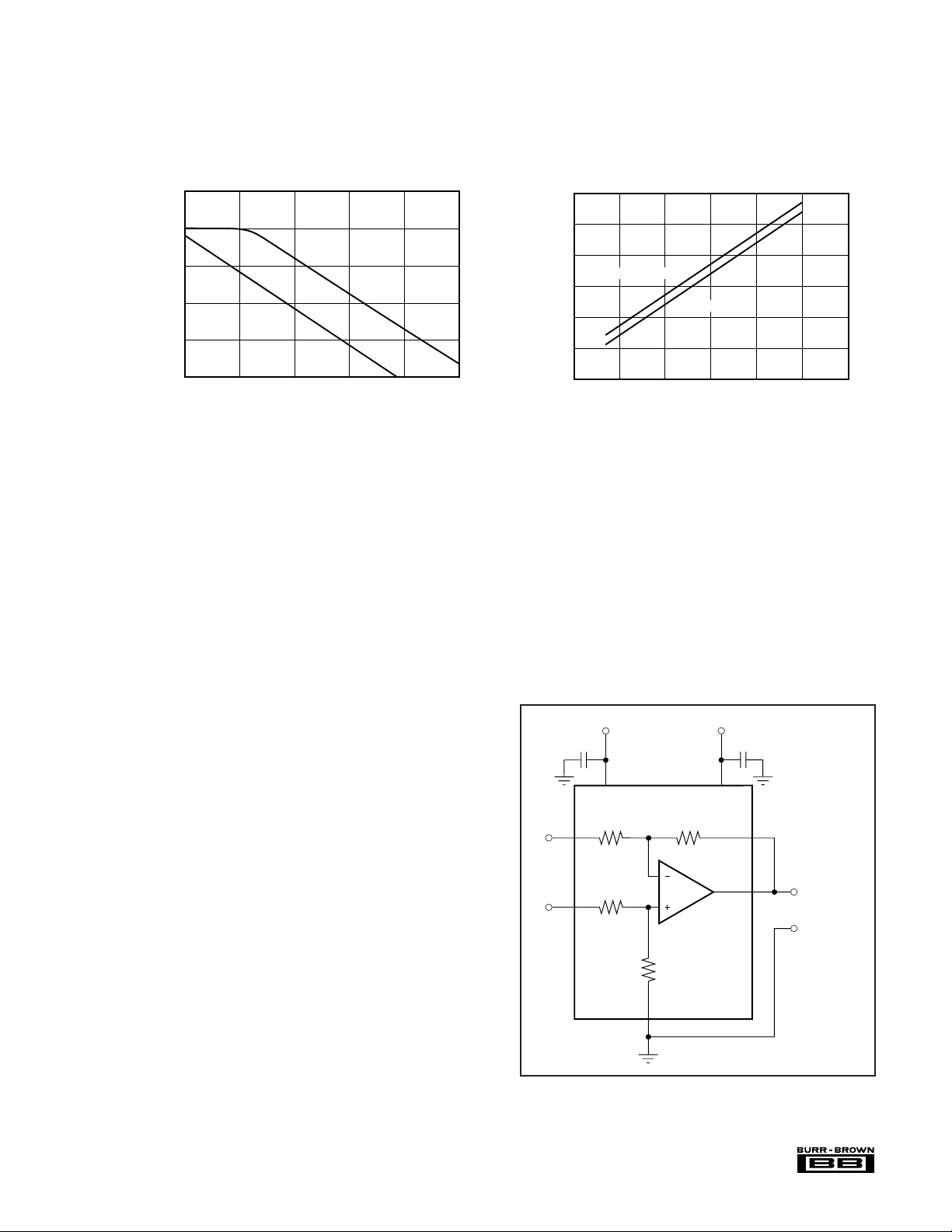
TYPICAL PERFORMANCE CURVES (CONT)
V
3
5
6
3
INA105
V
OUT
= V3 – V
2
2
R
3
R
1
R
2
R
4
V
2
25k
Ω
25k
Ω
25k
Ω
25k
Ω
1µF
V–
4
1µF
V+
7
1
At TA = 25°C, VS = ±15V, unless otherwise noted.
140
120
100
80
PSRR (dB)
60
40
1
POWER SUPPLY REJECTION
vs FREQUENCY
V–
V+
10 100 1k 10k 100k
Frequency (Hz)
36
30
24
18
12
Input Range (V)
6
0
±3
COMMON-MODE INPUT RANGE vs SUPPLY
(Difference Amplifier Connected, V
Negative CMV
Positive CMV
±6 ±9 ±12 ±15 ±18 ±21
Supply Voltage (V)
OUT
= 0)
APPLICATION INFORMATION
Figure 1 shows the basic connections required for operation
of the INA105. Power supply bypass capacitors should be
connected close to the device pins.
The differential input signal is connected to pins 2 and 3 as
shown. The source impedances connected to the inputs must
be nearly equal to assure good common-mode rejection. A
5Ω mismatch in source impedance will degrade the common-mode rejection of a typical device to approximately
FIGURE 1. Basic Power Supply and Signal Connections.
5
INA105
®
80dB. If the source has a known mismatch in source impedance, an additional resistor in series with one input can be
used to preserve good common-mode rejection.
The output is referred to the output reference terminal (pin
1) which is normally grounded. A voltage applied to the Ref
terminal will be summed with the output signal. This can be
used to null offset voltage as shown in Figure 2. The source
impedance of a signal applied to the Ref terminal should be
less than 10Ω to maintain good common-mode rejection.
nominal resistor values are equal. These resistors are laser
trimmed for precise resistor ratios to achieve accurate gain
Do not interchange pins 1 and 3 or pins 2 and 5, even though
and highest CMR. Interchanging these pins would not provide specified performance.

