Page 1
Installation Instructions
Enwatch Unit
Catalog Number
EK-44750C
Topic Page
Important User Information 2
Enwatch Unit Overview 3
Install the Enwatch Unit 6
Wire the Enwatch Unit 8
Apply Power 12
Network Configuration 13
Monitoring and Troubleshooting 15
Enwatch Measurement Capabilities 17
Configure and Enwatch Board with Emonitor Software 25
Add an Enwatch Unload Station 25
Specifications 31
Additional Resources 32
Page 2
2 Enwatch Unit
Important User Information
Solid-state equipment has operational characteristics differing from those of electromechanical equipment. Safety Guidelines for the Application, Installation and Maintenance of Solid
State Controls (publication
differences between solid-state equipment and hard-wired electromechanical devices. Because of this difference, and also because of the wide variety of uses for solid-state equipment,
all persons responsible for applying this equipment must satisfy themselves that each intended application of this equipment is acceptable.
In no event will Rockwell Automation, Inc. be responsible or liable for indirect or consequential damages resulting from the use or application of this equipment.
The examples and diagrams in this manual are included solely for illustrative purposes. Because of the many variables and requirements associated with any particular installation,
Rockwell Automation, Inc. cannot assume responsibility or liability for actual use based on the examples and diagrams.
No patent liability is assumed by Rockwell Automation, Inc. with respect to use of information, circuits, equipment, or software described in this manual.
Reproduction of the contents of this manual, in whole or in part, without written permission of Rockwell Automation, Inc., is prohibited.
Throughout this manual, when necessary, we use notes to make you aware of safety considerations.
SGI-1.1 available from your local Rockwell Automation sales office or online at http://www.rockwellautomation.com/literature/) describes some important
WARNING: Identifies information about practices or circumstances that can cause an explosion in a hazardous environment, which may lead to personal injury or death,
property damage, or economic loss.
ATTENTION: Identifies information about practices or circumstances that can lead to personal injury or death, property damage, or economic loss. Attentions help you
identify a hazard, avoid a hazard and recognize the consequences.
SHOCK HAZARD: Labels may be on or inside the equipment, for example, a drive or motor, to alert people that dangerous voltage may be present.
BURN HAZARD: Labels may be on or inside the equipment, for example, a drive or motor, to alert people that surfaces may reach dangerous temperatures.
IMPORTANT Identifies information that is critical for successful application and understanding of the product.
ATTENTION: This equipment is intended for use in a Pollution Degree 2 industrial environment, in overvoltage Category II applications (as
defined in IEC 60664-1), at altitudes up to 2000 m (6562 ft) without derating.
Rockwell Automation Publication GMSI10-IN001A-EN-P - May 2013
Page 3

