Page 1

Nighthawk X8
AC5300 Tri-Band
WiFi Router
User Manual
Model R8500
September 2015
202-11555-01
350 E. Plumeria Drive
San Jose, CA 95134
USA
Page 2

Support
Thank you for purchasing this NETGEAR product.
You can visit http://support.netgear.com to register your product, get help, access the latest downloads and user manuals,
and join our community.We recommend that you use only official NETGEAR support resources.
Conformity
For regulatory compliance information, visit http://kb.netgear.com/app/answers/detail/a_id/11621..
Compliance
For regulatory compliance information, visit http://www.netgear .com/about/regulatory. See the regulatory compliance document
before connecting the power supply.
Trademarks
© NETGEAR, Inc., NETGEAR and the NETGEAR Logo are trademarks of NETGEAR, Inc. An y non_NETGEAR trademarks
are used for reference purposes only.
2
Page 3

Contents
Chapter 1 Hardware Setup
Unpack Your Router...............................................................................................9
Front View..............................................................................................................9
USB Ports on the Right Panel..............................................................................11
Rear Panel...........................................................................................................12
Position Your Router.............................................................................................12
Cable Your Router................................................................................................13
How Active Antennas Improve WiFi Performance................................................14
Position the Active Antennas...............................................................................15
Chapter 2 Connect to the Network and Access the Router
Connect to the Network.......................................................................................18
Wired Connection............................................................................................18
WiFi Connection..............................................................................................18
WiFi Connection Using WPS...........................................................................19
Label...............................................................................................................19
Types of Logins....................................................................................................19
Use a Web Browser to Access the Router...........................................................20
Automatic Internet Setup.................................................................................20
Log In to the Router........................................................................................21
Change the Language.........................................................................................21
Access the Router With NETGEAR genie Apps..................................................22
Chapter 3 Specify Your Internet Settings
Use the Internet Setup Wizard.............................................................................24
Manually Set Up the Internet Connection............................................................24
Specify an Internet Connection Without a Login.............................................25
Specify an Internet Connection That Uses a Login.........................................26
Specify IPv6 Internet Connections.......................................................................28
Requirements for Entering IPv6 Addresses.........................................................30
Use Auto Config for an IPv6 Internet Connection................................................30
Use Auto Detect for an IPv6 Internet Connection................................................31
Set Up an IPv6 6to4 Tunnel Internet Connection.................................................33
Set Up an IPv6 DHCP Internet Connection.........................................................34
Set Up an IPv6 Fixed Internet Connection...........................................................36
Set Up an IPv6 Pass Through Inter net Connection.............................................37
Set Up an IPv6 PPPoE Internet Connection........................................................38
Set Up an IPv6 6rd Internet Connection..............................................................39
Change the MTU Size..........................................................................................41
Chapter 4 Control Access to the Internet
Set Up Parental Controls.....................................................................................45
3
Page 4

Allow or Block Access to Your Network................................................................46
Use Keywords to Block Internet Sites..................................................................48
Block Services From the Internet.........................................................................50
Delete Keywords From the Blocked List...............................................................51
Avoid Blocking on a Trusted Computer................................................................52
Manage Network Access Control Lists................................................................53
Schedule When to Block Internet Sites and Services..........................................54
Set Up Security Event Email Notifications...........................................................55
Chapter 5 Tri-Band WiFi Connections
Tri-Band WiFi........................................................................................................59
How Tri-Band WiFi Improves Speed and Performance...................................59
Load Balancing...............................................................................................61
Benefits of Tri-Band WiFi.................................................................................62
Smart Connect.....................................................................................................62
Enable or Disable Smart Connect...................................................................63
Beamforming........................................................................................................64
Enable or Disable Implicit Beamforming.........................................................64
Chapter 6 Network Settings
View or Change WAN Settings............................................................................67
Set Up a Default DMZ Server..............................................................................68
Set Up Ethernet Port Aggregation.......................................................................69
View Ethernet Port Aggregation Status...............................................................71
Change the LAN TCP/IP Settings........................................................................71
Change the Router’s Device Name......................................................................73
Specify the IP Addresses That the Router Assigns.............................................74
Disable the DHCP Server Feature in the Router.................................................75
Manage Reserved LAN IP Addresses.................................................................76
Reserve an IP Address...................................................................................76
Edit a Reserved IP Address............................................................................77
Delete a Reserved IP Address Entry..............................................................77
Custom Static Routes..........................................................................................78
Set Up a Static Route......................................................................................78
Edit a Static Route..........................................................................................80
Delete a Static Route......................................................................................80
Set Up a Bridge for a Port Group or VLAN Tag Group.........................................81
Set Up a Bridge for a Port Group....................................................................81
Set Up a Bridge for a VLAN Tag Group...........................................................82
Use the WPS Wizard for WiFi Connections.........................................................84
Specify Basic WiFi Settings.................................................................................85
Change the WiFi Password or Security Level......................................................88
Change the WiFi Mbps Settings...........................................................................88
Set Up a Guest WiFi Network..............................................................................89
Control the WiFi Radios.......................................................................................91
Use the WIFI Button........................................................................................91
Enable or Disable the WiFi Radios..................................................................91
Set Up a WiFi Schedule.......................................................................................92
4
Page 5

Specify WPS Settings..........................................................................................93
Use the Router as a WiFi Access Point...............................................................94
Use the Router in Bridge Mode............................................................................97
Chapter 7 Optimize Performance
Use Dynamic QoS to Optimize Internet Traffic Management.............................101
Enable Dynamic QoS....................................................................................101
Enable or Disable the Automatic QoS Database Update..............................102
Manually Update the Dynamic QoS Database..............................................103
Participate in Dynamic QoS Analytics...........................................................104
Improve Network Connections With Universal Plug and Play............................104
Wi-Fi Multimedia Quality of Service...................................................................105
Chapter 8 Manage Your Network
Update the Router Firmware..............................................................................108
Change the admin Password.............................................................................108
Set Up Password Recovery...............................................................................109
Recover the admin Password............................................................................110
View Router Status............................................................................................111
Display Internet Port Statistics...........................................................................112
Check the Internet Connection Status...............................................................113
View and Manage Logs of Router Activity.........................................................114
View Devices Currently on the Network.............................................................116
Monitor Internet Traffictraffic metering................................................................116
Manage the Router Configuration File...............................................................118
Back Up Settings...........................................................................................118
Erase the Current Configuration Settings......................................................119
Restore Configuration Settings.....................................................................119
Set Up Remote Management............................................................................120
Use Remote Access..........................................................................................122
Access the Router with NETGEAR genie Apps.................................................122
Remotely Access Your Router Using the genie App..........................................122
Chapter 9 Share USB Storage Devices Attached to the Router
USB Device Requirements................................................................................124
Connect a USB Device to the Router.................................................................124
Access a USB Storage Device Connected to the Router From a Windows
Computer...........................................................................................................125
Map a USB Device to a Windows Network Drive...............................................126
Access a USB Storage Device That Is Connected to the Router From a Mac....126
Back Up Windows Computers With ReadySHARE Vault...................................127
Back Up Mac Computers With Time Machine....................................................128
Set Up a USB Hard Drive on a Mac..............................................................128
Prepare to Back Up a Large Amount of Data................................................128
Use Time Machine to Back Up Onto a USB Hard Disk.................................129
Use FTP Within the Network..............................................................................130
View or Change Network Folders on a USB Storage Device.............................131
Add a Network Folder on a USB Storage Device..............................................132
5
Page 6

Edit a Network Folder on a USB Storage Device...............................................133
Remotely Access a USB Device Using ReadyCLOUD......................................133
Create a ReadyCLOUD Account...................................................................134
Register Your Router With ReadyCLOUD.....................................................134
Safely Remove a USB Device............................................................................136
Chapter 10 Use Dynamic DNS to Access USB Storage Devices Through the
Internet
Access USB Storage Devices Through the Inter net..........................................139
Set Up FTP Access Through the Internet..........................................................140
Your Personal FTP Server.................................................................................140
Dynamic DNS....................................................................................................141
Set Up a New Dynamic DNS Account...........................................................141
Specify a DNS Account That You Already Created.......................................142
Change the Dynamic DNS Settings..............................................................144
Set Up Your Personal FTP Server.................................................................144
Chapter 11 Use the Router as a Media Server
Specify ReadyDLNA Media Server Settings......................................................147
Play Music From a USB Storage Device With iTunes Server.............................147
Set Up the Router's iTunes Server with iTunes.............................................148
Set Up the Router's iTunes Server with the Remote app..............................149
Play Media From a USB Device on TiVo............................................................151
Set Up the Router to Work With TiVo............................................................151
Play Videos on TiVo.......................................................................................152
Play Music or View Photos on TiVo...............................................................153
Chapter 12 Share a USB Printer
Install the Printer Driver and Cable the Printer..................................................155
Download the ReadySHARE Printer Utility........................................................155
Install the ReadySHARE Printer Utility..............................................................156
Print Using the NETGEAR USB Control Center................................................157
View or Change the Status of a Printer..............................................................158
Use the Scan Feature of a Multifunction USB Printer........................................159
Change NETGEAR USB Control Center Settings.............................................159
Turn Off Automatic Startup for NETGEAR USB Control Center....................159
Change the Language for the NETGEAR USB Control Center....................160
Specify the USB Control Center Time-Out....................................................160
Chapter 13 Use VPN to Access Your Network
Set Up a VPN Connection..................................................................................162
Specify VPN Service in the Router....................................................................162
Install OpenVPN Software on Your Computer....................................................163
Use a VPN Tunnel..............................................................................................166
Use VPN to Access the Router’s USB Device and Media..................................168
Use VPN to Access Your Internet Service at Home...........................................168
Set Up VPN Client Internet Access in the Router.........................................168
Block VPN Client Internet Access in the Router............................................169
6
Page 7

Use a VPN Tunnel to Access Your Internet Service at Home........................170
Chapter 14 Customize Internet Traffic Rules for Ports
Set Up Port Forwarding to a Local Server.........................................................172
Edit a Port Forwarding Service..........................................................................174
Delete a Port Forwarding Entry..........................................................................174
Application Example: Make a Local Web Server Public.....................................175
How the Router Implements the Port Forwarding Rule......................................175
Port Triggering....................................................................................................176
Add a Port Triggering Service........................................................................176
Enable Port Triggering...................................................................................178
Application Example: Port Triggering for Internet Relay Chat port triggering.178
Chapter 15 Troubleshooting
Quick Tips..........................................................................................................181
Sequence to Restart Your Network...............................................................181
Check Ethernet Cable Connections..............................................................181
Network Settings...........................................................................................181
WiFi Settings.................................................................................................181
Troubleshoot With the LEDs...............................................................................181
Standard LED Behavior When the Router Is Powered On............................181
Power LED Is Off or Blinking.........................................................................182
Power LED Stays Amber...............................................................................182
LEDs Never Tur n Off.....................................................................................182
2.4 GHz, 5 GHz-1, and 5 GHz-2 WiFi LEDs Are Off.....................................183
Internet or Ethernet Port LEDs Are Off.........................................................183
Cannot Log In to the Router...............................................................................183
Cannot Access the Internet................................................................................183
Troubleshoot Internet Browsing.........................................................................186
Troubleshoot PPPoE..........................................................................................186
Changes Not Saved...........................................................................................187
WiFi Connectivity...............................................................................................187
Troubleshoot Your Network Using the Ping Utility..............................................187
Test the LAN Path to Your Router..................................................................188
Test the Path From Your Computer to a Remote Device...............................188
Chapter 16 Supplemental Information
Factory Settings.................................................................................................191
Technical Specifications.....................................................................................192
7
Page 8

Hardware Setup
The Nighthawk X8 AC5300 Tri-Band WiFi Router is the next wave in WiFi with Tri-Band Quad Stream performance,
Nighthawk delivers combined WiFi speeds of up to 5.3 Gbps. Four external active antennas combined with four internal
antennas amplify and maximize WiFi range .The X8’s pow erful 1.4 Ghz dual-core processor gives you a high-perf ormance
networking engine for faster connections. Aggregate two of the Gigabit ports to double your wired speeds to
network-attached storage. Quad-Stream with MU-MIMO support allows you to enjoy simultaneous streaming to your
devices for speeds up to four times faster than traditional WiFi.
This chapter contains the following sections:
• Unpack Your Router on page 9
• Front View on page 9
• USB Ports on the Right Panel on page 11
• Rear Panel on page 12
• Position Your Router on page 12
• Cable Your Router on page 13
1
• How Active Antennas Improve WiFi Performance on page 14
• Position the Active Antennas on page 15
For more information about the topics covered in this manual, visit the support website at http://support.netgear.com.
8
Page 9

Unpack Your Router
Your package contains the Nighthawk X8 AC5300 Tri-Band WiFi Router, the power adapter, and a yellow Ethernet
cable.
Figure 1. Package contents
Front View
The status LEDs are located on the top of the router. Buttons are on the front, and the USB ports are on the right
panel.
Figure 2. Router LEDs and buttons
Hardware Setup
9
Page 10
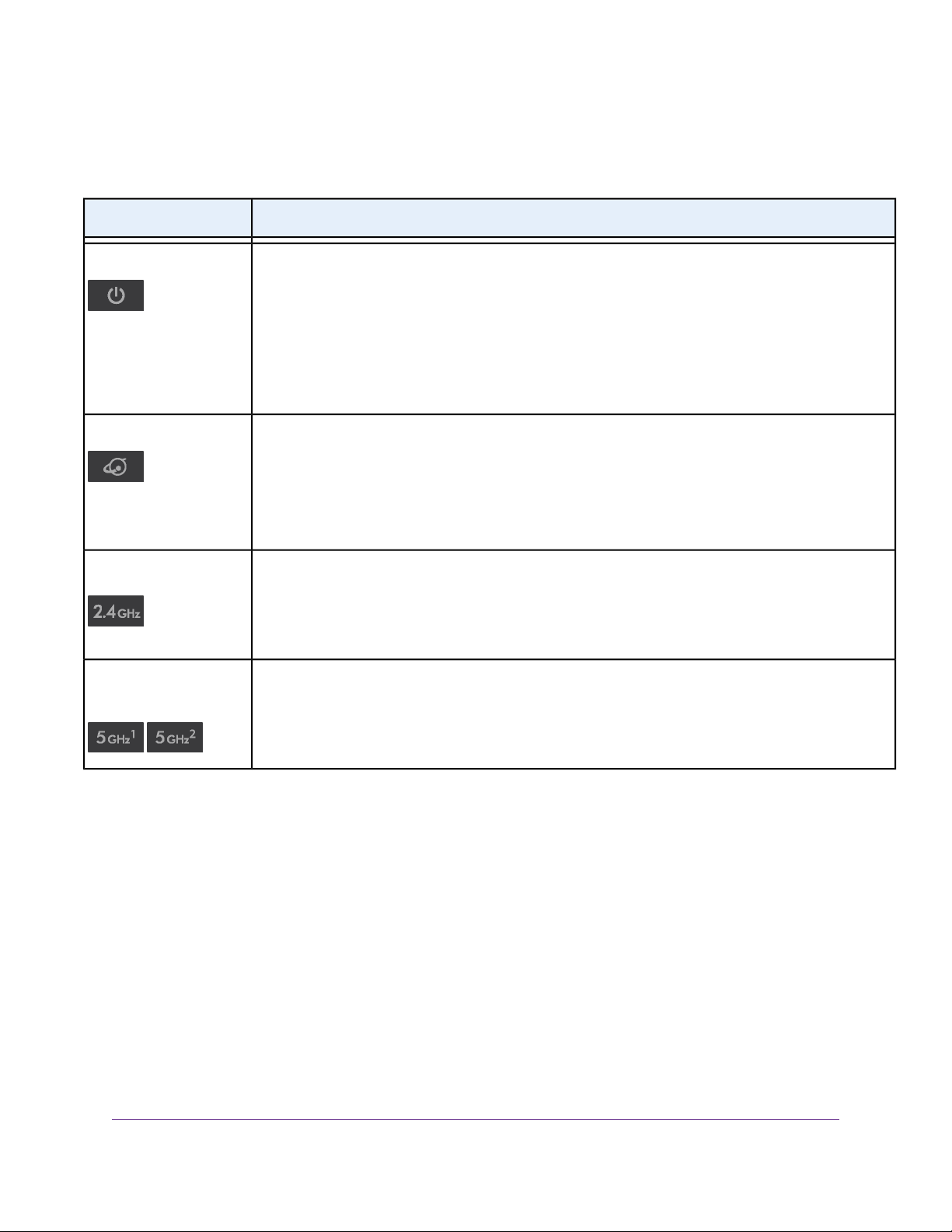
Table 1. LED descriptions
DescriptionLED
Power
Internet
2.4 GHz WiFi
5 GHz WiFi 1 and 5 GHz
WiFi 2
• Solid amber.The router is starting.
• Blinking amber.The firmware is upgrading, or the Reset button was pressed.
• Solid white.The router is ready.
• Blinking white.The firmware is corrupted.
• Off. Power is not supplied to the router.
• Solid white.The Internet connection is ready.
• Solid amber.The router detected an Ethernet cable connection to the modem.
• Blinking white.The port is sending or receiving traffic.
• Off. No Ethernet cable is connected between the router and the modem.
• Solid white.The 2.4 GHz WiFi radio is operating.
• Blinking.The router is sending or receiving WiFi traffic.
• Off.The 2.4 GHz WiFi radio is off.
• Solid white.The 5 GHz WiFi radio is operating.
• Blinking.The router is sending or receiving WiFi traffic.
• Off.The 5 GHz WiFi radio is off.
Hardware Setup
10
Page 11

