Page 1

Colour television Chassis
FTP2.4E
AA
Service Manual FHP plasma panels: 3122 785 14580
Service Manual SDI plasma panels: 3122 785 14990
E_14650_000.eps
160604
Contents Page Contents Page
1. Technical Specifications, Connections, and Chassis
Overview 2
2. Safety Instructions, Warnings, and Notes 5
3. Directions for Use 6
4. Mechanical Instructions 7
5. Service Modes, Error Codes, and Fault Finding 12
6. Block Diagrams, Testpoint Overviews, and
Waveforms
Wiring Diagram 42 Inch FHP Step 23
Wiring Diagram 50 Inch SDI Step 24
Block Diagram Supply 42 Inch FHP 25
Block Diagram Video 26
Block Diagram Audio & Control 27
I2C IC’s overview 28
Supply Lines Overview FHP 29
Supply Lines Overview SDI 30
7. Circuit Diagrams and PWB Layouts Diagram PWB
PDP Supply Panel: Filter Standby (A2) 31 36-41
PDP Supply Panel: Protection (A3) 32 36-41
PDP Supply Panel: Pre-Conditioner (A5) 33 36-41
PDP Supply Panel: LLC Supply (A6) 34 36-41
PDP Supply Panel: AUX Supply (A7) 35 36-41
Ambi Light (AL) 42 43
SSB: IF, I/O Video Processing (B2) 44 78-89
SSB: PICNIC (B3A) 45 78-89
SSB: (FEM) Falconic Embedded Memory (B3B) 46 78-89
SSB: Eagle (B3C) 47 78-89
SSB: Columbus (B3D) 48 78-89
SSB: FBX Supply (B3E) 49 78-89
SSB: HOP (B4) 50 78-89
SSB: OTC-Flash (B5A) 51 78-89
SSB: Backlight Control (B5B) 52 78-89
SSB: OTC-Flash (B5C)52 78-89
SSB: Audio Demodulator (B6A) 53 78-89
©
Copyright 2005 Philips Consumer Electronics B.V. Eindhoven, The Netherlands.
All rights reserved. No part of this publication may be reproduced, stored in a
retrieval system or transmitted, in any form or by any means, electronic,
mechanical, photocopying, or otherwise without the prior permission of Philips.
SSB: Dolby Digital Decoder (B6B) 54 78-89
SSB: Dolby Pro Logic Processor (B6C) 55 78-89
SSB: Audio Delay (B6D) 56 78-89
SSB: DC/DC Convertor (B12) 57 78-89
SSB: Main Tuner (B13A) 58 78-89
SSB: Sub Tuner (B13B) 59 78-89
SSB: DC/DC Converter (B13C) 60 78-89
SSB: I/O1: MMC (B14A) 61 78-89
SSB: I/O2: Connections (B14B) 62 78-89
SSB: I/O3: Switch (B14C) 63 78-89
SSB: I/O4: Audio (B14D) 64 78-89
SSB: I/O: 5 (B14E) 65 78-89
SSB: I/O6: Digital Input (B14F) 66 78-89
SSB: I/O: 7 (B14G) 67 78-89
SSB: PIP HIP (B15A)68 78-89
SSB: PIP Switch (B15B) 69 78-89
SSB: PIP Muppet (B15C) 70 78-89
SSB: HDI A/D Converter (B19A) 71 78-89
SSB: EPLD Control (B19B) 72 78-89
SSB: EPLD OSD (B19C)73 78-89
SSB: EPLD I/O (B19D) 74 78-89
SSB: Backlight Control (B19E) 75 78-89
SSB: Screen Interface (B20)76 78-89
SSB: Connection (B21)77 78-89
PDP Audio Amplifier (C) 90 91
Side I/O Panel (D) 92 93
Top Control Panel (E) 94 95
SCART 3 Panel (H) 96 97
LED and Switch Panel (J) 98 99
8. Alignments 101
9. Circuit Descriptions, Abbreviation List, and IC Data
Sheets 107
10. Spare Parts List 110
11. Revision List 123
Published by EL 0564 TV Service Printed in The Netherlands Subject to modification EN 3122 785 15460
Page 2
EN 2 FTP2.4E AA1.
Technical Specifications, Connections, and Chassis Overview
1. Technical Specifications, Connections, and Chassis Overview
Index of this chapter:
1.1 Technical Specifications
1.2 Connections
1.3 Chassis Overview
Notes:
• Figures can deviate due to the different set executions.
• Specifications are indicative (subject to change).
1.1 Technical Specifications
1.1.1 Vision
Display type : Plasma, 16:9
Screen size : 42” (106 cm), FHP
Resolution (HxV pixels) : 42" - 1024x1024i
Contrast ratio : 1000:1
Light output (cd/m
2
) : 42" - 1200
Viewing angle (HxV degrees) : 160 x 160
Tuning system : PLL
Colour systems : PAL B/G, D/K, I
Supported computer formats : 640x480
Supported video formats : 640x480i - 1fH
AV (playback only) : NTSC, PAL, SECAM
Presets/channels : 100 presets
Tuner bands : UHF, VHF, S, H-band
1.1.2 Sound
Sound systems : AV stereo,
Maximum power (W
) : 2 x 15
RMS
: 50” (127 cm), SDI
: 50" - 1366x768p
: 50" - 1000
: SECAM B/G, D/K, L/L’
: 800x600
: 1024x768 (50”)
: 720x576i - 1fH
: 640x480p - 2fH
: 720x576p - 2fH
: 1920x1080i - 2fH
: 1920x1152i - 2fH
: 1280x720p - 3fH
: FM/FM B/G(5.5-5.74),
: NICAM B/G(5.5-5.85)
: NICAM D/K(5.5-5.85),
: NICAM I (6.0-6.52)
1.2 Connections
Note: The following connector colour abbreviations are used
(acc. to DIN/IEC 757): Bk= Black, Bu= Blue, Gn= Green, Gy=
Grey, Rd= Red, Wh= White, and Ye= Yellow.
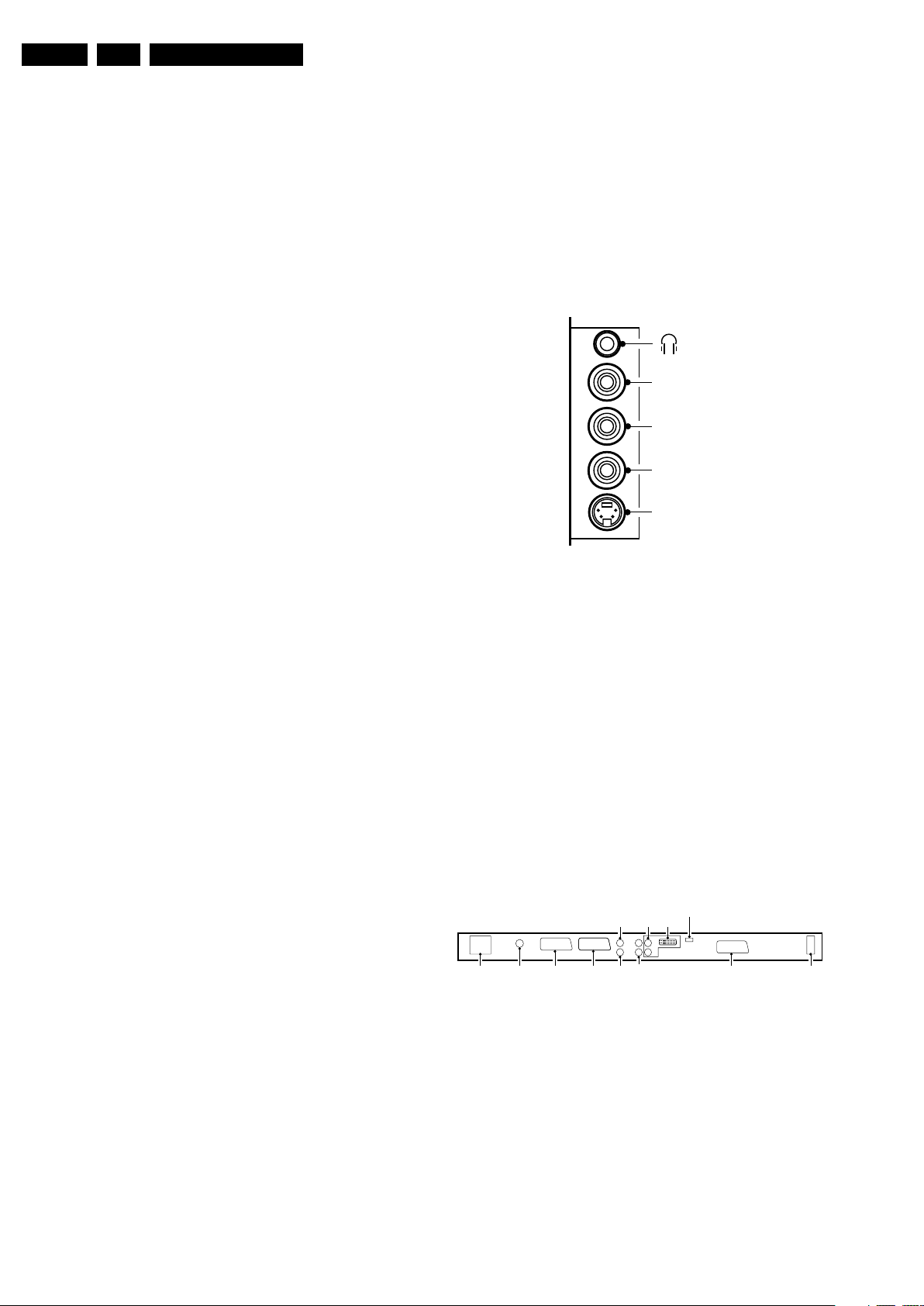
1.2.1 Side I/O
SIDE I/O
R
AUDIO
L
CVBS
SVHS
E_14620_022.eps
050404
Figure 1-1 Side I/O connections
Mini Jack: Audio Head phone - Out
Bk - Head phone 32 - 600 ohm / 10 mW ot
Cinch: Video CVBS - In, Audio - In
Ye -Video CVBS 1 V
Wh - Audio L 0.5 V
Rd - Audio R 0.5 V
SVHS (Hosiden): Video Y/C - In
1 -Ground Y Gnd H
2 -Ground C Gnd H
3 -Video Y 1 V
4 -Video C 0.3 V
1.2.2 Rear Connections
/ 75 ohm jq
PP
/ 10 kohm jq
RMS
/ 10 kohm jq
RMS
/ 75 ohm j
PP
P / 75 ohm j
PP
1.1.3 Miscellaneous
Power supply:
- Mains voltage (V
) : 220 - 240
AC
- Mains frequency (Hz) : 50 / 60
Ambient conditions:
- Temperature range (°C) : +5 to +40
- Maximum humidity : 90% R.H.
Power consumption
- Normal operation (W) : 42" - 257
: 50" - 375
- Stand-by (W) : < 2
Dimensions (WxHxD cm) : 42" - 111x78x10
: 50" - 128x88x10
Weight (kg) : 42" - 42, 50” - 58
MAINS
(PLASMA SETS)
AERIAL IN EXT2 EXT1
CENTRE
IN
SUBW
OUT
AUDIO
IN
RLR
AUDIO
OUT
L
DVI
SERVICE
EXT3
Figure 1-2 Rear connections
Aerial - In
- - IEC-type (EU) Coax, 75 ohm D
MAINS
(LCD SETS)
E_14620_023.eps
170604
Page 3

Technical Specifications, Connections, and Chassis Overview
EN 3FTP2.4E AA 1.
EXT2: Video RGB/YC - In, CVBS - In/Out, Audio - In/Out
21
20
E_06532_001.eps
2
1
050404
Figure 1-3 SCART connector
1 -Audio R 0.5 V
2 -Audio R 0.5 V
3 -Audio L 0.5 V
/ 1 kohm k
RMS
/ 10 kohm j
RMS
/ 1 kohm k
RMS
4 -Ground Audio Gnd H
5 -Ground Blue Gnd H
6 -Audio L 0.5 V
7 -Vid. Blue-in/C-out 0.7 V
8 -Function Select 0 - 2 V: INT
/ 10 kohm j
RMS
/ 75 ohm jk
PP
4.5 - 7 V: EXT 16:9
9.5 - 12 V: EXT 4:3 j
9 - Ground Green Gnd H
10 - Easylink P50 0 - 5 V / 4.7 kohm jk
11 - Video Green 0.7 V
12 - n.c.
/ 75 ohm j
PP
13 - Ground Red Gnd H
14 - Ground P50 Gnd H
15 - Video Red/C 0.7 V
16 - FBL 0 - 0.4 V: INT
/ 75 ohm j
PP
1 - 3 V: EXT / 75 ohm j
17 - Ground Video Gnd H
18 - Ground FBL Gnd H
19 - Video CVBS 1 V
20 - Vid. CVBS/Y-in 1 V
21 - Shield Gnd H
/ 75 ohm k
PP
/ 75 ohm j
PP
EXT1: Video RGB-in, CVBS - In/Out, Audio - In/Out
1 - Audio R 0.5 V
2 - Audio R 0.5 V
3 - Audio L 0.5 V
4 - Ground Audio Gnd H
/ 1 kohm k
RMS
/ 10 kohm j
RMS
/ 1 kohm k
RMS
5 - Ground Blue Gnd H
6 - Audio L 0.5 V
7 - Video Blue 0.7 V
8 - Function Select 0 - 2 V: INT
/ 10 kohm j
RMS
/ 75 ohm j
PP
4.5 - 7 V: EXT 16:9
9.5 - 12 V: EXT 4:3 j
9 - Ground Green Gnd H
10 - n.c.
11 - Video Green 0.7 V
12 - n.c.
/ 75 ohm j
PP
13 - Ground Red Gnd H
14 - Ground Data Gnd H
15 - Video Red 0.7 V
/ 75 ohm j
PP
16 - FBL 0 - 0.4 V: INT
1 - 3 V: EXT / 75 ohm j
17 - Ground Video Gnd H
18 - Ground FBL Gnd H
19 - Video CVBS 1 V
20 - Video CVBS 1 V
21 - Shield Gnd H
/ 75 ohm k
PP
/ 75 ohm j
PP
Cinch: Sub woofer - Out, Centre - In
Bu -Centre 0.5 V
Bk - Sub woofer 0.5 V
/ 10 kohm jq
RMS
/ 10 kohm kq
RMS
Cinch: Audio - Out
Rd - Audio - R 0.5 V
Wh - Audio - L 0.5 V
/ 10 kohm kq
RMS
/ 10 kohm kq
RMS
DVI-I: Digital/Analogue Video - In
18
916
17
C1 C2
C5
24
C3 C4
E_06532_004.eps
050404
Figure 1-4 DVI-I connector
1-D2- j
2-D2+ j
3 - Shield Gnd H
4-D4- j
5-D4+ j
6 - DDC_SCL DDC clock k
7 - DDC_SDA DDC data jk
8 - V-sync 0 - 5 V TTL j
9-D1- j
10 - D1+ j
11 - Shield Gnd H
12 - D3- j
13 - D3+ j
14 - +5V j
15 - Ground Gnd H
16 - HPD Hot Plug Detect j
17 - D0- j
18 - D0+ j
19 - Shield Gnd H
20 - D5- j
21 - D5+ j
22 - Shield Gnd H
23 - CLK+ j
24 - CLK- j
C1 - Video Red 0.7 V
C2 - Video Green 0.7 V
C3 - Video Blue 0.7 V
/ 75 ohm j
PP
/ 75 ohm j
PP
/ 75 ohm j
PP
C4 - H-sync 0 - 5 V TTL j
C5 - Ground Gnd H
Service connector (ComPair)
1 - SDA-S I
2 - SCL-S I
2
C Data (0 - 5 V) jk
2
C Clock (0 - 5 V) j
3 - Ground Gnd H
EXT3: Video CVBS - In, Audio - In
1-n.c.
2 - Audio R 0.5 V
/ 10 kohm j
RMS
3-n.c.
4 - Ground Audio Gnd H
5 - Ground Blue Gnd H
6 - Audio L 0.5 V
7-n.c.
/ 10 kohm j
RMS
8 - Function Select 0 - 2 V: INT
4.5 - 7 V: EXT 16:9
9.5 - 12 V: EXT 4:3 j
9 - Ground Green Gnd H
10 - n.c.
11 - n.c.
12 - n.c.
13 - Ground Red Gnd H
14 - Ground Data Gnd H
15 - n.c.
16 - n.c.
17 - Ground Video Gnd H
18 - Ground FBL Gnd H
19 - n.c.
20 - Video CVBS 1 V
21 - Shield Gnd H
/ 75 ohm j
PP
Cinch: DVI Audio - In
Rd - Audio - R 0.5 V
Wh - Audio - L 0.5 V
/ 10 kohm jq
RMS
/ 10 kohm jq
RMS
Page 4
EN 4 FTP2.4E AA1.
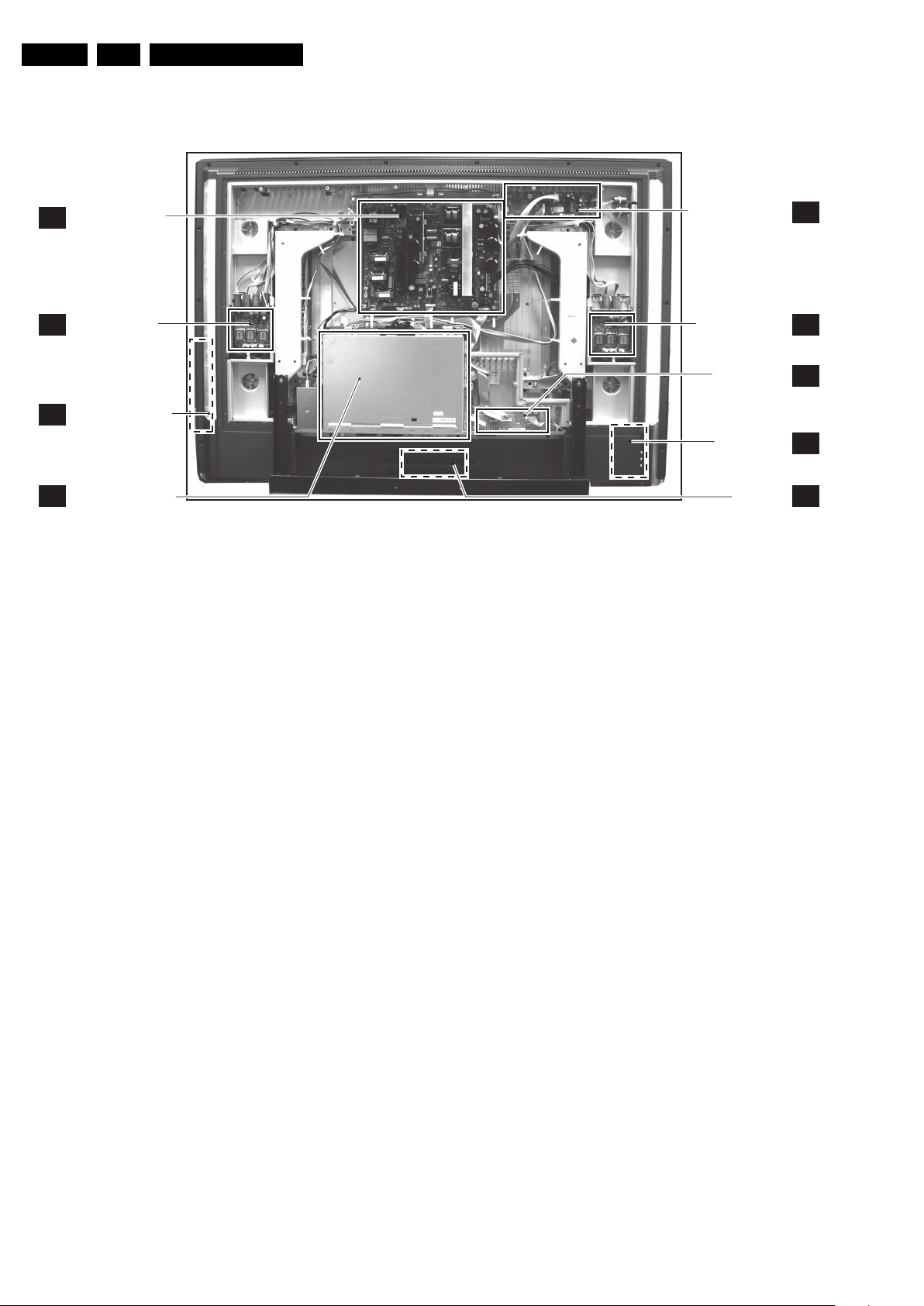
1.3 Chassis Overview
Technical Specifications, Connections, and Chassis Overview
PDP SUPPLY PANEL
A
(ONLY FOR FHP SETS)
AMBI LIGHT PANE
AL
TOP CONTROL PANEL
E
SMALL SIGNAL BOARD
B
PDP AUDIO PANEL
L
AMBI LIGHT PANEL
SCART 3 PANEL
SIDE I/O PANEL
LED PANEL
F_15460_076.eps
C
AL
H
D
J
130405
Figure 1-5 PWB location (photo from 42” FHP model)
Page 5

Safety Instructions, Warnings, and Notes
2. Safety Instructions, Warnings, and Notes
EN 5FTP2.4E AA 2.
Index of this chapter:
2.1 Safety Instructions
2.2 Warnings
2.3 Notes
2.1 Safety Instructions
Safety regulations require the following during a repair:
• Connect the TV to the Mains (AC Power) via an isolation
transformer (> 800 VA).
• Replace safety components, indicated by the symbol h,
only by components identical to the original ones. Any
other component substitution (other than original type) may
increase risk of fire or electrical shock hazard.
Safety regulations require that after a repair, the TV must be
returned in its original condition. Pay in particular attention to
the following points:
• Route the wire trees correctly and fix them with the
mounted cable clamps.
• Check the insulation of the Mains (AC Power) lead for
external damage.
• Check the strain relief of the Mains (AC Power) cord for
proper function.
• Check the electrical DC resistance between the Mains (AC
Power) plug and the secondary side (only for sets that have
a Mains (AC Power) isolated power supply):
1. Unplug the Mains (AC Power) cord and connect a wire
between the two pins of the Mains (AC Power) plug.
2. Set the Mains (AC Power) switch to the "on" position
(keep the Mains (AC Power) cord unplugged!).
3. Measure the resistance value between the pins of the
Mains (AC Power) plug and the metal shielding of the
tuner or the aerial connection on the TV. The reading
should be between 4.5 Mohm and 12 Mohm.
4. Switch "off" the TV, and remove the wire between the
two pins of the Mains (AC Power) plug.
• Check the cabinet for defects, to prevent touching of any
inner parts by the customer.
2.2 Warnings
• All ICs and many other semiconductors are susceptible to
electrostatic discharges (ESD w). Careless handling
during repair can reduce life drastically. Make sure that,
during repair, you are connected with the same potential as
the mass of the TV by a wristband with resistance. Keep
components and tools also at this same potential. Available
ESD protection equipment:
– Complete kit ESD3 (small tablemat, wristband,
connection box, extension cable and earth cable) 4822
310 10671.
– Wristband tester 4822 344 13999.
• Be careful during measurements in the high voltage
section.
• Never replace modules or other components while the unit
is switched "on".
• When you align the TV, use plastic rather than metal tools.
This will prevent any short circuits and the danger of a
circuit becoming unstable.
2.3 Notes
2.3.1 General
• Measure the voltages and waveforms with regard to the
chassis (= tuner) ground (H), or hot ground (I), depending
on the tested area of circuitry. The voltages and waveforms
shown in the diagrams are indicative. Measure them in the
Service Default Mode (see chapter 5) with a colour bar
signal and stereo sound (L: 3 kHz, R: 1 kHz unless stated
otherwise) and picture carrier at 475.25 MHz for PAL, or
61.25 MHz for NTSC (channel 3).
• Where necessary, measure the waveforms and voltages
with (D) and without (E) aerial signal. Measure the
voltages in the power supply section both in normal
operation (G) and in stand-by (F). These values are
indicated by means of the appropriate symbols.
• The semiconductors indicated in the circuit diagram and in
the parts lists, are interchangeable per position with the
semiconductors in the unit, irrespective of the type
indication on these semiconductors.
• Manufactured under license from Dolby Laboratories.
“Dolby”, “Pro Logic” and the “double-D symbol”, are
trademarks of Dolby Laboratories.
2.3.2 Schematic Notes
• All resistor values are in ohms, and the value multiplier is
often used to indicate the decimal point location (e.g. 2K2
indicates 2.2 kohm).
• Resistor values with no multiplier may be indicated with
either an "E" or an "R" (e.g. 220E or 220R indicates 220
ohm).
• All capacitor values are given in micro-farads (µ= x10
nano-farads (n= x10
• Capacitor values may also use the value multiplier as the
decimal point indication (e.g. 2p2 indicates 2.2 pF).
• An "asterisk" (*) indicates component usage varies. Refer
to the diversity tables for the correct values.
• The correct component values are listed in the Spare Parts
List. Therefore, always check this list when there is any
doubt.
2.3.3 Rework on BGA (Ball Grid Array) ICs
General
Although (LF)BGA assembly yields are very high, there may
still be a requirement for component rework. By rework, we
mean the process of removing the component from the PWB
and replacing it with a new component. If an (LF)BGA is
removed from a PWB, the solder balls of the component are
deformed drastically so the removed (LF)BGA has to be
discarded.
Device Removal
As is the case with any component that, is being removed, it is
essential when removing an (LF)BGA, that the board, tracks,
solder lands, or surrounding components are not damaged. To
remove an (LF)BGA, the board must be uniformly heated to a
temperature close to the reflow soldering temperature. A
uniform temperature reduces the risk of warping the PWB.
To do this, we recommend that the board is heated until it is
certain that all the joints are molten. Then carefully pull the
component off the board with a vacuum nozzle. For the
appropriate temperature profiles, see the IC data sheet.
Area Preparation
When the component has been removed, the vacant IC area
must be cleaned before replacing the (LF)BGA.
Removing an IC often leaves varying amounts of solder on the
mounting lands. This excessive solder can be removed with
either a solder sucker or solder wick. The remaining flux can be
removed with a brush and cleaning agent.
After the board is properly cleaned and inspected, apply flux on
the solder lands and on the connection balls of the (LF)BGA.
Note: Do not apply solder paste, as this has been shown to
result in problems during re-soldering.
-9
), or pico-farads (p= x10
-12
-6
),
).
Page 6

EN 6 FTP2.4E AA3.
Directions for Use
Device Replacement
The last step in the repair process is to solder the new
component on the board. Ideally, the (LF)BGA should be
aligned under a microscope or magnifying glass. If this is not
possible, try to align the (LF)BGA with any board markers.
So as not to damage neighbouring components, it may be
necessary to reduce some temperatures and times.
More Information
For more information on how to handle BGA devices, visit this
URL: www.atyourservice.ce.philips.com (needs subscription,
not available for all regions). After login, select “Magazine”,
then go to “Workshop Information”. Here you will find
Information on how to deal with BGA-ICs.
2.3.4 Lead-free Solder
Philips CE is producing lead-free sets (PBF) from 1.1.2005
onwards.
Identification: The bottom line of a type plate gives a 14-digit
serial number. Digits 5 and 6 refer to the production year, digits
7 and 8 refer to production week (in example below it is 1991
week 18).
• Use only adequate solder tools applicable for lead-free
soldering tin. The solder tool must be able:
– To reach a solder-tip temperature of at least 400°C.
– To stabilise the adjusted temperature at the solder-tip.
– To exchange solder-tips for different applications.
• Adjust your solder tool so that a temperature of around
360°C - 380°C is reached and stabilised at the solder joint.
Heating time of the solder-joint should not exceed ~ 4 sec.
Avoid temperatures above 400°C, otherwise wear-out of
tips will increase drastically and flux-fluid will be destroyed.
To avoid wear-out of tips, switch “off” unused equipment or
reduce heat.
• Mix of lead-free soldering tin/parts with leaded soldering
tin/parts is possible but PHILIPS recommends strongly to
avoid mixed regimes. If this cannot be avoided, carefully
clear the solder-joint from old tin and re-solder with new tin.
• Use only original spare-parts listed in the Service-Manuals.
Not listed standard material (commodities) has to be
purchased at external companies.
• Special information for lead-free BGA ICs: these ICs will be
delivered in so-called "dry-packaging" to protect the IC
against moisture. This packaging may only be opened
shortly before it is used (soldered). Otherwise the body of
the IC gets "wet" inside and during the heating time the
structure of the IC will be destroyed due to high (steam-)
pressure inside the body. If the packaging was opened
before usage, the IC has to be heated up for some hours
(around 90°C) for drying (think of ESD-protection!).
Do not re-use BGAs at all!
• For sets produced before 1.1.2005, containing leaded
soldering tin and components, all needed spare parts will
be available till the end of the service period. For the repair
of such sets nothing changes.
E_06532_024.eps
230205
Figure 2-1 Serial number example
Regardless of the special lead-free logo (which is not always
indicated), one must treat all sets from this date onwards
according to the rules as described below.
P
b
Figure 2-2 Lead-free logo
Due to lead-free technology some rules have to be respected
by the workshop during a repair:
• Use only lead-free soldering tin Philips SAC305 with order
code 0622 149 00106. If lead-free solder paste is required,
please contact the manufacturer of your soldering
equipment. In general, use of solder paste within
workshops should be avoided because paste is not easy to
store and to handle.
In case of doubt whether the board is lead-free or not (or with
mixed technologies), you can use the following method:
• Always use the highest temperature to solder, when using
SAC305 (see also instructions below).
• De-solder thoroughly (clean solder joints to avoid the
mixing of two alloys).
Caution: For BGA-ICs, you must use the correct temperature
profile, which is coupled to the 12NC. For an overview of these
profiles, visit the website www.atyourservice.ce.philips.com
(needs subscription, but is not available for all regions).
You will find this and more technical information within the
"Magazine", chapter "Workshop information".
For additional questions please contact your local repair help
desk.
2.3.5 Practical Service Precautions
• It makes sense to avoid exposure to electrical shock.
While some sources are expected to have a possible
dangerous impact, others of quite high potential are of
limited current and are sometimes held in less regard.
• Always respect voltages. While some may not be
dangerous in themselves, they can cause unexpected
reactions that are best avoided. Before reaching into a
powered TV set, it is best to test the high voltage insulation.
It is easy to do, and is a good service precaution.
3. Directions for Use
You can download this information from the following websites:
http://www.philips.com/support
http://www.p4c.philips.com
Page 7
4. Mechanical Instructions
Mechanical Instructions
EN 7FTP2.4E AA 4.
Index of this chapter:
4.1 Cable Dressing
4.2 Service Position
4.3 Assy/PWB Removal
4.4 Plasma Panel / Glass Plate (Dis)Assembly
4.5 Set Re-assembly
4.1 Cable Dressing
4.1.1 Chassis
Notes:
• Figures below can deviate slightly from the actual situation,
due to the different set executions.
• All photo’s are made of the 42” FHP model, however the
50” SDI model will not deviate much from it.
• Follow the disassemble instructions in described order.
• Be aware that the internal (gold coloured) frame is made of
conducting material. So, be cautious during electrical
measurements!
4.2 Service Position
For easy servicing of this set, there are a few possibilities
created:
• The buffers from the packaging.
• Foam bars (created for Service).
• Aluminium service stands (created for Service).
4.2.1 Foam Bars
E_06532_018.eps
Figure 4-2 Foam bars
The foam bars (order code 3122 785 90580 for two pieces) can
be used for all types and sizes of Flat TVs. By laying the TV
face down on the (ESD protective) foam bars, a stable situation
is created to perform measurements and alignments.
Figure 4-1 Chassis cable dressing
By placing a mirror under the TV, you can monitor the screen.
4.2.2 Aluminium Stands
170504
The new (MkII) aluminium stands (order code 3122 785 90690)
can also be used to do measurements, alignments, and
duration tests. The stands can be (dis)mounted quick and easy
by means of sliding them in/out the "mushrooms".
Important: For (older) FTV sets without these "mushrooms", it
is obligatory to use the provided screws, otherwise it is possible
to damage the monitor inside!.
F_15460_075.eps
140405
E_06532_019.eps
170504
Figure 4-3 Aluminium stands (MkI)
Page 8
EN 8 FTP2.4E AA4.
Mechanical Instructions
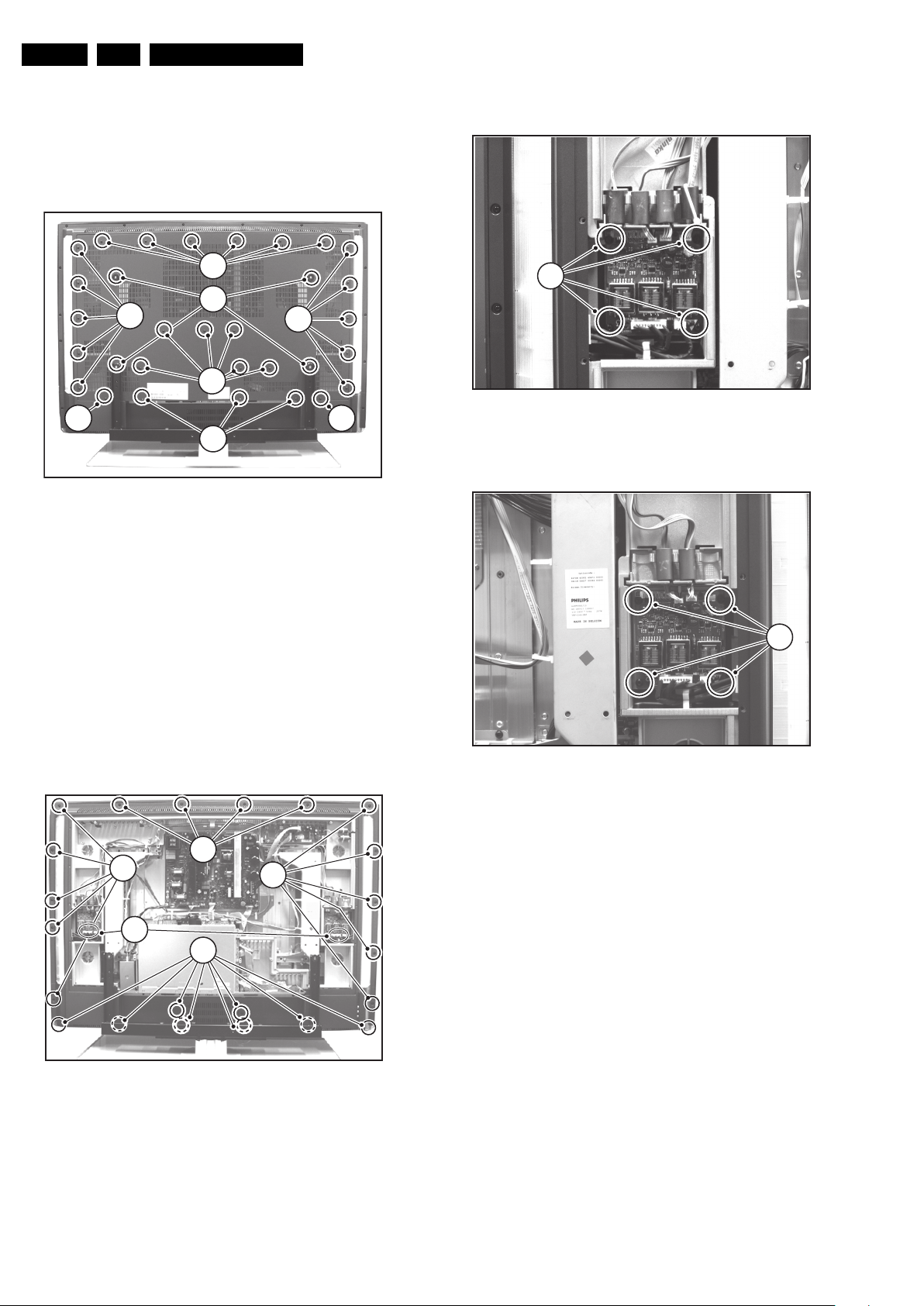
4.3 Assy/PWB Removal
4.3.1 Metal Back Plate
Caution: Disconnect the mains power cord before you remove
the metal back plate.
1
3
1
1
2
Figure 4-4 Metal back plate
1
11
F_15460_074.eps
140405
4.3.3 Ambient Light Panel(s)
1
Figure 4-6 Ambient light inverter (left side)
F_15460_071.eps
130405
1. Place the TV set upside down on a table top, using the
foam bars (see part "Foam Bars").
Caution: do not put pressure on the display, but let the
monitor lean on the speakers or the Front cover.
2. Remove all T10 parker screws (1) from the top, centre, and
left and right sides of the back plate.
3. Remove all T10 tapping screws (2) from the bottom of the
back plate.
4. Remove the four "mushrooms" (3) from the back plate.
5. Lift the back plate from the TV. Make sure that wires and
flat foils are not damaged during the back plate removal.
4.3.2 Rear Cover
2
2
2
1
2
Figure 4-7 Ambient light inverter (right side)
Later models are equipped with two Ambient Light Inverter
panels. For the earlier models with one panel, reference is
made to the FTP2.2x Service Manual for the correct
mechanical instructions.
1. Disconnect all cables from the Ambient Light Inverter
panel.
2. Remove all mounting screws (1) from the Ambient Light
Inverter panel.
3. Take out the Ambient Light Inverter panel.
4.3.4 Power Supply Panel
1
F_15460_072.eps
130405
F_15460_073.eps
140405
Figure 4-5 Rear cover
1. Disconnect all connectors (1) at both Ambient Light
Inverters that go to the Ambient Lights in the rear cover.
2. Remove all T10 tapping screws (2) around the edges of the
rear cover.
3. Lift the rear cover from the TV.
1. Disconnect all cables from the Power Supply panel.
2. Remove all mounting screws from the Power Supply panel.
3. Take out the Power Supply panel.
4.3.5 SCART3 Panel
1. Disconnect all cables from the SCART3 panel.
2. Remove the two mounting screws (7) near the SCART3 at
the connector plate (see figure "Connector plate").
3. Take out the SCART3 panel.
Page 9

Mechanical Instructions
EN 9FTP2.4E AA 4.
4.3.6 Audio Panel
1
Figure 4-8 Audio panel
1. Disconnect all cables from the Audio panel.
2. Remove all mounting screws (1) from the Audio panel.
3. Take out the Audio panel.
4.3.7 Side I/O Panel
1. Disconnect the cable from the Side I/O panel.
2. Release the clamps and take out the Side I/O panel from
its bracket.
F_15460_070.eps
140405
4.3.11 SSB
2b
1
2a
2
Figure 4-9 SSB top shielding
4
Figure 4-10 Connector plate
F_15460_069.eps
73
140405
E_14620_031.eps
130504
4.3.8 Top / Side Control
1. Remove the mounting screws from the Top / Side Control
panel bracket.
2. Disconnect the cable.
3. Release the clamps and take out the Top / Side Control
panel.
4.3.9 LED Panel
1. Disconnect all cables from the LED panel.
2. Remove the mounting screws from the LED panel.
3. Take out the LED panel.
4.3.10 Speakers
1. Remove all mounting screws.
2. After removing the cover plate, you can access the
speakers.
3. Be sure that the foam that makes the unit airtight is not
damaged.
6
5
F_15460_067.eps
130405
Figure 4-11 SSB removal
1. Remove the LVDS locking bracket (1).
2. Remove all fixing screws (2).
3. Disconnect the grounding wire from the mains filter (2a).
4. Shift, and lift the shielding at the top. The panel hinges at
the SCART side.
Caution: do not damage the EMC shielding foam while
you remove the shielding.
5. Remove mounting screws (3) from the connector plate.
Use a 5 mm socket screwdriver to remove both DVI
connector distance bolts (4).
6. Remove the mounting screws from the SSB (5).
7. Disconnect the LVDS cable (6).
8. Lift the SSB, disconnect all cables, and take out the SSB.
Page 10
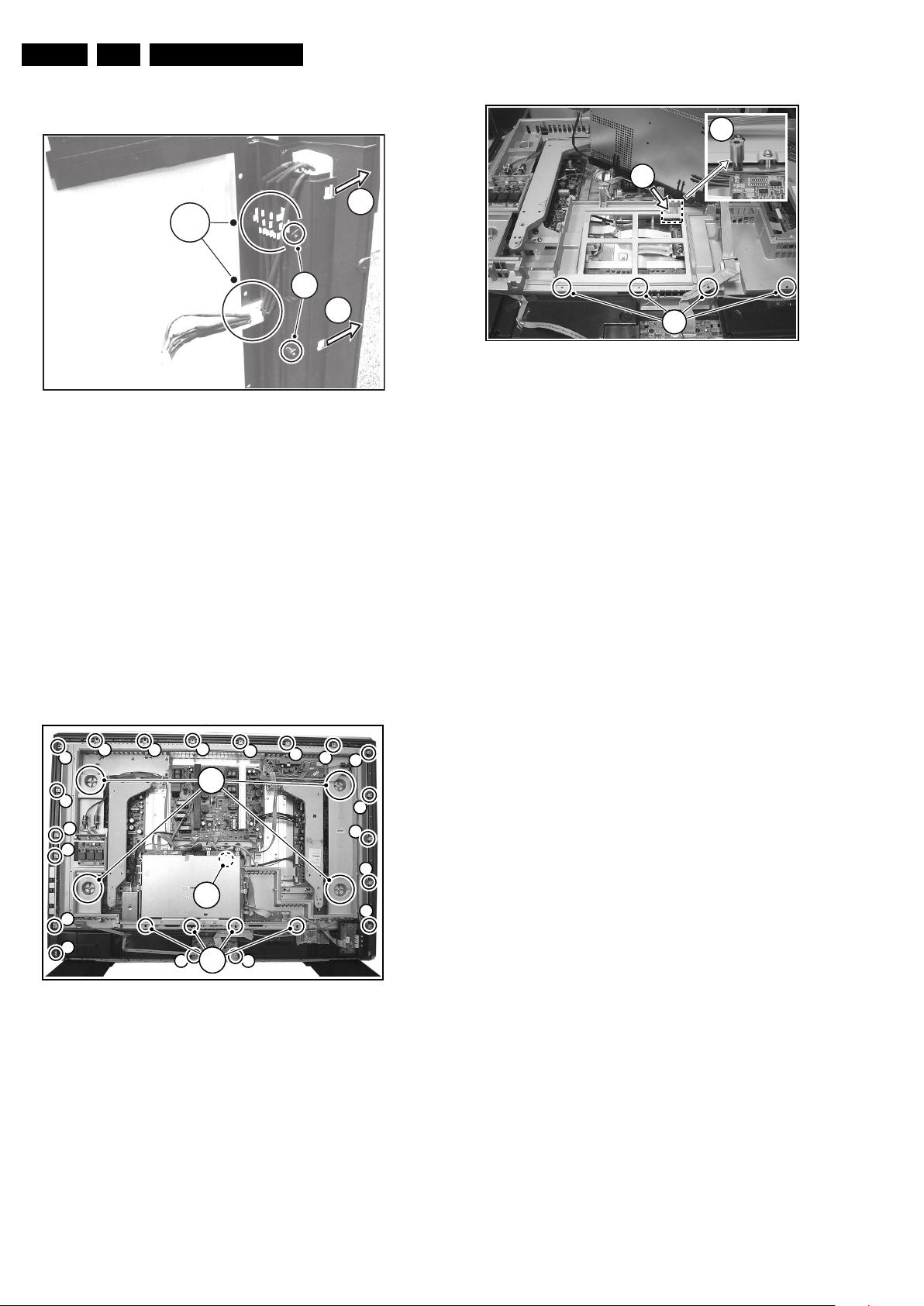
EN 10 FTP2.4E AA4.
4.3.12 Ambient Lights
Mechanical Instructions
5
4
3
2
1
3
2
E_14650_010.eps
170604
F_15460_066.eps
120405
Figure 4-12 Ambient light (partly shown)
Ambient lights are located in the rear cover of the TV.
1. Unplug the connectors.
2. Remove all mounting Ambient Light screws (1).
3. Move the Ambient light unit to the side (3) and take out the
unit.
4.4 Plasma Panel / Glass Plate (Dis)Assembly
Important: Be sure to work in a dust free environment during
the following activities. In addition, the use of (fabric) hand
gloves is advised.
4.4.1 Plasma Display Panel
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
Figure 4-13 Plasma panel removal
4
4
4
4
4
1
4
4
3
2
4
4
E_14650_009.eps
170604
Figure 4-14 Hidden screw
Disassembly
1. Place the TV set face down on the foam bars. Place the
bars at the edges of the TV so they will support the front
frame, and not only the glass plate!
2. Remove the four T25 screws (1) that hold the plasma
panel.
Note: In some models, the upper left T25 screw is hidden
under the Ambient Light Inverter panel. Remove this panel
to get access to it.
3. Remove the fifth T25 screw that is located near the SSB.
Note: In some models, this fifth screw is hidden under the
SSB. To get access, you have to remove the four T10
screws (2) that mount the "SSB connector plate" to the
frame. Then, lift the complete SSB unit away, so you can
remove the hidden screw (4).
4. Remove all T10 tapping screws around the frame (4).
5. Next step is to unplug the following connectors (see also
Wiring Diagram in chapter 6):
– Mains plug on PSU.
– Audio panel supply plug on PSU.
– LVDS plug on SSB (first remove the fixation clamp).
– Ambilight supply plug on PSU.
– SSB supply plugs on PSU.
– Side/Top Control plug on LED panel.
– Side I/O plug on LED panel.
– SSB grounding wire.
– Loosen all necessary cables from their clamps.
6. Lift the plastic frame together with all PWBs from the PDP
4
panel.
7. Now the PDP (incl. the PSU panel) can be removed. Lift the
panel at the two metal bars from the glass plate.
4
8. Before sending the plasma panel to the NSO for repair or
exchange, remove the PSU panel and the spacer (5) that
is placed upon the centre mounting stud.
Assembly
In order to centre the (new) plasma panel correctly w.r.t. the
glass plate, do the following:
1. Place the (new) plasma panel face down on foam bars.
2. Also, place the front assy (front panel with glass plate) on
two other foam bars.
3. Mount the plastic frame on the plasma panel.
Important: Be sure that the spacer (order code 3104 301
62781) is placed upon the centre mounting stud (5).
4. Lift this module (frame and PDP) and place it onto the front
assy.
5. Now follow the above described disassembly process in
reverse order.
4.4.2 Glass Plate
1. Follow the above-described PDP disassembly instructions.
2. After removing the PDP, the glass plate is now accessible.
Page 11
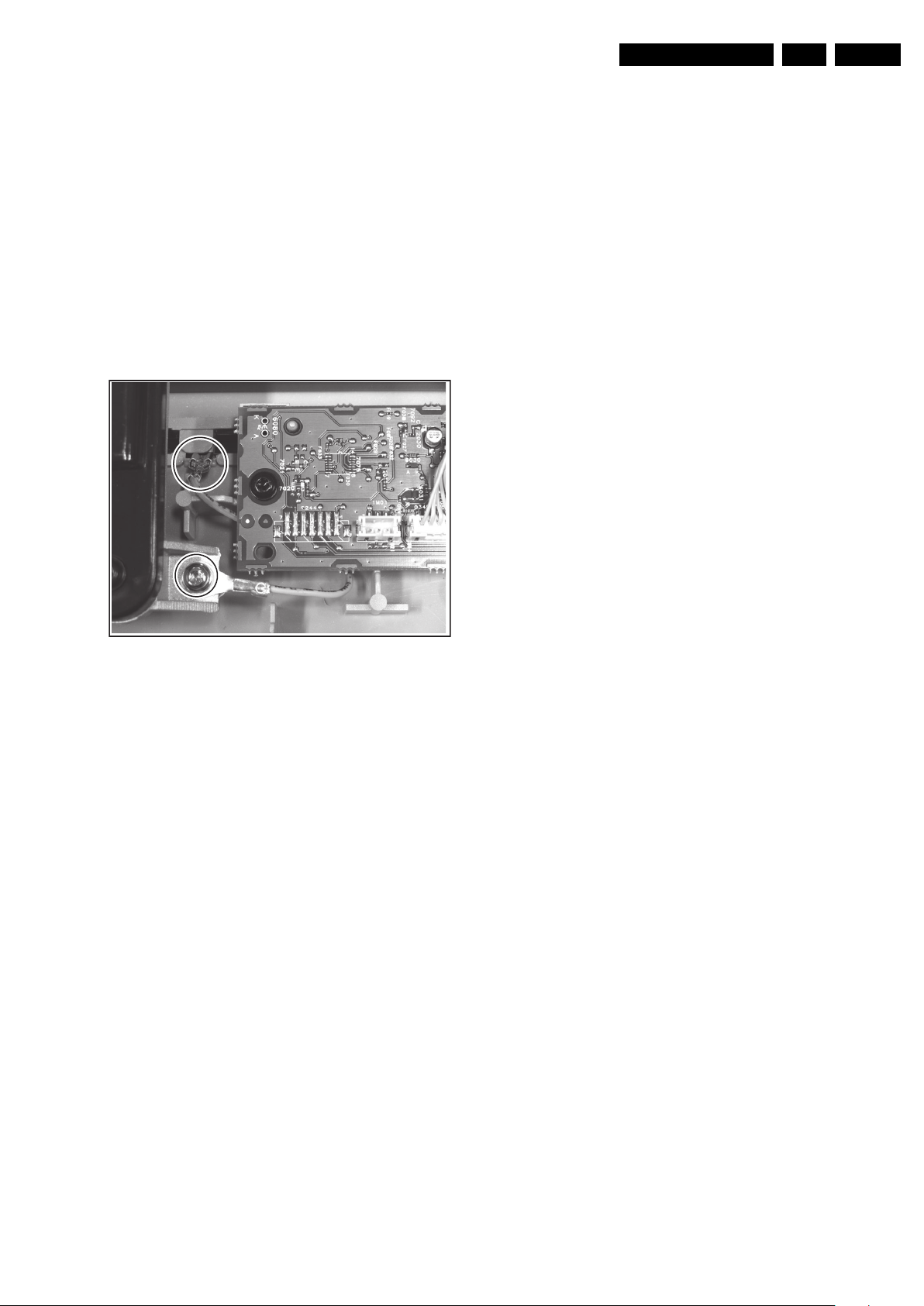
4.5 Set Re-assembly
To re-assemble the whole set, execute all processes in reverse
order.
Note: While re-assembling the TV, make sure that:
• All cables are placed and connected in their original
position (see figure “Cable dressing”).
• EMC Shielding foam is intact.
• LVDS connector (SSB) is secured with plastic clamp.
• All "grounding" wires are re-connected:
– Between metal speaker grid and frame (near the LED
panel).
– Between the Mains Filter and the SSB Top Shielding
(see figure SSB Top shielding item 2a).
– Between the SSB Top Shielding and the PSU (see
figure SSB Top shielding item 2b).
Mechanical Instructions
EN 11FTP2.4E AA 4.
F_15460_065.eps
Figure 4-15 Grounding wire of metal speaker grid
120405
Page 12
EN 12 FTP2.4E AA5.
Service Modes, Error Codes, and Fault Finding
5. Service Modes, Error Codes, and Fault Finding
Index of this chapter:
5.1 Test Points
5.2 Service Modes
5.3 Problems and Solving Tips (related to CSM)
5.4 ComPair
5.5 Error Codes
5.6 The Blinking LED Procedure
5.7 Protections
5.8 Repair tips
5.9 Software Downloading
5.1 Test Points
The chassis is equipped with test points printed on the circuit
board assemblies.
Perform measurements under the following conditions:
• Service Default Mode.
• Video: colour bar signal.
• Audio: 3 kHz left, 1 kHz right.
5.2 Service Modes
Service Default Mode (SDM) and Service Alignment Mode
(SAM) offer several features for the service technician, while
the Customer Service Mode (CSM) is used for communication
between a Philips Customer Care Centre (P3C) and a
customer.
There is also the option of using ComPair, a hardware interface
between a computer (see requirements below) and the TV
chassis. It offers the ability of structured troubleshooting, test
pattern generation, error code reading, software version readout, and software upgrading.
Minimum requirements: a Pentium processor, Windows 95/
98, and a CD-ROM drive (see also paragraph “ComPair”).
Remark: The silk screen printing is not correct for the SAM/
SDM indication. For the correct location of these pins, see
figure ”Service pads”.
5.2.1 Service Default Mode (SDM)
Purpose
• To create a pre-defined setting, to get the same
measurement results as given in this manual.
• To override SW protections.
• To start the blinking LED procedure.
– Smart modes.
– Auto store of personal presets.
– Auto user menu time-out.
How to activate SDM
Use one of the following methods:
• Use the standard RC-transmitter and key in the code
“062596”, directly followed by the “MENU” button.
Note: It is possible that, together with the SDM, the main
menu will appear. To switch it off, push the “MENU” button
again.
SDM
SAM
SW UPGRADE
MODE
Figure 5-1 Service pads
• Short for a moment the two solder pads on the SSB, with
the indication “SDM” (see figure ”Service pads”). Activation
can be performed in all modes, except when the TV has a
problem with the main microprocessor.
Caution: If the SDM is activated via the pins, all the
software-controlled protections are de-activated.
• Use the DST-emulation feature of ComPair.
• Use the “DEFAULT” button on the Dealer Service Tool
(RC7150).
How to navigate
When you press the “MENU” button on the RC transmitter, the
TV will toggle between the SDM and the normal user menu
(with the SDM mode still active in the background).
NORMAL
TV MODE
E_14620_151.eps
290704
Specifications
Table 5-1 SDM default settings
Default
Region Freq. (MHz)
Europe, AP-PAL/Multi 475.25 PAL B/G
NAFTA, AP-NTSC, LATAM 61.25 (ch. 3) NTSC M
• All picture settings at 50% (brightness, colour, contrast).
• All sound settings at 50%, except volume at 25%.
• All service-unfriendly modes (if present) are disabled, like:
– (Sleep) timer.
– Child/parental lock.
–Blue mute.
– Automatic volume limiter (AVL).
– Auto switch-off (when no video signal was received for
10 minutes).
– Skip/blank of non-favourite pre-sets.
system
How to exit SDM
Use one of the following methods:
• Switch the TV to STANDBY via the RC-transmitter.
• Press the “EXIT” button on the DST.
• Via a standard customer RC-transmitter: key in “00”sequence.
5.2.2 Service Alignment Mode (SAM)
Purpose
• To perform (software) alignments.
• To change option settings.
• To easily identify the used software version.
• To view operation hours.
• To display (or clear) the error code buffer.
Specifications
• Operation hours counter.
• Software version.
Page 13

Service Modes, Error Codes, and Fault Finding
EN 13FTP2.4E AA 5.
• Option settings.
• Error buffer reading and erasing.
• Software alignments.
How to activate SAM
Use one of the following methods:
• Via a standard RC transmitter: key in the code “062596”
directly followed by the “OSD [i+]” button. After activating
SAM with this method a service warning will appear on the
screen, you can continue by pressing any digit key on the
RC.
• Short for a moment the two solder pads on the SSB with
the indication "SAM" (see figure ”Service pads”).
Depending on the software version, it is possible that a
service warning will appear. You can continue by pressing
any digit key on the RC.
• Use the DST-emulation feature of ComPair.
• Press the ALIGN button on the DST while the TV is in the
normal operation
After activating this mode, “SAM” will appear in the upper right
corner of the screen.
Contents of SAM:
• Operation Hours. Displays the accumulated total of
operation hours (not the stand-by hours).
• Hardware Info.
– ROM Version. Displays the date of the software and
the software version of the ROM
Ex.: TX24EU_1.0_01234 = AAAABB_X.Y_NNNNN.
• AAAA= the chassis name.
• BB= the region: EU= Europe, AP= Asia Pacific
PAL/Multi, AN= Asia Pacific NTSC, US= USA, LT=
LATAM.
• X.Y= the software version, where X is the main
version number (different numbers are not
compatible with one another) and Y is the sub
version number (a higher number is always
compatible with a lower number).
• NNNNN= last five digits of 12nc code software.
– FBX Version. Displays the software version of the
FBX
– SW VERSION EPLD. Displays the software version of
the EPLD.
• Errors. (followed by maximal 10 errors). The most recent
error is displayed at the upper left (for an error explanation
see paragraph “Error Codes”).
• Defective Module. Here the module that generates the
error is displayed. If there are multiple errors in the buffer,
which are not all generated by a single module, there is
probably another defect. It will then display the message
“UNKNOWN” here.
• Reset Error Buffer. When you press the “OK” button, the
error buffer is reset.
• Alignments. This will activate the “ALIGNMENTS” submenu.
• Dealer Options. Extra features for the dealers.
• Service Options. Extra features for Service.
• Initialise NVM. When an NVM was corrupted (or replaced)
in the former EM3 chassis, the microprocessor replaces
the content with default data (to assure that the TV can
operate). However, all pre-sets and alignment values are
gone now, and option numbers are not correct. Therefore,
this was a very drastic way. In this chassis, the procedure
is implemented in another way: The moment the processor
recognises a corrupted NVM, the “initialise NVM” line will
be highlighted. Now, you can do two things (dependent of
the service instructions at that moment):
– Save the content of the NVM via ComPair for
development analysis, before initialising. This will give
the Philips Service department an extra possibility for
diagnosis (e.g. when Development asks for this).
– Initialise the NVM (same as in the past, however now it
happens conscious).
• Store. All options and alignments are stored when
pressing the “OK”-button
• Functional Test. All devices are tested via the “OK”
button. Eventual errors are displayed in the error buffer.
The error buffer is not erased, the content returns when this
test is terminated.
• Daily Menus. With the “OK” button, you can go to the
normal user menu. SAM is still active in the background.
With the “MENU” button, you return from the user menu to
SAM menu. This feature can be helpful to quickly change
some settings in the user menu.
• SW Maintenance.
• Upgrade. More info see paragraph Software
downloading.
• Events. Not useful for service purposes. In case of
specific software problems, the development
department can ask for this info.
• BDM Info. Broadcast Debug Menu info. The purpose
of this menu is to debug the broadcast, not the TV. The
menu gives an overview of what is received on the
current preset.
Following items are displayed:
P r e s e t n r : -- UTC: - - : - - : --
P r e s e t n a m e : ----- LTO: - - : - - : --
Time: - - : - - : --
C N I N V M : ---- Date: - - / - - / ----
C N I F 1 : ----
C N I F 2 : ---- Time TXT: - - : - - : --
C N I V P S : ---- Time 8/30 F1: - - : - - : --
M o r n i n g P r o g : --- Date 8/30 F1: - - / - - / ----
N a m e 8 / 3 0 F 1 : ----- LTO 8/30 F1: - - : - - : --
N a m e 8 / 3 0 F 2 : -----
N a m e T X T : ----- WSS G1: - - - -
S i g n a l S t r e n g t h :--- WSS G2: - - - -
WSS G3: - - -
E P G S e r v i c e : --- WSS G4: - - -
E_14620_050.eps
170504
Figure 5-2 Broadcast debug menu overview
Table 5-2 Broadcast debug menu explanation
Item Source Description
Presetnr Set Preset number of the current selected preset.
Presetname Set Preset name of the current selected preset.
CNI NVM Broadcaster CNI number stored in NVM for the current preset.
CNI F1 Broadcaster CNI number from transmitted Packet 8/30 Format
CNI F2 Broadcaster CNI number from transmitted Packet 8/30 Format
CNI VPS Broadcaster CNI number from transmitted VPS line.
Morning Prog Broadcaster "ARD" or "ZDF" according to dedicated bit in 8/30
Name 8/30 F1 Broadcaster Name extracted from status message of 8/30
Name 8/30 F2 Broadcaster Name extracted from status message of 8/30
Name TXT Broadcaster Name extracted from TXT header.
Signal Strength FBX Noise figure measured for selected preset.
EPG Service Set EPG Service stored in NVM for current preset
UTC Set UTC (Universal Time Code formerly known as
LTO Set LTO (Local Time Offset) used in the TV. Used by
Time Set Current time running in the TV. Was extracted at
Date Set Current date running in the TV. Was extracted at
Time TXT Broadcaster TXT header time from the selected preset.
Time 8/30 F1 Broadcaster UTC time from 8/30 Format 1.
Date 8/30 F1 Broadcaster Date from 8/30 Format 1.
LTO 8/30 F1 Broadcaster LTO from 8/30 Format 1.
WSS G1 Broadcaster WSS Group 1 (Aspect Ratio) bits 0 1 2 3
WSS G2 Broadcaster WSS Group 2 (Enhanced Services) bits 4 5 6 7
1.
2.
Format 1.
Format 1.
Format 2.
displayed as "TXT", "MCP", "SCP", "OCP".
Greenwich Mean Time) used in the TV.
EPG for all NextView displays. (= Time TXT
header - Time 8/30 F1)
start-up, then maintained by software.
start-up, then maintained by software.
Page 14

EN 14 FTP2.4E AA5.
Service Modes, Error Codes, and Fault Finding
Item Source Description
WSS G3 Broadcaster WSS Group 3 (Subtitles) bits 8 9 10
WSS G4 Broadcaster WSS Group 4 (Reserved) bits 11 12 13
How to navigate
• In SAM, you can select the menu items with the “CURSOR
UP/DOWN” key on the RC-transmitter. The selected item
will be highlighted. When not all menu items fit on the
screen, move the “CURSOR UP/DOWN” key to display the
next/previous menu items.
• With the “CURSOR LEFT/RIGHT” keys, it is possible to:
– (De) activate the selected menu item.
– Change the value of the selected menu item.
– Activate the selected sub-menu.
How to exit SAM
Use one of the following methods:
• Press the “MENU” button on the RC-transmitter, or
• Switch the TV to STANDBY via the RC-transmitter, or
• Press the “EXIT” button on the DST.
5.2.3 Customer Service Mode (CSM)
Purpose
When a customer is having problems with his TV-set, he can
call his dealer. The service technician can than ask the
customer to activate the CSM, in order to identify the status of
the TV. Now, the service technician can judge the severity of
the complaint. In many cases, he can advise the customer how
to solve the problem, or he can decide if it is necessary to visit
the customer.
The CSM is a read only mode; therefore, modifications in this
mode are not possible.
How to activate CSM
Use the following method:
Key in the code “123654” via the standard RC transmitter.
Note: Activation of the CSM is only possible if there is no (user)
menu on the screen!
How to navigate
By means of the “CURSOR-DOWN/UP” knob on the RCtransmitter, you can navigate through the menus.
Contents of CSM
CUSTOMER SERVICE MENU 1
• Software Version (example: TX24EU_1.0_01234).
Displays the built-in software version. In case of field
problems related to software, software can be upgraded
(for more details, see paragraph Software downloading).
You will find details of the software versions in the chapter
“Software Survey” of the “Product Survey - Colour
Television” publication. This publication is generated four
times a year.
• Feature Box. The 12NC-number of the built-in Feature
Box software.
• Set Type. This information is very helpful for a help desk/
workshop as reference for further diagnosis. In this way, it
is not necessary for the customer to look at the rear of the
TV-set.
• Code 1. Gives the latest five errors of the error buffer. As
soon as the built-in diagnose software has detected an
error the buffer is adapted. The last occurred error is
displayed on the left most position. Each error code is
displayed as a 3-digit number. When less than 10 errors
occur, the rest of the buffer is empty (000). See also
paragraph Error Codes for a description.
• Code 2. Gives the first five errors of the error buffer. See
also paragraph Error Codes for a description.
• Volume. Gives the last status of the volume as set by the
customer. The value can vary from 0 (volume is minimum)
to 100 (volume is maximum). Volume values can be
changed via the volume key on the RC-transmitter.
• Brightness. Gives the last status of the brightness as set
by the customer. The value can vary from 0 (brightness is
minimum) to 100 (brightness is maximum). Brightness
values can be changed via the “CURSOR LEFT” and
“CURSOR RIGHT” keys on the RC-transmitter after
pressing the “MENU” button and selecting “PICTURE” and
“BRIGHTNESS”.
• Contrast. Gives the last status of the contrast as set by the
customer. The value can vary from 0 (contrast is minimum)
to 100 (contrast is maximum). Contrast values can be
changed via “CURSOR LEFT” and “CURSOR RIGHT”
keys on the RC-transmitter after pressing the “MENU”
button and selecting “PICTURE” and “CONTRAST”.
• Colour. Gives the last status of the colour saturation, as
set by the customer. The value can vary from 0 (colour is
minimum) to 100 (colour is maximum). Colour values can
be changed via “CURSOR LEFT” and “CURSOR RIGHT”
keys on the RC-transmitter after pressing the “MENU”
button and selecting “PICTURE” and “COLOUR”.
• Hue. Only relevant for NTSC-signals (e.g. some NTSCDVD-discs).
CUSTOMER SERVICE MENU 2
• Sharpness. Gives the sharpness value. The value can
vary from 0 (sharpness is minimum) to 7 (sharpness is
maximum). In case of bad antenna signals, a too high
value of the sharpness can result in a noisy picture.
Sharpness values can be changed via the “CURSOR
LEFT” and “CURSOR RIGHT” keys on the RC-transmitter
after pressing the “MENU” button and selecting “PICTURE”
and “SHARPNESS”.
• Headphone Volume. Gives the last status of the head
phone volume, as set by the customer. The value can vary
from 0 (volume is minimum) to 100 (volume is maximum).
Head phone volume values can be changed via the
“CURSOR LEFT” and “CURSOR RIGHT” keys on the RCtransmitter after pressing the “MENU” button and selecting
“SOUND” and “HEADPHONE VOLUME”.
• Dolby. Indicates whether the received transmitter
transmits Dolby sound (“ON”) or not (“OFF”). Attention: The
presence of Dolby can only be tested by the software on
the Dolby Signalling bit. If a Dolby transmission is received
without a Dolby Signalling bit, this indicator will show “OFF”
even though a Dolby transmission is received.
• Surround Mode. Indicates the by the customer selected
surround mode (or automatically chosen mode). Possible
values are “OFF”, “INCREDIBLE SURROUND” OR
“DOLBY VIRTUAL”. These settings can be influenced after
pressing the “MENU” button and selecting “SOUND” and
SURROUND MODE”. It can also have been selected
automatically by signalling bits (internal software).
• Tuner Frequency. Indicates the frequency the selected
transmitter is tuned to. The tuner frequency can be
changed via the “CURSOR LEFT” and “CURSOR RIGHT”
keys for fine tune after opening the installation menu and
selecting “INSTALL” and “MANUAL INSTALL”.
• Digital Option. Gives the selected digital mode,
“PROGRESSIVE SCAN”, “MOVIE PLUS” or “PIXEL
PLUS”. Change via “MENU”, “PICTURE”, “DIGITAL
OPTIONS”.
• Centre Trim. Not applicable for this set.
• TV System. Gives information about the video system of
the selected transmitter.
– BG: PAL BG signal received.
– DK: PAL DK signal received.
– I: PAL I signal received.
– L/La: SECAM L/La signals received.
– M: NTSC M signal received with video carrier on 38.9
MHz.
Page 15

Service Modes, Error Codes, and Fault Finding
EN 15FTP2.4E AA 5.
CUSTOMER SERVICE MENU 3
• Balance. Indicates the balance settings, between “-50”
and “+50”. Change via “MENU”, “SOUND”, and
“BALANCE”. Not applicable for Dolby Pro Logic sets.
• Centre Mode. Not applicable for this TV.
• DNR. Gives the selected DNR setting (Dynamic Noise
Reduction), “OFF”, “MINIMUM”, “MEDIUM”, or
“MAXIMUM”. Change via “MENU”, “PICTURE”, “DNR”
• Noise Figure. Gives the noise ratio for the selected
transmitter. This value can vary from 0 (good signal) to 127
(average signal) and to 255 (bad signal). For some
software versions, the noise figure will only be valid when
“Active Control” is set to “medium” or “maximum”.
• Source. Indicates which source is used and the video/
audio signal quality of the selected source.
Example: Tuner, Video/NICAM) Source: “TUNER”,
“EXT1”, “EXT2”, “EXT3”, “EXT4”, “SIDE”, “AV1”, “AV2”,
“AV3” or “AV4”. Video signal quality: “VIDEO”, “S-VIDEO”,
“RGB 1FH”, “YPBPR 1FH 480P”, “YPBPR 1FH 576P”,
“YPBPR 1FH 1080I”, “YPBPR 2FH 480P”, “YPBPR 2FH
576P”, “YPBPR 2FH 1080I”, “RGB 2FH 480P”, “RGB 2FH
576P” or “RGB 2FH 1080I”. Audio signal quality:
“STEREO”, “SPDIF 1”, “SPDIF 2”, or “SPDIF”.
• Audio System. Gives information about the audio system
of the selected transmitter: “ANALOGUE MONO”,
“ANALOGUE STEREO”, “PCM 2/0”, “DD 1/0”, “DD 2/0
LtRt”, “DD 2/0 L0R0”, “DD 2/1”, “DD 2/2”, “DD 3/0”, “DD 3/
1”, “DD 3/2”, “DD 1+1”, “MPEG 1/0”, “MPEG 2/0”, “MPEG
2/0 LtRt”, “MPEG 2/1”, “MPEG 2/2”, “MPEG 3/0”, “MPEG
3/1”, “MPEG 3/2”, “MPEG 1+1” or “MPEG 2+2”.
• Tuned Bit. Gives information about the tuning method of
the stored pre-set. If a channel is found via “automatic
installation”, you will see the value “YES”. When you
change this (automatically found) frequency via “fine tune”
adjustment (installation menu - manual installation), the
displayed value will change to “NO”. Therefore, when you
see the value “NO” in this line, it is an indication that the
received channel is a non-standard signal (e.g. of a VCR).
• Surround Speakers. Not applicable in this set.
• On Timer. Indicates if the “On Timer” is set “ON” or “OFF”
and if the timer is “ON” also displays start time, start day
and program number. Change via “MENU”, “TV”,
“FEATURES”, and “ON TIMER”.
• Preset Lock. Indicates if the selected preset has a child
lock: “LOCKED” or “UNLOCKED”. Change via “MENU”,
“TV”, “FEATURES”, “CHILD LOCK”, and “CUSTOM
LOCK”.
CUSTOMER SERVICE MENU 4
• Child Lock. Indicates the last status of the general child
lock: “UNLOCK”, “LOCK”, or “CUSTOM LOCK”. Change
via “MENU”, “TV”, “FEATURES”, “CHILD LOCK”, and
“LOCK”.
• Age Lock. Indicates the last status of the EPG rating for
child lock: “OFF”, “4 YEARS”, “6 YEARS”, “8 YEARS”, “10
YEARS”, “12 YEARS”, “14 YEARS” or “16 YEARS”. This is
only displayed if child lock is set to “CUSTOM LOCK”
• Lock After. Indicates at what time the child lock is set:
“OFF” or e.g. “18:45” (lock time). This is only displayed if
child lock is set to “CUSTOM LOCK”
• Category Lock. Indicates the last status of the EPG theme
child lock: “MOVIES”, “NEWS”, “SHOWS”, “SPORTS”,
“CHILDREN”, “MUSIC”, “CULTURE”, or “SERIES”. This is
only displayed if child lock is set to “CUSTOM LOCK”. It is
possible that more than one value is shown.
• Program Category. Indicates the theme of the selected
transmitter: “MOVIES”, “NEWS”, “SHOWS”, “SPORTS”,
“CHILDREN”, “MUSIC”, “CULTURE”, or “SERIES”.
• TV Ratings Lock. Only applicable for US.
• Movie Ratings Lock. Only applicable for US.
• V-Chip TV Status. Only applicable for US.
CUSTOMER SERVICE MENU 5
• V-Chip Movie Status. Only applicable for US.
• Options 1. Gives the option codes of option group 1 as set
in SAM (Service Alignment Mode).
• Options 2. Gives the option codes of option group 2 as set
in SAM (Service Alignment Mode).
• AVL. Indicates the last status of AVL (Automatic Volume
Level): “ON” or “OFF”. Change via “MENU”, “TV”,
“SOUND”, “AVL”
• Delta Volume. Indicates the last status of the delta volume
for the selected preset as set by the customer: from “-12”
to “+12”. Change via “MENU”, “TV”, “SOUND”, “DELTA
VOLUME”.
• Front Spkr Dist. Not applicable for this TV.
• Front Spkr Dist. Not applicable for this TV.
How to exit CSM
Use one of the following methods:
• After you press a key on the RC-transmitter (with exception
of the “CHANNEL”, “VOLUME” and digit (0-9) keys), or
• After you switch the TV-set “OFF” with the mains switch.
Note: When you de-activate CSM, it is possible (depending on
the software version) that the size of the picture changes. This
can be solved by pushing “P+” and then “P-”.
5.3 Problems and Solving Tips (related to CSM)
Note: Below described problems are all related to the TV
settings (visible in the CSM menu). The procedures to change
the value (or status) of the different settings are described
above. New value(s) are automatically stored.
5.3.1 Picture Problems
Snowy/noisy picture
1. Check in CSM line NOISE FIGURE. In case the value is
"127" or higher, and the value is also high on other
programs, check the aerial cable/aerial system. For some
software versions, the noise figure will only be valid when
“Active Control” is set to “medium” or “maximum”.
2. Check in CSM lines SHARPNESS and NOISE FIGURE. In
case the value of line SHARPNESS is "3" or "4" and the
value of line NOISE FIGURE is high ("127" or higher),
decrease the "Sharpness” value.
Picture too dark
1. Press “Menu”, “TV”, “Picture”, “Smart Picture”. In case the
picture improves, increase the “Brightness” or the
“Contrast” value. The new value(s) are automatically
stored (in “personal” pre-set) for all TV channels.
2. Check in CSM line BRIGHTNESS and CONTRAST. If the
value of these lines is low (< "10"), increase the
“Brightness” or the “Contrast” value via the user menu.
Picture too bright
1. Press “Menu”, “TV”, “Picture”, “Smart Picture”. In case the
picture improves, decrease the “Brightness” or the
“Contrast” value. The new value(s) are automatically
stored (in “personal” pre-set) for all TV channels.
2. Check in CSM lines BRIGHTNESS and CONTRAST. If the
value of these line is high (> 50), decrease the “Brightness”
value or increase the “Contrast” value via the user menu.
White line around picture elements and text
1. Press “Menu”, “TV”, “Picture”, “Smart Picture”. In case the
picture improves, decrease the “Sharpness” value. The
new value is automatically stored (in “personal” pre-set) for
all TV channels.
2. Check in CSM line “Sharpness”. If the value is high,
decrease it. The new value is automatically stored for all
TV channels.
Page 16

EN 16 FTP2.4E AA5.
Service Modes, Error Codes, and Fault Finding
No picture
Check in CSM line TUNED BIT. In case the value is “No”, install
the required program again. Open the installation menu and
perform manual installation.
No picture or unstable picture
A scrambled or decoded signal is received.
Black and white picture
Check in CSM line COLOUR. In case the value is low (< "10"),
increase the “Colour” value via the user menu. The new value
is automatically stored for all TV channels.
No colours/colour lines around picture elements or colours not correct or unstable picture
1. Check in CSM line TV SYSTEM. If a “strange” system pops
up, something has gone wrong during installation. Reinstall the channel.
2. If in CSM line TV SYSTEM is “L”, then the installed system
for this pre-set is “France” (SECAM standard). if the
country requires a PAL standard, “West Europe” is
required. Install the required program again: open the
installation menu and perform manual installation. Select
system “West Europe”.
Menu text not sharp enough
1. Press “MENU”, “TV”, “PICTURE”, “SMART PICTURE”. In
case picture improves, decrease the contrast value. The
new value(s) are automatically stored for all TV channels.
2. Check line “Contrast”. If the value is high, decrease the
contrast value.
5.3.2 Sound Problems
No sound from left and right speaker
Check line 6 “Volume”. The value is low. Increase the value of
“Volume”. The new value(s) are automatically stored (in
“personal” pre-set) for all TV channels.
The ComPair fault finding program is able to determine the
problem of the defective television. ComPair can gather
diagnostic information in two ways:
• Automatic (by communication with the television): ComPair
can automatically read out the contents of the entire error
buffer. Diagnosis is done on I
2
the I
C bus of the television. ComPair can send and
receive I
2
C commands to the micro controller of the
television. In this way, it is possible for ComPair to
communicate (read and write) to devices on the I
2
C level. ComPair can access
2
C buses
of the TV-set.
• Manually (by asking questions to you): Automatic
diagnosis is only possible if the micro controller of the
television is working correctly and only to a certain extends.
When this is not the case, ComPair will guide you through
the fault finding tree by asking you questions (e.g. Does the
screen give a picture? Click on the correct answer: YES /
NO) and showing you examples (e.g. Measure test-point I7
and click on the correct oscillogram you see on the
oscilloscope). You can answer by clicking on a link (e.g.
text or a waveform picture) that will bring you to the next
step in the fault finding process.
By a combination of automatic diagnostics and an interactive
question / answer procedure, ComPair will enable you to find
most problems in a fast and effective way.
Beside fault finding, ComPair provides some additional
features like:
• Emulation of the Dealer Service Tool (DST), which is not
supported any more.
• If both ComPair and SearchMan (Electronic Service
Manual) are installed, all the schematics and the PWBs of
the TV are available by clicking on the appropriate
hyperlink.
Example: Measure the DC-voltage on capacitor C2568
(Schematic/Panel) at the Mono-carrier.
– Click on the “Panel” hyperlink to automatically show
the PWB with a highlighted capacitor C2568.
– Click on the “Schematic” hyperlink to automatically
show the position of the highlighted capacitor.
5.4 ComPair
5.4.1 Introduction
ComPair (Computer Aided Repair) is a service tool for Philips
Consumer Electronics products. ComPair is a further
development on the European DST (service remote control),
which allows faster and more accurate diagnostics. ComPair
has three big advantages:
• ComPair helps you to quickly get an understanding on how
to repair the chassis in a short time by guiding you
systematically through the repair procedures.
• ComPair allows very detailed diagnostics (on I
is therefore capable of accurately indicating problem areas.
You do not have to know anything about I
yourself because ComPair takes care of this.
• ComPair speeds up the repair time since it can
automatically communicate with the chassis (when the
microprocessor is working) and all repair information is
directly available. When ComPair is installed together with
the SearchMan electronic manual of the defective chassis,
schematics and PWBs are only a mouse click away.
5.4.2 Specifications
ComPair consists of a Windows based fault finding program
and an interface box between PC and the (defective) product.
The ComPair interface box is connected to the PC via a serial
or RS232 cable.
For this chassis, the ComPair interface box and the TV
communicate via a bi-directional service cable via the service
connector.
2
C level) and
2
C commands
5.4.3 Stepwise Start-up
Under normal circumstances, a fault in the power supply, or an
error during start-up, will switch the television to protection
mode. ComPair can take over the initialisation of the television.
In this way, it is possible to distinguish which part of the startup routine (hence which circuitry) is causing the problem.
Take notice that the transition between two steps can take
some time, so give the TV some time to reach a stable state.
During the transition time, the LED can blink strangely.
Stepwise start-up explanation
This is realised via ComPair and is very helpful when a
protection is activated (see also chapter “Protections”). The
following diagram shows the start-up procedure of the TV.
Every step of the stepwise start-up (also called trapped startup) in the diagram corresponds with the number of times the
LED blinks.
Page 17

Service Modes, Error Codes, and Fault Finding
EN 17FTP2.4E AA 5.
start time extraction
start P50 recording
start EPG loading
Standby bit = off
Ambient light ON
Trapped Startup 1
Trapped Startup 2
Start up LCD
opt 3,4,5,6
Mains cord IN
Stand-by
Put Stand-by line LOW
CPU GO becomes HIGH
Set STBYEN,VCCON,PFCON = 1
Only FHP (opt 2, 8)
Keep sound amplifiers muted with
sound enable = high
+5V and +8V is switched on
+8V and +5V get their nominal level,
detected by the OTC
activate protection algorithms for +8V and +5V and
I²C (start I²C protection the moment the component
Initialize HIP: IF, source selection, 2fh input, video
Switch on the syncoutput: set_syncout_tristate= off
is initialised).
Read rest of NVM information
processing
Initialize tuner
Initialize 3D Combfilter
or Initialize Columbus
Initialize PICNIC + screen info
Initialize rest of PIP/DW module
Start TXT acquisition
and time extraction
Reset Audio = low
and Initialize MSP
Initialize EBILD
Screen type
Initialize PDP FHP
opt 2,8
OUT
OTC gets supply voltage
OTC resets, Initialise IO pins
Reset Audio=high
Read NVM identification
enable watchdog
Figure 5-3 Stepwise start-up
OFF
Stand-by bit = OFF
Initialize PDP SDI
opt 0,1,7
400msec>t>200msec
Tact switch
E_14620_048.eps
170504
Initialize PDP SDI
PDP ON
yes
Ebild: POWER OFF
Trapped Startup 3
Semi stand by
START
Set Fixed settings
Ebild: POWER ON
Wait 200 msec
Power OK (POR OTC)?
Stby bit set?
no
Ebild/ Output blanking: OFF
PDP ON
Max 3.04 sec after 5V and 8V =OK
Stable LVDS
no
Time out 5 sec?
Goto protection
Trapped Startup 4
Figure 5-5 Stepwise start-up part 2: Initialise SDI (*)
Notes (*):
• When the TV is in stepwise mode and, due to stepping-up,
a protection is activated, the TV will really go into protection
(blinking LED). The TV will not leave the stepwise mode
however. If state X is the state where the TV went to
protection, stepwise start-up will return to state X-1. At
state (X-1) diagnostic measurements can be performed.
Also, in the short time the TV is in state X but not yet in
protection, you can also do some measurements.
• Stepwise start-up can NOT be used for Samsung displays
(SDI). The TV will not react in a proper way, due to other
timing specifications.
5.4.4 How To Connect
This is described in the chassis fault finding database in
ComPair.
TO
UART SERVICE
CONNECTOR
yes
I2C SERVICE
CONNECTOR
no
E_14660_003.eps
TO
150704
Semi stand by
Init
ialize PDP FHP
PDP ON
Trapped Startup 3
yes
START
Set Fixed settings
Set default settings
Stand by bit set?
no
PDP: PDP ON =1
Wait 200 msec
Power OK (POR OTC)?
yes
Wait 200 msec
Read CNDC
CNDC = 4 ?
yes
Ebild/ Power ON
Output blanking: OFF
PDP: ADEN = 1
PDP ON
no
Time out 5 sec?
no
no
Time out 5 sec?
Trapped Startup 4
Goto protection
Trapped Startup 4
yes
Figure 5-4 Stepwise start-up part 2: Initialise FHP
no
yes
E_14660_002.eps
150704
PC VCR I2CPower
9V DC
E_06532_021.eps
Figure 5-6 ComPair interface connection
5.4.5 How To Order
ComPair order codes (EU/AP/LATAM):
• Starter kit ComPair32/SearchMan32 software and
ComPair interface (excl. transformer): 3122 785 90450.
• ComPair interface (excl. transformer): 4822 727 21631.
• Starter kit ComPair32 software (registration version): 3122
785 60040.
• Starter kit SearchMan32 software: 3122 785 60050.
• ComPair32 CD (update): 3122 785 60070 (year 2002),
3122 785 60110 (year 2003 onwards).
• SearchMan32 CD (update): 3122 785 60080 (year 2002),
3122 785 60120 (year 2003), 3122 785 60130 (year 2004).
• ComPair firmware upgrade IC: 3122 785 90510.
• Transformer (non-UK): 4822 727 21632.
• Transformer UK: 4822 727 21633.
• ComPair interface cable: 3122 785 90004.
• ComPair interface extension cable: 3139 131 03791.
• ComPair UART interface cable: 3122 785 90630.
Note: If you encounter any problems, contact your local
support desk.
180804
Page 18

