Philips PCF8576U-10, PCF8576U-12, PCF8576U-2, PCF8576U-5, PCF8576U-7 Datasheet

INTEGRATED CIRCUITS
DATA SH EET
PCF8576
Universal LCD driver for low
multiplex rates
Product specification
Supersedes data of 1997 Nov 18
File under Integrated Circuits, IC12
1998 Feb 06
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
Universal LCD driver for low multiplex
rates
CONTENTS
1 FEATURES
2 GENERAL DESCRIPTION
3 ORDERING INFORMATION
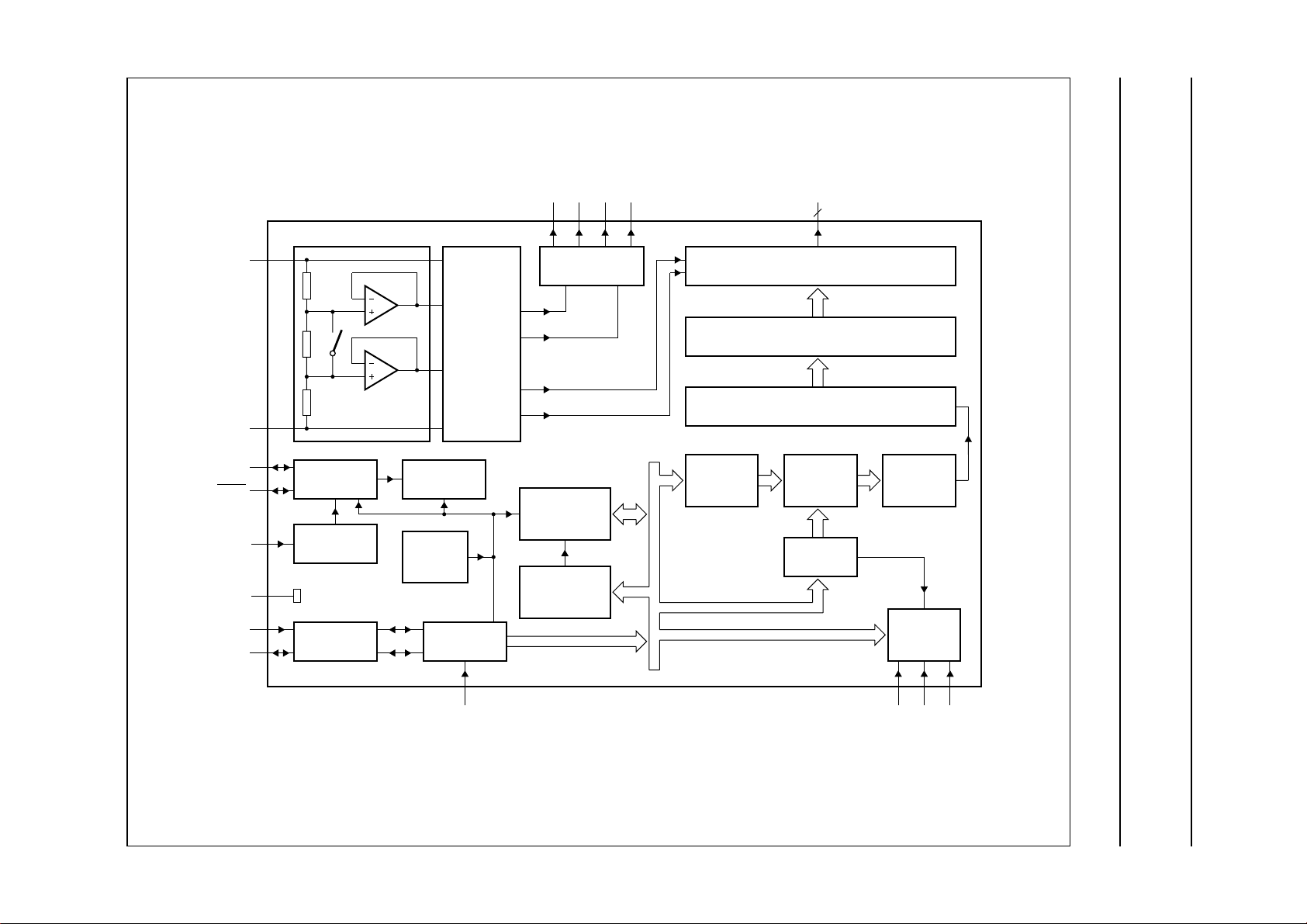
4 BLOCK DIAGRAM
5 PINNING
6 FUNCTIONAL DESCRIPTION
6.1 Power-on reset
6.2 LCD bias generator
6.3 LCD voltage selector
6.4 LCD drive mode waveforms
6.4.1 Static drive mode
6.4.2 1 : 2 multiplex drive mode
6.4.3 1 : 3 multiplex drive mode
6.4.4 1 : 4 multiplex drive mode
6.5 Oscillator
6.5.1 Internal clock
6.5.2 External clock
6.6 Timing
6.7 Display latch
6.8 Shift register
6.9 Segment outputs
6.10 Backplane outputs
6.11 Display RAM
6.12 Data pointer
6.13 Subaddress counter
6.14 Output bank selector
6.15 Input bank selector
6.16 Blinker
PCF8576
7 CHARACTERISTICS OF THE I2C-BUS
7.1 Bit transfer
7.2 START and STOP conditions
7.3 System configuration
7.4 Acknowledge
7.5 PCF8576 I2C-bus controller
7.6 Input filters
7.7 I2C-bus protocol
7.8 Command decoder
7.9 Display controller
7.10 Cascaded operation
8 LIMITING VALUES
9 HANDLING
10 DC CHARACTERISTICS
11 AC CHARACTERISTICS
11.1 Typical supply current characteristics
11.2 Typical characteristics of LCD outputs
12 APPLICATION INFORMATION
12.1 Chip-on-glass cascadability in single plane
13 BONDING PAD LOCATIONS
14 PACKAGE OUTLINES
15 SOLDERING
15.1 Introduction
15.2 Reflow soldering
15.3 Wave soldering
15.4 Repairing soldered joints
16 DEFINITIONS
17 LIFE SUPPORT APPLICATIONS
18 PURCHASE OF PHILIPS I2C COMPONENTS
1998 Feb 06 2

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
Universal LCD driver for low multiplex
rates
1 FEATURES
• Single-chip LCD controller/driver
• Selectable backplane drive configuration: static or 2/3/4
backplane multiplexing
• Selectable display bias configuration: static,1⁄2 or1⁄
• Internal LCD bias generation with voltage-follower
buffers
• 40 segment drives: up to twenty 8-segment numeric
characters; up to ten 15-segment alphanumeric
characters; or any graphics of up to 160 elements
• 40 × 4-bit RAM for display data storage
• Auto-incremented display data loading across device
subaddress boundaries
• Display memory bank switching in static and duplex