R
V
2
10
Ω
V
3
= V3 – V
V
O
Offset Adjustment
3
2
3
1
R
3
1
Range = ±300µV
FIGURE 2. Offset Adjustment.
INA105
R
4
10
V
1
–In
A
R
2
5
6
V
O
1
R
R
1
R
2
2
2
3
A
+15V
499k
Ω
100k
Ω
Ω
–15V
V
+In
For low source impedance applications, an input stage using OPA27 op
amps will give the best low noise, offset, and temperature drift performance.
At source impedances above about 10kΩ, the bias current noise of the
OPA27 reacting with the input impedance begins to dominate the noise
2
1
VO = (1 + 2R2/R1) (V2 –V1)
INA105
5
6
V
0
0utput
1
performance. For these applications, using the OPA111 or dual OPA2111
FET input op amp will provide lower noise performance. For lower cost use
the OPA121 plastic. To construct an electrometer use the OPA128.
INA105BM
–In
V
2
+In
V
3
R
2
3
1
25k
Ω
R
3
25k
Ω
V
= V3 – V
0
Gain Error = 0.005%
2
R
25k
R
25k
2
Ω
4
Ω
CMR = 100dB
Nonlinearity = 0.0002%
FIGURE 3. Precision Difference Amplifier.
R
A
, A
1
2
1R2
(Ω)(Ω) (V/V) (dB) I
GAIN CMRR MAX NOISE AT 1kHz
(nV/√HZ)
B
OPA27A 50.5 2.5k 100 128 40nA 4
5
6
V
0
1
OPA111B 202 10k 100 110 1pA 10
OPA128LM 202 10k 100 118 75fA 38
FIGURE 4. Precision Instrumentation Amplifier.
INA105
2
100
Ω
1%
V–
100
Ω
I
IN
0 to 20mA
1%
3
5
6
V
0
0 to 2V
1
FIGURE 5. Current Receiver with Compliance to Rails.
®
INA105
6

