Texas Instruments BQ25155 Datasheet
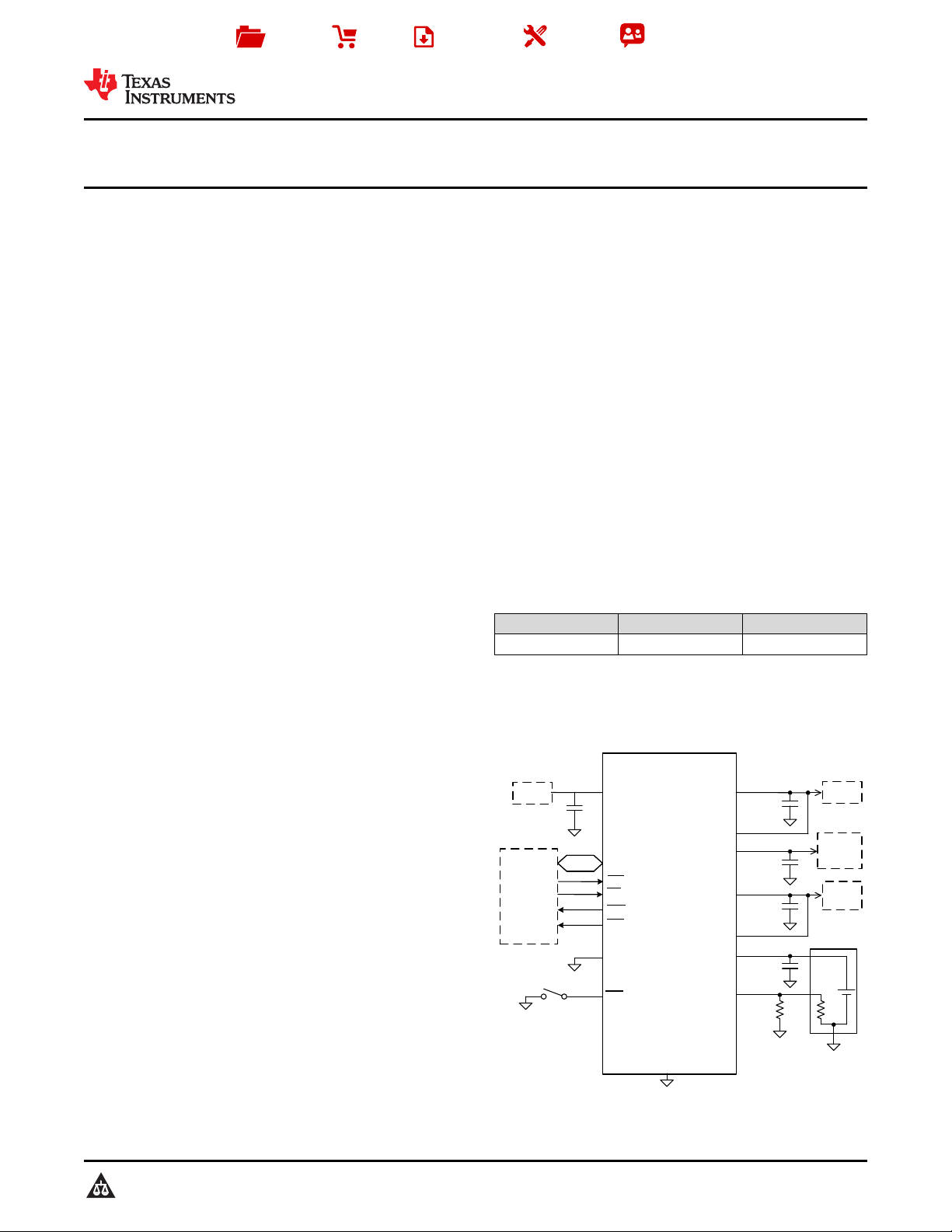
BQ25155
VINLS
PMID
LS/LDO
VDD
BAT
TS
+
±
NTC
GND
IN
VIO
Host
USB
I2C Bus
<150mA
Load
<10mA
Load
System
ADCIN
MR
PG
INT
LP
CE
C
4
C
5
C
3
C
2
C
1
Product
Folder
Order
Now
Technical
Documents
Tools &
Software
Support &
Community
BQ25155
SLUSDO1A –JUNE 2019–REVISED JULY 2019
BQ25155 I2C Controlled 1-Cell 500-mA Linear Battery Charger With 10-nA Ship Mode,
PowerPath With Regulated System (PMID) Voltage, ADC, and LDO
1 Features
1
• Linear battery charger with 1.25-mA to 500-mA
fast charge current range
– 0.5% Accurate I2C programmable battery
regulation voltage ranging from 3.6 V to 4.6 V
in 10-mV steps
– Configurable termination current supporting
down to 0.5 mA
– 20-V Tolerant input with typical 3.4-V to 5.5-V
input voltage operating range
– Programmable thermal charging profile, fully
configurable hot, warm, cool and cold
thresholds
• PowerPath management for powering system and
charging battery
– I2C Programmable regulated system voltage
(PMID) ranging from 4.4V to 4.9V in addition to
battery voltage tracking and Input pass-though
options
– Dynamic power path management optimizes
charging from weak adapters
– Advanced I2C control allows host to disconnect
the battery or adapter as needed
• I2C Configurable load switch or up to 150-mA
LDO output
– Programmable range from 0.6 V to 3.7 V in
100-mV steps
• Ultra low Iddq for extended battery life
– 10-nA Ship mode battery Iq
– 400-nA Iq While powering the system (PMID
and VDD on)
• One push-button wake-up and reset input with
adjustable timers
– Supports system power cycle and HW reset
• 16-Bit ADC
• Always on 1.8-V VDD LDO supporting loads up to
• 20-Pin 2-mm x 1.6-mm CSP package
• 12-mm2Total solution size
1
– Monitoring of charge current, battery thermistor
and battery, input and system (PMID) voltages
– General purpose ADC input
10 mA
2 Applications
• Headsets, earbuds and hearing aids
• Smart watches and smart trackers
• Wearable fitness & activity monitors
• Blood glucose monitors
3 Description
The BQ25155 is a highly integrated battery charge
management IC that integrates the most common
functions for wearable and portable devices, namely
a charger, a regulated output voltage rail for system
power, ADC for battery and system monitoring, a
LDO, and push-button controller.
The BQ25155 IC integrates a linear charger with
PowerPath that enables quick and accurate charging
for small batteries while providing a regulated voltage
to the system. The regulated system voltage (PMID)
output may be configured through I2C based on the
recommended operating condition of downstream
IC's and system loads for optimal system operation.
Device Information
PART NUMBER PACKAGE BODY SIZE (NOM)
BQ25155 DSBGA (20) 2.00 mm x 1.60 mm
(1) For all available packages, see the orderable addendum at
the end of the data sheet.
Simplified Schematic
(1)
An IMPORTANT NOTICE at the end of this data sheet addresses availability, warranty, changes, use in safety-critical applications,
intellectual property matters and other important disclaimers. PRODUCTION DATA.

BQ25155
SLUSDO1A –JUNE 2019–REVISED JULY 2019
www.ti.com
Table of Contents
1 Features.................................................................. 1
2 Applications ........................................................... 1
3 Description ............................................................. 1
4 Revision History..................................................... 2
5 Description (continued)......................................... 3
6 Pin Configuration and Functions......................... 4
7 Specifications......................................................... 5
7.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings...................................... 5
7.2 ESD Ratings.............................................................. 5
7.3 Recommended Operating Conditions....................... 6
7.4 Thermal Information.................................................. 6
7.5 Electrical Characteristics........................................... 6
7.6 Timing Requirements................................................ 9
7.7 Typical Characteristics............................................ 11
8 Detailed Description............................................ 14
8.1 Overview................................................................. 14
8.2 Functional Block Diagram....................................... 14
8.3 Feature Description................................................. 15
8.4 Device Functional Modes........................................ 33
8.5 Register Map .......................................................... 37
9 Application and Implementation ........................ 92
9.1 Application Information............................................ 92
9.2 Typical Application ................................................. 92
10 Power Supply Recommendations ..................... 98
11 Layout................................................................... 99
11.1 Layout Guidelines ................................................. 99
11.2 Layout Example .................................................... 99
12 Device and Documentation Support............... 100
12.1 Device Support.................................................... 100
12.2 Documentation Support ..................................... 100
12.3 Community Resources........................................ 100
12.4 Trademarks......................................................... 100
12.5 Electrostatic Discharge Caution.......................... 100
12.6 Glossary.............................................................. 100
13 Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable
Information......................................................... 100
4 Revision History
Changes from Original (June 2019) to Revision A Page
• Changed from Advance Information to Production Data ....................................................................................................... 1
2
Submit Documentation Feedback Copyright © 2019, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Product Folder Links: BQ25155

BQ25155
www.ti.com
SLUSDO1A –JUNE 2019–REVISED JULY 2019
5 Description (continued)
The device supports charge current up to 500 mA and supports termination current down to 0.5 mA for maximum
charge. The battery is charged using a standard Li-Ion charge profile with three phases: pre-charge, constant
current and constant voltage regulation.
The device integrates advanced power path management and control that allows the device to provide power to
the system while charging the battery even with poor adapters. The host may also control the power path
through I2C allowing it to disconnect the input adapter and/or battery without physically removing them. The
single push-button input eliminates the need of a separate button controller IC reducing the total solution
footprint. The push-button input can be used for wake functions or to reset the system.A 16-bit ADC enables
accurate battery voltage monitoring and can be used to enable a low Iq gauging to monitor battery health. It can
also be used to measure the battery temperature using a thermistor connected to the TS pin as well as external
system signals through a pin. The low quiescent current during operation and shutdown enables maximum
battery life. The input current limit, charge current, LDO output voltage, and other parameters are programmable
through the I2C interface making the BQ25155 a very flexible charging solution. A voltage-based JEITA
compatible (or standard HOT/COLD) battery pack thermistor monitoring input (TS) is included that monitors
battery temperature and automatically changes charge parameters to prevent the battery from charging outside
of its safe temperature range. The temperature thresholds are also programable through I2C allowing the host to
customize the thermal charging profile. The charger is optimized for 5-V USB input, with 20-V absolute maximum
tolerance to withstand line transients. The device also integrates a linear regulator to provide a quiet rail for
radios or processors and can be independently sourced and controlled through I2C.
Product Folder Links: BQ25155
Submit Documentation FeedbackCopyright © 2019, Texas Instruments Incorporated
3
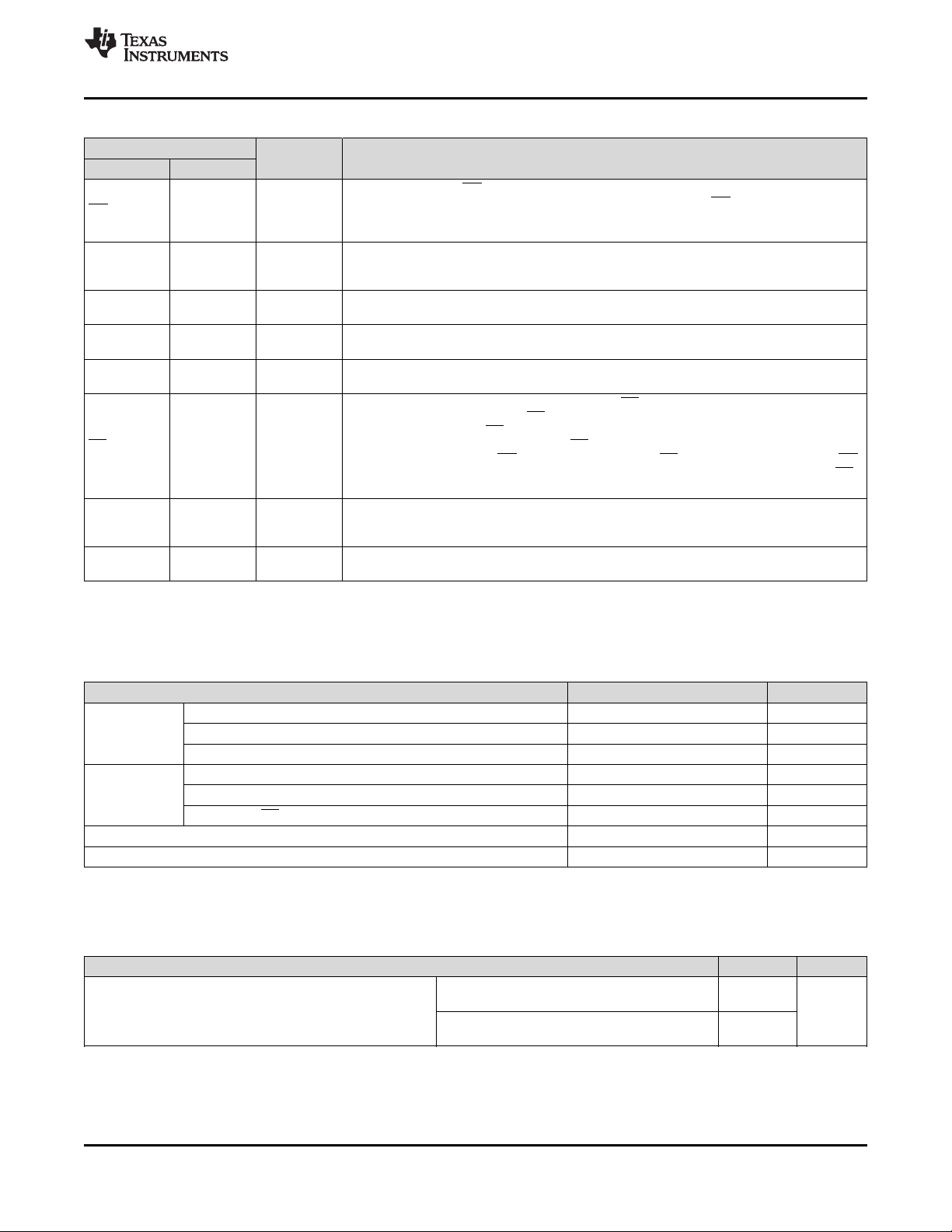
IN PMID BAT GND
/PG PMID BAT TS
/MR /CE NC ADCIN
VDD /INT /LP LSLDO
VIO SDA SCL VINLS
A
B
C
D
E
1 2 3 4
BQ25155
SLUSDO1A –JUNE 2019–REVISED JULY 2019
6 Pin Configuration and Functions
www.ti.com
YFP Package
20-Pin DSBGA
Top View
Pin Functions
PIN
NAME NO.
IN A1 I
PMID A2, B2 I/O
GND A4 PWR Ground connection. Connect to the ground plane of the circuit.
VDD D1 O
CE C2 I
SCL E3 I/O I2C Interface Clock. Connect SCL to the logic rail through a 10-kΩ resistor.
SDA E2 I I2C Interface Data. Connect SDA to the logic rail through a 10-kΩ resistor.
LP D3 I
INT D2 O
ADCIN C4 I Input Channel to the ADC. Maximum ADC range 1.2 V.
I/O DESCRIPTION
DC Input Power Supply. IN is connected to the external DC supply. Bypass IN to GND with
at least 1-µF of capacitance using a ceramic capacitor.
Regulated System Output. Connect 22-µF capacitor from PMID to GND as close to the PMID
and GND pins as possible. If operating in VIN Pass-Through Mode (PMID_REG = 111) a
lower capacitor value may be used (at least 3-µF of ceramic capacitance with DC bias derating). Note: Shorting PMID to IN pin is not recommended as it may cause large discharge
current from battery to IN if IN pin is not truly floating.
Digital supply LDO. Connect a 2.2-µF from this pin to ground. A 4.7-µF capacitor to ground
recommended if loaded externally.
Charge Enable. Drive CE low or leave disconnected to enable charging when VIN is valid.
Drive CE high to disable charge when VIN is present. CE is pulled low internally with 900-kΩ
resistor. CE has no effect when VIN is not present.