DescriptionLED
USB 3.0 port 1 and USB
2.0 port 2
Ethernet ports 1–6
• Solid white. A USB device is connected and is ready.
• Blinking. A USB device is plugged in and is trying to connect.
• Off. No USB device is connected, or someone clicked the Safely Remove Hardware button and it
is now safe to remove the attached USB device.
The LED color indicates the speed: white for Gigabit Ethernet connections and amber for 100 Mbps or
10 Mbps Ethernet connections.
• Solid. A powered-on device is connected to the Ethernet port.
• Blinking.The port is sending or receiving traffic.
• Off. No device is connected to this Ethernet port.
Table 2. Front panel button descriptions
DescriptionButton
LED
Pressing this button changes the LED mode.
• Mode one. All LEDs stay on and blink.
• Mode two. All LEDs stay on but don't blink.
• Mode three. Only the Power LED stays on and the other LEDs are off.
WPS
Pressing this button lets you use WPS to join the WiFi network without typing the WiFi password. For
more information, see Join the WiFi Network on page 9 on page 19.
Pressing this button for two seconds turns the 2.4 GHz, 5 GHz 1, and 5 GHz 2 WiFi radios on and off.WIFI
USB Ports on the Right Panel
Two USB ports are located on the right panel.To access the ports, open the USB port cover as shown.
Hardware Setup
11
Page 12

Figure 3. A USB 3.0 port and a USB 2.0 port are located on the right
Rear Panel
The rear panel connections and buttons are shown in the following figure.
Figure 4. Rear panel
Position Your Router
The router lets you access your network anywhere within the operating range of your WiFi network. However, the
operating distance or range of your WiFi connection can vary significantly depending on the physical placement of
your router. For example, the thickness and number of walls the WiFi signal passes through can limit the range.
Hardware Setup
12
Page 13

Additionally, other WiFi access points in and around your home might affect your router’s signal. WiFi access points
are routers, repeaters, WiFi range extenders, and any other device that emits a WiFi signal for network access.
Position your router according to the following guidelines:
• Place your router near the center of the area where your computers and other devices operate, and within line
of sight to your WiFi devices.
• Make sure that the router is within reach of an AC power outlet and near Ethernet cables for wired computers.
• Place the router in an elevated location, minimizing the number walls and ceilings between the router and your
other devices.
• Place the router away from electrical devices such as these:
• Ceiling fans
• Home security systems
• Microwaves
• Computers
• Base of a cordless phone
• 2.4 GHz cordless phone
• Place the router away from large metal surf aces , large glass surf aces, insulated w alls, and items such as these:
• Solid metal door
• Aluminum studs
• Fish tanks
• Mirrors
• Brick
• Concrete
Cable Your Router
To cable your router:
1. Unplug your modem’s power, leaving the modem connected to the wall jack for your Internet service.
If your modem uses a battery backup, remove the battery.
2. Plug in and turn on your modem.
If your modem uses a battery backup, put the battery back in.
Hardware Setup
13
Page 14
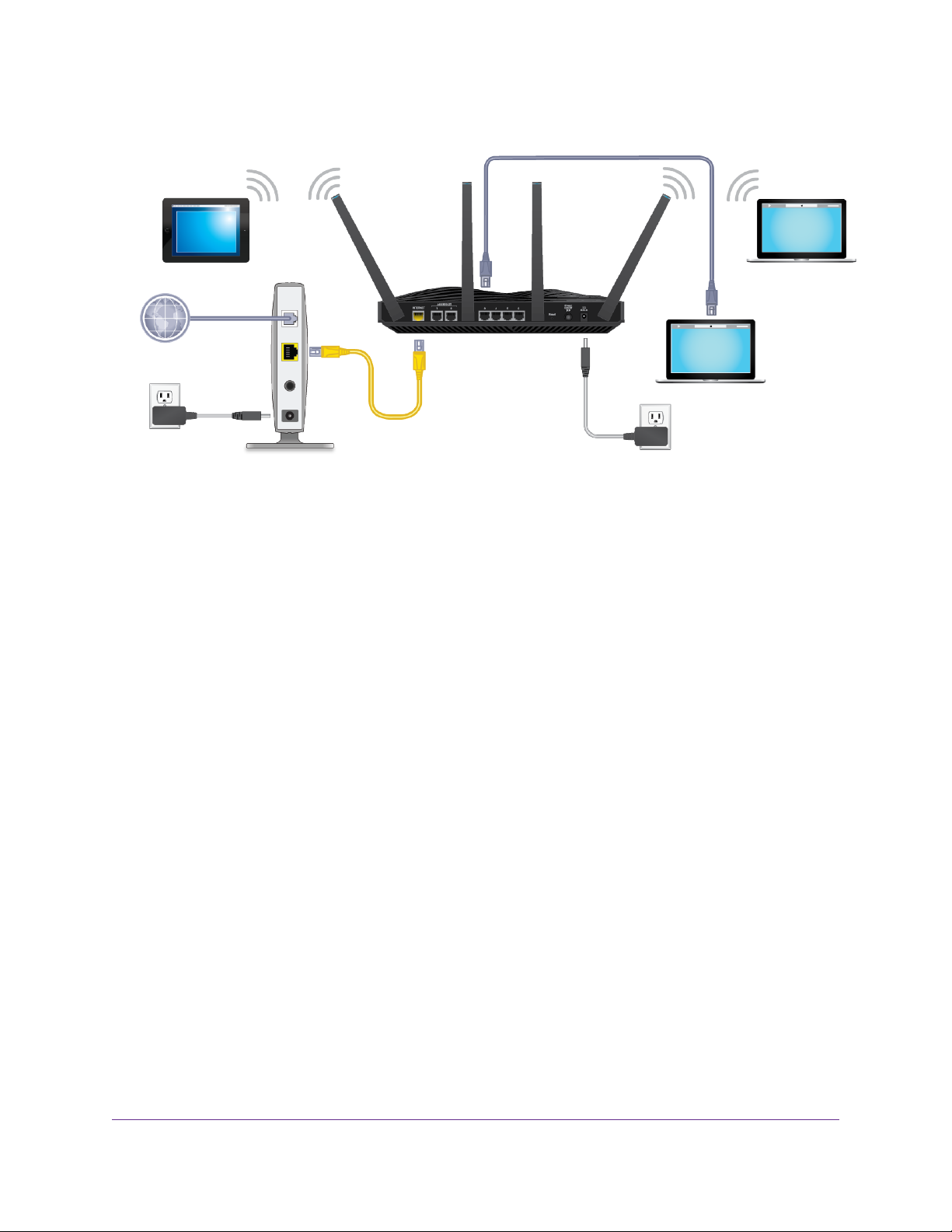
3. Connect your modem to the Internet port of your router with the yellow Ethernet cable that came with your router.
4. Connect the power adapter to your router and plug the power adapter into an outlet.
5. Press the Power On/Off button on the rear panel of the router.
6. To change the LED mode, press the LED button on the front panel. Pressing the LED button turns off blinking.
Pressing the LED button again turns off all LEDs except the Power LED.
How Active Antennas Improve WiFi Performance
The growing number of WiFi devices in the home combined with the increasing demand for high-speed WiFi
connectivity, places extraordinary demands on the WiFi infrastructure.To meet this demand, many WiFi routers
now use external antennas and high-power amplifiers to maximize signal po wer and extend WiFi cov erage throughout
your home.
Increased signal power on the router is important, but effective WiFi connectivity requires two-way communication
between the router and clients such as smartphones, tablets, and laptops.The client must acknowledge every WiFi
data packet sent by the router; otherwise the router resends the data pac k et. A strong signal from the router without
a corresponding boost in signal from the client to the router does not provide you with the full benefit.
Mobile devices continue to get smaller, while adding more features and reducing power consumption to extend
battery life. Since mobile de vice WiFi signal power and performance has not been improving, router technology has
evolv ed to find ways to compensate and impro ve the client-to-router WiFi signal. One passive approach to addressing
this problem is to add low noise amplifiers (LNA) on the router board to amplify the received signal.The router's
external antennas transmit the received WiFi signal to the router board.The issues with this approach are twofold.
Transmitting the signal from the external antenna to the router board reduces the signal strength and quality. In
addition, the router board injects noise from other components.The received signal deteriorates and noise is injected,
which reduces the efficacy of the received transmission.
Active antennas solve these problems. Active antennas move the powered amplification component (LNA) to the
antenna itself instead of using the router board.This eliminates signal loss during transmission since the active
antenna directly amplifies the received signal. In addition, since no noise from the router board components are
present in the antenna, the amplified signal is cleaner.
Hardware Setup
14
Page 15

The router receives a much cleaner and less noisy signal for amplification, significantly impro ving the received signal
and providing a clean, powerful signal that extends WiFi coverage and performance. Active antennas help reduce
the mismatch between the sent and the received signal by compensating for the relatively poor WiFi on the client
side.This WiFi improv ement is seen across all devices-new and old b ut helps mobile devices the most, which present
the greatest connectivity challenges today.
Position the Active Antennas
The router’s f our active antennas include a built-in receiv er low noise amplifier (LNA), f or high-speed WiFi connections
and excellent range. Both the 2.4 GHz and the 5 GHz low band (WiFi Channels 36-48, and 52-64) use the active
antennas.The 5 GHz high band (WiFi Channels 100-140, and 149-65) uses the passive antenna.
The best position for the active antennas depends on the la yout f or your home or office.We recommend the following
antenna positions:
• For a large single-story home (about 2,500 to 4,000 square feet in size), position all f our antennas vertically and
place the router on a table.
• For a multi-level home, position the two antennas in the center vertically, and position the other antennas at a
45-degree outward angle.
Hardware Setup
15
Page 16

Hardware Setup
16
Page 17

Connect to the Network and Access the Router
You can connect to the router’s WiFi networks or use a wired Ethernet connection.This chapter explains the ways you
can connect and how to access the router and log in.
The chapter contains the following sections:
• Connect to the Network on page 18
• Types of Logins on page 19
• Use a Web Browser to Access the Router on page 20
• Change the Language on page 21
• Access the Router With NETGEAR genie Apps on page 22
2
17
Page 18
Connect to the Network
You can connect to the router’s network through a wired or WiFi connection. If you set up your computer to use a
static IP address, change the settings so that it uses Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP).
Wired Connection
You can connect your computer to the router using an Ethernet cable and join the router’s local area network (LAN).
The router has six Ethernet ports. Ports 1 and 2 can be used as Ethernet LAN ports or as aggregation ports to
connect to a NAS or Smart Switch that supports port aggregation (LACP).
To connect your computer to the router with an Ethernet cable:
1. Make sure that the router is receiving power (its Power LED is lit).
2. Connect an Ethernet cable to an Ethernet port on your computer.
3. Connect the other end of the Ethernet cable Ethernet port 3 on the router.
To get the fastest performance with port aggregation, for wired connections use Ethernet
Note
port 3 for the first computer, and use Ethernet port 4, 5 or 6 for the second computer, which
allows for speeds up to 2 Gbps with port aggregation.The maximum speed between port 4,
5 and 6 is limited to 1 Gbps.
Your computer connects to the local area network (LAN). A message might display on your computer screen
to notify you that an Ethernet cable is connected.
WiFi Connection
To find and select the WiFi network:
1. Make sure that the router is receiving power (its Power LED is lit).
2. On your computer or WiFi device, find and select the WiFi network.
The WiFi network name is on the router’s label.
3. Join the WiFi network and enter the WiFi password.
The password is on the router’s label.
Your WiFi device connects to the WiFi network.
Connect to the Network and Access the Router
18
Page 19

WiFi Connection Using WPS
You can connect to the router’s WiFi network with Wi-Fi Protected Setup (WPS) or you can find and select the WiFi
network.
To use WPS to connect to the WiFi network:
1. Make sure that the router is receiving power (its Power LED is lit).
2. Check the WPS instructions for your computer or WiFi device.
3. Press the WPS button on the router.
4. Within two minutes, on your computer or WiFi device, press its WPS button or follow its instructions for WPS
connections.
Your computer or WiFi device connects to the WiFi network.
Label
The label on the router shows the login information, WiFi netw ork name and network key (pass word), MA C address,
and serial number.
Figure 5. Product label
Types of Logins
Separate types of logins serve different purposes. It is important that you understand the difference so that you kno w
which login to use when.
Several types of logins are associated with the router:
• ISP login.The login that your ISP gave you logs you in to your Internet service.Your service provider gave you
this login information in a letter or some other way. If y ou cannot find this login information, contact your service
provider.
• WiFi network key or password.Your router is preset with a unique WiFi network name (SSID) and password
for WiFi access.This information is on the router label.
• Router login.This logs you in to the router interface from a web browser as admin.
Connect to the Network and Access the Router
19
Page 20

Use a Web Browser to Access the Router
When you connect to the network (either with WiFi or with an Ethernet cable), y ou can use a web browser to access
the router to view or change its settings.When you access the router, the software automatically checks to see if
your router can connect to your Internet service.
Automatic Internet Setup
You can set up your router automatically, or you can use a web browser to access the router and set up your router
manually. Before you start the setup process, get your ISP information and make sure that the computers and
devices in the network are using the settings described here.
When your Internet service starts, your Internet service provider (ISP) typically gives you all the inf ormation needed
to connect to the Internet. For DSL service, you might need the following information to set up your router:
• The ISP configuration information for your DSL account
• ISP login name and password
• Fixed or static IP address setting (special deployment by ISP; this setting is rare)
If you cannot locate this information, ask your ISP to provide it.When your Internet connection is working, you no
longer need to launch the ISP login program on your computer to access the Internet.When you start an Internet
application, your router automatically logs you in.
NETGEAR genie runs on any device with a web browser. Installation and basic setup takes about 15 minutes to
complete.
To automatically set up your router:
1. Turn the router on by pressing the On/Off button.
2. Make sure that your computer or WiFi device is connected to the router with an Ethernet cable (wired) or over
WiFi with the preset security settings listed on the label.
If you want to change the router’s WiFi settings, use a wired connection to avoid being
Note
disconnected when the new WiFi settings take effect.
3. Launch a web browser.
The page that displays depends on whether you accessed the router before:
• The first time you set up the Internet connection for your router, the browser goes to
http://www.routerlogin.net and the Configuring the Internet Connection page displays.
• If you already set up the Internet connection, enter http://www.routerlogin.net in the address field for your
browser to start the installation process.
4. Follow the onscreen instructions.
The router connects to the Internet.
Connect to the Network and Access the Router
20
Page 21
5. If the browser does not display a router page, do the following:
• Make sure that the computer is connected to one of the LAN Ethernet ports or over WiFi to the router.
• Make sure that the router is receiving power and that its Power LED is lit.
• Close and reopen the browser or clear the browser cache.
• Browse to http://www.routerlogin.net.
• If the computer is set to a static or fixed IP address (this setting is uncommon), change it to obtain an IP
address automatically from the router.
6. If the router does not connect to the Internet, do the following:
a. Review your settings. Make sure that you selected the correct options and typed everything correctly.
b. Contact your ISP to verify that you are using the correct configuration information.
c. Read Cannot Access the Internet on page 183. If problems persist, register your NETGEAR product and
contact NETGEAR technical support.
When the router connects to the Internet, you are prompted to download and install the free NETGEAR Desktop
genie app and the free ReadySHARE Vault app.
Log In to the Router
When you first connect to your router and launch a web browser, the browser automatically displays the router’s
web page. If you want to view or change settings for the router later, you can use a browser to log in to the router’s
web page.
To log in to the router:
1. Launch a web browser from a computer or WiFi device that is connected to the network.
2. Enter http://www.routerlogin.net.
You can also enter http://www.routerlogin.com or http://192.168.1.1.The procedures in
Note
this manual use http://www.routerlogin.net.
A login window opens.
3. Enter the router user name and password.
The user name is admin.The default password is password.The user name and password are case-sensitive .
The BASIC Home page displays.
Change the Language
By default, the language is set to Auto.
Connect to the Network and Access the Router
21
Page 22

