Philips 74HCT138U, 74HCT138NB, 74HCT138N, 74HCT138DB, 74HCT138D Datasheet
...
DATA SH EET
Product specification
File under Integrated Circuits, IC06
September 1993
INTEGRATED CIRCUITS
74HC/HCT138
3-to-8 line decoder/demultiplexer;
inverting
For a complete data sheet, please also download:
•The IC06 74HC/HCT/HCU/HCMOS Logic Family Specifications
•The IC06 74HC/HCT/HCU/HCMOS Logic Package Information
•The IC06 74HC/HCT/HCU/HCMOS Logic Package Outlines
September 1993 2
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
3-to-8 line decoder/demultiplexer; inverting 74HC/HCT138
FEATURES
• Demultiplexing capability
• Multiple input enable for easy expansion
• Ideal for memory chip select decoding
• Active LOW mutually exclusive outputs
• Output capability: standard
• ICCcategory: MSI
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
The 74HC/HCT138 are high-speed Si-gate CMOS devices
and are pin compatible with low power Schottky TTL
(LSTTL). They are specified in compliance with JEDEC
standard no. 7A.
The 74HC/HCT138 decoders accept three binary
weighted address inputs (A
0
, A1, A2) and when enabled,
provide 8 mutually exclusive active LOW outputs (Y0to
Y7).
The “138” features three enable inputs: two active LOW
(E1and E2) and one active HIGH (E3). Every output will be
HIGH unless E1and E2are LOW and E3is HIGH.
This multiple enable function allows easy parallel
expansion of the “138” to a 1-of-32 (5 lines to 32 lines)
decoder with just four “138” ICs and one inverter.
The ”138” can be used as an eight output demultiplexer by
using one of the active LOW enable inputs as the data
