Page 1

PSEN op4F/H-A series
Safety light curtain
Operating Manual-1003067-EN-02
Page 2

Preface
This document is a translation of the original document.
All rights to this documentation are reserved by Pilz GmbH & Co. KG. Copies may be made
for internal purposes. Suggestions and comments for improving this documentation will be
gratefully received.
Pilz®, PIT®, PMI®, PNOZ®, Primo®, PSEN®, PSS®, PVIS®, SafetyBUS p®, SafetyEYE®,
SafetyNET p®, the spirit of safety® are registered and protected trademarks of Pilz GmbH
& Co. KG in some countries.
SD means Secure Digital
Page 3

1 GENERAL INFORMATION ......................................................... 5
1.1 General description ................................................................................................. 5
1.1.1 General description of the safety light curtain.......................................................... 5
1.1.2 Package content ..................................................................................................... 6
1.2 Guidelines for selecting the protective device ......................................................... 7
1.2.1 Resolution ............................................................................................................... 7
1.2.2 Height of protected field .......................................................................................... 8
1.2.3 Minimum safety distance ........................................................................................ 9
1.3 Typical application areas .......................................................................................12
1.4 Safety information ..................................................................................................13
2 INSTALLATION ........................................................................ 14
2.1 Precautions to be taken during selection and installation of a light curtain .............14
2.2 General information on positioning the device........................................................15
2.2.1 Minimum distance from reflective surfaces ............................................................16
2.2.2 Distances between identical light curtains ..............................................................17
2.2.3 Aligning transmitter and receiver ............................................................................20
2.2.4 Using deviating mirrors ..........................................................................................20
2.2.5 Inspections following a first-time installation ...........................................................21
3 MECHANICAL ASSEMBLY ...................................................... 23
4 ELECTRICAL CONNECTIONS ................................................. 25
4.1 Connection guidelines ............................................................................................28
5 ALIGNMENT ............................................................................. 31
6 SETTING THE FUNCTIONS ..................................................... 33
6.1 Reset to factory configuration ................................................................................35
6.2 Function list ...........................................................................................................36
7 FUNCTIONS .............................................................................. 38
7.1 Restart function ......................................................................................................38
7.2 Test .......................................................................................................................40
7.3 Reset .....................................................................................................................41
7.4 EDM ......................................................................................................................41
7.5 EDM selection ........................................................................................................43
7.6 Reduced range ......................................................................................................43
7.7 Muting ....................................................................................................................44
7.7.1 Disabling the muting function .................................................................................45
7.7.2 Muting display devices ...........................................................................................45
7.7.3 Typical muting application and sensor connection .................................................46
7.7.4 Muting direction .....................................................................................................46
7.7.5 Muting timeout .......................................................................................................50
7.7.6 Muting filter ............................................................................................................51
7.7.7 Partial muting .........................................................................................................52
7.8 Override .................................................................................................................53
7.8.1 Override mode .......................................................................................................54
7.8.2 Override timeout ....................................................................................................55
7.8.3 Override restart ......................................................................................................56
7.9 Blanking .................................................................................................................59
7.9.1 Fixed blanking ........................................................................................................60
7.9.2 Fixed blanking with increased tolerance .................................................................61
7.9.3 Floating blanking with total surveillance .................................................................61
7.9.4 Floating blanking with partial surveillance ..............................................................61
Page 4

7.9.5 Reduced resolution ................................................................................................62
7.9.6 Tolerance ...............................................................................................................62
7.9.7 Blanking mode in the basic configuration ...............................................................64
7.9.8 Blanking mode in advanced configuration ..............................................................65
7.10 Cascading ..............................................................................................................68
7.11 PNP/NPN ...............................................................................................................68
7.12 Coding ...................................................................................................................70
8 DIAGNOSTICS .......................................................................... 73
8.1 Status of LEDs .......................................................................................................73
9 REGULAR CHECKS AND MAINTENANCE ............................. 76
9.1 Regular checks ......................................................................................................76
9.2 Maintenance ..........................................................................................................76
10 TECHNICAL DETAILS .............................................................. 77
11 LIST OF AVAILABLE MODELS ............................................... 78
12 DIMENSIONS ............................................................................ 80
13 FITTINGS .................................................................................. 81
14 ACCESSORIES ........................................................................ 83
14.1 Rotating mounting bracket .....................................................................................83
14.2 Cascading cable ....................................................................................................84
14.3 Connection cable ...................................................................................................85
14.4 PSEN op Advanced Programming Adapter ............................................................86
14.5 Axial connection cable, unshielded ........................................................................88
14.6 Ethernet cable for PSEN op Advanced Programming Adapter ...............................88
Page 5

OPERATING MANUAL PSEN op4F/H-A series
1003067-EN-02
5
The information contained in paragraphs marked by this symbol is
particularly relevant to safety and is important for accident
strictly observed.
1 GENERAL INFORMATION
1.1 General description
1.1.1 General description of the safety light curtain
The safety light curtains in the PSE N op4F/H-A series are multibeam active optoelectronic
protective devices for work areas in which machines, robots and automated plants in general
could endanger the physical integrity of operators who could come into contact with moving
parts, even if only by chance.
Light curtains in the PSEN op4F/H-A series are designed as inherent ly safe Type 4 systems
for accident prevention in accordance with applicable international safety standards, in
particular the following:
IEC 61496-1: 2004 Safety of machinery: Electrosensitive protective equipment. Part 1:
General requirement s and tests.
IEC 61496-2: 2006 Safety of machinery: Electrosensitive protective equipment –
Particular requirements for equipment using active optoelectronic protective devices.
A light curtain pair consists of a transmitter and a receiver. They produce an infrared
protected field, which is able to detect an opaque object within the specific resolution. Both
the transmitter and the receiver have control and monitoring functions. The connections are
made via an M12 connector, which is located in the lower profile area. The transmitter and
receiver are synchronised optically, so the two units do not have to be connected directly to
each other. The infrared beams that are transmitted and received are controlled and
monitored via a microprocessor, which provides the user with information about the operating
state of the lig ht curtain via LED indicators (see Chapter 8).
A light curtain pair consists of 2 units, which may comprise one or more transmitter and
receiver modules, depending on the respective model. The receiver is the main control unit
for all functions. If an error occurs, it checks all the safety actions and decides on the
measures that are to be implement ed in terms of safety, as well as performing other general
functions.
During the installation phase the user interface makes it easier to align the two units (see
Chapter 5).
As soon as the beams emitted from the transmitter are interrupted by an object, a limb or the
body of an operator, both output signal switching devices (OSSD) ar e opened immediately.
This controls the stopping of the corresponding machine, which is connected to the OSSD.
Some parts or paragraphs of this manual, which are of particular importance to the user or
installation engineer, are highlighted as follows:
prevention.
This information must be read with particular attention and must be
Page 6

PSEN op4F/H-A series OPERATING MANUAL
6
1003067-EN-02
This manual contains all the information you need to select and operate the protective
devices.
Specialised knowledge of safety issues is required to integ rate a safety light curt ain correctly
in a plant.
PILZ’s technical customer service team is available to provide any information you need
regarding the functionality of the PSEN op4F/H-A safety light curtains and the safety
regulations concerning correct installation.
1.1.2 Package content
The following components are included:
• Receiver (RX)
• Transmitter (TX)
• Shortform for installing the safety light curtains in the PSEN op4F/H-A series
• CD with operating manual and other documents
• 4 fastening brackets and corresponding mounting accessories
• 2 fastening brackets for models with a height between 1200 and 1800 mm
Page 7
OPERATING MANUAL PSEN op4F/H-A series
1003067-EN-02
7
1 = Opaque object
2 = Height of protect ed
field
3 = Operating range
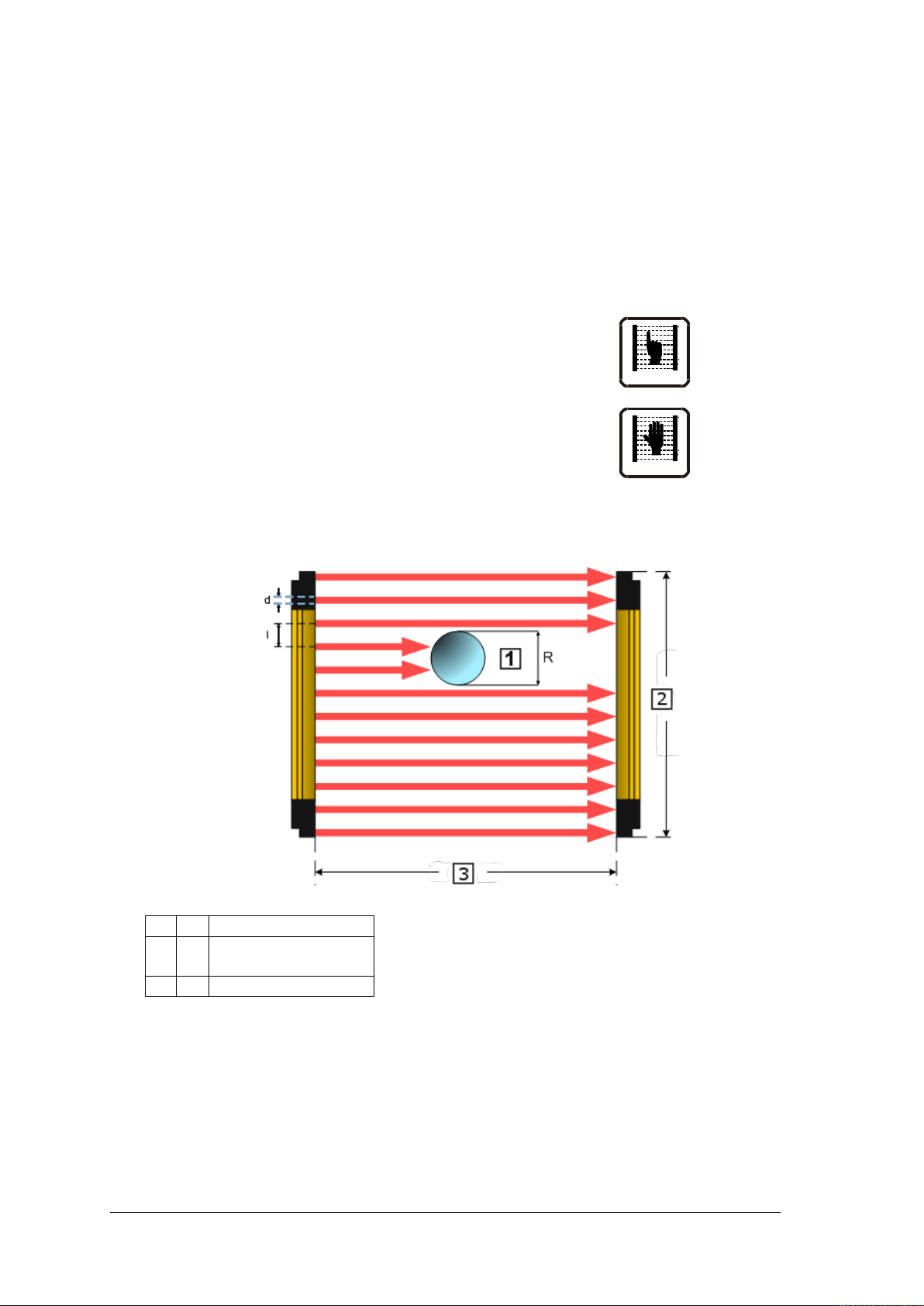
1.2 Guidelines for selecting the protective device
Once the hazards have been assessed appropriately, there are at least three essential
features to consider when selecting a safety light curtain:
1.2.1 Resolution
The device’s resolution is understood to be the minimum size that an opaque object must be
to safely interrupt at least one of the beams that form the area of the protected field.
The resolution is closely linked to the part of the body that requires protection.
R = 14 mm Finger protection
Type 4
R = 30 mm Hand protection
Type 4
As shown in Fig. 1, the resolution depends solely on the geometric properties of the lenses,
the diameter and the distance and so is unaffected by the light curtain’s ambient and
operating conditions.
The resolution value can be calculated using the following formula:
where:
I = Distance between two adjacent lenses
d = Lens diameter
Fig. 1– Resolution
R = I + d
Page 8
PSEN op4F/H-A series OPERATING MANUAL
8
1003067-EN-02
1 = Protected field
2 = Height of protect ed
field
3 = Operating range
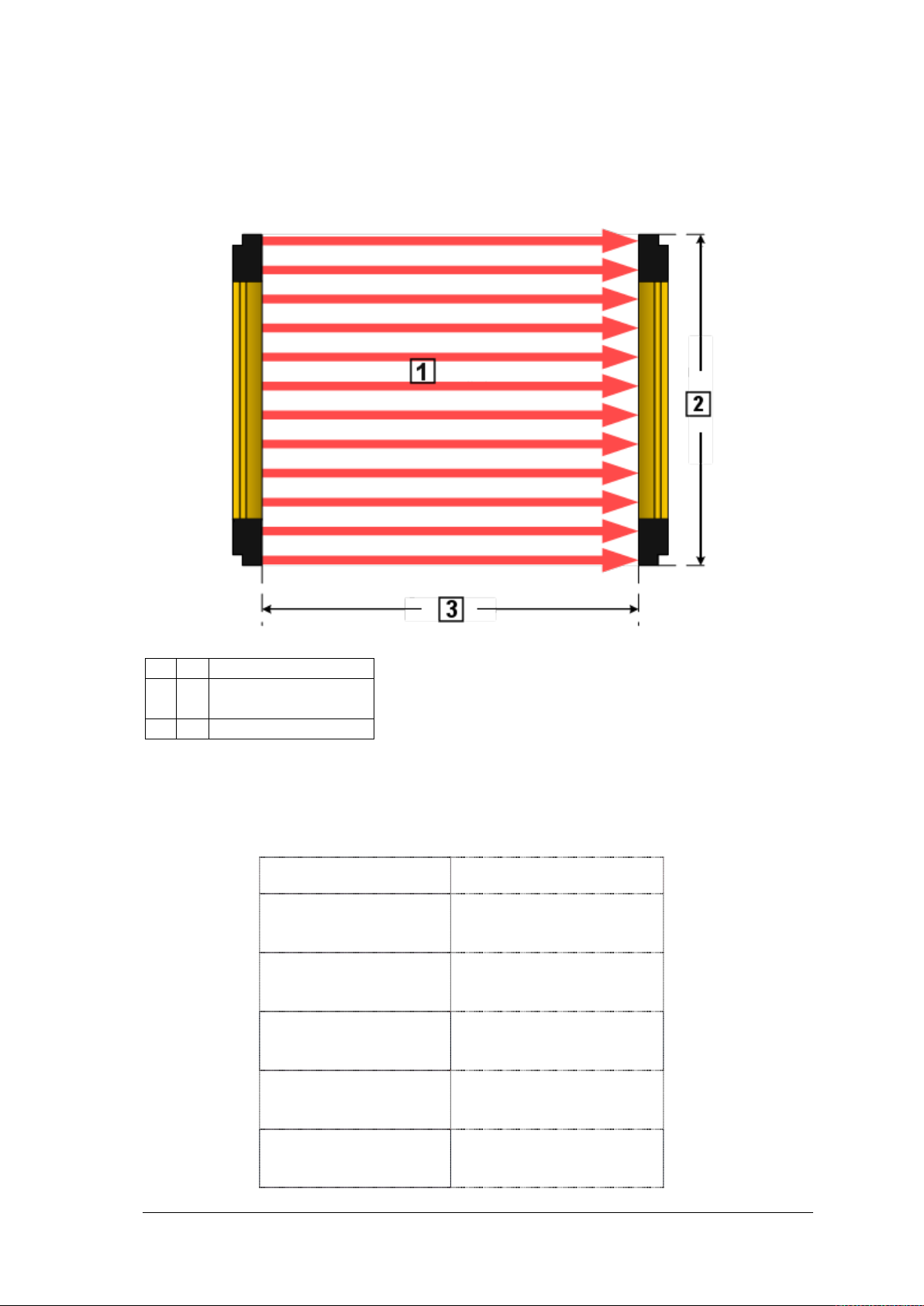
Height of protected field
(mm)
1.2.2 Height of protected field
The height of the protected field is understood to be the height pr otected by the safety light
curtain.
Fig. 2 – Height of protected field
The height monitored by the PSEN op4F/H-A corresponds to the overall height of the light
curtain.
With reference to the previous diagram, the height of the protected field can be taken from
the table below.
Model
PSEN op4F-A-14-030/1
PSEN op4H-A-30-030/1
PSEN op4F-A-14-045/1
PSEN op4H-A-30-045/1
PSEN op4F-A-14-060/1
PSEN op4H-A-30-060/1
300
450
600
PSEN op4F-A-14-075/1
750
PSEN op4H-A-30-075/1
PSEN op4F-A-14-090/1
900
PSEN op4H-A-30-090/1
Page 9
OPERATING MANUAL PSEN op4F/H-A series
1003067-EN-02
9
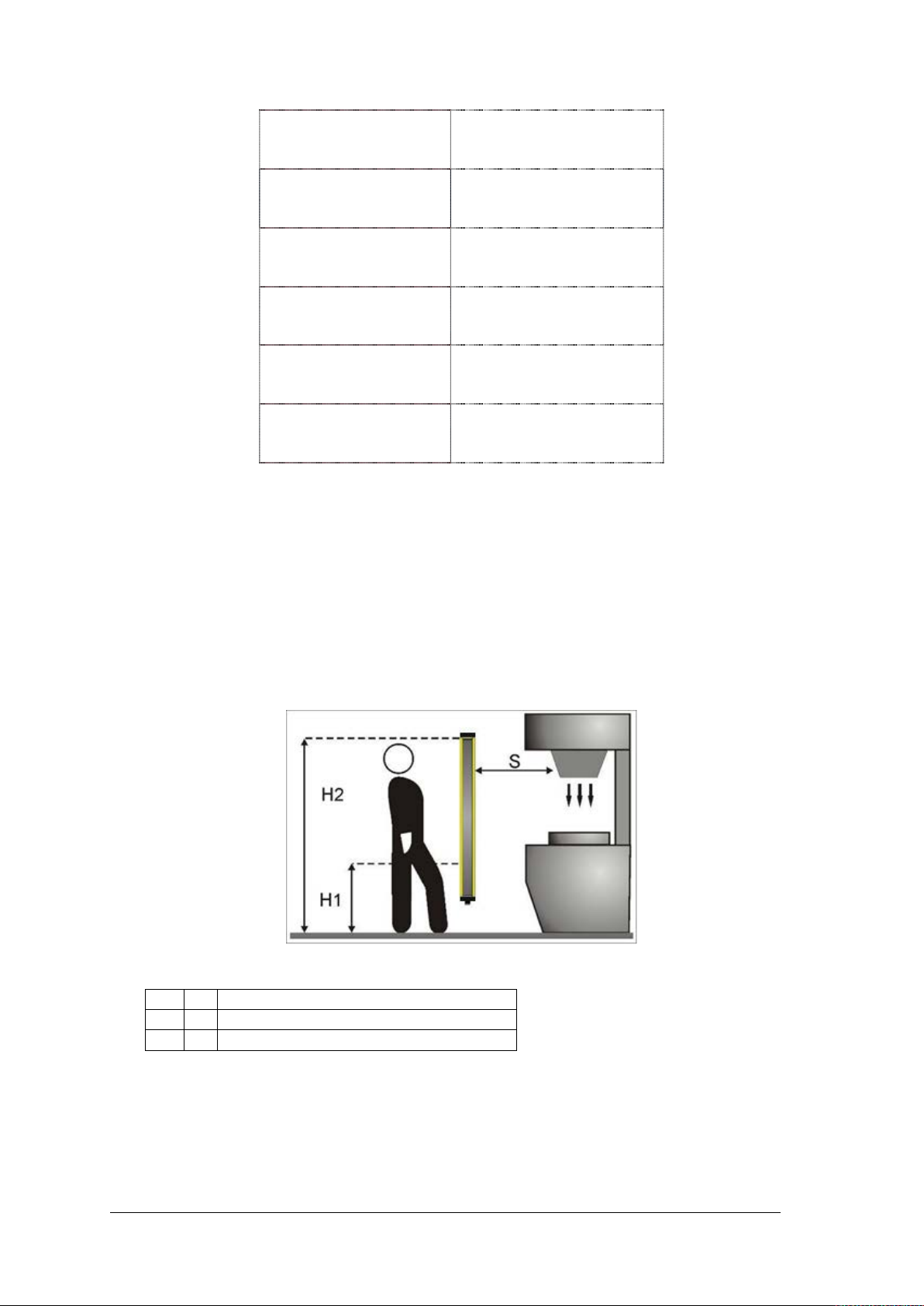
H1 = ≥ 900 mm at a resolution > 40 mm
H2 = ≤ 300 mm at a resolution > 40 mm
S = Minimum safety distance in mm
PSEN op4F-A-14-105/1
PSEN op4H-A-30-105/1
PSEN op4F-A-14-120/1
PSEN op4H-A-30-120/1
PSEN op4F-A-14-135/1
PSEN op4H-A-30-135/1
PSEN op4F-A-14-150/1
PSEN op4H-A-30-150/1
PSEN op4F-A-14-165/1
PSEN op4H-A-30-165/1
PSEN op4F-A-14-180/1
PSEN op4H-A-30-180/1
1050
1200
1350
1500
1650
1800
1.2.3 Minimum safety distance
The protective device must be positioned at a specific safety distance (Fig. 3), which
guarantees that the operator cannot reach the danger zone until the hazardous machine
movement has come to a standstill by triggering the light curtain.
In accordance with the standard ISO 13855, this distance depends on 4 factors:
• Response time of the light curtain (the time that elapses between the beams being
effectively interrupted and the OSSD contacts opening).
• Machine’s stopping performance (time that elapses between the light curtain contacts
opening and the hazardous machine movement effectively stopping).
• Light curtain’s resolution
• Approach speed of the object to be detected.
Fig. 3 – Safety distance (vertical)
Page 10
PSEN op4F/H-A series OPERATING MANUAL
10
1003067-EN-02
S
Minimum safety distance in mm
K
Speed of the object (limb or body) approaching the danger zone in mm/s
t1
Light curtain’s response time in seconds (see Chapter 11)
t2
Machine’s stopping performance in seconds
C
Additional distance based on the possibility of placing the body or limb into the danger
zone before the protective device responds
C
8 (d -14) for devices with a resolution ≤ 40 mm
C
850 mm for devices with a resolution > 40 mm
d
Device’s resolution
S
Minimum safety distance in mm
t1
Light curtain’s response time in seconds (see Chapter 11)
t2
Machine’s stopping performance in seconds
H
Height of the beams above the floor. This height must always be less than 1000 mm.
The safety dist ance is calculated using the following formula:
S = K (t1 + t2) + C
Therefore:
Note:
The value K corresponds to:
• 2000 mm/s, if the calculated value S is ≤ 500 mm
• 1600 mm/s, if the calculated value S is > 500 mm
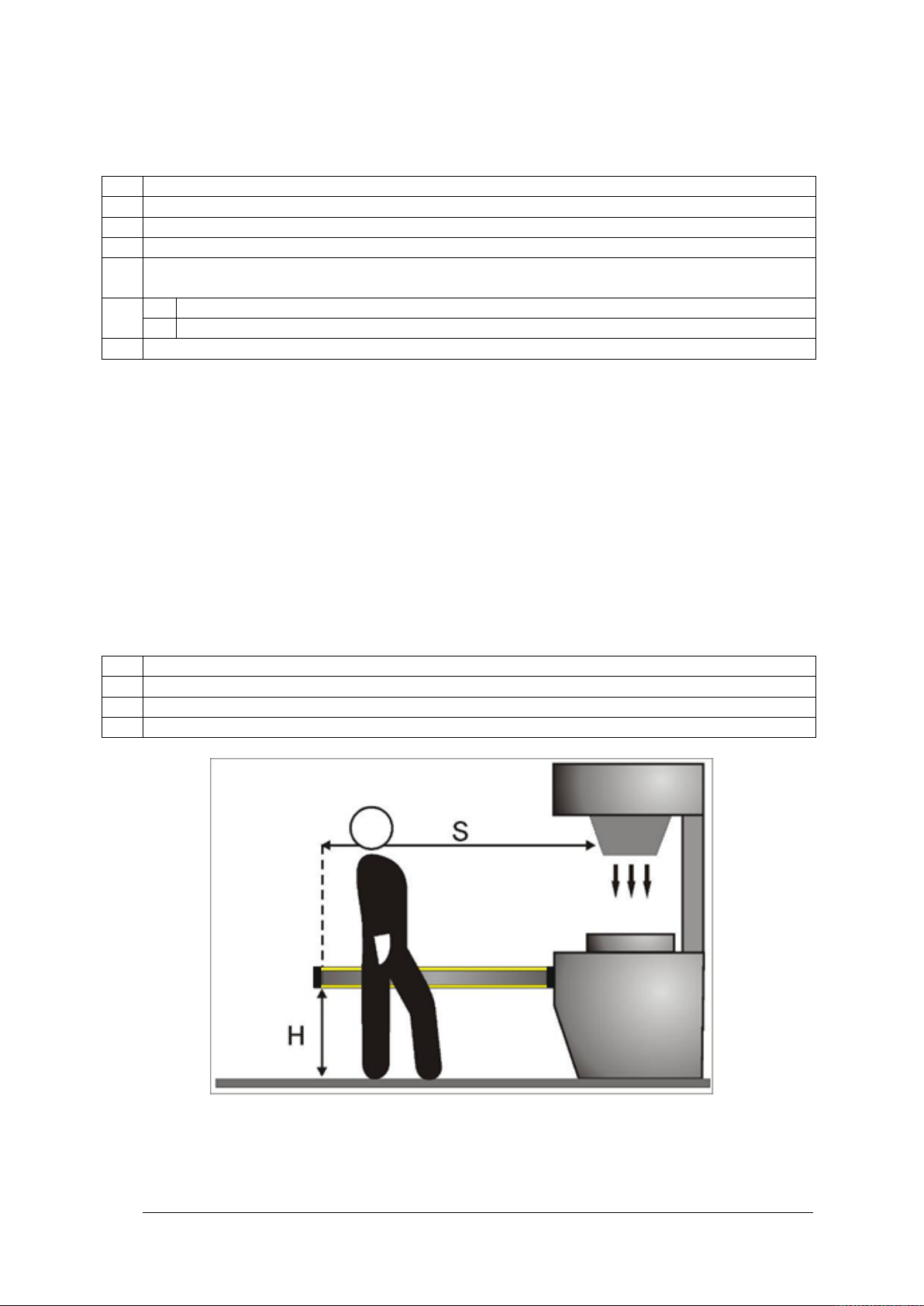
When using light curtains with a resolution of > 40 mm, the upper beam must be posit ioned
at a height of ≥ 900 mm (H2) from the supporting base, while the lower beam must be
positioned at a height of ≤ 300 mm (H1).
Where the light curtain must be installed horizontally (Fig. 4), the distance between the
danger zone and the most distant optical beam must correspond to the value calculated
using the following formula:
S = 1600 mm/s (t1 + t2) + 1200 – 0.4 H
Therefore:
Fig. 4 – Safety distance (horizontal)
Page 11