Enwatch Unit 3
Enwatch Unit Overview
The following sections give an overview of the hardware and electrical
components of the Enwatch® unit.
Hardware Overview
The Enwatch unit contains a printed circuit board and power supply on a
mounting base plate and housed in a metal enclosure. Use the key on the door of
the enclosure to access the enclosure.
The unit is pre-wired with mains input terminals connected to an internal 24V
power supply. The power supply and internal wiring are fitted to a mounting
base.
The output of the 24V power supply connects to the printed circuit board. The
circuit board is mounted on six stand-offs to the mounting base plate. The
printed circuit board and terminal connectors are packed separately.
To correctly install the unit, follow the steps in
page 6.
Install the Enwatch Unit on
Rockwell Automation Publication GMSI10-IN001A-EN-P - May 2013
Page 4
4 Enwatch Unit
Electrical Overview
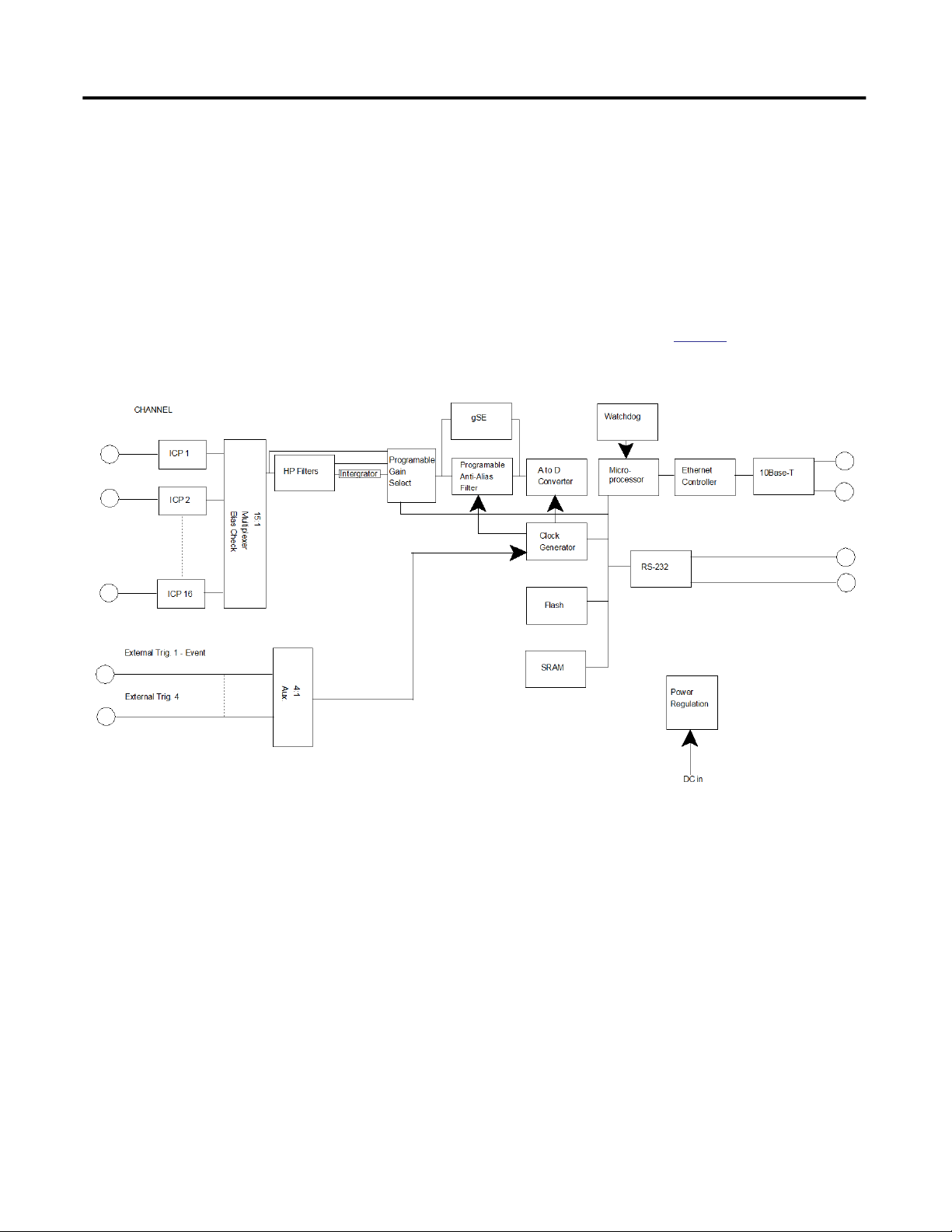
Enwatch is a distributed network system providing 16 channels of analog inputs
together with 4 trigger channels. The unit includes signal conditioning and
analog to digital conversion. It lets you connect 16 two-wire ICP or other sensors
into your Emonitor® Online system. Each Enwatch unit is a
microprocessor-based system, complete with a network controller that carries out
data acquisition tasks as directed by an Emonitor unload station.
A typical diagram for an Enwatch unit is shown in
Figure 1 - Enwatch Block Diagram
Figure 1.
The Enwatch unit responds to all relevant network data exchanges as defined by
the Ethernet protocol using the UDP/IP standard. In addition, there is a
comprehensive on-board monitor program that can exercise all functions via the
on-board serial RS232 port.
Rockwell Automation Publication GMSI10-IN001A-EN-P - May 2013
Page 5
Enwatch Unit 5
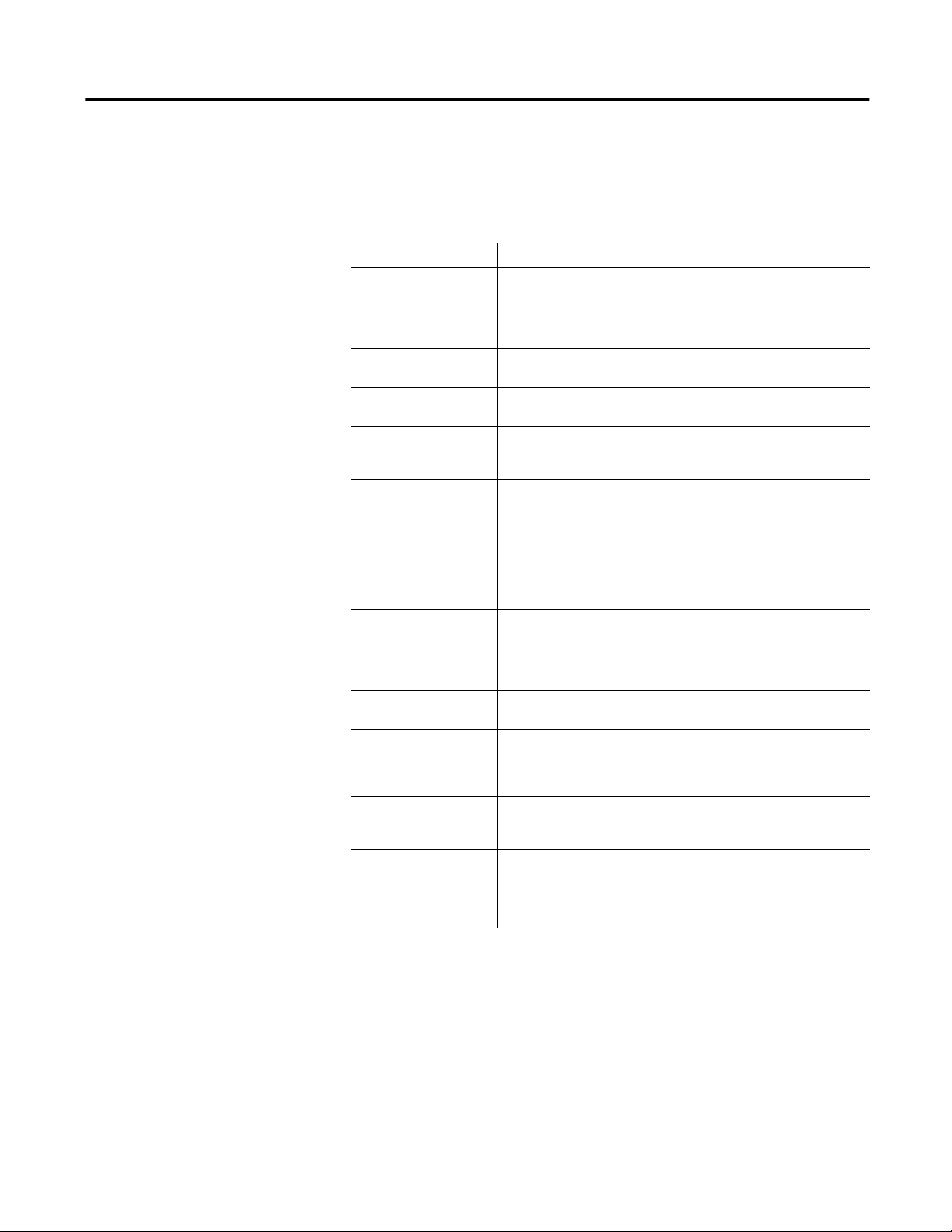
The circuit board is a completely self-contained, 16-channel analog input to
Ethernet interface, including power regulation and local communication
facilities. Each block of the diagram in
Table 1 - Electrical Block Descriptions
Block Description
ICP interface Each of the 16 channels has its own ICP interface that is capable of powering a typical
Multiplexer The multiplexer circuit selects one of the 16 input channels under software control.
High-pass filters Four software-programmable high-pass filters (0.36 Hz, 2.67 Hz, 5.3 Hz, and 23.8
Integrator An on-board hardware integrator is available for getting a velocity measurement
Spike Energy™ function (gSE™) gSE provides a conditioned signal suitable for measurement of bearing condition.
Anti-aliasing filter This filter removes high-frequency components from the incoming analog signal
Analog-to-digital converter
(ADC)
Clock generator The timer varies the sampling rate under microprocessor control. Sampling can be
Gain amplifier The Enwatch unit automatically sets the input gain in auto-range mode as each
Microprocessor subsystem This contains the microprocessor, flash memory, and SRAM memory. The
Watchdog The microprocessor subsystem incorporates a watchdog that, if a power glitch or
Ethernet controller/buffer
memory/10Base-T
Power regulation Input DC power is derived from an AC to DC converter and the Power Regulation
two-wire ICP transducer. The nominal voltage is 24 V with a constant current of 3.6
mA. A typical transducer has a bias voltage value of around 11 V, so that the system
can accommodate a full ±10V input range. The ICP interface can be disabled for AC
and DC coupling of voltage signals.
All inputs are over-voltage and ESD protected.
Hz) are available to remove unwanted low frequency signals.
from an accelerometer, as well as displacement from a velocity sensor. The host
software can perform a second level of integration if required.
that can alias back into the sampled signal, resulting in incorrect data in the
spectrum. The filter has a very high roll-off and removes all alias effects in standard
sampling/spectral analysis applications.
The ADC samples up to 51.2 kHz and has 16-bit resolution, providing a theoretical
dynamic range of 96 dB.
synchronized to one of 4 external triggers (typically a once-per-rev TTL signal from a
rotating shaft). This system can also take a preprogrammed number of samples per
revolution. The external trigger acts as a tachometer to determine shaft speed. Pre
and post-trigger functions are available.
channel is selected by the multiplexer.
microprocessor controls the Enwatch unit under instructions stored in the flash
memory. The SRAM memory acts as a temporary data storage area if buffering is
required before data is transferred over the network.
other external effect interrupts the system, automatically resets without the need for
user intervention.
These functions control data transfer over the Ethernet network. The system uses the
UDP/IP standard protocol and implements 10 Base-T as the physical network layer.
function provides the secondary DC voltages as required.
Figure 1 on page 4 is described below.
Rockwell Automation Publication GMSI10-IN001A-EN-P - May 2013
Page 6
6 Enwatch Unit
Install the Enwatch Unit
Use these installation instructions to install, test, and configure the Enwatch
hardware. For information on collecting data with the Enwatch unit, refer to the
Emonitor User's Guide, publication
