Telect ADF User Manual

Advanced Distribution Frame (ADF) Systems
User Manual

Advanced Distribution Frame (ADF) Systems
Advanced Distribution Frame (ADF) Systems
User Manual
User Manual
User Manual 119736-4
Copyright 2016, Telect Inc., All Rights Reserved
Telect and Connecting the Future are registered trademarks of Telect, Inc.
22425 East Appleway Ave., # 11
Liberty Lake, WA 99019
Telect assumes no liability from the application or use of these products. Neither does Telect convey any
license under its patent rights nor the patent rights of others. This document and the products described herein
are subject to change without notice.
Connecting the Future for Over 30 Years
Telect challenges the status quo and looks beyond what is possible in network connectivity and
power management.
Founded in 1982, Telect is driven by the principles of innovation and customer service. Headquartered in
Liberty Lake, WA, the privately held company supports a global network of customers with a comprehensive
product portfolio and a values-driven corporate culture.
Our products and solutions are found across communications service-provider networks, data centers and
utility networks around the globe.
At Telect, we pride ourselves on our ability to respond to customer challenges, building a reputation among
communications service providers for delivering solutions uniquely tailored to their needs.
We simplify networks.™
• Exceptional lead-times
• Custom integrated solutions
• Rapid collaborative development and prototyping
• UL and NEBs expertise
Technical Support
E-mail: getinfo@Telect.com
Phone: 509-926-6000
© Telect, Inc., All Rights Reserved, 12.7.16 v.4
© Telect, Inc., All Rights Reserved, 12.7.16 v.4
1.509.926.6000 :: telect.com
1.509.926.6000 :: telect.com
Page ii

Advanced Distribution Frame (ADF) Systems
Advanced Distribution Frame (ADF) Systems
User Manual
User Manual
Table of Contents
Chapter 1: Description ........................................................................................................................... 1
1.1 Overview.......................................................................................................................................... 1
1.1.1 ADF System Features ............................................................................................................... 3
1.2 ADF System Bays............................................................................................................................ 4
1.2.1 ADF XIs ..................................................................................................................................... 7
1.2.2 ADF ICs (after Trough Removed) .............................................................................................. 9
1.3 ADF Modules ..................................................................................................................................11
1.4 Telect ADF Feature Comparison ................................................................................................... 14
1.5 Specications ................................................................................................................................ 16
1.5.1 Weight ..................................................................................................................................... 16
1.5.2 Overall Dimensions ................................................................................................................. 17
Chapter 2: Applications ....................................................................................................................... 19
2.1 Cross-Connect - IFCs to NEs ........................................................................................................ 19
2.2 Cross-Connect - NEs to NEs ......................................................................................................... 20
2.3 Cross-Connect - IFC to IFCs ......................................................................................................... 21
2.4 Interconnect - IFC to IFC ............................................................................................................... 22
2.5 Interconnect - NEs to NEs ............................................................................................................. 23
2.6 Interframe Cross-Connecting ........................................................................................................ 24
2.7 Cross-Connect - IFC to NEs - Working/Protect ............................................................................. 25
2.8 Cross-Connect - IFC to NEs - Working/Protect - Standalone ........................................................ 26
Chapter 3: Frame Installation .............................................................................................................. 27
3.1 Installation Considerations ............................................................................................................ 27
3.1.1 Location & Space .................................................................................................................... 27
3.1.2 Tools & Equipment ................................................................................................................... 27
3.2 Inspection ...................................................................................................................................... 28
3.3 Main & Interbay Storage Panel Installation ................................................................................... 28
3.3.1 Unpacking Main & Interbay Storage Panels ............................................................................ 28
3.3.2 Installing Main & Interbay Storage Panels Directly on a Concrete Floor ................................. 29
3.3.3 Table of Footprint Dimensions ................................................................................................. 31
3.3.4 Installing Lower Trough Junction ............................................................................................. 32
3.3.5 Installing Upper Trough Junction on ADF XI Bays................................................................... 32
3.3.6 Securing ADF to the Lineup..................................................................................................... 33
3.3.7 Installing Rear Cable Tie-Down Bars....................................................................................... 34
© Telect, Inc., All Rights Reserved, 12.7.16 v.4
© Telect, Inc., All Rights Reserved, 12.7.16 v.4
1.509.926.6000 :: telect.com
1.509.926.6000 :: telect.com
Page iii

Advanced Distribution Frame (ADF) Systems
Advanced Distribution Frame (ADF) Systems
User Manual
User Manual
3.3.8 Installing Cable Management System (CMS).......................................................................... 36
3.3.9 Grounding ADF ........................................................................................................................ 36
3.3.10 Securing ADF Lineup............................................................................................................. 36
3.3.11 Wiring Facility Power ............................................................................................................. 36
Chapter 4: Module Installation ............................................................................................................ 39
4.1 Installation Considerations ............................................................................................................ 39
4.1.1 Pre-Cabled vs. Uncabled ADF Modules .................................................................................. 39
4.1.2 Tools & Equipment Required ................................................................................................... 39
4.2 Inspection ...................................................................................................................................... 39
4.3 Unpacking an ADF Module ............................................................................................................ 39
4.4 Installing an ADF Module to a Main ADF ....................................................................................... 40
Chapter 5: Outboard Cabling .............................................................................................................. 43
5.1 Intrafacility Cable to Uncabled IFC Module ................................................................................... 43
5.2 Network Cabling to Network Element Module ............................................................................... 47
Chapter 6: Inboard Cabling ................................................................................................................. 51
6.1 Installing Inboard Cabling .............................................................................................................. 51
6.2 Routing & Storing Inboard Cabling ................................................................................................ 54
6.2.1 Interconnection ........................................................................................................................ 54
6.2.2 Cross-Connection .................................................................................................................... 56
Chapter 7: Service ................................................................................................................................ 59
7.1 Owner Maintenance ...................................................................................................................... 59
7.2 Technical Support .......................................................................................................................... 59
7.3 In-Warranty Service ....................................................................................................................... 59
7.4 Out-of-Warranty Service ................................................................................................................ 59
7.5 Repacking for Shipment ................................................................................................................ 59
Chapter 8: Bays and Accessories ....................................................................................................... 61