To change the language:
1. Launch a web browser from a computer or WiFi device that is connected to the network.
2. Enter http://www.routerlogin.net.
A login window opens.
3. Enter the router user name and password.
The user name is admin.The default password is password.The user name and password are case-sensitive .
The BASIC Home page displays.
4. In the upper right corner, select a language from the menu.
5. When prompted, click the OK button to confirm this change.
The page refreshes with the language that you selected.
Access the RouterWith NETGEAR genie Apps
The genie app is the easy dashboard for managing, monitoring, and repairing your home network.The genie app
can help you with the following:
• Automatically repair common WiFi network problems.
• Easily manage router features like Live Parental Controls, guest access, Internet traffic meter, speed test, and
more.
To use the genie app to access the router:
1. Visit the NETGEAR genie web page at www.NETGEAR.com/genie.
2. Follow the onscreen instructions to install the app on your smartphone, tablet, or computer.
3. Launch the genie app.
The genie app dashboard page displays.
Connect to the Network and Access the Router
22
Page 23
Specify Your Internet Settings
Usually, the quickest way to set up the router to use your Internet connection is to allow the genie to detect the Internet
connection when you first access the router with a web browser .Y ou can also customiz e or specify your Internet settings.
This chapter contains the following sections:
• Use the Internet Setup Wizard on page 24
• Manually Set Up the Internet Connection on page 24
• Specify IPv6 Internet Connections on page 28
• Change the MTU Size on page 41
3
23
Page 24
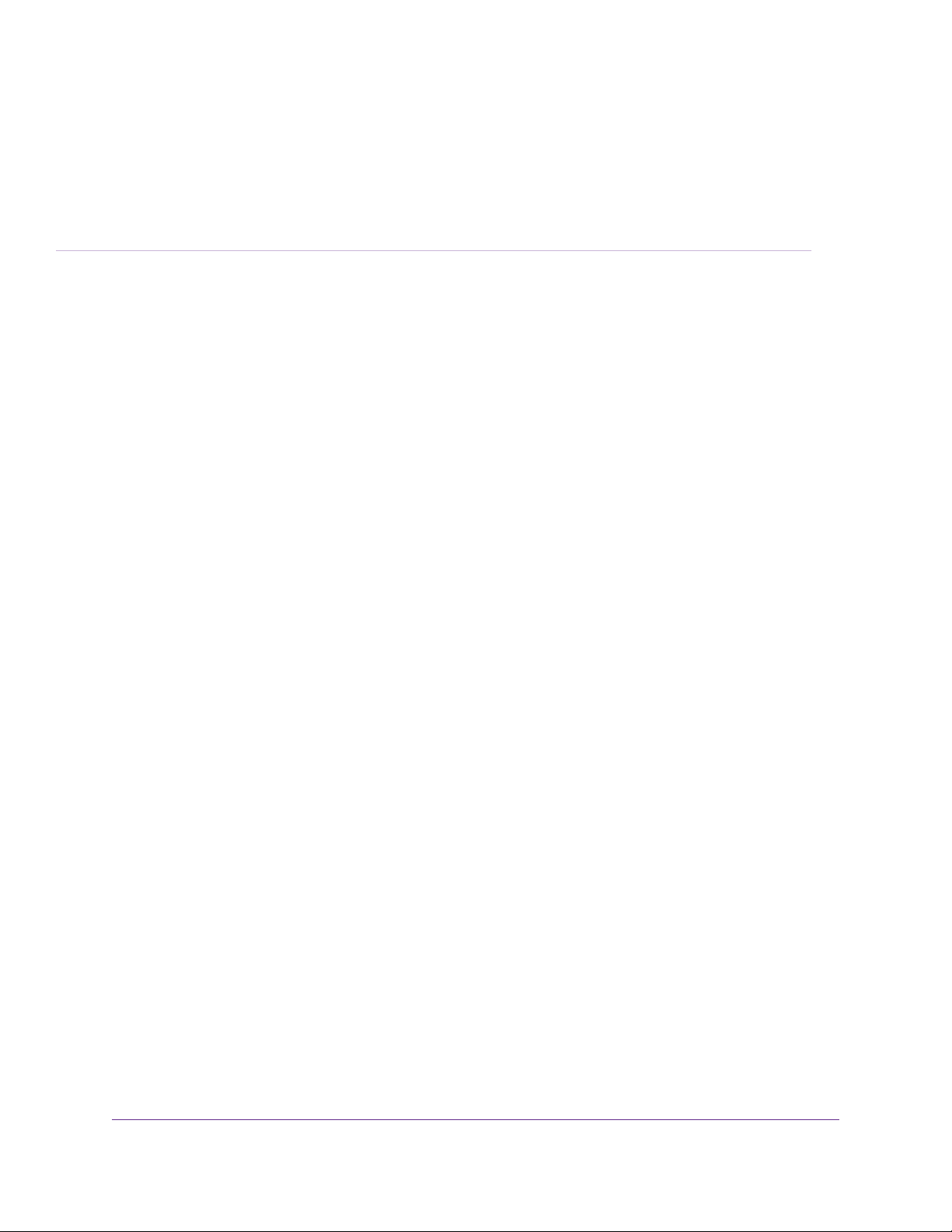
Use the Internet Setup Wizard
You can use the Setup Wizard to detect your Internet settings and automatically set up your router.The Setup
Wizard is not the same as the pages that display the first time you connect to your router to set it up.
To use the Setup Wizard:
1. Launch a web browser from a computer or WiFi device that is connected to the network.
2. Enter http://www.routerlogin.net.
A login window opens.
3. Enter the router user name and password.
The user name is admin.The default password is password.The user name and password are case-sensitive .
The BASIC Home page displays.
4. Select ADVANCED > Setup Wizard.
5. Select the Yes radio button.
If you select the No radio button, you are taken to the Internet Setup page (see Manually Set Up the Internet
Connection on page 24).
6. Click the Next button.
The Setup Wizard searches your Internet connection for servers and protocols to determine your Internet
configuration.
When the router connects to the Internet, you are prompted to download and install the free NETGEAR Desktop
genie app and the free ReadySHARE Vault app.
Manually Set Up the Internet Connection
You can view or change the router’s Internet connection settings.
Specify Your Internet Settings
24
Page 25
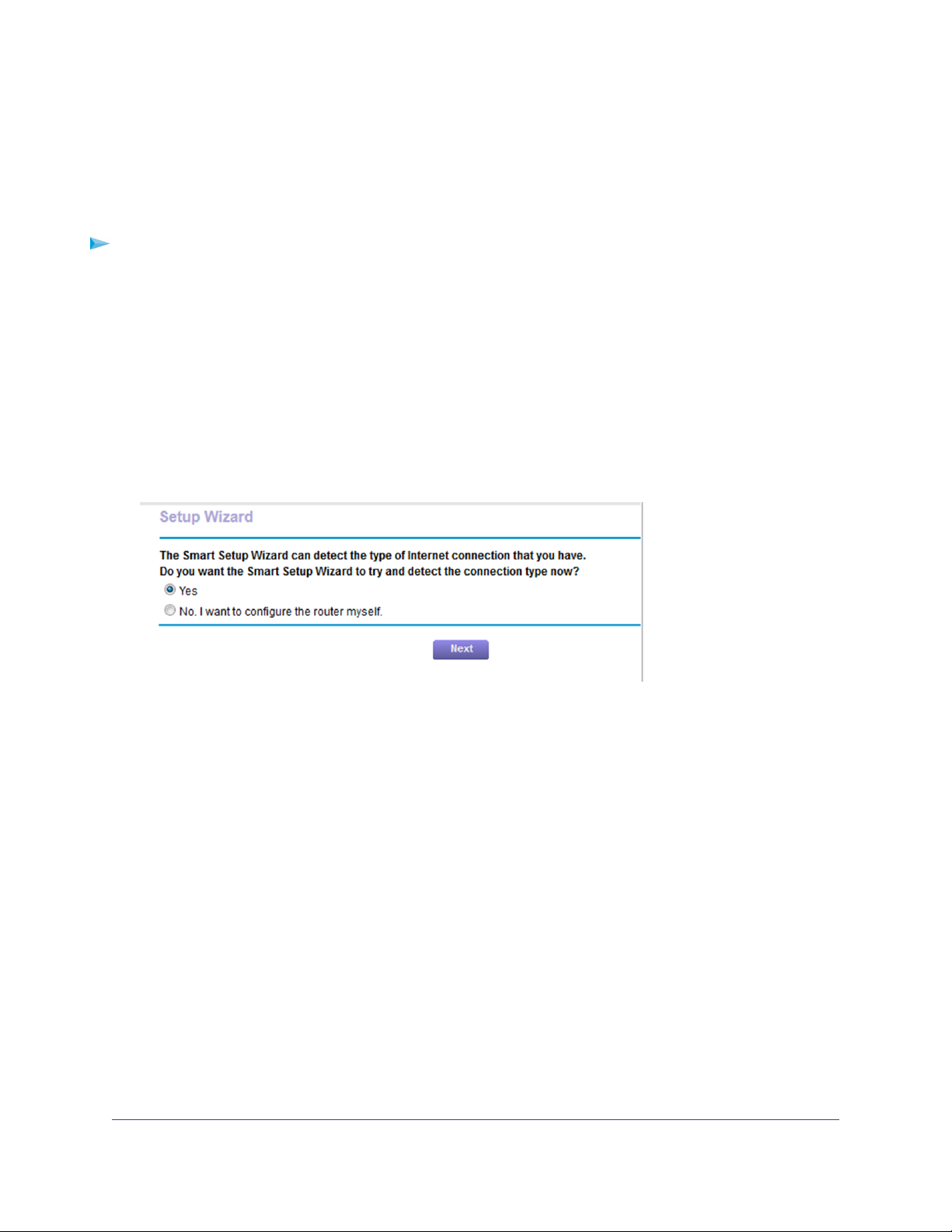
Specify an Internet Connection Without a Login
To specify the Internet connection settings:
1. Launch a web browser from a computer or WiFi device that is connected to the network.
2. Enter http://www.routerlogin.net.
A login window opens.
3. Enter the router user name and password.
The user name is admin.The default password is password.The user name and password are case-sensitive .
The BASIC Home page displays.
4. Select Internet.
Your router might display information that is different from this example.
5. For the Does your Internet connection require a login? setting, leave the No radio button selected.
6. If your Internet connection requires an account name or host name, type it in the Account Name (If Required)
field.
7. If your Internet connection requires a domain name, type it in the Domain Name (If Required) field.
For the other sections on this page, the default settings usually work, but you can change them.
8. Select an Internet IP Address radio button:
• Get Dynamically from ISP.Your ISP uses DHCP to assign your IP address.Your ISP automatically assigns
these addresses.
• Use Static IP Address. Enter the IP address, IP subnet mask, and the gateway IP address that your ISP
assigned.The gateway is the ISP router to which your router connects.
9. Select a Domain Name Server (DNS) Address radio button:
Specify Your Internet Settings
25
Page 26

• Get Automatically from ISP.Your ISP uses DHCP to assign your DNS servers.Your ISP automatically
assigns this address.
• Use These DNS Servers. If you know that your ISP requires specific servers, select this option. Enter the
IP address of your ISP’s primary DNS server. If a secondary DNS server address is available, enter it also.
10. Select a Router MAC Address radio button:
• Use Default Address. Use the default MAC address.
• Use Computer MAC Address.The router captures and uses the MAC address of the computer that you
are now using.You must use the one computer that the ISP allows.
• Use This MAC Address. Enter the MAC address that you want to use.
11. Click the Apply button.
Your settings are saved.
12. Click the Test button to test your Internet connection.
If the NETGEAR website does not display within one minute, see Cannot Access the Internet on page 183
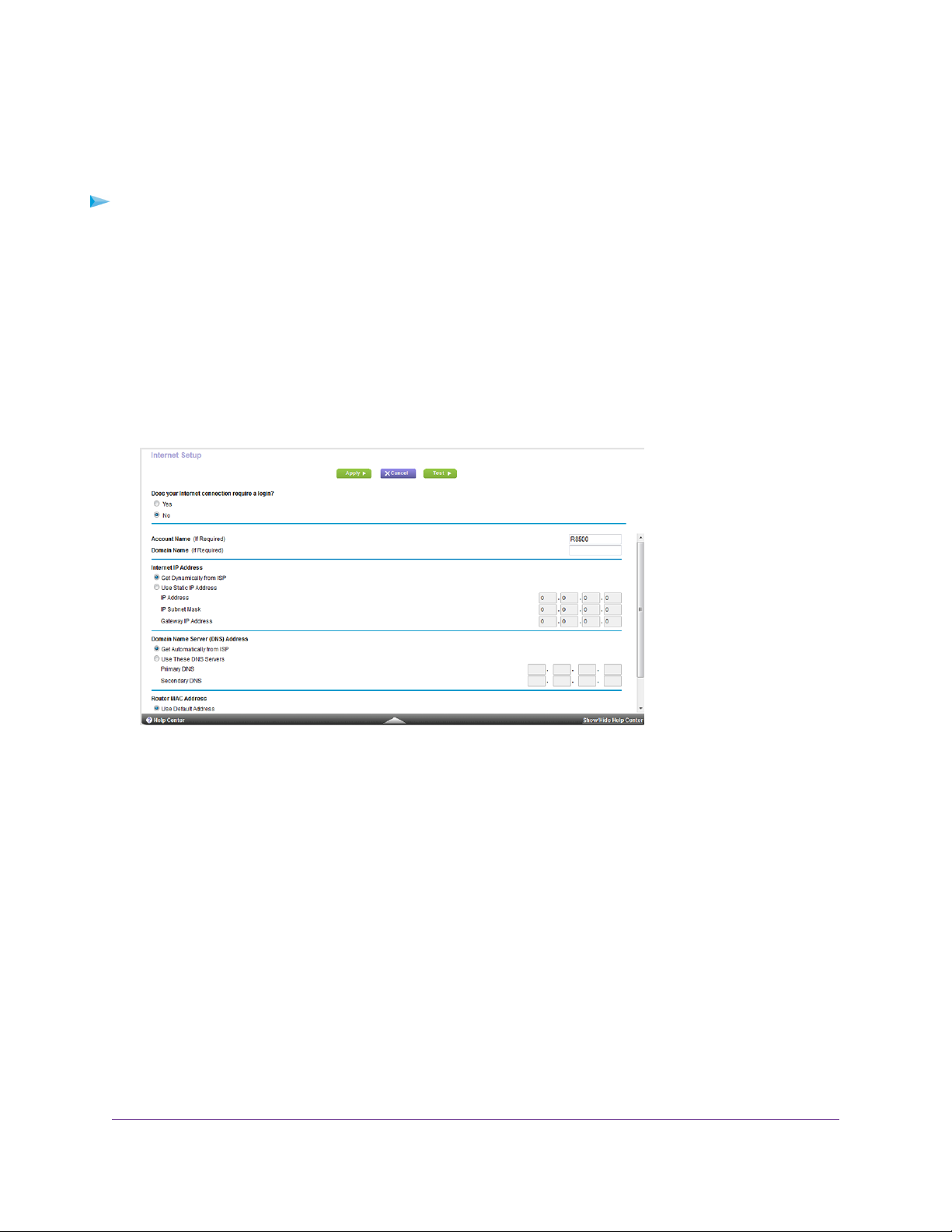
Specify an Internet Connection That Uses a Login
To view or change the basic Internet setup:
1. Launch a web browser from a computer or WiFi device that is connected to the network.
2. Enter http://www.routerlogin.net.
A login window opens.
3. Enter the router user name and password.
The user name is admin.The default password is password.The user name and password are case-sensitive .
The BASIC Home page displays.
4. Select Internet.
5. For the Does your Internet connection require a login? setting, select the Yes radio button.
Specify Your Internet Settings
26
Page 27
6. From the Internet Service Provider menu, select the encapsulation method: PPPoE, L2TP, or PPTP.
7. In the Login field, enter the login name that your ISP gave you.
This login name is often an email address.
8. In the Password field, type the password that you use to log in to your Internet service.
9. If your ISP requires a service name, type it in the Service Name (if Required) field.
10. From the Connection Mode menu, select Always On, Dial on Demand, or Manually Connect.
11. To change the number of minutes until the Internet login times out, in the Idle Timeout (In minutes) field, type
the number of minutes.
This is how long the router keeps the Internet connection active when no one on the network is using the Internet
connection. A value of 0 (zero) means never log out.
12. Select an Internet IP Address radio button:
• Get Dynamically from ISP.Your ISP uses DHCP to assign your IP address.Your ISP automatically assigns
these addresses.
• Use Static IP Address. Enter the IP address, IP subnet mask, and the gateway IP address that your ISP
assigned.The gateway is the ISP router to which your router connects.
13. Select a Domain Name Server (DNS) Address radio button:
• Get Automatically from ISP.Your ISP uses DHCP to assign your DNS servers.Your ISP automatically
assigns this address.
• Use These DNS Servers. If you know that your ISP requires specific servers, select this option. Enter the
IP address of your ISP’s primary DNS server. If a secondary DNS server address is available, enter it also.
14. Select a Router MAC Address radio button:
• Use Default Address. Use the default MAC address.
• Use Computer MAC Address.The router captures and uses the MAC address of the computer that you
are now using.You must use the one computer that the ISP allows.
Specify Your Internet Settings
27
Page 28