input and the remaining enable inputs as strobes. Unused
enable inputs must be permanently tied to their
appropriate active HIGH or LOW state.
The ”138” is identical to the “238” but has inverting outputs.
QUICK REFERENCE DATA
GND = 0 V; T
amb
= 25 °C; tr= tf= 6 ns
Notes
1. C
PD
is used to determine the dynamic power dissipation (PDin µW):
PD= CPD× V
CC
2
× fi+∑(CL× V
CC
2
× fo) where:
fi= input frequency in MHz
fo= output frequency in MHz
∑ (CL× V
CC
2
× fo) = sum of outputs
CL= output load capacitance in pF
VCC= supply voltage in V
2. For HC the condition is VI= GND to V
CC
For HCT the condition is VI= GND to VCC− 1.5 V
ORDERING INFORMATION
See
“74HC/HCT/HCU/HCMOS Logic Package Information”
.
SYMBOL PARAMETER CONDITIONS
TYPICAL
UNIT
HC HCT
propagation delay C
L
= 15 pF; VCC= 5 V
t
PHL
/ t
PLH
Anto Y
n
12 17 ns
t
PHL
/ t
PLH
E3to Y
n
Ento Y
n
14 19 ns
C
I
input capacitance 3.5 3.5 pF
C
PD
power dissipation capacitance per package notes 1 and 2 67 67 pF
September 1993 3
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
3-to-8 line decoder/demultiplexer; inverting 74HC/HCT138
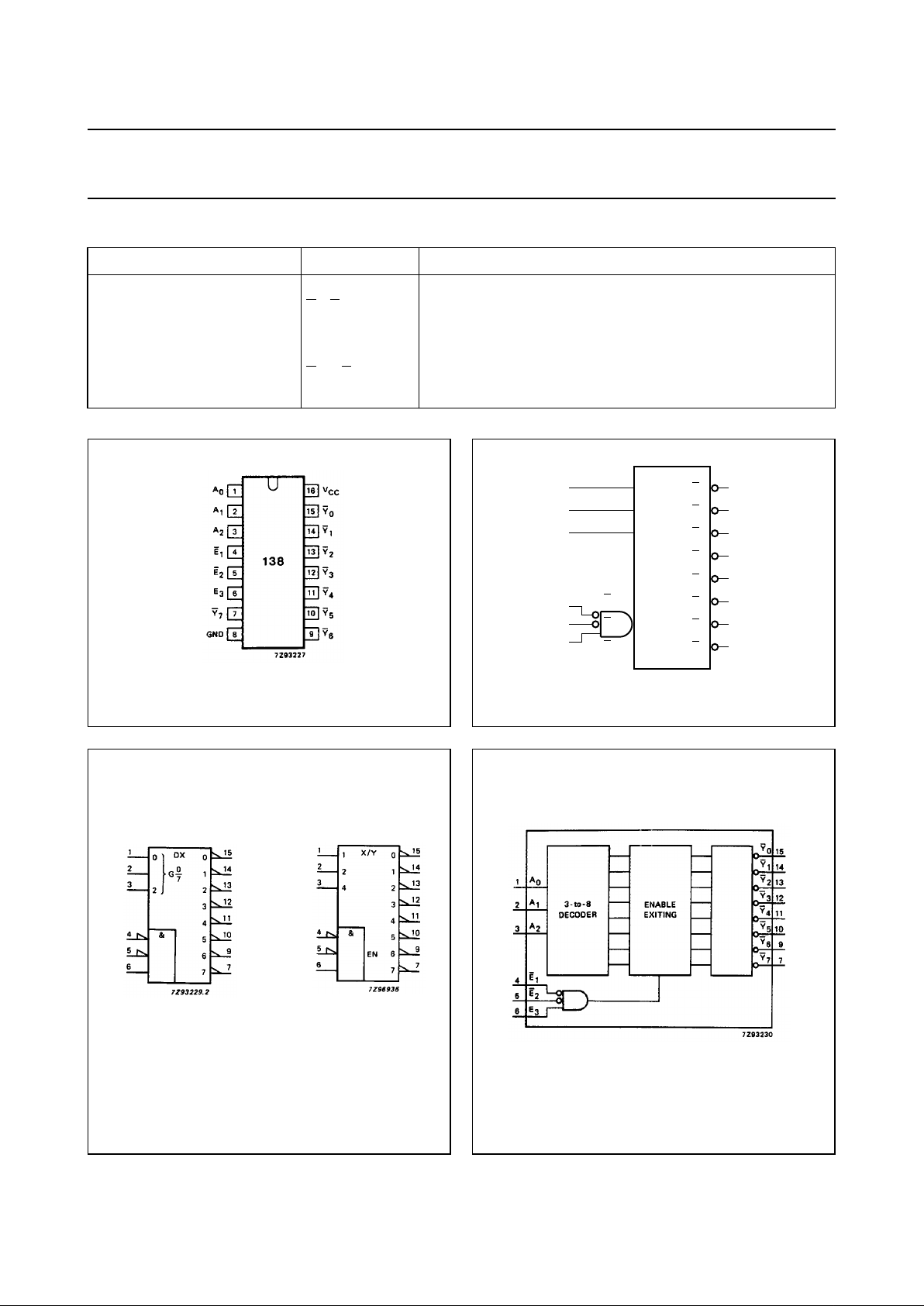
PIN DESCRIPTION
PIN NO. SYMBOL NAME AND FUNCTION
1, 2, 3 A
0
to A
2
address inputs
4, 5
E1, E
2
enable inputs (active LOW)
6E
3
enable input (active HIGH)
8 GND ground (0 V)
15, 14, 13, 12, 11, 10, 9, 7
Y0 to Y
7
outputs (active LOW)
16 V
CC
positive supply voltage
Fig.1 Pin configuration. Fig.2 Logic symbol.
handbook, halfpage
MLB312
A
0
A
1
A
2
1
2
3
15
13
11
7
9
10
12
14
Y
0
Y
1
Y
2
Y
3
Y
4
Y
5
Y
6
Y
7
4
5
6
E
1
E
2
E
3
Fig.3 IEC logic symbol.
(a) (b)
Fig.4 Functional diagram.
 Loading...
Loading...