drive modes
• Versatile blinking modes
• LCD and logic supplies may be separated
• Wide power supply range: from 2 V for low-threshold
LCDs and up to 9 V for guest-host LCDs and
high-threshold (automobile) twisted nematic LCDs
• Low power consumption
• Power-saving mode for extremely low power
consumption in battery-operated and telephone
applications
2
C-bus interface
• I
• TTL/CMOS compatible
3
PCF8576
• Compatible with any 4-bit, 8-bit or 16-bit
microprocessors/microcontrollers
• May be cascaded for large LCD applications (up to
2560 segments possible)
• Cascadable with 24-segment LCD driver PCF8566
• Optimized pinning for plane wiring in both single and
multiple PCF8576 applications
• Space-saving 56-lead plastic very small outline package
(VSO56)
• Very low external component count (at most one
resistor, even in multiple device applications)
• Compatible with chip-on-glass technology
• Manufactured in silicon gate CMOS process.
2 GENERAL DESCRIPTION
The PCF8576 is a peripheral device which interfaces to
almost any Liquid Crystal Display (LCD) with low multiplex
rates. It generates the drive signals for any static or
multiplexed LCD containing up to four backplanes and up
to 40 segments and can easily be cascaded for larger LCD
applications. The PCF8576 is compatible with most
microprocessors/microcontrollers and communicates via a
two-line bidirectional I2C-bus. Communication overheads
are minimized by a display RAM with auto-incremented
addressing, by hardware subaddressing and by display
memory switching (static and duplex drive modes).
3 ORDERING INFORMATION
TYPE NUMBER
NAME DESCRIPTION VERSION
PCF8576T VSO56 plastic very small outline package; 56 leads SOT190-1
PCF8576U − chip in tray −
PCF8576U/2 − chip with bumps in tray −
PCF8576U/5 − unsawn wafer −
PCF8576U/7 − chip with bumps on tape −
PCF8576U/10 FFC chip on film frame carrier (FFC) −
PCF8576U/12 FFC chip with bumps on film frame carrier (FFC) −
1998 Feb 06 3
PACKAGE
This text is here in white to force landscape pages to be rotated correctly when browsing through the pdf in the Acrobat reader.This text is here in
_white to force landscape pages to be rotated correctly when browsing through the pdf in the Acrobat reader.This text is here inThis text is here in
white to force landscape pages to be rotated correctly when browsing through the pdf in the Acrobat reader. white to force landscape pages to be ...