• Use This MAC Address. Enter the MAC address that you want to use.
15. Click the Apply button.
Your settings are saved.
16. Click the Test button to test your Internet connection.
If the NETGEAR website does not display within one minute, see Cannot Access the Internet on page 183.
Specify IPv6 Internet Connections
You can set up an IPv6 Internet connection if the router does not detect it automatically.
To set up an IPv6 Internet connection:
1. Launch a web browser from a computer or WiFi device that is connected to the network.
2. Enter http://www.routerlogin.net.
A login window opens.
3. Enter the router user name and password.
The user name is admin.The default password is password.The user name and password are case-sensitive .
The BASIC Home page displays.
4. Select ADVANCED > Advanced Setup > IPv6.
The Basic Settings page displays.
5. From the Internet Connection Type menu, select the IPv6 connection type:
• If your ISP did not provide details, select IPv6 Tunnel.
• If you are not sure, select Auto Detect so that the router detects the IPv6 type that is in use.
• If your Internet connection does not use PPPoe or DHCP, or is not fixed, but is IPv6, select Auto Config.
Your Internet service provider (ISP) can provide this information. For more information about IPv6 Internet
connection, see the following sections:
• Use Auto Detect for an IPv6 Internet Connection on page 31
• Use Auto Config for an IPv6 Internet Connection on page 30
• Set Up an IPv6 6to4 Tunnel Internet Connection on page 33
• Set Up an IPv6 Pass Through Internet Connection on page 37
• Set Up an IPv6 Fixed Internet Connection on page 36
• Set Up an IPv6 DHCP Internet Connection on page 34
Specify Your Internet Settings
28
Page 29

• Set Up an IPv6 PPPoE Internet Connection on page 38
• Set Up an IPv6 6rd Internet Connection on page 39
6. Click the Apply button.
Your settings are saved.
Specify Your Internet Settings
29
Page 30
Requirements for Entering IPv6 Addresses
IPv6 addresses are denoted by eight groups of hexadecimal quartets that are separated by colons.You can reduce
any four-digit group of zeros within an IPv6 address to a single zero or omit it.The following errors invalidate an
IPv6 address:
• More than eight groups of hexadecimal quartets
• More than four hexadecimal characters in a quartet
• More than two colons in a row
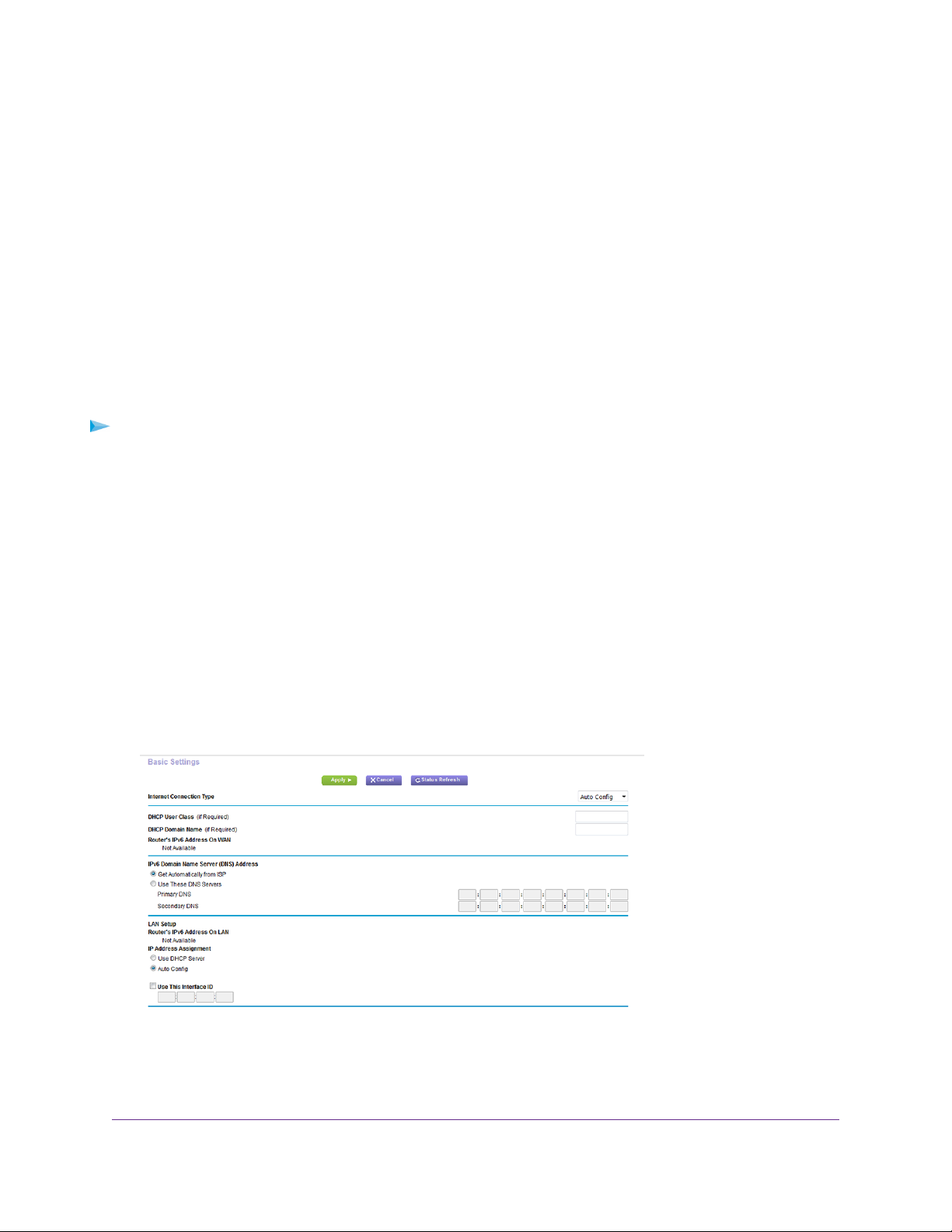
Use Auto Config for an IPv6 Internet Connection
To set up an IPv6 Internet connection through autoconfiguration:
1. Launch a web browser from a computer or WiFi device that is connected to the network.
2. Enter http://www.routerlogin.net.
A login window opens.
3. Enter the router user name and password.
The user name is admin.The default password is password.The user name and password are case-sensitive .
The BASIC Home page displays.
4. Select ADVANCED > Advanced Setup > IPv6.
The IPv6 page displays.
5. From the Internet Connection Type menu, select Auto Config.
The router automatically detects the information in the following fields:
Specify Your Internet Settings
30
Page 31

• Router’s IPv6 Address on WAN.This field shows the IPv6 address that is acquired for the router’s WAN
(or Internet) interface.The number after the slash (/) is the length of the prefix, which is also indicated by
the underline (_) under the IPv6 address. If no address is acquired, the field displays Not Available.
• Router’s IPv6 Address on LAN.This field shows the IPv6 address that is acquired for the router’s LAN
interface.The number after the slash (/) is the length of the prefix, which is also indicated by the underline
(_) under the IPv6 address. If no address is acquired, the field displays Not Available.
6. (Optional) In the DHCP User Class (If Required) field, enter a host name.
Most people can leave this field blank, but if your ISP gave you a specific host name, enter it here.
7. (Optional) In the DHCP Domain Name (If Required) field, enter a domain name.
You can type the domain name of your IPv6 ISP. Do not enter the domain name for the IPv4 ISP here. For
example, if your ISP’s mail server is mail.xxx.yyy.zzz, type xxx.yyy .zzz as the domain name. If your ISP provided
a domain name, type it in this field. For example, Earthlink Cable might require a host name of home, and
Comcast sometimes supplies a domain name.
8. Select an IP Address Assignment radio button:
• Use DHCP Server.This method passes more information to LAN devices but some IPv6 systems might not
support the DHCPv6 client function.
• Auto Config.This is the default setting.
This setting specifies how the router assigns IPv6 addresses to the devices on your home network (the LAN).
9. (Optional) Select the Use This Interface ID check box and specify the interface ID to be used for the IPv6
address of the router’s LAN interface.
If you do not specify an ID here, the router generates one automatically from its MAC address.
10. Click the Apply button.
Your settings are saved.
Use Auto Detect for an IPv6 Internet Connection
To set up an IPv6 Internet connection through autodetection:
1. Launch a web browser from a computer or WiFi device that is connected to the network.
2. Enter http://www.routerlogin.net.
A login window opens.
3. Enter the router user name and password.
The user name is admin.The default password is password.The user name and password are case-sensitive .
Specify Your Internet Settings
31
Page 32

The BASIC Home page displays.
4. Select ADVANCED > Advanced Setup > IPv6.
The IPv6 page displays.
5. From the Internet Connection Type menu, select Auto Detect.
The router automatically detects the information in the following fields:
• Connection Type.This field indicates the connection type that is detected.
• Router’s IPv6 Address on WAN.This field shows the IPv6 address that is acquired for the router’s WAN
(or Internet) interface.The number after the slash (/) is the length of the prefix, which is also indicated by
the underline (_) under the IPv6 address. If no address is acquired, the field displays Not Available.
• Router’s IPv6 Address on LAN.This field shows the IPv6 address that is acquired for the router’s LAN
interface.The number after the slash (/) is the length of the prefix, which is also indicated by the underline
(_) under the IPv6 address. If no address is acquired, the field displays Not Available.
6. Select an IP Address Assignment radio button:
• Use DHCP Server.This method passes more information to LAN devices but some IPv6 systems might not
support the DHCPv6 client function.
• Auto Config.This is the default setting.
This setting specifies how the router assigns IPv6 addresses to the devices on your home network (the LAN).
7. (Optional) Select the Use This Interface ID check box and specify the interface ID to be used for the IPv6
address of the router’s LAN interface.
If you do not specify an ID here, the router generates one automatically from its MAC address.
8. Click the Apply button.
Your settings are saved.
Specify Your Internet Settings
32
Page 33

Set Up an IPv6 6to4 Tunnel Internet Connection
The remote relay router is the router to which your router creates a 6to4 tunnel. Make sure that the IPv4 Internet
connection is working before you apply the 6to4 tunnel settings for the IPv6 connection.
To set up an IPv6 Internet connection by using a 6to4 tunnel:
1. Launch a web browser from a computer or WiFi device that is connected to the network.
2. Enter http://www.routerlogin.net.
A login window opens.
3. Enter the router user name and password.
The user name is admin.The default password is password.The user name and password are case-sensitive .
The BASIC Home page displays.
4. Select ADVANCED > Advanced Setup > IPv6.
The IPv6 page displays.
5. From the Internet Connection Type menu, select 6to4 Tunnel.
The router automatically detects the information in the Router’s IPv6 Address on LAN field.This field shows the
IPv6 address that is acquired for the router’s LAN interface.The number after the slash (/) is the length of the
prefix, which is also indicated by the underline (_) under the IPv6 address. If no address is acquired, the field
displays Not Available.
6. Select a Remote 6to4 Relay Router radio button:
• Auto.Your router uses any remote relay router that is available on the Internet.This is the default setting.
• Static IP Address. Enter the static IPv4 address of the remote relay router.Your IPv6 ISP usually provides
this address.
7. Select an IP Address Assignment radio button:
Specify Your Internet Settings
33
Page 34

• Use DHCP Server.This method passes more information to LAN devices but some IPv6 systems might not
support the DHCPv6 client function.
• Auto Config.This is the default setting.
This setting specifies how the router assigns IPv6 addresses to the devices on your home network (the LAN).
8. (Optional) Select the Use This Interface ID check box and specify the interface ID to be used for the IPv6
address of the router’s LAN interface.
If you do not specify an ID here, the router generates one automatically from its MAC address.
9. Click the Apply button.
Your settings are saved.
Set Up an IPv6 DHCP Internet Connection
To set up an IPv6 Internet connection with a DHCP server:
1. Launch a web browser from a computer or WiFi device that is connected to the network.
2. Enter http://www.routerlogin.net.
A login window opens.
3. Enter the router user name and password.
The user name is admin.The default password is password.The user name and password are case-sensitive .
The BASIC Home page displays.
4. Select ADVANCED > Advanced Setup > IPv6.
The IPv6 page displays.
Specify Your Internet Settings
34
Page 35

5. From the Internet Connection Type menu, select DHCP.
The router automatically detects the information in the following fields:
• Router’s IPv6 Address on WAN.This field shows the IPv6 address that is acquired for the router’s WAN
(or Internet) interface.The number after the slash (/) is the length of the prefix, which is also indicated by
the underline (_) under the IPv6 address. If no address is acquired, the field displays Not Available.
• Router’s IPv6 Address on LAN.This field shows the IPv6 address that is acquired for the router’s LAN
interface.The number after the slash (/) is the length of the prefix, which is also indicated by the underline
(_) under the IPv6 address. If no address is acquired, the field displays Not Available.
6. (Optional) In the User Class (If Required) field, enter a host name.
Most people can leave this field blank, but if your ISP gave you a specific host name, enter it here.
7. (Optional) In the Domain Name (If Required) field, enter a domain name.
You can type the domain name of your IPv6 ISP. Do not enter the domain name for the IPv4 ISP here. For
example, if your ISP’s mail server is mail.xxx.yyy.zzz, type xxx.yyy .zzz as the domain name. If your ISP provided
a domain name, type it in this field. For example, Earthlink Cable might require a host name of home, and
Comcast sometimes supplies a domain name.
8. Select an IP Address Assignment radio button:
• Use DHCP Server.This method passes more information to LAN devices but some IPv6 systems might not
support the DHCPv6 client function.
• Auto Config.This is the default setting.
This setting specifies how the router assigns IPv6 addresses to the devices on your home network (the LAN).
9. (Optional) Select the Use This Interface ID check box and specify the interface ID to be used for the IPv6
address of the router’s LAN interface.
Specify Your Internet Settings
35
Page 36

If you do not specify an ID here, the router generates one automatically from its MAC address.
10. Click the Apply button.
Your settings are saved.
Set Up an IPv6 Fixed Internet Connection
To set up a fixed IPv6 Internet connection:
1. Launch a web browser from a computer or WiFi device that is connected to the network.
2. Enter http://www.routerlogin.net.
A login window opens.
3. Enter the router user name and password.
The user name is admin.The default password is password.The user name and password are case-sensitive .
The BASIC Home page displays.
4. Select ADVANCED > Advanced Setup > IPv6.
The IPv6 page displays.
5. From the Internet Connection Type menu, select Fixed.
6. Configure the fixed IPv6 addresses for the WAN connection:
• IPv6 Address/Prefix Length.The IPv6 address and prefix length of the router WAN interface.
• Default IPv6 Gateway.The IPv6 address of the default IPv6 gateway for the router’s WAN interface.
• Primary DNS Server.The primary DNS server that resolves IPv6 domain name records for the router.
• Secondary DNS Server.The secondary DNS server that resolves IPv6 domain name records for the router.
Specify Your Internet Settings
36
Page 37