ATTENTION: If the Enwatch unit is used in a manner not specified by Rockwell
Automation, the protection provided by the Enwatch unit may be compromised.
EMONTR-UM001.
Install the Enclosure and Mounting Base Assembly
Follow these steps to install the enclosure and mounting base assembly.
ATTENTION:
• Only properly trained and certified professionals should complete these steps.
• All local safety regulations regarding mains powered equipment must be followed.
• Do not tamper with or deface safety or rating labels - they are there to ensure safe
operation and servicing.
• A switch or circuit breaker must be included in the installation of the Enwatch unit,
and must be:
– suitably located and easily reached; and
– marked as the disconnecting device for the equipment.
• The Enwatch unit must have an Earth Ground.
• The incoming supply must be in the range 100 to 240V AC and 50 or 60 Hz.
• The incoming mains power supply must be fused at 3A with a single spur, Enwatch
units can not be daisy chained from a single fused source.
1. Remove the four screws and washers from the corners of the mounting
base-plate, then remove the power supply and mounting base assembly.
2. Drill the enclosure for conduit connection and other required cables.
3. Use the included bracket set to mount the unit to the wall.
4. Fit the power supply and mounting base assembly back into position and
replace the four mounting base-plate screws and washers.
5. To connect mains power to the Enwatch unit, follow these steps.
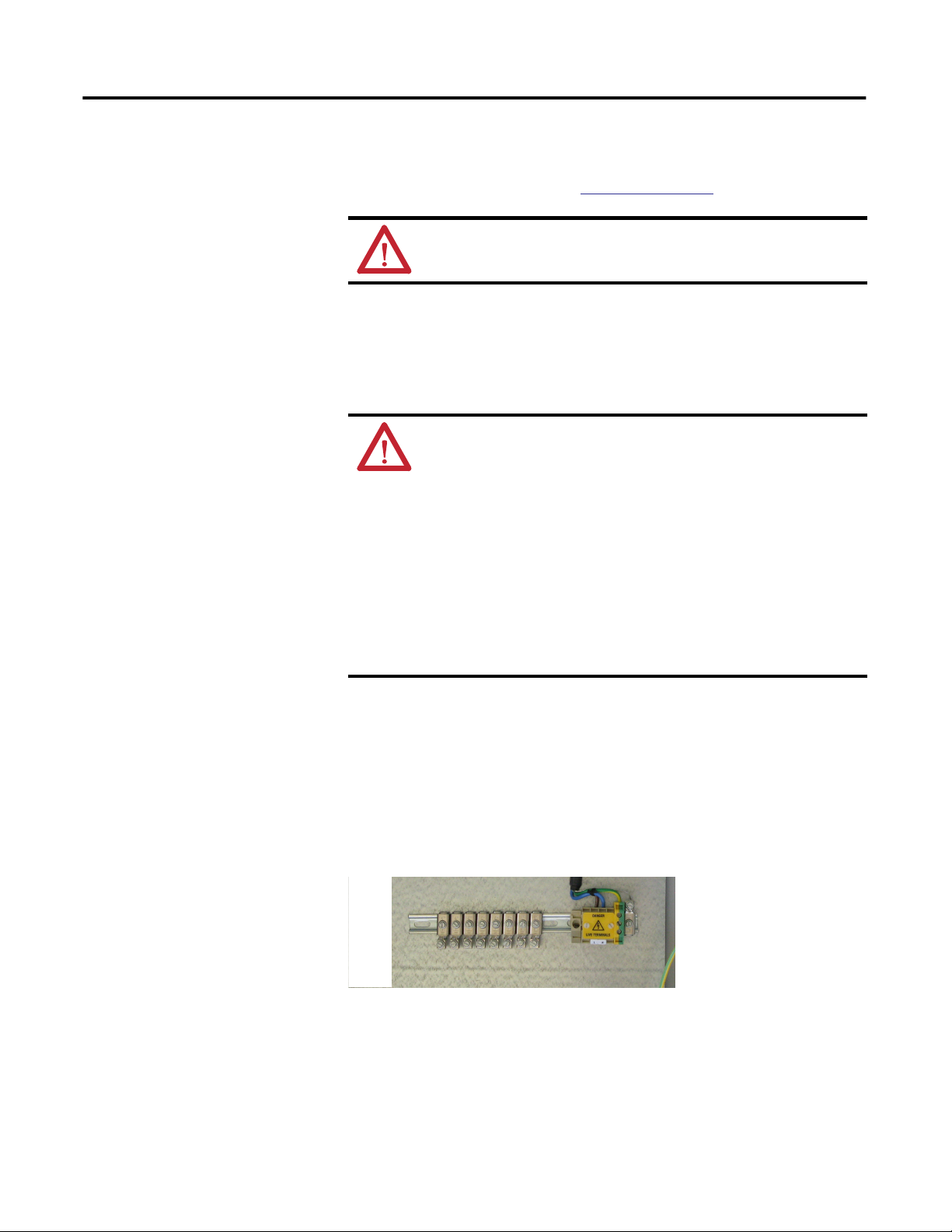
Earth Ground Terminal Strip
Mains Power Input and
Earth Ground Terminals
a. Ensure that the mains input cables are isolated at source from mains
power.
b. Connect the earth grounding wire at the bottom-right corner.
c. Remove the yellow safety cover from the live (L) and neutral (N)
terminals.
Rockwell Automation Publication GMSI10-IN001A-EN-P - May 2013
Page 7
RX LK OB
TX
11
10
7
13
15
A - B A - B A - B A - B A - B A - B
1 - 2 - 3 - 4 - 5 - 6 - 7 - 8 9-10-11-12-13-14-15-16 1 - 2 - 3 - 4 - 5 - 6 - 7 - 8
A - B A - B A - B A - B A - B
A - B
1
d. Connect mains input wires, paying attention to terminal markings
live (L) and neutral (N).
e. Verify that all connections are safely made, then replace the yellow
safety cover.
Install the Enwatch Board
Use the following information to install the Enwatch board.
12
9
9-10-11-12-13-14-15-16
2
_
+
8
6
5
4
3
14
A - B
16
A - B
A - B
A - B
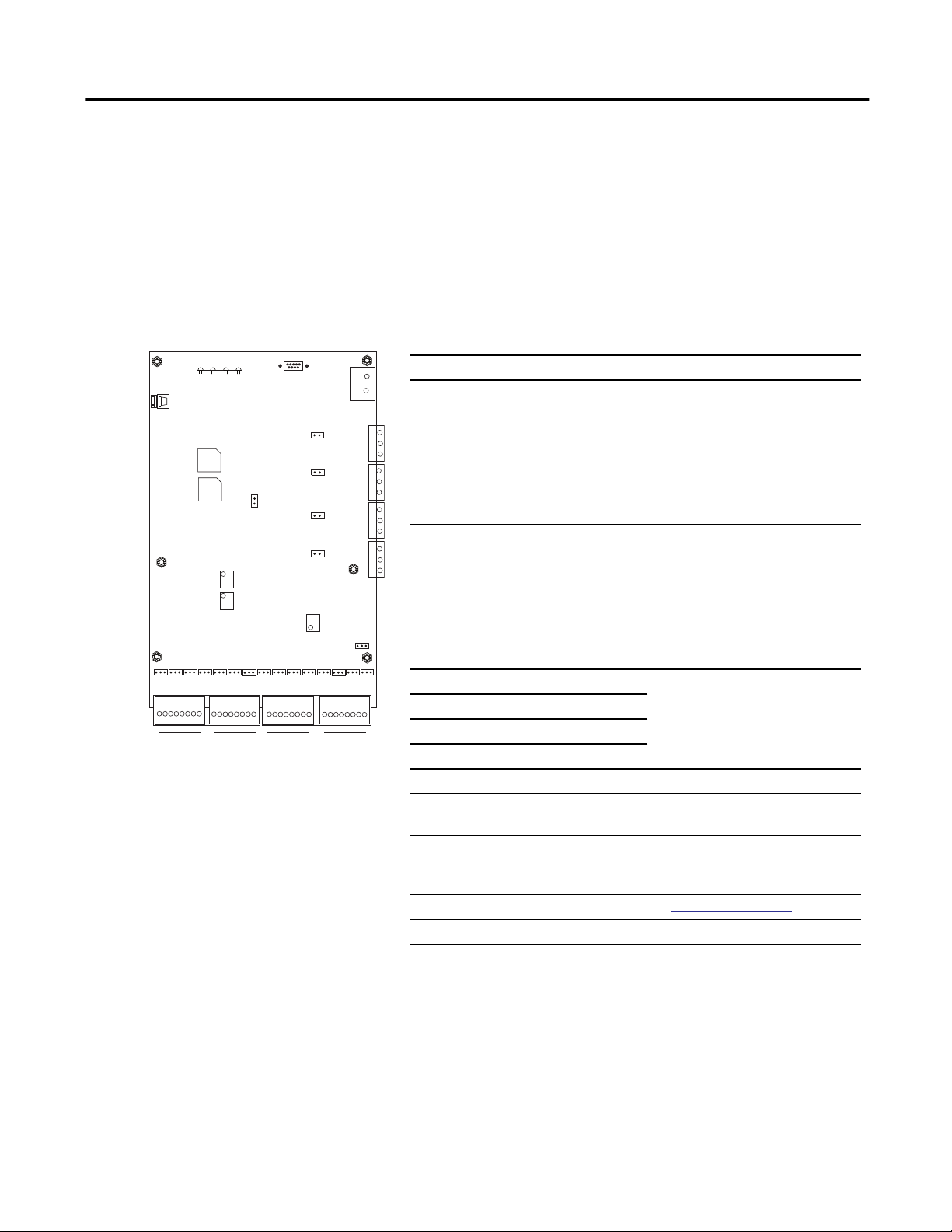
Connector Description Pin No./name - Signal
1 Analog input channels 1–8 1 - CH 1 input
33
22
1
33
22
1
33
22
1
2 Analog input channels 9–16 1 - CH 9 input
33
22
1
3 External trigger 1 / event 1 1 - Power supply
4 External trigger 2 / event 2
5 External trigger 3
6 External trigger 4
7 Ethernet interface RJ-45
8 Supply voltage + (plus) - Positive supply voltage
9 Serial port (RS-232)
(1)
10 Status Indicators See
11…16 Screws
2 - CH 1 ground
3 - CH 2 input
4 - CH 2 ground
5 - CH 3 input
6 - CH 3 ground
7 - CH 4 input
8 - CH 4 ground
2 - CH 9 ground
3 - CH 10 input
4 - CH 10 ground
5 - CH 11 input
6 - CH 11 ground
7 - CH 12 input
8 - CH 12 ground
(2)
(3)
2 - Input
3 - Ground
- (minus) - Common
2 - RXD
3 - TXD
5 - Ground
Status Indicators on page 16
Enwatch Unit 7
9 - CH 5 input
10 - CH 5 ground
11 - CH 6 input
12 - CH 6 ground
13 - CH 7 input
14 - CH 7 ground
15 - CH 8 input
16 - CH 8 ground
9 - CH 13 input
10 - CH 13 ground
11 - CH 14 input
12 - CH 14 ground
13 - CH 15 input
14 - CH 15 ground
15 - CH 16 input
16 - CH 16 ground
(1) To connect to a host computer, use a null modem 9-pin female to 9-pin female cable.
(2) A supply voltage is available on pin 1 of the connector to power an external trigger device. The voltage is equal to
the voltage of the incoming power supply to the board (on connector J9). The limit on the power supply pin on
each external trigger is limit 50 mA.
(3) The external trigger is compatible with a CMOS/TTL logic level (5 V logic). Alternatively, any voltage input in the
range 5 to 24 V can be accommodated. The trigger can be isolated or non-isolated.
1. Place the Enwatch board on the mounting base-plate standoffs and insert
the screws.
2. Connect the Ethernet cable.
Rockwell Automation Publication GMSI10-IN001A-EN-P - May 2013
Page 8
8 Enwatch Unit
Wire the Enwatch Unit
For optimum performance, use shielded cables for all connections to the Enwatch
unit. For sensors such as accelerometers, connect the screens on the cables to
chassis ground at only one point. The optimal place for this is inside the Enwatch
enclosure and eight ground terminals are provided for this purpose. Connect the
screen at only one end; do not connect to ground at both ends.
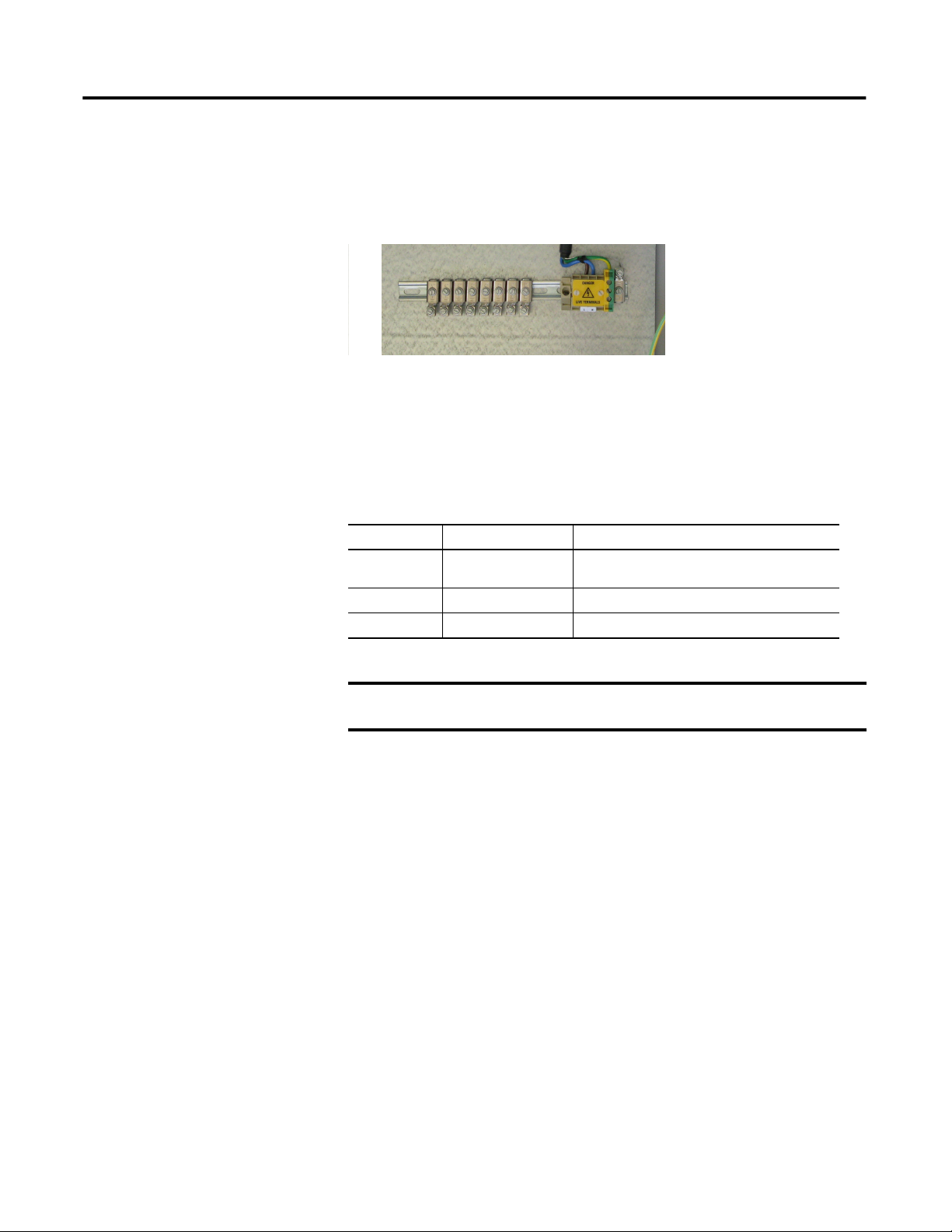
Earth Ground Terminal Strip
Mains Power Input and
Earth Ground Terminals
Analog Input Configuration
Each channel (16 total) has a 3-way header associated with it. These are labeled
with the channel number and ‘A’ or ‘B’. The three jumper options and couplings
are the following.
Coupling Fitted to Position Description
ICP x A
DC x B
AC Not Fitted AC coupled
(1)
(1)
ICP power (nominal 24 V at 3.6 mA constant current for
transducer powering)
DC coupled
(1) Where x is the channel number, 1-16.
IMPORTANT
The -3dB point of the high-pass coupling for the ICP interface and AC Coupled
configuration is 0.07 Hz.
Rockwell Automation Publication GMSI10-IN001A-EN-P - May 2013
Page 9