© Telect, Inc., All Rights Reserved, 12.7.16 v.4
© Telect, Inc., All Rights Reserved, 12.7.16 v.4
1.509.926.6000 :: telect.com
1.509.926.6000 :: telect.com
Page iv

Advanced Distribution Frame (ADF) Systems
Advanced Distribution Frame (ADF) Systems
User Manual
User Manual
List of Figures
Figure 1 - Advanced Distribution Frame System ...................................................................................... 1
Figure 2 - Typical Lineup Using ADF Cross-Connect/Interconnect (XI) Bays .......................................... 2
Figure 3 - Main ADF (Typical, Front View with Tray Modules) .................................................................. 4
Figure 4 - Main ADFs (as Shipped, without Tray Modules) ...................................................................... 5
Figure 5 - End Panel................................................................................................................................. 6
Figure 6 - XI Cross-Connect IFC to NE22 ................................................................................................ 7
Figure 7 - Interconnect IFC to NE33......................................................................................................... 8
Figure 8 - Cross-Connect NFC to IE ........................................................................................................ 8
Figure 9 - IFC to NE Interconnection Using ADF ICs in an ADF Lineup................................................... 9
Figure 10 - IFC to NE Interconnection Using ADF ICs in an ADF Lineup (with ISP Storage) ................ 10
Figure 11 - Outboard View of Right-Hand, Intrafacility Cable (IFC) Module ............................................11
Figure 12 - Outboard View of Right-Hand, Network Element (NE) Module ............................................ 12
Figure 13 - Fan-Out Module ................................................................................................................... 12
Figure 14 - Patch Tray (Physically the Same for IFC, NE and FO Modules).......................................... 13
Figure 15 - ADF Comparisons ................................................................................................................ 14
Figure 16 - ADF Comparisons ................................................................................................................ 15
Figure 17 - Cross-Connect - IFC to NEs ................................................................................................ 19
Figure 18 - Cross-Connect - NEs to NEs ............................................................................................... 20
Figure 19 - Cross-Connect - IFC to IFCs................................................................................................ 21
Figure 20 - Interconnect - IFC to IFC...................................................................................................... 22
Figure 21 - Interconnect - NEs to NEs.................................................................................................... 23
Figure 22 - Interframe Cross-Connecting ............................................................................................... 24
Figure 23 - Cross-Connect - IFC to NEs - Working/Project .................................................................... 25
Figure 24 - Cross-Connect - IFC to NEs - Working/Project - Standalone .............................................. 26
Figure 25 - Installation Location ............................................................................................................. 27
Figure 26 - ADF and Interbay Storage Panel Installation Template ........................................................ 29
Figure 27 - ADF and Interbay Storage Panel Footprints ........................................................................ 30
Figure 28 - Lower ADF Junction ............................................................................................................. 32
Figure 29 - Lower Trough Junction Being Secured to the Main ADF XI ................................................. 32
Figure 30 - Rear Corner View of an ADF XI in an ADF Lineup ............................................................... 33
Figure 31 - Rear Corner View of ADF ICs in an ADF Lineup .................................................................. 33
Figure 32 - Recommended Top Feed Conguration .............................................................................. 34
Figure 33 - Recommended Bottom Feed Conguration ......................................................................... 35
Figure 34 - Connect CMS to Main ADF XIs ............................................................................................ 36
Figure 35 - Electrical Raceway (Front of Base) on ADF XI and IC Lineups ........................................... 37
Figure 36 - Installing a Module on a Main ADF ...................................................................................... 41
© Telect, Inc., All Rights Reserved, 12.7.16 v.4
© Telect, Inc., All Rights Reserved, 12.7.16 v.4
1.509.926.6000 :: telect.com
1.509.926.6000 :: telect.com
Page v

Advanced Distribution Frame (ADF) Systems
Advanced Distribution Frame (ADF) Systems
User Manual
User Manual
Figure 37 - Adjusting Latch Bars (ADF Module Not Shown) .................................................................. 42
Figure 38 - Intrafacility Clamp and Cable ............................................................................................... 43
Figure 39 - Riser Cabling to Uncabled IFC Module ................................................................................ 44
Figure 40 - Securing Connector to Adapter ............................................................................................ 45
Figure 41 - Routing Cable to Breakout Area........................................................................................... 45
Figure 42 - Excess Cable Routing .......................................................................................................... 46
Figure 43 - Network Element Cabling (Example) ................................................................................... 47
Figure 44 - Opening Trays ...................................................................................................................... 48
Figure 45 - Securing Connector to Adapter ............................................................................................ 48
Figure 46 - Routing Cable to Channel .................................................................................................... 49
Figure 47 - Cable Routing through Channel to Rear of Module ............................................................. 49
Figure 48 - Cable Preparation ................................................................................................................ 51
Figure 49 - Connecting Patch Cord ........................................................................................................ 52
Figure 50 - Cable Routing in Tray........................................................................................................... 52
Figure 51 - Cable Routing in Module ...................................................................................................... 52
Figure 52 - Interconnecting Cable Routing ............................................................................................. 53
Figure 53 - Cross-Connecting Cable Routing......................................................................................... 53
Figure 54 - Cable Routing Down Cascade ............................................................................................. 53
Figure 55 - Interconnection within a Single Frame ................................................................................. 54
Figure 56 - Interconnection with Storage on ISP .................................................................................... 55
Figure 57 - Patching to Same Side of Same ADF .................................................................................. 56
Figure 58 - Patching to Opposite Side of Same ADF ............................................................................. 56
Figure 59 - Patching to Same Side of Different ADFs ............................................................................ 57
Figure 60 - Patching to Opposite Side of Different ADFs (without ISP) .................................................. 57
Figure 61 - Patching to Opposite Side of Different ADFs (with ISP) ....................................................... 58
© Telect, Inc., All Rights Reserved, 12.7.16 v.4
© Telect, Inc., All Rights Reserved, 12.7.16 v.4
1.509.926.6000 :: telect.com
1.509.926.6000 :: telect.com
Page vi
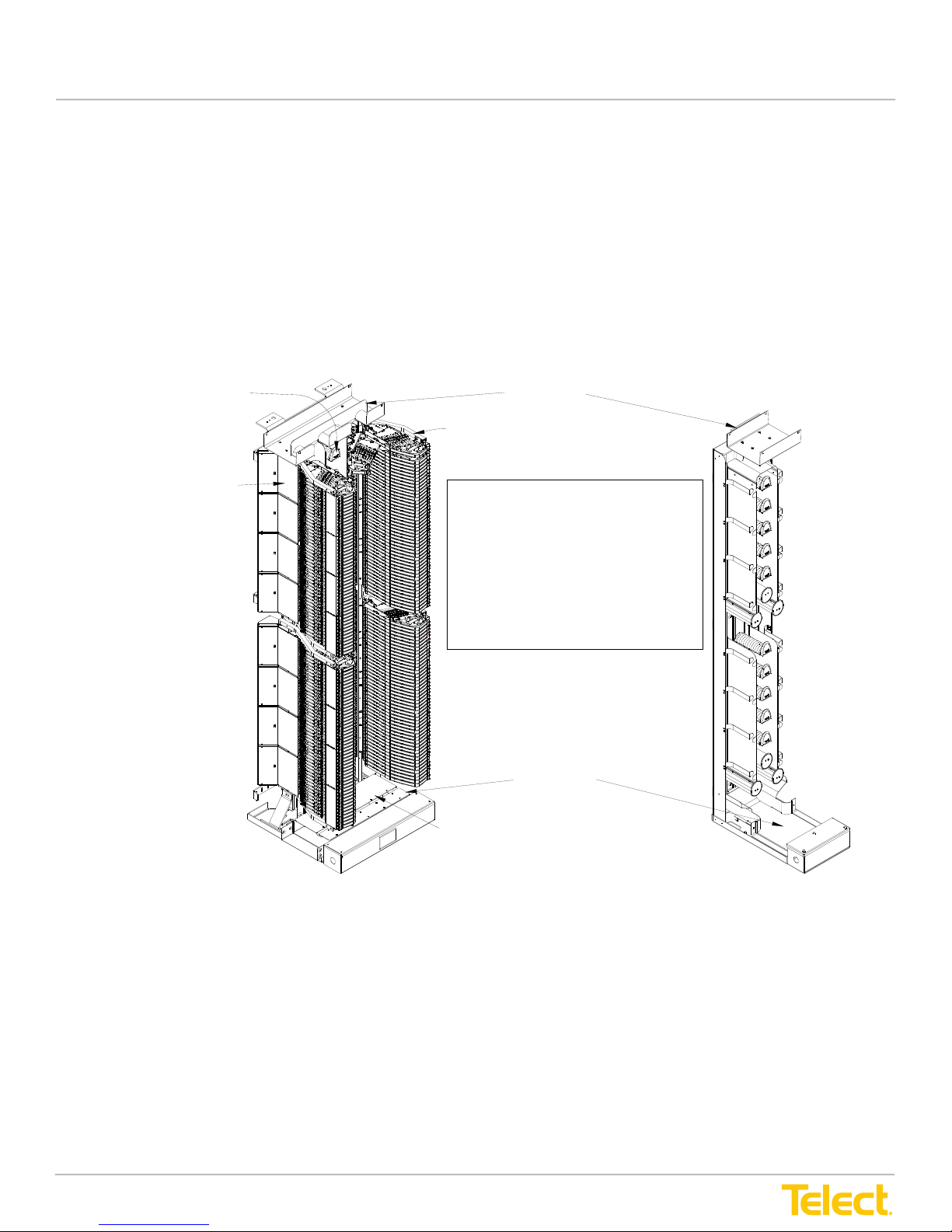
Advanced Distribution Frame (ADF) Systems
Chapter 1: Description
Advanced Distribution Frame (ADF) Systems
1.1 Overview
Telect’s ADF Systems provide inter-connectivity and cross-connectivity of intrafacility cables,
network elements, and patch cords.
• Each Main ADF consists of an upright frame holding a vertical array of modules on each side
of a patch cord interconnect routing area.
• Each module holds trays for interconnections or cross-connections.
Each swing-out tray supports 6, 8, or 12 optical connections, depending on the type of adapter.
User Manual
Chapter 1: Description
1.1 Overview
The Telect ADF Systems provide inter-connectivity and cross-connectivity of intrafacility cables, network
elements and patch cords.
• Each Main ADF consists of an upright frame holding a vertical array of modules on each side of a patch
cord interconnect routing area
• Each module holds trays for interconnections or cross-connections
Each swing-out tray supports 6,8 or 12 optical connections, depending on the type of adapter.
Vertical Spoo l Array for
R ou tin g P a tch Ca b ling
Between Modules
Trays H old 6, 8, or 12 O ptical Adapters
Upper Trough
Modules With Trays
Covers Protect Cable in Bottom Troughs
ADF Types & Versions
The Telect ADF-XI comes as pictured.
The trough can be removed to provide
inter-connectivity. [ADF-IC]
Two versions of ADF XI are offered,
an ETSI versions and a North American
version. The ETSI version is shown here.