EN 18 FTP2.4E AA5.
Service Modes, Error Codes, and Fault Finding
5.5 Error Codes
5.5.1 Introduction
The error code buffer contains all detected errors since the last
time the buffer was erased. The buffer is written from left to
right, new errors are logged at the left side, and all other errors
shift one position to the right.
When an error has occurred, the error is added to the list of
errors, provided the list is not full or the error is a protection
error.
When an error occurs and the error buffer is full, then the new
error is not added, and the error buffer stays intact (history is
maintained), except when the error is a protection error.
To prevent that an occasional error stays in the list forever, the
error is removed from the list after 50+ operation hours.
When multiple errors occur (errors occurred within a short time
span), there is a high probability that there is some relation
between them.
5.5.2 How to read the Error Buffer
Use one of the following methods:
• On screen via the SAM (only if you have a picture).
Examples:
– 0 0 0 0 0: No errors detected
– 6 0 0 0 0: Error code 6 is the last and only detected
error
– 9 6 0 0 0: Error code 6 was first detected and error code
9 is the last detected error
• Via the blinking LED procedure (when you have no
picture). See next paragraph.
•Via ComPair.
5.5.3 How to clear the Error Buffer
Use one of the following methods:
• By activation of the “RESET ERROR BUFFER” command
in the SAM menu.
• With a normal RC, key in sequence “MUTE” followed by
“062599” and “OK”.
• When you transmit the commands “DIAGNOSE” - “99” “OK” with ComPair (or with a DST).
• If the content of the error buffer has not changed for 50+
hours, it resets automatically.
5.5.4 Error Codes
In case of non-intermittent faults, clear the error buffer before
you begin the repair. This to ensure that old error codes are no
longer present. Before clearing the buffer, write down the
content, as this history can give you significant information.
If possible, check the entire contents of the error buffer. In
some situations, an error code is only the result of another error
code and not the actual cause (e.g., a fault in the protection
detection circuitry can also lead to a protection).
There are various errors:
2
•I
C device errors.
2
•I
C bus errors.
• Protection errors.
• Errors not related to an I
2
C device, but of importance:
– FEM (Falconic with Embedded Memory) (Error 26):
at start-up, after initialisation of the PICNIC, the
presence of the FEM can be checked.
Table 5-3 Error Code Overview
Error Device Description Def. item Def. Module indication Diagr.
1 M24Cxx NVM, spontaneous blinking error 1 7011 - B5a
3 SAA4978 PICNIC 7713 Feature Box B3a
4 Supply 5 V 5V protection - +5V Supply B5a
5 Supply 8 V 8V protection - +8V Supply B5a
6Slow I
2
C bus blocked Spontaneous blinking error 6 - Slow I2C Blocked 8 TDA932x HIP High-end Input Processor 7323 Chroma IF IO B2
13 UV1318/... Tuner protection 1T01 Tuner B13a
14 MSPxxxx ITT sound processor 7A02 Audio module B6a
2
18 Fast I
C bus blocked Spontaneous blinking error 18 - Fast I2C Blocked 21 M62320 I/O Expander 7P56 Video Dual Screen B15b
26 SAA4998 FEM (Falconic with Embedded Memory) 7760 +3V (FBX) Supply B3b
27 T6TX5 Eagle 1C 7720 +3V (FBX) Supply B3c
32 M29W400xx Flash Ram (EPG) 7012 EPG Memory B5a
35 T6TU5 Columbus 7752 Video Control B3d
55 DC/DC converter One of the voltages is not ok + protection error - MSB 76 Audio supply Audio supply protection - - 118 AD9883A AD converter 7L01 HD B19a
121 EPLD EPLD error 7V01 Video control B19d
Note: If error 3 or error 55 appears, sometimes error 16 is also logged. Error 16 is a non existing error.
Note:
• Error codes 1, 6, or 18 are protection codes and in this
case, supplies of some circuits will be switched “off”. Also,
in protection, the LED will blink the number of times
equivalent to the most recent error code.
Page 19
Service Modes, Error Codes, and Fault Finding
EN 19FTP2.4E AA 5.
5.6 The Blinking LED Procedure
5.6.1 Introduction
Via this procedure, you can make the contents of the error
buffer visible via the front LED. This is especially useful for fault
finding, when there is no picture.
When the SDM is activated, the front LED will show (blink) the
contents of the error-buffer. Error-codes > 10 are shown as
follows:
– A long blink of 750 ms (which is an indication of the decimal
digit),
– A pause of 1.5 s,
– “n” short blinks (where “n” = 1 - 9),
– When all the error-codes are displayed, the sequence
finishes with a LED blink of 3 s,
– The sequence starts again.
Note: For error codes >100, the first two digits (hundred-andten) are considered as one digit (one long blink)
Example: Error 12 9 6 121 0.
After activation of the SDM, the front LED will show:
– 1 long blink of 750 ms (which is an indication of the decimal
digit) followed by a pause of 1.5 s,
– 2 short blinks followed by a pause of 3 s,
– 9 short blinks followed by a pause of 3 s,
– 6 short blinks followed by a pause of 3 s,
– 12 long blinks of 750 ms (which is an indication of “120”)
followed by a pause of 1.5 s,
– 1 short blink followed by a pause of 3 s,
– 1 long blink of 3 s to finish the sequence,
– The sequence starts again.
Note: If errors 1, 6, or 18 occur, the LED always gives the last
occurred error even if the TV is NOT in service mode.
5.6.2 How to Activate
Use one of the following methods:
• Activate the SDM (only via soldering pads marked “SDM”
on SSB, see figure “Service pads”). The blinking front LED
will show the entire contents of the error buffer (this works
in “normal operation” mode and in “protection” mode).
• Transmit the commands “MUTE” - “062500” - “OK” with a
normal RC. The complete error buffer is shown. Take
notice that it takes some seconds before the blinking LED
starts.
• Transmit the commands “MUTE” - “06250x” - “OK” with a
normal RC (where “x” is a number between 1 and 5). When
x= 1 the last detected error is shown, x= 2 the second last
error, etc.... Take notice that it takes some seconds before
the blinking LED starts.
• “DIAGNOSE X” with the DST (where “x” is a number
between 1 and 5). When x= 1 the last detected error is
shown, x= 2 the second last error, etc.... When x = 0 all
errors are shown.
5.7 Protections
Note: With Samsung PDP displays (SDI V4) boards it is
possible that for some errors the blinking LED procedure does
not start immediately (e.g. error 18). When the error occurs, the
TV goes to protection and it is possible that you have to wait 30
seconds before the blinking LED procedure starts.
5.7.1 Introduction
This chassis has only one microprocessor (OTC), which
remains active during Stand-by. This because power of the
microprocessor and the attached memory chip set is coming
from the 3V3 supply, which is derived from the 5V Stand-bycircuitry. Therefore, in both Power-on as in Stand-by mode, the
microprocessor is connected to this power supply.
If a fault situation is detected, an error code will be generated
and if necessary, the TV is put in protection mode. The
protection mode is indicated by the blinking of the front LED at
a frequency of 3 Hz (or by a coded blinking in special cases).
The content of the error buffer can be read via the service menu
(SAM), the blinking LED procedure or via DST/ComPair.
To get a quick diagnosis, this chassis has three service-modes
implemented:
• The Customer Service Mode (CSM).
• The Service Default Mode (SDM). Start-up of the TV in a
predefined way.
• The Service Alignment Mode (SAM). In this mode, items
of the TV can be adjusted via a menu.
You can activate both SDM and SAM modes via the “service
pads” on the SSB (see figure “Service pads”), via an RCtransmitter (DST or standard RC), or via ComPair. It is not
possible to activate the SAM in “stand-by”; the TV has to be in
“normal operation” mode.
The “Protection Diagram” shows the structure of the protection
system. See diagram below.
TUNER
FAST I2C BUS BLOCKED
SLOW I2C BUS BLOCKED
EPLD
+
FBX
+
3D COMB
DC_PROT (from audio)
+8V_CON
+5V_CON
DC/DC
PROTECTION
IRQ-DIGITAL (98)
+8V SENSE (105)
+5V SENSE (106)
I2C
Figure 5-7 Protection diagram
There are several types of protections:
2
•I
C related protections.
• OTC related protections (via polling on I/O pins or via
algorithms).
• Hardware protection
All protections are explained below.
5.7.2 I
2
C Related Protections
2
In normal operation, some registers of the I
are refreshed every 200 ms. During this sequence, the I
buses and the I
2
An I
C protection will take place if the SDA and SCL lines are
2
C ICs are checked.
C controlled ICs
short-circuited to ground, or to each other. An I
occur, if the power supply of the IC is missing.
DC/DC protection: When a 3V3 supply is short-circuited, the
DC/DC converter switches “off” and goes in protection. The
FBX, EPLD IC, and 3D comb IC have no supply voltage and
give no acknowledge. In this case, the TV should go into
protection. An error code is written in the NVM: DC/DC error.
FBX protection: the FBX protection is not available any more.
It is replaced by the DC/DC protection.
OTC
E_14650_032.eps
170604
2
C
2
C error will also
Page 20

EN 20 FTP2.4E AA5.
Service Modes, Error Codes, and Fault Finding
5.7.3 OTC Related Protections
If a protection is detected at an OTC input, the OTC will start to
scan all protection inputs every 200 ms for 5 times. If the
protection on one of the inputs is still active after 1 s, the
microprocessor will put the TV in the protection mode. Before
the scanning is started, a so-called “ESD refresh” is carried out.
This is done, because the interrupt on one of the inputs is
possibly caused either by a flash or by ESD. As a flash or ESD
can influence IC settings, the HIP, MSP, 3D Comb and wireless
module (not used in this set) are initialised again, to ensure the
normal picture and sound conditions of the TV.
8 V and 5 V protections: The microprocessor senses the
presence of the 8 V and 5 V (via the “+5V_CON” and
“+8V_CON” lines). If one (or both) of these voltages is (are) not
present, an error code is stored in the error buffer of the NVM,
and the TV is put in the protection mode.
Audio Supply protection: The OTC senses if the audio
module is in protection via IRQ-DIGITAL (pin 98 of OTC). If this
is the case, the OTC puts the TV in protection.
5.7.4 Hardware Protection
Short-circuiting the 3V3 supply from the DC/DC converter will
shut down the DC/DC converter. The absence of the 3V3
supply line is also sensed via I
2
C (see description Audio Supply
protection above), this is useful if there is something wrong in
the detection circuit of the DC/DC converter.
2. 25V_HOT_SW (from Preconditioner) present?
3. 17V on pin 15 of item 7001 present?
4. Vcego= “H” and LATCH= “H”?
5. Vrs present? (Vrs=Vs/67).
6. Remark: Vs_unswitched = 65V when switch 7050 is open.
Va Supply
1. Vs_unswitched present?
2. 30V on item 3133 present?
3. Vsa_control= “L” (Vsago= “H” and Vs_lowlim= “H”)
4. Vra present? (Vra=Va/48).
Vcc Supply
1. Vs_switched present?
2. Vccgo= “H”? (Vcego= “H”).
Vs (switched)
1. 95V present on cathode of item 6054?
2. POK= “H” and Vsa_control= “L”? (POK= “H” when Vs, Va,
Vcc, 12V, and 8V6 are above their lower limit)
5.8.2 Power Supply Unit (for Samsung - SDI - plasma displays)
This PSU is for Service a “black box”. When defective (this can
be traced via error-codes in the error buffer, or by strange
phenomena), a new panel must be ordered and after receipt,
the defective panel must be send for repair.
Audio DC Protection: This protection occurs when there is a
DC voltage on the speakers. In that case, the Main Supply is
switched “off”. The Stand-by Supply is still working. For the
Samsung SDI V4 displays, all internal supplies (except the
5V2), are switched “off” and the LED on the Samsung SDI V4
display (on PSU Alarm board) blinks 11 times., which means
there is an overvoltage protection.
Repair tip: If there is an audio DC protection (DC voltage on
your speakers), you will probably see error 18 blink. To be sure
this is an audio DC protection, disconnect the cable between
the SSB and the audio PWB and also the cable between the
Main Supply and the Audio PWB. If the TV starts up, it is very
likely that there is DC on the speakers. Check, and replace if
necessary, the audio amplifiers.
Note: It is also possible that you have an Audio DC Protection
because of an interruption in one or both speakers (the DC
voltage that is still on the circuit can not disappear through the
speakers).
5.8 Repair tips
5.8.1 Power Supply Unit (for Fujitsu - FHP - plasma displays)
Below a troubleshoot sequence for the FHP power supply is
given (so this is not valid for the SDI power supply, this is
explained further on).
Stand-by Supply
1. 400V present?
2. +9V_STDBY, +5V_STDBY, and 25V_HOT present?
Preconditioner
1. Relay 1450 and 1440 “on” = switch “on” and supply “on”
(LATCH= “H” and STANDBY= “L”).
2. 400V or rectified mains present on item 2616?
3. 40V present on item 2664?
4. 15V present on item 2662?
1
Figure 5-8 SDI PSU Alarm board
A simple troubleshoot method for the SDI PSU is given below.
When the TVis in protection check the LED on the PSU Alarm
board (see (1) in figure “SDI PSU Alarm board”). In normal
working mode, this LED is "on". However, if this LED is blinking,
the PSU is in protection. See table:
Nr. of blinks Fault Description Remark
1V
2 12V block
3 D5VL Display voltage
4 D3V3 Display voltage
5V
6V
7V
8V
9 Thermal protection
10 PFC_OK Display voltage driving signal
11 OVP Overvoltage protection OR DC-prot
12 Time_Over A control signal to the PSU is missing af-
13 V
block problem Display voltages
A
S
CC/VG
SET
E
SCAN
Display voltage
Display voltage
Display voltage
Display voltage
ter a certain time period
Display voltage
5.8.3 3V3 Supply (DC/DC converter on the SSB)
F_15460_079.eps
140405
LLC Supply
1. 25V_HOT (from Stand-by supply) present?
As mentioned above, the DC/DC converter is switched “off”
when something goes wrong (detection of a missing 3V3
supply at one of the devices supplied by the 3V3). Because of
Page 21
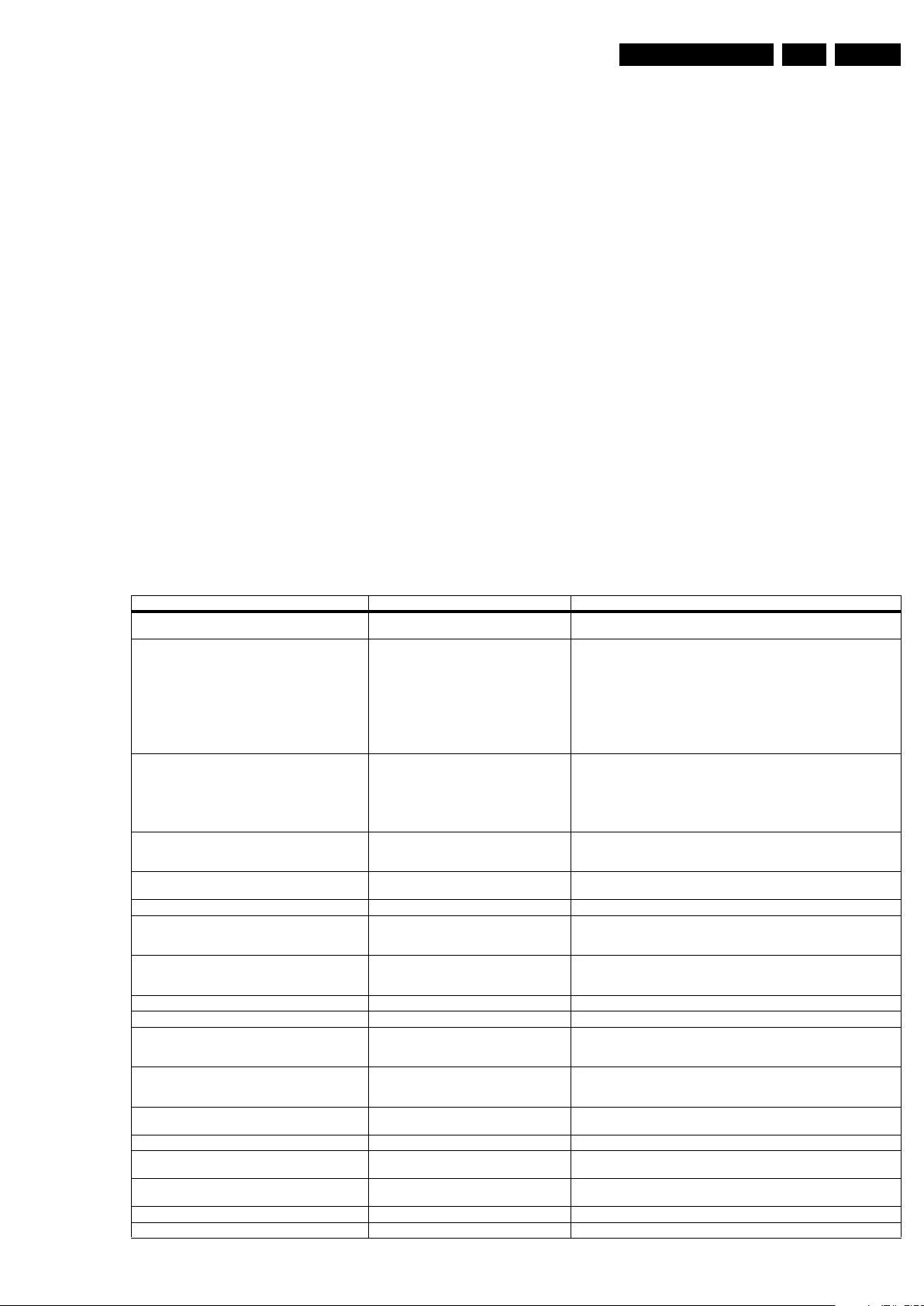
Service Modes, Error Codes, and Fault Finding
EN 21FTP2.4E AA 5.
this, the TV goes to protection (I2C protection). Error code “55”
is logged.
For further diagnoses, you need to overrule the I
put the TV in Service Default Mode by means of the solder
pads on the SSB (see figure “Service pads”).
The DC/DC converter is still not working because it is switched
“off” by the 3V3_FAULT line (schematic B12). Now you have
some possibilities:
1. First, measure the impedance over diode 6U06. In normal
conditions, you should measure approximately 120 ohm (if
possible, verify this with another set). If the impedance is
much too low, do not try to start up the converter as
mentioned below. Remind that if FET 7U03 is shortcircuited, this will also influence your measurement.
2. Desolder coils 5U05 and 5U06, connect an external 3V3
supply at capacitor 2U23 (current limitation to 500 mA) and
a second external 3V3 supply at capacitor 2U31 (current
limitation to 800 mA). The normal working current of the
3V3_SIM line is approximately 400 mA and the normal
working current for the 3V3_DCDCFBX line is
approximately 700 mA. Therefore, if one of the currents
exceeds their nominal value you can determine in which
circuit the overload is situated. If the TV would start up and
you have normal picture, there is probably no overload but
a problem in the detection circuits.
3. If you do not have two external power supplies, you can do
the following: Desolder coils 5U02, 5U03, and 5U04 (you
5.8.5 Repair tip table
2
C protection:
must desolder all three, otherwise the circuit could be
damaged), connect an external power supply of 3V3 at the
cathode of diode 6U06. Make sure to limit the current of this
external supply to approximately 1200 mA. If the supplied
current exceeds 1100 mA (approximately normal working
current) you can conclude that one of the devices supplied
by 3V3 is short-circuited.
4. Another possibility is to force the converter to start up by
short-circuiting (and keep short-circuited) resistor 3U25
(B12).
Caution: Be aware that this can damage the TV. Even if
you measure approximately 120 ohm over diode 6U06,
there can still be something wrong in the converter itself.
By short-circuiting resistor 3U25, the internal protection of
the converter is disabled.
5.8.4 Protections
Activating SDM via the “service pads” will overrule the
processor-controlled protections, but not the hardware
protections. This means, that the A/D-input protections (5 and
8 V) and the I
2
C “not-acknowledging” info of FBX + EPLD + 3D
Comb and of the tuner are overruled.
Caution: When doing this, the service technician must know
what he is doing, as it could lead to damaging the TV.
Table 5-4 Repair tips
Phenomenon Possible Cause Repair tip
“F” in right corner of the screen and set is not reacting on
remote control. The local keyboard is functioning.
No picture, LED blinking at 3 Hz. Set is in protection due to various causes.
No picture, LED blinking with code 6-6-6 or 18-18-18. No communication on slow I
No picture, LED blinking with code 1-1-1. No communication on NVM-I
No RC-reception. Blue LED does not echo RCcommands.
Picture is not synchronised. The sync is derived in the HIP. Check crystals in the HIP circuit on bad contacts.
Picture is distorted. Check video-path in Service Default Mode. Investigate whether there is an error code present in the error buffer. In case
Picture with horizontal stripes. Pixel Plus processing is malfunctioning Check functionality on circuitry (B3a, B3b, B3c and B3d) of PICNIC, FEM,
No NextView (EPG). IC7012 defective or not powered. Check circuitry around IC7012 on diagram “B5a”.
No Teletext. IC7007 defective or not powered. Check circuitry around IC7007 on diagram “B5a”.
Problems caused by EPG (Electronic Program Guide).
The TV set "hangs".
NexTView EPG is not functioning only Teletext guide. EPG version 2C3 is switched “off” during
Various symptoms, due to missing local supply voltage. An interrupted fuse, NFR-resistor or connection. When no symptom or error code leads you to a specific circuitry, use the supply
No sound at the speakers but sound at monitor out. Possible problem with the class D amplifier Check circuitry around IC7700 on diagram “SA3” (LCD) or “C” (PDP).
No sound at the speakers but sound at monitor out. Sound enable from OTC is HIGH, speakers are
No sound at the speakers not at monitor out, but sound
at SCART 1 output.
No sound from any output (except headphone) Reset audio is high or MSP is not properly reset Check pin 16 of MSP (diagram “B6a”) and circuitry around MSP.
No sound from the tuner but sound from any other input. Problem with the delay line (PDP sets only) Check circuitry on diagram “B6d”.
TV is in factory mode. Press MENU button on local keyboard for at least 3 seconds. Set will leave
For error codes see error-code list.
2
C- or fast I2C-bus. As processor cannot communicate with one of the 2 buses, the Stand-by-LED
2
C bus to the uP. As the uP cannot communicate with the NVM I2C bus, it spontaneously starts
uP circuitry or RC-receiver is defective. In case the TV does react on a local keyboard operation, you must check the
Problems with NexTView EPG broadcasts. To switch from EPG 2C3 to Teletext guide, press for 4 seconds, simultaneously
production.
muted
POR line is low, anti plop circuit mutes the sound Check pin 8 on connector 1739 on audio panel. Diagram “C” for PDP sets and
factory mode and function normally again.
You have no picture, so:
- Read the error buffer via ComPair (error buffer is accessible when set is in
protection, ComPair-file will guide you to this).
- Read the blinking LED information via standard remote command
<mute>06250x<ok>.
- Or you read the error code sequence via standard remote command
<mute>062500<ok>.
When you have found the error, check the circuitry related to the supply voltage
2
and I
C-communication or the circuitry that triggers the protection.
spontaneously starts blinking 6-6-6-etc. or 18-18-18-etc...
If in the error buffer somewhere is an error 6 or 18, these will have the highest
priority starting the mentioned blinking.
Measure, dependent of the error on the I
2
C-overview).
(use I
blinking 1-1-1. Note: when there is no access to the NVM, a lot of picture setting
can go wrong.
RC-receiver circuitry (diagram “J”).
2
there is one, check the I
Measure and check signal path Tuner-HIP-FBX-EPLD.
EAGLE, COLUMBUS and/or field memories. Tip: the whole Pixel Plus chipset
can be diagnosed via ComPair.
the MENU button on the TV and digit 0 on the remote. The option settings for
NexTView type and FlashRAM will not change.
To switch from Teletext guide to EPG 2C3, press for 4 seconds, simultaneously
the MENU button on the TV and digit 1 on the remote. The option settings for
NexTView type and Flashram will not change.
lines overview (see supply lines overview), for a quick scan of all supply lines.
Check pin 95 of OTC on diagram “B5a”.
diagram “SA3” for LCD sets
C-bus and/or supply lines (see overview supply lines).
2
C-bus, which device is loading the bus
Page 22

EN 22 FTP2.4E AA5.
5.9 Software Downloading
In this chassis, you can upgrade the main software via
ComPair without removing the back cover of the TV (it is
possible that early production sets don’t have a hole in the back
plate, in this case you have to remove the back plate). The
switch, which is needed for the software downloading
procedure, can be reached through a gap in the back cover or
the SSB shielding. The switch can be operated with a toothpick
or something like that. Make sure that you do not damage the
PWB with sharp objects. You can find more information on how
this procedure works in the ComPair file. It is possible that not
all sets are equipped with the hardware, needed to make
software upgrading possible. To speed up the programming
process the firmware of the ComPair interface can be
upgraded. See paragraph “How To Order” for the order
number.
Service Modes, Error Codes, and Fault Finding
Page 23
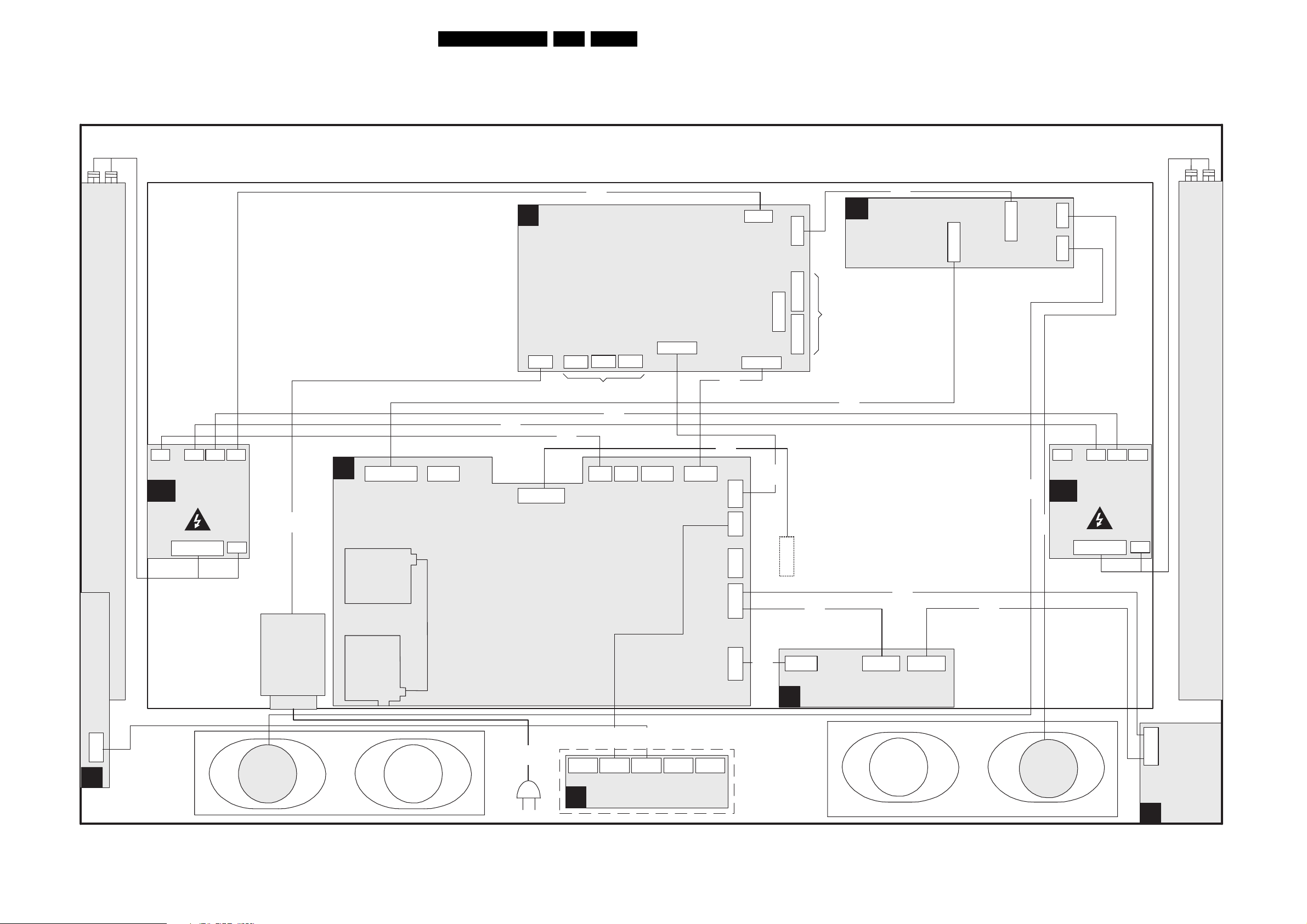
Block Diagrams, Testpoint Overviews, and Waveforms
6. Block Diagrams, Testpoint Overviews, and Waveforms
Wiring Diagram 42 Inch FHP Step
WIRING 42” FHP
EN 23FTP2.4E AA 6.
Ambient light lamps right
1M49
4P
AL
1M48
3P
Ambient
LIGHT 1
11P
1M11
1M08
4P
1M10
4P
3P
1M12
8199
B
1M52
2nd Tuner
(OPTIONAL)
1T02
1M48
9P N.C.
8548
A
2P
0308
1G50
31P
8310
PDP SUPPLY 42”
10P
1M03
1M17
0307
8349
20P
0311
TO DISPLAY
1M51
4P
9P 6P
0306
8508
1M49
3P 7P 11P
SSB
1M46
10P
12P
N.C.
11P
8346
8250
1M10
1M03
1M20
1M01
1M36
4P
10P
11P
1M46
1002
7P
7P
0352
0323
8303
(With 3th SCART)
DISPLAY
0342
7P
LVDS CONNECTOR
DISPLAY
8337
C
TO
8352
(Without 3th SCART)
8302
AUDIO AMPLIFIER
9P
1M52
8336
8336
(With 3th SCART)
7P
1M02
8736
3P
3P
1M49
AL
8735
1735
1736
4P
1M08
1M48
3P
AMBIENT
LIGHT 2
11P
1M11
4P
1M10
4P
3P
1M12
Ambient light lamps left
Top ControL
6P
0345
E
DELTA
MODULE
AC inlet
LS
RIGHT
Tu ne r
Splitter
1T01
8191
8345
8220
1M20 1M01
0350
N.C. 12P 6P N.C.
J
LED panel
0345 0244
N.C.
5P
1M07
8307
1M07
5P 11P 11P
H
3th SCART
1M37
1M36
LS
LEFT
11P
1M36
Side I/O
D
F_15460_077.eps
130405
Page 24
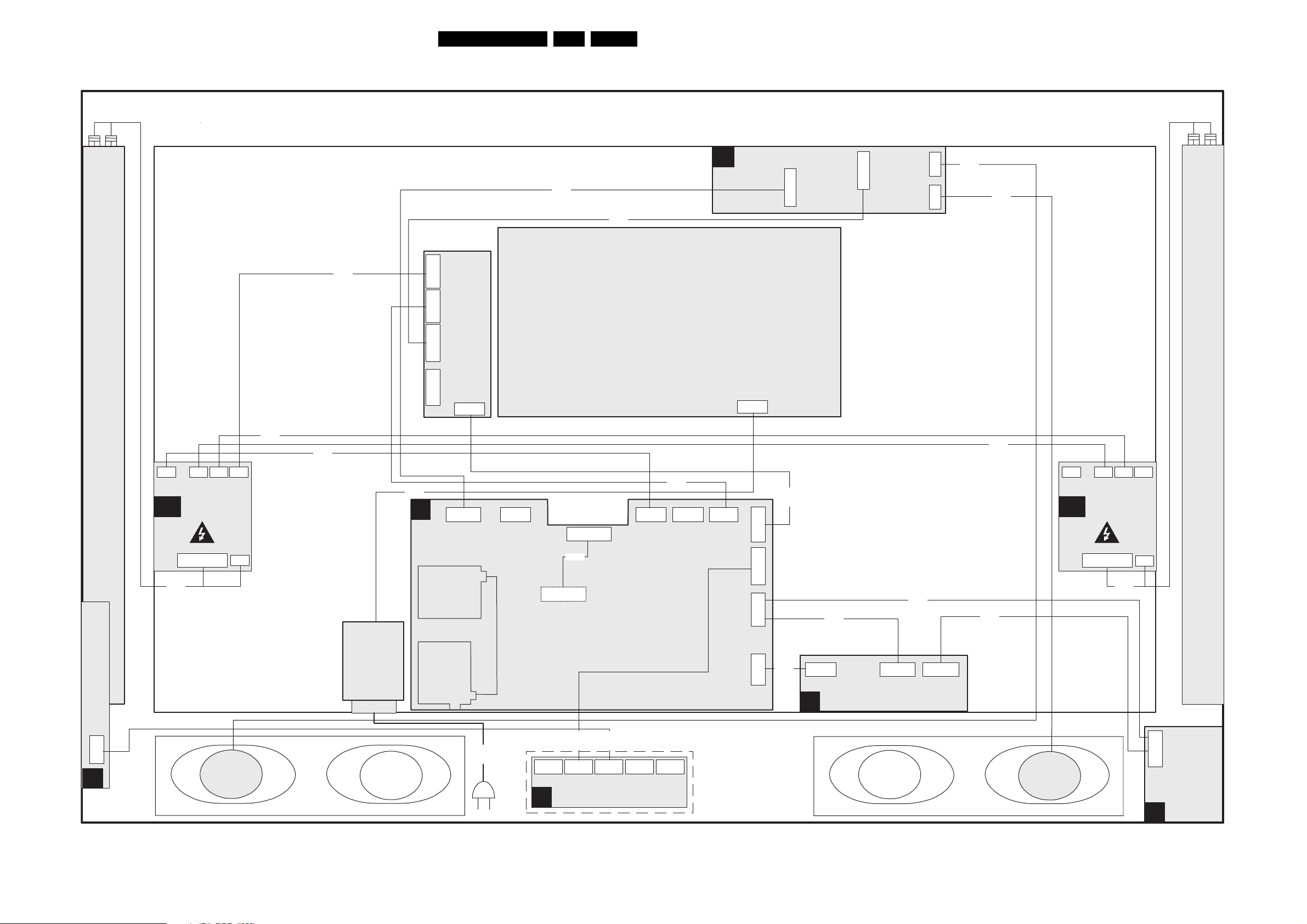
Block Diagrams, Testpoint Overviews, and Waveforms
Wiring Diagram 50 Inch SDI Step
WIRING 50” SDI
8352
EN 24FTP2.4E AA 6.
AUDIO AMPLIFIER
8302
C
1M52
9P
7P
1M02
3P
3P
1735
1736
8735
8736
(OPTIONAL)
Ambient light lamps right
1M49
4P
AL
8313
1M08
1M48
3P
AMBIENT
LIGHT 2
11P
1M11
4P
1M10
4P
3P
1M12
8508
8349
8310
CN9007
11P
CN9004
7P
CN9006
8199
B
2nd Tuner
(OPTIONAL)
1T02
4P
SUB
PSU
5P
10P
CN9005
1M52 1M48
9P N.C.
1G50
31P
8250
SSB
LVDS CONNECTOR
DISPLAY
PSU PDP
8346
1M51
1M17
4P 7P 11P
1M46
10P
12P
11P
2P3
1M03
1M20
1M36
8303
8337
(With 3th SCART)
(Without 3th SCART)
8336
8548
8336
(With 3th SCART)
1M49
4P
AL
1M08
1M48
3P
8736
AMBIENT
LIGHT 2
8735
11P
1M11
8311
4P
1M10
4P
3P
1M12
(OPTIONAL)
Ambient light lamps left
Top Control
6P
0345
E
LS
RIGHT
DELTA
MODULE
AC inlet
Tuner
splitter
1T01
8191
8345
8220
1M20 1M01
0350
N.C. 12P 6P N.C.
J
LED panel
0345 0244
N.C.
5P
1M07
8307
1M07
5P 11P 11P
H
3th SCART
1M37
1M36
LS
LEFT
11P
1M36
Side I/O
D
F_15460_078.eps
130405
Page 25
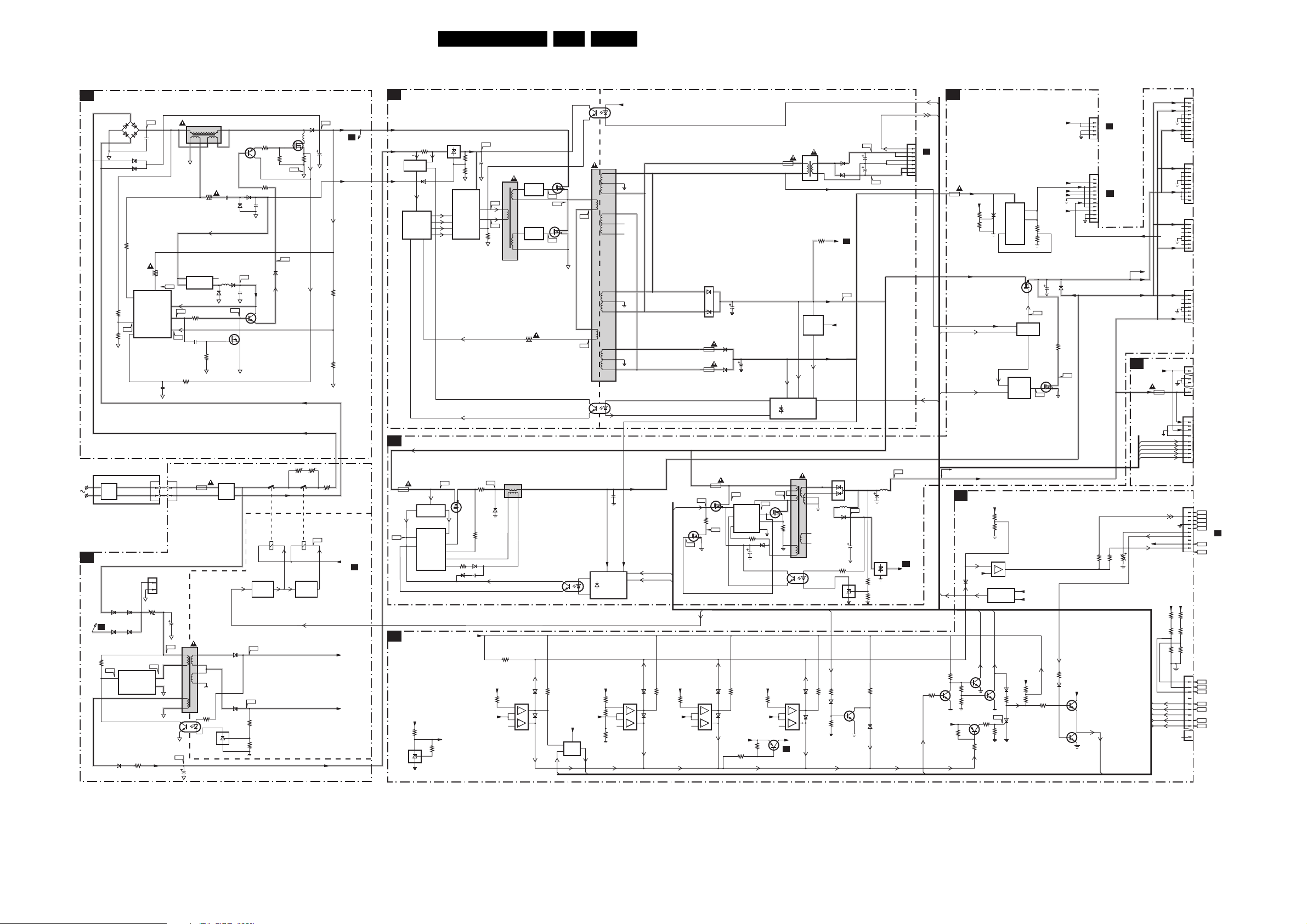
Block Diagrams, Testpoint Overviews, and Waveforms
Block Diagram Supply 42 Inch FHP
SUPPLY 42” FHP
PRECONDITIONER
A5
I622
VCC
VFB
2666
0308
F500
TCET1102
12
11
3
2
1
7501
F610
I629
2503
236
4
1
4
3
I504
5500
PRECONDITIONER
5600
1246
3663
7661
MC34063AD
8
DC TO DC
7
CONVERTOR
3641
2640
3666
1400
T6.3A
7
8
9
3501
1
7502
TS2431
2
2505
14
7608
2663
1
6665
5660
2
6663
I625
G
3640
5005
5401
5402
MAINS
FILTER
- STANDBY SUPPLY -
6504
RS1G
6505
SB34
1
2
3
6661
6660 2664
F609
2662
D
7640
BSN20
S
7460
ACTIVATING
F502
F503
3505
3503
3610
3608
BIAS
7641
MAINS FILTER UNIT
MAINS
FILTER
FILTERS STANDBY
A2
400V-HOT
A
A5
3507
I508
6600
3
GBU8J
F601
1
416
+
-
2603
2
6606
6605
3660
3668
7650
MC33368
16
LINE
7
ZC
CONTROL
3605
5
MULT
I618
CS
3651
6
2
1
1M05
1
2
6513
6512
BYG10
BYG10
3506
6511
BYG10
CONTROL
SOURCE
3508
DRAIN
+t
I510
5
7-8
6510
BYG10
RS1G
4
6503
7500
TNY256
ENABLE
GATE
SECOND
STANDBY
+25V-HOT +25V-HOT
12
1450
43
STW26NM50
3611
F608
6641
7610
D
G
S
3614
F604
AC3 100-230VAC2
AC5 100-230VAC1
3450
0
+t
+t
12
1460
43
7465
7470
ACTIVATING
DELAY
EN 25FTP2.4E AA 6.
LLC SUPPLY
A6
HOT
- LLC-CONVERTER -
F600
6611
400V-HOT
5612
3451
0
F411
A2
A
400V-HOT
2616
SW25V-HOT
3680
3671
3452
0
-t
HOT
COLD
+9V_STBY_SW
A3
SUPPLY_ON
+9V_STBY
+5V_STBY_SW
COLD
HOT
400V-HOT
- BIAS-SUPPLY -
25V-HOT
7090 :
7092
PROT
SW25V-HOT
7017
7018
SOFT
START
CURRENT
PROTECTION
AUX-SUPPLY
A7
70-90V
1110
TA5
1
I105
3
PROTECTIONS
A3
2V5 CIRCUIT
+5V_STBY_SW
7304
TL43IC2
3092
6095
15
+
7110
CONTROL
7112
TEA1507
VCC
CTRL
CONTROL
3304
1
3
2
VCC &
DRAIN
DRAIN
DRIVER
SENCE
DEMAG
3324
I101
8
6
5
2
4
2V5
7093
LM317T
7001
MC34067P
3
6
8
7
D
G
+5V_STBY_SW
CONTROL
S
7117
PSMN035
F001
BIAS
3095
3096
15
VCC
14
OA
12
OB
10
FI
3118
3117
61133113
21146111
2053
5001
F003
4
2
F004
3011
- VA-SUPPLY -
5121
I107
2
3
6120
VS PROTECTION
3308
VS_UNSW
70-90V
3300
7308 A+B
7
6
2V5
5
4
10
11
14
13
4
7007
7020
7008,
7021, 7012
3050
1
HIGH
SIDE
DRIVE
LOW
SIDE
DRIVE
1
2
6312
6313
STU16NB501
G
I038
F005
BZG03
G
I057
7120
TCET1102
3312
VSAGO
HOT COLD
+5V_STBY_SW
4
1
7005
D
S
7006
D
S
41
32
TCET1102
TCET1102
7003
I083
I083
7002
HOT COLD
2
3
5002
3
6
3
6
1
4
3
2
VA
VA
ADJ.
VS-SUPPLY
16
14
12
11
10
9
6044
STTH2003C
VS_UNSW
70-90V
VCC_GO
A3
A3
3
2
1083
F2,5A
1082
F2,5A
1200
BSN304
G
3202
A3
SUPPLY-ON
T2A
7200
I208
6021
BYU28
6045
BYU28
D
S
I214
1
3
4
2020
- VCC SUPPLY -
7212
TEA1507
VCC
CTRL
DEMAG
1
I213
7202
BSN20
D
G
S
I220
16
14
12
11
10
9
VA
2121
A3
+30V
VSA_CONTROL
VRA
VA PROTECTION VCC PROTECTION 12V PROTECTION
+9V_STBY
7375
7376
VSA-
CONTROL
LOGIC
VA
3311
7308 C+D
11
13
10
3313
2V5
9
14
8
3317
VSA CONTROL
A7
VCC
6321
6322
3320
2V5
7330 A+B
7
6
5
4
1
2
6333
6334
+5V_STBY_SW
3388
AUX-SUPPLY
A7
LATCH
A3
DC_PROT
GND_SND
F140
DC_PROT
A3
1002
TO 1002
7
6
C
5
PDP AUDIO
4
3
2
1
+30V
+12V_OVP
3345
3346
VCC
PROTECTIONS
+9V_STBY_SW
3360
3363
5
6
+2.5V
ref
6378
7326
7327
A7
VCC_GO
+12V SUPPLY
7260
L4973
6348
CONTROL
12
VS- SWITCHED
7050
PSMN035
VB
SWITCH
LOGIC
SEQUENCE
DISCHARGE
7366-2
7
DETECTION
CIRCUIT
A6
LATCH
1200
T2A
V.S._UNSW
70-90V
POK
A3
VSA-CONTROL
A3
VRS
A3
A3
A3
+8V6
POK
A7
7,8
3
2
D
S
G
SWITCH ON
LOGIC
VS
+5V_STBY_SW
+8V6
+8V6 UNDER
VOLTAGE PROT.
+5V_STBY_SW
3345
3346
I200
G
I202
+9V_STBY
VTUN
2021
D
S
VCEGO LATCH DC_PROT
OVERVOLTAGE
3353
+5V_STBY_SW
VCEGO
A2
3349
3350
7352
3354
7341
3341
3342
+5V_STBY_SW
7351
6347
3345
7348
3346
3347
3391
F343
7004
3344
3343
+12V
+8V6
6142
BYD33D
VA
3053
I201
7052
IRFR18N15D
STANDBY
STANDBY
3390
6366
+5V_STBY_SW
1M10
TO 1M10
1
2
AL
3
AMBIENT
4
LIGHT
0323
11
10
9
+12V
TO 1M46
8
7
B21
6
VCC
SSB
5
4
3
2
1
VCC
VS
VS
FITER STANDBY
A2
+3V3_STBY_SW
VCC
A3
A3
A3
A3
A3
- ERROR LOGGING -
t
3372
3355
3356
7391
7393
SUPPLY_ON
A2
2x
2x
A2
A3
A2
A3
E_14650_041.eps
- AUDIO SUPPLY -
VTUN
F293
VSND_POS
2292
6291
6292
A7
F016
6225
2
5229
F116
6230
2230
3228
7227
TL431CZ
3358
6364
3364
VSND_NEG
2294
F294
5225
2225
FAN CONTROL
7230
L4940
3224
3225
3361
7362
6362
6291
D458L20U
5290
1084
4
2
F1A
3
1
VB
3072
VS_UNSW
70-90V
VS
CONTROL
CONTROL
CIRCUIT
5220
1
3
2
4
5
7
3
+30V
VRS
FEEDBACK
3
14
13
12
1
11
18
16
124
7220
TCET1102
A6
DC_PROT
333833333321
6340
13
6341
14
2022
7010,7011
I236
7217
8
I216
PSMN070
DRAIN
D
G
6
DRIVE
S
5
SENCE
3218
GND
3214
6211
2210
+12V
3332
7330 C+D
11
10
2V5
9
8
7389
+12V_OVP
3389
A7
VA
VCC
VS
VCC
VS
VA
VCC
VAVA
VCC
1004
T2A
VRA
VRS
VCEGO
VSAGO
PFCGO
POR
STANDBY
+9V_STBY_SW
POWER_OK
VA V S
3396
3397
3316
PFCGO
VCEGO
VSAGO
0323
NC
NC
10
0333
NC
0342
NC
NC
NC
0352
NC
NC
NC
0306
0311
0319
10
3302
3303
3305
0307
VSK
VAK
VRS
VRA
11
13
15
20
NC
140405
1
2
3
4
TO
5
CN23
6
PDP
7
8
9
1
2
3
4
TO
5
CN33
6
PDP
7
8
9
1
2
3
TO
4
CN42
5
PDP
6
7
1
2
3
TO
4
CN52
5
PDP
6
7
1
3
TO
4
CN6
PDP
6
1
2
3
4
TO
5
CN11
6
PDP
7
8
9
1
F300
2
F301
3
F302
4
F304
5
TO 1M03
F305
6
B21
7
8
SSB
9
F309
F310
1
I900
2
I943
3
I901
5
7
I903
TO
9
CN7
I904
PDP
I905
I906
Page 26
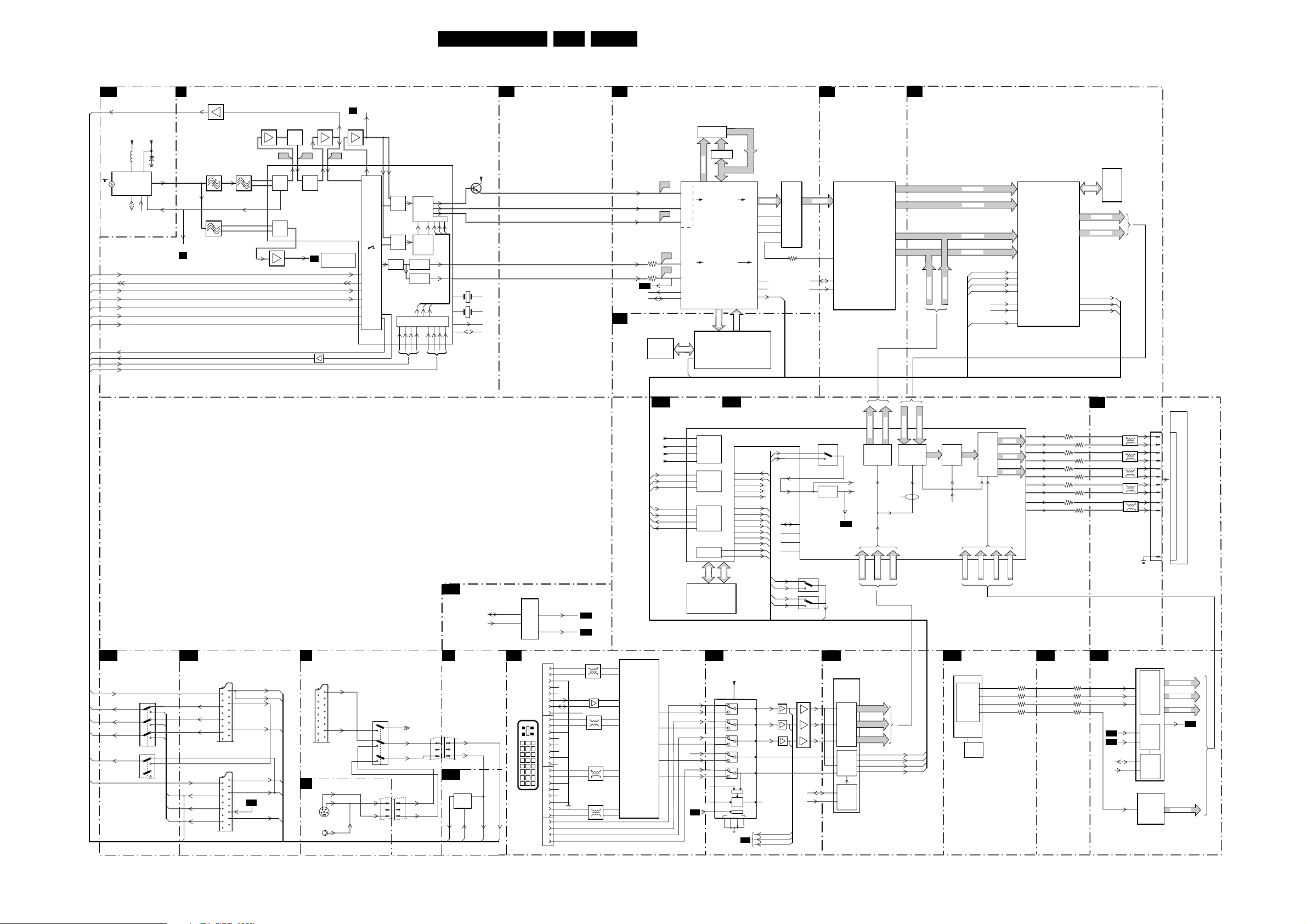
Block Diagrams, Testpoint Overviews, and Waveforms
Block Diagram Video
VIDEO
MAIN TUNER
B13A
B14b
B14b
B14b
B15a
B14b
B14b
B14a
B14a
N.C.
B14b
B14c
B14g
CVBS-TER-OUT
+5V
1T01
UV1318ST
MAIN TUNER
CVBS-SC1_AV1-IN
SEL-SVHS-RR_STATUS2
CVBS-AV3-IN
Y-CVBS-SC2_AV2-IN
C-SC2_SVHS-IN
Y-CVBS-FRONT-IN
C-FRONT-IN
CVBS-SC2-MON-OUT
R/G/B-SC1-Y/U/V-IN
SC2-FBL-IN
SC2-R_C-IN_AV2
SC2-G-IN
SC2-B-IN_C-OUT
5T25
7,3
5
S-SDA-PIP
PIP-OUT
+33V
9
4
S-SCL-PIP
6TO8
11
1
AGC
IF, I/O VIDEOPROCESSING
B2
MONITOR
7402
5403
IF-TER
40,4
SAW FILTER
AUDIO
1409-A
AGC
B5A
SAW FILTER
VIDEO
1410
1408
TUNER AGC
VIF1
VIF2
SIF2
SIF1
7411
EF
I6
7323
TDA9321H
2
PLL
3
DEM
62
QSS
64
MIXER
63
AM
DEMO
SOUND-OUTPUT
7410
1407
7322
SOUND
FILTER
V1
10 12 13 14
GROUP
DELAY
COR.
QSS-AM
5
QSS-AM
B6A
EF
V2
HIP
SEE
BLOCK DIAGRAM
AUDIO
7415
EN 26FTP2.4E AA 6.
AUDIO
B6A
DEMODULATOR
CVBS-TXT
B5A
OTC
7320
EF
12
26 29
28
CY
Y
Y
PROC.
VIDEO
SWITCH
+
CONTROL
C
C
PROC.
SYNC
32
32 34
SEPAR.
R
SCART1
36 37 38 39
16
17
18
20
21
23
24
Y/U/V
SWITCH
UU
VY V
DECODER
PAL
NTSC
SECAM
H-SYNC
PROC.
V-SYNC
PROC.
UY
RGB/YUV
MATRIX
GB
41 42 43 40
Y
U
V
V
RGB
+8VP
7414
49
50
51
60
61
54
57
46
47
SCART2
Y50
U50
V50
HA50
VA50
1305
PAL
4.43MHz
1308
NTSC M
3.57MHz
SCL-F
SDA-F
B3A
B3D
HA50
VA50
PICNIC
Y-PIP+MAIN-OUT
U-PIP+MAIN-OUT
V-PIP+MAIN-OUT
3727
3728
B19d
COLUMBUS
7753
MSN56V16160F-7TS
SDRAM
64K
7711
PROM
M27C512
7713
SAA4978H
F162
23
3x
ADC
25
F164
26
F165
28
F166
29
VA
SCL-F
4
SDA-F
5
7752-1
T6TU5XB
COL_SD
Href-EXT
B3a
74HC573
LATCH
AD(0-7)
DIGITAL
SIGNAL PROCESSING
PICNIC
SYNC PROCESSING
BUS A
UVA / YA
COLUMBUS
I/O
7712
BUS B
UVB / YB
BUS C
DA (0-15)
CLI6
WEC
RSTW
1
2
30
CLK32FM1
SN-DA
SN-CL
Href-EXT
7714
MS81V04160A
FIELD
MEMORY
FM1
3724
B3c,d,B19d
SNDA
SNCL
CLK32
B3B
MF (1-17)
FALCONIC
7760
SAA4998H
FALCONIC
EMBEDDED
MEMORY
83
34
41
B3C
EAGLE
UVF (0-7)
YF (0-7)
B19b
B19d
B19d
B19d
B19d
YG (0-7)
UVG (0-7)
YF (0-7)
UVF (0-7)
CLK32I
FALREF
REFIN
Vref
SNDA
SNCL
HREF_EXT_E
7719
118
26
27
EAG_SD
MSM56V16160F
512KX16X2
Y-OUT (0-9)
U-VOUT (0-9)
CLK64
HD-E
VD-E
DRAM
B19b
B3a
B3a
7720
TBF24EF
EAGLE
163
46
47
32
33
24
35
7I55
BA7657F
R1-IN
1
R2-IN
7
G1-IN
3
G2-IN
9
B1-IN
5
B2-IN
VD1-IN
VD2-IN
HD1-IN
HD2-IN
HD-S-SIG-DET
2
C-V-IN
CTL
B19D
SD-DQ
I/O7
+5VIO
VCC
1
2
1
2
1
2
1
2
1
2
GROUND
468
VD-OTC
HD3-OTC
PWR-OK-PDP
LCD-PWR-ON
LAMP-ON
CLK32E
Vref
Href
RSTR
REF
FALREF
REFIN
SWITCH-1FH
SWITCH-2FH
20
DET
SYNC
SEPA
LOGIC
EPLD I/O
R-OUT
G-OUT
B-OUT
VD-OUT
HD-OUT
C-S-OUT
10
B2
B19a
B3c
B3a
B3a
B19d
B3c
B3c
B3c
B3c
B3c
B19b
B19b
B19b
CLK32P_EPLD
SWITCH-2FH
B19d
B19d
SWITCH-2FH
B19d
R-VGA
21
G-VGA
19
B-VGA
15
14
22
17
SC2-R_C-IN_AV2
SC2-G-IN
SC2-B-IN_C-OUT
CLK32E
7I56
7I57
7I58
CLK-2FH
CLK-64
CLK-VID
SDA-F3
SCL-F3
SN-CL
SN-DA
7154
TSH95
SCREEN
B20
INTERFACE
YF (0-7)
UVF (0-7)
CONVERTION
CLKP
1:2
CLK-OSD
B19C
7E03
7E04
CLK32I
B3c
U-AD (0-7)
B19A
7L01
AD9883AKST
48
54
43
30
49
31
A/D
COVERTER
SYNC
PROC.
+
CLOCK
GENERATOR
SERIAL
REGISTER
+
POWER
MAN.
2-9
70-77
12-19
66
64
65
67
B15a
H-2FH-AD-OUT
V-2FH-AD-OUT
SYNCDET
CLK-2FH
Y-2 F H
V-2F H
11
U-2FH
10
SDA-F3
SCL-F3
UV
UV-AD (0-7)
PATH
FOR
3FH
ONLY
Y-AD (0-7)
Y-OUT (0-9)
UV DEMUX
CONTRAST
SATURATION
BRIGHTNESS
EPLD
U-VOUT (0-9)
B19d
B19d
B19d
B19b
YUV
RGB
CLKP
B5A
R-OSD (0-5)
OSD
INSERTION
G-OSD (0-5)
to
OTC
7001
SAA5801H
OTC
77 R-TXT 2FHR-GFX
78 G-TXT 2FHG-GFX
DIPLAY
INTERFACE
79 B-TXT 2FHB-GFX
80 FB-TXT 2FHFB-GFX
SEE ALSO
BLOCK
DIAGRAM
CONTROL
R (0-7)
G (0-7)
B (0-7)
B-OSD (0-5)
BL-OSD (0-4)
3064-1
3064-2 3859
3064-3 3860
3064-4 3861
R7
R5
G6
G7
G5
B0
B5
PAR IT Y
B1
CLK-OUT
B3A
PICNIC
3V25
3V26
3V27
3V28
4V29
3V30
3V31
3V32
3V33
3V24
3858
TXLCD0-
TXLCD0+
TXLCD1-
TXLCD1+
TXLCD2-
TXLCD2+
TXLCD3-
TXLCD3+
TXCLKLCD-
TXCLKLCD+
11,14,17,20,23,26,27,28,29
EPLD OSD
B19C
B3a
B3a
BL-OSD
SDA-F3
SCL-F3
5Z01
5Z02
5Z03
5Z05
5Z04
R-OSD
G-OSD
B-OSD
HD3-OTC
VD-OTC
7E23
AD9883AKST
7E24
AD9283BRS-80
1G50
18
17
16
15
14
13
10
12
11
A/D
COVERTER
SYNC
PROC.
+
CLOCK
GENERATOR
SERIAL
REGISTER
+
POWER
MAN.
8-BIT
ADC
9
DISPLAY
R-OSD (0-5)
G-OSD (0-5)
B-OSD (0-5)
CLK-OSD
B19d
BL-OSD (0-5)
E_14650_019.eps
110405
EPLD CONTROL
B19B
7V01
EP1C12F256C8
+2V5-IO
+3V3-IO
+1V5-INT
+1V5-PLL
H-2FH-AD-OUT
V-2FH-AD-OUT
B19a
B19a
SYNCDET
B19a
B3a
VA
B3a
Href-EXT
B3a
HD_E
B3a
VD_E
PIP SWITCH
B15B
IO3 SWITCH
B14C
B2
CVBS-TER-OUT
R-SC1_V-IN
B2
G-SC1-IN_Y-IN
B2
B-SC1-IN_U-IN
B2
B2
FBL-SC1-IN
B2
15
14
4
B2
15
7I12
74HC4053
4
7I32
74HC4053
3
5
e
1
2
f
13
12
g
3
5
1
2
B14B
CVBS-SC2_MON-OUT
e
f
g
B2
B14B CONNECTIONS
SCART 1
21
19
15
SC1-R
11
SC1-G
7
SC1-B
SCART 2
21
19
C-SC2_SVHS-IN
15
SC2-G
11
SC2-B_C-OUT
7
CVBS-SC1_AV1-IN
20
IN-CVBS-SC1_AV1-SUB
16
SC1-FBL
8
SC1-STATUS
20
Y-CVBS-SC2_AV2-IN
16
SC2-FBL
B5A
P50
SEL-SVHS-RR_STATUS2
8
OTC
SCART3
H
SCART 3
21
CVBS-SC3-IN
20
19
B2
B15A
B2
B2
B14a
B2
D
SVHS
SIDE I/O
CVBS
15
11
7
251
16
8
34
STATUS-SC3-F
C
Y
3
5
1
2
13
12
C
7516
74HC4053
1M36
4
15
14
24Y
3
SEL_FRONT_SC3
FRONT-SC3-Y-CVBS
FRONT-SC3-Y-C
1M36
FRONT-Y-CVBS
2
3
FRONT-C
4
1M36
2
3
4
B21
1M36
2
3
4
B14A
7I35
7I36
7I37
SC2-B_C-OUT
B14b,c
CONNECT
FRONT-Y-CVBS-IN
FRONT-C-IN
MMC
CONTROL
SC2-FBL
B14b
C-FRONT-IN
B2
7P56
M62320
SWITCH-MAIN
I/O
3
SDA-S
SCL-S
B14F
Y-CVBS-FRONT-IN
B2
10
EXP
2
SWITCH-SUB
12
DIGITAL INPUT
1D01
1
2
3
4
5
6
DVI-I INPUT
CONNECTOR
7
8
9
10
C5
11
C3 C4
C1 C2
12
13
24
14
15
16
17
18
19
18
916
17
20
21
22
23
24
C1
C2
C3
C4
SCL_DVI
SDA_DVI
AV6-V
B14C
B14C
7I18
1I59
SII907
RX2-
49
RX2+
48
7I51
7I52
SCLS
1I56
SDAS
RX1-
52
RX1+
51
RECEIVER
1I57
3
RX0-
2
RX0+
1I53
RXC+
5
RXC-
6
DVI
IOR
IOG
IOB
VSYNC
HSYNC
23
26
31
19
18 HDVI
7V03
MSM56V16160F
AV6-R
R-DV1
AV6-G
G-DVI
AV6-B
B-DVI
AV6-V
V-DVI
AV6-H
SWITCH-MAIN
B15B
SUPPLY
STANDARD
DEFLECTION
SYNC
CONTROL
INPUT
CONTROL
SD-A
DRAM
512KX16X2
B14G
11
12
13
24
23
18
16
Page 27