OPERATING MANUAL PSEN op4F/H-A series
1003067-EN-02
11
WARNING: In this case the reference standard is EN ISO 13855
protective equipment in
binding. Please refer to the complete standard ISO
13855 for details of how to calculate safety distances correctly.
Application examples
This example is based on a light curtain with a height = 600 mm.
To calculate the distance of the device from the light curtain in a vertical position, the
following formula is applied:
S = K*T + C
Therefore:
T = t
t
1
With a reaction time of the light curtain of 15 ms the result is a max. of 35 ms for t
+ t2
1
= Response time of light curtain + release time of relay (specific tim e of PNOZ S3: 20ms)
1
t2 = Machine’s overall stopping performance in seconds
C = 8 * (d – 14) for devices with resolution <= 40 mm
D = Resolution
In each case, if K = 2000 mm/sec, then S > 500 mm. The safety distance will then need to be
recalculated, based on K = 1600 mm/sec.
“Safety of machinery – Positioning of
respect of approach speeds of parts of the human body”.
The information provided here should be regarded as a summary
and is non-
Page 12
PSEN op4F/H-A series OPERATING MANUAL
12
1003067-EN-02
1.3 Typical application areas
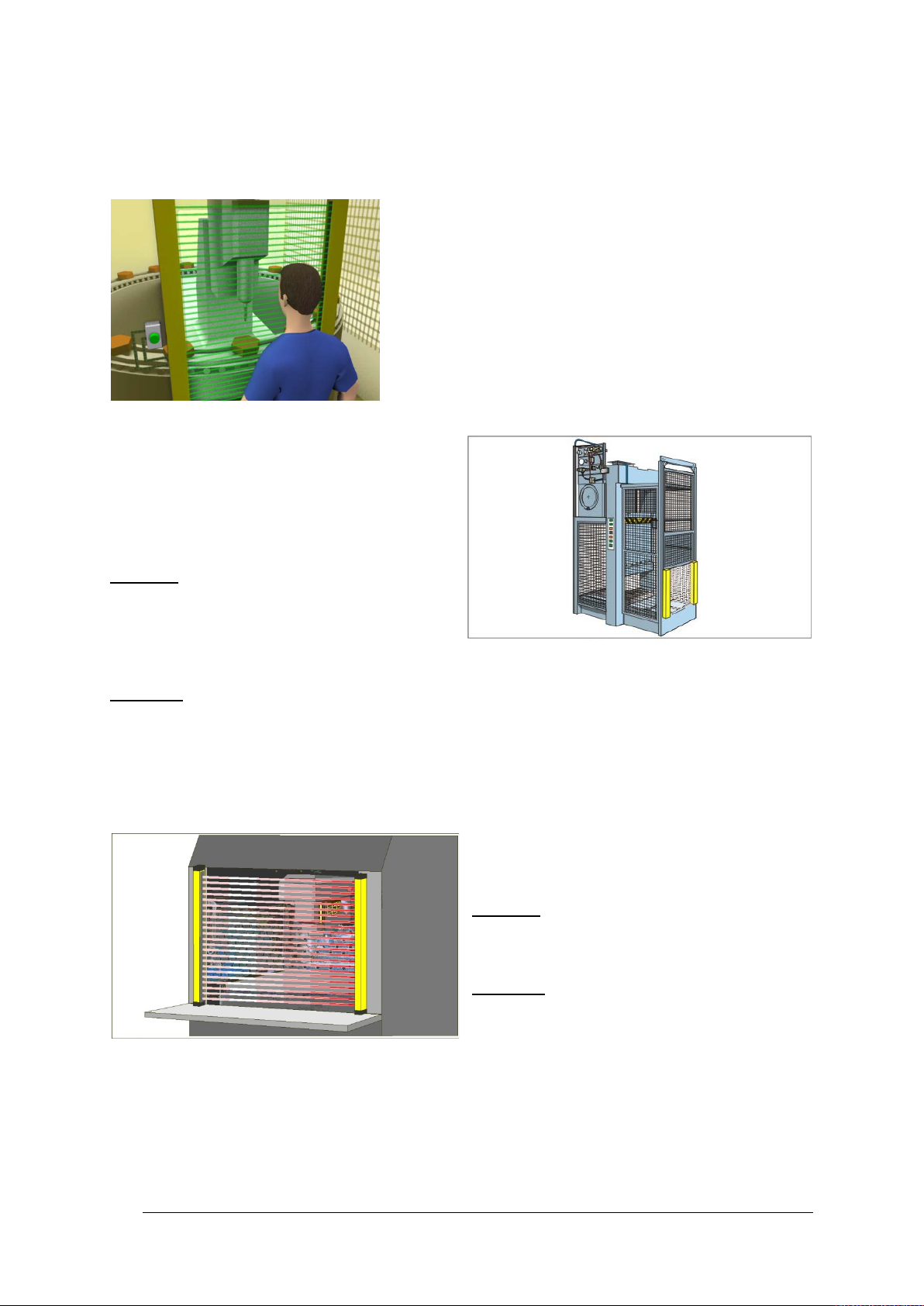
Example 1: Protecting the operating area on drilling machines
The operator inserts the workpiece and removes it after
machining. The operator must be protected from injury
during the machining process.
Solution: The safety light curtain PSEN op4F/H-A is
particularly suitable for this application, as the device
needs to be installed directly on the machine.
Benefits: The small dimensions of the light curtain
guarantee maximum flexibility during installation, as it
can be adapted to the machine dimensions.
Rotatable mounting brackets are included,
guaranteeing fast, simple attachment.
Example 2: Bending presses
The safety device must protect the bending
process operator from the crushing hazard
that exists between the upper and lower tool
or from the workpiece that is being
machined, if this approaches at high speed.
Solution: Even if just one light axis on the
safety light curtain PSEN op4F/H-A is
interrupted during the downward phase, the
movable workpiece carrier is stopped
immediately.
Benefits: The simple installation options and the small dimensions of the safety light curtain
mean it can be used in most bending operations. PSEN op4F/H-A not only guarantees a high
level of reliability but also increases production on the plant, as the standstill times needed
for access, settings and machine maintenance can be reduced.
Example 3: Paper cutting machine
A typical application for these protective devices is on paper cutting machinery for magazines
and special formats. The purpose of the light
curtain is to pr otect the operator from cuts or
abrasions from the cutting machine.
Solution: The safety light curtain PSEN
op4F/H-A is particularly suitable for this
application, as the device needs to be
installed directly on the machine.
Benefits: The small dimensions of the light
curtain and the guide rails at either end
guarantee maximum flexibility, as they can
be adapted to the machine’s mechanical
dimensions.
Page 13

