Page 1
User's Guide
SNLU237–September 2018
DP83869EVM User's Guide
This User’s Guide discusses how to properly operate and configure the DP83869EVM. For best layout
practices, schematic files, and Bill of Materials, see the associated support documents.
SNLU237–September 2018
Submit Documentation Feedback
Copyright © 2018, Texas Instruments Incorporated
DP83869EVM User's Guide
1
Page 2

www.ti.com
Contents
1 Definitions .................................................................................................................... 3
2 Introduction ................................................................................................................... 4
3 Board Setup Details ......................................................................................................... 9
4 Configuration Options ..................................................................................................... 11
5 Schematics.................................................................................................................. 18
List of Figures
1 DP83869EVM – Top Side.................................................................................................. 5
2 DP83869EVM – Bottom Side ............................................................................................. 6
3 Onboard Power Supply Connection ...................................................................................... 7
4 Jumper Placements for Onboard Power ................................................................................. 7
5 DP83869EVM Block Diagram.............................................................................................. 9
6 EVM Strap Jumpers ....................................................................................................... 11
7 Onboard Clock.............................................................................................................. 15
8 External Clock Input ....................................................................................................... 15
9 Schematic Page 1 ......................................................................................................... 18
10 Schematic Page 2.......................................................................................................... 19
11 Schematic Page 3.......................................................................................................... 20
12 Schematic Page 4.......................................................................................................... 21
13 Schematic Page 5.......................................................................................................... 22
14 Schematic Page 6.......................................................................................................... 23
1 Terminology .................................................................................................................. 3
2 EVM Applications .......................................................................................................... 10
3 4 Level Straps .............................................................................................................. 11
4 2 Level Straps .............................................................................................................. 11
5 PHY Strap Table ........................................................................................................... 12
6 Functional Mode Strap Table............................................................................................. 12
7 Copper Ethernet Strap Table............................................................................................. 12
8 1000Base-X Strap Table .................................................................................................. 13
9 100Base-X Strap Table.................................................................................................... 13
10 Bridge Mode Strap Table.................................................................................................. 13
11 100M Media Convertor Strap Table ..................................................................................... 13
12 1000M Media Strap Table ................................................................................................ 14
13 4-Pin Dip Switch Modes ................................................................................................... 15
Trademarks
All trademarks are the property of their respective owners.
List of Tables
2
DP83869EVM User's Guide
Copyright © 2018, Texas Instruments Incorporated
SNLU237–September 2018
Submit Documentation Feedback
Page 3
www.ti.com
1 Definitions
PHY Physical Layer Transceiver
MAC Media Access Controller
SMI Serial Management Interface
MDIO Management Data I/O
MDC Management Data Clock
MII Media Independent Interface
RMII Reduced Media Independent Interface
RGMII Reduced Gigabit Media Independent Interface
SGMII Serial Gigabit Media Independent Interface
VDDA Analog Core Supply Rail
VDDIO Digital Supply Rail
PD Pulldown
PU Pullup
Definitions
Table 1. Terminology
ACRONYM DEFINITION
SNLU237–September 2018
Submit Documentation Feedback
Copyright © 2018, Texas Instruments Incorporated
DP83869EVM User's Guide
3
Page 4