Enwatch Unit 9
Trigger Isolation Jumpers
These jumpers cause the four trigger inputs to be isolated or non-isolated.
Non-isolated means the common of the trigger input can be connected to the
common of the Enwatch unit. With a jumper removed, the trigger is isolated.
The following table describes the jumper positions.
20
19
18
17
33
22
1
33
22
1
33
22
1
33
22
1
Mode Jumper Position
External trigger 1 isolated 17 Out
External trigger 1 non-isolated 17 In
External trigger 2 isolated 18 Out
External trigger 2 non-isolated 18 In
External trigger 3 isolated 19 Out
External trigger 3 non-isolated 19 In
External trigger 4 isolated 20 Out
External trigger 4 non-isolated 20 In
IMPORTANT
If an external sensor is powered from pin 1 of the external trigger terminals, the
jumper corresponding to the trigger channel must be inserted to provide a ground
return path for the sensor power.
Rockwell Automation Publication GMSI10-IN001A-EN-P - May 2013
Page 10
10 Enwatch Unit
Serial Port (RS-232)
An RS-232 compatible serial port is available for providing local communication
with the board (independent of the Ethernet network). Only RXD and TXD
lines are supported, and so a null modem cable must be used. An on-board
software monitor is provided to communicate through the serial port.
If you do not use a 9-pin female to female null modem cable, the recommended
cable connection to a computer is defined in the table below.
OB
RS-232 Pin 9-Pin D-Shell Connector
RX 2
TX 3
Gnd 5
9
_
Transducers
The following sections show how to connect transducers to the Enwatch
terminals.
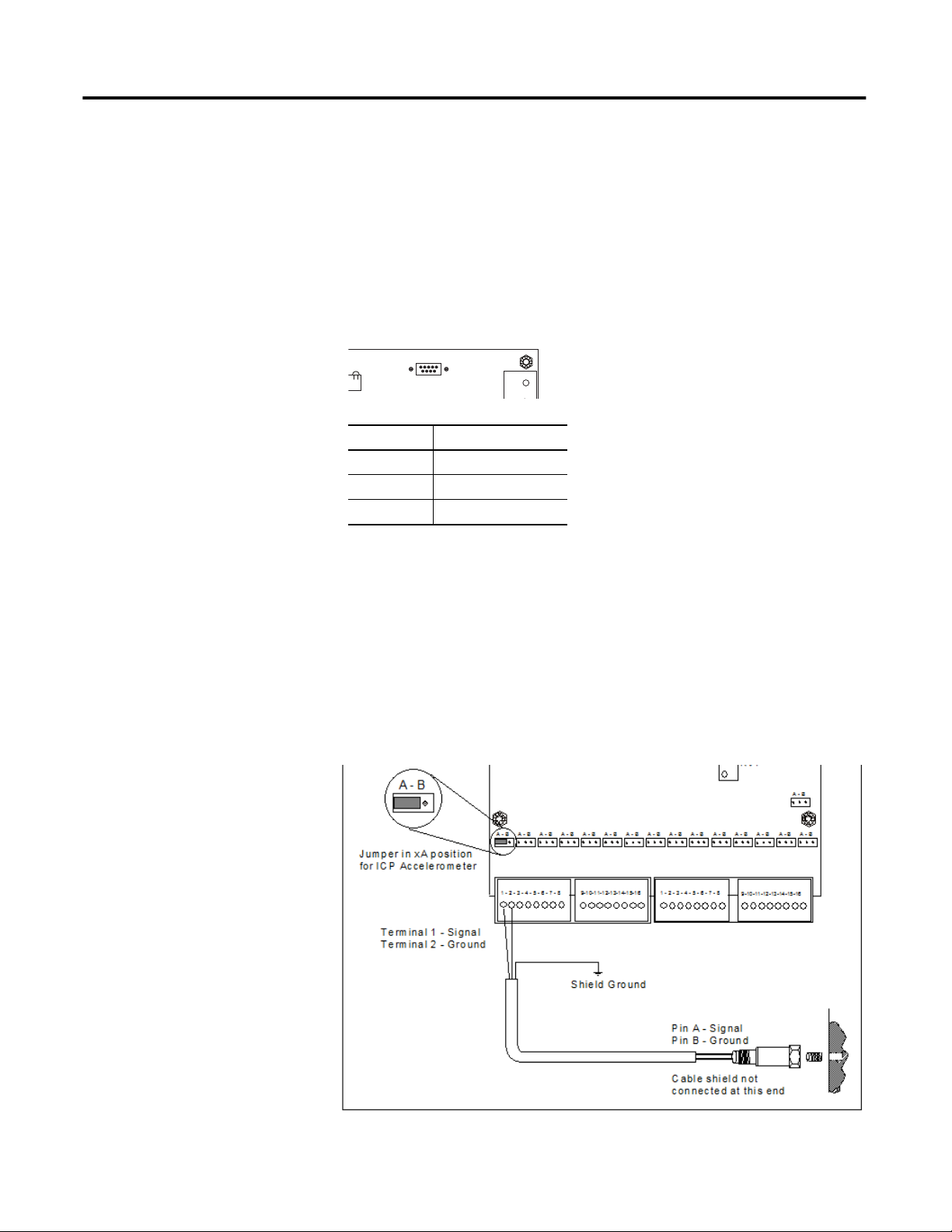
Connecting an ICP Accelerometer
The following diagram shows the wiring from an ICP accelerometer to the
terminals of the Enwatch unit.
Rockwell Automation Publication GMSI10-IN001A-EN-P - May 2013
Page 11