If you do not specify the DNS servers, the router uses the DNS servers that are configured
Note
for the IPv4 Internet connection on the Internet Setup page. (See Manually Set Up the Internet
Connection on page 24.)
7. Select an IP Address Assignment radio button:
• Use DHCP Server.This method passes more information to LAN devices but some IPv6 systems might not
support the DHCPv6 client function.
• Auto Config.This is the default setting.
This setting specifies how the router assigns IPv6 addresses to the devices on your home network (the LAN).
8. In the IPv6 Address/Prefix Length fields, specify the static IPv6 address and prefix length of the router’s LAN
interface.
If you do not specify an ID here, the router generates one automatically from its MAC address.
9. Click the Apply button.
Your settings are saved.
Set Up an IPv6 Pass Through Internet Connection
In pass-through mode, the router works as a Layer 2 Ethernet switch with tw o ports (LAN and WAN Ethernet ports)
for IPv6 packets.The router does not process any IPv6 header packets.
To set up a pass-through IPv6 Internet connection:
1. Launch a web browser from a computer or WiFi device that is connected to the network.
2. Enter http://www.routerlogin.net.
A login window opens.
3. Enter the router user name and password.
The user name is admin.The default password is password.The user name and password are case-sensitive .
The BASIC Home page displays.
4. Select ADVANCED > Advanced Setup > IPv6.
The IPv6 page displays.
5. From the Internet Connection Type menu, select Pass Through.
The page adjusts, but no additional fields display.
6. Click the Apply button.
Specify Your Internet Settings
37
Page 38

Your settings are saved.
Set Up an IPv6 PPPoE Internet Connection
To set up a PPPoE IPv6 Internet connection:
1. Launch a web browser from a computer or WiFi device that is connected to the network.
2. Enter http://www.routerlogin.net.
A login window opens.
3. Enter the router user name and password.
The user name is admin.The default password is password.The user name and password are case-sensitive .
The BASIC Home page displays.
4. Select ADVANCED > Advanced Setup > IPv6.
The IPv6 page displays.
5. From the Internet Connection Type menu, select PPPoE.
The router automatically detects the information in the following fields:
• Router’s IPv6 Address on WAN.This field shows the IPv6 address that is acquired for the router’s WAN
(or Internet) interface.The number after the slash (/) is the length of the prefix, which is also indicated by
the underline (_) under the IPv6 address. If no address is acquired, the field displays Not Available.
• Router’s IPv6 Address on LAN.This field shows the IPv6 address that is acquired for the router’s LAN
interface.The number after the slash (/) is the length of the prefix, which is also indicated by the underline
(_) under the IPv6 address. If no address is acquired, the field displays Not Available.
6. In the Login field, enter the login information for the ISP connection.
Specify Your Internet Settings
38
Page 39

This is usually the name that you use in your email address. For example, if your main mail account is
JerAB@ISP.com, you would type JerAB in this field. Some ISPs (like Mindspring, Earthlink, and T-DSL) require
that you use your full email address when you log in. If your ISP requires your full email address, type it in this
field.
7. In the Password field, enter the password for the ISP connection.
8. In the Service Name field, enter a service name.
If your ISP did not provide a service name, leave this field blank.
The default setting of the Connection Mode menu is Always On to provide a steady IPv6
Note
connection.The router never terminates the connection. If the connection is terminated, for
example, when the modem is turned off, the router attempts to reestablish the connection
immediately after the PPPoE connection becomes available again.
9. Select an IP Address Assignment radio button:
• Use DHCP Server.This method passes more information to LAN devices but some IPv6 systems might not
support the DHCPv6 client function.
• Auto Config.This is the default setting.
This setting specifies how the router assigns IPv6 addresses to the devices on your home network (the LAN).
10. (Optional) Select the Use This Interface ID check box and specify the interface ID to be used for the IPv6
address of the router’s LAN interface.
If you do not specify an ID here, the router generates one automatically from its MAC address.
11. Click the Apply button.
Your settings are saved.
Set Up an IPv6 6rd Internet Connection
The 6rd protocol makes it possible to deploy IPv6 to sites using a service provider's IPv4 network. 6rd uses the
service provider’s own IPv6 address prefix.This limits the operational domain of 6rd to the service provider’ s network
and is under direct control of the service provider.The IPv6 service provided is equivalent to native IPv6.The 6rd
mechanism relies upon an algorithmic mapping between the IPv6 and IPv4 addresses that are assigned for use
within the service provider’s network.This mapping allows for automatic determination of IPv4 tunnel endpoints from
IPv6 prefixes, allowing stateless operation of 6rd.
With a 6rd tunnel configuration, the router follows the RFC5969 standard, supporting two ways to establish a 6rd
tunnel IPv6 WAN connection:
Specify Your Internet Settings
39
Page 40

• Auto mode. In IPv6 Auto Detect mode, when the router receives option 212 from the DHCPv4 option, auto
detect selects the IPv6 as 6rd tunnel setting.The router uses the 6rd option information to establish the 6rd
connection.
• Manual mode. Select 6rd Tunnel. If the router receives option 212, the fields are automatically completed.
Otherwise, you must enter the 6rd settings.
To set up an IPv6 6rd Internet connection:
1. Launch a web browser from a computer or WiFi device that is connected to the network.
2. Enter http://www.routerlogin.net.
A login window opens.
3. Enter the router user name and password.
The user name is admin.The default password is password.The user name and password are case-sensitive .
The BASIC Home page displays.
4. Select ADVANCED > Advanced Setup > IPv6.
5. From the Internet Connection Type menu, select 6rd Tunnel.
The page adjusts.The router automactially detects the information in the following sections:
• 6rd (IPv6 Rapid Development) Configuration.The router detects the service provider’ s IPv4 network and
attempts to establish an IPv6 6rd tunnel connection. If the IPv4 network returns 6rd parameters to the router ,
the page adjusts to display the correct settings in this section.
• Router's IPv6 Address on LAN.This field shows the IPv6 address that is acquired for the router’s LAN
interface.The number after the slash (/) is the length of the prefix, which is also indicated by the underline
(_) under the IPv6 address. If no address is acquired, the field displays Not Available.
• MTU size (in bytes).The normal MTU (maximum transmit unit) value for most Ethernet networks is 1500
bytes, or 1492 bytes for PPPoE connections. Change the MTU only if you are sure that it is necessary for
Specify Your Internet Settings
40
Page 41

your ISP connection. For more inf ormation about changing the MTU size, see Change the MTU Size on page
41.
6. Select an IPv6 Domain Name Server (DNS) Address radio button:
• Get Automatically from ISP.Your ISP uses DHCP to assign your DNS servers.Your ISP automatically
assigns this address.
• Use These DNS Servers. If you know that your ISP requires specific servers, select this option. Enter the
IP address of your ISP’s primary DNS server. If a secondary DNS server address is available, enter it also.
7. Select an IP Address Assignment radio button:
• Use DHCP Server.This method passes more information to LAN devices but some IPv6 systems might not
support the DHCPv6 client function.
• Auto Config.This is the default setting.
This setting specifies how the router assigns IPv6 addresses to the devices on your home netw ork (the LAN).
8. (Optional) Select the Use This Interface ID check box and specify the interface ID that you want to be used for
the IPv6 address of the router’s LAN interface.
If you do not specify an ID here, the router generates one automatically from its MAC address.
9. Click the Apply button.
Your settings are saved.
Change the MTU Size
The maximum transmission unit (MTU) is the largest data packet a network device transmits.When one network
device communicates across the Internet with another, the data pac k ets trav el through man y de vices along the wa y.
If a device in the data path uses a lower MTU setting than the other devices, the data packets must be split or
“fragmented” to accommodate the device with the smallest MTU.
The best MTU setting for NETGEAR equipment is often the default value. In some situations, changing the value
fixes one problem but causes another. Leave the MTU unchanged unless one of these situations occurs:
• You experience problems connecting to your ISP or other Internet service, and the technical support of either
the ISP or NETGEAR recommends changing the MTU setting.These web-based applications might require an
MTU change:
• A secure website that does not open, or displays only part of a web page
• Yahoo email
Specify Your Internet Settings
41
Page 42

• MSN portal
• America Online’s DSL service
• You use VPN and experience severe performance problems.
• You used a program to optimize MTU for performance reasons and now you are experiencing connectivity or
performance problems.
An incorrect MTU setting can cause Internet communication problems. For example, you
Note
might not be able to access certain websites, frames within websites, secure login pages, or
FTP or POP servers.
To change the MTU size:
1. Launch a web browser from a computer or wireless device that is connected to the network.
2. Enter http://www.routerlogin.net.
A login window opens.
3. Enter the router user name and password.
The user name is admin.The default password is password.The user name and password are case-sensitive .
The BASIC Home page displays.
4. Select ADVANCED > Setup > WAN Setup.
The WAN Setup page displays.
5. In the MTU Size field, enter a value from 64 to 1500.
6. Click the Apply button.
Your settings are saved.
If you suspect an MTU problem, a common solution is to change the MTU to 1400. If you are willing to experiment, you
can gradually reduce the MTU from the maximum value of 1500 until the problem goes away.The following table
describes common MTU sizes and applications.
Table 3. Common MTU sizes
ApplicationMTU
1500
The largest Ethernet packet size.This setting is typical for connections that do not use PPPoE or VPN
and is the default value for NETGEAR routers, adapters, and switches.
Used in PPPoE environments.1492
Specify Your Internet Settings
42
Page 43

ApplicationMTU
Maximum size to use for pinging. (Larger packets are fragmented.)1472
Used in some DHCP environments.1468
Usable by AOL if you do not send or receive large email attachments, for example.1460
Used in PPTP environments or with VPN.1436
Maximum size for AOL DSL.1400
Typical value to connect to dial-up ISPs.576
Specify Your Internet Settings
43
Page 44

Control Access to the Internet
The router comes with a built-in firewall that helps protect y our home network from unwanted intrusions from the Internet.
This chapter includes the following sections:
• Set Up Parental Controls on page 45
• Allow or Block Access to Your Network on page 46
• Use Keywords to Block Internet Sites on page 48
• Manage Network Access Control Lists on page 53
• Schedule When to Block Internet Sites and Services on page 54
• Set Up Security Event Email Notifications on page 55
4
44
Page 45

Set Up Parental Controls
The first time that you select Parental Contr ols from the BASIC Home page, your bro wser goes to the Live P arental
Controls website, where you can learn more about Parental Controls and download the application.
After you set up and enable parental controls, y ou can change the web filtering le v el f or each device on the network
through the network map page on the genie app.
To set up Parental Controls:
1. Launch a web browser from a computer or wireless device that is connected to the network.
2. Enter http://www.routerlogin.net.
A login window opens.
3. Enter the router user name and password.
The user name is admin.The default password is password.The user name and password are case-sensitive .
The BASIC Home page displays.
4. Select Parental Controls.
The Live Parental Controls website opens.
5. Click the button for the app or version that you want to download and use.
6. Follow the onscreen instructions to download and install the genie app.
7. Open the genie app and select Parental Controls.
After installation, Live Parental Controls automatically starts.
8. Click the Next button, read the note, and click the Next button again.
Because Live Parental Controls uses free OpenDNS accounts, you are prompted to log in or create a free
account.
9. Select a radio button as follows:
• If you already own an OpenDNS account, leave the Yes radio button selected.
• If you do not own an OpenDNS account, select the No radio button.
If you are creating an account, the Create a free OpenDNS account page displays. Do the following:
Control Access to the Internet
45
Page 46

a. Complete the fields.
b. Click the Next button.
After you log on or create your account, the filtering level page displays.
10. Select a filtering level and click the Next button.
The Setup is complete page displays.
11. Click the Take me to the status screen button.
The Status page displays. Parental controls are now set up for the router.
12. To enable Parental Controls, click the Enable Live Parental Controls.
After you set up and enable Parental Controls, you can change the web filtering level for each device on the
network through the network map page of the genie app.
Allow or Block Access to Your Network
You can use access control to block or allow access to your network.
To set up access control:
1. Launch a web browser from a computer or wireless device that is connected to the network.
2. Enter http://www.routerlogin.net.
A login window opens.
3. Enter the router user name and password.
The user name is admin.The default password is password.The user name and password are case-sensitive .
The BASIC Home page displays.
Control Access to the Internet
46
Page 47

4. Select ADVANCED > Security > Access Control.
5. Select the Turn on Access Control check box.
You must select this check box before you can specify an access rule and use the Allow and Block buttons.
When this check box is cleared, all devices are allowed to connect, even if a device is in the blocked list.
6. Select an access rule:
• Allow all new devices to connect.With this setting, if you add a new device, it can access your network.
You don’t need to enter its MAC address on this page.We recommend that you leave this radio button
selected.
• Block all new devices from connecting.With this setting, if you add a new device, before it can access
your network, you must enter its MAC address for an Ethernet connection and its MAC address for a WiFi
connection in the allowed list.
The access rule does not affect previously blocked or allowed devices. It applies only to devices joining your
network in the future after you apply these settings.
7. To view allowed or blocked devices that are not connected, click one of the following links:
• View list of allowed devices not currently connected to the network
• View list of blocked devices not currently connected to the network
The list displays.
8. To allow the computer or device you’re currently using to continue to access the network, select the check box
next to your computer or device, and click the Allow button.
9. Click the Apply button.
Your settings are saed
Control Access to the Internet
47
Page 48

Use Keywords to Block Internet Sites
You can use keywords to block certain Internet sites from your network.You can use blocking all the time or based
on a schedule.
To block Internet sites:
1. Launch a web browser from a computer or wireless device that is connected to the network.
2. Enter http://www.routerlogin.net.
A login window opens.
3. Enter the router user name and password.
The user name is admin.The default password is password.The user name and password are case-sensitive .
The BASIC Home page displays.
4. Select ADVANCED > Security > Block Sites.
5. Select a keyword blocking option:
• Per Schedule.Turn on keyword blocking according to a schedule that you set. (See Schedule When to
Block Internet Sites and Services on page 54.)
• Always.Turn on keyword blocking all the time, independent of the Schedule page.
6. In the Type keyword or domain name here field, enter a keyword or domain that you want to block.
For example:
• Specify XXX to block http://www.badstuff.com/xxx.html.
• Specify .com if you want to allow only sites with domain suffixes such as .edu or .gov.
• Enter a period (.) to block all Internet browsing access.
Control Access to the Internet
48
Page 49

7. Click the Add Keyword button.
The keyword is added to the keyword list.The keyword list supports up to 32 entries.
8. Click the Apply button.
Keyword blocking takes effect.
Control Access to the Internet
49
Page 50

Block Services From the Internet
You can block Internet services on your network based on the type of service.You can block the services all the
time or based on a schedule.
To block services:
1. Launch a web browser from a computer or wireless device that is connected to the network.
2. Enter http://www.routerlogin.net.
A login window opens.
3. Enter the router user name and password.
The user name is admin.The default password is password.The user name and password are case-sensitive .
The BASIC Home page displays.
4. Select ADVANCED > Security > Block Services.
5. Specify when to block the services:
• To block the services all the time, select the Always radio button.
• To block the services based on a schedule, select the Per Schedule radio button.
For information about how to specify the schedule, see Schedule When to Block Internet Sites and Services on
page 54.
Control Access to the Internet
50
Page 51

6. Click the Add button.
7. To add a service that is in the Service Type menu, select the application or service.
The settings for this service automatically display in the fields.
8. To add a service or application that is not in the menu, select User Defined, and do the following:
a. If you know that the application uses either TCP or UDP, select the appropriate protocol. Otherwise, select
TCP/UDP (both).
b. Enter the starting port and ending port numbers.
If the service uses a single port number, enter that number in both fields.To find out which port numbers
the service or application uses, you can contact the publisher of the application, ask user groups or
newsgroups, or search on the Internet.
9. Select a filtering option:
• Only This IP Address. Block services for a single computer.
• IP Address Range. Bloc k services for a range of computers with consecutiv e IP addresses on your network.
• All lP Addresses. Block services for all computers on your network.
10. Click the Add button.
Your settings are saved.
Delete Keywords From the Blocked List
To delete keywords from the list:
1. Launch a web browser from a computer or WiFi device that is connected to the network.
2. Enter http://www.routerlogin.net.
Control Access to the Internet
51
Page 52