5
6
2
(V+)/2
INA105
V+
1
7
4
V+
CommonCommon
3
INA105
V
1
5
6
1
3
2
V
0
INA105
V
0
= V
1
Gain Error = 0.001% maximum
2
V
2
13
= – V
V
0
Gain Error = 0.01% maximum
5
6
V
0
2
Nonlinearity = 0.001% maximum
Gain Drift = 2ppm/°C
FIGURE 6. Precision Unity-Gain Inverting Amplifier.
+15V
2
+10V Out
–10V Out
5
6
REF10
4
6
2
1
INA105
FIGURE 9. Precision Unity-Gain Buffer.
FIGURE 7. ±10V Precision Voltage Reference.
13
FIGURE 8. ±5V Precision Voltage Reference.
3
2
INA105
5
6
V+
REF10
FIGURE 10. Pseudoground Generator.
INA105
2
6
+5V Out
4
–5V Out
1
V
1
V
3
3
V
= (V1 + V3)/2, ±0.01% maximum
0
2
5
6
V
0
FIGURE 11. Precision Average Value Amplifier.
®
7
INA105

INA105
V
1
6
1
3
V
0
INA105
V
3
25
R
1
R
2
V
0
= 1 +
R
2
R
1
V1 + V
3
2
( )( )
For G=10,
See INA106.
2
1
V
1
3
5
6
V
0
1
–10V
to
+10V
INA105
0 to +10V Output
±2ppm/°C
2
5
6
Output
(1)
Input
= 2 • V
V
0
1
Gain Error = 0.01% maximum
Gain Drift = 2ppm/°C
FIGURE 12. Precision (G = 2) Amplifier.
INA105
2
1
V
1
V
3
3
= V1 + V3, ±0.01% maximum
V
0
FIGURE 13. Precision Summing Amplifier.
3
2
6
Device
VFC320
VFC100
DAC80
DAC703
XTR110
Output
0-10kHz
/2
0-F
CLOCK
0-FS (12 bits)
0-FS (16 bits)
4-20mA
REF10
10V
4
5
NOTE: (1) Unipolar Input Device.
FIGURE 15. Precision Bipolar Offsetting.
6
V
0
INA105
2
5
FIGURE 16. Precision Summing Amplifier with Gain.
6
V
3
V
3
±20V
1
V0 = V3/2, ±0.01%
FIGURE 14. Precision Gain = 1/2 Amplifier.
®
INA105
= 1/2 V
0
3
8

Transducer or
Analog Signal
Noise (60Hz hum)
Offset
Adjust
8
76
INA101AG
3
A
20k
20k
1
10k
Ω
Ω
Ω
10k
10k
Ω
A
3
Output
1
Ω
4
5
R
G
10
11
A
12
2
10k
Ω
Noise (60Hz hum)
Shield
100k
INA105
2
5
6
FIGURE 17. Instrumentation Amplifier Guard Drive Generator.
INA105
2
3
V
1
5
6
Ω
2
+V
13
–V
CC
9 14 Common
CC
3
1
INA105
2
5
V
2
1
V
= V3 + V4 – V1 – V
0
2
FIGURE 18. Precision Summing Instrumentation Amplifier.
3
V
3
V
4
1
9
6
V
0
INA105
®

INA105
2
V
2
5
R
2
INA105
5
6
R
3
V
1
IO = (V1 – V2) (1/25k + 1/R)
≅
For R 200 , Figure 24 will
provide superior performance.
Ω
1
Load
I
O
FIGURE 19. Precision Voltage-to-Current Converter with
Differential Inputs.
INA105
2
V
2
3
V
3
5
6
R
1
V
1
3
V
2
6
1
INA105
2
5
6
3
– V
= 2 (V2 – V1)
V
01
02
1
FIGURE 22. Differential Output Difference Amplifier.
V
01
V
02
= (V3 – V2)/R
I
O
Load
I
O
FIGURE 20. Differential Input Voltage-to-Current Converter
for Low I
2
V
2
3
V
3
I
= (V3 – V2) (1/25k + 1/R)
O
OUT
INA105
.
5
R
6
1
Load I
R
R < 200Ω
Gate can be
–5V
+V
S
O
FIGURE 21. Isolating Current Source.
2
V
2
INA105
5
6
R 200
Ω≥
R
V
3
3
I
= (V3 – V2)/R
O
1
Gate can be
–5V
+V
CC
Load I
O
FIGURE 23. Isolating Current Source with Buffering Ampli-
fier for Greater Accuracy.
®
INA105
10