Enwatch Unit 11
Connecting a Coil-Based Velocity Sensor
The following diagram shows the wiring from a coil-based velocity sensor to the
terminals of the Enwatch unit.
Connecting an Process DC Voltage Signal
The following diagram shows the wiring from a process DC voltage signal to the
terminals of the Enwatch unit.
Rockwell Automation Publication GMSI10-IN001A-EN-P - May 2013
Page 12

12 Enwatch Unit
Connecting a Magnetic Hall Effect Sensor
The following diagram shows the external trigger wiring from a magnetic Hall
effect sensor (magnetic interrupter) to the terminals of the Enwatch unit.
Ground
33
17
3
A - B
Input
22
1
Power
Apply Power
A - B
A - B
A - B
IMPORTANT
A - B A - B A - B A - B A - B A - B
1 - 2 - 3 - 4 - 5 - 6 - 7 - 8 9-10-11-12-13-14-15-16 1 - 2 - 3 - 4 - 5 - 6 - 7 - 8
A - B A - B A - B A - B A - B
A - B
If an external sensor is used that is powered from pin 1 of
9-10-11-12-13-14-15-16
any of the trigger connectors (3, 4, 5 or 6), then the jumper
corresponding to the trigger channel must be inserted to
provide a ground return path for the sensor power.
Trigger Isolation Jumpers on page 9.
See
Use the following instructions to apply power to the Enwatch unit.
1. Connect the DC power supply cable to connector 8 on the Enwatch
board.
Maintenance and Service
_
8
+
2. Apply power at mains source.
3. Verify that the DC power input status indicator is green.
The device requires little ongoing maintenance except for periodic checking of
the wiring inside the enclosure. In very dirty environments, occasional lubrication
of the hinges and lock, together with cleaning of the door seal is recommended.
IMPORTANT
Rockwell Automation Publication GMSI10-IN001A-EN-P - May 2013
Only properly trained and certified professionals should perform maintenance
operations.
Page 13

Enwatch Unit 13
Network Configuration
Contact your IT department to obtain a unique IP address, Subnet Mask, and
Gateway IP address (if available) for each Enwatch unit and record them here.
IP Address 1: ___________________ IP Address 6: ____________________
IP Address 2: ___________________ IP Address 7: ____________________
IP Address 3: ___________________ IP Address 8: ____________________
IP Address 4: ___________________ IP Address 9: ____________________
IP Address 5: ___________________ IP Address 10: ___________________
To assign the IP address, Subnet Mask and Gateway IP address (if available),
complete the following steps.
TIP
The network configuration can be done while the Enwatch board is on a bench with
24V applied from an external source. The board does not have to be in the enclosure for
network configuration.
1. Attach the Enwatch unit to a terminal (or computer in terminal mode) via
the RS-232 serial port by using a null modem cable.
2. Insert a jumper into the normal/monitor mode connector (21).
3. Start up a terminal program (Hyperterminal) and set it up to
communicate through the serial port with the following settings:
• 9600 Baud
• No parity
• 8 data bits
• 1 stop bit
4. Turn on the Enwatch unit.
The configuration menu is displayed in the terminal window.
Main Menu:
1 - Exercise Hardware Control
2 - Exercise Memory Devices
3 - Exercise Ethernet Controller
4 - Exercise Combined Sub-Systems
5 - Configure Adapter Settings
Make your selection (1-5) :
5. Select 5- Configure Adapter Settings.
6. Select 2 - Assign Host MAC, and set it to the MAC address from the
board (press Esc if the MAC address shown is the correct one).
Rockwell Automation Publication GMSI10-IN001A-EN-P - May 2013
Page 14