A login window opens.
3. Enter the router user name and password.
The user name is admin.The default password is admin.The user name and password are case-sensitive.
The BASIC Home page displays.
4. Select ADVANCED > Security > Block Sites.
The Block Sites page displays.
5. Do one of the following:
• To delete a single word, select it and click the Delete Keyword button.
The keyword is removed from the list.
• To delete all keywords on the list, click the Clear List button.
All keywords are removed from the list.
6. Click the Apply button.
Your settings are saved.
Avoid Blocking on a Trusted Computer
You can exempt one trusted computer from bloc king.The computer you exempt m ust be assigned a fixed IP address.
You can use the reserved IP address feature to specify the IP address. See Manage Reserved LAN IP Addresses
on page 76.
To specify a trusted computer:
1. Launch a web browser from a computer or WiFi device that is connected to the network.
2. Enter http://www.routerlogin.net.
A login window opens.
3. Enter the router user name and password.
The user name is admin.The default password is password.The user name and password are case-sensitive .
The BASIC Home page displays.
4. Select ADVANCED > Security > Block Sites.
The Block Sites page displays.
5. Scroll down and select the Allow trusted IP address to visit blocked sites check box.
6. In the Trusted IP Address field, enter the IP address of the trusted computer.
7. Click the Apply button.
Control Access to the Internet
52
Page 53

Your settings are saved.
Manage Network Access Control Lists
You can use access control to block or allow access to your network.
To manage devices that are allowed or blocked:
1. Launch a web browser from a computer or wireless device that is connected to the network.
2. Type http://www.routerlogin.net.
A login window opens.
3. Enter the router user name and password.
The user name is admin.The default password is password.The user name and password are case-sensitive .
The BASIC Home page displays.
4. Select ADVANCED > Security > Access Control.
5. Select the Turn on Access Control radio button.
6. Click the View list of allowed devices not currently connected to the network link.
Control Access to the Internet
53
Page 54

The list displays.
7. Select the check box for a device.
8. Use the Add button, Edit button, and Remove from the list button as needed.
9. Click the Apply button.
Your changes take effect.
Schedule When to Block Internet Sites and Services
When you schedule blocking, the same schedule is used to block sites and to block services. For information about
how to specify what you want the router to block, see Use Keywords to Block Internet Sites on page 48 and Block
Services From the Internet on page 50.
To schedule blocking:
1. Launch a web browser from a computer or wireless device that is connected to the network.
2. Enter http://www.routerlogin.net.
A login window opens.
3. Enter the router user name and password.
The user name is admin.The default password is password.The user name and password are case-sensitive .
The BASIC Home page displays.
Control Access to the Internet
54
Page 55

4. Select ADVANCED > Security > Schedule.
5. Specify when to block keywords and services:
• Days to Block. Select the check box for each day that you want to block the keywords, or select the Every
Day check box, which automatically selects the check boxes for all days.
• Time of Day to Block. Select a start and end time in 24-hour format, or select the All Day check box for
24-hour blocking.
6. Select your time zone from the menu.
7. If you live in a region that observes da ylight sa ving time , select the A utomaticall y adjust f or da ylight sa vings
time check box.
8. Click the Apply button.
Your settings are saved.
Set Up Security Event Email Notifications
The router can email you its logs of router activity .The log records router activity and security events such as attempts
to access blocked sites or services.
To set up email notifications:
1. Launch a web browser from a computer or WiFi device that is connected to the network.
2. Enter http://www.routerlogin.net.
A login window opens.
3. Enter the router user name and password.
Control Access to the Internet
55
Page 56

The user name is admin.The default password is password.The user name and password are case-sensitive .
The BASIC Home page displays.
4. Select ADVANCED > Security > E-mail.
5. Select the Turn E-mail Notification On check box.
6. In the Your Outgoing Mail Server field, enter the name of your ISP outgoing (SMTP) mail server (such as
mail.myISP.com).
You might be able to find this information in the configuration window of your email program. If you leave this
field blank, log and alert messages are not sent.
7. In the Send to This E-mail Address field, type the email address to which logs and alerts are to be sent.
This email address is also used for the F rom address. If this field is b lank, log and alert messages are not sent.
8. If your outgoing email server requires authentication, select the My Mail Server requires authentication check
box, and do the following:
a. In the User Name field, type the user name for the outgoing email server.
b. In the Password field, type the password for the outgoing email server.
9. To send alerts when someone attempts to visit a blocked site, select the Send Alerts Immediately check box.
Email alerts are sent immediately when someone attempts to visit a blocked site.
10. To send logs based on a schedule, specify these settings:
Control Access to the Internet
56
Page 57

a. From Send logs according to this schedule menu, select the schedule type.
b. From the Day menu, select the day.
c. From the Time menu, select the time, and select the am or pm radio button.
11. Click the Apply button.
Your settings are saved.
Logs are sent automatically according to the schedule that you set. If the log fills before the specified time, it is
sent. After the log is sent, it is cleared from the router memory. If the router cannot email the log and the log
buffer fills, the router overwrites the log.
Control Access to the Internet
57
Page 58

Tri-Band WiFi Connections
This chapter explains how the router manages WiFi connections f or its WiFi bands and ho w y ou can control the rele vant
router settings.
The chapter contains the following sections:
• Tri-Band WiFi on page 59
• Smart Connect on page 62
• Beamforming on page 64
5
58
Page 59

Tri-Band WiFi
Tri-band WiFi delivers 3.2 Gbps combined WiFi speeds through three dedicated WiFi bands—a 2.4 GHz band plus
two 5 GHz bands.This additional 5 GHz WiFi band allows you to double the WiFi bandwidth for dual-band devices .
Figure 6.Tri-band WiFi doubles the available bandwidth for dual-band devices
Smart Connect intelligently selects the best WiFi band for each dual-band device to optimiz e connection speed and
performance based on that device’s speed and performance capabilities.This additional WiFi bandwidth combined
with the intelligence to segregate traffic based on WiFi speed and load balancing pro vides the best perf ormance f or
multiple WiFi devices in your home.
How Tri-Band WiFi Improves Speed and Performance
Tri-band WiFi increases the available WiFi bandwidth for your network to reduce network congestion.
Typically, a dual-band WiFi router shares bandwidth among all connected devices that are downloading data at the
same time. So if you are watching a Netflix movie on your Internet-enabled large-screen TV while your kids are
watching a YouTube video on a smartphone, the router shares the bandwidth across these two devices.This is
particularly unfair for the faster 802.11ac devices or three-stream (3x3) 802.11n devices because their speeds are
reduced to the speed of the slowest device in the network. Even one slow device can bring down the entire network
speed.
In this simplified example, the 5 GHz band is capable of a maximum speed of 1733 Mbps, but the actual speed
could be limited by the device capability. For example, an Apple MacBook Pro with support for three streams is
capable of the maximum 1300 Mbps, but the Tri-Band WiFi Connections iPhone 5S with support for only single-stream
802.11n can achieve a maximum WiFi speed of only 150 Mbps. As more devices connect and begin downloading,
the bandwidth is shared among them as well.
The following example of shared bandwidth shows a dual-band router in which the GHz WiFi band is capable of a
fast 640 Mbps speed. If only one computer or device connects, the router can allocate a speed of up to 640 Mbps
to that connection, assuming that the device is capable of that speed.When more devices connect to the 5 GHz
Tri-Band WiFi Connections
59
Page 60

band, they must share the bandwidth. If four devices connect, then the router divides its 640 Mbps capacity by 5,
as shown in the following figure.
Figure 7. Dual-band WiFi network with one 5 GHz WiFi band
That means that in the network shown, a computer with a 1,300 Mbps capacity provides an effectiv e WiFi connection
speed of 160 Mbps (13005 ), and other devices would also see their WiFi speeds divided by 5.
Tri-band WiFi adds a second 5 GHz WiFi band to the network.This increases the available WiFi bandwidth, which
can be compared to widening the road. In addition to widening the road, using two 5 GHz bands means that the
router has dedicated 5 GHz bands.That’s like tri-band WiFi connections using two lanes in the wider road instead
of one.The router automatically uses Smart Connect to allocate the fastest devices to the fast lane.
Tri-Band WiFi Connections
60
Page 61

Figure 8. A tri-band network includes two dedicated 5 GHz bands
In this tri-band network, the first 5 GHz band provides a speed of 200 Mbps, and the second 5 GHz band provides
a speed of 1,300 Mbps.
The slower and faster devices are separated in different WiFi connections to ensure that you get the best speed on
each device. So in the previous figure , all the three mobile devices are on one 5 GHz band with a combined maximum
speed of 200 Mbps, and the other 5 GHz WiFi band is used f or the faster 802.11ac de vices with a combined maximum
speed of 1300 Mbps. Effectiv ely both slower and faster de vices can run faster and the ov erall network speed increases
by more than two times, from 640 Mbps to 1500 Mbps.
Load Balancing
The router uses load balancing to distribute WiFi connections among all three WiFi bands, to ensure that both the
WiFi bands are utilized. Load balancing prevents overloading a single 5 GHz band and ensures that both the WiFi
bands are utilized and device connections are spread across the two bands.
For example , if three mobile devices are connected to one 5 GHz band, the f ourth device is automatically connected
to the other 5 GHz band.
Tri-Band WiFi Connections
61
Page 62

Figure 9. Load balancing
Slower devices like printers, older computers, or IP cameras connect to the 2.4 GHz band.The presence of two 5
GH bands prevents overloading when many devices use WiFi at the same time.
Benefits of Tri-Band WiFi
The tri-band WiFi network outperforms the dual-band network in several ways:
• More bandwidth is available.
Even with more devices connected to the network, because the connections are spread across two different
bands, each device gets a larger share of the available WiFi bandwidth.
• Smart Connect directs WiFi traffic to the appropriate lane.
With Smart Connect, older devices do not slow down faster devices.
• The router uses load balancing to avoid network congestion in each WiFi band.
With load balancing, you don’t need to share your WiFi connection with as many devices.
Smart Connect
Smart Connect balances your 5 GHz WiFi connections into two different radio bands: the 5 GHz radio 1 band and
the 5 GHz radio 2 band.The router uses Smart Connect to choose the best radio band for your device to give you
the best WiFi performance.
Tri-Band WiFi Connections
62
Page 63

iTunes Server lets you play music with your Windows or Mac iTunes app from a storage device that is connected
to the router.You can also use the Apple Remote app from an iPhone or iPad to pla y m usic on an y AirPlay devices,
such as Apple TV or AirPlay-supported receivers.
Figure 10. Smart Connect
For Smart Connect to work, both 5 GHz radio bands must use the same WiFi network name (SSID) and network
key (password).That means that when you connect to the router with WiFi, you see only one 5 GHz SSID that
connects to both 5 GHz radio bands.
If you enable Smart Connect and the SSID and passwords for both 5 GHz radio bands do
Note
not match, the WiFi settings for 5 GHz radio 1 overwrite the WiFi settings for 5 GHz radio 2.
Enable or Disable Smart Connect
To enable or disable Smart Connect:
1. Launch a web browser from a computer or WiFi device that is connected to the network.
2. Enter http://www.routerlogin.net.
A login window opens.
3. Enter the router user name and password.
The user name is admin.The default password is password.The user name and password are case-sensitive .
Tri-Band WiFi Connections
63
Page 64

The BASIC Home page displays.
4. Select Wireless.
The Wireless Setup page displays.
5. Select or clear the the Smart Connect – One Wireless Network Name (SSID) for both 5 GHz radios check
box.
Selecting this check box turns on Smart Connect and clearing this check box turns off Smart Connect.
6. Click the Apply button.
Your settings are saved.
Beamforming
Beamforming means that your router actively tracks clients and directs Wifi to the client, rather than just blasting it
out in all directions.This means better WiFi range and performance for your WiFi devices.
The router uses explicit and implicit beamforming to improve WiFi performance. Explicit beamforming requires the
client to support beamforming.Typically, 802.11ac clients support beamforming. Implicit beamforming means that
the router can support beamforming even with clients that do not support beamforming.This router supports implicit
beamforming for both 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz clients, which means that it will provide beamforming benefits of better
range and performance for all WiFi devices, even older 802.11a/b/g/n devices, not just the latest WiFi clients.
Enable or Disable Implicit Beamforming
Implicit beamforming means that the router can use information from client devices that support beamforming to
improve the WiFi signal.
To enable or disable implicit beamforming:
1. Launch a web browser from a computer or WiFi device that is connected to the network.
2. Enter http://www.routerlogin.net.
A login window opens.
3. Enter the router user name and password.
The user name is admin.The default password is password.The user name and password are case-sensitive .
The BASIC Home page displays.
4. Select ADVANCED > Advanced Setup > Wireless Settings.
The Wireless Settings page displays.
5. Scroll down below the WPS Settings section and select or clear the Enable Implicit BEAMFORMING check
box.
6. Click the Apply button.
Tri-Band WiFi Connections
64
Page 65

Your settings are saved.
Tri-Band WiFi Connections
65
Page 66

Network Settings
The router comes ready for WiFi, Ethernet, and USB connections.You can customize the router’s network settings.We
recommend that you install the router and connect it to the Internet before you change its network settings.
This chapter includes the following sections:
• View or Change WAN Settings on page 67
• Set Up a Default DMZ Server on page 68
• Set Up Ethernet Port Aggregation on page 69
• Change the LAN TCP/IP Settings on page 71
• Change the Router’s Device Name on page 73
• Specify the IP Addresses That the Router Assigns on page 74
• Disable the DHCP Server Feature in the Router on page 75
• Manage Reserved LAN IP Addresses on page 76
6
• Custom Static Routes on page 78
• Set Up a Bridge for a Port Group or VLAN Tag Group on page 81
• Use the WPS Wizard for WiFi Connections on page 84
• Specify Basic WiFi Settings on page 85
• Set Up a Guest WiFi Network on page 89
• Control the WiFi Radios on page 91
• Set Up a WiFi Schedule on page 92
• Specify WPS Settings on page 93
• Use the Router as a WiFi Access Point on page 94
• Use the Router in Bridge Mode on page 97
66
Page 67

View or Change WAN Settings
You can view or configure wide area network (WAN) settings f or the Internet port.Y ou can set up a DMZ (demilitarized
zone) server, change the maxim um transmit unit (MTU) size, and enable the router to respond to a ping to its WAN
(Internet) port.
To view or change the WAN settings:
1. Launch a web browser from a computer or WiFi device that is connected to the network.
2. Enter http://www.routerlogin.net.
A login window opens.
3. Enter the router user name and password.
The user name is admin.The default password is password.The user name and password are case-sensitive .
The BASIC Home page displays.
4. Select ADVANCED > Setup > WAN Setup.
The following settings display:
5. View or change the following settings:
• Disable Port Scan and DoS Protection. DoS protection protects your LAN against denial of service attacks
such as Syn flood, Smurf Attack, Ping of Death, and many others. Select this check box only in special
circumstances.
• Default DMZ Server.This feature is sometimes helpful when you are playing online games or
videoconferencing, but it makes the firewall security less effective. See Set Up a Default DMZ Server on
page 68.
• Respond to Ping on Internet Port.This feature allows your router to be discovered. Use this feature only
as a diagnostic tool or for a specific reason.
• Disable IGMP Proxying. IGMP proxying allows a computer on the local area network (LAN) to receive the
multicast traffic it is interested in from the Internet. If y ou do not need this feature, you can select this check
box to disable it.
Network Settings
67
Page 68

• MTU Size (in bytes).The normal MTU (maximum transmit unit) value for most Ethernet networks is 1500
bytes, or 1492 bytes for PPPoE connections. Change the MTU only if you are sure that it is necessary for
your ISP connection. See Change the MTU Size on page 41.
• NAT Filtering. Network Address Translation (NAT) determines how the router processes inbound traffic.
Secured NAT protects computers on the LAN from attacks from the Internet but might prevent some Internet
games, point-to-point applications, or multimedia applications from working. Open NAT provides a much
less secured firewall but allows almost all Internet applications to work.
6. Click the Apply button.
Your settings are saved.
Set Up a Default DMZ Server
The default DMZ server feature is helpful when y ou are using some online games and videoconferencing applications
that are incompatible with Network Address Translation (NAT).The router is programmed to recognize some of
these applications and to work correctly with them, but other applications might not function well. In some cases,
one local computer can run the application correctly if the IP address for that computer is entered as the default
DMZ server.
WARNING:
DMZ servers pose a security risk. A computer designated as the default DMZ server
loses much of the protection of the firewall and is exposed to exploits from the
Internet. If compromised, the DMZ server computer can be used to attack other
computers on your network.
The router usually detects and discards incoming traffic from the Internet that is not a response to one of your local
computers or a service that you configured on the Port Forwarding/Port Triggering page. Instead of discarding this
traffic, you can specify that the router forwards the traffic to one computer on your network.This computer is called
the default DMZ server.
To set up a default DMZ server:
1. Launch a web browser from a computer or WiFi device that is connected to the network.
2. Enter http://www.routerlogin.net.
A login window opens.
3. Enter the router user name and password.
The user name is admin.The default password is password.The user name and password are case-sensitive .
The BASIC Home page displays.
4. Select ADVANCED > Setup > WAN Setup.
The WAN Setup page displays.
Network Settings
68
Page 69

