Philips 74HCT193U, 74HCT193DB, 74HCT193D, 74HC193U, 74HC193PW Datasheet
...
DATA SH EET
Product specification
File under Integrated Circuits, IC06
December 1990
INTEGRATED CIRCUITS
74HC/HCT193
Presettable synchronous 4-bit
binary up/down counter
For a complete data sheet, please also download:
•The IC06 74HC/HCT/HCU/HCMOS Logic Family Specifications
•The IC06 74HC/HCT/HCU/HCMOS Logic Package Information
•The IC06 74HC/HCT/HCU/HCMOS Logic Package Outlines

December 1990 2
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
Presettable synchronous 4-bit binary
up/down counter
74HC/HCT193
FEATURES
• Synchronous reversible 4-bit binary counting
• Asynchronous parallel load
• Asynchronous reset
• Expandable without external logic
• Output capability: standard
• ICC category: MSI
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
The 74HC/HCT193 are high-speed Si-gate CMOS devices
and are pin compatible with low power Schottky TTL
(LSTTL). They are specified in compliance with JEDEC
standard no. 7A.
The 74HC/HCT193 are 4-bit synchronous binary up/down
counters. Separate up/down clocks, CP
U
and
CPDrespectively, simplify operation. The outputs change
state synchronously with the LOW-to-HIGH transition of
either clock input. If the CPUclock is pulsed while CPDis
held HIGH, the device will count up. If the CPDclock is
pulsed while CPUis held HIGH, the device will count down.
Only one clock input can be held HIGH at any time, or
erroneous operation will result. The device can be cleared
at any time by the asynchronous master reset input (MR);
it may also be loaded in parallel by activating the
asynchronous parallel load input (PL).
The “193” contains four master-slave JK flip-flops with the
necessary steering logic to provide the asynchronous
reset, load, and synchronous count up and count down
functions.
Each flip-flop contains JK feedback from slave to master,
such that a LOW-to-HIGH transition on the CPDinput will
decrease the count by one, while a similar transition on the
CPUinput will advance the count by one.
One clock should be held HIGH while counting with the
other, otherwise the circuit will either count by two’s or not
at all, depending on the state of the first flip-flop, which
cannot toggle as long as either clock input is LOW.
Applications requiring reversible operation must make the
reversing decision while the activating clock is HIGH to
avoid erroneous counts.
The terminal count up (TCU) and terminal count down
(TCD) outputs are normally HIGH. When the circuit has
reached the maximum count state of 15, the next
HIGH-to-LOW transition of CPUwill cause TCUto go
LOW.
TCUwill stay LOW until CPUgoes HIGH again, duplicating
the count up clock.
Likewise, the TCDoutput will go LOW when the circuit is in
the zero state and the CPDgoes LOW. The terminal count
outputs can be used as the clock input signals to the next
higher order circuit in a multistage counter, since they
duplicate the clock waveforms. Multistage counters will not
be fully synchronous, since there is a slight delay time
difference added for each stage that is added.
The counter may be preset by the asynchronous parallel
load capability of the circuit. Information present on the
parallel data inputs (D0to D3) is loaded into the counter
and appears on the outputs (Q0to Q3) regardless of the
conditions of the clock inputs when the parallel load
(PL) input is LOW. A HIGH level on the master reset (MR)
input will disable the parallel load gates, override both
clock inputs and set all outputs (Q0to Q3) LOW. If one of
the clock inputs is LOW during and after a reset or load
operation, the next LOW-to-HIGH transition of that clock
will be interpreted as a legitimate signal and will be
counted.