Block Diagrams, Testpoint Overviews, and Waveforms
Block Diagram Audio & Control
AUDIO
B2
7323
TDA9321H
HIP
MAIN
B14B
EXT 1
AUDIO
L/R IN
EXT 2
AUDIO
L/R IN
H
EXT 3
AUDIO
L/R IN
D
FRONT
AUDIO
L/R IN
B14C
DVI
AUDIO
L/R IN
B14B
CENTER
IN
IF
SCART 1
6
3
2
1
SCART 2
6
3
2
1
SCART 3
SCART 3
6
1
3
2
SIDE I/O
1002
1I07
1I06
SEE ALSO
BLOCK DIAGRAM
VIDEO
3380
5
I/O
AL-SC1-IN
AR-SC1-IN
AL-SC2-IN
AR-SC2-IN
SNDL-SC3-IN
SNDR-SC3-IN
FRONT-L
FRONT-R
SNR-DVI-IN
SND-DVI-IN
SND-CENTER-IN
SOUND-OUTPUT
3
5
1
2
13
12
SEL_FRONT_SC3
7515
74HC4053
+8VP
7410
QSS_AM
B21
SNDR-IN
4
15
SNDL-IN
14
B6a
B6a
B6a
B14D
9I32
9I33
9I34
9I35
9I31
9I30
AUDIO I/O
SNDL-MAIN-IN
SNDR-MAIN-IN
SNDLSC2-IN
SNDR-SC2-IN
SNDR-SEC-IN
SNDL-SEC-IN
EN 27FTP2.4E AA 6.
1M36
9ID0
10
11
11
7
7
B21
B14B
DH
1M36
10
11
7
SIDE I/O
CONNECTIONS
IRQ-AUDIOSUPPLY
B5A
I/O
1I06
SUBW
SCART 1
6
3
1
SCART 2
6
3
1
1I05
HEADPHONE-OUT
L
R
DETECT
SUBW
OUT
EXT 1
AUDIO
L/R OUT
EXT 2
AUDIO
L/R OUT
AUDIO
L/R OUT
AUDIO-R
AUDIO-L
+5V2-STBY
B5A
B5A
SA
GND-AUD
7010
SOUND-ENABLE
POR
N.C.
AUDIO-SW
7Y01
AUDIO I/O
B6A
B65
SND-CENTRE-IN
B14b
SNDR-MAIN-IN
B14d
SNDL-MAIN-IN
B14d
B6a
B6a
B6a
B6a
B6a
B6a
SNDR-SC2-IN
B14d
SNDLSC2-IN
B14d
B14c
SNDR-DVI-IN
SNDL-DVI-IN
B14c
SNDR-SEC-IN
B14d
B14d
SNDL-SEC-IN
B6D
AUDI O
DELAY
50
47
45
44
42
41
39
38
36
35
7A02
MSP3411G
IF1
IF2
N.C.
I2S-MSP-OUT
I2S-MSP-IN
I2S-MSP-CLK
SC4
SC1
SC3
I2S-DPL-OUT
I2S-DPL-CLK
I2S-DPL-WS
ADC
MONO-IN
12
15
14
SELECT
MODULATOR
SCART
DSP
INPUT
AUDI O
DELAY
7A03
B68
B66
DE-
PRESCALE
PRE-PROCESSING
ADC
(Optional)
PRESCALE
SOURCE
SELECT
INTERFACE
HPN-L
HPN-R
LOUD-
SPEAKER
SOUND
PROCESSING
HEADPHONE/
SURROUND
SOUND
PROCESSING
DAC
DAC
I2S
7A07
MC33178D
3
1
5
7
DAC
DAC
SCART
OUTPUT
SELECT
I2S-MSP-OUT
5
I2S-MSP-IN
6
I2S-MSP-CLK
3
HEADPHONE-L
HEADPHONE-R
LOUD
DACM-SUB
FRONT-DECT
SC
B21
20
5
21
3
B67
23
3
17
HPN-R
18
HPN-L
18
MSP-CENTER
18
MSP-SURR
DACM-SUB
23
SNDR-SC1-OUT-DC
28
SNDL-SC1-OUT-DC
29
SNDR-MON-OUT
25
SNDL-MON-OUT
26
61
CONNECTIONS
FRONT-DETECT
B5A
LM833D
7A00-A
7
1
1
1M36
AUDIO-R
AUDIO-L
B69
AUDIO-SW
N.C.
N.C.
5
7A00
LM833D
7
AUDIO_SW
B6C
B14D
2IA2
SNDR-SC1-OUT
SNDL-SC1-OUT
2I99
7I20
2
SNDR-SC2-OUT
15
1
5
SNDL-SC2-OUT
4
3
9.10
REG-SW
7I22-B
SNDR-MON-OUT
SNDL-MON-OUT
SCART 3
1M37
FRONT-L
10
10
11
7
FRONT-R
11
7
1M52
1M52
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
AUDIO AMPLIFIER
C
AUDIO-L
1
2
AUDIO-R
3
4
5
5701
6
7
8
9
2701
+
5
7
-
6
12
3
+
-
SOUND-ENABLE
POR
PROT-AUDIO-SUPPLY
7701
TDA8925ST
1
SW1
17
SW2
4
EN1
7706 : 7713
CLASS-D
AMPLIFIER
SOUND
ENABLE
AUDIO
SUPPLY
PROT, CIRCUIT
+19-16V
5
OUT1
OUT2
810
-19-16V
DCPROT
DC
13
7
12
5700
3704
DC
5702
DC
3716
3742
6704
3752
6705
+19-16V
-19-16V
DCPROT
1736
L
1
3
1735
1
3
15W/
8Ω
R
15W/
8Ω
1M06
7
6
5
TO 1002
4
A6
3
SUPPLY
2
1
CONTROL
SIDE I/O
D
HEADPHONE-OUT
TOP CONTROL
E
LED + SWITCH
J
J
6060
6051
1040
SENSOR
7070
LM358P
6070
LIGHT SENSOR
BLUE
RED
IR
CONNECTIONS
B21
1M36
FRONT
DETECT
BLACKLIGHT-TC
6x
KEYBOARD
ON / OFF
CHANNEL+
CHANNEL-
VOLUME+
VOLUME-
MENU
7030
7031
7032
BLACKLIGHT-TC
CONTROL
KEYBOARD
6061
LED1
RC-IN
LIGHT-SENSOR
+8V
72
+5V2-STBY
SDA-S
LED2
SCL-S
1M36
7
7
0345
4
2
0345
4
2
1M20
1M20
1
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
KEYBOARD
CON-SND
2
LED1
3
RC
4
LIGHT_SENSOR
5
5Y11
6
7
8
9
LED2
+5V2-STBY
9Y06
10
SCL-SF
11
SDA-SF
12
B14E
9ID0
+8V
OTC FLASH
B5A B3A
CVBS-TXT
SEE ALSO
BLOCK DIAGRAM
VIDEO
+5V2-CON
7005
LF33AB
IN
1
3073-2
B2
B3A
B3A
N.C.
OUT
+3V3
INTOTC
B14B
B14B
B14B
ON-OFFOLED
B4
N.C.
N.C.
N.C.
HD3-EPLD
VD-EPLD
CVBS-Y-RECORD-IN
7002 :
7004
RESET
RESET
FLASH
RAM
STATUS_SC3
STATUS_SC4
CON-SND
P50
7008
+3V3
LED2
+3V3
RC
LIGHTSENSOR
7015
7016
7013, 7014
7001
SAA5801H
83
OTC
84
7
114
74
RESET
RP
109
108
99POR-FLASH
98IRQ-DIGITAL
93HD@HOME
96IRQ-FTV
118
7009
97
120
7022
115
7022
115
100
107KEYBOARD
110
R-TXT
775
G-TXT
78
B-TXT
79
FBL-TXT
80
88 SDA-F
87 SCL-F
86 SDA-S
85 SCL-S
90 TXD
N.C.
89
RXD
3099-3 3081
119
3074-4 3097
96
104 STANDBY
95 SOUND-ENABLE
94 RESET AUDIO
117
116
103
SDA
91
92
SCL
ADDRESS
DATA
CONTROL
16
17
5
6
7011
MC24C32
EEPROM
1001
6Mhz
4kByte
2060
NVM.
SAM
SDM
2061
SEL_IN_2
SEL_IN_1
PWW-BLACKLIGHT
7007
MSM51V18165F
DRAM
(TXT)
16Mbit
3858
3859
3860
3861
SEE ALSO
IIC DIAGRAM
6005
SA
B6A
N.C.
B5B
7006
LH28F320BJE
FLASH-RAM
9006
9018
PROGRAM
SET SW
32Mbit
9005
A-PLOP
7516
74HC4053
B19C
SEE ALSO
BLOCK DIAGRAM
VIDEO
9017
B14B
7012
M29W400BT
EPG-
FLASH-RAM
4Mbit
R-OSD
G-OSD
B-OSD
BL-OSD
SA
H
B5C
RP
AMBI LIGHT
AL
1M49
1
TO 1M49
2
B5E
VIPER
3
See also
block diagram
4
I2C
1M48
1
TO 2nd
2
AMBI LIGHT
PWB
3
(Optional)
OTC-F LASH
(OCTAL BUS TRANSCEIVER)
7018
74LVC245APW
7019
74LVC245APW
AUXILIARY
FLASH
PROGRAM
CIRCUIT
FOR
FLASH RAM
1404
SSSS811
SWITCH FOR
SOFTWARE
DOWNLOAD
7001
P87LPC760
7
SCL
CONTROLLER
6
SDA
8
RXD
MICRO
1M12
1M11
RED
11
BLUE
6
GREEN
1
1
7018
7009
14
7019
7010
12
7020
7011
13
5014
7015
5015
7016
5016
7017
2
3
F_15460_080.eps
140405
Page 28
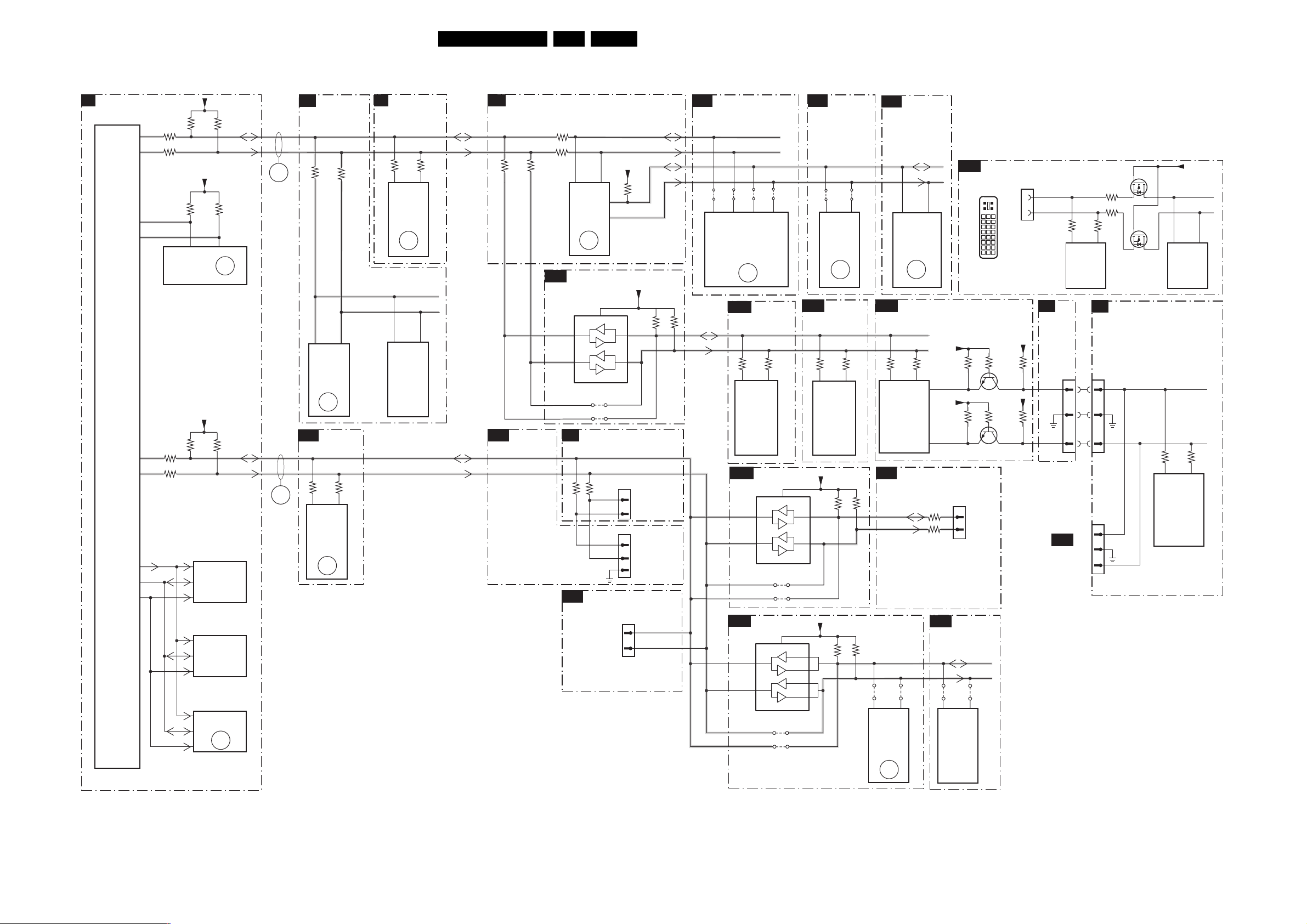
I2C IC’s overview
IIC
OTC
B5
88
87
7001
SAA5801H
SET
PROCESSOR
91
92
86
85
ADDRESS
DATA
CONTROL
Block Diagrams, Testpoint Overviews, and Waveforms
3064-4
3064-3
SDA
SCL
M24C64
EEPROM
3064-2
3064-1
7011
(NVM)
+5V2_CON
3069
3079
+3V3-INTOTC
3001 3002
56
ERR
+5V2_CON
3088
7006
M29W320DT
PROGRAM
FLASH-RAM
7007
MSM51V18165F
DRAM
(TXT)
7012
M29W400DT
ERR
32
1
3092
SDA-F
SCL-F
SDA-S
SCL-S
ERR
ERR
AUDIO
B6A
DEMODULATOR
3A17
2
7A02
AUDIO
ERR
14
PIP SWITCH
3P66
7P56
I/O
ERR
21
3A19
SDA-F-AUD
SCL-F-AUD
1
3P65
18
MSP3411G
DEMODUL
B15B
6
32
M62320FP
EXPANDER
B2
I2S-DPL-OUTI2S-DPL-OUTI2S-DPL-OUT
I/O, VIDEO
PROCESSING
3377 3376
47
7323
TDA9321H
HIP
ERR
8
45
7A06
TDA7309
AUDIO
DECODER
EN 28FTP2.4E AA 6.
PICNIC
B3A
6
7
3758
3E69
SDA-D
SCL-D
SN-DA
SN-CL
3E70
SDA-F
SCL-F
3826
46
SDA-EPLD
3827
SCL-EPLD
B19B
3710
3709
7E10
PCA9515DP
SAA4978H
EPLD
CONTROL
3
2
+5V2Pr
54
7713
1
2
PICNIC
ERR
3
+3V3-EPLD
8
VCC
I2C BUFFER
9E57
RES
9E58
RES
SDA-S
SCL-S
B14E
I/O5
B21
3Y09
SDA-SF
B14B
RES
CONNECTIONS
1M20
3Y40
SCL-SF
I/O2 CONNECTIONS
RES
FOR MMC
11
12
1M15
1I11
19
20
1
2
3
LED SWITCH
PA NE L
(ITV)
COMPAIR
SERVICE
CONNECTOR
SDA-S
B3D
SDA-F3
SCL-F3
SCL-S
COLUMBUS
9817 9818
A15 B15
7752-2
T6TU5XB
COLUMBUS
CTRL
B19A
AD9883AKST
CONVERTER
B14E
B13A
9815 9816
C14 D14
ERR
35
HDI A/D
CONVERTER
3L06 3L03
57 56
7L01
A/D
I/05
7I10
PCA9515DP
3
2
MAIN TUNER
7T50
P82B96TD
1
7
VCC
9I06
9I05
VCC
9T50
9T12
8
8
RES
RES
RES
B3C
B19C
57 56
AD9883AKST
CONVERTER
+3V3_SIM
6
7
+5V
3
2
5
6
EAGLE
9757 9755
33 24
7720
T6TX5AF
EAGLE1C
ERR
27
EPLD OSD
3E18 3E19
7E23
A/D
3IB3
3IB1
3T05
3T06
FALCONIC
B3B
SN-DA
34 41
7760
SAA4998H/V1
FEM
ERR
EPLD I/0
B19D
3V38 3V37
21
7V01-4
EP1C12F256C8
BANK3
SCREEN
B20
INTERFACE
SDA-DISP
SCL-DISP
9T08
9T07
54
1T01
UV1318ST
MAIN
TUNER
ERR
13
+3V3-IO
AL-CL-IN
+3V3-IO
AL-DA-IN
1M15
3Z51
3Z50
B13B
S-SDA-PIP
S-SCL-PIP
9T10
54
1T02
UV1318S
SUB
TUNER
B14F
3V50
3V55
1
2
SUB TUNER
SN-CL
26
Only for SDI Displays
I/O6 DIGITAL INPUT
DVI INPUT
CONNECTOR
C1 C2
18
3V51
3V54
TO
DISPLAY
9T09
1xxx
C5
C3 C4
24
916
17
+5V
3V52
7V04-1
+5V
3V53
7V04-2
RES
7
SDA-DVI
SCL-DVI
6
B21
AL-CL
AL-DA
TO 1M48
2nd AMBI LIGHT
(Optional)
3I49 3I46
7I19
M24C02
EEPROM
CON.
1M51
11
22
33
AL
65
AL
1M49
1M48
1
2
3
3IQ7
3IQ6
AMBI LIGHT
7I52
7I51
P87LPC760
CONTROLLER
3V3-Si-IO
14 15
7I18
SII907BCQ
DVI
RECEIVER
3002 3001
67
7001
MICRO
F_15460_081.eps
140405
Page 29
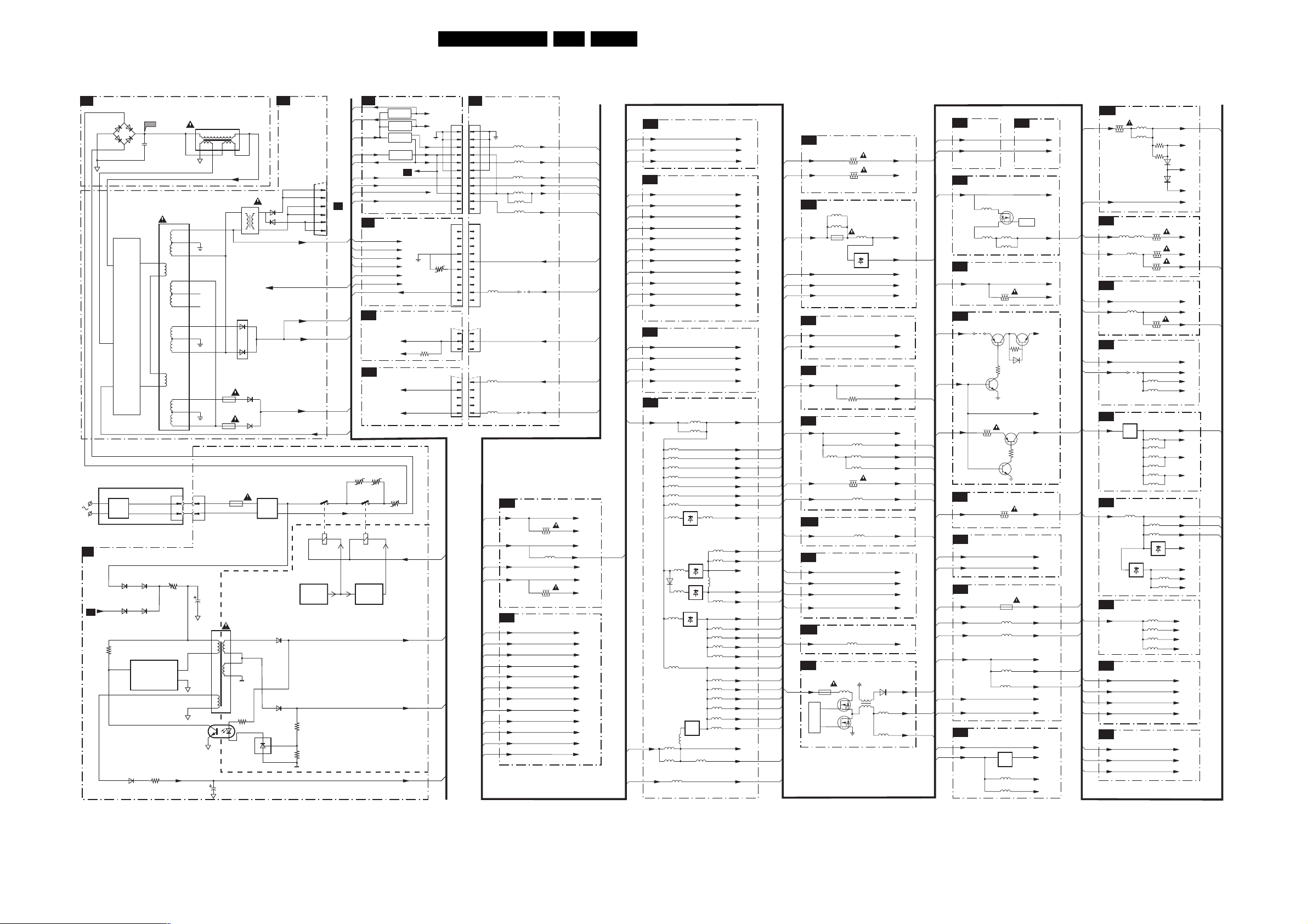
Block Diagrams, Testpoint Overviews, and Waveforms
Supply Lines Overview FHP
EN 29FTP2.4E AA 6.
SUPPLY LINES OVERVIEW FHP 42”
PRE CONDITIONER
A5
A
6600
3
GBU8J
1
F601
416
+
-
2603
2
5002
3
6
LCC
SUPPLY
3
6
MAINS FILTER UNIT
MAINS
FILTER
FILTERS STANDBY
A2
6513
6512
BYG10
BYG10
3506
6510
3507
BYG10
BYG10
CONTROL
7500
TNY256
4
ENABLE
6503
RS1G
6511
DRAIN
SOURCE
3508
400V-HOT
A5
PRECONDITIONER
5600
1246
16
14
12
11
10
9
16
14
12
11
10
9
0308
2
2
1
1
+t
2503
5
7-8
7501
TCET1102
3
+25V-HOT
1082
F2,5A
1082
F2,5A
5500
236
4
1
4
2505
400V-HOT
3
1
1400
T6.3A
7
8
9
3501
1
2
COLD
HOT
14
5290
VS
6044
STTH2003C
2
6021
BYU28
6045
BYU28
5005
5401
5402
MAINS
FILTER
- STANDBY SUPPLY -
1
7502
TS2431
3
2
6504
RS1G
6505
SB34
A6
VB
LLC SUPPLY
VSND_POS
GND_SND
VSND_NEG
VTUN
VS_UNSW
70-90
+30V
+25V-HOT
7460
ACTIVATING
3505
3503
1002
6
5
4
3
2
1
12
43
TO 1MO2
AUDIO
1450
AUX SUPPLY
A7
A6
VA
A3
70-90V
A6
+30V
A6
VCC
A3
+5V_STBY_SW
A2
VTUN
A5
+9V_STBY
A2
A5
PDP
A7
A3,A7
PROTECTION
A3
VA
A7
70-90V
A6
VCC
A7
+12V
A7
+5V_STBY_SW
A2
+9V_STBY
A2
A7
A2
A7
SCART 3
H
LED SWITCH PANEL
J
VS SWITCHED
VA SUPPLY
VCC SUPPLY
7260
L4973
CONTROL
AMBIENT LIGHT
+11V_SF
+11V_SFS
VS
VA
+8V6
+12V
VCC
AL
VB
+9V_STBY_SW
3511-3516
1M46
3372
0
+t
1M07
+8V
A7
A2
+t
3450
0
12
43
7465
7470
ACTIVATING
DELAY
+5V2-STBY
3451
0
+t
3452
0
-t
HOT
1460
COLD
+9V_STBY_SW
+9V_STBY
+5V_STBY_SW
+25V-HOT
A3
A3,A7
A3,A7
A6
10
11
1M03
1M20
6
7
8
9
10
CONNECTIONS
B21
1M46
1
1
2
2
3
3
4
4
5
5
6
6
7
7
8
8
9
9
10
11
1M03
1
1
2
2
3
3
4
4
5
5
6
6
7
7
8
8
9
10
5Y00
9
10
1M07
3
3
4
4
5
5
1M20
5Y11
6
7
8
9
5Y12
10
B14e
5Y06
5Y15
5Y07
5Y02
5Y03
5Y09
9Y15
9Y06
IF,I/O VIDEOPROCESSING
B2
+5V_VDP
+8V
+5V
+5V2-STBY
+33V
+11V
9V_STBY
+5V
9V_STBY
+11V_SF
+8V
+5V2-STBY
3402
+8V
B21
5416
+5VS
B14e
+8V_VDP
B4
3400
PICNIC
B3A
+3V3_DCDCFBXA
B3e
+1V8FA
B3e
+1V5_FBXA
B3e
+3V3_FBXB
B3e
+2V5_FBXA
B3e
+5V2Pr
B3e
+3V3PA
B3e
+8VPA
B3e
+3V3PB
B3e
+3V3Pr
B3e
+3V3PC
B3e
+3V3GA
B3e
B2,B6a,
B14a,d,e,g,B15a
B6a,b,B13a,b,B14b,
c,d,e,f,B15a,b,19a,d
B5a,B14b,e,
B13a,B13b
B14b,e,B20
B21
B21
B21
B14e
B21
B21
+5V_VDP
+5VCOM
+8V
+8V_CON
+5VS
+8V_VDP
+8VP
+3V3_DCDCFBXA
+1V8FA
+1V5_FBXA
+3V3_FBXA
+2V5_FBXA
+5V2Pr
+3V3PA
+8VPA
+3V3PB
+3V3Pr
+3V3PC
+3V3GA
B3e,B5a,B5b
B3e
B3e
B3e
B3e
B3e
B3e
B3e
B3e
B3e
B3e
B3e
B3e
B3e
B3e
B3e
B3e
B3e
B3e
B12
B6a
B2
B3B
+3V3FA
+3V3FB
+1V8FA
B3C
+2V5EC
+2V5ED
+1V5EA
+1V5EB
+2V5EA
+2V5EB
+3V3EA
+3V3EB
+3V3EC
+5V2Pr
+3V3ED
B3D
+3V3CB
+3V3CA
+1V5CA
+5V2Pr
B3E
+3V3_DCDCFBX
+5VF
+8V_CON
FALCONIC EMBEDDED MEMORY
EAGLE
COLUMBUS
FBX SUPPLY
+3V3_DCDCFBXA
5719
5720
5767
5779
5768
5769
5770
5771
5773
RES
7773
5772
5763
5758
5759
7701
5709
6719
5760
5761
7770
5753
7774
5775
5752
5764
5713
5762
5777
5750
5751
5780
5801
5756
7774
5753
IN OUT
RES
5764
5721
5722
5775
5702
+3V3FA
+3V3FB
+1V8FA
+2V5EC
+2V5ED
+1V5EA
+1V5EB
+2V5EA
+2V5EB
+3V3EA
+3V3EB
+3V3EC
+5V2Pr
+3V3ED
+3V3CB
+3V3CA
+1V5CA
+5V2Pr
+3V3PA
+3V3GA
+3V3PB
+3V3PC
+3V3FA
+3V3FB
+3V3Pr
+1V8FA
+1V5EB
+1V5CA
+1V5_FBXB
+1V5_FBXA
+1V5EA
+2V5_FBXA
+2V5ED
+2V5EC
+2V5EA
+2V5EB
+3V3_FBXB
+3V3EA
+3V3EB
+3V3ED
+3V3EC
+3V3CA
+3V3CB
+5V_FBXA
+5V2Pr
+8VPA
B3a,B3b
B3a,B3c,B3d
HOP
B4
+5V_VDP +5VS
B14e
+8V_VDP +8VS
B14e
OTC FLASH
B5A
+5V2-STBY
B21
B5c
B2
B5c
B14e
B2
B5a
B3a
B21
B3a
B3a
B3a
B3a
B21
B3b
B3b
B14b
B3a
B21
B3c
B3d
B6a
B6a
B3a
B6a
B3c
B6a
B3a
B3c
B3c
B6b
B3c
B3c
B3a
B3c
B3c
B21
B3c
B3c
B3d
B3d
B3a
F500mA
VPP-SW
+8V_CON
EAn
BACKLIGHT CONTROL
B5B
+5V_CON
+8V_CON
BACKLIGHT CONTROL
B5C
+3V3_INTOTC
AUDIO DEMODULATOR
B6A
+5V
5A02
+8V
+11V_S
DOLBY DIGITAL DECODER
B6B
+5V
DOLBY PROLOGIC PROCESSOR
B6C
+5DB
+8VC
+11V_AUD
+5DA
AUDIO DELAY
B6D
+5M
MAIN TUNER
B12
1U01
+11V
T1500mA
7U04
7U03
CONTROL
5000
5001
1000
5U02
3304
3C01
3A03
5A07
3329
5A06
5A00
5A03
5A01
5A38
5003
7005
RES
5U01
+5V2_CON
+3V3_INTOTC
VPP_SW
+8V_CON
EAn
+3V3_INTOTC
6U02
5U05
5U06
+5V_CON
+8V_CON
EAn
+5V
+5VF
+5DA
+5DB
+8VC
+11V_AUD
+5M
+5DB
+8VC
+11V_AUD
+5DA
+5D
+3V3-LINK
+3V3_SIM
+3V3_
DCDCFBX
B5a
B3e
B6c
B6c
B6c
B6b
N.C.
B14e,B15c,
B19b,B20
B3a,B3c
B2
B3c
B21
B6c
MAIN TUNER
B13A
+5V
B21
+33V
B21
DC-DC CONVERTER
B13C
+11V_DC
B14e
5T10
7T01-1
5T11
5T14
5T15
I/O1 MMC
B14A
+8V
B21
3IK7
I/O2 CONNECTIONS
B14B
9IA5
2
3IC1
I/O3 SWITCH
I/O4 AUDIO
I/O5
7I21-2
4
6
1
3
5
3ID9
7I21-1
1
3IN4
1I79
T300mA
5IEE
5I47
+5V2-STBY
+5V
B21
+11V
B21
B14C
+5V +5VIO
B21
B14D
+8V
B21
+5V
B21
B14E
+11V
B21
+11V_S
B14b
+8V
B21
+5V
B21
5I46
5I45
+5V2_STBY
B21
+3V3_SIM
B12
I/O6 DIGITAL INPUTS
B14F
+8V-VIDEO
B14g
+5V
B21
7I65
3
IN OUT
5I35
5I34
SUB TUNER
B13B
B21
+5V
+33V
7TO4
DC-DC
+11V_DC
VDISP
B14c
B20
+8V
+8VA
B21
7I05-1
+5V2-APLOP
3I37
6I11
B15b
B12
+5V
B6a,B14e
B21
B14g
B12
+11V_S
7I07
3ID0
3
7I09
2
+8V
+5V
+11V_DC
+11V_SF
+8V_VDP
+5V
RES
+5V_CON
+5V_VDP
+5V2_STBY
+3V3_SIM
B13c
B2,B4
B5a,B5b
B2,B4
B19a
B21
B19b
B19b
B21
B19b
+8V-VIDEO
+3V3-SI
2
3V3-TMDS
B21
3V3-Si-IO
B21
B21
B15a
B12
B13c
I/O7
B14G
3I40
+8V
+5VIO
PIP HIP
B15A
+5V
+8V
PIP SWITCH
B15B
+8VPIP
+5V
PIP MUPPET
B15C
+5VPIP
+3V3_SIM
HDI A/D CONVERTER
B19A
+5V
EPLD CONTROL
B19B
+3V3-SIM
EPLD OSD
B19C
+3V3-AD
EPLD I/O
B19D
+3V3-IO
+3V3-SD
+5V
+3V3_EPLD
SCREEN INTERFACE
B20
+3V3_SIM
VDISP
+11V
5P03
3
5P01
5P51
7L02
IN OUT
5E53
1
9PB2
5I13
5I12
3IG9
+8V-VIDEO
REF1
B14f
3IW1
6I80
REF2
6IA1
REF3
+5VIO
3P00
5P00
3P01
3P02
+5VHIP
+8VHIP
+8VPIP
B15b
+8VPIP
+5VD
3P74
+5VPIP
B15c
+5VPIP
+3.3V
5PA9
+3V
5PB0
+3VD
+3V3-AD
2
2
5L16
5L13
5L17
5L14
5L18
5L15
+3V3-EPLD
5E54
+3V3-SD
5E51
+3V3-IO
7E01
+2V5-IO
1
3
7E05
3
5E00
5E01
5E02
5E03
5E52
5E50
+1V5
+1V5-PLL
+1V5-INT
VBL
VDO
VDDO
PVDO
VD
VDD
PVD
B19c
B19d
B19d
B19d
+3V3-IO
+3V3-SD
+5V
+3V3_EPLD
+3V3_SIM
VDISP
+11V
F_15460_083.eps
140405
Page 30
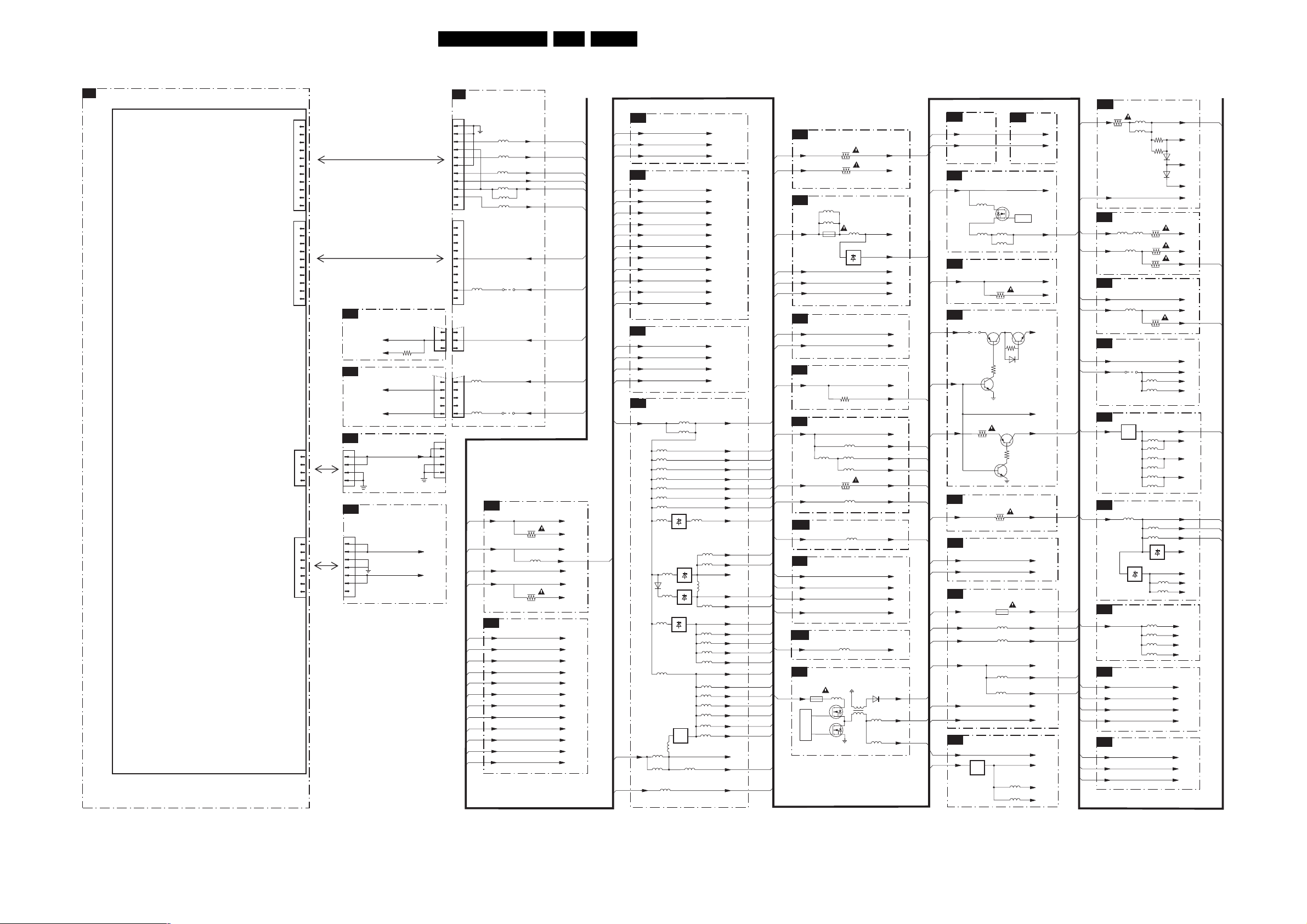
Block Diagrams, Testpoint Overviews, and Waveforms
Supply Lines Overview SDI
SUPPLY LINES OVERVIEW SDI 42” / 50”
SUPPLY
A
SUB
SUPPLY
SDI
CN9004
CN9005
CN9007
CN9006
EN 30FTP2.4E AA 6.
CONNECTIONS
B21
1M46
1M07
1M20
1M08
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
1M03
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
5Y09
9
10
1M07
3
3
4
4
5
5
1M20
TO 2nd
AMBI
LIGHT
5Y11
6
7
8
9
5Y12
10
B14e
6
7
8
9
10
1
2
3
4
+8V
5Y06
+5V
5Y15
+5V2-STBY
5Y07
+33V
5Y02
+11V
5Y03
9V_STBY
5Y09
+5V
9V_STBY
9Y15
+11V_SF
+8V
+5V2-STBY
9Y06
IF,I/O VIDEOPROCESSING
B2
+5V_VDP
3402
+8V
B21
5416
+5VS
B14e
+8V_VDP
B4
3400
PICNIC
B3A
+3V3_DCDCFBXA
B3e
+1V8FA
B3e
+1V5_FBXA
B3e
+3V3_FBXB
B3e
+2V5_FBXA
B3e
+5V2Pr
B3e
+3V3PA
B3e
+8VPA
B3e
+3V3PB
B3e
+3V3Pr
B3e
+3V3PC
B3e
+3V3GA
B3e
B2,B6a,
B14a,d,e,g,B15a
B6a,b,B13a,b,B14b,
c,d,e,f,B15a,b,19a,d
B5a,B14b,e,
B13a,B13b
B14b,e,B20
B14e
+5V_VDP
+5VCOM
+8V
+8V_CON
+5VS
+8V_VDP
+8VP
+3V3_DCDCFBXA
+1V8FA
+1V5_FBXA
+3V3_FBXA
+2V5_FBXA
+5V2Pr
+3V3PA
+8VPA
+3V3PB
+3V3Pr
+3V3PC
+3V3GA
B21
B21
B21
B21
B21
B3e,B5a,B5b
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
SCART 3
H
+11V_SF
+11V_SFS
3511-3516
LED SWITCH PANEL
J
+8V
+5V2-STBY
AMBIENT LIGHT
AL
1M10
C
1M02
1
2
3
4
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
PDP AUDIO
1
2
3
4
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
+12V
-16V-19V
+16V+19V
B3e
B3e
B3e
B3e
B3e
B3e
B3e
B3e
B3e
B3e
B3e
B3e
B3e
B3e
B3e
B3e
B3e
B3e
B12
B6a
B2
B3B
+3V3FA
+3V3FB
+1V8FA
B3C
+2V5EC
+2V5ED
+1V5EA
+1V5EB
+2V5EA
+2V5EB
+3V3EA
+3V3EB
+3V3EC
+5V2Pr
+3V3ED
B3D
+3V3CB
+3V3CA
+1V5CA
+5V2Pr
B3E
+3V3_DCDCFBX
+5VF
+8V_CON
FALCONIC EMBEDDED MEMORY
+3V3FA
+3V3FB
+1V8FA
EAGLE
+2V5EC
+2V5ED
+1V5EA
+1V5EB
+2V5EA
+2V5EB
+3V3EA
+3V3EB
+3V3EC
+5V2Pr
+3V3ED
COLUMBUS
+3V3CB
+3V3CA
+1V5CA
+5V2Pr
FBX SUPPLY
+3V3_DCDCFBXA
5719
5720
5767
5779
5768
5769
5770
5771
5773
RES
7773
5772
5763
5758
5759
7701
5709
6719
5760
5761
7770
5753
7774
5775
5752
5764
5713
5762
5777
5750
5751
5780
5801
5756
7774
5753
IN OUT
RES
5764
5721
5722
5775
5702
+3V3PA
+3V3GA
+3V3PB
+3V3PC
+3V3FA
+3V3FB
+3V3Pr
+1V8FA
+1V5EB
+1V5CA
+1V5_FBXB
+1V5_FBXA
+1V5EA
+2V5_FBXA
+2V5ED
+2V5EC
+2V5EA
+2V5EB
+3V3_FBXB
+3V3EA
+3V3EB
+3V3ED
+3V3EC
+3V3CA
+3V3CB
+5V_FBXA
+5V2Pr
+8VPA
B3a,B3b
B3a,B3c,B3d
HOP
B4
+5V_VDP +5VS
B14e
+8V_VDP +8VS
B14e
OTC FLASH
B5A
+5V2-STBY
B21
B5c
B2
B5c
B14e
B2
B5a
B3a
B21
B3a
B3a
B3a
B3a
B21
B3b
B3b
B14b
B3a
B21
B3c
B3d
B6a
B6a
B3a
B6a
B3c
B6a
B3a
B3c
B3c
B6b
B3c
B3c
B3a
B3c
B3c
B21
B3c
B3c
B3d
B3d
B3a
F500mA
VPP-SW
+8V_CON
EAn
BACKLIGHT CONTROL
B5B
+5V_CON
+8V_CON
BACKLIGHT CONTROL
B5C
+3V3_INTOTC
AUDIO DEMODULATOR
B6A
+5V
5A02
+8V
+11V_S
DOLBY DIGITAL DECODER
B6B
+5V
DOLBY PROLOGIC PROCESSOR
B6C
+5DB
+8VC
+11V_AUD
+5DA
AUDIO DELAY
B6D
+5M
MAIN TUNER
B12
1U01
+11V
T1500mA
7U04
7U03
CONTROL
5000
5001
1000
5U02
3304
3329
3C01
3A03
5A07
5A00
5A03
5A06
5A01
5A38
5003
7005
RES
5U01
+5V2_CON
+3V3_INTOTC
VPP_SW
+8V_CON
EAn
+3V3_INTOTC
6U02
5U05
5U06
+5V_CON
+8V_CON
EAn
+5V
+5VF
+5DA
+5DB
+8VC
+11V_AUD
+5M
+5DB
+8VC
+11V_AUD
+5DA
+5D
+3V3-LINK
+3V3_SIM
+3V3_
DCDCFBX
B3c
B5a
B3e
B6c
B6c
B6c
B6c
B6b
N.C.
B14e,B15c,
B19b,B20
B3a,B3c
B21
B21
B2
B14e
B21
B21
B21
B21
B21
B21
B21
B21
B14b
B21
B21
B12
B21
MAIN TUNER
B13A
+5V
+33V
DC-DC CONVERTER
B13C
+11V_DC
5T10
7T01-1
5T11
5T14
5T15
I/O1 MMC
B14A
+8V
3IK7
I/O2 CONNECTIONS
B14B
9IA5
2
3IC1
I/O3 SWITCH
I/O4 AUDIO
7I21-2
4
6
1
3
5
3ID9
7I21-1
1
3IN4
+5V2-STBY
+5V
+11V
B14C
+5V +5VIO
B14D
+8V
+5V
I/O5
B14E
+11V
+11V_S
+8V
B21
1I79
T300mA
5IEE
5I47
+5V
5I46
5I45
+5V2_STBY
+3V3_SIM
I/O6 DIGITAL INPUTS
B14F
+8V-VIDEO
B14g
7I65
+5V
2
3
IN OUT
SUB TUNER
B13B
B21
+5V
+33V
7TO4
DC-DC
+11V_DC
VDISP
B14c
B21
B20
B21
+8V
+8VA
7I05-1
+5V2-APLOP
3I37
6I11
B15a
B21
B15b
B12
+5V
B6a,B14e
B21
B14g
B12
+11V_S
7I07
3ID0
3
7I09
2
+8V
+5V
+11V_DC
+11V_SF
+8V_VDP
+5V
RES
+5V_CON
+5V_VDP
+5V2_STBY
+3V3_SIM
+8V-VIDEO
+3V3-SI
5I35
3V3-TMDS
5I34
3V3-Si-IO
B13c
B2,B4
B5a,B5b
B2,B4
B19a
B21
B19b
B19b
B21
B19b
B12
B13c
B21
B14G
3I40
+8V
+5VIO
PIP HIP
B15A
+5V
+8V
B15B
+8VPIP
+5V
PIP MUPPET
B15C
+5VPIP
+3V3_SIM
HDI A/D CONVERTER
B19A
+5V
EPLD CONTROL
B19B
+3V3-SIM
EPLD OSD
B19C
+3V3-AD
EPLD I/O
B19D
+3V3-IO
+3V3-SD
+5V
+3V3_EPLD
SCREEN INTERFACE
B20
+3V3_SIM
VDISP
+11V
I/O7
5P03
5P00
5P01
PIP SWITCH
5P51
9PB2
7L02
3
IN OUT
5E53
7E05
1
5I13
5I12
3IG9
+8V-VIDEO
REF1
B14f
3IW1
6I80
REF2
6IA1
REF3
+5VIO
3P00
+5VHIP
3P01
+8VHIP
3P02
+8VPIP
B15b
+8VPIP
+5VD
3P74
+5VPIP
B15c
+5VPIP
+3.3V
5PA9
+3V
5PB0
+3VD
5L16
5L13
5L17
5L14
5L18
5L15
5E54
5E51
1
5E00
5E01
5E02
5E03
+3V3-AD
VD
VDD
PVD
+3V3-EPLD
+3V3-SD
+3V3-IO
7E01
+2V5-IO
3
+1V5
5E52
+1V5-PLL
5E50
+1V5-INT
VBL
VDO
VDDO
PVDO
2
2
3
B19c
B19d
B19d
B19d
+3V3-IO
+3V3-SD
+5V
+3V3_EPLD
+3V3_SIM
VDISP
+11V
F_15460_084.eps
130405
Page 31

Circuit Diagrams and PWB Layouts
EN 31FTP2.4E AA 7.
7. Circuit Diagrams and PWB Layouts
PDP Supply Panel: Filter Standby
1234
A2 A2
FILTER STANDBY
56789
I405
MAINS
I400
470n
3400
V
AC2
495
1003
V_NOM
1402
500V
DSP-501N
2322595
3404
220R
ERC12
AC2
5401
12
2003
4
3
DMF28
AC3
2404
47p
1000V
FILTER
I402
470n
2408
470n
2001
I403
250V
2405
470p
12
470n
34
DMF28
47p
250V
470p
2019
COLD
GROUND
5005
2406
1000V
+T
232266293
I521
5402
1
2
2403
470n
2401
470n
470n
2004
AC3
250V
2407
470p
3
4
DMF28
I404
I520
1450
12
34
SDT-SS-109DM
I407
I406
12
3
SDT-SS-109DM
A
B
MAINS
INPUT
95-264Vac
F401
0308
2
1
B2P-VA-BF
AC3
F402
F406
F403
F407
F404
3401
F405
T6,3AH/250V
1M0
VR37
F408
F409
1400
19181
F410
2400
470n
2402
470n
I401
2002
C
GROUND
GROUND
D
400V_HOT
400V_HOT
6510
BYG10
I501
6511
BYG10
I502
GROUND
1M05
1
2
B2P-VA-BF
SECOND STBY
6512
BYG10
I503
6513
BYG10
STANDBY SUPPLY
E
F
G
H
MEASURED DC-VOLTAGES
I
3104 313 6066.3
123
25V_HOT
NORMAL . . .
STANDBY (. . .)
CONTROL
+T
3507
I524
3035
I525
3026
2504
HEATSINK
0203
123
680K
680K
680K
50V
1n0
100n
2513
600V
10R
3506
232266293
I504
2505
I508
7500
S5
EN|UV
8
S4
7
S3
6
S2
3
2
I509
25V
123
S1
HEATSINK
0201
BP
TNY256P
4
3509
12R
I518
I505
6503
3508
PR02
10R
35V1m0
F500
2503
F501
4
D
5
1
RS1G
47u 400V
I510
6501
9025
1000V
RES
2410
47p
9023
6502
BZT03-C
TCET1102(G)
6506
7501
GROUND
I506
5500
5
4
3
2
1
BZT03-C
I511
BZT03-C
I523
4
32
HOT
BS16421-00
6
7
8
9
1
7502
TS2431
COLD
GROUND
45678910
I522
2507
6504
RS1G
2509
6505
3501
1K0
I513
2502
50V
220p
F502
2508
50V
2
3502
2511
2512
470R
100n
16V
16V
100n
2510
F505
100u 16V
1m0 16V
I514
3503
1%
4K7
F503
+3V3_STBY_SW
1%
4K7
3505
33K
3504
5503
22u
1004
VCC
1404
9028
I519
TO
CN6
PDP
(DISPLAY)
F513
0306
B6B-PH-K
F506
19382
T2A/250V
EMC HOLE
1
2
3
4
5
6
VPR2
NC
GND
NC
VCC
220p
I507
100p
SS34
F504
I512
1
K
R
A
3
10 11 12 13 14
AC3
3450
10R
600V
1460
GROUND
1405
AC5
PFCGO
VSAGO
VCEGO
VRS
VRA
GROUND
I408
4
EMC HOLE
+T
232266293
I412
3460
F508
F510
F512
3451
600V
10R
2K2
3452
-T
1R0
6W7
B57464
3036
6W7
-T
1R0
6461
BAS316
I411
6460
BAS316
3463
10K
7460
BC817-25W
10K
3461
RELAY CONTROL
TO
CN11
F507
F509
F511
B9B-PH-K
0311
0309
9
8
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
2540
0-106451-1
RES
2531
9401
7461
BC869
LD1117DT33C
32
COM
1
16V
100u
B57464
I410I409
10K
3467
I413
16V
2465
100u
3465
I414
6520
RES
BAS316
I515
10R
RES
3520
I516
RES
RES
16V10u
2530
3530
10u 16V
1u0
2534
I526
I517
OUTIN
7540
2541
10K
100K
16V100u
7465
BC857BW
I415
4K7
3469
I416
10K
3470
F412
SWITCH
7530-1
SI4936ADY
RES
2
G
6530
BZX384-C18
3471
1K0
3472
1K0
SWITCH
7530-2
SI4936ADY
RES
4
G
6531
BZX384-C18
RES
100-230VAC2
AC5
100-230VAC1
6471
BAS316
I417
F411
6470
BAS316
7470
BC817-25W
SUPPLY_ON
9021
RES
7
8
D
S
1
16V
RES
100u
2532
6
5
9022
D
S
3
16V
2533
100u
11 12 13 14
+9V_STBY_SW
+9V_STBY
+3V3_STBY_SW
+5V_INT_SW
+5V_INT
+5V_STBY_SW
HOT
GROUND
COLD
GROUND
F_15460_002.eps
050405
A
B
C
D
E
F
G
H
I
0201 I5
0203 I4
0306 G9
0308 B1
0309 I11
0311 G11
1003 A3
1004 H9
1400 B2
1402 A3
1404 I9
1405 I10
1450 A8
1460 A10
1M05 D5
2001 B4
2002 B3
2003 B4
2004 B5
2019 C4
2400 B2
2401 B6
2402 B2
2403 B5
2404 B3
2405 C4
2406 B5
2407 C5
2408 B4
2410 G6
2465 C11
2502 E8
2503 F5
2504 G4
2505 F5
2507 E7
2508 F7
2509 F7
2510 F7
2511 I7
2512 I7
2513 G4
2530 G11
2531 G11
2532 G13
2533 I13
2534 H12
2540 I11
2541 I12
3026 G4
3035 F4
3036 A11
3400 B3
3401 B1
3404 A4
3450 A10
3451 A10
3452 A11
3460 D10
3461 D10
3463 D11
3465 D12
3467 C12
3469 D12
3470 D12
3471 G12
3472 H12
3501 H7
3502 H7
3503 I8
3504 I8
3505 H8
3506 E4
3507 F4
3508 E5
3509 E5
3520 F11
3530 G12
5005 B5
5401 B3
5402 B6
5500 F6
5503 F9
6460 D11
6461 C11
6470 D13
6471 C13
6501 G6
6502 H6
6503 E6
6504 E7
6505 F7
6506 G6
6510 E3
6511 E4
6512 E5
6513 E5
6520 F11
6530 F12
6531 I12
7460 D11
7461 G11
7465 C12
7470 D13
7500 G5
7501 H6
7502 I7
7530-1 F12
7530-2 I12
7540 I11
9021 F13
9022 I13
9023 G6
9025 G6
9028 E9
9401 G11
F401 B1
F402 B1
F403 B1
F404 B1
F405 B1
F406 B1
F407 B1
F408 B2
F409 B2
F410 B2
F411 D13
F412 E12
F500 F5
F501 G5
F502 E8
F503 F8
F504 F7
F505 F7
F506 H9
F507 G11
F508 G10
F509 G10
F510 G10
F511 G10
F512 G10
F513 G9
I400 A3
I401 A3
I402 B4
I403 B4
I404 B6
I405 A7
I406 A9
I407 C8
I408 A10
I409 A10
I410 A12
I411 C11
I412 D10
I413 C12
I414 D12
I415 D12
I416 D12
I417 C13
I501 E4
I502 E5
I503 E5
I504 E5
I505 E6
I506 E7
I507 F7
I508 F4
I509 G4
I510 G6
I511 G6
I512 H7
I513 H7
I514 I8
I515 F11
I516 F12
I517 H12
I518 E6
I519 F9
I520 A7
I521 B6
I522 E7
I523 G6
I524 F4
I525 F4
I526 H12
Page 32

PDP Supply Panel: Protection
0307 F8
1M03 A15
2303 F4
2304 D1
2305 D1
2306 D3
2316 F3
2322 D4
2324 E5
2343 E8
2350 D9
2352 E9
2364 E11
2366 F15
2376 G2
2377 G10
2380 F4
2381 H1
2385 H4
2396 F3
2397 C13
2398 C1
3068 F10
3074 G9
3102 E1
3103 C4
3300 B1
3301 C1
3302 F3
3303 F3
3304 D1
3305 F3
3306 D1
3307 E1
3308 C2 3357 D14
3311 C3
3312 C3
3313 D3
3316 F2
3317 E3
3320 B4
3321 C4 3364 E11
3322 D4
3323 E4
3324 D1
Circuit Diagrams and PWB Layouts
3325 G12
3326 G12
3327 G13
3328 F13
3332 C6
3333 C6
3334 D6
3335 E6
3340 C7
3341 C7
3342 D7
3343 E7
3344 D8
3345 C8
3346 C8
3347 D8
3348 C8
3349 C9
3350 D9
3351 D9
3352 E9
3353 E10
3354 E9
3355 D13
3356 D14
3358 C11
3359 C11
3360 D10
3361 C10
3362 D15
3363 E10
3366 D12
3367 D12
3368 D13
3369 D13
3370 D13
3372 B13
3373 F1
3374 F2
3376 G2
3377 G1
3378 E13
3380 H2
3381 H2
3382 F4
3383 E15
3384 F15
3385 H4
3386 G6
3387 G6
3388 F8
3389 F9
3391 F11
3396 F2
3397 F2
3800 F3
3801 F3
3802 F3
3803 F4
3804 F4
3805 F4
3806 H10
3807 H11
3808 G10
3809 F10
3811 G11
4300 F7
6312 C2
6313 D2
6321 C4
EN 32FTP2.4E AA 7.
6322 D4
6325 F12
6333 C5
6334 D5
6335 H10
6340 C7
6341 D7
6344 D8
6347 C8
6362 D10
6364 D11
6365 E12
6366 G11
6375 F1
6376 G1
6378 F14
7004 D8
7304 E1
7308-1 D4
7308-2 D4
7308-3 D2
7308-4 D2
7326 G13
7327 G14
7330-1 D6
7330-2 D6
7330-3 D5
7330-4 D5
7341 D8
7348 D8
7351 D10
7352 D9
7362 D11
7366-1 G5
7366-2 E14
7366-3 D12
7366-4 F10
7375 F1
7376 H1
7389 F9
7391 F11
9003 G4
9004 G5
9005 C1
9006 B13
9020 B14
F312 F9
F313 F7
F314 F7
F315 F7 I339 E11F368 C3
F316 F7
F317 G7
F318 G7
F319 H7
F320 H7
F321 G7
F322 H7
F323 H7
F324 F7
F325 D13
F326 D2
F327 D4
F328 D5
F329 D7
F330 C1
F335 C12
F343 D7
F370 A14
F371 B15
F372 B14
F374 B15
F375 B14
F376 B15
F377 B14
F378 B15
F379 B13
F381 F13
F390 F9
I302 C2
I303 F1
I304 D1
I305 F1
I306 E1
I307 E1
I308 F2
I309 F2
I310 G1
I311 H2
I313 C1
I316 D3
I318 C8
I319 D8
I320 D10
I321 D11
I322 D4
I323 D12
I325 G12
I326 G13
I327 F13
I330 D4
I332 C6
I335 D6
I341 D7
I344 D8
I345 D8
I347 D8
I348 D8
I349 C9
I350 D9
I351 D9
I352 D9
I363 D11
I364 D11
I367 D11
I379 E14
I380 E15
I381 F10
I382 F1
I383 D1
I384 C4
I385 H4
I386 H5
I387 G5
I388 F3
I389 F9
I390 B13
I392 F11
I900 F6
I901 F6
I902 F6
I903 F6
I904 G6
I905 G6
I906 H6
I934 F6
I935 F11
I936 D14
I937 D14
I939 G10
I942 G10
1
234567
89
10 11
12 13 14 15
PROTECTION
A3 A3
2397
3355
3372
3378
POK
1M03
F370
F372
I936
5
6
BAT54 COL
4
11
F375
F377
POWER_OK
I937
3356
7366-2
LM324
560R
3362
7
9020
STANDBY
100u 16V
2K7
3357
100R
I379
10K
6378
F371
F374
F378
F376
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
2K7
10K
3383
4V(0V1)
I380
10K
2366
3384
8V6 UNDER VOLTAGE
7327
BC847BW
PROTECTION
POK
A
+5V_INT_SW
B
2398
C
D
E
F
10u 16V
3304
I304
50V
2V5 (2V5)
2304
1n0
1
TS2431
K
A
3
+9V_STBY
I305
70-90V +12V
+5V_INT
VS
1%
PROTEC-
TION
3300
220K
I313
9005
RES
1%
3301
2.5 Vref
1K0
7304
2R
220K
F330
3308
1K0
16V
3
7308-4
7
2305
100n
3306
I383
1K0
3324
3102
I306
LM339P
61
12
1%
+5V_INT_SW
10K
3
7308-3
5
LM339P
4
1%
1K0
I307
3307
2
12
1%
12K
VSA
CONTROL
I303
3373
4K7
I382
6375
7375
6376
BAS316
BAS316
BC847BW
2376
47K
3374
I308
0V7
(0V6)
47K
3376
100n 16V
G
4K7
3377
I310
7376
BC847BW
H
0V7(0V)
2381
100n
I311
3380
47K
16V
47K
3381
VA
(0V3)
5V
I302
F326
5V(0V3)
LATCH
1K0
6347
BAT54 COL
I347
3347
330R
7348
BC847BW
P0102BL
3388
1K0
0307
NC
NC
NC
NC
20FMN-BMT-A-TFT
5V1(4V2)
3348
330R
I348
I350
I389
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
TO
11
12
13
(DISPLAY)
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
3350
3354
3389
1K0
PDP
4K7
7352
4K7
CN7
VCEGO
3351
10K
BC847BW
+5V_INT_SW
7389
BC857BW
F312
I349
I351
3352
I318
7341
BC857BW
3344
I345
6344
2343
+5V_INT
1K0
3346
I344
1K0
7004
BZX384-C3V3
50V
2u2
3345
I319
VA
VA
PROTEC-
TION
1%
3311
220K
F368
1K0
3312
6312
BAT54 COL
16V
6313
3313
2306
BAT54 COL
100n
I316
3317
0,1%
0,1%
3800
3396
RES
100K
I309
0,1%
0,1%
3801
3397
3316
0,1%
7K5 100K
3802
RES
0,1%
RES
2396
220n
2316
1%
7K5
1%
7K5
16V
100n
11
10
9
8
VS
3
12
+5V_INT_SW
3
12
0,1%0,1%
3302
100K
I388
3303
100K
0,1%
3305
6K2
7308-2
LM339P
13
7308-1
LM339P
3803
3804
3805
F327
14
0,1%
RES
RES
0,1%
3382
RES 0,1%
6321
6322
2303
1%
220K
3321
BAT54 COL
BAT54 COL
2322
220n
2380
I385
3385
16V
100n
16V
100n
VCC
3320
3103
1K0
3322
I322
3323
9003
100K
PROTEC-
1%
TION
10K
I384
1%
1K0
7
I330
6
1%
3K9
5
4
1%
10K
2385
1u0 10V
VCC
3
3
IAK
BUFFER
3
2
7330-4
LM339P
12
7330-3
LM339P
12
12V
PROTEC-
TION
1%
68K
3332
LATCH
I332
10K
3341
1K0
6333
3333
BAT54 COL
F328
1
6334
BAT54 COL
9004
3334
16V100n
I335
2324
3335
I387
3387
470R
3386
100K
2
4
7366-1
LM324
1
11
I386
3
7330-2
11
LM339P
10
1%
9
10K
8
1%
15K
I934
12
3
12
I900
I901
I902
I903
I904
I905
I906
13
7330-1
LM339P
14
VSK
S_GND
VAK
VRS
VRA
VCEGO
VSAGO
F320
6340
6341
4300
IAK
1V8(0V6)
1V9(0V7)
BAT54 COL
F329
BAT54 COL
RES
3340
F313
F324
F314
F315
F316
F317
F321
F318
F319
F322F323
1K0
I341
10K
3342
F343
1K0
3343
2350
3349
F390
1K0
16V
100u
I352
10K
2352
+12V_OVP
16V
100n
VCC_GO
7351
BC847BW
3353
3074
15K
10K
+9V_STBY_SW
1K2
3360
I320
3363
10K
3809
3068
I939
2377
100n
3806
470R
4K7
3361
I321
6362
BAS316
1K0
STANDBY
27K
I381
12
13
11
10K
3808
I942
4
6335
BAS316
7366-4
LM324
7362
BC847BW
3391
10K
14
0V(0V)
DC_PROT
3358
I367
6364
2364
I392
3811
100R
2K2
BAS316
16V100n
3359
I363
I339
6366
DCPROT
5K6
F335
I364
1K0
3364
6365
7391
I935
BAS316
3807
7366-3
LM324
8
BAS316
BC857BW
10K
VCC
+9V_STBY_SW
+5V_INT
4
10
11
+8V6
6325
BZX384-C6V8
I325
3325
470R
+T
KTY81
I390
9006
F379
232267191
+T
120R
10K
3366
3368
3370
470R
+T
F325
9
I323
1K0
10K
3369
3367
+5V_INT_SW
F381
10K
3328
3326
I326
4K7
3327
I327
7326
BC847BW
10K
100n 16V
TO
1M03
FTP2.X
A
B
C
D
E
F
G
H
VSA_CONTROL
3104 313 6066.3
123
IAKS
VRS
VRA
PFCGO
VCEGO
4567
VSAGO
SUPPLY_ON
8 9 10 11 12 13 14
F_15460_003.eps
15
050405
Page 33

Circuit Diagrams and PWB Layouts
EN 33FTP2.4E AA 7.
PDP Supply Panel: Pre-Conditioner
1
A5 A5
PRECONDITIONER
2345
A
S3J
6606
100-230VAC2
B
1000V
2601
100-230VAC1
1n0
C
D
3602
I602
3601
F602
3
6600
GBU8J
1
2
4M7
RES
4M7
RES
COLD GROUND
4
2604
E
MEASURED DC-VOLTAGES
NORMAL . . .
F
STANDBY ( . . . )
G
10K
3654
I663
6654
BAS316
1K8
3656
H
I615
2654
3655
1K0
16V47u
I617
I633
BC857BW
7654
2656
100n
2600
S3J
6605
5600
BS42228-02
16
1000V
F601
1n0
1u
RES
RES
2605
2603
3609
3604 3603
6601
BZX384-C39
3605
I647
3607
220K
10V
3651
2655
1u0
I603 I604
470K
I650
470K
I651
470K
I637
470K
I621
I618
I619
16V
22K
3612
2651
10n
50V
2K2
3666
2666
100R
4n7
6652
3652
2
3608
3660
4
I605
6608
SS14
2612
50V
1n0
2602
I654
2n2
3606
100R
12R
RES
I610
I631
270R
I653
1
PRECONDITIONER
3661
270R
I652
3659
220R
I616
1M0
I620
50V
2653
BAT54 COL
680p
6653
BZX384-C8V2
SS14
6651
I
HOT GROUND
3104 313 6066.3
1 23456789
6789
PRECONDITIONER
2611
6666
3614
100u
3690
3691
50V
47K
33K
I614
2W
0R27
2661
I623
2665
PDZ8.2-B
3K9
8K2
3615
1n0
3678
I630
7601
BC847BW
50V
470p
220p 2000V
6611
BYV29X-500
5601
2W
3620
0R27
I639
3675
I656
I641
4K7
3676
47K
3K3
3619
I645
10K
3613
I644
2672
100n
I609
2W
0R27
MC34063AD
1R0
3677
47K
50V
2608
1n0
2R2
3621
7661
8 DCOL
7IS
6
VCC
5 CIN_NEG
7602
BC857BW
I646
2640
1K0
3639
3640
3616
2616
2R2
3622
IPK
OSC
3665
12K
50V
470p
I624
330R
614
I634
I606
BC369
7608
2613
3662
NFR25
1R0
3663
I632
NFR25
1R0
CONTROL
I649
6602
3623
1K0
BZX384-C15
7650
MC33368P
2
CONTROL
RD
3
FB
4
COMP
5
MULT
9
LEB
6
CS
7
ZCDET
AGND PGND
8
3667
10K
I664 I665
3693
2K2
7656
BC847BW
50V
1n0
3611
3610
I611
VCC
BZG03-C18
2677
2n2
I612
6660
16
1
11
13
14
15
3692
10K
1n0
6609
I635
BYG22D
I622
7655
BC847BW
6661
BYG22D
5612
3686
I608
2610
1n8
15R
32V
(0V)
I613
2664
I643
3618 3617
I667
I668
1n0
2691
7610
STW26NM50
I607
3R3
I601
2614
2n2
I655
1K0
2663
50V1u0
12
LINE
VREF
GATE
FC
NC1
NC2
10
2690
I666
SRQ
F609
270K
6643
400V220u
F610
BZX384-C18
2617
REFERENCE
REGULATOR
3641
470R
7640
G
BSN20
11 12 13
F998
F999
F608
I640
6665
SL04
BIAS
2662
1m0 25V
3673
(0V)
6642
5V
I627
500V
500V
2675
2674
10n
10n
I628
SS14
I629
2676
3683
330K
I657
3684
330K
2673
I658
3685
330K
16V
3664
2671
100n
I636
16V
3669
100n
2670
7642
3643
220R
3642
220R
6640
SS14
BCP56
2642
50V
1n0
220u 400V
I625
GND
3668
1K0
NFR25H
6641
D
S
F600
F604
F606
10
1SWC
2SWE
3TIMC
4
BAS316
I642
2660
F997F996
I638
470p
7641
BC817-25W
F605
6663
3999
1K0
5660
220u
SL04
15V(1V8)
I626
10 11 12 13
400V_HOT
SW25V_HOT
1K0
NFR25H
3679
150K
I659
10n
3680
220K
I660
3681
220K
500V
I661
10n
3682
220K
1%
1K0
120K
3104
I648
I662
1%
10K
3671
120K
F_15460_005.eps
050405
2600 B3
2601 B2
2602 C6
2603 C3
2604 C2
2605 C3
2608 H8
2610 B7
2611 B8
2612 B5
2613 C6
A
2614 C6
2616 C9
2617 C9
2640 H8
2642 G11
2651 H3
2653 H5
2654 H1
2655 H3
2656 H2
B
2660 E10
2661 F8
2662 F11
2663 E6
2664 E7
2665 H8
2666 H4
2670 H12
2671 H12
2672 H8
C
2673 G12
2674 G12
2675 G11
2676 G12
2677 C7
2690 I6
2691 I7
3104 H12
3601 D2
D
3602 D2
3603 E3
3604 E3
3605 F3
3606 C5
3607 F3
3608 C5
3609 D3
3610 C6
3611 C6
E
3612 H4
3613 G8
3614 C7
3615 C8
3616 G9
3617 G7
3618 G7
3619 F8
3620 C8
3621 C8
F
3622 C9
3623 G6
3639 H8
3640 H8
3641 H9
3642 G11
3643 F11
3651 H3
3652 G5
3654 G1
G
3655 H1
3656 H1
3659 G5
3660 F5
3661 F5
3662 E6
3663 E6
3664 H12
3665 F9
H
3666 H4
3667 H6
3668 F10
3669 H12
3671 H12
3673 F12
3675 E8
3676 F8
3677 F8
3678 F8
I
3679 F12
3680 G12
3681 G12
3682 H12
3683 G12
3684 G12
3685 H12
3686 C7
3690 I7
3691 I7
3692 I7
3693 I6
3999 A10
5600 A5
5601 B8
5612 B7
5660 E10
6600 B2
6601 F3
6602 G6
6605 A3
6606 A2
6608 B6
6609 C7
6611 B8
6640 G11
6641 H10
6642 H11
6643 H9
6651 H5
6652 H4
6653 H5
6654 G1
6660 F7
6661 E7
6663 E10
6665 E11
6666 H7
7601 G8
7602 F8
7608 C6
7610 B7
7640 H9
7641 G10
7642 G11
7650 G6
7654 H2
7655 I7
7656 I6
7661 D8
F600 B10
F601 B3
F602 D2
F604 C10
F605 D10
F606 I10
F608 D11
F609 F9
F610 G9
F996 A10
F997 A10
F998 A11
F999 A11
I601 C7
I602 D2
I603 B4
I604 B7
I605 B5
I606 C6
I607 C6
I608 B7
I609 C8
I610 E5
I611 E6
I612 E7
I613 E7
I614 B8
I615 H1
I616 G5
I617 G2
I618 H4
I619 H4
I620 H5
I621 G4
I622 G7
I623 H8
I624 H9
I625 G10
I626 H10
I627 F12
I628 G11
I629 H11
I630 C8
I631 E5
I632 E6
I633 H1
I634 B6
I635 C7
I636 H12
I637 F3
I638 E10
I639 D8
I640 E11
I641 E8
I642 E10
I643 G7
I644 G8
I645 G8
I646 G8
I647 F3
I648 H12
I649 G6
I650 E3
I651 E3
I652 G5
I653 F5
I654 C5
I655 C7
I656 E8
I657 G12
I658 H12
I659 G12
I660 G12
I661 G12
I662 H12
I663 G1
I664 I6
I665 I7
I666 I6
I667 I7
I668 I7
Page 34

Circuit Diagrams and PWB Layouts
PDP Supply Panel: LLC Supply
2034 E1
U13 E9
U14 E6
0204 H9
1000 G6
1001 G7
1002 H14
1006 G8
1008 G9
1009 G8
1082 F11
1083 F11
1084 G10
2000 G9
2005 C1
2006 C2
2007 F1
2008 F3
2009 E5
2010 F5
2011 E9
2012 D9
2013 C9
2014 F6
2015 F5
2016 E6
2017 C9
2018 C1
2020 C11
2022 E11
2023 E14
2024 E12
2025 E13
2026 F3
2027 E2
2028 C11
2029 G11
2030 F12
2031 F15
2032 D2
2033 D1
2035 F1
2036 D2
2037 E2
2038 C13
2039 D7
2040 D7
2041 D8
2042 D9
2043 D13
2044 D11
2045 F11
2046 C8
2047 E1
2048 F6
2049 C1
2052 B3
2053 B5
2060 F6
2062 A4
2070 E7
2071 C7
2090 B2
2290 H10
2291 G11
2292 H11
2293 H11
2294 H11
2295 G11
2296 H11
3001 E6
3002 C6
3003 C1
3004 C1
3005 C2
3006 D2
3007 E2
3008 E2
3009 F1
3010 E4
3011 E5
3012 F3
3013 F4
3014 C7
3015 C7
3016 C7
3017 D7
3018 D7
3019 E7
3020 F5
3021 F5
3032 F14
3022 C12
3033 D8
3034 F13
3023 E12
3024 E13
3037 C13
3025 F13
3038 C13
3027 F2
3039 C14 3065 E4
3028 F13
3040 E13
3029 E13
3041 F13
3042 D1
3030 F12
3043 D1
3031 F13
3044 D1
3045 E2
3046 E1
3047 E2
3048 D1
3049 D3
3050 F7
3052 E12
3054 D6
3056 E4
3057 D12
3059 D8
3060 C8
3061 D8
3064 F3
3066 F2
3067 F5
3069 E1
3070 E5
3071 F2
3072 B13
3073 D7
3075 B8
3076 C8
3077 E8
3078 E8
3080 C12
3081 A4
3082 B5
3089 A4
3090 A2
3091 B2
3092 A3
3093 B2
3094 A3
3095 A5
3096 A5
3097 B5
3098 F15
EN 34FTP2.4E AA 7.
3100 F14
3292 H10
5001 C6
5002 C9
5004 E9
5290 G10
5291 H12
5292 H12
5293 G12
6002 A4
6018 C8
6003 A3
6019 E7
6004 D6
6021 F11
6005 D5
6023 E13
6006 D7
6027 C7
6007 C7
6008 D7
6028 E7
6009 F4
6029 B11
6010 F4
6031 D2
6011 F4 F007 F3
6032 D2
6012 B11
6033 E1
6034 D2
6035 D2
6042 C13
6044 C11
6045 F11
6075 B8
6077 D8
6095 A5
6291 H11
6292 H11
7001 B3
7002 B9
7003 A9
7005 B8
7006 E8
7007 C7
7008 E7
7009 E4
7010 E12
7011 F13
7012 D7
7013 A3
7017 F3
7018 F3
7020 C8
7021 D8
7042 C13
7090 A2
7091 A3
7092 A3
7093 A4
9007 A3
F001 A6
F002 C7
F003 C5
F004 C5
F005 C9
F006 D8
F008 D5
F009 D6
F014 E12
F016 B13
F017 C11
F040 B14
F290 H12
F292 H12
F293 G12
F294 H12
F295 H12
F296 G13
F297 H12
F298 H12
I001 A2
I002 A3
I003 A5
I004 A5
I005 B2
I006 B4
I007 C2
I008 C2
I009 C2
I010 D2
I011 D1
I012 D4
I013 D2
I014 E1
I015 D2
I016 E2
I017 E2
I018 E2
I019 E1
I020 E3
I021 E1
I022 F2
I023 F3
I024 F3
I025 F2
I026 F1
I027 C2
I028 G3
I029 G3
I030 E5
I031 E4
I032 E5
I033 F4
I034 F5
I035 F5
I036 F5
I037 C8
I038 C8
I039 D6
I041 B8
I042 B7
I043 B7
I044 B8
I045 C6
I046 C7
I047 D7
I048 D7
I049 D8
I050 D8
I051 E7
I052 D7
I053 E7
I054 E7
I055 E8
I056 A2
I057 D7
I059 E8
I060 A10
I061 A10
I062 B10
I063 B10
I064 B8
I065 C9
I066 C8
I067 C8
I070 B11
I071 F10
I072 D11
I073 F10
I074 F11
I075 C13
I077 F11
I078 C13
I079 C13
I080 G10
I081 F7
I082 F7
I083 F8
I084 F8
I085 E12
I088 E13
I089 E12
I090 E13
I091 E14
I092 F13
I093 F12
I094 F12
I095 H6
I096 H7
I098 H8
I282 D1
I283 F14
I284 E15
I285 A4
I286 A4
I287 A4
I288 B5
I289 A5
I290 G11
I291 H11
I292 H10
I293 H11
I294 D13
I295 D6
I296 F6
I297 E7
I298 C7
I299 B11
1234
5678910
11 12 13 14 15
LLC SUPPLY
A6 A6
25V_HOT
18V(22V5)
BC857BW
A
7090
B
VS-CONTROLLER
GND4
3043
470R
3046
5M6
VR25
100K
15K
4K7
470R
50V
1n0
2018
2005
3044
1K0
I014
BZX384-C47
I021
3009
GND4
3048
6033
100p
100p
I011
47p
1K0
2007
50V
2049
I009
50V
4K7
2033
BZX384-C5V6
3045
1K0
2034
1000V
100n
I026
6031
2032
I017
3008
1K0
16V
100p
1n0
100n
C
D
E
2047
GND4
3003
3004
GND4
3042
I282
100n
3069
I019
2035
F
50V
2006
50V
25V
22n
16V
I015
BZX384-C5V6
2037
47p
3047
150K
2090
I008
3006
6034
BAS316
6035
BAS316
6032
3007
3090
100R
4u7 35V
3091
1K0
I007
3005
27K
10K
2036
4K7
I025
I022
19V3
(24V)
3093
25V
22n
I010
I016
3071
47K
I005
2027
3066
I001
I056
1K0
I027
I013
I018
15n
10K
F007
3027
3094
1K0
I002
3092
1K0
7092
BC807-25W
18V6
6003
(0V)
7091
BC857BW
35V1m0
2052
CONTROL
3049
12K
SOFTSTART
CONTROL
I020
16V
BC857BW
7017
I023
10K
3064
50V
47K
2026
2n2
I028
9007
BCP56
7013
BZX384-C33
7001
MC34067P
9
1
2
3
16
6
8
7
11
4K7
3012
7018
BC847BW
I029
EN|UA
OSCC
OSCR
OSCCC
OS
EAO
Ip
In
SOST
I024 I033
2008
G
MEASURED DC-VOLTAGES
NORMAL . .
H
STANDBY ( . . . )
3104 313 6066.3
1
2345
BIAS SUPPLY
18V6
I285
(22V1)
10K
3089
3081
I286
1K0
2062
2u2 50V
GND4
I006
15
VCC
VREF
OA
OB
PGND
FI
GND
I012
4
1K0
3056
3065
CURRENT
PROTECTION
6011
BAS316
50V
10K
3013
10n
7093
LM317T
16V2(4V7)
IN OUT
32
ADJ
1
I003
15V9
I287
6002
I004
BAS316
5
14
12
13
10
3010
15K
330R
7009
BC847BW
I031
I032
2015
10n
50V
6009
I035
BAS316
2010
6010
BAS316
HOT GROUND
3095
3096
3097
10n
F001
2
2
2290
10n 50V
3292
560R
5V1(4V2)
3
5290
1
1084
I060
I061
I062
I063
STTH2003C
I071
I073
F1A/250V
I080
4
2
I292
6044
I072
T2,5A/250V
19382
T2,5A/250V
19382
19370
BD15403
2291
470p 50V
2293
470p
LATCH
I070
1
1082
1083
50V
BZX384-C6V8
2028
220p
3
2
2044
220p
+5V_INT_SW
6029
200V
200V
2022
1m0
I077
6045
BY328/20
2045
220p
I074
6021
BY328/20
2029
220p
2295
470p
6291
6292
2296
470p
I299
BZX384-C5V6
2020
50V
200V
200V
STPS745F
STPS745F
6012
F017
I290
I291
100V
3m3
I293
86V(6V)
2292
2294
3057
100R
3030
35V(4V)
35V(4V)
F040
3072
4K7
F016
10K
3037
3038
1u0
I294
I088
3040
I079
I090
7011
TS2431
33K
100K
2038
I078
FEEDBACK
2025
4K7
3029
100K
3031
10K
1
K
R2
A
3
VRS
1%
50V
1n0
3039
1M0
I091
I283
3080
680R
3022
680R
I085
1
K
A
3
18K
3023
47K
7010
TS2431
R2
I094
I089
2V5(0V6)
2030
3052
150K
2024
3n3
50V
F014
16V
100n
I093
3024
3025
3034
PMST5401
6042
BZX384-C47
2043
1u0
50V
150K
6023
BAS316
3028
7K5
1K8
220R
7042
I075
34V(4V)
50V
1%
I092
3041
Vs_unsw
70-90V
VS
3100
1K0
1%
VTUN
2023
100n
3032
10K
I284
3098
1K0
1%
10n
2031
+30V
VB
F293
5293
22u
F297
1m0
5291
22u
1m0
5292
22u
F298
F294
F292
F290
F295
VSND_POS
GND_SND
VSND_NEG
F296
1002
7
TO 1MO2
6
5
4
3
2
PDP AUDIO
1
TCET1102(G)
TCET1102(G)
2000V
2013
330p
2017
F005
2000V
2012
330p
2011
EMC HOLE
HEATSINK
123
1008
0204
4
7003
3
4
7002
3
1600V
15n
I065
BS42315-02
1600V
15n
BS42315-02
5002
3
6
5004
3
6
470p
BAS316
470R
I289
6095
5K6
3082
I288
820R
2053
1K0
22u 35V
HIGH SIDE
I042
6007
I045
5001
S13932-04
F003
4
3
F004
2
6005
6004
BAS316
F008
I030
2009
3011
2u2 50V
I036
3020
56K
50V
3067
BAS316
F009
3054
470R
10K
3070
560R
GND4
I034
20602048
6R8
3021
15K
PR02
GND4
50V2u2
2016
2014
1n5
220n
I296
220n
HOT
BAS316
3016
6
1K0
3002
470R
2071
7
I298
1n0
9
LOW SIDE
10
I295
U14
2000V
EMC HOLE
I095
1000
7012
BC847BW
GND4
GND4 GND4
6008
I039
BAS316
3019
1K0
470R
3001
I053
2070
I297
1n0
I081
COLD
6 7 10 11 12 13 14
6027
BAS316
3073
I052
6028
BAS316
EMC HOLE
I096
400V_HOT
I043
3014
33R
DRIVE
I048
BAS316
1M0
2039
GND4
3017
33R
6019
BAS316
1001
SW25V_HOT
DRIVE
F002
I046
6006
2n2
GND4
3018
I051
I064
3075
I044
6018
I038
BAS316
7020
10R
3015
BC517
I037
BC327-25
7007
2046
33p
I047 I050
3033
180K
27p
2040
I057
10R
BC517
I059
BC327-25
7008
I054
3050
3R9
NFR25
EMC HOLE
1009
I098
GND4
F006
7021
3076
I067
3060
220K
3059
56K
2041
100p
3077
3078
I055
I084I082 I083
COLD GROUND
89
I041
6075
BZG03-C270
7005
1M0
STP15NK50ZFP
100K
I066
3061
6077
BZG03-C270
I049
STP15NK50ZFP
1M0
100K
GND3
EMC HOLE
1006
18K
2042
330p
7006
U13
2000
250V
1
1
16
14
12
11
10
9
16
14
12
11
10
9
VRS
1V9(0V7)
DC_PROT
F_15460_006.eps
140405
15
A
B
C
D
E
F
G
H
Page 35

Circuit Diagrams and PWB Layouts
EN 35FTP2.4E AA 7.
PDP Supply Panel: AUX Supply
12
AUX SUPPLY
A7 A7
A
B
C
D
E
F
G
H
I
VB
6054
I159
POK
3055
I158
2054
2056
BAS321
10K
50V
220p
220p
BAS321
VCC_GO
SFR16
6055
2113
6111
I105
3106
I164
3112
BAS316
25V
220u
SEQUENCE
DISCHARGE
+5V_INT_SW
10K
3084
5V2(0V)
47K
3085
I225
47K
3087
3104 313 6066.3
6086
BAS316
I207
7058
BC847BW
1234
70-90V
F110
1110
19382
T5A/250V
I101
3110
2K7
3107
2K7
1K0
2112
50V
2111
220p
I113
6112
3086
47K
I203
47K
3088
2059
I109
50V
1n0
2114
220n
BAS316
3108
2K7
I115
I160
104V(0V)
16V
100n
I162I163
3
4
5
3113
470K
3058
3083
PMST5401
3109
2K7
7112
TEA1507P
SMPS CONTROL
CTRL
DEM
ISENSE
I204
7059
PMST5550
7110
I147
1
VCC
Φ
CONTROL
DRIVER
DRAIN
GND
2
3114
I114
1M0
I161
250V
2058
1u0
1K0
3062
560K
HVS
6113
BAS316
2055
1n5
1K0
2061
1K0
50V
3051
8K2
I202
16V
100n
34
I102
7117
PSMN035
I106
6117
3116
1K0
220K
I110
BZX384-C18
3117
2117
330n
6
7
8
I112
I117I116
3115
Vs_unsw
70-90V
I165
2057
1n5
87V
(0V5)
105V
I200
(0V)
50V
2050
6050
0V1(8V)
6061
BZX384-C18
7052
IRFR18N15D
BZX384-C18
22n
10K
16V
7050
PSMN035
I244
3053
I201
2214
2213
I248
I118
VS
10R
+T
4n7
4n7
2118
3118
0R051
F113
600V
232266293
2021
1n0 1000V
6142
100V3m3
+30V
+30V
87V
(0V5)
VA
I222
4
3
I107
6120
BZX384-C5V6
S3J
6202
1K0
3203
BAS316
F260
PROTECTION
7120
TCET1102(G)
5121
64V (0V5)
BD21232
21
34
I108
BYW29EX-200
I211
6204
BAS316
1200
T2A/250V
19382
BSN20
I220
16V
2203
100n
3204
100K
567
1260
5260
MP200
39812
FROM
6206
0V
(0V5)
3202
7202
F265
BT151X-500R
+5V_INT_SW
6133
1
2
3111
I249
I111
4K7
3143
I210
I213
47R
I208
3205
5
100u
10K
3138
1
6
BC857BS
7140-1
3200
6205
100K
6260
BAS316
I246
I135
RES
1%
220R
RES
BSH114
220K
BZX384-C18
2205
9002
3145
0R51
3146
0R51
2W 1%
2138
I156
2
7200
50V
2u2
2260
3140
+12V_OVP
I172
3261
I104
1u0
3260
RES
RES
RES
10V1u0
5
RES
1%
RES
75K
I212
2210
1K0
1K0
3139
I157
3141
3212
2215
470p
16V47u
2261
I153
4
7140-2
BC857BS
3
PMST5401
3206
2K7
I215
6
1%
220R
1%
75K
1K0
6062
2262
50V
1m0
RES
RES
2212
220n
I155
7142
3142
11V5(0V7)
I166
16V
220n
2051
BZX384-C18
2211
470p
6211
SS14
I103
10K
3262
I173
10K
3263
I139
I142
2270
2n7
2263
I154
3150
RES
1%
1%
RES
1K0
3148
I167
3207
2K7
I214
3
4
5
I218
120K
3214
I221
100n
6213
I223
3213
+12V-SUPPLY
7
8
16
V5.1
12
VFB
1
OSC
9
BOOT
25V
47u
1K8
3120
I124
I121
3121
47K
7121
1
TS2431
K
R
2V5
2
(0V3)
A
3
1M0
VA
RES
5K6
Adj.
I168
3209
3208
2K7
2K7
7212
1
TEA1507P
VCC
Φ
SMPS CONTROL
CONTROL
CTRL
DRIVER
DEM
HVS
ISENSE
DRAIN
GND
2
I217
1K0
3216
BAS316
10K
3215
3219
270K
33K
I224
78
7260
L4973V3.3
REGULATOR
GND
456
2123
3n3
50V
I127
3126
I131
3132
2219
10p
Φ
2K2
220R
6
7
8
8 9 10 11 12 13
35V(4V)
6268
SS14
5268
I175
100u
BAS316
I176
560R
3063
1K0
10n
I129
I233
STPS20L40CFP
I238
2229
470u
16V
3269
3268
VA
3
3135
3229
2223
100p
2222
100p
IAKS
47K
I122
220u
I170
12V6(ON)
2K7
1K0
VRA
560R
50V
6225
50V
5229
6230
SS34
2232
100p
BC857BS
2269
7060-2
VSA_CONTROL
3V3
(8V4)
F125
2225
50V
2230
2m2
33R
3153
4
3
I179 I180
3154
VA
3224
I235
25V
2m2
10V4(0V7)
16V
470u
9009
3156
0R051
I178
5
10K
I230
I231
1%
12K
100n
I237
3225
10K
1%
2234
F126
5225
4u7
2226
+9V_STBY_SW
33R
3152
I177
1
2
7060-1
F124
BC857BS
6
7061
BC857BW
10K
3155
I181
2K2
2K2
3158
3157
100V
2121
2200u
F127
F128
VCC
I234
2227
100p
50V
3226
10K
3210
7230
L4940P
COM
1
7227
TS2431
K
R
2
A
3
1%
1K0
F116
F114
OUTIN
2
2235
16V
2V5(0V3)
I171
13
1u0
I243
+9V_STBY
+5V_STBY_SW
F122
F102
F130
F131
F119
F120
F134
3228
150R
F135
F136
F140
2228
1u0
2231
RES
12
16V
47u
VTUN
VCC
+8V6
+12V
F118
NC
NC
VCC
6.3V
10u
131415
3122
2126
2
3
OUTVCC
11
COMP
18
SYNC
I141
17
SS
10
INH
I140
1K0
3265
2264
BZX384-C5V6
2122
1%
75K
6123
BAS316
3124
7K5
3125
7K5
16V
100n
1u0
I120
18K
3123
I126
I128
1%
TS2431
1%
33K
3128
VCC-SUPPLY
I216
3149
4R7
I169
NFR25
6216
BZX384-C18
I219
I245
6201
63V
7130
PSMN070
G
3217
10K
2217
330n
16V
6269
6270
7217
3133
3130
K
A
3
470n
3264
2266
+30V
1
BYG10
BYG10
I138
4n7
6267
220n
2268
SB540
I134
I136
6271
3151
I152
F111
1%
3147
10K
2133
4
7220
3
5220
1
4
5
78
BS29238-00
33R
3079
50V22u
680R
I125
3134
3136
47K
14
13
12
11
2274
680R
7134
BC847BW
I247
R
I236
D
S
I133
100R
12K
3218
I130
560R
4u7
I174
3101
2265
2267
6114
BZX384-C6V8
I123
3131
10K
1%
1K0
2
I132
1600V
2218
3n3
I209
I240
3220
0R051
330p
1%
TCET1102(G)
I148
91011
F115
9000
F264
9001
I137
+12V
F380
1M46
B11B-PH-K
11
10
9
8
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
1M10
1
2
3
4
B4B-PH-K
VA
VS
VCC
100n
2273
0323
F129
VA
NC
0342
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
B7B-PH-K
F138
2236
F133
16V
F121
F123
F132
F106
F107
F137
F139
2233
10u
B7B-PH-K
6.3V
10u
B10P-VH
0352
2237
VA
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
10u 16V
NC
NC
NC
VCC
10
9
8
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
VCC
+8V6
MEASURED DC-VOLTAGES
NORMAL . . .
STANDBY (. . . )
13
TO
1M46
FTP2.X
TO
1M10
AMBI LIGHT
TO
VS
CN23
PDP
NC
(DISPLAY)
NC
VA
TO
CN42
PDP
(DISPLAY)
TO
CN52
PDP
(DISPLAY)
F_15460_007.eps
050405
0323 E13
0342 G12
0352 G13
1110 B1
1200 G4
1260 A5
1M10 C13
1M46 B13
2021 I4
2050 G3
2051 H6
2054 C1
2055 E2
A
2056 C1
2057 E3
2058 G2
2059 I1
2061 I2
2111 D1
2112 D1
2113 E1
2114 E2
2117 D3
2118 C4
2121 E11
2122 D8
2123 D7
2126 E8
B
2133 E9
2138 D6
2203 I4
2205 I5
2210 I6
2211 I6
2212 G6
2213 I4
2214 I4
2215 I6
2217 H8
2218 G9
2219 I7
C
2222 G10
2223 F10
2225 H10
2226 G11
2227 G11
2228 H12
2229 H10
2230 I10
2231 I12
2232 I10
2233 H13
2234 I11
D
2235 I12
2236 H12
2237 H13
2260 A6
2261 A6
2262 A6
2263 B6
2264 B8
2265 A9
2266 B8
2267 B9
2268 B9
2269 A10
E
2270 B7
2273 D12
2274 D10
3051 G2
3053 H3
3055 B1
3058 G2
3062 H2
3063 D10
3079 D9
3083 H2
3084 I1
3085 I1
F
3086 I1
3087 I1
3088 I1
3101 D9
3106 C1
3107 C1
3108 C2
3109 C2
3110 C2
3111 C5
3112 D1
3113 D2
3114 D2
G
3115 D3
3116 D3
3117 D3
3118 C4
3120 D7
3121 D7
3122 D8
3123 D8
3124 D8
3125 E8
3126 E7
3128 E8
H
3130 D8
3131 D9
3132 E7
3133 C8
3134 D10
3135 E10
3136 E10
3138 D5
3139 D6
3140 E6
3141 E6
3142 E6
3143 E5
I
3145 C6
3146 C6
3147 D9
3148 E7
3149 G8
3150 D7
3151 B10
3152 B11
3153 B11
3154 C11
3155 C11
3157 D11
3158 D11
3200 G5
3202 H5
3203 I4
3204 I5
3205 I5
3206 F6
3207 F6
3208 F7
3209 F7
3210 H11
3212 G6
3213 I7
3214 H7
3215 I7
3216 H7
3217 H8
3218 I9
3219 I7
3220 I9
3224 G11
3225 H11
3226 G11
3228 F12
3229 F10
3260 A6
3261 A6
3262 A6
3263 A6
3264 A9
3265 B8
3268 B10
3269 A10
5121 C5
5220 G9
5225 G11
5229 H10
5260 A5
5268 A10
6050 G3
6054 E1
6055 E1
6061 I3
6062 H6
6086 I1
6111 D1
6112 E1
6113 D2
6114 B9
6117 C3
6120 D4
6123 D8
6133 B5
6142 G4
6201 B8
6202 I4
6204 F4
6205 I5
6206 F5
6211 I6
6213 H7
6216 H8
6225 G10
6230 I10
6260 A5
6267 B9
6268 A9
6269 H8
6270 I8
6271 B10
7050 G3
7052 I3
7058 I1
7059 I2
7060-1 B11
7060-2 B11
7061 C11
7110 C2
7112 C2
7117 C3
7120 B5
7121 D7
7130 E8
7134 D10
7140-1 D5
7140-2 D6
7142 D6
7200 G6
7202 H5
7212 G7
7217 G8
7220 F9
7227 H12
7230 I11
7260 A8
9000 A12
9001 A12
9002 C6
9009 A11
F102 D12
F106 E13
F107 G13
F110 A1
F111 D9
F113 G4
F114 I12
F115 A12
F116 I12
F118 E12
F119 E12
F120 F12
F121 E13
F122 B12
F123 E13
F124 B12
F125 E10
F126 E11
F127 E11
F128 E11
F129 E12
F130 D12
F131 D12
F132 E13
F133 E12
F134 F12
F135 F12
F137 G13
F138 H12
F139 H12
F140 G12
F260 A5
F264 A12
F265 A5
F380 B13
I101 B2
I102 B3
I103 A7
I104 A6
I105 B1
I106 C3
I107 C4
I108 D4
I109 C2
I110 D3
I111 C5
I112 D3
I113 D1
I114 E2
I115 D2
I116 D2
I117 D3
I118 D4
I120 D8
I121 D7
I122 D10
I123 D9
I124 D7
I125 D9
I126 D8
I127 D7
I128 D8
I129 E10
I130 A9
I131 E7
I132 E9
I133 B9
I134 B10
I135 C6
I136 B10
I137 B13
I138 A9
I139 A7
I140 B8
I141 A8
I142 A6
I147 C2
I148 H9
I152 C9
I153 D6
I154 D6
I155 D6
I156 D6
I157 E6
I158 C1
I159 E1
I160 E2
I161 G2
I162 C2
I163 C1
I164 C1
I165 E3
I166 F6
I167 F7
I168 F7
I169 H8
I170 H10
I171 H11
I172 A6
I173 A6
I174 D9
I175 A10
I176 B10
I177 B11
I178 B11
I179 B11
I180 B11
I181 C11
I200 G3
I201 H3
I202 I3
I203 I1
I204 I2
I207 I1
I208 H5
I209 H9
I210 G5
I211 F5
I212 F6
I213 G5
I214 G7
I215 G6
I216 G8
I217 H7
I218 H7
I219 H8
I220 H4
I221 H7
I222 I4
I223 I7
I224 I7
I225 I1
I230 F11
I231 F11
I233 F10
I234 G11
I235 G11
I236 G9
I237 H11
I238 G10
I240 H9
I243 I11
I244 I3
I245 I8
I246 B6
I247 B9
I248 C4
I249 C5
F136 G12
3156 B11
Page 36

Circuit Diagrams and PWB Layouts
Layout PDP Supply Panel (Overview Top Side)
2028 C8
2021 D8
2014 B5
2007 A5
2000 A5
0201 B4
0311 G3
0203 D3
0323 F8
0204 D7
0342 F8
0306 G4
0352 E8
0307 G2
1002 A8
0308 G1
1003 F1
1004 F8
0309 G1
Part 1
F_15460_008a.eps
3104 313 6066.3
1082 C8
1083 B8
1084 A8
1110 D6
1200 E6
1260 F8
1400 F1
1402 F1
1450 F4
1460 E4
1M03 G5
1M05 G3
1M10 A8
1M46 G8
2001 E2
2002 G1
2003 E2
2004 E2
2005 A4
2006 A4
2008 A4
2009 A4
2010 A3
2011 B5
2012 A5
2013 C5
2016 A4
2017 C5
2018 A4
2019 E1
2020 B8
2023 E5
2024 E5
2025 E8
2026 A4
2027 A4
2022 B8
2015 A4
Part 3
F_15460_008c.eps
2029 C8
2030 E5
2031 E5
2032 A4
2033 A4
2034 B5
2035 A5
2036 A4
2037 B5
2038 D8
2039 B3
2040 B3
2041 B3
2042 B4
2043 E8
2044 C8
2045 C8
2046 B3
2047 A4
2048 A5
2049 A4
2050 E8
2051 F6
2052 B4
2053 A4
2054 D8
2055 D8
2056 D8
2057 D8
2058 C8
2059 D8
2060 A5
2061 D8
2062 A4
2070 B4
2071 B4
2090 B3
2111 D5
2112 D5
2113 D5
2114 D5
2117 D6
2118 C6
2121 C8
2122 E6
2123 D5
2126 D6
2133 E5
2138 E6
2203 F5
2205 F5
2210 F6
2211 F6
2212 F6
2213 D8
EN 36FTP2.4E AA 7.
2214 D8
2215 F6
2217 F6
2218 E6
2219 F5
2222 F8
2223 F8
2226 E8
2227 E8
2228 E8
2229 E6
2230 E6
2231 E7
2233 E8
2234 E8
2235 E8
2236 E8
2237 E8
2260 F8
2232 E6
2225 F8
Part 2
F_15460_008b.eps
2261 G8
2262 G8
2263 G8
2264 G8
2265 G8
2266 G8
2267 G8
2269 F8
2270 G8
2273 G8
2274 D6
2290 B8
2291 B8
2293 C8
2294 A8
2295 B8
2296 C8
2303 G7
2304 G7
2292 A8
2268 G8
Part 4
F_15460_008d.eps
2305 G7
2306 G7
2316 G7
2322 G7
2324 G7
2343 G6
2350 G7
2352 G6
2364 G6
2366 G6
2376 G6
2377 G6
2380 G7
2381 G6
2385 G6
2396 G7
2397 G4
2398 G7
2400 G1
2401 E1
2402 G1
2403 E1
2404 F2
2405 E1
2406 E2
2407 D1
2408 E2
2410 F3
2465 E5
2502 F5
2503 F4
2504 G4
2505 B3
2507 F5
2508 F5
2509 F5
2510 F5
2511 G4
2512 G4
2513 G4
2530 G4
2531 G4
F_15460_008.eps
120405
2532 G3
2533 G4
2534 G5
2540 G5
2541 G5
2600 E2
2601 D2
2602 B2
2603 B1
2604 C1
2605 C1
2608 A2
2610 C2
2611 D2
2612 B2
2613 B2
2614 B2
2616 D4
2617 C4
2640 A2
2642 A2
2651 A2
2653 A2
2654 B2
2655 A3
2656 B3
2660 A2
2661 A1
2662 A3
2663 A2
2664 A2
2665 B3
2666 A2
2670 A3
2671 A3
2672 A2
2673 B2
2674 B2
2675 B2
2676 B2
2677 B2
2690 B3
2691 B3
3001 B4
3002 B4
3003 A4
3004 A4
3005 A4
3006 A4
3007 A4
3008 A5
3009 A5
3010 A4
3011 A4
3012 A4
3013 A4
3014 C4
3015 C4
3016 C4
3017 B4
3018 B4
3019 B4
3020 A3
3021 B5
3022 E5
3023 E5
3024 D8
3025 E5
3026 G4
3027 A4
3028 E5
3029 E5
3030 E5
3031 E5
3032 E5
3033 B3
3034 E5
3035 F4
3036 D1
3037 D8
3038 D8
3039 D8
3040 E5
3041 E5
3042 A4
3043 A4
3044 A4
3045 A4
3046 A5
3047 A4
3048 A4
3049 A3
3050 B5
3051 D8
3052 D8
3053 D8
3054 B3
3055 C8
3056 A3
3057 E5
3058 D8
3059 B4
3060 B3
3061 B4
3062 D8
3063 D6
3064 A4
3065 A4
3066 A4
3067 A4
3068 G5
3069 A4
3070 A4
3071 A4
3072 D8
3073 B3
3074 G6
3075 C4
3076 C4
3077 A5
3078 B4
3079 D5
3080 E5
3081 B4
3082 B3
3083 D8
3084 D8
3085 D8
3086 D8
3087 D8
3088 D8
3089 A4
3090 A3
3091 B3
3092 A3
3093 B3
3094 A3
3095 A4
3096 A4
3097 A4
3098 E5
3100 E5
3101 D6
3102 G7
3103 G7
3104 A3
3106 D6
3107 D6
3108 D6
3109 D6
3110 D6
3111 E5
3112 D5
3113 D5
3114 D5
3115 D5
3116 D6
3117 D6
3118 D7
3120 D5
3121 D5
3122 E6
3123 E6
3124 D6
3125 D6
3126 E6
3128 E6
3130 D5
3131 D6
3132 E5
3133 E5
3134 D5
3135 D5
3136 D5
3138 E6
3139 E6
3140 E6
3141 E6
3142 E6
3143 E6
3145 E6
3146 E6
3147 D6
3148 E6
3149 F5
3150 D5
3151 G7
3152 G7
3153 G8
3154 G7
3155 G7
3156 G7
3157 G7
3158 G7
3200 F5
3202 F5
3203 G6
3204 F5
3205 F5
3206 F5
3207 F5
3208 F5
3209 F5
3210 E8
3212 F6
3213 F6
3214 F6
3215 F6
3216 F6
3217 F6
3218 F6
3219 F5
3220 G6
3224 E8
3225 E8
3226 E8
3228 E8
3229 E8
3260 F8
3261 F8
3262 G8
3263 G8
3264 G8
3265 G8
3268 G8
3269 G7
3292 B8
3300 E6
3301 E6
3302 F8
3303 G7
3304 G7
3305 G7
3306 G7
3307 G7
3308 G6
3311 F8
3312 G7
3313 G7
3316 G7
3317 G7
3320 G7
3321 G7
3322 G7
3323 G7
3324 G7
3325 F7
3326 G7
3327 F7
3328 G8
3332 G7
3333 G7
3334 G7
3335 G7
3340 G7
3341 G6
3342 G6
3343 G6
3344 G6
3345 G6
3346 G6
3347 G6
3348 G6
3349 G7
3350 G7
3351 G7
3352 G6
3353 G6
3354 G6
3355 G5
3356 G4
3357 G5
3358 G6
3359 G6
3360 G5
3361 G5
3362 G4
3363 G5
3364 G6
3366 G7
3367 G6
3368 F7
3369 G6
3370 F7
3372 G4
3373 G6
3374 G6
3376 G6
3377 G6
3378 G5
3380 G6
3381 G6
3382 G7
3383 G6
3384 G6
3385 G6
3386 G6
3387 G6
3388 G7
3389 G7
3391 G6
3396 F8
3397 G7
3400 F2
3401 G1
3404 E1
3450 E4
3451 E4
3452 C1
3460 E5
3461 E5
3463 F5
3465 F5
3467 F5
3469 E5
3470 F5
3471 G5
3472 G5
3501 G4
3502 F4
3503 F4
3504 G4
3505 F5
3506 E4
3507 F4
3508 D4
3509 D4
3520 G3
3530 G3
3601 A5
3602 A5
3603 A2
3604 A2
3605 A2
3606 B2
3607 A2
3608 B2
3609 A2
3610 B2
3611 B2
3612 A2
3613 B2
3614 C2
3615 C2
3616 B2
3617 A2
3618 A2
3619 B2
3620 C2
3621 C2
3622 C2
3623 A3
3639 A2
3640 A2
3641 A2
3642 A2
3643 A2
3651 A2
3652 B2
3654 B2
3655 A3
3656 B2
3659 A2
3660 A2
3661 A2
3662 A2
3663 A2
3664 A3
3665 B2
3666 A2
3667 A2
3668 B2
3669 A3
3671 A3
3673 B2
3675 A1
3676 A1
3677 A1
3678 A1
3679 B2
3680 B2
3681 B2
3682 B2
3683 B2
3684 B2
3685 B2
3686 B2
3690 B3
3691 B3
3692 B3
3693 A2
3800 F8
3801 G7
3802 G7
3803 F8
3804 G7
3805 G7
3806 G6
3807 G6
3808 G6
3809 G6
3811 G6
3999 A7
4300 G2
5001 B4
5002 A5
5004 C5
5005 E1
5121 D6
5220 E7
5225 E8
5229 E8
5260 G8
5268 G8
5290 A8
5291 A8
5292 A8
5293 A8
5401 F3
5402 D2
5500 F4
5503 F5
5600 B2
5601 B3
5612 C2
5660 A1
6002 A4
6003 B4
6004 B4
6005 B4
6006 B3
6007 C4
6008 B4
6009 A4
6010 A4
6011 A3
6012 E5
6018 C4
6019 B4
6021 C8
6023 E5
6027 C4
6028 B4
6029 E5
6031 A4
6032 A4
6033 A5
6034 A4
6035 A4
6042 D8
6044 C8
6045 C8
6050 E8
6054 D8
6055 D8
6061 D8
6062 F6
6075 D5
6077 B5
6086 D8
6095 A3
6111 D5
6112 D5
6113 D5
6114 E5
6117 D7
6120 D8
6123 D6
6133 D6
6142 E8
6201 E5
6202 F5
6204 G6
6205 F6
6206 G6
6211 F6
6213 F5
6216 F6
6225 F8
6230 E6
6260 F8
6267 G8
6268 G8
6269 E5
6270 E5
6271 G7
6291 B8
6292 B8
6312 G6
6313 G7
6321 G6
6322 G7
6325 F7
6333 G7
6334 G7
6335 G6
6340 G7
6341 G7
6344 G6
6347 G6
6362 G5
6364 G6
6365 G6
6366 G6
6375 G6
6376 G6
6378 G6
6460 F5
6461 E5
6470 E5
6471 E5
6501 F3
6502 F3
6503 D4
6504 F4
6505 F5
6506 F3
6510 E3
6511 E3
6512 E3
6513 F3
6520 G3
6530 G3
6531 G3
6600 E3
6601 A2
6602 A3
6605 D3
6606 E3
6608 B2
6609 B2
6611 C3
6640 A2
6641 A2
6642 A2
6643 A2
6651 A3
6652 A2
6653 A2
6654 B2
6660 A3
6661 A3
6663 A2
6665 A1
6666 B2
7001 A4
7002 D5
7003 E5
7004 G6
7005 D5
7006 B5
7007 C4
7008 B4
7009 A3
7010 E5
7011 E5
7012 B3
7013 B4
7017 A4
7018 A4
7020 C4
7021 B4
7042 D8
7050 D8
7052 D8
7058 D8
7059 D8
7060 G8
7061 G7
7090 A3
7091 B3
7092 B4
7093 A3
7110 D6
7112 D5
7117 D6
7120 D5
7121 D6
7130 D6
7134 D5
7140 E7
7142 E6
7200 F6
7202 F5
7212 G6
7217 F6
7220 E8
7227 E8
7230 E8
7260 G8
7304 G7
7308 G7
7326 F8
7327 G8
7330 G7
7341 G6
7348 G6
7351 G6
7352 G6
7362 G5
7366 G6
7375 G6
7376 G6
7389 G7
7391 G6
7460 E5
7461 G5
7465 F5
7470 E5
7500 G4
7501 G4
7502 G4
7530 G4
7540 F5
7601 B2
7602 B2
7608 B2
7610 B3
7640 A2
7641 A2
7642 A2
7650 A2
7654 A3
7655 B3
7656 B3
7661 A2
9000 G6
9001 G8
9002 E7
9003 G6
9004 G6
9005 G6
9006 G5
9007 B4
9009 G7
9020 G5
9021 G3
9022 G4
9023 F3
9025 F3
9028 G6
9401 G5
Page 37