Introduction
2 Introduction
The DP83869 is a low power, fully-featured Physical Layer transceiver with integrated PMD sublayers to
support 10BASE-Te, 100BASE-TX, and 1000BASE-T Ethernet protocols. It also supports Fiber protocols
1000BASE-X and 100BASE-FX. Optimized for ESD protection, the DP83869 exceeds 8-kV IEC 61000-4-2
(direct contact). This device interfaces to the MAC layer through Reduced GMII (RGMII) and SGMII.
Integrated Termination Impedance on RGMII helps reduce system BOM. The DP83869EVM will
demonstrate all features of DP83869. The EVM will support Copper Ethernet protocols like 10BASE-Te,
100BASE-TX, and 1000BASE-T. It also supports Fiber protocols 1000BASE-X and 100BASE-FX. The
EVM has connections to use the DP83869 MAC Inerface in RGMII and SGMII mode. The EVM will also
be optimized to demonstrate the robust EMI. EMC, and ESD performance of the DP83869 device.
2.1 Key Features
• Multiple Operating Modes
– Media Support: Copper and Fiber
– Media Conversion: Copper to Fiber
– Bridge Conversion: RGMII to SGMII, SGMII to RGMII
• RGMII and SGMII MAC Interfaces
• 1000Base-X, 100Base-T, 100Base-TX, 10Base-Te
• USB-2-MDIO Support Through Onboard MSP430 for Easy Register Access
• Onboard LDO and External Power Supply Options
• Status LEDs
– Link
– Activity
– Power
• Bootstraps for Hardware Configuration
www.ti.com
4
DP83869EVM User's Guide
Copyright © 2018, Texas Instruments Incorporated
SNLU237–September 2018
Submit Documentation Feedback
Page 5
www.ti.com
Introduction
SNLU237–September 2018
Submit Documentation Feedback
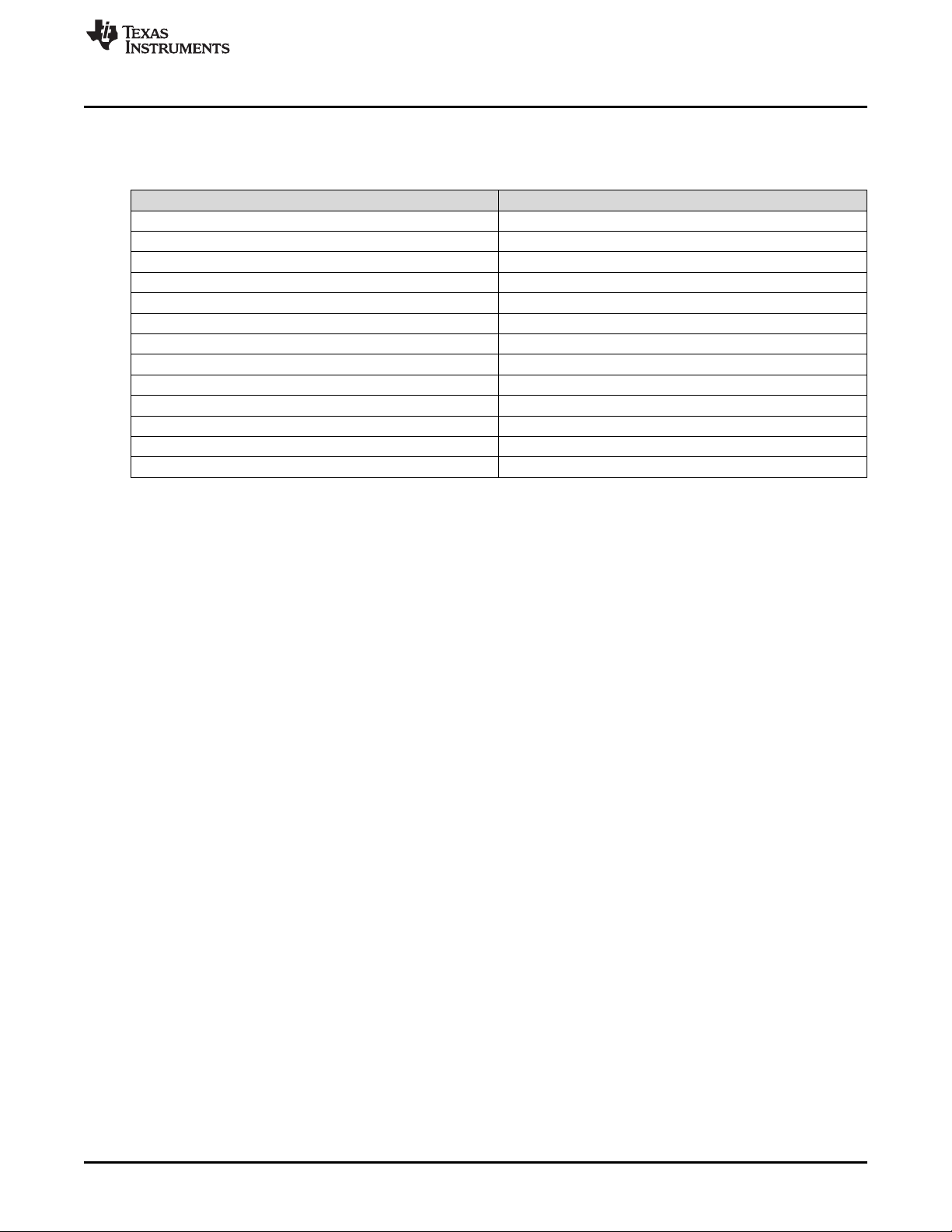
Figure 1. DP83869EVM – Top Side
Copyright © 2018, Texas Instruments Incorporated
DP83869EVM User's Guide
5
Page 6
Introduction
www.ti.com
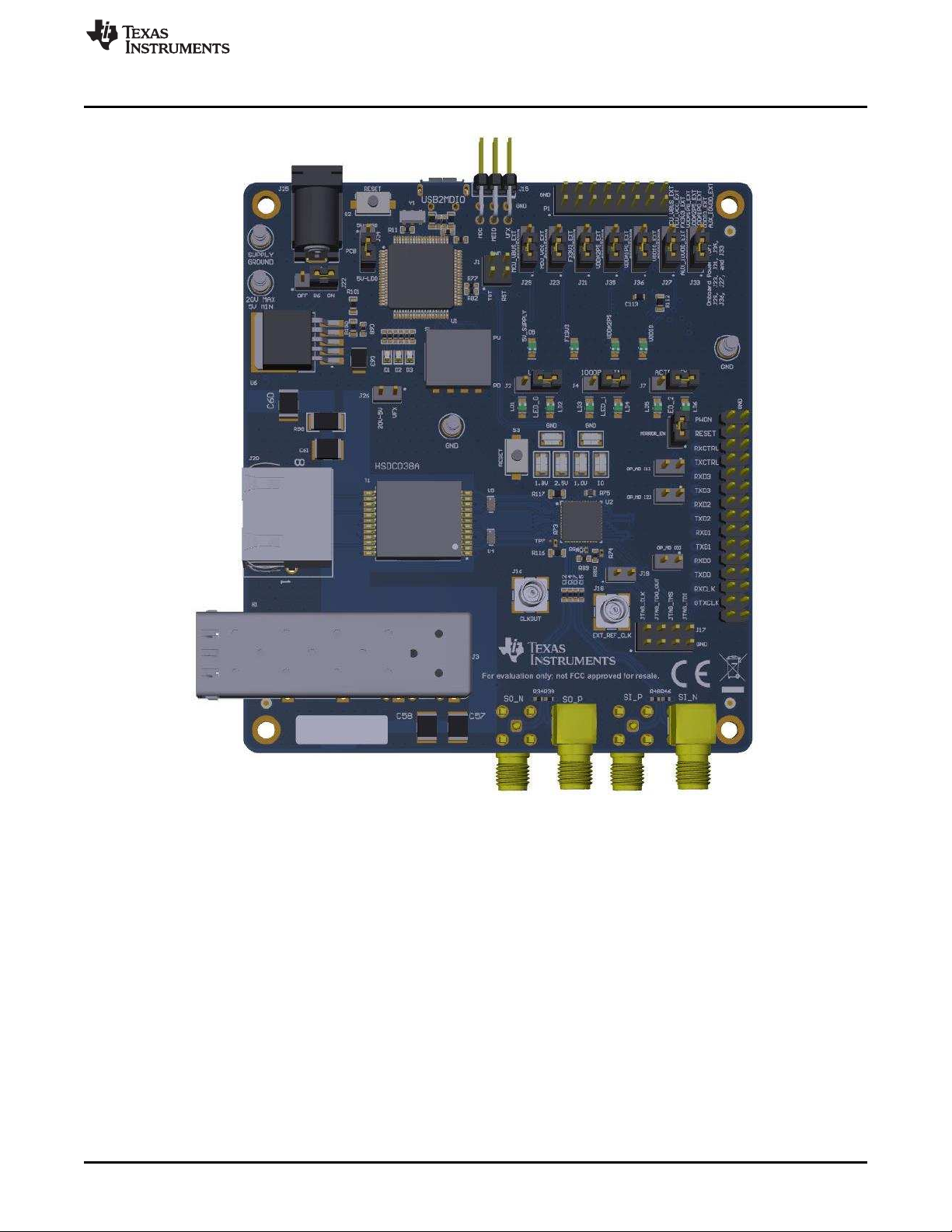
Figure 2. DP83869EVM – Bottom Side
6
DP83869EVM User's Guide
Copyright © 2018, Texas Instruments Incorporated
SNLU237–September 2018
Submit Documentation Feedback
Page 7