Lower Trough
ADF-26F-XI ADF-12INT-XI
Figure 1 - Advanced Distribution Frame System
• ADFs with 12 adapters per tray have up to 2304 junctions per bay (LC)
• ADFs with 8 adapters per tray have up to 1536 junctions per bay
• ADFs with 6 adapters per tray have up to 1152 junctions per bay
© Telect, Inc., All Rights Reserved, 12.7.16 v.4
1.509.926.6000 :: telect.com
1

Advanced Distribution Frame (ADF) Systems
Figure 1, “Advanced Distribution Frame System” on page 1, depicts a multipurpose ADF XI bay
with a complete array of modules and an ADF InterBay Storage panel.
The area between right-side and left-side modules contains various spools for routing patch
cords and/or pigtail interconnects. Bulk patch cord storage is provided by InterBay Storage
Panels (ISPs) located between Main ADFs in ADF System lineups.
User Manual
Figure 1, “Advanced Distribution Frame System” on page 1, depicts a multi-purpose ADF XI bay with a
complete array of modules and an ADF InterBay Storage Panel.
The area between right-side and left-side modules contains various spools for routing patch cords and/or pigtail interconnects. Bulk patch cord storage is provided by Interbay Storage Panels (ISPs) located between Main
ADFs in ADF System lineups.
Normally, the top tray of ea ch
qua drant is covered to protect cab les
and ad apters from overhead hazards.
Bottom-Up IFC Cabling (IFC can be routed from the top-down
or bottom-up on all Main ADFs)
Rear View of Main ADF Showing IFC
Front View
Cable at Rear of ADF Module
Figure 2 - Typical Lineup Using ADF Cross-Connect/Interconnect (XI) Bays
ADF system lineups consist of Main ADF, ISPs and end panels.
Cable, patch cord and pigtail access differs somewhat between the Telect ADF Cross-Connect/Interconnect
(XI) and Interconnect (IC) Systems, but generally IFC, OSP or network element
© Telect, Inc., All Rights Reserved, 12.7.16 v.4
1.509.926.6000 :: telect.com
2

Advanced Distribution Frame (ADF) Systems
User Manual
(NE) access are connected at the rear of the modules. Patch cords, as well as NE pigtail interconnects, are
connected at the front of the modules. In cross-connect applications, patch cords are routed between modules
on different Main ADFs through upper and/or lower ADF troughs.
1.1.1 ADF System Features
• Industry-leading termination density
• Simple, straight-forward cable management, access, circuit identication and isolation
• No shing of cables
• Total front access for patching
• Designed for compliance (ber bend radius control, ammability safety, structural reliability) throughout
ADF design
• No line-of-sight laser hazards
• Easy access to riser/network/patch cord interconnections and cross-connections
• Light-weight, heavy-duty frame certied for Zone 4 earthquake reliability
• Easy installation
• 600-mm and 26-in. rack widths that accommodate standard lineups
• Diverse routing with reduced cable congestion, diverse routing between ADFs using upper and/or
lower troughs
• 4.5 m standard, single-length patch cords for ADF cross connections
• Unique storage spools with wave-like ridges for grouping patch cords
• Variable placement of tray modules on ADF mounting rails
• Compatible with WaveTrax™ Cable Management System and other cable management systems
© Telect, Inc., All Rights Reserved, 12.7.16 v.4
1.509.926.6000 :: telect.com
3
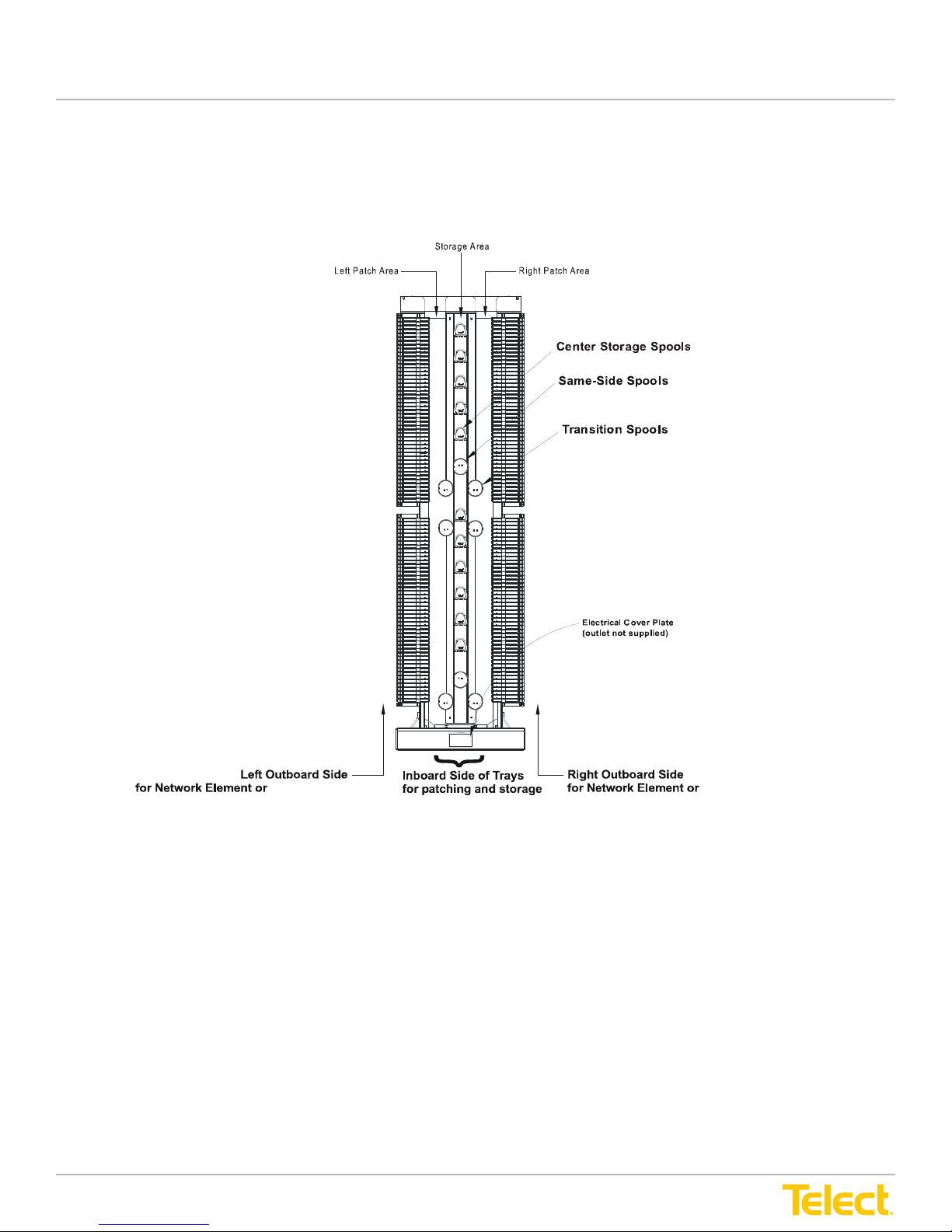
Advanced Distribution Frame (ADF) Systems
1.2 ADF System Bays
As mentioned, ADF Systems consist of Main ADFs with modules, InterBay Storage Panels
(ISPs), and end panels.
User Manual
1.2 ADF System Bays
As mentioned, ADF Systems consist of Main ADFs with modules, Interbay Storage Panels (ISPs)
and End Panels.
Intrafacility Cabling
Figure 3 - Main ADF (Typical, Front View with Tray Modules)
Main ADFs, such as the Main ADF XI in Figure 3, above, consist of a central cable storage area with mounting
rails for the ber tray modules. The routing area contains several types of spools for directing and redirecting
patch cords and pigtail interconnects.
Interconnect and cross-connect cabling differs somewhat between the Main ADF XI and IC bays:
• Main ADF XI - Interconnection and cross-connection cabling to the inboard patch areas is provided by
either upper and/or lower cable troughs. Drops in the troughs ensure cable bend radius control. Junctions
are provided for coupling the upper and lower troughs to other Main ADFs or Interbay Storage Panels in
the lineup.
Intrafacility Cabling
• Main ADF IC (Specialized for Interconnections) - Interconnect cabling to the inboard patch area is by direct
access from a cable management system above the ADF lineup. Junctions are provided for coupling the
lower troughs of all Main and Interbay Storage Panels in the lineup.