Circuit Diagrams and PWB Layouts
Layout PDP Supply Panel (Part 1 Top Side)
Part 1
EN 37FTP2.4E AA 7.
F_15460_008a.eps
120405
Page 38

Circuit Diagrams and PWB Layouts
Layout PDP Supply Panel (Part 2 Top Side)
EN 38FTP2.4E AA 7.
Part 2
F_15460_008b.eps
120405
Page 39

Circuit Diagrams and PWB Layouts
Layout PDP Supply Panel (Part 3 Top Side)
EN 39FTP2.4E AA 7.
Part 3
F_15460_008c.eps
120405
Page 40

Circuit Diagrams and PWB Layouts
Layout PDP Supply Panel (Part 4 Top Side)
EN 40FTP2.4E AA 7.
Part 4
F_15460_008d.eps
120405
Page 41

Circuit Diagrams and PWB Layouts
Layout PDP Supply Panel (Bottom Side)
EN 41FTP2.4E AA 7.
3104 313 6066.3
F_15460_009.eps
060405
Page 42
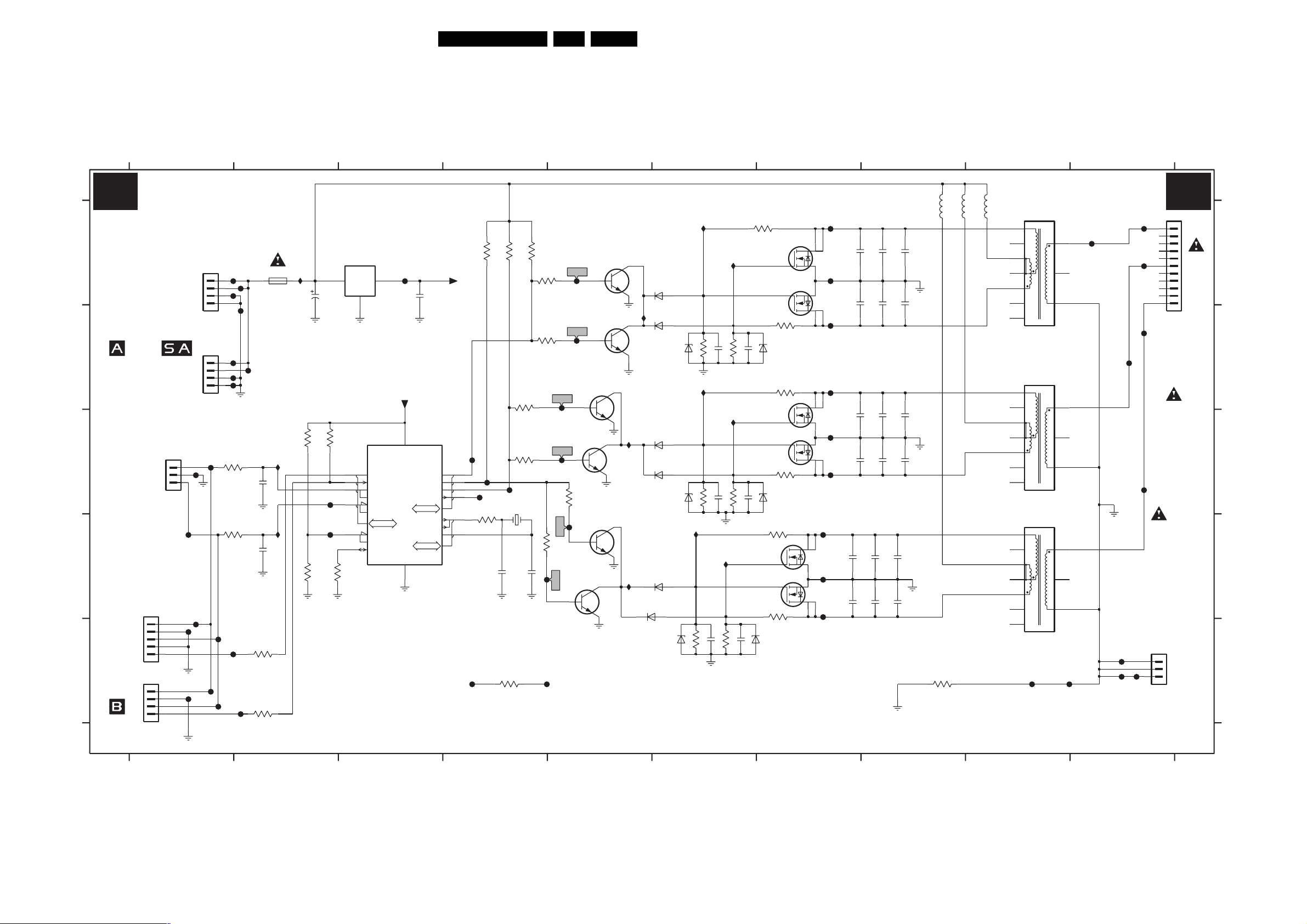
Ambi Light
1004 D1
1010 A2
1050 C4
1M08 A1
1M10 B1
1M11 B10
1M12 E10
1M48 C1
1M49 E1
2001 A2
2002 A3
2003 C2
2004 D2
2005 D4
2006 D4
2007 E6
2008 E6
2009 C6
Circuit Diagrams and PWB Layouts
2010 C6
2011 B6
2012 B6
2020 A7
2021 A8
2022 A8
2030 B7
2031 B8
2032 B8
2040 C7
2041 C8
2042 C8
2050 C7
2051 C8
2052 C8
2060 D7
2061 D8
2062 D8
2070 D7
2071 D8
2072 D8
3001 C1
3002 D1
3003 D4
3004 E6
3005 E6
3006 D7
123
3007 D7
3008 C6
3009 C6
3010 C7
3011 B7
3012 B6
3013 B6
3014 B7
3015 A7
3016 C2
3017 B4
3018 A4
3019 A4
3020 A4
3022 E2
3023 E2
3024 D4
3025 C4
EN 42FTP2.4E AA 7.
3026 D2
3027 D2
3028 C2
3029 A4
3030 B4
3031 C5
3042 E8
3999 E4
5002 A9
5007 A8
5008 A8
5014 A9
5015 B9
5016 C9
6000 A6
6001 B6
6002 C6
6003 C6
6004 D6
6005 D5
6006 B6
6007 B6
6008 C6
6009 C6
6010 E6
6011 E6
7001 C3
7002 A3
7009 B5
7010 C5
7011 E5
7015-1 A7
7015-2 A7
7016-1 C7
7016-2 C7
7017-1 D7
7017-2 D7
7018 A5
7019 B5
7020 D5
A001 E10
A002 B10
A003 A10
A004 A10
F001 C4
F002 C4
F003 C4
F004 C4
F005 C2
F006 D2
F007 E2
F008 E1
F009 E1
F010 E1
F011 E1
F012 E1
F013 E1
F014 E1
F015 D1
F016 C1
F017 C1
F018 B2
F019 B2
F020 B2
F021 B1
F022 B1
F023 A2
F024 A2
F025 A1
F026 A3
F027 A10
F028 B10
F029 C10
F030 E10
F031 E10
F032 E9
F033 E9
F034 E7
F035 D7
F036 D7
F037 C7
F038 C7
F040 B7
F041 B7
F042 A7
F043 A7
F045 B5
F046 C5
F047 D5
F048 A5
F050 B5
F060 D5
F098 E4
F099 E4
I001 A2
I002 C2
I003 D2
I004 D5
I005 C5
45678910
I006 B5
I007 A6
I008 A6
I009 B6
I010 C6
I011 D6
I012 D6
AL AL
A
TO 2nd AMBI
LIGHT PWB
(OPTIONAL)
TO
1M10 TO
B
OR
PDP
SUPPLY
OR
TO SDI SUPPLY
C
TO 2nd AMBI
LIGHT PWB
(OPTIONAL)
D
1004
1
2
3
NC
4
5
SSB
B5B-PH-K
1M49
1
2
3
4
B4B-PH-K
E
TO 1M49
3104 313 6072.6
1M10
AUDIO
STANDBY
1M48
B3B-PH-K
1
2
3
F015
F013
F009
1
2
3
4
B4B-PH-K
1
2
3
4
B4B-PH-K
F016
F014
F010
1M08
1M10
F017
F022
F012
F008
F025
F021
560R
3001
560R
3002
F011
F007
F019
F018
F024
F023
F020
2003
2004
3022
100R
3023
100R
1010
F 3A
I002
1n0
I003
1n0
I001
2001
3028
3026
10K
1K0
1m0 16V
3016
F005
F006
3
4K7
3027
7002
LD1117DT
OUTIN
COM
1
7001
P87LPC760BDH
9
TXD
8
RXD
7
SCL
T0
6
INT0
SDA
2
RST
P1.5
1
P1.7
1K0
F026
2
2002
+5V
113
VDD
Φ
MICROCONTROLLER
CMPREF
P0<3:6>
P1<0:3>
CLKOUT
P2<0:1>
VSS
100n
CIN1B
CIN1A
CMP1
I007
6006
3012 470R
BZX384-C18
I009
470R
6008
3008
BZX384-C18
I011
3004 470R
BZX384-C18
RED
6n82011
BLUE
6n82009
GREEN
I012
2007 6n8
3005 560R
F002
1050
20M
15p
4K7
3030
4K7
3025
4K7
3020
2006
4K7
3029
4K7
3017
4K7
3024
15p
F099
F050
F046
4K7
F060
4K7
F047
7011
BC847BW
F048
F045
3031
7018
BC847BW
7010
BC847BW
I006
7009
BC847BW
7019
BC847BW
I005
7020
BC847BW
I004
6000
BAS316
6001
BAS316
6002
BAS316
6003
BAS316
6004
BAS316
6005
BAS316
6010
4K7
3018
3019
+5V
F001
14
F003
13
12
10
F004
DSX840GA
3003
5
X2
X1
4
F098
220R
2005
3999
10K
I008
3013 560R
I010
560R
3009
6n82008
6n82012
2010 6n8
3015
1K0
2
4
3014
1K0
6007
BZX384-C18
3011
1K0
2
4
3010
1K0
6009
BZX384-C18
3007
1K0
2
4
3006
1K0
6011
BZX384-C18
12345678910
7
7017-1
SI4946
1
3
SI4946
7017-2
5
7
8
7015-1
SI4946
1
3
SI4946
7015-2
5
6
7
8
7016-1
SI4946
1
3
SI4946
7016-2
6
5
F036
8
F035
6
F034
F043
F042
F041
F040
F038
F037
2060
47n
2070
47n
47n
2020
47n
2030
47n
2040
47n
2050
47n2021
2022 47n
47n2032
2031 47n
47n2042
2041 47n
47n2051
2052 47n
47n2061
2062 47n
47n2072
2071 47n
WARNING HIGH VOLTAGE
5007
3042
1M0
22u
5008
22u
5002
22u
1
3
4
5
6
7
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
5014
BD21416-00
5015
BD21416-00
5016
BD21416-00
F033
F032
B11B-XASK-1
F027
A004
132
A003
11
9
A002
F028
13
11
9
F029
GND-HV
13
11
9
F030
F031
A001
B03B-XASK-1
TO
CCFL
1M12
F_15460_010.eps
AMBI LIGHT
1M11
TO
CCFL
1
2
CCFL
3
TO
11
10
9
8
7
6
CCFL
5
4
3
2
1
060405
TO
A
B
C
D
E
Page 43

Circuit Diagrams and PWB Layouts
EN 43FTP2.4E AA 7.
Layout Ambi Light (Top Side)
1004 B2
1010 B1
1050 B2
1M08 B1
1M10 B1
1M11 A2
1M12 A1
1M48 B2
1M49 B2
2001 B1
2002 B2
2003 B2
2004 B2
2005 B2
2006 B2
2007 B1
2008 B1
2009 B2
2010 B2
2011 B2
2012 B2
2020 A2
2021 A2
2022 A2
2030 A2
2031 A2
2032 A2
2040 A1
2041 A1
2042 A2
2050 A2
2051 A2
2052 A2
2060 A1
2061 A1
2062 A1
2070 A1
2071 A1
2072 A1
3001 B2
3002 B2
3003 B2
3004 B1
3005 B1
3006 B1
3007 B1
3008 B2
3009 B2
3010 B2
3011 B2
3012 B2
3013 B2
3014 B2
3015 B2
3016 B2
3017 B2
3018 B2
3019 B2
3020 B2
3022 B2
3023 B2
3024 B2
3025 B2
3026 B2
3027 B2
3028 B2
3029 B2
3030 B2
3031 B2
3042 A1
3999 B1
5002 B2
5007 B1
5008 B1
5014 A2
5015 A1
5016 A1
6000 B2
6001 B2
6002 B2
6003 B2
6004 B1
6005 B1
6006 B2
6007 B2
6008 B2
6009 B2
6010 B1
6011 B1
7001 B2
7002 B2
7009 B2
7010 B2
7011 B1
7015 B2
7016 B2
7017 B1
7018 B2
7019 B2
Layout Ambi Light (Bottom Side)
7020 B1
3104 313 6072.6
F_15460_011.eps
060405
3104 313 6072.6
F_15460_012.eps
060405
Page 44

Circuit Diagrams and PWB Layouts
EN 44FTP2.4E AA 7.
SSB: IF, I/O Video Processing
12
345678910
11 12 13 14
IF,I/O VIDEOPROCESSING
B2 B2
A
B
+5V_VDP
B13a
IF-TER
C
330n
5411
F437
D
B2(3x)
B15a(4x)
LMN
E
F
G
B2(3x)
B15a(4x)
H
LMN
3423
5K6
I
8204 000 8483.1
B5a
AGC
B13a
+8V_VDP
+5VS
3400
I444
I445
2K2
3415
I411
4K7
3463
3408
100R
22K
3441
A409
A410
+8V_VDP
9416
3416
2413
3419
390R
9418
5402
3421
3u9
1406
TPWKA
O
I
GND
I461
5K6
7406
BC847BW
7407
BC857BW
I462
3417
5K6
+8VP
4K7
3435
7410
BC847BW
F451
1K0
3405
I458
13
2
F413
4R7
+8VP
78
1
MODULATOR
COIL
2
6R8
34
I447
I446
47u
9417
9409
5406
3u3
1407
TPWKA
1
I
2
GND
9420
+8VP
4K7
3456
I463
SFSKA
O
4M5
4K7
3457
F411
1411
GND
I443
1u0
2377
2394
5CCB
5408
6
7411
BC847BW
I448
3
O
3445
120R
1K0
3420
13
I
2
9422
100u
2401
2416 1u0
2436 1u0
2404 1u0
3436
3439
+8V_VDP
3412
2414 100u
3404
9412
270R
2415
2411
100n
I450
10n
1K2
560R
1u02409
2417
470n
100n
3401
100K
V1
+8VP
2402
4R7
5404
5405
2418
F401
9414
7322
9413
9404
2300 47p
330p
7402
BC847BW
2387
I402
F403
3418
390R
5p6
12p
3437
1K0
BC847BW
560R
3300
1K0
9427
9408
2376
3382
3R9
3402
2412
4n7
BC847BW
2425
7405
I452
2405
3433
100u
+8VP
AGC-MONITOR
5416
+8V
100n
2391
+5VCOM
SAW-FILTER AUDIO
+8VP
2K7
3411
4n7
1SS356
3K9
6403
BA591
6u8
5401
3414
0V4
4K7
7403
BC847BW
9403
6402
1SS356
9405
6405
1SS356
3434
4K7
BC847BW
I460
3407
+8VP
3409
3406
27R
6404
6
78
1234
9402
7401
5K6
4K7
2406
220p
5
5403
5CCE
A400
+8VP
9415
9401
3410
2407
2408
2
3
1
4
5
6
9
10
13
14
15
18
4K7
2
3
1
4
5
6
9
10
13
14
15
18
68p
3p3
+8V_CON
1409
OFWK3953L
I1
I2
SAW-FILTER-VIDEO
SAW-FILTER VIDEO
GND
I
ISWI
GND
2
3
1
4
5
6
9
10
13
14
15
18
38M9
OFWK9656L
40M4
OFWK3953L
I1
I2
GND
NC
1410
38M9
O1
O2
O1
O2
NC
1408
9410
9407
I440
A411
A412
7
8
11
12
16
17
7
8
11
12
16
17
7
O1
8
O2
11
12
NC
16
17
COIL 40.4 SUPPRESSION
LMN
B2(3x),B15a(4x)
QSS_AM
B6a
SOUND-OUTPUT
B2
BG
CVBS-PIP_TUN1-2-CVBS-IN
B15a
CVBS-TER-OUT
B14b
B2,B15a(2x)
123456
B2
SOUND-OUTPUT
7V7
3380
100R
I441
1u0
100n
2378
100n
4V5
2V8
2419
I6
9419
7V7
I442
64
63
1
2
3
4
6
7
8
62
10
12
13
5
QSS_AM
SIF2
SIF1
AGCSIF
VIF1
VIF2
AGCDEC
PLLRILT
VCO1
VCO2
TUNERAGC
VIFOUT
GROUP
DELAY COR.
IN
OUT
F440
IF DEM
c002
1u0
2392
22n
2375
9
45
+8_2
GND_2
SUPPLY CTRL
1u0
2374
I421
2373
100n
I422
5V0
4V1
44
35
33
GND_1
DEC
DIGDEC
31
DIGGND
11
+8_1
HIP
TDA9321H/N2
I/O SWITCH
I467
14
CVBSINT
V2
100n
2384
I449
5318
33u
3385
470R
RES
CVBS116CVBS2
2365
9428
2339
2366
100n
10p
18
2367
100n
9322
I415
Y_CVBS320Y_CVBS4
C321C4
23
100n
100n
2369
2370
2368
100n
I417
2420150p
RES
PIPOUT
CVBSOUT
32
34
24
3370
I464
100n
10R
3474
BC847BW
I465
2410
RES
CVBS-SC1_AV1-IN
AV3-CVBS-IN
B14a,B14g,B15a
B14b
Y-CVBS-SC2_AV2-IN
CVBS-AV3-IN
nc
B14a,b
C-SC2_SVHS-IN
Y-CVBS-FRONT-IN
B14a
B14a(2x)
B14a,b,c(2x)
C-FRONT-IN
PIP-OUT
B14a
789
B14b
SC1-STATUS
48
ADSEL
7323
COMBOUT
26
100R
7320
+8V_VDP
3475
100u
3476
AV115AV2
+8VP
7415
BC847BW
B2,B15a(2x)
B14b
B2(3x),B15a(4x)
BG
LMN
SCL-F
SEL-SVHS-RR_STATUS2
3376
5V0
0V4
19
22
46
17
SCL
SW0
SW01
LUMA & CHROMA PROC.
YCOMBIN
CCOMBIN
28
29
2403
100n
2434
3413
100n
270R
1K0
3422
10R
2433
560R
1n0
2435
100n
47R
3371
3372
470R
I401
CVBS-TXT
CVBS-SC2_MON-OUT
B14b
B2(2x),B5a
B3a,B6a
B3a,B6a
SDA-F
100R
2372
3377
V9
3378
100R
V10
47
SDA
SYS125SYS2
27
0V
5V
COMB-C-OUT
SYS1
SYS2
COMB-Y_CVBS-OUT
B2
B2
B2
1u0
2371
15K
61
58
VA
HPLL
SYNC
SVBCOUT
SCOUT
30
59
FSC
B2
B2
VA50
F407
4n7
60
HA
R1IN
G1IN
B1IN
FBL1IN
R2IN
G2IN
B2IN
OUTP SWITCH
FBL2IN
YOUT
UOUT
VOUT
X3.579
X3.575
X3.582
X4.43
COL_PLL
SEC_DEC
+5VCOM
2424
100n
3303
100K
CVBS-TXT
SC
B2
HA50
F408
3468
50
57
9319
9318
2350
2351
100n
2352
100n
100n
+8VP
7408
2388
220n
I453
BC857BW
I454
3444
3447
680K
2305
36
37
38
39
41
42
43
9426
40
49
33p
2430
51
56
55
54
52
53
3393
100K
2357
2356
2358
100n
100n
2
INPSEL
12
Y|CVBS1
I434
3
Y|CVBS2
1
CIN
I435
7
SC
100K
I433
SC
100n
2316
100n
3n3
7307
TDA9181
2322
100n
1305
2359
7414
BC847BW
NR-18
4M433619
15p
2360
CLAMP
CLAMP
SAND-
CASTLE
AGND
13
9423
9424
3473
1p2
DGND
4
7307-p4
B2
39K
9425
+8VP
1306
B2
2389
2355
1K0
2379
G-SC1-IN_Y-IN
B-SC1-IN_U-IN
+8VP
3448
1u0
3449
SC2-R_C-IN_AV2
10p
2364
10p
SC2-B-IN_C-OUT
2383 10p
10p 2327
100n
2432
F404
F405
F406
NR-18
PAL N
3M582056
15p
2380
+5VCOM
2354
100n
FILTER
TUNING
I432
2353
FSC
B2
R-SC1_V-IN
7409
BC857BW
I455
10K
2K2
FBL-SC1-IN
SC2-G-IN
SC2-FBL-IN
B2,B6a
Y50
U50
V50
1307
2p2
2381
VCC6VDD
2H/4H DELAY
ADAPTIVE
COMB FILTER
FSC9FSCSEL
3301
100K
100n
B2(2x),B5a
10 11 12 13
NR-18
3M575611
15p
2382
CLOCK
GEN
SYS1
8
B2
B14c
B14c
B14c
B14c
B14b,g,B15a
B14b,g,B15a
B14c,g,B15a
B14b,B15a
Y50
B2,B6a
B6a
B6a
1308
PAL M
2p2
2362
2385
100n
5
SYS2
11
10
4V2
4V2
SYS1
SYS2
B2
NR-18
10p
Y|CVBSO
OUTSEL
15
BFR93AW
NTSC M
3M579545
2361
COUT
2p7
I456
+8VP
7413
3460
14
16
+8VP
3K3
100n
2422
9406
3451
I428
270R
I430
10p2426
CVBS-3D-COMB
COUT-3D-COMB
nc
nc
3461
I457
3462
I424
10p
2427
1K8
1K2
COMB-Y_CVBS-OUT
I426
3452
150R
5312
33u
2302
I431
100n
5309
5310
10p2428
YOUT-3D-COMB
nc
+5VS
I425
7412
BC857BW
I427
2421
10p
2423
7307-p4
YOUT-3D
COUT-3D
COMB-C-OUT
CVBS-TXT
COUT-3D
YOUT-3D
5311
F_15460_013.eps
14
3450
1K0
6p8
B2
B2
B2
B2
B2
B2(2x)
B5a
B2
B2
070405
A
B
C
D
E
F
G
H
I
1305 E11
1306 E12
1307 E12
1308 E13
1406 E5
1407 E5
1408 G4
1409 C3
1410 E4
1411 G6
2300 F7
2302 G14
2305 C11
2316 C11
2322 C11
2327 D12
2339 H8
2350 A11
2351 A11
2352 A11
2353 I12
2354 G12
2355 C12
2356 F11
2357 F11
2358 F11
2359 F11
2360 F11
2361 F13
2362 F13
2364 C12
2365 F8
2366 F8
2367 F8
2368 F8
2369 F8
2370 F8
2371 B10
2372 B10
2373 B8
2374 B8
2375 B8
2376 B7
2377 B6
2378 B7
2379 F12
2380 F12
2381 F12
2382 F12
2383 D12
2384 F7
2385 G13
2387 B7
2388 A11
2389 B12
2391 B3
2392 B8
2394 B6
2401 C6
2402 G6
2403 F9
2404 C7
2405 D1
2406 G2
2407 G3
2408 H3
2409 C7
2410 G9
2411 D6
2412 C1
2413 D5
2414 H6
2415 H6
2416 C7
2417 E6
2418 D6
2419 D7
2420 G8
2421 F14
2422 E13
2423 G14
2424 G10
2425 B1
2426 H13
2427 I14
2428 I14
2430 D11
2432 D12
2433 G9
2434 F10
2435 G9
2436 C7
3300 F7
3301 I12
3303 H10
3370 F9
3371 H9
3372 H9
3376 B9
3377 B10
3378 B10
3380 B7
3382 F7
3385 G7
3393 F11
3400 B5
3401 B7
3402 B1
3404 I6
3405 H5
3406 G2
3407 F2
3408 B5
3409 G2
3410 E3
3411 D2
3412 G6
3413 F9
3414 D2
3415 B5
3416 D5
3417 G5
3418 D7
3419 E5
3420 G6
3421 F5
3422 G9
3423 H1
3433 G1
3434 E2
3435 G5
3436 E6
3437 D7
3439 E6
3441 B5
3444 B11
3445 F6
3447 B11
3448 B12
3449 B12
3450 E14
3451 F14
3452 F14
3456 G5
3457 H5
3460 D13
3461 D14
3462 D14
3463 B5
3468 H10
3473 D11
3474 F9
3475 G9
3476 H9
5309 H14
5310 H14
5311 I14
5312 F14
5318 F7
5401 D2
5402 E5
5403 H2
5404 B7
5405 B7
5406 E6
5408 D6
5411 C1
5416 A3
6402 E2
6403 D2
6404 G2
6405 E2
7307 G11
7320 F9
7322 E7
7323 D9
7401 F2
7402 H7
7403 D2
7405 H1
7406 F5
7407 F5
7408 A11
7409 A12
7410 H5
7411 D6
7412 F14
7413 D13
7414 D11
7415 H9
9318 G11
9319 G11
9322 G8
9401 F3
9402 E2
9403 E2
9404 F7
9405 E2
9406 F13
9407 B4
9408 H7
9409 E6
9410 B4
9412 G6
9413 F7
9414 E7
9415 D2
9416 D5
9417 D6
9418 E5
9419 E7
9420 F6
9422 H6
9423 C11
9424 C11
9425 C12
9426 D11
9427 G7
9428 H8
A400 G3
A409 C5
A410 C5
A411 C4
A412 C4
F401 D7
F403 C7
F404 D12
F405 E12
F406 E12
F407 B10
F408 B10
F411 C6
F413 B6
F437 D1
F440 B8
I401 H10
I402 C7
I411 B5
I415 H8
I417 F8
I421 B8
I422 B8
I424 E14
I425 F14
I426 F14
I427 F14
I428 F13
I430 G14
I431 H14
I432 H12
I433 I11
I434 G11
I435 H11
I440 B4
I441 B7
I442 B7
I443 B6
I444 B5
I445 B5
I446 D5
I447 D5
I448 E6
I449 F7
I450 H6
I451 H5
I452 B1
I453 B11
I454 B12
I455 B12
I456 D13
I457 D14
I458 E4
I460 F2
I461 F5
I462 G5
I463 G5
I464 F9
I465 G9
I467 E7
c002 A8
Page 45

SSB: PICNIC
123
B3A
A
B
C
D
E
F
G
H
I
J
K
L
M
N
8204 000 8481.1
12
Circuit Diagrams and PWB Layouts
4
5678910111213
PICNIC
9809
3747
+3V3_DCDCFBXA
3903
3K9
7707
BC847BW
3755
3719
3K3
3720
10K
RES
5706
6u8
9707
680RRES
2915
RES
6u8
5708 RES
47p
680R
3933
RES
+5V2Pr
I810
2931
RES
150p
47K
100K
4K7
PMBT2369
9709
BC847BW
+3V3Pr
9776
7715
2916
HREF_EXT
B3c,d,B19d
+3V3_DCDCFBXA
3736
7709
I820
3739
12K
3756
+1V8FA
+1V5_FBXA
2747
2740
150p
22n
2741
22n
2742
22n
150p
F164
RES
F165
F166
2935
N.C.
1710
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
89
07FMN-BMT-A-TFT
+1V8FA
3748
100R
F709
10K
3741
5723
5724
RES
9701
RES
68p
F162
F163
18p
RES
B19d
B3a(2x),b
B3e,B19d
B3b,c(2x),d
B3b,c(2x),d
B3a(2x)
B3c(2x),d
B2,B6a
B2,B6a
B3c,d
B19d
B19b
B19b
B3b
B3d
B3c
B3d
B3d
B3e
B6a
B6a
B6a
B3e
RST-FEM
RST_COL
RST_PIC_EAG
RST-FBX
MF(17)
HD_E_T0
SN-DA
SN-CL
SCL-D
SDA-D
SCL-F
SDA-F
RSTW
RSTR_I
3V3_FAULT_FBX
F108
Y-PIP+MAIN-IN
U-PIP+MAIN-IN
F109
V-PIP+MAIN-IN
F110
3V3_FAULT_FBX
HA50
VA50
VAP
VA
SDA-EPLD
SDA-F
SCL-EPLD
SCL-F
I814
1K0
3722
22p
1K0
2707
3733
F115
3709
100R
F114
3710
100R
22p
2713
res
3713
180R
3714
180R
2719
3715
180R
2720
F119
F112
2722
100p
3826
100R
3827
100R
22p
2714
res
RES
3922
15p
2718
3716
100K
220R
680R
RES
3928
RES
+8VPA
3927
7776
BC857BW
RES
3929
220R
15p
220R
RES
100K
3717
9826
RES
3930
220R
15p
3718
100K
9827
2721
3728
3730
150R
560R
1K2
3726
9720
22p
2840
res
22p
2841
res
+8VPA
BC857BW
7775
7703
BC847BW
680R
3923
RES
9825
RES 2900
100p
RES
47p
RES
3926
BC857BW
7777
RES
3725
3734
100R
9726
680R
RES
3932
680R
3931
220R
9710
res
3924 RES
220R
RES
RES
3727
150R
3K3
9729
I720
3749
+3V3PA
+5V2Pr
2901
3925
47p
RES
5707
6u8
9708
+8VPA
RES 2902
* SEE MAPPING I1 ON B3c
** SEE MAPPING G1 ON B3c
3
3740
3732
47K
120K
2743
I815
3737
1K0
1K0
3738
3742
RES
+3V3_FBXB
+3V3_DCDCFBXA
+3V3PA
5714
2749
100n
3721 100R
2800
3706
100R
5705 6u8
3723
1M0
RES
1703
12MHz
CSTCV
1702
3
1
12M
2
F127
4K7
I813
+3V3_DCDCFBXA
7708
BC847BW
F145
100n
2744
I805
22K
3743
4K7
3905
F128
F129
100n
27p2881
RES
2929
RES
F122
F123
F124
F125
F126
100n
F708
7710
BC847BW
3750
10K
+2V5_FBXA
2806
100n
I804
I803
18p
B3c
7705
BC847BW
3K3
3751
F706
F707
3754
100R
+3V3_DCDCFBXA
3K9
2748
100n
2724
100p
2737
100p
F155
F156
I727
BAS316
3759
220R
2804
100n
F710
9706
TDOC
TRST
B3b,c,d
EN 45FTP2.4E AA 7.
14 15
5703
F107
5
7706
74LVC1G14GW
VCC
1
NC
A2
2917
100n
3752
1R0
3753
1R0
3K9
3746
9702
RES
4K7
3758
N.C.
9703
RES
F157
F158
6710
F159
F161
2757
22n
BAS316
6703
2920
100n
2807
1K0
3701
47K
+3V3PB
TMS
B3b,c,d
GND
220n
2918
res
9700
RES
+5V2Pr
+3V3Pr
5727
5728
RES
2754
2746
100n
74HC573PW
F784
F785
1
SN-DA
2
SN-CL
3
VSSO6
4
SCL
5
SDA
6
UP-RST
7
WD-RST
8
RSTW
9
RSTR
F788
10
FBL
11
VDDA1
12
Y-OUT
13
VSSA1
14
U-OUT
15
V-OUT
16
VSSA2
17
BGEXT
F160
18
H-D
19
V-D
20
AGND
21
DIFFIN
F118
22
VDDA2
23
Y-IN
24
VDDA3
25
U-IN
26
VIN
27
VSSA3
28
H-A
29
V-A
30
HREF-EXT
31
VDDA4
32
VSSA4
33
VSSX
100n
34
OSC-I
35
OSC-O
36
TEST
37
TRST
38
TMS
39
TDI
40
TDO
3712
F152
TCK
TDO
B3d
B3b,c,d
Y4
2709
3
+5V2Pr
+3V3Pr
AD(00)
RES
5726
5725
32
VCC
1n0
2732
2745
100n
M27C512-90-C1
1n0
1918171615
7712
20
ENC11D
11
1
23456
B3a
ALE
AD(02)
AD(00)
AD(01)
B3c
INT1
F786
AD(00)
F787
159T1160
158
157
T0
INT0
INT1
ANALOG
PROCESSING
PLL
OSC
BST
VSSO1
UVA043UVA1
TCK
42
44
41
UVA(0)
UVA(1)
UVA(2)
BAS316
Q013Q114Q215Q318Q419Q520Q6
A011A1
AD(03)
156
P0-0
CLK
TIMING
UVA245UVA346UVA447UVA548UVA649UVA750UVA8
+3V3_DCDCFBXA
I802
6701
100n
AD(01)
AD(02)
AD(03)
7711
A29A38A47A56A65A7
10
141312
10
GND
8
9
7
AD(04)
AD(05)
AD(06)
AD(07)
AD(01)
AD(02)
AD(03)
155
154
153
P0-1
P0-2
P0-3
3909
100R
AD(04)
AD(05)
AD(06)
21Q722
AD(04)
AD(05)
AD(06)
152
151
P0-4
P0-5
P0
3V3_FAULT_FBX
AD(07)
PROM
4
100n
AD(07)
150
149
P0-6
P0-7
A829A9
2731
148
VDDO3
B3e
A1024A1127A123A13
28
147
146
P2-0
P2-1
MICRO-PROCESSOR
PSP
3 X DAC
7713
PICNIC
SAA4978H/V203
3 X ADC
FRONT
END
BUS A
YA255YA356YA457YA558YA659YA760YA8
YA053YA1
VDDO1
54
52
51
100n
2735
+3V3PB
YA(2)
YA(1)
UVA(6)
UVA(7)
UVA(8)
YA(0)
UVA(3)
UVA(4)
UVA(5)
YA(3)
145
P2-2
17
DU11DU2
144
P2-3
YA(4)
12
NC2
30
143
P2-4
P2
YA(5)
26
NC1
A1431A15
142
P2-5
16
VSS
FBX
E_23G_
SOFTWARE
2
25
B3a
10R
ALE
3702
F151
139
141
140
137
136
138
ALE
P2-6
EAN
P2-7
PSEN
VSSD4
CLK
TIMING
BACK END
MID END
HISTOGRAM
REDUCTION
TIMING
WE-A
VSSO2
VSSD1
VDDD1
61
62
63
65
64
2736
100n
+3V3PB
YA(8)
YA(7)
YA(6)
WE-A
+3V3PB
2727
100n
1K0
intern
3711
RES
134
133
135
132
131
UVC0
UVC1
VSSD3
VSSO5
VDDD4
PEAKING
MUX
NOISE
TBC/SRC
MUX
WE-B
67
66
YB(5)
WE-B
YB(8)
YB(7)
YB(6)
11 12
UVB(0)
RES
3761
100R
9820
CL16
CLK32NE
100R
CLK32FM1
B3a
MF(17)
B3a,b
B3a(2x)
RSTW
RSTR_O
B3a,b,c
MF(17)
B3a,b
B3a(2x)
RSTW
RSTR_O
B3a,b,c
DA(00)
DA(01)
DA(02)
DA(03)
DA(04)
DA(05)
DA(06)
DA(07)
DA(15)
DA(14)
DA(13)
DA(12)
DA(11)
DA(10)
DA(09)
DA(08)
F148
F149
2733
100n
100n
2734
A139
F140
CLK-AS
CLK32P
CL16
+3V3PB
+3V3PB
B3a(2x),c
B3a,d
B3a,b
CLK32NE
B19b(2x)
CLK32P_EPLDCLK32G
100n
100n
2712
MS81V04160A
RES
3760
9728
B3a
CLK32P
B3a(2x),c
CLK32G
15 16 1745678910
B3a(2x),c
CLK32G
B3a(2x),c
B3a,d
B3a,b
DA(15)
DA(14)
DA(13)
DA(12)
DA(11)
DA(10)
DA(09)
+3V3PB
2726 100n
122
123
130
129
UVC2
UVC3
124
128
127
126
125
YC0
UVC8
UVC4
UVC5
UVC6
UVC7
VDDO2
BUS C
BUS D
CLK
BUS B
YB174YB273YB372YB471YB570YB669YB768YB8
YB0
75
76
YB(4)
YB(2)
YB(1)
YB(0)
UVB(6)
UVB(5)
UVB(4)
UVB(7)
UVB(8)
YB(3)
DA(08)
121
DA(07)
YC1
120
DA(06)
YC2
119
DA(05)
YC3
118
DA(04)
YC4
117
DA(03)
YC5
116
DA(02)
YC6
115
DA(01)
YC7
114
DA(00)
YC8
113
WE-C
112
IE-C
111
VSSO4
110
RE-D
109
YD8
108
YD7
107
YD6
106
YD5
105
YD4
104
YD3
103
YD2
102
YD1
101
YD0
100
VDDD3
99
UVD8
98
UVD7
97
UVD6
96
UVD5
95
UVD4
94
UVD3
93
UVD2
92
UVD1
91
UVD0
90
VSSD2
89
CLK32
CLK16
VDDD2
VSSO3
CLK-AS
UVB480UVB579UVB678UVB777UVB8
3700
88
22R
87
86
85
84
UVB0
83
UVB1
82
UVB2
81
UVB3
UVB(2)
UVB(1)
UVB(3)
13 14
16 17 18 19
+3V3PC
100n
2725
2717
2716
100n
7714
13
SWCK
63
SRCK
85
MODE1
41
MODE2
32
WE1
45
RE1
31
IE1
46
OE1
30
RSTW1
44
RSTR1
94
WE2
81
RE2
95
IE2
80
OE2
96
RSTW2
82
RSTR2
29
28
11
27
12
24
13
22
14
21
15
20
16
19
17
97
20
98
21
99
22
2
23
4
24
5
25
6
26
7
27
9772
3
2708
101617
9771
+3V3GA
100n
3437435162
11
121415
DUAL FIFO
(262,214 x 8) x 2
FM1
VSS
233335
39
4849545967
3703
9770
9769
VCC
Φ
+3V3GA
4K7
CY2302S
7702
1
2
4
5
6475838992
7277788791993
7
VDD
FBIN
FREQ.
MULTI.
IN
& ZDB
0
FS1OUT
1
2710
100n
2711
100n
1
8
18
25
26
36
38
40
42
47
NC
50
76
79
84
86
88
90
100
52
1010
53
11
55
12
56
13
57
14
58
15
60
16
61
17
74
20
73
21
71
22
70
23
69
24
68
25
66
26
65
27
+3V3GA
3704
100R
9768
+3V3GA
Φ
GND
3
3705
6
8
9767
2
RESERVED
B5a
VD-EPLD
B19d
VD-OTC
B5a
HD3-EPLD
B19c,d
B19c
B19c
B19c
B19c
B5a
B5a
B5a
B5a
HD3-OTC
2FHR-GFX
R-OSD
2FHG-GFX
G-OSD
2FHB-GFX
B-OSD
2FHFB-GFX
BL-OSD
3857
10R
2838
100p
3859
10R
100p
2926
RES
3861
10R
100p
2927
RES
1702 K6
3928 I3
1703 K6
3929 I3
1710 L5
3930 J3
2707 C2
3931 J4
2708 I16
3932 J4
2709 A8
A
B
C
D
E
F
G
H
I
J
K
L
M
N
2710 C17
2711 C17
2712 C15
2713 G2
2714 G3
2716 C16
2717 C15
2718 H3
2719 I3
2720 J3
2721 K3
2722 K3
2724 F6
2725 C16
2726 F13
2727 E11
2731 E9
2732 C7
2733 I14
2734 K14
2735 L9
2736 L10
2737 F6
2738 C18
2740 I5
2741 I5
2742 I5
2743 C6
2744 C6
2745 C8
2746 D7
2747 H5
2748 E6
2749 H6
2754 D7
2757 I7
2800 I6
2804 J6
2806 G6
2807 K7
2837 J18
2838 K17
2839 K18
2840 L3
2841 L3
2881 J6
2900 I4
2901 I4
2902 J4
2915 I5
2916 I5
2917 A7
2918 A7
2920 J7
2926 L17
2927 M17
2928 L18
2929 K6
2931 I5
2935 K5
3700 K14
3701 L6
3702 E11
3703 H16
3704 G17
3705 H18
3706 I6
3709 F3
3710 F3
3711 E11
3712 L7
3713 H3
3714 I3
3715 J3
3716 H3
3717 J3
3718 J3
3719 G5
3720 H5
3721 H6
3722 C3
3723 K6
3724 H18
3725 K4
3726 K3
3727 J4
3728 K3
3730 K3
3732 A6
3733 C3
3734 B4
3736 C5
3737 C6
3738 D5
3739 D5
3740 A6
3741 D5
3742 D6
3743 D6
3746 C6
3747 C5
3748 B5
3749 C4
3750 D6
3751 B6
3752 B7
3753 C6
3754 C6
3755 D5
3756 D5
3758 F7
3759 I6
3760 D15
3761 A14
3826 L3
3827 L3
3856 J18
3857 J17
3858 K18
3859 K17
3860 L18
3861 L18
3903 C5
3905 E6
3909 A9
3922 H3
3923 H4
3924 H4
3925 I4
3926 I4
3927 I3
3933 J4
5703 A8
5705 I6
5706 H5
5707 I4
5708 J4
5714 G6
5723 E5
5724 E5
5725 C8
5726 C7
5727 C7
5728 C7
6701 A8
6703 I7
6710 H6
7702 H17
7703 C4
7705 A6
7706 A7
7707 D5
7708 B6
7709 C5
7710 D6
7711 C8
7712 D7
7713 I9
7714 D16
7715 G5
7775 H4
7776 I3
7777 J4
9700 B7
9701 F5
9702 E6
9703 G7
9706 K6
9707 I5
9708 I4
9709 J5
9710 F4
9720 L3
9726 G4
9727 D18
9728 D15
9729 A4
9767 I18
9768 H17
9769 I16
9770 I16
9771 H16
9772 H16
9776 G5
9809 B5
9820 B14
9825 I4
9826 J3
9827 J3
A139 K14
F107 A8
F108 H2
F109 I2
F110 J2
F112 K3
F114 F3
F115 F3
F118 I7
F119 J3
F122 L6
F123 L6
F124 L6
F125 L6
F126 M6
F127 L5
F128 F6
F129 F6
F140 K14
F145 B6
F148 G14
F149 G14
F151 F10
F152 L7
F155 G6
F156 G6
F157 H7
F158 H7
F159 H7
F160 I7
F161 I7
F162 I5
F163 I5
F164 J5
F165 J5
F166 J5
F706 B6
F707 C6
F708 C6
F709 D5
F710 K6
F784 E7
F785 F7
F786 E8
F787 F8
F788 G7
I720 A4
I727 G6
I802 A8
I803 I6
I804 H6
I805 D6
I810 H5
I813 A6
I814 C3
I815 C5
I820 D5
B3A
100n
2738
RES
9727
+3V3PC
MF(16)
MF(15)
MF(14)
B3b
MF(13)
MF(12)
MF(11)
MF(10)
MF(9)
MF(1)
MF(2)
MF(3)
MF(4)
B3b
MF(5)
MF(6)
MF(7)
MF(8)
3724
100R
100R
3856
10R
100p
2837
3858
10R
2839
100p
RES
3860
10R
100p
2928
RES
18
B3a
CLK32FM1
B3b,c
CLK32
F_15460_014.eps
120405
19
Page 46
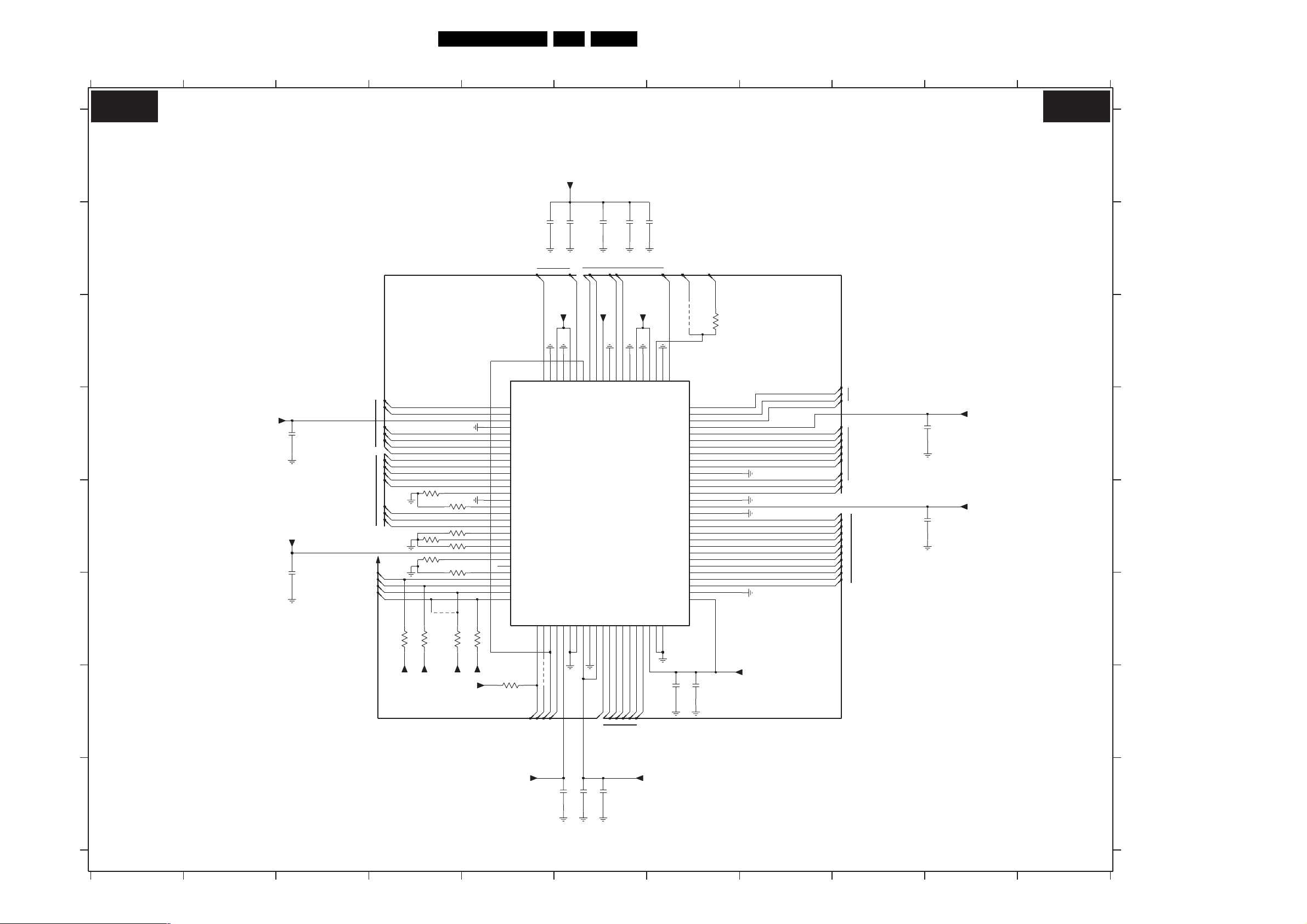
Circuit Diagrams and PWB Layouts
SSB: (FEM) Falconic Embedded Memory
123
B3B
FEM
FALCONIC EMBEDDED MEMORY
A
B
C
+3V3FA
D
E
F
2886
+3V3FB
2885
100n
100n
B3c,B19d
B3c,B19d
B3a,c,d
B3a,c,d
B3d
B3c
TRST
TMS
TDOA
TDOB
YG(5)
YG(4)
YG(3)
YG(2)
YG(1)
YG(0)
UVG(7)
UVG(6)
UVG(5)
UVG(4)
UVG(3)
UVG(2)
UVG(1)
UVG(0)
3880
3890
47K
EN 46FTP2.4E AA 7.
4
3885
1K0
3886
1K0
1K0
3891
3882
47K
3889
1K0
1K0
3887
1K0
3883
3881
3888
1K0
9810
47K
567891011
B3B
+1V8FA
100n
47K
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
YG5|DPIP5
YG4|DPIP4
VDDE1
VSSE1
YG3|DPIP3
YG2|DPIP2
YG1|DPIP1
YG0|DPIP0
UVG7|QPIP7
UVG6|QPIP6
UVG5|QPIP5
UVG4|QPIP4
UVG3|QPIP3
NC|LLC
VSSE2
NC|SWCK2
UVG2|QPIP2
UVG1|QPIP1
UVG0|QPIP0
NC|RSTW2
NC|OIE2
NC|IE2
VDDP
NC|WE2
ACV|RE2
NC|RSTR2
TRSTN
TMS
TDI
TDO
2876
2875
100n
B3c,B19d
YG(7)
97
99
98
96
100
VSSM3
VSSM4
VDDM4
VDDM3
YG6|DPIP695YG7|DPIP7
VDDE2
PIPON
RST
SNDA33SNRST
TCK
37
35
36
32
34
31
2877
UVF(0)
UVF(1)
+1V8FA
94VD91
93
UVF092UVF189UVF2
FEM
7760
SAA4998H/V1
VSSM139VSSM2
VDDM140VDDM2
38
41
90
VDDA
SNCL
42
2887
100n
B3c
UVF(3)
UVF(2)
87
88
UVF3
VSSA
UVA043UVA144UVA2
45
2888
100n
+1V8FA+1V8FA
85
84
86
VSSS2
VSSD3
VDDD3
UVA346UVA447UVA5
48
100n
83
CLK32
VDDS2
VSSD1
VDDD1
49
UVF(4)
82
81
UVF4
VSSE4
UVF5
UVF6
UVF7
VDDE3
VSSE3
REF
VSSD2
VDDD2
REA
UVA7
UVA6
VSSS1
VDDS1
TWOFMON
50
YF0
YF1
YF2
YF3
YF4
YF5
YF6
YF7
YA7
YA6
YA5
YA4
YA3
YA2
YA1
YA0
B3a,c
CLK32
9808
IE
80
79
78
77
76
75
74
73
72
71
70
69
68
67
66
65
64
63
62
61
60
59
58
57
56
55
54
53
52
51
B3a
CLK32NE
3876
100R
RES
UVF(5)
UVF(6)
UVF(7)
YF(0)
YF(1)
YF(2)
YF(3)
YF(4)
YF(5)
YF(6)
YF(7)
RE_F
MF(17)
MF(16)
MF(15)
MF(14)
MF(13)
MF(12)
MF(11)
MF(10)
MF(9)
MF(8)
MF(7)
B3c
B3c
B3c(2x)
B3a
2878
2879
+3V3FA
100n
+1V8FA
100n
A
B
C
D
E
F
2723 G7
2875 B5
2876 B6
2877 B6
2878 D9
2879 E9
2880 G7
2882 H6
2883 H6
2884 H6
2885 F3
2886 D3
2887 B6
2888 B6
3876 C7
3880 F4
3881 F4
3882 F4
3883 F5
3884 G5
3885 E4
3886 E4
3887 E5
3888 E4
3889 E5
3890 E4
3891 E4
7760 E6
9808 C7
9810 F4
9811 G5
G
H
8204 000 8481.1
1234
+3V3FA
+3V3FA
+3V3FA +3V3FA
+3V3FA
3884
47K
TCK
9811
RST-FEM YG(6)
RSTR_O
SN-DA
SN-CL
MF(1)
MF(2)
MF(3)
MF(4)
MF(5)
MF(6)
2723
100n
2880
100n
+1V8FA
B3a
+3V3FA
B3a,c,d
B3a(2x),c
B3a,c(2x),d
2884
100n
2883
B3a,c(2x),d
2882
100n
B3a
+1V8FA
100n
5678910
F_15460_015.eps
070405
11
G
H
Page 47
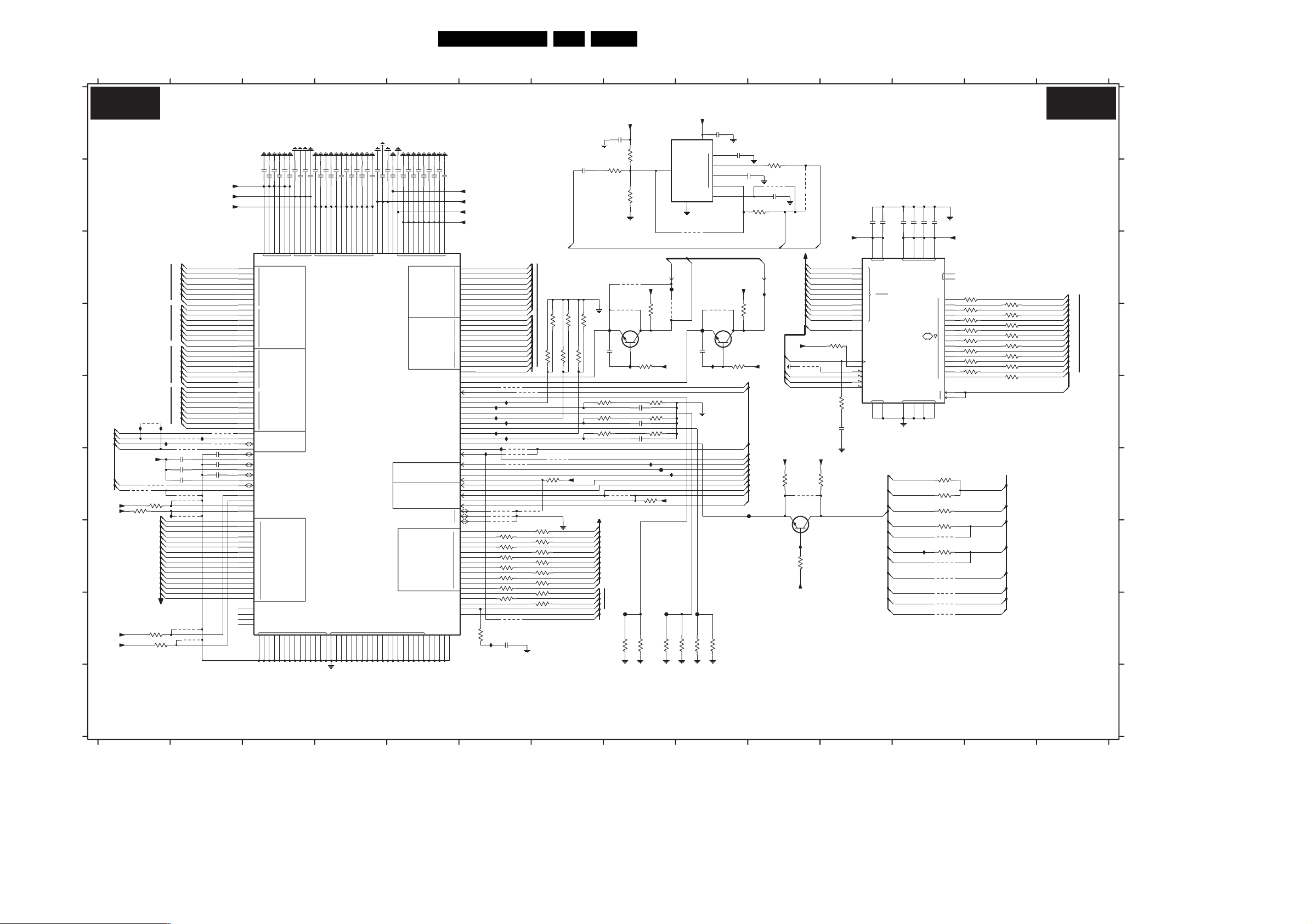
Circuit Diagrams and PWB Layouts
EN 47FTP2.4E AA 7.
SSB: Eagle
1
B3C B3C
EAGLE
A
B
C
B3b
B3b
D
B3b,B19d
B3b,B19d
E
F
G
B3a,b,c,d
B3a,c,d
B3a,b,c,d
B3a(2x),b
B3c
B3a
+3V3EA
+3V3EA
I731
SN-CL
RSTR_I
SN-DA
RSTR_O
+2V5EA
EAG_DQM
RST_PIC_EAG
9763
3799
RES
3798
RES
9712
4K7
I732
I714
100n
100n
100n
9723
RES
4K7
I733
EAG_SD_DQ(0)
EAG_SD_DQ(1)
EAG_SD_DQ(2)
EAG_SD_DQ(3)
EAG_SD_DQ(4)
EAG_SD_DQ(5)
EAG_SD_DQ(6)
EAG_SD_DQ(7)
EAG_SD_DQ(8)
EAG_SD_DQ(9)
EAG_SD_DQ(0:15)
EAG_SD_DQ(10)
EAG_SD_DQ(11)
EAG_SD_DQ(12)
EAG_SD_DQ(13)
EAG_SD_DQ(14)
EAG_SD_DQ(15)
B3c
H
+3V3EA
+3V3EA
3819
3820
RES
4K7
4K7
2345
2782
2784
2785
2799
1n0
1n0
1n0
1n0
1n0
2251125
61
LUMINANCE
COLOUR DIFFERENCE
ADDRESS SDRAM
156
161
168
178
2760
139
183
2762
2761
1n0
1n0
149
162
63
200
UVF(0:7)
YF(0:7)
UVG(0:7)
YG(0:7)
9756
9758
9740
9765
9766
9704
UVF(0)
UVF(1)
UVF(2)
UVF(3)
UVF(4)
UVF(5)
UVF(6)
UVF(7)
YF(0)
2789
2791
2793
9705
RES
YF(1)
YF(2)
YF(3)
YF(4)
YF(5)
YF(6)
YF(7)
UVG(0)
UVG(1)
UVG(2)
UVG(3)
UVG(4)
UVG(5)
UVG(6)
UVG(7)
YG(0)
YG(1)
YG(2)
YG(3)
YG(4)
YG(5)
YG(6)
YG(7)
I713
100n
100n
100n
2805
2750
2756
2759
2808
2753
2755
2809
2752
2751
1n0
1n0
1n0
1n0
1n0
+2V5EC
+2V5ED
+1V5EA
9755
9757
2788
2790
2824
1n0
7720
EAGLE1C
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
190
191
192
193
194
195
196
197 32
201
202
203
204
205
206
207
208
24
25
33
23
57
58
66
67
73
74
146
48
159
158
49
50
176
175
174
171
170
169
166
165
177
179
180
181
186
187
188
189
53
153
154
164
29
0
1
2
3
UVF
4
5
6
7
0
1
2
3
YF
4
5
6
7
0
1
2
3
UVG
4
5
6
7
0
1
2
3
YG
4
5
6
7
SNCL
SNRST
SNDA
SNRSTO
VREFY
VBSY
VREFU
VBSU
VREFV
VBSV
DQM
RESET
IS0
IS1
BISTEN
PLLND2
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
DQ
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
1
28
95
83
90
VDD
INPUT BUS F
INPUT BUS G
DATA SDRAM
52
85
98
104
111
SNERT
VSS
107
117
2768
2769
2771
2794
2770
1n0
1n0
1n0
1n0
1n0
1n0
1n0
1n0
1n0
113
10
214478
3087101
VDD2 VDDC VDDS
96
112
VIDEO ENHANCEMENT
PROCESSOR
EAGLE - IC
2034437786
11
184
124
135
145
148
160
173
2778
2797
2796
2777
2795
2773
2772
1n0
1n0
1n0
131
143
2780
2798
2781
1n0
1n0
1n0
1n0
1n0
1n0
1n0
1n0
151
167
182
199
697660
152
AVDDV
AVDDY
AVDDU
108
VSS2
114
123
130
AVDPLL
CLOCK
BOUNDARY SCAN
144
150
Φ
97
2763
2764
1n0
1n0
172
OUTP_VAL
TESTSEL
SDCLKOUT
AVSSV
AVSSU
70
2821
1n0
185
198
AOUTNY
AOUTPY
FSADJY
AOUTNU
AOUTPU
FSADJU
AOUTNV
AOUTPV
FSADJV
FALREF
CLK32O
CLK64O
CLKSEL
ADDR
SDCLKIN
AVSSY
54
155
2822
Y
UV
HD
HREF
INTR
REFIN
CLKI
TRST
TMS
TDI
TDO
TCK
RASN
CASN
WEN
DVSS
AVSPLL
62
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
VD
VA
0
1
2
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
I
8204 000 8481.1
123456
67891011121314
F766
3814
150R
150R
150R
REF
HD_E
F714
9731
I719
+3V3EA
75R
ZERO
DELAY
BUFFER
GND
4
9730
B3a,19d
res
3815
+3V3ED
6
Φ
HD_E_T0
F715
75R
3817
VDD
CLK
CLKOUT
2787
RES
F767
1
2
3
4
7718
PMBT2369
68p
I819
75R
3818
2758
1n0
3
2
5
7
8
9751
HREF_EXT_E
75R
2815
10p
RES
3783
1K0
VAP_E
RE_F
FALREF
CLK32IN
CLK32O
CLK64
TRST
TMS
TDOB
TDOC
TCK
3898
100R
2816
10p
9711
2814
15p
3729
100R
VD_E
B19d
+3V3EA
I736
1K0
RES
3765
RES
+2V5ED+2V5ED
B3c
B3c
EAG_SD_CLK
EAG_SD_A(0:11)
EAG_SD_CLK
EAG_SD_CASN
EAG_SD_WEN
B3c
+3V3EB
9821 9822
EAG_SD_A(0)
EAG_SD_A(1)
EAG_SD_A(2)
EAG_SD_A(3)
EAG_SD_A(4)
EAG_SD_A(5)
EAG_SD_A(6)
EAG_SD_A(7)
EAG_SD_A(8)
EAG_SD_A(9)
EAG_SD_A(10)
EAG_SD_A(11)
9752
+3V3EB
EAG_SD_CLKIN
MSM56V16160F-6TS
3778
4K7
75R
RES
3906
1n0
RES
2936
2830
2832
2831
100n
100n
7719
25
1
VDD
21
0
22
1
23
512K X 16 X 2
2
24
3
27
4
0
28
A
5
512K-1
29
6
30
7
31
8
32
9
20
10
19
A11
35
CLK
34
CKE
18
CS
17
RAS
16
CAS
15
WE
VSS
26
50
100n
71338
Φ
DRAM
4
2833
100n
100n
VDDQ
VSSQ
104147
2834
D
DQM
100n
2835
+3V3EC
44
33
NC
37
2
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
U
L
3762
3
68R
5
3764
6
68R
8
3768
9
68R
11
3770
12
68R
39
3775
40
68R
42
3779
43
68R
45
3781
46
68R
48
3804
49
68R
36
14
EAG_SD_DQ(0)
3763
EAG_SD_DQ(1)
68R
EAG_SD_DQ(2)
3767
EAG_SD_DQ(3)
68R
EAG_SD_DQ(4)
3769
EAG_SD_DQ(5)
68R
EAG_SD_DQ(6)
3774
EAG_SD_DQ(7)
68R
EAG_SD_DQ(8)
3777
EAG_SD_DQ(9)
68R
EAG_SD_DQ(10)
3780
EAG_SD_DQ(11)
68R
EAG_SD_DQ(12)
3784
EAG_SD_DQ(13)
68R
EAG_SD_DQ(14)
3803
EAG_SD_DQ(15)EAG_SD_RASN
68R
EAG_DQM
B3b,c
F720
B19d
B3c
B3c
B19b
B3a,b,d
B3a,b,d
B3b
B3a
B3a,b,d
+3V3EA
2K2
3793
PMBT2369
1K0
9777
7725
I816
+3V3EA
3745
+5V2Pr
B19b
2K2
3744
B3a,d,B19d
CLK32I
B3a(3x)
CLK32G
B3c
CLK32O CLK32
INT1
B3a
B3a,d
VAP
B19d
VREF
HREF_EXT
B19d
HREF
B3b,c
RE_F
B3a,b,c,d
SN-DA
B3a,b,c,d
SN-CL
B3a,c,d
RSTR_I
3821
33R
3822
RES
27R
3823
68R
3824
RES
10R
9717
I734
3825
RES
10R
9718
9719
9713
9714
9721
HREF_EXT_E
SN-DA_EPLD
SN-CL_EPLD
CLK32IN
VAP_E
RSTR_EPLD
B3c
B3a,b
B3c
B3c
B19d
REF
B19d
B19d
B19d
12 13 14
+1V5EB
+2V5EA
+2V5EB
+3V3EA
116
115
110
109
106
105
103
102
100
99
94
93
92
91
89
88
84
82
81
80
79
26
27
35
55
56
59
64
65
68
71
72
75
31
46
47
163
147
118
157
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
45
136
134
133
132
119
120
121
122
126
127
137
138
140
141
142
128
129
3850
+3V3ED
9750
F765
3811
3895
3897
9732
res
7721
CY2305SC-1
2K2
1
2K2
+3V3EA
1K0
3766
7717
PMBT2369
I730
3782
1K0
3802
2825
100n
3757
2827
100n
3795
2823
100n
I717
F718
3797
4K7
75R
75R
3812
2765
1n0
2812
3896
82R
1n0
EAG_SD_CLKOUT
B19d
YOUT(0)
YOUT(1)
YOUT(2)
YOUT(3)
YOUT(4)
YOUT(5)
YOUT(6)
YOUT(7)
YOUT(8)
YOUT(9)
U_VOUT(0)
U_VOUT(1)
U_VOUT(2)
U_VOUT(3)
U_VOUT(4)
U_VOUT(5)
U_VOUT(6)
U_VOUT(7)
U_VOUT(8)
U_VOUT(9)
O_VAL
9753
9754
I818
I817
I811
I808
I812
I809
I715
I716
RES
9759
9760
9761
9773
9774
9775
3912-4
68R
3919
68R
3911-3
68R
3911-1
68R
3921
68R
3912-1
68R
3901
68R
9715
82R
2925
I806
1n0
9762
75R
75R
75R
I735
3773
3771
3772
75R
75R
75R
3776
3800
3794
9716
4K7
3796
+3V3EA
RES
3801
3792
3894
2786
68p
RES
150R
150R
150R
RES
9764
B3c
3912-3
3918
3911-4
3911-2
9823
3912-2
3900
3902
EAG_SD_CLKOUT
EAG_SD_A(0)
EAG_SD_A(1)
EAG_SD_A(2)
EAG_SD_A(3)
EAG_SD_A(4)
EAG_SD_A(5)
EAG_SD_A(6)
EAG_SD_A(7)
EAG_SD_A(8)
EAG_SD_A(9)
EAG_SD_A(10)
EAG_SD_A(11)
EAG_SD_RASN
EAG_SD_CASN
EAG_SD_WEN
EAG_SD_CLKIN
REFIN
EAG_SD_A(0:11)
B3c
B19d
68R
68R
68R
68R
68R
68R
68R
68R
7 8 9 10 11
B3c
EAG_SD_DQ(0:15)
B3c
F_15460_016.eps
070405
A
B
C
D
E
F
G
H
I
2750 B3
2751 B3
2752 B3
2753 B3
2755 B3
2756 B3
2758 A9
2759 B3
2760 B5
2761 B5
2762 B5
2763 B5
2764 B5
2765 A8
2768 B4
2769 B4
2770 B4
2771 B4
2772 B4
2773 B4
2777 B4
2778 B4
2780 B4
2781 B5
2782 B5
2784 B5
2785 B5
2786 D8
2787 D9
2788 F2
2789 F2
2790 F2
2791 F2
2793 F2
2794 B4
2795 B4
2796 B4
2797 B4
2798 B4
2799 B5
2805 B3
2808 B3
2809 B3
2812 B7
2814 B10
2815 A9
2816 B10
2821 B5
2822 B5
2823 E8
2824 F2
2825 E8
2827 E8
2830 B11
2831 B11
2832 B12
2833 B12
2834 B12
2835 B12
2925 H6
2936 E11
3729 B10
3744 F11
3745 G10
3757 E8
3762 C13
3763 D13
3764 D13
3765 D9
3766 D8
3767 D13
3768 D13
3769 D13
3770 D13
3771 D7
3772 D7
3773 D7
3774 D13
3775 D13
3776 D7
3777 D13
3778 D11
3779 D13
3780 D13
3781 D13
3782 D8
3783 D9
3784 D13
3792 E7
3793 F10
3794 D7
3795 E8
3796 F7
3797 F8
3798 F1
3799 F1
3800 D7
3801 E7
3802 E8
3803 E13
3804 D13
3811 H8
3812 H8
3814 H8
3815 H9
3817 H9
3818 H9
3819 H1
3820 H1
3821 F12
3822 F12
3823 F12
3824 G12
3825 G12
3850 H6
3894 E7
3895 B8
3896 B8
3897 A8
3898 B10
3900 H7
3901 H6
3902 H7
3906 E11
3911-1 G6
3911-2 G7
3911-3 G6
3911-4 G7
3912-1 G6
3912-2 G7
3912-3 G7
3912-4 G6
3918 G7
3919 G6
3921 G6
7717 D8
7718 D9
7719 C11
7720 C3
7721 A8
7725 F10
9704 H2
9705 H2
9711 B10
9712 E1
9713 H12
9714 H12
9715 H6
9716 F7
9717 G12
9718 G12
9719 G12
9721 H12
9723 F1
9730 C9
9731 D8
9732 C8
9740 F2
9750 D8
9751 D9
9752 D10
9753 E6
9754 E6
9755 E2
9756 E2
9757 F2
9758 F2
9759 F6
9760 F6
9761 F6
9762 F7
9763 F1
9764 F8
9765 F2
9766 F2
9773 F6
9774 G6
9775 G6
9777 F10
9821 B10
9822 B10
9823 G7
F714 C9
F715 D9
F718 F8
F720 G10
F765 H8
F766 H8
F767 H9
I713 E2
I714 E1
I715 E6
I716 F6
I717 F8
I719 F8
I730 D8
I731 E1
I732 E1
I733 F1
I734 G12
I735 D7
I736 C10
I806 H6
I808 E6
I809 E6
I811 E6
I812 E6
I816 G10
I817 E6
I818 E6
I819 D9
Page 48

Circuit Diagrams and PWB Layouts
EN 48FTP2.4E AA 7.
SSB: Columbus
12345
B3D B3D
A
B
B3d
C
B3d
D
COLUMBUS
+3V3CB
2854
100n
2853
100n
2851
2852
4K7
3846
100n
9803
9802
9801
9800
2850
100n
COL_SD_A0
COL_SD_A1
COL_SD_A2
COL_SD_A3
COL_SD_A4
COL_SD_A5
COL_SD_A6
COL_SD_A7
COL_SD_A8
COL_SD_A9
COL_SD_A10
COL_SD_A11
COL_SD_CLK
+3V3CB
COL_SD_RASN
COL_SD_CASN
COL_SD_WEN
100n
2855
B3d
100n
+3V3CB
COL_DQM
B3d
1
25
VDD
21
0
22
1
23
2
24
3
27
4
28
A
5
29
6
30
7
31
8
32
9
20
10
19
A11
35
CLK
34
CKE
18
CS
17
RAS
16
CAS
15
WE
VSS
71338
Φ
DRAM
512K X 16 X 2
0
512K-1
SDRAM
MSM56V16160F-7TS
4
26 50
VDDQ
7753
VSSQ
104147
44
33
37
NC
2
1
3
2
5
3
6
4
8
5
9
6
11
7
DQM
12
8
39
9
40
10
42
11
43
12
45
13
46
14
48
15
49
16
36
U
14
L
D
COL_SD_DQ1
COL_SD_DQ2
COL_SD_DQ3
COL_SD_DQ4
COL_SD_DQ5
COL_SD_DQ6
COL_SD_DQ7
COL_SD_DQ8
COL_SD_DQ9
COL_SD_DQ10
COL_SD_DQ11
COL_SD_DQ12
COL_SD_DQ13
COL_SD_DQ14
COL_SD_DQ15
COL_SD_DQ16
COL_DQM
B3d
B3d
B3d
E
(ONLY FOR 3D COMB)
F
G
B3a
B3a,b,c
B3a
B3b
B3a,b,c
B3a,b,c
RST_COL
TCK
TDO
TDOA
TMS
TRST
3853
+3V3CA
+3V3CA
47K
100n
100n
+3V3CA
P13/N14
L13
G13
N11
2868
2860
100n
100n
N9
2869
C12
2861
100n
C11
2870
100n
100n
2862
E13
2819
100n
100n
2863
H13
2836
100n
100n
2864
100n
N8
2859
100n
+1V5CA
K3
N6
100n
2867
COLUMBUS_CTRL
G3
M3/N3
C4
2856
100n
100n
2857
2858
H
C7/B8
2865
100n
D3
2866
9804
+3V3CA
4K7
3847
9806
9807
678
7752-1
COL_SD_RASN
COL_SD_CASN
COL_SD_CLK
COL_SD_WEN
COL_SD_A0
COL_SD_A1
COL_SD_A2
COL_SD_A3
COL_SD_A4
COL_SD_A5
COL_SD_A6
COL_SD_A7
COL_SD_A8
COL_SD_A9
COL_SD_A10
COL_SD_A11
B3a,c,B19d
4K7
3848
9805
B3a
B3a,c
B3a
T6TU5XBG
I801
7752-2
G15
H15
H14
G14
A7
D15
F15
E15
E14
F14
A8
F1
H3
9812
CL16
WE-A
YA(0)
YA(1)
YA(2)
YA(3)
YA(4)
YA(5)
YA(6)
YA(7)
YA(8)
VAP
HREF_EXT
UVA(0)
UVA(1)
UVA(2)
UVA(3)
UVA(4)
UVA(5)
UVA(6)
UVA(7)
UVA(8)
C4
RESET
CLKSEL
CLKEXT
A0IIC
656SEL
TCK
TDI
TDO
TMS
TRST
TST1
TST2
TST3
G3
C12
B14
B2
+3V3CA
N3
M3
L13
G13
VDDS
C3C5C6C9C10
T6TU5XBG
L14
K15
K14
J14
J15
P6
R6
P5
R5
R1
R2
R3
P3
R4
P4
P7
H1 G1
B13
B7
B9
A9
B10
A10
B11
A11
B12
A12
A13
A14
A2
B3
A3
B4
A4
B5
A5
B6
A6
+3V3CA
4K7
3854
I807
4K7
3855
N8
P13
N11
N14
CTRL
VSS
C13
D13
F13J3J13
K13L3M13N4N5
E3
F3
ΙΟ
DQM
RAS
CAS
CLK
WE
0
1
2
38
4
5
6
A
7
8
9
10
11
CLKASA
WEA
DAVA
DI9
0
1
2
3
4
YA
5
6
7
8
VA
HREF
0
1
2
3
UVA
4
5
DI
6
7
8
B8
BISTEN
C7
C8
N7
N10
CLKASB
UVB
+1V5CA
D3
E13
C11
VDDC
N12
N13P2P14R9R11
DQ
WEB
DAVB
DO9
YB
DO
K3
H13
9 101112
B3a
B3a
3849
68R
68R
68R
68R
4K7
+5V2Pr
3830
3833
68R
3836
3840
3844
9815
9816
9722
9817
9818
68R
68R
68R
68R
COL_SD_DQ1
COL_SD_DQ2
COL_SD_DQ3
COL_SD_DQ4
COL_SD_DQ5
COL_SD_DQ6
COL_SD_DQ7
COL_SD_DQ8
COL_SD_DQ9
COL_SD_DQ10
COL_SD_DQ11
COL_SD_DQ12
COL_SD_DQ13
COL_SD_DQ14
COL_SD_DQ15
COL_SD_DQ16
B3d
SN-DA
SN-CL
RSTR_I
SDA-D
SCL-D
B3a,b,c(2x)
B3a,b,c(2x)
B3a,B3c(2x)
B3a
B3a
P12
1
R12
2
P11
3
P10
4
R10
5
P9
6
P8
7
R8
R13
9
R14
10
R15
11
P15
12
N15
13
M14
14
M15R7
15
L15
16
A1
3914-1
22R
G2
0
F2
3915-1
1
E2
2
E1
3
D2
4
D1
5
C2
6
C1
7
B1
8
M2
0
M1
1
L2
2
L1
3
K2
4
K1
5
J2
6
J1
7
H2
8
N6
N9
AVD
SNDA
SNCL
SNRST
AVS
P1
3913-3
3914-3
3917-2
3917-4
3916-2
3915-4
N1
SDA
SCL
NC1
NC2
3913-1
C14
D14
C15
A15
B15
D4
N2
22R
22R
22R
22R
22R
22R
22R
22R
+1V5CA
5800
2792
I718
100n
3916-4
3915-2
3913-4
3913-2
3914-4
3914-2
3917-1
3917-3
3916-3
3916-1
3915-3
F735
F736
3831
3834
3837
3839
3842
3845
22R
22R
22R
22R
22R
22R
22R
22R
22R
22R
22R
CLK-AS
UVB(0)
UVB(1)
UVB(2)
UVB(3)
UVB(4)
UVB(5)
UVB(6)
UVB(7)
UVB(8)
+5V2Pr
68R
68R
68R
68R
68R
68R
WE-B
YB(0)
YB(1)
YB(2)
YB(3)
YB(4)
YB(5)
YB(6)
YB(7)
YB(8)
3851
3832
3835
68R
3838
3841
3843
4K7
A
B
C
D
G
H
2792 F9
2819 H3
2836 H3
2850 A1
2851 A1
2852 A1
2853 A2
2854 A2
2855 A2
2856 G2
2857 G2
2858 G2
2859 G2
2860 G3
2861 G3
2862 G3
2863 G3
2864 G4
2865 H2
2866 H2
2867 H2
2868 H2
2869 H3
2870 H3
3830 B11
3831 B10
3832 B10
3833 B11
3834 B10
3835 B10
3836 B11
3837 B10
3838 B10
3839 B10
3840 B11
3841 B10
3842 C10
3843 C10
3844 C11
3845 C10
3846 D1
3847 G5
3848 G6
3849 H10
3851 H10
3853 H5
3854 F8
3855 F8
3913-1 D9
3913-2 D9
3913-3 D9
3913-4 C9
3914-1 C9
3914-2 D9
3914-3 D9
E
3914-4 D9
3915-1 C9
3915-2 C9
3915-3 E9
3915-4 E9
3916-1 E9
3916-2 E9
3916-3 E9
3916-4 C9
3917-1 D9
3917-2 D9
F
3917-3 D9
3917-4 E9
5800 F9
7752-1 A8
7752-2 G7
7753 C3
9722 H11
9800 D2
9801 D2
9802 D2
9803 D2
9804 G6
9805 G6
9806 H5
9807 H5
9812 B7
9815 G11
9816 G11
9817 H11
9818 H11
F735 H10
F736 H10
I718 F9
I801 G6
I807 F8
I
8204 000 8481.1
12345
67891011
12
F_15460_017.eps
070405
I
Page 49

SSB: FBX Supply
B3E
B3e
A
B
C
D
E
F
3V3_FAULT_FBX
B3e
3V3_FAULT_FBX
+3V3_DCDCFBXA
2739
B3e
3V3_FAULT_FBX
B3e
3V3_FAULT_FBX
B3e
3V3_FAULT_FBX
B3e
3V3_FAULT_FBX
B3e
3V3_FAULT_FBX
B3e
3V3_FAULT_FBX
B3e
3V3_FAULT_FBX
8204 000 8481.1
Circuit Diagrams and PWB Layouts
1 234
EN 49FTP2.4E AA 7.
56789
FBX SUPPLY
+8V_CON
3
2919
+3V3_DCDCFBXA
GND
5709
res
6719
S1D
6704
res
S1D
F795
2730
100u
5775
2895
5763
100u
2802
10u
10u
2715
res
5760
2898
B3a(3x)B3e(14x)
F796
2817
I748
1
100n
GND
2897
res
+1V8FA
100n
IN
10u
B12
7774
KF25BDT25
OUTIN
COM
LF15ABDT
1
IN
res
100n
1
IN
100n
2899
3V3_FAULT_FBX
3V3_FAULT
GND
2
GND
7701
OUTIN
COM
GND
2
7772
LF15ABDT
COM
OUT
OUTIN
2
3
2889
GND
GND
I743
OUT
3
OUT
100u
2896
3
2871
2922
GND
F799
F713
10n
2938
2924
GND
100u
220u
16V10u
100n
+1V5_FBXB
5761
+1V5_FBXA
5778
6u8
100n
2932
+2V5_FBXA
2923
+2V5_FBXA
220u
2939
16V100u
3869
100R
3870
100R
I744
5779
RES
5768
3707
100R
6712
RES
3875
100R
3829
100R
3871
100R
3872
100R
3873
100R
3874
100R
5772
I756
I758
BAS316
F734
F791
I753
I721
I759
I747
5769
I749
5770
I750
5771
I751
5773
6705
BAS316
BAS316
6711
5767
RES
BAS316
6722
BAS316
6702
BAS316
6713
BAS316
6714
I752
10u
2728
F790
RES
F793
BAS316
6715
BAS316
6716
2914
100n
2891
100n
2892
100n
2893
100n
2894
100n
2843
100n
2729
+3V3PA
2890
100n
+3V3GA
+3V3_DCDCFBXA
F792
F794
F748
LF18ABDT
1
IN
COM
100n
+3V3PB
+3V3PC
+3V3FA
+3V3FB
+3V3Pr
7773
OUTIN
GND
2
OUT
1 2345
RESERVED
5702
+3V3_DCDCFBX
+5VF
+2V5_FBXA
+2V5_FBXA
10n
+2V5_FBXA
2933
5719
5720
5722
5752
5764
5713
5762
100n
RES5721
+8VPA
+3V3_DCDCFBXA
+3V3_DCDCFBXA
F798
100n
2849
F712
2921
100n
F711
100n
2872
F797
2873
100n
B3E
B3e
3V3_FAULT_FBX
RES
7770
LD1117DT33C
OUTIN
COM
1
F750
2847
5757
5758
5759
+3V3_DCDCFBXA
5777
I745
100u
2829
10u
2848
100n
F745
+1V5EA
2844
100n
F746
+1V5EB
100n
2826
F747
+1V5CA
2874
100n
+3V3_FBXB
2937
220u 4V
B3e
+5V2Pr
B3e
B3e
B3e
B3e
3V3_FAULT_FBX
3V3_FAULT_FBX
3V3_FAULT_FBX
+3V3_FBXB
3V3_FAULT_FBX
3V3_FAULT_FBX
+5V_FBXA
+2V5ED
+2V5EC
+2V5EA
+2V5EB
+5V_FBXA
+5V_FBXA
2828
5754
32
10u
100n
2820
F749
5755
5776
+1V5_FBXA
+1V5_FBXB
+1V5_FBXB
6789
3868
100R
+3V3_FBXB
3867
100R
+3V3_FBXB
3877
100R
+3V3_FBXB
3805
100R
3865
100R
+3V3_FBXB
3864
100R
+3V3_FBXB
I742
I746
I712
I760
I754
I755
BAS316
6717
5750
BAS316
6718
5751
BAS316
6709
5780
5801
5756
5753
6723
BAS316
BAS316
6720
BAS316
6721
2811
2810
2818
F789
2813
2845
2846
F740
100n
F741
100n
100n
100n
F744
100n
F743
100n
+3V3EA
+3V3EB
+3V3ED
+3V3EC
+3V3CA
+3V3CB
F_15460_018.eps
070405
5777 B7
2715 C3
2728 F2
5778 E4
2729 F2
5779 B1
2730 F3
5780 C9
2739 B1
5801 D9
2802 B3
6702 C2
2810 B9
6704 D3
2811 A9
6705 F1
6709 C9
2813 D9
2817 F3
6711 A2
2818 C9
6712 B1
2820 B6
2826 E7
2828 B6
2829 B7
2843 F2
2844 E7
2845 E9
2846 F9
2847 D7
2848 D7
2849 D6
2871 D4
2872 E6
2873 F6
2874 F7
2889 B4
2890 B2
2891 C2
2892 D2
2893 D2
2894 E2
2895 B3
2896 C4
2897 C3
2898 D3
2899 D4
2914 C2
2919 F2
2921 E6
2922 E4
2923 E5
2924 B4
2932 A5
2933 A5
2937 B7
2938 A4
2939 B1
3707 F1
3805 D9
3829 C1
3864 F9
3865 E9
3867 B9
3868 A9
3869 A1
3870 A1
3871 C1
3872 D1
3873 E1
3874 E1
3875 B1
3877 C9
5702 A5
5709 B3
5713 E5
5719 B5
5720 C5
5721 C5
5722 C5
5750 A9
5751 B9
5752 D5
5753 F9
5754 B6
5755 C7
5756 E9
5757 D7
5758 E7
5759 F7
5760 C3
5761 C4
5762 F5
5763 F3
5764 D5
5767 B2
5768 C1
5769 D1
5770 D1
5771 E1
5772 F1
5773 E1
5775 A3
5776 C7
6713 D2
6714 D2
6715 E2
6716 E2
6717 A9
6718 B9
6719 C3
6720 E9
6721 F9
6722 B2
6723 D9
7701 B4
7770 B7
7772 C4
7773 F2
7774 A4
F711 E6
F712 D6
F713 C4
F734 B1
F740 A9
F741 B9
F743 F9
F744 E9
F745 D7
F746 E7
F747 F7
F748 E2
F749 C6
F750 C7
F789 D9
F790 B2
F791 C1
F792 D2
F793 D2
F794 E2
F795 F3
F796 F3
F797 F6
F798 D6
F799 B4
I712 C9
I721 B1
I742 A9
I743 A4
I744 B1
I745 B7
I746 B9
I747 C1
I748 C3
I749 D1
I750 E1
I751 E1
I752 F2
I753 F1
I754 E9
I755 F9
I756 A1
I758 A1
I759 C1
I760 D9
A
B
C
D
E
F
Page 50