Low Power Mode Enable. Drive this pin low to enable the device in low power mode when
powered by the battery. LP is pulled low internally with 900-kΩ resistor. This pin has no
effect when VIN is present.
INT is an open-drain output that signals fault interrupts. When a fault occurs, a 128-µs pulse
is sent out as an interrupt for the host. INT is enabled/disabled using the MASK_INT bit in
the control register.
4
Submit Documentation Feedback Copyright © 2019, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Product Folder Links: BQ25155
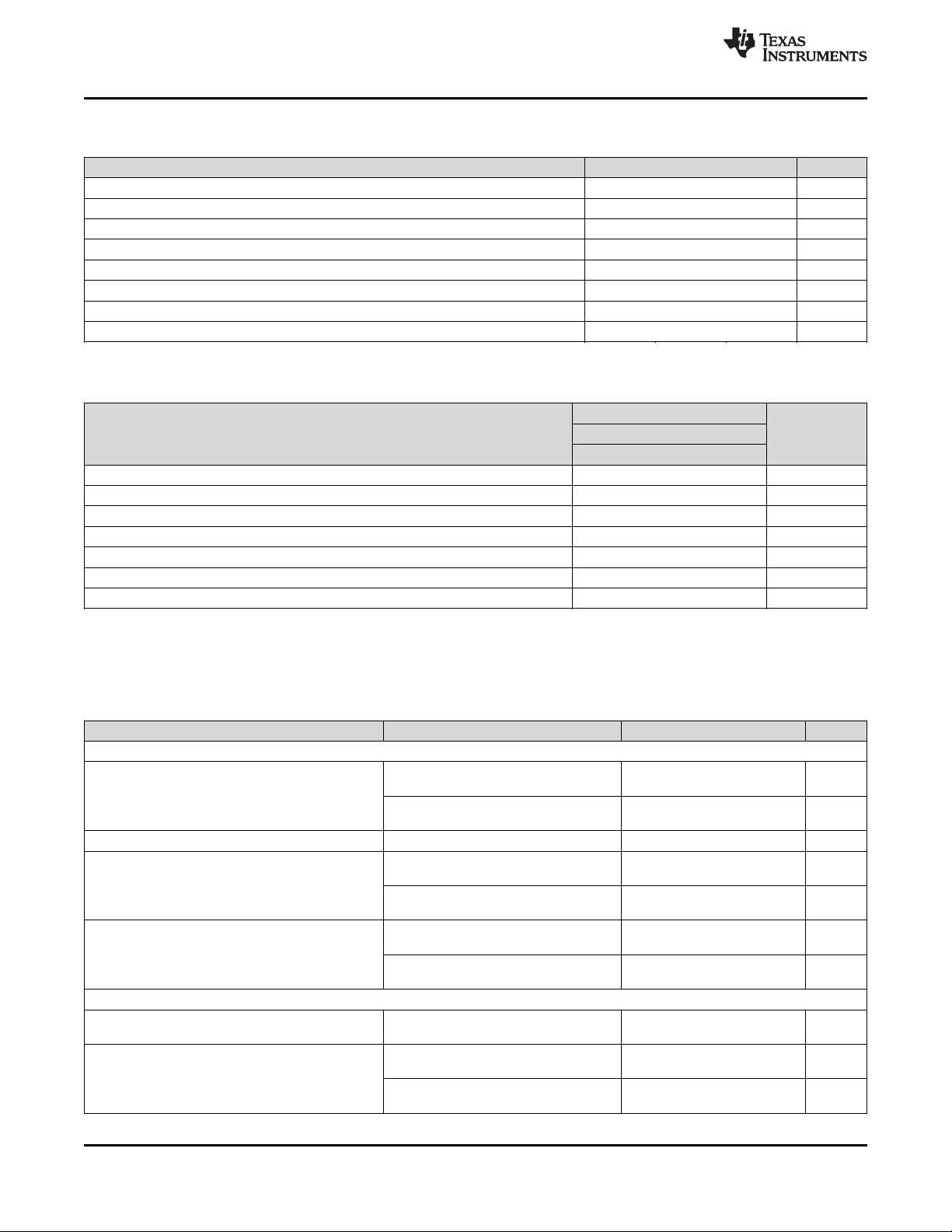
www.ti.com
PIN
NAME NO.
MR C1 I
LS/LDO D4 O
VINLS E4 I
BAT A3, B3 I/O
TS B4 I
PG B1 O
VIO E1 I
NC C3 I
SLUSDO1A –JUNE 2019–REVISED JULY 2019
Pin Functions (continued)
I/O DESCRIPTION
Manual Reset Input. MR is a general purpose input that must be held low for greater than
t
HWRESET
up the device out of Ship Mode when pressed for at least t
pull-up resistor to BAT.
Load Switch or LDO output. Connect 2.2 µF of ceramic capacitance to this pin to assure
stability. Be sure to account for capacitance bias voltage derating when selecting the
capacitor.
Input to the Load Switch / LDO output. Connect at least 1 µF of ceramic capacitance from
this pin to ground.
Battery Connection. Connect to the positive terminal of the battery. Bypass BAT to GND with
at least 1 µF of ceramic capacitance.
Battery Pack NTC Monitor. Connect TS to a 10-kΩ NTC thermistor in parallel to a 10-kΩ
resistor. If TS function is not to be used connect a 5-kΩ resistor from TS to ground.
Open-drain Power Good status indication output. PG is pulled to GND when VIN is above
V
specified limits. Connect PG to the desired logic voltage rail using a 1-kΩ to 100-kΩ resistor,
or use with an LED for visual indication. PG can also be configured through I2C as a pushbutton level shifted output (MR), where the output of the PG pin reflects the status of the MR
input, but pulled up to the desired logic voltage rail using a 1-kΩ to 100-kΩ resistor. The PG
pin can also be configured as a general purpose open drain output.
System IO supply. Connect to system IO supply to allow level shifting of input signals (SDA,
SCL, LP and CE) to the device internal digital domain. Connect to VDD when external IO
supply is not available.
No Connect. Connect to ground if possible for better thermal dissipation or leave floating. Do
not connect to a any voltage source or signal to avoid higher quiescent current.
to go into HW Reset and power cycle the output rails. If MR is also used to wake
+ V
BAT
and less than V
SLP
. PG is high-impedance when the input power is not within
OVP
. MR has in internal 125-kΩ
WAKE1
BQ25155
7 Specifications
7.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
over operating free-air temperature range (unless otherwise noted)
IN –0.3 20 V
Voltage
TS, ADCIN, VDD, NC –0.3 1.95 V
All other pins –0.3 5.5 V
IN 0 800 mA
Current
BAT, PMID –0.5 1.5 A
INT, ADCIN, PG 0 10 mA
Junction temperature, T
Storage temperature, T
J
stg
(1) Stresses beyond those listed under Absolute Maximum Rating may cause permanent damage to the device. These are stress ratings
only, which do not imply functional operation of the device at these or any other conditions beyond those indicated under Recommended
Operating Condition. Exposure to absolute-maximum-rated conditions for extended periods may affect device reliability.
7.2 ESD Ratings
Human body model (HBM), per
V
(ESD)
Electrostatic discharge
(1) JEDEC document JEP155 states that 500-V HBM allows safe manufacturing with a standard ESD control process.
(2) JEDEC document JEP157 states that 250-V CDM allows safe manufacturing with a standard ESD control process.
ANSI/ESDA/JEDEC JS-001, all pins
Charged device model (CDM), per JEDEC
specification JESD22-C101, all pins
(1)
MIN MAX UNIT
–40 125 °C
–55 150 °C
VALUE UNIT
(1)
±2000
V
(2)
±500
Product Folder Links: BQ25155
Submit Documentation FeedbackCopyright © 2019, Texas Instruments Incorporated
5
BQ25155
SLUSDO1A –JUNE 2019–REVISED JULY 2019
www.ti.com
7.3 Recommended Operating Conditions
over operating free-air temperature range (unless otherwise noted)
MIN NOM MAX UNIT
V
BAT
V
IN
V
INLS
V
IO
V
ADCIN
I
LDO
I
PMID
T
A
(1) Based on minimum V
Battery voltage range 2.4 4.6 V
Input voltage range 3.15 5.25
LDO input voltage range 2.2 5.25
(1)
(1)
V
V
IO supply voltage range 1.2 3.6 V
ADC input voltage range 0 1.2 V
LDO output current 0 100 mA
PMID output current 0 500 mA
Operating free-air temperature range –40 85 °C
value. 5.5V under typical conditions
OVP
7.4 Thermal Information
BQ25155
THERMAL METRIC
R
θJA
R
θJA
R
θJC(top)
R
θJB
Ψ
JT
Ψ
JB
R
θJC(bot)
Junction-to-ambient thermal resistance
Junction-to-ambient thermal resistance 74.4 °C/W
Junction-to-case (top) thermal resistance 0.5 °C/W
Junction-to-board thermal resistance 17.6 °C/W
Junction-to-top characterization parameter 0.3 °C/W
Junction-to-board characterization parameter 17.7 °C/W
Junction-to-case (bottom) thermal resistance N/A °C/W
(1) For more information about traditional and new thermal metrics, see the Semiconductor and IC Package Thermal Metrics application
report.
(2) Measured in BQ25155EVM board.
(1)
UNITYFP (DSBGA)
20-PIN
(2)
36.1 °C/W
7.5 Electrical Characteristics
VIN= 5V, V
INPUT CURRENTS
I
IN
I
BAT_SHIP
I
BAT_LP
I
BAT_ACTI
VE
POWER PATH MANAGEMENT AND INPUT CURRENT LIMIT
V
PMID_RE
G
V
PMID_RE
G_ACC
= 3.6V. -40°C < TJ< 125°C unless otherwise noted. Typical data at TJ= 25°C
BAT
PARAMETER TEST CONDITIONS MIN TYP MAX UNIT
PMID_MODE = 01, VIN= 5V, V
Input supply current
3.6V
0°C <TJ< 85°C , VIN= 5V, V
Charge Disabled
Battery Discharge Current in Ship Mode 0°C <TJ< 60°C ,VIN= 0V , V
0°C <TJ< 60°C ,VIN= 0V , V
Battery Quiescent Current in Low-power
Mode
LDO Disabled
0°C <TJ< 60°C ,VIN= 0V , V
LDO Enabled
0°C <TJ< 85°C ,VIN= 0V , V
Battery Quiescent Current in Active
Mode
LDO Disabled
0°C <TJ< 85°C ,VIN= 0V , V
LDO Enabled
Default System (PMID) Regulation
Voltage
VIN= 5V, V
System Regulation Voltage Accuracy
100mA, TJ= 25°C
VIN= 5V, V
500mA
PMID_REG
PMID_REG
= 4.5V. I
= 4.5V. I
=
BAT
= 3.6V
BAT
= 3.6V 10 150 nA
BAT
= 3.6V,
BAT
BAT
BAT
BAT
= 3.6V,
= 3.6V,
= 3.6V,
0.46 1.2 µA
1.7 3.5 µA
18 25 µA
21 27 µA
500 µA
4.5 V
=
PMID
PMID
= 0-
-1 1 %
–3 3 %
2 mA
6
Submit Documentation Feedback Copyright © 2019, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Product Folder Links: BQ25155
www.ti.com
Electrical Characteristics (continued)
BQ25155
SLUSDO1A –JUNE 2019–REVISED JULY 2019
VIN= 5V, V
R
ON(IN-
PMID)
V
BSUP1
V
BSUP2
I
ILIM
= 3.6V. -40°C < TJ< 125°C unless otherwise noted. Typical data at TJ= 25°C
BAT
Input FET ON resistance
Enter supplements mode threshold
Exit supplements mode threshold
Input Current Limit
Input DPM voltage threshold where
V
IN_DPM
current in reduced
Accuracy –3 3 %
BATTERY CHARGER
V
DPPM
R
ON(BAT-
PMID)
V
BATREG
PMID voltage threshold when charge
current is reduced
Battery Discharge FET On Resistance V
Charge Voltage Programmable charge voltage range 3.6 4.6 V
Voltage Regulation Accuracy 0.5 0.5 %
Fast Charge Programmable Current
I
CHARGE
Range
Fast Charge Current Accuracy TJ= 25°C, I
I
PRECHAR
GE
Precharge current Precharge current programmable range 1.25 77.5 mA
Precharge Current Accuracy -40°C < TJ< 85°C –10 10 %
Termination Charge Current
I
TERM
Accuracy
V
LOWV
V
SHORT
I
SHORT
V
RCH
R
PMID_PD
Programmable voltage threshold for precharge to fast charge transitions
Battery voltage threshold for short
detection
Charge Current in Battery Short
Condition
Recharge Threshold voltage
PMID pull-down resistance V
VDD
V
DD
I
LOAD_VD
D
VDD LDO output voltage
Maximum VDD External load capability V
LS/LDO
PARAMETER TEST CONDITIONS MIN TYP MAX UNIT
I
= 500mA (ILIM = 110), VIN= 5V, I
ILIM
= 150mA
V
> V
BAT
BAT
> V
BATUVLO
BATUVLO
Charge disabled
V
Charge disabled
, DPPM enabled or
, DPPM enabled or
IN
280 520 mΩ
V
<
PMID
V
–
BAT
40mV
V
<
PMID
V
–
BAT
20mV
mV
mV
Programmable Range 50 600 mA
I
= 50mA 45 50 mA
ILIM
I
= 100mA 90 100 mA
ILIM
I
= 150mA 135 150 mA
ILIM
I
= 500mA 450 500 mA
ILIM
Programmable Range 4.2 4.9 V
V
- V
PMID
BAT
V
BAT
LOWV
= 4.35V, I
< V
BAT
= 100mA 100 175 mΩ
BAT
< V
BATREG
> 5mA –5 5 %
CHARGE
Termination Current Programmable
Range
TJ= 25°C, I