OPERATING MANUAL PSEN op4F/H-A series
1003067-EN-02
13
To use the safety light curtains in the PSEN op4F/H-A series safely
and correctly, the following information must be considered:
Example 4: Moulding machine
The moulding machine is used to create
complex shapes from metallic parts or parts
made from other materials. In this case it is
necessary to prevent the operator’s hands or
other limbs being dragged, entangled or cut
by the tool itself or being injured by the
spindle.
Solution: The safety light curtain from the
PSEN op4F/H-A series is the best solution
for protecting the operator in terms of the required safety level and the application type. As
soon as even a single beam on the light curtain is interrupted, the machine is stopped
immediately.
Benefits: The small dimensions of the light curtain with no dead zones guarantees maximum
flexibility during installation, as it can be adapted to the machine dimensions.
1.4 Safety information
• The system intended to stop the machine must be electrically controllable.
• This control system must be able to stop hazardous machine movements
- inside the overall stopping performance of the machine T,
- in accordance with the details in Chapter 1.2.3 of the operating manual (see CD provided)
- and in each phase of the processing cycle.
• The protective device must be positioned at a distance that exceeds the minimum safety
distance S or that correspo nds to it, so that the operator cannot reach the danger zone until the
movement of the hazardous object has come to a standstill by triggering the light curtain.
• The safety light curtains may only be installed and connected by qualified personnel. It is
essential to follow the instr uctions provided in the relevant sections of the manuals provided
(see Chapters 2, 3, 4 and 5) and to comply with the applicable directives.
• Ensure that the c orrect ope ration of the light cur tain is not distur bed by stron g electromagnet ic
interference.
• Ensure that the light curtain, particularly the receiver, is not installed close to particularly
intense and/or flashing light sources.
• The saf et y light curtain must be positioned so th at it saf ely preve nts ac cess to the dan ger zone
without interrupting the beams (see Chapters 2, 3).
• Only qualified personnel with appropriate knowledge of all the operating procedures of the
safety light curtain should be permitted to work within the danger zone.
• The RESET button must be positioned outside the area of the pr otected field and in such a
way that the operator can see into the danger zone when carrying out a reset and test
procedure.
• Reflective surfaces close to the beams emitted from the protective device (whether from
above, below or from the side) can cause passive reflections th at adversely affect the correct
operation of the light curtain.
The instructions provided for correct operation must be strict ly followed before switching on
the light curtain.
Page 14
PSEN op4F/H-A series OPERATING MANUAL
14
1003067-EN-02
Ensure that the safety level guaranteed by the PSEN op4F/H-A
to be monitored, as well as the level defined by the standard
EN ISO 13849.
Ensure that the light curtain’s outputs (OSSD) are used as
machine must have a separate START control.
Ensure that the correct operation of the light curtain is not
Ensure that the light curtain, particularly the receiver, is not
2 INSTALLATION
2.1 Precautions to be taken during selection and installation of a light curtain
(Type 4) complies with the actual risk assessment of the machine
machine stopping devices and not as control devices. The
disturbed by strong electromagnetic interference.
installed close to particularly intense and/or flashing light sources.
• The size of the smallest object to be detected must be greater than the device’s resolution.
• The light curtain must be installed in an env ironment t hat com plies with t he techn ical prop erties
stated in Chapter 11.
• Smoke, mist or dust in the working environment can reduce the operating range of the
protective device.
• Sudden, large-scale temperatur e variations, particularly with l ow temperatures can generate a
slight layer of condensation on the device’s lens, adversely affecting its function.
• Reflective surfaces close to the beam s em itted from the protect ive device ( whether from above,
below or from the s ide) can cause pas sive r eflect ions t hat adv ersel y aff ect the correct operation
of the light curtain.
• The protective device must be positioned at a distance that exceeds the minimum safety
distance S or that correspo nds to it, so that the operator cannot reach the dang er zone until the
movement of the hazardous object has come to a standstill by triggering the light curtain.
Page 15
OPERATING MANUAL PSEN op4F/H-A series
1003067-EN-02
15
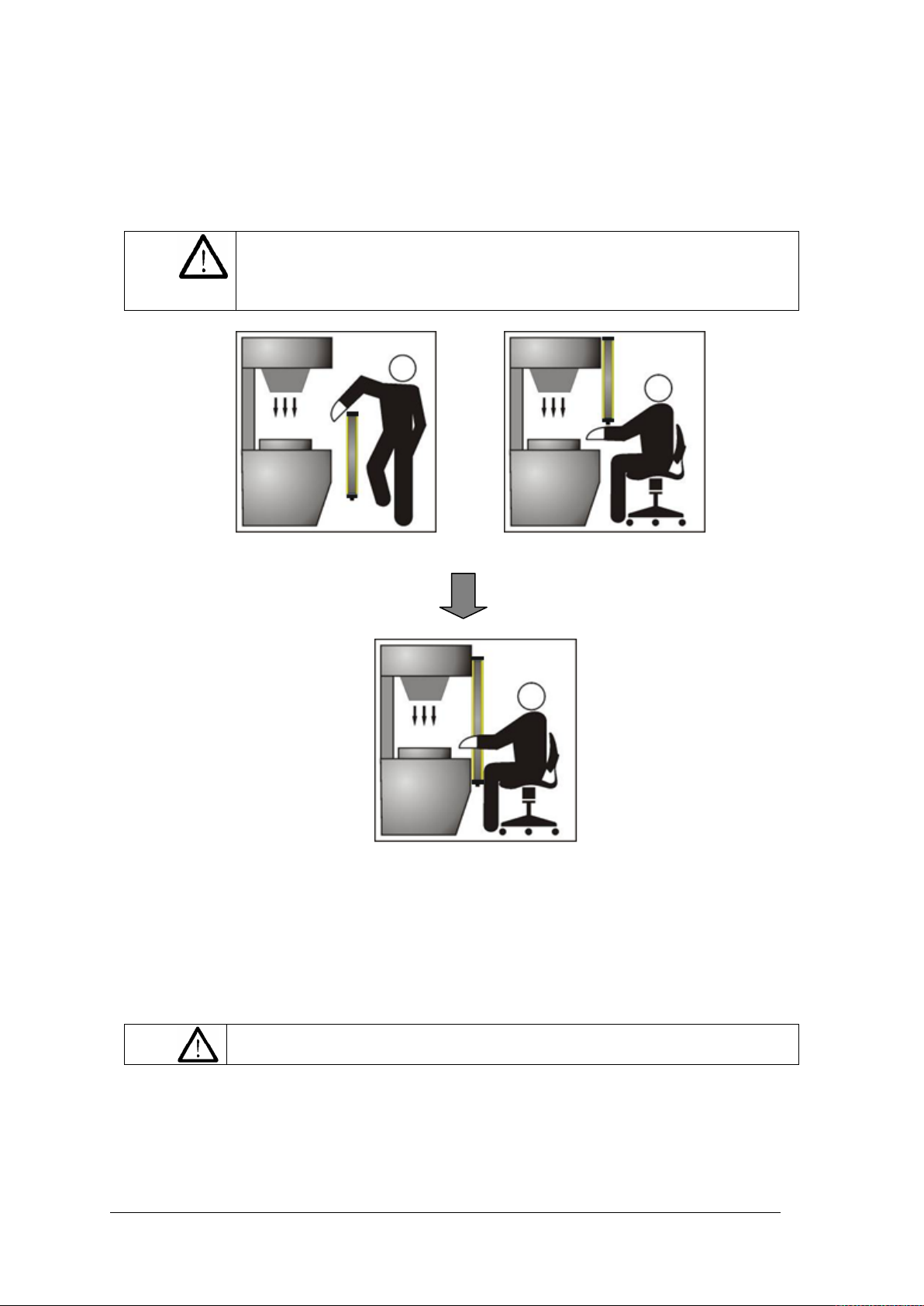
Fig. 5 shows some possibilities for accessing the machine from above
which access to the danger zone can be covered in full (Fig. 6).
If the operator is able to enter the danger zone, additional
mechanical protection must be installed to exclude access.
NO
YES
2.2 General information on positioning the device
Special care should be taken when positioning the safety light curtain to ensure it provides
efficient protection. The device must be installed so that the danger zone cannot be
accessed without interrupting the protected field.
and below. Situations like this could turn out to be extremely dangerous.
For this reason, the safety light curtain must b e installed at a height from
Fig. 5 – Device positioned incorrectly
Fig. 6 – Device positioned correctly
Under normal operating conditions, the machine may only be started if the operator is
outside the danger zone.
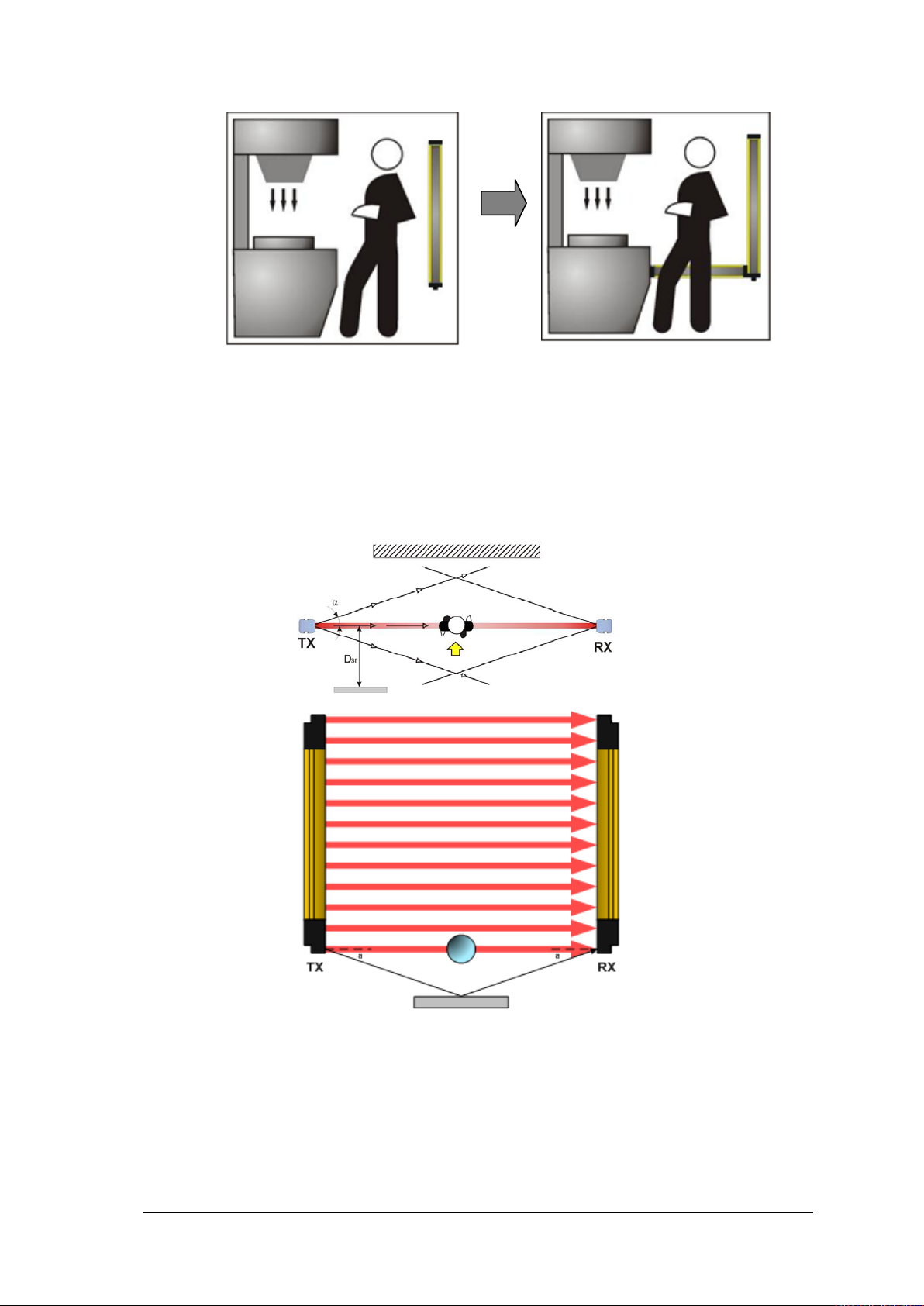
If it is impossib le to install the light curtain in the immediate vicinity of the danger zone, t he
possibility of access from the side must be excluded, for example, by installing a second
horizontal light curtain. See Fig. 8.
Page 16
PSEN op4F/H-A series OPERATING MANUAL
16
1003067-EN-02
Fig. 7
Fig. 8
NO
YES
2.2.1 Minimum distance from reflective surfaces
Reflective surfaces close to the beams emitted from the protective device (whether from
above, below or from the side) can cause passive reflect ions. These passive reflections can
adversely affect how the object is detected within the protected area. If the receiver RX
detects a secondary beam (reflected by the side-reflecting surface), the object may not be
detected even if it interrupts the main beam.
DANGER ZONE
Reflective surface
Reflective surface
Fig. 9 Minimum distance from reflective surfaces
When installing the safet y light curtain it is important to maintain a minimum distance from
reflective surfaces.
Page 17
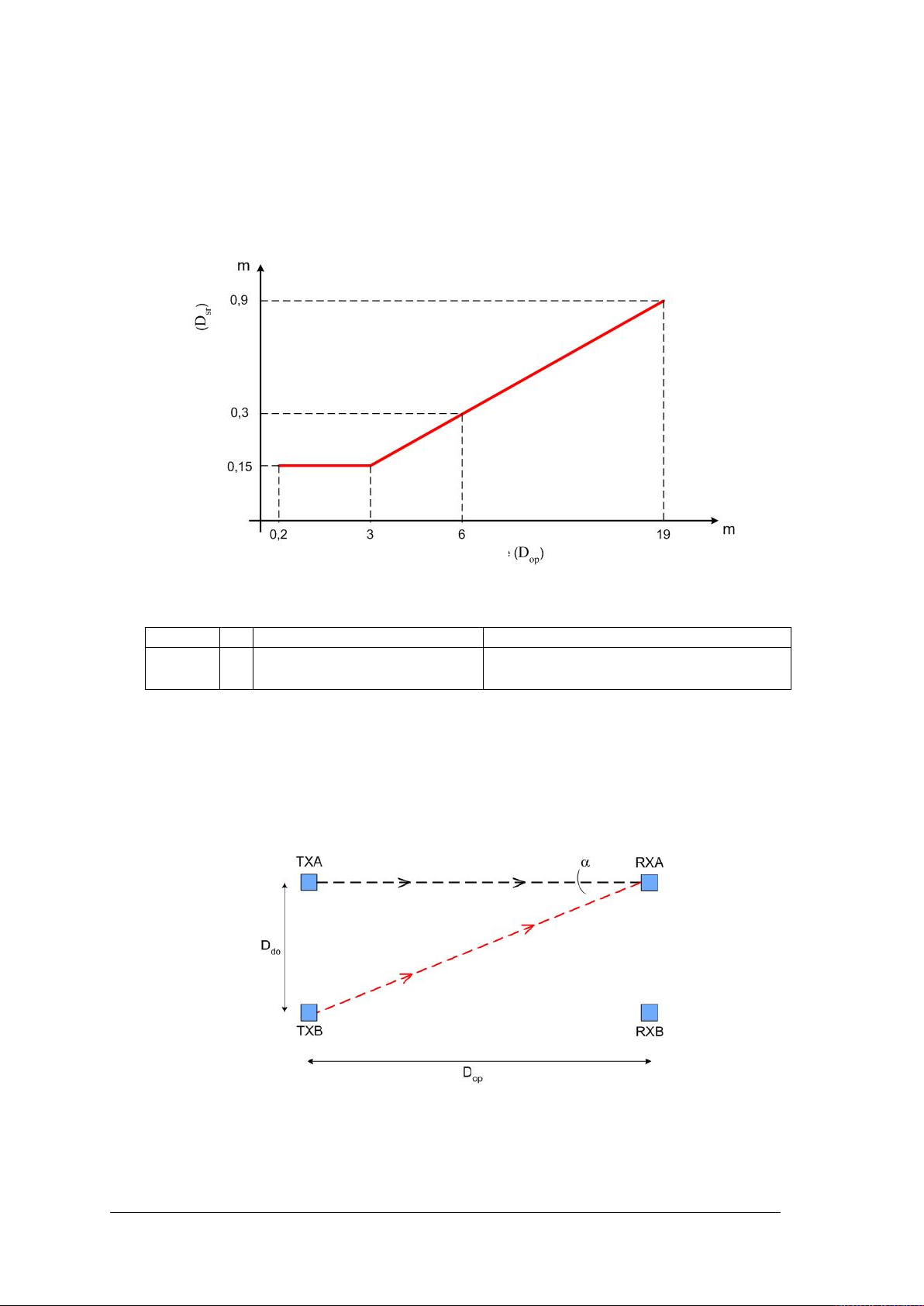
OPERATING MANUAL PSEN op4F/H-A series
1003067-EN-02
17
Dsr (m)
=
0.15
With operating ranges < than 3 m
Dsr (m)
=
0.5 x operating range (m) x
tg 2α
Light
Operating range
This minimum distance depends on the following factors:
• The distance between the transmitter (TX) and receiver (RX)
• The actual opening angle of the light curtain; in particular:
when Type 4 light curtain = 5° (α = ± 2.5°)
The illustration in Fig. 10 shows the minimum distance from the reflective surface (D
) based
sr
on the operating range:
curtain
Type 4
Distance from
reflective surface
Fig. 10
Formula for calculating Dsr:
With operating ranges ≥ than 3 m
2.2.2 Distances between identical light curtains
Should it be necessary to install several protective devices in adjacent areas, care must be
taken to ensure that the transmitter on one of the pairs does not dangerously interfere with
the receiver on another pair.
The interfering transmitter, TX B, must be installed outside the minimum distance D
the TX A - RX A axis of the transmitter/receiver pair.
from
do
This minimum distance D
• The distance between the transmitter (TX A) and receiver (RX A);
• The actual opening angle of the light curtain.
Fig. 11 – Distance between devices of the same type
depends on the following factors:
do
Page 18
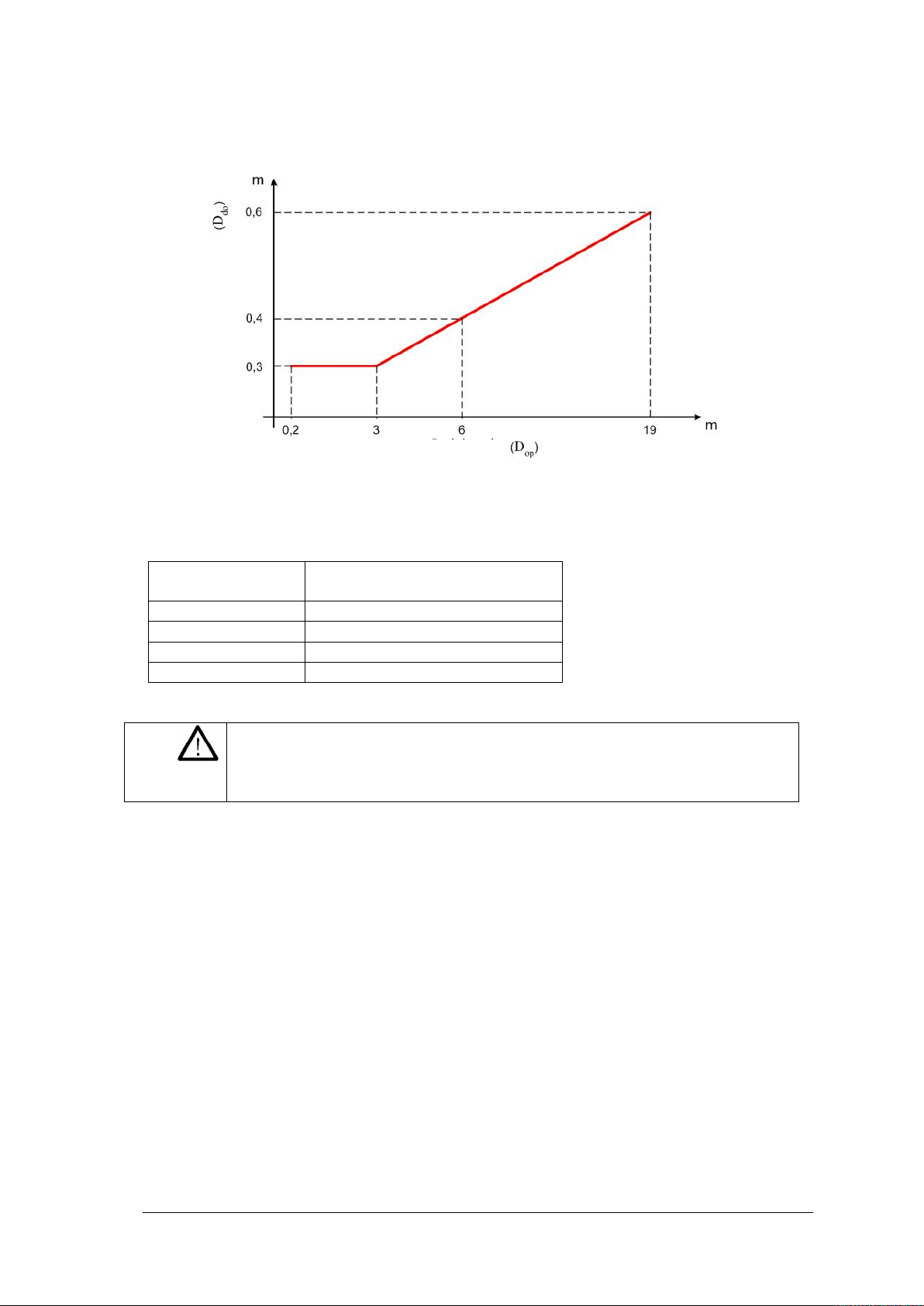
PSEN op4F/H-A series OPERATING MANUAL
18
1003067-EN-02
Operating range
(m)
Minimum safety distance
(m)
3
0.3 6 0.4
10
0.5
19
0.6
WARNING: The interfering transmitter (TX B) must be positioned at
even if the distance
RX A.
Reichweite
Operating range
Distance between two
The following graphic shows the distance from the interfering devices (Ddo), based on the
operating range (D
) of the pair (TX A – RX A).
op
devices of the same type
Fig. 12
For the purpose of simplification, the table below states the values of the minimum safety
distances required for installation, with reference to some operating ranges.
the same distance Ddo, as calculated above,
from the other transmitter TX A is shorter than from the receiver
Page 19
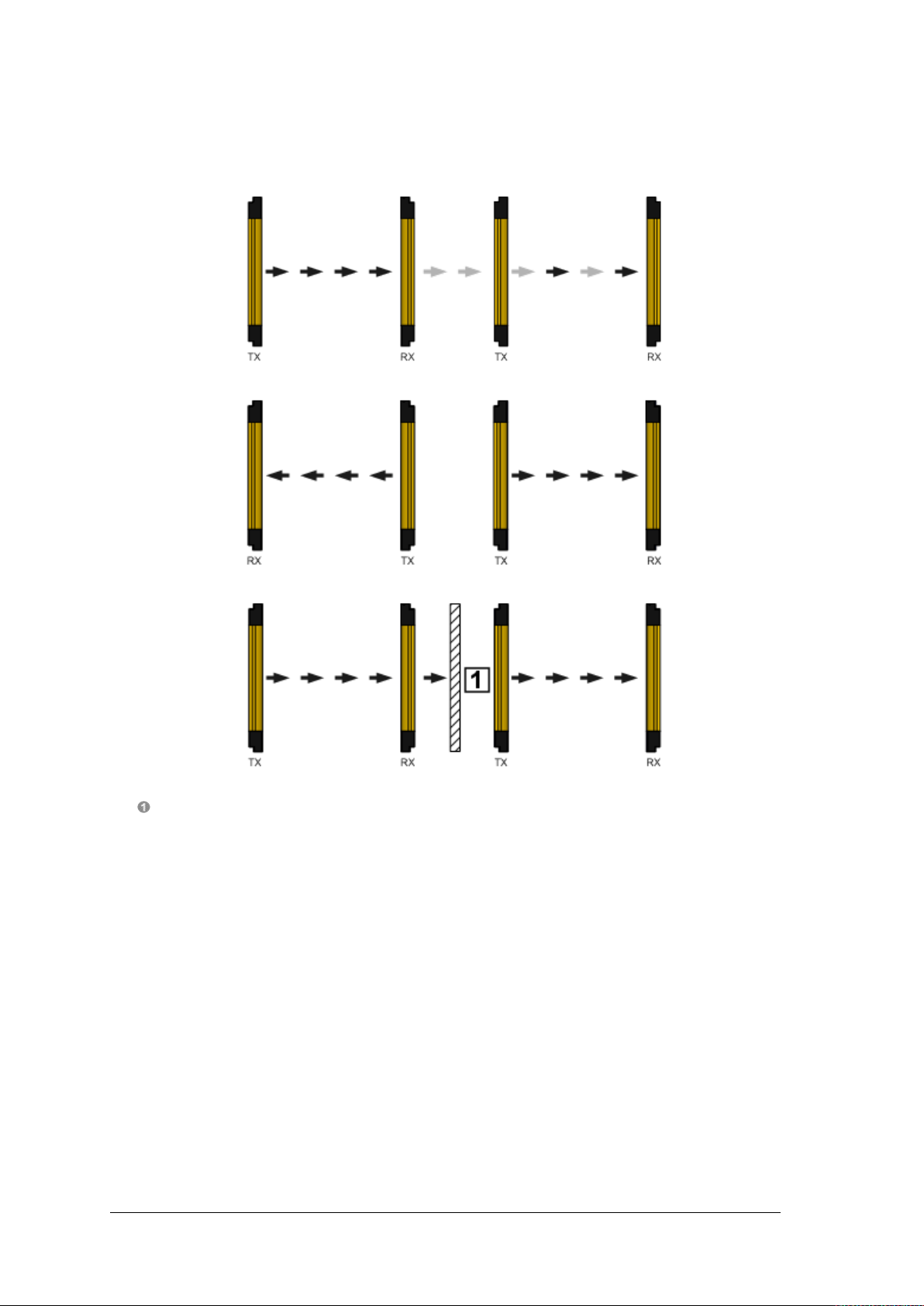
OPERATING MANUAL PSEN op4F/H-A series
1003067-EN-02
19
NO
YES
YES
Fig. 13 shows an example of an installation in which interference may occur, along with two
potential remedies.
Opaque partition
Fig. 13 – Interference between adjacen t lig ht cur tains
Should it be necessary to install two light curtains adjacently, as shown in the example in Fig.
13, the coding function is available as a possible solution (see section 7.12).
Page 20
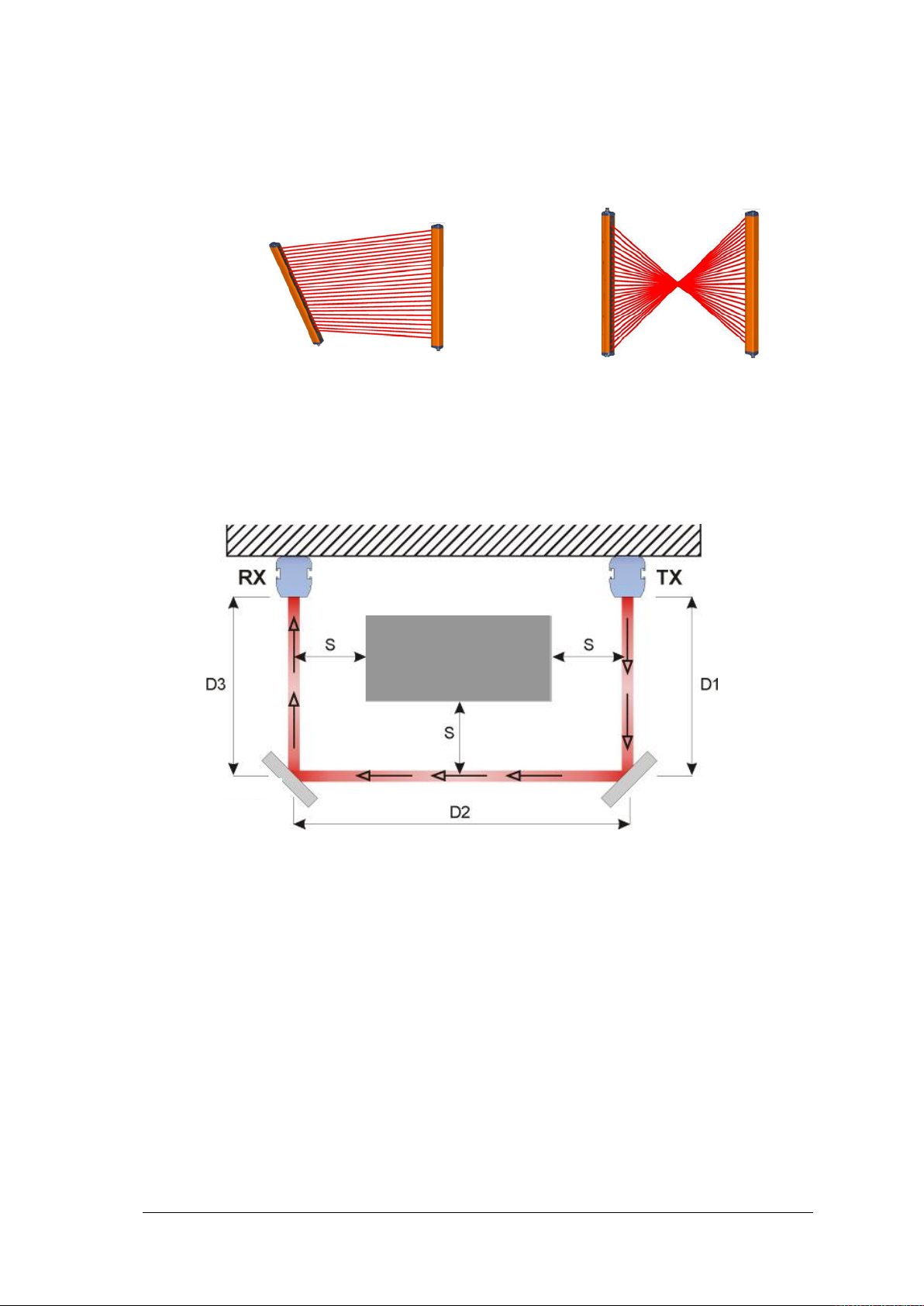
PSEN op4F/H-A series OPERATING MANUAL
20
1003067-EN-02
NO
Mirror
Mirror
2.2.3 Aligning transmitter and receiver
The light curtain pair must be arranged in parallel to each other. Transmitter and receiver
have connections underneath. Both units must be installed at the same time.
Make sure that the light curtains are not configured as shown in Fig. 14.
NO
Fig. 14 – Light curtain alignment
2.2.4 Using deviating mirrors
If a single safety device is used, danger zones with different but adjacent access sides can
be monitored using well-positioned deviating mirrors.
Fig. 15 shows a possible solution, which can be used to protect three access sides using two
mirrors. The deviating mirrors should be positioned at a 45° angle to the light axes.
DANGER
ZONE
Fig. 15- Using deviating mirrors
When deviating mirrors are used, the following precautions must be taken and conditions
considered:
• When deviating mirrors are used, the alignment of the transmitters and receivers requires
higher precision. Perfect ali gnment can be lost even with only a minor ang ular displacement of
the mirror. In this case we recommend you use the laser pointer, which is available as an
accessory.
• The minimum safety distance (S) must be maintained for all sections of the beam.
• Use of a single deviating mirror reduces the effective operating range by about 15%. This
percentage increases when two or more deviati ng mirrors are used (m ore detailed information
is provided in the technical specifications for the relevant mirror).
Page 21
OPERATING MANUAL PSEN op4F/H-A series
1003067-EN-02
21
Number
of mirror s
Operating range
(14 mm)
Operating range
(30 mm)
1
5.1 m
16.5 m
2
4.3 m
13.7 m
3
3.7 m
11.6 m
The table below states the operating ranges based on the number of mirrors used.
• Never use more than three mirrors per device.
• Any dust or dirt on the mirror’s reflective surface will drastically reduce the operating range.
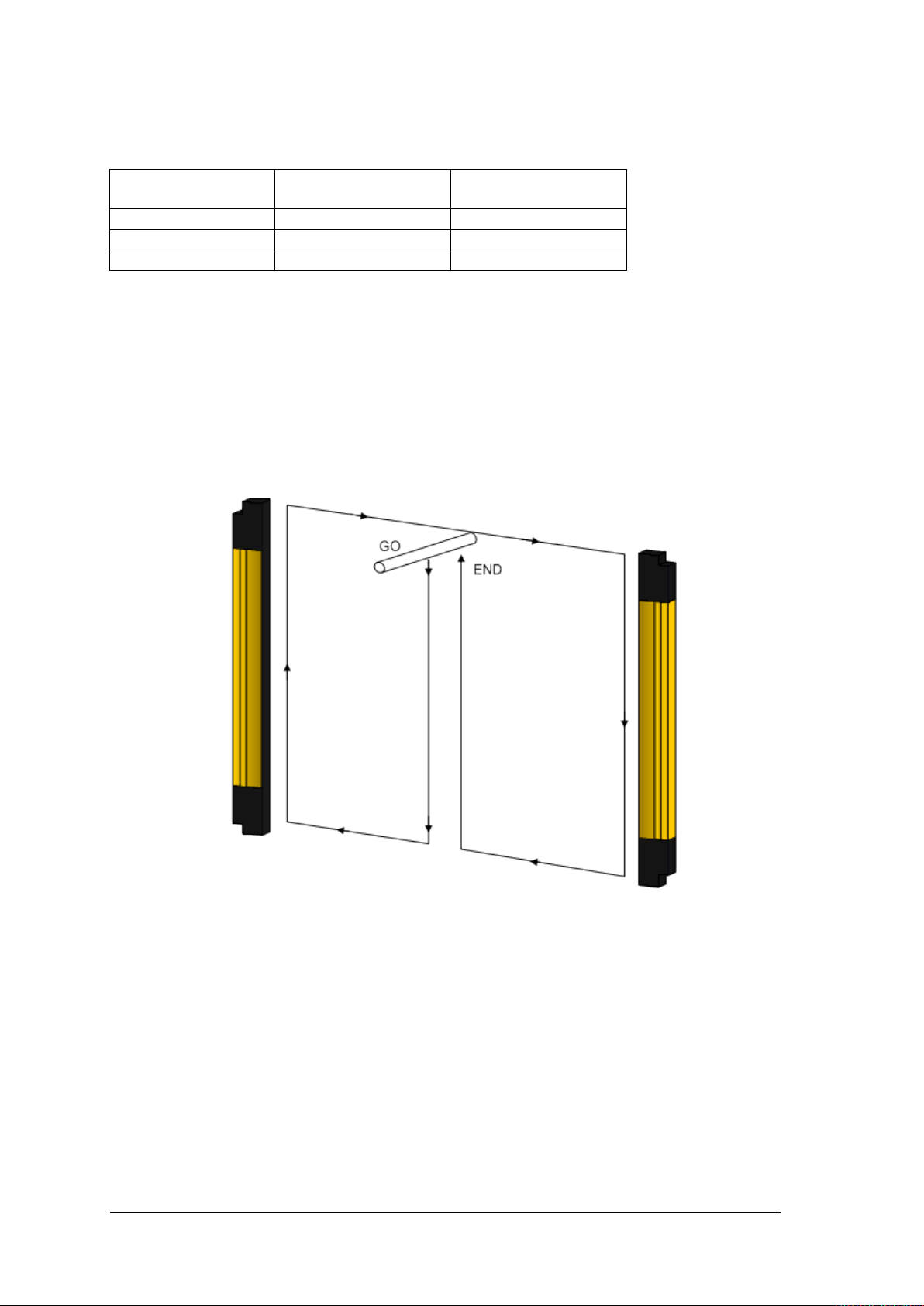
2.2.5 Inspections following a first-time installation
Listed below are the control measures that must be taken following a first-time installation,
prior to starting the machine. Tests must be carried out by qualified personnel or directly by
the person in charge of machinery safety / under his or her supervision.
Fig. 16 – Path of test object
Page 22