5. Select the Default DMZ Server check box.
6. Type the IP address.
7. Click the Apply button.
Your settings are saved.
Set Up Ethernet Port Aggregation
Ethernet aggregation lets you combine two Gigabit Ethernet ports to improve the aggregated file transfer speed.
Note that Ethernet port aggregation is also referred to as link aggregation, teaming port, and port trunking. If a device
supports Ethernet aggregation, you can use the Ethernet aggregate ports 1 and 2 to cable the device that supports
Ethernet port aggregation to the router.
To get the fastest performance with port aggregation, for wired connections use Ethernet
Note
port 3 for the first computer, and use Ethernet port 4, 5 or 6 for the second computer, which
allows for speeds up to 2 Gbps with port aggregation.The maximum speed between port 4,
5 and 6 is limited to 1 Gbps.
NETGEAR ReadyNAS equipment with two Ethernet ports such as model RN100/200/300/500/700 desktop series
and the ReadyNAS RN2000/3000/4000 rack-mount series support Ethernet aggregation.
Figure 11. Ethernet port aggregation
Network Settings
69
Page 70

To set up Ethernet port aggregation:
1. If you are connecting a switch, make sure that the switch supports 802.3ad LACP.
You must configure the switch before you connect the Ethernet cables to the router.
WARNING:
To avoid causing broadcast looping, which can shut down your network, do not
connect an unmanaged switch to Ethernet aggregate port 1 and port 2 on the router .
2. Use Ethernet cables to connect a device that supports Ethernet port aggregation, such as a NAS or network
switch, to Ethernet port 1 and port 2 on the router.
3. Set up Ethernet port aggregation on the device that is connected to Ethernet port 1 and port 2 on the router.
For information about how to set up Ethernet port aggregation on your device, see the documentation that came
with your device.
For information about viewing the status of the Ethernet port aggregation, see View Ethernet Port Aggregation
Status on page 71.
Network Settings
70
Page 71

View Ethernet Port Aggregation Status
You can view the status of Ethernet aggregation for a device that is connected to the router's designated Ethernet
aggregation ports.The device must support Ethernet aggregation.
To view the status of the Ethernet port aggregation:
1. Launch a web browser from a computer or WiFi device that is connected to the network.
2. Enter http://www.routerlogin.net.
A login screen displays.
3. Enter the router user name and password.
The user name is admin.The default password is password.The user name and password are case-sensitive .
The BASIC Home screen displays.
4. Select ADVANCED > Advanced Setup > Ethernet Port Aggregation.
The Ethernet Port Aggregation Status displays.
Change the LAN TCP/IP Settings
The router is preconfigured to use private IP addresses on the LAN side and to act as a DHCP server.The router’s
default LAN IP configuration is as follows:
• LAN IP address. 192.168.1.1
• Subnet mask. 255.255.255.0
These addresses are part of the designated private address range for use in private networks and are suitable for
most applications. If your network requires a different IP addressing scheme, you can change these settings.
You might want to change these settings if you need a specific IP subnet that one or more devices on the network
use, or if you use competing subnets with the same IP scheme.
Network Settings
71
Page 72

To change the LAN TCP/IP settings:
1. Launch a web browser from a computer or WiFi device that is connected to the network.
2. Enter http://www.routerlogin.net.
A login window opens.
3. Enter the router user name and password.
The user name is admin.The default password is password.The user name and password are case-sensitive .
The BASIC Home page displays.
4. Select ADVANCED > Setup > LAN Setup.
Your router might display information that is different from this example.
5. In the IP Address field, type the IP address.
6. In the IP Subnet Mask, type the subnet mask of the router.
The IP address and subnet mask identify which addresses are local to a specific device and which must be
reached through a gateway or router.
7. Change the RIP settings.
Router Information Protocol (RIP) allows a router to exchange routing information with other routers.
Network Settings
72
Page 73

a. Select the RIP direction:
• Both.The router broadcasts its routing table periodically and incorporates information that it receives.
• Out Only.The router broadcasts its routing table periodically.
• In Only.The router incorporates the RIP information that it receives.
b. Select a RIP version:
• Disabled.This is the default setting.
• RIP-1.This format is universally supported. It is adequate for most networks, unless you are using an
unusual network setup.
• RIP-2.This format carries more information. Both RIP-2B and RIP-2M send the routing data in RIP-2
format. RIP-2B uses subnet broadcasting. RIP-2M uses multicasting.
8. Click the Apply button.
Your settings are saved.
If you changed the LAN IP address of the router, you are disconnected when this change takes effect.
9. To reconnect, close your browser, relaunch it, and log in to the router
Change the Router’s Device Name
The router’s default device name is based on its model number, which is R8500.This device name displays in the
file manager when you browse your network.
To change the router’s device name:
1. Launch a web browser from a computer or WiFi device that is connected to the network.
2. Enter http://www.routerlogin.net.
A login window opens.
3. Enter the router user name and password.
The user name is admin.The default password is password.The user name and password are case-sensitive .
The BASIC Home page displays.
4. Select ADVANCED > Setup > LAN Setup.
The LAN Setup page displays.
5. In the Device Name field, type a new name.
6. Click the Apply button.
Network Settings
73
Page 74

Your settings are saved.
Specify the IP Addresses That the Router Assigns
By default, the router acts as a Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) server.The router assigns IP, DNS
server, and def ault gatewa y addresses to all computers connected to the LAN.The assigned default gatewa y address
is the LAN address of the router.
These addresses must be part of the same IP address subnet as the router’s LAN IP address. Using the default
addressing scheme, define a range between 192.168.1.2 and 192.168.1.254, although you can save part of the
range for devices with fixed addresses.
To specify the pool of IP addresses that the router assigns:
1. Launch a web browser from a computer or wireless device that is connected to the network.
2. Enter http://www.routerlogin.net.
A login window opens.
3. Enter the router user name and password.
The user name is admin.The default password is password.The user name and password are case-sensitive .
The BASIC Home page displays.
4. Select ADVANCED > Setup > LAN Setup.
Your router might display information that is different from this example.
5. Make sure that the Use Router as DHCP Server check box is selected.
6. Specify the range of IP addresses that the router assigns:
Network Settings
74
Page 75

a. In the Starting IP Address field, type the lowest number in the range.
This IP address must be in the same subnet as the router.
b. In the Ending IP Address field, type the number at the end of the range of IP addresses.
This IP address must be in the same subnet as the router.
7. Click the Apply button.
Your settings are saved.
The router delivers the following parameters to any LAN device that requests DHCP:
• An IP address from the range that you define
• Subnet mask
• Gateway IP address (the router’s LAN IP address)
• DNS server IP address (the router’s LAN IP address)
Disable the DHCP Server Feature in the Router
By default, the router acts as a DHCP server.The router assigns IP, DNS server, and default gateway addresses
to all computers connected to the LAN.The assigned default gateway address is the LAN address of the router.
You can use another device on your network as the DHCP server or specify the network settings of all your computers.
To disable the DHCP server feature in the router:
1. Launch a web browser from a computer or wireless device that is connected to the network.
2. Enter http://www.routerlogin.net .
A login window opens.
3. Enter the router user name and password.
The user name is admin.The default password is password.The user name and password are case-sensitive .
The BASIC Home page displays.
4. Select ADVANCED > Setup > LAN Setup.
The LAN Setup page displays.
5. Clear the Use Router as DHCP Server check box.
6. Click the Apply button.
Network Settings
75
Page 76

Your settings are saved.
7. (Optional) If this service is disabled and no other DHCP server is on your network, set your computer IP addresses
manually so that the computers can access the router.
Manage Reserved LAN IP Addresses
When you specify a reserved IP address for a computer on the LAN, that computer always receives the same IP
address each time it accesses the router’s DHCP server. Assign reserved IP addresses to computers or servers
that require permanent IP settings.
Reserve an IP Address
To reserve an IP address:
1. Launch a web browser from a computer or WiFi device that is connected to the network.
2. Enter http://www.routerlogin.net.
A login window opens.
3. Enter the router user name and password.
The user name is admin.The default password is password.The user name and password are case-sensitive .
The BASIC Home page displays.
4. Select ADVANCED > Setup > LAN Setup.
The LAN Setup page displays.
5. In the Address Reservation section, click the Add button.
The page adjusts.
6. In the IP Address field, type the IP address to assign to the computer or server.
Choose an IP address from the router’s LAN subnet, such as 192.168.1.x.
7. Type the MAC address of the computer or server.
If the computer is already on your network, you can copy its MAC address from the Attached
Tip
Devices page and paste it here.
8. Click the Apply button.
The reserved address is entered into the table.
Network Settings
76
Page 77

The reserved address is not assigned until the next time the computer contacts the router’s DHCP server. Reboot
the computer, or access its IP configuration and force a DHCP release and renew.
Edit a Reserved IP Address
To edit a reserved address entry:
1. Launch a web browser from a computer or WiFi device that is connected to the network.
2. Enter http://www.routerlogin.net.
A login window opens.
3. Enter the router user name and password.
The user name is admin.The default password is password.The user name and password are case-sensitive .
The BASIC Home page displays.
4. Select ADVANCED > Setup > LAN Setup.
The LAN Setup page displays.
5. Select the radio button next to the reserved address.
6. Click the Edit button.
7. Change the settings.
8. Click the Apply button.
Your settings are saved.
Delete a Reserved IP Address Entry
To delete a reserved address entry:
1. Launch a web browser from a computer or WiFi device that is connected to the network.
2. Enter http://www.routerlogin.net.
A login window opens.
3. Enter the router user name and password.
The user name is admin.The default password is password.The user name and password are case-sensitive .
The BASIC Home page displays.
4. Select ADVANCED > Setup > LAN Setup.
The LAN Setup page displays.
Network Settings
77
Page 78

5. Select the radio button next to the reserved address.
6. Click the Delete button.
The address is removed.
Custom Static Routes
T ypically, you do not need to add static routes unless you use multiple routers or multiple IP subnets on y our network.
As an example of when a static route is needed, consider the following case:
• Your main Internet access is through a cable modem to an ISP.
• Your home network includes an ISDN router for connecting to the company where you are employed.This
router’s address on your LAN is 192.168.1.100.
• Your company’s network address is 134.177.0.0.
When you set up your router, two implicit static routes were created. A default route was created with your ISP as
the gateway, and a second static route was created to your local network for all 192.168.1.x addresses.With this
configuration, if you try to access a device on the 134.177.0.0 network, your router f orwards y our request to the ISP.
The ISP forwards your request to the company where you are employed, and the company firewall is likely to deny
the request.
In this case you must define a static route, telling your router to access 134.177.0.0 through the ISDN router at
192.168.1.100. Here is an example:
• The Destination IP Address and IP Subnet Mask fields specify that this static route applies to all 134.177.x.x
addresses.
• The Gateway IP Address field specifies that all traffic for these addresses will be forwarded to the ISDN router
at 192.168.1.100.
• A metric value of 1 works because the ISDN router is on the LAN.
• The Private check box is selected only as a precautionary security measure in case RIP is activated.
Set Up a Static Route
To set up a static route:
1. Launch a web browser from a computer or WiFi device that is connected to the network.
2. Enter http://www.routerlogin.net.
A login window opens.
3. Enter the router user name and password.
The user name is admin.The default password is password.The user name and password are case-sensitive .
Network Settings
78
Page 79

The BASIC Home page displays.
4. Select ADVANCED > Advanced Setup > Static Routes.
The Static Routes page displays.
5. Click the Add button.
6. In the Route Name field, type a name for this static route (for identification purposes only).
7. So limit access to the LAN only, select the Private check box.
If the Private check box is selected, the static route is not reported in RIP.
8. Select the Active check box to make this route effective.
9. Type the IP address of the final destination.
10. Type the IP subnet mask for this destination.
If the destination is a single host, type 255.255.255.255.
11. Type the gateway IP address, which must be on the same LAN segment as the router.
12. Type a number from 1 through 15 as the metric value.
This value represents the number of routers between your network and the destination. Usually, a setting of 2
or 3 works, but if this is a direct connection, set it to 1.
13. Click the Apply button.
The static route is added.
Network Settings
79
Page 80

Edit a Static Route
To edit a static route:
1. Launch a web browser from a computer or WiFi device that is connected to the network.
2. Enter http://www.routerlogin.net.
A login window opens.
3. Enter the router user name and password.
The user name is admin.The default password is password.The user name and password are case-sensitive .
The BASIC Home page displays.
4. Select ADVANCED > Advanced Setup > Static Routes.
The Static Routes page displays.
5. In the table, select the radio button for the route.
6. Click the Edit button.
The Static Routes page adjusts.
7. Edit the route information.
8. Click the Apply button.
Your settings are saved.
Delete a Static Route
To delete a static route:
1. Launch a web browser from a computer or WiFi device that is connected to the network.
2. Enter http://www.routerlogin.net.
A login window opens.
3. Enter the router user name and password.
The user name is admin.The default password is password.The user name and password are case-sensitive .
The BASIC Home page displays.
4. Select ADVANCED > Advanced Setup > Static Routes.
The Custom Static Routes page displays.
Network Settings
80
Page 81

5. In the table, select the radio button for the route.
6. Click the Delete button.
The route is removed from the table.
Set Up a Bridge for a Port Group or VLAN Tag Group
Some devices, such as an IPTV, cannot function behind the router’s network address translation (NAT) service or
firewall. Based on what your Internet service provider (ISP) requires, for the device to connect to the ISP’s network
directly, you can enable the bridge between the device and the router’s Internet port or add new VLAN tag groups
to the bridge.
If your ISP provides directions on how to set up a bridge for IPTV and Internet service, follo w
Note
those directions.
Set Up a Bridge for a Port Group
If the devices that are connected to the router’s Ethernet LAN port or WiFi network include an IPTV device, your
ISP might require you to set up a bridge for a port group for the router’s Internet interface.
A bridge with a port group prevents packets that are sent between the IPTV device and the router’s Internet port
from being processed through the router’s network address translation (NAT) service.
To configure a port group and enable the bridge:
1. Launch a web browser from a computer or WiFi device that is connected to the network.
2. Enter http://www.routerlogin.net.
A login window opens.
3. Enter the router user name and password.
The user name is admin.The default password is password.The user name and password are case-sensitive .
The BASIC Home page displays.
4. Select ADVANCED > Advanced Setup > VLAN/Bridge Settings.
The VLAN / Bridge Settings page displays.
5. Select the Enable VLAN/Bridge Group check box.
The page expands.
Network Settings
81
Page 82

6. Select the By bridge group radio button.
7. Select a Wired Ports check box or a Wireless check box:
• If your device is connected to an Ethernet port on the router, select the Wired Ports check box that
corresponds to the Ethernet port on the router to which the device is connected.
• If your device is connected to your router’s WiFi network, select the Wireless check box that corresponds to
the router’s WiFi network to which the device is connected.
You must select at least one Wired Ports or Wireless check box.You can select more than
Note
one check box.
8. Click the Apply button.
Your settings are saved.
Set Up a Bridge for a VLAN Tag Group
If the devices that are connected to the router’s Ethernet LAN ports or WiFi network include an IPTV device, your
ISP might require you to set up a bridge for a VLAN tag group for the router’s Internet interface.
If you are subscribed to IPTV service, the router might require VLAN tags to distinguish between the Internet traffic
and the IPTV traffic. A bridge with a VLAN tag group prevents packets that are sent between the IPTV device and
the router’s Internet port from being processed through the router’s network address translation (NAT) service.
You can add VLAN tag groups to a bridge and assign VLAN IDs and priority values to each VLAN tag group.
To add a VLAN tag group and enable the bridge:
1. Launch a web browser from a computer or WiFi device that is connected to the network.
2. Enter http://www.routerlogin.net.
A login window opens.
3. Enter the router user name and password.
Network Settings
82
Page 83