= 100mA
-10°C < TJ< 85°C, I
I
= 100mA
CHARGE
TERM
= 10% I
TERM
CHARGE
= 10% I
, I
CHARGE
CHARGE
1.25 500 mA
1 31 %
–5 5 %
,
–10 10 %
200 mV
VBAT rising. Programmable Range 2.8 3 V
VBAT falling, VIN = 5V 2.41 2.54 2.67 V
I
V
< V
BAT
SHORT
V
falling, V
BAT
140mV setting
V
falling, V
BAT
200mV setting
= 3.6V 25 Ω
PMID
V
= 3.6V, VIN= 0V, 0 < I
BAT
10mA
> 3V 10 mA
PMID
BATREG
BATREG
= 4.2V, V
= 4.2V, V
LOAD_VDD
RCH
RCH
=
=
<
PRECHAR
GE
140 mV
200 mV
1.8 V
mA
Product Folder Links: BQ25155
Submit Documentation FeedbackCopyright © 2019, Texas Instruments Incorporated
7
BQ25155
SLUSDO1A –JUNE 2019–REVISED JULY 2019
Electrical Characteristics (continued)
www.ti.com
VIN= 5V, V
= 3.6V. -40°C < TJ< 125°C unless otherwise noted. Typical data at TJ= 25°C
BAT
PARAMETER TEST CONDITIONS MIN TYP MAX UNIT
Input voltage range for Load switch
Mode
V
INLS
Input voltage range for LDO Mode
LDO programmable output voltage range 0.6 3.7 V
V
LDO
ΔV
OUT
ΔV
V
IN
R
DOSN_L
DO
R
DSCH_LS
LDO
I
OCL_LDO
LDO output accuracy
/ΔI
OUT
DC Load Regulation
/Δ
OUT
DC Line Regulation
Switch On resistance V
Discharge FET On-resistance for LS V
Output Current Limit V
LDO VINLS quiescent current in LDO
I
IN_LDO
mode
OFF State Supply Current V
ADC
Resolutio
n
t
ADC_CON
V
Resolutio
n
Bits reported by ADC 16 Bits
Conversion-time
Effective Resolution
ADC TS Accuracy
Accuracy
ADC ADCIN Accuracy
ADC VBAT Accuracy
BATTERY PACK NTC MONITOR
V
HOT
V
WARM
V
COOL
V
COLD
V
OPEN
V
HYS
I
TS_BIAS
High temperature threshold VTSfalling, -10°C < TJ< 85°C 0.182 0.185 0.189 V
Warm temperature threshold VTSfalling, -10°C < TJ< 85°C 0.262 0.265 0.268 V
Cool temperature threshold VTSrising, -10°C < TJ< 85°C 0.510 0.514 0.518 V
Cold temperature threshold VTSrising, -10°C < TJ< 85°C 0.581 0.585 0.589 V
TS Open threshold VTSrising, -10°C < TJ< 85°C 0.9 V
Threshold hysteresis 4.7 mV
TS bias current -10°C < TJ< 85°C 78.4 80 81.6 µA
PROTECTION
V
UVLO
IN active threshold voltage
0.8 5.5 V
2.2 or
V
LDO
500mV
+
5.5 V
TJ= 25°C –2 2 %
V
= 1.8V, V
LDO
0°C < TJ< 85°C, 1 mA < I
V
= 1.8V
LDO
0°C < TJ< 85°C, Over V
= 100mA, V
= 3.6V 250 450 mΩ
INLS
= 3.6V 40 Ω
INLS
= 0V 200 300 mA
LS/LDO
V
= V
BAT
INLS
= V
BAT
INLS
LDO
INLS
= 1.8V
=3.6V. I
= 1mA –3 3 %
LOAD
< 150mA,
INLS
OUT
range, I
OUT
1.2 %
0.5 %
=3.6V 0.9 µA
=3.6V 0.25 µA
ADC_SPEED = 00 24 ms
ADC_SPEED = 01 12 ms
ADC_SPEED = 10 6 ms
ADC_SPEED = 11 3 ms
ADC_SPEED = 00 12 Bits
ADC_SPEED = 10 10 Bits
ADC_SPEED = 00, VTS= 0.4V, -10°C <
TJ< 85°C
ADC_SPEED = 00, V
< TJ< 85°C
ADC_SPEED = 00, V
TJ< 85°C
= 0.4V, -10°C
ADCIN
= 4.2V, -10°C <
BAT
–1. 1 %
–1 1 %
–0.4 0.4 %
VINrising 3.4 V
VINfalling 3.25 V
8
Submit Documentation Feedback Copyright © 2019, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Product Folder Links: BQ25155

www.ti.com
Electrical Characteristics (continued)
BQ25155
SLUSDO1A –JUNE 2019–REVISED JULY 2019
VIN= 5V, V
= 3.6V. -40°C < TJ< 125°C unless otherwise noted. Typical data at TJ= 25°C
BAT
PARAMETER TEST CONDITIONS MIN TYP MAX UNIT
Battery undervoltage Lockout Threshold
Voltage
V
BATUVLO
Accuracy –3 3 %
Battery undervoltage Lockout Threshold
Voltage at Power Up
V
SLP_ENT
RY
V
SLP_EXIT
V
OVP
Sleep Entry Threshold (VIN- V
Sleep Exit Threshold (VIN- V
Input Supply Over Voltage Threshold
Battery Over Current Threshold
I
BAT_OCP
Programmable range
Current Limit Accuracy –30 30 %
T
SHUTDO
WN
T
HYS
Thermal shutdown trip point 125 °C
Thermal shutdown trip point hysteresis 15 °C
I2C INTERFACE (SCL and SDA)
I2C Frequency 100 400 kHz
V
V
V
I
IL
IH
OL
LKG
Input Low threshold level V
Input High Threshold level V
Output Low threshold level V
High-level leakage Current V
/MR INPUT
R
PU
V
IL
Internal pull up resistance 90 125 170 kΩ
/MR Input Low threshold level V
/INT, /PG OUTPUTS
V
I
OL
LKG
Output Low threshold level V
/INT Hi level leakage Current High Impedance, V
/CE, /LP INPUTS
R
PDOWN
V
IL
V
IH
/CE pull down resistance 900 kΩ
Input Low threshold level VIO= 1.8V 0.45 V
/CE Input High Threshold level VIO= 1.8V 1.35 V
) 2.0V < V
BAT
) 2.0V < V
BAT
Programmable range, 150 mV
Hysteresis
V
rising, VIN= 0V, TJ= 25°C 3.15 V
BAT
BAT
BAT
< V
< V
, VINfalling 80 mV
BATREG
BATREG
2.4 3 V
130 mV
VINrising 5.35 5.5 5.8 V
VINfalling (125mV hysteresis) 5.4 V
I
BAT_OCP
increasing 1200 1600 mA
= VIO= 1.8V
PULLUP
= VIO= 1.8V
PULLUP
= VIO= 1.8V, I
PULLUP
= VIO= 1.8V 1 µA
PULLUP
> V
BAT
BUVLO
= VIO= 1.8V, I
PULLUP
PULLUP
= 5mA
LOAD
= 5mA
LOAD
= VIO= 1.8V 1 µA
0.75 *
V
IO
0.25 *
V
IO
0.25 *
V
IO
0.3 V
0.25 *
V
IO
V
V
V
V
7.6 Timing Requirements
PARAMETER TEST CONDITIONS MIN TYP MAX UNIT
BATTERY CHARGE TIMERS
t
MAXCHG
t
PRECHG
WATCHDOG TIMERS
t
WATCHDO
G_SW
t
HW_RESE
T_WD
LDO
t
ON_LDO
Charge safety timer Programmable range 180 720 min
Precharge safety timer 0.25 * t
SW Watchdog timer 25 50 s
HW reset watchdog timer WATCHDOG_15S_ENABLE = 1 15 s
Turn ON time 100mA load, to 90% V
LDO
Product Folder Links: BQ25155
MAXCHG
500 µs
Submit Documentation FeedbackCopyright © 2019, Texas Instruments Incorporated
9
BQ25155
SLUSDO1A –JUNE 2019–REVISED JULY 2019
Timing Requirements (continued)
PARAMETER TEST CONDITIONS MIN TYP MAX UNIT
t
OFF_LDO
t
PMID_LDO
_DELAY
PUSHBUTTON TIMERS (/MR)
t
WAKE1
t
WAKE2
t
RESET_W
ARN
t
HW_RESE
T
t
RESTART(
AUTOWAK
E)
PROTECTION
t
DGL_SLP
t
DGL_OVP
t
DGL_OCP
t
REC_SC
t
RETRY_S
C
t
DGL_SHT
DWN
I2C INTERFACE
t
WATCHDO
G
t
I2CRESET
INPUT PINS (/CE and /LP)
t
LP_EXIT_I
2C
Turn OFF time 100mA load, to 10% V
Delay between PMID and LDO enable
during power up
WAKE1 Timer. Time from /MR falling
edge to INT being asserted.
WAKE2 Timer. Time from /MR falling
edge to INT being asserted.
RESET_WARN Timer. Time prior to HW
RESET
HW RESET Timer. Time from /MR falling
edge to HW Reset
RESTART Timer. Time from /MR HW
Reset to PMID power up
Deglitch time for supply rising above
V
+ V
SLP
SLP_HYS
Deglitch time for V
Threshold VIN falling below V
OVP
Battery OCP deglitch time 30 µs
Recovery time, BAT Short Circuit during
Discharge Mode
Retry window for PMID or BAT short
circuit recovery
Deglitch time, Thermal shutdown TJrising above T
I2C interface reset timer for host When enabled 50 s
I2C interface inactive reset timer 500 ms
Time for device to exit Low-power mode
and allow I2C communication
www.ti.com
LDO
30 µs
Startup 20 ms
MR_WAKE1_TIMER = 0 106 125 144 ms
MR_WAKE1_TIMER = 1 425 500 575 ms
MR_WAKE2_TIMER = 0 0.85 1 1.15 s
MR_WAKE2_TIMER = 1 1.7 2 2.3 s
MR_RESET_WARN = 00 0.42 0.5 0.58 s
MR_RESET_WARN = 01 0.85 1 1.15 s
MR_RESET_WARN = 10 1.27 1.5 1.73 s
MR_RESET_WARN = 11 1.7 2 2.3 s
MR_HW_RESET = 00 3.4 4 4.6 s
MR_HW_RESET = 01 6.8 8 9.2 s
MR_HW_RESET = 10 8.5 10 11.5 s
MR_HW_RESET = 11 11.9 14 16.1 s
AUTOWAKE = 00 0.52 0.6 0.68 s
AUTOWAKE = 01 1.05 1.2 1.35 s
AUTOWAKE = 10 2.11 2.4 2.69 s
AUTOWAKE = 11 4.4 5 5.6 s
120 µs
OVP
32 ms
250 ms
2 s
SHUTDOWN
10 µs
VIN= 0V. 1 ms
10
Submit Documentation Feedback Copyright © 2019, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Product Folder Links: BQ25155
V
INLS
(V)
R
DSON
(:)
1 1.5 2 2.5 3 3.5 4 4.5 5
0
0.2
0.4
0.6
0.8
1
1.2
D015
TJ = -40C
TJ = 25C
TJ = 85C
I
LOAD
(A)
V
LDO
(V)
0.1 0.11 0.12 0.13 0.14 0.15 0.16 0.17 0.18 0.19 0.2
0.7984
0.7992
0.8
0.8008
0.8016
0.8024
0.8032
0.804
0.8048
0.8056
0.8064
D009
TJ = -40C
TJ = 25C
TJ = 85C
I
PRECHARGE
(A)
Error (%)
0 5 10 15 20 25 30 35 40 45 50 55 60 65 70 75 80
-1.2
-1
-0.8
-0.6
-0.4
-0.2
0
0.2
0.4
0.6
0.8
1
1.2
D013
TJ = 25C
TJ = 0C
TJ = -40C
TJ = 60C
TJ = 125C
I
PRECHARGE
(mA)
Error (%)
0 5 10 15 20 25 30 35 40
-1.5
-1
-0.5
0
0.5
1
1.5
D012
TJ = 25C
TJ = 0C
TJ = -40C
TJ = 60C
TJ = 125C
V
BATREG
(V)
Error (%)
3.6 3.7 3.8 3.9 4 4.1 4.2 4.3 4.4 4.5 4.6
-0.5
-0.45
-0.4
-0.35
-0.3
-0.25
-0.2
-0.15
-0.1
-0.05
0
D011
TJ = 25C
TJ = 0C
TJ = -40C
TJ = 60C
TJ = 125C
I
CHARGE
(A)
Error (%)
0 0.05 0.1 0.15 0.2 0.25 0.3 0.35 0.4 0.45 0.5
-1.75
-1.5
-1.25
-1
-0.75
-0.5
-0.25
0
0.25
0.5
0.75
1
1.25
D014
TJ = -40C
TJ = 0C
TJ = 25C
TJ = 60C
TJ = 125C
www.ti.com
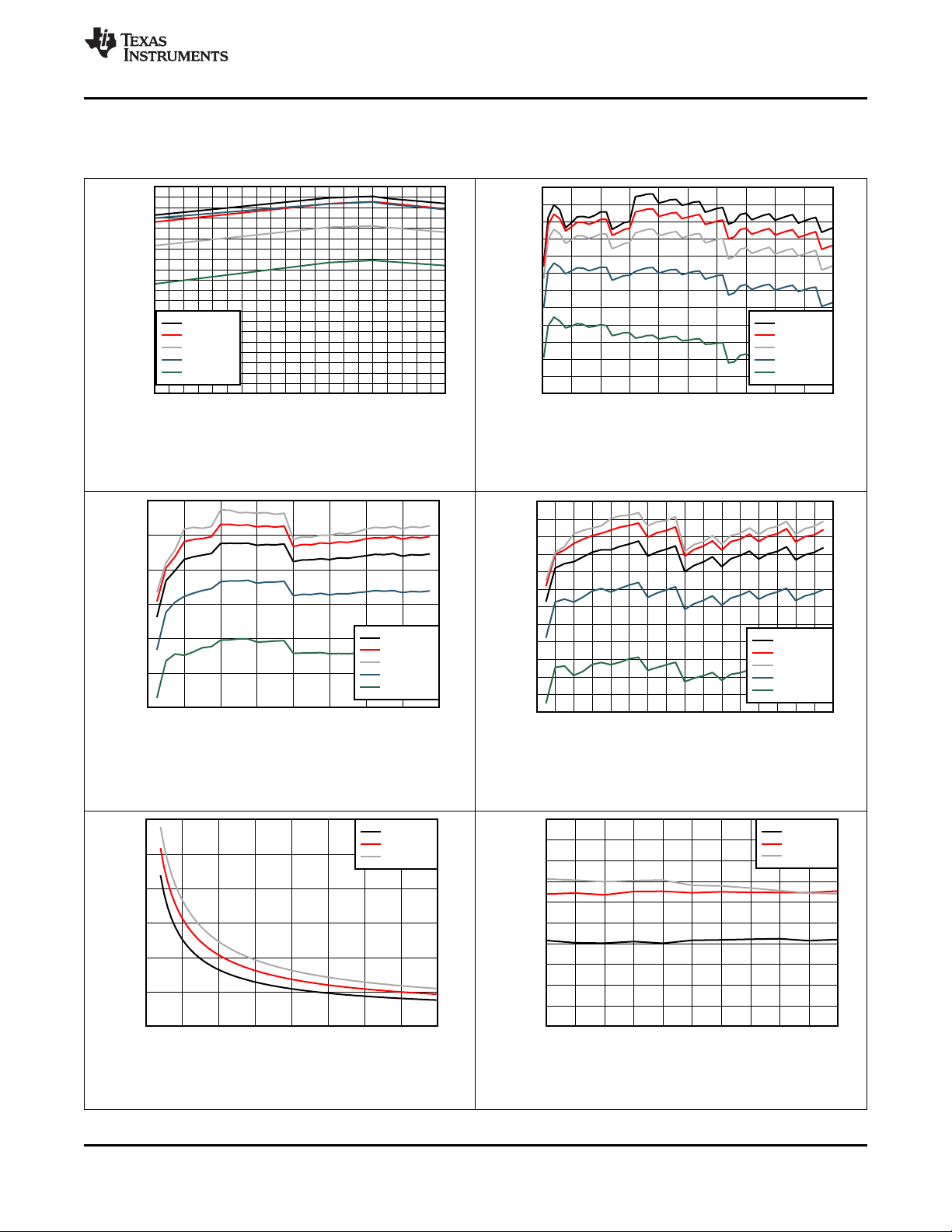
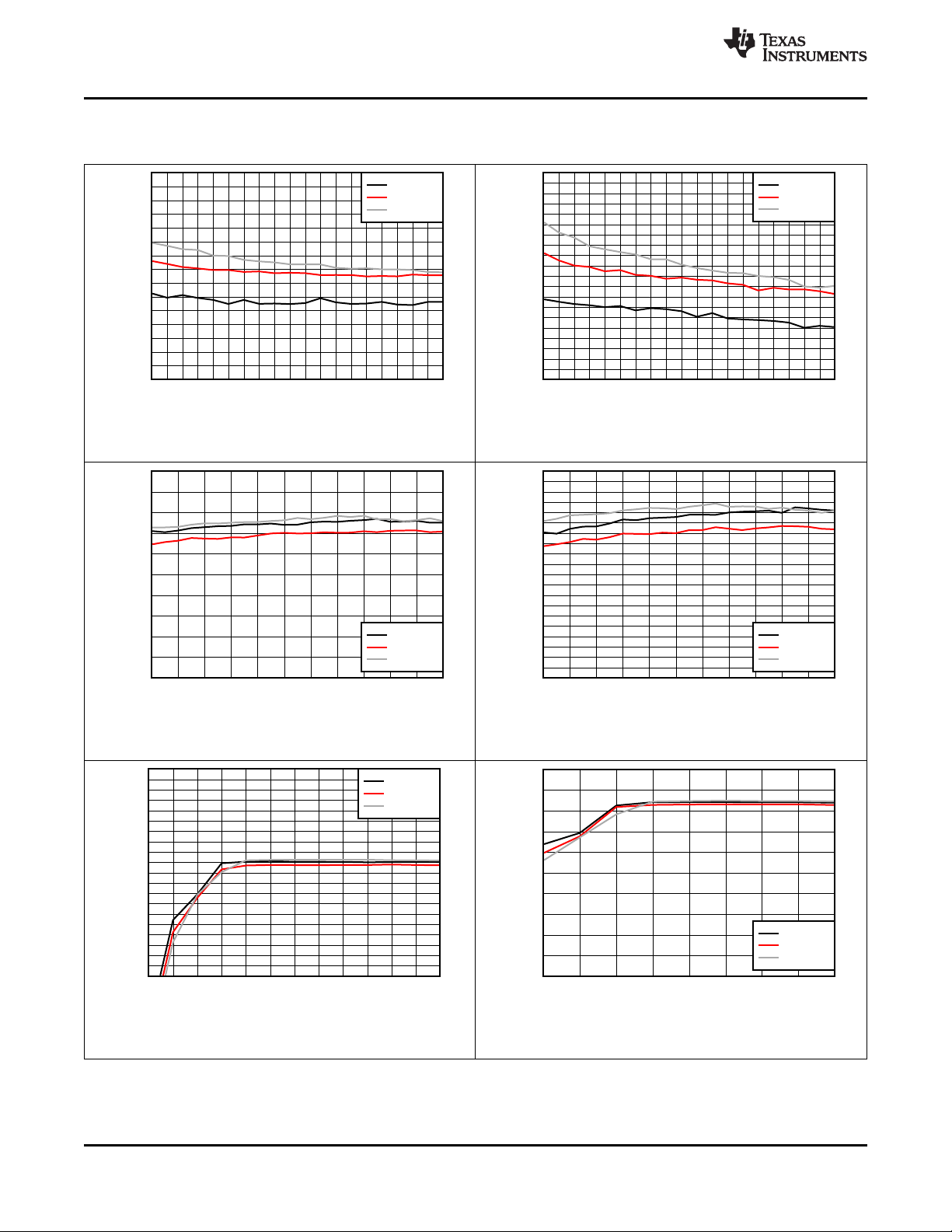
7.7 Typical Characteristics
CIN= 1 µF, C
= 10 µF, C
PMID
LSLDO
= 2.2 µF, C
= 1 µF (unless otherwise specified)
BAT
BQ25155
SLUSDO1A –JUNE 2019–REVISED JULY 2019
VIN = 5 V PMID_REG_CTRL = 111 (Pass-Through)
Figure 1. Battery Regulation Voltage Accuracy vs.