14 Enwatch Unit
7. Select 3 - Assign Host IP, and set your Enwatch unit to one of your plant
specific IP addresses (press Esc if the IP address shown is the correct one).
Please note, you must enter all of the digits of the IP address, including
zeros that are placeholders. For example, the IP address 192.168.1.2 must
be entered as 192.168.001.002.
8. Select 4 - Assign Host UDP Port, and set it to 4242. This is the default
port number and cannot be any other number.
9. Select 5 - Assign Subnet Mask, and set it to the number obtained from
your IT department. Normally it is 255.255.255.000.
10. Select 6 - Assign Gateway IP, and set it to the number obtained from your
IT department.
11. Select 7 - Assign Name (the default is blank) and enter a name.
12. Select 8 - Assign Network Name, and enter a name for the network (the
default network name will be used unless overwritten here).
13. Select 9 - Assign Debug Level, and select which level of debug messages
you want to receive.
• 0 - no messages (use this for normal operation)
• 1 - Basic system sampling and message processing
• 2 - Basic system sampling and message processing, plus full Rx & Tx
messages
• 2 - Basic system sampling and message processing, full Rx & Tx
messages, plus interrupt firing notifications
IMPORTANT
Do not change options A and B. They are to assist in debug only.
14. Shut down the Enwatch unit by removing the AC power, and then turn it
back on. Look at the configuration settings and make sure the MAC and
IP address are correct.
15. Shut down the Enwatch unit by removing the AC power, then remove the
jumper from the normal/monitor mode connector (21) and connect the
board to an active Ethernet connection. You do not have to disconnect the
RS-232 port.
16. Open a DOS prompt on a networked computer. Type ping, then a
space, and then the first IP address.
EXAMPLE
ping 200.100.200.100
If configured correctly, a response is returned from the Enwatch unit.
Rockwell Automation Publication GMSI10-IN001A-EN-P - May 2013
Page 15

Enwatch Unit 15
Monitoring and Troubleshooting
Use the following sections to help you monitor and troubleshoot the
Enwatch unit.
On Board Monitor
When you insert a jumper into the normal/monitor mode connector (21), the
Enwatch unit operates in its internal monitor mode. This enables you to change
the IP address as well as modify other options.
21
Mode Connector 21
Normal Jumper out
Monitor Jumper in
To invoke monitor mode, complete these steps.
1. Connect a terminal (or computer in terminal mode) to the serial port
2. Insert a jumper into the normal/monitor mode connector (21).
3. Remove the power and then reconnect the power to reset the unit.
The configuration menu is displayed in the terminal window.
Main Menu:
1 - Exercise Hardware Control
2 - Exercise Memory Devices
3 - Exercise Ethernet Controller
4 - Exercise Combined Sub-Systems
5 - Configure Adapter Settings
Make your selection (1-5) :
4. Use menu selections 1…4 to exercise the various sections on the Enwatch
board.
For information about selection 5, Configure Adapter Settings, see
Network
Configuration on page 13.
To exit monitor mode, remove the jumper from the normal/monitor mode
connector (21), then remove and reconnect the power to reset the unit.
Rockwell Automation Publication GMSI10-IN001A-EN-P - May 2013
Page 16

16 Enwatch Unit
Status Indicators
These status indicators indicate the status of the Ethernet communication.
RX LK OB
TX
Name Description
TX Flashes green when a response is sent from the board.
Note: If the Enwatch board has an IP address that is not compatible with the network
the TX indicator will not blink.
RX Flashes green when a message is received.
LK Solid green when the Enwatch unit is connected the network. Otherwise the indicator
OB Flashes green when the on-board processor and the on-board LAN controller are
In the event of a system problem, use a portable computer to diagnose the
problem via the RS-232 serial interface on the Enwatch board.
is off.
exchanging data.
Flash Memory
23
22
If you need to change the firmware, the flash memory is located as shown above.
This flash memory is socket mounted to allow you to change the EPROM. Make
sure that the orientation of the chip is correct when installing.
Rockwell Automation Publication GMSI10-IN001A-EN-P - May 2013
Page 17

Enwatch Unit 17
Enwatch Measurement
This section lists the measurement capabilities of the Enwatch unit.
Capabilities
Table 2 - Enwatch measurement capabilities
Product Feature Capability
Signal Control Raw input signal
Integrated input signal via HP filter
Hp filter input signal
gSE 200 Hz input signal
gSE 5000 Hz input signal
Bias Voltage
Combining measurements in the Enwatch driver The Enwatch driver can combine measurements at the same location in the Emonitor software. The following items must to
How does the Enwatch driver choose the high-pass
filter?
be the same to combine measurements.
Signal route control (Integrate/non integrate/gSE/Raw)
Tachometer on/off
gSE time constant
Sample rate/maximum frequency
Phase lock loop
Number of averages
Measurement filter
Number of lines
X=2 x FMAX/lines
If X > 5.3 then set to 23.8
else if X > 2.67 set to 5.3
else if X > 0.36 set to 2.67
else if the Smart HP filter is on in the Emonitor software, then set to 2.67, otherwise set to 0.36
Note: The Smart HP filter in the Emonitor software does not use 0.36Hz HP filter.
Trigger usage Sample on trigger (the first version of Enwatch always uses this option)
Sample on post-trigger
Sample on pre-trigger
Tachometer usage Use tachometer for PLL (phase loop locked)
Autorange Always on, maximum input ±10 V
Integrator reset control Reset before first sampling of a measurement
Sampling rate 64 to 51200 Hz by 1
FMAX Sampling Rate FMAX Sampling Rate
25 64 2000 5120
50 128 3200 8192
100 256 4000 10240
200 512 5000 12800
400 1024 6400 16384
500 1280 8000 20480
800 2048 10000 25600
1000 2560 16000 40960
1600 4096 20000 51200
Number of synchronous time averages 1, 2, 4, 8, 32... 32768
Rockwell Automation Publication GMSI10-IN001A-EN-P - May 2013
Page 18

18 Enwatch Unit
Table 2 - Enwatch measurement capabilities
Product Feature Capability
Sample length Multiple of 256 bytes, maximum sample 32768 bytes if no trigger, 16384 bytes with pre-trigger (not used in first version of
Filter settling time HP 0.36 Hz 18 seconds
Trigger delay 0-32768 samples. The Emonitor software always uses 0.
Trigger channel 1-4 channels, TTL input 5-20 V
Gain control X1, X10, X100, X1000, X5, X50, X500, X5000
Anti-Alias filter 20 kHz, 2 kHz, 500 Hz, 100 Hz. This is read only. The Enwatch unit selects the proper filter.
gSE time constant 0.03, 0.006, 0.0012, 0.00024 seconds, the default is 0.03 seconds
Enwatch)
HP 2.67 Hz 3 seconds
HP 5.3 Hz 1.2 seconds
HP 23.8 Hz 0.3 seconds
Integrator HP 0.36 Hz 25 seconds
Integrator HP 2.67 Hz 8 seconds
Integrator HP 5.3 Hz 1.5 seconds
Integrator HP 23.8 Hz 0.8 seconds
gSE 200 Hz 88 milliseconds
gSE 5 kHz 2 milliseconds
Core 0.7 seconds
Time constant of 0.03 seconds 300 milliseconds
Time constant of 0.006 seconds 60 milliseconds
Time constant of 0.0012 seconds 12 milliseconds
Time constant of 0.00024 seconds 3 milliseconds
Maximum combined trigger current (channels 1-4), not to exceed 100mA.
Download X1 always. The Enwatch unit autoranges and returns back the current gain for rescaling.
if FMAX > 350Hz set to 0.00024 seconds
else if FMAX > 150 Hz set to 0.0012 seconds
else if FMAX > 37.5 Hz set to 0.006 seconds
If the measurement is overall only (no spectrum) then set to 0.03 seconds.
Integrator One level of hardware integration
The hardware has a gain factor of:
2.67/f for the 0.36 Hz and the 2.67 Hz filter ranges (INTHI = 0)
38.9/f for the 5.3 Hz and 23.7 Hz filter ranges (INTHI = 1)
To convert from g->ips:
Velocity (ips peak) = [integrator output (volts peak)] x [1 / (gain factor)] x [accel scale factor
(g peak / mv peak)] x [61.24 / frequency]
Sample sequence allowed 4096 - one sample sequence uses one configuration table
Configuration tables 128 - one measurement point uses one table so the total is 128 points
Storage overhead 18 bytes per allocation
Flash memory lifetime 100,000 writes
Total available memory 640 Kilobytes
HOST software support (Emonitor) Window types: Hanning, Hamming, Rectangular, Kaiser Bessel, Flattop
Number of lines 100, 200, 400, 800, 1600, 3200
Number of averages 1-99
Rockwell Automation Publication GMSI10-IN001A-EN-P - May 2013
Page 19