The user name is admin.The default password is password.The user name and password are case-sensitive .
The BASIC Home page displays.
4. Select ADVANCED > Advanced Setup > VLAN/Bridge Settings.
The VLAN / Bridge Settings page displays.
5. Select the Enable VLAN/Bridge Group check box.
6. Select the By VLAN tag group radio button.
7. Specify the settings as described in the following table.
DescriptionField
Name
Enter a name for the VLAN tag group.
The name can be up to 10 characters.
Enter a value from 1 to 4094.VLAN ID
Network Settings
83
Page 84

DescriptionField
Enter a value from 0 to 7.Priority
Select the check box for a wired LAN port or WiFi port.
If your device is connected to an Ethernet port on the router, select the LAN port check box that corresponds to the Ethernet
port on the router to which the device is connected. If your device is connected to your router’s WiFi network, select the
WiFi check box that corresponds to the router’s WiFi network to which the device is connected.
You must select at least one LAN port or WiFi port.You can select more than one port.
8. Click the Add button.
The VLAN tag group is added.
9. Click the Apply button.
Your settings are saved.
Use the WPS Wizard for WiFi Connections
The WPS Wizard helps you add a computer or WiFi device to your WiFi network without typing the WiFi password.
To use the WPS Wizard:
1. Launch a web browser from a computer or WiFi device that is connected to the network.
2. Enter http://www.routerlogin.net.
A login window opens.
3. Enter the router user name and password.
The user name is admin.The default password is password.The user name and password are case-sensitive .
The BASIC Home page displays.
4. Select ADVANCED > WPS Wizard.
A note explaining WPS displays.
5. Click the Next button.
The WPS page displays.
6. Select a setup method:
• Push button. Click the WPS button on this screen.
Network Settings
84
Page 85

• PIN Number.The page adjusts. Enter the client security PIN and click the Next button.
7. Within two minutes, go to the client device and use its WPS software to connect to the WiFi network.
The WPS process automatically sets up your computer with the netw ork password when it connects .The router
WPS page displays a confirmation message.
Specify Basic WiFi Settings
The router comes with preset security.This means that the WiFi network name (SSID), network key (password),
and security option (encryption protocol) are preset in the factory.You can find the preset SSID and password on
the router label.
The preset SSID and password are uniquely generated for every device to protect and
Note
maximize your WiFi security.
We recommend that you do not change your preset security settings. If you change your preset security settings,
make a note of the new settings and store it in a safe place where you can easily find it.
If you use a WiFi connection to change the SSID or other WiFi security settings, you are disconnected when you
click the Apply button.To avoid this problem, use a computer with a wired connection to access the router.
To specify basic WiFi settings:
1. Launch a web browser from a computer or WiFi device that is connected to the network.
2. Enter http://www.routerlogin.net.
A login window opens.
3. Enter the router user name and password.
The user name is admin.The default password is password.The user name and password are case-sensitive .
The BASIC Home page displays.
Network Settings
85
Page 86

4. Select Wireless.
You can specify the settings for the 2.4 GHz, 5 GHz-1, and 5 GHz-2 bands.
Your router might display information that is different from this example.
5. From the Region menu, select your region.
In some locations, you cannot change this setting.
6. To control the SSID broadcast, select or clear the Enable SSID Broadcast check box.
When this check box is selected, the router broadcasts its network name (SSID) so that it displays when you
scan for local WiFi networks on your computer or WiFi device.
7. To change the network name (SSID), type a new name in the Name (SSID) field.
The name can be up to 32 characters long and it is case-sensitive.The default SSID is randomly generated and
is on the router’s label. If you change the name, make sure to write down the new name and keep it in a safe
place.
8. To change the WiFi channel, select a number from the Channel menu.
In some regions, not all channels are available. Do not change the channel unless you experience interference
(shown by lost connections or slow data transfers). If this happens, experiment with different channels to see
which is the best.
When you use multiple access points, it is better if adjacent access points use different channels to reduce
interference.The recommended channel spacing between adjacent access points is four channels (f or example ,
use Channels 1 and 5, or 6 and 10).
9. Click the Apply button.
Network Settings
86
Page 87

Your settings are saved.
If you connected to the WiFi network and you changed the SSID, you are disconnected from the network.
10. Make sure that you can use WiFi to connect to the network's new new settings.
If you cannot connect with WiFi, check the following:
• Is your computer or WiFi device connected to another wireless network in your area? Some WiFi devices
automatically connect to the first open network without WiFi security that they discover.
• Is your computer or WiFi device trying to connect to your network with its old settings (before you changed
the settings)? If so, update the WiFi network selection in your computer or WiFi device to match the current
settings for your network.
Network Settings
87
Page 88

Change the WiFi Password or Security Level
Your router comes with preset WPA2 or WPA security.The password that you enter to connect to your network is
unique to your router and is on the router label.We recommend that you use the preset security, but you can change
the settings. Do not disable security.
To change the WPA settings:
1. Launch a web browser from a computer or WiFi device that is connected to the network.
2. Enter http://www.routerlogin.net.
A login window opens.
3. Enter the router user name and password.
The user name is admin.The default password is password.The user name and password are case-sensitive .
The BASIC Home page displays.
4. Select Wireless.
The Wireless Setup page displays.
5. Under Security Options, select a WPA option.
The WPA2 options use the newest standard for the strongest security.
The Passphrase field displays.
6. In the Passphrase field, enter the network key (password).
It is a text string from 8 to 63 characters.
7. Write down the new password and keep it in a secure place for future reference.
8. Click the Apply button.
Your settings are saved.
Change the WiFi Mbps Settings
The data rate for high-speed transmissions is commonly giv en in megabits per second (Mbps). By def ault, the router
is set to operate at up to 600 Mbps in the 2.4 GHz WiFi band and up to 1,733 Mbps in the 5 GHz WiFi band.You
can select slower settings.
To change the WiFi Mbps settings:
1. Launch a web browser from a computer or WiFi device that is connected to the network.
2. Enter http://www.routerlogin.net.
A login window opens.
Network Settings
88
Page 89

3. Enter the router user name and password.
The user name is admin.The default password is password.The user name and password are case-sensitive .
The BASIC Home page displays.
4. Select Wireless.
Your router might display information that is different from this example.
5. For the 2.4 GHz WiFi band, in the Wireless Network (2.4 GHz b/gn/n) section, select a setting from the Mode
menu.
Up to 1000 Mbps is the default setting.The other settings are Up to 433 Mbps and Up to 54 Mbps.
6. For each the 5 GHz WiFi band, select a setting from the Mode menu.
Up to 2165 Mbps is the default setting, which allows 802.11ac and 802.11a WiFi devices to join the network.
The other settings are Up to 1000 Mbps and Up to 433 Mbps.
7. Click the Apply button.
Your settings are saved.
Set Up a Guest WiFi Network
Guest networks allow visitors at your home to use the Internet without using your WiFi security key.You can add a
guest network for the 2.4 GHz WiFi band and the 5.0 GHz WiFi band.
Network Settings
89
Page 90

To set up a guest network:
1. Launch a web browser from a computer or WiFi device that is connected to the network.
2. Enter http://www.routerlogin.net.
A login window opens.
3. Enter the router user name and password.
The user name is admin.The default password is password.The user name and password are case-sensitive .
The BASIC Home page displays.
4. Select Guest Network.
Your router might display information that is different from this example.
5. Scroll to the section of the page for the guest WiFi network that you want to set up.
The default guest WiFi network names (SSIDs) are as follows:
• NETGEAR-Guest is for the 2.4 GHz WiFi band.
• NETGEAR-5G-Guest is for the 5 GHz WiFi band.
6. Leave the Enable SSID Broadcast check box selected.
Allowing the router to broadcast its wireless network name (SSID) makes it easier to find your network and
connect to it. If you clear this check box, that creates a hidden network.
7. Give the guest network a name.
The guest network name is case-sensitive and can be up to 32 characters.You then manually configure the
WiFi devices in your network to use the guest network name in addition to the main SSID.
Network Settings
90
Page 91

8. For the WiFi channel and mode, leave the default settings selected.
9. Select a security option.
The WPA2 options use the newest standard for the strongest security.
10. Click the Apply button.
Your settings are saved.
Control the WiFi Radios
The router’s internal WiFi r adios broadcast signals in the 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz ranges . By default, they are on so that
you can connect over WiFi to the router. When the WiFi radios are off, you can still use an Ethernet cable for a LAN
connection to the router.
You can turn the WiFi radios on and off with the WiFi On/Off button on the router, or you can log in to the router
and enable or disable the WiFi radios. If y ou are close to the router, it might be easier to press its WiFi On/Off button.
If you are away from the router or already logged in it might be easier to enable or disable them.You can also turn
the WiFi radios off and on based on a schedule. (See Set Up a WiFi Schedule on page 92.)
Use the WIFI Button
To turn the WiFi radios off and on with the WIFI button:
• Press the WIFI button on the front of the router for two seconds.
If you turned off the WiFi radios, the 2.4 GHz, 5 GHz-1, and 5 GHz-2 LEDs turn off. If you turned on the WiFi
radios, the 2.4 GHz, 5 GHz-1, and 5 GHz-2 LEDs light.
Enable or Disable the WiFi Radios
If you used the WIFI button to turn off the WiFi radios, you can’t log in to the router to turn them back on.You must
press the WIFI button again for two seconds to turn the WiFi radios back on.
To enable or disable the WiFi radios:
1. Launch a web browser from a computer or WiFi device that is connected to the network.
2. Enter http://www.routerlogin.net.
A login window opens.
3. Enter the router user name and password.
The user name is admin.The default password is password.The user name and password are case-sensitive .
The BASIC Home page displays.
Network Settings
91
Page 92

4. Select ADVANCED > Advanced Setup > Wireless Settings.
Your router might display information that is different from this example.
5. In the 2.4 GHz, 5 GHz-1, and 5 GHz-2 sections, select or clear the Enable Wireless Router Radio check bo xes .
Clearing these check boxes turns off the WiFi feature of the router for each band.
6. Click the Apply button.
If you turned off the WiFi radios, the WiFi On/Off LED and the WPS LED turn off. If y ou turned on the WiFi radios,
the WiFi On/Off LED and the WPS LED light.
Set Up a WiFi Schedule
You can turn off the WiFi signal from your router at times when you do not need a WiFi connection. For example,
you might turn it off for the weekend if you leave town.
To set up the WiFi schedule:
1. Launch a web browser from a computer or WiFi device that is connected to the network.
2. Enter http://www.routerlogin.net.
A login window opens.
3. Enter the router user name and password.
The user name is admin.The default password is password.The user name and password are case-sensitive .
The BASIC Home page displays.
4. Select ADVANCED > Advanced Setup > Wireless Settings.
Network Settings
92
Page 93

5. Click the Add a new period button.
6. Use the menus, radio buttons, and check boxes to set up a period during which you want to turn off the WiFi
signal.
7. Click the Apply button.
The Wireless Settings page displays.
8. Select the Turn off wireless signal by schedule check box to activate the schedule.
9. Click the Apply button.
Your settings are saved.
Specify WPS Settings
Wi-Fi Protected Setup (WPS) lets you join the WiFi network without typing the WiFi password.
To specify WPS settings:
1. Launch a web browser from a computer or WiFi device that is connected to the network.
2. Enter http://www.routerlogin.net.
Network Settings
93
Page 94

A login window opens.
3. Enter the router user name and password.
The user name is admin.The default password is password.The user name and password are case-sensitive .
The BASIC Home page displays.
4. Select ADVANCED > Advanced Setup > Wireless Settings.
TheWireless Settings page displays.The Router’s PIN field displays the PIN that you use on a registrar (for
example, from the Network Explorer on a Vista Windows computer) to configure the router’ s WiFi settings through
WPS.
5. (Optional) Select or clear the Enable Router’s PIN check box.
The PIN function might temporarily be disabled when the router detects suspicious attempts to break into the
router’s wireless settings by using the router’s PIN through WPS.You can manually enable the PIN function by
selecting the Enable Router’s PIN check box.
6. (Optional) Select or clear the Keep Existing Wireless Settings check box.
By default, the Keep Existing Wireless Settings check box is selected.We recommend that you leave this
check box selected.
If you clear this check box, the next time a new WiFi client uses WPS to connect to the router, the routerWiFi
settings change to an automatically generated random SSID and security key.
7. Click the Apply button.
Your settings are saved.
Use the Router as a WiFi Access Point
You can set up the router to run as an access point (AP) on the same local network as another router.
Network Settings
94
Page 95

To set up the router as an AP:
1. Use an Ethernet cable to connect the yellow Internet port of this router to a LAN port in the other router.
2. Launch a web browser from a computer or WiFi device that is connected to the network.
3. Enter http://www.routerlogin.net.
A login window opens.
4. Enter the router user name and password.
The user name is admin.The default password is password.The user name and password are case-sensitive .
The BASIC Home page displays.
Network Settings
95
Page 96

5. Select ADVANCED > Advanced Setup > Wireless AP.
6. Select the Enable AP Mode check box.
7. Scroll down and select an IP address setting:
• Get dynamically from existing r outer.The other router on the network assigns an IP address to this router
while this router is in AP mode.
• Enable fixed IP settings on this device (not recommended). Use this setting if you want to manually
assign a specific IP address to this router while it is in AP mode. Using this option effectiv ely requires advanced
network experience.
To avoid interference with other routers or gateways in your network, we recommend that
Note
you use different WiFi settings on each router.You can also turn off the WiFi radio on the
other router or gateway and use the router only for WiFi client access.
8. Click the Apply button.
The IP address of the router changes, and you are disconnected.
9. To reconnect, close and restart your browser and enter http://www.routerlogin.net.
Network Settings
96
Page 97

Use the Router in Bridge Mode
You can use your router in bridge mode to connect multiple devices with WiFi at the faster 802.11ac speed.To do
this, you need two WiFi routers: one set up as a router and the other set up as a bridge.
Figure 12. Router in bridge mode
Installing your router as a bridge offers the following benefits:
• You can take advantage of gigabit WiFi speeds on current devices.
• Use gigabit WiFi for applications like video and gaming.
• Connect multiple devices like a NAS, Smart TV, NeoTV, Blu-ray player, and game consoles at gigabit WiFi
speeds using a WiFi link.
• Avoid the need for separate WiFi adapters for each device.
For example, you could install the first router in a room such as a home office where your Internet connection is
located.
Then set up the second router in bridge mode. Place the router in bridge mode in a diff erent room such as the room
where your home entertainment center is located. Cable the router in bridge mode to your Smart TV, DVR, game
console, or Blu-ray player, and use its 802.11ac WiFi connection to the first router.
Network Settings
97
Page 98

To set up bridge mode:
1. Make a note of the WiFi settings of the other router to which this router will connect.
You must know the SSID, WiFi security mode, WiFi password, and operating frequency (either 2.4 GHz or 5
GHz).
2. Launch a web browser from a computer or WiFi device that is connected to the network of the router that will
run in bridge mode.
3. Enter http://www.routerlogin.net.
A login window opens.
4. Enter the router user name and password.
The user name is admin.The default password is password.The user name and password are case-sensitive .
The BASIC Home page displays.
5. Select ADVANCED > Advanced Setup > Wireless Bridge.
The Wireless Bridge page displays.
6. Select the Enable Bridge Mode check box.
7. Click the setup bridge mode wireless Settings button.
The page adjusts.
8. Enter the settings of the other router:
a. Select the WiFi network frequency (2.4 GHz or 5 GHz).
b. For 802.11ac mode, select 5 GHz.
c. In the Name (SSID) field, enter the WiFi network name (SSID).
d. In the Security Option section, select a radio button.
e. If prompted, type the passphrase (the WiFi pass w ord that y ou use to connect with WiFi to the other router).
9. Click the Apply button.
Network Settings
98
Page 99

The settings for the other router are saved and theWireless Settings page displays.
10. Click the Apply button on the Wireless Settings page.
Your settings are saved.
Network Settings
99
Page 100

Optimize Performance
You can set up the router to optimize performance for applications such as Internet gaming, high definition video streaming,
and VoIP communication. By default, the router uses Wi-Fi Multimedia Quality of Service (WMM QoS).
This chapter contains the following sections:
• Use Dynamic QoS to Optimize Internet Traffic Management on page 101
• Improve Network Connections With Universal Plug and Play on page 104
• Wi-Fi Multimedia Quality of Service on page 105
7
100
 Loading...
Loading...