VBATREG Setting
VIN = 5 V VBAT = 2.7 V ICHARGE_RANGE = 0
Figure 3. Pre-Charge Current Accuracy vs. IPRECHARGE
setting (ICHARGE_RANGE = 0)
VIN = 5 V VBAT = 3.6 V ICHARGE_RANGE = 1
Figure 2. Charge Current Accuracy vs. ICHARGE Setting
VBUS = 5 V VBAT = 2.7 V ICHARGE_RANGE = 1
Figure 4. Pre-Charge Current Accuracy vs. IPRECHARGE
Setting (ICHARGE_RANGE = 1)
VBUS = 5 V
Figure 5. LS/LDO Switch On Resistance vs. VINLS
Product Folder Links: BQ25155
VIN = 0 V VBAT = 3.6 V VINLS = VPMID
Figure 6. LDO Load Regulation (VLDO = 0.8 V)
Submit Documentation FeedbackCopyright © 2019, Texas Instruments Incorporated
11
V
INLS
(V)
VLDO (V)
3.2 3.3 3.4 3.5 3.6 3.7 3.8 3.9 4 4.1 4.2 4.3 4.4
3.2
3.22
3.24
3.26
3.28
3.3
3.32
3.34
3.36
3.38
3.4
D006
TJ = -40C
TJ = 25C
TJ = 85C
V
INLS
(V)
V
LDO
(V)
3.6 3.7 3.8 3.9 4 4.1 4.2 4.3 4.4
3.4
3.425
3.45
3.475
3.5
3.525
3.55
3.575
3.6
3.625
3.65
D007
TJ = -40C
TJ = 25C
TJ = 85C
V
INLS
(V)
V
LDO
(V)
2.2 2.4 2.6 2.8 3 3.2 3.4 3.6 3.8 4 4.2 4.4
1.19
1.192
1.194
1.196
1.198
1.2
1.202
1.204
1.206
1.208
1.21
D004
TJ = -40C
TJ = 25C
TJ = 85C
V
INLS
(V)
V
LDO
(V)
2.2 2.4 2.6 2.8 3 3.2 3.4 3.6 3.8 4 4.2 4.4
1.79
1.792
1.794
1.796
1.798
1.8
1.802
1.804
1.806
1.808
1.81
D005
TJ = -40C
TJ = 25C
TJ = 85C
I
LOAD
(A)
V
LDO
(V)
0.01 0.03 0.05 0.07 0.09 0.11 0.13 0.15 0.17 0.19
1.79
1.792
1.794
1.796
1.798
1.8
1.802
1.804
1.806
1.808
1.81
1.812
1.814
1.816
1.818
1.82
D008
TJ = -40C
TJ = 25C
TJ = 85C
I
LOAD
(A)
V
LDO
(V)
0.01 0.03 0.05 0.07 0.09 0.11 0.13 0.15 0.17 0.19
3.29
3.294
3.298
3.302
3.306
3.31
3.314
3.318
3.322
3.326
3.33
D010
TJ = -40C
TJ = 25C
TJ = 85C
BQ25155
SLUSDO1A –JUNE 2019–REVISED JULY 2019
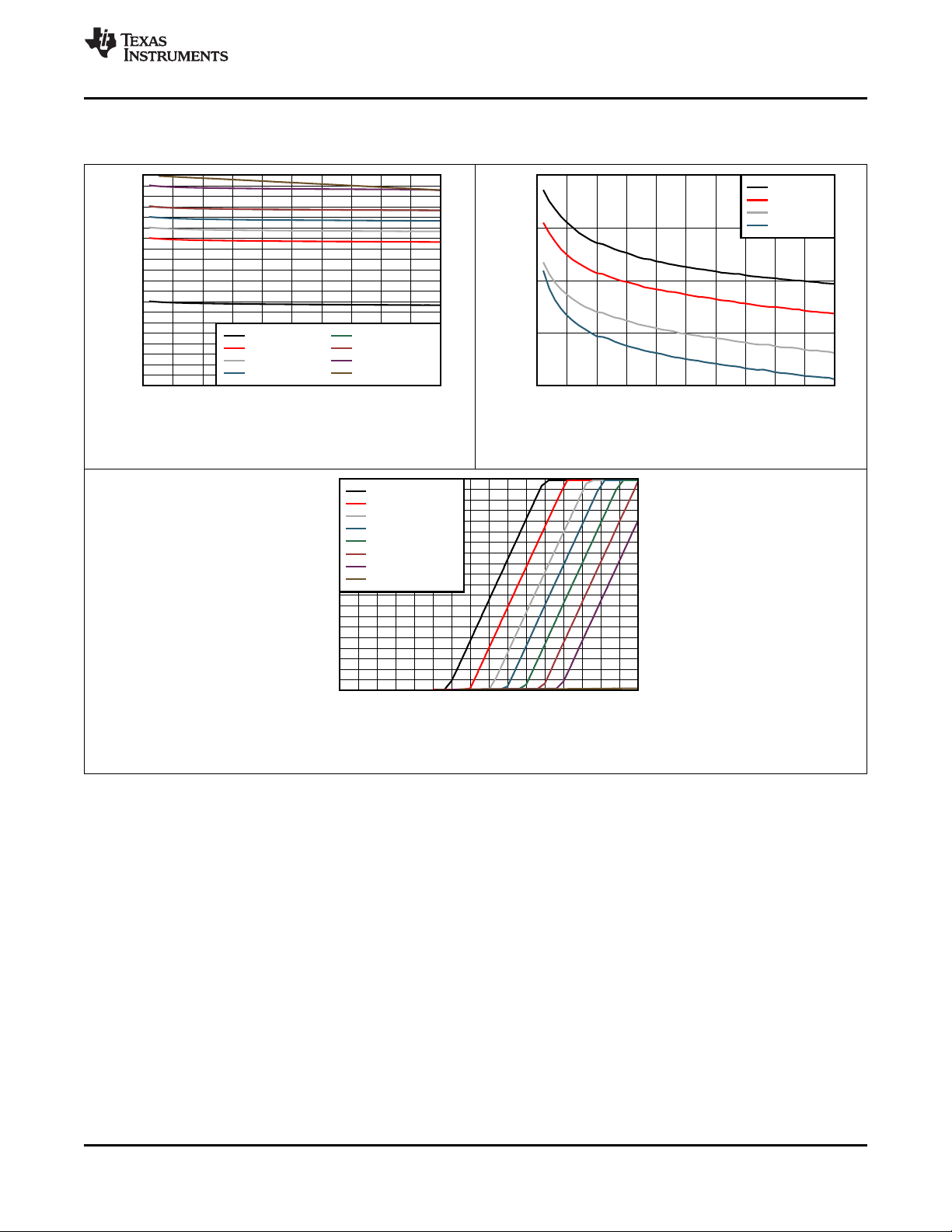
Typical Characteristics (continued)
www.ti.com
CIN= 1 µF, C
= 10 µF, C
PMID
LSLDO
= 2.2 µF, C
= 1 µF (unless otherwise specified)
BAT
VIN = 0 V VBAT = 3.6 V VINLS = VPMID
Figure 7. LDO Load Regulation (VLDO = 1.8 V)
VIN = 0 V VBAT = 3.6 V VINLS= VPMID
Figure 8. LDO Load Regulation (VLDO = 3.3 V)
VBAT = 4.4 V ILOAD = 150 mA
Figure 9. LDO Line Regulation (VLDO = 1.2 V)
12
VBAT = 4.4 V ILOAD = 150 mA
Figure 11. LDO Line Regulation (VLDO = 3.3 V)
Submit Documentation Feedback Copyright © 2019, Texas Instruments Incorporated
VBAT = 4.4 V ILOAD = 150 mA
Figure 10. LDO Line Regulation (VLDO = 1.8 V)
VBAT = 4.4 V ILOAD = 150 mA
Figure 12. LDO Line Regulation (VLDO = 3.6 V)
Product Folder Links: BQ25155
Temperature(qC)
Charge Current Reduction (%)
50 60 70 80 90 100 110 120 130
0
10
20
30
40
50
60
70
80
90
100
D004
THERM_REG = 0
THERM_REG = 1
THERM_REG = 2
THERM_REG = 3
THERM_REG = 4
THERM_REG = 5
THERM_REG = 6
THERM_REG = 7
PMID Load Current (A)
V
PMID
(V)
0 0.05 0.1 0.15 0.2 0.25 0.3 0.35 0.4 0.45 0.5
3
3.2
3.4
3.6
3.8
4
4.2
4.4
4.6
4.8
5
D001
PMID_REG = 0
PMID_REG = 1
PMID_REG = 2
PMID_REG = 3
PMID_REG = 4
PMID_REG = 5
PMID_REG = 6
PMID_REG = 7
PMID Load (A)
V
PMID
(V)
0 0.05 0.1 0.15 0.2 0.25 0.3 0.35 0.4 0.45 0.5
4.44
4.46
4.48
4.5
4.52
D003
TJ = -40°C
TJ = 25°C
TJ = 85°C
TJ = 125°C
www.ti.com
Typical Characteristics (continued)
BQ25155
SLUSDO1A –JUNE 2019–REVISED JULY 2019
CIN= 1 µF, C
= 10 µF, C
PMID
LSLDO
= 2.2 µF, C
VBAT = 0 V
Figure 13. PMID Load Regulation
= 1 µF (unless otherwise specified)
BAT
Figure 14. PMID Load Regulation vs. Temperature
VBAT = 3.6 V VIN = 5 V
VBAT = 3.6 V VIN = 5 V
Figure 15. Charge Current Thermal Regulation
Product Folder Links: BQ25155
Submit Documentation FeedbackCopyright © 2019, Texas Instruments Incorporated
13
LDO, and BAT FET Control
Device Control
V
IN
Charge
Enable
I2C
Interface
Low Power Mode
Control
Charge Control
LDO / Load Switch
Control
Thermal
Shutdown
I
BATREG
LDO
Control
UVLO
V
BATREG
V
IN_DPM
BAT
VIN
+
±
ADC
/Power Good
GP Output
Interrupt
JEITA/Temp
Battery Voltage
Charge Current
Information
For Charge Control
VDD
VIN
IIN
PMID
VIN
IIN
VPMID
ICHG
VBAT
VTS
Ext.
S
G
D
S
G
D
Q7
Q8
IN
GND
VIO
/CE
SCL
SDA
/LP
/MR
/INT
/PG
PMID
VDD
VINLS
LDO
BAT
TS
ADCIN
V
BATUVLO
Q5/Q6
1.045 x V
BAT
PMID_REG
BQ25155
SLUSDO1A –JUNE 2019–REVISED JULY 2019
www.ti.com
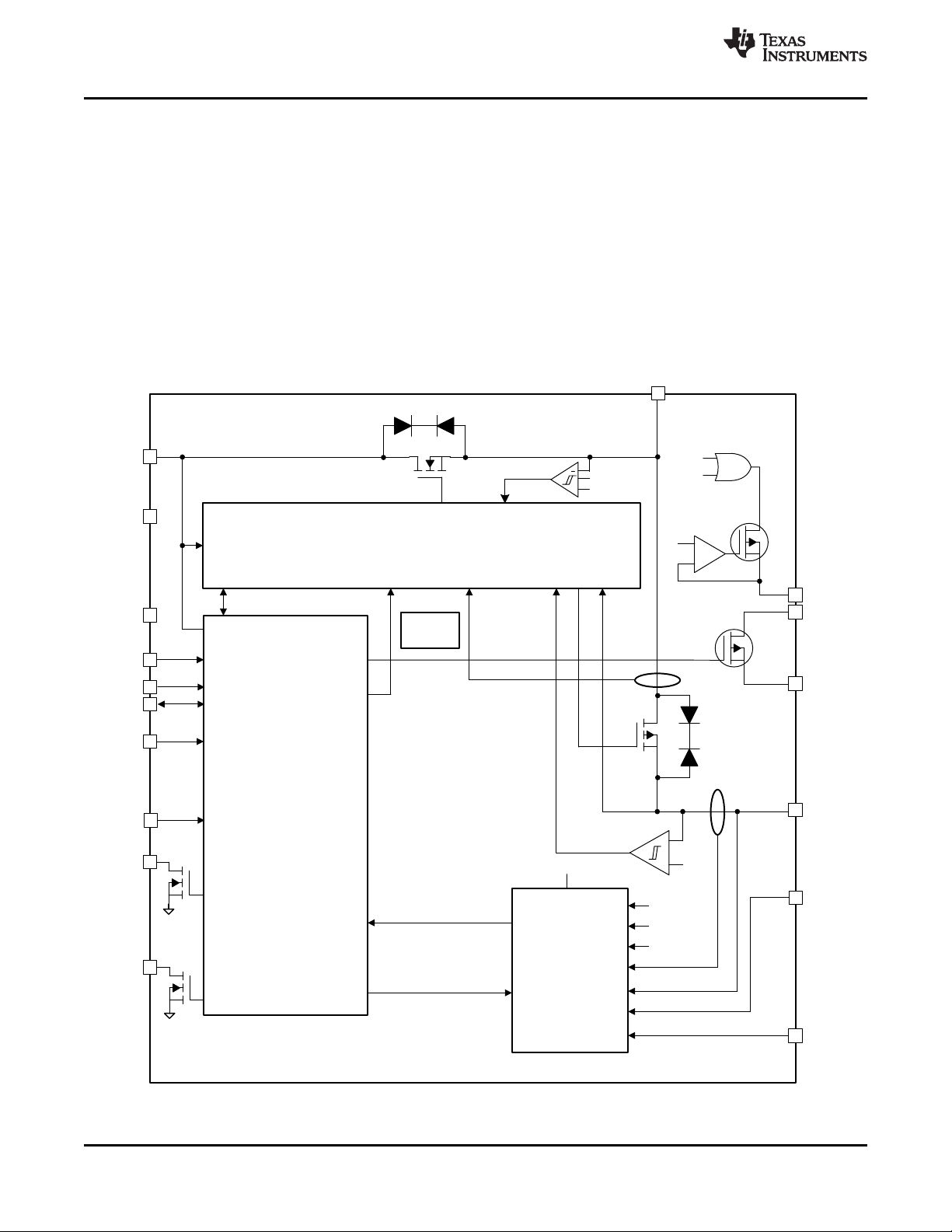
8 Detailed Description
8.1 Overview
The BQ25155 IC is a highly programmable battery management device that integrates a 500-mA linear charger
for single cell Li-Ion batteries, a 16-bit ADC, a general purpose LDO that may be configured as a load switch,
and a push-button controller. Through it's I2C interface the host may change charging parameters such as
battery regulation voltage and charge current, and obtain detailed device status and fault information. The host
may also read ADC measurements for battery and input voltage among other parameters, including the ADCIN
pin voltage. The push-button controller allows the user to reset the system without any intervention from the host
and wake up the device from Ship Mode.