Enwatch Unit 19
Table 2 - Enwatch measurement capabilities
Product Feature Capability
Bias voltage reading When you define a process measurement of DC in the Emonitor software, the Enwatch unit reads the transducer bias
Maximum number of averages that can be supported Number of samples required: Lines x 2.56 + lines x 2.56(#avg -1) x (1 -%overlap)
voltage.
24V means open circuit, 10V is OK.
Max number of samples per configuration: 32768
Max number of averages = ((32768 / (lines x 2.56)) - 1) / (1 -%overlap) + 1)
The following table shows the maximum number of averages versus the number of lines and percent overlap for non-trigger
point.
Max samples-non trigger points 32768
% overlapping % overlapping % overlapping % overlapping
#lines 0 0.25 0.5 0.75
100 128 170 255 509
200 64 85 127 253
400 32 42 63 125
800 16 21 31 61
1600 8 10 15 29
3200 4 5 7 13
6400 2 2 3 5
12800 1 1 1 1
The following table shows the maximum number of averages versus the number of lines and percent overlap for pre-trigger
point.
Max samples-trigger points 16384
% overlapping % overlapping % overlapping % overlapping
#lines 0 0.25 0.5 0.75
100 64 85 127 253
200 32 42 63 125
400 16 21 31 61
800 8 10 15 29
1600 4 5 7 13
3200 2 2 3 5
6400 1 1 1 1
12800 - - - -
Signal detection RMS, Peak, Peak-Peak
Configuration downloading Route mode configuration downloads to Flash memory
Live mode configuration downloads to RAM
Note: You can reduce number of average or increase percent overlap to reduce amount of memory used.
Rockwell Automation Publication GMSI10-IN001A-EN-P - May 2013
Page 20

20 Enwatch Unit
Setting Up Sample Measurements
This section gives examples of setting up measurement definitions in the
Emonitor software.
DC or Other Numeric Measurements
Suppose you have a transducer with an output of -2 V to 2 V and a linear scale
from -10° F to 100° F. How do you set up the transducer in the Emonitor
software?
If the volts reading is R, then the data stored in the Emonitor software is:
(R / calibration + DC offset)
Input range volts: (X, Y)
Scale value: (A, B) volts
Data in the Emonitor software = (R - X) x ((B-A) / (Y-X)) + A
Calibration value in transducer setup: [(Y-X) x 1000mv / eu]/(B-A)
DC Offset in transducer setup: A - (B-A) x X / (Y-X)
EXAMPLE
Input range: (-1.31 V, +0.87 V)
Scale value: (100° F, 200° F)
Calibration: [(0.87 - (-1.31)) x 1000] / (200 - 100) = 21.8
Offset: 100 - (200 - 100) x (-1.31) / (0.87-(-1.31)) = 160.09
Input type should be DC coupled and the jumper setting on board needs to be set
as DC couple as well.
1. In the Emonitor software, select Setup>Calibration and set up the
calibration for the Temperature transducer.
Rockwell Automation Publication GMSI10-IN001A-EN-P - May 2013
Page 21

Enwatch Unit 21
2. Select Setup>Tr a n s d u c e r to select the “Temperature” transducer in the
collection specification.
3. In the Emonitor software, define a numeric measurement definition with
the temperature units and the “Temperature” collection specification.
Transducer Bias Reading
The Enwatch board can take transducer bias readings; however, this is not a
transducer check function that detects transducer failure before taking data. The
bias reading is an independent reading with a different signal path on the
Enwatch board.
1. In the Emonitor software, select Setup>Transducer.
2. To define a new transducer name (for example, “Transducer Check”) click
New.
3. Enter a name and click OK.
Rockwell Automation Publication GMSI10-IN001A-EN-P - May 2013
Page 22

22 Enwatch Unit
4. Select Setup>Calibration to select “Bias Voltage” as the input type for
this transducer. Set the calibration to 1000 and the offset to 0.
5. Click OK.
6. Select Setup>Collection to define a new collection specification. Select
“Transducer Check” as the transducer.
7. In the Emonitor software, define a numeric measurement definition with
V DC units and the “Transducer Bias” collection specification.
Magnitude And Phase Reading
A magnitude/phase reading is similar to any other data collector in the Emonitor
software. Use the “Mag & Phase” collection specification to set up an overall
measurement. Then select “1st Order” as the measurement filter (or any other
desired order).
Rockwell Automation Publication GMSI10-IN001A-EN-P - May 2013
Page 23

Enwatch Unit 23
Order Normalized Measurements
Enable order normalized measurements in the collection specification.
1. In the Emonitor software, select Setup>Collection.
2. Edit an existing collection specification or create a new one.
3. Veri fy tha t Order normalization is checked.
The Enwatch unit then finds the machine speed and applies it to the
number of orders to select the proper sampling rate before collecting data.
IMPORTANT
You must also define a trigger channel for the Enwatch
channel so that the Enwatch unit can find the machine
speed.
Rockwell Automation Publication GMSI10-IN001A-EN-P - May 2013
Page 24

24 Enwatch Unit
DSP Functions in the Enwatch Driver
The Enwatch unit takes only time domain data and returns that data to the host
software. All DSP functions are done by the host driver. In this way, the firmware
can focus on data collection speed. Because the Enwatch board does not handle
calculating the average time waveform, the host driver software must tell the
Enwatch unit to collect a time waveform of sufficient length to calculate the
average.
Limitation on the Number of Points in the Enwatch Unit
The Enwatch unit has 640 K bytes memory for data storage. If you attempt to
collect data on more points than can fit in memory, the unit returns an error
message. The message appears in the Unload Station Manager window (refer to
the Online Applications Guide for more on the Unload Station Manager). The
Enwatch driver can combine measurements in some cases (see “Combining
measurements in the Enwatch driver” on page 17).
If a route has 5 points per channel and 400 lines, 4 averages, no overlap averaging:
Bytes required: 5 points x 16 channels x 1024 bin x 2 byte/bin x 4 averages =
655360 bytes
If a route has 2 points per channel and 800 lines, 4 averages, no overlap averaging:
Bytes required: 2 points x 16 channels x 2048 bin x 2 byte/bin x 4 averages =
524288 bytes
To best use the 640K memory, try to use overlap averaging. For examples, see
“Maximum number of averages that can be supported” on page 19.
Rockwell Automation Publication GMSI10-IN001A-EN-P - May 2013
Page 25