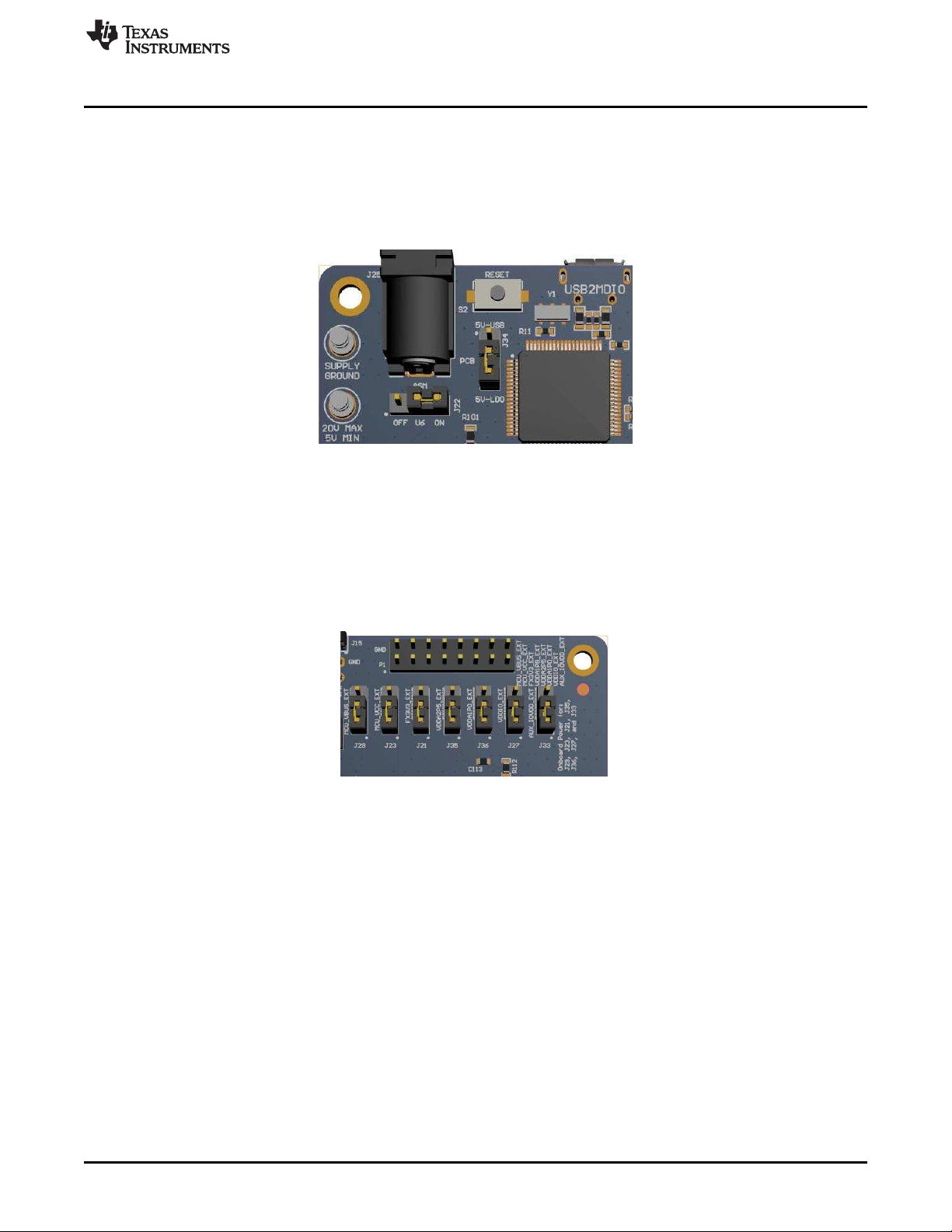
www.ti.com
2.2 Quick Setup
2.2.1 Onboard Power Supply Operation
The EVM can be supplied power through multiple options. Single-supply operation uses onboard LDOs to
generate the voltages required for operating various sections of the EVM (PHY, MSP430, FO transceiver,
and so forth).
Figure 3. Onboard Power Supply Connection
The EVM can be supplied power by either a J26 barrel jack connector, power-supply turrets, or a USB
• For Barrel Jack and Turret, connect the jumper in the ON position to J22 and the jumper on 5V-LDO to
J34.
• For USB power, connect the Jumper on 5V-USB position to J35. J23 is don’t care.
Introduction
2.2.2 External Power Supply Operation
Figure 4. Jumper Placements for Onboard Power
The jumpers shown in Figure 4 can be used to choose whether a particular voltage rail is supplied through
onboard LDOs or an external power supply. If an external power supply is desired on a voltage rail,
change its respective jumper from position 1-2 (LDO) to 2-3 (External). Then connect the appropriate
voltage on its corresponding pin to the P1 connector. For example, if the VDDA2P5 is to be supplied from
an external supply, then change jumper position of J36 from 1-2 to 2-3. Then connect the 2.5-V external
supply on pins 9-10 on the P1 connector. Note that pin 9 is supply and pin 10 is ground.
2.2.3 Software
The onboard MSP430 comes pre-programmed and ready to use. When using this EVM for the first time
on a Windows 7 (or above) PC, MSP430 drivers and USB2MDIO software utility will have to be installed.
The USB2MDIO software can be used for accessing registers.
2.2.3.1 MSP430 Driver
Install the latest MSP430 drive from this website: http://software-
dl.ti.com/msp430/msp430_public_sw/mcu/msp430/MSP430_FET_Drivers/latest/index_FDS.html.
SNLU237–September 2018
Submit Documentation Feedback
Copyright © 2018, Texas Instruments Incorporated
DP83869EVM User's Guide
7
Page 8