8.2 Functional Block Diagram
14
Submit Documentation Feedback Copyright © 2019, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Product Folder Links: BQ25155

BQ25155
www.ti.com
SLUSDO1A –JUNE 2019–REVISED JULY 2019
8.3 Feature Description
8.3.1 Linear Charger and Power Path
The BQ25155 IC integrates a linear charger that allows the battery to be charged with a programmable charge
current of up to 500 mA. In addition to the charge current, other charging parameters can be programmed
through I2C such as the battery regulation voltage, pre-charge current, termination current, and input current limit
current.
The power path allows the system to be powered from PMID, even when the battery is dead or charging, by
drawing power from IN pin. It also prioritizes the system load connected to PMID, reducing the charging current,
if necessary, in order support the load when input power is limited. If the input supply is removed and the battery
voltage level is above V
BATUVLO
There are several control loops that influence the charge current: constant current loop (CC), constant voltage
loop (CV), input current limit, VDPPM, and VINDPM. During the charging process, all loops are enabled and the
one that is dominant takes control regulating the charge current as needed. The charger input has back to back
blocking FETs to prevent reverse current flow from PMID to IN. They also integrate control circuitry regulating the
input current and prevents excessive currents from being drawn from the IN power supply for more reliable
operation.
The device supports multiple battery regulation voltage regulation settings (V
options to support multiple battery chemistries for single-cell applications.
A more detailed description of the charger functionality is presented in the following sections of this document.
, PMID will automatically and seamlessly switch to battery power.
) and charge current (I
BATREG
CHARGE
)
8.3.1.1 Battery Charging Process
The following diagram summarizes the charging process of the BQ25155 charger.
Product Folder Links: BQ25155
Submit Documentation FeedbackCopyright © 2019, Texas Instruments Incorporated
15
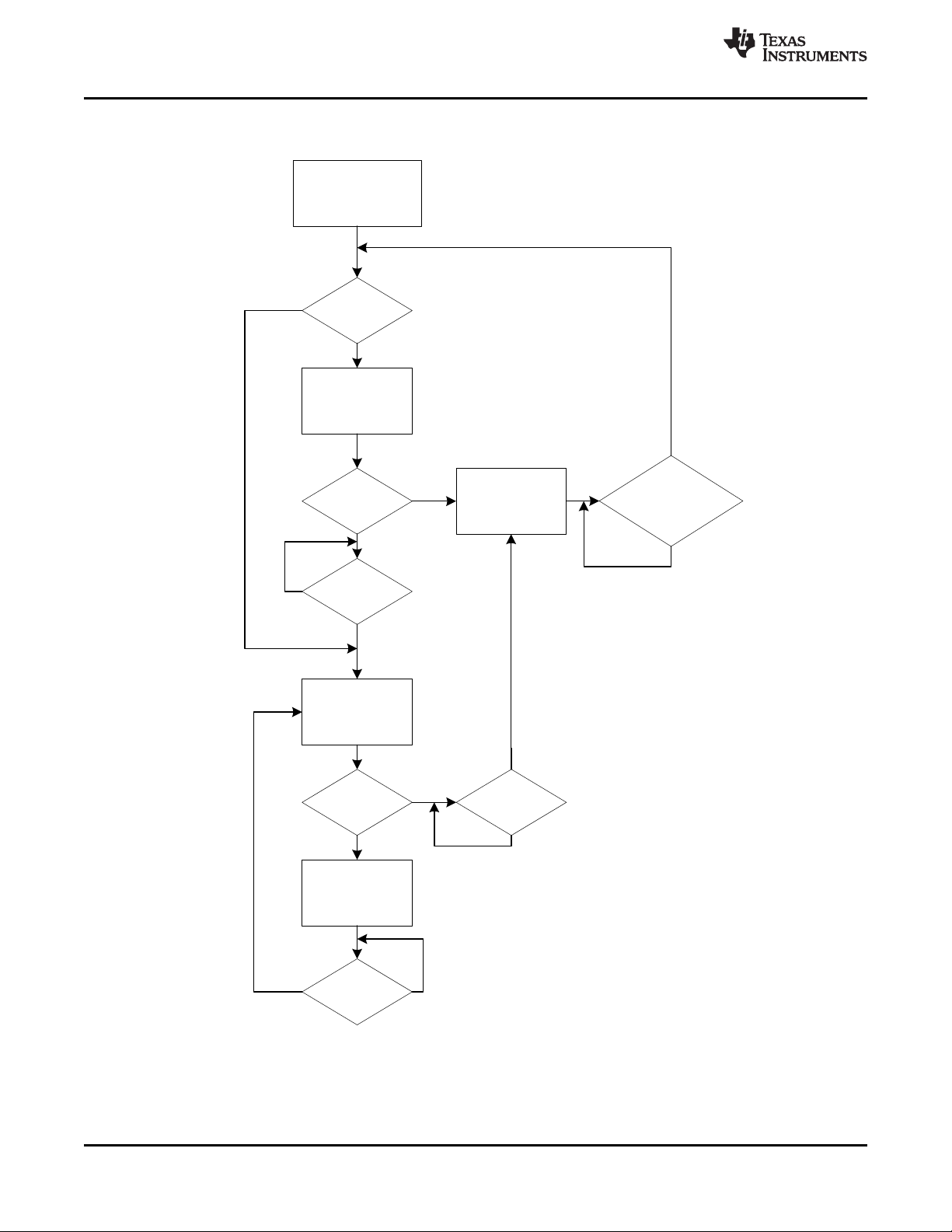
V
BAT
< V
LOWV
Start Precharge
Icharge set by I2C
Connect VIN
Precharge safety
timer expired?
Stop Charging and set
Fault bits
/CE toggled or VIN and
removed and
reconnected?
V
BAT
> V
LOWV
Start FastCharge
Icharge set by I2C
I
BAT
< I
TERM
Fast Charge safety
timer expired?
Charge Done (Set bit
and interrupt and
disconnect BATFET)
V
BAT
< V
BAT
- V
RCH
Yes
No
Yes
No
Yes
No
Yes
No
Yes
No
Yes
No
Yes No
BQ25155
SLUSDO1A –JUNE 2019–REVISED JULY 2019
Feature Description (continued)
www.ti.com
16
Figure 16. BQ25155 Charger Flow Diagram
Submit Documentation Feedback Copyright © 2019, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Product Folder Links: BQ25155
www.ti.com
Feature Description (continued)
BQ25155
SLUSDO1A –JUNE 2019–REVISED JULY 2019
When a valid input source is connected (VIN> V
UVLO
and V
BAT+VSLP
< VIN< V
), the state of the CE pin
OVP
determines whether a charge cycle is initiated. When the CE input is high and a valid input source is connected,
the battery charge FET is turned off, preventing any kind of charging of the battery. A charge cycle is initiated
when the CHARGE_DISABLE bit is written to 0 and CE pin in low. Table 1 shows the CE pin and bit priority to
enable/disable charging.
Table 1. Charge Enable Function Through CE Pin and CE Bit
CE PIN CHARGE _DISABLE BIT CHARGING
0 0 Enabled
0 1 Disabled
1 0 Disabled
1 1 Disabled
Figure 17 shows a typical charge cycle.
Figure 17. BQ25155 Typical Charge Cycle
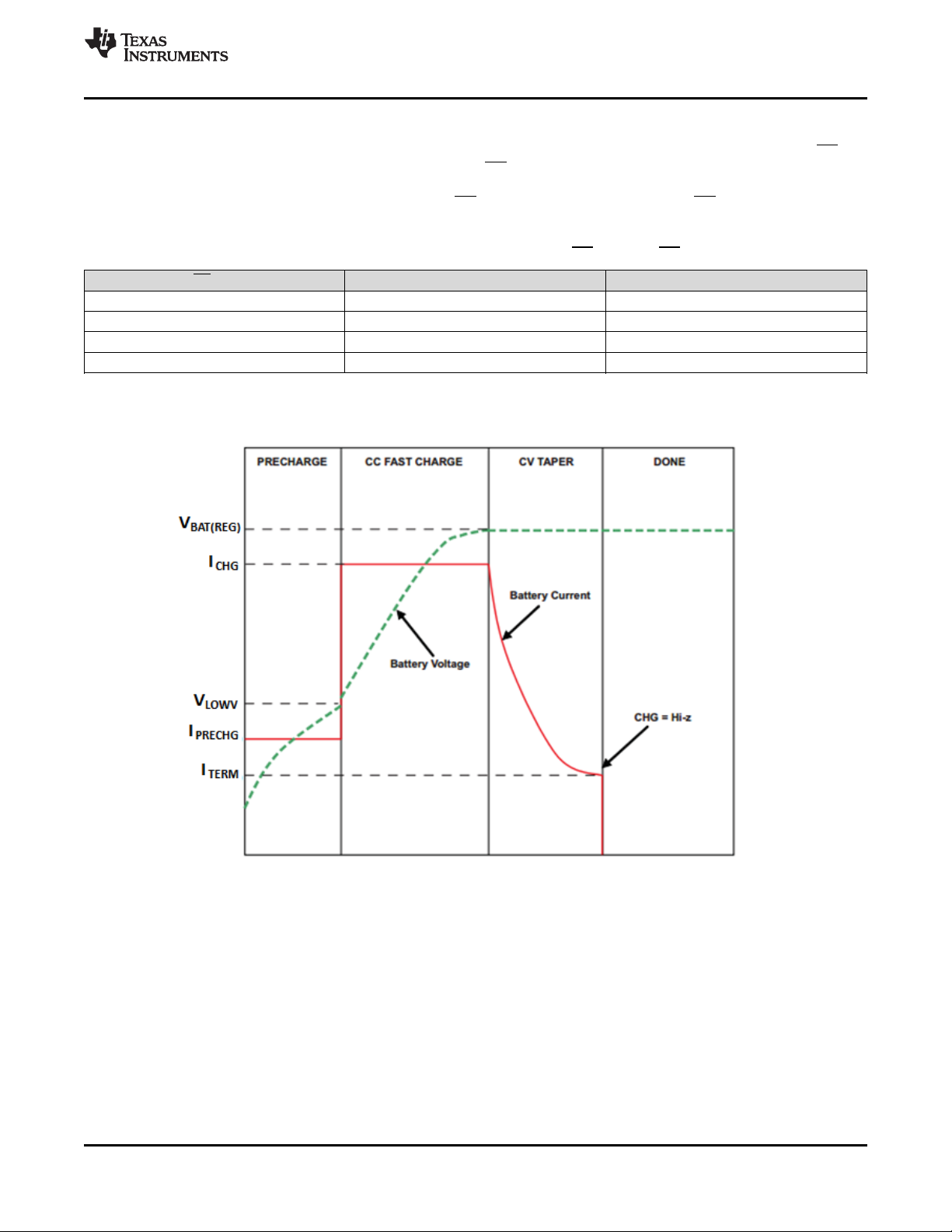
8.3.1.1.1 Pre-Charge
In order to prevent damage to the battery, the device will charge the battery at a much lower current level when
the battery voltage (V
through I2C. Once the battery voltage reaches V
charging the battery at I
) is below the V
BAT
.
CHARGE
level. The pre-charge current (I
LOWV
, the charger will then operate in Fast Charge Mode,
LOWV
PRECHARGE
) can be programmed
During pre-charge, the safety timer is set to 25% of the safety timer value during fast charge.
Submit Documentation FeedbackCopyright © 2019, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Product Folder Links: BQ25155
17

BQ25155
SLUSDO1A –JUNE 2019–REVISED JULY 2019
8.3.1.1.2 Fast Charge
The charger has two main control loops that control charging when V
BAT
> V
LOWV
Constant Voltage (CV) loops. When the CC loop is dominant, typically when V
is charged at the maximum charge current level I
, unless there is a TS fault condition (JEITA operation),
CHARGE
: the Constant Current (CC) and
BAT
< V
BATREG
– 50 mV, the battery
www.ti.com
thermal charge current foldback is active, VINDPM is active, or DPPM is active. (See respective sections for
details on these modes of operation.) Once the battery voltage approaches the V
BATREG
level, the CV loop
becomes more dominant and the charging current starts tapering off as shown in Figure 17. Once the charging
current reaches the termination current (I
charged to V
8.3.1.1.3 Pre-Charge to Fast Charge Transitions and Charge Current Ramping
BATREG
level, the regulated PMID voltage should be set to at least 200mV above V
) charging is stopped. Note that to ensure that the battery is
TERM
BATREG
.
Whenever a change in the charge current setting is triggered, whether it occurs due to I2C programming by the
host, Pre-Charge/Fast Charge transition or JEITA TS control, the device will temporarily disable charging (for ~ 1
ms) before updating the charge current value.
8.3.1.1.4 Termination
The device will automatically terminate charging once the charge current reaches I
, which is programmable
TERM
through I2C.
After termination the charger will operate in high impedance mode, disabling the BATFET to disconnect the
battery. Power is provided to the system (PMID) by IN supply as long and VIN> V
V
.
OVP
UVLO
and V
BAT+VSLP
< VIN<
Termination is only enabled when the charger CV loop is active in fast charge operation. No termination will
occur if the charge current reaches I
while VINDPM or DPPM is active as well as the thermal regulation
TERM
loop. Termination is also disabled when operating in the TS WARM region. The charger only goes to termination
when the current drops to I
due to the battery reaching the target voltage and not due to the charge current
TERM
limitation imposed by the previously mentioned control loops.
8.3.1.2 JEITA and Battery Temperature Dependent Charging
The charger can be configured through I2C setting to provide JEITA support, automatically reducing the charging
current and voltage depending on the battery temperature as monitored by an NTC thermistor connected to the
BQ25155 TS pin. See External NTC Monitoring (TS) section for details.
8.3.1.3 Input Voltage Based Dynamic Power Management (VINDPM)
The VINDPM loop prevents the input voltage from collapsing to a point where charging would be interrupted by
reducing the current drawn by charger in order to keep VINfrom dropping below V
. The VINDPM function is
IN_DPM
disabled by default and may be enabled through I2C command.
