Page 1
<For System Sales Company / SI,SE>
*Plasma Display Panel Division
If power is ON where a sine wave voltage is 0V, a rush current is
POWER CONSUMPTION
OVERVIEW
Power Consumption-related items are described for installation of a plasma display.
PDP SE Referencece
No.PDP006-Ver02
*TV System Products Division
*Overseas Solution Business Dept.
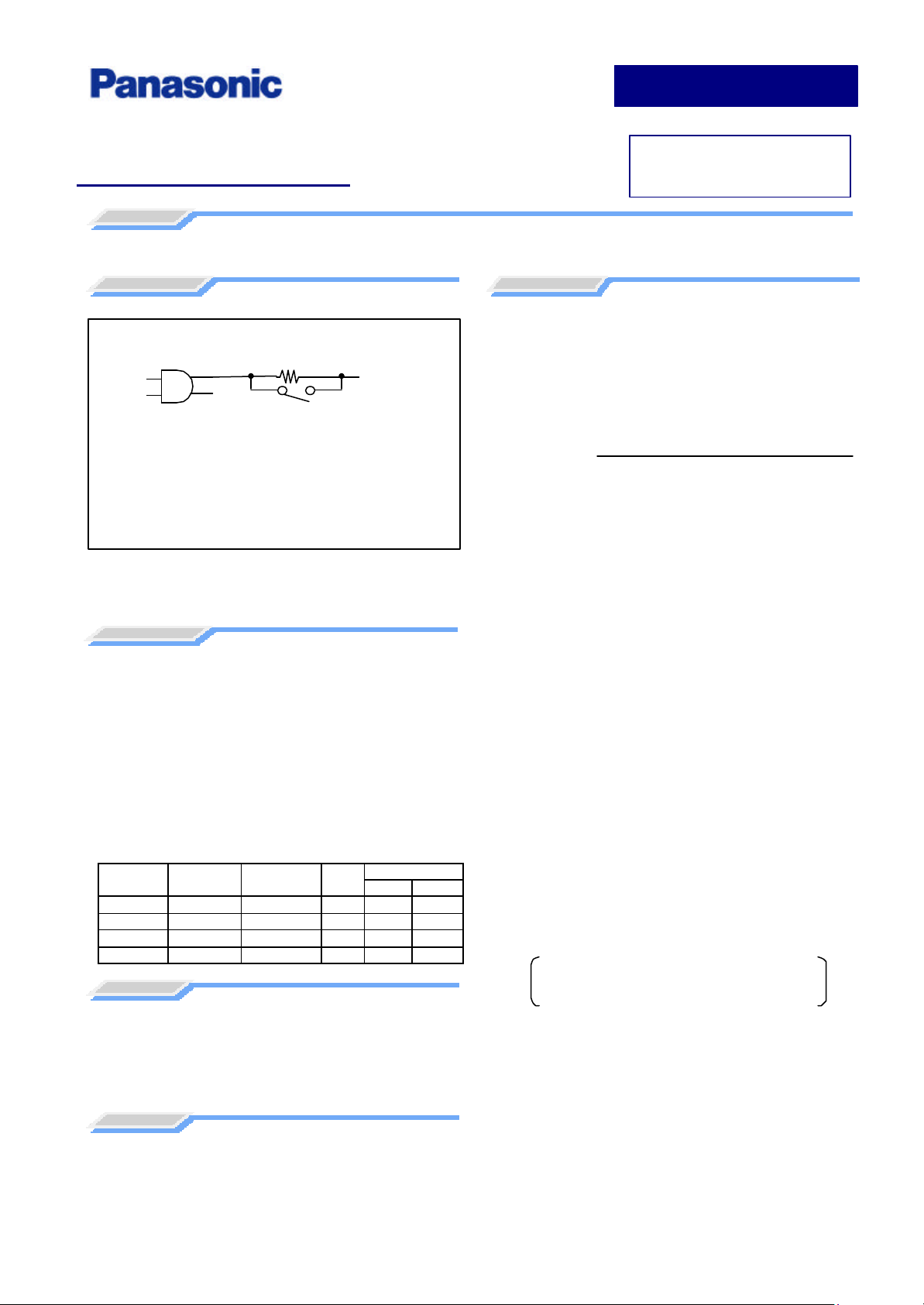
RUSH CURRENT
TH-42PWD5 for example:
Input resistance 3.4 ohm in US model
Soft start relay
TH- 42PWD5 US model I=120Vx1.41/3.4 ohm= 49.8 [A]
0 to maximum 49.8[A].