PSEN op4F/H-A series OPERATING MANUAL
22
1003067-EN-02
Perform the following checks:
• The light curtain is in a safe state (OSSDs off)
- T he beams are interrupted across the whole area of the protected field using a test
object (test rod) (TP-14 or TP-30) with an appropriate resolution, in accordance with
the diagram in Fig. 16.
• Is the light curtain aligned correctly?
- Press gently on the side of the product in both directions. The red LED must not lig ht
during this process
• Activate the TEST function on the TX side.
- The OSSD outputs are opened (r ed LED, OSSD on the RX side, ON and stop of the
controlled machine).
• The response time to the status of the machine STOP, including the response time of
the light curtain and machine, is within the limit values defined f or calculating the safety
distance (see Chapter 2.2).
• The safety distance between the danger zones and the light curtain complies with the
details specified in Chapter 2.2.
• Access and exposure of persons between the light curtain and hazardous machine
components is prevented.
• It is impossible to access the machine’s danger zones from an unprotected side.
• In order to guarantee that the light curtain remains in NORMAL FUNCTION MODE for at
least 10-15 minutes and, after positioning the specific test object in the protected field,
stays in a SAFE STATE for the same time span, there must be no interference from
external light sources.
• Check that all additional functions comply by activating them several times under
different operating conditions.
Page 23