During the normal charging process, if the input power source is not able to support the programmed or default
charging current and system load, the voltage at the IN pin decreases. Once the IN voltage drops to V
IN_DPM
, the
VINDPM current and voltage loops will reduce the input current through the blocking FETs, to prevent the further
drop of the supply voltage. The V
threshold is programmable through the I2C register from 4.2 V to 4.9 V in
IN_DPM
100-mV steps. It can be disabled completely as well. When the device enters this mode, the charge current may
be lower than the set value and the V
V
IN_DPM
is active. Additionally, termination is disabled.
INDPM_STAT
bit is set. If the 2X timer is set, the safety timer is extended while
8.3.1.4 Dynamic Power Path Management Mode (DPPM)
With a valid input source connected, the power-path management circuitry monitors the input voltage and current
continuously. The current into IN is shared at PMID between charging the battery and powering the system load
connected at PMID. If the sum of the charging and load currents exceeds the preset maximum input current set
by ILIM, PMID starts to drop. If PMID drops below the DPPM voltage threshold, the charging current is reduced
by the DPPM loop through the BATFET. If PMID continues to drop after BATFET charging current is reduced to
zero, the part will enter supplement mode when PMID falls below the supplement mode threshold (V
V
). Battery termination is disabled while in DPPM mode. The V
BSUP1
V
. This will enable supporting lower input voltages to minimize losses through the linear charger.
BAT
threshold is typically 200 mV above
DPPM
BAT
-
18
Submit Documentation Feedback Copyright © 2019, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Product Folder Links: BQ25155

/DISS PMID LS LDO BAT
P P P P
BQ25155
www.ti.com
SLUSDO1A –JUNE 2019–REVISED JULY 2019
8.3.1.5 Battery Supplement Mode
While in DPPM mode, if the charging current falls to zero and the system load current increases beyond the
programmed input current limit, the voltage at PMID reduces further. When the PMID voltage drops below the
battery voltage by V
load when the voltage on the PMID pin rises above the battery voltage by V
, the battery supplements the system load. The battery stops supplementing the system
BSUP1
. During supplement mode, the
BSUP2
battery supplement current is not regulated, however, the Battery Over-Current Protection mechanism is active.
Battery charge termination is disabled while in supplement mode.
8.3.2 Protection Mechanisms
8.3.2.1 Input Over-Voltage Protection
The input over-voltage protection protects the device and downstream components connected to PMID, and BAT
against damage from over-voltage on the input supply. When VIN> V
an OVP fault is determined to exist.
OVP
During the OVP fault, the device turns the input FET off, sends a single 128-µs pulse on INT, and the
VIN_OVP_FAULT FLAG and STAT bits are updated over I2C. Once the OVP fault is removed, the STAT bit is
cleared and the device returns to normal operation. The FLAG bit is not cleared until it is read through I2C after
the OVP condition no longer exists. The OVP threshold for the device is 5.5 V to allow operation from standard
USB sources.
8.3.2.2 Safety Timer and I2C Watchdog Timer
At the beginning of the charge cycle, the device starts the safety timer. If charging has not terminated before the
programmed safety time, t
t
MAXCHG
. When a safety timer fault occurs, a single 128-µs pulse is sent on the INT pin and the
MAXCHG
, expires, charging is disabled. The pre-charge safety time, t
PRECHG
, is 25% of
SAFETY_TMR_FAULT_FLAG bit in the FLAG3 register is updated over I2C. The CE pin or input power must be
toggled in order to reset the safety timer and exit the fault condition. Note that the flag bit will be reset when the
bit is read by the host even if the fault has not been cleared. The safety timer duration is programmable using the
SAFETY_TIMER bits. When the safety timer is active, changing the safety timer duration resets the safety timer.
The device also contains a 2X_TIMER bit that doubles the timer duration prevent premature safety timer
expiration when the charge current is reduced by a high load on PMID (DPM operation), VIN DPM, thermal
regulation, or a NTC (JEITA) condition. When 2X_TIMER function is enabled, the timer is allowed to run at half
speed when any loop is active other than CC or CV.
In addition to the safety timer, the device contains a 50-second I2C watchdog timer that monitors the host
through the I2C interface. The watchdog timer is enabled by default and may be enabled by the host through I2C.
Once the watchdog timer is enabled, the watchdog timer is started. The watchdog timer is reset by any
transaction by the host using the I2C interface. If the watchdog timer expires without a reset from the I2C
interface, all charger parameters registers (ICHARGE, IPRECHARGE, ITERM,VLOWV, etc.) are reset to the
default values.
8.3.2.3 Thermal Protection and Thermal Charge Current Foldback
During operation, to protect the device from damage due to overheating, the junction temperature of the die, TJ,
is monitored. When TJreaches T
operation when TJfalls below T
During the charging process, to prevent overheating in the device, the device monitors the junction temperature
of the die and reduces the charging current at a rate of (0.04 x I
foldback threshold, T
the PMID output. The thermal regulation threshold may be set through I2C by setting the THERM_REG bits to
the desired value.
To ensure that the system power dissipation is under the limits of the device. The power dissipated by the device
can be calculated using Equation 1:
Where:
SHUTDOWN
SHUTDOWN
. If the charge current is reduced to 0, the battery supplies the current needed to supply
REG
the device stops operation and is turned off. The device resumes
by T
.
HYS
Product Folder Links: BQ25155
CHARGE
)/°C once TJexceeds the thermal
Submit Documentation FeedbackCopyright © 2019, Texas Instruments Incorporated
(1)
19

J A JA DISS
T T P
T
u
( )
BAT PMID BAT BAT
P V V I u
/ / /
( )
LS LDO INLS LS LDO LS LDO
P V V I u
( )
PMID IN PMID IN
P V V I u
BQ25155
SLUSDO1A –JUNE 2019–REVISED JULY 2019
www.ti.com
(2)
(3)
(4)
The die junction temperature, TJ, can be estimated based on the expected board performance using Equation 5:
(5)
The θJAis largely driven by the board layout. For more information about traditional and new thermal metrics, see
the Semiconductor and IC Package Thermal Metrics Application Report. Under typical conditions, the time spent
in this state is very short.
8.3.2.4 Battery Short and Over Current Protection
In order to protect the device from over current and prevent excessive battery discharge current, the BQ25155
detects if the current on the battery FET exceeds I
(t
DGL_OCP
t
REC_SC
), the battery discharge FET is turned off and start operating in hiccup mode, re-enabling the BATFET
(250 ms) after being turned off by the over-current condition. If the over-current condition is triggered
BAT_OCP
. If the short circuit limit is reached for the deglitch time
upon retry for 3 to 7 consecutive times, the BATFET will then remain off until the part is reset or until Vin is
connected and valid. If the over-current condition and hiccup operation occurs while in supplement mode where
VIN is already present, VIN must be toggled in order for BATFET to be enabled and start another detection
cycle.
This process protects the internal FET from over current. During this event PMID will likely droop and cause the
system to shut down. It is recommended that the host read the Faults Register after waking up to determine the
cause of the event.
In the case where the battery is suddenly shorted while charging and VBAT drops below V
comparator quickly reduces the charge current to I
PRECHARGE
preventing fast charge current to be momentarily
SHORT
, a fast
injected to the battery while shorted.
8.3.2.5 PMID Short Circuit
A short on the PMID pin is detected when the PMID voltage drops below 1.6 V (PMID short threshold). PMID
short threshold has a 200-mV hysteresis. When this occurs, the input FET temporarily disconnects IN for up to
200 µs to prevent stress on the device if a sudden short condition happens, before allowing a softstart on the
PMID output.
8.3.3 ADC
The device uses a 16-bit ADC to report information on the input voltage, input current, PMID voltage, battery
voltage, battery charge current, and TS pin voltage of the device. It can also make measurements from an
external source through the ADCIN pin.
The host may select the function desired, perform an ADC read, and then read the values in the ADC registers.
The details for the register functions are in the Register Map section.
8.3.3.1 ADC Operation in Active Battery Mode and Low Power Mode
When the device is powered by the battery it is imperative that power consumption is minimized in order to
maximize battery life. In order to limit the number of ADC conversions, and hence power consumption, the ADC
conversions when in Active Battery Mode may be limited to a period determined by the ADC_READ_RATE bits.
On the case where the ADC_READ_RATE is set to Manual Mode, the host will have to set the
ADC_CONV_START bit to initiate the ADC conversion. Once the ADC conversion is completed and the data is
ready, the ADC_READY flag will be set and an interrupt will be sent to the host. In Low Power Mode the ADC
remains OFF for minimal IC power consumption. The host will need to switch to Active Battery Mode (set LP
high) before performing an ADC measurement.
20
Submit Documentation Feedback Copyright © 2019, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Product Folder Links: BQ25155
16
16
_
% 100
0.8 2
bit
CHARGE
ADCDATA ICHG
I u
u
16
16
_
1.2
2
bit
ADCIN
ADCDATA ADCIN
V V u
16
16
_
1.2
2
bit
TS
ADCDATA TS
V V u
16
16
_
6
2
bit
ADCDATA VBAT
VBAT V u
16
16
_
750
2
bit
IN
ADCDATA IIN
I mA u
16
16
_
375
2
bit
IN
ADCDATA IIN
I mA u
16
16
_
6
2
bit
PMID
ADCDATA PMID
V V u
16
16
_
6
2
bit
IN
ADCDATA VIN
V V u
BQ25155
www.ti.com
SLUSDO1A –JUNE 2019–REVISED JULY 2019
8.3.3.2 ADC Operation When VIN Present
When VIN is present and VDD is powered from VIN, the ADC is constantly active, performing conversions
continuously. The device will not send an interrupt after a conversion is complete since this would force the
device to constantly send ADC_READY interrupts that would overwhelm the host. The host will be able to read
the ADC results registers at any time. This is true even when VIN> V
OVP.
8.3.3.3 ADC Measurements
Table 2 below lists the ADC measurements done by the ADC.
Table 2. ADC Measurement Channels
MEASUREMENT
VIN 6 V 2 V - 5 V
PMID 6 V 2 V - 5 V
FULL SCALE RANGE
(ABSOLUTE MAX CODE)
FULL LINEAR RANGE
(RECOMMENDED
OPERATING RANGE)
FORMULA
(6)
(7)
For ILIM ≤ 150mA:
(8)
IIN 750 mA 0 - 600 mA
For ILIM >150mA:
(9)
VBAT 6 V 2 V - 5 V
Note: IIN reading only valid when VIN> V
V
OVP
UVLO
and VIN<
(10)
TS 1.2 V 0 - 1 V
(11)
ADCIN 1.2 V 0 - 1 V
(12)
% ICHARGE - -
where I
the device is in pre-charge or in the TS COLD region,
I
CHARGE
is the charge current setting. Note that if
CHARGE
will be the current set by the IPRECHRG and
TS_ICHRG bits respectively.
(13)
8.3.3.4 ADC Programmable Comparators
The BQ25155 has three programmable ADC comparators that may be used to monitor any of the ADC channels
as configured through the ADCTRL0 and ADCCTRL1 registers. The comparators will send an interrupt whenever
the ADC measurement the comparator is monitoring crosses the thresholds programmed in their respective
ADC_ALARM_COMPx registers in the direction indicated by the x_ADCALARM_ABOVE bit. The comparators
are only 12 bit compared to the 16 bits reported by the ADC, so only the first 12 bits of the ADC measurements
are used to make the comparison. Note that the interrupts are masked by default and must be unmasked by the
host to use this function.
Product Folder Links: BQ25155
Submit Documentation FeedbackCopyright © 2019, Texas Instruments Incorporated
21
BQ25155
SLUSDO1A –JUNE 2019–REVISED JULY 2019
www.ti.com
When configuring the ADC comparators, it is recommended to first disable the comparator through the
ADCCTRLx registers and allow the ADC to complete a measurement on the desired channel before enabling or
reconfiguring the comparator by setting the ADC_COMPx_2:0 bits to the desired channel. This would prevent the
comparator from sending an interrupt based on an outdated ADC reading when the comparator is enabled or
reconfigured, specially in battery only operation where the ADC is not continuously performing measurements in
all the channels.
8.3.4 VDD LDO
The device integrates a low current always-on LDO that serves as the digital I/O supply to the device. This LDO
is supplied by VIN or by BAT. The end user may be able to draw up to 10 mA of current through the VDD pin to
power a status LED or provide an IO supply. The VDD LDO will remain on through all power states with the
exception of Ship Mode.
8.3.5 Load Switch/LDO Output and Control
The device integrates a low Iq load switch which can also be used as a regulated output. The LDO/LS has a
dedicated input pin VINLS and can support up to 150 mA of load current.
The LSCTRL may be enabled/disabled through I2C. To limit voltage drop or voltage transients, a small ceramic
capacitor must be placed close to VINLS pin. Due to the body diode of the PMOS switch, it is recommended to
have the capacitor on VINLS ten times larger than the output capacitor on LS/LDO output.
The output voltage is programmable using the LS_LDO bits in the registers. The LS_LDO output can only be
changed when the EN_LS_LDO or LSCTRL pin have disabled the output. The LS/LDO voltage is calculated
using the following equation: V
= 0.6 V + LS_LDOCODE × 100 mV up to 3.7 V. All higher codes will set the
LSLDO
output to 3.7 V.
Table 3. LDO Mode Control
I2C EN_LS_LDO LS_CONFIG LS/LDO OUTPUT
0 0 Pulldown
0 1 Pulldown
1 0 LDO
1 1 Load Switch
The current capability of the LDO will depend on the VINLS input voltage and the programmed output voltage.
When the LS/LDO output is disabled through the register, an internal pull-down will discharge the output.
The LDO has output current limit protection, limiting the output current in the event of a short in the output. When
the LDO output current limit trips and is active for at least 1 ms, the device will set a flag and send an interrupt to
the host. The LDO may be set to operate as a load switch by setting the LS_SWITCH_CONFG bit. Note that in
order to change the configuration the LDO must be disabled first, then the LS_SWITCH_CONFG bit is set for it
to take effect.
8.3.6 PMID Power Control
The BQ25155 offers the option to control PMID through the I2C PMID_MODE bits. These bits can force PMID to
be supplied by BAT instead of IN, even if VIN> V
BAT
+ V
. They can also disconnect PMID, pulling it down or
SLP
leaving it floating. Table 4 shows the expected device behavior based on the PMID_MODE setting as detailed in
Table 4 below.
Table 4. PMID_MODE Control
PMID_MODE DESCRIPTION PMID SUPPLY PMID PULL-DOWN
00 Normal Operation IN or BAT Off
01 Force BAT Power BAT Off
10 PMID Off - Floating None Off
11 PMID Off - Pulled Down None On
22
Submit Documentation Feedback Copyright © 2019, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Product Folder Links: BQ25155
BQ25155
www.ti.com
SLUSDO1A –JUNE 2019–REVISED JULY 2019
PMID_MODE = 00
This is the default state/normal operation of the device. PMID will be powered from IN if VIN is valid or it will be
powered by BAT. PMID will only be disconnected from IN or BAT and pulled down when a HW Reset occurs or
the device goes into Ship Mode.
PMID_MODE = 01
When this configuration is set, PMID will be powered by BAT if V
BAT>VBATUVLO
regardless of VIN or CE state.
This allows the host to minimize the current draw from the adapter while it is still connected to the system. If
PMID_MODE = 01 is set while V
BAT
< V
BATUVLO
, the PMID_MODE = 01 setting will be ignored and the device will
go to PMID_MODE = 00. If VBAT drops below VBATUVLO while PMID_MODE = 01 the device will automatically
switch to PMID_MODE=00. This prevents the device from needing a POR in order to restore power to the
system and allow battery charging. If PMID_MODE = 01 is set during charging, charging will be stopped and the
battery will start to provide power to PMID as needed.
PMID_MODE = 10
When this configuration is set, PMID will be disconnected from the supply (IN or BAT) and left floating. VDD and
the digital remain on and active. The LDO will be disabled. When floating, PMID can only be forced to a voltage
up to VBAT level. Note that this mode can only be exited through I2C or MR HW Reset.