© Telect, Inc., All Rights Reserved, 12.7.16 v.4
1.509.926.6000 :: telect.com
4
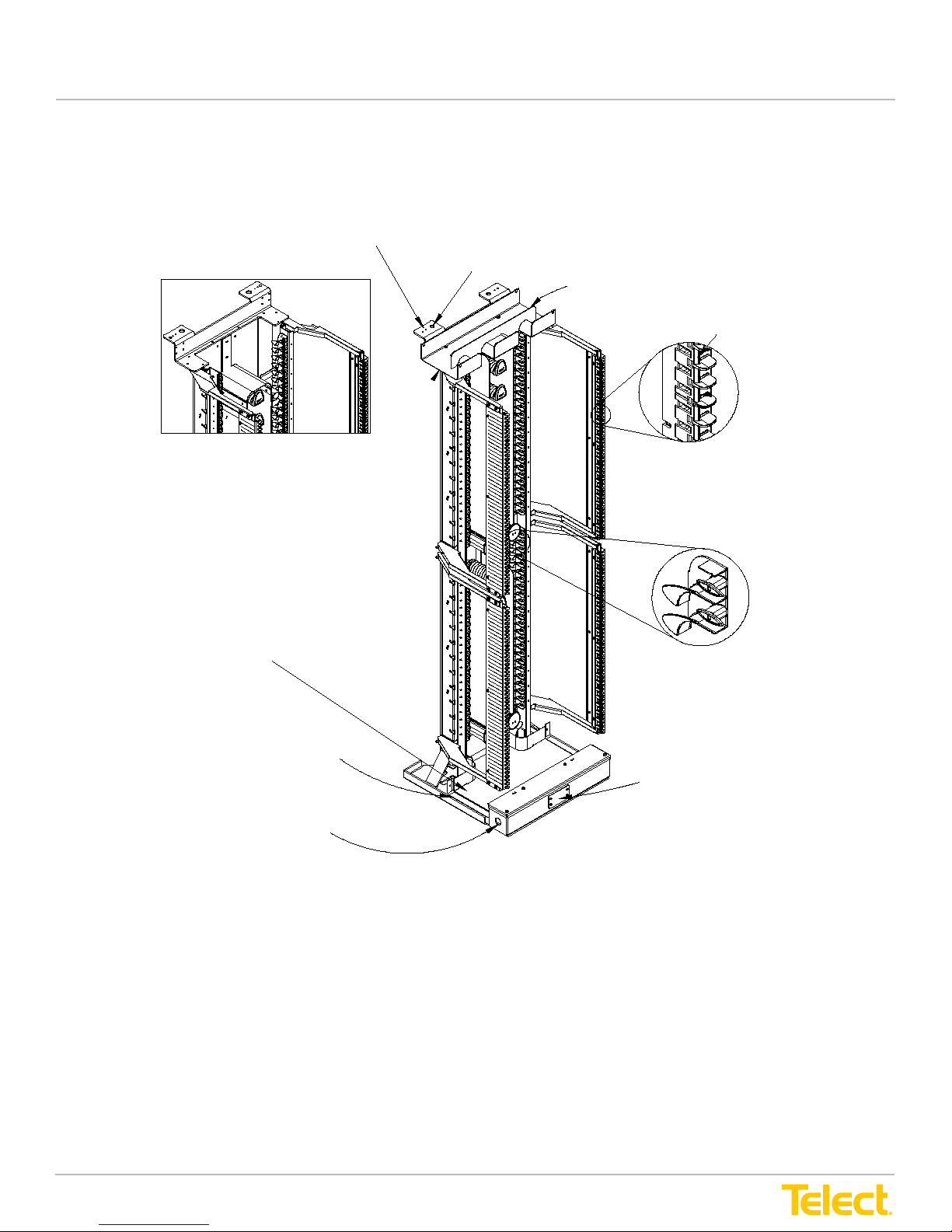
Advanced Distribution Frame (ADF) Systems
are provided for coupling the lower troughs of all Main and InterBay Storage Panels
in the lineup.
At the bottom is an electrical raceway for power cabling and conduit. The raceway provides a
mounting area for a standard recessed receptacle or other wiring device.
Small holes are tappedto connect dual-hole grounding
Main ADF XI only
User Manual
At the bottom is an electrical raceway for power cabling and conduit. The raceway provides a mounting area
for a standard recessed receptacle or other wiring device.
lug usin g M5 scr ews
Main ADF Interconnect (IC)
(shown with top trough removed)
Junction (not shown) fits on the edge to
connect the upper trough to the adjacent
frame in the lineup (Main ADF XI [cross-connect] only)
Main ADF IC
(shown without top trough)
Lar g e hole s f or s ecur i ng ADF
to th e CMS or a la dder ra ck
Upper ADF Trough (Main ADF XI Only)
Catch for Tray Latch
Lower ADF Trough
Patch Cord Cascade
With Turn stiles
Coupling (not shown) fits on lip to
connect lower troughto adjacent
frame in lineup
Cover Plate for Standard Electrical
Receptacle
31.8 mm/1.25 in. (Diameter) AccessHole
on Both Ends of Raceway
Main ADF XI
Figure 4 - Main ADFs (as Shipped, without Tray Modules)
An Interbay Storage Panel (ISP) is used for storage of either patch cord cabling from an overhead CMS and/or
inboard cabling terminated at IFC or NE modules. Except for the tray modules, cable routing through an
Interbay Storage Panel is similar to that of a Main ADF.
The Main ADF and ISP can be mounted directly to a concrete oor or on a raised equipment oor. (A template
is provided for mounting panels to the oor.) Support is provided at the top for added earthquake security and
for attaching to a cable management or ladder rack system.
© Telect, Inc., All Rights Reserved, 12.7.16 v.4
1.509.926.6000 :: telect.com
5
Advanced Distribution Frame (ADF) Systems
Normally, ADF lineups are terminated at each end by ADF End Panels secured to adjacent ISPs.
User Manual
Normally, ADF lineups are terminated at each end by ADF End Panels secured to adjacent ISPs.
Doors (2)
Access Covers (2)
Figure 5 - End Panel
You can congure two types of ADF System bays that t North American and ETSI footprints:
1. ADF Cross-Connect/Interconnect (XI) Bays
2. ADF Interconnect (IC) Bays
The subsections that follow describe and illustrate various cabling scenarios provided by each of these types
of ADF systems. Chaper 2, “Applications” on page 19, provides comprehensive and comparative analyses of
cabling using these two systems.
© Telect, Inc., All Rights Reserved, 12.7.16 v.4
1.509.926.6000 :: telect.com
6
Advanced Distribution Frame (ADF) Systems
1.2.1 ADF XIs
ADF Cross-Connect/Interconnect bays are used in either cross-connect or interconnect
applications, depending on the type of module installed on the Main ADFs. Lineup access to the
patch cord area on the Main ADFs is through either the bottom or upper troughs with access to/
from patch cord storage on the ISPs via the bottom trough.
Two models are available:
1. The North American model is based on a 26 in. by 24 in. Main ADF footprint. ISPs for the
North
American model are 12 in. by 24 in.
2. The ETSI model is based on a 600 mm by 600 mm Main ADF footprint. ISPs for the ETSI
model are 30
0 mm by 600 mm.
The following figures show a few typical cross-
connection and interconnection schemes between
IFC and network element (NE) cabling. In these examples, IFC routing to the rear of the IFC ADF
modules is from the facilities cable (ladder) rack with NE cabling through a cable management
system (CMS).
Ladder Rack
User Manual
1.2.1 ADF XIs
ADF Cross-Connect/Interconnect bays are used in either cross-connect or interconnect applications,
depending on the type of module installed on the Main ADFs. Lineup access to the patch cord area on the
Main ADFs is through either the bottom or upper troughs with access to/from patch cord storage on the ISPs
via the bottom trough.
Two models are available:
1. The North American model is based on a 26" by 24" Main ADF footprint. ISPs for the North American model
are 12" by 24".
2. The ETSI model is based on a 600 mm by 600 mm Main ADF footprint. ISPs for the ETSI model are 300
mm by 600 mm.
The following gures show a few typical cross-connection and interconnection schemes between IFC and
network element (NE) cabling. In these examples, IFC routing to the rear of the IFC ADF modules is from the
facilities cable (ladder) rack with NE cabling through a cable management system (CMS).