Introduction
2.2.3.2 USB-2-MDIO Software
Download the software from http://www.ti.com/tool/usb-2-mdio. The Web page also contains a User’s
Guide for installing and using the software.
The MSP430 is on board the EVM, so it is not required to purchase a separate MSP430 Launchpad kit
and connect to the PHY using wires. The entire EVM can be powered and controlled through a USB
connector. MSP430 and USB2MDIO utility can be used even when power is not supplied through a USB.
In case the onboard MSP430 cannot be used due to some reason, MDIO and MDC pins are also broken
out on the J15 connector. Customers can connect a MSP430 launchpad or their own MDIO-MDC utility on
J15 to access the PHY registers.
www.ti.com
8
DP83869EVM User's Guide
Copyright © 2018, Texas Instruments Incorporated
SNLU237–September 2018
Submit Documentation Feedback
Page 9

DP83869
DUT
5V
LDO
1.0V
LDO
2.5V
LDO
3.3V IO
LDO
MSP-430
EVM BLOCK
3.3V
LDO
LEDs
LED SPEED
LED ACT
LED LINK
SMI
Connector
Magnetics/
Capacitive
Coupling
RJ-45
FO
Transceiver
RGMII Header
& Samtec
SMA
USB
External Supply
Header
25MHz Clock in
MDC
MDIO
SGMII
Fiber IO
ESD
Diodes
RESET
Turrets
Barrel Jack
3.3V from
MSP430 LDO
1x3
Header
Power
DATA
Jumper
(LDO vs External)
1.0VI/O 2.5V 1.8V
I/OCORE
Strap
Resistors
JTAG
www.ti.com
3 Board Setup Details
3.1 Block Diagram
Board Setup Details
Figure 5. DP83869EVM Block Diagram
SNLU237–September 2018
Submit Documentation Feedback
Copyright © 2018, Texas Instruments Incorporated
DP83869EVM User's Guide
9
Page 10