1998 Feb 06 4
4 BLOCK DIAGRAM
Universal LCD driver for low multiplex
rates
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
V
DD
V
LCD
CLK
SYNC
OSC
V
SS
SCL
SDA
5
R
R
LCD BIAS
R
12
4
3
6
11
2
1
GENERATOR
TIMING BLINKER
OSCILLATOR
INPUT
FILTERS
VOLTAGE
SELECTOR
POWER-
ON
RESET
2
I C - BUS
CONTROLLER
LCD
10
BP014BP215BP116BP3
13
BACKPLANE
OUTPUTS
PCF8576
DISPLAY
CONTROLLER
COMMAND
DECODER
INPUT
BANK
SELECTOR
S0 to S39
40
17 to 56
DISPLAY SEGMENT OUTPUTS
DISPLAY LATCH
SHIFT REGISTER
DISPLAY
RAM
40 x 4 BITS
DATA
POINTER
OUTPUT
BANK
SELECTOR
SUBADDRESS
COUNTER
9
SA0
Fig.1 Block diagram (for VSO56 package; SOT190-1).
handbook, full pagewidth
A07A18A2
MBK276
PCF8576
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
Universal LCD driver for low multiplex
rates
5 PINNING
SYMBOL PIN DESCRIPTION
2
SDA 1 I
SCL 2 I
SYNC 3 cascade synchronization input/output
CLK 4 external clock input/output
V
DD
5 supply voltage
OSC 6 oscillator input
A0 to A2 7 to 9 I
SA0 10 I
V
V
SS
LCD
11 logic ground
12 LCD supply voltage
BP0, BP2, BP1 and BP3 13 to 16 LCD backplane outputs
S0 to S39 17 to 56 LCD segment outputs
C-bus serial data input/output
2
C-bus serial clock input
2
C-bus subaddress inputs
2
C-bus slave address input; bit 0
PCF8576
1998 Feb 06 5

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
Universal LCD driver for low multiplex
rates
handbook, halfpage
SDA
SCL
SYNC
CLK
V
DD
OSC
A0
A1
A2
SA0
V
SS
V
LCD
BP0
BP2
BP1
BP3
S0
S1
S2
S3
S4
S5
S6
S7
S8
S9
S10
S11
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
PCF8576T
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
MBK278
PCF8576
56
S39
55
S38
54
S37
53
S36
52
S35
51
S34
50
S33
49
S32
48
S31
47
S30
46
S29
45
S28
44
S27
43
S26
42
S25
41
S24
40
S23
39
S22
38
S21
37
S20
36
S19
35
S18
34
S17
33
S16
32
S15
31
S14
30
S13
29
S12
Fig.2 Pin configuration; SOT190-1.
1998 Feb 06 6
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
Universal LCD driver for low multiplex
rates
6 FUNCTIONAL DESCRIPTION
The PCF8576 is a versatile peripheral device designed to
interface to any microprocessor/microcontroller to a wide
variety of LCDs. It can directly drive any static or
multiplexed LCD containing up to four backplanes and up
to 40 segments. The display configurations possible with
the PCF8576 depend on the number of active backplane
