Page 1
User’s Manual
78K0/FC2
8-Bit Single-Chip Microcontrollers
μ
PD78F0881(A)
μ
PD78F0882(A)
μ
PD78F0883(A)
μ
PD78F0884(A)
μ
PD78F0885(A)
μ
PD78F0886(A)
The 78K0/FC2 has an on-chip debug function.
Do not use this product for mass production after the on-chip debug function has been used because its reliability cannot
be guaranteed, due to issues with respect to the number of times the flash memory can be rewritten. NEC Electronics
does not accept complaints concerning when use this product for mass production after the on-chip debug function has
been used.
Document No. U17555EJ4V0UD00 (4th edition)
Date Published March 2007 NS CP(K)
μ
PD78F0881(A2)
μ
PD78F0882(A2)
μ
PD78F0883(A2)
μ
PD78F0884(A2)
μ
PD78F0885(A2)
μ
PD78F0886(A2)
Printed in Japan
2005
Page 2

[MEMO]
2
User’s Manual U17555EJ4V0UD
Page 3

NOTES FOR CMOS DEVICES
1
VOLTAGE APPLICATION WAVEFORM AT INPUT PIN
Waveform distortion due to input noise or a reflected wave may cause malfunction. If the input of the
IL
CMOS device stays in the area between V
malfunction. Take care to prevent chattering noise from entering the device when the input level is fixed,
and also in the transition period when the input level passes through the area between V
IH
(MIN).
V
HANDLING OF UNUSED INPUT PINS
2
Unconnected CMOS device inputs can be cause of malfunction. If an input pin is unconnected, it is
possible that an internal input level may be generated due to noise, etc., causing malfunction. CMOS
devices behave differently than Bipolar or NMOS devices. Input levels of CMOS devices must be fixed
high or low by using pull-up or pull-down circuitry. Each unused pin should be connected to V
via a resistor if there is a possibility that it will be an output pin. All handling related to unused pins must
be judged separately for each device and according to related specifications governing the device.
3
PRECAUTION AGAINST ESD
A strong electric field, when exposed to a MOS device, can cause destruction of the gate oxide and
ultimately degrade the device operation. Steps must be taken to stop generation of static electricity as
much as possible, and quickly dissipate it when it has occurred. Environmental control must be
adequate. When it is dry, a humidifier should be used. It is recommended to avoid using insulators that
easily build up static electricity. Semiconductor devices must be stored and transported in an anti-static
container, static shielding bag or conductive material. All test and measurement tools including work
benches and floors should be grounded. The operator should be grounded using a wrist strap.
Semiconductor devices must not be touched with bare hands. Similar precautions need to be taken for
PW boards with mounted semiconductor devices.
(MAX) and VIH (MIN) due to noise, etc., the device may
IL
(MAX) and
DD
or GND
4
STATUS BEFORE INITIALIZATION
Power-on does not necessarily define the initial status of a MOS device. Immediately after the power
source is turned ON, devices with reset functions have not yet been initialized. Hence, power-on does
not guarantee output pin levels, I/O settings or contents of registers. A device is not initialized until the
reset signal is received. A reset operation must be executed immediately after power-on for devices
with reset functions.
5
POWER ON/OFF SEQUENCE
In the case of a device that uses different power supplies for the internal operation and external
interface, as a rule, switch on the external power supply after switching on the internal power supply.
When switching the power supply off, as a rule, switch off the external power supply and then the
internal power supply. Use of the reverse power on/off sequences may result in the application of an
overvoltage to the internal elements of the device, causing malfunction and degradation of internal
elements due to the passage of an abnormal current.
The correct power on/off sequence must be judged separately for each device and according to related
specifications governing the device.
6
INPUT OF SIGNAL DURING POWER OFF STATE
Do not input signals or an I/O pull-up power supply while the device is not powered. The current
injection that results from input of such a signal or I/O pull-up power supply may cause malfunction and
the abnormal current that passes in the device at this time may cause degradation of internal elements.
Input of signals during the power off state must be judged separately for each device and according to
related specifications governing the device.
User’s Manual U17555EJ4V0UD
3
Page 4
EEPROM is trademark of NEC Electronics Corporation.
Windows, Windows NT and Windows XP are either registered trademarks or trademarks of Microsoft
Corporation in the United States and/or other countries.
PC/AT is a trademark of International Business Machines Corporation.
HP9000 series 700 and HP-UX are trademarks of Hewlett-Packard Company.
SPARCstation is a trademark of SPARC International, Inc.
Solaris and SunOS are trademarks of Sun Microsystems, Inc.
SuperFlash
is a registered trademark of Silicon Storage Technology, Inc. in several countries including the
United States and Japan.
®
Caution: This product uses SuperFlash
technology licensed from Silicon Storage Technology, inc.
•
The information in this document is current as of March, 2007. The information is subject to change
without notice. For actual design-in, refer to the latest publications of NEC Electronics data sheets or
data books, etc., for the most up-to-date specifications of NEC Electronics products. Not all
products and/or types are available in every country. Please check with an NEC Electronics sales
representative for availability and additional information.
•
No part of this document may be copied or reproduced in any form or by any means without the prior
written consent of NEC Electronics. NEC Electronics assumes no responsibility for any errors that may
appear in this document.
•
NEC Electronics does not assume any liability for infringement of patents, copyrights or other intellectual
property rights of third parties by or arising from the use of NEC Electronics products listed in this document
or any other liability arising from the use of such products. No license, express, implied or otherwise, is
granted under any patents, copyrights or other intellectual property rights of NEC Electronics or others.
Descriptions of circuits, software and other related information in this document are provided for illustrative
•
purposes in semiconductor product operation and application examples. The incorporation of these
circuits, software and information in the design of a customer's equipment shall be done under the full
responsibility of the customer. NEC Electronics assumes no responsibility for any losses incurred by
customers or third parties arising from the use of these circuits, software and information.
•
While NEC Electronics endeavors to enhance the quality, reliability and safety of NEC Electronics products,
customers agree and acknowledge that the possibility of defects thereof cannot be eliminated entirely. To
minimize risks of damage to property or injury (including death) to persons arising from defects in NEC
Electronics products, customers must incorporate sufficient safety measures in their design, such as
redundancy, fire-containment and anti-failure features.
•
NEC Electronics products are classified into the following three quality grades: "Standard", "Special" and
"Specific".
The "Specific" quality grade applies only to NEC Electronics products developed based on a customerdesignated "quality assurance program" for a specific application. The recommended applications of an NEC
Electronics product depend on its quality grade, as indicated below. Customers must check the quality grade of
each NEC Electronics product before using it in a particular application.
"Standard":
"Special":
"Specific":
Computers, office equipment, communications equipment, test and measurement equipment, audio
and visual equipment, home electronic appliances, machine tools, personal electronic equipment
and industrial robots.
Transportation equipment (automobiles, trains, ships, etc.), traffic control systems, anti-disaster
systems, anti-crime systems, safety equipment and medical equipment (not specifically designed
for life support).
Aircraft, aerospace equipment, submersible repeaters, nuclear reactor control systems, life
support systems and medical equipment for life support, etc.
The quality grade of NEC Electronics products is "Standard" unless otherwise expressly specified in NEC
Electronics data sheets or data books, etc. If customers wish to use NEC Electronics products in applications
not intended by NEC Electronics, they must contact an NEC Electronics sales representative in advance to
determine NEC Electronics' willingness to support a given application.
(Note)
(1)
"NEC Electronics" as used in this statement means NEC Electronics Corporation and also includes its
majority-owned subsidiaries.
(2)
"NEC Electronics products" means any product developed or manufactured by or for NEC Electronics (as
defined above).
4
User’s Manual U17555EJ4V0UD
M8E 02. 11-1
Page 5

[MEMO]
User’s Manual U17555EJ4V0UD
5
Page 6
INTRODUCTION
Readers This manual is intended for user engineers who wish to understand the functions of the
78K0/FC2 and design and develop application systems and programs for these devices.
The target products are as follows.
78K0/FC2:
Purpose This manual is intended to give users an understanding of the functions described in the
Organization below.
Organization The 78K0/FC2 manual is separated into two parts: this manual and the instructions
edition (common to the 78K/0 Series).
• Pin functions
• Internal block functions
• Interrupts
• Other on-chip peripheral functions
• Electrical specifications
How to Read This Manual It is assumed that the readers of this manual have general knowledge of electrical
engineering, logic circuits, and microcontrollers.
• When using this manual as the manual for (A) and (A2) grade products:
→ Only the quality grade differs between (A) grade products and (A2) grade
• μPD78F0881→ μPD78F0881 (A), 78F0881 (A2)
•
•
•
•
•
• To gain a general understanding of functions:
→ Read this manual in the order of the CONTENTS. The mark <R> shows major
• How to interpret the register format:
→ For a bit number enclosed in brackets, the bit name is defined as a reserved word
• To check the details of a register when you know the register name:
→ Refer to APPENDIX C REGISTER INDEX.
Conventions Data significance: Higher digits on the left and lower digits on the right
Active low representations: ××× (overscore over pin and signal name)
Note: Footnote for item marked with Note in the text.
Caution: Information requiring particular attention
Remark: Supplementary information
Numerical representations: Binary
Decimal
Hexadecimal
μ
PD78F0881 (A), 78F0882 (A), 78F0883 (A), 78F0884 (A), 78F0885 (A),
78F0886 (A), 78F0881 (A2), 78F0882 (A2), 78F0883 (A2), 78F0884 (A2),
78F0885 (A2), 78F0886 (A2)
78K0/FC2
User’s Manual
(This Manual)
products.
Read the part number as follows.
μ
PD78F0882→ μPD78F0882 (A), 78F0882 (A2)
μ
PD78F0883→ μPD78F0883 (A), 78F0883 (A2)
μ
PD78F0884→ μPD78F0894 (A), 78F0894 (A2)
μ
PD78F0885→ μPD78F0885 (A), 78F0885 (A2)
μ
PD78F0886→ μPD78F0886 (A), 78F0886 (A2)
revised points.
in the assembler, and is already defined in the header file named sfrbit.h in the C
compiler.
• CPU functions
• Instruction set
• Explanation of each instruction
...
×××× or ××××B
...
××××
...
××××H
78K/0 Series
User’s Manual
Instructions
6
User’s Manual U17555EJ4V0UD
Page 7
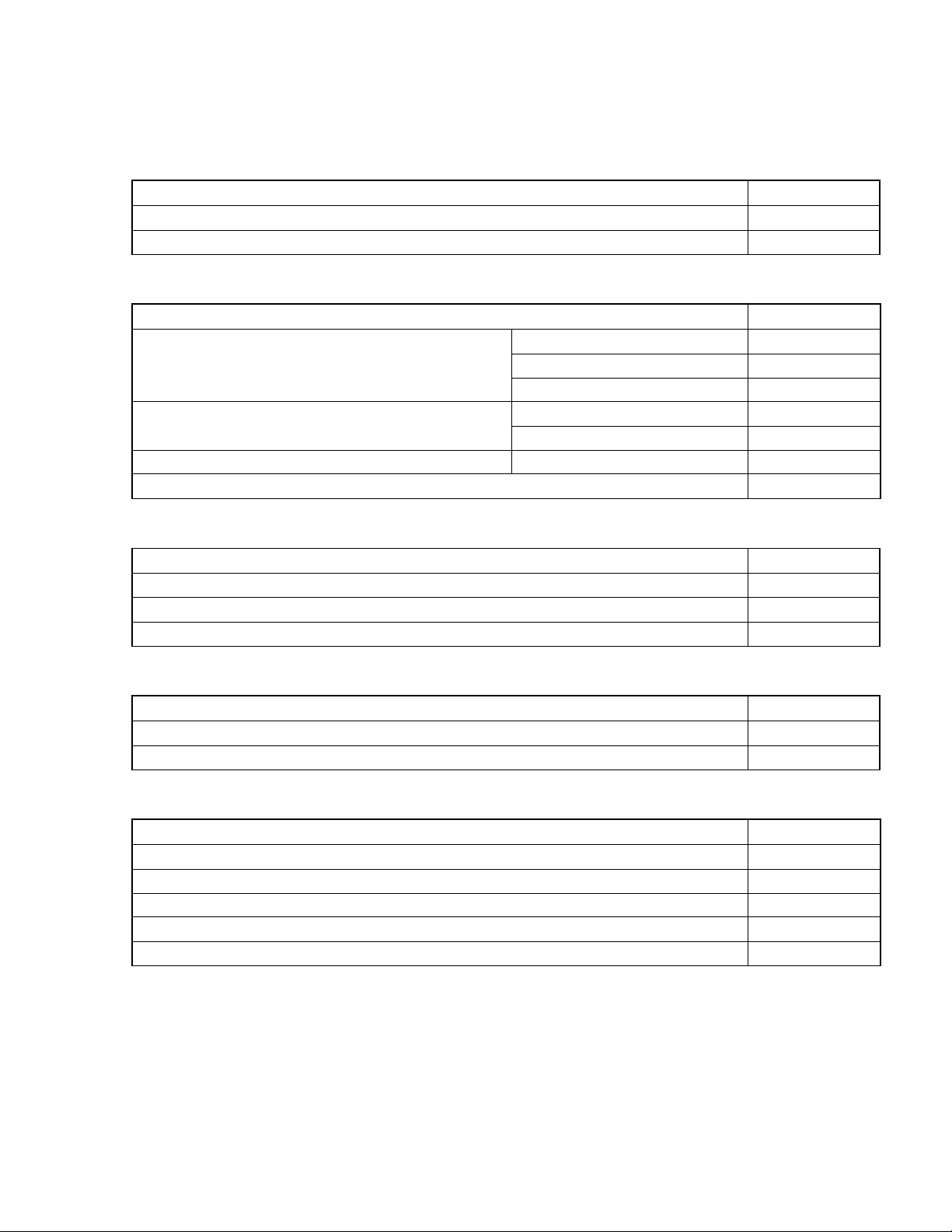
Related Documents The related documents indicated in this publication may include preliminary versions.
However, preliminary versions are not marked as such.
Documents Related to Devices
Document Name Document No.
78K0/FC2 User’s Manual This manual
78K/0 Series Instructions User’s Manual U12326E
Documents Related to Development Tools (Software) (User’s Manuals)
Document Name Document No.
RA78K0 Ver.3.80 Assembler Package
ID78K0-QB Ver. 2.90 Integrated Debugger Operation U17437E
PM plus Ver. 5.20 U16934E
Operation U17199E
Language U17198E
Structured Assembly Language U17197E
Operation U17201E CC78K0 Ver.3.70 C Compiler
Language U17200E
Documents Related to Development Tools (Hardware) (User’s Manuals)
<R>
<R>
Document Name Document No.
QB-78K0FX2 In-Circuit Emulator U17534E
QB-78K0MINI ON-CHIP DEBUG Emulator U17029E
QB-MINI2 On-Chip Debug Emulator with Programming Function U18371E
Documents Related to Flash Memory Programming
Document Name Document No.
PG-FP4 Flash Memory Programmer User’s Manual U15260E
PG-FPL3 Flash Memory Programmer User’s Manual U17454E
Other Documents
Document Name Document No.
SEMICONDUCTOR SELECTION GUIDE − Products and Packages − X13769X
Semiconductor Device Mount Manual Note
Quality Grades on NEC Semiconductor Devices C11531E
NEC Semiconductor Device Reliability/Quality Control System C10983E
Guide to Prevent Damage for Semiconductor Devices by Electrostatic Discharge (ESD) C11892E
Note See the “Semiconductor Device Mount Manual” website (http://www.necel.com/pkg/en/mount/index.html).
Caution The related documents listed above are subject to change without notice. Be sure to use the latest
version of each document when designing.
User’s Manual U17555EJ4V0UD
7
Page 8

CONTENTS
CHAPTER 1 OUTLINE ............................................................................................................................ 17
1.1 Features......................................................................................................................................... 17
1.2 Applications .................................................................................................................................. 18
1.3 Ordering Information ................................................................................................................... 18
1.4 Pin Configuration (Top View) ...................................................................................................... 19
1.5 Fx2 Series Lineup......................................................................................................................... 22
1.5.1 78K0/Fx2 product lineup ................................................................................................................... 22
1.6 Block Diagram .............................................................................................................................. 24
1.7 Outline of Functions .................................................................................................................... 26
CHAPTER 2 PIN FUNCTIONS ............................................................................................................... 28
2.1 Pin Function List .......................................................................................................................... 28
2.2 Description of Pin Functions ...................................................................................................... 32
2.2.1 P00, P01, P06 (port 0)....................................................................................................................... 32
2.2.2 P10 to P17 (port 1) ............................................................................................................................ 33
2.2.3 P30 to P33 (port 3) ............................................................................................................................ 34
2.2.4 P40, P41 (port 4) ............................................................................................................................... 34
2.2.5 P60 to P63 (port 6) ............................................................................................................................ 34
2.2.6 P70 to P73 (port 7) ............................................................................................................................ 35
2.2.7 P80 to P87 (port 8) ............................................................................................................................ 35
2.2.8 P90 (port 9) ....................................................................................................................................... 36
2.2.9 P120 to P124 (port 12) ...................................................................................................................... 36
2.2.10 P130, P131 (port 13) ....................................................................................................................... 37
2.2.11 AVREF............................................................................................................................................... 37
2.2.12 AVSS ................................................................................................................................................ 37
2.2.13 RESET ............................................................................................................................................ 37
2.2.14 REGC.............................................................................................................................................. 37
2.2.15 VDD and EVDD .................................................................................................................................. 37
2.2.16 VSS and EVSS................................................................................................................................... 37
2.2.17 FLMD0 ............................................................................................................................................ 38
2.3 Pin I/O Circuits and Recommended Connection of Unused Pins ........................................... 39
CHAPTER 3 CPU ARCHITECTURE ...................................................................................................... 43
3.1 Memory Space .............................................................................................................................. 43
3.1.1 Internal program memory space........................................................................................................ 48
3.1.2 Internal data memory space.............................................................................................................. 49
3.1.3 Special function register (SFR) area ................................................................................................. 49
3.1.4 Data memory addressing .................................................................................................................. 50
3.2 Processor Registers .................................................................................................................... 54
3.2.1 Control registers ................................................................................................................................ 54
3.2.2 General-purpose registers................................................................................................................. 58
3.2.3 Special Function Registers (SFRs) ................................................................................................... 59
3.3 Instruction Address Addressing................................................................................................. 65
3.3.1 Relative addressing........................................................................................................................... 65
3.3.2 Immediate addressing ....................................................................................................................... 66
8
User’s Manual U17555EJ4V0UD
Page 9

3.3.3 Table indirect addressing ...................................................................................................................67
3.3.4 Register addressing ...........................................................................................................................67
3.4 Operand Address Addressing .................................................................................................... 68
3.4.1 Implied addressing .............................................................................................................................68
3.4.2 Register addressing ...........................................................................................................................69
3.4.3 Direct addressing ...............................................................................................................................70
3.4.4 Short direct addressing ......................................................................................................................71
3.4.5 Special function register (SFR) addressing........................................................................................72
3.4.6 Register indirect addressing............................................................................................................... 73
3.4.7 Based addressing ..............................................................................................................................74
3.4.8 Based indexed addressing.................................................................................................................75
3.4.9 Stack addressing................................................................................................................................76
CHAPTER 4 PORT FUNCTIONS ........................................................................................................... 77
4.1 Port Functions.............................................................................................................................. 77
4.2 Port Configuration ....................................................................................................................... 78
4.2.1 Port 0 .................................................................................................................................................79
4.2.2 Port 1 .................................................................................................................................................81
4.2.3 Port 3 .................................................................................................................................................84
4.2.4 Port 4 .................................................................................................................................................86
4.2.5 Port 6 .................................................................................................................................................87
4.2.6 Port 7 .................................................................................................................................................88
4.2.7 Port 8 .................................................................................................................................................91
4.2.8 Port 9 .................................................................................................................................................92
4.2.9 Port 12 ...............................................................................................................................................94
4.2.10 Port 13 .............................................................................................................................................97
4.3 Registers Controlling Port Function .......................................................................................... 99
4.4 Port Function Operations.......................................................................................................... 106
4.4.1 Writing to I/O port.............................................................................................................................106
4.4.2 Reading from I/O port.......................................................................................................................106
4.4.3 Operations on I/O port......................................................................................................................106
4.5 Cautions on 1-Bit Manipulation Instruction for Port Register n (Pn).................................... 107
CHAPTER 5 CLOCK GENERATOR .................................................................................................... 108
5.1 Functions of Clock Generator................................................................................................... 108
5.2 Configuration of Clock Generator ............................................................................................ 109
5.3 Registers Controlling Clock Generator ................................................................................... 111
5.4 System Clock Oscillator ............................................................................................................ 120
5.4.1 X1 oscillator .....................................................................................................................................120
5.4.2 XT1 oscillator ...................................................................................................................................120
5.4.3 When subsystem clock is not used ..................................................................................................123
5.4.4 Internal high-speed oscillator ...........................................................................................................123
5.4.5 Internal low-speed oscillator.............................................................................................................123
5.4.6 Prescaler..........................................................................................................................................123
5.5 Clock Generator Operation ....................................................................................................... 124
5.6 Controlling Clock ....................................................................................................................... 128
5.6.1 Controlling high-speed system clock................................................................................................128
5.6.2 Example of controlling internal high-speed oscillation clock............................................................. 131
User’s Manual U17555EJ4V0UD
9
Page 10