Board Setup Details
3.2 EVM High-Level Summary
The DP83869EVM supports SMI through J2 using pin 26 for MDIO and 28 for MDC. These pins can be
connected to an MSP430 Launchpad, which can be used for USB-2-MDIO control.
NO. DP83869 MODE APPLICATIONS HOW TO USE
1 RGMII to Copper Run traffic between RGMII and Copper. Connect to DP83867 RGMII EVM or MAC
Perform IEEE and UNH compliance testing Use onboard MSP430 to activate test mode
Run EMI/EMC Test on EVM Use internal PRBS and loopback
Measure Power Dissipation Connect external power supplies.
External MAC loopback Connect external MAC to headers/Samtech
2 SGMII to Copper Run traffic between SGMII and Copper. Connect to DP83867 SGMII EVM or MAC
Perform IEEE and UNH compliance testing Use onboard MSP430 to activate test mode
Run EMI/EMC Test on EVM Use internal PRBS and loopback
External SGMII loopback Use SMA cable for Passive Loopback.
3 RGMII to Fiber
Ethernet
4 100M Media Convertor Demonstrate 100M functionality on EVM Use SFP and RJ45 connector for fiber and
5 1000M Media
Convertor
6 RGMII to SGMII bridge Demonstrate SGMII as MAC able to link with
7 SGMII to RGMII bridge Demonstrate RGMII of DP83869 is able to link-
Run traffic between RGMII and Fiber Ethernet. Straps to enable Fiber Ethernet. Connect to
Perform IEEE and UNH compliance testing Use onboard MSP430 to activate test mode
Run EMI/EMC Test on EVM Use internal PRBS and loopback
Measure Power Dissipation Connect external power supplies.
Demonstrate FAR End fault capability
Demonstrate unmanaged mode of Media
convertor
Demonstrate 1000M functionality on EVM Use SFP and RJ45 connector for fiber and
Demonstrate Link Loss Pass Thru Capability
Demonstrate unmanaged mode of Media
Convertor
SGMII i/f of Phy ( DP83867)
Demonstrate SGMII link speed is reflected on
RGMII
Demonstrate Complete Data path Use-case Use DP83867 RGMII EVM and SGMII EVM with
up with RGMII of DP83867
Demonstrate SGMII link speed is reflecting
RGMII speed
Demonstrate Complete Data path Use-case Use DP83867 RGMII EVM and SGMII EVM with
www.ti.com
Table 2. EVM Applications
System using Header pins/Samtech connector.
waveform on DP83869
connector.
System using SMA connector.
waveform on DP83869.
DP83867 RGMII EVM or MAC System using
Header/Samtech.
waveforms.
copper ethernet. Straps will be used for
unmanaged mode and MDIO for managed
mode.
copper ethernet. Straps will be used for
unmanged mode and MDIO for managed mode.
Connect to DP83867 SGMII EVM over SMA
connectors and monitor RGMII header on 869
EVM.
DP83869EVM.
Connect to DP83867 RGMII EVM over Samtech
connectors and monitor SGMII SMA on 869
EVM.
DP83869EVM.
10
DP83869EVM User's Guide
Copyright © 2018, Texas Instruments Incorporated
SNLU237–September 2018
Submit Documentation Feedback
Page 11

www.ti.com
4 Configuration Options
4.1 Bootstrap Options
Except PHYADD straps, all other straps are only two-level straps in DP83869. EVM will support one
pullup and one pulldown resistor pad on RX_D0 and RX_D2 for PHY address straps. There will be only
one pullup resistor on all other strap pins with an jumper option to disconnect it.
STRAP VALUE MODE 1 MODE 2 MODE 3 MODE 4
Resistor PU (kΩ) Open 10 5.76 2.49
Resistor PD (kΩ) Open 2.49 2.49 Open
STRAP VALUE MODE 1 MODE 2
Resistor PU (kΩ) 2.49 Open
Resistor PD (kΩ) Open 2.49
Configuration Options
Table 3. 4 Level Straps
Table 4. 2 Level Straps
SNLU237–September 2018
Submit Documentation Feedback
Figure 6. EVM Strap Jumpers
Copyright © 2018, Texas Instruments Incorporated
DP83869EVM User's Guide
11
Page 12

Configuration Options
4.1.1 Straps for PHY Address
Table 5. PHY Strap Table
PIN NAME STRAP NAME PIN NO. DEFAULT
RX_D0 PHY_ADD[1:0] 33 00
RX_D1 PHY_ADD[3:2] 34 00
4.1.2 Strap for DP83869 Functional Mode Selection
Table 6. Functional Mode Strap Table
www.ti.com
PHY_ADD1 PHY_ADD0
MODE 0 0 0
MODE 1 0 1
MODE 2 1 0
MODE 3 1 1
PHY_ADD3 PHY_ADD2
MODE 0 0 0
MODE 1 0 1
MODE 2 1 0
MODE 3 1 1
PIN NAME STRAP NAME PIN NO. DEFAULT
JTAG_TDO/GP
IO_1
RX_D3 OPMODE_1 36 0
RX_D2 OPMODE_2 35 0
OPMODE_0 22 0
4.1.3 Straps for RGMII/SGMII to Copper
Table 7. Copper Ethernet Strap Table
PIN NAME STRAP NAME PIN NO. DEFAULT
LED_0 ANEG_DIS 47 0
LED_1 ANEGSEL_0 46 0
OPMO
DE_2
ANEG
OPMO
DE_1
0 0 0
0 0 1 RGMII to 1000Base-X
0 1 0 RGMII to 100Base-FX
0 1 1 RGMII-SGMII Bridge Mode
1 0 0 1000Base-T to 1000Base-X
1 0 1 100Base-T to 100Base-FX
1 1 0
1 1 1 JTAG for boundary scan
_DIS
ANEG
SEL_1
0 0 0
0 0 1
0 1 0
0 1 1
1 0 0
OPMO
DE_0
ANEG
SEL_0
FUNCTIONAL MODES
RGMII to Copper( 1000Base-
T/100Base-TX/10Base-Te)
SGMII to Copper( 1000Base-
T/100Base-TX/10Base-Te)
FUNCTION
Auto-negotiation, 1000/100/10
advertised, Auto MDI-X
Auto-negotiation, 1000/100
advertised, Auto MDI-X
Auto-negotiation, 100/10
advertised, Auto-MDI-X
Reserved (JTAG for boundary
scan)
Forced 1000M, master, MDI
mode
12
DP83869EVM User's Guide
SNLU237–September 2018
Submit Documentation Feedback
Copyright © 2018, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Page 13