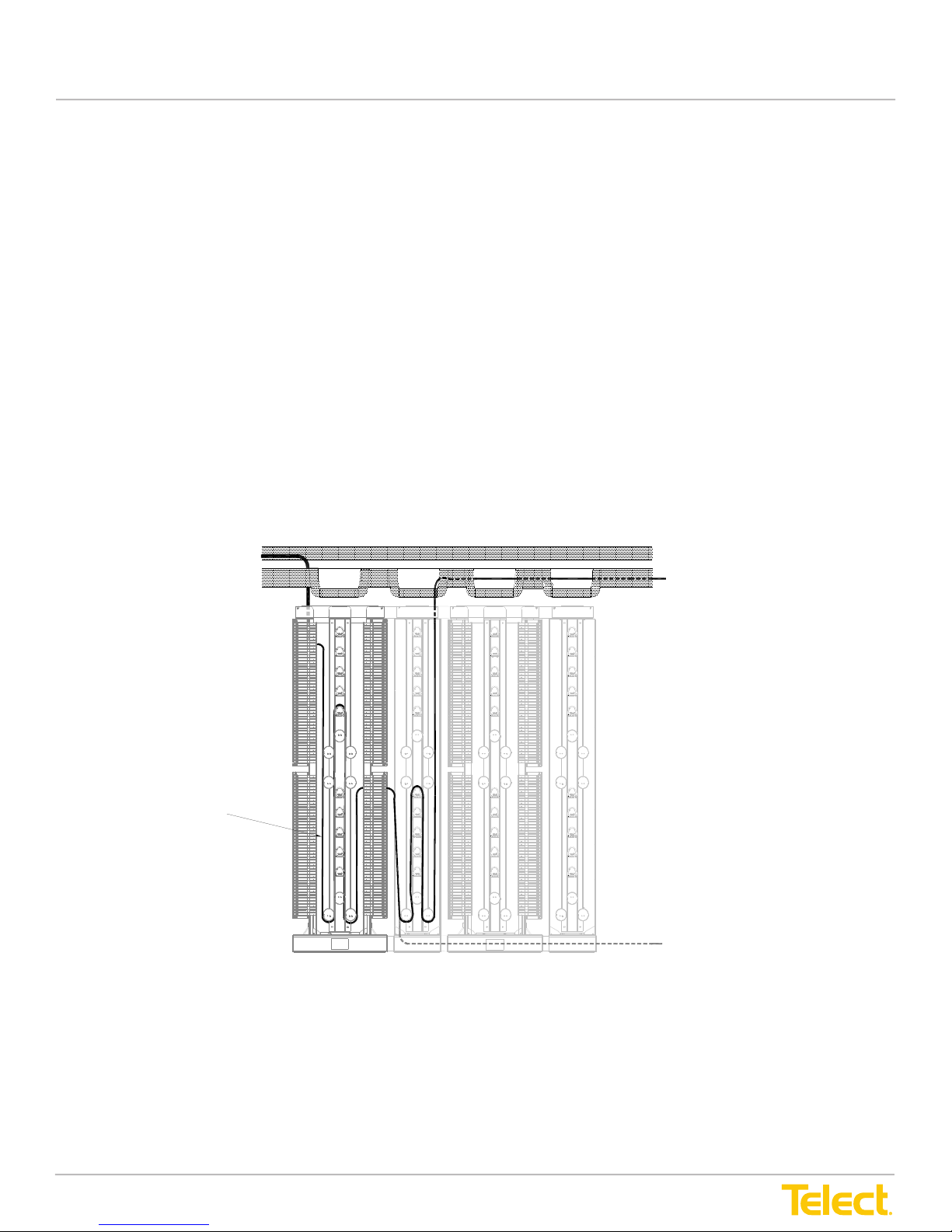
IFC Cabling to Rear
(Outboard Side)
of IFC Module
CMS
Preferred Pigtail
Route from Outboard
Side of NE Module
Via CMS to Network
Element
Patch Cord
Alternate Route
Figure 6 - XI Cross-Connect IFC to NE22
© Telect, Inc., All Rights Reserved, 12.7.16 v.4
1.509.926.6000 :: telect.com
7
Advanced Distribution Frame (ADF) Systems
CMS
Alternate Route
Alternate Route
Ladder Rack
IFC Cabling to Rear
(Outboard Side)
of IFC Module
Preferred Pigtail
Route from Inboard
Side of IFC Module
Via CMS to Network
Element
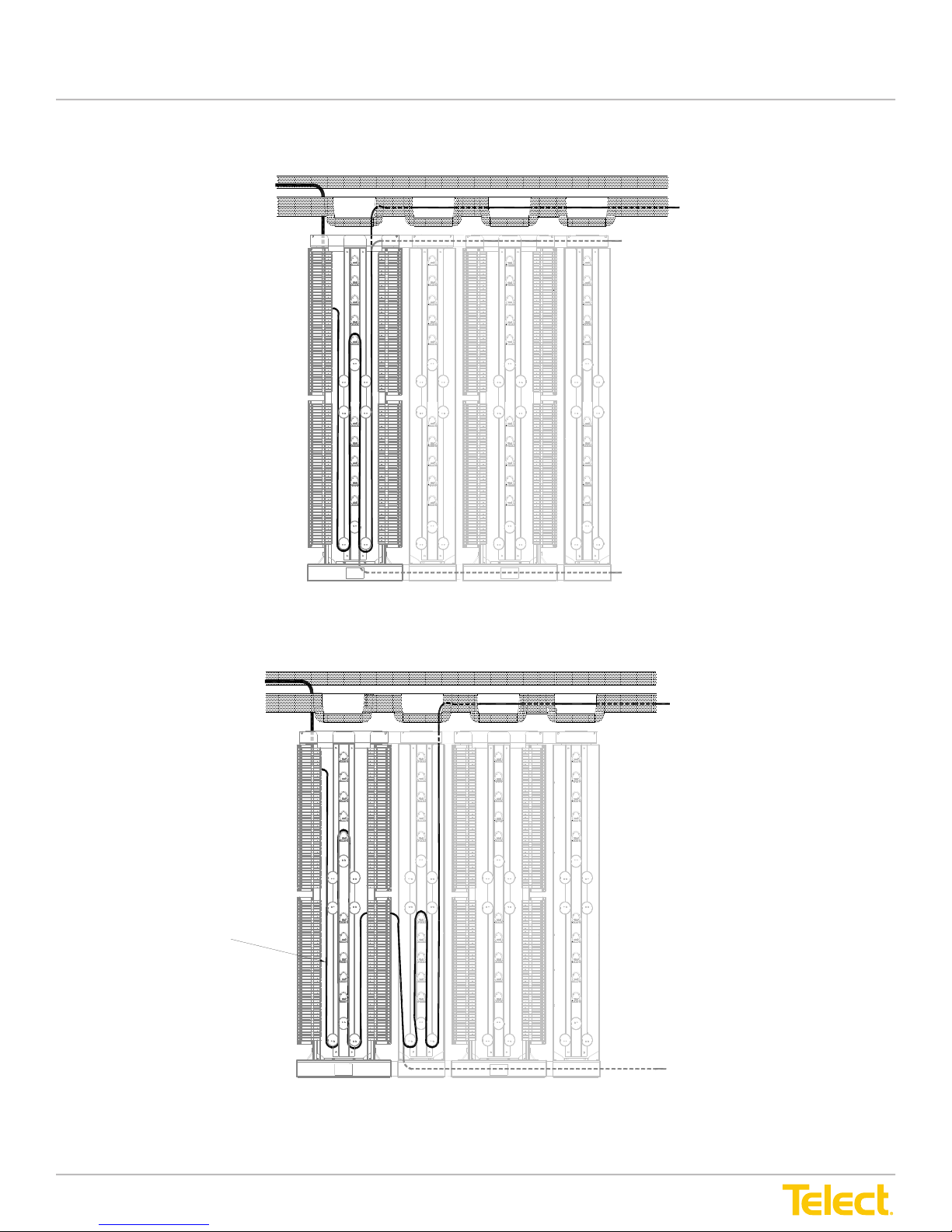
Figure 7 - Interconnect IFC to NE33
User Manual
IFC Cabling to Rear
(Outboard Side)
of IFC Module
Ladder Rack
CMS
Figure 7 - Interconnect IFC to NE33
Preferred Pigtail
Route from Inboard
Side of IFC Module
Via CMS to Network
Element
Alternate Route
Alternate Route
IFC C abling to R ea r
(Outboard Side)
of IFC Module
Patch Cord
Ladder Rack
CMS
Figure 8 - Cross-Connect NFC to IE
Preferred Pigtail
Route from Outboard
Side of NE Module
Via CMS to Network
Element
Alternate Route
© Telect, Inc., All Rights Reserved, 12.7.16 v.4
1.509.926.6000 :: telect.com
8
Advanced Distribution Frame (ADF) Systems
1.2.2 ADF ICs (after Trough Removed)
ADF Interconnect (IC) bays are physically similar to but functionally quite different from the ADF
XI bays.
To convert XI to IC, remove the top trough. With the top trough removed, the overhead access to
the patch area of a Main and ISP ADF ICs is confined to a center drop from an overhead cable
management system. Both Main and ISP ADF ICs feature an interconnected bottom trough for
routing cable between the ADF IC bays.