5.6.3 Example of controlling subsystem clock...........................................................................................133
5.6.4 Controlling internal low-speed oscillation clock ................................................................................135
5.6.5 Clocks supplied to CPU and peripheral hardware ............................................................................135
5.6.6 CPU clock status transition diagram.................................................................................................136
5.6.7 Condition before changing CPU clock and processing after changing CPU clock ...........................141
5.6.8 Time required for switchover of CPU clock and main system clock .................................................142
5.6.9 Conditions before clock oscillation is stopped ..................................................................................143
CHAPTER 6 16-BIT TIMER/EVENT COUNTERS 00 AND 01......................................................... 144
6.1 Functions of 16-Bit Timer/Event Counters 00 and 01............................................................. 145
6.2 Configuration of 16-Bit Timer/Event Counters 00 and 01 ...................................................... 146
6.3 Registers Controlling 16-Bit Timer/Event Counters 00 and 01.............................................. 154
6.4 Operation of 16-Bit Timer/Event Counters 00 and 01............................................................. 166
6.4.1 Interval timer operation.....................................................................................................................166
6.4.2 PPG output operations .....................................................................................................................169
6.4.3 Pulse width measurement operations ..............................................................................................172
6.4.4 External event counter operation......................................................................................................180
6.4.5 Square-wave output operation .........................................................................................................183
6.4.6 One-shot pulse output operation ......................................................................................................185
6.5 Special Use of TM0n .................................................................................................................. 190
6.5.1 Rewriting CR01n during TM0n operation .........................................................................................190
6.5.2 Setting LVS0n and LVR0n ...............................................................................................................190
6.6 Cautions for 16-Bit Timer/Event Counters 00 and 01 ............................................................. 192
CHAPTER 7 8-BIT TIMER/EVENT COUNTERS 50 AND 51........................................................... 196
7.1 Functions of 8-Bit Timer/Event Counters 50 and 51............................................................... 196
7.2 Configuration of 8-Bit Timer/Event Counters 50 and 51 ........................................................ 198
7.3 Registers Controlling 8-Bit Timer/Event Counters 50 and 51................................................ 200
7.4 Operations of 8-Bit Timer/Event Counters 50 and 51............................................................. 205
7.4.1 Operation as interval timer ...............................................................................................................205
7.4.2 Operation as external event counter ................................................................................................207
7.4.3 Square-wave output operation .........................................................................................................208
7.4.4 PWM output operation......................................................................................................................209
7.5 Cautions for 8-Bit Timer/Event Counters 50 and 51 ............................................................... 213
CHAPTER 8 8-BIT TIMERS H0 AND H1 .......................................................................................... 214
8.1 Functions of 8-Bit Timers H0 and H1 ....................................................................................... 214
8.2 Configuration of 8-Bit Timers H0 and H1................................................................................. 214
8.3 Registers Controlling 8-Bit Timers H0 and H1 ........................................................................ 218
8.4 Operation of 8-Bit Timers H0 and H1........................................................................................ 223
8.4.1 Operation as interval timer/square-wave output ...............................................................................223
8.4.2 Operation as PWM output mode ......................................................................................................226
8.4.3 Carrier generator mode operation (8-bit timer H1 only)....................................................................232
CHAPTER 9 WATCH TIMER................................................................................................................ 239
9.1 Functions of Watch Timer ......................................................................................................... 239
9.2 Configuration of Watch Timer................................................................................................... 240
9.3 Register Controlling Watch Timer ............................................................................................ 241
10
User’s Manual U17555EJ4V0UD
Page 11

9.4 Watch Timer Operations............................................................................................................ 243
9.4.1 Watch timer operation ...................................................................................................................... 243
9.4.2 Interval timer operation ....................................................................................................................244
9.5 Cautions for Watch Timer ......................................................................................................... 245
CHAPTER 10 WATCHDOG TIMER ..................................................................................................... 246
10.1 Functions of Watchdog Timer ................................................................................................ 246
10.2 Configuration of Watchdog Timer.......................................................................................... 247
10.3 Register Controlling Watchdog Timer ................................................................................... 248
10.4 Operation of Watchdog Timer................................................................................................. 249
10.4.1 Controlling operation of watchdog timer.........................................................................................249
10.4.2 Setting overflow time of watchdog timer.........................................................................................251
10.4.3 Setting window open period of watchdog timer..............................................................................252
CHAPTER 11 CLOCK OUTPUT/BUZZER OUTPUT CONTROLLER............................................... 254
11.1 Functions of Clock Output/Buzzer Output Controller.......................................................... 254
11.2 Configuration of Clock Output/Buzzer Output Controller ................................................... 255
11.3 Register Controlling Clock Output/Buzzer Output Controller............................................. 255
11.4 Clock Output/Buzzer Output Controller Operations............................................................. 258
11.4.1 Clock output operation ...................................................................................................................258
11.4.2 Operation as buzzer output............................................................................................................258
CHAPTER 12 A/D CONVERTER ......................................................................................................... 259
12.1 Function of A/D Converter ...................................................................................................... 259
12.2 Configuration of A/D Converter .............................................................................................. 260
12.3 Registers Used in A/D Converter ........................................................................................... 262
12.4 A/D Converter Operations ....................................................................................................... 271
12.4.1 Basic operations of A/D converter.................................................................................................. 271
12.4.2 Input voltage and conversion results..............................................................................................273
12.4.3 A/D converter operation mode .......................................................................................................274
12.5 How to Read A/D Converter Characteristics Table .............................................................. 276
12.6 Cautions for A/D Converter..................................................................................................... 278
CHAPTER 13 SERIAL INTERFACES UART60 AND UART61.......................................................... 282
13.1 Functions of Serial Interfaces UART60 and UART61 ........................................................... 282
13.2 Configurations of Serial Interface UART60 and UART61..................................................... 287
13.3 Registers Controlling Serial Interfaces UART60 and UART61 ............................................ 291
13.4 Operations of Serial Interface UART60 and UART61 ........................................................... 310
13.4.1 Operation stop mode......................................................................................................................310
13.4.2 Asynchronous serial interface (UART) mode .................................................................................311
13.4.3 Dedicated baud rate generator ......................................................................................................326
CHAPTER 14 SERIAL INTERFACE CSI10 ........................................................................................ 332
14.1 Functions of Serial Interface CSI10........................................................................................ 332
14.2 Configuration of Serial Interface CSI10 ................................................................................. 333
14.3 Registers Controlling Serial Interface CSI10......................................................................... 335
14.4 Operation of Serial Interface CSI10........................................................................................ 338
14.4.1 Operation stop mode......................................................................................................................338
User’s Manual U17555EJ4V0UD
11
Page 12

14.4.2 3-wire serial I/O mode ....................................................................................................................339
CHAPTER 15 CAN CONTROLLER ..................................................................................................... 349
15.1 Outline Description .................................................................................................................. 349
15.1.1 Features .........................................................................................................................................349
15.1.2 Overview of functions .....................................................................................................................350
15.1.3 Configuration ..................................................................................................................................351
15.2 CAN Protocol ............................................................................................................................ 352
15.2.1 Frame format..................................................................................................................................352
15.2.2 Frame types ...................................................................................................................................353
15.2.3 Data frame and remote frame ........................................................................................................353
15.2.4 Error frame .....................................................................................................................................361
15.2.5 Overload frame...............................................................................................................................362
15.3 Functions .................................................................................................................................. 363
15.3.1 Determining bus priority .................................................................................................................363
15.3.2 Bit stuffing ......................................................................................................................................363
15.3.3 Multi masters..................................................................................................................................363
15.3.4 Multi cast ........................................................................................................................................363
15.3.5 CAN sleep mode/CAN stop mode function ....................................................................................363
15.3.6 Error control function ......................................................................................................................364
15.3.7 Baud rate control function ..............................................................................................................370
15.4 Connection With Target System ............................................................................................. 374
15.5 Internal Registers of CAN Controller...................................................................................... 375
15.5.1 CAN controller configuration...........................................................................................................375
15.5.2 Register access type ......................................................................................................................376
15.5.3 Register bit configuration................................................................................................................385
15.6 Bit Set/Clear Function.............................................................................................................. 389
15.7 Control Registers ..................................................................................................................... 391
15.8 CAN Controller Initialization.................................................................................................... 426
15.8.1 Initialization of CAN module ...........................................................................................................426
15.8.2 Initialization of message buffer.......................................................................................................426
15.8.3 Redefinition of message buffer.......................................................................................................426
15.8.4 Transition from initialization mode to operation mode ....................................................................427
15.8.5 Resetting error counter C0ERC of CAN module ............................................................................428
15.9 Message Reception.................................................................................................................. 429
15.9.1 Message reception .........................................................................................................................429
15.9.2 Receive Data Read ........................................................................................................................430
15.9.3 Receive history list function............................................................................................................431
15.9.4 Mask function .................................................................................................................................433
15.9.5 Multi buffer receive block function ..................................................................................................435
15.9.6 Remote frame reception.................................................................................................................436
15.10 Message Transmission.......................................................................................................... 437
15.10.1 Message transmission..................................................................................................................437
15.10.2 Transmit history list function.........................................................................................................439
15.10.3 Automatic block transmission (ABT).............................................................................................441
15.10.4 Transmission abort process .........................................................................................................442
15.10.5 Remote frame transmission..........................................................................................................443
15.11 Power Save Modes................................................................................................................. 444
12
User’s Manual U17555EJ4V0UD
Page 13

15.11.1 CAN sleep mode .......................................................................................................................... 444
15.11.2 CAN stop mode............................................................................................................................ 446
15.11.3 Example of using power saving modes........................................................................................447
15.12 Interrupt Function .................................................................................................................. 448
15.13 Diagnosis Functions and Special Operational Modes ....................................................... 449
15.13.1 Receive-only mode ......................................................................................................................449
15.13.2 Single-shot mode .........................................................................................................................450
15.13.3 Self-test mode..............................................................................................................................451
15.13.4 Receive/Transmit Operation in Each Operation Mode ................................................................. 452
15.14 Time Stamp Function............................................................................................................. 453
15.14.1 Time stamp function.....................................................................................................................453
15.15 Baud Rate Settings ................................................................................................................ 455
15.15.1 Baud rate settings ........................................................................................................................455
15.15.2 Representative examples of baud rate settings ...........................................................................459
15.16 Operation of CAN Controller................................................................................................. 463
CHAPTER 16 INTERRUPT FUNCTIONS ............................................................................................ 489
16.1 Interrupt Function Types......................................................................................................... 489
16.2 Interrupt Sources and Configuration ..................................................................................... 489
16.3 Registers Controlling Interrupt Functions ............................................................................ 493
16.4 Interrupt Servicing Operations ............................................................................................... 501
16.4.1 Maskable interrupt acknowledgement............................................................................................501
16.4.2 Software interrupt request acknowledgement ................................................................................503
16.4.3 Multiple interrupt servicing .............................................................................................................504
16.4.4 Interrupt request hold .....................................................................................................................507
CHAPTER 17 STANDBY FUNCTION .................................................................................................. 508
17.1 Standby Function and Configuration..................................................................................... 508
17.1.1 Standby function ............................................................................................................................508
17.1.2 Registers controlling standby function............................................................................................508
17.2 Standby Function Operation................................................................................................... 511
17.2.1 HALT mode....................................................................................................................................511
17.2.2 STOP mode ...................................................................................................................................516
CHAPTER 18 RESET FUNCTION ....................................................................................................... 523
18.1 Register for Confirming Reset Source................................................................................... 531
CHAPTER 19 MULTIPLIER/DIVIDER................................................................................................... 532
19.1 Functions of Multiplier/Divider ............................................................................................... 532
19.2 Configuration of Multiplier/Divider......................................................................................... 532
19.3 Register Controlling Multiplier/Divider .................................................................................. 536
19.4 Operations of Multiplier/Divider.............................................................................................. 537
19.4.1 Multiplication operation ..................................................................................................................537
19.4.2 Division operation...........................................................................................................................539
CHAPTER 20 POWER-ON-CLEAR CIRCUIT ..................................................................................... 541
20.1 Functions of Power-on-Clear Circuit ..................................................................................... 541
20.2 Configuration of Power-on-Clear Circuit ............................................................................... 542
User’s Manual U17555EJ4V0UD
13
Page 14

20.3 Operation of Power-on-Clear Circuit...................................................................................... 542
20.4 Cautions for Power-on-Clear Circuit ...................................................................................... 545
CHAPTER 21 LOW-VOLTAGE DETECTOR ....................................................................................... 547
21.1 Functions of Low-Voltage Detector........................................................................................ 547
21.2 Configuration of Low-Voltage Detector ................................................................................. 548
21.3 Registers Controlling Low-Voltage Detector......................................................................... 548
21.4 Operation of Low-Voltage Detector........................................................................................ 551
21.4.1 When used as reset .......................................................................................................................552
21.4.2 When used as interrupt ..................................................................................................................557
21.5 Cautions for Low-Voltage Detector ........................................................................................ 562
CHAPTER 22 OPTION BYTE............................................................................................................... 565
22.1 Functions of Option Bytes ...................................................................................................... 565
22.2 Format of Option Byte ............................................................................................................. 567
CHAPTER 23 FLASH MEMORY .......................................................................................................... 570
23.1 Internal Memory Size Switching Register.............................................................................. 570
23.2 Internal Expansion RAM Size Switching Register ................................................................ 571
23.3 Writing with Flash Memory Programmer ............................................................................... 572
23.4 Programming Environment ..................................................................................................... 578
23.5 Communication Mode.............................................................................................................. 578
23.6 Connection of Pins on Board.................................................................................................. 580
23.6.1 FLMD0 pin......................................................................................................................................580
23.6.2 Serial interface pins........................................................................................................................580
23.6.3 RESET pin......................................................................................................................................582
23.6.4 Port pins .........................................................................................................................................582
23.6.5 REGC pin .......................................................................................................................................582
23.6.6 Other signal pins ............................................................................................................................582
23.6.7 Power supply..................................................................................................................................583
23.7 Programming Method .............................................................................................................. 584
23.7.1 Controlling flash memory................................................................................................................584
23.7.2 Flash memory programming mode.................................................................................................584
23.7.3 Selecting communication mode......................................................................................................585
23.7.4 Communication commands ............................................................................................................586
23.8 Security Settings ...................................................................................................................... 587
23.9 Processing Time for Each Command When PG-FP4 Is Used (Reference)......................... 589
23.10 Flash Memory Programming by Self-Programming ........................................................... 590
23.10.1 Registers used for self-programming function ..............................................................................596
23.11 Boot Swap Function............................................................................................................... 600
CHAPTER 24 ON-CHIP DEBUG FUNCTION ..................................................................................... 602
24.1 Outline of Functions ................................................................................................................ 602
24.2 Connection with MINICUBE..................................................................................................... 603
24.3 Connection Circuit Examples ................................................................................................. 604
24.4 On-Chip Debug Security ID ..................................................................................................... 606
24.5 Restrictions and Cautions on On-Chip Debug Function ..................................................... 606
14
User’s Manual U17555EJ4V0UD
Page 15

CHAPTER 25 INSTRUCTION SET ...................................................................................................... 607
25.1 Conventions Used in Operation List...................................................................................... 607
25.1.1 Operand identifiers and specification methods ..............................................................................607
25.1.2 Description of operation column.....................................................................................................608
25.1.3 Description of flag operation column ..............................................................................................608
25.2 Operation List........................................................................................................................... 609
25.3 Instructions Listed by Addressing Type ............................................................................... 617
CHAPTER 26 ELECTRICAL SPECIFICATIONS ((A) GRADE PRODUCTS) .................................. 620
26.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings .................................................................................................... 620
26.2 Oscillator Characteristics........................................................................................................ 622
26.3 DC Characteristics ................................................................................................................... 624
27.4 AC Characteristics ................................................................................................................... 631
27.5 Data Retention Characteristics............................................................................................... 641
27.6 Flash EEPROM Programming Characteristics...................................................................... 642
CHAPTER 27 ELECTRICAL SPECIFICATIONS ((A2) GRADE PRODUCTS)................................ 643
27.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings .................................................................................................... 643
27.2 Oscillator Characteristics........................................................................................................ 645
27.3 DC Characteristics ................................................................................................................... 647
27.4 AC Characteristics ................................................................................................................... 653
27.5 Data Retention Characteristics............................................................................................... 663
27.6 Flash EEPROM Programming Characteristics...................................................................... 664
CHAPTER 28 PACKAGE DRAWINGS ................................................................................................ 665
CHAPTER 29 RECOMMENDED SOLDERING CONDITIONS........................................................... 667
CHAPTER 30 CAUTIONS FOR WAIT ................................................................................................ 668
30.1 Cautions for Wait ..................................................................................................................... 668
30.2 Peripheral Hardware That Generates Wait ............................................................................ 669
30.3 Example of Wait Occurrence .................................................................................................. 671
APPENDIX A DEVELOPMENT TOOLS .............................................................................................. 672
A.1 Software Package...................................................................................................................... 676
A.2 Language Processing Software............................................................................................... 676
A.3 Control Software........................................................................................................................ 677
A.4 Flash Memory Programming Tools ......................................................................................... 678
A.4.1 When using flash memory programmer FG-FP4, FL-PR4, PG-FPL3, and FP-LITE3......................678
A.4.2 When using on-chip debug emulator with programming function QB-MINI2 ...................................678
A.5 Debugging Tools (Hardware) ................................................................................................... 679
A.5.1 When using in-circuit emulator QB-78K0FX2 ..................................................................................679
A.5.2 When using on-chip debug emulator QB-78K0MINI ........................................................................ 679
A.5.3 When using on-chip debug emulator with programming function QB-MINI2 ...................................680
A.6 Debugging Tools (Software)..................................................................................................... 680
User’s Manual U17555EJ4V0UD
15
Page 16

APPENDIX B NOTES ON TARGET SYSTEM DESIGN ................................................................... 681
APPENDIX C REGISTER INDEX ......................................................................................................... 683
C.1 Register Index (In Alphabetical Order with Respect to Register Names)............................ 683
C.2 Register Index (In Alphabetical Order with Respect to Register Symbol)........................... 688
APPENDIX D REVISION HISTORY ..................................................................................................... 692
D.1 Main Revisions in this Edition.................................................................................................. 692
D.2 Revision History of Preceding Editions .................................................................................. 693
16
User’s Manual U17555EJ4V0UD
Page 17
CHAPTER 1 OUTLINE
1.1 Features
{ Minimum instruction execution time can be changed from high speed (0.1
speed system clock) to ultra low-speed (122
{ General-purpose register: 8 bits × 32 registers (8 bits × 8 registers × 4 banks)
{ ROM, RAM capacities
μ
s: @ 32.768 kHz operation with subsystem clock)
μ
s: @ 20 MHz operation with high-
Part Number
μ
PD78F0881, 78F0884
μ
PD78F0882, 78F0885
μ
PD78F0883, 78F0886
Program Memory
(ROM)
Flash memory
48 KB 2048 bytes
60 KB
Note
32 KB 1024 bytes 1024 bytes
Internal High-Speed RAM
Data Memory Item
Note
Internal Expansion RAM
Note The internal flash memory, internal high-speed RAM capacities, and internal expansion RAM capacities
can be changed using the internal memory size switching register (IMS) and the internal expansion RAM
size switching register (IXS).
{ On-chip single-power-supply flash memory
{ Self-programming (with boot swap function)
{ On-chip debug function
{ On-chip power-on-clear (POC) circuit and low-voltage detector (LVI)
{ Short startup is possible via the CPU default start using the on-chip internal high-speed oscillator
{ On-chip watchdog timer (operable with on-chip internal low-speed oscillator clock)
{ On-chip multiplier/divider
{ On-chip clock output/buzzer output controller
{ I/O ports:
{ Timer: 8 channels
μ
PD78F0881, 78F0882, 78F0883: 37 (N-ch open drain: 3)
μ
PD78F0884, 78F0885, 78F0886: 41 (N-ch open drain: 4)
Note 1
{ Serial interface: 3 channels
(UART (LIN (Local Interconnect Network)-bus supported): 1 channel,
CSI/UART
{ 10-bit resolution A/D converter:
{ Supply voltage: V
(with internal high-speed oscillator clock or subsystem clock: V
{ Operating ambient temperature: T
Note 2
: 1 channel, CAN: 1 channel)
μ
PD78F0881, 78F0882, 78F0883: 8 channels
μ
PD78F0884, 78F0885, 78F0886: 9 channels
DD = 4.0 to 5.5 V when 20 MHz, VDD = 2.7 to 5.5 V when 10 MHz, VDD = 1.8 to 5.5 V when 5 MHz
DD = 1.8 to 5.5 V)
A = −40 to +85°C, −40 to +125°C
Notes 1. Since TM01 does not have the following terminal at 78K0/FC2, the function is restricted in part.
μ
PD78F0881, 78F0882, and 78F0883: TI001, TI011, TO01
μ
PD78F0884, 78F0885, and 78F0886: TI001
2. Select either of the functions of these alternate-function pins.
Note
User’s Manual U17555EJ4V0UD
17
Page 18