outputs required; a selection of display configurations is
given in Table 1.
All of the display configurations given in Table 1 can be
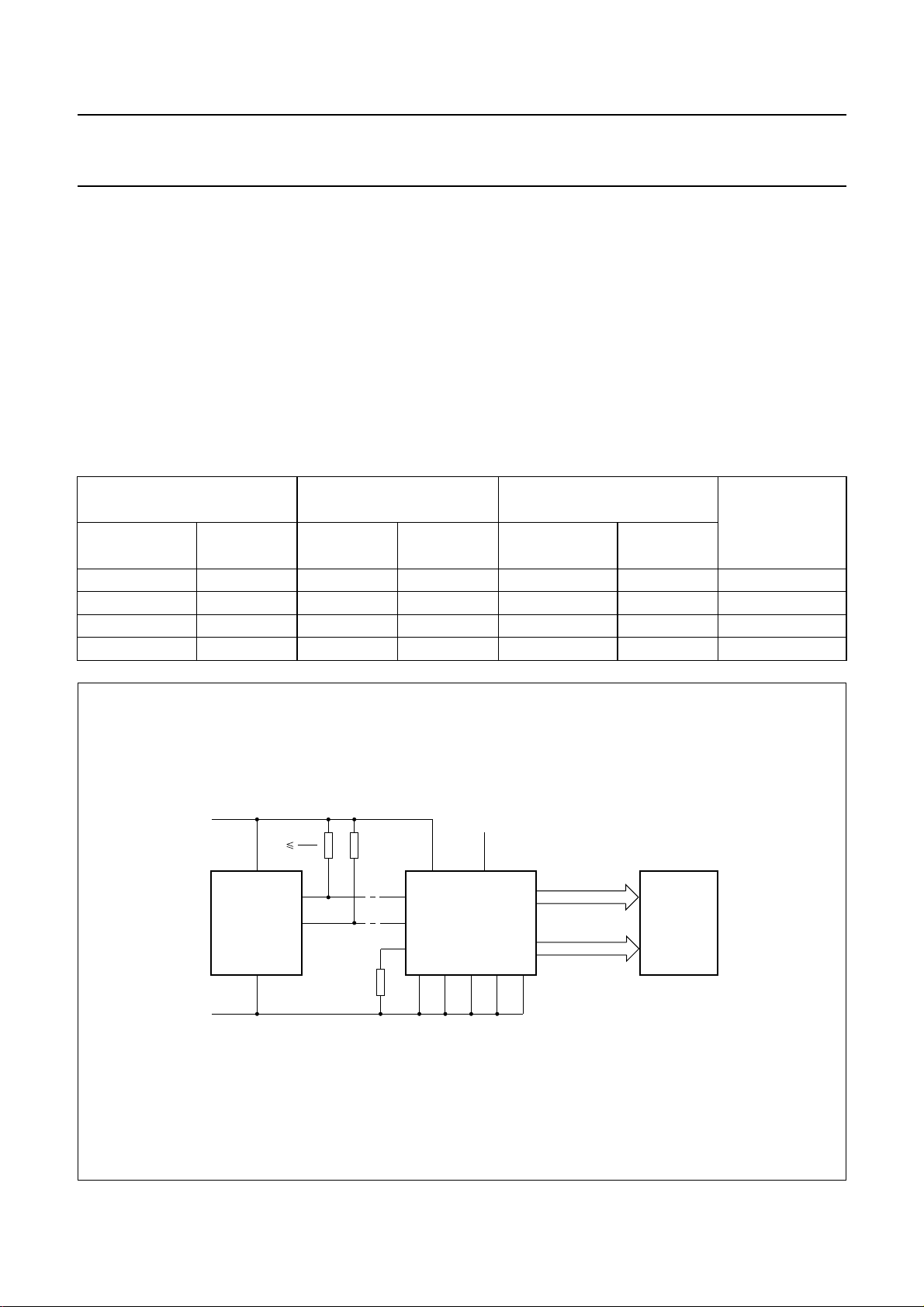
implemented in the typical system shown in Fig.3.
Table 1 Selection of display configurations
NUMBER OF 7-SEGMENTS NUMERIC
BACKPLANES SEGMENTS DIGITS
4 160 20 20 10 20 160 dots (4 × 40)
3 120 15 15 8 8 120 dots (3 × 40)
2 80 10 10 5 10 80 dots (2 × 40)
1 40 5 5 2 12 40 dots (1 × 40)
INDICATOR
SYMBOLS
PCF8576
The host microprocessor/microcontroller maintains the
2
2-line I
The internal oscillator is selected by connecting pin OSC
to pin VSS. The appropriate biasing voltages for the
multiplexed LCD waveforms are generated internally.
The only other connections required to complete the
system are to the power supplies (VDD, VSS and V
the LCD panel chosen for the application.
C-bus communication channel with the PCF8576.
LCD
14-SEGMENTS
ALPHANUMERIC
DOT MATRIX
CHARACTERS
INDICATOR
SYMBOLS
) and
handbook, full pagewidth
V
DD
HOST
MICRO-
PROCESSOR/
MICRO-
CONTROLLER
V
SS
t
r
R
2C
B
SDA
SCL
OSC
R
OSC
V
DD
512
1 17 to 56
2
PCF8576
6
78
A0 A1 A2SSSA0 V
Fig.3 Typical system configuration.
1998 Feb 06 7
V
LCD
13 to 16
91011
40 segment drives
4 backplanes
LCD PANEL
(up to 160
elements)
MBK277
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
Universal LCD driver for low multiplex
rates
6.1 Power-on reset
At power-on the PCF8576 resets to a starting condition as
follows:
1. All backplane outputs are set to VDD.
2. All segment outputs are set to VDD.
3. The drive mode ‘1 : 4 multiplex with1⁄3bias’ is selected.
4. Blinking is switched off.
5. Input and output bank selectors are reset (as defined
in Table 5).
6. The I2C-bus interface is initialized.
7. The data pointer and the subaddress counter are
cleared.
2
Data transfers on the I
following power-on to allow completion of the reset action.
6.2 LCD bias generator
The full-scale LCD voltage (V
VDD− V
. The LCD voltage may be temperature
LCD
compensated externally through the V
Fractional LCD biasing voltages are obtained from an
internal voltage divider of the three series resistors
connected between VDD and V
be switched out of the circuit to provide a1⁄2bias voltage
level for the 1 : 2 multiplex configuration.