Window Span
0 to +5V
Window Center–Window Span
2
5
6
3
INA105
1
Lower Limit
2
5
Window
Center
±10V
3
1
INA105
6
FIGURE 24. Window Comparator with Window Span and Window Center Inputs.
–In
V
1
+In
V
2
(1)
R
2
R
1
R
2
(1)
I
= (E2 – E1) (1 +2R2/R1) (1/25k + 1/R)
O
NOTE: (1) See Figure 5 for op amp recommendation.
2
3
INA105
V
IN
Upper Limit
5
6
1kΩ
1
5
4115
3
Window
Comparator
2
10
9
7
8
Window Center + Window Span
V+
R
R
Load
I
O
HI
GO
LO
FIGURE 25. Precision Voltage-Controlled Current Source with Buffered Differential Inputs and Gain.
INA105
V
1
DG188
2
5
V
O
6
3
1
V
O
0
–V
1
+V
Logic
In
1
Logic In
FIGURE 26. Digitally Controlled Gain of ±1 Amplifier.
11
INA105
1
1
®

INA105
V
1
A
1
R
1
49.5Ω
R
1
R
1
49.5Ω
R
2
R
2
A
3
1
2
5
6
V0 = 200 (V2 – V1)
3
R
A
2
V
2
2
R
2
Conventional
Instrumentation
Amplifier (e.g., INA101 or INA102)
INA105
A = 2
A = 100
FIGURE 27. Boosting Instrumentation Amplifier Common-Mode Range From ±5 to ±7.5V with 10V Full-Scale Output.
INA105
V
Input
R
2
D
1
10pF
3
D
1
OPA111
2
1
R
5
2k
Ω
1
R
3
R
4
R
2
5
6
V0 = |V1|
FIGURE 28. Precision Absolute Value Buffer.
12.5k
0 to 10V
Ω
In
50k
Ω
+15V
OPA27
2
REF10
6
10V
4
FIGURE 29. Precision 4-20mA Current Transmitter.
®
INA105
1k
Ω
2
INA105
5
50.1
Ω
6
50.1
Ω
3
4 to 20mA
1
R
LOAD
Out
12