CHAPTER 1 OUTLINE
1.2 Applications
{ Automotive electrical appliances (Body control, Door control, Front light control)
{ Industrial equipment (Industrial robot, Building control)
1.3 Ordering Information
• Flash memory version
Part Number Package Quality Grade
μ
PD78F0881GB(A)-GAF-AX 44-pin plastic LQFP (10x10) Special
μ
PD78F0881GB(A2)-GAF-AX 44-pin plastic LQFP (10x10) Special
μ
PD78F0882GB(A)-GAF-AX 44-pin plastic LQFP (10x10) Special
μ
PD78F0882GB(A2)-GAF-AX 44-pin plastic LQFP (10x10) Special
μ
PD78F0883GB(A)-GAF-AX 44-pin plastic LQFP (10x10) Special
μ
PD78F0883GB(A2)-GAF-AX 44-pin plastic LQFP (10x10) Special
μ
PD78F0884GA(A)-GAM-AX 48-pin plastic LQFP (Fine pitch) (7x7) Special
μ
PD78F0884GA(A2)-GAM-AX 48-pin plastic LQFP (Fine pitch) (7x7) Special
μ
PD78F0885GA(A)-GAM-AX 48-pin plastic LQFP (Fine pitch) (7x7) Special
μ
PD78F0885GA(A2)-GAM-AX 48-pin plastic LQFP (Fine pitch) (7x7) Special
μ
PD78F0886GA(A)-GAM-AX 48-pin plastic LQFP (Fine pitch) (7x7) Special
μ
PD78F0886GA(A2)-GAM-AX 48-pin plastic LQFP (Fine pitch) (7x7) Special
Remark All these products are lead free products.
18
User’s Manual U17555EJ4V0UD
Page 19
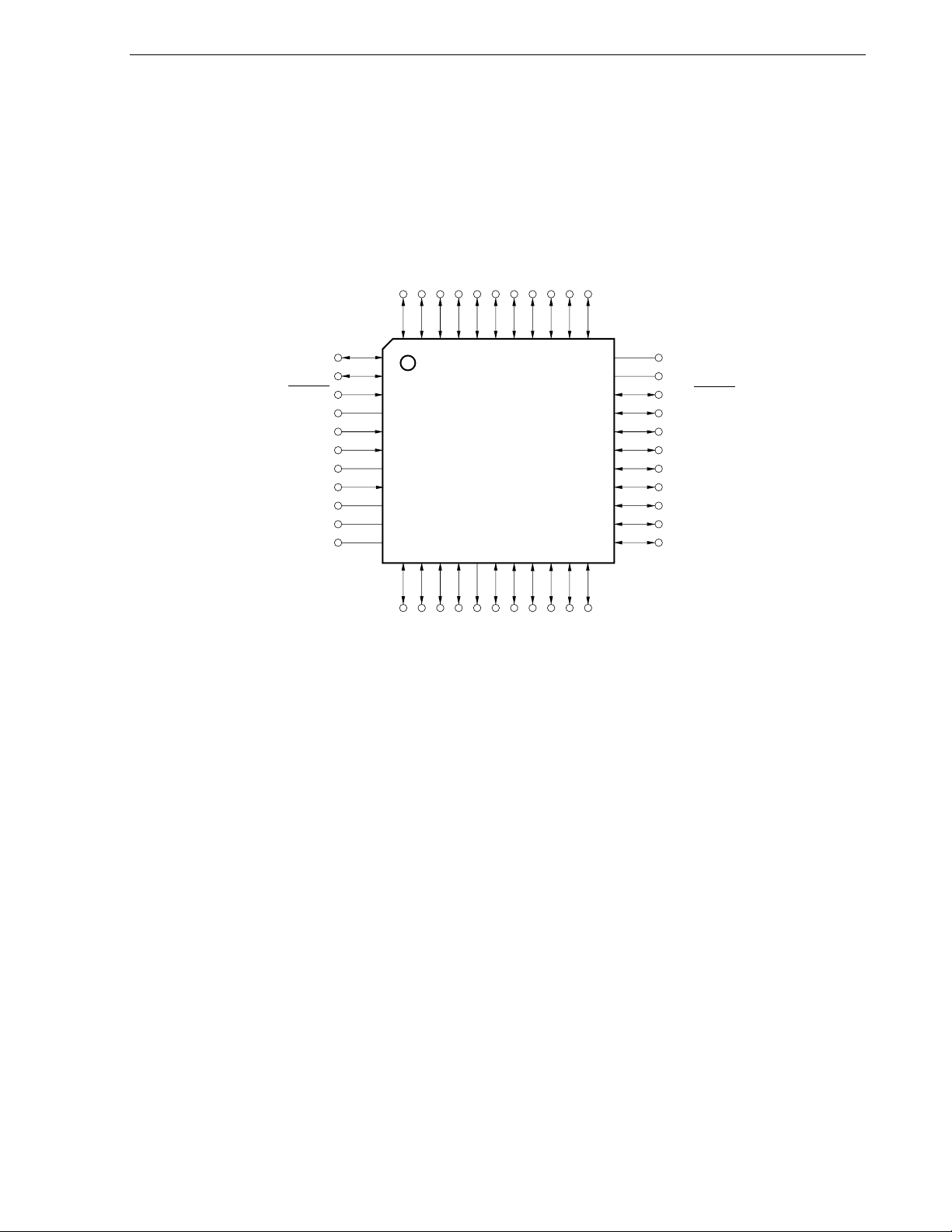
1.4 Pin Configuration (Top View)
• 44-pin plastic LQFP (10x10)
P41
P40
RESET
P124/XT2/EXCLKS
P123/XT1
FLMD0
P122/X2/EXCLK
P121/X1
REGC
V
SS
/EV
SS
VDD/EV
DD
CHAPTER 1 OUTLINE
P120/INTP0/EXLVI
P00/TI000
P01/TI010/TO00
P80/ANI0
P81/ANI1
P82/ANI2
P83/ANI3
P84/ANI4
P85/ANI5
44 43 42 41 40 39 38 37 36 35 34
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22
P86/ANI6
P87/ANI7
33
32
31
30
29
28
27
26
25
24
23
AV
SS
AV
REF
P10/SCK10/TxD61
P11/SI10/RxD61
P12/SO10
P13/TxD60
P14/RxD60
P15/TOH0
P16/TOH1/INTP5
P17/TI50/TO50
P30/INTP1
P60
P61
P62
P130
P70/CTxD
P71/CRxD
P32/INTP3
P31/INTP2
P72/PCL/INTP6
P73/BUZ/INTP7
P33/TI51/TO51/INTP4
Cautions 1. Make AV
SS the same potential as VSS/EVSS.
2. Connect the REGC pin to VSS via a capacitor (0.47 to 1 μF: recommended).
3. ANI0/P80 to ANI7/P87 are set in the analog input mode after release of reset.
User’s Manual U17555EJ4V0UD
19
Page 20
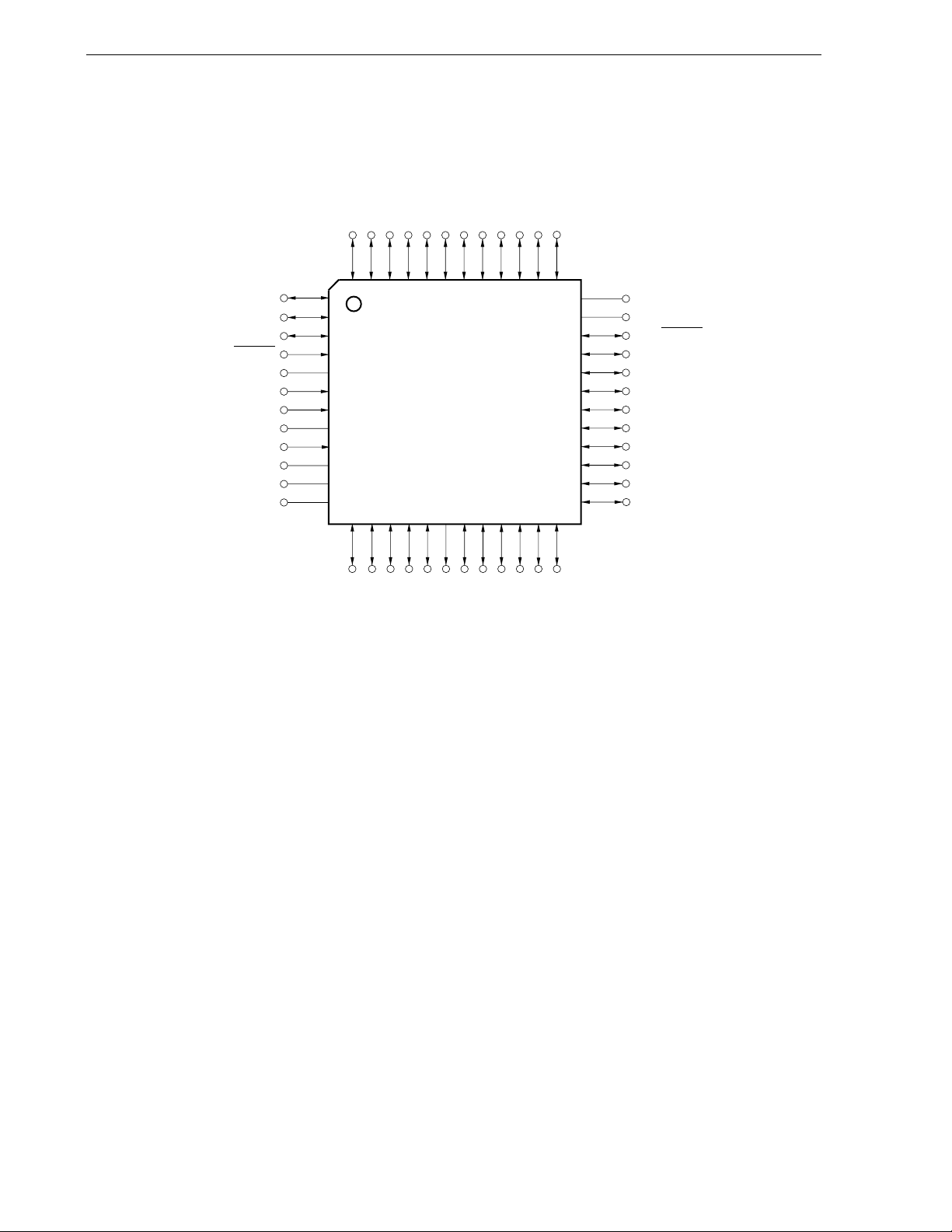
• 48-pin plastic LQFP (Fine pitch) (7x7)
48 47 46 45 44 43 42 41 40 39 38 37
P120/INTP0/EXLVI
P41
P40
RESET
P124/XT2/EXCLKS
P123/XT1
FLMD0
P122/X2/EXCLK
P121/X1
REGC
V
SS
/EV
VDD/EV
SS
DD
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24
CHAPTER 1 OUTLINE
P131
P00/TI000
P01/TI010/TO00
P80/ANI0
P81/ANI1
P82/ANI2
P83/ANI3
P84/ANI4
P85/ANI5
P86/ANI6
P87/ANI7
P90/ANI8
36
35
34
33
32
31
30
29
28
27
26
25
AV
SS
AV
REF
P10/SCK10/TxD61
P11/SI10/RxD61
P12/SO10
P13/TxD60
P14/RxD60
P15/TOH0
P16/TOH1/INTP5
P17/TI50/TO50
P30/INTP1
P31/INTP2
P60
P61
P62
P63
P130
P70/CTxD
P71/CRxD
P72/PCL/INTP6
P73/BUZ/INTP7
P32/INTP3
P06/TI011/TO01
P33/TI51/TO51/INTP4
Cautions 1. Make AVSS the same potential as VSS/EVSS.
2. Connect the REGC pin to V
SS via a capacitor (0.47 to 1
μ
F: recommended).
3. ANI0/P80 to ANI7/P87 are set in the analog input mode after release of reset.
20
User’s Manual U17555EJ4V0UD
Page 21