C-bus should be avoided for 1 ms
) is obtained from
op
supply to pin 12.
LCD
. The centre resistor can
LCD
PCF8576
6.3 LCD voltage selector
The LCD voltage selector co-ordinates the multiplexing of
the LCD in accordance with the selected LCD drive
configuration. The operation of the voltage selector is
controlled by MODE SET commands from the command
decoder. The biasing configurations that apply to the
preferred modes of operation, together with the biasing
− V
characteristics as functions of V
op=VDD
resulting discrimination ratios (D), are given in Table 2.
A practical value for Vop is determined by equating V
with a defined LCD threshold voltage (Vth), typically when
the LCD exhibits approximately 10% contrast. In the static
drive mode a suitable choice is Vop>3Vth approximately.
Multiplex drive ratios of 1 : 3 and 1 : 4 with
possible but the discrimination and hence the contrast
ratios are smaller ( = 1.732 for 1 : 3 multiplex or
21
= 1.528 for 1 : 4 multiplex).
---------3
3
The advantage of these modes is a reduction of the LCD
full-scale voltage V
• 1 : 3 multiplex (
Vop= = 2.449 V
6V
×
as follows:
op
1
⁄2bias):
off rms〈〉
off(rms)
• 1 : 4 multiplex (1⁄2bias):
V
43×()
= = 2.309 V
op
----------------------- 3
off(rms)
and the
LCD
1
⁄2bias are
off(rms)
These compare with Vop=3V
Table 2 Preferred LCD drive modes: summary of characteristics
NUMBER OF
LCD DRIVE MODE
BACKPLANES LEVELS
CONFIGURATION
static 1 2 static 0 1 ∞
1:2 2 3
1:2 2 4
1:3 3 4
1:4 4 4
1998 Feb 06 8
LCD BIAS
1
⁄
2
1
⁄
3
1
⁄
3
1
⁄
3
when1⁄3bias is used.
off(rms)
V
off(rms)
-------------------- V
op
V
on(rms)
-------------------- V
op
=
D
0.354 0.791 2.236
0.333 0.745 2.236
0.333 0.638 1.915
0.333 0.577 1.732
V
on(rms)
-------------------- V
off(rms)

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
Universal LCD driver for low multiplex
rates
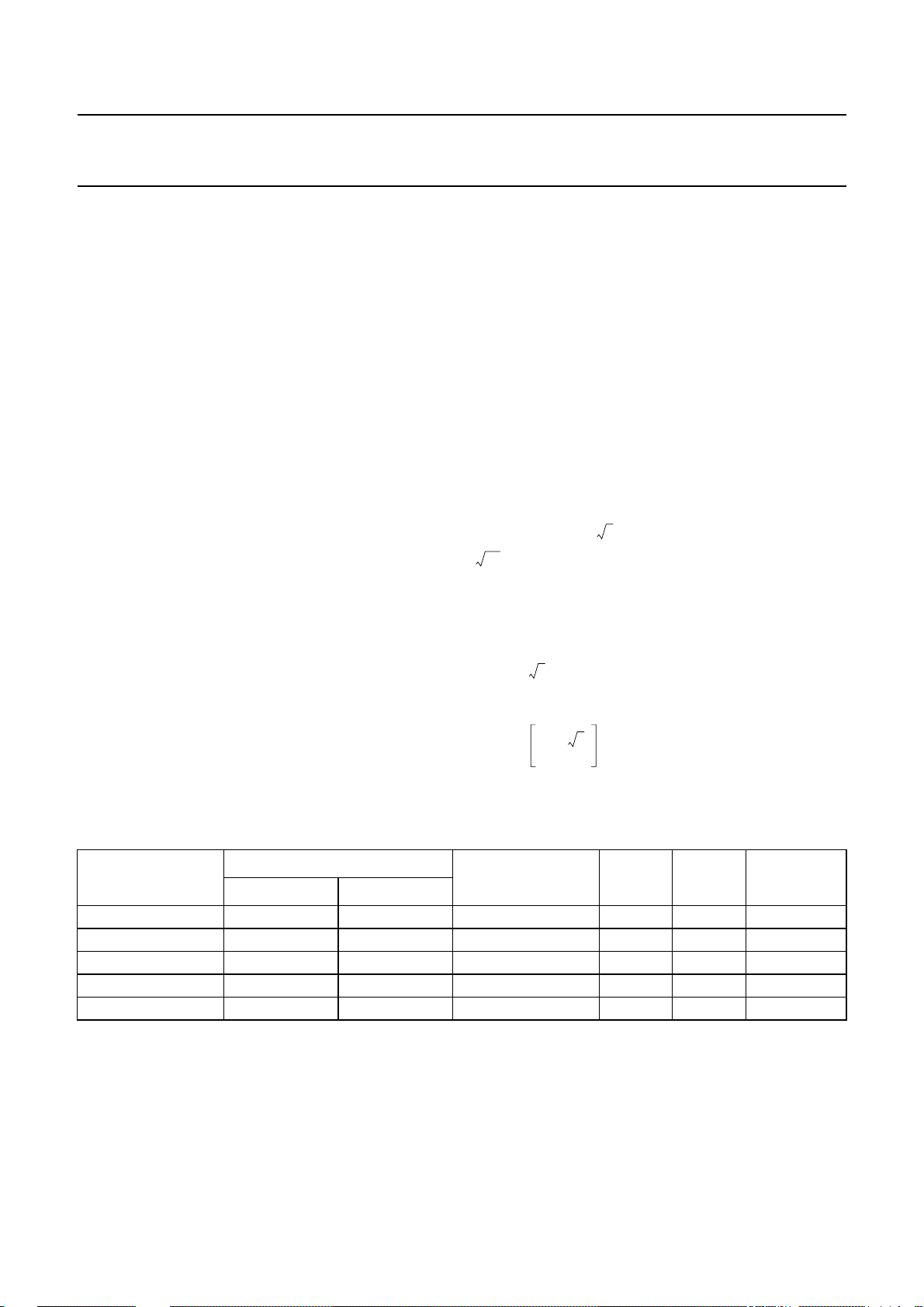
6.4 LCD drive mode waveforms
6.4.1 S
The static LCD drive mode is used when a single
backplane is provided in the LCD. Backplane and
segment drive waveforms for this mode are shown in
Fig.4.
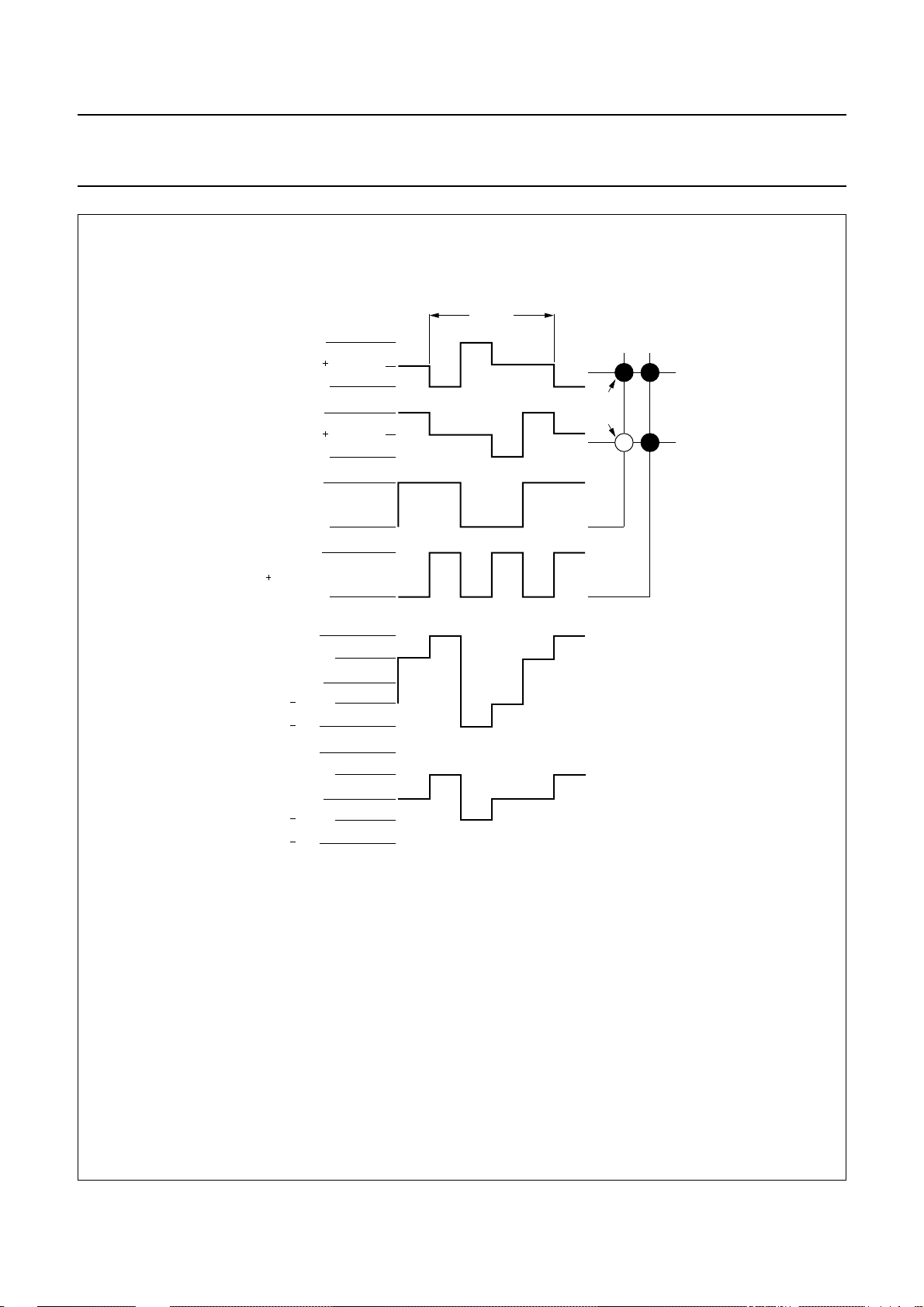
6.4.2 1 : 2
When two backplanes are provided in the LCD, the 1 : 2
multiplex mode applies. The PCF8576 allows use of
1
⁄2bias or1⁄3bias in this mode as shown in Figs 5 and 6.