www.ti.com
Table 7. Copper Ethernet Strap Table (continued)
PIN NAME STRAP NAME PIN NO. DEFAULT
LED_2 ANEGSEL_1 45 0
RX_CTRL MIRROR_EN 38 0
4.1.4 Straps for RGMII to 1000Base-X
PIN NAME STRAP NAME PIN # DEFAULT
LED_0 ANEG_DIS 47 0
LED_1 ANEGSEL_0 46 0
1 0 1 Forced 1000M, slave, MDI mode
1 1 0
1 1 1
0 Port Mirroring Disabled
1 Port Mirroring Enabled
Table 8. 1000Base-X Strap Table
0 Fiber Auto-negotiation ON
1 Fiber Force mode
0 Signal Detect disable on Pin 24
1 Configure Pin 24 as Signal Detect Pin
Configuration Options
Forced 100M, full duplex, MDI
mode
Forced 100M, full duplex, MDI-X
mode
4.1.5 Straps for RGMII to 100Base-FX
Table 9. 100Base-X Strap Table
PIN NAME STRAP NAME PIN # DEFAULT
LED_1 ANEGSEL_0 46 0
4.1.6 Straps for Bridge Mode (SGMII-RGMII)
Table 10. Bridge Mode Strap Table
PIN NAME STRAP NAME PIN # DEFAULT
RX_CTRL MIRROR_EN 38 0
4.1.7 Straps for 100M Media Convertor
Table 11. 100M Media Convertor Strap Table
PIN NAME
LED_1
LED_2
STRAP
NAME
ANEGSEL_
0
ANEGSEL_
1
PIN # DEFAULT
46 0
45 0
0 Signal Detect disable on Pin 24
1 Configure Pin 24 as Signal Detect Pin
RGMII to SGMII ( RGMII : MAC I/F, SGMII : Phy
0
SGMII to RGMII ( SGMII : MAC I/F, RGMII : Phy
1
ANEGSEL_1ANEGSEL_
0 0
1 1
0
I/F)
I/F)
Copper : Auto-negotiation ( 100/10
Advertised), Auto MDIX
Copper : Auto Negotiation ( 100
Advertised), Auto MDIX
SNLU237–September 2018
Submit Documentation Feedback
Copyright © 2018, Texas Instruments Incorporated
DP83869EVM User's Guide
13
Page 14

Configuration Options
Table 11. 100M Media Convertor Strap Table (continued)
PIN NAME
RX_CTRL
RX_CLK LINK_LOSS 32 0
STRAP
NAME
MIRROR_E
N
PIN # DEFAULT
38 0
4.1.8 Straps for 1000M Media Convertor
Table 12. 1000M Media Strap Table
www.ti.com
0 Copper: Mirror Disable
1 Copper: Mirror Enable
0 Link Loss Pass Thru Enabled
1 Link Loss Pass Thru Disabled
PIN NAME
LED_0 ANEG_DIS 47 0
LED_1
LED_2
STRAP
NAME
ANEGSEL_
0
ANEGSEL_
1
4.2 SGMII/Fiber Interface
SGMII Pins from the DUT are multipurpose pins functioning as SGMII and Fiber IO pins. By default, the
EVM will be configured for Fiber operation.
NOTE: Fiber Transceiver is not a part of the EVM package. SFP cage and SFP connector will be
mounted.
For routing signals to Fiber Transceiver, populate R31, R38, R45, and R47. Remove C12, C14, C15, and
C17.
For routing signals to SGMII SMAs, populate C12, C14, C15, and C17. Remove R31, R38, R45, and R47.
4.3 RGMII
RGMII signals are routed to standard 2.54-mm header connectors on J14. RGMII can be used both in
Copper mode and Fiber mode.
PIN # DEFAULT
46 0
45 0
0 Fiber Auto Negotiation
1 Fiber Force Mode
ANEGSEL_1ANEGSEL_
0
0 0
1 1
Copper : Auto-negotiation ( 1000/100
Advertised), Auto MDIX
Copper : Auto Negotiation ( 1000
Advertised), Auto MDIX
4.4 Clock Output
The EVM has a SMB connector to output clock from the PHY. A 50-Ω Coax cable with a SMB connector
should be used for accessing the clock output.
4.5 Clock Input
The EVM is configured for default crystal input clock operation. It supports the option to provide clock from
25-MHz crystal, 25-MHz CMOS oscillator, and the External clock from the SMB connector. A 50-Ω Coax
cable with a SMB connector should be used for providing clock input from external sources.
14
DP83869EVM User's Guide
Copyright © 2018, Texas Instruments Incorporated
SNLU237–September 2018
Submit Documentation Feedback
Page 15