CHAPTER 1 OUTLINE
Pin Identification
ANI0 to ANI8: Analog input
AV
REF: Analog reference voltage
AV
SS: Analog ground
BUZ: Buzzer output
CRxD: Receive data for CAN
CTxD: Transmit data for CAN
EV
DD: Power supply for port
EV
SS: Ground for port
EXCLK: External clock input
(Main system clock)
EXCLKS: External clock input
(Subsystem clock)
EXLVI: External potential input
for low-voltage detector
FLMD0: Flash programming mode
INTP0 to INTP7: External interrupt input
P00, P01,
P06
: Port 0
P10 to P17: Port 1
P30 to P33: Port 3
P40, P41: Port 4
P60 to P63: Port 6
P70 to P73: Port 7
P80 to P87: Port 8
P90: Port 9
P120 to P124: Port 12
P130, P131: Port 13
PCL: Programmable clock output
REGC: Regulator Capacitance
RESET: Reset
RxD60, RxD61: Receive data
SCK10: Serial clock input/output
SI10: Serial data input
SO10: Serial data output
TI000, TI010,
TI011, TI50, TI51: Timer input
TO00, TO01,
TO50, TO51,
TOH0, TOH1: Timer output
TxD60, TxD61: Transmit data
V
DD: Power supply
V
SS: Ground
X1, X2: Crystal oscillator (high-speed system clock)
XT1, XT2: Crystal oscillator (subsystem clock)
User’s Manual U17555EJ4V0UD
21
Page 22
CHAPTER 1 OUTLINE
1.5 Fx2 Series Lineup
1.5.1 78K0/Fx2 product lineup
•
44-pin LQFP (10 × 10 mm 0.8 mm pitch)
78K0/FC2
μ
PD78F0881
Single-power-supply flash
memory: 32 KB,
RAM: 2 KB
48-pin LQFP (7 × 7 mm 0.5 mm pitch)
•
78K0/FC2
μ
PD78F0884
Single-power-supply flash
memory: 32 KB,
RAM: 2 KB
•
64-pin LQFP (10 × 10 mm 0.5 mm pitch, 12 × 12 mm 0.65 mm pitch)
78K0/FE2
•
80-pin LQFP (12 × 12 mm 0.5 mm pitch, 14 × 14 mm 0.65 mm pitch)
78K0/FF2
Remark All product with on-chip debug function.
μ
PD78F0882
Single-power-supply flash
memory: 48 KB,
RAM: 3 KB
μ
PD78F0885
Single-power-supply flash
memory: 48 KB,
RAM: 3 KB
μ
PD78F0887
Single-power-supply flash
memory: 48 KB,
RAM: 3 KB
Single-power-supply flash
memory: 60KB,
RAM: 3 KB
Single-power-supply flash
memory: 60KB,
RAM: 3 KB
Single-power-supply flash
memory: 60 KB,
RAM: 3 KB
Single-power-supply flash
memory: 60 KB,
RAM: 3 KB
μ
PD78F0883
μ
PD78F0886
μ
PD78F0888
μ
PD78F0891
μ
PD78F0889
Single-power-supply flash
memory: 96 KB,
RAM: 5 KB
μ
PD78F0892
Single-power-supply flash
memory: 96 KB,
RAM: 5 KB
μ
PD78F0890
Single-power-supply flash
memory: 128 KB,
RAM: 7 KB
μ
PD78F0893
Single-power-supply flash
memory: 128 KB,
RAM: 7 KB
22
User’s Manual U17555EJ4V0UD
Page 23
<R>
CHAPTER 1 OUTLINE
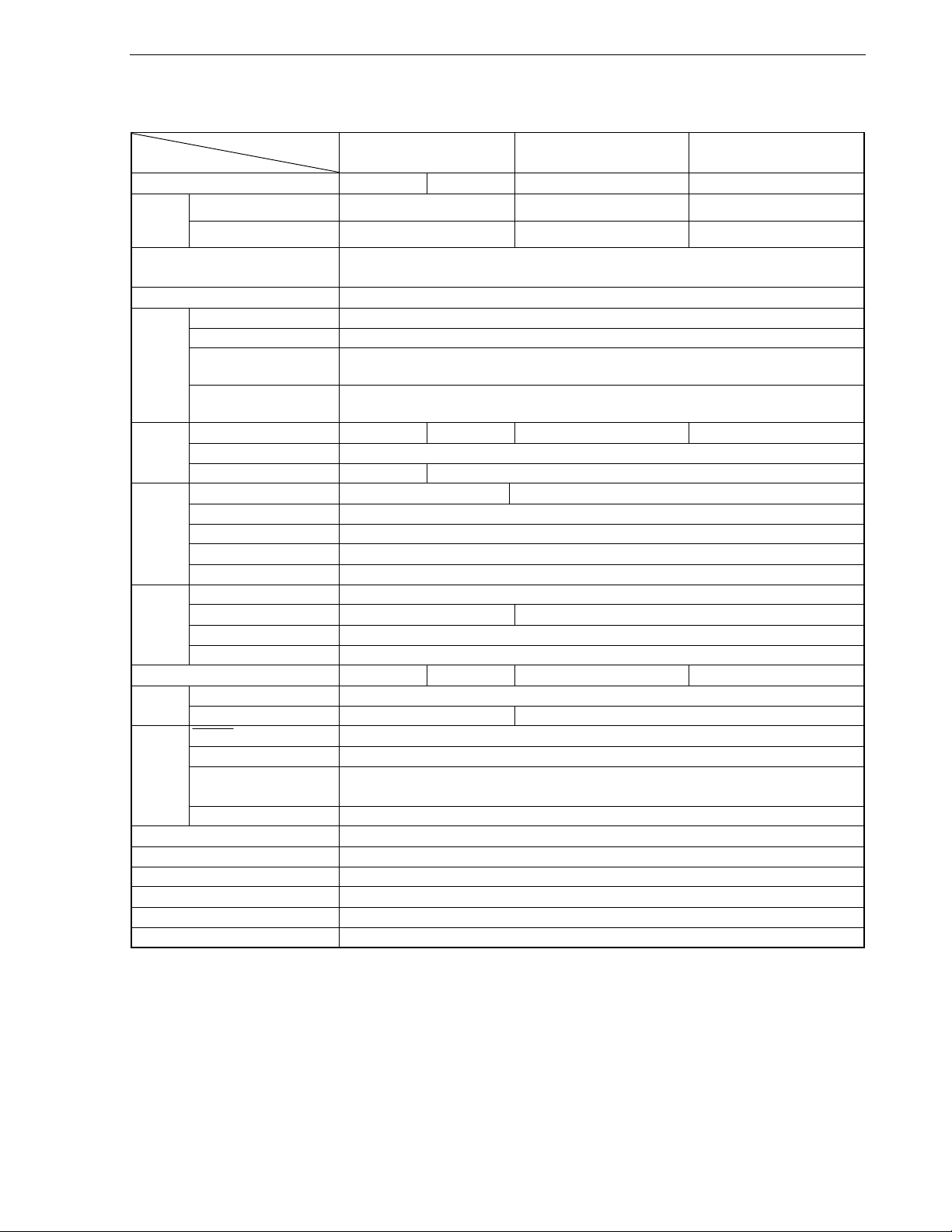
The list of functions in the 78K0/Fx2 is shown below.
Part Number
Item
Number of pins 44 pins 48 pins 64 pins 80 pins
Flash memory 32 K/48 K/60 K 48 K/60 K/96 K/128 K 60 K/96 K/128 K Internal
memory
(bytes)
Power supply voltage VDD = 4.0 to 5.5 V when 20 MHz, VDD = 2.7 to 5.5 V when 10 MHz,
Minimum instruction execution time 0.1 μs (when 20 MHz, VDD = 4.0 to 5.5 V)
Clock
Ports
Timer
Serial
interface
10-bit A/D converter 8 ch 9 ch 12 ch 16 ch
Interrupts
Reset
Multiplier/divider Provided
Clock output/buzzer output Provided
Self-programming function Provided
On-chip debug function Provided
Standby function HALT/STOP mode
Operating ambient temperature TA = −40 to +85°C, −40 to +125°C
RAM 2 K/3 K/3 K 3 K/3 K/5 K/7 K 3 K/5 K/7 K
Crystal/ceramic 4 to 20 MHz
Subclock 32.768 kHz
Internal low-speed
oscillator
Internal high-speed
oscillator
CMOS I/O 33 36 50 66
CMOS output 1
N-ch open-drain I/O 3 4
16 bits (TM0) 2 ch
8 bits (TM5) 2 ch
8 bits (TMH) 2 ch
For watch 1 ch
WDT 1 ch
CAN 1 ch
3-wire CSI
LIN-UART 1 ch
LIN-UART/CSI 1 ch
External 8
Internal 24 29
RESET pin Provided
POC 1.59 V ±0.15 V (detection voltage is fixed)
LVI 4.24/4.09/3.93/3.78/3.62/3.47/3.32/3.16/3.01/2.85/2.70/2.55/2.39/2.24/2.08/1.93 V
WDT Provided
78K0/FC2
DD = 1.8 to 5.5 V when 5 MHz
V
8 MHz (TYP., V
Note
4 ch
−
78K0/FE2 78K0/FF2
240 kHz (TYP.)
DD = 2.7 to 5.5 V)
1 ch
(selectable by software)
Note Since TM01 does not have the following terminal at 78K0/FC2, the function is restricted in part.
μ
μ
PD78F0881, 78F0882, and 78F0883: TI001, TI011, TO01
PD78F0884, 78F0885, and 78F0886: TI001
User’s Manual U17555EJ4V0UD
23
Page 24
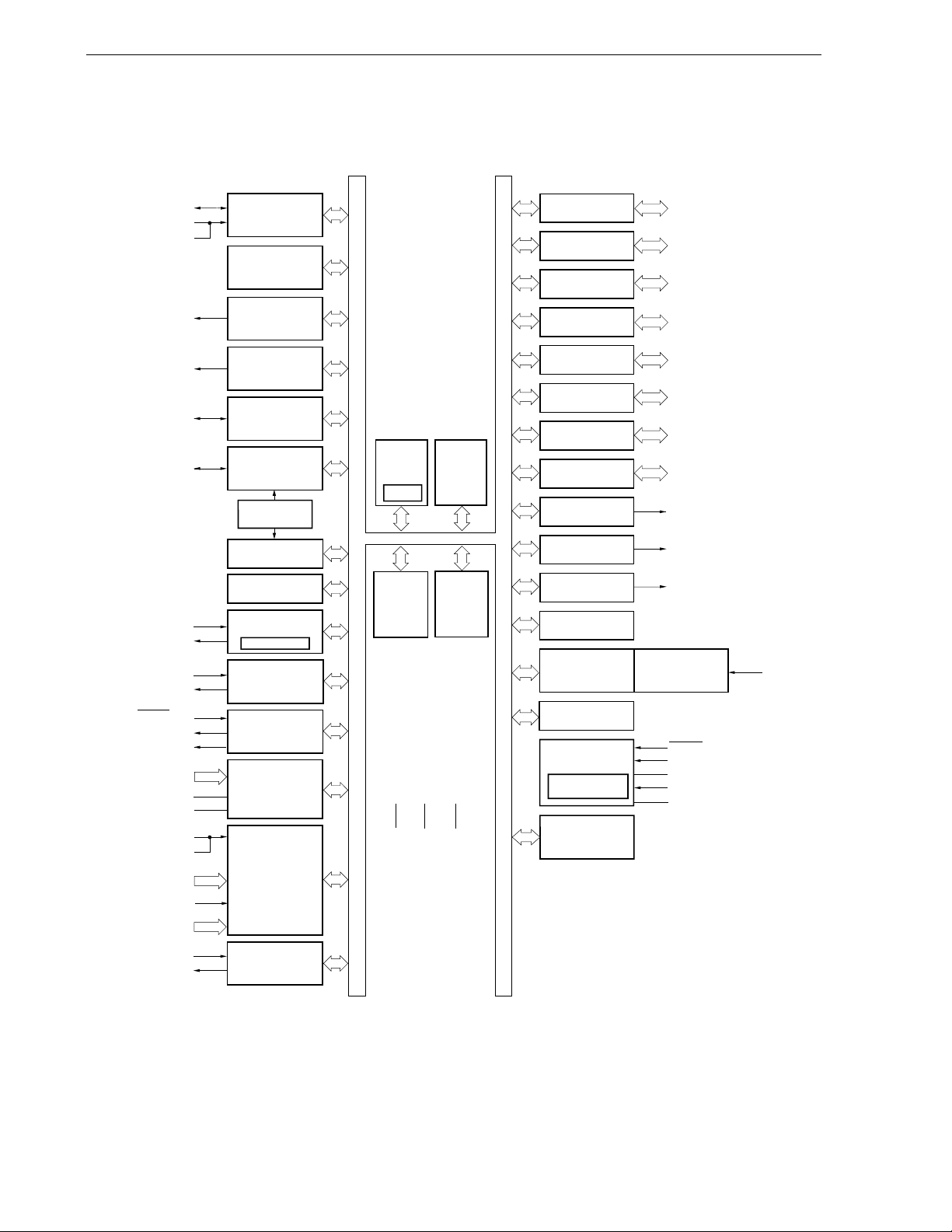
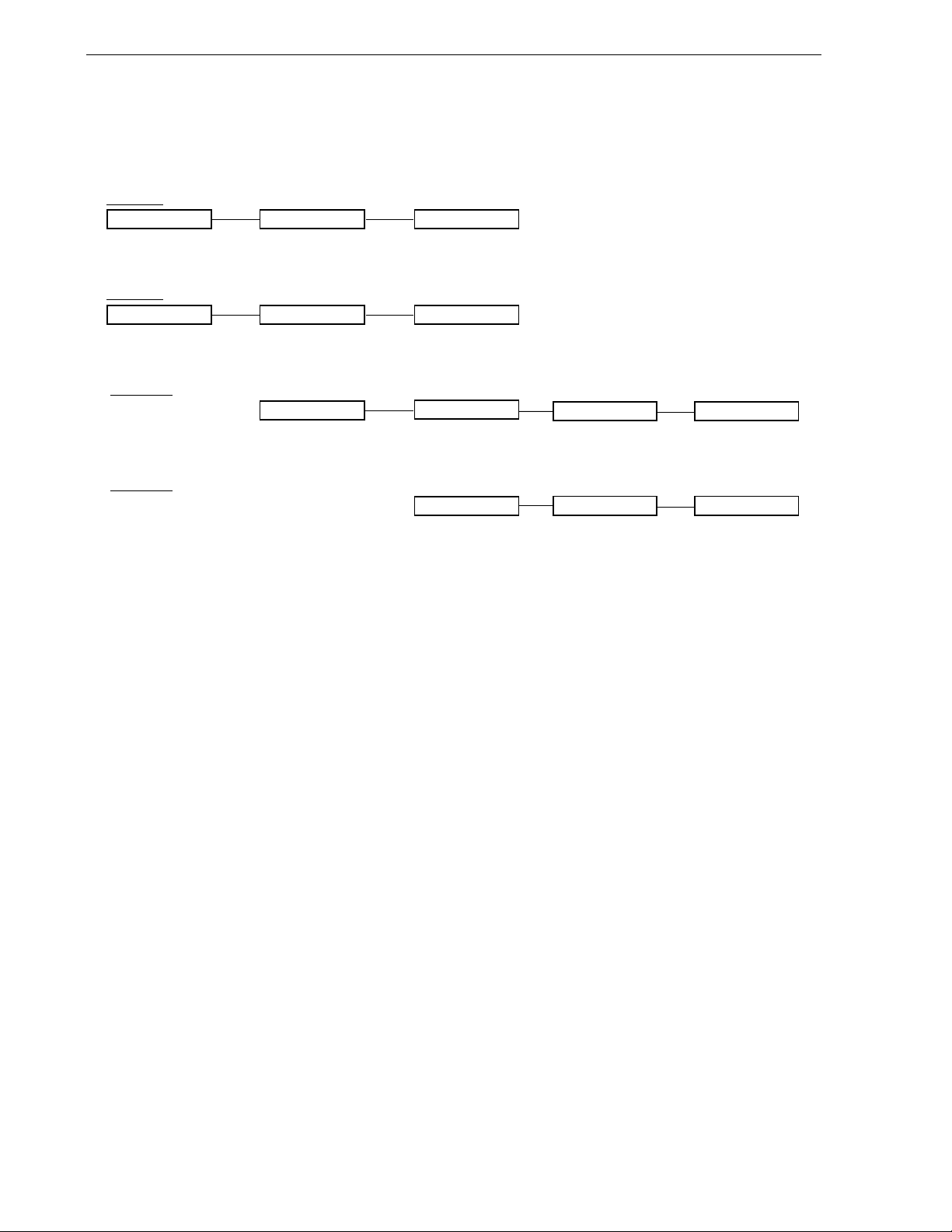
1.6 Block Diagram
• μ PD78F0881, 78F0882, 78F0883
CHAPTER 1 OUTLINE
TO00/TI010/P01
TI000/P00 (LINSEL)
RxD60/P14 (LINSEL)
TOH0/P15
TOH1/P16
TI50/TO50/P17
TI51/TO51/P33
RxD60/P14
TxD60/P13
RxD61/P11
TxD61/P10
16-bit timer/
event counter 00
16-bit timer/
event counter 01
8-bit timer H0
8-bit timer H1
8-bit timer/
event counter 50
8-bit timer/
event counter 51
Low-speed
internal oscillator
Watchdog timer
Watch timer
Serial
interface UART60
LINSEL
Serial
interface UART61
78K/0
CPU
core
Bank
Internal
high-speed
RAM
Flash
memory
Internal
expansion
RAM
Port 0
Port 1
Port 3
Port 4
Port 6
Port 7
Port 8
Port 12
Port 13
Buzzer output
Clock output control
Multiplier/Divider
Power on clear/
low voltage
indicator
2
8
4
2
3
P60-P62
4
P70-P73
8
P80-P87
5
P120-P124
POC/LVI
control
P00, P01
P10-P17
P30-P33
P40, P41
P130
BUZ/P73
PCL/P72
EXLVI/P120
SCK10/P10
SI10/P11
SO10/P12
ANI0/P80-ANI7/P87
AV
AV
INTP0/P120 (LINSEL)
RxD60/P14 (LINSEL)
INTP1/P30-
INTP4/P33
INTP5/P16
INTP6/P72
INTP7/P73
CRxD/P71
CTxD/P70
REF
Serial
interface CSI10
8
A/D converter
SS
VSS,
FLMD0VDD,
EV
EV
SS
DD
Interrupt control
4
2
Reset control
System control
High-speed
internal oscillator
On-chip
debugger
RESET
X1/P121
X2/EXCLK/P122
XT1/P123
XT2/EXCLKS/P124
CAN
24
User’s Manual U17555EJ4V0UD
Page 25
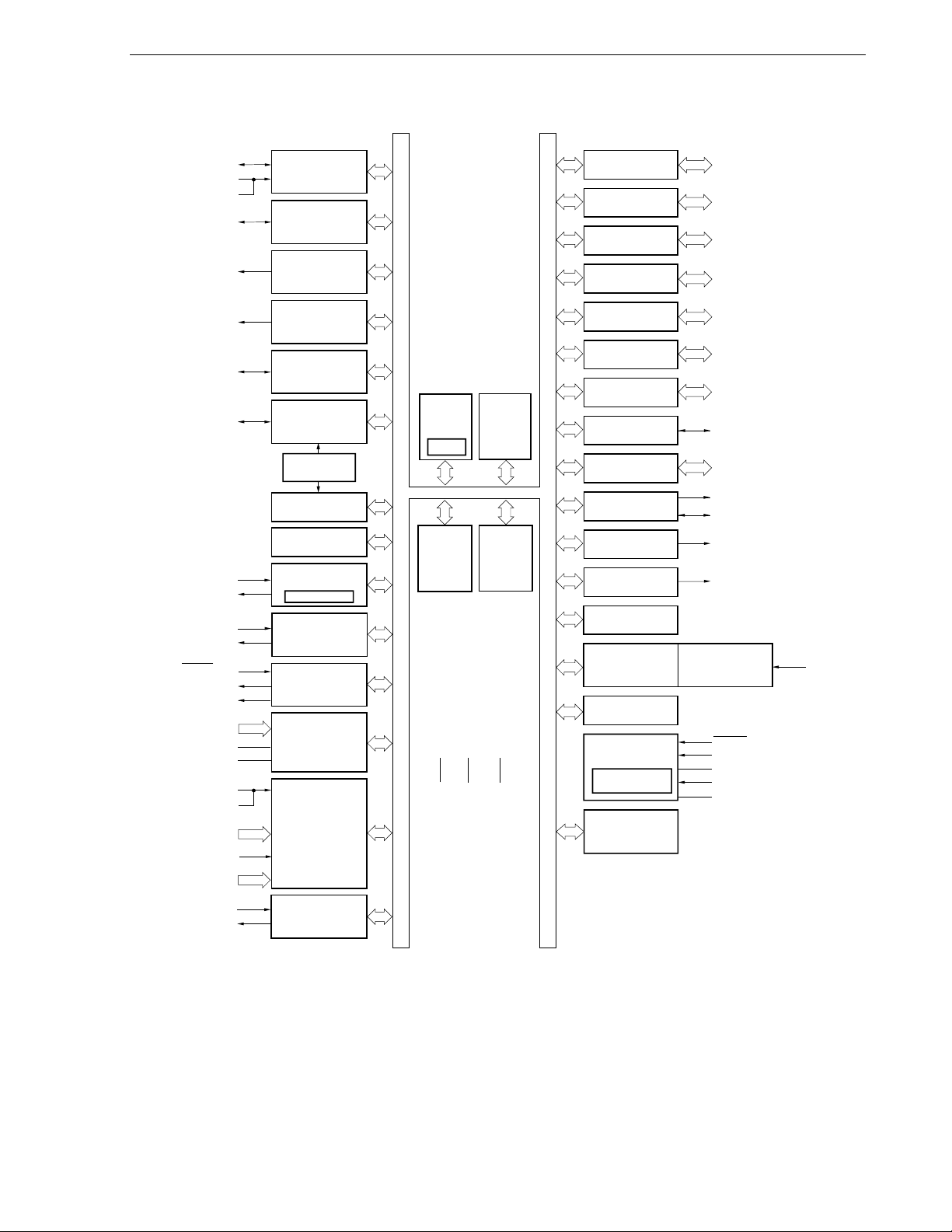
• μ PD78F0884, 78F0885, 78F0886
CHAPTER 1 OUTLINE
TO00/TI010/P01
TI000/P00 (LINSEL)
RxD60/P14 (LINSEL)
TO01/TI011/P06
TOH0/P15
TOH1/P16
TI50/TO50/P17
TI51/TO51/P33
RxD60/P14
TxD60/P13
RxD61/P11
TxD61/P10
SCK10/P10
SI10/P11
SO10/P12
ANI0/P80-ANI7/P87,
INTP0/P120 (LINSEL)
RxD60/P14 (LINSEL)
ANI8/P90
AV
AV
INTP1/P30-
INTP4/P33
INTP5/P16
INTP6/P72
INTP7/P73
CRxD/P71
CTxD/P70
REF
16-bit timer/
event counter 00
16-bit timer/
event counter 01
8-bit timer H0
8-bit timer H1
8-bit timer/
event counter 50
8-bit timer/
event counter 51
Low-speed
internal oscillator
Watchdog timer
Watch timer
Serial
interface UART60
LINSEL
Serial
interface UART61
Serial
interface CSI10
9
A/D converter
SS
Interrupt control
4
2
78K/0
CPU
core
Bank
Internal
high-speed
RAM
EV
DD
EV
VSS,
Flash
memory
Internal
expansion
RAM
FLMD0VDD,
SS
Port 0
Port 1
Port 3
Port 4
Port 6
Port 7
Port 8
Port 9
Port 12
Port 13
Buzzer output
Clock output control
Multiplier/Divider
Power on clear/
low voltage
indicator
Reset control
System control
High-speed
internal oscillator
On-chip
debugger
3
P00, P01, P06
8
P10-P17
4
P30-P33
2
P40, P41
4
P60-P63
4
P70-P73
8
P80-P87
P90
5
P120-P124
P130
P131
BUZ/P73
PCL/P72
POC/LVI
control
RESET
X1/P121
X2/EXCLK/P122
XT1/P123
XT2/EXCLKS/P124
EXLVI/P120
CAN
User’s Manual U17555EJ4V0UD
25
Page 26
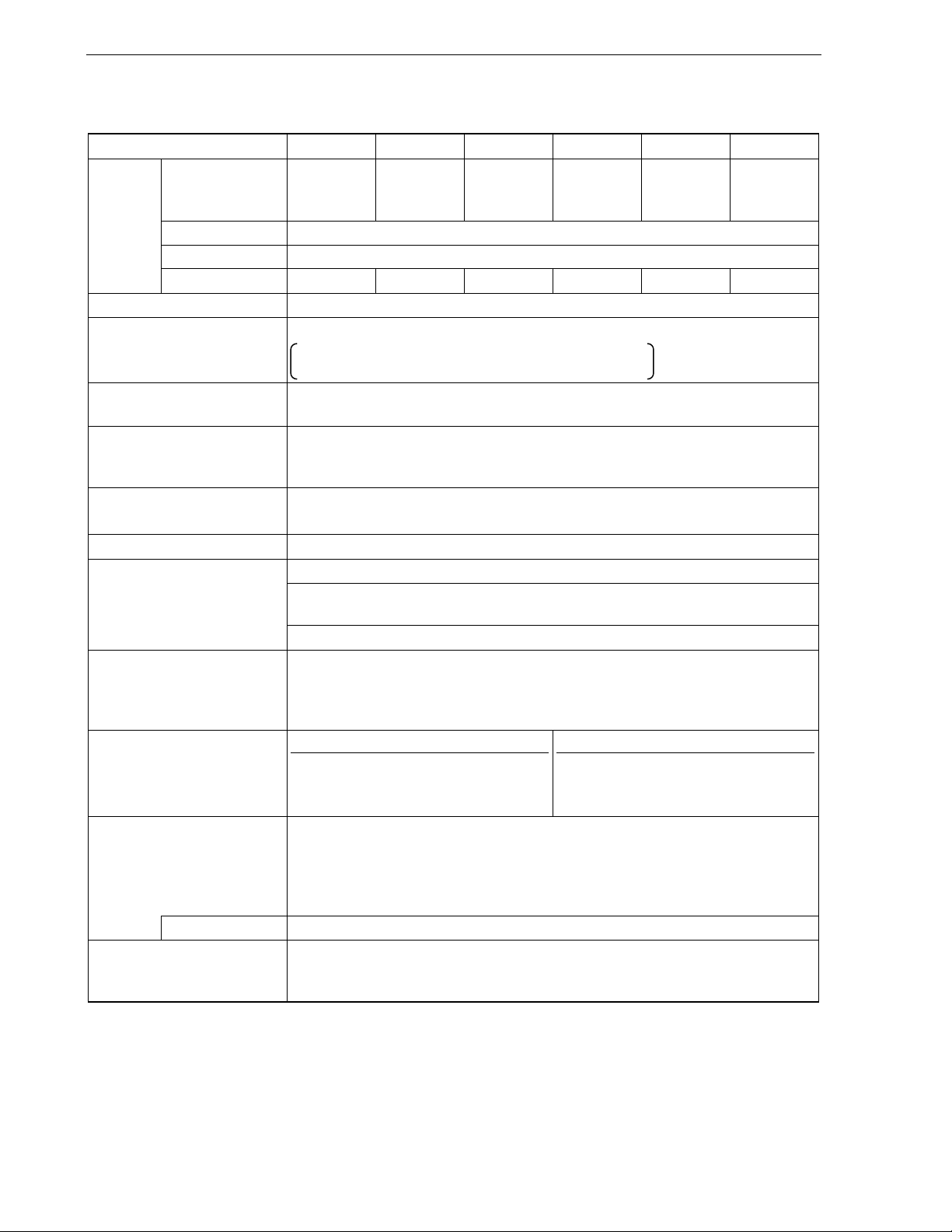
CHAPTER 1 OUTLINE
1.7 Outline of Functions
(1/2)
Item
Internal
memory
(bytes)
Flash memory
(self-programming
supported)
Note 1
Bank
High-speed RAM
Expansion RAM
Memory space 64 KB
High-speed system clock
(oscillation frequency)
Internal high-speed oscillation
clock (oscillation frequency)
Internal low-speed oscillation
clock
(oscillation frequency)
Subsystem clock
(oscillation frequency)
General-purpose registers 8 bits × 32 registers (8 bits × 8 registers × 4 banks)
Minimum instruction execution
time
Instruction set
I/O ports
Timers
Timer outputs 8 (PWM output: 4)
Clock output
Notes 1. The internal flash memory capacity, internal high-speed RAM capacity, and internal expansion RAM
capacity can be changed using the internal memory size switching register (IMS) and the internal
expansion RAM size switching register (IXS).
2. Since TM01 does not have the following terminal at 78K0/FC2, the function is restricted in part.
μ
μ
PD78F0881, 78F0882, and 78F0883: TI001, TI011, TO01
PD78F0884, 78F0885, and 78F0886: TI001
μ
PD78F0881 μPD78F0882 μPD78F0883 μPD78F0884 μPD78F0885 μPD78F0886
32 K 48 K 60 K 32 K 48 K 60 K
−
Note 1
1 K
Note 1
1 K 2 K 2 K 1 K 2 K 2 K
Crystal/ceramic oscillation (X1), external main system clock input (EXCLK)
4 to 20 MHz: V
4 to 5 MHz: V
On-chip internal oscillation (8 MHz (TYP.): V
DD = 4.0 to 5.5 V, 4 to 10 MHz: VDD = 2.7 to 5.5 V,
DD = 1.8 to 5.5 V
DD = 2.7 to 5.5 V)
On-chip internal oscillation (240 kHz (TYP.))
Crystal oscillation (XT1), external subsystem clock input (EXCLKS)
(32.768 kHz: V
DD = 1.8 to 5.5 V)
0.1 μs/0.2 μs/0.4 μs/0.8 μs/1.6 μs (high-speed system clock: @ fXP = 20 MHz operation)
0.25 μs/0.5 μs/1.0 μs/2.0 μs/4.0 μs (TYP.) (internal oscillator clock: @ fRH = 8 MHz (TYP.)
operation)
122
μ
s (subsystem clock: when operating at fXT = 32.768 kHz)
• 16-bit operation
• Multiply/divide (8 bits × 8 bits, 16 bits ÷ 8 bits)
• Bit manipulate (set, reset, test, and Boolean operation)
• BCD adjust, etc.
Total: 37
CMOS I/O 33
CMOS output 1
N-ch open-drain I/O 3
• 16-bit timer/event counter: 2 channels
Total: 41
CMOS I/O 36
CMOS output 1
N-ch open-drain I/O 4
Note 2
• 8-bit timer/event counter: 2 channels
• 8-bit timer: 2 channels
• Watch timer 1 channel
• Watchdog timer: 1 channel
• 78.125 kHz, 156.25 kHz, 312.5 kHz, 625 kHz, 1.25 MHz, 2.5 MHz, 5 MHz, 10 MHz
(high-speed system clock: 10 MHz)
• 32.768 kHz (subsystem clock: 32.768 kHz)
26
User’s Manual U17555EJ4V0UD
Page 27
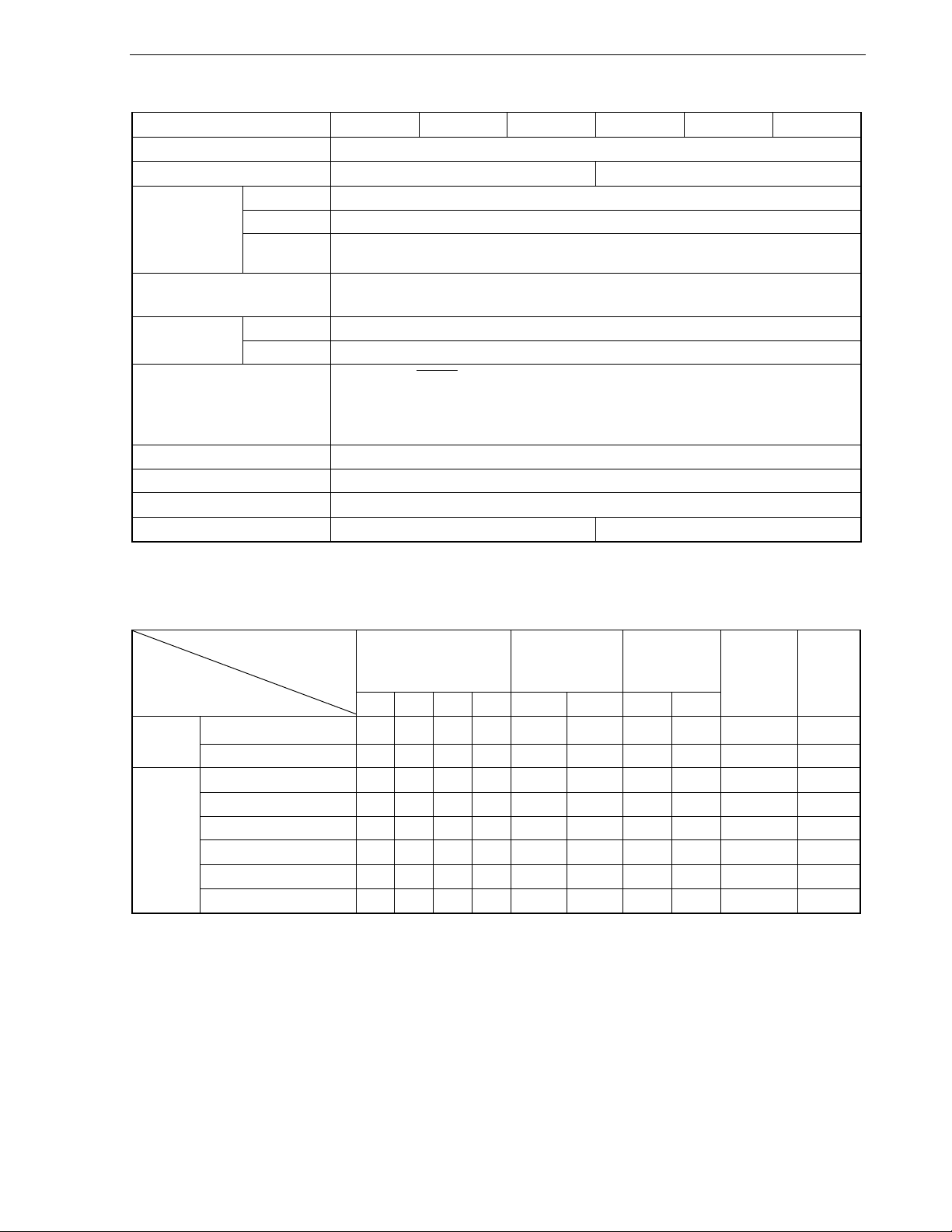
<R>
<R>
<R>
CHAPTER 1 OUTLINE
Item
μ
PD78F0881 μPD78F0882 μPD78F0883 μPD78F0884 μPD78F0885 μPD78F0886
Buzzer output 1.22 kHz, 2.44 kHz, 4.88 kHz, 9.77 kHz (high-speed system clock: 10 MHz)
A/D converter 10-bit resolution × 8 channels 10-bit resolution × 9 channels
Serial interface
Multiplier/divider
CAN
LIN-UART
LIN-UART/
Note
CSI
1 ch
1 ch
1 ch
• 16 bit x 16 bit = 32 bit (Multiplication)
• 32 bit ÷ 32 bit = 32 bit remainder of 16 bits (Division)
Vectored
interrupt sources
Reset
Internal 24
External 8
• Reset using RESET pin
• Internal reset by watchdog timer
• Internal reset by power-on-clear
• Internal reset by low-voltage detector
On-chip debug function Provided
Supply voltage VDD = 1.8 to 5.5 V
Operating ambient temperature TA = −40 to +85°C, −40 to +125°C
Package 44-pin plastic LQFP(10x10) 48-pin plastic LQFP (Fine pitch) (7x7)
Note Select either of the functions of these alternate-function pins.
An outline of the timer is shown below.
Watchdog
Note 1
1 channel
− −
− −
− −
Operation
mode
Function
16-Bit Timer/
Event Counters 00 to 03
TM00 TM01 TM02 TM03 TM50 TM51 TMH0 TMH1
Interval timer 1 ch 1 ch
External event counter 1 ch
Timer output 1 1
PPG output 1 1
PWM output
Pulse width measurement 2
Square-wave output 1 1
− − −
Note 2
Note 2
− − − −
− − − − − − − − −
Note2
Interrupt source 2 2
8-Bit Timer/
Event Counters
8-Bit Timers H0
and H1
Watch Timer
50 and 51
− −
− −
1 ch 1 ch 1 ch 1 ch
1 ch 1 ch
− − − −
1 1 1 1
1 channel
− − − − − − − −
1 1 1 1
− −
− −
1 1 1 1
1 1 1 1 1
Notes 1. In the watch timer, the watch timer function and interval timer function can be used simultaneously.
2.
μ
PD78F0884, 78F0885, and 78F0886 only.
Remark TM51 and TMH1 can be used in combination as a carrier generator mode.
(2/2)
Timer
−
User’s Manual U17555EJ4V0UD
27
Page 28
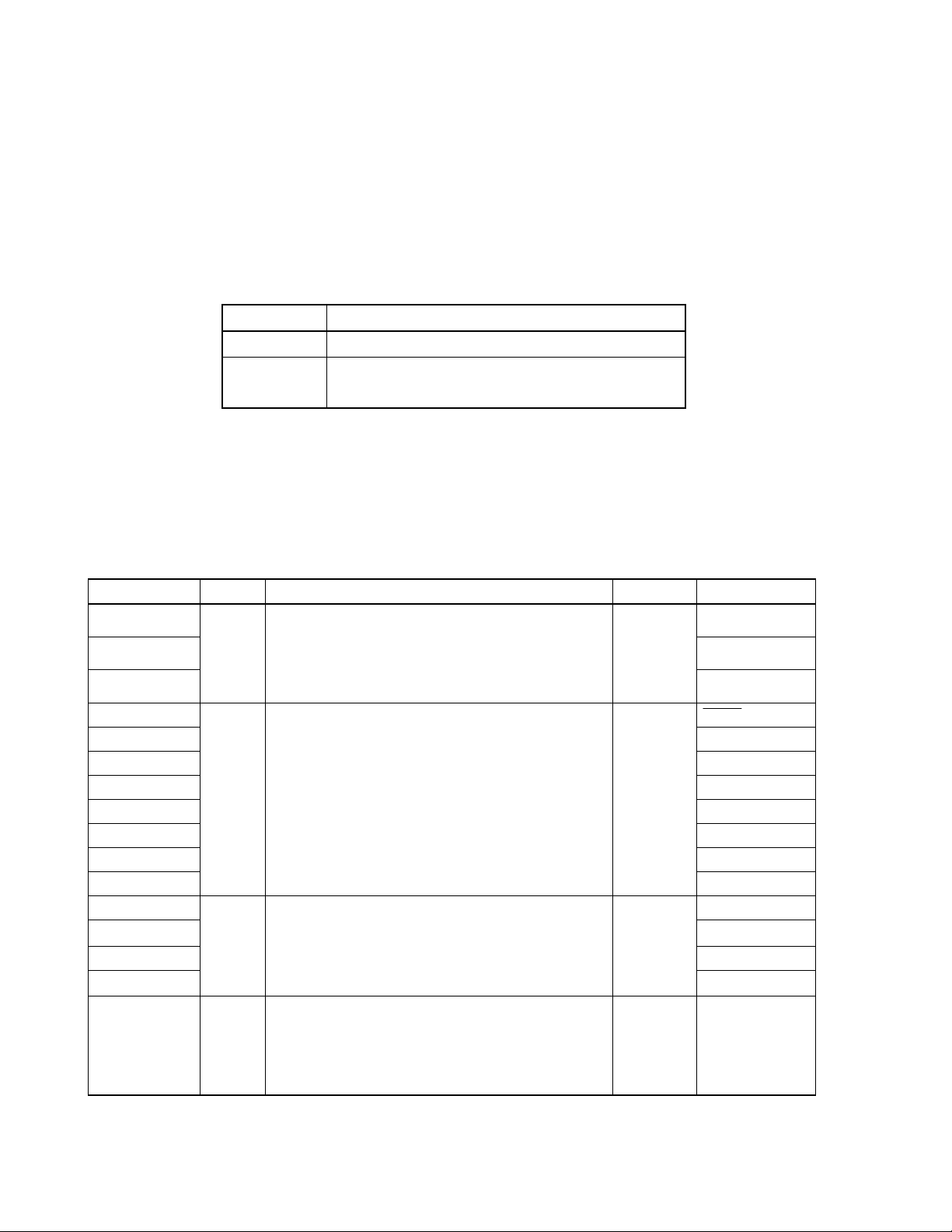
CHAPTER 2 PIN FUNCTIONS
2.1 Pin Function List
There are three types of pin I/O buffer power supplies: AV
supplies and the pins is shown below.
Table 2-1. Pin I/O Buffer Power Supplies
Power Supply Corresponding Pins
AVREF P80 to P87, P90
EVDD/VDD • Port pins other than P80 to P87, P90
• Non-port pins
Note
Note P90 is μPD78F0884, 78F0885, and 78F0886 only.
This section explains the names and functions of the pins of the 78K0/FC2.
(1) Port pins
REF, EVDD/VDD. The relationship between these power
Note
Table 2-2. Port pins (1/2)
Pin Name I/O Function After Reset Alternate Function
P00 TI000
P01 TI010/TO00
Note
P06
P10 SCK10/TxD61
P11 SI10/RxD61
P12 SO10
P13 TxD60
P14 RxD60
P15 TOH0
P16 TOH1/INTP5
P17
P30 INTP1
P31 INTP2
P32 INTP3
P33
P40, P41 I/O
I/O
I/O
I/O
Port 0.
3-bit I/O port.
Input/output can be specified in 1-bit units.
Use of an on-chip pull-up resistor can be specified by a
software setting.
Port 1.
8-bit I/O port.
Input/output can be specified in 1-bit units.
Use of an on-chip pull-up resistor can be specified by a
software setting.
Port 3.
4-bit I/O port.
Input/output can be specified in 1-bit units.
Use of an on-chip pull-up resistor can be specified by a
software setting.
Port 4.
2-bit I/O port.
Input/output can be specified in 1-bit units.
Use of an on-chip pull-up resistor can be specified by a
software setting.
Input
Input
Input
Input
TI011/TO01
TI50/TO50
INTP4/TI51/TO51
−
Note P06 is μPD78F0884, 78F0885, and 78F0886 only.
28
User’s Manual U17555EJ4V0UD
Page 29
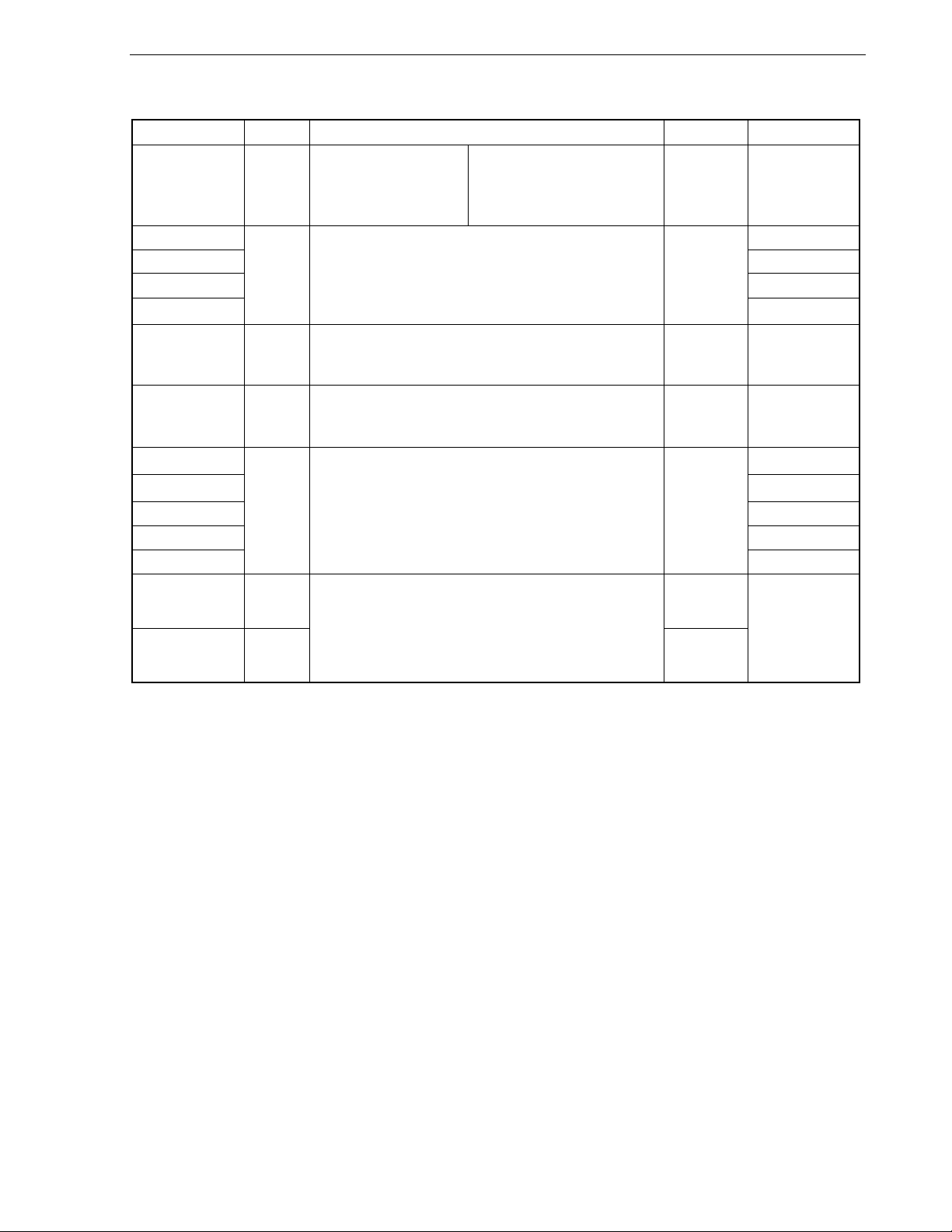
CHAPTER 2 PIN FUNCTIONS
Table 2-2. Port pins (2/2)
Pin Name I/O Function After Reset Alternate Function
P60 to P63
Note
I/O
Port 6.
N-ch open drain I/O port. Input
−
4-bit I/O port
Input/output can be
specified in 1-bit units.
P70 CTxD
I/O
P71 CRxD
P72 PCL/INTP6
P73
P80 to P87 I/O
Port 7.
4-bit I/O port.
Input/output can be specified in 1-bit units.
Use of an on-chip pull-up resistor can be specified by a
software setting.
Port 8.
Input
BUZ/INTP7
Input ANI0 to ANI7
8-bit I/O port.
Input/output can be specified in 1-bit units.
Note
P90
I/O
Port 9.
Input ANI8
1-bit I/O port.
Input/output can be specified in 1-bit units.
P120 INTP0/EXLVI
I/O
P121 X1
P122 X2/EXCLK
Port 12.
5-bit I/O port.
Only for P120, use of an on-chip pull-up resistor can be
specified by a software setting.
Input
P123 XT1
P124
P130 Output Output
Port 13.
XT2/EXCLKS
−
P130 is 1-bit output-only port.
Note
P131
I/O
P131 is 1-bit I/O port.
P131 use of an on-chip pull-up resistor can be specified by a
Input
software setting.
Note P63, P90 and P131 are μPD78F0884, 78F0885, and 78F0886 only.
User’s Manual U17555EJ4V0UD
29
Page 30
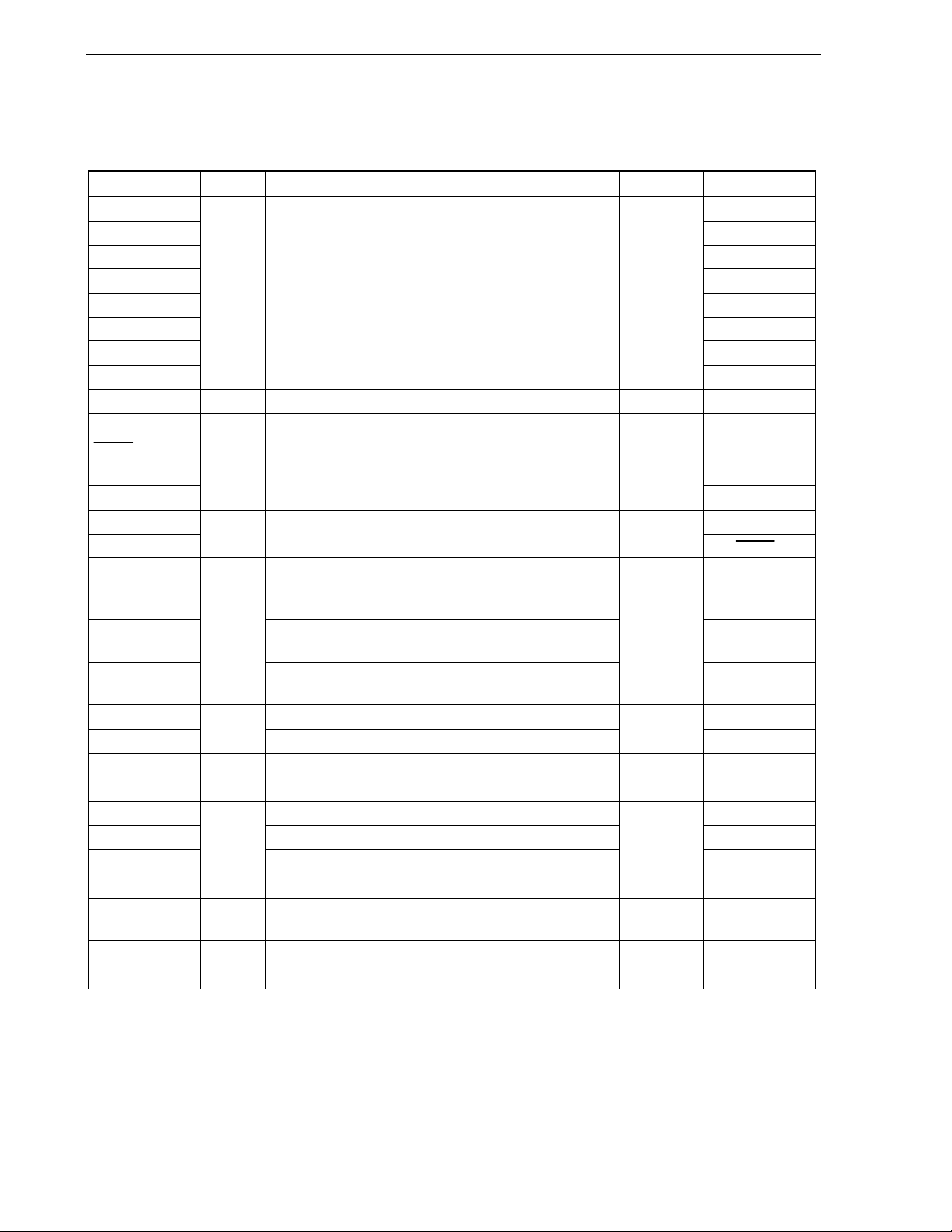
CHAPTER 2 PIN FUNCTIONS
(2) Non-port pins
Table 2-3. Non-port pins (1/2)
Pin Name I/O Function After Reset Alternate Function
INTP0 P120/EXLVI
INTP1 P30
INTP2 P31
INTP3 P32
INTP4 P33/TI51/TO51
INTP5 P16/TOH1
INTP6 P72/PCL
INTP7
SI10 Input Serial data input to serial interface Input P11/RxD61
SO10 Output Serial data output from serial interface Input P12
SCK10 I/O Clock input/output for serial interface Input P10/TxD61
RxD60 P14
RxD61
TxD60 P13
TxD61
TI000
TI010
TI011
TO00 16-bit timer/event counter 00 output P01/TI010
TO01
TI50 External count clock input to 8-bit timer/event counter 50 P17/TO50
TI51
TO50 8-bit timer/event counter 50 output P17/TI50
TO51 8-bit timer/event counter 51 output P33/TI51/INTP4
TOH0 8-bit timer H0 output P15
TOH1
PCL Output
BUZ Output Buzzer output Input P73/INTP7
ANI0 to ANI8
Input
Input Serial data input to asynchronous serial interface Input
Output Serial data output from asynchronous serial interface Input
Input
Output
Input
Output
Note
Input A/D converter analog input Input P80 to P87, P90
External interrupt request input for which the valid edge (rising
edge, falling edge, or both rising and falling edges) can be
specified
External count clock input to 16-bit timer/event counter 00
Capture trigger input to capture registers (CR000, CR010) of
16-bit timer/event counter 00
Capture trigger input to capture register (CR000) of 16-bit
timer/event counter 00
Capture trigger input to capture register (CR001) of 16-bit
timer/event counter 01
16-bit timer/event counter 01 output
External count clock input to 8-bit timer/event counter 51
8-bit timer H1 output
Clock output (for trimming of high-speed system clock,
subsystem clock)
Input
P73/BUZ
P11/SI10
P10/SCK10
Input
Input
Input
Input
Input P72/INTP6
P00
P01/TO00
P06/TO01
P06/TI011
P33/TO51/INTP4
P16/INTP5
Note ANI8 is μPD78F0884, 78F0885, and 78F0886 only.
30
User’s Manual U17555EJ4V0UD
Page 31