TATIC DRIVE MODE
MULTIPLEX DRIVE MODE
S
BP0
S
n 1
V
DD
V
LCD
V
DD
n
V
LCD
V
DD
V
LCD
(a) waveforms at driver
V
op
PCF8576
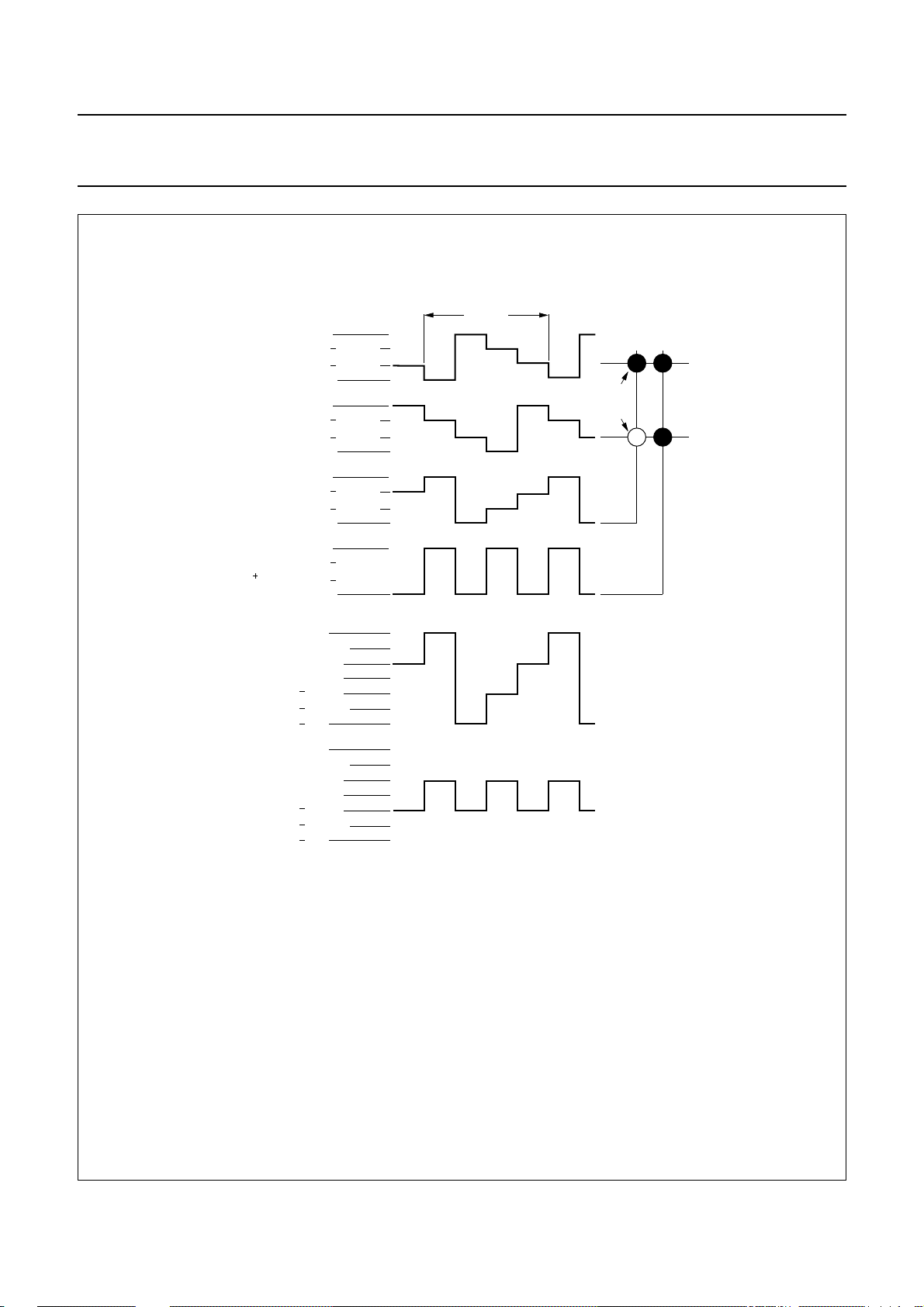
6.4.3 1 : 3
When three backplanes are provided in the LCD, the 1 : 3
multiplex drive mode applies, as shown in Fig.7.