OPERATING MANUAL PSEN op4F/H-A series
1003067-EN-02
23
3 MECHANICAL ASSEMBLY
The transmitter (TX) and receiver (RX) must be assembled with their sensing surfaces facing
each other. The connectors must be positioned on the same side and the distance must be
within the operating limits of the relevant model (see Chapter 11).
The pair of light cu rtains must be aligned to the best possible extent and must be as parallel
as possible.
The devices will be precision aligned in accordance with the description in Chapter 5.
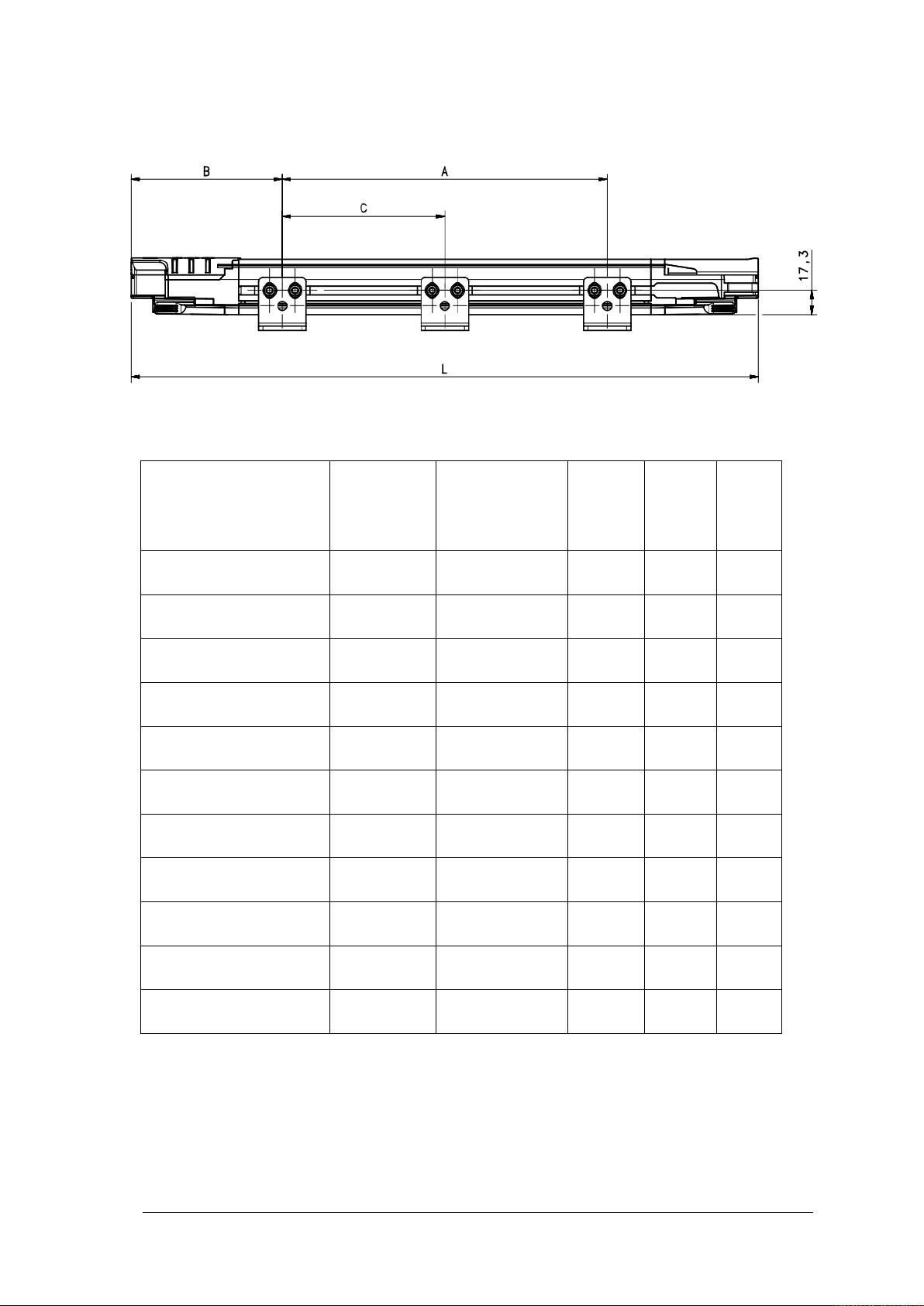
When positioning the pair of light curtains, please note that the length of the receiver is
increased by 56.9 mm if the PSEN op Advanced Programming Adapter is used and is built
into the light curtain.
The fastening kit supplied can be used as follows (Fig. 17).
To assemble the kit with the mounting brackets, place the bolts into the dedicated side guide
rail. Slide the insert along the groove of the metal profile. Attach the bracket by tightening the
M5 hexagonal nuts on the profile. It is possible to slide the bracket unit along the dedicated
rail and then reposition it by tightening the above-mentioned nuts.
Fig. 17 – Procedure with fixed mounting brackets
On applications where there is particularly heavy vibration, we recommend that you use antivibration rubbers with the mounting brackets to alleviate the effects of the vibration.
Fig. 18 - Anti-vibration rubbers
Page 24
PSEN op4F/H-A series OPERATING MANUAL
24
1003067-EN-02
MODEL
L (mm)
L (mm)
adapter
A (mm)
B (mm)
C (mm)
PSEN op4H-A-30-030/1
PSEN op4H-A-30-045/1
PSEN op4H-A-30-060/1
PSEN op4H-A-30-075/1
PSEN op4H-A-30-090/1
PSEN op4H-A-30-105/1
PSEN op4H-A-30-120/1
PSEN op4H-A-30-135/1
PSEN op4H-A-30-150/1
PSEN op4H-A-30-165/1
PSEN op4H-A-30-180/1
The mounting positions recommended based on the length of the light curt ain are stated in
Fig. 19 and in the following table.
Fig. 19 – Light curtain dimensions
incl. PSEN op
advanced
programming
PSEN op4F-A-14-030/1
PSEN op4F-A-14-045/1
PSEN op4F-A-14-060/1
PSEN op4F-A-14-075/1
PSEN op4F-A-14-090/1
PSEN op4F-A-14-105/1
PSEN op4F-A-14-120/1
PSEN op4F-A-14-135/1
PSEN op4F-A-14-150/1
PSEN op4F-A-14-165/1
PSEN op4F-A-14-180/1
306.3
456.3
606.2
756.2
906.1
1056.1
1206
1356
1505.9
1655.9
1805.8
363.2
513.2
663.1
813.1
963.0
1113.0
1262.9
1412.9
1562.8
1712.8
1862.7
86.3 110 -
236.3 110 -
306.2 150 -
406.2 175 -
506.1 200 -
606.1 225 -
966 150 453
1066 175 503
1166 200 553
1266 225 603
1366 250 652.9
Page 25
OPERATING MANUAL PSEN op4F/H-A series
1003067-EN-02
25
NOTE: The RX connections on the 12-pin M12 cable for the muting model and
muting configuration and one M12 for the blanking configuration).
PSENopt Advanced RX Muting
18 pin
M12 12 pin
M12 5 pin
M12 12-Pin:
M12 5-Pin:
4 ELECTRICAL CONNEC TIONS
18-pin rectangular pigtail cables are used at the light curtain for electrical connections. The
pigtail cable has M12 connectors with a different number of pins on the opposite side.
On muting models, the receiver is equipped with one 12-pin M12 connector and one 5-pin
M12 connector.
On blanking models, the receiver is equipped with one 12-pin M12 connector.
The transmitter has one 5-pin M12 connector (on both muting and blanking models).
After removing the cap shown in grey (see Fig.) the cables must be connected at the bot tom
of the light curtain (the end with LEDs and buttons).
Make sure that the terminator cap (see Chapter 13) is connected on the top of the light
curtain. If this connection is missing, the Master and Slave units will switch to a critical
communication state.
the 12-pin M12 cable for the blanking model are different, so it is important to
use the right cable for each configuration (connector with two
M12s for the
1. 24 V (brown)
2. 0 V (blue)
3. RESET/RESTART/ALIGN (white)
4. OVERRIDE1 (green)
5. OSSD2 (pink)
6. EDM (yellow)
7. MUTING DEACTIVATION (black)
8. OSSD1 (grey)
9. OVERRIDE2 (red)
10. MUTING LAMP (purple)
11. OVERRIDE STATUS (grey-pink)
12. EARTHING (red-blue)
1. 24 V (brown)
2. MUTING2 (white)
3. 0 V (blue)
4. MUTING1 (black)
5. NC (grey)
Page 26
PSEN op4F/H-A series OPERATING MANUAL
26
1003067-EN-02
PSENopt Advanced RX Bl a nking
18 pin
M12 12 pin
M12 12-Pin:
12. EARTHING (red-blue)
PSENopt Advanced TX
18 pin
M12 5 pin
M12 5-Pin:
5. REDUCED RANGE (grey)
Assignment of M12 connector
12-pin
5-pin
PSENopt Advanced RX Muting
CONNECTION
LINE
BEHAVIOUR
24Vdc
IN line
N.O.
24Vdc
IN line
N.O.
24Vdc
IN line
N.O.
24Vdc
IN line
N.O.
IN line
N.O.
connections
with EDM enabled
24Vdc
IN line
N.O.
1. 24 V (brown)
2. 0 V (blue)
3. RESET/RESTART/ALIGN (white)
4. TEACH IN (green)
5. OSSD2 (pink)
6. EDM (yellow)
7. NC (black)
8. OSSD1 (grey)
9. TOLERANCE (red)
10. LAMP (purple)
11. NC (grey-pink)
1. 24 V (brown)
2. TEST (white)
3. 0 V (blue)
4. EARTH (black)
RESET
RESTART
ALIGNMENT
OVERRIDE 1
Is connected – when in disabled state the
RESET/RESTART/ALIGN button is operated
Is connected – when during operation the
RESET/RESTART/ALIGN button is operated
Has to be set to 24 V DC at startup
Is connected – when Override is active during
operation
OVERRIDE 2
EDM
MUTING
DEACTIVATION
No voltage – during operation
See section 7.4 for
Must be non-equiva lent to OSSD during oper at io n
Muting is disabled when connecting
Page 27
OPERATING MANUAL PSEN op4F/H-A series
1003067-EN-02
27
PSENopt Advanced RX Muting
CONNECTION
LINE
BEHAVIOUR
0V
OSSDs
0V
OSSDs
This line signals the state of the override
24Vdc
LAMP
24Vdc
IN line
N.O.
FUNCTION EARTH
Connect to earth
PSENopt Advanced RX Blanking
CONNECTION
LINE
BEHAVIOUR
24Vdc
IN line
N.O.
Is connected – when in disabled state the
24Vdc
IN line
N.O.
24Vdc
IN line
N.O.
24Vdc
IN line
N.O.
24Vdc
IN line
N.O.
connections
with EDM enabled
0V
OSSDs
24Vdc
LAMP
FUNCTION
EARTH
PSENopt Advanced TX
CONNECTION
LINE
BEHAVIOUR
24Vdc
IN line
N.O.
is connected, when the RESET button is
24Vdc
IN line
N.O.
FUNCTION EARTH
Connect to earth
OSSD1 / OSSD 2
OVERRIDE
STATUS
MUTING LAMP
MUTING1/MUTING2
RESET
RESTART
ALIGNMENT
Protected field clear
No voltage = Protected field not clear
High level = Override function active
Low level = Override function inactive
NOTE:
signal inputs
The open collector connection is activated when
muting is activated.
Is connected – when muting is active during
operation
RESET/RESTART/ALIGN button is operated
Is connected – when during operation the
RESET/RESTART/ALIGN button is operated
Has to be set to 24 V DC at startup
TEACH-IN
TOLERANCE
EDM
OSSD1 / OSSD 2
BLANKING LAMP
TEST
REDUCED RANGE
See Chapter 7.4 for
Is connected – when TEACH-IN button is operated
during operation
Has to be set to 24 V DC at startup
Must be non-equiva lent to OSSD during oper at io n
Protected field clear
No voltage = Protected field not clear
The open collector connection is switched when
blanking is activated.
Connect to earth
operated during operation
Has to be set to 24 V DC at startup
Page 28

PSEN op4F/H-A series OPERATING MANUAL
28
1003067-EN-02
The RESET button must be positioned so that the user can check
the protected field during each test.
The RESET/RESTART/ALIGN button m ust be positioned so that the
user can check the protected field during all reset operations.
4.1 Connection guidelines
The following section contains some guidelines regarding the connections, which should be
followed to ensure the correct operation of the safety light curtain from the PSEN op4F/HA series.
• Never place connection cable close to or in contact with cables featuring high voltage
ratings and/or current fluctuations (e.g.: motor supply, inverters etc.).
• Never combine the OSSD wires from several safety light curtains into one multi-pole
cable.
• The TEST wire must be connected to the light curtain’s operating voltage via a
pushbutton with N/O contact.
• Use the light curtain with protection class III and SEL/PELV power supplies for the
voltage.
• Use the light curtain with protection class III and SELV/PELV power supplies for the
voltage supply.
Example: Connection to the safety relay
Automatic start
Fig. 20 – Connection to safety relay – automatic start
Page 29

OPERATING MANUAL PSEN op4F/H-A series
1003067-EN-02
29
connection (I)
(II)
connection (III)
NO
NO
YES
NO
Manual start
Fig. 21 – Connection to safety relay – manual start
The diagrams show the connection between the safety light curtains and the safety relay
PNOZ s3 in automatic start mode (Fig. 20) and monitored manual start mode (Fig 21).
• Avoid using varistors, RC circuits or LEDs in parallel to the relay inputs or in series
connection to the OSSD outputs.
• The safety contacts of OSSD1 and OSSD2 may not be connected in series or in
parallel, but must be used separately (Fig. 22).
• Should one of these configurations be used by mistake, the device switches to an
output error condition (see Chapter 8.).
• Connect both OSSDs outputs individually to the safety relay. Other configurations have
a negative effect on the safety of the system and are not permitted.
Fig. 22 – Correct OSSD signal load connection Fig. 23 – Incorrect OSSD signal load
Fig. 24 – Incorrect OSSD signal load connection
Fig. 25 – Incorrect OSSD signal load
Page 30

PSEN op4F/H-A series OPERATING MANUAL
30
1003067-EN-02
NOTE: The OSSDs are pulsed. The following diagram shows the time
characteristic of the OSSDs.
115 µs
500 ms
1000 ms
OSSD in safe state
OSSD2
OSSD1
24 V DC
GND
24 V DC
GND
Fig. 26 – Time characteristic of the OSSDs
Page 31

OPERATING MANUAL PSEN op4F/H-A series
1003067-EN-02
31
1 = First beam SYNC1
2 = Beam of protected field
3 = Last beam SYNC2
OFF
ON
RESET/RESTART/ALIGN
STATE OF LIGHT CURTAIN (POWER ON)
0 V DC
24 V DC
ON
OFF
RED LED FLASHES
ON
OFF
STATE OF LIGHT CURTAIN (ALIGN)
5 ALIGNMENT
The transmitter and receiver must be aligned to ensure the device operates correctly.
Good alignment prevents the light curtain switching incorrectly due to dust or vibration.
The optimum alig nment is achieved when the optical axes of the first and last beam from the
transmitter coincide with the optical axes of the corresponding elements on the receiver.
The light curtain has two synchronisation beams. The lower synchronisation beam, the first
beam in the protected field, is called SYNC1 and the synchronisation beam on the opposite
side of the light curtain, the last beam in the protected field, is called SYNC2.
The illustration shows that the first beam is on the lower edge of the light c urta in, next to the
LED display. The last beam is on the opposite side, next to the terminator cap.
Fig. 27 – Beam description
The alignment function can be activated by simultaneously switching 24 V at the input
RESET/RESTART/ALIGN (Pin 3/ 12-pin connect or) during startup. The activated alignment
mode is shown when the second LED starts flashing (red) (see Fig. 28). Then the
RESET/RESTART/ALIGN input can be switched without voltage again. When successful
alignment has been reached, the light curtain is returned to normal operating mode by
switching off and then on again.
Fig. 28 – Alignment timings
Page 32

PSEN op4F/H-A series OPERATING MANUAL
32
1003067-EN-02
Alignment
operating mode
No sync, check
SYNC1
One or more
not aligned
All light axes are
aligned
POOR
All light axes are
aligned
All light axes are
aligned
All light axes are
aligned
In alignment mode, the light curtain is always in a safe state and the OSSD outputs are OFF.
The quality and level of the alignment is determined via the signal strength of each individual
beam in alignment mode. The two synchronization beams have a higher value level. The
user can see the alignment quality from the LED state at the lower end of the receiver.
A. Hold the receiver in a stable position and align the transmitter until the yellow SYNC1
LED goes out. This state confirms that the first synchronisation beam has been
aligned.
B. Rotate the transmitter around the axis of the lower lens until the yellow SYNC2 LED
goes out.
C. For precision adjustment, m ake minor movements of the transmitter and receiver to
achieve the optimum quality
D. Attach both units firmly using the mounting brackets. Check that the LEVEL of the
receiver does not decrease in quality and that the light axes are not interrupted. Then
check that all LEDs on the LEVEL display go out, even if only one beam is
interrupted. This test is conducted using a test object TP-14 or TP-30 corresponding
to the resolution (see Chapter 2.2.5).
E. Switch off the light curtain pair and then switch it back on in normal operating mode.
The alignment level is also monitored by the display during normal operation (see
Chapter 8.1). Once the light curtain has been aligned and fastened appropriately, the
LED display proves perfect for checking the alignment and displaying any change in
the ambient conditions (e.g. dust).
Display Configuration LED RX
Alignment
status
Status of OSSD
in normal
NONE OFF
SYNC1 aligned
SYNC2 aligned
intermediate
beams
NONE OFF
NONE OFF
NONE OFF
ON
ON
EXCELLENT
ON
ON
Fig. 29 –Status of the LED displays in alignment mode
Page 33

OPERATING MANUAL PSEN op4F/H-A series
1003067-EN-02
33
CAUTION: Configuration via ACM will overwrite a configuration
accidental changes.
6 SETTING THE FUNCTIONS
There are two options for configuring the light curtain’s functions and operating
configurations:
- Basis configuration mode (BCM):
In basic configuration mode you have the option to use the buttons and the LED interface
(transmitter/receiver) to select basic functions/parameters.
- Advanced configuration mode (ACM):
In advanced configuration mode you have the option to use the PC software
PSENopt Configurator (only for the receiver) to select advanced functions/parameters. For
configuration via software the PSEN op Advanced Programming Adapter is required.
created via BCM! A new BCM configuration can only be created when
the ACM configuration is deleted. This protects the light curtain from
Basic configuration mode
The user interface consists of 8 LEDs and 3 protected pushbuttons and enables the user to
perform the basic configuration. The LEDs are the same LEDs used to display status in
normal operating mode.
A plastic pen is provided (see Chapter 13), which the user must use to activate the
pushbuttons, thus preventing unwanted access to the safety configuration.
Basic configuration steps
On the right-hand side of the operator panel at transmitter and receiver there is a settings
interface, consisting of three pushbuttons. The interfaces give users the option to set the lig ht
curtain locally, without using the PSENopt Configurator.
• CONFIRM button activates the BCM configuration mode
• SELECT button: The different functions are run through.
• ENABLE button: Activates and deactivates the currently selected function.
The individual steps are described below:
1. Press the CONFIRM button and keep it held down to switch to basic configuration
mode.
2. The light curtain runs through a test cycle. With the transmitter the LEDs 2 and 3 light
up one after the other, with the receiver the LEDs 2 to 8. The Power LED 1 is
constantly lit.
After the test cycle is completed, the current configuration is displayed
3. Use the SELECT function to choose the function that is to be set. The LED for the
selected function will flash.
4. Now configure the selected function by pressing the ENABLE but t on (LED lights/goes
out).
5. Repeat steps 3 and 4 until the required configuration is displayed.
6. Press the CONFIRM button and keep it held down to save the new configuration.
If an advanced configuration has already been set on the light curtain (via the
PSENopt Configurator on the PC), pressing the button just once dur ing s tep 2 will generate a
Page 34

PSEN op4F/H-A series OPERATING MANUAL
34
1003067-EN-02
Operator
Password
System integrator
SystemIntegrator
Maintenance engineer
Maintainer
Machine operator
No password required
light curtain configuration error, which prevents non-authorised changes to the advanced
configuration.
Advanced configuration mode
With the PSENopt Configurat or (graphical user interface for PC), t he user has the option to
configure advanced light curtain parameters. A variety of parameters can be used to adapt
the light curtain operation to your applications.
As the configuration of the light curtain is a safety-related component, the software must only
be handled by qualified personnel.
Such qualified personnel must ensure that nobody has access to the hazardous parts of the
machinery during the configuration procedure.
PSENopt Configurator has three different user levels with different authorizations.
System integrator: Has all possible access rights and can modify any setting in the
PSENopt Configurator.
Maintenance engineer: Can upload a configuration stored in the PSENopt Config urator to
the light curtain and use the PSENopt Configurator to monitor the system. He cannot create
any new configurations.
Machine operator: Uses the PSENopt Configurator exclusively to monitor the system.
Each user category is assigned different passwords to protect some functions.
1) Selecting the light curtain: User selects the light curtain to be configured from
among the light curtains that are identified within the network.
2) Configuring the parameters: User sets the configuration for the selected light
curtain.
Once completed, the user saves the configuration; the light curtain switches to a
SAFE state; the “Configuration in progress” message is displayed on the light
curtain’s LED interface and the previous light curtain configuration is deleted.
3) Checking the report: The light curtain sends the received configuration back to the
PSENopt Configurator and PSENopt Configurator generates a printable SAFETY
REPORT, which contains all the safety-related information about the present
configuration (Fig. 30). Once all the content of the report has been checked, the user
can accept the configuration: the light curtain restarts normal operation with the new
configuration.
4) Checking the light curtain: User checks that the light curtain is operating in
accordance with the specifications in the SAFETY REPORT (checks the resolution
using the appropriate test object, parameter check, ...).
Page 35

OPERATING MANUAL PSEN op4F/H-A series
1003067-EN-02
35
Identification of light curtain
Configuration ID (check sum of configuration parameters)
Position of light curtain in a cascading
Model name and characteristic data of the light curtain (resolution)
Current protected field configuration (muting or blanking)
Configuration parameters for blanking/muting
NOTE: Restoring the factory settings will delete the BCM and the ACM
configuration.
Fig. 30 – Safety report
• Serial no.
• Firmware version
•
6.1 Reset to factory configuration
The user has the option to re -establish the light curtain’s factory configuration by operating
the pushbuttons as described below:
1. Press the CONFIRM button and keep it held down for at least 9 s (but not more than
30 s, so that the light curtain is not blocked)
2. The LEDs flash briefly, indicating that the light curtain has been reset to the factory
configuration
3. After the reset has occurred, the light curtain resumes its normal operation with the
factory configuration.
Page 36