ADF XI and IC bays can be used in the same lineup; cross-aisle connections between lineups
are common applications for ADF ICs.
The following figures show a few typical interconnection schemes between IFC and network
element (NE) cabling. In these examples, IFC routing to the rear of the IFC ADF modules is from
the facilities ladder rack with NE cabling dropped from an overhead cable management system
(CMS).
User Manual
1.2.2 ADF ICs (after Trough Removed)
ADF Interconnect (IC) bays are physically similar to but functionally quite different from the ADF XI bays.
To convert XI to IC, remove the top trough. With the top trough removed, the overhead access to the patch
area of a Main and ISP ADF ICs are conned to a center drop from an overhead cable management system.
Both Main and ISP ADF ICs feature an interconnected bottom trough for routing cable between the ADF
IC bays.
ADF XI and IC bays can be used in the same lineup; cross-aisle connections between lineups are common
applications for ADF ICs.
The following gures show a few typical interconnection schemes between IFC and network element (NE)
cabling. In these examples, IFC routing to the rear of the IFC ADF modules is from the facilities ladder rack
with NE cabling dropped from an overhead cable management system (CMS).
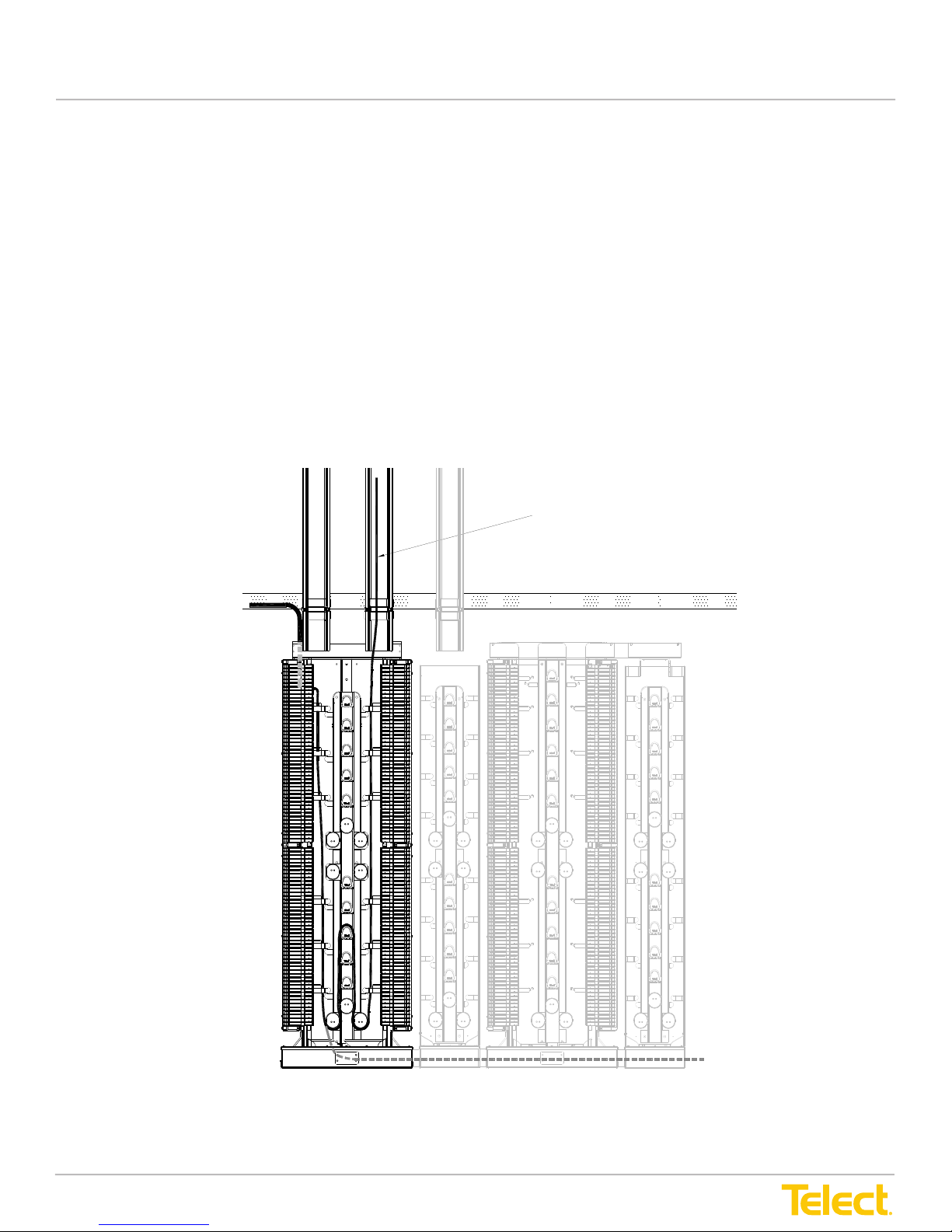
CMS
(Optional)
IFC Cabling to Rear
(Outboard Side) of
of IFC Module
Ladder Rack
Preferred Pigtail Route from
Inboard Side of IFC Module Via
CMS to Network Element
Figure 9 - IFC to NE Interconnection Using ADF ICs in an ADF Lineup
© Telect, Inc., All Rights Reserved, 12.7.16 v.4
1.509.926.6000 :: telect.com
Alternate Route
9
Advanced Distribution Frame (ADF) Systems
User Manual
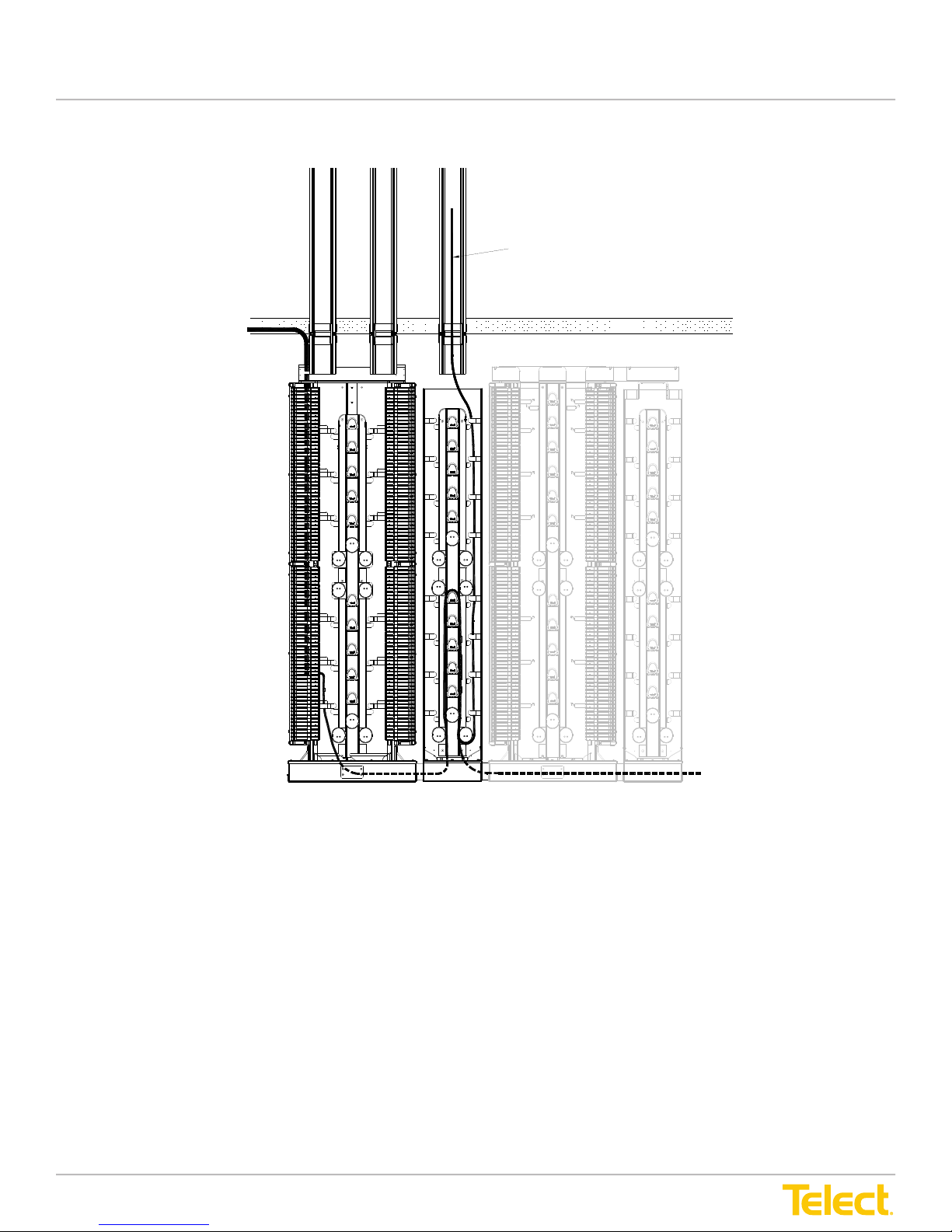
IFC Cabling to Rear
(Outboard Side)
of IFC Module
CMS
(Optional)
Preferred Pigtail Route from Inboard Side of
IFC Module Via CMS to Network Element
Ladder Rack