CHAPTER 2 PIN FUNCTIONS
Table 2-3. Non-port pins (2/2)
Pin Name I/O Function After Reset Alternate Function
CTxD Input CAN transmit data output Input P70
CRxD Output CAN receive data input Input P71
AVREF Input
A/D converter reference voltage input and positive power
− −
supply for port 2
AVSS
RESET Input System reset input
X1 Input Input P121
X2
XT1 Input Input P123
XT2
A/D converter ground potential. Make the same potential as
−
SS or VSS.
EV
Connecting resonator for high-speed system clock
−
Connecting resonator for subsystem clock
−
− −
− −
Input P122/EXCLK
Input P124/EXCLKS
EXCLK Input External clock input for main system clock Input P122/X2
EXCLKS Input External clock input for subsystem clock Input P124/XT2
EXLVI Input Potential input for external low-voltage detection Input P120/INTP0
VDD
EVDD
VSS
EVSS
FLMD0
REGC
Positive power supply (except for ports)
−
Positive power supply for ports
−
Ground potential (except for ports)
−
Ground potential for ports
−
Flash memory programming mode setting.
−
This is the pin for connecting regulator output (2.5 V)
−
− −
− −
− −
− −
− −
− −
stabilization capacitance for internal operation. Connect this
SS via a capacitor (0.47 to 1
pin to V
μ
F: recommended).
User’s Manual U17555EJ4V0UD
31
Page 32