PMID_MODE = 11
When this configuration is set, PMID will be disconnected from the supply (IN or BAT)and pulled down to ground.
VDD and the digital remain on and active. The LDO will be disabled. Note that this mode can only be exited
through I2C or MR HW Reset.
8.3.7 System Voltage (PMID) Regulation
The BQ25155 has a regulated system voltage output (PMID) that is programmable through I2C. PMID regulation
is only active when the adapter is connected and VIN> V
UVLO
, VIN> V
BAT
_ V
and VIN< V
SLP
. In Battery
OVP
Tracking operation (PMID_REG_CTRL = 000), the PMID voltage will be regulated to about 4.7% over battery
level (V
be at least 200mV higher than V
PMID
= V
x 1.047) or 3.8 V, whichever is higher. Note that the PMID regulation target should be set to
BAT
BATREG
.
8.3.8 MR Wake and Reset Input
The MR input has three main functions in the BQ25155. First, it serves as a means to wake the device from Ship
Mode. Second, it serves as a short button press detector, sending an interrupt to the host when the button
driving the MR pin has been pressed for a given period of time. This allows the implementation of different
functions in the end application such as menu selection and control. And finally it serves as a mean to get the
BQ25155 to reset the system by performing a power cycle (shut down PMID and automatically powering it back
on) or go to Ship Mode after detecting a long button press. The timing for the short and long button press
duration is programmable through I2C for added flexibility and allow system designers to customize the end user
experience of a specific application. Note that if a specific timer duration is changed through I2C while that timer
is active and has not expired, the new programmed value will be ignored until the timer expires and/or is reset by
MR. The MR input has an internal pull-up to BAT.
8.3.8.1 MR Wake or Short Button Press Functions
There are two programmable wake or short button press timers, WAKE1 and WAKE2. When the MR pin is held
low for t
WAKE1
the device sends an interrupt (128 µs active low pulse in the INT pin) and sets the
MRWAKE1_TIMEOUT flag when it expires. If the MR pin continues to be driven low after WAKE1 and the
WAKE2 timer expires, the BQ25155 sends a second interrupt and sets the MRWAKE2_TIMOUT flag. WAKE1 is
used as the timer to wake the device from ship mode. WAKE2’s only function is to send the interrupt and has no
effect on other BQ25155 functions. These flags are not cleared until they have been read by the host. Note that
interrupts are only sent when the flags are set and the flags must be cleared in order for another interrupt to be
sent upon MR press. The timer durations can be set through the MR_WAKEx_TIMER bits in the MRCTRL
Register section.
Product Folder Links: BQ25155
Submit Documentation FeedbackCopyright © 2019, Texas Instruments Incorporated
23

/MR
INT
SHIPMODE
VDD
twake1
twake2
treset_warn
thwreset
128us
twake1
Output Rails
(PMID, LDO if enabled)
VIN
MR_LPRESS_ACTION
Go to Ship Mode
'RQ¶WFDUH
twake1
twake2
thwreset
128us
twake1
No WAKE interrupts
are sent or reset
actions are taken
until /MR is toggled
after Ship Mode exit
Go to Ship Mode
/MR
INT
SHIPMODE
VDD
Output Rails
(PMID, LDO if enabled)
MR_LPRESS_ACTION 'RQ¶WFDUH
twake1
Thwreset_warn
BQ25155
SLUSDO1A –JUNE 2019–REVISED JULY 2019
www.ti.com
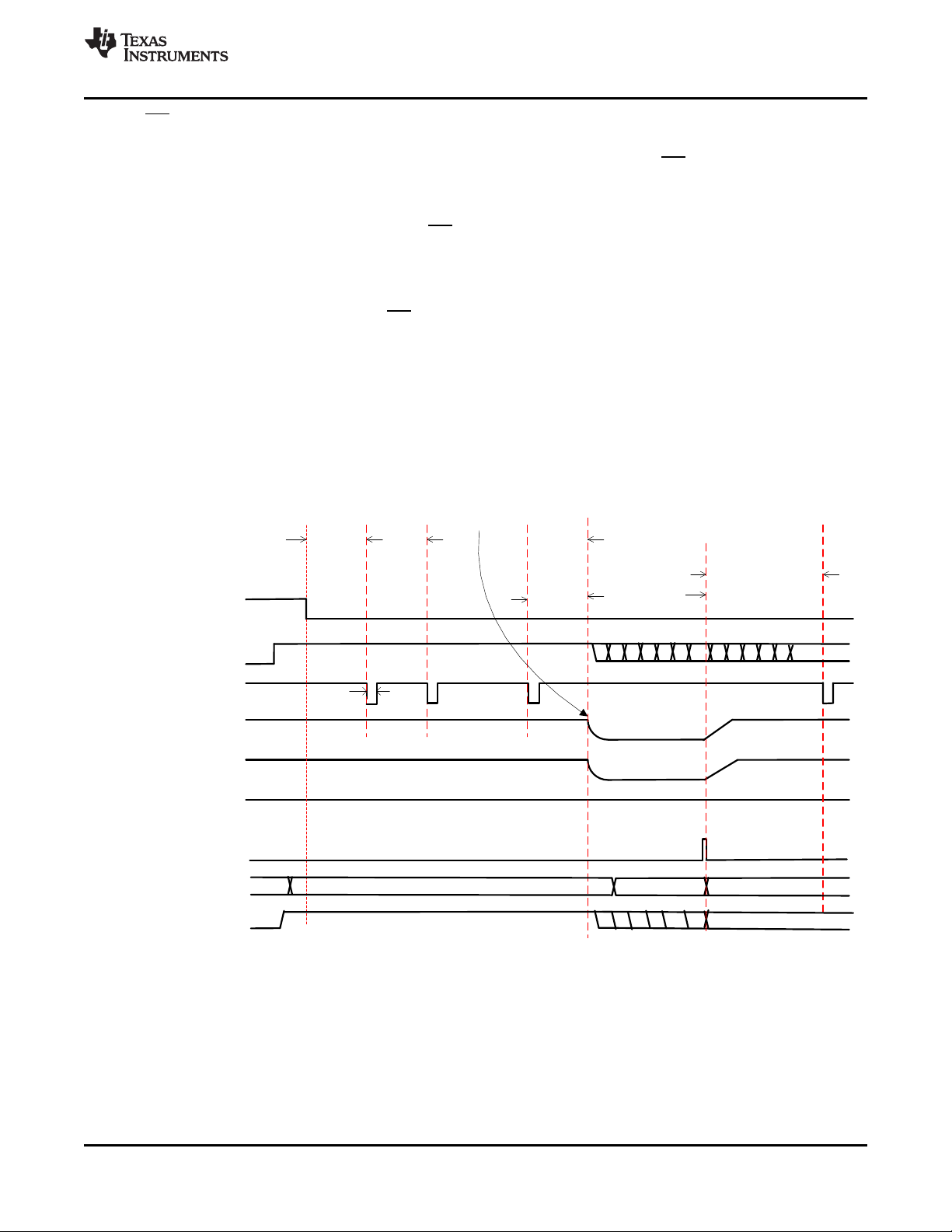
One of the main MR functions is to wake the device from Ship Mode when the MR is asserted. The device will
exit the Ship Mode when the MR pin is held low for at least t
. Immediately after the MR is asserted, VDD
WAKE1
will be enabled and the digital will start the WAKE counter. If the MR signal remains low until after the WAKE1
timer expires, the device will power up PMID and LDO (If enabled) completing the exit from the ship mode. If the
MR signal goes high before the WAKE1 timer expires, the device will go back to the Ship Mode operation, never
powering up PMID or the LDO. Note that if the MR pin remains low after exiting Ship Mode the wake interrupts
will not be sent and the long button press functions like HW reset will not occur until the MR pin is toggled. In the
case where a valid VIN(VIN> V
) is connected prior to WAKE2 timer expiring, the device will exit the ship
UVLO
mode immediately regardless of the MR or wake timer state. Figure 18 and Figure 19 show these different
scenarios.
Figure 18. MR Wake from Ship Mode (MR_LPRESS_ACTION = Ship Mode, VIN not valid)
24
Submit Documentation Feedback Copyright © 2019, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Figure 19. MR Wake from Ship Mode – VIN Dependencies
Product Folder Links: BQ25155
/MR
INT
PMID
LDO
VDD
SW reset
twake1
twake2
treset_
warn
thwreset
t_restart
128us
twake1
VIN
Once thwreset timer
expires and decision to
power cycle is done,
the device will always
complete the wake
after t_restart, no
matter change in VIN,
or bit control
MR_LPRESS_ACTION
'RQ¶WFDUH
00 - PowerCycle (AutoWake)
MR_RESET_VIN
Default
Default
BQ25155
www.ti.com
SLUSDO1A –JUNE 2019–REVISED JULY 2019
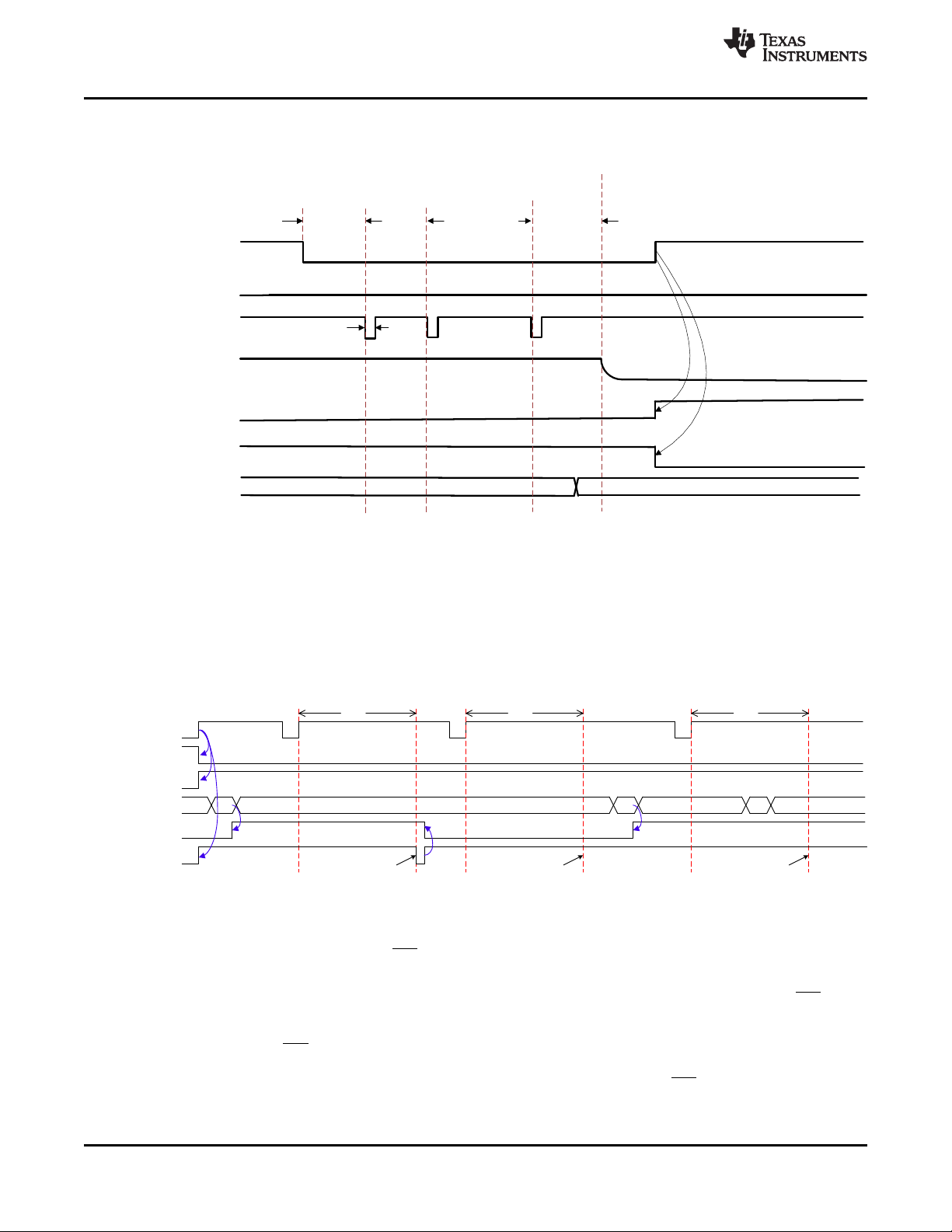
8.3.8.2 MR Reset or Long Button Press Functions
The BQ25155 device may be configured to perform a system hardware reset (Power Cycle/Autowake), go into
Ship Mode, or simply do nothing after a long button press (for example, when the MR pin is driven low until the
MR_HW_RESET timer expires).The action taken by the device when the timer expires is configured through the
MR_LPRESS_ACTION bits in the ICCTRL1 Register section. Once the MR_HW_RESET timer expires the
device immediately performs the operation set by the MR_LPRESS_ACTION bits. The BQ25155 sends an
interrupt to the host when the device detects that MR has been pressed for a period that is within t
from reaching t
HW_RESET
. This may warn the host that the button has been pressed for a period close to t
HW_RESET_WARN
HW_RESET
which would trigger a HW Reset or used as another button press timer interrupt like the WAKE1 and WAKE2
timers. This interrupt is sent before the MR_HW_RESET timer expires and sets the MRRESET_WARN flag. The
t
HW_RESET_WARN
may be set through I2C by the MR_RESET_WARN bits in the MRCTRL register. The host may
change the reset behavior at any time after MR going low and prior to the MR_HW_RESET timer expiring. It may
not change it however from another behavior to a HW reset (Power Cycle/Autowake) since a HW reset can be
gated by other condition requirements, such as VIN presence (controlled by MR_RESET_VIN bit), throughout the
whole duration of the button press. This flexibility allows the host to abort any reset or power shutdown to the
system by overriding a long button press command.
A HW reset may also be started by setting the HW_RESET bit. Note that during a HW reset , VDD remains on.