www.ti.com
Configuration Options
Figure 7. Onboard Clock
4.6 Switch Configuration Options
The DP83869EVM includes a 4-pin dip switch (S3), which can be used for various test modes and feature
displays. Some of the switch settings can also be used with the USB-2-MDIO GUI for additional control.
Except for switch mode 15, all switch modes are hard-coded and can be used without USB-2-MDIO or any
other serial com port. Refer to Table 13 for switch configurations and LED outputs. For each switch, PU is
1 and PD is 0.
Mode SW[4:1] Feature LED Description
0 0000 Normal Operation
1 0001
2 0010
3 0011
Test Mode 1 Droop
Test Mode 2 Clock Frequency,
Master Jitter
Test Mode 3 Slave Jitter
Figure 8. External Clock Input
Table 13. 4-Pin Dip Switch Modes
LED
D14
USB-2-MDIO Active (Flashes very briefly
red during read and green during write)
Program failed to read PHY register Red Off Off
Program failed to write PHY register Green Off Off
Successfully entered Test Mode 1
Failed to enter Test Mode 1 (Flashing
LEDs)
Successfully entered Test Mode 2
Failed to enter Test Mode 2 (Flashing
LEDs)
Successfully entered Test Mode 3
Failed to enter Test Mode 3 (Flashing
LEDs)
Red
Green
Red
Green
Red Red Red No
Red
Green
Red Red Red No
Red
Green
Red Red Red No
LED
D15
Off Off Yes
Off Green Yes
Off Red Yes
Off
LED
D16
Red
Green
USB2MDIO
No
Yes
SNLU237–September 2018
Submit Documentation Feedback
Copyright © 2018, Texas Instruments Incorporated
DP83869EVM User's Guide
15
Page 16

Configuration Options
Mode SW[4:1] Feature LED Description
4 0100
5 0101 Test Mode 5
6 0110 Force 100Mbps
7 0111 Force 10Mbps
8 1000 Reverse Loopback
9 1001 xMII Loopback
10 1010 Enable BIST
11 - 14
15 1111
(1)
During the loop for Mode 15, USB-2-MDIO is not operational. However, other serial port terminals (that is, PuTTY) can be used
to view real-time data.
1011 -
1110
www.ti.com
Table 13. 4-Pin Dip Switch Modes (continued)
LED
D14
Test Mode 4 Distortion
RESERVED RESERVED - - - No
LOOP: Read data
continuously from a
list of registers
loaded to the MC
Successfully entered Test Mode 4
Failed to enter Test Mode 4 (Flashing
LEDs)
Successfully entered Test Mode 5
Failed to set Test Mode 5 (Flashing
LEDs)
Force 100-Mbps speed with force MDI
Program failed to program the PHY
registers
Force 10-Mbps speed with force MDI
and PRBS on.
Program failed to program the PHY
registers
Successfully entered Reverse Loopback
Failed to enter Reverse Loopback
(Flashing LEDs)
Successfully entered xMII Loopback
Failed to enter xMII Loopback (Flashing
LEDs)
Enable BIST in Copper Ethernet Mode Red Green
Program failed to program the PHY
registers
To upload a list of registers to
continuously read from with USB-2MDIO: Write the hex value of the register
you want to add to the list to the register
address "LOAD"
To begin reading data continuously with
USB-2-MDIO: Read the register address
"OPEN"
To stop reading data continuously with
USB-2-MDIO: Read the register address
"STOP"
Red
Green
Red Red Red No
Red
Green
Red Red Red No
Red
Green
Off Green Red No
Off Green Red
Red Red Red
Red
Green
Red Red Red No
Red
Green
Red Red Red No
Red Red Red
Red
Green
LED
D15
Green Off Yes
Green Green Yes
Green Red Yes
Red Off Yes
Red Green Yes
Red
Green
LED
D16
Red
Green
Red
Green
USB2MDIO
No
No
Yes
(1)
16
When running switch mode 15, data is constantly sent to the serial port. USB-2-MDIO is not capable of
supporting the constant read feature. However, other serial port terminals, that is, PuTTY, can be used.
When using a serial port terminal, copy and paste data. Do not enter in the data slowly, because the
firmware will execute as soon as the data is received.
To load a list of registers to read data from, follow this data format:
##LOADAAAAB/
• ## = Two digit PHY ID expressed in decimal form
• LOAD = the string 'LOAD' indicates to the MC to add a register to the list
• AAAA = Four character Register Address to read data from in hex form (that is, Read register 0x133h,
set AAAA = 0133)
DP83869EVM User's Guide
Copyright © 2018, Texas Instruments Incorporated
SNLU237–September 2018
Submit Documentation Feedback
Page 17

www.ti.com
• B = use '*' for an extended access read and '=' for a direct access read
• / = end string with '/'
For example, to load register 0x462h with PHY_ID = 1 with extended access, copy and paste the following
command into a serial com terminal: 01LOAD0462*/
To start reading data, continuously copy and paste the following into the serial com terminal: OPEN
To stop reading data, continuously copy and paste the following into the serial com terminal: STOP
Configuration Options
NOTE: The "OPEN" and "STOP" commands are in no particular position, so the designer can copy
"OPENSTOP" and paste it into the serial com terminal once to start reading data and then
paste it again to stop reading data, for example.
NOTE: When the read loop is stopped, the list of registers to read is cleared.
SNLU237–September 2018
Submit Documentation Feedback
Copyright © 2018, Texas Instruments Incorporated
DP83869EVM User's Guide
17
Page 18