CHAPTER 2 PIN FUNCTIONS
2.2 Description of Pin Functions
2.2.1 P00, P01, P06 (port 0)
P00, P01 and P06 function as a 3-bit I/O port. These pins also function as timer I/O.
The following operation modes can be specified in 1-bit units.
(1) Port mode
P00, P01 and P06 function as 3-bit I/O port. P00, P01 and P06 can be set to input or output in 1-bit units using
port mode register 0 (PM0). Use of an on-chip pull-up resistor can be specified by pull-up resistor option register
0 (PU0).
(2) Control mode
P00, P01 and P06 function as timer I/O.
(a) TI000
These is the pin for inputting an external count clock to 16-bit timer/event counters 00 and are also for
inputting a capture trigger signal to the capture registers (CR000) of 16-bit timer/event counters 00.
(b) TI010, TI011
These are the pin for inputting a capture trigger signal to the capture register (CR010, CR011) of 16-bit
timer/event counters 00 and 01.
(c) TO00, TO01
These are timer output pin.
Caution P06 is
μ
PD78F0884, 78F0885, and 78F0886 only.
32
User’s Manual U17555EJ4V0UD
Page 33

CHAPTER 2 PIN FUNCTIONS
2.2.2 P10 to P17 (port 1)
P10 to P17 function as an 8-bit I/O port. These pins also function as pins for external interrupt request input, serial
interface data I/O, clock I/O, and timer I/O.
The following operation modes can be specified in 1-bit units.
(1) Port mode
P10 to P17 function as an 8-bit I/O port. P10 to P17 can be set to input or output in 1-bit units using port mode
register 1 (PM1). Use of an on-chip pull-up resistor can be specified by pull-up resistor option register 1 (PU1).
(2) Control mode
P10 to P17 function as external interrupt request input, serial interface data I/O, clock I/O, and timer I/O.
(a) SI10
This is a serial interface serial data input pin.
(b) SO10
This is a serial interface serial data output pin.
(c) SCK10
This is a serial interface serial clock I/O pin.
(d) RxD60, RxD61
These are the serial data input pins of the asynchronous serial interface.
(e) TxD60, TxD61
These are the serial data output pins of the asynchronous serial interface.
(f) TI50
This is the pin for inputting an external count clock to 8-bit timer/event counter 50.
(g) TO50, TOH0, and TOH1
These are timer output pins.
(h) INTP5
This is an external interrupt request input pin for which the valid edge (rising edge, falling edge, or both rising
and falling edges) can be specified.
User’s Manual U17555EJ4V0UD
33
Page 34

CHAPTER 2 PIN FUNCTIONS
2.2.3 P30 to P33 (port 3)
P30 to P33 function as a 4-bit I/O port. These pins also function as pins for external interrupt request input and
timer I/O.
The following operation modes can be specified in 1-bit units.
(1) Port mode
P30 to P33 function as a 4-bit I/O port. P30 to P33 can be set to input or output in 1-bit units using port mode
register 3 (PM3). Use of an on-chip pull-up resistor can be specified by pull-up resistor option register 3 (PU3).
(2) Control mode
P30 to P33 function as external interrupt request input pins and timer I/O pins.
(a) INTP1 to INTP4
These are the external interrupt request input pins for which the valid edge (rising edge, falling edge, or both
rising and falling edges) can be specified.
(b) TI51
This is an external count clock input pin to 8-bit timer/event counter 51.
(c) TO51
This is a timer output pin.
Cautions 1. Be sure to pull the P31/INTP2 pin down before a reset release, to prevent malfunction.
2. Connect P31/INTP2 as follows when writing the flash memory with a flash programmer.
- P31/INTP2: Connect to EV
SS via a resistor (10 kΩ: recommended).
The above connection is not necessary when writing the flash memory by means of self
programming.
Remark P31/INTP2 and P32/INTP3 can be used as on-chip debug mode setting pins when the on-chip debug
function is used. For details, refer to CHAPTER 24 ON-CHIP DEBUG FUNCTION.
2.2.4 P40, P41 (port 4)
P40, P41 function as a 2-bit I/O port. P40, P41 can be set to input or output in 1-bit units using port mode register
4 (PM4). Use of an on-chip pull-up resistor can be specified by pull-up resistor option register 4 (PU4).
2.2.5 P60 to P63 (port 6)
P60 to P63 function as a 4-bit I/O port. P60 to P63 can be set to input port or output port in 1-bit units using port
mode register 6 (PM6)
P60 to P63 are N-ch open-drain pins.
Caution P63 is
μ
PD78F0884, 78F0885, and 78F0886 only.
34
User’s Manual U17555EJ4V0UD
Page 35

CHAPTER 2 PIN FUNCTIONS
2.2.6 P70 to P73 (port 7)
P70 to P73 function as a 4-bit I/O port. These pins also function as external interrupt request input, clock output
pins, buzzer output pins, CAN I/F I/O.
The following operation modes can be specified in 1-bit units.
(1) Port mode
P70 to P73 function as a 4-bit I/O port. P70 to P73 can be set to input or output in 1-bit units using port mode
register 7 (PM7). Use of an on-chip pull-up resistor can be specified by pull-up resistor option register 7 (PU7).
(2) Control mode
P70 to P73 function as external interrupt request input, output pins, buzzer output pins, CAN I/F I/O.
(a) INTP6, INTP7
These are the external interrupt request input pins for which the valid edge (rising edge, falling edge, or both
rising and falling edges) can be specified.
(b) CRxD
This is the CAN serial receive data input pin.
(c) CTxD
This is the CAN serial transmit data output pin.
(d) PCL
This is a clock output pin.
(e) BUZ
This is a buzzer output pin.
2.2.7 P80 to P87 (port 8)
P80 to P87 function as an 8-bit I/O port. These pins also function as pins for A/D converter analog input.
The following operation modes can be specified in 1-bit units.
(1) Port mode
P80 to P87 function as an 8-bit I/O port. P80 to P87 can be set to input or output in 1-bit units using port mode
register 8 (PM8).
(2) Control mode
P80 to P87 function as A/D converter analog input pins (ANI0 to ANI7). When using these pins as analog input
pins, see (5) P80/ANI0 to P87/ANI7, P90/ANI8 in 12.6 Cautions for A/D Converter.
Caution P80/ANI0 to P87/ANI7 is set in the analog input mode after release of reset.
User’s Manual U17555EJ4V0UD
35
Page 36

CHAPTER 2 PIN FUNCTIONS
2.2.8 P90 (port 9)
P90 function as a 1-bit I/O port. These pins also function as pins for A/D converter analog input.
The following operation modes can be specified in 1-bit units.
(1) Port mode
P90 function as a 1-bit I/O port. P90 can be set to input or output in 1-bit units using port mode register 9 (PM9).
(2) Control mode
P90 function as A/D converter analog input pins (ANI8). When using these pins as analog input pins, see (5)
P80/ANI0 to P87/ANI7, P90/ANI8 in 12.6 Cautions for A/D Converter.
Cautions 1. P80/ANI0 to P87/ANI7 is set in the analog input mode after release of reset.
2. P90 is
μ
PD78F0884, 78F0885, and 78F0886 only.
2.2.9 P120 to P124 (port 12)
P120 to P124 function as a 5-bit I/O port. These pins also function as pins for external interrupt request input,
external clock input for main system clock, external clock input for subsystem clock and potential input for external
low-voltage detection. The following operation modes can be specified in 1-bit units.
(1) Port mode
P120 to P124 function as a 5-bit I/O port. P120 to P124 can be set to input or output using port mode register 12
(PM12). Only for P120, use of an on-chip pull-up resistor can be specified by pull-up resistor option register 12
(PU12).
(2) Control mode
P120 to P124 function as pins for external interrupt request input, potential input for external low-voltage
detection, resonator connection for main system clock, resonator connection for subsystem clock, external clock
input for main system clock and external clock input for subsystem clock.
(a) INTP0
This functions as an external interrupt request input for which the valid edge (rising edge, falling edge, or
both rising and falling edges) can be specified.
(b) EXLVI
This is a potential input pin for external low-voltage detection.
(c) X1, X2
These are the pins for connecting a resonator for high-speed system clock.
When supplying an external clock, input a signal to the X1 pin and input the inverse signal to the X2 pin.
Caution Connect P121/X1 as follows when writing the flash memory with a flash programmer.
- P121/X1: When using this pin as a port, connect it to V
SS via a resistor (10 kΩ:
recommended) (in the input mode) or leave it open (in the output mode).
The above connection is not necessary when writing the flash memory by means of self
programming.
Remark The X1 and X2 pins can be used as on-chip debug mode setting pins when the on-chip debug
function is used. For details, refer to CHAPTER 24 ON-CHIP DEBUG FUNCTION.
36
User’s Manual U17555EJ4V0UD
Page 37

CHAPTER 2 PIN FUNCTIONS
(d) EXCLK
This is an external clock input pin for main system clock.
(e) XT1, XT2
These are the pins for connecting a resonator for subsystem clock.
When supplying an external clock, input a signal to the XT1 pin and input the inverse signal to the XT2 pin.
(f) EXCLKS
This is an external clock input pin for subsystem clock.
2.2.10 P130, P131 (port 13)
P130 functions as a 1-bit output-only port. P131 function as a 1-bit I/O port. P131 can be set to input or output in
1-bit units using port mode register 13 (PM13). Use of an on-chip pull-up resistor can be specified by pull-up resistor
option register 13 (PU13).
Caution P131 is
μ
PD78F0884, 78F0885, and 78F0886 only.
2.2.11 AV
REF
This is the A/D converter reference voltage input pin.
When the A/D converter is not used, connect this pin directly to EV
DD or VDD
Note
.
Note Connect port 8 and port 9 directly to EVDD when it is used as a digital port.
2.2.12 AVSS
This is the A/D converter ground potential pin. Even when the A/D converter is not used, always use this pin with
the same potential as the EV
SS pin or VSS pin.
2.2.13 RESET
This is the active-low system reset input pin.
2.2.14 REGC
This is the pin for connecting regulator output (2.5 V) stabilization capacitance for internal operation. Connect this
pin to V
SS via a capacitor (0.47 to 1 µF: recommended).
REGC
SS
V
Caution Keep the wiring length as short as possible for the broken-line part in the above figure.
2.2.15 V
DD and EVDD
DD is the positive power supply pin for other than ports.
V
EVDD is the positive power supply pin for ports.
2.2.16 V
SS and EVSS
SS is the ground potential pin for other than ports.
V
SS is the ground potential pin for ports.
EV
User’s Manual U17555EJ4V0UD
37
Page 38

CHAPTER 2 PIN FUNCTIONS
2.2.17 FLMD0
This is a pin for setting flash memory programming mode.
Connect to EV
SS or VSS in the normal operation mode. In flash memory programming mode, be sure to connect
this pin to the flash programmer.
38
User’s Manual U17555EJ4V0UD
Page 39

CHAPTER 2 PIN FUNCTIONS
2.3 Pin I/O Circuits and Recommended Connection of Unused Pins
Table 2-4 shows the types of pin I/O circuits and the recommended connections of unused pins.
Refer to Figure 2-1 for the configuration of the I/O circuit of each type.
Table 2-4. Pin I/O Circuit Types (1/2)
Pin Name I/O Circuit
I/O Recommended Connection of Unused Pins
Type
P00/TI000
P01/TI010/TO00
P06/TI011/TO01
Note 1
5-AH
I/O
Input: Independently connect to EV
EV
Output: Leave open.
P10/SCK10/TxD61
P11/SI10/RxD61
P12/SO10
5-H
P13/TxD60
P14/RxD60 5-AH
P15/TOH0 5-H
P16/TOH1/INTP5
5-AH
P17/TI50/TO50
P30/INTP1
P31/INTP2
Note 2
P32/INTP3
P33/TI51/TO51/INTP4
P40, P41 5-H
P60 to P63
Note 1
13-P Input: Connect to EVSS.
Output: Leave this pin open at low-level
output after clearing the output latch of the
port to 0.
DD or
SS via a resistor.
P70/CTxD 5-H
P71/CRxD
5-AH
P72/PCL/INTP6
Input: Independently connect to EV
SS via a resistor.
EV
Output: Leave open.
DD or
P73/BUZ/INTP7
P80/ANI0 to P87/ANI7
P90/ANI8
Note 1
Note 3
11-G I/O
<Analog setting>
Connect to AV
REF or AVSS.
<Digital setting>
Input: Independently connect to EV
SS via a resistor.
EV
DD or
Output: Leave open.
Notes 1. P06, P63 and P90 are μPD78F0884, 78F0885, and 78F0886 only.
2. Connect P31/INTP2 as follows when writing the flash memory with a flash
programmer.
- P31/INTP2: Connect to EV
SS via a resistor (10 kΩ: recommended).
The above connection is not necessary when writing the flash memory by means
of self programming.
3. P80/ANI0 to P87/ANI7 and P90/ANI8 is set in the analog input mode after release
of reset.
User’s Manual U17555EJ4V0UD
39
Page 40

CHAPTER 2 PIN FUNCTIONS
Table 2-4. Pin I/O Circuit Types (2/2)
Pin Name I/O Circuit
I/O Recommended Connection of Unused Pins
Type
P120/INTP0/EXLVI 5-AH I/O Input: Independently connect to EVDD or
EV
SS via a resistor.
Output: Leave open.
P121/X1
P122/X2/EXCLK
P123/XT1
Note 1, 2
Note 1
Note 1
P124/XT2/EXCLKS
Note 1
37 I/O Input: Independently connect to EV
EV
SS via a resistor.
Output: Leave open.
DD or
P130 3-C Output Leave open.
Note 3
P131
5-AH I/O Input: Independently connect to EVDD or
EV
SS via a resistor.
Output: Leave open.
RESET 2 Input Connect to EVDD or VDD.
AVREF Connect directly to EVDD or VDD
− −
Note 4
.
AVSS Connect directly to EVSS or VSS.
FLMD0
Connect to EVSS or VSS.
Notes 1. Use the recommended connection above in I/O port mode (see Figure 5-6 Format
of Clock Operation Mode Select Register (OSCCTL)) when these pins are not
used.
2. Connect P121/X1 as follows when writing the flash memory with a flash
programmer.
- P121/X1: When using this pin as a port, connect it to V
SS via a resistor (10 kΩ:
recommended) (in the input mode) or leave it open (in the output mode).
The above connection is not necessary when writing the flash memory by means
of self programming.
3. P131 is
μ
PD78F0884, 78F0885, and 78F0886 only.
4. Connect port 8 directly to EVDD when it is used as a digital port.
40
User’s Manual U17555EJ4V0UD
Page 41

CHAPTER 2 PIN FUNCTIONS
Figure 2-1. Pin I/O Circuit List (1/2)
Type 2
Type 5-H
EV
DD
IN
Schmitt-triggered input with hysteresis characteristics
Type 3-C
EV
DD
P-ch
Data
OUT
N-ch
Vss
Pullup
enable
Output
data
Output
disable
Input
enable
Type 11-G
Data
Output
disable
Comparator
(threshold voltage)
+
_
AV
REF
AV
P-ch
DD
EV
P-ch
IN/OUT
N-ch
EVss
REF
AV
P-ch
IN/OUT
N-ch
AV
SS
P-ch
N-ch
SS
Type 5-AH
Pull-up
enable
Data
Output
disable
Input
enable
EV
EV
DD
P-ch
N
SS
-ch
EV
DD
P-ch
IN/OUT
Input enable
Type 13-P
Data
Output disable
input enable
IN/OUT
N-ch
EVss
User’s Manual U17555EJ4V0UD
41
Page 42