6.4.4 1 : 4
When four backplanes are provided in the LCD, the 1 : 4
multiplex drive mode applies, as shown in Fig.8.
T
frame
MULTIPLEX DRIVE MODE
MULTIPLEX DRIVE MODE
LCD segments
state 1
(on)
state 2
(off)
state 1 0
V
op
V
op
state 2 0
V
op
(b) resultant waveforms
at LCD segment
V
t() V
t() V
t() V
BP0
BP0
t()–=
t()–=
state1
V
on(rms)Vop
t() V
V
state2
V
off(rms)
S
n
=
S
n1+
0V=
Fig.4 Static drive mode waveforms (Vop=VDD− V
1998 Feb 06 9
MBE539
LCD
).
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
Universal LCD driver for low multiplex
rates
V
DD
(V )/2V
BP0
BP1
S
S
n 1
state 1 0
state 2
n
DD LCD
V
LCD
V
DD
(V )/2V
DD
V
LCD
V
DD
V
LCD
V
DD
V
LCD
V
op
V /2
op
V /2
op
V
op
V
op
V /2
op
0
V /2
op
V
op
LCD
(a) waveforms at driver
(b) resultant waveforms
T
frame
at LCD segment
PCF8576
LCD segments
state 1
state 2
MBE540
V
t() V
t() V
op
t() V
op
BP0
BP1
t()–=
t()–=
state1
V
on(rms)
V
state2
V
off(rms)
0.791V
=
t() V
0.354V
=
S
n
S
n
Fig.5 Waveforms for the 1 : 2 multiplex drive mode with1⁄2bias (Vop=VDD− V
1998 Feb 06 10
LCD
).
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
Universal LCD driver for low multiplex
rates
V
DD
V V /3
op
BP0
BP1
S
n
S
n 1
state 1 0
state 2 0
DD
V 2V /3
V
V
V V /3
V 2V /3
V
V
V V /3
V 2V /3
V
V
V V /3
V 2V /3
V
DD
LCD
DD
DD
DD
LCD
DD
DD
DD
LCD
DD
DD
DD
LCD
V
op
2V /3
op
V /3
op
V /3
op
2V /3
op
V
op
V
op
2V /3
op
V /3
op
V /3
op
2V /3
op
V
op
op
op
op
op
op
op
op
(a) waveforms at driver
(b) resultant waveforms
T
frame
at LCD segment
PCF8576
LCD segments
state 1
state 2
MBE541
V
t() V
t() V
op
t() V
op
BP0
BP1
t()–=
t()–=
state1
V
on(rms)
V
state2
V
off(rms)
0.745V
=
t() V
0.333V
=
S
n
S
n
Fig.6 Waveforms for the 1 : 2 multiplex drive mode with1⁄3bias (Vop=VDD− V
1998 Feb 06 11
LCD
).

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
Universal LCD driver for low multiplex
rates
T
V
DD
V V /3
op
n
DD
V 2V /3
V
V
V V /3
V 2V /3
V
V
V V /3
V 2V /3
V
V
V V /3
V 2V /3
V
V
V V /3
V 2V /3
V
V
V V /3
V 2V /3
V
DD
LCD
DD
DD
DD
LCD
DD
DD
DD
LCD
DD
DD
DD
LCD
DD
DD
DD
LCD
DD
DD
DD
LCD
V
op
2V /3
op
V /3
op
V /3
op
2V /3
op
V
op
V
op
2V /3
op
V /3
op
V /3
op
2V /3
op
V
op
op
op
op
op
op
op
op
op
op
op
op
(a) waveforms at driver
(b) resultant waveforms
at LCD segment
V
state1
V
on(rms)
V
state2
V
off(rms)
t() V
0.638V
=
t() V
0.333V
=
S
S
t() V
n
t() V
n
op
op
BP0
BP1
BP2/S23
S
S
n 1
S
n 2
state 1 0
state 2 0
t()–=
BP0
t()–=
BP1
PCF8576
frame
LCD segments
state 1
state 2
MBE542
Fig.7 Waveforms for the 1 : 3 multiplex drive mode (Vop=VDD− V
1998 Feb 06 12
LCD
).
 Loading...
Loading...