Circuit Diagrams and PWB Layouts
EN 50FTP2.4E AA 7.
SSB: HOP
12345678
9 101112
13
HOP
B4 B4
B4(2x)
B4(2x)
A
B4
Y100
B4
U100
B4
V100
B
SDA-F
SCL-F
B5a,B21
LIGHT-SENSOR
B3a,B4(3x)
B5a
B4(2x)
B4(2x)
B4(2x)
B4(2x)
B4
HD100
SANDCASTLE
FBL_2FH
R_2FH
G_2FH
B_2FH
SCL-F
SDA-F
C
D
E
B4
GND-RGB-CRT
F
G
NC
B4(3x),B5a
B4(2x)
B4(2x)
B4(2x)
B4(2x)
B3a,B4(3x),B5a
VD100
B4
NOHOP1A
B4
VD
HD100
R_2FH
G_2FH
B_2FH
FBL_2FH
HD100
B4
VD
H
B4,B5a
HFB
B4,B5a
VSYNC
B4
NOHOP1B
B4
NOHOP1A
B4(3x)
I
B5a
HD100
B4
NOHOP2B
8204 000 8483.1
2398
2301
3397
100R
2332
3387
100R
DEC
5301
10p
100n
GND
SPECTRAL
PROC
ADC
AD24AD3
AD1
3
15
100n
I333
3305
3396
100R
3398
100R
6u8
100n
2315
100n
I321
F348
F349
F350
F351
F352
F353
10p
10p
2344
2345
9314
9315
3454
100R
9311
9312
+8VS
7302
TDA9178T
3455
100R
5303
5304
5305
5306
5307
5308
2349
122 102324
NC
YIN
6
8
9
22
I302
+5VS
10p
UIN
VIN
CF
F311
+8V_VDP
3329
2314
2348
LUMA
PROCESSING
CHROMA
PROCESSING
CONTROL
SCL11SDA
ADR
14
6308
BAS316
3453
33K
6R8
5302
6u8
100u
3349
4K7
7304
PDTC144EU
10p
10p
2347
7
2346
ONLY FOR NO HOP
12
1813
5
68K
VCC
SOUT
YOUT
UOUT
VOUT
WINDOW
2396
100n
3320
100R
3321
100R
2317
B4
V100
+8VS
V21
20
21
19
17
16
2321
SC
1
I366
6K8
3339
3395
100R
2395
100n
2397
100n
10p
2309
10p
2310
I312
1u0
22n
2318
c200
3363
1K0
+5VS
2363
1K0
3333
3331
1K0
1304
10p
2320
N.C.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
F362
2FH-VD100
B14b
B14b
V20
9302
I332
100n
3302
1K0
I338
2307
100n
470p
2FH-FBL
2FH-B
2FH-HD100
nc
nc
nc
B4
2431
I339
0V2
2FH-G
V22
V23
F17
L12
nc
9303
U100
I358
2FH-R
B4
Y100
V19
9304
I330
I331
2323
100n
100n
28
YIN
27
UIN
26
VIN
33
BL1
30
RI1
31
GI1
32
BI1
10
SCL
B4
Yltp
9305
2429
100n
ONLY FOR NO HOP
9308
9309
9310
7301
TDA9330H/N1
SWITCH
VUY
RGB-YUV
MATRIX
+8VS
10R
3399
3388
SATUR’N
CONTROL
COLOUR
DIFF
MATRIX
Y
BLACK
STRETCH
R
G
B
SAT
CONTRAST
BRIGHTNESS
CONTR
Y
U
V
I2C
11
SDA
17
7V9
VP1
SYNC+GEO
39
7V9
VP2
RGB
18
DECBG
BANDGAP
19
GND2
ANAGND
I303
7
DECVD
6
GND1
I359
23
VD
24
HD
12
HSEL
XTALI20XTALO
1V3
CSTCV
2
F364
12M
DIGSUP
DIGGND
Hsel
13
1PHI-
1V1
1301
SANDCASTLE
B4
SUPPLY
PHI-2
SC
SCO
HFB
V31
6334
I363
3334
DPC
9
13
14
I305
0V8
2325
RES
3323
BAS316
1K0
4K7
3324
6306
HFB_X-RAY-PROT
I306
100n
100K
BZX384-C5V6
RES
3326
RES
2311
6307
21
HFB
B4
B4,B5a
345
nc
B5a
B5a
B5a
7340
BC847BW
10K
BCL
2329
R-TXT
35
RI2
2330
100n
G-TXT
36
GI2
B-TXT
100n
2331
37
BI2
R
AND
G
RGB-INSERTION
B
CONTROL
BRIGHT
HOP
START/STOP
H-DRIVE
LPSU
FBCSO29FLASH
22
5
I307
0V
0V2
3327
100K
100K
3336
68p
3472
BAT54 COL
9316
B14b,B21(2x)
POR
DYN-FASE-COR
nc
6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13
1K0
22K
B5a
BC847BW
2324
POR_FLASH
7362
PDTC144EU
10n
FBL-TXT
100n
38
BL2
B4,B5a
R
G
7361
B4(2x)
B_2FH
G_2FH
1K0
1K03335
3332
WHITE
POINT
CONTROL
PWL +
BEAM CURR
LIMITER
+8VS
47K
3361
1K03330
I368
2328
22p
WHITE P.
R_2FH
3311
B4
B4
B4(2x)
3467
7305
I311
I315
2334
I357
F20
F19
+8VS
3315
10K
3465
6316
BAS316
3345
10K
2u2
2336
3306
220R
F312
F18
+8VS
3318
2308
1K0
6303
BZX384-C47
6313
BZX384-C22
Yltp
V28
V30
+8VS
V29
6319
BAS316
2u2
3325
33K
3394
1K0
10p
3317
220R
6304
BAS316
BAS316
I316
6314
100K
4K7
2303
3347
V32
1u0
2312
33n
+8VS
+8VS
6312
FBL_2FH
3471
100K
7375
33K
3470
BC847BW
BC847BW
40
RO
41
GO
42
BO
44
BLKIN
43
BCL
25
DACOUT
3
EWO
4
EHTIN
2
1V1
VDOB
1
VDOA
1V5
16
IREF
4V0
VSC 15
8
2V5
HOUT
L13
10K
+8VS
7303
BC857BW
BAS316
3360
100K
I369
2342
100n
33K
3355
I326
34
PWL
R
OUTPUT
AMPL
G
+ BUFFER
+ BLUE
BB
STRETCH
CONTIN’S
CATHODE
CALIBR’N
6-BITS
DAC
EW
FRAME
RAMP
GENERATOR
10p
100K
2304
3314
+8VS
TILT
+8VS+8VS
BC847BW
7306
3351
I314
22K
BZX384-C6V8
3390
220R
3307
F329
2306
10K
3308
18K
470p
2343
100n
2313
100n
9421
3346
33K
3328
39K
+8VS
3352
3359
3348
2K2
6310
+8VS
470K
3310
7312
PDTC144EU
3316
47K
+8VS
47K
BC847BW
100K
I370
100K
7314
2333
2u2
7318
BC857BW
+8VS
3350
nc
Y-SCAVEM
1K0
I367
2319
1n0
+8VS
1K0
3353
3354
I320
7315
PMBT2369
3344
2K2
I365
2335
1n0
+8VS
36
680K
3364-3
680K
3364-4
45
2K2
7313
PMBT2369
3312
+8VS
680K
3364-2
27
18
3364-1
680K
220R
B4,B5a
FBL-TXT
3358
3459
I304
F309
3313
100K
100K
2
+8VS
3338
680R
7316
1K8
3337
820R
I319
2K2
5313
BC857BW
I308
5u6
2337
6p8
GND-RGB-CRT
BC857BW
I309
3369
820R
5314
7317
I310
5u6
2338
6p8
GND-RGB-CRT
BC857BW
5315
5u6
6301
BAS316
6317
BAS316
5
3343
3322
I317
68K
1K0
3391
10K
+5VS
7319
2341
6p8
GND-RGB-CRT
3442
22K
3319
100R
+8VS
100K
C001
3366
BAS316
3367
220R
+8VS
3K9
I313
6309
3362
6
7310-1
BC847BS
1
+5V_VDP
3304
2340
2K2
3384
820R
BZX384-C22
6311
2326
+8VS
3K9
3
4
3356
3R9
5V2
10u
F347
10n
3357
2386
1n0
7310-2
BC847BS
I371
+8VS
3383
1412
3386
220K
680R
+8VS
3389
3443
+8VS
3365
3340
R-CRT
47R
3341
G-CRT
47R
680R
3342
B-CRT
47R
CUTOFF
EHT-INFO
EW-DRIVE
EHT-INFO
1u0
2393
HFB_X-RAY-PROT
ANTI-MOIRE
BACKLIGHT-CNTRL
9313
4K7
RES ONLY PTV
VSYNC
7309
BC847BW
NOHOP1B
FRAMEDRIVE+
HD@HOME
LINEDRIVE1
GND-LINEDRIVE
NOHOP2B
EHT-INFO
F_15460_019.eps
1301 G4
1304 G3
1412 E13
2301 B2
2303 E9
2304 G7
2306 H9
2307 F4
2308 G9
2309 D3
A
2310 E3
B
C
D
E
F
G
H
I
2311 H6
2312 F9
2313 F9
2314 E2
2315 E3
2317 E3
2318 E3
2319 G10
2320 G3
2321 B3
2323 B4
2324 I6
2325 G5
2326 E12
2328 B7
2329 A6
2330 A6
2331 A6
2332 E2
2333 D10
2334 D8
2335 F11
2336 D9
2337 B12
2338 B12
2340 I11
2341 C12
2342 A7
2343 A9
2344 H3
2345 H2
2346 H2
2347 H2
2348 H2
2349 H2
2363 F3
2386 F12
2393 E13
2395 D3
2396 D3
2397 D3
2398 A3
2429 A4
2431 B4
3302 C4
3304 I11
3305 C3
3306 E9
3307 E9
3308 E9
3310 E10
3311 G7
3312 E11
3313 E11
3314 G8
3315 H8
3316 H10
3317 G9
3318 F9
3319 E13
3320 D3
3321 D3
3322 D12
3323 H5
3324 I5
3325 A9
3326 G5
3327 G6
3328 F9
3329 E2
3330 A7
3331 G3
3332 A7
3333 F3
3334 H5
3335 A7
3336 H6
3337 A11
3338 A12
3339 C3
3340 A13
3341 B13
nc
nc
nc
nc
B4(2x)
B4
TILT
nc
B4(2x)
B4
B5b
B20
B4,B5a
B4
nc
B5a
nc
nc
B4
B4(2x)
140405
3342 C13
3343 D12
3344 D10
3345 D9
3346 C9
3347 D9
3348 D10
3349 F2
3350 B10
3351 B9
3352 A10
3353 A10
3354 A11
3355 B8
3356 G12
3357 F12
3358 A11
3359 B10
3360 A8
3361 G7
3362 F11
3363 F3
3364-1 F11
3364-2 F11
3364-3 G10
3364-4 G10
3365 F13
3366 H11
3367 F11
3369 B12
3383 B13
3384 C12
3386 F13
3387 G2
3388 B5
3389 C13
3390 D9
3391 F12
3394 D9
3395 C3
3396 D3
3397 D2
3398 D3
3399 B6
3442 E13
3443 E13
3453 C2
3454 B2
3455 C2
3459 B11
3465 A9
3467 A8
3470 A8
3471 A8
3472 I6
5301 E2
5302 E2
5303 G2
5304 G2
5305 G2
5306 H2
5307 H2
5308 H2
5313 A12
5314 B12
5315 C12
6301 E12
6303 H9
6304 H9
6306 I5
6307 I6
6308 C2
6309 D11
6310 D10
6311 D12
6312 H8
6313 H9
6314 H9
6316 C9
6317 E12
6319 D9
6334 H5
7301 B4
7302 A1
7303 H8
7304 F2
7305 B9
7306 A9
7309 G13
7310-1 G11
7310-2 G12
7312 F10
7313 A11
7314 A10
7315 A10
7316 A12
7317 B12
7318 E10
7319 C12
7340 A6
7361 H7
7362 H7
7375 A8
9302 A3
9303 A4
9304 A4
9305 A4
9308 B5
9309 B5
9310 B5
9311 I1
9312 I1
9313 F13
9314 H1
9315 H1
9316 I6
9421 B9
C001 H12
F309 D11
F311 C2
F312 E9
F329 H9
F347 D12
F348 G3
F349 G3
F350 G3
F351 H3
F352 H3
F353 H3
F362 H3
F364 F4
I302 E2
I303 E4
I304 B11
I305 G5
I306 G5
I307 G7
I308 A12
I309 B11
I310 B12
I311 D9
I312 E3
I313 C12
I314 C9
I315 D8
I316 D9
I317 C12
I319 A11
I320 A11
I321 F3
I326 B7
I330 B4
I331 B4
I332 B3
I333 C3
I338 E3
I339 E4
I357 E8
I358 D4
I359 F4
I363 H5
I365 E10
I366 B3
I367 D10
I368 A7
I369 A8
I370 A10
I371 I12
c200 F3
Page 51

Circuit Diagrams and PWB Layouts
EN 51FTP2.4E AA 7.
SSB: OTC-Flash
12345678910111213
B5A B5A
B5a
IRQ-FTV
B14d
B21
B14e
B4,B21
B14e
Nc
Nc
B14b,B21
B14b
B14b,B21
B6a,B14b
B5a
B5a
B5a
B4(2x)
B3a,B4 (4X)
B4(2x)
B3a
B2(3x)
B21
B21
B21
B21
B2
B21
B5b
B4
B4
B3a
SEL_IN_2
LED2
+3V3_INTOTC
9024
FRONT-DETECT
CON-SND
ON-OFF-LED
SEL_IN_1
LIGHT-SENSOR
AGC-MONITOR
STATUS-SC3
+5V2_CON
RES
STATUS-SC4
KEYBOARD
STANDBY
STATUS_SC3
PWM_BACKLIGHT
RC
POR_FLASH
IRQ-DIGITAL
P50
SDA-F
SCL-F
SDA-S
SCL-S
SOUND-ENABLE
RESET-AUDIO
HD@HOME
SDA-S
SDA-F
SCL-S
SCL-F
TxD
RxD
RESET
+3V3_INTOTC
HFB
HD100
HD3-EPLD
+3V3_INTOTC
VSYNC
VD-EPLD
CVBS-TXT
A
B
C
B14e(2x),B21
D
E
F
G
H
I
J
OTC-FLASH
+3V3_INTOTC
2K7
3068
3009180R
+5V2_CON
9021
3058
6K8
3075
10K
7008
BC847BW
3025
220R
FC69
3C10
100R
IC05
2041
150p
3041
3C09
RES
9003
RES
9004
RES
3094
47K
4K7
10K
3095
47K
3042
4K7
3C11
100R
BC857BW
7022
3038
10K
2071
100n
2072
100n
9014
+3V3_INTOTC
3059
9015
2020
220p
IC07
IC09
3
2
1
9001
IC45
3040
3096
2070
620R
3027
3011
2 SDA
1
0
4K7
9002
47K
2068
FC57
+8V_CON+5V_CON
SDM
9006
10K
10K
3018
3020
3080 10K
4K7
3019
10K
3021
3078-3
100n
IC03
2058
100p
3047
470R
+3V3_INTOTC
+5V2_CON
6001
47K
1PS76SB10
+3V3_INTOTC
4K7
3053
ADR
NVM
EEPROM
(4Kx8)
Φ
+3V3_INTOTC
7015
PMBT2369
IC46
PMBT2369
2n2
36
470R
180R 3039
+3V3_INTOTC
+5V2_CON
2059
100p
3091
470R
10K
18
7011
M24C32-WMN6T
84
6004
BAT54
2022
3074-1
470R
SCL
WC
9016
7016
IC48
100n
100n
2073
3024
27K
1K8
3033
27
3069
+3V3_INTOTC
5
6
7
3097
100p
2061
9018
3074-4
3078-2
7
2
470R
2V8
9022
9023
7010
100K
BC857BW
+3V3_INTOTC
3077
4K7
3076-2
470R
1PS76SB10
IC40
6003
+5V2_CON
1K8
1K8
3088
3079
3074-3
36
470R
3001
FC48
FC49
IC21
IC26
2007
100n
2006
CVBS-Y-RECORD-IN
B14a,b,B15b
6005
PLVA2650A
470R
4
470R
5
9025
IC41
BZX384-C3V9
3090-3
36
470R
3090-1
18
470R
2074
100n
3103
470R
3076-3
36
470R
+3V3_INTOTC
7009
BC847BW
1K8
3092
45
3064-3
36
100R
27
3064-1
18
100R
3074-2
27
470R
4K7
4K7
3002
2018
3
1001
33p
2002
1
27p
2008
100n
2014
100n
2005
100n
100n
FC60
SAM
100p
9005
2060
3081
470R
SAA5801H/015
36
470R
3099-3
2V9
3099-4
45
470R
3099-2
27
3099-1
470R
18
470R
3073-4
45
3073-3
470R
36 72
470R
3073-2
27
470R
3073-1
6006
18
470R
3090-4
45
470R
3090-2
27
470R
3078-1
0V2
18
470R
3076-4
45
470R
0V2
3076-1
18
470R
3V4
4K7
3026
3064-4
100R
3064-2
100R
IC37
3100
42
24K
3003
FC61
220R
220R
3101
6M0
0V
IC17
IC22
1V3
2003
220n
220n
2004
2023
100n
9017
9
7023
105 P2-2|ADC0
106 P2-3|ADC1
120 P3-7|CBB
119 P3-6|TTC
118 P3-5|TTD
117 P3-4
116 P3-3
115 P3-2
114 P3-1|LED1
113 P3-0|LED0
110 P2-7|ADC5
109 P2-6|ADC4
108 P2-5|ADC3
107 P2-4|ADC2
104 P2-1|PWM1
103 P2-0|PWM0
100 P1-7|RC
99 P1-6|INT3
98 P1-5|INT2
97 P1-4|INT1
96 P1-3|INT0
95 P1-2|T2
92 P0-7
91 P0-6|CORN
90 P0-5|TxDo
89 P0-4|RxDo
88 P0-3|SDA1
87 P0-2|SCL1
86 P0-1|SDA0
85 P0-0|SCL0
93 P1-0|T0
94 P1-1|T1
16 OSCOUT
17 OSCIN
18 OSCGND
74 RESET
83 HSYNC
84 VSYNC
82 FRAME
5 CVBS0
4 CVBS0_R
7 CVBS1
6 CVBS1_R
1 IREF_DEC
2 IREF
3 REF+
8 STN|BLACK
VSSA21VSSD176VSSD2
10
VDDA
2024
100n
19
VDDN1
OTC
VSSP150VSSP2
39
2025
100n
49
20
38
VDD1
VDDP2
VDDP1
EXTERNAL CODE AND DATA INTERFACE
AND
DISPLAY TIMING
CLOCK GENERATOR
TXT
CAPTION
EPG
CLOSE
TXT
USA
VSSP3
VSSD3
112
102
3006
470R
2026
2027
100n
100n
75
VDDD2
DISPLAY
TEST012TEST113TEST2
11
3007-1470R
470R 3007-2
101
VDDD3
RAM_CSn
INTERFACE
3007-3470R
2028
100n
111
VIDEOn
TEST315TEST4
14
470R 3007-4
100n
VDDP3
2029
OTC
FC47
+3V3_INTOTC
45A1
AA(0)
47A2
AA(1)
51A3
AA(2)
53A4
AA(3)
55A5
AA(4)
57A6
AA(5)
59A7
AA(6)
61A8
AA(7)
62A9
AA(8)
60A10
AA(9)
58A11
AA(10)
56A12
AA(11)
54A13
AA(12)
52A14
AA(13)
48A15
AA(14)
46A16
AA(15)
44A17
AA(16)
63A18
AA(17)
65A19
AA(18)
64A20
AA(19)
66A21
AA(20)
67A22
68A23
36D0
32D1
28D2
24D3
23D4
27D5
31D6
35D7
34D8
30D9
26D10
DD(10)
22D11
DD(11)
25D12
DD(12)
29D13
DD(13)
33D14
DD(14)
37D15
DD(15)
3034-1
18
40ROM_OEn
100R
41RAM_OEn
3034-4
45
43ROM_CSn
100R
42
3035-4
69RASn
45
100R
72CASLn
3035-2
71CASHn
27
100R
70WEn
FC66
73EAn
77R
78G
79B
80FADING
81DATA
AA(0)
AA(2)
AA(4)
AA(6)
AA(7)
AA(8)
AA(9)
AA(10)
AA(11)
AA(13)
AA(15)
AA(16)
AA(17)
AA(18)
+3V3_INTOTC
C
DD(0)
DD(1)
DD(2)
DD(3)
DD(4)
DD(5)
DD(6)
DD(7)
DD(8)
DD(9)
+5V2-STBY
3034-2
27
100R
3034-3
36
100R
3035-1
IC20
18
100R
3035-3
36
100R
2067
100n
3008-1
3008-2
100R
18
27
FC02
FC22
FC24
FC26
FC28
FC30
FC06
FC08
FC10
FC15
FC51
B5c(3x)
B5c(3x)
B5c(3x)
ROM_OE
RAM_OE
ROM_CS
RAM_CS
EAn
3008-3
100R
36
3089
63
54
81
72
63
54
72
81
81
FC03
6
54
8
72
63
FC09
54
8
54
7
63
SW_CS
SW_WE
SW_OE
F
5000
5001
1000
500mA F
B5c(3x)
RAS
CASL
CASH
WE
3008-4
100R
45
3C12
100R
3049-3
3049-4
3050-1
3050-2
3050-3
3050-4
3049-2
3048-1
3051-1
3051-2
3051-3
3051-4
3052-1
3052-2
3052-3
3052-4
3049-1
3048-4
3048-2
3048-3
2075
E
B5a(2x),C(3x)
B5c(3x)
B5c(3x)
B5a(2x)
B5a(2x)
2033
B5a(2x)
B5c(3x)
3012-1
100R
3012-3
100R
100R
68R
+3V3_INTOTC
FC04
3
1
FC07
FC11
1
FC12
2
3084
10K
+3V3_INTOTC
100n
82p
18
36
2031
100n
25
A(0)
A(0)
A(1)AA(1)
A(2)
A(3)AA(3)
A(4)
A(5)AA(5)
A(6)
A(7)
A(8)
A(9)
A(10)
A(11)
A(12)AA(12)
A(13) EP_WE
A(14)AA(14)
A(15)
A(16)
A(17)
A(18)
A(19)AA(19)
A(20)AA(20)
FC50
10K
3010
5003
IC14
82p
2034
3012-2
100R
3012-4
5
100R
IC29
FC16
FC18
FC19
IC15
2035
A(1)
A(2)
A(3)
A(4)
A(5)
A(6)
A(7)
A(8)
A(9)
A(10)
A(11)
A(12)
A(13)
A(14)
A(15)
A(16)
A(17)
A(18)
A(19)
A(20)
3V4
+5V2_CON
F
IC18
82p
27
IC28
4
2009
RES
2036
24
23
22
21
20
19
18
8
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
48
17
16
9
10
47
26
11
28
12
14
CASL
CASH
RAM_OE
FC45
82p
47p
A0
A1
A2
LH28F320BJE-PTTL90
A3
A4
A5
A6
A7
A8
A9
A10
A11
A12
A13
A14
A15
A16
A17
A18
A19
A20
BYTE_
CE_
WE_
OE_
RP_
WP_
RAS
WE
2037
IC27
2010
RES
FC01
37
VCC
7006
DQ10
DQ11
DQ12
DQ13
DQ14
DQ15|A_1
PROGRAM
FLASH-RAM
(Set SW)
RY|BY_
GND
27
46
G
MSM51V18165F-60JS
A(6)
A(2)
FC33
A(1)
A(7)
A(8)
FC39
A(3)
A(4)
FC35
A(5)
FC37
A(9)
A(0)
B5a(2x)
RAS
B5a(2x)
CASL
B5a(2x)
CASH
B5a(2x),C(3x)
WE
B5a(2x),C(3x)
RAM_OE
82p
FC46
E
IC24
47p
47p
2011
RES
13
VCCW
DQ0
DQ1
DQ2
DQ3
DQ4
DQ5
DQ6
DQ7
DQ8
DQ9
IC23
2012
17
18
19
20
23
24
25
26
27
28
14
31
30
13
29
11
12
15
RES
100n
2038
29
31
33
35
38
40
42
44
30
32
34
36
39
41
43
45
15
A0
A1
A2
A3
A4
A5
A6
A7
A8
A9
RAS_
LCAS_
UCAS_
WE_
OE_
NC
47p
VPP-SW
H
D(0)
D(1)
D(2)
D(3)
D(4)
D(5)
D(6)
D(7)
D(8)
D(9)
D(10)
D(11)
D(12)
D(13)
D(14)
D(15)
FC17
1
VCC16VCC221VCC3
7007
DRAM
(TXT)
VSS1
VSS2
VSS2
VSS1
22
D(15)
37
D(0)
D(1)
D(2)
D(3)
D(4)
D(5)
D(6)
D(7)
D(8)
D(9)
D(10)
D(11)
D(12)
D(13)
D(14)
FC13
VSS3
VSS3
42
DQ10
DQ11
DQ12
DQ13
DQ14
DQ15
DQ16
DQ16
3055-3
63
3055-1
81
3056-1
18
3056-3
6
3
3057-1
18
3057-3
36
3054-4
45
3054-2
27
3055-2
72
3055-4
54
3056-2
27
3056-4
45
3057-2
27
3057-4
45
3054-3
36
3054-1
18
+3V3_INTOTC
100n
2019
2
DQ1
3
DQ2
4
DQ3
5
DQ4
7
DQ5
8
DQ6
9
DQ7
10
DQ8
33
DQ9
34
35
36
38
39
40
41
16
NC
32
9008
RxD
B5a
FC05
3098
100R
FC29
FC34
FC42
FC41
FC38
FC40
FC44
FC21
FC23
FC25
FC27
FC36
FC31
FC43
DD(0)
DD(1)
DD(2)
DD(3)
DD(4)
DD(5)
DD(6)
DD(7)
DD(8)
DD(9)
DD(10)
DD(11)
DD(12)
DD(13)
DD(14)
DD(15)
D(15)
D(14)
D(13)
D(10)
D(11)
D(12)
A
C
AA(0)
AA(1)
4
AA(2)
AA(3)
27
AA(4)
AA(5)
45
AA(6)
AA(7)
18
AA(8)
AA(9)
AA(10)
27
AA(11)
45
AA(12)
AA(13)
27
AA(14)
AA(15)
45
AA(16)
AA(17)
10K3093
F
B5c(3x)
H
D(2)
D(5)
D(4)
D(3)
D(1)
D(0)
D(6)
D(7)
D(9)
D(8)
FC70
2053
10p
TxD
100R3087
3086-3
36
3086-4
5
3029-1
18
3029-2
3029-3
36
3029-4
3086-2
27
3031-1
3085-1
18
3085-2
3085-3
36
3085-4
3061-1
18
3061-2
3061-3
36
3061-4
3086-1
18
3V4
EP_OE
EP_CS
3062
+3V3_INTOTC
+5V2_CON
2013
100u
BC857BW
7002
9010
9011
9012
9013
9009
B5a
100R
100R
6002
3015
470K
IC13
3067
470K
100R
3046-4
100R
3046-3
8
+3V3_INTOTC
M29W400BT-90N1
25
24
23
22
21
20
19
18
8
7
6
5
4
3
2
48
17
15
12
11
28
26
47
10K
9007
BAS316
3014
6K8
FC32
2017
FC68
2039
45
36
27
3046-2
1
3046-1
10p
2054
3045
100R
2040
100n
7012
37
EPROM
512Kx8/256Kx16
0
1
EPG-
2
3
FLASH-RAM
4
5
6
7
8
0
A
9
4M-1
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
RB
RP
WE
OE
CE
BYTE
27
5V3
15K
3004
RES
RES
IC42
7003
BC847BW
100n
1K5
3016
3065
7013
BC847BW
100n
FC52
FC53
RES
1401
10
FC54
9
8
7
6
5
4
3
FC55
2
1
10p
2052
D
NC
46
7005
LF33ABDT
1
OUTIN
COM
2
3013
10K
IC43
+3V3_INTOTC
4K7
3066
47K
1112
IC38
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
A-1
IC44
10p
2057
29
31
33
35
38
40
42
44
30
32
34
36
39
41
43
451
10
13
14
16
+3V3_INTOTC
3V4
3
IC11
7004
BC847BW
10p
2056
FC56
FC58
3072-3
3
3082-1
8
3083-1
81
3102-4
5
3072-2
27
3082-2
72
3083-2
7
3102-3
63
3031-2
9
72
3031-4
54
10K
3005
3017
+3V3_INTOTC
7014
BC857BW
3V4
FC67
2055
N.C.
8204 000 8482.1
123
4
5
678910111213
6
DD(0)
3072-1
1
8
DD(1)
1
DD(2)
3082-3
3
DD(3)
6
DD(4)
3083-3
63
DD(5)
4
DD(6)
3102-2
72
DD(7)
DD(8)
3072-4
45
DD(9)
DD(10)
3082-4
54
DD(11)
2
DD(12)
3083-4
54
DD(13)
DD(14)
8
1
DD(15)
3102-1
AA(19)
3031-3
63
AA(20)
VPP-EPG
AA(18)
FC20
+3V3_INTOTC
100u
2016
4K7
RESET
B5a
B4
R-TXT
B4
G-TXT
B4
B-TXT
B4 (2X)
FBL-TXT
B3a
2FHFB-GFX
B3a
2FHB-GFX
B3a
2FHG-GFX
10p
B3a
2FHR-GFX
B5a
IRQ-FTV
F_15460_020.eps
100R
100R
100R
100R
100R
C
100R
100R
B5c(3x)
100R
A
070405
100R
100R
100R
100R
100R
100R
100R
100R
100R
100R
100R
A
B
C
D
E
F
G
H
I
J
1000 F7
1001 G3
1401 I12
2002 G3
2003 J4
2004 J4
2005 J3
2006 J3
2007 J3
2008 H4
2009 J8
2010 J9
2011 J9
2012 J9
2013 F11
2014 I4
2016 F13
2017 G12
2018 G3
2019 F10
2020 E1
2022 E2
2023 A5
2024 A5
2025 A5
2026 A6
2027 A6
2028 A6
2029 A6
2031 A8
2033 H8
2034 H8
2035 H8
2036 H8
2037 H8
2038 F9
2039 H12
2040 A12
2041 H1
2052 J12
2053 J11
2054 J11
2055 J13
2056 I13
2057 I12
2058 C2
2059 C2
2060 A4
2061 A3
2067 I7
2068 J2
2070 B2
2071 B1
2072 B1
2073 C3
2074 D4
2075 F8
3001 F3
3002 F3
3003 J4
3004 F12
3005 D13
3006 J6
3007-1 J6
3007-2 J6
3007-3 J6
3007-4 J6
3008-1 J7
3008-2 J7
3008-3 J7
3008-4 J7
3009 A1
3010 E8
3011 E2
3012-1 I8
3012-2 I8
3012-3 I8
3012-4 I8
3013 F12
3014 F12
3015 G11
3016 G12
3017 F13
3018 A2
3019 B2
3020 A2
3021 B2
3024 D3
3025 E1
3026 E4
3027 E2
3029-1 B11
3029-2 B11
3029-3 B11
3029-4 B11
3031-1 B11
3031-2 C13
3031-3 C13
3031-4 C13
3033 C3
3034-1 G7
3034-2 H7
3034-3 H7
3034-4 H7
3035-1 H7
3035-2 H7
3035-3 H7
3035-4 H7
3038 B1
3039 B2
3040 I1
3041 I1
3042 J1
3045 J11
3046-1 J12
3046-2 J12
3046-3 I11
3046-4 I11
3047 C2
3048-1 B8
3048-2 D8
3048-3 D8
3048-4 D8
3049-1 D8
3049-2 B8
3049-3 A8
3049-4 A8
3050-1 B8
3050-2 B8
3050-3 B8
3050-4 B8
3051-1 B8
3051-2 C8
3051-3 C8
3051-4 C8
3052-1 C8
3052-2 C8
3052-3 C8
3052-4 C8
3053 E2
3054-1 D10
3054-2 C10
3054-3 D10
3054-4 B10
3055-1 B10
3055-2 C10
3055-3 B10
3055-4 C10
3056-1 B10
3056-2 C10
3056-3 B10
3056-4 C10
3057-1 B10
3057-2 C10
3057-3 B10
3057-4 C10
3058 C1
3059 C1
3061-1 B11
3061-2 B11
3061-3 C11
3061-4 C11
3062 C11
3064-1 F3
3064-2 F4
3064-3 E3
3064-4 E4
3065 G12
3066 G12
3067 H11
3068 A2
3069 E3
3072-1 B13
3072-2 B13
3072-3 A13
3072-4 B13
3073-1 C4
3073-2 C4
3073-3 C4
3073-4 B4
3074-1 F2
3074-2 F4
3074-3 F3
3074-4 A3
3075 C1
3076-1 D4
3076-2 D3
3076-3 D3
3076-4 D4
3077 D3
3078-1 D4
3078-2 B3
3078-3 B3
3079 E3
3080 A2
3081 A4
3082-1 B13
3082-2 B13
3082-3 B13
3082-4 B13
3083-1 B13
3083-2 B13
3083-3 B13
3083-4 B13
3084 D8
3085-1 B11
3085-2 B11
3085-3 B11
3085-4 B11
3086-1 C11
3086-2 B11
3086-3 B11
3086-4 B11
3087 A11
3088 E3
3089 A8
3090-1 C4
3090-2 C4
3090-3 C4
3090-4 C4
3091 C2
3092 E3
3093 C11
3094 H1
3095 I1
3096 J2
3097 A3
3098 J10
3099-1 B4
3099-2 B4
3099-3 A4
3099-4 B4
3100 F4
3101 F4
3102-1 C13
3102-2 B13
3102-3 B13
3102-4 B13
3103 D3
3C09 I1
3C10 I1
3C11 J1
3C12 J7
5000 F7
5001 F7
5003 F8
6001 E2
6002 F11
6003 E3
6004 D2
6005 A3
6006 C4
7002 F11
7003 G12
7004 G13
7005 E12
7006 A9
7007 F10
7008 E1
7009 D3
7010 C3
7011 F2
7012 A12
7013 H12
7014 G13
7015 I2
7016 J2
7022 B1
7023 A4
9001 H2
9002 J2
9003 G1
9004 G1
9005 A4
9006 A3
9007 F12
9008 J10
9009 J11
9010 I11
9011 I11
9012 I11
9013 J11
9014 C2
9015 D2
9016 C2
9017 A4
9018 A3
9021 A1
9022 B3
9023 B3
9024 A1
9025 C4
FC01 A9
FC02 A7
FC03 C7
FC04 C8
FC05 C10
FC06 C7
FC07 C8
FC08 C7
FC09 C7
FC10 C7
FC11 D8
FC12 D8
FC13 D10
FC15 D7
FC16 D8
FC17 D10
FC18 D8
FC19 E8
FC20 F13
FC21 F10
FC22 A7
FC23 F10
FC24 B7
FC25 F10
FC26 B7
FC27 F10
FC28 B7
FC29 B10
FC30 B7
FC31 G10
FC32 G12
FC33 F9
FC34 C10
FC35 G9
FC36 F10
FC37 G9
FC38 C10
FC39 G9
FC40 C10
FC41 C10
FC42 C10
FC43 G10
FC44 C10
FC45 H8
FC46 H9
FC47 J6
FC48 G3
FC49 G3
FC50 E8
FC51 D7
FC52 I12
FC53 I12
FC54 J12
FC55 J12
FC56 J13
FC57 A3
FC58 J13
FC60 A4
FC61 E4
FC66 I7
FC67 H13
FC68 H12
FC69 J1
FC70 J11
IC03 B2
IC05 D1
IC07 E2
IC09 F1
IC11 G13
IC13 G11
IC14 G8
IC15 H8
IC17 H4
IC18 H8
IC20 H7
IC21 H3
IC22 H4
IC23 I9
IC24 I9
IC26 I3
IC27 I9
IC28 I8
IC29 D8
IC37 F4
IC38 J12
IC40 E3
IC41 C3
IC42 F12
IC43 G12
IC44 G12
IC45 I1
IC46 J2
IC48 E3
Page 52

Circuit Diagrams and PWB Layouts
EN 52FTP2.4E AA 7.
SSB: Backlight Control
2063 C3
3022 B1
3023 C1
3028 B2
3030 B2
3032 B2
1234
3036 B4
3037 C4
3070 C3
7020 B2
7021-1 B4
7021-2 B4
9019 C4
FC72 B4
IC50 B4
IC51 B3
IC52 B2
BACKLIGHT CONTROL
B5B B5B
A
+5V_CON+5V_CON
*
1K2
3022
B
B5a
PWM_BACKLIGHT
3028
4K7
*
IC52
*
4K7
3030
7020
BC847BW
10K
3032
IC51
*
*
*
2K2
C
D
3023
*
2063
100n
*
3070
*
+8V_CON
*
RES
27K
4K7
3036
IC50
BC847BPN
7021-2
9019
*
*
RES
3037
RES
7021-1
BC847BPN
FC72
ANTI-MOIRE
BACKLIGHT
CONTROL
(
10K
SSB: OTC-Flash
1402 C1
1404 B1
2C00 A2
2C01 B3
2C02 E3
3C00 A2
3C01 A2
3C03 B2
3C04 D2
3C05 D2
3C06-1 B4
3C06-2 C4
3C06-3 C4
3C06-4 C4
3C07-1 C4
3C07-2 C4
3C07-3 C4
3C07-4 D4
3C08 B2
7017 B1
7018 B3
7019 E3
9C00 A2
9C01 C1
9C02 D1
FC62 F3
FC63 F3
FC64 F3
FC65 C1
FC71 C2
1234
OTC-FLASH
B5C B5C
A
A
B
B4
)
C
B
SSSS8
1404
1402
SSSS8
C
D
SWITCH
FOR SOFTWARE
DOWNLOAD
9C02 9C01
+3V3_INTOTC
7017
PDTC144EU
b5a,c(2x)
b5a(3x),c(2x)
FC65
b5a,c(2x)
b5a(3x),c(2x)
3C00
2C00
b5a,c(2x)
b5c(2x)
b5c(2x)
2K2
100n
3C01
10R
3C03
10K
FC71
ROM_CS
RAM_OE
RAM_CS
WE
WP
VCCW
9C00
10K
3C08
0V1
3V3
EAn
+3V3_INTOTC
100n
2C01
B
A
10R
3C07-1
10R
3C07-3
10R
B5a,c
ROM_OE
ROM_CS
RAM_OE
RAM_CS
WE
WP
WP
VCCW
b5a,c(2x)
b5a,c(2x)
b5a(3x),c(2x)
b5a,c(2x)
b5a(3x),c(2x)
b5c(2x)
b5c(2x)
b5c(2x)
C
7018
74LVC245APW
3EN1
3EN2
G3
2
20
SWITCH
1
10
18
17
16
15
14
13
12
VPP-EPG
11
b5a,c(2x)
SW_OEROM_OE
b5a,c(2x)
SW_CS
EP_OE
EP_CS
EP_WE
SW_WE
VPP-SW
SW_OE
SW_CS
b5a,c(2x)
EP_OE
b5a,c(2x)
EP_CS
b5a,c(2x)
EP_WE
b5a,c(2x)
SW_WE
b5a,c(2x)
VPP-EPG
b5a,c(2x)
VPP-SW
3C06-1
10R
3C06-2
10R
3C06-4
10R
3C07-2
10R
3C07-4
10R
3C06-3
1
19
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
8204 000 8482.1
123
F_15460_021.eps
4
070405
D
E
F
8204 000 8482.1
b5c(2x)
b5c(2x)
b5a(3x),c(2x)
b5a,c(2x)
b5a(3x),c(2x)
b5a,c(2x)
b5a,c(2x)
VCCW
WP
WE
RAM_CS
RAM_OE
ROM_CS
ROM_OE
3C05
470R
3V3
10K
3C04
7019
74LVC245APW
3EN1
3EN2
G3
2
20
SWITCH
1
10
1
19
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
+3V3_INTOTC
2C02
18
17
16
FC64
15
14
13
12
FC63
11
FC62
100n
VPP-EPG
VPP-SW
EP_WE
SW_WE
SW_CS
SW_OE
EP_CS
EP_OE
b5a,c(2x)
b5a,c(2x)
b5a,c(2x)
b5a,c(2x)
b5a,c(2x)
b5a,c(2x)
b5a,c(2x)
b5a,c(2x)
F_15460_022.eps
080405
D
E
F
1234
Page 53

Circuit Diagrams and PWB Layouts
EN 53FTP2.4E AA 7.
SSB: Audio Demodulator
12345
6789
10 11 12 13
AUDIO DEMODULATOR
B6A B6A
5
6
3A20
100K
GND-AUD
INPUT
SUPPLY
VS
16
B6a
DACM-SUB
7A03-2
8
LM833D
4
6V5
2A30
100p
3A23
68K
1
RECL
SERIAL BUS DECODER
AGND7CREF
15
IA21
4V2
22u
2A90
+11V_AUD
2A20
1u0
7
LOUDL
VOLUME+
LOUDNESS
+ LATCHES
VOLUME+
LOUDNESS
RECR
10
1u0
2A89
GND-AUD
19
3A21
27K
IA04
LOUDR
12
2A88
47K
3A12
3
2
3A18
33K
2A25
100p
9A00
9A01
2A64 100n
100n
3A15
8
7A00-1
1
LM833D
4
6V5
GND-AUD
MUTE
SOFT
MUTE
MUTE
B14c,B15c
HA50-PIP
VA50-PIP
B14c,B15b,c
12 13
2AB8
100K
OUTL
DGND
ADDR
CSM
OUTR
+5V
+5VF
1u0
2A15
GND-AUD
SDA
SCL
FA12
100u
3A11
2A16
2
6
4
5
8
3
9
3V6
3V6
100K
100n
2A14
9A03
2A76
100n
GND-AUD
9A16
5
1n0
6
9A02
9A18
2A10
100n
8
LM833D
7A00-2
4
3A16
100R
SNDR-SC1-OUT-DC
SNDL-SC1-OUT-DC
9A17
5A06
2A95
220p
FA17
SNDR-MON-OUT
SNDL-MON-OUT
A
+5V
5A02
B
B6a,b,c
B6a,b,c
C
D
B14d(2x)
B14d(2x)
E
B2
B14b
B14d
B14d
B14c
B14c
2A05
SCL-F
SCL-F-AUD
SDA-F
SDA-F-AUD
QSS_AM
SND-CENTER-IN
SNDR-MAIN-IN
SNDL-MAIN-IN
SNDR-SC2-IN
SNDL-SC2-IN
SNDR-DVI-IN
SNDL-DVI-IN
F
B6a,B14d(2x)
B6a,B14d(2x)
SNDR-SEC-IN
SNDL-SEC-IN
G
B2(2x)
Y50
B2
U50
B2
V50 IN-V50
H
B3a
Y-PIP+MAIN-IN
B3a
U-PIP+MAIN-IN
B3a
V-PIP+MAIN-IN
I
8204 000 8477.1
+5DA
IA10
5A00
1u0
2A01
2A02
1n0
2A06
5A03
5A19
22u
IA12
2A08
3A19
100R
3A17
100R
IA23
IA24
100u 16V
2A32
100p
+11V_S
2A00
1n0
+5DB
1u0
2A07
IA25
2A33
100n
2A39
2A46
FA26
FA27
2A49
IA13
2A53
2A56
IA14
IA15
2A59
2A62
IA16
9A67
IA17
1n0
5A01
2A04
2A03
100u
1n0
7A02
MSP4450
1
I2C-CL
2
I2C-DA
2A29
52 ANA-IN2+
100p
50 ANA-IN1+
2A37
51
100p
1u0
1u0
1u0
1u0
1u0
1u0
1u0
ANA-IN-
47 MONO-IN
45 SC1-IN-R
44 SC1-IN-L
42 SC2-IN-R
41 SC2-IN-L
39 SC3-IN-R
38 SC3-IN-L
SCART 3
36 SC4-IN-R
35 SC4-IN-L
SCART 4
9A71
IA18
9A10
9A11
9A12
9A05
9A06
9A04
9A13
9A14
9A15
12
B15b,c
IN-Y50
B15b,c
IN-U50
B15b,c
B14c,B15b
Y-PIP+MAIN-OUT
B14c,B15b
U-PIP+MAIN-OUT
B14c,B15b
V-PIP+MAIN-OUT
B6a
B6a
DACM-SUB
HPN-L
REF-AUD
B6A(3X)B6C(3X)
2AB3
1u0
3A45
47K
8ADR-WS
IDENT
A/D
A/D
nc
57
AUD-CL-OUT
B14d
REG-SW
SUBW-SPI-SW
61
60
D-CTR-IO0
D-CTR-IO1
FM1
FM2
NICAM A
NICAM B
IDENT
SCART-L
SCART-R
S1...4
B6c
I2S-DPL-CLK
14
I2S-CL3
I2SL/R
DSP
B6c
B6c
I2S-DPL-WS
I2S-DPL-OUT
15
12I2S-DA-IN2
I2S-WS3
I2S
I2SL/R
LOUDSPEAKER R
LOUDSPEAKER L
HEADPHONE R
B6b,d
I2S-MSP-OUT
5I2S-DA-O1
interface
+11V_AUD
FA28
1u0
MONO
B6c
SYS-CLK0
10n
2A09
7ADR-DA
9ADR-CL
interface
ADR
DEMODULATOR
HEADPHONE L
SCART-R
SCART-L
Switching Facilities
SCART
NC159NC264NC322NC4
58
2AB7
1n0
IA00
56K
3A52
GND-AUD
2A99
3A46 3A49
4K7
*
NC
NC524NC8
13
3A04
100K
7A09
BC857B
3A55
2AB2
1n0
IA02
3A48
IA48
330R
2AB6
1n0
2A79
100n
8
MC33178D3
1
7A07-1
2
4
IA49
2A91
100p
3A22
100K
1u0
47K
*
DACM-SUB
ADR-SEL
23
62
MSP-SURR
MSP-CENTER
HEADPHONE-L
100K
TESTEN
53
AVSS
48
B21
ASG040ASG137ASG2
43
+5DA
B6c
B6c
B6a
HPN-R
B6a(3x),C(3x)
3A47
REF-AUD
33
2AB4
1u0
47K
345
B6d
I2S-MSP-IN
6I2S-DA-IN1
VREF119VREF2
AHVSS
cA01
IA01
3A53
GND-AUD
3A51
4K7
10u
B6b,c
SYS-RESET
2A23
100n
2A31
FA23
2A40
1u0
100n
REF-AUD
3A13
IA06
2A41
B6a(3x),C(3x)
+11V_AUD
47K
3
2
3A66
100K
10u
8
4
2A36
100p
3A26
68K
7A03-1
LM833D
2A22
100n
6V5
100n
2A11
1
2A26
IA05
3A14
47K
1u0
3A27
4K7
B6b,d
I2S-MSP-CLK
3I2S-CL
D/A
D/A
D/A
D/A
B6b
+8V
I2S-MSP-WS
3A03
4I2S-WS
31
AHVSUP
LOUDSPEAKER
HEADPHONE
6R8
2A18
FA13
100u
+8VC
2A17
RESETQ
VREFTOP
AGNDC
CAPL-M
CAPL-A
B5a,B14b
+5DB
RESET-AUDIO
2K2
3A01
22K
7A01
IA35
IA36
IA07
IA08
2V7
3A00
IA22
22K
100n
2A21
3A09
2A27
1n0
2A35
1n0
FA24
3V9
2A42
16V
10u
2AB5
16V
10u
2A50
1n0
2A54
1n0
BC847BW
GND-AUD
2A44
FA14
100n
3A28
4K7
2A43
1n0
6A00
PDZ10-B
16
20DACM-R
21DACM-L
46
34
32
30
17DACA-R
18DACA-L
D/A
XTAL-IN55XTAL-OUT
54
DSX840GA
18M432
1A01
1n0
2AA9
3p3
7A04
BC857B
IA42
3A61
330R
BC847BS
3A63
100K
3A62
7A08-2
28SC1-OUT-R
29SC1-OUT-L
25SC2-OUT-R
26SC2-OUT-L
B6a,B14d(2x)
SNDL-SEC-IN
*
6A02
BZX384-C3V3
POR
22K
SYS-RESET
IA41
6A01
IA40
1u0
3A24
2A51
*
180R
B21
B6a,B14d(2x)
SNDR-SEC-IN
1u0
IA03
100K
3
4
2AB0
3p3
+5V
3A06
7A08-1
BC847BS
+11V_AUD
+5V
BC847BS
9A78
5
3A07
100K
100K
6
1
IA46
5
7A31-1
9A07
9A08
6
1
3
7A31-2
BC847BS
4
IA47
2
3A64
47K
HEADPHONE-R
2
9A79
1M0
3A65
2A47
3A05
BAS316
2A70
1u0
2A69
1u0
2A72
1u0
2A74
1u0
2A75
1u0
2A66
1u0
7A06 TDA7309D-TR
IN1L
17
IN2L
18
IN3L
20
IN1R
14
IN2R
13
IN3R
11
+8VC
2A83
100n
1n0
1u0
2A80
2A81
SELECTOR
D/A
SCART 1
SCART 2
STANDBYQ
DVSS10DVSUP
AVSUP
56TP27
IA09
GND-AUD
56K
2A92
*
63
11
49
0V
5V2
5V2
5V2
1n0
2AA6
2AA7
+5DB
+5DA
8
MC33178D
5
6
1u0
2AA5
100p
3A60
100K
3A40
7
7A07-2
4
IA43
47K
*
67891011
B6a(3x),
REF-AUD
7
6V3
SDA-F-AUD
C(3x)
B6c,B21
AUDIO-SW
B6c,B21
AUDIO-R
B6c,B21
AUDIO-L
B6a
HPN-R
B6a
HPN-L
B14b(2x)
B14b(2x)
B14b,d(2x)
B14b,d(2x)
B6a,b,c
B6a,b,c
SCL-F-AUD
B2 , B3a
HA50
B2 , B3a
VA50
B15b
F_15460_023.eps
070405
A
B
C
D
E
F
G
H
I
1A00 G7
1A01 G7
2A00 A3
2A01 B2
2A02 B2
2A03 B2
2A04 B3
2A05 B1
2A06 B1
2A07 B2
2A08 B2
2A09 B3
2A10 B13
2A11 B10
2A14 B13
2A15 B12
2A16 B12
2A17 B7
2A18 B6
2A20 B11
2A21 B7
2A22 C10
2A23 C9
2A25 C11
2A26 C10
2A27 C8
2A29 C2
2A30 C11
2A31 D9
2A32 D1
2A33 D2
2A35 D8
2A36 C9
2A37 D2
2A39 D2
2A40 D9
2A41 D9
2A42 D8
2A43 D8
2A44 D8
2A46 D2
2A47 I8
2A49 E2
2A50 E8
2A51 I9
2A53 E2
2A54 E8
2A56 E2
2A59 F2
2A62 F2
2A64 F11
2A66 F9
2A69 G9
2A70 G9
2A72 G9
2A74 G9
2A75 H9
2A76 H13
2A79 H3
2A80 I10
2A81 I10
2A83 I10
2A88 I11
2A89 I11
2A90 I11
2A91 I3
2A92 I6
2A95 I13
2A99 I3
2AA5 I6
2AA6 G6
2AA7 G6
2AA9 H7
2AB0 H7
2AB2 G4
2AB3 H3
2AB4 H5
2AB5 D8
2AB6 G4
2AB7 G3
2AB8 B12
3A00 B8
3A01 B8
3A03 B6
3A04 H4
3A05 H8
3A06 I7
3A07 I8
3A09 B8
3A11 B12
3A12 B11
3A13 B9
3A14 B10
3A15 B12
3A16 B13
3A17 C2
3A18 C11
3A19 C2
3A20 C10
3A21 B11
3A22 I3
3A23 C10
3A24 I8
3A26 D9
3A27 D10
3A28 D9
3A40 I6
3A45 H3
3A46 I3
3A47 H5
3A48 I4
3A49 I3
3A51 I6
3A52 I3
3A53 I6
3A55 I4
3A60 I6
3A61 I7
3A62 I7
3A63 H7
3A64 I8
3A65 I8
3A66 C9
5A00 A1
5A01 B2
5A02 B1
5A03 B1
5A06 I13
5A19 D2
6A00 B7
6A01 I8
6A02 H8
7A00-1 B12
7A00-2 B13
7A01 B8
7A02 B3
7A03-1 C9
7A03-2 B11
7A04 I7
7A06 G10
7A07-1 H3
7A07-2 H6
7A08-1 I7
7A08-2 I7
7A09 I4
7A31-1 H8
7A31-2 H8
9A00 E11
9A01 E11
9A02 G13
9A03 G13
9A04 H1
9A05 H1
9A06 H1
9A07 G8
9A08 G8
9A10 G1
9A11 H1
9A12 H1
9A13 H1
9A14 I1
9A15 I1
9A16 I13
9A17 I13
9A18 B13
9A67 F2
9A71 G2
9A78 H7
9A79 H8
FA12 B12
FA13 B7
FA14 B8
FA17 B13
FA23 D9
FA24 D8
FA26 D2
FA27 E2
FA28 B3
IA00 H3
IA01 H6
IA02 H4
IA03 I7
IA04 B11
IA05 C10
IA06 C9
IA07 C7
IA08 D7
IA09 G6
IA10 A2
IA12 B2
IA13 E2
IA14 E2
IA15 F2
IA16 F2
IA17 F2
IA18 G2
IA21 I11
IA22 B8
IA23 D2
IA24 D2
IA25 B2
IA35 D7
IA36 E7
IA40 I8
IA41 I8
IA42 I7
IA43 I6
IA46 I8
IA47 I8
IA48 I4
IA49 I4
cA01 G6
Page 54

Circuit Diagrams and PWB Layouts
EN 54FTP2.4E AA 7.
SSB: Dolby Digital Decoder
123456789
DOLBY DIGITAL DECODER
B6B B6B
A
+5M
SID
SIC
_PCS
PR
XTI
XTO
_POR
SCL
SDA
2AD0
2AD4
SII
TE
1n0
+5M
1u0
100u
5A38
+5V
+5M
2AF4
100n
2AF3
A5
21
20
19
A6
I2S-MSP-OUT
A7
I2S-MSP-WS
I2S-MSP-CLK
+5M
IA71
2AE3
36
37
3V1
39
38
40
9
10
2AE5
2AF0
10n
10n
IA75
10n
IA72
3A74
75R
3A77
75R
2AE2
1n0
SPDIF-IN1
SPDIF-BO-OUT
SYS-CLK1
A8
6
4V9
5
4
3
SYS-RESET
SCL-F-AUD
SDA-F-AUD
VSS
2AD1
2AD6
1
1u0
1n0
SPREF
SPDI_1
SPDI_2
+5M
B
7A30
IC MAS3528E
18
PI4
24
PI8
28
C
D
E
B6c
B6c
B6c
I2S-DD-CLK
I2S-DD-WS
I2S-DD-OUT
A2
A3
A4
F
PI12
29
PI13
30
SID_PI14
31
SII_PI15
32
SIC_PI16
33
PI17
34
PI18
35
PI19
41
_RTW
42
_RTR
43
_EOD
44
SYNC
17
SPDIFOUT
25
SOC
26
SOI
27
SOD
14
SOD1
15
SOD2
16
SOD3
13
CLKO
2AC1
220p
2AD3
DOLBY DIGITAL
MPEG-1 LAYER-2
AUDIO DECODER
1u0
2AD5
AND
NC2
12
1n0
NC1
11
23
XVDD
8
AVDD
XVSS
22
2
VDD
AVSS
7
B6a,d
B6a,d
B6a
B14b
B14b
B6c
B6a,C
B6a(2x),C
B6a(2x),C
A
B
C
D
E
F
2AC1 B4
2AD0 B6
2AD1 B6
2AD3 B4
2AD4 B6
2AD5 B5
2AD6 B6
2AE2 D8
2AE3 D7
2AE5 D7
2AF0 E6
2AF3 C8
2AF4 C7
3A74 D7
3A77 E7
5A38 B8
7A30 B4
IA71 D7
IA72 D7
IA75 D7
8204 000 8477.1
12345
678
F_15460_024.eps
070405
9
Page 55

Circuit Diagrams and PWB Layouts
EN 55FTP2.4E AA 7.
SSB: Dolby Pro Logic Processor
12345678
B6C B6C
A
B
C
B6a(2x),b
SCL-F-AUD
B6a(2x),b
SDA-F-AUD
D
E
F
DOLBY PRO LOGIC PROCESSOR
B6a
B6a
I2S-DPL-WS
I2S-DPL-CLK
+5DB
A10
A9
A11
7
100n
2AK6
10u
2AK7
IAA5
7A63
DPL4519G
1
I2C_CL
2
I2C_DA
0V2
46 VREFTOP
51 ANA_IN-
8
ADR-WS
ADR-DA
ADR-CL
62
ADR_SEL
DEMODULATOR
52 ANA-IN2+
50 ANA_IN1+
NICAM
DECODER
IDENT
47 MONO_IN
SCART 4
36 SC4-IN-R
35
SC4-IN-L
SCART 3
39 SC3-IN-R
38 SC3-IN-L
SCART 2
42 SC2_IN_R
41 SC2_IN_L
SCART 1
45 SC1_IN_R
44 SC1_IN_L
A/D
A/D
FM1
FM2
NICAM A
NICAM B
IDENT
SCART-L
SCART-R
4I2S-WS
SCART
3I2S-CL
DSP
Switching Facilities
B6b
B6b
I2S-DD-WS
I2S-DD-CLK
A12
15I2S-WS3
14
I2S-CL3
I2S INTERFACE
I2SL/R
LOUDSPEAKER R
LOUDSPEAKER L
B6a
A13
5I2S-DA-OUT1
I2SL/R
HEADPHONE R
HEADPHONE L
B6b
I2S-DD-OUT
I2S-DPL-OUT
6I2S-DA-IN1
12I2S-DA-IN2|3
SCART-R
SCART-L
B6a,b
SYS-RESET
+8VC
1n0
2AK4
10u
2AK9
IAA9
30
32
CAPL-A
CAPL-M
STANDBYQ
DACM-SUB
LOUDSPEAKER
1u0
10u
DVSUP
RESETQ
AGNDC
2AK5
A14
2AK8
IAA8
31
AHVSUP
D/A
D/A
D/A
HEADPHONE
D/A
D/A
D/A
SC1_OUT_L
+5DB
1n0
1u0
2AK3
2AK2
63
+5DB
10
16
23
3V8
34
IAB0
20DACM_R
21DACM_L
17DACA-R
18DACA-L
25SC2-OUT-R
26SC2-OUT-L
28SC1_OUT_R
29
2AM3
1n0
2AN5
100n
2AN6
B6a
MSP-SURR
9A60
IAA2
2AL3
IAA4
10u
2AM7
AUDIO PLL
48 9
AVSS
TP1
56
VREF1
VREF2
AHVSS
27
19
G
33
A
37
ASG2
ASG0
ASG1
43
40
H
11
DVSS
TESTEN
53
A15
AUD-CL-OUT
57
10n
2AN7
NC1
NC2
D-CTR-IO0
D-CTR-IO1
58
59
61
60
+5DA
1u0
2AK0
2AK1
XTAL_IN
NC3
AVSUP
54
64
49
A16
1n0
NC422NC524NC6
55 XTAL_OUT
13
9 10111213
2AM5
470n
1n0
B6a(4x),C(2x)
REF-AUD
6K8
47K
3AA6
3AA0
IA52
2AL1
1u0
1n0
IA50
GND-AUD
3AA1
18K
LM833D
IAB1
3AB2
3AB9
4K7
7A61-2
5
6
47K
3AB4
IAA3
+11V_AUD
47K
5
6
2AN0
8
4
3AA4
47K
2AM0
100p
+11V_AUD
8
4
2AN1
100p
3AB6
100K
1u0
3AB8
68K
B6a,B21
AUDIO-SW
9A65
7
6V5
7A62-2
LM833D
B14b
SUBW
IA51
2AL2
2AL4
IAA6
7
6V5
IAA7
2ALA
470n
1n0
GND-AUD
1n0
GND-AUD
2AM2
100n
3AC1
18K
3AA9
4K7
3AB7
6K8
3AB0
IA53
IAA1
IAB2
3AC0
47K
2AM6
+11V_AUD
2AL0
100n
47K
7A61-1
8
LM833D
3
2
1u0
2AL8
3
2
100n
3AB3
100K
3AB5
68K
100p
3AA5
100K
3AA7
68K
8
4
2AM9
100p
9A61
4
2AL9
7A62-1
LM833D
1
6V5
9A20
1
6V5
9A19
2AM1
SURR-R
AUDIO-R
REF-AUD
AUDIO-L
SURR-L
B6a(4x),C(2x)
REF-AUD
+11V_AUD
100n
AUDIO-C
MSP-CENTER
B14b,e
B6a,B21
B6a(4x),C(2x)
B6a,B21
B14b,e
B21
B6a
2AK0 G5
2AK1 G5
2AK2 B7
2AK3 B7
2AK4 B6
2AK5 B6
2AK6 D2
2AK7 D2
2AK8 B6
2AK9 B6
A
2AL0 B12
2AL1 B9
2AL2 B11
2AL3 B9
2AL4 B11
2AL8 C12
2AL9 C12
2ALA F11
2AM0 C10
B
2AM1 E13
2AM2 E11
2AM3 E7
2AM5 D9
2AM6 F12
2AM7 D8
2AM9 E12
2AN0 E9
2AN1 E10
2AN5 D7
C
2AN6 D8
2AN7 G5
3AA0 B9
3AA1 D9
3AA4 C10
3AA5 C12
3AA6 B9
3AA7 C12
3AA9 C11
D
3AB0 E11
3AB2 D9
3AB3 F12
3AB4 D9
3AB5 F12
3AB6 E10
3AB7 F11
3AB8 E10
3AB9 E9
E
3AC0 B12
3AC1 B11
7A61-A B12
7A61-B B10
7A62-A E12
7A62-B D10
7A63 C3
9A19 C13
9A20 D13
9A60 B8
F
9A61 F12
9A65 B10
IA50 D9
IA51 B11
IA52 B9
IA53 E12
IAA1 E12
IAA2 B8
IAA3 E9
G
IAA4 C9
IAA5 D2
IAA6 C11
IAA7 F11
IAA8 C6
IAA9 C7
IAB0 D7
IAB1 C9
IAB2 C12
H
8204 000 8477.1
123456
SYS-CLK1
B6b
SYS-CLK0
B6a
7 8 9 101112
13
F_15460_025.eps
070405
Page 56

SSB: Audio Delay
B6D B6D
A
B
C
D
+5D
+5D
Circuit Diagrams and PWB Layouts
12345678 9
AUDIO DELAY
7A11
M74HC590T
14
13
12
11
10
M74HC590T
7A12
14
13
12
11
10
EN3
C2
G1
1+
CT=0
CTR8
(CT=255)Z4
EN3
C2
G1
(CT=255)Z4
1+
CT=0
16
8
CTR8
9
4
15
2D 3
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
16
4
+5D
9
+5D
2A12
2A13
100n
100n
EN 56FTP2.4E AA 7.
2A12 B2
2A13 D2
2A19 F5
2A24 C7
2A34 C9
2A38 B9
2A45 B7
3A02 F5
A
3A67 E5
5A07 B9
B
7A11 A1
7A12 D1
7A13 E5
7A14 D7
7A15 D9
7A16 A5
9A21 D9
9A22 D9
9A23 D9
9A24 D9
9A25 F8
9A72 D9
CY7C199B-15ZC
14
GND
A1
21A023
A2
25A326A41A52A63A74A85
24
A9
A107A118A129A1310A14
6
7A16
I|O012I|O113I|O215I|O316I|O417I|O518I|O6
11
I|O722OE_
19
20
CE_
WE_
27
VCC
+5D
28
100n
2A45
+5M
5A07
FA00
2A38
+5D
1u0
9A73 D9
9A74 D9
9A75 D9
FA00 B9
FA01 E5
FA02 E5
FA03 D9
FA04 E6
C
+5D
74HCT573PW
1
EN
11
C1
2
1D
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
20
10
7A14
+5D
100n
2A24
19
18
17
16
15
14
13
12
74HCT573PW
1
EN
11
C1
2
1D
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
20
10
7A15
+5D
100n
2A34
19
9A72
18
9A73
17
9A74
16
9A75
15
9A21
14
9A22
13
9A23
12
9A24
FA03
D
E
F
8204 000 8477.1
15
2D 3
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
1
2345678 9
FA02
BC847BW
7A13
3A67
470R
FA01
3A02
47K
27p
2A19
B6a,b
I2S-MSP-CLK
FA04
B6a,b
I2S-MSP-OUT
9A25
B6a
I2S-MSP-IN
F_15460_026.eps
070405
E
F
Page 57

SSB: DC/DC Convertor
1U01 A1
2U01 A8
2U02 B9
2U04 B5
2U05 C2
2U06 C3
2U07 C3
2U08 C8
2U09 D6
2U10 A3
2U11 E102U03 B4
2U13 E14
2U14 B5
2U15 A1
2U16 C2
2U17 D5
2U18 B2
2U19 H1
2U20 H4
2U21 B3
2U22 H6
12
Circuit Diagrams and PWB Layouts
2U24 G8
2U25 H5
2U26 H6
2U27 D2
2U28 E2
2U29 C9
2U30 C1
2U31 D13
2U32 C1
2U33 F10
2U34 G11
2U35 H8
2U36 B6
2U37 B6
2U38 A3
2U39 F6
2U40 F3
2U41 F7
2U42 E6
3U01 C14
3U02 B1
3U03 C1
3U04 C2
3U05 C3
345
3U06 C12
3U07 C9
3U08 C11
3U09 C4
3U10 D14
3U11 D4
3U12 G10
3U13 D7
3U14 D1
3U15 D14
3U16 D11
3U17 D7
3U18 E112U12 E7
3U19 E8
3U20 E14
3U21 E2
3U22 E12
3U23 E14
3U24 G6
3U25 F2
3U26 H4
3U27 H10
3U28 E1
3U29 C22U23 C13
3U30 C2
3U31 B2
3U32 H1
3U33 H2
3U34 H4
3U35 H5
3U36 H10
3U37 F9
EN 57FTP2.4E AA 7.
3U38 G9
3U39 G9
3U40 G9
3U41 H6
3U42 H5
3U43 G6
3U44 D2
3U45 E2
3U46 C10
3U51 A5
3U52 F10
3U53 F10
3U54 H7
3U55 E9
3U56 B6
3U57 A6
3U58 G12
3U59 G12
3U60 F4
3U61 F5
3U62 F7
3U63 F6
3U64 F7
3U65 F5
3U66 F4
3U67 G5
3U68 G6
3U69 F6
3U70 C14
5U01 B8
5U02 A2
5U03 B7
5U04 C7
5U05 C12
5U06 D12
5U07 B8
6U01 A2
6U02 A8
6U03 A4
6U04 B5
6U05 B1
6U06 C9
6U07 D14
6U08 E3
6U09 E3
6U10 H1
6U11 H2
6U12 F9
6U13 E10
6U14 H8
6U16 F7
6U17 D14
7U01 B2
7U02 C4
7U03 C7
7U04 C5
678910111213
7U05 D9
7U06-A D12
7U06-B D12
7U07-1 G10
7U07-2 F8
7U08 D5
7U09 E1
7U10 G4
7U11 E3
7U12 H3
7U13-1 F5
7U13-2 F4
FU03 B9
FU04 B9
FU05 C8
FU06 G6
FU07 H1
FU08 C9
FU09 D13
IU01 B2
IU02 C1
IU03 D1
IU04 E3
IU05 D3
IU06 D4
IU07 D4
IU08 C4
IU09 B4
IU10 A4
IU11 A5
IU13 D8
IU14 D6
IU15 A8
IU16 C11
IU17 D9
IU18 D11
IU19 C14
IU20 D10
IU21 D14
IU22 E12
IU25 H4
IU26 E2
IU27 G3
IU28 H2
IU30 C3
IU31 C2
IU32 E2
IU34 H6
IU35 G7
IU36 G9
IU37 F8
IU38 G9
IU39 G9
IU40 G10
IU41 H9
IU42 C6
IU43 E10
IU44 F11
IU45 F9
IU46 F5
IU47 F6
cU01 H12
14
B12 B12
DC/DC - CONVERTOR
+11V
A
B
C
3U03
D
E
3U28
F
G
3U32
H
18K
8204 000 8480.1
1U01
1500mAT
420
GND GND
3U02
1K0
6U05
2U30
120p
33K
IU02
2U32
3n3
IU03
3U14
BC817-25
7U09
47K
GND_SUPPLY
6U10
FU07
BZX384-C15
GND_SUPPLY
12345678910 14
5U02
100u
2U15
IU01
21V4
2U18
BZX384-C12
IU31
2U05
3U44
1K0
3U45
GND_SUPPLY
100n
2U19
10u
6U01
21V6
3U31
120p
3U30
3U04
1n0
6n8
1M0
2U27
IU32
6n8
1M0
2U28
IU26
IU28
6U11
BAS316
GND_SUPPLY
2U10
BAS316
7U01
BC857B
120R
3U29
120R
IU30
120R
2U16
47K
3U21
220K
3U25
GND_SUPPLY
0V7
3U33
GND_SUPPLY
10R
4n7
IU04
10K
22u
2U06
GND
6U08
BAT54 COL
7U11
BC847BW
GND_SUPPLY
2U38
GND
3U05
1K0
22u
IU05
2n2
IU27
7U12
BC847BW
res
220u 16V
IU10
470n
2U21
GND_SUPPLY
IU08
82p
2U07
IU07
3U11
120R
6U09
BAT54 COL
10K
2U40
3U66
BC847BW
2U20
GND_SUPPLY
1u0
3U09
7U10
2U03
BC857B
5K6
IU06
1K0
BC847BPN
7U13-2
3U34
7U02
3U60
IU25
330K
6U03
BAS316
1u0
IU09
GND_SUPPLY
3U61
3U26
GND_SUPPLY
3U51
22R
6U04
567841
2U17
7U08
BC817-25
GND_SUPPLY
10K
IU46
3U65
1K0
7U13-1
BC847BPN
GND_SUPPLY
22K
100n
BAS316
470n
2U25
3U67
10K
3U42
3U35
10K
IU11
2U14
2U04
23
7U04
SI4410DY
100R
GND_SUPPLY
470n
470n
IU34
3U56
4K7
47n
1K0
3U68
2U42
3U69
3U63
IU47
10K
22K
3U43
2U22
1u0
2U36
100n
GND_SUPPLY
IU42
IU14
2K2
GND_SUPPLY
3V3_FAULT
B3e,B14a,B19b,B13c
FU06
3U24
100n
2U26
GND_SUPPLY
3U41
GND_SUPPLY
10K
3U57
GND-ILINK
2U37
2U09
2U39
100n
22K
1K0
2n2
SI4410DY
7U03
10K
1n0
10n
2U12
GND_SUPPLY
3U64
1K0
6n8
2U41
GND_SUPPLY
IU35
3U54 3U13
100R
5
6
5U03
5U04
4
GND_SUPPLY
3U17
4R7
1K0
BZX384-C5V1
1
3
5U01
10
res
5U07
10u
FU05
5678
123
IU13
3U19
GND_SUPPLY
3U62
2U35
4
3
1u0
7U07-2
6U16
6U14 BAV99 COL
IU15
STPS2L30A
2U08
GND_SUPPLY
4K7
BC847BPN
2U01
2n2
6U02
22u
IU37
5
2U24
1n0
res
res
2U02
res
FU04
GND-ILINK
FU08
6U06
BZG05C3V9
7U05
BC857BW
3U38
2K2
150K
3U40
IU36
IU41
FU03
47u
3U07
IU17
3U55
22K
22K
3U39
+3V3-ILINK
2U29
22R
GND_SUPPLY
1K0
IU45
6U12
BZX384-C5V1
GND_SUPPLY
3U37
IU38
7U07-1
IU39
GND_SUPPLY
res
330u 6.3V
2U33
6
1
3U36
6U13
PDZ8.2-B
IU43
18K
3U53
1u0
GND_SUPPLY
BC847BPN
2K2
3U46
IU20
2U11
GND_SUPPLY
1K0
3U52
2
IU40
GND_SUPPLY
47K
1n0
IU16
1%
3U12
3U27
3V4
3U06
1%
1K5
3U08
120R
3U16
1%
1K0
3U18
IU44
2U34
22K
GND_SUPPLY
22K
1V6
IU18
2
22n
7U06-1
BC847BS
470R
6
BC847BS
1
3U22
270R
GND_SUPPLY
7U06-2
IU22
5U06
10u
3
4
GND
11 12 13
5U05
10u
1V7
3U58
1R0
3U59
1R0
cU01
3V4
2U23
GND_SUPPLY
100u
2U31
GND_SUPPLY
5
res
res
GND_SUPPLY
+3V3_SIM
100u
+3V3_DCDCFBX
FU09
3U01
6V9
3U10
3U15
2U13
GND_SUPPLY
1K0
3U70
IU19
1R0
6U07
1%
3K3
GND_SUPPLY
IU21
3U20
220n
3U23
F_15460_027.eps
1K0
6U17
PDZ6.8-B
1%
1K0
1R0
A
B
C
PDZ6.8-B
D
E
F
G
H
070405
Page 58
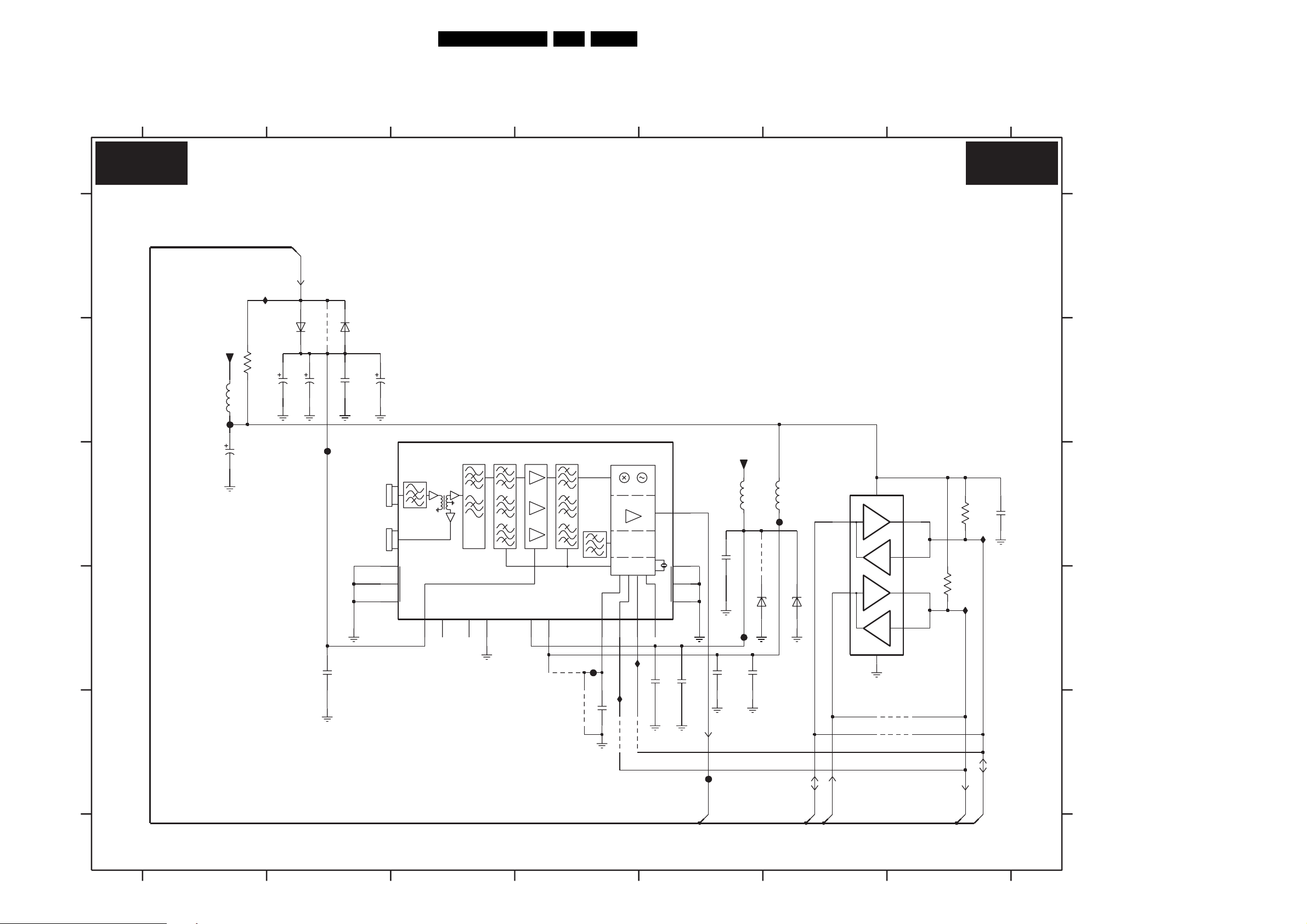
SSB: Main Tuner
1T01 B3
2T01 B2
2T04 C5
2T05 C1
2T06 E4
2T09 D5
2T12 C7
2T13 B2
2T15 D5
Circuit Diagrams and PWB Layouts
2T17 D2
2T60 B2
2T61 B2
2T62 D5
2T63 D5
3T03 B1
3T05 C7
3T06 D7
5T20 B1
5T22 C5
5T25 C6
6T01 B2
6T03 B2
6T05 D6
6T08 D5
7T50 C6
9T01 B2
9T04 D4
9T05 E4
9T07 E4
9T08 E4
9T12 E7
9T14 C5
9T50 E7
EN 58FTP2.4E AA 7.
AT00 E5
FT50 B1
FT51 C2
FT52 D4
FT53 C6
FT54 D5
IT50 A1
IT51 D4
IT52 D4
IT53 C7
IT54 D7
123
4567
MAIN TUNER
B13A B13A
B2
A
AGC
IT50
9T01
6T01
+5V
3T03
RES
B
5T20
FT50
220u
2T05
RES
2T01
220u
C
D
E
BAS316
2T60
220u 6.3V
FT51
2T17
6T03
BAS316
10n
2T13
UV1318ST/AIH-MK3
2T61
1T01
RF
IN
RF
OUT
12
13
14
0V5
10n
47u 6.3V
PRE-FIL
MT
BOOSTER
SPLITTER
AGC1
PRE-FIL
TRACK
FILTER
GAIN
CTRL
PRE-AMP
TRACK
FILTER
INTMED
FILTER
MIX-OSC
IF AMP
IFOUT 11
+33V
5T22
5T25
10u
FT53
7T50
P82B96TD
RES
8
VCC
SX1
TX 3
3T05
RES
10K
IT53
2T12
AGC
DET
2T04
2T09
FT54
22n
47n
9T14
2T15
6T08
PDZ33-B
1u0
SY7
6T05
SML4752-33V
MT
ADC
8
220n
2T63
15
16
17
220n
PLL
NC1
TU2
NC2
6
10
933V
5V7
FT52
9T04
9T05
10n
AS3
IT51
SCL4SDA5
IT52
2T06
9T07
2T62
9T08
GND
4
RX 2
RY 6
9T50
9T12
RES
3T06
10K
IT54
5TY
A
B
C
100n
D
E
8204 000 8479.1
AT00
IF-TER
B2
SDA-S
SCL-S
S-SDA-PIP
S-SCL-PIP
B13b
B13b
F_15460_028.eps
080405
1234567
Page 59

Circuit Diagrams and PWB Layouts
EN 59FTP2.4E AA 7.
SSB: Sub Tuner
1234567
SUB TUNER
B13B B13B
B15A
A
AGC2
IT10
BAS316
220u
2T20
9T02
220u 6.3V
2T14
6T04
10n
BAS316
2T11
1T02
UV1318S
FT04
12
13
6.3V47u
MT1
MT2
+5V
5T04
IT17
47n
+33V
5T02
6T06
33V5
PDZ33-B
RES
IT09
5T03
2T10
10u
22n
2T16
220u
2T19
L
H
M
PLL
TU2
AGC1
SCL4
AS3
NC1
SDA5
VS7
6
VST
ADC8
9
L
H
M
14
MT3
15
MT4
IF111
IF2|NC210
2T02
6T02
10K
3T04
RES
B
2T03
C
1u0
A
B
C
1T02 B4
2T02 C6
2T03 B3
2T07 D4
2T10 D7
2T11 B4
2T14 B3
2T16 D7
2T18 D4
2T19 C6
2T20 B3
2T21 D6
2T22 D6
3T04 B3
5T02 C6
5T03 C7
5T04 B6
6T02 B3
6T04 B4
6T06 C6
6T07 D6
9T02 B3
9T03 D4
9T06 D4
9T09 D4
9T10 D5
FT04 C4
FT05 D6
IT07 D4
IT09 C7
IT10 A3
IT17 B6
IT18 D4
IT19 D5
D
E
8204 000 8476.1
123
2T18
6T07
RES
PDZ33-B
10n
IT07
2T07
RES
10n
9T06
9T03
IT18
9T10
9T09
S-SCL-PIP
B13a
B13a
IT19
S-SDA-PIP
5V1
IF-TER2
B15A
2T21
220n
2T22
FT05
220n
F_15460_029.eps
080405
4567
D
E
Page 60

SSB: DC/DC Converter
Circuit Diagrams and PWB Layouts
EN 60FTP2.4E AA 7.
1234 8567
9
DC - DC CONVERTER
B13C B13C
A
B
C
D
E
F
8204 000 8476.1
5V-ENABLE
IT08
12
IT00
2T30
GND-P GND-P
47K
3T14
IT44
GND5V
1u0
2T36
3T15
10K
FT10
10K
3T17
GND5V GND5V
345678
3T10
10K
2T35
3T16
2T37
GND5V
GND-P
22u
2T31
2T34
100K
2T50
10n
10n
1n0
100n
IT01
22u
GND5V
2
9T11
1T03
2T33
2T32
100n
IT04
IT05
GND5V
100n
3T33
IT02
7T04
L6910
1
4
IT06
2
8
6
7T10-1
BC847BS
1
GND-P
2T54
100n
10R
IT45
VREF
SS
OSC
EAREF
1T04
6T11
BZX384-C9V1
IT26
1K0
3T51
3T13
9
15
VCC
PGOOD
Monitor
Protection & Ref
OSC
IT30
10K
COMP
5
3T113T12
IT42
3
OCSET
10K
1K0
2T49
2T47
470p
2T48
100n
FT15
2
10K
2
2T53
IT63
4
4K7
3T23
1K0
330R
3T57
100R
7T13-1
BC847BPN
6
7T11-1
BC847BPN
1
78
7T01-1
SI4936ADY
1
3n3
56
7T01-2
SI4936ADY
3
GND-P
3K9
3T24
IT48
2T52
IT43IT16
3T30
3
7T11-2
BC847BPN
4
6T10
IT34
IT11
IT12
4
3
IT46
FT11
BAS316
2T38
3T27
10R
3T26
2R2
GND5V
3T20
3T58
10K
100n
1K0
GND5V
5
47K
3T29
IT13
FT12
3T60
4R7
IT15
3T22
IT22
3T19
IT47
5
1n0
BOOT
12
HGATE
11
10
PHASE
LGATE
14
13
PGND
GND-P
GND
7
VFB
6
NC
16
2K7
3T18
IT32
BC847BS
7T10-2
10K
3T59
IT25
3T31
1K0
5T12
res
5T13
res
5T10
10u
3T32
1K0
10K 10K
3T56
1u0
3T53
470K
2T40
IT62
100n
2T42
3T25
IT20
IT33
3T55
22n
6K8
3V3_FAULT
2T41
1n0
5T11
10u
2T44
10n
IT23
2T43
GND-P
IT21IT41
2T45
+11V_DC
BC847BPN
7T13-2
IT61
10K
3T54
IT60
10K
3T52
B12
22u
10n
5T15
2T46
1n0
FT13
5T14
1u0
7T12
BC847BW
+11V_DC
IT24
3T28
FT14
2T51
9
10R
VDISP
F_15460_030.eps
080405
A
B
C
D
E
F
1T03 E4
1T04 E5
2T30 B4
2T31 B4
2T32 B4
2T33 B4
2T34 B4
2T35 B4
2T36 C4
2T37 D4
2T38 B7
2T40 B8
2T41 B8
2T42 C8
2T43 C8
2T44 D8
2T45 D8
2T46 B9
2T47 D6
2T48 E6
2T49 B6
2T50 C4
2T51 E9
2T52 E7
2T53 C7
2T54 A5
3T10 A4
3T11 A6
3T12 B6
3T13 B5
3T14 C4
3T15 C3
3T16 C4
3T17 D4
3T18 D6
3T19 E7
3T20 D7
3T22 D7
3T23 E7
3T24 D7
3T25 C8
3T26 C7
3T27 B7
3T28 B9
3T29 B7
3T30 A7
3T31 A8
3T32 D8
3T33 B5
3T51 B5
3T52 F8
3T53 F8
3T54 F8
3T55 E8
3T56 E8
3T57 E7
3T58 F7
3T59 F6
3T60 C7
5T10 B8
5T11 C8
5T12 B8
5T13 B8
5T14 D9
5T15 D9
6T10 B6
6T11 A5
7T01-1 B7
7T01-2 C7
7T04 B5
7T10-1 C5
7T10-2 E6
7T11-1 A7
7T11-2 A6
7T12 F9
7T13-1 F7
7T13-2 E8
9T11 D4
FT10 C4
FT11 B7
FT12 C7
FT13 D9
FT14 E9
FT15 A7
IT00 A4
IT01 A4
IT02 B5
IT04 B5
IT05 B5
IT06 C5
IT08 C3
IT11 B7
IT12 C6
IT13 B7
IT15 C7
IT16 A7
IT20 D8
IT21 C9
IT22 E7
IT23 B9
IT24 B9
IT25 A8
IT26 A5
IT30 D5
IT32 E6
IT33 C8
IT34 B7
IT41 C7
IT42 B6
IT43 A7
IT44 C4
IT45 B5
IT46 F7
IT47 E7
IT48 E7
IT60 F9
IT61 F9
IT62 E8
IT63 C7
Page 61