December 1990 3
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
Presettable synchronous 4-bit binary
up/down counter
74HC/HCT193
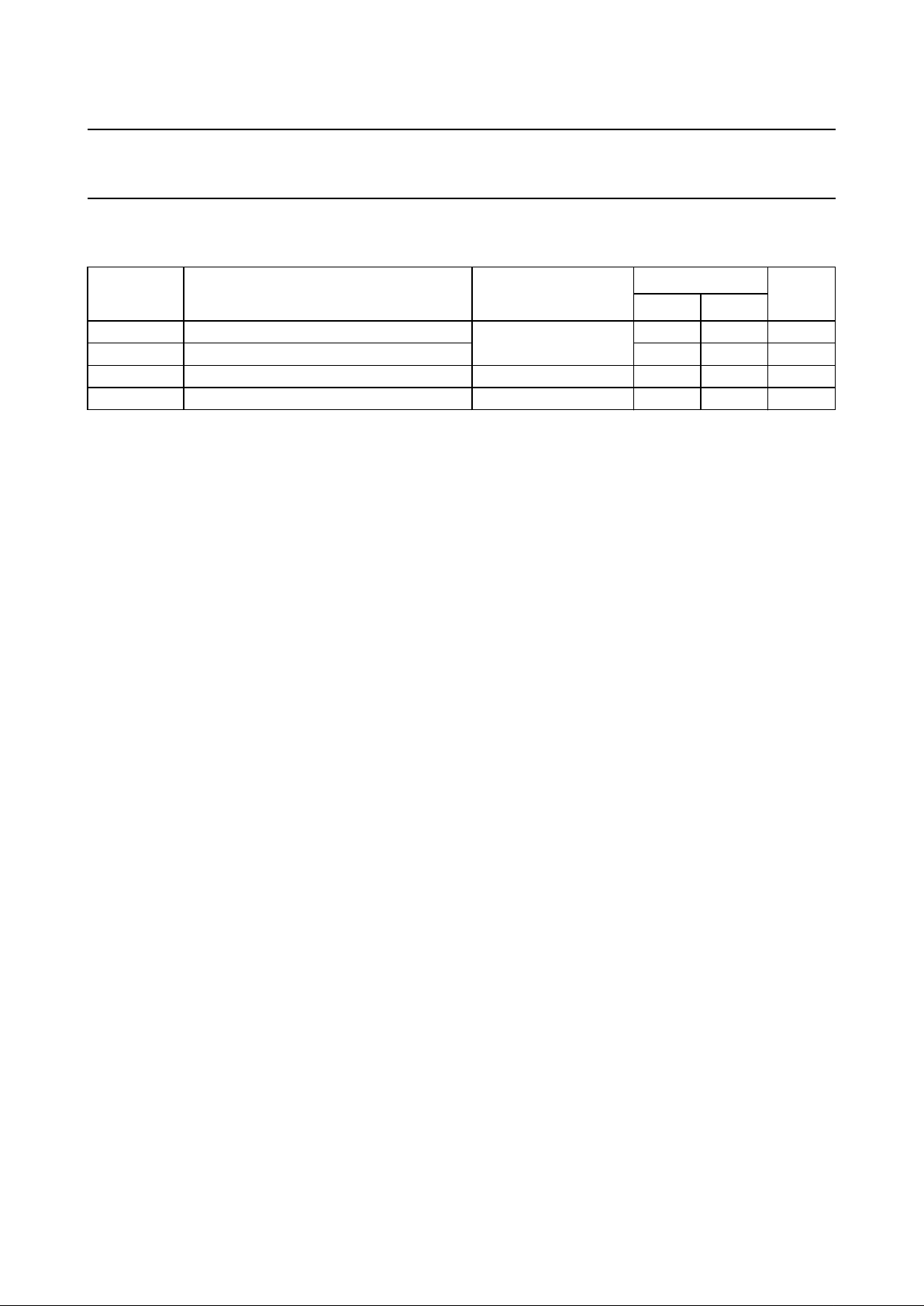
QUICK REFERENCE DATA
GND = 0 V; T
amb
= 25 °C; tr= tf= 6 ns
Notes
1. C
PD
is used to determine the dynamic power dissipation (PDin µW):
PD= CPD× V
CC
2
× fi+∑(CL× V
CC
2
× fo) where:
fi= input frequency in MHz
fo= output frequency in MHz
∑ (CL× V
CC
2
× fo) = sum of outputs
CL= output load capacitance in pF
VCC= supply voltage in V
2. For HC the condition is VI= GND to V
CC
For HCT the condition is VI= GND to VCC− 1.5 V
ORDERING INFORMATION
See
“74HC/HCT/HCU/HCMOS Logic Package Information”
.