Type 37
Reset
Data
Output
disable
Input
enable
Reset
Data
Output
disable
Input
enable
EV
EVSS
EV
EVSS
DD
P-ch
N
DD
P-ch
N
-ch
CHAPTER 2 PIN FUNCTIONS
Figure 2-1. Pin I/O Circuit List (2/2)
X2,
-ch
N-ch
P-ch
XT2
X1,
XT1
42
User’s Manual U17555EJ4V0UD
Page 43

CHAPTER 3 CPU ARCHITECTURE
3.1 Memory Space
Products in the 78K0/FC2 can each access a 64 KB memory space. Figures 3-1 to 3-3 show the memory map.
Caution Regardless of the internal memory capacity, the initial values of the internal memory size
switching register (IMS) and internal expansion RAM size switching register (IXS) of the
78K0/FC2 is fixed (IMS = CFH, IXS = 0CH). Therefore, set the value corresponding to each
product as indicated below.
Table 3-1. Set Values of Internal Memory Size Switching Register (IMS)
and Internal Expansion RAM Size Switching Register (IXS)
Flash Memory Version IMS IXS
μ
PD78F0881, 78F0884
μ
PD78F0882, 78F0885
μ
PD78F0883, 78F0886
C8H 0AH
CCH 08H
CFH 08H
User’s Manual U17555EJ4V0UD
43
Page 44

CHAPTER 3 CPU ARCHITECTURE
Figure 3-1. Memory Map (μPD78F0881, 78F0884)
Data memory
space
RAM space in
which instruction
can be fetched
Program
memory space
FFFFH
FF00H
FEFFH
FEE0H
FEDFH
FB00H
FAFFH
FA00H
F9FFH
F800H
F7FFH
F400H
F3FFH
8000H
7FFFH
0190H
018FH
0083H
0082H
0000H
Special function registers
(SFR)
256 × 8 bits
General-purpose
registers
32 × 8 bits
Internal high-speed RAM
1024 × 8 bits
Note 1
AFCAN area
(256 × 8 bits)
Reserved
Internal expansion RAM
1024 × 8 bits
Reserved
Flash memory
32768 × 8 bits
Note 2
FF20H
FF1FH
FE20H
FE1FH
FE10H
FE0FH
Short direct
addressing
7FFFH
1085H
1084H
1080H
107FH
1000H
0FFFH
0800H
07FFH
0085H
0084H
0080H
007FH
0040H
003FH
0000H
Program area
Option byte area
5 × 8 bits
Program area
CALLF entry area
2048 × 8 bits
Program area
1915 × 8 bits
Option byte area
5 × 8 bits
CALLT table area
64 × 8 bits
Vector table area
64 × 8 bits
Note 3
Note 3
1FFFH
Boot cluster 1
Boot cluster 0
Notes 1. During on-chip debugging, use of this area is disabled since it is used as the user data backup area for
communication.
2. During on-chip debugging, use of this area is disabled since it is used as the communication command
area (269 bytes).
3. When boot swap is not used: Set the option bytes to 0080H to 0084H.
When boot swap is used: Set the option bytes to 0080H to 0084H and 1080H to 1084H.
4. Writing boot cluster 0 can be prohibited depending on the setting of security (see 23.8 Security
Setting).
Remark The flash memory is divided into blocks (one block = 1 KB). For the address values and block numbers,
see Table 3-2 Correspondence Between Address Values and Block Numbers in Flash Memory.
7FFFH
EC00H
EBFFH
Block 1FH
Note 4
44
07FFH
0400H
03FFH
0000H
Block 01H
Block 00H
User’s Manual U17555EJ4V0UD
1 KB
Page 45

CHAPTER 3 CPU ARCHITECTURE
Figure 3-2. Memory Map (μPD78F0882, 78F0884)
Data memory
space
RAM space in
which instruction
can be fetched
Program
memory space
FFFFH
FF00H
FEFFH
FEE0H
FEDFH
FB00H
FAFFH
FA00H
F9FFH
F800H
F7FFH
F000H
EFFFH
C000H
BFFFH
0190H
018FH
0083H
0082H
0000H
Special function registers
(SFR)
256 × 8 bits
General-purpose
registers
32 × 8 bits
Internal high-speed RAM
1024 × 8 bits
Note 1
AFCAN area
(256 × 8 bits)
Reserved
Internal expansion RAM
2048 × 8 bits
Reserved
Flash memory
49152 × 8 bits
Note 2
FF20H
FF1FH
FE20H
FE1FH
FE10H
FE0FH
Short direct
addressing
BFFFH
1085H
1084H
1080H
107FH
1000H
0FFFH
0800H
07FFH
0085H
0084H
0080H
007FH
0040H
003FH
0000H
Program area
Option byte area
5 × 8 bits
Program area
CALLF entry area
2048 × 8 bits
Program area
1915 × 8 bits
Option byte area
5 × 8 bits
CALLT table area
64 × 8 bits
Vector table area
64 × 8 bits
Note 3
Note 3
1FFFH
Boot cluster 1
Boot cluster 0
Notes 1. During on-chip debugging, use of this area is disabled since it is used as the user data backup area for
communication.
2. During on-chip debugging, use of this area is disabled since it is used as the communication command
area (269 byte).
3. When boot swap is not used: Set the option bytes to 0080H to 0084H.
When boot swap is used: Set the option bytes to 0080H to 0084H and 1080H to 1084H.
4. Writing boot cluster 0 can be prohibited depending on the setting of security (see 23.8 Security
Setting).
Remark The flash memory is divided into blocks (one block = 1 KB). For the address values and block numbers,
see Table 3-2 Correspondence Between Address Values and Block Numbers in Flash Memory.
BFFFH
EC00H
EBFFH
Block 2FH
Note 4
07FFH
0400H
03FFH
0000H
Block 01H
Block 00H
User’s Manual U17555EJ4V0UD
1 KB
45
Page 46

CHAPTER 3 CPU ARCHITECTURE
Figure 3-3. Memory Map (μPD78F0883, 78F0886)
Data memory
space
RAM space in
which instruction
can be fetched
Program
memory space
FFFFH
FF00H
FEFFH
FEE0H
FEDFH
FB00H
FAFFH
FA00H
F9FFH
F800H
F7FFH
F000H
EFFFH
0190H
018FH
0083H
0082H
0000H
Special function registers
(SFR)
256 × 8 bits
General-purpose
registers
32 × 8 bits
Internal high-speed RAM
1024 × 8 bits
Note 1
AFCAN area
(256 × 8 bits)
Reserved
Internal expansion RAM
2048 × 8 bits
Flash memory
61440 × 8 bits
Note 2
FF20H
FF1FH
FE20H
FE1FH
FE10H
FE0FH
Short direct
addressing
EFFFH
1085H
1084H
1080H
107FH
1000H
0FFFH
0800H
07FFH
0085H
0084H
0080H
007FH
0040H
003FH
0000H
Program area
Option byte area
5 × 8 bits
Program area
CALLF entry area
2048 × 8 bits
Program area
1915 × 8 bits
Option byte area
5 × 8 bits
CALLT table area
64 × 8 bits
Vector table area
64 × 8 bits
Note 3
Note 3
1FFFH
Boot cluster 1
Boot cluster 0
Notes 1. During on-chip debugging, use of this area is disabled since it is used as the user data backup area for
communication.
2. During on-chip debugging, use of this area is disabled since it is used as the communication command
area (269 bytes).
3. When boot swap is not used: Set the option bytes to 0080H to 0084H.
When boot swap is used: Set the option bytes to 0080H to 0084H and 1080H to 1084H.
4. Writing boot cluster 0 can be prohibited depending on the setting of security (see 23.8 Security
Setting).
Remark The flash memory is divided into blocks (one block = 1 KB). For the address values and block numbers,
see Table 3-2 Correspondence Between Address Values and Block Numbers in Flash Memory.
EFFFH
EC00H
EBFFH
Block 3BH
Note 4
46
07FFH
0400H
03FFH
0000H
Block 01H
Block 00H
User’s Manual U17555EJ4V0UD
1 KB
Page 47

CHAPTER 3 CPU ARCHITECTURE
Correspondence between the address values and block numbers in the flash memory are shown below.
Table 3-2. Correspondence Between Address Values and Block Numbers in Flash Memory
(1)
μ
PD78F0881, 78F0882, 78F0883, 78F0884, 78F0885, 78F0886
Address Value
0000H to 03FFH 00H 4000H to 43FFH 10H 8000H to 83FFH 20H C000H to C3FFH 30H
0400H to 07FFH 01H 4400H to 47FFH 11H 8400H to 87FFH 21H C400H to C7FFH 31H
0800H to 0BFFH 02H 4800H to 4BFFH 12H 8800H to 8BFFH 22H C800H to CBFFH 32H
0C00H to 0FFFH 03H 4C00H to 4FFFH 13H 8C00H to 8FFFH 23H CC00H to CFFFH 33H
1000H to 13FFH 04H 5000H to 53FFH 14H 9000H to 93FFH 24H D000H to D3FFH 34H
1400H to 17FFH 05H 5400H to 57FFH 15H 9400H to 97FFH 25H D400H to D7FFH 35H
1800H to 1BFFH 06H 5800H to 5BFFH 16H 9800H to 9BFFH 26H D800H to DBFFH 36H
1C00H to 1FFFH 07H 5C00H to 5FFFH 17H 9C00H to 9FFFH 27H DC00H to DFFFH 37H
2000H to 23FFH 08H 6000H to 63FFH 18H A000H to A3FFH 28H E000H to E3FFH 38H
2400H to 27FFH 09H 6400H to 67FFH 19H A400H to A7FFH 29H E400H to E7FFH 39H
2800H to 2BFFH 0AH 6800H to 6BFFH 1AH A800H to ABFFH 2AH E800H to EBFFH 3AH
2C00H to 2FFFH 0BH 6C00H to 6FFFH 1BH AC00H to AFFFH 2BH EC00H to EFFFH 3BH
3000H to 33FFH 0CH 7000H to 73FFH 1CH B000H to B3FFH 2CH
3400H to 37FFH 0DH 7400H to 77FFH 1DH B400H to B7FFH 2DH
3800H to 3BFFH 0EH 7800H to 7BFFH 1EH B800H to BBFFH 2EH
3C00H to 3FFFH 0FH 7C00H to 7FFFH 1FH BC00H to BFFFH 2FH
Block
Number
Address Value
Block
Number
Address Value
Block
Number
Address Value
Remark μPD78F0881, 78F0884: Block numbers 00H to 1FH
μ
PD78F0882, 78F0885: Block numbers 00H to 2FH
μ
PD78F0883, 78F0886: Block numbers 00H to 3BH
Block
Number
User’s Manual U17555EJ4V0UD
47
Page 48

CHAPTER 3 CPU ARCHITECTURE
3.1.1 Internal program memory space
The internal program memory space stores the program and table data. Normally, it is addressed with the program
counter (PC).
78K0/FC2 products incorporate internal ROM (flash memory), as shown below.
Table 3-3. Internal ROM Capacity
Internal ROM Part Number
Structure Capacity
μ
PD78F0881, 78F0884
μ
PD78F0882, 78F0885 49152 × 8 bits (0000H to BFFFH)
μ
PD78F0893, 78F0886
Flash memory
32768 × 8 bits (0000H to 7FFFH)
61440 × 8 bits (0000H to EFFFH)
The internal program memory space is divided into the following areas.
(1) Vector code area
The 64-byte area 0000H to 003FH is reserved as a Vector code area. The program start addresses for branch
upon reset signal input or generation of each interrupt request are stored in the Vector code area.
Of the 16-bit address, the lower 8 bits are stored at even addresses and the higher 8 bits are stored at odd
addresses.
Table 3-4. Vector Code
Vector Code Address Interrupt Source Vector Code Address Interrupt Source
RESET input, POC, LVI,
WDT
0004H INTLVI 0024H INTP7/INTST61
0006H INTP0 0026H INTTMH1
0008H INTP1 0028H INTTMH0
000AH INTP2 002AH INTTM50
000CH INTP3 002CH INTTM000
000EH INTP4 002EH INTTM010
0010H INTP5 0030H INTAD
0012H INTC0ERR 0032H INTWTI/INTDMU
0014H INTC0WUP 0034H INTTM51
0016H INTC0REC 0036H INTWT
0018H INTC0TRX 003AH INTTM001
001AH INTSRE60 003CH INTTM011
001CH INTSR60 003EH BRK
001EH INTST60
0020H INTCSI10/INTSRE61 0000H
0022H INTP6/INTSR61
(2) CALLT instruction table area
The 64-byte area 0040H to 007FH can store the subroutine entry address of a 1-byte call instruction (CALLT).
(3) Option byte area
The option byte area is assigned to the 1-byte area of 0080H. Refer to CHAPTER 22 OPTION BYTE for details.
48
User’s Manual U17555EJ4V0UD
Page 49

CHAPTER 3 CPU ARCHITECTURE
(4) CALLF instruction entry area
The area 0800H to 0FFFH can perform a direct subroutine call with a 2-byte call instruction (CALLF).
(5) On-chip debug security ID setting area
A 10-byte area of 0085H to 008EH and 1085H to 108EH can be used as an on-chip debug security ID setting
area. Set the on-chip debug security ID of 10 bytes at 0085H to 008EH when the boot swap is not used and at
0085H to 008EH and 1085H to 108EH when the boot swap is used. For details, see CHAPTER 24 ON-CHIP
DEBUG FUNCTION.
3.1.2 Internal data memory space
78K0/FC2 products incorporate the following RAM.
(1) Internal high-speed RAM
Table 3-5. Internal High-Speed RAM Capacity
Part Number Internal High-Speed RAM
μ
PD78F0881, 78F0884
μ
PD78F0882, 78F0885
μ
PD78F0883, 78F0886
1024 × 8 bits (FB00H to FEFFH)
The 32-byte area FEE0H to FEFFH is assigned to four general-purpose register banks consisting of eight 8-bit
registers per one bank.
This area cannot be used as a program area in which instructions are written and executed.
The internal high-speed RAM can also be used as a stack memory.
(2) Internal expansion RAM
Table 3-6. Internal Expansion RAM Capacity
Part Number Internal Expansion RAM
μ
PD78F0881, 78F0884 1024 × 8 bits (F400H to F7FFH)
μ
PD78F0882, 78F0885 2048 × 8 bits (F000H to F7FFH)
μ
PD78F0883, 78F0886
The internal expansion RAM can also be used as a normal data area similar to the internal high-speed RAM, as
well as a program area in which instructions can be written and executed.
The internal expansion RAM cannot be used as a stack memory.
3.1.3 Special function register (SFR) area
On-chip peripheral hardware special function registers (SFRs) are allocated in the area FF00H to FFFFH (refer to
Table 3-7 Special Function Register List in 3.2.3 Special Function Registers (SFRs)).
Caution Do not access addresses to which SFRs are not assigned.
User’s Manual U17555EJ4V0UD
49
Page 50

CHAPTER 3 CPU ARCHITECTURE
3.1.4 Data memory addressing
Addressing refers to the method of specifying the address of the instruction to be executed next or the address of
the register or memory relevant to the execution of instructions.
Several addressing modes are provided for addressing the memory relevant to the execution of instructions for the
78K0/FC2, based on operability and other considerations. For areas containing data memory in particular, special
addressing methods designed for the functions of special function registers (SFR) and general-purpose registers are
available for use. Figure 3-4 to 3-6 show correspondence between data memory and addressing. For details of each
addressing mode, refer to 3.4 Operand Address Addressing.
50
User’s Manual U17555EJ4V0UD
Page 51

CHAPTER 3 CPU ARCHITECTURE
Figure 3-4. Correspondence Between Data Memory and Addressing (μPD78F0881, μPD78F0884)
FFFFH
FF00H
FEFFH
FEE0H
FEDFH
FB00H
FAFFH
FA00H
F9FFH
F800H
F7FFH
Special function registers (SFR)
256 × 8 bits
General-purpose registers
32 × 8 bits
Internal high-speed RAM
1024 × 8 bits
Note 1
AFCAN area
(256 × 8 bits)
Reserved
Internal expansion RAM
1024 × 8 bits
SFR addressing
FF20H
FF1FH
Register addressing
FE20H
FE1FH
FE10H
FE0FH
Short direct
addressing
Direct addressing
Register indirect addressing
Based addressing
Based indexed addressing
F400H
F3FFH
Reserved
8000H
7FFFH
0190H
018FH
0083H
0082H
0000H
Flash memory
32768 × 8 bits
Note 2
Notes 1. During on-chip debugging, use of this area is disabled since it is used as the user data backup area for
communication.
2. During on-chip debugging, use of this area is disabled since it is used as the communication command
area (269 bytes).
User’s Manual U17555EJ4V0UD
51
Page 52

CHAPTER 3 CPU ARCHITECTURE
Figure 3-5. Correspondence Between Data Memory and Addressing (μPD78F0882, 78F0885)
FFFFH
FF00H
FEFFH
FEE0H
FEDFH
FB00H
FAFFH
FA00H
F9FFH
F800H
F7FFH
Special function registers (SFR)
256 × 8 bits
General-purpose registers
32 × 8 bits
Internal high-speed RAM
1024 × 8 bits
Note 1
AFCAN area
(256 × 8 bits)
Reserved
Internal expansion RAM
2048 × 8 bits
SFR addressing
FF20H
FF1FH
Register addressing
FE20H
FE1FH
FE10H
FE0FH
Short direct
addressing
Direct addressing
Register indirect addressing
Based addressing
Based indexed addressing
F000H
EFFFH
Reserved
C000H
BFFFH
Flash memory
49152 × 8 bits
0190H
018FH
0083H
0082H
0000H
Note 2
Notes 1. During on-chip debugging, use of this area is disabled since it is used as the user data backup area for
communication.
2. During on-chip debugging, use of this area is disabled since it is used as the communication command
area (269 bytes).
52
User’s Manual U17555EJ4V0UD
Page 53

FFFFH
CHAPTER 3 CPU ARCHITECTURE
Figure 3-6. Correspondence Between Data Memory and Addressing (μPD78F0883, 78F0886)
FF00H
FEFFH
FEE0H
FEDFH
FB00H
FAFFH
FA00H
F9FFH
F800H
F7FFH
Special function registers (SFR)
256 × 8 bits
General-purpose registers
32 × 8 bits
Internal high-speed RAM
1024 × 8 bits
Note 1
AFCAN area
(256 × 8 bits)
Reserved
Internal expansion RAM
2048 × 8 bits
SFR addressing
FF20H
FF1FH
Register addressing
FE20H
FE1FH
FE10H
FE0FH
Short direct
addressing
Direct addressing
Register indirect addressing
Based addressing
Based indexed addressing
F000H
EFFFH
Flash memory
61440 × 8 bits
0190H
018FH
0083H
0082H
0000H
Note 2
Notes 1. During on-chip debugging, use of this area is disabled since it is used as the user data backup area for
communication.
2. During on-chip debugging, use of this area is disabled since it is used as the communication command
area (269 bytes).
User’s Manual U17555EJ4V0UD
53
Page 54

CHAPTER 3 CPU ARCHITECTURE
3.2 Processor Registers
78K0/FC2 products incorporate the following processor registers.
3.2.1 Control registers
The control registers control the program sequence, statuses and stack memory. The control registers consist of a
program counter (PC), a program status word (PSW) and a stack pointer (SP).
(1) Program counter (PC)
The program counter is a 16-bit register that holds the address information of the next program to be executed.
In normal operation, the PC is automatically incremented according to the number of bytes of the instruction to be
fetched. When a branch instruction is executed, immediate data and register contents are set.
Reset signal generation sets the reset Vector code values at addresses 0000H and 0001H to the program
counter.
Figure 3-7. Format of Program Counter
15 0
PC PC15 PC14 PC13 PC12 PC11 PC10 PC9 PC8 PC7 PC6 PC5 PC4 PC3 PC2 PC1 PC0
(2) Program status word (PSW)
The program status word is an 8-bit register consisting of various flags set/reset by instruction execution.
Program status word contents are automatically stacked upon interrupt request generation or PUSH PSW
instruction execution and are restored upon execution of the RETB, RETI and POP PSW instructions.
Reset signal generation sets the PSW to 02H.
Figure 3-8. Format of Program Status Word
7 0
PSW IE Z RBS1 AC RBS0 0 ISP CY
(a) Interrupt enable flag (IE)
This flag controls the interrupt request acknowledge operations of the CPU.
When 0, the IE flag is set to the interrupt disabled (DI) state, and all maskable interrupt requests are disabled.
Other interrupt requests are all disabled.
When 1, the IE flag is set to the interrupt enabled (EI) state and interrupt request acknowledgement is
controlled with an in-service priority flag (ISP), an interrupt mask flag for various interrupt sources, and a
priority specification flag.
The IE flag is reset (0) upon DI instruction execution or interrupt acknowledgement and is set (1) upon EI
instruction execution.
(b) Zero flag (Z)
When the operation result is zero, this flag is set (1). It is reset (0) in all other cases.
(c) Register bank select flags (RBS0 and RBS1)
These are 2-bit flags to select one of the four register banks.
In these flags, the 2-bit information that indicates the register bank selected by SEL RBn instruction
execution is stored.
54
User’s Manual U17555EJ4V0UD
Page 55