PSEN op4F/H-A series OPERATING MANUAL
36
1003067-EN-02
Legend for LED display in RX/TX function list
LED off, LED is not relevant for the information in the “Function” column
LED off, LED is relevant for the information in the “Function” column
“Function” column
LED red, value in the “Setti ng” column is valid for the inf ormation in the “Functi on”
column
“Function” column
List of RX functions in muting mode
(LED 3 lights up yellow)
PWR
OSSD
EDM
ACM
LEVEL
Coding
Selection of
EDM
4
Restart mode
5
Muting direction
Activation of
6.2 Function list
PSEN op4F/H-A has two main operating modes: blanking and muting. The settings of the
functions at the receiver associated with LEDs 5 to 8 will change, depending on whether
blanking or muting is selected.
NOTE: The table highlights the default configuration in bold.
LED yellow, value in the “Setting” column is valid for the information in the
LED green, value in the “Setting” column is valid for the information in the
Function
muting/blanking
LED
No.
2
3
6
Code 1
Code 2
No code
Muting
Blanking
Activated
Deactivated
Auto
Manual
T (bidirectional)
Setting
LED status
L (one-directional)
Muting timeout 7
override
8
10 min
Infinite
Level
Edge
Page 37

OPERATING MANUAL PSEN op4F/H-A series
1003067-EN-02
37
List of RX functions in blanking mode
(LED 3 OFF)
LED status
PWR
OSSD
EDM
ACM
LEVEL
Coding
2
Selection of
3
EDM
4
Restart mode
5
Floating blanking
deactivated
Selection of fixed
8
List of TX functions
LED status
PWR
TST
SR
LR
CODE
Selection of
3
Function
muting/blanking
Selection of
floating blanking
LED
No.
Code 1
Code 2
No code
Muting
Blanking
Activated
Deactivated
Auto
Manual
Setting
6-7
blanking
Coding
operating range
Function
LED
No.
2
Floating blanking 1 beam
Floating blanking 2 beams
Reduced resolution 4 beams
1 fixed blanking zone
2 fixed blanking zones
Setting
Code 1
Code 2
No code
Normal
Reduced
Page 38

PSEN op4F/H-A series OPERATING MANUAL
38
1003067-EN-02
7 FUNCTIONS
7.1 Restart function
If the beams detect an opaque object, the OSSD output switching elements will switch (i.e.
the safety contacts will open, SAFETY conditions). The restart f unction enables the user to
define how the light curtain returns from the safe state to normal operation.
There are two ways to restart the light curtain (i.e. close the OSSD safety contacts –
SAFETY condition): automatic or manual restart.
Automatic restart: If an opaque object is detected, the light curtain switches to a SAFE
CONDITION. If the object is then removed from the protected field, the light curtain will
resume its normal operation.
The response time is the time that elapses between the object being introduced to the
protected field and the OSSD achieving the OFF state (SAFETY); the reset time is the time it
takes for the OSSD to switch to the ON state (SAFETY) after all the objects have been
removed.
All these times are functions that are dependent on length, as illustrated below.
Fig. 31 – Restart timings (auto)
In automatic restart mode, the RESET/RESTART/ALIGN input (Pin 3 of the 12-pin M12
connector – RX-side) must not be activated.
Fig. 32 – Restart connection (auto)
Page 39

OPERATING MANUAL PSEN op4F/H-A series
1003067-EN-02
39
WARNING: Hazardous conditions and the reset mode should be
When access to danger zones is protected,
manual restart on the relay PNOZ s3 (see Chapter 4.).
Manual restart: W hen the light curtain has detected an opaque object in the protected f ield,
the light curtain does not resume its normal operation until the object has been removed from
the protected field and the reset button has been operated.
The OSSD output switching elements switch back to normal operation when the RESTART
signal voltage is removed again, and not after 500 ms. If the RESTART signal is present for
longer than 5 s an error is generated, which blocks the light curtain.
Fig. 33 – Restart timings (manual)
In manual restart mode, the RESET/RESTART/ALIGN input (Pin 3 of the 12-pin M12
connector – RX-side) must be connected to a 24 VDC N/O contact.
Fig. 34 – Restart connection (manual)
assessed carefully.
automatic reset mode is potentially unsafe if it enables the operator
to pass through the zone before the sensing area is active. In this
case it will be necessary to use a manual restart or, for example, the
Page 40

PSEN op4F/H-A series OPERATING MANUAL
40
1003067-EN-02
PWR
OSSD
EDM
ACM
LEVEL
The section below describes how the restart mode can be selected via the pushbutton as
well as via the user interface.
BCM configuration: Restart mode
Auto LED 5 red (ON)
Manual LED 5 OFF
ACM configuration: Restart mode
7.2 Test
The TEST function can be activated by operating the 24 VDC N/O pushbutton connected to
the TEST input on the TX device (Pin 2 of the 5-pin M12 connector) for at least 0.5 seconds.
The TEST disables the transmission level, so the RX-side sees the beams as interrupted and
the OSSD go low within the response time. As shown on the timing diagram below, the
OSSDs switch to the OFF state (INTERRUPTION STATE) after 500 ms (plus one cycle time)
and after the light curtain's response time.
Fig. 35 – Test timings
Page 41

OPERATING MANUAL PSEN op4F/H-A series
1003067-EN-02
41
PNP configuration
NPN configuration
7.3 Reset
If the light curtain is blocked in a fault state, you can restore normal operation by switching
the light curtain on and off or by activating the RESET function (only with critical errors).
To activate the RESET function, the RESET/RESTART/ALIGN connection (Pin 3 of the 12pin connector) must be supplied with 24 V for at least 5 seconds.
If the light curtain does not return to normal operating mode, the light curtain has to be
switched off and on again
. Errors in the internal connections can be cancelled this way.
Fig. 36 – Reset timings
If the error has not been rectified, the light curtain will again switch to a blocked state.
7.4 EDM
The external device monitoring function (EDM) monitors the external devices and checks the
OSSD status.
EDM enabled:
If EDM is enabled in the PNP configuration, the EDM input (Pin 6 of the 12-pin M12
connector - RX) must be connected to a 24 VDC N/C contact on the device to be monitored.
If the EDM is enabled in the NPN configuration, the EDM input (Pin 6 of the 12-pin M12
connector - RX) must be connected to a 24 VDC N/O contact on the device to be monitored.
NOTE: In normal operating mode, the third LED switched on in the user interface
indicates that the function is active.
The following diagrams describe how to connect the EDM input in the event of a PNP
and NPN configuration.
The function monitors the switching of the 24 VDC N/C contact, based on the OSSD status
changes.
Page 42

PSEN op4F/H-A series OPERATING MANUAL
42
1003067-EN-02
PNP configuration
NPN configuration
PNP configuration
NPN configuration
Fig. 37 – EDM timings
The EDM status is not equivalent to that of the OSSD: the timing diagram illustrates the
relationship between cause (OSSD) and effect (EDM), with the maximum permitted delay.
Tc ≥ 350 ms (time betwee n t he O SSD transition from OFF-O N a nd t he EDM test)
To ≥ 100 ms (time betwee n t he O SSD transition from OFF-O N a nd the EDM test)
(two different times for the mechanical, positive-guided contact)
EDM disabled:
If EDM is disabled, the EDM input may not be connected.
Fig. 38 – EDM connections
Page 43

OPERATING MANUAL PSEN op4F/H-A series
1003067-EN-02
43
PWR
OSSD
EDM
ACM
LEVEL
Resolution 30 mm
RX long range
RX short range
TX long range
20 m
6 m
TX short range
12 m
4 m
Resolution 14 mm
RX long range
RX short range
TX long range
7 m
2 m
TX short range
4 m
1 m
7.5 EDM selection
This function enables users to select or exclude monitoring of the external switching devices.
BCM configuration: EDM selection
Activated LED 4 ON yellow
Deactivated LED 4 OFF
ACM configuration: EDM selection
To increase the safety level when EDM is OFF when the light curtain is commissioned,
ensure that the EDM input is not connected.
7.6 Reduced range
This function enables you to select the maximum operating range for the light curtain’s
assembly.
The table below summarises the different operating ranges for both resolutions, if the
reduced operating range is changed.
You can select this function via ACM for the receiver and via BCM for the transmitter.
Fig. 39 – Reduced range
Page 44

PSEN op4F/H-A series OPERATING MANUAL
44
1003067-EN-02
PWR
OSSD
EDM
ACM
LEVEL
L-Version with integrated
one direction
T-Version with integrated muting
directions
Linear version with external
BCM configuration (TX-side): Reduced range
Long LED 3 ON yellow
Reduced LED 3 OFF
ACM configuration (RX-side): Reduced range
If long range is selected, the TX and RX can be installed at the maximum permitted operating
range. A reduced operating range is recommended for cases in which several pairs of light
curtains need to be assembled side by side and the coding function cannot be used.
7.7 Muting
The muting function guarantees that the safety function is automatically disabled over all or
part of the height of the detection zone, to enable specific, cyclical work operations to be
carried out without having to stop the machine operation.
In accordance with safety requirements, the light curtain is equipped with two inputs for
activating the muting function, MUTING1 and MUTING2.
The muting sensors must be able to detect the conveyed material (pallets, vehicles,…)
based on their length and speed. Where there are variable conveyor speeds within the
muting area, you must consider the effect this will have on the overall duration of the muting
process.
• The muting function excludes the light curtain during operation and maintains the
OSSD output switching elements in an activated state, based on the specific operating
requirements (Fig. 40).
muting sensors for muting in
• In accordance with the applicable standards, the safety light curtain has two inputs
(MUTING1 and MUTING2) to activate this function.
• This function is particularly suitable for cases in which an object, but not a person,
needs to pass through the danger zone under certain conditions.
sensors for muting in two
Fig. 40 – Application examples for the muting function
muting sensors
Page 45

OPERATING MANUAL PSEN op4F/H-A series
1003067-EN-02
45
Particular attention should be paid to the choice of configuration, as
incorrectly and reduce the safety level.
The muting sensors must be arranged in such a way that the
• It is important to not e that the muting function represents a hazardous situation of the
device. So it must be applied only in keeping with the necessary preventive measures.
• The muting sensors must be corr ectly positioned t o avoid unintended mut ing becom ing
potentially dangerous for the operator.
• MUTING1 and MUTING2 cannot be activated simultaneously.
• The muting status is displayed via an external muting lamp (which can be connected to
the light curtain via Pin 10 of the 12-pin M12 connector) and via various LEDs on the
user interface. If the muting function is ON, the LAMP and LEDs start to flash.
• During installation, ensure that the lamp is positioned so that it is as visible as possible.
• If the external lamp is broken and/or not connected, a muting call will result in a
SAFETY BLOCKING CONDITION and the relevant error message will be displayed.
an incorrect configuration can cause the muting function to operate
muting function cannot be activated by an operator who happens to
pass through.
7.7.1 Disabling the muting function
The muting function can be enabled and disabled dynamically during operation of the PSEN
op4F/H-A. When disabled, no muting call is accepted at the inputs MUTING X and the safety
function is constantly active.
Users can deactivate the muting function during operation by applying 24 V at the DISABLE
signal (Pin 7 of the 12-pin connector).
7.7.2 Muting display devices
The corresponding display device (lamp) must be connected in order to use the muting
function. If this device is not present, the light curtain will switch to a blocked state due to a
defect.
Both incandescent lamps and LED lamps are permitted. If you are using an LED lamp, make
sure that the connection has the right polarity.
When the lamp is switched on, a lamp TEST is carried out as part of each cycle, to ensure
that any functional failure is detected. If the lamp is found to be broken, the light curtain will
switch to a safe s t ate and a corresponding message is shown on the display (see Chapter 10
for further informatio n on the lam p).
Page 46

PSEN op4F/H-A series OPERATING MANUAL
46
1003067-EN-02
A11
A12
A21
A22
Safety sensor
7.7.3 Typical muting application and sensor connection
Fig. 41 – Typical muting application
The diagram above shows a typical muting application: t he protection device installed on t he
conveyor must allow the package to pass through but not the operator. The light curtain
temporarily suspends its safety function when the sensors A11, A21, A12, A22 are activated
in the correct sequence.
These may be optical or mechanical sensors that switch 24 V when the object is detected.
7.7.4 Muting direction
The light curtain can be used for bidirectional muting (T-type, four sensors) as well as onedirectional muting (L-type, two sensors).
• T-muting is used when objects can move through the light curtain in both directions.
• L-muting is used when objects move only in one direction.
In BC M mode the maximum activation delay between MUTING1 and MUTING2 (T12max) is
4 seconds
T-Muting
With T-type operation, the device switches to the muting function if the signal from the
MUTING2 input switches within a fixed T12max, after the MUTING1 signal has switched (or
vice versa). The muting function ends as soon as the sig nal at MUTING1 or MUTING2 goes
low. Users can set the maximum activation delay between MUTING1 and MUTING2 (or vice
versa) from a minimum of 1 second to a maximum of 16 seconds (T12max). Once this time
has elapsed, if users wish to switch to muting st atus they will need to deactivate the muting
input and start the sequence again.
Page 47

OPERATING MANUAL PSEN op4F/H-A series
1003067-EN-02
47
Fig. 42 – T muting timings
The sensors labelled A1/A2 are connected to the muting input (MUTING1) and the sensors
labelled B1/B2 are connected to the MUTING2 input. Sensors ending in “1” are on the same
side of the light curtain and therefore on the opposite side to the sensors ending in “2”.
“D” stands for the distance at which the sensors A1/A2 or B1/B2 must be installed and
depends on the package length (L):
D < L
“d1” stands for the maximum distance required between the muting sensors and depends on
the package speed (V):
d1
[cm] = V [m/s] * T12 [s] * 100,
max
“d2” stands for the maximum distance required to accept a muting request and depends on
the package speed (V):
d2
[cm] = V [m/s] * T12 [s] * 100,
max
“T12” stands for the activation delay between MUTING1 and MUTING2, which the operator
can select via ACM.
Fig. 43 – T-Muting connection
Page 48

PSEN op4F/H-A series OPERATING MANUAL
48
1003067-EN-02
L-Muting
With L-muting, the light curtain is muted if the input signals switch to 24 VDC in accordance
with a certain sequence: MUTING1 must be activated first; only then can MUTING2 be
activated.
If MUTING2 should activate before MUTING1, the device will not switch to muting mode;
“T12” represents the activation delay between MUTING1 and MUTING2, which users can
select via ACM.
The muting function ends once the time has elapsed, which corresponds to a multiple of the
activation delay between the two sensors (this time corresponds to m * T12). The value “m”
(multiplier T12) must be selected by the user. With BCM, 2 is the default value.
In the ACM configuration, users can set the maximum activation delay between MUTING1
and MUTING2 (or vice versa) from a minimum of 1 second to a maximum of 16 seconds
(T12max). Once this time has elapsed, if users wish to switch to muting status they will need
to deactivate the muting input and start the sequence again.
Fig. 44 – L-muting timings
The sensor labelled A is positioned furthest away from the light curtain, which is why its
beam is recorded first. With reference to the diagram below and in consideration of the fact
that the package only passes from right to left, sensor B cannot be recorded first. If this
should happen, the light curtain is not muted.
“V” indicates a constant velocity. As a result, “d1” can be calculated in accordance with the
following formula:
d1 [cm] = V [m/s] * T12 [s] * 100
Fig. 45 – L-Muting connection
Page 49

OPERATING MANUAL PSEN op4F/H-A series
1003067-EN-02
49
PWR
OSSD
EDM
ACM
LEVEL
BCM configuration: Muting direction
T (bidirectional) LED 6 ON green
L (one-directional) LED 6 OFF
ACM configuration: Muting direction
Page 50

PSEN op4F/H-A series OPERATING MANUAL
50
1003067-EN-02
NOTE: This does not comply with the standard IEC 61496-1 and the user is
informed of this fact via a message
PWR
OSSD
EDM
ACM
LEVEL
NOTE: The infinite timeout option does not comply with the standard
IEC 61496-1 and the user is warned accordingly.
7.7.5 Muting timeout
The muting timeout describes the time for the maximum duration of the muting function; once
the timeout has elapsed, muting is ended.
Users have the option to set this time in BCM as well as ACM mode.
In BCM mode they can select the timeout to be 10 minutes long or infinite; “infinite” means
that the muting timeout may potentially never end: as long as the muting conditions are
present, the muting function will be maintained.
Fig. 46 – Muting timeout
Users have the option in the ACM mode set the muting timeout in increments of 1 minute
between 10 min und 1080 min. Alternatively, it can also be set to be infinite.
BCM configuration: Muting timeout
10 min LED 7 ON green
Infinite LED 7 OFF
ACM configuration: Muting-Timeout
Page 51

OPERATING MANUAL PSEN op4F/H-A series
1003067-EN-02
51
.
7.7.6 Muting filter
This function prevents muting from being activated unintentionally.
The muting filter is a filter arranged on the muting inputs: Transitions of the muting signal
from high to low are only considered valid if they are maintained for a period (Tf) of over
100 ms.
If this function is disabled, the logic level of the muting sensors will correspond to the signal
level on the wire.
ACM configuration: Muting filter
Fig. 47 – Muting filter disabled
Fig. 48 – Muting filter enabled
Page 52

PSEN op4F/H-A series OPERATING MANUAL
52
1003067-EN-02
7.7.7 Partial muting
The muting type can be configured: total or partial muting. Partial muting can prove useful
when the user wishes to limit the effects of the muting function exclusively to the selected
zones.
With ACM configuration, the user can select a maximum of 5 muting zones, each of which is
defined in accordance with the following parameters:
- Position: First beam of muting zone (starting from the user display cover).
- Dimensions: Number of beams in muting zone
ACM configuration: Selection of parti al muting
Select to enable the "partial muting" function.
• To add a new muting zone above the selected area:
Click the "Add area" button and then select: "Add after selected beam"
• To add a new muting zone below the selected area:
Click the "Add area" button and then select: "Add before selected beam"
• To remove an existing muting area:
Click the "Remove selected area" button.
• Set ting the muting zone :
Enter the values for dimensions and position of an area in the soft ware. The display of the
software is adapted accordingly. W hen performing step "2 Programming" and the report has
been accepted, these values are also set in the light cur tain or in the PSEN op Advanced
Programming Adapter.
Page 53

OPERATING MANUAL PSEN op4F/H-A series
1003067-EN-02
53
7.8 Override
The override function allows the user to disable the safety f unctions if the machine needs to
be restarted, even though one or more of the light curtain beams have detected an object in
the protected field. For example, a typical application would be to examine recurring
blockages more precisely and to rectify the cause. These may be work materials between
the light curtain’s transmitter and receiver, which trigger the light curtain.
The override’s redundant inputs must be connected to a 24 VDC N/O contact and an earthed
N/O contact.
In accordance with the guidelines, the light curtain is equipped with two override activation
inputs: OVERRIDE1 and OVERRIDE2 (respectively, Pin 4 of the 12-pin M12 connector and
Pin 9 of the 12-pin M12 connector – of the receiver).
Fig. 49 – Override connection
The condition for the override is t hat t he light curtain must be in a SAFE STATE and at least
one muting sensor must have been interrupted.
If this condition is met, the user interface shows “override call stat us”
on the OSSDs and the LEDs for the alignment function flash.
OVERRIDE CALL
STATUS
As a result, the override request will only be accepted if the signals at the OVERRIDE X
inputs comply with the timings shown below.
The override function is ended automatically if any of the following conditions is present:
• All muting sensors are deactivated (with a T-muting configuration).
• All muting sensors are deactivated and no beams are interrupted (with an L-muting
configuration).
• The preset time limit has elapsed.
• The requirements for activation are no longer met (e.g. an override input is deactivated).
and both the red LED
Page 54