Enwatch Unit 25
Configure and Enwatch Board with Emonitor Software
Add an Enwatch Unload Station
The Enwatch unit is specially designed to operate over an Ethernet connection.
Each Enwatch unit has a unique IP address that can be changed through the
RS232 port inside the unit. Ideally, one Enwatch unload station can serve an
unlimited number of Enwatch units. However, to improve unload speed,
multiple Enwatch unload stations are suggested.
Each Enwatch unit has 16 vibration channels and 4 tachometer channels. In
addition, the Allen Bradley Enlive software (live mode analysis) can be used to
“lock onto” one channel at a time. During live mode analysis, regularly scheduled
unload continues to unload whatever data is in the Enwatch unit buffers before
entering live mode analysis. The Enlive software has a default timeout of 30
minutes to prevent an extended break in unloading scheduled data.
For more information on setting up an Enwatch unit in an Emonitor system,
refer to the Emonitor User's Guide, publication
The Unload Station Manager is a graphical representation of all of the Enwatch
units on your network. It is used for Enwatch configuration of Enwatch IP
addresses, subnet address, and mapping measurement points to Enwatch
channels.
EMONTR-UM001.
1. Click Start>All Programs>Rockwell Software>Emonitor>Online Data
Management Console.
The Online Data Management Console opens.
2. Enter your User Name and Password and click OK.
3. To create a new data source, click New.
4. For Type, enter Enwatch/6600 Online Data.
Rockwell Automation Publication GMSI10-IN001A-EN-P - May 2013
Page 26

26 Enwatch Unit
5. Enter a Name and click OK.
6. Select the new data source, and click Edit.
The Setup window opens.
7. Right-click Emonitor Online and select Insert.
The Insert Unload Station window opens.
8. Select Enwatch Unload Station and click Next.
The General tabs opens.
9. Enter the IP address of the computer on which the Online Data
Management Console is installed (not the IP address of the Enwatch
board), or click Browse to find the computer name.
10. Add a description of the computer and click Finish.
The Enwatch Unload Station icon is added to the window.
The red OFF indicates that there are no Enwatch units or there is no
connection to an Enwatch unit.
Rockwell Automation Publication GMSI10-IN001A-EN-P - May 2013
Page 27

Add Enwatch Units
1. Right-click the Enwatch Unload Station and select Insert.
2. Click the Insert and instrument radio button and click Next.
3. Select the type of Enwatch unit you are installing and click Next.
Enwatch Unit 27
The Enwatch window opens.
Configuring the Enwatch Unit
1. On the General tab, enter a Description and the IP address of the Enwatch
unit.
Rockwell Automation Publication GMSI10-IN001A-EN-P - May 2013
Page 28

28 Enwatch Unit
2. Select the Channel tab.
This tab is used to map the Enwatch channel to the measurement point in
the database.
3. On the Channel tab, double-click the first square to the left of the channel
number.
A connection to the database opens and the hierarchy tree from the
Emonitor database is displayed.
4. Expand the tree and select the measurement point to which you want to
map the Enwatch channel and click OK.
The machine name and location are populated. All measurement points
associated with the machine name are collected by the Enwatch board.
5. Click Finish.
Rockwell Automation Publication GMSI10-IN001A-EN-P - May 2013
Page 29

The Enwatch unit appears under the Enwatch Unload Station.
Save the Machine Speed with a Spectrum
To add or edit an Enwatch unit, click the Trigger Channel tab.
Enwatch Unit 29
The Timeout is defined in seconds (the default is 5 seconds). The Number of
pulse per rev default is 1 pulse per revolution.
Click the Channel tab and assign the correct Trigger channel to the vibration
channel. This example uses trigger channel 1 for the measurement on input
channel 1.
When the Enwatch unit collects data for channel 1, the unit checks trigger
channel 1 to get the machine speed reading. The speed reading comes back with
time waveform data and gets stored into the database with the vibration data.
Rockwell Automation Publication GMSI10-IN001A-EN-P - May 2013
Page 30

30 Enwatch Unit
Validating Enwatch Measurements
To add or edit an Enwatch unit, you can set up a validation function to allow the
driver to check the channel’s data before updating the database. This function can
be used to filter unwanted data when the machine is not running, or when some
other parameter is not within the correct bounds.
Click the Channel tab, then double-click in the Va l i d a t e column to set up the
validation parameters.
You can reference any channel in any order.
Rockwell Automation Publication GMSI10-IN001A-EN-P - May 2013
Page 31
Specifications
Enwatch Technical Specifications
Product Feature Specification
Inputs Number of Channels 16 vibration and 4 tachometer (synchronizer)
Voltage Protection Protects against over-voltage (channel auto-switch off)
2000 V ESD protection
Input Impedance 1 M
Ranges ±10 mV… ±10 V, 7 ranges (software selectable)
ICP Interface 3.6 mA @ 24V DC, configurable per channel
Coupling AC/DC (numeric measurements), configurable per channel
DC offset removal by optional use of channel 16
PGA Gains Set when a route is loaded by the Emonitor software
Anti-alias Filter Compound analog filter with roll-off better than 20th order filter; cut-off frequency related to sample rate.
High-pass Filters 4th order with corner frequencies 0.36, 2.67, 5.3, and 23.8 Hz
Channel Cross-Talk -80 dB
Amplitude Accuracy ±2% typical in pass-band
Phase Accuracy ±3%
Harmonic Distortions -70 dB (typical)
Integration One 2-stage with ideal stop-band edge at 0.36 Hz
Acquisition Modes Mode 1: Timed pickup
Mode 2: Data Ready flag
Mode 3: Data broadcast
Spike Energy Measurement gSE Filters High pass at 200 Hz & 5 kHz 2nd order
Triggers Types TTL Isolated or Non-Isolated, or any voltage up to +24 V
Maximum combined current for all channels, not to exceed 100mA
Machine Speed Range 1 to 60,000 RPM
Time to Lock 2 revolutions
Averaging 1, 2, 4, ... 32,000 averages, programmable
Tachometer Information RPM using trigger input
Trigger Delays Post-trigger delays up to 32,768 samples
Pre-trigger delays up to 16,384 samples
(not used with the Emonitor software)
Processing Time Domain ADC 16 bit
Sampling Rate 64 Hz to 51.2 kHz
Dynamic Range 96 dB (theoretical)
Block Lengths 256, 512, 1024, 2048, 4096, or 8192 with averaging
up to 16,384 without averaging
Overall Units Acceleration, velocity, or displacement (double integration in one level hardware & one level software), and Spike
Energy data
Outputs Status LEDs indicate system functions
Interface Port RS232C, 9600 baud for diagnostics
Storage Memor y Buffer 640 KB
Enwatch Unit 31
Rockwell Automation Publication GMSI10-IN001A-EN-P - May 2013
Page 32

Enwatch Technical Specifications
Product Feature Specification
Mechanical Protection NEMA 4, IP66
Environmental Temperature -10 to 70° C
Humidity 80% for temperatures up to 31 ºC, decreasing linearly to 50% at 40 ºC
Relative Humidity maximum 80% noncondensing
(1)
Power
Communication Network Ethernet
(1) Mains supply voltage fluctuations are not to exceed -15%…10% of the nominal supply voltage.
Power Supply 100…240V AC, 50 or 60 Hz
Power Consumption 12 W maximum
Medium 10BASE-T
Connectors Weidmuller terminal blocks, 500V AC
Speed 10 Mbits/sec
Isolation 1000 Vrms
Additional Resources
These documents contain additional information concerning related products
from Rockwell Automation.
Resource Description
Industrial Automation Wiring and Grounding
Guidelines, publication
Product Certifications website,
http://www.ab.com
1770-4.1
Provides general guidelines for installing a Rockwell Automation
industrial system.
Provides declarations of conformity, certificates, and other
certification details.
You can view or download publications at
http://www.rockwellautomation.com/literature/. To order paper copies of
technical documentation, contact your local Allen-Bradley distributor or
Rockwell Automation sales representative.
Allen-Bradley, Rockwell Software, Rockwell Automation, Enwatch and Emonitor are trademarks of Rockwell
Automation, Inc.
Trademarks not belonging to Rockwell Automation are property of their respective companies.
Rockwell Otomasyon Ticaret A.Ş., Kar Plaza İş Merkezi E Blok Kat:6 34752 İçerenköy, İstanbul, Tel: +90 (216) 5698400
Publication GMSI10-IN001A-EN-P - August 2013
Supersedes Publication GMSI10-UM031C-EN-E - July 2009 Copyright © 2013 Rockwell Automation, Inc. All rights reserved. Printed in the U.S.A.
 Loading...
Loading...