* TH-42PWD5 except US I=240Vx1.41/6.8 ohm= 49.8 [A]
* TH-50PHD5 US model I=120Vx1.41/6.8 ohm= 24.9 [A]
l
A rush current is an instantaneous large current flowing at a time of
Power ON and depends on an input resistance of power supply circuit
(in parallel with a soft start relay).
MAXIMUM POWER CONSUMPTION & CURRENT
* Maximum Power Consumption
The power Consumption values described on the catalog resulted from
the measurement of power Consumption for a certain sound and
image for European models. The PDP must make every pixel
discharge light repetitively on a not-constant base, thus resulting in a
huge value of power Consumption.(US models)
* Maximum Current
Current can be normally found by the formula: Current A = Power P ÷
Voltage V, but it depends heavily on the power factor of a power
circuit.
*Values of the existing models
Power
Consumption
TH-50PHD5 495W Approx. 550W
TH-42PHD5 375W Approx. 450W
TH-42PWD5 295W Approx. 395W
TH-37PWD5 225W Approx. 325W
CALORIFIC VALUE
Calorific Value[J]=Power Consumption[W]xTime[S]
Calorific value per hour[Kcal/H] = 0.24xPowerConsumptionx3600
=Power Consumptionx0.864
* TH-42PWD5UY = 295Wx0.864 = 255[Kcal/H]
Max. Power
Consumption
Power
Factor
100%
100%
British Thermal Units VALUE
British Thermal Units = Power Consumption [W] × 3.41 = [BTU/h]
* TH-42PWD5UY = 295 W × 3.41 = 1,006 BTU/h
Max. Current (Approx.)
AC100v AC200v
75%
70%
5.5A 2.8A
5.0A 2.5A
5.3A 2.7A
4.4A 2.2A
1
J=0.24cal
HEAT COOLING
* PDP operation conditions
Temperature: 0 deg – 40 degHumidity : 20% - 80%(not dewing)
NOTICE:
NOTICE:※
*Ambient Temp
*Operating airflow
(Example) Ambient temp. =25 deg: Q’ = 0.98m3/min.
Ambient temp. =30 deg: Q’ = 1.48m3/min.
When it exceeds the above range, you have to consider cooling.
* Method of choosing a cooling fan
●
Operating airflow rate needed for cooling (Q’)
Q’
[m3/min]
The formula is based on the assumption that heat eradication is
done by a cooling airflow of a fan.
●
Choice of a fan
Since the operating airflow is generally 1/2 to 2/3 the maximum
airflow, it is recommended that you choose the fan 1.5 to 2.0 times
the calculated airflow Q’.
Assuming that an operating airflow is 2/3 the maximum airflow, the
maximum airflow Q[m3/min]=Q’ x 3/2.
: Calculation example for placing TH-42PWD4 inside the housing:
* Power Consumption
*Temp inside Housing
Q’ = 295 / [ 20x(40-35) ) = 2.95 [m3/min]
Q = 2.95 x 3/2 = 4.425 [m3/min]
Heat tends to focus on the upper part. A fan had better be placed to
ventilate this area.
Example) Two fans whose maximum airflow is 2.3[m
or 3 fans whose maximum airflow is 1.5[m
=
20x [Temp inside the housing case - Housing case ambient Temp
PDP Power Consumption
:
295W
:
Need to be below 40 deg
:
35 deg (example)
:
2/3 the maximum airflow
3
/min]
3
/min.]
)
* Other cautions
*Never fail to attach the fan the PDP inside.
*The values mentioned above are the theoretical ones. You
are required to make enough tolerance in actual design and
to perform a mounting experiment at the time of studying.
*When you study the outdoor use, you have to take into
account the heat inflow from outside such as solar heat.
 Loading...
Loading...