Circuit Diagrams and PWB Layouts
EN 61FTP2.4E AA 7.
SSB: I/O1: MMC
1
B14A B14A
I/O1: MMC
23
45678
A
+8VA
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
100K
3I23
9I78
IN1
DATA
IN2
CLK
IN3
IN4
PROG
IN5
VCC
IN6
2I08
100n
9I00
9I01
IIC6
3I06
7I24
TEA6415CD
+8VA
9I02
9I03
*
*
75R
GND2
GND1
OUT6
OUT5
OUT4
OUT3
OUT2
OUT1
100K
B
2I02
220n
100R
2I03
220n
100R
2I04
220n
2I05
220n
2I06
220n
3I04
3I05
res
9I95
II00
II03
3I01
100K
res
II01
68K
3I02
II04
II02
II05
3I09
68K
B2,B14a,B15a
B
From HIP MAIN
B14b
B14b
B2
AV3-CVBS-IN
Y-CVBS-MMC-OUT
C-MMC-OUT
res
SDA-S
PIP-OUT
3I03
IIC7
75R
res
9I96
C
SCL-S
B21
FRONT-Y-CVBS-IN
From Front
75R
3IK4
2IJ1
D
B2,B14b
From Scart 4
(USA AV3)
B15a
From PIP/DW
res
Y-CVBS-SC2_AV2-IN
PIP-OUT1
100p
res
E
B2,B14b,c (2x)
For US (AV3)
F
B21
C-SC2_SVHS-IN
FRONT-C-IN
3IK5
9I15
2I07
res
220n
+8VA
75R
2IJ0
470p
res
res
2I01
100n
res
G
RESERVED FOR MMC
II08
220n
2IE0
3I11
560R
3I13
560R
3I15
560R
3I17
560R
3I19
100R
3I21
100R
3I24
1K0
3I10
20
IN8
19
18
17
16
15
14
13
12
11
IN7
II06
3I25
68K
IIC5
3I12
470R
res
II07
3I14
470R
res
II09
1K5
3I16
res
II10
3I18
470R
res
II11
3I20
470R
res
C-PIPDW-OUT
Y-CVBS-PIPDW-OUT
C-FRONT-IN
Y-CVBS-FRONT-IN
B15a
TO PIP/DW (HIP SUB)
B15a
B2
B2
C-FRONT-IN
B2
+8V
B14b,c
4R7
3IK8
2IJ3
100n
IIC2
7I06
BC847BW
3IQ2
IIC3
2IJ2
3IQ3
75R
3I27
C-RECORD-IN
75R
1K0
CVBS-Y-RECORD-IN
B5a,B14b,B15b
9I21
100u
IIC1
3
7I60
BC847BW
2
3I26
9I20
100n
1K0
II12
3I22
470R
2IA6
res
1
SC2-FBL
B14b
RES FOR MMC
H
3IK7
+8V
IIC8
4R7
2IA5
+8VA
100u
I
8204 000 8478.1
1234567891011
910
+8VA
2R2
3IP5
1K0
7I35
BC847BW
2I55
10n
II14
7I36
BC847BW
3IP2
5I01
3IP6
220R
6u8
*
3IP4
270R
IIC9
BC857BW
7I37
II15
3IQ0
10R
3IT9
330R
IIC0
*
10n
2I56
res
8K2
3IP0
II16
2IG1
3IP7
2K7
100n
2K2
3IP1
IIG2
3I08
330R
B12
3V3_FAULT 3V3_FAULT_PIP
*
res
11 12 13
10p
3IN1
2IJ4
7I62
BC847BW
B15c
1K0
II13
IIG1
100n
2IL0
3IP8
res
3IQ4
7I38
BC847BW
1K0
res
1K2
1K2
3IQ1
3IHG
1K8
SC2-B_C-OUT
3IP3
75R
IIC4
1K0
3IJ8
B14b,c(2x)
B
12 13
F_15460_031.eps
080405
A
B
C
D
E
F
G
H
I
2I01 F4
2I02 B3
2I03 C3
2I04 D3
2I05 D3
2I06 D3
2I07 F4
2I08 E5
2I55 I10
2I56 I10
2IA5 I4
2IA6 F7
2IE0 B5
2IG1 C9
2IJ0 F3
2IJ1 D3
2IJ2 F7
2IJ3 E8
2IJ4 C11
2IL0 B11
3I01 B4
3I02 C4
3I03 B3
3I04 C3
3I05 C3
3I06 B5
3I08 E9
3I09 E4
3I10 B6
3I11 B6
3I12 B7
3I13 C6
3I14 C7
3I15 C6
3I16 C7
3I17 D6
3I18 D7
3I19 D6
3I20 D6
3I21 F6
3I22 F6
3I23 E5
3I24 E5
3I25 E6
3I26 G7
3I27 F8
3IHG C12
3IJ8 D12
3IK4 D3
3IK5 F3
3IK7 H4
3IK8 E7
3IN1 B11
3IP0 B9
3IP1 D9
3IP2 D10
3IP3 C12
3IP4 C10
3IP5 B10
3IP6 B10
3IP7 C9
3IP8 B11
3IQ0 C11
3IQ1 C11
3IQ2 F8
3IQ3 G8
3IQ4 C11
3IT9 E10
5I01 I10
7I06 F8
7I24 C1
7I24 D5
7I35 D10
7I36 C10
7I37 C11
7I38 C11
7I60 G7
7I62 E11
9I00 A5
9I01 B5
9I02 F5
9I03 F5
9I15 F4
9I20 F7
9I21 G7
9I78 B5
9I95 B4
9I96 B3
II00 C4
II01 B4
II02 D4
II03 D3
II04 D4
II05 D5
II06 E6
II07 C7
II08 B6
II09 C7
II10 D7
II11 D6
II12 F6
II13 C11
II14 C10
II15 C11
II16 C9
IIC0 I10
IIC1 G7
IIC2 F7
IIC3 F8
IIC4 D12
IIC5 B7
IIC6 B5
IIC7 B3
IIC8 H4
IIC9 C10
IIG1 C11
IIG2 D9
Page 62

Circuit Diagrams and PWB Layouts
EN 62FTP2.4E AA 7.
SSB: I/O2: Connections
12345678910111213
I/O 2: CONNECTIONS
B14B B14B
1I39
FI48
1I40
14 15
1I75
HR-AG0741S-0
B14a
9I04
9I22
1I04-2
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
16
17
18
19
20
21
MT
9I60
SCART2
1I04-1
2223
9I09
9I11
9I93
9I08
9I97
FI59
3I79
6I45
100R
BZX384-C6V8
1I471I46
6I46
FI58
3I80
6I47
100R
BZX384-C6V8
6I48
FI57
1I45
FI55
1I44
1I43
FI54
II34
1I76
FI50
FI69
FIA9
FI96
FI16
FI18
FI19
FI20
FIC1
FI14
II35
3I82
3K9
3I81
BZX384-C12
6I49
3I83
100R
BZX384-C6V8
75R
3I84
6I50
FI56
6I51
75R
3I86
BZX384-C6V8
3I87
100R
6I52
75R
BZX384-C6V8
6I77
BZX384-C6V8
Multi Media Connector (MMC)
9I94
9I92
FI21
FI22
FI13
FI12
FI94
9I10
FI11
9I12
8
II37
3IK2
100p
2I23
II36
3IK3
100p
2I24
SEL-SVHS-RR_STATUS2
2I25
8K2
330p
9I16
BZX384-C6V8
6I75
3I35
100R
9I19
*
100R
AR-SC2-IN
AL-SC2-IN
SC2-R_C-IN
SC2-FBL
30FMN-BMT-A-TFT
B14d (2x)
B14d (2x)
B2
B15a
B2,B14a,c (2x)
B14a,c
B15a
B2,B14a
1I11
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
B14b(4x)
B14b
B14b(4x)
B14b
B14b(4x)
B14b
B14b(4x)
B14b
B14b(4x)
B14b
B14b(4x)
B14b
B14b(3x)
B14b
B14b(4x)
B14b(3x)
+5V2-APLOP
A-PLOP
AP-SNDL-SC2-OUT
A-PLOP
AP-SNDR-SC2-OUT
A-PLOP
AP-FRONT-L
A-PLOP
AP-FRONT-R
A-PLOP_E
AP_SUBW
A-PLOP_E
AP-SURR-L
A-PLOP_E
AP-SURR-R
IID2
+5V2-APLOP
BC847BPN
A-PLOP
A-PLOP_E
3ID8
100K
BC847BPN
+5V
II49
22K
22K
BC847BS
BC847BS
BC847BS
BC847BS
BC847BW
BC847BS
BC847BS
7I05-2
II44
7I50-1
3IB4
3IB5
7I01-1
7I01-2
7I02-1
7I02-2
7I04
3
7I03-2
4
4V2
6
7I03-1
1
4V9
4V2
BC847BPN
7I50-2
4V2
II46
1n0
2I46
2I39
47n
IIB0
4V1
+5V2-APLOP
4V2
IID4
0V7
3I38
BC847BW
1
IIG3
IIG4
IIG5
IIG6
IIG7
IIG8
5
IIG9
2
5V2
9I50
BC847BPN
7I05-1
3I36
22K
7I09
3IA4
1K0
3IA5
1K0
3IA6
1K0
3IA7
1K0
3IA8
1K0
3IA9
1K0
3IB0
1K0
1u0
2I11
3I07
10K
IIH2
3V6
22K
SOUND-ENABLE
3
2
IID7
B5a,B21
II47
3I34
10K
3IC6
22K
100R
3IS2
22K
*
C-SC2_SVHS-IN
IN-Y-CVBS-SC2_AV2
Y-CVBS-SC2_AV2-IN
FI10
91011
IIH0
3ID0
4K7
+5V2-STBY
9IA5
47K
9I51
IID1
+5V2-STBY
3I37
22K
+5V2-APLOP
6I11
BAS316
3ID7
BAS316
IIA9
6IA7
1u0
2IA4
IID3
BAS316
6I12
BAS316
6I13
BC847BS
1u0
2I12
12 13
+11V_S
+5V
9IA4
4
3
7I44-1
+11V
3IC1
BC869
7I07
IID0
BC847BPN
7I21-2
7I21-1
BC847BPN
PDTC144EU
100K
II45
6
1
5
3IH1
3
4
II48
3IC9
6
1
47K
7I49
BC847BS
1R5
7I44-2
2
+5V
22K
6I10
BAS316
3ID1
2
150K
2I15
+11V_S
+5V
9IA6
9IA7
3IW4
*
0V
5
3IC2
0V
2I47
6K8
POR-LINEOUT
*
3IW5
2K7
IID6
3IC3
RESET-AUDIO
0V
22K
22K
1n0
2IH3
3I98
IID5
100K
1n0
3IA1
100K
F_15460_032.eps
1I71
1I72
1I73
1I34
FI34
1I35
FI35
FI36
FI37
FI38
FI40
HR-AG0741S-0
SCART1
1I01-1
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
MT
1I01-2
2223
FI42
FI43
1I36
3I66
3I67
FI41
6I30
BZX384-C6V8
1I38
6I31
6I32
BZX384-C6V8
1I37
6I33
BZX384-C12
FI44
75R
FI45
75R
6I35
3I61
100R
3I62
100R
3I63
3K9
6IA0
BZX384-C6V8
6I36
1I03
6I68
IIA1
100p
IIA2
100p
II29
3I64
1I08
3I68
100R
*
BZX384-C6V8
BZX384-C6V8
100R
3IB2
22K
3IN5
2I18
100R
3IC4
22K
3IN6
2I19
2I20
8K2
3I65
100R
CVBS-SC1_AV1-IN
9I18
IN-CVBS-SC1_AV1-SUB
A
B14d
SNDR-SC1-OUT SNDR-SC2-OUT
B14d
SNDL-SC1-OUT
B
B14c(2x)
B14c(2x)
SC1-G
C
B14c(2x)
SC1-R
B15a
TER-CVBS-OUT-SUB
9I17
CVBS-TER-OUT
res
B2
D
270R
II25
3I50
270R
II26
3I52
3I54
100R
II27
100R
IIA0
100R
FI32
3I51
6I22
100R
BZX384-C6V8
2I16
2I17
75R
3I56
3I58
100p
3I53
100R
100p
3I55
3I60
75R
BZX384-C6V8
BZX384-C6V8
6I27
BZX384-C6V8
6I28
BZX384-C6V8
BZX384-C6V8
6I23
FI33
6I24
6I25
6I26
75R
3I57
75R
3I59
FI39
6I29
1I74
E
F
G
H
I
B14b
b6a,B14d (2x)
B14b
b6a,B14d (2x)
B14b
B6c,B14c
B14b
B6c,B14c
B14b
B6c
B6b
B6a
AP-FRONT-L
SNDL-MON-OUT
AP-FRONT-R
SNDR-MON-OUT
AP-SURR-L
FI91
SURR-L
AP-SURR-R
FI92
SURR-R
AP_SUBW
FI93
SUBW
SPDIF-IN1
SND-CENTER-IN
100R
2IC0
10u
2IC1
10u
2IC2
10u
2I31
10u
2I32
10u
9I13
3I28
II38
FI60
6I54
FI61
6I56
FI62
6I58
FI63
6I60
FI64
6I62
1I58
3IT0
IIA5
3IT2
3IT3
3IT4
3IA2
100R
47K
IIA4
II41
II42
47K
2I26
2I27
47K
2I28
47K
2I29
47K
2I30
BZX384-C6V8
100p
100p
100p
100p
100p
6I69
3I90
100R
3I92
100R
3I95
100R
3I97
100R
3IA0
100R
6I53
BZX384-C6V8
6I55
BZX384-C6V8
6I57
BZX384-C6V8
6I59
BZX384-C6V8
6I61
BZX384-C6V8
FI68
6I70
3I89
270R
3I91
270R
3IT1
3I94
270R
3I96
270R
3I99
270R
II43
22K
2I36
3IA3
100p
1I48
1I49
1I50
1I52
1I54
YKC21-3226
1
3
1I05
2
1
3
YKC21-3226
1I09
YKC21-4591N
12
3
1I06
J
8204 000 8478.1
1234567
B14d(2x)
AR-SC1-IN
B14d(2x)
AL-SC1-IN
SC1-STATUS
330p
SC1-FBL
2
VARIABLE LEVEL
VARIABLE LEVEL
SUBWOOFER
B14d
AP-SNDR-SC2-OUT
B14b
SNDL-SC2-OUT
B14d
AP-SNDL-SC2-OUT
B14b
SC2-B_C-OUTSC1-B
B2
B14a,c (2x)
P50
B5a
B14c
SC2-G
B14c (2x)
B2
CVBS-SC2_MON-OUT
B2
B15a
SURROUND
DOLBY DIGITAL
RES
TO B4
270R
3I71
270R
3I73
100R
res
3I75
100R
3I76
100R
2FH-HD100
2FH-VD100
3I69
9I39
II32
2I22
II33
2I21
BZX384-C6V8
BZX384-C6V8
BZX384-C6V8
B15b,B5a,B14a
9IB1
9IB2
B2,B14g,B15a
B2,B14g,B15a
B2,B14g,B15a
100p
100p
6I41
6I42
FI52
6I44
3I78
75R
2IC9
220p
HD-ANA
VD-ANA
B5a,B21
3I70
100R
3I72
100R
75R
75R
B14d
B14d
B14a
B6b
B14d
B14d
B14f
B14a
B14b
B14b
FI46
6I37
BZX384-C6V8
6I38
6I39
BZX384-C6V8
6I40
1I02
RES
1I41
1I42
3I77
6I43
BZX384-C6V8
SNDR-BO-IN
SNDL-BO-IN
CVBS-Y-RECORD-IN
C-RECORD-IN
SPDIF-BO-OUT
SNDR-BO-OUT
SNDL-BO-OUT
HD-ANA
VD-ANA
Y-CVBS-MMC-OUT
SDA-S
SCL-S
IRQ-DIGITAL
MMC-R
C-MMC-OUT
MMC-G
MMC-B
SC2-B-IN_C-OUT
SC2-G-IN
SC2-R_C-IN_AV2
FI47
FI49
IIA3
FI51
FI53
B14b,f
B14b,f
1u0
B14b
IIH1
POR
B4,B21(2x)
B5a,B6a
POR-LINEOUT
B14b
080405
A
B
C
D
E
F
G
H
I
J
1I01-1 A3
1I01-2 E3
1I02 C6
1I03 D3
1I04-1 A7
1I04-2 E7
1I05 F4
1I06 I4
1I08 D4
1I09 H4
1I11 F9
1I34 A2
1I35 B2
1I36 C3
1I37 B3
1I38 A3
1I39 A7
1I40 B7
1I41 C6
1I42 D6
1I43 D8
1I44 C8
1I45 C8
1I46 B8
1I47 A8
1I48 F4
1I49 F4
1I50 G4
1I52 H4
1I54 I4
1I58 J3
1I71 C2
1I72 C2
1I73 D2
1I74 D2
1I75 D7
1I76 D8
2I11 H11
2I12 J12
2I15 F13
2I16 A1
2I17 B1
2I18 B4
2I19 B4
2I20 C4
2I21 B6
2I22 A6
2I23 B9
2I24 B9
2I25 C9
2I26 F2
2I27 F2
2I28 G2
2I29 H2
2I30 I2
2I31 H2
2I32 H2
2I36 J2
2I39 H11
2I46 B11
2I47 J13
2IA4 I12
2IC0 F1
2IC1 F1
2IC2 G1
2IC9 D6
2IH3 I13
3I07 I11
3I28 I1
3I34 I11
3I35 D9
3I36 J11
3I37 H12
3I38 J11
3I50 A1
3I51 A2
3I52 B1
3I53 B2
3I54 B1
3I55 C2
3I56 C1
3I57 C2
3I58 C1
3I59 D2
3I60 D2
3I61 A4
3I62 B4
3I63 B4
3I64 C4
3I65 D4
3I66 D3
3I67 D3
3I68 D4
3I69 A5
3I70 A6
3I71 B5
3I72 B6
3I73 B5
3I75 C5
3I76 D5
3I77 D6
3I78 D6
3I79 A8
3I80 B8
3I81 C8
3I82 B8
3I83 C8
3I84 C8
3I86 D8
3I87 D8
3I89 F2
3I90 F3
3I91 F2
3I92 F3
3I94 G2
3I95 G3
3I96 H2
3I97 H3
3I98 J13
3I99 H2
3IA0 H3
3IA1 J13
3IA2 I2
3IA3 J2
3IA4 C11
3IA5 D11
3IA6 E11
3IA7 E11
3IA8 F11
3IA9 G11
3IB0 G11
3IB2 A4
3IB4 B11
3IB5 B11
3IC1 B12
3IC2 I13
3IC3 I13
3IC4 B4
3IC6 A9
3IC9 F12
3ID0 B12
3ID1 F13
3ID7 H12
3ID8 J10
3IH1 H12
3IK2 A9
3IK3 B9
3IN5 A4
3IN6 B4
3IS2 B9
3IT0 F2
3IT1 F2
3IT2 G2
3IT3 H2
3IT4 I2
3IW4 H13
3IW5 H13
6I10 F13
6I11 H12
6I12 I12
6I13 I12
6I22 A2
6I23 A2
6I24 B2
6I25 B2
6I26 C2
6I27 C2
6I28 D2
6I29 D2
6I30 A3
6I31 B3
6I32 B3
6I33 B3
6I35 D3
6I36 D3
6I37 A6
6I38 A6
6I39 B6
6I40 B6
6I41 C6
6I42 C6
6I43 D6
6I44 D6
6I45 A8
6I46 B8
6I47 B8
6I48 B8
6I49 C8
6I50 C8
6I51 D8
6I52 D8
6I53 F3
6I54 F3
6I55 F3
6I56 G3
6I57 G3
6I58 H3
6I59 H3
6I60 H3
6I61 H3
6I62 I3
6I68 E4
6I69 I3
6I70 J3
6I75 C9
6I77 E8
6IA0 C3
6IA7 I12
7I01-1 C11
7I01-2 D11
7I02-1 E11
7I02-2 E11
7I03-1 G11
7I03-2 G11
7I04 F11
7I05-1 H11
7I05-2 I11
7I07 B12
7I09 B11
7I21-1 F12
7I21-2 E13
7I44-1 J12
7I44-2 I13
7I49 H13
7I50-1 J11
7I50-2 I11
9I04 I7
9I08 H7
9I09 G7
9I10 I8
9I11 H7
9I12 I8
9I13 I1
9I16 C9
9I17 D1
9I18 D4
9I19 D9
9I22 I7
9I39 B5
9I50 H11
9I51 F12
9I60 I7
9I92 G8
9I93 H7
9I94 G8
9I97 I7
9IA4 E12
9IA5 E12
9IA6 G13
9IA7 G13
9IB1 G6
9IB2 H6
FI10 H9
FI11 I8
FI12 I8
FI13 I8
FI14 H8
FI16 G8
FI18 G8
FI19 G8
FI20 G8
FI21 H8
FI22 H8
FI32 A2
FI33 B2
FI34 B2
FI35 B2
FI36 C2
FI37 C2
FI38 C2
FI39 D2
FI40 D2
FI41 A3
FI42 B3
FI43 B3
FI44 D3
FI45 D3
FI46 A6
FI47 B7
FI48 B7
FI49 B7
FI50 E8
FI51 C7
FI52 D6
FI53 D7
FI54 D8
FI55 C8
FI56 D8
FI57 B8
FI58 B8
FI59 A8
FI60 F4
FI61 F3
FI62 G3
FI63 H3
FI64 I3
FI68 J3
FI69 F8
FI91 G1
FI92 H1
FI93 H1
FI94 I8
FI96 F8
FIA9 F8
FIC1 H8
II25 A1
II26 B1
II27 C1
II29 B4
II32 A6
II33 B6
II34 D8
II35 B8
II36 B9
II37 A9
II38 E2
II41 H2
II42 H2
II43 I2
II44 I11
II45 I12
II46 B11
II47 B11
II48 B12
II49 B10
IIA0 C1
IIA1 A4
IIA2 B4
IIA3 C7
IIA4 G2
IIA5 F2
IIA9 I12
IIB0 I11
IID0 B12
IID1 H12
IID2 H10
IID3 I12
IID4 J11
IID5 J13
IID6 I13
IID7 H11
IIG3 C11
IIG4 D11
IIG5 E11
IIG6 E11
IIG7 F11
IIG8 G11
IIG9 G11
IIH0 B12
IIH1 H13
IIH2 I11
Page 63

Circuit Diagrams and PWB Layouts
EN 63FTP2.4E AA 7.
SSB: I/O3: Switch
1234
B14C B14C
A
B2,B14a,b,c
C-SC2_SVHS-IN
B14b,c
SC1-R
B14b,c
SC1-G
B14b,c
SC2-G SWITCH-MAIN
C
B14b,c
SC1-B
D
B14a,b,c
SC2-B_C-OUT
E
IO3: SWITCH
9I67
res
9I66
res
9I65
res
8
7
GND
VEE
75R
3IS4
3y1
3
res
75R
3I85
res
75R
3I93
res
75R
3IP9
res
75R
3IN2
res
75R
3IN3
res
s2
3y0
2y1
2y0
1y1
1y0
MUXDX
3z
s1
2z
s0
1z
G3
VCC
74HC4053PW
7I12
16
9
4
10
15
11
14
6
2I50
100n
5
1
2
13
12
+5VIO
res
9I64
9I63
res
9I62
res
3ID5
10R
3IE7
10R
3IN8
10R
+5VIO
3IC8
+5VIO
3ID9
+5VIO
3IH7
BC857BW
7I27
BC857BW
7I29
BC857BW
7I31
560R560R
R-SC1_V-IN
560R
G-SC1-IN_Y-IN
B-SC1-IN_U-IN
F
B6a
SNDR-DVI-IN
B6a
B6a,B15b
SNDL-DVI-IN
G
H
I
8204 000 8478.1
II50
FIB0
1I07
YKC21-3226
3IF7
6I90
3IE3
100R
BZX384-C6V8
1I68
100R
3IE9
22K
2I57
100p
IIB2
3
6I91
2FH
3IE2
FIB1
100R
3IF5
22K
2I58
II51
100p
3IF6
100R
6I92
IIB3
BZX384-C6V8
6I93
1I69
B6a,B15b
B6a,B15b
1
2
12345 789
5 6 7 8 9 10111213
9I41
B2,B14a,b,c
B14b,c
B2
B14b,c
B2
B14c(2x),f,g,B15b
B2
B2
B14b,c
B14b,c
B14a,b,c
V-PIP+MAIN-OUT
Y-PIP+MAIN-OUT
U-PIP+MAIN-OUT
RESERVED
C-SC2_SVHS-IN
SC1-R
SC1-G
SC2-G
SC1-B
SC2-B_C-OUT
9I87
IID8
3IFA
res
9I89
IID9
3IFB
res
9I90
IIE0
3IFC
res
6
100K
100K
100K
res
9I59
*
res
9I61
*
9I37
RES
*
8
7
GND
VEE
3y1
3
s2
3y0
2y1
2y0
1y1
1y0
*
MUXDX
VCC
3z
s1
2z
s0
1z
G3
16
9
4
10
15
11
14
6
74HC4053PW
7I33
2I49
*
100n
5
1
2
13
12
10R
3IM0
10R
+5VIO
*
3IL1
560R
B15a
3IL3
*
*
SUB-V
BC857BW
7I26
*
SWITCH-SUB
+5VIO
*
3IL8
560R
SUB-Y
BC857BW
7I28
*
B14c,B15b
B15a
B2,B15a
SC2-FBL-IN
B14a,b
SC2-FBL
B14b
SC1-FBL
9I42
+5VIO
3IO6
*
res
*
res
9IA2
+5VIO
+5VIO
RES
9I25
*
9I26
*
RES
9I27
*
RES
9IF0
res
8
7
GND
VEE
3y1
3
3y0
s2
2y1
2y0
1y1
1y0
MUXDX
16
9
3z
4
s1
10
2z
15
s0
11
1z
14
G3
VCC
6
74HC4053PW
7I80
2IR0
100n
TRI-STATE-DVI
+5VIO
5
1
2
13
12
3IN0
10R
R-VGA
G-VGA
B-VGA
*
3IM4
560R
B15a
+5V
BC857BW
7I30
B14g(2x)
B14g(2x)
B14c(2x),f,g
B14g(2x)
SUB-U
*
3IN4
2R2
2IA9
IIB1
+5VIO
100u
B6a,B15c
VA50-PIP
res
3IFF
B6a,B15b,c
HA50-PIP
IIE1
res
3IFD
100K
*
+5VIO
4K7
BC847BW
3IFE
IIH3
3IFL
7I82
TRI-STATE-DVI
1K0
B14c(2x),f,g
RESERVED
9IF1
res
9IF2
res
10 11 12 13 14
10K
3IO5
10K
3
5
1
2
13
12
+5VIO
100K
VEE
3y1
3y0
2y1
2y0
1y1
1y0
MUXDX
9I79
II39
7
GND
s2
3z
s1
2z
s0
1z
G3
VCC
16
res
res
8
9
4
10
15
11
14
6
74HC4053PW
7I32
2IC3
100n
res
3
5
1
2
13
12
SWITCH-MAIN
FBL-SC1-IN
SWITCH-SUB
SC1-FBL-IN
SWITCH-MAIN
9IF4
7
8
GND
VEE
3y1
3y0
s2
2y1
2y0
1y1
1y0
MUXDX
VCC
3z
s1
2z
s0
1z
G3
16
9
4
10
15
11
14
6
74HC4053PW
7I81
2IR1
100n
VS-2FH
TRI-STATE-DVI
HS-2FH
+5VIO
9IF3
res
14
B14c(2x),f,g,B15b
B2
B14c,B15b
B15a
B14c(2x),f,g,B15b
B14g,B19a
B14c(2x),f,g
B14g,B19a
F_15460_033.eps
080405
A
BB
C
D
E
F
G
H
I
1I07 I2
1I68 I2
1I69 I3
2I49 D7
2I50 D3
2I57 H2
2I58 H3
2IA9 E9
2IC3 D12
2IR0 H7
2IR1 H12
3I85 B1
3I93 C1
3IC8 B4
3ID5 B3
3ID9 C4
3IE2 G3
3IE3 G2
3IE7 D3
3IE9 G2
3IF5 G3
3IF6 H3
3IF7 H2
3IFA G6
3IFB H6
3IFC H6
3IFD H11
3IFE I8
3IFF G11
3IFL I8
3IH7 D4
3IL1 A8
3IL3 B8
3IL8 C8
3IM0 C8
3IM4 D8
3IN0 D8
3IN2 B2
3IN3 C2
3IN4 E9
3IN8 E3
3IO5 B11
3IO6 B11
3IP9 D1
3IS4 B2
6I90 H2
6I91 I2
6I92 H3
6I93 I3
7I12 D3
7I26 B8
7I27 B4
7I28 C8
7I29 D4
7I30 D8
7I31 E4
7I32 D12
7I33 C7
7I80 H7
7I81 H12
7I82 I8
9I25 D7
9I26 D7
9I27 D7
9I37 A7
9I41 A12
9I42 B11
9I59 A7
9I61 A7
9I62 E2
9I63 D2
9I64 D2
9I65 A2
9I66 A2
9I67 A2
9I79 A12
9I87 G6
9I89 G6
9I90 H6
9IA2 B11
9IF0 F7
9IF1 I7
9IF2 I7
9IF3 I12
9IF4 F12
FIB0 I2
FIB1 I3
II39 G12
II50 H2
II51 H3
IIB1 E9
IIB2 H2
IIB3 H3
IID8 G6
IID9 G6
IIE0 H6
IIE1 H11
IIH3 I8
Page 64

Circuit Diagrams and PWB Layouts
EN 64FTP2.4E AA 7.
SSB: I/O4: Audio
1
B14D B14D
I/O4: AUDIO
23456
78
91011
A
B14d,B21
R-FRONT-INL-FRONT-IN
SNDR-BO-OUT
1u0
1u0
2I75
9IA1
R419R518R6
DECODER
1u0
9IA3
1u0
2I84
SNDL-BO-OUT
B14d,B21
B6a,B14b,B14d
SNDR-MON-OUT
2I76
1u0
BUS
2I85
1u0
SNDL-MON-OUT
B6a,B14b,B14d
IIE7
1u0
ROUT1
ROUT2
ROUT3
SDA
SCL
ADDR
LOUT1
LOUT2
LOUT3
1u0
B14b.d
B14b
B14b.d
AR-SC2-IN
AR-SC1-IN
B
1u0
2I71
2I73
2I72
25R124R223R320
7I17
TEA6422
C
D
E
F
2I77
+8V
VS
3
II72
CAP
2
SUPPLY
GND
1
1u0
1u0
2I78
B15b
3I39
4K7
PIP-FM
2I79
IIE6
2I13
22u
7
NC1
8
NC2
21
NC
NC3
22
NC4
L15L26L39L410L511L6
4
2I81
1u0
2I80
2I82
10n
AL-SC2-IN
AL-SC1-IN
B14b
B14b,d
B14b,d
G
H
2I14
B15a
PIP-AM
3I43
4K7
2n2
13
15
17
3IJ0
28
27
26
12
14
16
100R
3IJ1
100R
9I30
L-FRONT-IN
B14d,B21
B14d,B21
9I31
9I32
R-FRONT-IN
AL-SC1-IN
B14b.d
9I33
AR-SC1-IN
B14b.d
B14b.d
9I34
AL-SC2-IN
9I35
AR-SC2-IN
B14b.d
SNDR-MAIN-IN
SNDR-SEC-IN
SNDR-BO-IN
SDA-S
SCL-S
SNDL-MAIN-IN
SNDL-SEC-IN
SNDL-BO-IN
SNDL-SEC-IN
SNDR-SEC-IN
SNDL-MAIN-IN
SNDR-MAIN-IN
SNDL-SC2-IN
SNDR-SC2-IN
B6a ,B14d
B6a (2x),B14d
B14b
B6a,B14d
B6a (2x),B14d
B14b
B6a (2x),B14d
B6a (2x),B14d
B6a,B14d
B6a,B14d
B6a
B6a
II67
B6a
REG-SW
B14b
SNDL-SC2-OUT
B14b
SNDR-SC2-OUT
2I99
10u
IIE5
10u
2IA2
IIE4
SNDL-SC1-OUT
SNDL-SC1-OUT-DC
SNDR-SC1-OUT-DC
SNDR-SC1-OUT
TRI-STATE-DVI
3IH9
47K
3II4
47K
B14b
B6a , B14d
B6a , B14d
B14b
B14c(3x),f
3II1
22K
3II2
IIE2
3IH8
IIE3
3II3
+8V
3II0
10K
+8V
7I22
BC847BW
22K
2IA0
16V10u
47K
2IA1
16V10u
47K
74HC4053PW
16
7I20
6
G3
14
MUXDX
1z
11
s0
15
2z
10
s1
4
3z
9
s2
GND
8
+5V
7I23-2
BC847BS
RES
10K
3IJ2
3
II69
5
4
22K
RES
9I68
RES
3IJ3
22K
3IJ4
SEL_IN_1_B
SEL_IN_2
B5a
B14e
+5V
RES
3II5
10K
12 13
VCC
12
1y0
13
1y1
2
2y0
1
2y1
5
3y0
3
3y1
VEE
7
9I57
9I58
SNDL-MON-OUT
SNDL-SC1-OUT-DC
SNDR-MON-OUT
SNDR-SC1-OUT-DC
B6a,B14b,B14d
B6a , B14d
B6a,B14b,B14d
B6a , B14d
A
B
C
D
E
F
G
H
2I13 F2
2I14 B4
2I71 B3
2I72 B3
2I73 B3
2I75 B3
2I76 B3
2I77 D1
2I78 D1
2I79 D2
2I80 E3
2I81 E3
2I82 E3
2I84 E3
2I85 E3
2I99 F7
2IA0 D10
2IA1 E10
2IA2 F7
3I39 E2
3I43 B4
3IH8 D10
3IH9 E7
3II0 C10
3II1 C10
3II2 C10
3II3 E10
3II4 F7
3II5 H7
3II6 I7
3II7 I7
3IJ0 D4
3IJ1 D5
3IJ2 G7
3IJ3 G7
3IJ4 H7
7I17 C2
7I20 C12
7I22 C10
7I23-1 I7
7I23-2 G7
9I30 E5
9I31 E5
9I32 E5
9I33 E5
9I34 E5
9I35 E5
9I57 E12
9I58 E12
9I68 G8
9IA1 B3
9IA3 E3
II67 C10
II69 G7
II70 I7
II72 D2
IIE2 D9
IIE3 D10
IIE4 F7
IIE5 E7
IIE6 E2
IIE7 B4
I
8204 000 8478.1
7I23-1
BC847BS
6
II70
3II7
2
1
22K
3II6
22K
SEL_IN_1
B5a
123456789
10 11
12 13
F_15460_034.eps
080405
I
Page 65

SSB: I/O: 5
1I10 G2
1I12 G2
1I79 H3
1I99 H2
1M15 F2
2I00 H2
2I10 A3
2I33 D9
2I34 D10
2I37 B10
2I38 G3
2I40 C10
2I48 E3
2I52 C5
2I59 E11
Circuit Diagrams and PWB Layouts
2I60 E2
2I62 H10
2I64 G9
2I65 G3
2IA3 G8
2IB7 D4
2IJ5 D6
2IJ6 H9
2IJ7 I9
2IK5 G5
2IK6 G5
2IK7 G6
2IS6 H4
3I00 H8
3IB1 E11
3IB3 E11
3IB6 D8
3IB7 D9
3IB8 G10
3IB9 G9
3IBA E9
3IBB E9
3IC0 C9
3IC5 C9
3IC7 C10
3ID2 C4
3ID3 A12
3ID4 C12
3ID6 D6
3IE0 A11
3IF0 F8
3IF1 D1
3IF2 D2
3IF3 D2
3IF4 D3
3IF8 D4
3IF9 E3
3IGA A12
3IGB C12
3IGC B11
3IGD B11
3IGE C11
3IGF C11
3IGH H8
3IH0 A12
EN 65FTP2.4E AA 7.
3IH2 B11
3IH4 C12
3IS3 H9
3IS6 I9
3IW3 B5
3IW9 B5
5I02 E9
5I04 D10
5I05 F3
5I06 G3
5I10 C5
5I21 G8
5I22 H2
5I45 G5
5I46 G5
6I03 F12
6I04 E12
6I05 D5
6I99 F1
7I08 B4
7I10 E10
7I11 G8
7I13 E5
7I15 E45I47 G6
7I16-1 E3
7I16-2 E1
7I40 C11
7I45 C8
7I46 C10
9I05 F10
9I06 F10
9I99 C12
9ID0 G8
FI15 G2
FIC4 G2
FIC5 F2
II75 D4
II76 E3
II77 C4
II78 E2
II79 B12
II80 E1
II81 C11
II82 B11
II83 E4
II84 E3
II85 E10
II86 C5
II87 C6
II88 C12
II89 E11
II95 E12
II96 E97I14 B11
IIE8 H8
IIE9 G9
IIF1 C13
IIH4 B11
IIH5 C11
123456789
10 11 12 13
I/O: 5
B14E B14E
3IF3
FIC5
FIC4
+11V_SF
+5V
*
10n
2I10
B5a,B14e,B21
8
7I08
*
LM75ADP
+5V
+VS
7
A0
6
A1
5
A2
GND
4
+8V
10K
II84
5I05
5I06
2I48
3IF4
470R
II76
1n0
6
2
7I16-1
BC847BS
1
2I65
2I38
100p
+11V
3IF9
3K3
SDA-SF
SCL-SF
100p
T3A 420
1I79
T3000mA
B21
B21
II83
1
2IS6
100u 16V
TEMPERATURE
3
OS
1
SDA
2
SCL
3ID2
1R0
2K2
3IF8
II75
3
7I15
BC847BW
2
+11V_DC
SENSOR
*
*
3IW3
100R
II77
5I10
1m0
2IB7
100n
2IK5
3IW9
100R
5I46
100n
+5V
II86
+5V_CON
2IK6
SDA-S
SCL-S
BAS316
7I13
BC817-25W
+5V_VDP
5I45
100n
+5V
2I52
220p
6I05
RES
B5a,B14e,B21
II87
2IK7
3ID6
2K2
2IJ5
100n
5I47
100n
+8V
+33V
+8V_VDP
B6c,B14b
STANDBY
STANDBY
+5V2-STBY
3IC5
100p
100p
*
5I02
*
PCA9515DP
220R
7I46
BC847BW
3 SDA0 6SDA1
2SCL0
5EN
1K0
7I45
TS2431
A3K
R
2
3IB6
1
1K0
3IC0
2I33
1n0
3IB7
330R
II96
+3V3_SIM
SDA-S
SCL-S
3I00
3IF0
100R
5I21
IIE8
10K
3IGH
9ID0
7I11
BC847BW
100K
2IA3
1n0
IIE9
B5a
STATUS-SC3 STATUS-SC3-F
B14d
B5a
ON-OFF-LED
SURR-R
3IBA
100R
3IBB
100R
2I64
3IB9
100R
3IS3
100R
2IJ6
A
B
C
D
E
G
H
RES
+5V
2K7
II78
2I60
1n0
5
SERVICE
CONNECTOR
1I10
5I22
EMC HOLE
FI15
3IF2
2I00
1I12
1M15
1
2
3
S3B-EH
100p
3IF1
470R
II80
3
7I16-2
BC847BS
4
F
6I99
21
PLVA2656A
3
+11V_S
1I99
2I34
3IC7
220R
10u 16V
VCC
GND
II85
9I05
9I06
RES
3IE0
47K
II82
IIH4
2I37
3IGC
10K
47K
1u0
3IGD
*
3IH2
47K
7I14
BC847BW
RES
IIH5
3IGE
10K
*
7I40
BC847BW
*
10K
2I59
100n
II89
II95
*
*
II81
*
*
2I40
5I04
8
7I10
NC
4
47K
3IGF
100n
*
*
10K
3IB1
3IB3
7SCL1
1
RES
II79
+5V
2K2
3IH4
II88
*
BAV99 COL
BAV99 COL
+5V
4K7
3IH0
+5V2-STBY
3ID4
RES
6I04
6I03
+5V2-STBY
3ID3
9I99
4K7
+3V3_SIM
4K7
3IGA
+3V3_SIM
*
RES
3IGB
4K7
PDP-GO
4K7
IIF1
CPU-GO
SDA-DISP
SCL-DISP
RES
+5V2-STBY
3IB8
100p
10K
2I62
SEL_IN_1_BFSEL_IN_1_B
LED1
SURR-RF
NC
NC
B21
B21
B21
B21
NC
A
B
C
D
E
F
G
H
I
8204 000 8478.1
1234
B6c,B14b
3IS6
100R
2IJ7
100p
56NC78910
SURR-LFSURR-L
11 12 13
B21
F_15460_035.eps
080405
I
Page 66

Circuit Diagrams and PWB Layouts
EN 66FTP2.4E AA 7.
SSB: I/O6: Digital Input
123 5
B14F B14F
I/O6: DIGITAL INPUT
A
B
1I21
FI00
FI09
FI08
FIC3
FI01
FI70
FI71
FI06
FI07
SCL_DVI
SDA_DVI
FI02
FI03
HOT PLUG
FI04
RX2+
RX1+
RX0+
RXC+
RXC-
RX2-
RX1-
RX0-
1I61
1I60
6I01
BAV99 COL
1I62
1I14
1I56
DLW21S
1I65
1I64
+5V
3I42
1K0
1I66
FI05
1I67
1I55
DLW21S
1I16
1I15
C
DVI INPUT
CONNECTOR
D
E
F
G
YKF45-7005
1D01-1
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
H
I
J
4678910
7I65
LD1117DT33C
FI80
+8V-VIDEO
3V3-TMDS
6I20
6I65
6I66
1I53
BAS316
BAS316
B14g
B14b
AV6-R
9ID1
R
1I20
BAV99 COL
75R
3I29
BAV99 COL
3I44
MMC-R
9ID2
res
+8V-VIDEO
6I06
6I21
DLW21S
DLW21S
10K
3I45
FI81
BAV99 COL
1I57
1I59
47K
B14g
AV6-G
9ID3
3I30
2IB9
B14b
MMC-G
9ID4
res
1I19
+8V-VIDEO
6I07
BAV99 COL
75R
100n
3I47
2K2
3I46
100R
FI82
1
3V3-TMDS
6I14
5I39
3I48
RES
FI72
B14g
B14b
AV6-B
9ID5
75R
3I31
BAV99 COL
2K2
MMC-B
DVI INPUT
CONNECTOR
9ID6
res
C428
FI83
1I18
3
6I08
6I15
BAV99 COL
2IB8
2IH1
100n
100n
7I19
M24C02-WDW6
(256x8)
EEPROM
1
0
2
ADR
1
3
2 SDA
32
2
1
Φ
30
6I16
2IC5
84
C1 25C226
29
3I32
PLVA2656A
BAV99 COL
100n
WC
SCL
1D01-4
YKF45-7005
27C3
31
1K0
2IC7
6I17
3IQ5
7
6
5
3I33
100R
47p
BAV99 COL
47K
6I63
3I49
B14b(2x)
VD-ANA
9ID7
res
6I18
BAS316
100R
B14g
AV6-V
9ID8
6I64
B14g
V
BAV99 COL
3V3-Si-IO
AV6-H
9ID9
H
BAS316
IIG0
B14b(2x)
HD-ANA
9IB3
res
3I40
100R
3V3-Si-IO
3IV1
3IV2
+5V
B14f
B14c (3x),g,B15b
FI84
2
1K0
2
470R
1K0
2IC6
BAV99 COL
BSH112
6
7I53-1
BC847BPN
1
3IV3
3I41
3IQ7
100R
1K0
3
6I09
3IR2
7I51
4K7
1
BSH112
PLVA2656A
3IR3
7I52
1I17
1u0
2IB5
2IB3
100n
DVI-PWR-DOWN
B14f
4K7
1u0
1u0
2IJ9
2IJ8
3IV0
FI74
8K2
47p
6I19
3IQ6
100R
32
2IB0
100n
DVI-PWR-DOWN
SWITCH-MAIN
+3V3-SI
22u
2IE9
100n
2I97
2I98
100n
100n
3IR4
6-M7
100R
3V3-Si-IO
3K3
3IQ8
IIH6
5
7I53-2
BC847BPN
4
3
3IQ9
OUTIN
COM
1
3IK9
1K0
res
2IG3
100n
2IG2
II66
3V3-Si-IO
FI75
FI73
1K0
1K2
3IR0
res
FI76
5I33
II60
2 RX0+
3IR1
1u0
SII905CQ52
RX0-3
RX1+51
RX1-52
RX2+48
RX2-49
RXC+5
RXC-6
PD_11
PD-DAC_20
SCLM34
SDAM36
SCLS15
SDAS14
RESET_39
RSET29
270R
+3V3-SI
7I61
BC847BW
2IG4
100n
5I34
II65
2IC8
7I18
RX0+
RX0-
PANELLINK
RX1+
RX1-
RX2+
RX2-
RXC+
RXC-
PD
PD_
PD-DAC_
SCLM
SDAM
SCLS
SDAS
RESET_
RSET
VREF-IN VREF-OUT
AGND1
AGND1
47
res
1u0
100n
22
46
VCC3
VCC2
VCC3
VCC2
RECEIVER
PLLCK
CLK
CIPHER
RESET_
C
AGND2
AGND3
AGND2
AGND3
50
4
HDCP
8204 000 8478.1
1234
57
6
8 9 10 11 12
11 12 13 14
+3V3-SI
3II9
1K0
II68
2IH5
100n
II63
II64
37
32
27
DACVCC
DACVCCB
DACVCCR
DACVCCG
DACVCC
DACVCCB
DACVCCG
DVI
RECEIVER
MODE
SELECT
DACPD
OGND1
OGND2
DACGNDR
OGND1
OGND2
DACGNDG
DACGNDR
16
43
25
RES
3II8
1K0
2IG6
100n
2IE5
24
AVCC2
AVCC2
DACVCCR
DACGNDG
DACGNDB
DACGNDB
28
TRI-STATE-DVI
5I40
2IH4
100n
2IE6
1
7
AVCC1
AVCC1
SCDT
RESERVED
EXT-RES 8
EXT-RES
ODCK
HSYNC 18
HSYNC
VSYNC 19
VSYNC
COMP
DACGND
DACGND
35
33
1u0
100n
SCDT 40
ODCK 42
DE 44
DE
IOB 31
IOB
IOG
IOR 23
IOR
COMP 30
B14c (3x),g,B15b
2IG8
100n 100n
5I31
1u0
2IE8
38RESERVED
2I91
26IOG
3IS5
2IE7
100n
2IG7
2IG9
100n
5I32
1u0
2I95
2I94
100n
1u0
2I90
120R
2I66
RES
5I41
2I96
100n
2I93
100n
3IR7
3IR5
1u0
2I89
47R
3IR6
47R
3IS0
3IR9
120R
120R
47p
47p
2I67
2I68
RES
2IE1
DR[7:0]
DG[7:0]
DB[7:0]
CNTL3
HSYNC
VSYNC
2IG5
100n
VCC1
SCDT
DE
PGND
2IE3
13
VCC1
PGND
10
BC847BW
100n
100n
OVCC2
GND1
7I64
VCC-Si
5I30
II62
2IE4
2IE2
17
41
OVCC1
OVCC1
OVCC2
DB
8
DG
8
DR
8
DE
HSYNC
VSYNC
TRIPPLE 8-
BIT DAC
GND1
GND2
GND2
21
12
RES
II61
9
PVCC
PVCC
FORMATTER
GND3
GND3
45
13 14
2IH2
100n
II92
1u0
5I35
3V3-TMDS
II97
3V3-Si-IO
1u0
2I92
3K3
3IR8
470R
II93
2I88
100p
2I87
5I36
220n
5I37
220n
5I38
220n
3IS1
47p
RES
100p
FI79
120R
2I69
9I07
II94
9I14
RES
FI30
FI29
FI77
FI78
3IT6
3IT5
120R
33p
33p
2I70
B14g,B19d
HS-DET
9I85
H-DVI
B14g
V-DVI
B14g
B-DVI
B14g
G-DVI
B14g
R-DVI
B14g
120R
33p
2I86
F_15460_036.eps
080405
A
B
C
D
E
F
G
H
J
I
1D01-1 D1
1D01-4 B6
1I14 D2
1I15 G2
1I16 G2
1I17 D8
1I18 D5
1I19 C5
1I20 C4
1I21 C3
1I53 G4
1I55 F2
1I56 E3
1I57 F4
1I59 G4
1I60 C2
1I61 C2
1I62 D2
1I64 E2
1I65 E2
1I66 F2
1I67 F2
2I66 I12
2I67 I13
2I68 I13
2I69 I13
2I70 I14
2I86 I14
2I87 H13
2I88 G13
2I89 G13
2I90 G12
2I91 G12
2I92 F13
2I93 F13
2I94 F12
2I95 F12
2I96 F13
2I97 F9
2I98 F9
2IB0 A9
2IB3 F9
2IB5 F8
2IB8 H5
2IB9 H4
2IC5 H6
2IC6 D7
2IC7 D6
2IC8 E10
2IE1 E10
2IE2 E11
2IE3 D11
2IE4 D11
2IE5 D12
2IE6 E12
2IE7 E12
2IE8 D12
2IE9 D9
2IG2 D9
2IG3 C10
2IG4 C10
2IG5 C11
2IG6 C12
2IG7 C13
2IG8 C12
2IG9 D13
2IH1 H5
2IH2 D13
2IH4 D12
2IH5 D11
2IJ8 I8
2IJ9 I9
3I29 D4
3I30 D4
3I31 D5
3I32 D6
3I33 C7
3I40 C7
3I41 D8
3I42 E2
3I44 I4
3I45 I4
3I46 I5
3I47 I5
3I48 I5
3I49 I7
3II8 B12
3II9 B11
3IK9 B9
3IQ5 I6
3IQ6 I7
3IQ7 I8
3IQ8 I9
3IQ9 I9
3IR0 I9
3IR1 I10
3IR2 H8
3IR3 H8
3IR4 H9
3IR5 G13
3IR6 H13
3IR7 F13
3IR8 F13
3IR9 I13
3IS0 I13
3IS1 I13
3IS5 I12
3IT5 I14
3IT6 I14
3IV0 I9
3IV1 J7
3IV2 J7
3IV3 J7
5I30 D11
5I31 D12
5I32 D13
5I33 D10
5I34 D10
5I35 F13
5I36 H13
5I37 H13
5I38 I13
5I39 H5
5I40 C12
5I41 E13
6I01 D3
6I06 D4
6I07 C5
6I08 C6
6I09 C8
6I14 F5
6I15 F5
6I16 F6
6I17 F6
6I18 F7
6I19 F7
6I20 E4
6I21 E4
6I63 I7
6I64 I7
6I65 I4
6I66 J4
7I18 F10
7I19 I6
7I51 I8
7I52 I8
7I53-1 J8
7I53-2 I9
7I61 B10
7I64 B11
7I65 A9
9I07 F14
9I14 G14
9I85 G14
9IB3 B7
9ID1 B4
9ID2 B4
9ID3 B4
9ID4 B5
9ID5 B5
9ID6 B5
9ID7 B7
9ID8 B7
9ID9 B7
FI00 C2
FI01 C2
FI02 E2
FI03 E2
FI04 F2
FI05 F2
FI06 G2
FI07 G2
FI08 E2
FI09 E2
FI29 H14
FI30 G14
FI70 D2
FI71 D2
FI72 I5
FI73 I10
FI74 I8
FI75 H10
FI76 C10
FI77 H14
FI78 H14
FI79 I14
FI80 B4
FI81 C4
FI82 C5
FI83 C6
FI84 C8
FIC3 F2
II60 B10
II61 D11
II62 D11
II63 D11
II64 E11
II65 E10
II66 E10
II68 B11
II92 E13
II93 G13
II94 G14
II97 F14
IIG0 J7
IIH6 I9
Page 67

Circuit Diagrams and PWB Layouts
EN 67FTP2.4E AA 7.
SSB: I/O: 7
12 5
B14G B14G
I/O: 7
34
67891011
A
HDI : RGB-YPbPr
RES
9I29
9I91
RES
9I98
RES
B
RGB-OUTPUT SELECTION
BA7657F
7I55
20
C
D
B14f
AV6-R
B14f
R-DVI
B14f
AV6-G
B14f
G-DVI
B14f
AV6-B
B14f
B-DVI
B14f
AV6-V
V-DVI
B14f
AV6-H
B14g
H-DVI
B14f
E
B14g (3x),f,B15b
SWITCH-MAIN
2IH9
6.3V
22u
2IH8
6.3V
22u
2IH7
6.3V
22u
2IH6
6.3V
22u
2IF9
6.3V
22u
2IF8
6.3V
22u
5I42
FIC2
100n
100n
1
7
3
9
5
11
12
13
24
23
II30
2IN8
2
II31
2IN9
18
16
R1-IN
R2-IN
G1-IN
G2-IN
B1-IN
B2-IN
VD1-IN
VD2-IN
HD1-IN
HD2-IN
HD-S-SIG-DET
C-V-IN
CTL
468
VCC
1
2
1
2
1
2
1
2
1
2
DET
SYNC
SEPA
LOGIC
GROUND
R-OUT
G-OUT
B-OUT
VD-OUT
HD-OUT
C-S-OUT
10
+5VIO
IIF2
2IK1
220n
21
19
15
14
22
17
IIF4
res
1K0
3IV6
res
3IV4
IIF3
res
1K0
3IV5
B14c,g
B14c,g
R-VGA
R-VGA
1K0
B14c,g
G-VGA
B14c,g
B-VGA
B14c,g
VS-2FH
HS-2FH
HS-DET
G-VGA
B14c,B19a
B14f,B19d
B14c,B19a
9I84
res
3IG7
10R
IIF5
3IG4
10R
IIF6
F
9I88
res
9I81
B19a,d
B19d
H-2FH-DIV-2
FIB2
G
3IT7
1K0
3IT8
1K0
1K0
3IK0
H
res
5I13
3IU0
+8V
2R2
5I12
16V47u
2IF4
B2,B14a,B15a
AV3-CVBS-INV-2FH-AD-OUT
+8V-VIDEO
FIB5
2IF5
100n
B14c,g
B-VGA
3IG1
10R
IIF7
7I56
BC847BW
7I57
BC847BW
7I58
BC847BW
+8V-VIDEO
3IG6
560R
+8V-VIDEO
3IG3
560R
+8V-VIDEO
3IG0
560R
2IF3
100R
3IHC
100R
3IHA
2IF2
100R
3IHB
2IF1
100n
SC2-R_C-IN_AV2
100n
B2,B14b,B15a
100n
SC2-B-IN_C-OUT
B14g (2x)
B14g
R-VGA-BUF
B14g (2x)
G-VGA-BUF
SC2-G-IN
B14g (2x)
B-VGA-BUF
REF1
REF2
REF3
R-VGA-BUF
G-VGA-BUF
B14g (2x)
B-VGA-BUF
B2,B14b,B15a
B14g (2x)
R-VGA-BUF
B14g
B-VGA-BUF
B14g (2x)
B2,B14b,B15a
3IG9
6I80
6IA1
+8V-VIDEO
3IW1
680R
FIB8
BAS316
FIB9
BAS316
FIB3
680R
100n
3IZ3
3IW7
1K0
1K0
IIB4
3IZ4
1K0
3IW8
3IZ5
1K2
3IU5
3K3
3IU9
3K3
REF2
3K9
+8V-VIDEO
3IJ6
100R
IIH8
RES
9I45
IIB6
10K
3IW2
IIB8
47K
3IV8
9I49
RES
RESERVED
2IK3
100n
2IK2
I
16V
10u
2I09
2IF0
2IK4
100n
47u
res
6I81
BZX384-C3V9
8204 000 8478.1
12
34
5
67891011
12 13 14
3IJ7
3IU6
REF3
3IZ0
REF3
3IZ7
7I41
BFR93AW
470R
1K2
1K0
REF2
330R
9I28
RES
IIH7
1K2
3IU7
1K2
3IZ1
IIB9
+8V-VIDEO
1K0
3IZ9
2
3
IIB5
REF2
+8V-VIDEO
11
12
IIB7
+8V-VIDEO
15
14
SB1
3IU2
100K
SB2_
SB2_
2IF6
7I54-1
4
TSH95ID
1
13
8
3IZ8
2K2
RES
6
100K
5
3IZ6
7I54-3
4
TSH95ID
10
13
9
3IU8
3K3
3IV7
18K
7I54-4
4
TSH95ID
16
13
9
3IZ2
2K2
3IV9
res
100K
+8V-VIDEO
10K
3IU1
FIB6
12 13 14
220n
+8V-VIDEO
SB1
8
3IU3
9I23
7I54-2
4
TSH95ID
13
STANDBY1
Y-2FH
7
B14g (2x)
STANDBY1
B19a
V-2FH
B14g (2x)
STANDBY2
B19a
U-2FH
STANDBY2
FIB7
10K
STANDBY1
STANDBY2
F_15460_037.eps
B14g (2x)
B19a(2x)
B14g (2x)
B14g (2x)
B14g (2x)
080405
A
B
C
D
E
F
G
H
I
2I09 I10
2IF0 I9
2IF1 F9
2IF2 D9
2IF3 B9
2IF4 H6
2IF5 H7
2IF6 A13
2IF8 D2
2IF9 D2
2IH6 D2
2IH7 D2
2IH8 C2
2IH9 C2
2IK1 C5
2IK2 H10
2IK3 H11
2IK4 I10
2IN8 E3
2IN9 E3
3IG0 G8
3IG1 F8
3IG3 E8
3IG4 D8
3IG6 C8
3IG7 C8
3IG9 H10
3IHA F9
3IHB E9
3IHC C9
3IJ6 C11
3IJ7 C12
3IK0 G3
3IT7 G3
3IT8 G3
3IU0 H5
3IU1 G13
3IU2 B13
3IU3 H13
3IU5 D11
3IU6 E12
3IU7 E12
3IU8 E13
3IU9 F11
3IV4 C7
3IV5 D6
3IV6 D6
3IV7 E13
3IV8 F11
3IV9 F13
3IW1 H10
3IW2 E11
3IW7 B11
3IW8 B11
3IZ0 F12
3IZ1 F12
3IZ2 F13
3IZ3 B11
3IZ4 B11
3IZ5 B11
3IZ6 C13
3IZ7 B12
3IZ8 B13
3IZ9 A12
5I12 H6
5I13 H6
5I42 E2
6I80 H10
6I81 I10
6IA1 H10
7I41 C12
7I54-A A13
7I54-B C13
7I54-C D13
7I54-D F13
7I55 C4
7I56 C8
7I57 D8
7I58 F8
9I23 B13
9I28 C12
9I29 B4
9I45 D11
9I49 F11
9I81 F4
9I84 E7
9I88 F4
9I91 B4
9I98 B4
FIB2 G2
FIB3 I10
FIB5 H6
FIB6 G13
FIB7 G13
FIB8 H10
FIB9 H10
FIC2 E2
II30 E3
II31 E3
IIB4 B11
IIB5 B12
IIB6 D11
IIB7 E12
IIB8 E11
IIB9 F12
IIF2 B6
IIF3 C6
IIF4 D6
IIF5 C8
IIF6 D8
IIF7 F8
IIH7 C12
IIH8 C11
Page 68

Circuit Diagrams and PWB Layouts
EN 68FTP2.4E AA 7.
SSB: PIP HIP
123456789101112
5P03
330n
2P03
4n7
BC847BW
*
7P02
2P04
*
3P19
PIP HIP
2R2
IP23
5P00
IP25
3P00
+8V
+8VHIP
2K7
3P07
4n7
7P00
BC847BW
9P04
6P00
1SS356
+8VHIP
3P18
47R
6P02
1SS356
3K9
*
COIL 40.4 SUPPRESSION
BA591
*
*
*
6P01
3P12
*
2K7
7P01
BC847BW
IP68
*
5K6
3P13
+8VHIP
*
2K7
3P17
*
5
6
8
5P07
7
1234
2P01
2P02
6P03
3P08
4K7
*
9P16
1SS356
*
2P06
220p
100u
100n
IP30
5P01
5P04
IP27
IP28
0V5
9P11
AP09
IP24
*
6u8
+8VHIP
3P09
*
*
2P07
2P08
9P01
*
9P10
3P01
2R2
3P02
1R0
2
3
1
4
5
6
9
10
13
14
15
18
4K7
2
3
1
4
5
6
9
10
13
14
15
18
68p
2p7
+5VHIP
IP26
IP31
8V0
IP29
8V0
IP32
SAW-FILTER AUDIO
1P04
OFWK9656L
I
ISWI
40M4
GND
SAW-FILTER VIDEO
1P05
OFWM1967L
I1
I2
45M75
GND
SAW-FILTER VIDEO
1P06
OFWK3953L
2
I1
3
I2
1
4
5
6
9
38M9
GND
10
13
14
15
18
NC
NC
O1
O2
*
O1
O2
+8VPIP
O1
O2
NC
+8VHIP
7
8
11
12
16
17
7
8
11
12
16
17
11
12
16
17
B13b
+5VHIP
AGC2
2K2
3P03
IP02
3P04
3P05
AP04
AP05
AP06
AP07
9P02
IP22
RES
IP01
1P08
TPWKA
13
I
2
GND
3P14
*
5K6
0V5
7
8
3P15
5K6
3P06
100R
4K7
IP00
5K6
3P10
2P05
9P05
5P05
3u9
BC847BW
IP69
IP70
*
3P16
FP08
+8VHIP
1
2
6R8
RES
3
FP27
MODULATOR COIL
47u
3P11
470R
IP03
*
*
13
O
2
7P03
*
7P04
BC857BW
4K7
5V0
1P09
TPWKA
I
GND
9P23
IP33
2P25
5P08
7
8
6
4
9P03
9P00
5P06
FP14
2u2
O
3P40
9P09
3P38
*
1K0
*
RES
9P17
5P09
IP34
100n
2P19
100n
3P28
5P10
3P21
100K
180R
*
9P07
1P07
SFSKA
4M5
IP35
*
*
22n
2P21 1u0
2P20 1u0
4p72P49
2P17
470n
+8VHIP
390R
7V6
FP13
9P30
3P71
560R
*
O
1u02PG0
1u02PG1
FP15
2V7
47p2PG2
2P24
2P23
FP16
3P25
390R
2P18
5p6
3P26
470R
V1
9P06
7P06
BC847BW
3P32
560R
9P18
RES
+8VHIP
*
3P39
*
3P37
100n
IP17
*
5P11
33u
4K7
2
4K7
10u
2P22
RES
5V4
7P05
BC847BW
2V4
3P27
120R
9P08
RES
RES
9P14
13
I
2
GND
2P99
2P98
V2
9P15
8V0
8V0
I6
IP71
2P16
100u
100u
64
63
1
2
3
4
6
7
8
62
10
12
13
14
100n
FP17
+8VHIP
3P36
SIF2
SIF1
AGCSIF
VIF1
VIF2
AGCDEC
PLLRILT
VCO1
VCO2
TUNERAGC
VIFOUT
IN
OUT
CVBSINT
6
7P07-1
1
1K0
B15a
cP01
cP00
MONO-HIP-OUT
3P48
100R
FP02
5
QSS_AM
9
1u0
22n
2P09
2P26
IP20
45
44
+8_111+8_2
GND_1
GND_2
SUPPLY CTRL
HIP
IF DEM
GROUP
DELAY COR.
I/O SWITCH
Y_CVBS3
CVBS2
C321C4
CVBS1
20
18
16
100n
100n
2P15
2P14
2P13
100n
100n
2P11
9P12
IP10
3P31
470R
FP41
BC847BS
2P10
2P27
35
DEC
Y_CVBS4
23
100n
2P12
24
1u0
2P28
IP21
33
DIGDEC
PIPOUT
32
3P44
100n
GND_DEC
+8VHIP
100n
31
DIGGND
CVBSOUT
34
100R
IP72
9P25
RES
FP12
48
TDA9321H/N2
COMBOUT
26
3P30
BC847BW
9P24
3P34
ADSEL
100R
FP42
47R
17
AV115AV2
7P09
+8VHIP
7P08
2V8
FP36
B2(2x),B15a
BG
19
7V6
3P35
B2(2x),B15a(3X)
SCL-S
LMN
3P22
22
46
5V0
0V5
SCL
SW0
SW01
LUMA & CHROMA PROC.
YCOMBIN
CCOMBIN
28
29
470R
+8VHIP
3
5
7P07-2
BC847BS
4
3P33
1K0
B14a
FP11
PIP-AM
SIF-OUT
IN-CVBS-SC1_AV1-SUB
CVBS-PIP_TUN1-2-CVBS-IN
B2
B15a
B14b
AV3-CVBS-IN
IN-Y-CVBS-SC2_AV2
B14b
B2,B14a,g
SC2-R_C-IN
Y-CVBS-PIPDW-OUT
B14a
B14b
C-PIPDW-OUT
B14a
B14a
PIP-OUT1
B15b
PIP-CVBS-COMB
PIP-CVBS-MON
B15a
PIP-COMB-C-OUT
PIP-COMB-Y_CVBS-OUT
B15a
B15a
LMN
B2(4x),B15a(3x)
BG
B2(2x),B15a
9P19
RES
TER-CVBS-OUT-SUB
MONO-HIP-OUT
B14b
B15a
SDA-S
3P23
100R
47
PIP-SYS1
B15a
100R
SDA
SYS125SYS2
27
0V5
PIP-SYS2
B15a
5V0
B15a
B15c
IP36
58
HPLL
SYNC
SVBCOUT
30
PIP-FSC
B15a
B15c
VS-HIP-OUT
HS-HIP-OUT
60
61
VA
HA
FBL1IN
OUTP SWITCH
FBL2IN
YOUT
UOUT
VOUT
X3.579
X3.575
X3.582
X4.43
COL_PLL
SEC_DEC
SCOUT
59
RES
RES
IP37
PIP-SC
PIP-CVBS-COMB
B15a
FP23
R1IN
G1IN
B1IN
R2IN
G2IN
B2IN
9P22
100n
3P45
RES
2P91
3P24
15K
36
37
38
39
41
42
43
40
49
50
51
57
56
55
54
52
53
+5VHIP
9P20
9P21
100K
3P46
RES
2P30
2P31
100n
2P32
100n
2P45
100n
2P47
100n
2P48
9P26
9P27
2P34
RES
RES
2 INPSEL
12 Y|CVBS1
3 Y|CVBS2
FP29
1
7SC
100K
PIP-SC
B15a
4n7
33p
100n
IP38
*
*
3P29
2P35
7P11
TDA9181
CIN
2P29
2P33
100n
1u0
100K
100n
2P46
100n
2P36
9P13
RES
1P00
3n3
2P37
13
FP38
FP39
FP40
FP24
FP25
FP26
4M433619
15p
CLAMP
CLAMP
SAND-
CASTLE
AGND
4
7P11-P4
B15a
FP37
SC2-R_C-IN_AV2
SC2-B-IN_C-OUT
HC-49/U
1p2
2P38
*
2P39
DGND
2P96
100n
TUNING
B14c
SUB-V
B14c
SUB-Y
B14c
SUB-U
B14c
SC1-FBL-IN
B2, B14b,g
B2, B14b,g
SC2-G-IN
B2, B14b,g
B2, B14c
SC2-FBL-IN
B15c
Y-HIP-OUT Y-HIP-OUT
B15c
U-HIP-OUT
B15c
V-HIP-OUT
3P90
560R
I
2
1
I
GND
1P12
O
O
3
SFSRH
9P28
*
15p
2P40
2p2
7P55-I
B15b
+5VHIP
RES
6
VCC5VDD
2H/4H DELAY
ADAPTIVE
COMB FILTER
FILTER
IP39
2P92
RES
PIP-FSC
B15a
100n
3P47
RES
CLOCK
GEN
9 FSC
8 FSCSEL
100K
12 13 14
B15A B15A
A
+5V
100n
2P00
B
B13b
AP02
IF-TER2
C
5P02
FP03
D
B2(4x),B15a(3x)
LMN
E
F
G
B2(4x),B15a(3x)
LMN
H
I
8204 000 8475.1
3P20
5K6
1234567891011
13 14
3K3
3P41
RES
BFR93AW
3P91
560R
I
1
I
5M5
1P10
O
O
3
9P29
*
*
15p
2p2
2P42
2P41
7P55-DK
B15b
RES
2P95
100n
SYS1
15 OUTSEL
11
10 SYS2
PIP-SYS1
PIP-SYS2
B15a
B15a
7P10
GND
+8VHIP
RES
RES
RES
1P03
5M5
SFSRH
14Y|CVBSO
16COUT
3P42
3P43
2P43
1K8
IP73
1K5
HC-49/U
10p
2P44
IP40
2P94
IP42
100n
3P92
560R
1
I
4M433619
O
1P11
2p7
3
7P55-BG
B15b
RES
100n
PIP-COMB-Y_CVBS-OUT
2P93
RES
PIP-COMB-C-OUT
F_15460_038.eps
I
O
SIF-OUT
680R
GND
*
SFSRH
7P11-P4
IP41
IP43
*
5M5
2n2
2P97
7P55-M
B15b
080405
B15a
3P93
B15a
B15a
B15a
A
B
C
D
E
F
G
H
I
1P00 E11
1P03 E13
1P04 C4
1P05 E4
1P06 G4
1P07 H7
1P08 E5
1P09 E6
1P10 E13
1P11 F14
1P12 E12
2P00 B1
2P01 B2
2P02 B2
2P03 C1
2P04 D2
2P05 D5
2P06 G3
2P07 G3
2P08 H3
2P09 B8
2P10 F8
2P11 F8
2P12 F8
2P13 F8
2P14 F8
2P15 F8
2P16 F7
2P17 E7
2P18 D7
2P19 D6
2P20 C7
2P21 C7
2P22 C6
2P23 B7
2P24 B7
2P25 B6
2P26 B8
2P27 B8
2P28 B9
2P29 B11
2P30 B11
2P31 C11
2P32 C11
2P33 C11
2P34 F11
2P35 F11
2P36 F11
2P37 F11
2P38 F12
2P39 F12
2P40 F12
2P41 F13
2P42 F13
2P43 F13
2P44 F14
2P45 C11
2P46 D11
2P47 D11
2P48 D11
2P49 D6
2P91 G11
2P92 I12
2P93 G14
2P94 G14
2P95 G13
2P96 G12
2P97 F14
2P98 B7
2P99 B7
2PG0 C7
2PG1 C7
2PG2 F7
3P00 B2
3P01 B3
3P02 B3
3P03 B5
3P04 B5
3P05 B5
3P06 B5
3P07 D2
3P08 D2
3P09 E3
3P10 D5
3P11 E5
3P12 E2
3P13 F2
3P14 F5
3P15 G5
3P16 G5
3P17 G2
3P18 G2
3P19 G2
3P20 H1
3P21 B7
3P22 B10
3P23 B10
3P24 B11
3P25 D7
3P26 D7
3P27 E6
3P28 E6
3P29 E11
3P30 F9
3P31 F8
3P32 F7
3P33 I6
3P34 G9
3P35 G9
3P36 H7
3P37 H7
3P38 H6
3P39 G7
3P40 F6
3P41 D13
3P42 D13
3P43 D13
3P44 F9
3P45 H11
3P46 H11
3P47 I12
3P48 B8
3P71 F7
3P90 E12
3P91 E13
3P92 E14
3P93 E14
5P00 A2
5P01 B3
5P02 C1
5P03 A1
5P04 D3
5P05 E5
5P06 E6
5P07 H2
5P08 C6
5P09 B7
5P10 B7
5P11 F7
6P00 E2
6P01 E2
6P02 G2
6P03 D2
7P00 D2
7P01 F2
7P02 H1
7P03 F5
7P04 G5
7P05 D6
7P06 E7
7P07-1 H7
7P07-2 I6
7P08 F9
7P09 D9
7P10 D13
7P11 G11
9P00 E6
9P01 C3
9P02 D5
9P03 D6
9P04 E2
9P05 E5
9P06 E7
9P07 F7
9P08 G6
9P09 F6
9P10 F3
9P11 E3
9P12 G8
9P13 D11
9P14 G6
9P15 E7
9P16 E3
9P17 H6
9P18 G7
9P19 H5
9P20 F11
9P21 G11
9P22 G11
9P23 H6
9P24 G9
9P25 F9
9P26 E11
9P27 E11
9P28 F12
9P29 F13
9P30 F7
AP02 C1
AP04 C4
AP05 C4
AP06 C5
AP07 C5
AP09 G3
FP02 B8
FP03 C1
FP08 B5
FP11 I7
FP12 G9
FP13 F7
FP14 E6
FP15 D7
FP16 C7
FP17 F7
FP23 B11
FP24 D12
FP25 D12
FP26 D12
FP27 D5
FP29 H11
FP36 G9
FP37 C12
FP38 C12
FP39 C12
FP40 C12
FP41 H8
FP42 H9
IP00 B5
IP01 E5
IP02 B5
IP03 E5
IP10 H8
IP17 C7
IP20 B8
IP21 B9
IP22 D5
IP23 A2
IP24 A3
IP25 B2
IP26 B4
IP27 B3
IP28 B3
IP29 B4
IP30 A3
IP31 B3
IP32 C3
IP33 B6
IP34 B7
IP35 B7
IP36 B10
IP37 H11
IP38 H11
IP39 H12
IP40 G13
IP41 G14
IP42 G13
IP43 G14
IP68 F2
IP69 F5
IP70 G5
IP71 E7
IP72 F9
IP73 D14
cP00 A8
cP01 A8
Page 69

SSB: PIP Switch
1P50 E2
2P50 E4
2P51 E1
2P52 F2
2P53 F2
2P54 F2
2P55 G2
2P56 G6
2P57 G6
2P58 F6
2P59 I5
2P60 H6
2P61 I6
2P62 F6
2P63 F7
1
2P65 F9
2P66 F9
2P70 E6
2P71 E15
2P72 E7
Circuit Diagrams and PWB Layouts
2P73 E9
2P74 C6
2P75 A9
2P76 E1
2P77 E4
2P78 E12
2P79 E7
2P80 F14
2P87 D2
2P88 D1
2P90 E6
2PE7 H7
2PE8 G7
2PE9 A13
2PG6 F8
3P49 B13
3P50 D1
3P51 E1
3P52 E4
3P53 E2
3P54 F2
3P55 I6
3P56 H5
3P57 G6
3P60 F5
3P62 H6
3P63 H6
3P64 H7
3P65 H15
3P66 H15
3P67 G14
3P68 F14
3P69 F14
3P70 F14
3P72 E14
3P74 E15
3P75 H6
3P76 F5
3P79 D4
3P80 C2
3P81 D4
3P82 D22P81 F14
EN 69FTP2.4E AA 7.
3P86 C10
3P87 C10
3P88 D6
3P94 D5
3P95 D4
3P96 G7
3P97 G7
3P98 G5
3P99 G6
3PG7 F7
3PG8 F7
3PJ0 B11
3PJ1 B12
3PJ2 B12
3PJ3 B12
2345678
3PJ4 B13
3PJ5 B143P61 E8
3PJ6 B14
3PJ7 B14
3PJ8 C14
3PJ9 C14
5P50 D4
5P51 E15
6P10 F8
7P51 D3
7P52-1 F5
7P52-2 G4
7P53-1 G6
7P53-2 H6
7P54 G9
7P55 B6
7P56 G12
7P58-1 G7
7P58-2 H7
7P59-1 G73P85 F14
7P59-2 F7
7P60 B15
7P61-1 B14
7P61-2 C14
7P62 B13
7P63 B12
9P31 H6
9P32 G6
9P52 F5
9P53 G5
9P54 I6
9P69 I13
9P70 I13
9P71 I13
9P72 F1
9P73 G9
9P74 G9
9P75 H9
9PB7 B11
FP50 E15
FP51 G10
FP52 G10
FP53 G10
FP55 E15
FP56 B10
FP57 I6
FP59 G15
FP60 H9
IP50 C2
IP51 E3
IP52 F5
IP53 E2
IP54 E2
IP55 G6
IP56 E14
IP57 E8
IP58 E7
IP59 B9
IP60 C6
IP61 D9
IP62 D14
IP63 F12
IP64 F12
IP74 G4
IP75 F5
9 101112131415
B15B B15B
PIP SWITCH
A
B15B
B15B
B
C
D
E
F
G
H
I
B15a
PIP-CVBS-MON
9P72
CVBS-Y-RECORD-IN
B5a,B14a,b
SDA-VCHIP
SCL-VCHIP
2P88
2P76
1u0
AUDIO DEMODULATOR
7P55
TDA9820
IN1M
3P88
2P90
2P74
3P75
100R
3P99
680R
2P57
680R
+5VPIP
RES
3
IN1B|G
1
IN11
16
IN1D|K
2
7 STAGE
LIMITER
AMPLIFIER 1
IP60
IN2
15
100n
7 STAGE
LIMITER
AMPLIFIER 2
VCO1
VCO2
SUPPLY
NC1
4
IP57
27K
3P61
1u0
100u
VCOREF
VP
CSTAB
100n
GND
11
14
12
13
4V4
IP58
1u0
2P79
2P72
3R9
7V9
2P70
VIDEO SWITCH
1u0
2P62
RES
47p
47p
BC857BS
7P53-1
3P63
680R
2P61
RES
+5VPIP
2P56
BC857BS
7P53-2
FP57
3PG7
4K7
2P63
RES
4K7
3P97
2PE8
1u0
4K7
3P96
47p
RES
0V
3P64
2PE7
7P59-2
BC847BS
6P10
BZX384-C2V7
3PG8
1K0
100n
4K7
1u0
2PG6
BC847BS
7P59-1
BC847BS
7P58-1
10u10V
BC847BS
7P58-2
BA7609F
1
16
2
14
11
12
8
9
7
VIDEO SWITCH
IN1A
IN1B
CTL1
IN2A
IN2B
CTL2
IN3A
IN3B
CTL3
7P55-M
B15a
7P55-BG
B15a
7P55-I
B15a
7P55-DK
+5VD
+5VD
IP50
3P80
*
6K8
*
1u0
2P87
*
22p
*
3P50
*
3P51
*
8p2
3P82
*
470K
10M
32K768
DMX-26S
*
1P50
10M
7P51
*
Z86130-12SSC
1
I2C-SEL
2
HSEL
3
XOUT
4
SEN
5
HIN-XIN
6
SMS
7
VIDEO
IP53
8
CSYNC
IP54
9
LPF
NC2
NC1
SDO
SCK
SDA
VIN-INTRO
VDD
VSS
RREF
18
3P79
17
100R
16
3P81
15
100R
14
13
*
12
11
10
2P77
3P52
*
10K
IP51
+5VD
*
4K7
3P94
*
4K7
3P95
*
+8VPIP
*
5P50
*
6u8
*
100n
2P50
100n
V-CHIP
2P51
3P53
100n
*
470R
2P54
68n
*
*
56p
2P52
2P53
100n
*
2P55
*
6n8
*
3P54
6K8
(US ONLY)
*
B6a,B15c
B6a,B15c
B15c
B15c
B15c
V34
IN-U50
HA50-PIP
DU
+5VPIP
V35
IN-V50
DV
IN-Y50
MUPPET_BLK
DY-IN
7P52-1BC847BS
+5VPIP
IP75
BC847BS7P52-2
3
5
IP74
3P56
IP52
9P53
2P58
1u0
3P60
680R
RES
+5VPIP
3P98
10R
RES
9P32
IP55
RES
47p
2P59
RES
V33
2P60
1u0
3P57
3P62
10R
9P31
3P55
RES
1K0
9P54
1
6
2
9P52
10R
3P76
4
10R
IP59
CONTROL
2V5
2P73
+5VPIP
Φ
3-CHANNEL
7P54
GND
4
10
VCC
FP60
9
C1C2
UNIT
10
13
OUT1
OUT2
OUT3
15
2V5
2P75
IP61
9PB7
3PJ0
VAF1
SEL_PIP_SOUND2
SEL_PIP_SOUND1
8
DY
SUB-ATTENUATION
+8VPIP
FP56
S1
5
S2
6
VAF2
7
1u0
2P65
10V
10u
2P66
100n
V38
9P74
3
V39
9P73
5
V37
9P75
6
0V1
0V1
10K
3P86
3P87
FP52
U-PIP+MAIN-OUT
FP51
V-PIP+MAIN-OUT
FP53
Y-PIP+MAIN-OUT
10K
B14d
PIP-FM
B15b
SEL_PIP_SOUND1
SEL_PIP_SOUND2
B15b
SUB-SYNC-INSERT
SUB-ATTENUATION
B6a,B14c
B6a,B14c
B6a,B14c
+5VPIP
3PJ1
680R
res
BC857BW
10R
7P63
3PJ2
330R
120R
3PJ3
2PE9
100n
3P49
3PJ4
680R
390R
1
4
DY-IN
+5VPIP
+5VPIP
1
2
1
X1
7P62
35
74LVC1G66GW
7P61-1
BC847BS
6
1
3PJ6
680R
res
7P61-2
BC847BS
+5VPIP
3PJ5
2
3PJ7
3
4
IP62
820R
2K2
+5VPIP
7P60
74LVC1G66GW
1
1
1
4
X1
35
SUB-SYNC-INSERT
3PJ9
5
4K7
1K8
3PJ8
+5VPIP
FP50
3P74
2R2
IP56
100u
3P85
4K7
5P51
2P81
FP59
3P66
3P65 100R
2P71
FP55
100n
100R
2P78
IP63
IP64
7P56
M62320FP
1
100n
SO
0V1
0V1
0V1
4
5D16D27D39
D0
DATA LATCHES
IN
8
REG
SHIFT
0V1
0V1
0V1
D410D511D612D7
I/O PORT
888
OUTI/O
88
TRANSCEIVER
C BUS
0V1
0V1
RES
PWR
I
2
GND
+5VD
5V2
3P72
4K7
3P70
3P69
3P68
3P67
2P80
4K7
4K7
4K7
4K7
+5VD
8
13
VDD
3
SDA
2
SCL
CHIP SELECT
CS015CS114CS2
16
I/O EXPANDER
9P71
9P70
9P69
8204 000 8475.1
1
23456
7 8 9 101112131415
HA50-PIP
2
B14c(3x),f,g
SWITCH-MAIN
B15c
PIP_RESET
+5V
10u
FBLK
B15c
SWITCH-SUB
B14c(2x)
SDA-S
SCL-S
F_15460_039.eps
080405
A
B
C
D
E
F
G
H
I
Page 70