SYMBOL PARAMETER CONDITIONS
TYPICAL
UNIT
HC HCT
t
PHL
/ t
PLH
propagation delay CPD, CPU to Q
n
CL= 15 pF; VCC= 5 V
20 20 ns
f
max
maximum clock frequency 45 47 MHz
C
I
input capacitance 3.5 3.5 pF
C
PD
power dissipation capacitance per package notes 1 and 2 24 26 pF
December 1990 4
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
Presettable synchronous 4-bit binary
up/down counter
74HC/HCT193
PIN DESCRIPTION
Note
1. LOW-to-HIGH, edge triggered
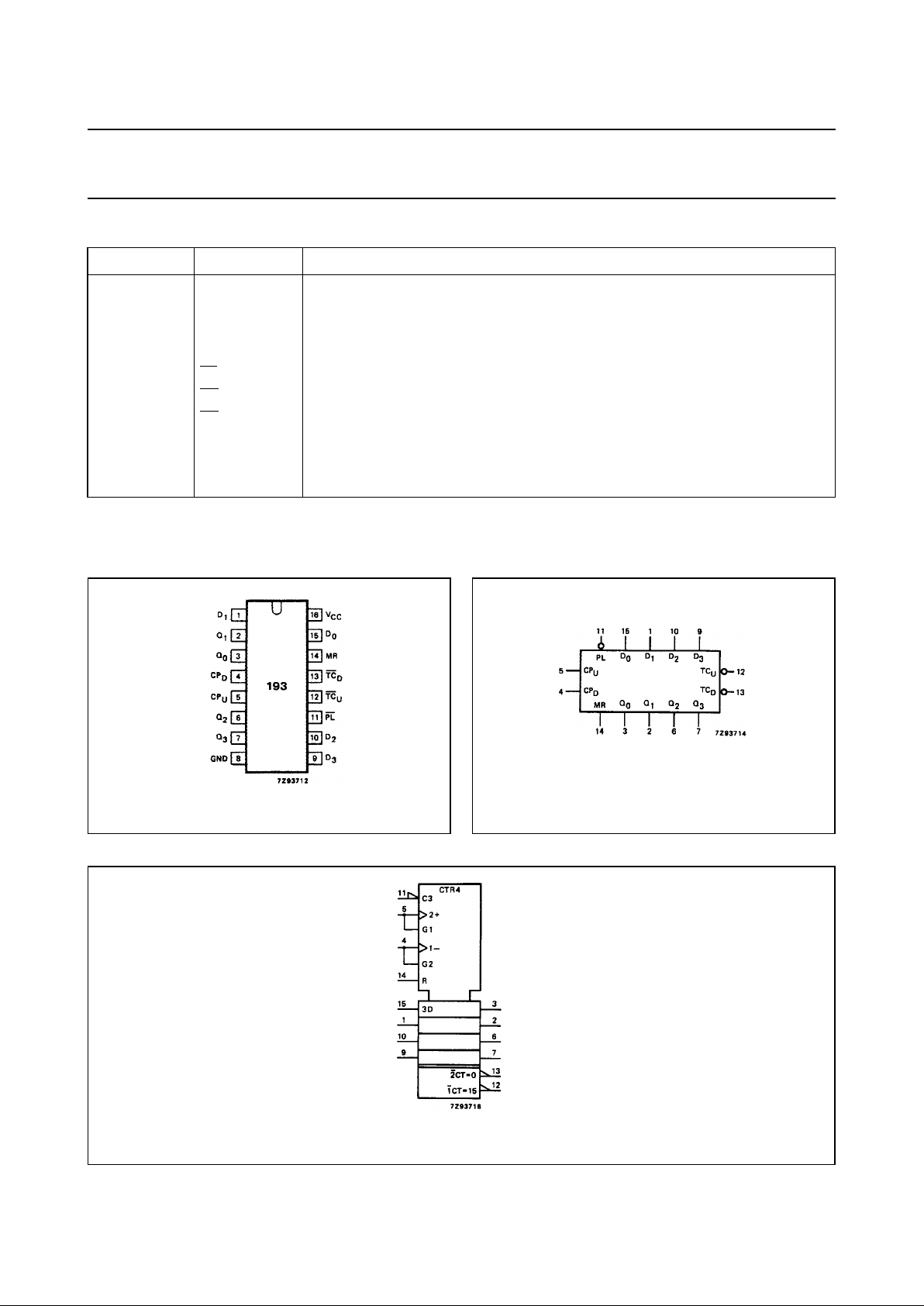
PIN NO. SYMBOL NAME AND FUNCTION
3, 2, 6, 7 Q
0
to Q
3
flip-flop outputs
4CP
D
count down clock input
(1)
5CP
U
count up clock input
(1)
8 GND ground (0 V)
11
PL asynchronous parallel load input (active LOW)
12
TC
U
terminal count up (carry) output (active LOW)
13
TC
D
terminal count down (borrow) output (active LOW)
14 MR asynchronous master reset input (active HIGH)
15, 1, 10, 9 D
0
to D
3
data inputs
16 V
CC
positive supply voltage
Fig.1 Pin configuration. Fig.2 Logic symbol.
Fig.3 IEC logic symbol.
 Loading...
Loading...