Figure 10 - IFC to NE Interconnection Using ADF ICs in an ADF Lineup (with ISP Storage)
© Telect, Inc., All Rights Reserved, 12.7.16 v.4
1.509.926.6000 :: telect.com
Alternate Route
10
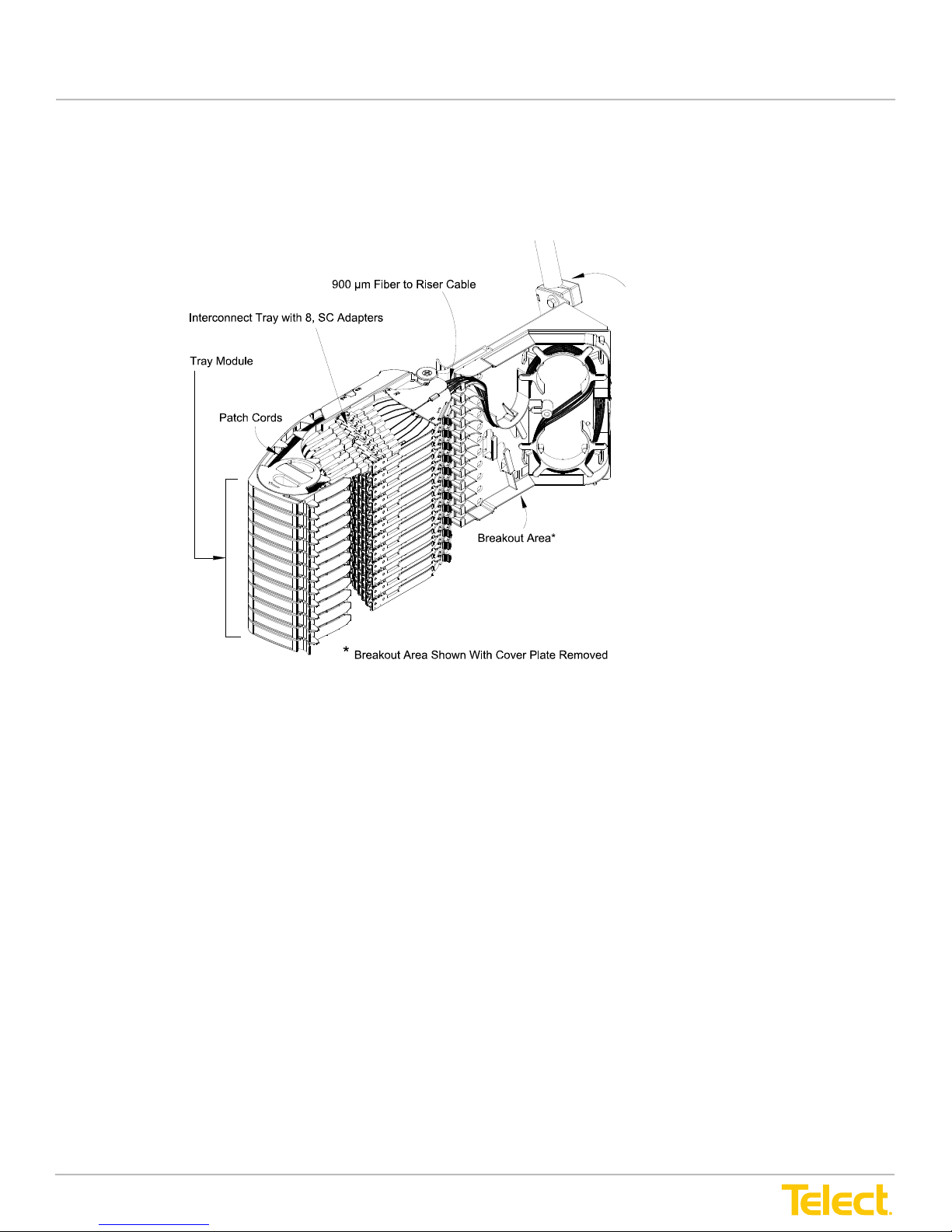
Advanced Distribution Frame (ADF) Systems
1.3 ADF Modules
Normally, Main ADFs are dedicated to either interconnection between intrafacility cabling and
facility elements, or cross-connection between the network elements. The difference lies in the
type of ADF modules on the right and left sides of the Main ADF Panels.
User Manual
1.3 ADF Modules
Normally, Main ADFs are dedicated to either interconnection between intrafacility cabling and facility elements
or cross-connection between the network elements. The difference lies in the type of ADF modules on the right
and left sides of the Main ADF Panels.
Clamp on Rear of Breakout Box
Secures Riser Cable to Module
Figure 11 - Outboard View of Right-Hand, Intrafacility Cable (IFC) Module
© Telect, Inc., All Rights Reserved, 12.7.16 v.4
1.509.926.6000 :: telect.com
11

Advanced Distribution Frame (ADF) Systems
Figure 12 - Outboard View of Right-Hand, Network Element (NE) Module
User Manual
Figure 12 - Outboard View of Right-Hand, Network Element (NE) Module
.
Figure 13 - Fan-Out Module
ADF modules are available for accommodating ribbon cabling, combining patching with ber splicing, splitting
and other capabilities. The modules come in right- and left-side versions, for the right and left sides of the
Main ADF.
© Telect, Inc., All Rights Reserved, 12.7.16 v.4
1.509.926.6000 :: telect.com
12
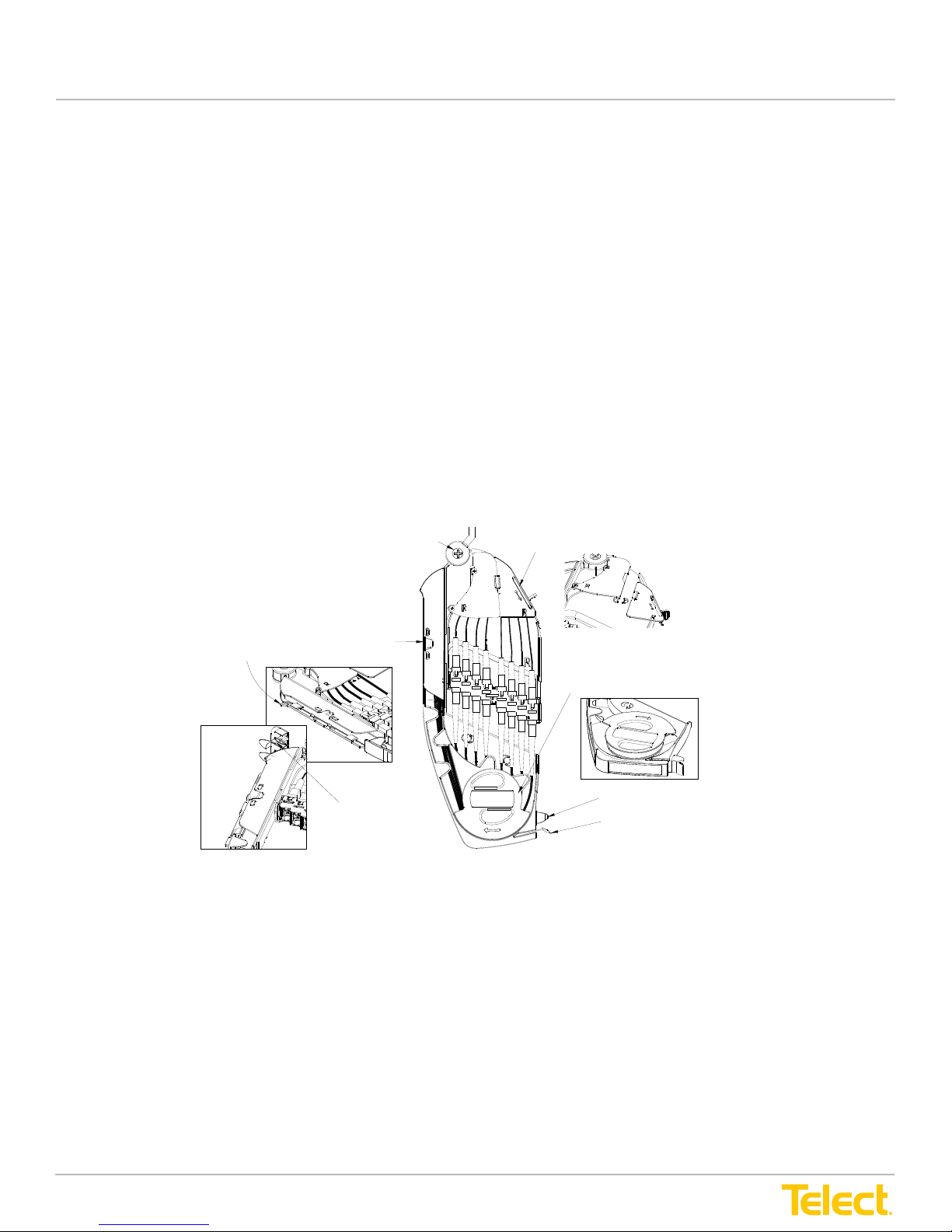
Advanced Distribution Frame (ADF) Systems
Three types of modules are available, depending on application:
1. The IntraFacility Cable (IFC) module contains a breakout area for routing standard 900
micron fiber cabling from a rear-side clamp holding the riser cable. The 900-micron fibers
are routed to optical adapters in the trays.