SSB: PIP Muppet
2PA0 B5
2PA1 B5
2PA2 B5
2PA3 B5
2PA4 C5
2PA5 C5
2PA6 E6
2PA7 D5
2PA8 F2
2PA9 E5
2PB0 F4
2PB1 G4
2PB2 G4
2PB3 G5
2PB4 G5
2PB5 H2
2PB6 G5
2PB7 H5
2PB9 B7
2PC0 B7
1
Circuit Diagrams and PWB Layouts
2PC8 C8
2PC9 C8
2PD0 B9
2PD1 B9
2PD2 B10
2PD3 B10
2PD4 B10
2PD5 B10
2PD6 B10
2PD7 C10
2PD8 C10
2PD9 C112PB8 B7
2PE0 B12
2PE1 E13
2PE2 E13
2PE3 F13
2PE4 G12
2PE5 F12
2PE6 H13
2PF1 D13
2PF2 D13
2PF3 F4
2PF5 D14
2PF6 D14
2PF7 D5
2PF8 G5
2PF9 G12
3PA0 B2
2PC1 B7
2PC2 B7
2PC3 B7
2PC4 B8
2PC5 B8
2PC6 B8
2PC7 C8
2345
3PA1 B4
3PA2 B4
3PA3 B4
3PA4 B4
3PA5 H12
3PA6 C4
3PA7 C4
3PA8 C3
3PA9 C5
3PB0 D4
3PB1 D3
3PB2 D2
3PB3 D3
3PB4 E3
3PB5 E5
3PB6 D5
3PB7 E2
3PB8 E3
3PB9 F2
3PC0 E3
3PC1 F4
3PC2 F3
3PC3 F3
3PC4 G2
3PC5 E4
3PC6 G5
3PC7 G2
3PC8 G3
EN 70FTP2.4E AA 7.
3PC9 G3
3PD0 H3
3PD1 H5
3PD2 H5
3PD3 H4
3PD4 H5
3PD5 I4
3PD6 I5
3PD7 I6
3PD8 I6
3PD9 E5
3PE0 B12
3PE1 B12
3PE2 C13
3PE3 A13
3PE4 B14
3PE5 B14
3PF0 F12
3PF1 G14
3PF2 F12
3PF3 G14
3PF4 F12
3PF5 F4
3PF6 E12
3PF7 E13
3PF8 E12
3PF9 E13
3PG0 F12
3PG1 F13
3PG2 B4
3PG3 B3
3PG4 C4
3PG5 G3
3PG6 H4
3PH2 A7
3PH3 A7
3PH4 A8
3PH5 A9
3PH6 A9
3PH7 A10
3PH8 A11
3PH9 A11
3PI0 A6
5PA0 B6
5PA1 B7
5PA2 B7
5PA3 B8
5PA4 B9
5PA5 B10
5PA6 B10
5PA7 B10
5PA8 B11
5PA9 C14
5PB0 D14
6PA0 D4
6PA1 E2
6PA2 B13
6PB1 B6
6PB2 B7
6PB3 B7
6PB4 B8
6PB5 B9
6PB6 B9
678910
6PB7 B10
6PB8 B10
6PB9 B11
7PA0 B3
7PA1 C3
7PA2 D3
7PA3 D4
7PA4 D5
7PA5 E3
7PA6 C6
7PA7 F2
7PA8 G3
7PA9 H4
7PB0 I5
7PB1 H13
7PB2 B12
7PB3 B13
7PB4 B14
7PB5 E5
7PB6 A4
9PA0 B3
FPA0 E5
FPA7 D15
IP77 C3
IP84 B14
9PA1 C3
9PA2 E4
9PA4 G2
9PA5 G2
9PA6 H3
9PA7 H5
9PA8 I5
9PB1 C14
9PB2 C13
9PB3 B4
9PB4 D3
9PB5 B13
9PB8 E12
FPA1 D5
FPA2 F5
FPA3 F5
FPA4 G6
FPA5 G6
FPA6 B15
FPA8 E15
FPA9 F15
FPB0 C14
FPB1 F5
FPB2 F6
IP76 B3
IP78 D4
IP79 E4
IP80 E2
IP81 H4
IP82 G2
IP83 I5
IP85 B12
IPA1 C14
IPA3 D14
IPA5 F12
IPA6 G12
IPA7 D5
IPA8 D6
IPA9 G6
IPB0 G69PA3 F3
IPB1 B14
IPB2 D2
IPB3 D4
IPB4 B5
IPB5 F3
IPB6 A7
IPB7 A6
IPB8 A8
IPB9 A8
IPC1 A10
IPC2 A9
IPC3 A9
IPC4 B11
IPC5 B11
11 12 13 14 15
B15C B15C
PIP MUPPET
A
B15a
B
C
B15a
U-HIP-OUT
V-HIP-OUT
D
B15a
HS-HIP-OUT
B15a
B15a
B15c(2x)
PIP_RESET
VS-HIP-OUT
SDA-S
HA
SCL-S
E
F
B6a,B15b
IN-Y50
G
B6a,B15b
IN-U50
H
B6a,B15b
IN-V50
B6a,B14c
VA50-PIP
I
B15c(2x)
HA
8204 000 8475.1
123456789101112
6PA1
BAS316
RES
3PB2
1K5
2PA8
100n
2PB5
3PC4
680R
B15a(2x)
+5VPIP
Y-HIP-OUT
9PB3
3PG2
7PA1
BC847BW
RES
7PA3
3PC0
2PB0
1u0
39K
IP81
3K3
RES
RES
680R
3PB0
1K5
3PC1
100R
+5VPIP
7PB6
BC847BW
3PA3
100R
3PA7
100R
680R
3PG4
RES
IPB3
9PA2
3PC5
4K7
2PF3
7PA9
BC847BW
3PG6
680R
3PA1
100R
39K
IP78
6PA0
BZX384-C3V9
150p
3PD3
1K8
3PD5
3K3
RES
3PA4
39K
RES
IP79
RES
2PB1
150p
2PB2
100n
3PA2
2PA2
100n
3PA6
IPB4
3PF5
39K
RES
2PB4
150p
RES
3PD1
39K
3PD2
100R
RES
2PA4
100n
3PB5
1K0
2PA0
1u0
2PA7
100n
RES
7PA4
BC857BW
1K0
2PB7
3PD6
10K
150p
3PB6
9PA7
1K2
RES
150p
2PF7
IP83
2PA1
7PB5
BC847BW
3PC6
100n
BC847BW
2PA3
10u 10V
IPA7
FPA1
39K
7PB0
2PA5
150p
3PA9
39K
FPB1
2PB6
RES
3PD9
RES
2PB3
100n
100n
+3.3V
3PD4
FPA0
2PA9
FPA2
FPA3
2PF8
1V0
2PA6
3K3
3V2
10V
10u
IPA9
IPB0
FPA4
16V10u
FPA5
4K7
RES
9PA8
+5VPIP
IP76
3PA0
220R
IPB2
3PB7
100R
IP80
3K3
3PB9
+5VPIP
7PA7
BC847BW
RES
9PA4
RES
9PA5
IP82
3PC7
220R
47p
+5VPIP
9PA0
BC847BW
7PA8
RES
3PA8
220R
9PA1
+5VPIP
RES
3PB1
3PB4
7PA5
BC847BW
3PG5
680R
3PC8
100R
7PA0
BC847BW
680R
3PG3
IP77
RES
470R
7PA2
BC847BW
1K5
3PC2
100R
RES
9PB4
9PA3
3PC9
3PB8
RES
3PD0
220R
1K8
RES
3PB3
220R
RES
IPB5
3PC3
39K
+5VPIP
BC847BW
9PA6
IPA8
2V7
1V0
2V7
100n
FPB2
47R
3PI0
IPB7
6PB1
BAS316
7PA6
SAB9081H/N4
83
SY
79
SU
81
SV
84
VBIASSA
82
VREFTSA
80
VREFBSA
87
SHSYNC
72
SVSYNC
75
POR
74
SDA
73
SCL
98
MY
2
MU
100
MV
97
VBIASMA
99
VREFTMA
1
VREFBMA
94
DHSYNC
70
DVSYNC
3PD7
21
+3V
+3V
5PA1
820n
5PA0
2PB8
2PC0
10u
2PB9
100n
4
5
3
VSSAMA
VDDAMF
VDDAMA
CLAMP
AND A/D
CONVERTER
PLL AND CLOCK
GENERATION
IIC BUS
CONTROL
CLAMP
AND A/D
CONVERTER
PLL AND CLOCK
GENERATION
NC223NC324NC425NC526NC627NC7
NC1
22
1K2
3K3
3PD8
12u
10u
2PC1
100n
6
VDDADA
47R
6PB2
7
3PH2
IPB6
BAS316
14
VSSADA
+3VD
5PA2
2PC2
15
VDDDDA
4u7
100n
16
VSSDDA
47R
IPB8
6PB3
2PC3
17
VSSDP1
3PH3
+3VD
5PA3
BAS316
10u
RES
20
VDDDP1
4u7
2PC4
2PC7
39
VDDDRP
100n
100n
40
VDDDRL
2PC5
VSSDRL
6PB4
100n
2PC8
41
VSSDRM
47R
2PC6
42
VDDDRM
3PH4
BAS316
10u
100n
61
RES
2PC9
64
VSSDRP
100n
65
VDDDP2
47R
6PB5
VSSDP2
66
VSSDD
3PH5
IPC2IPB9
BAS316
+3V
5PA4
67
VDDDD
820n
2PD0
10u
2PD1
100n
76
VDDASA
77
VSSASA
47R
6PB6
RES
78
VDDASF
3PH6
IPC3
BAS316
2PD2
10u
2PD3
100n
+3VD
5PA5
85
47R
3PH7
12u
90
VDDASP
IPC1
6PB7
2PD4
100n
2PD5
10u
2PD6
10u
2PD7
100n
91
VSSASP
BAS316
16V
VSSADP
+3V
5PA7
92
VDDADP
+3V +3VD
12u
5PA6
86
89
VSSDSA
VDDDSA
12u
95
VDDDMA
LINE MEMORYH/V FILTER
PROCESSING
MUPPET
T5
TEST
CONTROL
T7
88T693
DAC
TCLK
43
TCBD47TCBR
LINE MEMORYH/V FILTER
NC829NC9
NC1052NC1153NC1254NC1355NC1456NC1557NC1658NC17
28
31 71
NC1860NC19
59
37T036T135T234T333T432
47R
6PB8
45
3PH8
IPC4
BAS316
RES
2PD8
96
VSSDMA
DISPLAY
CONTROL
TCBC
46
B14a
+5VPIP
HA50-PIP
3V3_FAULT_PIP
3PF8
820R
270R
16V10u
3PE1
3PG0
560R
2PE5
100n
3PA5
220R
RES
9PB5
470R
7PB2
BC847BW
9PB2
74LVC1G32GW
1
2
RES
BC847BW
1K5
3PE2
2PF1
3PF7
470R
3PF9
120R
3PG1
68R
+3.3V
7PB1
35
47R
3PH9
12u
5PA8
IPC5
6PB9
BAS316
RES
10u
100n
2PD9
2PE0
3PE0
1K5
IP85
3n3
+3V3_SIM
18
VSSDT1
19
VSSDT2
30
VSSDT3
48
VSSDT4
49
VSSDT5
50
VSSDT6
51
VSSDT7
62
VSSDT8
63
VSSDT9
3PF6
560R
9PB8
120R
3PF0
8
DY
12
DU
10
DV
9
VBIASDA
11
VREFTDA
13
VREFBDA
69
PKOFF
68
FBL
TM
TC
DCLK
38
44
IPA6
1V2
0V2
2PE4
IPA5
100n
3PF2
3PF4
22K
2PF9
0V
10u
RES
7PB3
2PF2
RES
RES
RES
4
100n
100n
RES
RES
6PA2
2PE1
2PE2
2PE3
3PE3
IPB1
47p
47p
47p
2PE6
1K5
BZX384-C3V9
5PA9
5PB0
3K3
3PF3
RES
3PE4
220R
9PB1
IP84
FPB0
IPA1
IPA3
3PF1
BC857BW
7PB4
RES
FPA6
1K0
RES
3PE5
+3.3V
+3V
100n
2PF5
RES
+3VD
100n
2PF6
RES
FPA7
FPA8
FPA9
1K5
MUPPET_BLK
F_15460_040.eps
13 14 15
B15c(2x)
HA
B15b
DY
B15b
DU
B15b
DV
B15b
FBLK
B15b
A
B
C
D
E
F
G
H
I
080405
Page 71

Circuit Diagrams and PWB Layouts
EN 71FTP2.4E AA 7.
SSB: HDI A/D Converter
12345
B19A B19A
A
HDI A/D CONVERTER
+3V3-AD
7L02
2L33
100n
LD1117DT33C
3
COM
2
OUTIN
1
2L34
FL17
+5V
6.3V
2L19
22u
FE02
5L16
5L13
100n
5L17
5L14
2L58
IL10
6.3V22u
2L01
100n
2L02
100n
2L03
100n
2L04
100n
2L05
100n
2L06
100n
2L07
100n
2L10
100n
IL11
B
2L00
2L12
100n
2L13
22u 6.3V
5L18
5L15
6.3V
C
2L48
5L02
470n
4p7
RESRES
2L28
39p
B14g
V-2FH
AL06
3L04
100R
2L51
FL09
100n
2L08
2L09
22u
RES
3L19
680R
100n
100n
2L14
2L20
100n
100n
2L15
2L21
3L29
150R
100n
100n
2L16
100n
2L17
100n
IL12
D
2L49
RES
2L50
5L04
470n
4p7
5L06
470n
4p7
AL07
B14g(2x)B19a
Y-2FH
3L05
100R
E
AL08
B14g
B14c,g
U-2FH
HS-2FH
VS-2FH
Y-2FH
F
B14c(2x)
G
B14g(2x),B19a
3L11
100R
PVD
2L31
47n
2L26
H
33n
2L27
4n7
2L32
3n3
IL07
2L30
2L29
3L08
FL10
39p
39p
IL08
2K7
FL12
3L12
470R
RES
3L20
680R
FL11
RES
3L21
2L60
FL13
680R
47p
3L30
150R
3L31
150R
3L32
470R
2L56
1n0
3L33
470R
COAST
RES
2L18
3L06
100R
3L02
RES
470R
47p
RES
2L59
3L03
100R
1n0
VD
VD
VDD
PVD
2L54
47n
2L11
100n
470R
3L28
2L52
47n
2L57
47n
IL09
6
78910
A/D CONVERTER
VDD
7L01
AD9883AKST
112223
69
VDD
54 RAIN
48 GAIN
43 BAIN
IL06
37 MIDSCV
30 HSYNC
31 VSYNC
49 SOGIN
38 CLAMP
COAST 67DATACK
29
33 FILT
57 SDA
56 SCL
55 A0
CLAMP
CLAMP
PVD
78
79
39424546515259
266227
VD
A/D
A/DCLAMP
A/D
SYNC
PROCESSING
AND CLOCK
GENERATION
SERIAL REGISTER
AND
PWR MANAGMENT
8
8
8
REF
VD
34
PVD
ROUTA0
ROUTA1
ROUTA2
ROUTA3
ROUTA4
ROUTA5
ROUTA6
ROUTA7
GOUTA0
GOUTA1
GOUTA2
GOUTA3
GOUTA4
GOUTA5
GOUTA6
GOUTA7
BOUTA0
BOUTA1
BOUTA2
BOUTA3
BOUTA4
BOUTA5
BOUTA6
BOUTA7
REF-BYPASS
PVD
35
77
76
75
74
73
72
71
70
9
8
7
6
5
4
3
2
19
18
17
16
15
14
13
12
FL15
66HSOUT
FL03
64VSOUT
FL04
65SOGOUT
AL02
FL05
58
100n
to EPLD
UV-AD-0
UV-AD-1
UV-AD-2
UV-AD-3
UV-AD-4
UV-AD-5
UV-AD-6
UV-AD-7
H-2FH-AD-OUT
V-2FH-AD-OUT
SYNCDET
CLK-2FH
2L25
GND
202124
1
252832
4041444750
36
53606163681080
I
SDA-F3
8204 000 8484.1
12345
6
78910
Y-AD-0
Y-AD-1
Y-AD-2
Y-AD-3
Y-AD-4
Y-AD-5
Y-AD-6
Y-AD-7
U-AD-0
U-AD-1
U-AD-2
U-AD-3
U-AD-4
U-AD-5
U-AD-6
U-AD-7
SCL-F3
11
B19d
B19d
B19d
B19d
B14g,B19d
B19d
B19b
B19b,d
B19b,d
F_15460_041.eps
11
080405
A
B
C
D
E
F
G
H
I
2L00 B3
2L01 A4
2L02 A4
2L03 A4
2L04 A4
2L05 A4
2L06 A5
2L07 A5
2L08 C4
2L09 C4
2L10 A5
2L11 F6
2L12 B4
2L13 B4
2L14 B4
2L15 B4
2L16 B4
2L17 B5
2L18 E5
2L19 A1
2L20 C4
2L21 C4
2L25 H10
2L26 H2
2L27 H2
2L28 D3
2L29 E3
2L30 F3
2L31 H2
2L32 H2
2L33 A2
2L34 A3
2L48 D2
2L49 E2
2L50 F2
2L51 C3
2L52 C6
2L54 F6
2L56 G4
2L57 E6
2L58 A3
2L59 E5
2L60 G4
3L02 E5
3L03 H5
3L04 C2
3L05 E2
3L06 H5
3L08 H3
3L11 F2
3L12 G3
3L19 D4
3L20 E4
3L21 F4
3L28 G6
3L29 C4
3L30 E4
3L31 F4
3L32 G4
3L33 G5
5L02 C2
5L04 E2
5L06 F2
5L13 A3
5L14 B3
5L15 C3
5L16 A3
5L17 B3
5L18 B3
7L01 C6
7L02 A2
AL02 G10
AL06 C1
AL07 E1
AL08 F1
FE02 A3
FL03 G10
FL04 G10
FL05 H10
FL09 C3
FL10 E3
FL11 G4
FL12 F3
FL13 G4
FL15 G10
FL17 A1
IL06 F6
IL07 H3
IL08 H3
IL09 H6
IL10 A5
IL11 B5
IL12 C5
Page 72

Circuit Diagrams and PWB Layouts
EN 72FTP2.4E AA 7.
SSB: EPLD Control
123
B19B B19B
EPLD CONTROL
A
+3V3-IO
+3V3-IO
B
100n
2E84
C
+3V3-IO
7E02
EPCS4SI8
378
VCC
Φ
SCD
26
DATA
GND
1
CS_
DCLK
5
ASDI
4
3E00
10K
3E59
IE22
IE21
7E25
BC857BW
IE25
+3V3-IO
10K
3E64
10K
7E26
BC857BW
7E27
BC857BW
IE36
IE34
IE35
D
7E05
3E55
7E12-2
BC847BS
1
IE27
IN
10K
LF15ABDT
OUTIN
COM
2 GND
2D04
+3V3-SD
FE59
1n0
2D09
2E67
OUT
3
2E49
7E12-1
BC847BS
100n
2D10
100n
2E66
100n
FE60
1u0
100n
2E50
2D11
2E65
+1V5
47u 4V10n
2E82
100n
FE61
2D12
2E62
100n
2E83
10n
100n
+3V3-EPLD
100n
2E86
3E57
E
IE26
100K
3E56
2E51
FE67
1u0
33K
F
G
H
+1V5-PLL
+1V5-INT
+3V3-IO
I
2E81
1u0
2E78
100n
2E77
100n
2E75
100n
2E74
100n
2E73
100n
2E72
100n
2E71
8204 000 8484.1
12
34
456789
10K
3E60
3E77
47R
100p
2E88
RES
3E78
47R
FE55
FE51
FE54
100p
1E02
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
147279-2
FOR
FACTORY
USE
ONLY
CLK32P_EPLD
FE66
100p
2E89
RES
3E79
47R
100p
2E90
RES
3E80
47R
2E91
RES
res
2E96
100p
3E01
1K0
2E97
100p
3E02
1K0
2E98
100p
3E03
1K0
+3V3-EPLD
IE20
IE23
IE24
3E51
+3V3-IO
+3V3-IO
+3V3-IO
+3V3-IO
10K
3E50
1
IN
100n
10K
3E52
1K0
9E59
res
7E01
LF15ABDT
OUTIN
COM
GND
2
H2
K4
G4
K3
J3
J2
K13
J13
H3
J4
3E62
+3V3_SIM
3
OUT
2E41
DATA0
DCLK
CSO
ASDO
0
MSEL
1
CONF_DONE
STATUS
CONFIG
CE
6E51
BAS316
FE05
100n
2E80
7V01-1
EP1C12F256C8
Φ
CONTROL
5E53
10u
1n0
2D03
IE37
100n
100n
2E79
3E61
47R
2E42
SCAN
TDO
TMS
CEO
CLK
TDI
TCK
0
1
2
3
2E87
+2V5-IO
10n
2E99
H14
H15
J14
J15
G16
H16
100u 16V
H4
G1
H1
FE56
PROT
4V47u
10K
3E73
+3V3-EPLD
B19b
9E62
9E63
9E64
9E65
3E53
10K
10K
3E63
FE53
res
res
9E60
9E61
10K
2E43
I2C BUFFER
5E54
+3V3-EPLD
FOR FACTORY
B19b
USE ONLY
1E04
1
2
3
B3B-PH-SM3-TBT
B19b
SDA-EPLD
B3a
SCL-EPLD
B19b(5x),B19d(2x)
B12
7E10
PCA9515DP
+3V3-EPLD
5E58
100n
2E52
8
VCC
SDA03 SDA1 6
SCL02 SCL1 7
EN5
GND
9E58
9E57
NC
4
RES
RES
4K7
3E69
B3A
B3A
1
3E70
4K7
I2C BUFFER
891011
2E59
100n
10n
2E54
10n
2E70
2E58
100n
10n
2E01
10n
2E69
2E57
FE58
100n
10n
2E03
10n
2E68
2E56
FE57
100n
10n
2E06
10n
2E55
BAS316
6E54
100n
IE32
6E53
BAS316
5E52
6E52
BAS316
BAS316
1u0
6E55
5E51
IE31
3E74
47R
5E50
3E58
47R
IE29
3E54
47R
+1V5
IE30
3E88
47R
+3V3-EPLD
3E89
+1V5
47R
2D15
RES
10n
B19b
3V3_FAULT
PROT
PROT
B3a
PROT
PROT
567
FE52
CLK-VID
CLK64
CLK-2FH
REFCLK
B3a,B19b
B19b,d
B19d
B19b,d
SDA-F3
SCL-F3
B19b
+3V3-IO
2E92
RES
B19d
B3a,B19b
B3c
B19a
B19b
SWITCH-2FH
CLK32E
SWITCH-2FH
B19a,d,c
B19a,d,c
REFCLK
100p
CLK32P_EPLD
10 11 12 13
7V01-6
+2V5-IO
+3V3-IO
+1V5-INT
+1V5-PLL
EP1C12F256C8
BANK1
BANK2
BANK3
BANK4
VCCINT
PLL1
PLL2
POWER
VCCIO
VCCA
Φ
GNDG
C1
G6
P1
A14
F10
F7
A3
P16
K11
C16
T3
L7
L10
T14
A7
A10
G8
G10
H7
H9
J8
J10
K7
K9
T7
T10
H6
H11
GNDA
GND
PLL1
PLL2
PLL1
PLL2
A1
A16
A5
A12
F6
F8
F9
F11
G7
G9
G11
H8
H10
J7
J9
K6
K8
K10
L6
L8
L9
L11
T1
T5
T12
T16
J6
J11
J5
J12
+3V3-EPLD
5E55
IE33
3E84
6E56
BAS316
100n
2E94
7E03
74LVC1G126GW
3E83
10R
74LVC1G125GW
10R
3E86
10R
5
2
1
EN
3
3E20
10R
7E04
5
2
1
EN
3
3E21
10R
3E82
4
2E93
10R
100n
3E85
4
10R
3E81
47R
PROT
CLK32I
+3V3-EPLD
res
5E56
7E06
4
FXO-34FL
1
FE50
3E87
47R
2E95
res
100n
3
res
2
res
14M31818
F_15460_042.eps
12 13
B19b
B3c
080405
A
B
C
D
E
F
G
H
I
1E02 B9
1E04 G6
2D03 E5
2D04 F3
2D09 G3
2D10 G3
2D11 G3
2D12 G3
2D15 I5
2E01 G4
2E03 G4
2E06 G4
2E41 F5
2E42 F6
2E43 F4
2E49 E3
2E50 E3
2E51 E2
2E52 G8
2E54 G4
2E55 H4
2E56 H4
2E57 H4
2E58 H4
2E59 H4
2E62 H3
2E65 H3
2E66 H3
2E67 H3
2E68 I4
2E69 I4
2E70 I4
2E71 I4
2E72 I3
2E73 I3
2E74 I3
2E75 I3
2E77 I2
2E78 I2
2E79 F5
2E80 F5
2E81 I2
2E82 G3
2E83 G4
2E84 B1
2E86 E2
2E87 E6
2E88 A8
2E89 B8
2E90 B8
2E91 C8
2E92 B9
2E93 G12
2E94 E12
2E95 I12
2E96 B4
2E97 C4
2E98 C4
2E99 F6
3E00 B2
3E01 B4
3E02 C4
3E03 D4
3E20 F11
3E21 H11
3E50 B4
3E51 B4
3E52 B4
3E53 B7
3E54 G5
3E55 E2
3E56 E2
3E57 E2
3E58 G5
3E59 B3
3E60 A8
3E61 E6
3E62 D5
3E63 B7
3E64 B3
3E69 H8
3E70 H9
3E73 B6
3E74 I5
3E77 A8
3E78 A8
3E79 B8
3E80 C8
3E81 E12
3E82 F12
3E83 F11
3E84 G10
3E85 G12
3E86 G11
3E87 I11
3E88 H5
3E89 I5
5E50 H5
5E51 I5
5E52 G5
5E53 D6
5E54 F5
5E55 E11
5E56 H11
5E58 G8
6E51 E5
6E52 G5
6E53 G5
6E54 I5
6E55 H5
6E56 E12
7E01 E5
7E02 B2
7E03 F11
7E04 G11
7E05 D3
7E06 I12
7E10 H8
7E12-1 F3
7E12-2 E2
7E25 C3
7E26 B3
7E27 C3
7V01-1 B5
7V01-6 A12
9E57 I8
9E58 I8
9E59 E5
9E60 C7
9E61 D7
9E62 C7
9E63 C7
9E64 C7
9E65 D7
FE05 F5
FE50 I10
FE51 B8
FE52 A9
FE53 C7
FE54 C9
FE55 B8
FE56 D6
FE57 H4
FE58 I4
FE59 G3
FE60 F3
FE61 E3
FE66 B9
FE67 E2
IE20 B4
IE21 C3
IE22 B3
IE23 C4
IE24 C4
IE25 C3
IE26 E2
IE27 E2
IE29 G5
IE30 H5
IE31 I5
IE32 G5
IE33 E12
IE34 C3
IE35 C4
IE36 B4
IE37 E5
Page 73

Circuit Diagrams and PWB Layouts
EN 73FTP2.4E AA 7.
SSB: EPLD OSD
12345678910
B19C B19C
EPLD OSD
+3V3-AD
5E00
VBL
A
100n
100n
2E09
2E07
VBL
B
B3a
3E37
BL-OSD
100R
10p
2E39
C
1K5
3E05
2E02
D
E
F
B19c
CLK-BL
IE03
3E15
100R
2E32
3E13
1K0
10p
100n
+3V3-AD
3E09
7E22
BC847BW
3E04
3E90
100R
IE04
1K0
68R
G
H
7E24
5
8
AD9283BRS-50
7
AIN+
620
AIN-
1
PWRDWN
10
ENCODE
2
VREFOUT
3
VREFIN
100n
2E04
3E10
33R
RES
9E74
IE05
15
VDD
VD
Φ
4
8-BIT
ADC
GND
9
DATA
16
9E78
0
19
1
18
2
17
3
14
4
13
5
12
6
11
7
BACKLIGHT-DIMMING
BL-OSD-1
BL-OSD-2
BL-OSD-3
BL-OSD-4
BL-OSD-5
BL-OSD-6
BL-OSD-7
B3a
B3a
B3a
B3a,B19d
B3a
PVDO
2E28
47n
2E29
33n
2E30
4n7
2E34
3n3
R-OSD
G-OSD
B-OSD
HD3-OTC
VD-OTC
2E05
B19d
IE00
FL01
100n
3E16
2K7
5E01
5E02
5E03
IE01
2E10
2E16
2E08
100n
100n
100n
2E11
2E17
2E20
FE01
100n
100n
100n
2E12
2E18
FE03
100n
100n
2E13
2E19
100n
100n
2E53
3E11
470R
100n
100n
2E14
2E15
3E06
100R
3E07
100R
3E08
100R
10p
3E12
470R
2E48
10p
3E18
100R
2E22
2E24
2E26
22p
22p
22p
VDO
IL01
VDDO
IL02
PVDO
IL03
VDDO
7E23
AD9883AKST
2E21
54 RAIN
47n
2E23
48 GAIN
47n
2E25
2E27
100n
3E14
1K0
3E19
100R
43 BAIN
47n
IL05
37 MIDSCV
30 HSYNC
31 VSYNC
49 SOGIN
CLAMP
38
29 COAST 67DATACK
33 FILT
57 SDA
56 SCL
55 A0
A/D CONVERTER
PVDO
11
22
CLAMP
CLAMP
236978
VDD
79
PROCESSING
AND CLOCK
GENERATION
SERIAL REGISTER
27394245465152
26
VD
SYNC
AND
A/D
A/DCLAMP
A/D
59
8
8
8
REF
PWR MANAGMENT
I
20
1
2124252832
GND
36
404144
475053606163681080
11 12 13
PVDO
VDO
62
35
34
PVD
77
ROUTA0
76
ROUTA1
75
ROUTA2
74
ROUTA3
73
ROUTA4
72
ROUTA5
71
ROUTA6
70
ROUTA7
9
GOUTA0
8
GOUTA1
7
GOUTA2
6
GOUTA3
5
GOUTA4
4
GOUTA5
3
GOUTA6
2
GOUTA7
19
BOUTA0
18
BOUTA1
17
BOUTA2
16
BOUTA3
15
BOUTA4
14
BOUTA5
13
BOUTA6
12
BOUTA7
66HSOUT
64VSOUT
REF-BYPASS
65SOGOUT
58
FE04
100n
3E91
33R
AL10
2E35
R-OSD-0
R-OSD-1
R-OSD-2
R-OSD-3
R-OSD-4
R-OSD-5
R-OSD-6
R-OSD-7
G-OSD-0
G-OSD-1
G-OSD-2
G-OSD-3
G-OSD-4
G-OSD-5
G-OSD-6
G-OSD-7
B-OSD-0
B-OSD-1
B-OSD-2
B-OSD-3
B-OSD-4
B-OSD-5
B-OSD-6
B-OSD-7
B19c,d
CLK-OSD
CLK-BL
B19c
B19d
A
B
C
D
E
F
G
H
I
2E02 D1
2E04 D2
2E05 B4
2E07 A5
2E08 C5
2E09 A6
2E10 B5
2E11 B6
2E12 B6
2E13 B6
2E14 B6
2E15 B6
2E16 B5
2E17 B6
2E18 B6
2E19 B6
2E20 C6
2E21 D8
2E22 D7
2E23 E8
2E24 E7
2E25 F7
2E26 G7
2E27 G7
2E28 H4
2E29 H4
2E30 H4
2E32 F1
2E34 H4
2E35 I12
2E39 B1
2E48 G6
2E53 G6
3E04 D1
3E05 C1
3E06 D6
3E07 E6
3E08 F6
3E09 E1
3E10 E2
3E11 G6
3E12 G6
3E13 E1
3E14 G7
3E15 F1
3E16 H5
3E18 H7
3E19 H7
3E37 B1
3E90 D1
3E91 H12
5E00 A5
5E01 A5
5E02 B5
5E03 C5
7E22 E1
7E23 C8
7E24 B2
9E74 E2
9E78 B3
AL10 H12
FE01 G6
FE03 G6
FE04 H12
FL01 A4
IE00 H4
IE01 H5
IE03 E1
IE04 E2
IE05 F2
IL01 A7
IL02 B7
IL03 C7
IL05 G8
8204 000 8484.1
B19a,b,d
SDA-F3
B19a,b,d
SCL-F3
1
2
3456
7 8 9 10 11 12 13
F_15460_043.eps
080405
Page 74
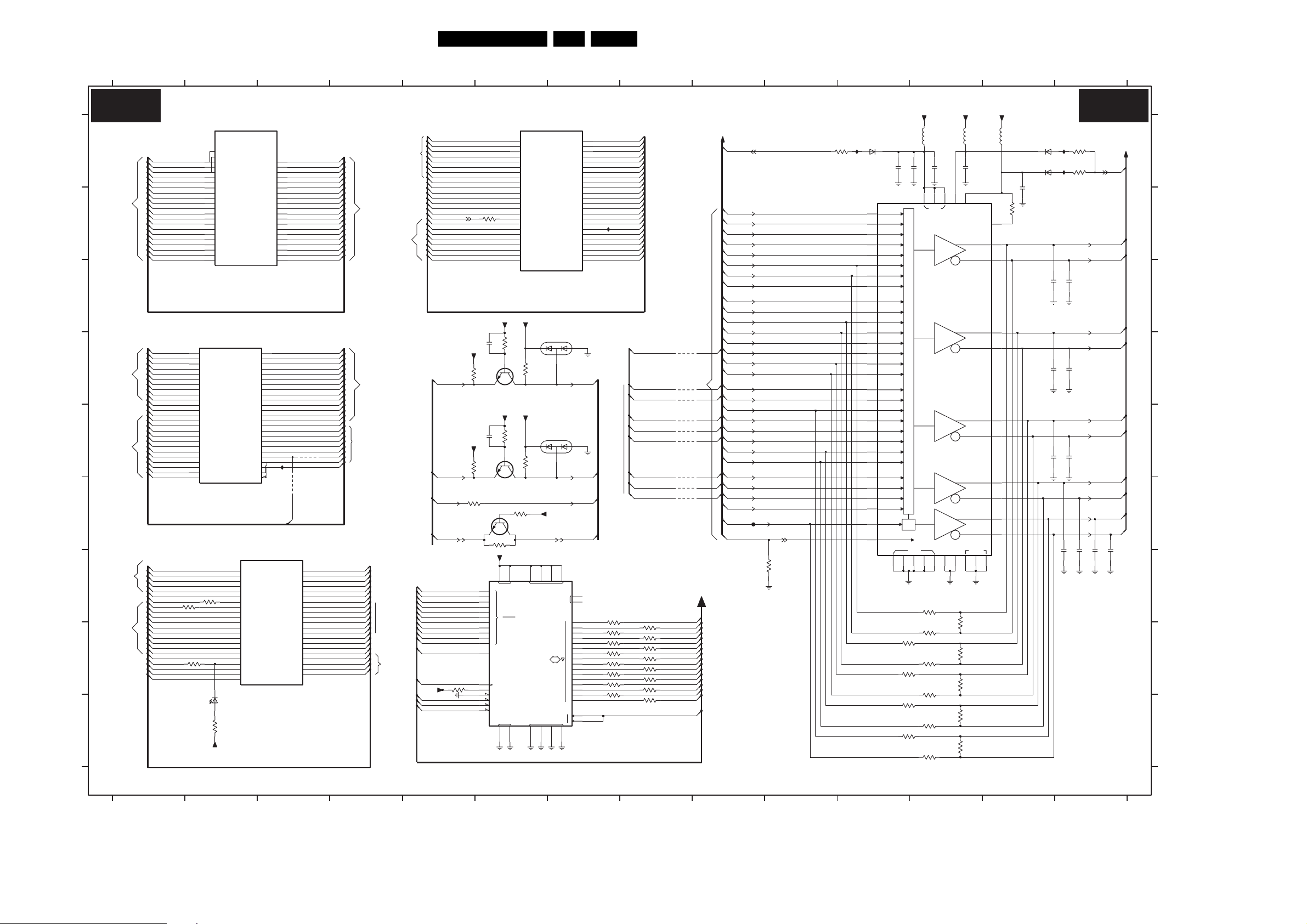
Circuit Diagrams and PWB Layouts
EN 74FTP2.4E AA 7.
SSB: EPLD I/O
B19d
B19d
B19b
R0
R1
R6
9
PROT
R0
R1
R2
R3
R4
R7
R5
G0
G1
G2
G6
G7
G3
G4
G5
B0
B6
B7
B1
B2
B3
B4
B5
PARITY
HS-OUT
VS-OUT
DE-OUT
R6
AV01
CLK-OUT
LVDS-PWR-DOWN
123456
B19D B19D
A
B19c
B
EPLD I/O
B-OSD-3
BL-OSD-7
B-OSD-2
BL-OSD-5
R-OSD-4
G-OSD-6
B-OSD-4
B-OSD-7
G-OSD-5
G-OSD-2
B-OSD-5
G-OSD-3
B-OSD-6
G-OSD-7
R-OSD-5
R-OSD-2
G-OSD-4
R-OSD-6
R-OSD-3
R-OSD-7
D4
C3
C2
B1
G5
F4
D3
E4
F5
E3
D2
E2
D1
F3
G3
F2
E1
G2
F1
H5
INIT_DONE
CLKUSR
IO_1
IO_2
IO_3
IO_4
IO_5
IO_6
IO_7
IO_8
IO_9
IO_10
IO_11
IO_12
IO_13
IO_14
IO_15
IO_16
IO_17
IO_18
IO_19
IO_20
7V01-2
EP1C12F256C8
Φ
BANK 1
IO_21
IO_22
IO_23
IO_24
IO_25
IO_26
IO_27
IO_28
IO_29
IO_30
IO_31
IO_32
IO_33
IO_34
IO_35
IO_36
IO_37
IO_38
IO_39
IO_40
J1
K2
L3
K1
L1
L2
M1
N1
M2
N2
M3
L5
M4
N3
K5
L4
R1
P2
P3
N4
CLK-OUT
HS-OUT
VS-OUT
LVDS-PWR-DOWN
PARITY
DE-OUT
7V01-5
EP1C12F256C8
IO_41
IO_42
IO_43
IO_44
IO_45
IO_46
IO_47
IO_48
IO_49
IO_50
IO_51
IO_52
IO_53
IO_54
IO_55
IO_56
IO_57
IO_58
IO_59
IO_60
IO_61
IO_62
IO_63
IO_64
Φ
BANK 4
100R
R2
T2
R3
P4
R4
T4
R5
P5
M5
M6
N5
N6
P6
R6
M7
T6
R7
P7
N7
R8
T8
M8
N8
P8
R6
R0
R1
B19d
G1
R2
B3b,c
B19d
B3b,c
B3b,c
B20,B21
R3
R4
G0
B2
UVG(0)
G3
UVG(1)
UVG(2)
LAMP
UVG(3)
LCD-PWR-ON
UVG(6)
UVG(5)
UVG(4)
YG(2)
YG(3)
UVG(7)
YG(0)
YG(1)
3V36
B1
B5
B6
B7
B0
G5
B3
G7
G6
B4
R5
R7
G2
G4
B19d
B19d,B3b,c
B13b,B20(2x)
B3b,c
78
M10
HREF_EXT
IO_65
IO_66
IO_67
IO_68
IO_69
IO_70
IO_71
IO_72
IO_73
IO_74
IO_75
IO_76
IO_77
IO_78
IO_79
IO_80
IO_81
IO_82
IO_83
IO_84
IO_85
IO_86
IO_87
IO_88
R9
T9
P9
N9
R10
T11
N10
P10
RSTR_EPLD
R11
SN-CL_EPLD
P11
SN-DA_EPLD
N11
N12
M9
M11
M12
P12
IV05
R12
T13
R13
R14
P13
T15
R15
YG(7)
VD-OTC
YG(6)
YG(5)
HD3-OTC
VREF
HREF
FALREF
YG(4)
VD_E
REFIN
HD_E
U_VOUT(9)
U_VOUT(8)
U_VOUT(5)
U_VOUT(7)
U_VOUT(4)
U_VOUT(3)
B3a,c,d
B3b,c
B3a
B3b,c
B3b,c
B3a,B19c
B3a
VA
B3a
B3c
B3c
B3c
B3c
B3c
B3b,c
B3a
B3c
REF
B3c
B3a,c
B3c
B3c
B3c
B3c
B3c
B3c
C
+5V+3V3-IO
6V06
VDDQ
VSSQ
6V07
+3V3-IO
D
BAV99 COL
BAV99 COL
44
NC
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
U
DQM
L
RES
AL-CL
B21
RES
B21
AL-DA
B21
B20,B21B3b,e,B19d
33
37
2
3V21-4 68R45
3
3V21-2 68R27
5
6
8
9
11
12
3V23-1 68R
39
40
42
3V23-3 68R36
43
45
3V24-1 1 8
46
48
49
36
14
BL-OSD-2 G1
B19c,d
BL-OSD-1
BACKLIGHT-DIMMING R3
G-OSD-1 B2
G-OSD-0 G0
B19c
B-OSD-1 R2
B-OSD-0
R-OSD-1
R-OSD-0 G3
36
3V21-3
3V21-1
18
68R3V22-4 4 5
3V22-3
68R3V22-2
3V22-1
3V23-2
3V23-4
68R
3V24-2
68R3V24-3 3 6
3V24-4
36
1 8 68R
27
45
27
18
68R
68R
68R
68R27
68R45
68R
68R
9E77
9E70
9E66
9E67
9E68
9E69
9E71
9E72
9E73
SD-DQ1
SD-DQ2
SD-DQ3
SD-DQ4
SD-DQ5
SD-DQ6
SD-DQ7
SD-DQ8
SD-DQ9
SD-DQ10
SD-DQ11
SD-DQ12
SD-DQ13
SD-DQ14
SD-DQ15
SD-DQ16
SD-DQM
UV-AD-2
UV-AD-4
UV-AD-3
B19d
B19a
Y-AD-7
UV-AD-5
UV-AD-6
UV-AD-7
UV-AD-0
U-AD-6
Y-AD-4
SD-DQM
Y-AD-3
SD-DQ1
SD-DQ2
SD-DQ16
SD-DQ15
SD-DQ13
SD-DQ14
SD-DQ3
SD-DQ12
SD-DQ11
SD-DQ6
SD-DQ5
SD-DQ4
SD-DQ7
D
E
B19a
B19d
B15
IO_132
IO_133
IO_134
IO_135
IO_136
IO_137
IO_138
IO_139
IO_140
IO_141
IO_142
IO_143
IO_144
IO_145
IO_146
IO_147
IO_148
IO_149
IO_150
IO_151
IO_152
IO_153
IO_154
IO_155
IO_156
Φ
BANK 2
A15
B14
C13
B13
A13
B12
C12
E12
E11
E9
D12
D11
C11
B11
A11
B10
C10
D10
A9
B9
D9
C9
E10
C8
F
IO_157
IO_158
IO_159
IO_160
IO_161
IO_162
IO_163
IO_164
IO_165
IO_166
IO_167
IO_168
IO_169
IO_170
IO_171
IO_172
IO_173
IO_174
IO_175
IO_176
IO_177
IO_178
IO_179
DEV_OE
DEV_CLR
D8
E8
A8
B8
D7
C7
B7
A6
E7
B6
C6
D6
D5
E6
E5
C5
B5
A4
B4
C4
B3
A2
B2
IV01
9E76
9E75
SD-DQ8
SD-WE
SD-DQ10
SD-DQ9
SD-RAS
SD-CAS
SD-A9
SD-A8
SD-A11
SD-A7
SD-A10
SD-A0
SD-A3
SD-A1
CLK-OSD
SD-A2
SD-A6
SD-A5
SD-A4
BL-OSD-6
BL-OSD-2
BL-OSD-3
BL-OSD-4
B19c(2x)
B19d
B19c(4x)
B19d
B19d
B19d
B19d
RST-FBX
+3V3-IO
3V50
AL-CL-IN
+3V3-IO
3V55
AL-DA-IN
3V56
R4 ODC
100R
BC847BW
7V06
7V01-3
EP1C12F256C8
LAMP LAMP-ON
7V01-4
EP1C12F256C8
U_VOUT(6)
B19a,b,c
B19a,b,c
B19b
U_VOUT(2)
U_VOUT(0)
U_VOUT(1)
YOUT(1)
YOUT(2)
SCL-F3
SDA-F3
YOUT(7)
YOUT(0)
YOUT(3)
YOUT(4)
YOUT(8)
YOUT(5)
YOUT(6)
YOUT(9)
O_VAL
CLK32E
FRAME
SWITCH-2FH
SD-CLK
SYNCDET
3V38
3V37
100R
3V40
G
B3c
B3c
H
B21,B19b(2x)
B19d
B19a
I
100R
6V05
3V18
+3V3-IO
100R
TLMG3100
390R
N13
P14
P15
R16
N15
N16
K12
K14
L12
N14
M13
M14
L13
M15
M16
L14
L15
L16
K16
K15
J16
H12
IO_89
IO_90
IO_91
IO_92
IO_93
IO_94
IO_95
IO_96
IO_97
IO_98
IO_99
IO_100
IO_101
IO_102
IO_103
IO_104
IO_105
IO_106
IO_107
IO_108
IO_109
IO_110
Φ
BANK 3
IO_111
IO_112
IO_113
IO_114
IO_115
IO_116
IO_117
IO_118
IO_119
IO_120
IO_121
IO_122
IO_123
IO_124
IO_125
IO_126
IO_127
IO_128
IO_129
IO_130
IO_131
G14
V-2FH-AD-OUT
G13
H-2FH-AD-OUT
G15
F16
F14
F13
F15
E16
E15
D16
D15
E14
F12
E13
D14
H13
G12
B16
C15
C14
D13
H-2FH-DIV-2
CLK-VID
COAST
AL-CL-IN
U-AD-0
AL-DA-IN
U-AD-2
U-AD-3
U-AD-7
Y-AD-0
U-AD-4
U-AD-1
U-AD-5
Y-AD-1
HS-DET
UV-AD-1
Y-AD-5
Y-AD-6
Y-AD-2
B14g,B19a
B19a
B19d
B19d
B19a
B19d
B19a
B14g
B14f,g
B19a
SD-A0
SD-A1
SD-A2
SD-A3
SD-A4
SD-A5
SD-A6
SD-A7
SD-A8
SD-A9
SD-A10
SD-A11
SD-CLK
+3V3-SD
SD-RAS
SD-CAS
SD-WE
MSM56V16160F-7T3
3V39
4K7
7V03
21
22
23
24
27
28
29
30
31
32
20
19
35
34
18
17
16
15
10K
10K
2V12
2V11
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
A11
CKE
CS
RAS
CAS
WE
470p
470p
3V35
100R
CLK
3V51
1
+3V3-IO
3V54
4
+3V3-SD
1
VDD
A
512K-1
VSS
26
BC847BS
BC847BS
10K
2
47K
3V52
6
7V04-1
+5V
10K
5
47K
3V53
3
7V04-2
3V57
*
10K
*
*
25
71338
Φ
DRAM
512K X 16 X 2
0
4
50
104147
8204 000 8484.1
1
32
45
678
10 11 12
IV04
BAS316
3V14
47R
6V01
7V02
DS90C385MTD
52
4
18
27
4K7
3V07
LVDS TRANSMITTER
109
100n
TXIN051
TXIN1
TXIN254
TXIN355
TXIN456
TXIN52
TXIN63
TXIN7
TXIN86
TXIN97
TXIN108
TXIN1110
TXIN1211
TXIN1312
TXIN1414
TXIN1515
TXIN1616
TXIN17
TXIN1819
TXIN1920
TXIN2022
TXIN2123
TXIN2224
TXIN2325
TXIN24
TXIN2528
TXIN2630
TXIN2750
TXCLKIN31
PWRDWN_32
513212953
+3V3-EPLD
5V06
100n
100n
2V10
2V07
2V09
9
1
26
VCC
TTL PARALLEL-TO-LVDS TTL PARALLEL-TO-LVDS
PLL
3V25
120R
3V26
120R
3V28
120R
3V30
120R
3V32
120R
3V34
120R
PLL
GND
35
GND
3V27
120R
3V29
120R
3V31
120R
3V33
120R
1211
+3V3-EPLD
5V07
12
2V08
34
44
PLLVCC
LVDSVCC
TXCLKOUT- 40
TXCLKOUT+ 39
LSVD
GND
33
364349
3V01
180R
3V02
180R
3V17
180R
3V19
180R
3V20
180R
+3V3-EPLD
100n
R-FB
TXOUT0- 48
TXOUT0+ 47
TXOUT1- 46
TXOUT1+ 45
TXOUT2-
TXOUT2+ 41
TXOUT3- 38
TXOUT3+ 37
13 14
5V08
17
42
3V08
2V06
1K0
BAS316
6V02
BAS316
6V03
100n
13
2V16
2V18
2V20
IV03
IV02
10p
10p
10p
2V22
2V17
2V19
2V21
10p
3V15
3V16
47R
47R
10p
10p
10p
2V23
10p
2V24
14
TXLCD0-
TXLCD0+
TXLCD1-
TXLCD1+
TXLCD2-
TXLCD2+
TXLCD3-
TXLCD3+
TXCLKLCD-
TXCLKLCD+
10p
2V25
F_15460_044.eps
PROT
10p
B19b
B20
B20
B20
B20
B20
B20
B20
B20
B20
B20
080405
A
B
C
D
E
F
G
H
I
2V06 B13
2V07 A11
2V08 A12
2V09 A12
2V10 A12
2V11 E6
2V12 D6
2V16 C13
2V17 C14
2V18 D13
2V19 D14
2V20 E13
2V21 E14
2V22 G14
2V23 G14
2V24 G14
2V25 G14
3V01 H12
3V02 H12
3V07 G10
3V08 B13
3V14 A11
3V15 A14
3V16 A14
3V17 H12
3V18 I2
3V19 I12
3V20 I12
3V21-1 H8
3V21-2 H7
3V21-3 H8
3V21-4 G7
3V22-1 H8
3V22-2 H7
3V22-3 H8
3V22-4 H7
3V23-1 H7
3V23-2 H8
3V23-3 H7
3V23-4 H8
3V24-1 H7
3V24-2 H8
3V24-3 H7
3V24-4 I8
3V25 G12
3V26 H12
3V27 H11
3V28 H12
3V29 H11
3V30 H12
3V31 I11
3V32 I12
3V33 I11
3V34 I12
3V35 F6
3V36 B6
3V37 G2
3V38 G1
3V39 H5
3V40 H1
3V50 D5
3V51 D6
3V52 D6
3V53 E6
3V54 E6
3V55 E5
3V56 F5
3V57 F6
5V06 A12
5V07 A12
5V08 A13
6V01 A11
6V02 A13
6V03 A13
6V05 I2
6V06 D7
6V07 E7
7V01-2 A2
7V01-3 D2
7V01-4 G3
7V01-5 A7
7V02 B11
7V03 G6
7V04-1 D6
7V04-2 F6
7V06 F6
9E66 D8
9E67 E8
9E68 E8
9E69 E8
9E70 D8
9E71 E8
9E72 F8
9E73 F8
9E75 E3
9E76 F3
9E77 D8
AV01 F9
IV01 E3
IV02 A14
IV03 A14
IV04 A11
IV05 B7
Page 75

SSB: Backlight Control
2L22 B3
3L40 A1
3L41 A2
3L42 A3
3L43 B2
1234
Circuit Diagrams and PWB Layouts
3L45 B2
3L46 B1
3L47 B1
3L48 B3
3L49 B4
7L03-1 B4
7L04-2 B3
7L05 B2
9L00 B4
9L01 B2
FL06 B4
IL13 B3
EN 75FTP2.4E AA 7.
IL14 B2
IL15 A33L44 B2
Personal Notes:
B19E B19E
BACKLIGHT CONTROL
3L48
*
27K
*
RES
+8V
3L42
4K7
IL15
BC847BPN
7L04-2
9L00
*
*
RES
7L03-1
BC847BPN
BACKLIGHT-CNTRL-DC
10K
RES
3L49
FL06
A
B
C
B5a
B10c
BACKLIGHT-CNTRL
BACKLIGHT-DIMMING
*
*
3L40
3L46
1K2
2K2
*
3L47
3L44
4K7
3L45
4K7
10K
IL14
*
+5V+5V
3L41
7L05
BC847BW
*
4K7
10K
3L43
9L01
*
*
2L22
100n
IL13
*
A
B4
B
C
8204 000 8484.1
1234
F_15460_045.eps
080405
E_06532_012.eps
131004
Page 76

SSB: Screen Interface
Circuit Diagrams and PWB Layouts
EN 76FTP2.4E AA 7.
1
B20 B20
B19d
LCD-PWR-ON
A
B
C FZ43 A2
D
E
(IRQ)
B19d,B21
LAMP-ON
(PDWN)
B14e
CPU-GO
B4
BACKLIGHT-CNTRL
PDP-GO
B14e
B19d
TXLCD0-
B19d
TXLCD0+
B19d
TXLCD1-
B19d
TXLCD1+
B19d
TXLCD2-
B19d
TXLCD2+
B19d
TXCLKLCD-
B19d
TXCLKLCD+
B19d
TXLCD3-
B19d
TXLCD3+
B19e
SCL-DISP
SCREEN INTERFACE
3Z37
3Z39
100R
3Z22
resres
res
3Z36
4K7
3Z34
3Z35
10K
1K0
1K0
5Z01 1
4
1
5Z02
4
1
5Z03
4
1
5Z04
4
1
5Z05
4
3Z50
100R
4K7
3Z54
100R
3Z55
100R
3Z52
100R
3Z53
100R
2Z62
res
2Z57
2Z60
2Z58
2
DLW21S
3
2
DLW21S
3
2
DLW21S
3
2
DLW21S
3
2
DLW21S
3
4K73Z38
100p
100p
2Z59
100p
100p
2Z44
22p
2Z45
22p
2Z46
22p
2Z47
22p
2Z48
22p
2Z49
22p
2Z50
22p
2Z51
2Z52
22p
2Z53
100p
234
+3V3_SIM
res
FZ43
22p
22p
FZ45
FZ46
FZ44
FZ02
FZ04
FZ07
FZ10
FZ12
FZ14
FZ16
FZ17
FZ18
FZ08
3Z26
1K0
res
3Z24
100R
res
3Z25
100R
FZ40
+3V3_SIM
+3V3_SIM
+3V3_SIM
+3V3_SIM
10K
3Z33
2Z55
IZ02
100n
10K
3Z32
IZ03
BC847BW
7Z00
567
1G50
33
B19c
32
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
A
B
C
TO
DISPLAY
D
E
2Z56
47K
3Z31
2Z65
IZ01
1
2
5
6
3Z56
1K0
100R
3Z23
1n0
IZ00
SI3441BDV
7Z01
10V10u
2Z64
BZX384-C5V6
6Z00
47K
3Z30
47R
3Z29
3
4
FZ21
100n
5V-ENABLE
LCD-PWR-ON
1u0
FZ66
2Z54
+11V
2.0AT
1Z28
VDISP
5Z06
5Z07
5Z08
2Z63
100n
FZ20
FZ42
FI-WE31P-HFE-E1500
1G50 C7
2Z44 C2
2Z45 C2
2Z46 C2
2Z47 D2
2Z48 D2
2Z49 D2
2Z50 E2
2Z51 E2
2Z52 E2
2Z53 E2
2Z54 B6
2Z55 B4
2Z56 A5
2Z57 B1
2Z58 A1
2Z59 A2
2Z60 F1
2Z61 F2
2Z62 B1
2Z63 C6
2Z64 C5
2Z65 C5
3Z22 A1
3Z23 A5
3Z24 B2
3Z25 B2
3Z26 A2
3Z28 C6
3Z29 B6
3Z30 B6
3Z31 B5
3Z32 B4
3Z33 B4
3Z34 B1
3Z35 B1
3Z36 A1
3Z37 A1
3Z38 A2
3Z39 B1
3Z50 F1
3Z51 F2
3Z52 B1
3Z53 B1
5Z05 E1
5Z06 C6
5Z07 C6
5Z08 D6
6Z00 B6
7Z00 A4
7Z01 B5
FZ02 C2
FZ04 C2
FZ07 C2
FZ08 D2
FZ10 D2
FZ12 D2
FZ14 D2
FZ16 E2
FZ17 E2
FZ18 E2
FZ20 D7
FZ21 C6
FZ40 E3
FZ41 F3
FZ42 F7
FZ44 A2
FZ45 B2
FZ46 B2
FZ66 A6
IZ00 B5
IZ01 A5
IZ02 B4
IZ03 A4
3Z54 A1
F
B14e
SDA-DISP
3Z51
100R
2Z61
FZ41
100p
LVDS
CONNECTOR
F
3Z55 A1
3Z56 A5
5Z01 C1
5Z02 C1
5Z03 D1
5Z04 E1
8204 000 8486.1
F_15460_046.eps
080405
1
234567
Page 77

Circuit Diagrams and PWB Layouts
EN 77FTP2.4E AA 7.
SSB: Connection
1M01 D10
1M02 E7
1M03 E5
1M07 F10
1M09 G10
1M17 A4
1M20 F8
1M36 B15
1M46 A1
1M48 G14
1M49 F14
1M51 E14
1M52 A10
1Y02 A10
1Y04 A10
1Y05 A10
1Y06 A10
1Y07 A10
1Y08 A10
1Y09 B10
1Y10 E3
1Y11 E4
1Y12 F4
1Y13 F4
1Y14 F4
1Y15 F4
1Y16 F4
1Y17 F4
1Y18 G4
1Y21 E8
1Y22 E8
1Y23 E8
1Y24 F8
1Y25 F8
1Y26 E8
1Y27 E8
1Y28 D10
1Y30 B15
1Y31 B15
1Y32 B15
1Y33 B15
1Y34 B15
1Y35 B15
1Y37 B15
1Y38 A10
1Y39 A10
2Y00 A3
2Y01 B3
2Y02 B2
2Y03 C3
2Y04 C3
2Y06 D2
2Y07 E2
2Y08 E2
2Y09 F2
2Y10 H3
123456789101112131415
B21 B21
A
10
11
B11B-PH-K
B
TO 1M46
AUDIO-STBY
SDI SUPPLY
CONNECTION
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
OR
1M46
FY48
FY00
FY05
9Y14
FY47
FY65
FY03
FY46
FY01
2Y02
2Y03
100p
100p
+8V
5Y06
100p
2Y00
+5V
5Y15
100p
2Y34
+5V2-STBY
5Y07
100p
2Y01
9Y13
+33V
res
5Y02
+11V
5Y03
C
9V_STBY
5Y09
100p
2Y04
100p
100p
100p
+5V2-STBY
3Y16
FY26
4K7
9Y07
FY22
FY23
FY24
3Y38
BC857BW
7Y02
3Y14
3Y05
100R
FY25
2K2
4K7
2Y52
2Y10
100n
FY28
FY79
100p
1Y10
1Y11
1Y12
1Y13
1Y14
1Y15
1Y16
1Y17
1Y18
FY30
100p
D
B19e
BACKLIGHT-CNTRL-DC
B21
PWR-OK-PDP
B4,B14b,B21
POR
E
B20,B19d
LAMP-ON
9Y03
+5V
FAN-SPEED
3Y03
100R
nc
F
B21
PROT-AUDIOSUPPLY
B14b,B5a
IRQ-DIGITAL
G
PDTC114EU
STANDBY
B5a,B14e(2x)
9Y09
7Y04
*
3Y30
*
2Y09
+5V2-STBY
15K
100p
3Y15
3Y00
100R
3Y01
100R
*
3Y02
100R
+5V
3Y37
10K
7Y03
PDTC114EU
*
2Y06
*
2Y07
2Y08
*
4K7
3Y39
10K
H
B21
9Y04
PWR-OK-PDP
3Y08
100R
*
FY31
100n
2Y13
*
STANDBY-IO4
8204 000 8485.1
12345
2Y11 A5
2Y12 G4
2Y14 G6
2Y15 H6
2Y16 H6
2Y17 G6
BM07B-SRSS-TBT
5Y00
2Y12
FY29
9V_STBY
3Y04
2K2
2Y18 F6
2Y19 F6
2Y20 E6
2Y21 E6
2Y22 A5
2Y23 D9
2Y25 A13
1M17
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
N.C.
B10P-PH-K-S
9Y15
2Y26 B13
2Y27 B13
2Y28 C13
2Y29 C13
2Y30 D13
2Y31 D13
2Y32 D13
FY74
*
*
100p
9
FY75
2Y11
*
+5V2-STBY
+5V
1M03
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
TO 1M03
AUDIO-STBY
OR
SDI SUPPLY
9Y01
+5V2-STBY
9Y12
2Y22
100p
*
B4,B5a
3Y06
100R
3Y13
100R
B14e
B5a
B5a
2Y33 D13
2Y34 A3
2Y37 A8
2Y38 A7
2Y39 B7
2Y40 C7
2Y41 C9
*
FY85
*
*
9Y16
9Y17
PDTC144EU
SCL-S
SDA-S
LED1
RC
LIGHT-SENSOR
+8V
LED2
+5V2-STBY
100p
2Y42 D7
2Y43 A6
2Y44 H13
2Y45 G13
2Y48 A5
2Y49 F13
2Y50 F13
2Y48
3Y24
100K
7Y01
3Y33
100R
5Y02 C3
5Y03 C3
5Y06 A3
5Y07 B3
5Y09 C3
5Y11 G6
5Y12 H6
FY60
9Y00
100p
FY57
2Y41
5Y23
5Y14 F6
5Y15 A3
5Y16 A13
5Y17 B13
5Y18 A7
5Y19 B7
5Y20 B7
FY56
FY62
100p
100p
2Y23
CON-SND
KEYBOARD
FY61
FY63
GND-AUD
FY32
5Y21 C8
5Y22 C7
5Y23 F9
7Y01 B5
7Y02 G3
7Y03 G2
7Y04 H2
1M52
B9B-PH-K
B5a
B5a
B14e
STATUS-SC3-F
B14e
SEL_IN_1_BF
B14e
SURR-RF
B14e
SURR-LF
9Y00 D9
9Y01 G4
9Y02 G6
9Y03 F1
9Y04 H2
9Y05 G6
9Y06 H6
1Y39
9
8
1Y04
7
6
1Y06
5
4
1Y08
3
2
1
TO 1793
AUDIO-STBY
PDP AUDIO
1M01
1
2
3
B3B-PH-K
+11V_SF
+11V_SF
1Y38
OR
*
+3V3_SIM
2Y43
100p
3Y07
1R0
9Y02
2Y51 A8
2Y52 G3
2Y53 F92Y13 H3
3Y00 D2
3Y01 E2
3Y02 E2
3Y03 F1
GND-AUD
POR-CLASSD
B4,B14b,B21
9Y05
9Y06
B19d
FRAME
ODC
POR
B19d
B21
3Y04 H4
3Y05 G3
3Y06 A5
3Y07 G6
3Y08 H3
3Y09 E6
3Y10 F6
B21
POR-CLASSD
B5a,B14b
SOUND-ENABLE
(SOUND PROTECT)
PROT-AUDIOSUPPLY
B6a,c
AUDIO-SW
B6b
AUDIO-C
B6a,c
AUDIO-R
B6a,c
AUDIO-L
B5a
KEYBOARD
100R
3Y40
2Y21
100R
3Y09
2Y20
5Y14
2Y19
3Y10
100R
2Y18
3Y11
100R
2Y17
5Y11
2Y14
5Y01
2Y15
5Y12
2Y16
3Y11 F6
3Y12 F8
3Y13 A5
3Y14 G3
3Y15 G2
3Y16 G2
3Y17 B13
100R
3Y25
B21
5Y19
5Y20
5Y22
N.C.
1M02
1
2
FY39
FY43
FY37
FY38
FY40
FY41
FY42
FY44
FY45
3
S3B-PH-K
10p
10p
100p
100p
100p
100p
100p
3Y18 B13
3Y19 C13
3Y20 C12
3Y21 D12
3Y22 D12
3Y23 D12
3Y24 B5
5Y18
100p
3Y25 A7
3Y27 H13
3Y28 G13
3Y30 E2
3Y33 A6
3Y34 E13
3Y35 F13
2Y37
2Y38
3Y36
100R
100p
2Y39
100p
2Y40
FY64
100p
2Y42
1Y21
FY78
FY77
3Y12 100R
FY76
TO 1M20
100p
2Y51
SDA-SF
SCL-SF
1Y26
1Y27
1Y22
1Y23
1Y24
1Y25
3Y36 A8
3Y37 F2
3Y38 F3
3Y39 G2
3Y40 E6
5Y00 G4
5Y01 G6
FY58
100p
FY59
B12P-PH-K
B14e
B14e
5Y21
1M20
1
2Y53
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
LED + SWITCH
100p
FY82
678910
9Y07 D3
9Y09 D2
9Y12 A5
9Y13 B3
9Y14 B1
9Y15 G4
9Y16 B5
1Y02
1Y05
1Y07
1Y09
1Y28
FY66
FY67
FY68
FY69
FY70
FY71
FY72
FY73
9Y17 B5
FY00 A2
FY01 B2
FY03 B2
FY05 B1
FY22 E3
FY23 E3
1M07
B5B-PH-K
1M09
B8P-PH-K
TO 1M07
1
2
3
4
5
SCART 3
1
2
3
4
N.C.
5
6
7
8
FY24 F3
FY25 F3
FY26 F3
FY28 H3
FY29 F4
FY30 G4
FY31 H3
B14d(2x)
B14d(2x)
FY32 D9
FY37 E7
FY38 E7
FY39 F7
FY40 F7
FY41 F7
FY42 F7
B14a
FRONT-Y-CVBS-IN
B14a
FRONT-C-IN
L-FRONT-IN
B5a
FRONT-DETECT
R-FRONT-IN
B6a
HEADPHONE-L
B6a
HEADPHONE-R
TO 1M01
LED + SWITCH
FY43 G7
FY44 F7
FY45 G7
FY46 B2
FY47 B2
FY48 A2
FY49 A13
FY50 A13
FY51 B13
FY52 B14
FY53 B14
FY54 B14
FY55 B14
FY56 A9
3Y20
68R
3Y21
68R
3Y22
68R
3Y23
68R
SDA-S
B19d
AL-CL
B19d
AL-DA
SCL-S
5Y16
5Y17
3Y17
100R
3Y18
100R
3Y19
100R
FY57 A9
FY58 A8
FY59 B8
FY60 B9
FY61 C7
FY62 C9
FY63 C8
2Y25
2Y26
2Y27
2Y28
2Y29
2Y32
2Y33
3Y34
100R
3Y35
100R
100p
100p
1n0
1n0
1n0
1n0
1n0
3Y28
100R
3Y27
100R
FY64 C8
FY65 A2
FY66 F10
FY67 F9
FY68 G9
FY69 G9
FY70 G9
FY49
FY50
2Y49
2Y50
res
2Y45
res
2Y44
FY51
16V 100u
2Y30
16V
100u
2Y31
FY86
10p
FY87
10p
10p
res
10p
res
FY52
FY53
FY71 G9
FY72 G9
FY73 G9
FY74 A5
FY75 A5
FY76 G8
FY77 F8
FY80
FY81
FY54
B4B-PH-K
B3B-PH-K
1M51
1M49
FY78 F8
FY79 F3
FY80 G14
FY81 H14
FY82 H7
FY85 A5
FY86 E13
FY55
1
2
3
4
1
2
3
1M48
B3B-PH-K
11 12 13 14 15
1
2
3
TO
res
FY87 F13
1M36
B11B-PH-K
TO 1M37
SCART 3
1
2
3
1Y31
4
5
1Y32
6
1Y33
7
8
9
1Y35
10
11
F_15460_047.eps
A
1Y30
B
1Y34
1Y37
C
D
E
F
G
H
110405
Page 78

Circuit Diagrams and PWB Layouts
Layout SSB (Top Side Overview)
Part 1
F_15460_048a.eps
EN 78FTP2.4E AA 7.
Part 2
F_15460_048b.eps
3104 313 6003.7
Part 3
F_15460_048c.eps
Part 4
F_15460_048d.eps
F_15460_048.eps
120405
Page 79

Layout SSB Mapping (Top Side)
1000 A6
1001 B6
1304 A5
1305 B5
1306 B4
1307 B5
1308 B4
1401 A6
1402 A6
1408 A4
1702 D5
1703 D5
1710 D7
1D01 A8
1E02 B8
1E04 C8
1I01 A5
1I04 A4
1I05 A7
1I07 A7
1I09 A6
1I11 B3
1I53 A8
1I56 A9
1I57 A8
1I59 A9
1I79 E1
1M01 D9
1M02 A9
1M03 E9
1M07 A9
1M09 A9
1M15 A9
1M17 F8
1M20 D9
1M36 C9
1M46 F8
1M48 F3
1M49 F7
1M51 F7
1M52 F2
1P00 C2
1P03 C2
1P06 B2
1P10 C2
1P11 C2
1P12 C2
1T01 A2
1T02 E2
1U01 F6
2002 B6
2004 C6
2005 C6
2006 C6
2007 C6
2008 C6
2009 C5
2011 C5
2012 C5
2013 B6
2014 B6
2016 B6
2018 B6
2020 C6
2025 B5
2027 C5
2028 B6
2029 C6
2031 A6
2034 B5
2035 B5
2037 B6
2039 B5
2058 A6
2059 A6
2067 B5
2070 C6
2071 C6
2073 C6
2075 A6
2301 C4
2305 B4
2314 C4
2315 C4
2316 B4
2317 B4
2318 B4
2322 B4
2324 C4
2327 B5
2329 C5
2330 C5
2331 C5
2332 C4
2333 C4
2334 C4
2336 C4
2339 A5
2340 C4
2344 A5
2347 A5
2348 A5
2349 A5
2350 B4
2351 B4
2352 B4
2353 B4
2355 A5
2356 B4
2357 B4
2358 B4
2359 B5
2360 B5
2361 B5
2362 B5
2363 C5
2364 A5
2365 B4
2367 B4
2368 B4
2373 B4
2376 B4
2377 B4
2379 B5
2380 B5
2381 B5
2382 B5
2383 A5
2388 B4
2389 C4
2391 A4
2393 C4
2394 C4
2395 C5
2396 C5
2397 C4
2398 C4
2401 B4
2403 B4
2404 B4
2405 A4
2406 A4
2407 A4
2408 A4
2409 B4
2410 C4
2411 B4
2412 A4
2413 A4
2414 C4
2416 B4
2417 B4
2425 C4
2427 A5
2428 A5
2429 C4
2430 B4
2432 B4
2433 C4
2434 B4
2435 B4
2436 B4
2707 D6
2708 D6
2709 D6
2710 D7
2711 D7
2712 D7
2715 C7
2716 E7
2717 D7
2718 C5
2719 C5
2720 D5
2721 D5
2722 D5
2723 D7
2724 C8
2725 E7
2726 E6
2728 E7
2729 E7
2730 D7
2732 E5
2733 D6
2735 D5
2736 D6
2738 D7
2739 E6
2740 D5
2741 D5
2742 D5
2743 D6
2744 D6
2745 E5
2747 D5
2749 D5
2750 A7
2751 A7
2752 B7
2753 B7
2755 B8
2756 B7
2758 B7
2759 B7
2760 B7
2761 B7
2762 B7
2763 B7
2764 C7
2765 B8
2768 A7
2770 B7
2771 B7
2772 B7
2773 B7
2777 B7
2778 B7
2780 B7
2781 B7
2782 B7
2784 B7
2785 B7
2787 B7
2788 B7
2790 B7
2792 C5
2794 B7
2795 B7
2796 B7
2797 B7
2798 B7
2799 B7
2800 D5
2802 A6
2805 B7
2809 A7
2810 C7
2811 C7
2813 C7
2814 B8
2815 B7
2816 B7
2818 B7
2819 D6
2820 C7
2821 B7
2822 B6
2824 B7
2826 B7
2828 B7
2829 C7
2830 C7
2831 C7
2832 C7
2833 C7
2834 C7
2835 C7
2836 C5
2837 A7
2838 A7
2839 A7
2840 C5
2841 C6
2843 E5
2844 B7
2845 D6
2846 D6
2847 E6
2848 E5
2849 B7
2850 C6
2851 C6
2852 D6
2853 D6
2854 D6
2855 C6
2856 C6
2857 C6
2858 C6
2859 C6
2860 C6
2861 C6
2862 C5
2863 C5
2864 C5
2865 C6
2866 D5
2867 D6
2868 C5
2869 C6
2870 D5
2871 A7
2872 B7
2873 B7
2874 D6
2875 D7
2876 C7
2877 D7
2878 D7
2879 D7
2880 D7
2881 D5
2886 D7
2887 D7
2888 D7
2889 A7
2890 D5
2891 E6
2895 A7
2896 C6
2897 C7
2898 A8
2899 A8
2900 C5
2901 D5
2902 D5
2914 D6
2915 C5
2916 D5
2917 E6
2918 E6
2919 E7
2921 B7
2922 E5
2923 E5
2924 A6
2925 B7
2926 A7
2927 A7
2928 A7
2929 D5
2931 D5
2935 D5
2936 C7
2937 C7
2938 C5
2939 E6
2A00 E4
2A02 D5
2A03 E4
2A04 E4
2A05 D4
2A06 D4
2A08 C4
2A09 D5
2A10 D4
2A11 D4
2A12 D3
2A13 D3
2A14 D4
2A15 D4
2A16 D4
2A17 D4
2A18 D4
2A20 D4
2A21 D4
2A22 D4
2A23 D4
2A25 D4
2A26 D4
2A27 D4
2A29 D5
2A30 D4
2A31 D4
2A32 D5
2A33 D5
2A35 D4
2A36 D4
2A37 D5
2A39 D5
2A40 D5
2A41 D5
2A42 D4
2A43 D4
2A44 D4
2A45 D3
2A46 D5
2A49 D4
2A50 D4
2A53 D4
2A54 D4
2A56 D4
2A59 D4
2A62 D4
2A66 D4
2A76 D4
2A95 E3
2AA6 D5
2AA7 D4
2AB2 D4
2AB5 D4
2AB6 D4
2AB7 D4
2AD1 E3
2AF3 E3
2AF4 E3
2AK0 E5
2AK1 E5
2AK2 D4
2AK3 D4
2AK4 E4
2AK5 E4
2AK6 E5
2AK7 E5
2AK9 E4
2AL0 D4
2AL1 E4
2AL2 E4
2AL3 E4
2AL4 D4
2AL8 E4
2AL9 E4
2ALA E4
2AM0 D4
2AM1 D4
2AM2 E4
2AM3 E4
2AM5 D4
2AM6 E4
2AM7 E4
2AM9 E4
2AN0 D4
2AN1 E4
2AN7 E5
2C01 A5
2D03 E7
2D09 C8
2D10 C8
2D11 C8
2D12 C8
2E01 C9
2E03 D9
2E06 C9
2E17 E9
2E21 D8
2E22 D8
2E23 E8
2E24 E8
2E25 E8
2E26 E8
2E28 E8
2E29 E8
2E30 E8
2E32 E9
2E34 E8
2E39 E9
2E41 D9
2E42 C8
2E43 D9
2E50 D9
2E54 C9
2E56 C8
2E57 C8
2E58 C8
2E59 C8
2E62 C8
2E65 C8
2E66 C8
2E67 C8
2E68 C8
2E69 C8
2E70 C8
2E71 C8
2E72 C8
2E73 C8
2E74 C8
2E75 C8
2E77 C8
2E78 C8
2E79 C8
2E80 D8
2E81 D8
2E82 C9
2E83 C9
2E87 D8
2E89 B8
2E90 B8
2E91 B8
2E95 C8
2E96 D8
2E97 D9
2E98 D8
2E99 D9
2I00 A9
2I03 B3
2I13 A2
2I14 A3
2I15 A5
2I16 A4
2I17 A4
2I18 A4
2I19 A4
2I20 A5
2I21 A2
2I22 A2
2I23 A2
2I24 A3
2I25 A3
2I26 A7
2I27 A7
2I28 A6
2I29 A6
2I30 A6
2I31 A7
2I32 A6
2I34 E2
2I36 A6
2I38 A9
2I49 A7
2I55 B2
2I56 B2
2I57 A7
2I58 A7
2I62 E3
2I64 A9
2I65 A9
2I66 B9
2I67 B8
2I68 B8
2I71 A3
2I72 A3
2I73 A3
2I75 A3
2I76 A3
2I77 A2
2I78 A3
2I79 A3
2I80 A2
2I81 A2
2I82 A2
2I84 A2
2I85 A2
2I86 B9
2I87 B8
2I88 B8
2I89 B9
2I90 B9
2I91 B9
2I92 A8
2I93 A8
2I94 A8
2I95 B8
2I96 B8
2I97 A9
Circuit Diagrams and PWB Layouts
2I98 B8
2I99 A4
2IA0 A2
2IA1 A2
2IA2 A4
2IA3 A9
2IA5 A3
2IA6 A3
2IA9 A7
2IB0 A8
2IB3 A8
2IB5 A9
2IC0 A7
2IC1 A7
2IC2 A6
2IC8 B9
2IC9 A4
2IE1 A9
2IE2 B8
2IE3 A8
2IE4 A8
2IE5 B9
2IE6 B9
2IE7 B9
2IE8 B9
2IE9 A9
2IF1 A8
2IF2 A8
2IF3 A8
2IF4 A7
2IF5 A8
2IF6 A8
2IG2 A9
2IG3 A9
2IG4 A9
2IG5 A8
2IG6 B9
2IG7 B9
2IG8 B9
2IG9 B8
2IH2 A8
2IH4 B9
2IH5 B9
2IJ2 A3
2IJ3 A3
2IJ6 A9
2IJ7 A9
2IJ8 B9
2IJ9 B9
2IK4 A9
2IK5 B3
2IK7 C4
2IR1 A8
2IS6 E2
2L00 C9
2L01 B9
2L02 B9
2L03 B9
2L04 B9
2L05 B9
2L06 B9
2L07 B9
2L08 C9
2L09 C9
2L10 B9
2L11 C9
2L12 C9
2L13 C9
2L14 C9
2L15 C9
2L16 C9
2L17 C9
2L19 F8
2L20 C9
2L21 C9
2L28 B9
2L29 B9
2L30 B9
2L33 F9
2L34 E9
2L48 B9
2L49 B9
2L50 B9
2L51 C9
2L52 B9
2L54 B9
2L57 B9
2L58 B9
2P00 B1
2P02 B1
2P03 B2
2P04 B2
2P05 B1
2P06 B2
2P07 B2
2P08 B2
2P09 C1
2P10 C1
2P13 C1
2P17 C1
2P19 C2
2P20 C2
2P21 C2
2P22 B2
2P26 D1
2P27 C1
2P28 C1
2P34 C2
2P35 C2
2P36 C2
2P37 C2
2P38 C2
2P39 C2
2P40 C2
2P41 C2
2P42 C2
2P43 C2
2P44 C2
2P48 C2
2P50 B2
2P80 B2
2P81 B3
2P90 B3
2P98 C1
2P99 C2
2PA4 C3
2PA5 C3
2PA6 C2
2PA7 C2
2PA8 C2
2PB3 C3
2PB4 C3
2PB5 C3
2PB6 C3
2PB7 C2
2PB8 B3
2PB9 C3
2PC0 C3
2PC1 C3
2PC2 C3
2PC3 B3
2PC4 B3
2PC5 C3
2PC6 B3
2PC7 B2
2PC8 B2
2PC9 C2
2PD1 C2
2PD2 D2
2PD3 C3
2PD4 C3
2PD5 D3
2PD6 C3
2PD7 C3
2PD8 C3
2PD9 C3
2PE0 C2
2PE1 D3
2PE2 C3
2PE3 C3
2PE4 C3
2PE5 C3
2PE6 B2
2PF1 B3
2PF3 C3
2PF8 C3
2PF9 C3
2PG0 C2
2PG1 C2
2U03 E7
2U04 E7
2U05 E7
2U07 E7
2U09 E7
2U11 E6
2U12 E6
2U13 F7
2U14 E7
2U15 E6
2U16 E7
2U17 F7
2U18 E7
2U20 E6
2U21 E7
2U23 E8
2U30 E7
2U31 F8
2U32 E7
2U34 F6
2U36 E6
2V06 D8
2V07 D8
2V08 D8
2V09 D8
2V10 D8
2V11 E9
2V12 E9
2V16 D8
2V17 D8
2V18 D8
2V19 D8
2V20 D8
2V21 D8
2V22 D8
2V23 D8
2V24 D8
2V25 D8
2Y06 E9
2Y07 E9
2Y08 E9
2Y09 E9
2Y12 F9
2Y13 F9
2Y15 E9
2Y16 E9
2Y19 D9
2Y20 D9
2Y21 D9
2Y30 B9
2Y31 C9
2Y32 D9
2Y33 D9
2Y37 F2
2Y38 F2
2Y39 F2
2Y40 F2
2Y41 F2
2Y42 F2
2Y43 F2
2Y44 F3
2Y45 F3
2Y51 F2
2Z44 F5
2Z45 F5
2Z46 F5
2Z47 F5
2Z48 F5
2Z49 F5
2Z50 F5
2Z51 F5
2Z52 F5
2Z53 F5
2Z57 F5
2Z58 F5
2Z59 F5
2Z60 F5
2Z61 F5
2Z62 F5
2Z63 F4
2Z65 F4
3003 C6
3011 C5
3012 B5
3018 C5
3019 C5
3020 C5
3021 C5
3024 C6
3025 C6
3026 C6
3027 C6
3033 C6
3035 B5
3039 C6
3047 A6
3058 C6
3059 C6
3065 B5
3066 B5
3068 C6
3073 C6
3074 C5
3075 C6
3076 C5
3077 C6
3078 C5
3084 A6
3089 B5
3090 C6
3091 A6
3099 C6
3302 C4
3304 C4
3306 C4
3317 C4
3318 C4
3320 B4
3321 B4
3322 C4
3329 C4
3330 C5
3332 C5
3335 C5
3336 C4
3340 C4
3341 B4
3342 B4
3343 C4
3344 C4
3345 C4
3346 C4
3347 C4
3348 C4
3349 B5
3353 C4
3361 C4
3363 C5
3370 B4
3371 B4
3372 B4
3376 B4
3377 B4
3387 C5
3388 C4
3390 C4
3393 B4
3394 C4
3395 C5
3396 C5
3397 C5
3398 C4
3399 C4
3400 C4
3402 C4
3404 B4
3406 A4
3409 A4
3411 B4
3412 C4
3413 B4
3416 A4
3418 B4
3422 B4
3423 A4
3433 A4
3436 A4
3437 B4
3439 B4
3442 C4
3443 C4
3444 B4
3447 B4
3448 C4
3449 C4
3460 B5
3461 B5
3462 B5
3472 C4
3473 B4
3474 C4
3475 B4
3476 B4
3701 D6
3703 D6
3704 D6
3705 D6
3706 D5
3707 E7
3712 D5
3713 C5
3714 C5
3715 D5
3716 C5
3717 C5
3718 D5
3719 D5
3720 D5
3721 D5
3722 D6
3723 D5
3724 D7
3725 D5
3726 D5
3727 D5
3728 D5
3729 B8
3730 D5
3732 E6
3733 D6
3734 D6
3736 D6
3737 D6
3738 D6
3739 D6
3740 E6
3741 D6
3742 D6
3743 D6
3744 D5
3745 B6
3746 D6
3747 D6
3748 D6
3749 D6
3750 D6
3751 E6
3752 D6
3753 D5
3754 D6
3755 D6
3756 D6
3760 D7
3765 B7
3766 B7
3778 C7
3782 B7
3783 B7
3796 B7
3798 B7
3805 C7
3819 C7
3820 B7
3821 C8
3823 B7
3824 B6
3826 C5
3827 C5
3829 E6
3830 D6
3831 D6
3832 D6
3833 C6
3834 C6
3835 C6
3836 C6
3837 C6
3838 C6
3839 C6
3840 C6
3841 C6
3842 C6
3843 D6
3844 D6
3845 D6
3846 C6
3847 C6
3848 C6
3849 D5
3850 B7
3851 D5
3853 C6
3854 C6
3855 C6
3856 A7
3857 A7
3858 A7
3859 A7
3860 A7
3861 A7
3864 D6
3865 D6
3867 C7
3868 C7
3869 D5
3870 E6
3874 E5
3875 D6
3876 D7
3877 C8
3885 D7
3886 D7
3887 D7
3888 D7
3889 D7
3890 D7
3891 D7
3895 B8
3897 B8
3898 B8
3903 D6
3905 D6
3906 C7
3909 D5
3913 D5
3914 D5
3915 C5
3916 C5
3917 C5
3922 D5
3923 D5
3924 D5
3925 D5
3926 C5
3927 C5
3928 C5
3929 C5
3930 D5
3931 D5
3932 D5
3933 D5
3A00 D5
3A01 D5
3A03 D4
3A05 D5
3A07 D5
3A09 D5
3A11 D4
3A12 D4
3A13 D4
3A14 D4
3A15 D4
3A16 D4
3A18 D4
3A20 D4
3A21 D4
3A23 D4
3A26 D4
3A27 D4
3A28 D4
3A66 D4
3AA0 E4
3AA1 E4
3AA4 D4
3AA5 E4
3AA6 D4
3AA7 E4
3AA9 E4
3AB0 E4
3AB2 E4
3AB3 E4
3AB4 E4
3AB5 E4
3AB6 D4
3AB7 E4
3AB8 D4
3AB9 D4
3AC0 E4
3AC1 E4
3C01 A5
3C03 A5
3C06 A5
3C07 B5
3C08 A5
3C09 C5
3E00 D8
3E01 D8
3E02 D9
3E03 D8
3E06 D8
3E07 E8
3E08 E8
3E09 E9
3E10 E9
3E13 E9
3E15 E9
3E16 E8
3E37 E9
3E50 C8
3E52 C8
3E53 B8
3E54 C8
3E59 D9
3E60 C8
3E61 C9
3E62 C8
3E63 C8
3E64 D9
3E73 B8
3E74 D8
3E77 C8
3E78 C8
3E79 B8
3E80 B8
3E87 C8
3E91 D8
3I00 E3
3I19 A3
3I20 A3
3I21 A3
3I22 A3
3I26 A3
3I27 A3
3I35 A4
3I39 A2
3I43 A3
3I50 A4
3I51 A4
3I52 A4
3I53 A4
3I54 A5
3I55 A5
3I56 A5
3I57 A5
3I58 A5
3I59 A5
3I60 A5
3I61 A4
3I62 A4
3I63 A5
3I64 A5
3I65 A5
3I66 A5
3I67 A5
3I68 A5
3I69 A2
3I70 A2
3I71 A2
3I72 A3
3I73 A3
3I74 A3
3I75 A3
3I76 A3
3I77 A3
3I78 A4
3I79 A2
3I80 A3
3I81 A3
3I82 A3
3I83 A3
3I84 A3
3I86 A4
3I87 A4
3I88 A4
3I89 A7
3I90 A7
3I91 A7
3I92 A7
3I93 A7
3I94 A6
3I95 A6
3I96 A6
3I97 A6
3I99 A6
3IA0 A6
3IA2 A6
3IA3 A6
3IB2 A4
3IB8 E3
3IB9 E3
3IC4 A4
3IC6 A2
3IC9 A6
3ID1 A5
3IE2 A7
3IE3 A7
3IE9 A7
3IF0 A9
3IF5 A7
3IF6 A7
3IF7 A7
3IFA A7
3IFB A7
3IFC A7
3IFD A8
3IFE A8
3IFF A8
3IFL A8
3IG0 A8
3IG1 A8
3IG3 A8
3IG4 A8
3IG6 A8
3IG7 A8
3IGH E3
3IH9 A4
3IHA A8
3IHB A8
3IHC A8
3II4 A4
3IJ0 A3
3IJ1 A3
3IK0 B8
3IK2 A2
3IK3 A3
3IK8 A3
3IL1 A7
3IL3 A7
3IL8 A7
3IM0 A7
3IM4 A7
3IN0 A7
3IN4 A7
3IN5 A4
3IN6 A4
3IQ2 A3
3IQ3 A3
3IQ8 B9
3IQ9 B9
3IR2 B8
3IR3 B8
3IR4 B8
3IR5 B8
3IR6 B8
3IR7 A8
3IR8 A8
3IR9 B8
3IS0 B8
3IS2 A3
3IS3 A9
3IS5 B9
3IS6 A9
3IT0 A7
3IT1 A7
3IT2 A6
3IT3 A6
3IT4 A6
3IT6 B9
3IT7 B8
3IT8 B8
3IU0 A8
3IU2 A8
3IU5 A9
3IU6 A9
3IU7 A8
3IU8 A8
3IU9 A9
3IV0 B9
3IV1 B9
3IV2 B9
3IV3 B9
3IV7 A8
3IV8 A9
3IV9 A8
3IW2 A9
3IW4 A5
3IW5 A5
3IZ0 A9
3IZ1 A8
3IZ2 A8
3IZ6 A8
3IZ7 A8
3IZ8 A8
3IZ9 A8
3L04 B9
3L05 B9
3L11 B9
3L19 B9
3L20 B9
3L21 B9
3L28 B9
3L29 B9
3L30 B9
3L31 B9
3L32 C8
3L33 C8
3P00 C1
3P01 C2
3P02 D2
3P07 B2
3P08 B2
3P10 B1
3P17 B2
3P18 B2
3P19 B1
3P20 B1
3P25 C2
3P26 C2
3P27 B1
3P28 C1
3P29 C2
3P30 C1
3P34 C1
3P35 C1
3P41 C2
3P42 C2
3P43 C2
3P44 C1
3P61 C3
3P90 C2
3P91 B2
3P93 B3
3PA0 C3
3PA1 D2
3PA2 D2
3PA3 C3
3PA4 C3
3PA5 C2
3PA6 C3
3PA7 C3
3PA8 C2
3PA9 C3
3PB0 C2
3PB1 C2
3PB2 C2
3PB3 C2
3PB4 C2
3PB5 C3
3PB6 C3
3PB7 C2
3PB8 C2
3PB9 C2
3PC1 C2
3PC2 D3
3PC3 D3
3PC4 D3
3PC6 C3
3PC7 C3
3PC8 C3
3PC9 C3
3PD0 C3
3PD1 C2
3PD2 C3
3PD3 C2
3PD4 C2
3PD5 C2
3PD6 C2
3PD8 C2
3PD9 C3
3PE0 C2
3PE1 C2
3PE2 C2
3PE3 C2
3PE4 C2
3PE5 C2
3PF0 C3
3PF1 C2
3PF2 C3
3PF3 C2
3PF4 C3
3PF6 C3
3PF7 D3
3PF8 C3
3PF9 C3
3PG0 C3
3PG2 D2
3PG3 C3
3PG4 C3
3PG5 C3
3PG6 C2
3PH2 C3
3PH3 B3
3PH4 B2
3PH6 C2
3PH7 D2
3PH8 C3
3U01 F6
3U02 E7
3U03 E7
3U04 E7
3U05 E7
3U06 E6
3U07 E6
3U08 E6
3U09 E7
3U10 F7
3U11 E7
3U13 E7
3U14 E7
3U15 F7
3U16 E6
3U17 E7
3U18 E6
3U19 E6
3U20 F6
3U21 E6
3U22 F6
3U23 F6
3U25 E6
3U26 E6
3U28 E7
3U29 E7
3U30 E7
3U31 E7
3U34 E6
3U46 E6
3U51 E7
3U52 F6
3U53 F6
3U56 E6
3U57 E6
3U70 F6
3V01 D8
3V02 D8
3V07 D8
3V08 D8
3V14 D8
3V15 D8
3V16 D8
3V17 D8
3V19 D8
3V20 D8
3V21 C9
3V22 C9
3V23 C9
3V24 C9
3V25 D8
3V26 D8
3V27 D8
3V28 D8
3V29 D8
3V30 D8
3V31 D8
3V32 D8
3V33 D8
3V34 D8
3V35 E8
3V36 C8
3V39 C9
3V50 E9
3V51 E9
3V52 E9
3V53 E9
3V54 E9
3V55 E9
3V56 D8
3V57 E8
3Y04 C9
3Y15 F9
3Y16 F9
3Y17 C9
3Y18 D9
3Y19 D9
3Y27 F3
3Y28 F3
3Y36 F2
3Y39 F2
3Z22 F5
3Z34 F5
3Z35 F5
3Z50 F5
3Z51 F5
3Z52 F5
3Z53 F5
3Z54 F4
3Z55 F5
5000 A6
5001 A6
5003 A6
5301 C4
5302 C4
5303 A5
5306 A5
5307 A5
5309 A5
5310 A5
5311 A5
5403 A4
5405 B4
5406 A4
5411 A5
5416 A4
5703 D6
5705 D5
5706 D5
5707 C5
5708 D5
5709 C7
5713 B7
5714 D5
5721 E5
5722 E5
5725 E5
5726 E5
5750 C7
5751 C7
5752 B7
5753 D6
5754 B7
5755 E5
5756 D6
5757 B7
5758 B7
5759 C7
5760 B8
5761 C7
5762 B7
5764 B7
5767 D5
5768 E6
5772 E7
5773 E5
5775 B7
5776 E6
5777 C7
5778 E5
5779 D6
5780 B7
5800 C5
5801 C7
5A00 D4
5A01 E4
5A02 C4
5A03 C4
5A06 E3
5A19 D5
5A38 E3
5E51 D8
5E52 C8
5E53 E7
5E56 C8
5I01 B2
5I05 A9
5I06 A9
5I12 A8
5I13 A8
5I21 A9
5I22 A9
5I30 A8
5I31 B9
5I32 B9
5I33 A9
5I34 A9
5I35 A8
5I36 B9
5I37 B8
5I38 B8
5I40 B9
5I41 B8
5I46 B3
5I47 C3
5L02 B9
5L04 B9
5L06 B9
5L13 C9
5L14 C9
5L15 C9
5L16 C9
5L17 C9
5L18 C9
5P00 B1
5P01 B1
5P02 B2
5P03 B1
5P04 B2
5P06 B1
5P07 B2
5P51 B2
5PA0 B3
5PA1 C3
5PA2 B3
5PA3 B3
5PA4 C3
5PA5 D2
5PA6 C3
5PA7 C3
5PA8 D3
5PB0 B3
5U01 F7
5U02 F6
5U03 E7
5U04 E7
5U05 E8
5U06 F8
5U07 E7
5V06 D8
5V07 D8
5V08 D8
5Y16 C9
5Y17 C9
5Z01 F5
5Z02 F5
5Z03 F5
5Z04 F5
5Z05 F5
5Z06 F4
6001 C6
6003 C6
6301 C4
6309 C4
6310 C4
6311 C4
6316 C4
6319 C4
6404 A4
6701 D5
6702 E6
6703 D5
6704 B7
6705 E7
6709 C8
6710 D5
6711 D5
6712 E6
6716 E5
6717 C7
6718 C7
6719 B7
6720 D6
6721 D6
6722 D6
6723 C7
6A00 D4
6E51 C9
6E52 C8
6E54 D8
6I10 A5
6I14 A9
6I15 A8
6I16 A9
6I17 A9
6I18 A8
6I19 A8
6I20 A8
6I21 A9
6I22 A4
6I23 A4
6I24 A4
6I25 A4
6I26 A5
6I27 A5
EN 79FTP2.4E AA 7.
6I28 A5
6I29 A5
6I30 A4
6I31 A4
6I32 A4
6I33 A4
6I35 A5
6I36 A5
6I37 A2
6I38 A2
6I39 A3
6I40 A3
6I41 A3
6I42 A3
6I43 A4
6I44 A3
6I45 A2
6I46 A2
6I47 A3
6I48 A3
6I49 A3
6I50 A3
6I51 A4
6I52 A4
6I53 A7
6I54 A7
6I55 A7
6I56 A7
6I57 A6
6I58 A6
6I59 A6
6I60 A6
6I61 A6
6I62 A6
6I68 A6
6I69 A6
6I70 A6
6I75 A3
6I77 A4
6I90 A7
6I91 A7
6I92 A7
6I93 A7
6I99 A9
6IA0 A5
6P02 B2
6P03 B2
6PA0 C2
6PA1 C2
6PA2 C2
6PB2 C3
6PB3 B3
6PB4 B2
6PB6 D2
6PB7 C2
6PB8 C3
6U01 F7
6U03 E7
6U04 E7
6U05 E7
6U06 F7
6U07 F6
6U08 E6
6U09 E6
6U13 F6
6U17 F6
6V01 D8
6V02 D8
6V03 D8
6V06 E9
6V07 E9
7005 A6
7006 A6
7008 C6
7009 C6
7010 C6
7013 B5
7014 B5
7017 A5
7018 A5
7019 B5
7023 B5
7304 B5
7320 B4
7323 B4
7340 C4
7361 C4
7362 C5
7402 B4
7405 A4
7408 B4
7409 C4
7411 B4
7413 B5
7414 B4
7415 B4
7701 C7
7702 D6
7703 E6
7705 E6
7706 D6
7707 D6
7708 D6
7709 D6
7710 D6
7711 D5
7715 D6
7717 B7
7718 B7
7721 B7
7725 B6
7770 C6
7772 B8
7773 E6
7774 B6
7775 D5
7776 C5
7777 D5
7A00 D4
7A01 D4
7A02 D4
7A03 D4
7A11 D3
7A12 D3
7A16 D3
7A31 D5
7A61 E4
7A62 E4
7A63 E4
7E01 D9
7E02 D8
7E06 B8
7E22 E9
7E25 D9
7E26 D9
7E27 D8
7I06 A3
7I11 E3
7I17 A3
7I18 B9
7I21 A6
7I24 B3
7I26 A7
7I28 A7
7I30 A7
7I33 A7
7I45 E2
7I53 B9
7I54 A8
7I56 A8
7I57 A8
7I58 A8
7I60 A3
7I65 A8
7I80 A7
7I81 A8
7I82 A8
7L02 F9
7P00 B2
7P02 B1
7P05 B1
7P08 C1
7P09 C2
7P10 C2
7PA0 C3
7PA1 C3
7PA2 C2
7PA3 C2
7PA4 C3
7PA5 C2
7PA6 C2
7PA7 D3
7PA8 C3
7PA9 C3
7PB0 C2
7PB1 B2
7PB2 C2
7PB3 C2
7PB4 C2
7PB6 D2
7U01 E7
7U02 E7
7U03 E7
7U04 E7
7U05 E6
7U06 E6
7U08 E7
7U09 E7
7U10 E6
7U11 E6
7U12 E6
7V04 E9
7V06 E8
7Y03 F9
7Y04 F9
9016 C6
9017 A6
9018 A6
9022 C6
9023 C6
9302 C4
9303 C4
9304 C4
9305 C4
9314 B5
9315 C5
9316 C4
9322 B4
9408 B4
9409 B4
9412 A4
9414 B4
9416 A4
9417 A4
9419 B4
9423 A5
9424 A5
9425 A5
9426 B5
9428 A5
9700 D6
9703 D5
9704 C7
9705 C7
9707 D5
9708 C5
9709 D5
9711 B8
9713 C8
9717 B6
9718 B6
9719 B7
9720 B6
9721 C7
9722 D5
9727 D7
9728 D7
9729 D6
9730 B8
9731 B7
9732 B7
9750 B7
9751 B7
9752 C7
9761 C7
9762 C7
9767 D6
9768 D6
9769 D6
9770 D6
9771 D6
9772 D6
9776 D5
9777 B6
9800 C6
9801 C6
9802 C6
9803 C6
9804 C6
9805 C6
9806 C6
9807 D6
9808 D7
9809 D6
9810 D7
9812 C6
9815 D6
9816 D6
9817 D6
9818 D6
9821 B8
9822 B8
9825 D5
9826 C5
9827 D5
9A04 C5
9A05 D5
9A06 D5
9A19 E4
9A21 D2
9A22 D3
9A23 D3
9A24 D3
9A25 D3
9A60 D4
9A61 E4
9A65 D4
9A67 D4
9A71 D4
9A72 D2
9A73 D2
9A74 D3
9A75 D3
9A78 D5
9A79 D5
9C00 A5
9C01 A6
9E59 C9
9E60 C8
9E61 C8
9E62 C8
9E63 C8
9E64 C8
9E65 C8
9E74 E9
9E78 E9
9I04 A4
9I07 B9
9I08 B3
9I10 B3
9I12 B3
9I13 A6
9I14 B9
9I17 A5
9I18 A5
9I20 A3
9I21 A3
9I22 A4
9I23 A8
9I25 A7
9I26 A7
9I27 A7
9I28 A9
9I30 A2
9I35 A2
9I37 A7
9I45 A8
9I49 A8
9I51 A6
9I59 A7
9I60 A3
9I61 A7
9I84 A8
9I85 B8
9I87 E1
9I89 E1
9I90 E1
9I95 B3
9I97 B3
9IA1 A3
9IA3 A2
9IA6 A5
9IA7 A5
9ID0 E3
9IF0 A7
9IF1 A7
9IF2 A7
9IF3 A8
9IF4 A8
9P00 B1
9P01 B2
9P02 B1
9P03 B1
9P06 C1
9P08 B1
9P13 C2
9P14 B1
9P15 C1
9P19 B1
9P26 C2
9P27 C2
9P29 B2
9P70 B3
9P72 B2
9PA0 C3
9PA1 C2
9PA2 C3
9PA3 C2
9PA4 D3
9PA5 C3
9PA6 C3
9PA7 C2
9PA8 C2
9PB1 C2
9PB2 B3
9PB3 C2
9PB4 C2
9PB5 C2
9PB8 D3
9Y01 F9
9Y04 F9
F_15460_048m.eps
110405
Page 80
Circuit Diagrams and PWB Layouts
Layout SSB (Top Side Part 1)
Part 1
EN 80FTP2.4E AA 7.
F_15460_048a.eps
080405
Page 81