Figure 20. MR Wake and Reset Timing with VIN Present or BAT Active Mode When
MR_LPRESS_ACTION = 00
Product Folder Links: BQ25155
Submit Documentation FeedbackCopyright © 2019, Texas Instruments Incorporated
25
R/W
VIN
SHIPMODE
VDD
I2C
HWRESET_14S_WD
PMID
14s 14s
R/W
14s
R/W
HW Reset due to no I2C
transaction after VIN
detected
No HW Reset since
function was not reenabled after boot up
No HW Reset since I2C
transaction occurred
within 14s window of
VIN detection
/MR
INT
SHIPMODE
VDD
twake1
twake2
Treset_warn
thwreset
128us
PMID & LDO
Shipmode enabled when both
MR has gone high and
thwreset has expired
VIN
MR_RESET_VIN has no effect
on this mode
MR_LPRESS_ACTION
'RQ¶WFDUH
Go to Shipmode
BQ25155
SLUSDO1A –JUNE 2019–REVISED JULY 2019
www.ti.com
Figure 21. MR Wake and Reset Timing Active Mode When MR_LPRESS_ACTION = 1x (Ship Mode) and
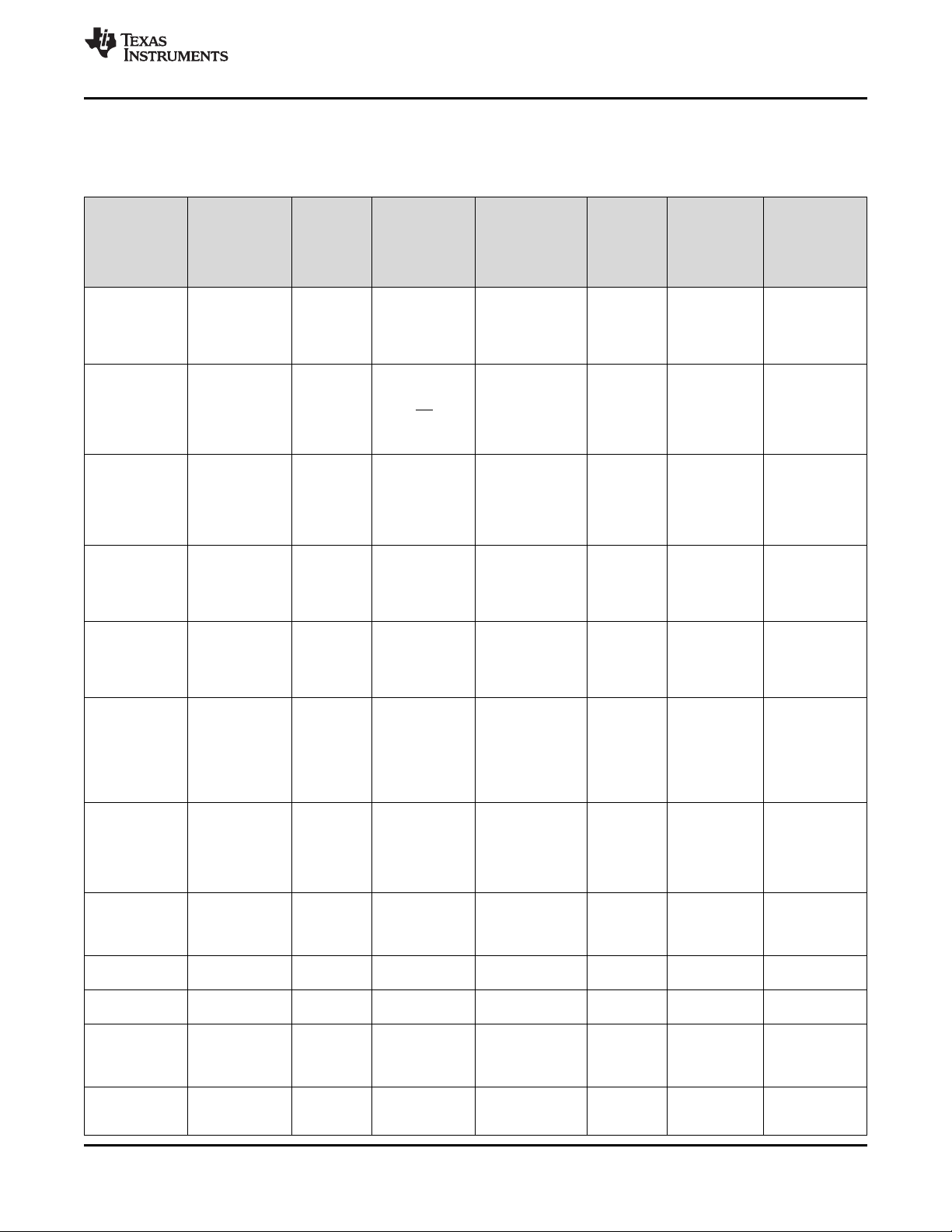
8.3.9 14-Second Watchdog for HW Reset
The BQ25155 integrates a 14-second watchdog timer that makes the BQ25155 perform a HW reset/power cycle
if no I2C transaction is detected within 14 seconds of a valid adapter being connected. If the adapter is connected
and the host responds with an I2C transaction before the 14-second watchdog window expires, the part
continues in normal operation. The 14-second watchdog is disabled by default and may be enabled through I2C
by setting the HWRESET_14S_WD bit. Figure 22 shows the basic functionality of this feature.
8.3.10 Faults Conditions and Interrupts (INT)
The device contains an open-drain output that signals an interrupt and is valid only after the device has
completed start-up into a valid state. If the part starts into a fault, interrupts will not be sent. The INT pin is
normally in high impedance and is pulled low for 128 µs when an interrupt condition occurs. When a fault or
status change occurs or any other condition that generates an interrupt such as CHARGE_DONE, a 128-µs
pulse (interrupt) is sent on INT to notify the host. All interrupts may be masked through I2C. If the interrupt
condition occurs while the interrupt is masked an interrupt pulse will not be sent. If the interrupt is unmasked
while the fault condition is still present, an interrupt pulse will not be sent until the INT trigger condition occurs
while unmasked.
26
Only BAT is Present
Figure 22. 14-Second Watchdog for HW Reset Behavior
Submit Documentation Feedback Copyright © 2019, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Product Folder Links: BQ25155
www.ti.com
8.3.10.1 Flags and Fault Condition Response
Table 5 below details the BQ25155 behavior when a fault condition occurs.
Table 5. Interrupt Triggers and Fault Condition Response
INTERRUP
T TRIGGER
FAULT / FLAG DESCRIPTION
Set when
CHRG_CV_FLA
G
charger enters
Constant
Voltage
operation
CHARGE_DON
E_FLAG
IINLIM_ACTIVE
_FLAG
VDPPM_ACTIV
E_FLAG
VINDPM_ACTIV
E_FLAG
Set when
charger reaches
termination
Set when Input
Current Limit
loop is active
Set when DPPM
loop is active
Set when
VINDPM loop is
active
Set when
Thermal Charge
THERMREG_A
CTIVE
Current
Foldback
(Thermal
Regulation) loop
is active
VIN_PGOOD_F
LAG
VIN_OVP_FAUL
T_FLAG
BAT_OCP_FAU
LT_FLAG
BAT_UVLO_FA
ULT_FLAG
Set when VIN
changes
PGOOD status
Set when VIN>
V
OVP
Set when I
Set when V
I
BATOCP
V
BATUVLO
BAT
BAT
TS_COLD_FLAGSet when VTS>
V
TS_COLD
TS_COOL_FLA
G
Set when
V
TS_COLD
> V
> V
TS_COOL
BASED ON
STATUS
BIT
CHANGE
Rising Edge Enabled No effect N/A
Rising Edge
Rising Edge
Rising Edge
Rising Edge
Rising Edge
Rising and
Falling Edge
Rising Edge
>
Rising Edge
<
Rising Edge Enabled No effect N/A
Rising Edge
Rising Edge
TS
CHARGER
BEHAVIOR
Paused-
Charging
resumes with
VIN or CE toggle
or when V
reached
RCH
Enabled.
Reduced charge
current.
Enabled.
Reduced charge
current.
Enabled.
Reduced charge
current.
Enabled.
Reduced charge
current.
If
VIN_PGOOD_S
TAT is low,
charging is
disabled.
Charging is
paused until
condition
disappears
Disabled (BAT
only condition)
Charging
paused until
condition is
cleared
Enabled.
Reduced charge
current.
CHARGER
SAFETY TIMER
Reset N/A
is
Doubled if option
is enabled
Doubled if option
is enabled
Doubled if option
is enabled
Doubled if option
is enabled
Reset N/A
Reset N/A BAT powered
N/A N/A
Paused N/A
Doubled if option
is enabled
SLUSDO1A –JUNE 2019–REVISED JULY 2019
LS/LDO
BEHAVIOR
PMID
BEHAVIOR
IN powered if
VINis valid
IN powered if
VINis valid
IN powered
VIN powered
N/A
unless
supplement
mode condition
is met.
VIN powered
unless
N/A
supplement
mode condition
is met.
VIN powered
unless
N/A
supplement
mode condition
is met.
VIN powered
unless
N/A
supplement
mode condition
is met.
VIN powered (if
VIN_PGOOD_
STAT=1)
unless
PMID_MODE
is not 00.
Interrupt will not
be sent if device
powers up with
VIN_PGOOD
condition and
V
BAT
Disconnect
BAT
IN powered of
VINis valid
IN powered of
VINis valid
N/A
IN powered of
VINis valid
BQ25155
NOTES
< V
BATUVLO
Product Folder Links: BQ25155
Submit Documentation FeedbackCopyright © 2019, Texas Instruments Incorporated
27
BQ25155
SLUSDO1A –JUNE 2019–REVISED JULY 2019
Table 5. Interrupt Triggers and Fault Condition Response (continued)
INTERRUP
T TRIGGER
FAULT / FLAG DESCRIPTION
TS_WARM_FLA
G
TS_HOT_FLAG
ADC_READY_F
LAG
Set when
V
TS_HOT
V
TS_WARM
< VTS<
Set when VTS<
V
HOT
Set when ADC
conversion is
completed
Set when ADC
COMP1_ALARM
_FLAG
measurement
meets
programmed
condition
Set when ADC
COMP2_ALARM
_FLAG
measurement
meets
programmed
condition
Set when ADC
COMP3_ALARM
_FLAG
measurement
meets
programmed
condition
TS_OPEN_FLAGSet when VTS>
V
TS_OPEN
WD_FAULT_FL
AG
Set when I2C
watchdog timer
expires
Set when safety
SAFETY_TMR_
FAULT_FLAG
Timer expires.
Cleared after
VIN or CE toggle
Set when LDO
LS_LDO_OCP_
FAULT_FLAG
output current
exceeds OCP
condition
MRWAKE1_TIM
EOUT_FLAG
MRWAKE2_TIM
EOUT_FLAG
MRRESET_WA
RN_FLAG
Set when MR is
low for at least
t
WAKE1
Set when MR is
low for at least
t
WAKE2
Set when MR is
low for at least
t
RESETWARN
No flag. Die
temperature
TSHUT
exceeds thermal
shutdown
threshold is
reached
BASED ON
STATUS
CHANGE
Rising Edge
Rising Edge
Rising Edge N/A N/A N/A N/A
Rising Edge N/A N/A N/A N/A
Rising Edge N/A N/A N/A N/A
Rising Edge N/A N/A N/A N/A
Rising Edge
Rising Edge Enabled N/A N/A N/A
Rising Edge
Rising Edge N/A N/A
Rising Edge N/A N/A N/A N/A
Rising Edge N/A N/A N/A N/A
Rising Edge N/A N/A N/A N/A
CHARGER
BEHAVIOR
CHARGER
SAFETY TIMER
LS/LDO
BEHAVIOR
PMID
BEHAVIOR
BIT
Enabled.
Reduce battery
regulation
No effect N/A
IN powered of
VINis valid
voltage.
Charging
paused until
condition is
Paused N/A
IN powered of
VINis valid
cleared
Charging is
paused until
condition
Paused N/A N/A
disappears
Disabled until
VIN or CE toggle
Reset after flag is
cleared
N/A
IN powered of
VINis valid
Enabled
(host must
take action
to disable
N/A
the LDO if
desired)
N/A Disabled Disabled Disabled Disabled
www.ti.com
NOTES
28
Submit Documentation Feedback Copyright © 2019, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Product Folder Links: BQ25155

BQ25155
www.ti.com
SLUSDO1A –JUNE 2019–REVISED JULY 2019
8.3.11 Power Good (PG) Pin
The PG pin is an open-drain output that by default indicates when a valid IN supply is present. It may also be
configured to be a general purpose output (GPO) controlled through I2C or to be a level shifted version of the MR
input signal. Connect PG to the desired logic voltage rail using a 1-kΩ to 100-kΩ resistor, or use with an LED for
visual indication. Below is the description for each configuration:
• In its default state, PG pulls to GND when the following conditions are met: VIN> V
VIN< V
. PG is high impedance when the input power is not within specified limits.
IN_OVP
UVLO
, VIN> V
BAT+VSLP
and
• MR shifted (MRS) output when the PG_MODE bits are set to 01. PG is high impedance when the MR input is
high, and PG pulls to GND when the MR input is low.
• General purpose open drain output when setting the PG_MODE bits to 1x. The state of the PG pin is then
controlled through the GPO_PG bit, where if GPO_PG is 0 , the PG pin is pulled to GND and if it is 1, the PG
pin is in high impedance.
8.3.12 External NTC Monitoring (TS)
The I2C interface allows the user to easily implement the JEITA standard for systems where the battery pack
thermistor is monitored by the host. Additionally, the device provides a flexible voltage based TS input for
monitoring the battery pack NTC thermistor. The voltage at TS is monitored to determine that the battery is at a
safe temperature during charging.
The part can be configured to meet JEITA requirements or a simpler HOT/COLD function only. Additionally, the
TS charger control function can be disabled. To satisfy the JEITA requirements, four temperature thresholds are
monitored: the cold battery threshold, the cool battery threshold, the warm battery threshold, and the hot battery
threshold. These temperatures correspond to the V
Characteristics table. Charging and safety timers are suspended when VTS< V
VTS< V
, the charging current is reduced to the value programmed in the TS_FASTCHGCTRL register. Note
COLD
COLD
, V
COOL
, V
WARM
, and V
HOT
thresholds in the Electrical
HOT
or VTS> V
COLD
. When V
COOL
that the current steps for fast charge in the COOL region, just as those in normal fast charge, are multiples of the
fast charge LSB value (1.25 mA by default). So in the case where the calculated scaled down current for the
COOL region falls in between charge current steps, the device will round down the charge current to the nearest
step. For example, if the fast charge current is set for 15 mA (ICHG = 1100) and TS_FASTCHARGE =111
(0.125*ICHG), the charge current in the COOL region will be 1.25 mA instead of the calculated 1.85 mA.
When V
< VTS< V
HOT
, the battery regulation voltage is reduced to the value programmed in the
WARM
TS_FASTCHGCTRL register.
Regardless of whether the part is configured for JEITA, HOT/COLD, or disabled, when a TS fault occurs, a 128µs pulse is sent on the INT output, and the FAULT bits of the register are updated over I2C. The FAULT bits are
not cleared until they are read over I2C. This allows the host processor to take action if a different behavior than
the pre-set function is needed. Alternately, the TS pin voltage can be read by the host if VIN is present or when
BAT is present, so the appropriate action can be taken by the host.
<
8.3.12.1 TS Thresholds
The BQ25155 monitors the TS voltage and sends an interrupt to the host whenever it crosses the V
V
COOL
and V
thresholds which correspond to different temperature thresholds based on the NTC resistance
COLD
HOT
, V
WARM
and biasing. These thresholds may be adjusted through I2C by the host. The device will also disable charging if
TS pin exceeds the V
TS_OPEN
threshold.
The TS biasing circuit is shown in Figure 23. The ADC range is set to 1.2 V. Note that the respective VTSand
hence ADC reading for T
COLD
(0°C), T
COOL
(10°C), T
WARM
(45°C) and T
(60°C) changes for every NTC,
HOT
therefore the threshold values may need to be adjusted through I2C based on the supported NTC type.
Submit Documentation FeedbackCopyright © 2019, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Product Folder Links: BQ25155
29
,
BQ25155
TS
VDD
NTC R
PARALLEL
R
PARALLEL
= R
NTC@25C
ADC
TS
measurement
control
TS I
BIAS
BQ25155
SLUSDO1A –JUNE 2019–REVISED JULY 2019
www.ti.com
Figure 23. TS Bias Functional Diagram
The BQ25155 supports by default the following thresholds for a 10-KΩ NTC.
Table 6. TS Thresholds for 10-KΩ Thermistor
THRESHOLD
Open -- >0.9
Cold 0 0.585
Cool 10 0.514
Warm 45 0.265
Hot 60 0.185
TEMPERATURE
(°C)
VTS (V)
For accurate temperature thresholds a 10-KΩ NTC with a 3380 B-constant should be used (Murata
NCP03XH103F05RL for example) with a parallel 10-KΩ resistor. Each threshold can be programmed via I2C
through the TS_COLD, TS_COOL, TS_WARM and TS_HOT registers. The value in the registers corresponds to
the 8 MSBs in the TS ADC output code.
8.3.13 External NTC Monitoring (ADCIN)
The ADCIN pin can be configured through I2C to support NTC measurements without the need of an external
biasing circuit. In this mode, the ADCIN pin is biased and monitored in the same manner as the TS pin.
Measurement data can be read by selecting one of the ADC data slots to read the ADCIN.
30
Submit Documentation Feedback Copyright © 2019, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Product Folder Links: BQ25155
 Loading...
Loading...