PSEN op4F/H-A series OPERATING MANUAL
54
1003067-EN-02
7.8.1 Override mode
It is possible to activate the override inputs: Level or edge.
As shown in the diagram below, the two types of activation sequence for the override are
recorded in the external inputs:
• Activated by level: The override remains activated until both contacts are closed and
at least one muting sensor has been interrupted.
OVERRIDE STATE: This is an output signal which provides the user with information
as to whether the override inputs are active and the override conditions are present.
Fig. 50 – Override timings (activated by level)
• Activated by edge: W hen the contacts are closed, the override rem ains activated until
at least one muting sensor has been interrupted. In this case, the override status is
also maintained if the override contacts are opened. The device switches the override
status if any of the following events occurs:
− The muting sensors are deactivated (T-Muting) or the muting sensors are
deactivated AND no beams are interrupted (L-Muting).
− The timeout time elapses.
OVERRIDE STATE: This is an output signal which provides the user with information
as to whether the override inputs are active and the override conditions are present.
Fig. 51 – Override timings (activated by edge)
Page 55

OPERATING MANUAL PSEN op4F/H-A series
1003067-EN-02
55
PWR
OSSD
EDM
ACM
LEVEL
BCM configuration: Override mode
Level LED 8 ON green
Edge LED 8 OFF
ACM configuration: Override mode
7.8.2 Override timeout
BCM mode
The timeout of the override status is 120 seconds in both operating modes. If the override
conditions remain active and both contacts remain closed for more than 120 seconds (this
condition only applies when the mode is activated by level), the override will go low after a
maximum of 120 seconds.
ACM mode
The override timeout represents the maximum duration of the override. This time can be set,
from a minimum of one minute to a maximum of 256 minutes.
Once the timeout has elapsed the override ends, even if the conditions that led to the
activation are still present and the override inputs are active.
OVERRIDE STATE: This is an output sig nal which provides the user with information as to
whether the override inputs are active and the override conditions are present.
Fig. 52 – Override timeout timings
Page 56

PSEN op4F/H-A series OPERATING MANUAL
56
1003067-EN-02
ACM configuration: Override timeout
7.8.3 Override restart
This can only be selected when the light curtain is in manual restart mode; users can select
the type of override restart: normal or automatic.
The RESET/RESTART/ALIGN input (Pin 3 of the 12-pin M12 connector – RX-s ide) m ust be
connected to a 24 V DC N/O contact.
Fig. 53 – Override restart connection
Page 57

OPERATING MANUAL PSEN op4F/H-A series
1003067-EN-02
57
NOTE: This selection does not comply with the standard IEC 61496-1 and the
user will be informed of this fact via a message.
Automatic override restart
The OSSD output switching elements resume normal operation when the RESTART signal
goes low and not after 500 ms. With a timeout of 5 s on RESTART with 24 V an error is
generated, which blocks the light curtain.
The output signals switch to 24 VDC after a time period that represents the maximum value
between the reset time and the high restart time (greater than or equal to 500 ms). This tim e
period may lie between 500 ms and 5 s.
Once the override is ended, the OSSDs return to a normal operating state if the beams are
not interrupted.
OVERRIDE STATE: This is an output sig nal which provides the user with information as to
whether the override inputs are active and the override conditions are present.
Fig. 54 – Override restart timings (auto)
ACM configuration: Selection of automati c override restart
Page 58

PSEN op4F/H-A series OPERATING MANUAL
58
1003067-EN-02
Normal override restart
The OSSD outputs switch to normal operation when the RESTART signal goes low and not
after 500 ms. With a timeout of over 5 s an error is generated, which blocks the light curtain.
The output signals switch to 24 V DC aft er a time period that represents the maximum value
between the reset time and switched restart (greater than or equal to 500 ms).This time
period may lie between 500 ms and 5 s.
Once the override is ended and if the beams are not interrupt ed, the lig ht curtain switches to
an interlock state, after which a restart must be performed in order to resume a normal
operating state.
OVERRIDE STATE: This is an output sig nal which provides the user with information as to
whether the override inputs are active and the override conditions are present.
Fig. 55 – Override restart timings (normal)
ACM configuration: Selection of normal override restart
Page 59

OPERATING MANUAL PSEN op4F/H-A series
1003067-EN-02
59
PWR
OSSD
EDM
ACM
LEVEL
7.9 Blanking
Blanking is a function of the safety light curtains, which enables an opaque object to be
inserted into the protected field without stopping the machine’s normal operation. Blanking
can only be used when certain safety conditions are present and in accordance with a
configurable operating log ic.
The blanking function is particularly useful when the light curtain's protected field will
inevitably be within moving parts or material of the machine. So it is possible to maintain the
light curtain’s safety outputs on working machinery under normal operating conditions, even
if a pre -defined number of beams in the protected area has been interrupted.
The blanking function can be selected in two ways: fixed blanking and floating blanking.
These two modes can be enabled individually or simultaneously.
Users also have the option to connect a lamp (properties are listed under Chapter 10), which
indicates that the blanking function is activated. It is not absolutely necessary to use a lamp
for a light curtain that is in blanking mode.
The lamp begins to flash in the following circumstances:
−
The light curtain is in a fixed blanking mode and the object is being removed from the
blanked zone;
−
The light curtain is in floating mode with total surveillance and the dimensions of the
detected object are changing or the object is being removed from the blanked zone.
To enable all blanking functions, the blanking function can be selected in either BCM or
ACM.
BCM configuration: Selection of muting/bl anking
Muting
Blanking LED 3 OFF
ACM configuration: Selection of muting/bl anking
LED 3 ON yellow
Page 60

PSEN op4F/H-A series OPERATING MANUAL
60
1003067-EN-02
7.9.1 Fixed blanking
Fixed blanking enables a certain part of the protected area (e.g. a certain number of beams)
to be hidden, while all other beams operate normally.
The blanking zone can be achieved using the teach-in process: the user must hold down the
24 V DC N/O teach-in contact (Pin 4 of the 12-pin M12 connector - RX) for at least
3 seconds, while an object interrupts the zone designed for blanking. The blanking zone
becomes active as soon as the teach-in contact is without voltage again.
If the teach-in contact is depressed for more than a minute, the light curtain is blocked
Teach-in can also occur in ACM. The user mus t place the object/objects within the protect ed
field and then press the teach-in button (“Reduced resolution / Blanking” in the blanking
section of the PSENopt Configurator).
ACM configuration: Teach-in
With fixed blanking, the beams from the blanked zone must be interrupted, otherwise the
light curtain switch es to a SAFE STATE.
The tolerance function can be activated by applying a voltage of 24 V DC at the tolerance
signal during restart (Pin 9 of the 12-pin M12 connector - RX). If the tolerance is activated,
the object can move 1 beam above and below the blanking zone. If the object moves out of
the blanking zone by more than 1 beam, the light curtain is blocked due to a blanking
tolerance error.
The tolerance function is useful if it is only possible for the object to move slightly from its
original position.
If the light curtain is switched of f, the tolerance is lost and it will be necessary to r epeat the
procedure for setting a tolerance value (described above).
If the tolerance is activated, two blanking zones must be separated by at least two beams
that have not been blanked.
Even if the supply is interrupted or the light curtain is reset, the teach-in configuration is
maintained until the next teach-in operation. The user can delete the teach-in conf iguration
by carrying out a new teach-in procedure with a protected area that is object-free.
If blanking errors occur, the teach-in configuration will be deleted after the reset.
If the user switches from the blanking configuration to the muting configuration and then back
to the blanking configuration, all potential teach-in zones that were saved initially will be
deleted. Fixed blanking can be combined with floating blanking; at least one synchronisation
beam must remain free.
Page 61

OPERATING MANUAL PSEN op4F/H-A series
1003067-EN-02
61
Please note that the actual resolution changes when using this
and that the installation of the light curtain must be adapted
accordingly.
7.9.2 Fixed blanking with increased tolerance
This is fixed blanking with a tolerance on only one side of the blanking zone, so the user
must select “top” or “bottom” tolerance.
This function is particularly helpful with conveyor belts (which use fixed blanking) with goods
transported along them (dimensions within the tolerance).
Only fixed blanking zones can be set on the tolerance side. On the other side it’s possible to
set fixed as well as floating blanking zones with total surveillance.
Only one zone can be set with fixed blanking and increased tolerance.
This function can only be set via ACM.
function. Ensure that the minimum distance has to be recalculated
7.9.3 Floating blanking with total surveillance
Floating blanking with total surveillance enables the object to move freely within the light
curtain’s pr otected field. The blanked beams must be occupied, which means that the object
must stay within the light curtain’s protected field to remain in normal operating mode.
This function can only be set via ACM.
7.9.4 Floating blanking with partial surveillance
Floating blanking with partial surveillance ensures that the object moves freely within the light
curtain’s protected field, although only a certain area in the light curtain is perm itted and the
hidden beams are adjacent and must not exceed the configured number.
This function can only be set via ACM.
The diagram below illustrates various blanking configurations.
ACM configuration: Blanking configuration
Page 62

PSEN op4F/H-A series OPERATING MANUAL
62
1003067-EN-02
NOTE: This function affect s the light curtain’s actual resolution and the user
is informed of this fact via a message.
Please note that the actual resolution changes when using this function.
7.9.5 Reduced resolution
Reduced resolution represents a particular type of floating blanking, in which multiple object s
can each interrupt a certain number of beams, while the light curtain remains in normal
operating mode.
The number below indicates how many adjacent beams the object can interrupt to guarantee
that the light curtain remains in normal operating mode. With reduced resolution 2, for
example, the object can interrupt 1 beam, 2 beams or no beam at all and the light curtain
remains in normal operating mode.
This function can only be set via ACM.
Ensure that the minimum distance has to be recalculated and that the
installation of the light curtain must be adapted accordingly.
7.9.6 Tolerance
There are two types of tolerance: position tolerance and dimension tolerance.
• Position tolerance
Indicates the number of beams in the blanking zone that can be interrupted above and
below the blanking zone, without causing the OSSD to switch off.
If heavy vibration is present, this function is useful to avoid the OSSD changing state.
• Dimension tolerance
Indicates the number of beams by which the object may be smaller in comparison with t he
number defined by the dimension value. It is a negative figure.
It is useful if an object interrupts half a lens. In this case, even minimum vibration could
cause the OSSD to change state.
The tolerance can be set in BCM and also in ACM.
To select this function via ACM, the user must have at least one blanking zone. Then he can
select either position tolerance or dimension tolerance. The tables below show various cases
in a blanking zone consisting of 3 beams.
Page 63

OPERATING MANUAL PSEN op4F/H-A series
1003067-EN-02
63
PWR
OSSD
EDM
ACM
LEVEL
The tolerance affects the light curtain's actual resolution. Make sure
that the new resolution is considered when calculating a new
mechanical assembly.
Position tolerance
Dimension tolerance
The existence of the tolerance is indicated by LEDs f lashing on the user interface, as shown
below.
Tolerance display
Tolerance active
LED 3 flashes yellow
Page 64

PSEN op4F/H-A series OPERATING MANUAL
64
1003067-EN-02
PWR
OSSD
EDM
ACM
LEVEL
PWR
OSSD
EDM
ACM
LEVEL
7.9.7 Blanking mode in the basic configuration
Only a reduced series of configurations can be implemented in basic configuration mode.
BCM configuration: Fixed blanking
1 fixed blanking zone
LED 8 ON green
2 fixed blanking zones LED 8 OFF
• 1 fixed blanking zone: only 1 zone can be configured as a blanking zone.
• 2 fixed blanking zones: 2 zones can be configured as blanking zones.
BCM configuration: Floating blanking
Floating blanking disabled
Floating blanking 1 beam (with
partial surveillance)
Floating blanking 2 beams (with
partial surveillance)
LED 6 ON green
LED 7 ON green
LED 6 ON green
LED 7 OFF
LED 6 OFF
LED 7 ON green
Reduced resolution 4 LED 6 OFF
LED 7 OFF
• Floating blanking disabled: Floating blanking is not permitted.
• 1 floating blanking beam: The lig ht c urtain remains in NORMAL OPERATIO N if 1 beam
or 0 beams are interrupted.
• 2 floating blanking beams: The light curtain remains in NORMAL OPERATION if 2
adjacent beams, 1 beam or 0 beams are interrupted.
• Reduced resolution 4: The light curtain switches to a SAFE state if more than 4
adjacent beams are interrupted.
Page 65

OPERATING MANUAL PSEN op4F/H-A series
1003067-EN-02
65
Number of
beams
Actual resolution of light curtain
14 mm
30 mm
1
23 mm
49 mm
2
33 mm
68 mm
3
42 mm
87 mm
4
51 mm
105 mm
7.9.8 Blanking mode in advanced configuration
A maximum of 5 blanking zones (fixed + floating) can be configured in ACM (however, at
least one separating beam is required between the zones).
The user can select the number of beams via ACM.
• Reduced resolution
ACM configuration
The software calculates the maximum object size (in mm) that the light curtain can detect
without triggering a SAFE STATE.
The actual resolution of the light curtain changes based on the varying value that is
assigned to the parameter N.
The safety distance must be calculated based on the actual resolution.
hidden light
Actual resolution based on the hidden light beams
Page 66

PSEN op4F/H-A series OPERATING MANUAL
66
1003067-EN-02
• FIXED blanking
The panel on the right shows the settings for the active blanking zone (in the example
shown below, the active blanking zone is 3 beams in size and is 7 beams from the bottom
of the light curtain; no tolerance is set).
• FIXED blanking with increased tolerance (top
or bottom )
The example shown below illustrates the settings with fixed blanking and an increased top
tolerance: only fixed blanking zones are permitted above this zone; fixed blank ing zones as
well as zones with total surveillance are permitted below this zone.
Page 67

OPERATING MANUAL PSEN op4F/H-A series
1003067-EN-02
67
• FLOATING blanking with total surveillance
Floating objects can move up and down, interrupting several beams in t he process. These
objects can overlap or change positions.
The object must be within the protected field at all times and interrupt the number of
configured beams with a fixed tolerance of one beam. This is necessary so that a moving
object always interrupts a different number of beams.
• FLOATING blanking with partial surveillance
Floating objects can move up and down, interrupting several beams in the process.
These objects can also
− leave the protected field or
− interrupt a lower number of beams than that configured.
Only fixed blanking can be configured around this zone. In these fixed blanking zones,
floating objects can overlap and even change position without causing the OSSDs to
switch.
Page 68

PSEN op4F/H-A series OPERATING MANUAL
68
1003067-EN-02
7.10 Cascading
An internal communication bus can be used to cascade several pairs of light curtains with
each other. The normal connections at the top and bottom of the light curtain are used with
the aid of a cascading cable. The OSSDs are only physically connected to the Master unit.
If transmission should fail due to a stuck-at fault or signal degradation, both the Master and
Slave units switch to a safe state.
A maximum of three units (Master and two Slaves) can be connected in a cascading
configuration: a maximum of 160 beams on models with a resolution of 30 mm and a
maximum of 320 beams on models with a resolution of 14 mm. The maximum length of the
Master unit is 1800 mm and the maximum length of each Slave unit is 1200 mm. The
corresponding cables must be used ( see Chapter 14) to ensure that the units are connected
correctly in the cascading configuration.
An auto-recognition procedure is run on start-up; it automatically synchronizes the topology
of the cascading structure and the light curtains
.
To enable auto-recognition, the terminator cap (contained in the kit) m ust be connected to all
the light curtains of the cascading system, both in the transmitter and in the receiver unit.
Without this connection, a critical communication error will be generated in the Master and
Slave units.
7.11 PNP/NPN
The PNP/NPN function enables the user to inform the light curtain of the mode in which the
OSSDs are connected.
PNP configuration
In this configuration, the load is connected between the OSSD output and GND.
In normal operation, the output voltage of the OSSD is 24 V DC
If an opaque object interrupts the beams, the OSSDs switch from 24 V CD to 0 V DC
Fig 56 PNP connection
Page 69

OPERATING MANUAL PSEN op4F/H-A series
1003067-EN-02
69
Fig. 57 – PNP timings
NPN configuration
With this configuration, the load is connected between 24 V DC and the OSSD output
switching element.
In normal operation, the output voltage of the OSSD is 0 V DC.
If an opaque object interrupts the beams, the OSSD status switches from 0 VDC to 24 V.
Fig. 58– NPN connection
Page 70

PSEN op4F/H-A series OPERATING MANUAL
70
1003067-EN-02
Fig. 59 – NPN timings
7.12 Coding
The coding function enables the light curtain to operate normally even if an interference
condition occurs with another light curtain. This is particularly true if the transmitter TX of the
first light curtain emits beams in the direction of the receiver RX of the second light curtain.
To counter this, both light curtains must be configured with different codes (see under
Chapter 2.2.2).
• No code
In this case, no code is selected and the light curtain must be installed at a certain
distance to other light curtains with no code, to avoid potentially dangerous interference.
Users who install the light curtains closer than the designated minimum distance must
install the TX from the first light curtains on the same side as the RX from the second.
Fig. 60 – No code
Page 71

OPERATING MANUAL PSEN op4F/H-A series
1003067-EN-02
71
NOTE: The configur ation performed using the GUI only changes the code on
the TX side with the same code via BCM.
PWR
OSSD
EDM
ACM
LEVEL
PWR
TST
SR
LR
CODE
• Code 1 or Code 2
If the two light curtains
− are installed at a distance that is lower than the minimum distance permitted for
identical devices
− and has RX on the same side,
the user must configure the light curtains with different codes.
the RX side; for the light curtain to operate correctly, the user must configure
Fig. 61 – Code 1 and Code 2
If one of the three options (no code, code 1 and code 2) has been selected and beams have
been interrupted, the following display appears on the user interface.
Normal operating mode (RX side): beams interrupted
LED Level
No Code LED 5 and 6 OFF
Code 1 LED 5 ON Red, LED 6 OFF
Code 2 LED 5 OFF LED 6 ON Green
Normal operating mode (TX side)
No Code LED 5 and 6 OFF
Code 1 LED 5 ON Red, LED 6 OFF
Code 2 LED 5 OFF LED 6 ON Green
Page 72