PACKAGE OPTION ADDENDUM
www.ti.com
22-Oct-2007
PACKAGING INFORMATION
Orderable Device Status
(1)
Package
Type
Package
Drawing
Pins Package
Qty
Eco Plan
INA105AM NRND TO-99 LMC 8 20 Green (RoHS &
no Sb/Br)
INA105BM NRND TO-99 LMC 8 20 Green (RoHS &
no Sb/Br)
INA105KP ACTIVE PDIP P 8 50 Green(RoHS &
no Sb/Br)
INA105KPG4 ACTIVE PDIP P 8 50 Green(RoHS &
no Sb/Br)
INA105KU ACTIVE SOIC D 8 100 Green (RoHS &
no Sb/Br)
INA105KU/2K5 ACTIVE SOIC D 8 2500 Green (RoHS &
no Sb/Br)
INA105KU/2K5E4 ACTIVE SOIC D 8 2500 Green (RoHS &
no Sb/Br)
INA105KUE4 ACTIVE SOIC D 8 100 Green (RoHS &
no Sb/Br)
(1)
The marketing status values are defined as follows:
ACTIVE: Product device recommended for new designs.
LIFEBUY: TI has announced that the device will be discontinued, and a lifetime-buy period is in effect.
NRND: Not recommended for new designs. Device is in production to support existing customers, but TI does not recommend using this part in
a new design.
PREVIEW: Device has been announced but is not in production. Samples may or may not be available.
OBSOLETE: TI has discontinued the production of the device.
(2)
Lead/Ball Finish MSL Peak Temp
AU N / A for Pkg Type
AU N / A for Pkg Type
CU NIPDAU N / A for Pkg Type
CU NIPDAU N / A for Pkg Type
CU NIPDAU Level-3-260C-168 HR
CU NIPDAU Level-3-260C-168 HR
CU NIPDAU Level-3-260C-168 HR
CU NIPDAU Level-3-260C-168 HR
(3)
(2)
Eco Plan - The planned eco-friendly classification: Pb-Free (RoHS), Pb-Free (RoHS Exempt), or Green (RoHS & no Sb/Br) - please check
http://www.ti.com/productcontent for the latest availability information and additional product content details.
TBD: The Pb-Free/Green conversion plan has not been defined.
Pb-Free (RoHS): TI's terms "Lead-Free" or "Pb-Free" mean semiconductor products that are compatible with the current RoHS requirements
for all 6 substances, including the requirement that lead not exceed 0.1% by weight in homogeneous materials. Where designed to be soldered
at high temperatures, TI Pb-Free products are suitable for use in specified lead-free processes.
Pb-Free (RoHS Exempt): This component has a RoHS exemption for either 1) lead-based flip-chip solder bumps used between the die and
package, or 2) lead-based die adhesive used between the die and leadframe. The component is otherwise considered Pb-Free (RoHS
compatible) as defined above.
Green (RoHS & no Sb/Br): TI defines "Green" to mean Pb-Free (RoHS compatible), and free of Bromine (Br) and Antimony (Sb) based flame
retardants (Br or Sb do not exceed 0.1% by weight in homogeneous material)
(3)
MSL, Peak Temp. -- The Moisture Sensitivity Level rating according to the JEDEC industry standard classifications, and peak solder
temperature.
Important Information and Disclaimer:The information provided on this page represents TI's knowledge and belief as of the date that it is
provided. TI bases its knowledge and belief on information provided by third parties, and makes no representation or warranty as to the
accuracy of such information. Efforts are underway to better integrate information from third parties. TI has taken and continues to take
reasonable steps to provide representative and accurate information but may not have conducted destructive testing or chemical analysis on
incoming materials and chemicals. TI and TI suppliers consider certain information to be proprietary, and thus CAS numbers and other limited
information may not be available for release.
In no event shall TI's liability arising out of such information exceed the total purchase price of the TI part(s) at issue in this document sold by TI
to Customer on an annual basis.
Addendum-Page 1

PACKAGE MATERIALS INFORMATION
www.ti.com
TAPE AND REEL INFORMATION
11-Mar-2008
*All dimensions are nominal
Device Package
INA105KU/2K5 SOIC D 8 2500 330.0 12.4 6.4 5.2 2.1 8.0 12.0 Q1
Type
Package
Drawing
Pins SPQ Reel
Diameter
(mm)
Reel
Width
W1 (mm)
A0 (mm) B0 (mm) K0 (mm) P1
(mm)W(mm)
Pin1
Quadrant
Pack Materials-Page 1

PACKAGE MATERIALS INFORMATION
www.ti.com
11-Mar-2008
*All dimensions are nominal
Device Package Type Package Drawing Pins SPQ Length (mm) Width (mm) Height (mm)
INA105KU/2K5 SOIC D 8 2500 346.0 346.0 29.0
Pack Materials-Page 2