Circuit Diagrams and PWB Layouts
Layout SSB (Top Side Part 2)
Part 2
EN 81FTP2.4E AA 7.
F_15460_048b.eps
120405
Page 82

Circuit Diagrams and PWB Layouts
Layout SSB (Top Side Part 3)
EN 82FTP2.4E AA 7.
Part 3
F_15460_048c.eps
120405
Page 83

Circuit Diagrams and PWB Layouts
Layout SSB (Top Side Part 4)
EN 83FTP2.4E AA 7.
Part 4
F_15460_048d.eps
120405
Page 84

Circuit Diagrams and PWB Layouts
Layout SSB (Overview Bottom Side)
Part 1
F_15460_049a.eps
EN 84FTP2.4E AA 7.
Part 2
F_15460_049b.eps
3104 313 6003.7
Part 3
F_15460_049c.eps
Part 4
F_15460_049d.eps
F_15460_049.eps
080405
Page 85

Circuit Diagrams and PWB Layouts
Layout SSB Mapping (Bottom Side)
1301 B5
2804 D5
2I33 E8
2PA0 C7
2Y49 F3
3357 C6
1404 A4
1406 A6
1407 A6
1409 A5
1410 B6
1411 B6
1A01 D5
1G50 F5
1P04 B8
1P05 C8
1P07 C8
1P08 B9
1P09 C9
1Z28 E5
2003 B4
2010 C5
2017 B5
2019 A5
2022 C4
2023 B4
2024 B4
2026 B5
2033 B5
2036 B4
2038 B4
2040 B4
2041 B5
2052 A4
2053 A4
2054 A4
2055 A4
2056 A4
2057 A4
2060 A4
2061 A4
2063 C4
2068 C5
2072 C5
2074 C5
2300 B6
2302 B6
2303 C6
2304 C6
2306 B6
2307 C6
2308 C6
2309 B6
2310 B6
2311 B6
2312 B6
2313 B6
2319 C6
2320 B5
2321 C5
2323 C5
2325 B6
2326 C6
2328 C5
2335 C6
2337 C6
2338 C6
2341 C6
2342 C6
2343 C6
2345 A5
2346 A5
2354 B6
2366 B6
2369 B6
2370 C6
2371 B6
2372 B6
2374 B6
2375 B6
2378 B6
2384 B6
2385 B6
2386 C6
2387 B6
2392 B6
2402 B6
2415 B6
2418 B6
2419 B6
2420 B6
2421 B6
2422 B6
2423 B6
2424 B6
2426 A5
2431 C5
2713 E5
2714 E5
2727 E4
2731 E5
2734 D4
2737 C2
2746 E5
2748 E5
2754 E5
2757 D5
2769 B3
2786 B4
2789 A3
2791 A3
2793 A3
2806 D5
2807 D5
2808 B4
2812 B3
2817 D3
2823 A3
2825 A3
2827 A3
2882 D3
2883 D3
2884 D3
2885 D3
2892 E3
2893 D3
2894 D3
2920 D5
2932 C5
2933 C5
2A01 D6
2A07 C6
2A19 D7
2A24 D7
2A34 D8
2A38 D7
2A47 D5
2A51 C5
2A64 D6
2A69 D6
2A70 D6
2A72 D6
2A74 D6
2A75 D6
2A79 D6
2A80 D6
2A81 D6
2A83 D6
2A88 D6
2A89 D6
2A90 D6
2A91 D5
2A92 D6
2A99 D5
2AA5 D6
2AA9 D5
2AB0 D5
2AB3 D6
2AB4 D6
2AB8 D6
2AC1 E7
2AD0 E7
2AD3 E7
2AD4 E8
2AD5 E7
2AD6 E8
2AE2 D7
2AE3 D8
2AE5 E8
2AF0 D7
2AK8 E6
2AN5 E6
2AN6 E6
2C00 A5
2C02 B5
2D04 D1
2D15 D1
2E02 E1
2E04 E1
2E05 E2
2E07 E1
2E08 E2
2E09 D1
2E10 E2
2E11 E2
2E12 D2
2E13 E2
2E14 E2
2E15 D2
2E16 E1
2E18 D2
2E19 D1
2E20 E2
2E27 E2
2E35 D2
2E48 E2
2E49 D1
2E51 D1
2E52 C2
2E53 E2
2E55 C2
2E84 D2
2E86 D1
2E88 C2
2E92 B2
2E93 B2
2E94 B2
2I01 B7
2I02 B8
2I04 A7
2I05 B7
2I06 B7
2I07 A8
2I08 A8
2I09 A1
2I10 A6
2I11 A4
2I12 A5
2I37 F6
2I39 A5
2I40 F6
2I46 A2
2I47 A5
2I48 E6
2I50 A3
2I52 E5
2I59 E8
2I60 F6
2I69 B2
2I70 B2
2IA4 A5
2IB7 E6
2IB8 A1
2IB9 B2
2IC3 A3
2IC5 B1
2IC6 A2
2IC7 A2
2IE0 B8
2IF0 A1
2IF8 A2
2IF9 A2
2IG1 A8
2IH1 B1
2IH3 A5
2IH6 A2
2IH7 A2
2IH8 A2
2IH9 A2
2IJ0 A8
2IJ1 A7
2IJ4 A8
2IJ5 E5
2IK1 A2
2IK2 A1
2IK3 A1
2IK6 C6
2IL0 A7
2IN8 A2
2IN9 A2
2IR0 A3
2L18 B1
2L22 F1
2L25 B1
2L26 C2
2L27 C2
2L31 C2
2L32 C2
2L56 B1
2L59 B1
2L60 B1
2P01 C8
2P11 C9
2P12 C9
2P14 C9
2P15 C9
2P16 C9
2P18 C8
2P23 C8
2P24 C8
2P25 C9
2P29 C8
2P30 C8
2P31 C9
2P32 D9
2P33 C9
2P45 C9
2P46 C9
2P47 C8
2P49 C8
2P51 C8
2P52 C7
2P53 C7
2P54 C7
2P55 C7
2P56 C7
2P57 C7
2P58 C7
2P59 D8
2P60 D7
2P61 D7
2P62 D7
2P63 C7
2P65 C7
2P66 C7
2P70 B7
2P71 C7
2P72 B7
2P73 B7
2P74 C7
2P75 B7
2P76 C7
2P77 C7
2P78 B8
2P79 B7
2P87 B8
2P88 B7
2P91 C9
2P92 C9
2P93 C9
2P94 C9
2P95 C8
2P96 C8
2P97 C7
2PA1 C7
2PA2 C7
2PA3 C7
2PA9 C8
2PB0 C7
2PB1 C7
2PB2 C7
2PD0 C8
2PE7 C7
2PE8 C7
2PE9 C7
2PF2 B7
2PF5 B7
2PF6 B7
2PF7 C8
2PG2 C9
2PG6 D7
2T01 A9
2T02 D9
2T03 D8
2T04 A9
2T05 A9
2T06 A9
2T07 D8
2T09 A9
2T10 D9
2T11 D8
2T12 A9
2T13 A9
2T14 D8
2T15 A9
2T16 D8
2T17 A9
2T18 D8
2T19 D8
2T20 D8
2T21 D9
2T22 D9
2T30 E9
2T31 E8
2T32 E9
2T33 E8
2T34 E8
2T35 E8
2T36 E9
2T37 E8
2T38 E9
2T40 D9
2T41 D8
2T42 E8
2T43 E8
2T44 E8
2T45 E8
2T46 D8
2T47 E9
2T48 E8
2T49 E9
2T50 E9
2T51 E8
2T52 E9
2T53 E8
2T54 E9
2T60 A9
2T61 A9
2T62 A9
2T63 A9
2U01 F3
2U02 E3
2U06 E4
2U08 F2
2U10 F3
2U19 E4
2U22 E4
2U24 E4
2U25 E4
2U26 F4
2U27 E3
2U28 E3
2U29 F2
2U33 F4
2U35 E4
2U37 E3
2U38 E4
2U39 E4
2U40 E4
2U41 E4
2U42 E4
2Y00 F2
2Y01 F2
2Y02 F2
2Y03 F2
2Y04 F2
2Y10 E1
2Y11 F2
2Y14 E1
2Y17 E1
2Y18 D1
2Y22 F2
2Y23 D1
2Y25 C1
2Y26 C1
2Y27 C1
2Y28 D1
2Y29 D1
2Y34 F2
2Y48 F2
2Y50 F3
2Y52 F8
2Y53 D1
2Z54 E5
2Z55 E5
2Z56 E5
2Z64 F6
3001 C5
3002 C5
3004 B5
3005 B5
3006 B4
3007 B4
3008 B5
3009 C4
3010 B5
3013 B5
3014 B5
3015 B5
3016 B5
3017 B5
3022 C4
3023 C4
3028 C4
3029 B5
3030 C4
3031 B5
3032 C4
3034 B4
3036 C4
3037 C4
3038 C4
3040 B5
3041 B5
3042 C5
3045 A4
3046 A4
3048 B5
3049 B5
3050 B5
3051 B5
3052 B4
3053 C5
3054 B4
3055 B4
3056 B4
3057 B4
3061 B4
3062 B4
3064 C5
3067 B5
3069 C5
3070 C4
3072 B4
3079 C5
3080 C4
3081 B4
3082 B4
3083 B4
3085 B5
3086 B5
3087 B4
3088 C5
3092 C5
3093 B5
3094 C5
3095 C5
3096 C5
3097 A4
3098 A4
3100 C5
3101 C5
3102 B4
3103 C4
3300 B6
3301 B6
3303 B6
3305 C6
3307 C6
3308 C6
3310 C6
3311 C6
3312 C6
3313 C6
3314 C6
3315 B6
3316 C6
3319 C6
3323 B6
3324 B6
3325 C6
3326 B6
3327 B6
3328 B6
3331 C5
3333 B5
3334 B6
3337 C6
3338 C6
3339 C6
3350 C6
3351 C6
3352 C6
3354 C6
3355 C6
3356 C6
3358 C6
3359 C6
3360 C6
3362 C6
3364 C6
3365 C6
3366 C6
3367 C6
3369 C6
3378 B6
3380 B6
3382 B6
3383 C6
3384 C6
3385 B6
3386 C6
3389 C6
3391 C6
3401 B6
3405 B6
3407 A6
3408 B6
3410 A6
3414 B6
3415 B6
3417 A6
3419 A6
3420 B6
3421 A6
3434 A6
3435 A6
3441 B6
3445 A6
3450 B6
3451 B6
3452 B6
3453 C6
3454 C6
3455 C6
3456 B6
3457 B6
3459 C6
3463 B6
3465 C6
3467 C6
3468 B6
3470 C6
3471 C6
3700 D4
3702 E4
3709 E5
3710 D5
3711 E4
3757 A3
3758 E5
3759 D5
3761 D4
3762 C3
3763 C3
3764 C3
3767 C3
3768 C3
3769 C3
3770 C3
3771 A3
3772 A3
3773 A3
3774 C3
3775 C3
3776 A3
3777 C3
3779 C3
3780 C3
3781 C3
3784 C3
3792 A3
3793 B4
3794 A3
3795 A3
3797 B4
3799 B4
3800 A3
3801 A3
3802 A3
3803 C3
3804 C3
3811 A3
3812 A3
3814 A3
3815 A3
3817 A3
3818 A3
3822 D4
3825 B4
3871 E3
3872 D3
3873 E3
3880 D3
3881 D3
3882 D3
3883 D3
3884 D3
3894 A3
3896 B2
3900 B3
3901 C3
3902 C3
3911 B3
3912 B3
3918 B3
3919 B3
3921 B3
3A02 D7
3A04 D5
3A06 D6
3A17 D6
3A19 D6
3A22 D5
3A24 C5
3A40 D6
3A45 D5
3A46 D5
3A47 D6
3A48 D5
3A49 D5
3A51 D6
3A52 D6
3A53 D6
3A55 D5
3A60 D6
3A61 D6
3A62 D6
3A63 D6
3A64 D5
3A65 C5
3A67 D7
3A74 E8
3A77 D7
3C00 A5
3C04 A5
3C05 A5
3C10 B5
3C11 C5
3C12 B5
3E04 E1
3E05 E1
3E11 E2
3E12 E2
3E14 E2
3E18 D2
3E19 D2
3E20 B2
3E21 B2
3E51 D1
3E55 D1
3E56 D1
3E57 D1
3E58 D1
3E69 C2
3E70 C2
3E81 C2
3E82 B2
3E83 C2
3E84 B2
3E85 B2
3E86 B2
3E88 D2
3E89 D1
3E90 E1
3I01 A8
3I02 B8
3I03 B8
3I04 A7
3I05 B7
3I06 B8
3I07 A5
3I08 A8
3I09 A8
3I10 B7
3I11 B7
3I12 B7
3I13 B7
3I14 B7
3I15 B7
3I16 B7
3I17 A7
3I18 A7
3I23 A8
3I24 A8
3I25 B8
3I28 A4
3I29 A3
3I30 A2
3I31 A3
3I32 A2
3I33 A2
3I34 A4
3I36 A4
3I37 A4
3I38 A4
3I40 A2
3I41 A2
3I42 B2
3I44 A1
3I45 A2
3I46 A1
3I47 B1
3I48 B1
3I49 A2
3I85 A3
3I98 A5
3IA1 A5
3IA4 A8
3IA5 A8
3IA6 A3
3IA7 A3
3IA8 A4
3IA9 A4
3IB0 A3
3IB1 E8
3IB3 E8
3IB4 A2
3IB5 A2
3IB6 E8
3IB7 E8
3IBA E8
3IBB E8
3IC0 E8
3IC1 A3
3IC2 A5
3IC3 A5
3IC5 E8
3IC7 E8
3IC8 A3
3ID0 A3
3ID2 E6
3ID3 F6
3ID4 F6
3ID5 A3
3ID6 E5
3ID7 A5
3ID8 A5
3ID9 A3
3IE0 F6
3IE7 A3
3IF1 E6
3IF2 E6
3IF3 F6
3IF4 E6
3IF8 E6
3IF9 E6
3IG9 A1
3IGA F6
3IGB F6
3IGC F6
3IGD F6
3IGE F6
3IGF F6
3IH0 F6
3IH1 A5
3IH2 F6
3IH4 F6
3IH7 A3
3IH8 A8
3IHG A7
3II0 A8
3II1 A8
3II2 A8
3II3 A8
3II5 A2
3II6 A2
3II7 A2
3II8 B2
3II9 B2
3IJ2 A2
3IJ3 A2
3IJ4 A2
3IJ6 A2
3IJ7 A2
3IJ8 A7
3IK4 A7
3IK5 A8
3IK7 A7
3IK9 B2
3IN1 A7
3IN2 A3
3IN3 A3
3IN8 A3
3IO5 A3
3IO6 A3
3IP0 A8
3IP1 A8
3IP2 A8
3IP3 A7
3IP4 A8
3IP5 A8
3IP6 A8
3IP7 A8
3IP8 A7
3IP9 A3
3IQ0 A7
3IQ1 A7
3IQ4 A7
3IQ5 B2
3IQ6 A2
3IQ7 A2
3IR0 B1
3IR1 B1
3IS1 B2
3IS4 A3
3IT5 B2
3IT9 A8
3IU1 A2
3IU3 A1
3IV4 A2
3IV5 A2
3IV6 A2
3IW1 A1
3IW3 A6
3IW7 A2
3IW8 A2
3IW9 A6
3IZ3 A2
3IZ4 A2
3IZ5 A2
3L02 B1
3L03 C2
3L06 C2
3L08 C2
3L12 B1
3L40 F1
3L41 F1
3L42 F1
3L43 F1
3L44 E1
3L45 E1
3L46 E1
3L47 E1
3L48 F1
3L49 E1
3P03 C8
3P04 C8
3P05 C8
3P06 C8
3P09 B8
3P11 B9
3P12 B8
3P13 B8
3P14 B8
3P15 B8
3P16 C9
3P21 C8
3P22 C8
3P23 C8
3P24 C8
3P31 C9
3P32 C9
3P33 C9
3P36 C9
3P37 C8
3P38 C9
3P39 C9
3P40 B9
3P45 C8
3P46 C8
3P47 C9
3P48 C8
3P49 C8
3P50 C7
3P51 C7
3P52 C7
3P53 C8
3P54 C7
3P55 D7
3P56 C7
3P57 C7
3P60 C7
3P62 C7
3P63 C7
3P64 C7
3P65 B8
3P66 B8
3P67 B7
3P68 B7
3P69 B7
3P70 B7
3P71 C8
3P72 B8
3P74 B7
3P75 D7
3P76 C7
3P79 C8
3P80 C8
3P81 C7
3P82 B7
3P85 B8
3P86 B7
3P87 B7
3P88 B7
3P92 C8
3P94 C8
3P95 C8
3P96 C7
3P97 D7
3P98 C7
3P99 C7
3PC0 C8
3PC5 B7
3PD7 C8
3PF5 B7
3PG1 C7
3PG7 D7
3PG8 C7
3PH5 D8
3PH9 D7
3PI0 B7
3PJ0 D8
3PJ1 D8
3PJ2 D8
3PJ3 D8
3PJ4 C7
3PJ5 C7
3PJ6 C7
3PJ7 C7
3PJ8 C7
3PJ9 C7
3T03 A9
3T04 D8
3T05 A9
3T06 A9
3T10 E9
3T11 E9
3T12 E9
3T13 E9
3T14 E9
3T15 E9
3T16 E8
3T17 E8
3T18 E8
3T19 E8
3T20 E9
3T22 E9
3T23 E8
3T24 E8
3T25 E8
3T26 E8
3T27 E9
3T28 D8
3T29 E9
3T30 E9
3T31 E9
3T32 E8
3T33 E9
3T51 E9
3T52 E9
3T53 E9
3T54 E9
3T55 E9
3T56 E9
3T57 E9
3T58 E9
3T59 E9
3T60 E9
3U12 F5
3U24 E4
3U27 E5
3U32 E3
3U33 E3
3U35 E4
3U36 F5
3U37 F4
3U38 F4
3U39 E4
3U40 E4
3U41 E4
3U42 E4
3U43 F4
3U44 E3
3U45 E3
3U54 E5
3U55 F4
3U58 E3
3U59 E3
3U60 E4
3U61 E4
3U62 E4
3U63 E4
3U64 E4
3U65 E4
3U66 E4
3U67 E4
3U68 E4
3U69 E4
3V18 C2
3V37 C2
3V38 C2
3V40 C2
3Y00 E1
3Y01 E1
3Y02 E1
3Y03 E1
3Y05 E1
3Y06 F2
3Y07 F1
3Y08 F1
3Y09 D1
3Y10 E1
3Y11 E1
3Y12 D1
3Y13 F2
3Y14 F8
3Y20 D1
3Y21 D1
3Y22 D1
3Y23 D1
3Y24 F9
3Y25 F8
3Y30 F1
3Y33 F2
3Y34 F3
3Y35 F3
3Y37 F8
3Y38 F8
3Y40 D1
3Z23 E5
3Z24 F5
3Z25 F5
3Z26 F5
3Z29 E5
3Z30 E5
3Z31 E5
3Z32 E5
3Z33 E5
3Z36 E5
3Z37 F5
3Z38 F6
3Z39 F5
3Z56 E5
5304 A5
5305 A5
5308 A5
5312 B6
5313 C6
5314 C6
5315 C6
5318 B6
5401 B6
5402 A6
5404 B6
5408 B6
5702 C5
5719 E4
5720 E4
5723 E5
5724 E5
5727 E5
5728 E5
5763 D3
5769 E3
5770 D3
5771 D3
5A07 D7
5E00 E1
5E01 E2
5E02 E2
5E03 E2
5E50 C2
5E54 D1
5E55 C2
5E58 C2
5I02 E8
5I04 E8
5I10 E6
5I39 B2
5I42 A2
5I45 C6
5P05 B9
5P08 C8
5P09 C8
5P10 C8
5P11 C9
5P50 C7
5PA9 B7
5T02 D9
5T03 D8
5T04 E8
5T10 D9
5T11 E8
5T12 D9
5T13 D9
5T14 E8
5T15 E8
5T20 A9
5T22 A9
5T25 A9
5Y00 F1
5Y01 E1
5Y02 F2
5Y03 F2
5Y06 F2
5Y07 F2
5Y09 F1
5Y11 E1
5Y12 E1
5Y14 D1
5Y15 F2
5Y18 F8
5Y19 F8
5Y20 F8
5Y21 F8
5Y22 F8
5Y23 D1
5Z07 F6
5Z08 F6
6002 A4
6004 C4
6005 A4
6006 C4
6303 B6
6304 B6
6306 B6
6307 B6
6308 C6
6312 B6
6313 B6
6314 C6
6317 C6
6334 B6
6402 A6
6403 B6
6405 A6
6713 E3
6714 D3
6715 E3
6A01 C5
6A02 C6
6E53 D1
6E55 D2
6E56 C2
6I01 A3
6I03 E8
6I04 E8
6I05 E5
6I06 A2
6I07 A3
6I08 A2
6I09 A2
6I11 A4
6I12 A5
6I13 A5
6I63 B2
6I64 A2
6I65 A1
6I66 A2
6I80 A1
6I81 A1
6IA1 A1
6IA7 A5
6P00 B8
6P01 B8
6P10 C7
6PB1 B7
6PB5 D8
6PB9 D7
6T01 A9
6T02 D8
6T03 A9
6T04 D8
6T05 A9
6T06 D9
6T07 D9
6T08 A9
6T10 E9
6T11 E9
6U02 E3
6U10 E3
6U11 E4
6U12 F4
6U14 E4
6U16 E4
6V05 C2
6Z00 E5
7002 B5
7003 B5
7004 B5
7007 A5
7011 C5
7012 B4
7015 C5
7016 C5
7020 C4
7021 C4
7022 C4
7301 C6
7302 C6
7303 B6
7305 C6
7306 C6
7307 B6
7309 C6
7310 C6
7312 B6
7313 C6
7314 C6
7315 C6
7316 C6
7317 C6
7318 C6
7319 C6
7322 B6
7375 C6
7401 A6
7403 B6
7406 A6
7407 A6
7410 B6
7412 B7
7712 E5
7713 D4
7714 D3
7719 C3
7720 B3
7752 C4
7753 C4
7760 D3
7A04 D6
7A06 D6
7A07 D6
7A08 D5
7A09 D5
7A13 D7
7A14 D7
7A15 D8
7A30 E8
7E03 B2
7E04 C2
7E05 D1
7E10 C2
7E12 D1
7E23 E2
7E24 E1
7I01 A8
7I02 A3
7I03 A4
7I04 A4
7I05 A5
7I07 A3
7I08 A6
7I09 A2
7I10 E8
7I12 A3
7I13 E5
7I14 F6
7I15 E6
7I16 E6
7I19 B1
7I20 A8
7I22 A8
7I23 A2
7I27 A3
7I29 A3
7I31 A3
7I32 A3
7I35 A8
7I36 A8
7I37 A8
7I38 A7
7I40 F6
7I41 A2
7I44 A5
7I46 E8
7I49 A5
7I50 A5
7I51 B2
7I52 B2
7I55 A2
7I61 B2
7I62 A8
7I64 B2
7L01 B1
7L03 F1
7L04 F1
7L05 E1
7P01 B8
7P03 B9
7P04 B9
7P06 C9
7P07 C9
7P11 C9
7P51 C7
7P52 C7
7P53 C7
7P54 C7
7P55 C7
7P56 B7
7P58 C7
7P59 C7
7P60 C8
7P61 C8
7P62 C8
7P63 D8
7PB5 B7
7T01 D9
7T04 E9
7T10 E8
7T11 E9
7T12 E9
7T13 E9
7T50 A9
7U07 F4
7U13 E4
7V01 C2
7V02 D2
7V03 C1
7Y01 F9
7Y02 F8
7Z00 E5
7Z01 E5
9001 C5
9002 C5
9003 C5
9004 B5
9005 A4
9006 A4
9007 A4
9008 C4
9009 C4
9010 C5
9011 C5
9012 C4
9013 C4
9014 B5
9015 C5
9019 C4
9021 C4
9024 C4
9025 C4
9308 C6
9309 C6
9310 C6
9311 C6
9312 C6
9313 C6
9318 B6
9319 B6
9401 A6
9402 A6
9403 A6
9404 B6
9405 A6
9406 B6
9407 B6
9410 B6
9413 B6
9415 B6
9418 A6
9IB1 A7
9420 A6
9IB2 A7
9421 C6
9IB3 A2
9422 B6
9ID1 A3
9427 B6
9ID2 A3
9701 E5
9ID3 A2
9702 E5
9ID4 A2
9706 D5
9ID5 A2
9710 D5
9ID6 A2
9712 B4
9ID7 A2
9714 C2
9ID8 A2
9715 B4
9ID9 A2
9716 B4
9L00 F1
9723 B3
9L01 F1
9726 D5
9P04 B8
9740 B4
9P05 B9
9753 B4
9P07 C9
9754 B4
9P09 B9
9755 B4
9P10 B8
9756 B4
9P11 B8
9757 B4
9P12 C9
9758 B4
9P16 B8
9759 B4
9P17 C8
9760 B4
9P18 B9
9763 B4
9P20 C8
9764 B4
9P21 C8
9765 B4
9P22 C9
9766 B4
9P23 C8
9773 B4
9P24 C9
9774 B4
9P25 C9
9775 B4
9P28 C8
9811 D3
9P30 C9
9820 D4
9P31 C7
9823 B3
9P32 C7
9A00 D6
9P52 C7
9A01 D6
9P53 C7
9A02 D6
9P54 D7
9A03 D6
9P69 B7
9A07 D6
9P71 B7
9A08 D6
9P73 D7
9A10 E6
9P74 D7
9A11 E6
9P75 D7
9A12 E6
9PB7 D8
9A13 E6
9T01 A9
9A14 E6
9T02 D8
9A15 E6
9T03 D8
9A16 E6
9T04 A9
9A17 E6
9T05 A9
9A18 D6
9T06 D8
9A20 E6
9T07 A9
9C02 A4
9T08 A9
9E57 C2
9T09 D8
9E58 C2
9T10 D8
9E66 D1
9T11 E8
9E67 D1
9T12 A9
9E68 D1
9T14 A9
9E69 D1
9T50 A9
9E70 D1
9Y00 D1
9E71 D1
9Y02 F1
9E72 D1
9Y03 F1
9E73 D2
9Y05 E1
9E75 D1
9Y06 E1
9E76 D1
9Y07 E1
9E77 D2
9Y09 F1
9I00 A7
9Y12 F2
9I01 A7
9Y13 F2
9I02 A7
9Y14 F2
9I03 B7
9Y15 F1
9I05 E8
9Y16 F9
9I06 E8
9Y17 F9
9I09 A7
9I11 A7
9I15 A8
9I16 A8
9I19 B7
9I29 A2
9I31 A7
9I32 A7
9I33 A7
9I34 A8
9I39 A7
9I41 A3
9I42 A3
9I50 A4
9I57 A8
9I58 A8
9I62 A3
9I63 A3
9I64 A3
9I65 A3
9I66 A3
9I67 A3
9I68 A2
9I78 B8
9I79 A3
9I81 A2
9I88 A2
9I91 A2
9I92 A7
9I93 A7
9I94 A7
9I96 B8
9I98 A2
9I99 F6
9IA2 A3
9IA4 A5
9IA5 A5
F_15460_049m.eps
110405
EN 85FTP2.4E AA 7.
Personal Notes:
E_06532_012.eps
131004
Page 86

Circuit Diagrams and PWB Layouts
Layout SSB (Bottom Side Part 1)
EN 86FTP2.4E AA 7.
Part 1
F_15460_049a.eps
120405
Page 87

Circuit Diagrams and PWB Layouts
Layout SSB (Bottom Side Part 2)
EN 87FTP2.4E AA 7.
Part 2
F_15460_049b.eps
120405
Page 88

Circuit Diagrams and PWB Layouts
Layout SSB (Bottom Side Part 3)
EN 88FTP2.4E AA 7.
Part 3
F_15460_049c.eps
120405
Page 89

Circuit Diagrams and PWB Layouts
Layout SSB (Bottom Side Part 4)
EN 89FTP2.4E AA 7.
Part 4
F_15460_049d.eps
120405
Page 90

PDP Audio Amplifier
0001 A15
1736 A13
1738 G13
1M02 A13
1M06 A14
1M52 E14
2700 A3
2701 B10
2702 H11
2703 A7
2704 A7
2705 B10
2706 A3
2707 C5
2708 F9
2709 A6
2710 A7
2711 A2
2712 A10
2713 A4
2714 G14
2715 A10
2716 A10
2717 A8
2718 B5
2719 A4
2720 B5
2721 B6
2722 B4
2723 B8
2724 H10
2725 H10
2726 B4
2727 C9
2728 H10
1234
2729 H10
2731 C91735 C12
2732 C10
2733 G9
2736 D10
2737 D10
2739 D6
2740 F11
2741 E6
2742 G11
2743 E5
2744 E3
Circuit Diagrams and PWB Layouts
2745 B7
2746 C7
2747 C2
2748 C2
2749 C3
2750 G9
2751 F4
2752 G5
2754 D15
2756 G7
2757 G7
2758 G5
2759 G11
2760 G6
2761 G1
2762 G2
2763 H5
2764 E8
2766 H11
2767 H11
2768 H5
2770 A15
2771 H6
2772 G2
2773 G3
2774 G3
2775 H5
2776 A6
2778 E9
2779 E8
2780 A10
2782 F8
2783 G8
2788 H8
2789 D10
2790 G15
2791 D14
2793 H1
2794 H3
2795 H3
2796 H3
2797 H4
2798 H4
2799 H9
3700 A2
3701 A10
3702 C2
EN 90FTP2.4E AA 7.
3703 A2
3704 A10
3705 A5
3706 A4
3707 A8
3708 A10
3709 A3
3710 B8
3711 B9
3712 B3
3713 C13
3714 B4
3715 B8
3716 C10
3717 C5
3718 C2
3719 C2
3720 D10
3721 C3
3722 A3
3723 A3
3724 C2
3726 D4
3727 D6
3728 D4
3729 D2
3730 D1
3731 D3
3732 E4
3733 E6
3734 E4
3735 F5
3736 F3
3737 F3
3738 F5
3739 F9
3740 F15
3741 G10
3742 G14
3743 G5
3744 G5
3745 G11
3746 G13
3747 G5
3748 G152755 G2
3749 G5
3750 G2
3751 H13
3752 H14
3753 H11
3754 G4
3755 H5
3756 H5
3757 G3
3758 G2
3759 G7
3760 E2
3761 H11
3762 H9
3763 H7
3764 A10
3765 D10
3766 H10
3767 H9
3768 G10
3769 H8
3770 H2
3771 H3
3772 H2
3773 H23725 D2
3774 H2
3775 H9
3776 H9
3777 D3
3778 D10
3999 A15
5700 A10
5701 D14
5702 C10
5704 G9
5705 A7
5706 G10
5708 C7
5709 E9
5714 H8
6700 D13
6702 D5
6703 E3
6704 G13
6705 H13
7700-1 C4
7700-2 A4
7701 A7
7702 C14
7705 D5
7706 D3
7707 D2
7708 E6
7709 E5
7710 E4
7711 F5
7712 G6
7713 G6
7714 F8
7715 G15
7716 G14
7717 H14
7718-1 G2
7718-2 G4
7719-1 H6
7719-2 H6
7720 H15
9700 E12
9701 E12
9702 E12
9703 E13
9704 G12
9705 H12
9706 G7
9707 H7
9708 H7
9709 G14
F700 A12
F701 A12
F702 A11
F703 B13
F704 A13
F705 B13
F706 B12
F707 C12
F708 C12
F709 C11
F710 E13
F711 E14
F712 E13
F713 D15
F714 F13
F715 F13
F716 F13
F717 F13
F718 F13
F719 G12
F720 G12
F721 G12
F722 H8
F723 H8
F724 H6
F725 G7
F726 A7
F727 A5
F728 B6
F729 C5
F730 D6
F731 B8
F733 H4
F734 A15
F735 A14
F740 A12
F741 A12
F742 A13
F743 B13
F744 C7
F745 C12
F747 E8
F748 G3
F749 G12
F750 G7
I700 G13
I701 H13
I702 G11
I703 A2
I704 A3
I705 A3
I706 A4
I707 C3
I708 D4
I709 D5
I710 A4
I711 G10
I712 A9
I713 C2
I714 C2
I715 A8
I716 A10
I717 D2
I718 A8
I719 A10
I720 B8
I721 B4
I722 C9
I723 B4
I724 B9
I725 C8
I726 B10
I727 D10
I728 G9
I729 D13
I730 D3
I731 G7
I732 D14
I733 D10
I734 D3
I735 H7
I736 D2
I737 D2
I738 D3
I739 D4
I740 E4
I741 G11
I742 E3
I743 F3
I744 F5
I745 F6
I746 F9
I747 G10
5 6 7 8 9 1011 12131415
I748 G15
I749 G1
I750 G3
I751 G14
I752 G5
I753 G5
I754 G5
I755 G2
I756 G4
I757 G5
I758 H11
I759 H5
I760 H14
I761 H4
I762 H9
I763 H5
I764 H3
I765 H15
I766 G1
I767 H3
I768 H10
I769 H11
I770 H3
I771 H1
I772 H2
I773 H10
I774 G10
I775 C9
I776 B10
I777 A11
C C
C (4x)
3104 313 6056.4
AUDIO AMPLIFIER
AUDIO-L
8K2
3703
2711
I703
1u0
3700
560R
AUDIO-R
3719
120K
2747
I714
1u0
1n5
2748
3724
1K0
47K
3725
I717
3729
3
47K
7707
BC847BW
2
2755
100n
84
3
7718-1
1
2
LM833D
2772
100n
3774
100K
3770
47K
10K
2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13
SOUND-ENABLE
POR
DC-PROT
DC
I766
AUDIO-C
8K2
3702
I713
3718
560R
+19-16VS1
I736
I737
3730
1
22K
22K
3760
VDDOPAMP
I749
3750
330R
2761
1u0
2793
120p
I755
2762
1u0
22K
3758
3773
-19-16VS2
I772
3K3
3772
I771
1
470R
1
I738
3721
I767
2795
220p
2744
2796
470n
3771
3K9
F740
F741
B3B-PH-K
-19-16V
+19-16V
F706
1735
3
2
1
B3B-PH-K
+19-16V
9700
9701
9702
F717
1738
F749
B3B-PH-K
TO
CENTER
SPEAKER
-19-16V
1736
3
2
1
F742
F704
F743
F705
1V2
TO
RIGHT
SPEAKER
9703
F710
F712
F716
F718
+19-16V
3
2
1
TO
LEFT
SPEAKER
1M02
1
2
F703
3
4
5
6
7
B7B-PH-K
3713
I729
6700
F714
F715
6704
I700
3746
3751
I701
6705
3K3
2791
BZX384-C15
F711
4V7
0V3
0V
BZX384-C10
3742
100K
2K2
2K2
3752
10K
BZX384-C10
1M06
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
B7B-EH-A
7702
BC847BW
1
220n
1M52
B9B-PH-K
2714
F735
TO 1M02
PDP
SUPPLY
3
I732
5701
2
1
TO 1M52
2
3
4
5
6
7
SSB
8
9
BP2.x / FTP2.x
I751
1
9709
100u 16V
I760
3999
1K0
I748
3
7716
BC847BW
2
2
7717
BC847BW
2754
1
2770
F713
3740
100K
F734
0001
1
GND screw
10n
OR
SUPPLY
VDDOPAMP
22u 100V
OR
3
1
7715
BC847BW
2
3748
100K
3
1
I765
VDD2
VSS2
2757
2704
13
BOOT1
BOOT2
10
F725
2K2
OUT1
DIAG
OUT2
3759
F750
2K2
100n
25V
470u
2745
220n
2746
470u 25V
-19-16VS1
+19-16VS2
-19-16VS2
-19-16VS2
5705
+19-16V
2710
-19-16VS1
220n
6
7
3
12
11
9706
I731
9707
F731
TDA8925ST
-19-16V
I720
F722
I725
2764
7714
1
2
4
9
15
17
16
14
2783
220n
2788
25V 470u
I715
1u0
2717
1u0
2723
F747
100V22u
2782
220n
VDD1
CLASS-D
AMPLIFIER
SW1
REL1
EN1
STAB
POWERUP
SW2
REL2
EN2
VSS1
3707
39K
I718
3710
39K
3715
5R6
220n
2779
5
VDD2
Φ
VSS2
8
F723
5714
3769
+19-16VS1
13
BOOT1
OUT1
DIAG
BOOT2
OUT2
10
-19-16VS2
3775
120K
5R6
I775
2778
+19-16VS1
I724
25V470u
6
7
3
12
11
3776
2799
470p
I712
5709
2708
220n
18K
2727
560p
2731
560p
I722
2750
2733
5700
33u
3764
100K
I726
3711
5R6
I776
+19-16VS1
-19-16VS1
5702
33u
3765
100K
+19-16V
-19-16VS2
I746
3739
39K
1u0
I747
1u0
3768
I728
39K
5704
I711
33u
2724
3767
100K
2725
3762
22R
I762
I719
I733
5706
33u
I773
2712
2780
3708
2701
560p
2705
560p
2732
2789
3720
+19-16VS2
470n
I768
470n
3704
I777
100K
470n
I716
470n
47R
47R
3701
470n
I727
470n
47R
47R
3778
I774
+19-16VS2
470n
2728
2729
2715
+19-16VS1
-19-16VS1
3716
100K
2736
3741
5R6
3766
100K
15n
470n
470n
2716
2737
15n
15n
2740
560p
2742
I702
I741
560p
3745
100K
2759
470n
2766
470n
2767
I758
2702
470n
3753
I769
22R
3761
100K
F709
+19-16VS2
-19-16VS2
15n
C (4x)
DC
DC-PROT
C (4x)
DC
AUDIO-L
AUDIO-R
PROT-AUDIOSUPLLY
SOUND-ENABLE
POR
PROT-AUDIOSUPLLY
C (4x)
DC
C (4x)
DC
AUDIO-C
F721
F707
F720
9704
9705
F700
F701F702
F745
F708
F719F748
SW1
REL1
EN1
STAB
POWERUP
SW2
REL2
EN2
I735
F726
220n
2703
5
VDD1
Φ
CLASS-D
AMPLIFIER
VSS1
8
F744
5708
1
2756
22u 100V
-19-16VS2
3763
9708
3n9
+19-16VS1
I742
3737
I743
3757
2719
470n
I710
2713
I706
4n7
3706
3K9
I721
2722
470n
2726
4n7
3714
3K9
I739
3
1
7710
BC847BW
2
47K
3754
470R
I756
5
6
8K2
2798
2797
560p
560p
5
6
7700-2
LM393PT
84
I723
7700-1
LM393PT
3732
22K
7718-2
LM833D
I761
84
3
2
3728
15K
BC857BW
7
F733
84
3726
15K
I708
BZX384-C39
I740
3734
7711
2751
22K
2775
7
2718
1
6702
2743
2
3
47u 25V
2752
120p
3749
10K
39n
-19-16VS1
VDDOPAMP
100n
100n
2707
I709
1
1n0
1
I752 I753
I757
2763
220p
2768
470n
3755
3K9
I759
F727
3705
3717
F729
3
1
2
3
7709
BC847BW
2
3735
270K
3738
I744
100K
3743
3K3
3747
2758
1u0
I763
3756
8K2
3709
4K7
3722
120K
I705
3723
I704
470R
2n7
2700
I707
2749
I730
3777
I734
100n
2773
1u0
2794
1u0
3n9
1K0
3
7706
BC847BW
2
6703
2706
3712
4K7
3731
1K0
BZX384-C3V3
3736
47K
I750
2774
1u0
-19-16VS2
+19-16VS2
I770
I764
2K2
2720
2K2
7705
BC847BW
+19-16VS1
47K
I754
2
3
VDDOPAMP
100V22u
2721
3727
7708
BC857BW
2
1
3744
100K
84
+19-16VS1
-19-16VS1
100n
10K
3
1
3
7712
BC847BW
2
2760
100n
1
LM393PT
7719-1
2771
100n
2739
-19-16VS2
6
5
F728
100n
3733
-19-16VS1
BC847BW
2776
22u 100V
2709
220n
7701
TDA8925ST
1
2
4
9
15
17
16
14
-6V7
-19-16V
F730
-19-16VS1
5K6
2741
220p
I745
3
7713
2
F724
7
LM393PT
7719-2
84
F_15460_050.eps
14 15
TO
SDI
TO 1J04
SSB
LC4.x
2790
3
7720
BC847BW
2
A
B
C
D
E
F
100n
G
H
110405
Page 91

Circuit Diagrams and PWB Layouts
EN 91FTP2.4E AA 7.
Layout PDP Audio Amplifier (Top Side)
3104 313 6056.4
F_15460_051.eps
110405
0001 C1
1735 E1
1736 E1
1738 B1
1M02 C1
1M06 C1
1M52 B1
2704 D1
2714 C1
2715 E1
2720 D1
2728 B1
2736 E1
2746 D1
2751 B1
2754 C1
2756 A1
2764 A1
2766 B1
2776 D1
2778 A1
2788 A1
3753 B1
3762 A1
5700 E1
5702 E1
5704 A1
5705 D1
5706 A1
5708 D1
5709 B1
5714 A1
7701 D1
7714 A1
9704 B1
9705 B1
9708 A1
9715 E1
9716 B1
9721 A1
9723 B1
9724 A1
9725 A1
9726 C1
9727 A1
9728 B1
9730 B1
9731 A1
9732 A1
9733 A1
9734 A1
9735 B1
9739 D1
9740 D1
9741 E1
9742 D1
9744 D1
9745 D1
9747 E1
9749 A1
9774 A1
9797 C1
9798 B1
9799 B1
9801 C1
9804 C1
9805 C1
9810 C1
9811 C1
Layout PDP Audio Amplifier (Bottom Side)
9800
3104 313 6056.4
F_15460_052.eps
140405
2700 D1
2701 D1
2702 B1
2703 E1
2705 D1
2706 D1
2707 C1
2708 A1
2709 E1
2710 E1
2711 D1
2712 E1
2713 D1
2716 E1
2717 D1
2718 C1
2719 C1
2721 E1
2722 C1
2723 D1
2724 B1
2725 B1
2726 C1
2727 E1
2729 B1
2731 E1
2732 E1
2733 A1
2737 E1
2739 E1
2740 A1
2741 E1
2742 A1
2743 B1
2744 B1
2745 D1
2747 C1
2748 C1
2749 C1
2750 A1
2752 A1
2755 A1
2757 A1
2758 A1
2759 B1
2760 A1
2761 A1
2762 A1
2763 A1
2767 B1
2768 A1
2770 B1
2771 A1
2772 A1
2773 A1
2774 A1
2775 A1
2779 A1
2780 E1
2782 A1
2783 A1
2789 E1
2790 D1
2791 C1
2793 A1
2794 A1
2795 A1
2796 A1
2797 A1
2798 A1
2799 A1
3700 C1
3701 E1
3702 C1
3703 D1
3704 E1
3705 D1
3706 D1
3707 D1
3708 E1
3709 C1
3710 D1
3711 D1
3712 C1
3713 C1
3714 C1
3715 D1
3716 E1
3717 D1
3718 C1
3719 C1
3720 E1
3721 C1
3722 D1
3723 D1
3724 B1
3725 B1
3726 E1
3727 E1
3728 E1
3729 B1
3730 B1
3731 B1
3732 B1
3733 E1
3734 B1
3735 B1
3736 C1
3737 B1
3738 B1
3739 A1
3740 C1
3741 A1
3742 C1
3743 A1
3744 A1
3745 B1
3746 C1
3747 A1
3748 D1
3749 A1
3750 A1
3751 D1
3752 D1
3754 A1
3755 A1
3756 A1
3757 A1
3758 A1
3759 A1
3760 B1
3761 B1
3763 A1
3764 E1
3765 E1
3766 A1
3767 A1
3768 A1
3769 A1
3770 A1
3771 A1
3772 A1
3773 A1
3774 A1
3775 A1
3776 A1
3777 B1
3778 E1
3999 A1
5701 C1
6700 C1
6702 E1
6703 B1
6704 C1
6705 D1
7700 C1
7702 C1
7705 E1
7706 B1
7707 B1
7708 B1
7709 B1
7710 B1
7711 B1
7712 B1
7713 B1
7715 C1
7716 C1
7717 D1
7718 A1
7719 A1
7720 D1
9700 C1
9701 C1
9702 B1
9703 C1
9706 A1
9707 A1
9709 C1
9710 D1
9711 E1
9712 D1
9713 D1
9748 D1
9757 D1
9758 D1
9759 D1
9760 D1
9761 D1
9762 D1
9763 D1
9764 D1
9765 D1
9766 D1
9768 D1
9770 D1
9775 A1
9776 A1
9777 A1
9778 A1
9779 A1
9780 A1
9781 A1
9782 A1
9783 A1
9784 A1
9785 A1
9786 A1
9787 A1
9788 A1
9789 A1
9790 C1
9792 A1
9793 A1
9795 D1
9796 B1
9800 B1
9802 B1
9803 C1
9806 B1
9807 C1
9808 C1
9809 C1
9812 C1
9813 C1
9814 C1
Page 92

Circuit Diagrams and PWB Layouts
EN 92FTP2.4E AA 7.
Side I/O Panel
123456789
D D
SIDE I/O
F001
A
B
C
D
E
F
3104 313 6058.4
C
2010
2008
1101
1102
1106
GND_AUD
1108
GND_AUD
22n
GNDB
22n
GNDB
1109
1111
1110
2
1001
1002-1
YELLOW
1002-2
WHITE
1002-3
RED
1010
Y / CVBS
134
5
F003
1
2
F004
9004
645
I001
9005
978
I003
F007
5
4
2
F008
F009
3
7
F019
8
1
GNDB
GND_AUD
F002
F005
F006
GNDB
123456
I009
I002
I010
GNDB
GNDB
GNDB
6000
6002
6003
6004
6005
6006
6007
PDZ6.8-B
I004
PDZ6.8-B
PDZ6.8-B
PDZ6.8-B
PDZ6.8-B
GND_AUD
PDZ6.8-B
PDZ6.8-B
GND_AUD
6010
PDZ6.8-B
I014
PDZ6.8-B
6008
I013
PDZ6.8-B
6009
6001
6011
GNDB
I005
PDZ6.8-B
GNDB
PDZ6.8-B
3004
2004
2006
I007
75R
680p
680p
75R
3000
F020
3010
GND_AUD
3013
GND_AUD
33K
33K
9011
9010
9009
9008
3009
1K0
3012
1K0
2005
2007
100p
100p
I008
3020
GNDB
I006
3016
JAGUAR ONLY
TO 1H01
VIPER
10n
10n
3008
2K2
10K
10K
3011
3K9
2011
GNDB
2009
GNDBGNDB
2003
RES
1u0
F025
9003
1H01
OR
1M60
5000
F012
1
2
3
4
56
F014
F016
1050
DLW31S
F013
F015
F017
1112
1005
56
1
2
3
4
USB
CONNECTOR
TO 1M36
1M36
F022
F021
F023
GNDB
1M37
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
B11B-PH-SM3-TBT
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
13
12
SSB EMGT
OR
TO 1M36
SCART 3
OR
TO 1M36
SSB JAGUAR
F024
F010
3999
150R
F011
I011
9006
F018
GNDB
9007
I012
GND_AUD
789
EMGT
F_15460_053.eps
110405
A
B
C
D
E
F
1001 B2
1002-1 B1
1002-2 C1
1002-3 D1
1005 A8
1010 E1
1050 A7
1101 A3
1102 B3
1106 C3
1108 D3
1109 E3
1110 F3
1111 E3
1112 A7
1H01 A6
1M36 B8
1M37 B8
2003 C5
2004 C3
2005 C4
2006 D3
2007 D4
2008 F2
2009 F5
2010 E2
2011 E5
3000 A4
3004 B3
3008 C5
3009 C4
3010 C4
3011 C5
3012 D4
3013 D4
3016 F5
3020 E5
3999 F9
5000 A7
6000 A3
6001 A3
6002 B3
6003 B3
6004 C3
6005 C3
6006 D3
6007 D3
6008 F3
6009 F3
6010 E3
6011 F3
9003 C6
9004 C2
9005 D2
9006 F7
9007 F8
9008 F4
9009 F4
9010 E4
9011 E4
F001 A2
F002 A2
F003 B2
F004 C2
F005 C2
F006 D2
F007 E2
F008 E2
F009 E2
F010 F8
F011 F9
F012 A6
F013 A7
F014 A6
F015 A7
F016 A6
F017 A7
F018 F7
F019 F2
F020 B4
F021 C6
F022 C6
F023 C6
F024 E6
F025 E6
I001 C2
I002 C3
I003 D2
I004 A3
I005 F4
I006 F4
I007 E4
I008 E4
I009 B3
I010 D3
I011 F7
I012 F8
I013 F3
I014 E3
Page 93
Circuit Diagrams and PWB Layouts
EN 93FTP2.4E AA 7.
Layout Side I/O Panel (Top Side)
1001 B1
1002 A1
1005 A1
1010 A1
1050 A1
1H01 A1
1M36 B1
1M37 B1
5000 A1
Layout Side I/O Panel (Bottom Side)
2003 A1
2004 A1
2005 A1
2006 A1
2007 A1
2008 A1
2009 A1
2010 A1
2011 A1
3000 B1
3004 B1
3008 A1
3009 A1
3010 A1
3011 A1
3012 A1
3013 A1
3016 A1
3020 A1
3999 B1
6000 B1
6001 B1
6002 B1
6003 B1
6004 A1
6005 A1
6006 A1
6007 A1
6008 A1
6009 A1
6010 A1
6011 A1
9003 A1
9004 A1
9005 A1
9006 A1
9007 B1
9008 A1
9009 A1
9010 A1
9011 A1
3104 313 6058.4
F_15460_054.eps
110405
3104 313 6058.4
F_15460_055.eps
110405
Page 94

Top Control Panel
Circuit Diagrams and PWB Layouts
EN 94FTP2.4E AA 7.
E E
A
B
C
D
E
3104 313 6020.3
1234567
TOP CONTROL
33R
3017
6001
SML512BC2T
1701
VOLUME -
I105
3014
SKQNAB
390R
33R
3018
6002
SML512BC2T
1702
SKQNAB
VOLUME +
I109
3013
200R
I112I111
3019
6003
1705
MENU
3011
33R
I113
SML512BC2T
6004
SKQNAB
CHANNEL -
2K0
33R
3020
SML512BC2T
1704
3010
I114I110
SKQNAB
1K1
33R
3021
6005
SML512BC2T
1703
SKQNAB
CHANNEL +
I107I106I108
3008
620R
I115
3022
6006
33R
I116
SML512BC2T
6007
36
25
14
33R
3023
SML512BC2T
ON / OFF
I117
6008
9000
1710
33R
3024
I118
SML512BC2T
KEYBOARD
33R
3025
6009
SML512BC2T
BACKLIGHT-TC
I119
3026
6010
9002
33R
3027
I120
6011
SML512BC2T
F002
F005
9001
33R
3028
I121
6012
SML512BC2T
0345
F001
BACKLIGHT-TC
33R
SML512BC2T
1
2
TO
3
4
5
LED + SWITCH
6
F006
3999
2K2
F_15460_056.eps
F007
110405
A
B
C
D
E
0345 C5
1701 D1
1702 D1
1703 D2
1704 D2
1705 D2
1710 E4
3008 D3
3010 D2
3011 D2
3013 D1
3014 D1
3017 B1
3018 B1
3019 B2
3020 B2
3021 B2
3022 B3
3023 B3
3024 B4
3025 B4
3026 B4
3027 B5
3028 B5
3999 E7
6001 B1
6002 B1
6003 B2
6004 B2
6005 B2
6006 B3
6007 B3
6008 B4
6009 B4
6010 B4
6011 B5
6012 B5
9000 D4
9001 D5
9002 D5
F001 C5
F002 C5
F005 C5
F006 E7
F007 E7
I105 D1
I106 D2
I107 D2
I108 D2
I109 D1
I110 B1
I111 B1
I112 B2
I113 B2
I114 B2
I115 B3
I116 B3
I117 B4
I118 B4
I119 B4
I120 B5
I121 B5
1234567
Page 95

Circuit Diagrams and PWB Layouts
Layout Top Control Panel (Top Side)
EN 95FTP2.4E AA 7.
0345 -1701 --
1702 -1703 --
1704 -1705 --
1710 -3008 --
3104 313 6020.3
Layout Top Control Panel (Bottom Side)
3010 -3011 --
3013 -3014 --
3017 -3018 --
3019 -3020 --
3021 -3022 --
3023 -3024 --
3025 -3026 --
3027 -3028 --
3999 -6001 --
6002 -6003 --
6004 -6005 --
6006 -6007 --
6008 -6009 --
6010 -6011 --
6012 -9000 --
9001 -9002 --
F_15460_057.eps
110405
3104 313 6020.3
F_15460_058.eps
110405
Page 96

Circuit Diagrams and PWB Layouts
EN 96FTP2.4E AA 7.
SCART 3 Panel
12345678910111213
1n0
2507
BZX384-C10
7501
BC847BW
2508
I580
3525
V-GND
3529
V-GND
F536
2511
100n
7502
+11V-SFS
1u0
F512
F514
F516
F544
F545
V-GND
3524
47R
1K0
2513
100n
V-GND
I583
3535
47R
1K0
SNDR-IN
SNDL-IN
SEL_FRONT_SC3
SEL_FRONT_SC3
SEL_IN_1_BF
SEL_FRONT_SC3
FRONT-SC3-Y-CVBS
SEL_FRONT_SC3
FRONT-SC3-C
STATUS-SC3-F
+11V-SF
SEL_IN_1_BF
FRONT-SC3-Y-CVBS
FRONT-SC3-C
SNDL-IN
SNDR-IN
HEADPHONE-L
HEADPHONE-R
2523
100p
F523
V-GND
2522
3533
100R
2520
2521
3532
100R
100p
2524
F549
F525
F526
F530
A-GND
9503
3530
100R
100p
3531
100R
100p
F519
9505
9504
3534
100R
100p
1M07
B5B-PH-K
1M37
B11B-PH-K
9506
F546
F518
1
2
3
4
5
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
F510
B7B-PH-K
F531
F513
F515
0244
F517
1005
440050-1
F547
F548
TO 1M07
SSB EMG
TO 1M36
SSB EMG
H H
SCART 3
+11V-SF
F532
3511
3512
3514
3513
47R
47R
3515
47R
A
I505
3501
100R
BZX384-C6V8
3502
BZX384-C6V8
I518
3504
100R
BZX384-C6V8
3505
BZX384-C6V8
330p
2510
9500
RES
2500
1u0
22K
2502
1u0
22K
STATUS-SC3-F
FRONT-SC3-Y-CVBS
FRONT-Y-CVBS
HEADPHONE-L
HEADPHONE-R
SNDR-SC3-IN
SNDL-SC3-IN
CVBS-SC3-IN
CVBS-SC3-IN
FRONT-C
FRONT-L
FRONT-R
SNDR-SC3-IN
FRONT-R
SNDL-SC3-IN
FRONT-L
STATUS-SC3-F
CVBS-SC3-IN
FRONT-Y-CVBS
F543
FRONT-C
I560
F539
I562
F540
F520
F542
I570
2515
2517
1u0
2505
1u0
2504
1u0
2516
1u0
7515
74HC4053PW
I576
A-GND
I577
+11V-SFS
74HC4053PW
I581
1u0
I571
V-GND
I582
7516
3
5
1
2
13
12
3
5
1
2
13
12
2509
V-GND
7
VEE
3y1
3y0
2y1
2y0
1y1
1y0
MUXDX
A-GND
7
VEE
3y1
3y0
2y1
2y0
1y1
1y0
MUXDX
16
2506
16
100n
8
GND
s2
3z
s1
2z
s0
1z
G3
VCC
100n
8
GND
s2
3z
s1
2z
s0
1z
G3
VCC
+11V-SFS
4
15
14
6
4
15
14
6
9
10
A-GND
11
A-GND
F541
V-GND
9
10
11
A-GND
I564
I565
I572
I579
I573
V-GND
c001
9501
RES
9521
9502
I575
A-GND
V-GND
3526
3509
100R
I503
6500
2501
100p
I508
6501
I516
6502
2503
100p
I519
6503
8K2
2K7
3522
75R
3500
100R
I549
3506
75R
I552
3508
6506
BZX384-C6V8
1500
1502
75R
6507
1506
75R
BZX384-C6V8
3510
6505
3503
100R
BZX384-C12
3543
75R
F521
1003
3999
1K0
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
F522
1509
1
F500
2
1511
3
I504
4
5
F501
6
7
B
8
F502
9
1512
1513
1514
1510
1501
1508
I550
G
F538
I551
R
1507
FBL
F503
3507
1505
1504
B
C
SCART
D
E
F
1M36
1
2
TO 1M36
SIDE I/O
G
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
B11B-PH-K
F527
F529
A-GND
F524
F528
V-GND
H
V-GND
3516
47R
47R47R
6508
6504
BAS316
100n
3527
3528
V-GND
3536
10K
BC847BW
68K
22K
+11V-SFS
+11V-SFS
47K
3517
I578
22K
3523
2512
V-GND
V-GND
+11V-SFS
95169517
V-GND
3104 313 6023.4
1234
567
8 9 10 11 12 13
7
ONLY
6
5
FOR
4
3
ITV
2
1
1
2
ONLY
3
FOR
4
5
ITV
6
F_15460_059.eps
110405
0244 B13
1003 B1
1005 C13
1500 B3
1501 C2
1502 C3
1504 F2
1505 E2
1506 E3
A
1507 D2
1508 C2
1509 B2
1510 E2
1511 B2
1512 C2
1513 D2
1514 E2
1M07 F12
1M36 F1
1M37 F12
2500 A4
B
2501 B3
2502 C4
2503 C3
2504 E6
2505 C5
2506 D6
2507 A9
2508 A9
2509 G6
2510 D4
2511 D9
2512 E8
C
2513 F9
2515 E5
2516 F6
2517 B5
2520 B12
2521 C12
2522 C12
2523 D11
2524 D12
3500 A3
3501 A3
D
3502 B4
3503 C3
3504 C3
3505 C4
3506 C2
3507 D2
3508 E2
3509 E3
3510 F3
3511 A6
3512 A6
3513 A7
E
3514 A7
3515 A7
3516 A8
3517 E8
3522 D3
3523 E8
3524 E9
3525 E9
3526 D3
3527 F8
3528 G8
3529 G9
F
3530 B12
3531 C12
3532 C12
3533 D12
3534 D12
3535 F9
3536 D9
3543 E3
3999 F1
6500 B3
6501 B3
G
6502 C3
6503 C3
6504 E8
6505 F2
6506 F2
6507 D2
6508 A8
7501 E9
7502 F9
7515 B6
7516 D6
9500 F4
H
9501 E7
9502 D7
9503 B12
9504 D12
9505 C12
9506 A12
9516 H8
9517 H7
9521 G7
F500 B2
F501 C2
F502 C2
F503 E2
F510 A12
F512 B12
F513 B13
F514 B12
F515 B13
F516 B12
F517 C13
F518 C12
F519 C12
F520 E5
F521 F1
F522 F1
F523 F12
F524 F2
F525 F12
F526 F12
F527 G1
F528 G2
F529 G1
F530 G12
F531 A12
F532 A5
F536 A9
F538 D2
F539 B5
F540 C5
F541 D7
F542 E5
F543 F5
F544 B10
F545 C10
F546 D12
F547 D12
F548 D13
F549 F12
I503 A3
I504 C2
I505 A4
I508 B3
I516 C3
I518 C4
I519 C3
I549 C2
I550 D2
I551 D2
I552 E2
I560 B5
I562 C5
I564 B7
I565 C7
I570 E5
I571 E6
I572 E7
I573 F7
I575 E7
I576 B6
I577 C6
I578 E8
I579 E7
I580 E9
I581 E6
I582 F6
I583 F9
c001 F7
Page 97

Circuit Diagrams and PWB Layouts
EN 97FTP2.4E AA 7.
Layout SCART 3 Panel (Top Side)
0244 A2 1003 A1 1005 A3 1M07 A1 1M36 A4 1M37 A3 9500 A3 9509 A3 9510 A3 9511 A4 9512 A1 9513 A2 9514 A1 9515 A3 9523 A2 9525 A4 9526 A4 9527 A4
3104 313 6023.4
Layout SCART 3 Panel (Bottom Side)
2500 A4
2501 A4
2502 A4
2503 A4
2504 A2
2505 A1
2506 A1
2507 A4
2508 A4
2509 A1
2510 A2
2511 A1
2512 A1
2513 A1
2515 A1
2516 A1
2517 A1
2520 A3
2521 A3
2522 A3
2523 A3
2524 A3
3500 A4
3501 A4
3502 A4
3503 A4
3504 A4
3505 A4
3506 A4
3507 A3
3508 A3
3509 A3
3510 A3
3511 A4
3512 A4
3513 A4
3514 A4
3515 A4
3516 A4
3517 A1
3522 A2
3523 A1
3524 A1
3525 A1
3526 A4
3527 A1
3528 A1
3529 A1
3530 A3
3531 A3
3532 A3
3533 A3
3534 A3
3535 A1
3536 A2
3543 A3
3999 A1
6500 A4
6501 A4
6502 A4
6503 A4
6504 A1
6505 A3
6506 A3
6507 A4
6508 A4
7501 A1
7502 A1
7515 A2
7516 A2
9501 A2
9502 A2
9503 A3
9504 A3
9505 A3
9506 A3
9508 A3
9516 A2
9517 A2
9521 A2
9524 A2
F_15460_060.eps
110405
3104 313 6023.4
F_15460_061.eps
110405
Page 98

Circuit Diagrams and PWB Layouts
EN 98FTP2.4E AA 7.
LED and Switch Panel
12345678910111213
LED & SWITCH PANEL
J J
F018
F019
F028
3027
220R
3092
7092
BC847BW
3010
100R
I023
I025
+5V2-STBY
10K
3096
3095
I024
F032
10K
10K
F016
F021
F029
F010
F011
F012
F015
F017
F013
F014
3012
100R
2014
7075
P87LPC760BDH
14
CIN1B
13
CIN1A
12
CMPREF
10
CMP1
P0<3:6>
5
CLKOUT
X2
4
X1
P2<0:1>
I094
+8V
+5V2-STBY
100n
F031
2021
100n
113
VDD
Φ
MICROCONTROLLER
P1<0:3>
VSS
I034
10K
3093
TXD
RXD
INT0
SDA
RST
P1.5
P1.7
SCL
T0
3030
3011
100R
+5V2-STBY
4K7
I039
7032
BC847BW
9015
KEYBOARD
COM-SND
9016
9017
9012
5020
9
8
7
F030
6
F033
2
1
6030
BAS316
6031
BAS316
LED1
RC
LIGHT-SENSOR
LED2
SCL-S
SDA-S
LED1
9010
STATUS-POWER
9018
9019
3025
+5V2-STBY
10K
3026
SDA-S
SCL-S
RC
KEYBOARD
+5V2-STBY
10K
9060
(RES)
RC2
PWM-OUT
I021
"PROXIMITY"
"LED DIMMING"
9031
3031
100K
3032
180K
I040
2030
I047
I033
I048
3033
1K0
16V10u
I062
I064
I019
(RES)
I061
3061
3060
LED1
PULSE-OUT
+8V
+5V2-STBY
3062
330R
(RES)
100R
6060
"BLUE"
RC
c001
3021
2K2
BC857BW
7030
560R
6061
BAS316
SML512BC4T
BC857CW
I030
I038
3034
1K0
STATUS-POWER
9061
I063
16V
2060
22u
+5V2-STBY
7020
I035
3035
I037
3022
75R
+5V2-STBY
4K7
I031
TSAL5300
3036
I049
BCP53
7031
9050
(RES)
I051
6080
+5V2-STBY
2R2
3037
BLACKLIGHT-TC
LED2
PWM-OUT
I032
7021
2R2
3053
BC857CW
I052
100R
OPT_LED
"RED"
+5V2-STBY
3K3
3024
I027
47K
3023
I036
2022
220n
(RES)
6051
+8V
+5V2-STBY
3051
3052
330R
560R
(RES)
12
TLMH3100
1040
VS
OUT
GND
TSOP34836YA1
"IR RECEIVER"
9041
9040
9081
9082
9083
2070
470n
3071
LM358P
84
7070-1
I073
16V10u
2071
0345
1
2
3
4
5
6
8
7
B6B-PH-SM3-TBT
0350
1
2
3
4
5
B5B-PH-SM3-TBT
I026
1
+8V
3077
TO 0345
TOP CONTROL
TO 0350
PROXIMITY SENSOR
+8V
84
5
6
I074
1K0
3K3
3072
7070-2
LM358P
3073
3K3
3074
10K
I076
7
3075
I072
LIGHT-SENSOR
4K7
3K3
3076
F083
F087
F084
F086
+5V2-STBY
3080
100R
3081
100R
3082
100R
I071
6070
I075
3070
TEMD5000
F088
F089
+5V2-STBY
4M7
2
3
4M7
KEYBOARD
BLACKLIGHT-TC
RC2
PWM-OUT
PULSE-OUT
RC
+5V2-STBY
9044
I046
3040
330R
I044
6K8
3042
9043
I045
I043
I042
10K
3041
9042
I041
2040
9013
16V100u
"LIGHT SENSOR"
F038
3999
10K
A
B
C
D
E
F
G
H
I
3104 313 6016.5
OR
OR
1M20
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
14
13
B12B-PH-SM3-TBT
FOR ITV
0244
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
B7B-PH-SM3-TBT
1M01
1
2
3
B3B-PH-SM3-TBT
F020
I020
9014
I022
TO 1M20
SSB JAGUAR
SSB EMG
TO 0244
SIDE I/O
TO 1M01
SSB JAGUAR
SSB EMG
+5V2-STBY
10K
3020
COM-SND
DSX840GA
PROX-DET
COM-SND
STATUS-POWER
PROX-DET
20M
I028
15p
3094
10K
+8V
3091
1020
9093
2023
F027
I029
15p
2020
I093
10K
12345678910111213
F039
F_15460_062.eps
110405
A
B
C
D
E
F
G
H
I
0244 C1
0345 B11
0350 C11
1020 E2
1040 F8
1M01 C1
1M20 A1
2014 D3
2020 F2
2021 E3
2022 F7
2023 F1
2030 I4
2040 F9
2060 C6
2070 F11
2071 G11
3010 B2
3011 A3
3012 B2
3020 E1
3021 E5
3022 E6
3023 E7
3024 E7
3025 E4
3026 F4
3027 E2
3030 H3
3031 H4
3032 I4
3033 H5
3034 H6
3035 H6
3036 H6
3037 H7
3040 E9
3041 G9
3042 F9
3051 B8
3052 B8
3053 C7
3060 C5
3061 B5
3062 B5
3070 G10
3071 F11
3072 G11
3073 G12
3074 F12
3075 F12
3076 G13
3077 G11
3080 C10
3081 C10
3082 C10
3091 H1
3092 G2
3093 H3
3094 G1
3095 I2
3096 H2
3999 I13
5020 D4
6030 H4
6031 I4
6051 C8
6060 C5
6061 B6
6070 G10
6080 E7
7020 E6
7021 F7
7030 H5
7031 H6
7032 I3
7070-1 F11
7070-2 F12
7075 E3
7092 H2
9010 C4
9012 B4
9013 E9
9014 C2
9015 A4
9016 A4
9017 A4
9018 C4
9019 C4
9031 H4
9040 G9
9041 F9
9042 G9
9043 F9
9044 E9
9050 C7
9060 C5
9061 B6
9081 B11
9082 B11
9083 C11
9093 H1
F010 A2
F011 A3
F012 A3
F013 B3
F014 B2
F015 A3
F016 B2
F017 A2
F018 B2
F019 B2
F020 B2
F021 D2
F027 E2
F028 E2
F029 E2
F030 E4
F031 D3
F032 E2
F033 F4
F038 I12
F039 I13
F083 B10
F084 B10
F086 B10
F087 C10
F088 B10
F089 B10
I019 E5
I020 C2
I021 E4
I022 C2
I023 C2
I024 C2
I025 C2
I026 F11
I027 E7
I028 F1
I029 F2
I030 E6
I031 E6
I032 E7
I033 I4
I034 G3
I035 E6
I036 F7
I037 H6
I038 H6
I039 H3
I040 H4
I041 G9
I042 G9
I043 F9
I044 E9
I045 F9
I046 E9
I047 H4
I048 H5
I049 H7
I051 D7
I052 B7
I061 C5
I062 B5
I063 C6
I064 D5
I071 F10
I072 F13
I073 G11
I074 G11
I075 F10
I076 F12
I093 G2
I094 G2
c001 E5
Page 99

Circuit Diagrams and PWB Layouts
EN 99FTP2.4E AA 7.
Layout LED and Switch Panel (Top Side)
3104 313 6023.4
F_15460_063.eps
110405
1020 C1
1040 A1
6051 A1
6060 A1
6070 A1
6080 C1
Layout LED and Switch Panel (Bottom Side)
3104 313 6023.4
F_15460_064.eps
110405
0244 C1
0345 B1
0350 A1
1M01 B1
1M20 A1
2014 C1
2020 C1
2021 B1
2022 C1
2023 C1
2030 B1
2040 A1
2060 A1
2070 B1
2071 B1
3010 B1
3011 B1
3012 B1
3020 B1
3021 C1
3022 C1
3023 C1
3024 C1
3025 C1
3026 B1
3027 C1
3030 B1
3031 B1
3032 B1
3033 B1
3034 B1
3035 B1
3036 B1
3037 B1
3040 A1
3041 A1
3042 A1
3051 A1
3052 A1
3053 A1
3060 A1
3061 A1
3062 A1
3070 B1
3071 B1
3072 A1
3073 A1
3074 A1
3075 A1
3076 A1
3077 B1
3080 A1
3081 A1
3082 A1
3091 B1
3092 B1
3093 B1
3094 B1
3095 B1
3096 B1
3999 B1
5020 B1
6030 B1
6031 B1
6061 A1
7020 C1
7021 C1
7030 B1
7031 B1
7032 B1
7070 A1
7075 C1
7092 B1
9010 B1
9012 B1
9013 A1
9014 A1
9015 B1
9016 A1
9017 A1
9018 C1
9019 C1
9031 B1
9040 A1
9041 A1
9042 A1
9043 A1
9044 A1
9050 A1
9060 A1
9061 A1
9081 B1
9082 B1
9083 B1
9093 A1
Page 100

Personal Notes:
Circuit Diagrams and PWB Layouts
EN 100FTP2.4E AA 7.
E_06532_013.eps
131004
 Loading...
Loading...