Schematics
5 Schematics
www.ti.com
18
DP83869EVM User's Guide
Figure 9. Schematic Page 1
SNLU237–September 2018
Submit Documentation Feedback
Copyright © 2018, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Page 19

www.ti.com
Schematics
SNLU237–September 2018
Submit Documentation Feedback
Figure 10. Schematic Page 2
Copyright © 2018, Texas Instruments Incorporated
DP83869EVM User's Guide
19
Page 20

Schematics
www.ti.com
20
DP83869EVM User's Guide
Figure 11. Schematic Page 3
SNLU237–September 2018
Submit Documentation Feedback
Copyright © 2018, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Page 21

www.ti.com
Schematics
SNLU237–September 2018
Submit Documentation Feedback
Figure 12. Schematic Page 4
Copyright © 2018, Texas Instruments Incorporated
DP83869EVM User's Guide
21
Page 22

Schematics
www.ti.com
22
DP83869EVM User's Guide
Figure 13. Schematic Page 5
SNLU237–September 2018
Submit Documentation Feedback
Copyright © 2018, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Page 23

www.ti.com
Schematics
SNLU237–September 2018
Submit Documentation Feedback
Figure 14. Schematic Page 6
Copyright © 2018, Texas Instruments Incorporated
DP83869EVM User's Guide
23
Page 24

24
DP83869EVM User's Guide
SNLU237–September 2018
Submit Documentation Feedback
Page 25

www.ti.com
Schematics
IMPORTANT NOTICE AND DISCLAIMER
TI PROVIDES TECHNICAL AND RELIABILITY DATA (INCLUDING DATASHEETS), DESIGN RESOURCES (INCLUDING REFERENCE
DESIGNS), APPLICATION OR OTHER DESIGN ADVICE, WEB TOOLS, SAFETY INFORMATION, AND OTHER RESOURCES “AS IS”
AND WITH ALL FAULTS, AND DISCLAIMS ALL WARRANTIES, EXPRESS AND IMPLIED, INCLUDING WITHOUT LIMITATION ANY
IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY, FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE OR NON-INFRINGEMENT OF THIRD
PARTY INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY RIGHTS.
These resources are intended for skilled developers designing with TI products. You are solely responsible for (1) selecting the appropriate
TI products for your application, (2) designing, validating and testing your application, and (3) ensuring your application meets applicable
standards, and any other safety, security, or other requirements. These resources are subject to change without notice. TI grants you
permission to use these resources only for development of an application that uses the TI products described in the resource. Other
reproduction and display of these resources is prohibited. No license is granted to any other TI intellectual property right or to any third
party intellectual property right. TI disclaims responsibility for, and you will fully indemnify TI and its representatives against, any claims,
damages, costs, losses, and liabilities arising out of your use of these resources.
TI’s products are provided subject to TI’s Terms of Sale (www.ti.com/legal/termsofsale.html) or other applicable terms available either on
ti.com or provided in conjunction with such TI products. TI’s provision of these resources does not expand or otherwise alter TI’s applicable
warranties or warranty disclaimers for TI products.
Mailing Address: Texas Instruments, Post Office Box 655303, Dallas, Texas 75265
Copyright © 2018, Texas Instruments Incorporated
SNLU237–September 2018
Submit Documentation Feedback
Copyright © 2018, Texas Instruments Incorporated
DP83869EVM User's Guide
25
Page 26

IMPORTANT NOTICE AND DISCLAIMER
TI PROVIDES TECHNICAL AND RELIABILITY DATA (INCLUDING DATASHEETS), DESIGN RESOURCES (INCLUDING REFERENCE
DESIGNS), APPLICATION OR OTHER DESIGN ADVICE, WEB TOOLS, SAFETY INFORMATION, AND OTHER RESOURCES “AS IS”
AND WITH ALL FAULTS, AND DISCLAIMS ALL WARRANTIES, EXPRESS AND IMPLIED, INCLUDING WITHOUT LIMITATION ANY
IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY, FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE OR NON-INFRINGEMENT OF THIRD
PARTY INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY RIGHTS.
These resources are intended for skilled developers designing with TI products. You are solely responsible for (1) selecting the appropriate
TI products for your application, (2) designing, validating and testing your application, and (3) ensuring your application meets applicable
standards, and any other safety, security, or other requirements. These resources are subject to change without notice. TI grants you
permission to use these resources only for development of an application that uses the TI products described in the resource. Other
reproduction and display of these resources is prohibited. No license is granted to any other TI intellectual property right or to any third
party intellectual property right. TI disclaims responsibility for, and you will fully indemnify TI and its representatives against, any claims,
damages, costs, losses, and liabilities arising out of your use of these resources.
TI’s products are provided subject to TI’s Terms of Sale (www.ti.com/legal/termsofsale.html) or other applicable terms available either on
ti.com or provided in conjunction with such TI products. TI’s provision of these resources does not expand or otherwise alter TI’s applicable
warranties or warranty disclaimers for TI products.
Mailing Address: Texas Instruments, Post Office Box 655303, Dallas, Texas 75265
Copyright © 2018, Texas Instruments Incorporated
 Loading...
Loading...