2. The Network Element (NE) module contains raceways for routing standard 2-mm network
element cabling to the adapters.
3. The Fan-Out (FO) module accommodates up to 12 different multifiber cable
clamp positions.
Individual trays swing toward the inboard area of the Main ADF to simplify the cabling process.
The trays contain a moveable adapter bridge that slides toward the rear when the tray is opened.
The sliding bridge provides slack management as the tray opens.
Fiber cables from the breakout area or raceways are routed under a cover to
the rear side of the
adapters. The patch cords connected to the front side of the adapters are routed around a spool
containing a retaining flange, through a raceway, to a vertical array of cascade guides with
turnstiles attached to the inboard patch area of the ADF. A door at the end of each raceway helps
guide cables downward into the patch area
Pivot Point of Tray
.
User Manual
Three types of modules are available, depending on application:
1. The IntraFacility Cable (IFC) module contains a breakout area of routing standard 900 micron ber cabling
from a rear-side clamp holding the riser cable. The 900 micron bers are routed to optical adapters
in the trays.
2. The Network Element (NE) module contains raceways for routing standard 2mm network element cabling
to the adapters.
3. The Fan-Out (FO) module accommodates up to 12 different multi-ber cable clamp positions.
Individual trays swing toward the inboard area of the Main ADF to simplify the cabling process. The trays
contain a moveable adapter bridge that slides toward the rear when the tray is opened. The sliding bridge
provides slack management as the tray opens.
Fiber cables from the breakout area or raceways are routed under a cover to the rear side of the adapters. The
patch cords connected to the front side of the adapters are routed around a spool containing a retaining ange,
through a raceway, to a vertical array of cascade guides with turnstiles attached to the inboard patch area of
the ADF. A door at the end of each raceway helps guide cables downward into the patch area.
S lid e O pe ns to Al low IFC or N etw ork E lem en t Cab lin g
Door Flips Down to Allow Patch Cord Cabling
toPatchCordCascade
Spool Rotates to Allow Patch Cord Cabling
Patch Cord Cascade
With Turns tile
Tab
Latch
Figure 14 - Patch Tray (Physically the Same for IFC, NE and FO Modules)
© Telect, Inc., All Rights Reserved, 12.7.16 v.4
1.509.926.6000 :: telect.com
13
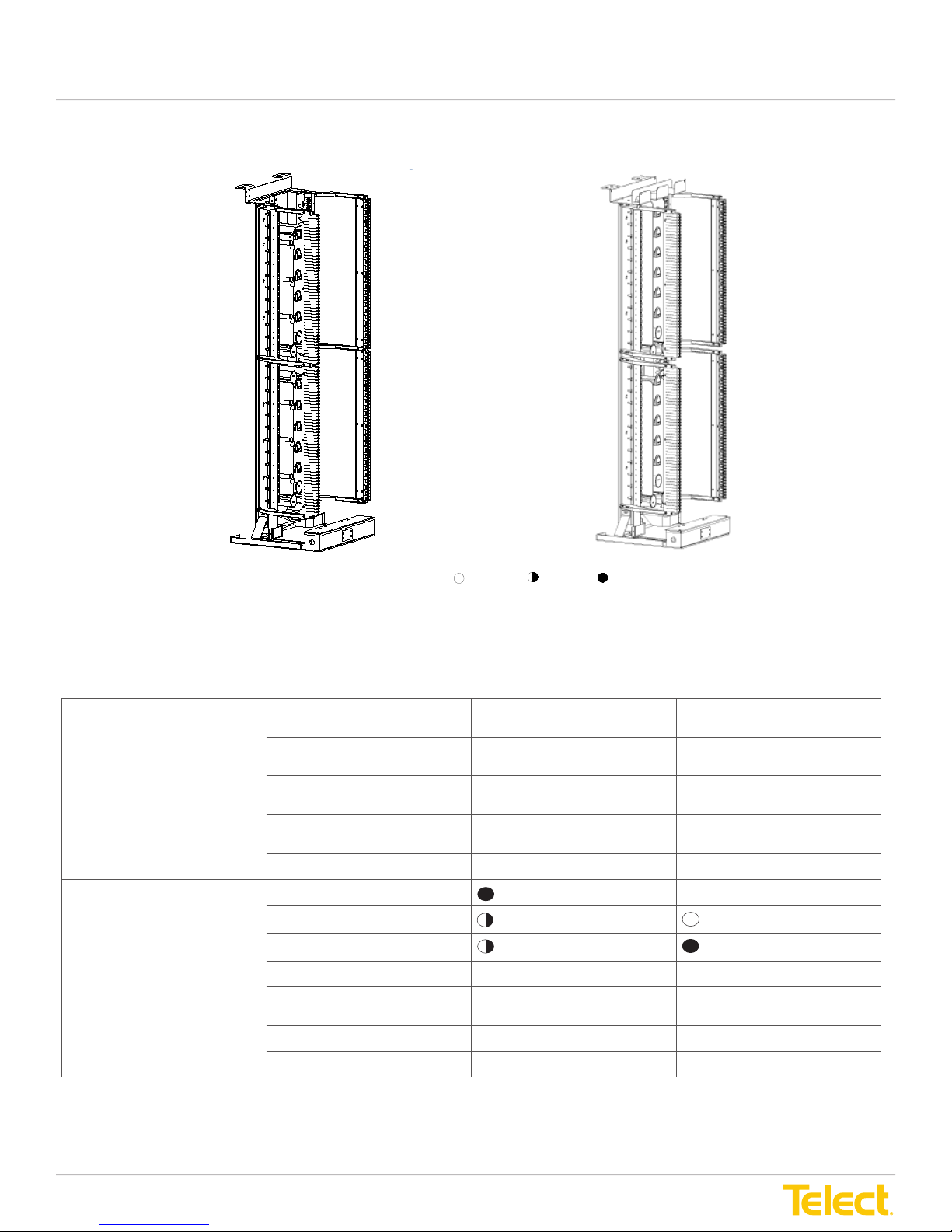
Advanced Distribution Frame (ADF) Systems
1.4 Telect ADF Feature Comparison
Legend: Good Better Best
User Manual
1.4 Telect ADF Feature Comparison
Telect IC
Figure 15 - ADF Comparisons
Max. Terminations/Ft
(Small Form Factor) LC
Capacity
Max. Frames in a Lineup
at Max. Density
Max. Terminations in a Lineup 16,128 (LC) 4,860 (LC)
Flexibility to Grow Yes Yes
Telect XI
1536
(2304)
2
396
(594)
7 (LC) 4 (LC)
1536
(2304)
396
(594)
(4 x 2304)
Inter-Bay Cross-Connect
Application
Single Jumper
(Cross-Connect Length)
On-frame splicing Ye s Ye s
Off-frame splicing Yes Yes
© Telect, Inc., All Rights Reserved, 12.7.16 v.4
1.509.926.6000 :: telect.com
Yes Yes
Yes
(4.5 m)
14
Yes
(4.5 m)
Advanced Distribution Frame (ADF) Systems
Legend: Good Better Best
User Manual
Telect IC
Figure 16 - ADF Comparisons
© Telect, Inc., All Rights Reserved, 12.7.16 v.4
1.509.926.6000 :: telect.com
15
 Loading...
Loading...