PSEN op4F/H-A series OPERATING MANUAL
72
1003067-EN-02
PWR
OSSD
EDM
ACM
LEVEL
PWR
TST
SR
LR
CODE
This function can be set in the RX unit as well as the TX unit via BCM. Two codes are
available.
BCM configuration: Coding selectio n (TX and RX)
No Code LED 2 OFF
Code 1 LED 2 ON Red
Code 2 LED 2 ON Green
ACM configuration: Coding selectio n
Page 73

OPERATING MANUAL PSEN op4F/H-A series
1003067-EN-02
73
Meaning of LED
Off On
Flash
Indifferent
Operating
light curtain
LED DISPLAY
Suggested action
First synchronisation
beam linked
Last synchronisation
beam linked
normal operating mode.
User must clear protected field
OSSD ON
(maximum alignment)
OSSD OFF
Code1
OSSD OFF
Code 2
No Code
None
Insufficient
Low
Good
Best
Configuration process running
instructions
LEVEL
ACM
EDM
OSSDs
Power
Sync
Fault Code
8 DIAGNOSTICS
8.1 Status of LEDs
On the bottom left-hand side of the light curtain 8 LEDs help users to monitor and check the
state of the light curtain in alignment mode, in normal mode and when troubleshooting. The
LEDs can be used to recognise the configuration that has been set via the pushbuttons.
Receiver side (RX):
mode of
Alignment
Normal
operating
mode
Manual restart
only
Normal
operating
mode
Information
Not aligned
Minimum signal level
Maximum signal level
Interlock
free beams
Interlock
interrupted beams
OSSD OFF
Signal level at beams
User can restart the device by
activating the RESTART in
before activating the
RESTART.
EDM a ctive
ACM active
ACM ready for
configuration
via PC, follow software
Page 74

PSEN op4F/H-A series OPERATING MANUAL
74
1003067-EN-02
Blanking zones not observed.
Check the actual resolution for
activation of the tolerance
function.
If the OSSDs swi tch off
muting configuration.
Activate the override button to
Check and repeat the override
connections.
Check the lamp connections
Activate RESET.
Activate RESET.
services.
services.
Activate RESET.
Check connection RESTART
Activate RESET.
correctly.
Perform basic configuration
Perform advanced configuration
services.
Switch light curtain on/off.
services.
Blanking valid
(OSSD ON)
Normal
operating
mode
Blanking only
Blanking invalid
(OSSD OFF)
Tolerance BCM active
Re-configure blanking (teach in
if BCM)
the light curtain and the i ntended
Normal
operating
mode
Muting only
Muting active
Override active
Override status
Override timing error
Lamp error
OSSD error
Microprocessor error
Lens error
EDM error
unintentionally and during
active muting, check the partial
bridge OSSDs to light
activation sequence.
Check the override
and check for any potential
defects on the lamp.
If the problem should persist,
please contact Pilz customer
services.
If the problem should persist,
please contact Pilz customer
Activate RESET.
If the problem should persist,
please contact Pilz customer
Check the EDM feedback line
and the EDM configuration.
Restart error
/RESET/REALIGN.
Error
information
Communication error
BCM Configuration error
ACM Configuration error
Critical error
Check the cascading
connection and check that the
terminator cap is installed
again.
If the problem should persist,
please contact Pilz customer
services.
again.
If the problem should persist,
please contact customer
If the problem should persist,
please contact Pilz customer
A critical error cannot be eliminated via a RESET.
The light curtain must be switched on and off. If the error should persist, please contact Pil z
customer services.
Page 75

OPERATING MANUAL PSEN op4F/H-A series
1003067-EN-02
75
Meaning of LED
Off On
Flash
Indifferent
Operating
curtain
LED DISPLAY
Suggested action
LEVEL
ACM
EDM
OSSDs
Power
Sync
Fault Code
Receiver side (TX):
mode of
light
Normal
operating
mode
Error
Light beams - reduced range
Light beams - long range
No code
Code 1
Code 2
Test
Light beams
Microprocessor error
Lens error
BCM configuration error
Communication error
Critical error
Information
Check the wiring of the TEST.
Activate RESET.
If the problem should persist,
please contact Pilz customer
services.
Activate RESET.
If the problem should persist,
please contact Pilz customer
services.
Perform basic configuration again.
If the problem should persist,
please contact Pilz customer
services.
Activate RESET.
Check the cascading connection
and check that the end cap is
installed correctly.
Switch light curtain on/off.
If the problem should persist,
please contact Pilz customer
services.
A critical error cannot be eliminated via a RESET.
The light curtain must be switched on and off. If the error should persist, please contact Pil z
customer services.
Page 76

PSEN op4F/H-A series OPERATING MANUAL
76
1003067-EN-02
9 REGULAR CHECKS AND M AINTENANCE
9.1 Regular checks
Check the following once a day
• The light curtain is in a safe state (OSSDs off).
− The beams are interrupted across the whole area of the protecte d field using a test object
(test rod) (TP-14 or TP-30) with an appropriate resolution, in acc ordance with the following
diagram.
• Is the light curtain aligned correctly?
− Press gently on the side of the product in both direc tions. The red LED m ust not light dur ing
this process.
• Activate the TEST function on the TX side.
− The OSSD outputs are opened (red LED, OSSD on the RX side, ON and stop of the
controlled machine).
• The response time to the status of the m achine STOP, including the respo nse time of the light
curtain and machine, is within the limit valu es defined for calculating the safet y distance (see
Chapter 2.2).
• The safety distance between th e danger zones and the light curtai n complies with the deta ils
specified in Chapter 2.2.
• Access and exposure of persons betwee n the light c urtain a nd hazard ous m ac hine components
is prevented.
• It is impossible to access the machine’s danger zones from an unprotected side.
• In order to guarantee that the ligh t curtain remains in NO RMAL FUNCTION MODE f or at least
10-15 minutes and, after positioning the specific test object in the protected field, stays in a
SAFE STATE for the same time span, there must be no interference from external light sources.
• Check that all additional functions comply by activating them several times under different
operating conditions.
9.2 Maintenance
The safety light curtain in the PSEN op4F/H-A series does not require any special
maintenance.
The front optical protective surfaces should be cleaned regularly to prevent any reduction in
the operating range.
Use moist cotton cloths. Do not apply excessive pressure or the surfaces may become
tarnished.
The following materials should not be used to clean plastic surf aces or paintwork on the light
curtain:
− Alcohol and solvents;
− Woollen cloths or synthetic materials;
− Paper or other abrasive materials.
Page 77

OPERATING MANUAL PSEN op4F/H-A series
1003067-EN-02
77
Electrical data
Operating voltage:
24 V DC ±20%
Current consumption transmitter (TX):
Max. 3 W
Current consumption receiver (RX):
5 W max (without load)
Outputs:
2 PNP or 2 NPN
- Short circuit protection:
1.4 A max
- Output current:
0.5 A max. at each output
- Output voltage – Status ON:
Operating voltage – 1 V min
- Output voltage – Status OFF:
0.2 V max.
- Capacitive load:
2.2 uF at 24 V DC max
Response times:
See table below
Reset time:
100 ms
Height of protected field:
300..1800 mm
Category:
Type 4 (ref. to EN 61496-1)
MTTFd [years] = 444
Auxiliary functions:
Test; manual/automatic restart; EDM; reset;
muting; blanking; GUI; coding; PNP/NPN
connection; cascading
Protection class:
Class III (see Ch. 4.1)
Current for external lamp:
20 mA min.; 300 mA max.
Cable length (for supply):
50 m max.
Optical data
Transmitter light (λ):
Infra-red, LED (950 nm)
Resolution:
14 - 30 mm
Operating range:
0.2…20 m for 30 mm
0.2…7 m for 14 mm
Ambient brightness:
IEC-61496-2
Environmental data and mechanical data
Operating temperature:
0…+ 50 °C
Storage temperature:
- 25…+ 70 °C
Temperature class:
T6
Humidity:
15…95 % (non-condensing)
Protection type:
IP 65 (EN 60529)
- 1 octave/min. (EN 60068-2-6)
Max. acceleration:
10 g
(EN 60068-2-29)
Housing material:
Varnished aluminium (yellow RAL 1003)
Front surface material:
PMMA
Terminator cap material:
PBT Valox 508 (RAL 7021)
Cover material:
PC LEXAN
Weight:
1.35 kg per running metre per individual unit
10 TECHNICAL DETAILS
SIL 3 (ref. to EN 61508)
SIL 3 (ref. to EN 62061)
PL and Cat. 4 (ref. to EN ISO 13849-1:2008)
PFHd [1/h] = 2.64E-09
Connections:
Vibration: - Amplitude 0.35 mm,
- M12 12-pin + M12 5-pin for receiver (muting
model)
- M12 12-pin for receiver (blanking model)
- M12 5-pin for transmitter (for both models)
- Frequency 10 … 55 Hz
- 20 sweeps per axis,
Page 78

PSEN op4F/H-A series OPERATING MANUAL
78
1003067-EN-02
Protected
(mm)
Response time
(ms)
Response time
(ms)
PSEN op4F-A-14-030/1
300
32
15
20
14
PSEN op4F-A-14-045/1
450
48
17
25
14
PSEN op4F-A-14-075/1
750
80
20
34
14
PSEN op4F-A-14-090/1
900
96
22
38
14
PSEN op4F-A-14-105/1
1050
112
24
43
14
PSEN op4F-A-14-120/1
1200
128
26
47
14
PSEN op4F-A-14-135/1
1350
144
27
52
14
PSEN op4F-A-14-150/1
1500
160
29
56
14
PSEN op4F-A-14-180/1
1800
192
33
65
14
PSEN op4H-A-30-030/1
300
16
13
16
30
PSEN op4H-A-30-060/1
600
32
15
20
30
PSEN op4H-A-30-075/1
750
40
16
23
30
PSEN op4H-A-30-090/1
900
48
17
25
30
PSEN op4H-A-30-105/1
1050
56
18
27
30
PSEN op4H-A-30-120/1
1200
64
19
29
30
PSEN op4H-A-30-135/1
1350
72
19
32
30
PSEN op4H-A-30-165/1
1650
88
21
36
30
PSEN op4H-A-30-180/1
1800
96
22
38
30
AIC OFF
(without code)
Response time of
Tmaster
Response time of
Tslave
Response time of
Tmaster AIC
Response time of
Tslave AIC
PSEN op4F-A-14-030/1
13.7
13.7
19.1
19.1
PSEN op4F-A-14-045/1
PSEN op4F-A-14-060/1
PSEN op4F-A-14-075/1
18.9
18.9
32.6
32.6
PSEN op4F-A-14-090/1
20.7
20.7
37.1
37.1
PSEN op4F-A-14-105/1
22.4
22.4
41.6
41.6
PSEN op4F-A-14-120/1
24.2
24.2
46.0
46
PSEN op4F-A-14-135/1
PSEN op4F-A-14-150/1
PSEN op4F-A-14-165/1
29.5 - 59.5
-
PSEN op4F-A-14-180/1
31.2 - 64.0
-
11 LIST OF AVAILABLE MODELS
Model
PSEN op4F-A-14-060/1 600 64 19 29 14
PSEN op4F-A-14-165/1 1650 176 31 61 14
PSEN op4H-A-30-045/1 450 24 14 18 30
PSEN op4H-A-30-150/1 1500 80 20 34 30
field height
No. of
beams
AIC OFF
AIC ON
Resolution
(mm)
With the following formulas (and with reference to the response times stated in the tables below),
users can calculate the response time of any cascading configurations they create.
Tcascade [ms] = Tmaster + Tslave1 + Tslave2 + 7.5
AIC ON
(with code)
Tcascade [ms] = Tmaster AIC + Tslave1 AIC + Tslave2 AIC + 7.5
Master AIC OFF
(ms)
15.4 15.4 23.6 23.6
17.2 17.2 28.1 28.1
26.0 - 50.5 -
27.7 - 55.0 -
Slave AIC OFF
(ms)
Master AIC ON
(ms)
Slave AIC ON
(ms)
Page 79

OPERATING MANUAL PSEN op4F/H-A series
1003067-EN-02
79
Response time of
Tmaster
Response time of
Tslave
Response time of
Tmaster AIC
Response time of
Tslave AIC
PSEN op4H-A-30-030/1
11.9
11.9
14.6
15
PSEN op4H-A-30-045/1
12.8
12.8
16.8
17
PSEN op4H-A-30-060/1
13.7
13.7
19.1
19
PSEN op4H-A-30-075/1
14.5
14.5
21.3
21
PSEN op4H-A-30-090/1
PSEN op4H-A-30-105/1
PSEN op4H-A-30-120/1
17.2
17.2
28.1
28
PSEN op4H-A-30-135/1
18.0 - 30.3
-
PSEN op4H-A-30-150/1
18.9 - 32.6
-
PSEN op4H-A-30-165/1
19.8 - 34.8
-
PSEN op4H-A-30-180/1
20.7 - 37.1
-
Master AIC OFF
(ms)
15.4 15.4 23.6 24
16.3 16.3 25.8 26
Slave AIC OFF
(ms)
Master AIC ON
(ms)
Slave AIC ON
(ms)
Page 80

PSEN op4F/H-A series OPERATING MANUAL
80
1003067-EN-02
Model
Lt (mm)
L (mm)
150
306.3
300
456.3
450
606.3
600
756.3
750
906.3
900
1056.3
1050
1206.3
1200
1356.3
1350
1506.3
1500
1656.3
1650
1806.3
12 DIMENSIONS
PSEN op4F/H-A-xx-030-1
PSEN op4F/H-A-xx-045-1
PSEN op4F/H-A-xx-060-1
PSEN op4F/H-A-xx-075-1
PSEN op4F/H-A-xx-090-1
PSEN op4F/H-A-xx-105-1
PSEN op4F/H-A-xx-120-1
PSEN op4F/H-A-xx-135-1
PSEN op4F/H-A-xx-150-1
PSEN op4F/H-A-xx-165-1
PSEN op4F/H-A-xx-180-1
xx = Resolution (14 mm – 30 mm)
Page 81

OPERATING MANUAL PSEN op4F/H-A series
1003067-EN-02
81
13 FITTINGS
Fastening bracket
Terminator cap
(fixed to the light curtain)
Page 82

PSEN op4F/H-A series OPERATING MANUAL
82
1003067-EN-02
Tool for BCM configuration
When not in use, the tool for the BCM configuration can be slotted into the profile groove or
into the upper section of the light curtain.
Page 83

OPERATING MANUAL PSEN op4F/H-A series
1003067-EN-02
83
Description
Order number
PSEN op cascading bracket
631 061
14 ACCESSORIES
14.1 Rotating mounting bracket
Page 84

PSEN op4F/H-A series OPERATING MANUAL
84
1003067-EN-02
Description
Order number
PSEN op cascading 0,05 m
631 058
PSEN op cascading 0,5m
631 059
PSEN op cascading 1 m
631 060
Cable length 500 mm for PSEN op cascading 0,5 m
Cable length 1000 mm for PSEN op cascading 1 m
14.2 Cascading cable
Cable length 50 mm for PSEN op cascading 0,05 m
Page 85

OPERATING MANUAL PSEN op4F/H-A series
1003067-EN-02
85
Description
Order Number
PSEN op pigtail emitter
631 055
Description
Order Number
PSEN op pigtail receiver b
631 056
Cable length 200 mm
Cable length 200 mm
14.3 Connection cable
Page 86

PSEN op4F/H-A series OPERATING MANUAL
86
1003067-EN-02
Description
Order Number
PSEN op pigtail receiver m
631 057
Cable length 200 mm
14.4 PSEN op Advanced Programming Adapter
Page 87

OPERATING MANUAL PSEN op4F/H-A series
1003067-EN-02
87
Page 88

PSEN op4F/H-A series OPERATING MANUAL
88
1003067-EN-02
Description
Length
(m)
Pins
Order number
PSEN op cable axial M12 4-pole 3 m
3 4 630 300
PSEN op cable axial M12 4-pole 5 m
5 4 630 301
PSEN op cable axial M12 4-pole 10 m
10 4 630 302
PSEN op cable axial M12 4-pole 30 m
30 4 630 296
PSEN op cable axial M12 4-pole 50 m
50 4 630 362
PSEN op cable axial M12 5-pole 3 m
3 5 630 310
PSEN op cable axial M12 5-pole 5 m
5 5 630 311
PSEN op cable axial M12 5-pole 10 m
10 5 630 312
PSEN op cable axial M12 5-pole 20 m
20 5 630 298
PSEN op cable axial M12 5-pole 30 m
30 5 630 297
PSEN op cable axial M12 5-pole 50 m
50 5 630 364
PSEN op cable axial M12 12-pole 3 m
3
12
631 080
PSEN op cable axial M12 12-pole 5 m
5
12
631 081
PSEN op cable axial M12 12-pole 10 m
10
12
631 082
PSEN op cable axial M12 12-pole 20 m
20
12
631 083
PSEN op cable axial M12 12-pole 30 m
30
12
631 084
PSEN op cable axial M12 12-pole 50 m
50
12
631 085
Description
Length (m)
Connection
Order number
PSEN op Ethernet cable 1 m
1
M12 / RJ45
631 071
PSEN op Ethernet cable 3 m
3
M12 / RJ45
631 072
PSEN op Ethernet cable 10 m
10
M12 / RJ45
631 073
14.5 Axial connection cable, unshielded
14.6 Ethernet cable for PSEN op Advanced Programming Adapter
EC declaration of conformity
This product/these products meet the requirements of the directive 2006/42/EC for
machinery of the European Parliament and of the Council. The complete EC Declaration of
Conformity is available on the Internet at
Representative: Norbert Fröhlich, Pilz GmbH & Co. KG, Felix-Wankel-Str. 2, 73760
Ostfildern, Germany
www.pilz.com/downloads.
Page 89

© Pilz GmbH & Co. KG, 2011
of the equipment. We accept no responsibility for the validity, accuracy and entirety of the text and graphics presented in this information. Please contact our Technical Support if you have any questions.
Titelseite
Sachnummer Printed in Germany
1003067-EN-02, 2014-02 Printed in Germany
© Pilz GmbH & Co. KG, 2011
...
In many countries we are
represented by our subsidiaries
and sales partners.
Please refer to our homepage
for further details or contact our
headquarters.
Technical support
+49 711 3409-444
support@pilz.com
are registered and protected trademarks
®
, the spirit of safety
®
, SafetyNET p
®
, SafetyEYE
®
, SafetyBUS p
®
, PVIS
®
, PSS
®
, PSEN
®
, Primo
®
, PNOZ
®
, PMI
®
Pilz GmbH & Co. KG
Felix-Wankel-Straße 2
73760 Ostfildern, Germany
Telephone: +49 711 3409-0
Telefax: +49 711 3409-133
E-Mail: pilz.gmbh@pilz.de
Internet: www.pilz.com
, PMCprotego
®
, PIT
®
, Pilz
®
of Pilz GmbH & Co. KG in some countries. We would point out that product features may vary from the details stated in this document, depending on the status at the time of publication and the scope
InduraNET p
 Loading...
Loading...