IMPORTANT NOTICE
Texas Instruments Incorporated and its subsidiaries (TI) reserve the right to make corrections, modifications, enhancements, improvements,
and other changes to its products and services at any time and to discontinue any product or service without notice. Customers should
obtain the latest relevant information before placing orders and should verify that such information is current and complete. All products are
sold subject to TI’s terms and conditions of sale supplied at the time of order acknowledgment.
TI warrants performance of its hardware products to the specifications applicable at the time of sale in accordance with TI’s standard
warranty. Testing and other quality control techniques are used to the extent TI deems necessary to support this warranty. Except where
mandated by government requirements, testing of all parameters of each product is not necessarily performed.
TI assumes no liability for applications assistance or customer product design. Customers are responsible for their products and
applications using TI components. To minimize the risks associated with customer products and applications, customers should provide
adequate design and operating safeguards.
TI does not warrant or represent that any license, either express or implied, is granted under any TI patent right, copyright, mask work right,
or other TI intellectual property right relating to any combination, machine, or process in which TI products or services are used. Information
published by TI regarding third-party products or services does not constitute a license from TI to use such products or services or a
warranty or endorsement thereof. Use of such information may require a license from a third party under the patents or other intellectual
property of the third party, or a license from TI under the patents or other intellectual property of TI.
Reproduction of TI information in TI data books or data sheets is permissible only if reproduction is without alteration and is accompanied
by all associated warranties, conditions, limitations, and notices. Reproduction of this information with alteration is an unfair and deceptive
business practice. TI is not responsible or liable for such altered documentation. Information of third parties may be subject to additional
restrictions.
Resale of TI products or services with statements different from or beyond the parameters stated by TI for that product or service voids all
express and any implied warranties for the associated TI product or service and is an unfair and deceptive business practice. TI is not
responsible or liable for any such statements.
TI products are not authorized for use in safety-critical applications (such as life support) where a failure of the TI product would reasonably
be expected to cause severe personal injury or death, unless officers of the parties have executed an agreement specifically governing
such use. Buyers represent that they have all necessary expertise in the safety and regulatory ramifications of their applications, and
acknowledge and agree that they are solely responsible for all legal, regulatory and safety-related requirements concerning their products
and any use of TI products in such safety-critical applications, notwithstanding any applications-related information or support that may be
provided by TI. Further, Buyers must fully indemnify TI and its representatives against any damages arising out of the use of TI products in
such safety-critical applications.
TI products are neither designed nor intended for use in military/aerospace applications or environments unless the TI products are
specifically designated by TI as military-grade or "enhanced plastic." Only products designated by TI as military-grade meet military
specifications. Buyers acknowledge and agree that any such use of TI products which TI has not designated as military-grade is solely at
the Buyer's risk, and that they are solely responsible for compliance with all legal and regulatory requirements in connection with such use.
TI products are neither designed nor intended for use in automotive applications or environments unless the specific TI products are
designated by TI as compliant with ISO/TS 16949 requirements. Buyers acknowledge and agree that, if they use any non-designated
products in automotive applications, TI will not be responsible for any failure to meet such requirements.
Following are URLs where you can obtain information on other Texas Instruments products and application solutions:
Products Applications
Amplifiers amplifier.ti.com Audio www.ti.com/audio
Data Converters dataconverter.ti.com Automotive www.ti.com/automotive
DSP dsp.ti.com Broadband www.ti.com/broadband
Clocks and Timers www.ti.com/clocks Digital Control www.ti.com/digitalcontrol
Interface interface.ti.com Medical www.ti.com/medical
Logic logic.ti.com Military www.ti.com/military
Power Mgmt power.ti.com Optical Networking www.ti.com/opticalnetwork
Microcontrollers microcontroller.ti.com Security www.ti.com/security
RFID www.ti-rfid.com Telephony www.ti.com/telephony
RF/IF and ZigBee® Solutions www.ti.com/lprf Video & Imaging www.ti.com/video
Mailing Address: Texas Instruments, Post Office Box 655303, Dallas, Texas 75265
Copyright © 2008, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Wireless www.ti.com/wireless
 Loading...
Loading...