CHAPTER 3 CPU ARCHITECTURE
(d) Auxiliary carry flag (AC)
If the operation result has a carry from bit 3 or a borrow at bit 3, this flag is set (1). It is reset (0) in all other
cases.
(e) In-service priority flag (ISP)
This flag manages the priority of acknowledgeable maskable vectored interrupts. When this flag is 0, low-
level vectored interrupt requests specified by a priority specification flag register (PR0L, PR0H, PR1L, PR1H)
(refer to 16.3 (3) Priority specification flag registers (PR0L, PR0H, PR1L, PR1H)) can not be
acknowledged. Actual request acknowledgement is controlled by the interrupt enable flag (IE).
(f) Carry flag (CY)
This flag stores overflow and underflow upon add/subtract instruction execution. It stores the shift-out value
upon rotate instruction execution and functions as a bit accumulator during bit operation instruction execution.
(3) Stack pointer (SP)
This is a 16-bit register to hold the start address of the memory stack area. Only the internal high-speed RAM
area can be set as the stack area.
Figure 3-9 Format of Stack Pointer
15 0
SP SP15 SP14 SP13 SP12 SP11 SP10 SP9 SP8 SP7 SP6 SP5 SP4 SP3 SP2 SP1 SP0
The SP is decremented ahead of write (save) to the stack memory and is incremented after read (restored) from
the stack memory.
Each stack operation saves/restores data as shown in Figures 3-10 and 3-11.
Caution Since reset signal generation makes the SP contents undefined, be sure to initialize the SP
before using the stack.
User’s Manual U17555EJ4V0UD
55
Page 56
CHAPTER 3 CPU ARCHITECTURE
Figure 3-10. Data to Be Saved to Stack Memory
(a) PUSH rp instruction (when SP = FEE0H)
SP
SP
FEE0H
FEDEH
FEE0H
FEDFH
FEDEH
Register pair higher
Register pair lower
(b) CALL, CALLF, CALLT instructions (when SP = FEE0H)
SP
SP
FEE0H
FEDEH
FEE0H
FEDFH
FEDEH
PC15 to PC8
PC7 to PC0
(c) Interrupt, BRK instructions (when SP = FEE0H)
SP
FEE0H
FEE0H
SP
FEDDH
FEDFH
FEDEH
FEDDH
PSW
PC15 to PC8
PC7 to PC0
56
User’s Manual U17555EJ4V0UD
Page 57

CHAPTER 3 CPU ARCHITECTURE
Figure 3-11. Data to Be Restored from Stack Memory
(a) POP rp instruction (when SP = FEDEH)
SP
SP
FEE0H
FEDEH
FEE0H
FEDFH
FEDEH
Register pair higher
Register pair lower
(b) RET instruction (when SP = FEDEH)
SP
SP
FEE0H
FEDEH
FEE0H
FEDFH
FEDEH
PC15 to PC8
PC7 to PC0
(c) RETI, RETB instructions (when SP = FEDDH)
SP
FEE0H
FEE0H
SP
FEDDH
FEDFH
FEDEH
FEDDH
PSW
PC15 to PC8
PC7 to PC0
User’s Manual U17555EJ4V0UD
57
Page 58

CHAPTER 3 CPU ARCHITECTURE
3.2.2 General-purpose registers
General-purpose registers are mapped at particular addresses (FEE0H to FEFFH) of the data memory. The
general-purpose registers consists of 4 banks, each bank consisting of eight 8-bit registers (X, A, C, B, E, D, L, and H).
Each register can be used as an 8-bit register, and two 8-bit registers can also be used in a pair as a 16-bit register
(AX, BC, DE, and HL).
These registers can be described in terms of function names (X, A, C, B, E, D, L, H, AX, BC, DE, and HL) and
absolute names (R0 to R7 and RP0 to RP3).
Register banks to be used for instruction execution are set by the CPU control instruction (SEL RBn). Because of
the 4-register bank configuration, an efficient program can be created by switching between a register for normal
processing and a register for interrupts for each bank.
Figure 3-12. Configuration of General-Purpose Registers
(a) Absolute name
16-bit processing 8-bit processing
FEFFH
FEF8H
FEF0H
FEE8H
FEE0H
BANK0
BANK1
BANK2
BANK3
RP3
RP2
RP1
RP0
15 0 7 0
R7
R6
R5
R4
R3
R2
R1
R0
(b) Function name
16-bit processing 8-bit processing
FEFFH
FEF8H
FEF0H
FEE8H
FEE0H
BANK0
BANK1
BANK2
BANK3
HL
DE
BC
AX
15 0 7 0
H
L
D
E
B
C
A
X
58
User’s Manual U17555EJ4V0UD
Page 59

CHAPTER 3 CPU ARCHITECTURE
3.2.3 Special Function Registers (SFRs)
Unlike a general-purpose register, each special function register has a special function.
SFRs are allocated to the FF00H to FFFFH area.
Special function registers can be manipulated like general-purpose registers, using operation, transfer and bit
manipulation instructions. The manipulatable bit units, 1, 8, and 16, depend on the special function register type.
Each manipulation bit unit can be specified as follows.
• 1-bit manipulation
Describe the symbol reserved by the assembler for the 1-bit manipulation instruction operand (sfr.bit).
This manipulation can also be specified with an address.
• 8-bit manipulation
Describe the symbol reserved by the assembler for the 8-bit manipulation instruction operand (sfr).
This manipulation can also be specified with an address.
• 16-bit manipulation
Describe the symbol reserved by the assembler for the 16-bit manipulation instruction operand (sfrp).
When specifying an address, describe an even address.
Table 3-7 gives a list of the special function registers. The meanings of items in the table are as follows.
• Symbol
Symbol indicating the address of a special function register. It is a reserved word in the RA78K0, and is defined
by the header file “sfrbit.h” in the CC78K0. When using the RA78K0, ID78K0-NS, ID78K0, or SM78K0, symbols
can be written as an instruction operand.
• R/W
Indicates whether the corresponding special function register can be read or written.
R/W: Read/write enable
R: Read only
W: Write only
• Manipulatable bit units
Indicates the manipulatable bit unit (1, 8, or 16). “−” indicates a bit unit for which manipulation is not possible.
• After reset
Indicates each register status upon reset signal generation.
User’s Manual U17555EJ4V0UD
59
Page 60

CHAPTER 3 CPU ARCHITECTURE
Table 3-7. Special Function Register List (1/5)
FF00H Port register 0 P0 R/W
FF01H Port register 1 P1 R/W
FF02H 8-bit timer H compare register 00 CMP00 R/W
FF03H Port register 3 P3 R/W
FF04H Port register 4 P4 R/W
FF06H Port register 6 P6 R/W
FF07H Port register 7 P7 R/W
FF08H Port register 8 P8 R/W
FF09H Port register 9 P9 R/W
FF0AH Receive buffer register 60 RXB60 R
FF0BH Transmit buffer register 60 TXB60 R/W
FF0CH Port register 12 P12 R/W
FF0DH Port register 13 P13 R/W
FF0EH 8-bit timer H compare register 10 CMP10 R/W
FF0FH Serial I/O shift register 10 SIO10 R
FF10H
16-bit timer counter 00 TM00 R
FF11H
FF12H
16-bit timer capture/compare register 000 CR000 R/W
FF13H
FF14H
16-bit timer capture/compare register 010 CR010 R/W
FF15H
FF16H 8-bit timer counter 50 TM50 R
FF17H 8-bit timer compare register 50 CR50 R/W
FF18H 10- bit A/D conversion result register ADCR R
FF19H 8-bit A/D conversion result register ADCRH R
FF1AH 8-bit timer H compare register 01 CMP01 R/W
FF1BH 8-bit timer H compare register 11 CMP11 R/W
FF1FH 8-bit timer counter 51 TM51 R
FF20H Port mode register 0 PM0 R/W
FF21H Port mode register 1 PM1 R/W
FF22H A/D port configuration register ADPC R/W
FF23H Port mode register 3 PM3 R/W
FF24H Port mode register 4 PM4 R/W
FF26H Port mode register 6 PM6 R/W
FF27H Port mode register 7 PM7 R/W
FF28H Port mode register 8 PM8 R/W
FF29H Port mode register 9
Note
PM9 R/W
FF2AH A/D converter mode register ADM R/W
FF2BH Analog input channel specification register ADS R/W
Note μPD78F0884, 78F0885, 78F0886 only.
Manipulatable Bit Unit Address Special Function Register (SFR) Name Symbol R/W
1 Bit 8 Bits 16 Bits
√ √ −
√ √ −
− √ −
√ √ −
√ √ −
√ √ −
√ √ −
√ √ −
√ √ −
− √ −
− √ −
√ √ −
√ √ −
− √ −
− √ −
− − √
− − √
− − √
− √ −
√ √ −
− − √
− √ −
− √ −
− √ −
− √ −
√ √ −
√ √ −
√ √ −
√ √ −
√ √ −
√ √ −
√ √ −
√ √ −
√ √ −
√ √ −
√ √ −
After
Reset
00H
00H
00H
00H
00H
00H
00H
00H
00H
FFH
FFH
00H
00H
00H
00H
0000H
0000H
0000H
00H
00H
0000H
00H
00H
00H
00H
FFH
FFH
00H
FFH
FFH
FFH
FFH
FFH
FFH
00H
00H
60
User’s Manual U17555EJ4V0UD
Page 61

CHAPTER 3 CPU ARCHITECTURE
Table 3-7. Special Function Register List (2/5)
After
Reset
FFH
FEH
01H
FF2CH Port mode register 12 PM12 R/W
FF2DH Port mode register 13 PM13 R/W
FF2EH
Asynchronous serial interface selection register
ASIM61 R/W
Manipulatable Bit Unit Address Special Function Register (SFR) Name Symbol R/W
1 Bit 8 Bits 16 Bits
√ √ −
√ √ −
√ √ −
61
FF2FH
Asynchronous serial interface reception error
ASIS61 R
− √ −
00H
status register 61
FF30H Pull-up resistor option register 0 PU0 R/W
FF31H Pull-up resistor option register 1 PU1 R/W
FF33H Pull-up resistor option register 3 PU3 R/W
FF34H Pull-up resistor option register 4 PU4 R/W
FF37H Pull-up resistor option register 7 PU7 R/W
FF38H
Asynchronous serial interface transmission
ASIF61 R
√ √ −
√ √ −
√ √ −
√ √ −
√ √ −
− √ −
00H
00H
00H
00H
00H
00H
status register 61
FF39H Clock selection register 61 CKSR61 R/W
FF3AH
Asynchronous serial interface Receive buffer
RXB61 R/W
− √ −
− √ −
00H
FFH
register 61
FF3BH
Asynchronous serial interface Transmit buffer
TXB61 R/W
− √ −
FFH
register 61
FF3CH Pull-up resistor option register 12 PU12 R/W
FF3DH Pull-up resistor option register 13
Note
PU13 R/W
FF3EH Baud rate generator control register 61 BRGC61 R/W
FF3FH Asynchronous serial interface control register 61 ASICL61 R/W
FF40H Clock output selection register CKS R/W
FF41H 8-bit timer compare register 51 CR51 R/W
FF42H Multiplier/divider control register 0 DMUC0 R/W
FF43H 8-bit timer mode control register 51 TMC51 R/W
FF44H
FF45H
Multiplier/divider data register 0 SDR0
SDR0L
SDR0H
R/W
FF48H External interrupt rising edge enable register EGP R/W
FF49H External interrupt falling edge enable register EGN R/W
FF4AH Multiplication/Division Data Register A0L MDA0L R/W
√ √ −
√ √ −
− √ −
√ √ −
√ √ −
√ √ −
√ √ −
√ √ −
− √ √
√ √ −
√ √ −
− √ √
00H
00H
FFH
16H
00H
00H
00H
00H
0000H
00H
00H
0000H
FF4BH
FF4CH Multiplication/Division Data Register A0H MDA0H R/W
− √ √
0000H
FF4DH
FF4FH Input switch control register ISC R/W
FF50H
Asynchronous serial interface operation mode
ASIM60 R/W
√ √ −
√ √ −
00H
01H
register 60
FF53H
Asynchronous serial interface reception error
ASIS60 R
− √ −
00H
status register 60
Note μPD78F0884, 78F0885, 78F0886 only.
User’s Manual U17555EJ4V0UD
61
Page 62

CHAPTER 3 CPU ARCHITECTURE
Table 3-7. Special Function Register List (3/5)
FF55H
FF56H Clock selection register 60 CKSR60 R/W
FF57H Baud rate generator control register 60 BRGC60 R/W
FF58H Asynchronous serial interface control register 60 ASICL60 R/W
FF60H
FF61H
FF62H
FF63H
FF64H
FF65H
FF66H
FF67H
FF68H Module Last Out Pointer Register C0LOPT R
FF69H 8-bit timer H mode register 0 TMHMD0 R/W
FF6AH Timer clock selection register 50 TCL50 R/W
FF6BH 8-bit timer mode control register 50 TMC50 R/W
FF6EH CAN Global Macro Clock Selection Register C0GMCS R/W
FF6FH
FF70H
FF71H
FF72H
FF73H
FF74H
FF75H
FF76H
FF77H
FF78H
FF79H
FF7AH
FF7BH
FF7CH
FF7DH
FF7EH
FF7FH
FF80H Serial operation mode register 10 CSIM10 R/W
FF81H Serial clock selection register 10 CSIC10 R/W
FF84H Transmit buffer register 10 SOTB10 R/W
Asynchronous serial interface transmission
status register 60
Module Receive History List Get Pointer
Register
Module Transmission History List Get Pointer
Register
CAN Global Macro Clock Selection C0GMCTRL R/W
CAN Global Macro Automatic Block
Transmission Delay Register
CAN Global Macro Automatic Block
Transmission Register
CAN Module Mask 1 Register L C0MASK1L R/W
CAN Module Mask 1 Register H C0MASK1H R/W
CAN Module Mask 2 Register L C0MASK2L R/W
CAN Module Mask 2 Register H C0MASK2H R/W
CAN Module Mask 3 Register L C0MASK3L R/W
CAN Module Mask 3 Register H C0MASK3H R/W
CAN Module Mask 4 Register L
CAN Module Mask 4 Register H C0MASK4H R/W
ASIF60 R
C0RGPT
C0TGPT R/W
C0GMABT R/W
C0GMABTD R/W
C0MASK4L R/W
R/W
Manipulatable Bit Unit Address Special Function Register (SFR) Name Symbol R/W
1 Bit 8 Bits 16 Bits
− √ −
− √ −
− √ −
√ √ −
− − √
− − √
− − √
− − √
− √ −
√ √ −
√ √ −
√ √ −
− √ −
− √ −
− − √
− − √
− − √
− − √
− − √
− − √
−
− − √
√ √ −
√ √ −
− √ −
−
After
Reset
00H
00H
FFH
16H
xx02H
xx02H
0000H
0000H
Undefined
00H
00H
00H
0FH
00H
Undefined
Undefined
Undefined
Undefined
Undefined
Undefined
Undefined
√
Undefined
00H
00H
00H
62
User’s Manual U17555EJ4V0UD
Page 63

CHAPTER 3 CPU ARCHITECTURE
Table 3-7. Special Function Register List (4/5)
Manipulatable Bit Unit Address Special Function Register (SFR) Name Symbol R/W
After Reset
1 Bit 8 Bits 16 Bits
FF8AH CAN module time stamp register C0TS R/W
− − √
0000H
FF8BH
FF8CH Timer clock selection register 51 TCL51 R/W
FF8FH Watch timer operation mode register WTM R/W
FF90H
CAN Module Control Register C0CTRL R/W
√ √ −
√ √ −
− − √
00H
00H
0000H
FF91H
FF92H CAN Module Last Error Code Register C0LEC R/W
FF93H CAN Module Information Register C0INFO R
FF94H
CAN Module Error Counters C0ERC R
− √ −
− √ −
− − √
00H
00H
0000H
FF95H
FF96H
CAN Module Interrupt Enable Register C0IE R/W
− − √
0000H
FF97H
FF98H
CAN Module Interrupt Pending Register C0INTS R/W
− − √
0000H
FF99H
FF9BH Watchdog timer enable register WDTE R/W
FF9CH
CAN Module Bit Rate Register C0BTR R/W
− √ −
− − √
1AH/9AH
Note1
370FH
FF9DH
FF9EH CAN Module bit rate Prescaler register C0BRP R/W
FF9FH CAN Module Last In Pointer Register C0LIPT R
FFA0H Internal oscillator mode register RCM R/W
FFA1H Main clock mode register MCM R/W
FFA2H Main OSC control register MOC R/W
FFA3H Oscillation stabilization time counter status register OSTC R
FFA4H Oscillation stabilization time select register OSTS R/W
FFACH Reset control flag register RESF R
FFAEH MDB0L
FFAFH
FFB0H
Multiplier/divider data register B0 MDB0
MDB0H
16-bit timer counter 01 TM01 R
R/W
− √ −
− √ −
√ √ −
√ √ −
√ √ −
√ √ −
√ √ −
− √ −
− √ √
− − √
FFH
Undefined
Note2
00H
00H
80H
00H
05H
Note3
00H
0000H
0000H
FFB1H
FFB2H 16-bit timer capture/compare register 001 CR001 R/W
− − √
0000H
FFB3H
FFB4H
16-bit timer capture/compare register 011 CR011 R/W
− − √
0000H
FFB5H
FFB6H 16-bit timer mode control register 01 TMC01 R/W
FFB7H Prescaler mode register 01 PRM01 R/W
FFB8H Capture/compare control register 01 CRC01 R/W
√ √ −
√ √ −
√ √ −
00H
00H
00H
Notes 1. The reset value of WDTE is determined by setting of option byte.
2. The value of this register is 00H immediately after a reset release but automatically changes to 80H after
internal high-speed oscillator oscillation has been stabilized.
3. This value varies depending on the reset source.
User’s Manual U17555EJ4V0UD
63
Page 64

CHAPTER 3 CPU ARCHITECTURE
Tables 3-7. Special Function Register List (5/5)
Manipulatable Bit Unit Address Special Function Register (SFR) Name Symbol R/W
After Reset
1 Bit 8 Bits 16 Bits
FFB9H 16-bit timer output control register 01 TOC01 R/W
FFBAH 16-bit timer mode control register 00 TMC00 R/W
FFBBH Prescaler mode register 00 PRM00 R/W
FFBCH Capture/compare control register 00 CRC00 R/W
FFBDH 16-bit timer output control register 00 TOC00 R/W
FFBEH Low-voltage detection register LVIM R/W
FFBFH Low-voltage detection level selection register LVIS R/W
FFC2H Flash status register PFS R/W
FFC4H Flash programming mode control register FLPMC R/W
FFE0H Interrupt request flag register 0L IF0 IF0L R/W
FFE1H Interrupt request flag register 0H IF0H R/W
FFE2H Interrupt request flag register 1L IF1 IF1L R/W
FFE3H Interrupt request flag register 1H IF1H R/W
FFE6H Interrupt mask flag register 1L MK1L R/W
FFE7H Interrupt mask flag register 1H
FFE8H Priority specification flag register 0L PR0L R/W
FFE9H Priority specification flag register 0H
FFEAH Priority specification flag register 1L PR1L R/W
FFEBH Priority specification flag register 1H
MK1
MK1H R/W
PR0
PR0H R/W
PR1
PR1H R/W
FFEEH 8-bit timer H carrier control register 1 TMCYC1 R/W
FFEFH Clock operation mode select register OSCCTL R/W
FFF0H Internal memory size switching register
FFF4H
Internal expansion RAM size switching
Note2
register
Note2
IMS R/W
IXS R/W
FFFAH 8-bit timer H mode register 1 TMHMD1 R/W
FFFBH Processor clock control register PCC R/W
√ √ −
√ √ −
√ √ −
√ √ −
√ √ −
√ √ −
√ √ −
√ √ −
√ √ −
√ √ √
√ √
√ √ √
√ √
√ √
√ √
√ √
√ √
√ √
√ √
√ √ −
√ √ −
− √ −
− √ −
√ √ −
√ √ −
00H
00H
√
√
√
00H
00H
00H
00H
00H
00H
00H
00H
08H/0CH
00H
00H
FFH
DFH
FFH
FFH
FFH
FFH
00H
00H
CFH
0CH
00H
01H
Note1
Notes 1. Varies depending on the operation mode.
• User mode: 08H
• On-board mode: 0CH
2. Regardless of the internal memory capacity, the initial values of the internal memory size switching
register (IMS) and internal expansion RAM size switching register (IXS) of the 78K0/FC2 is fixed (IMS =
CFH, IXS = 0CH). Therefore, set the value corresponding to each as indicated below.
Flash Memory Version IMS IXS
μ
PD78F0881, 78F0884 C8H 0AH
μ
PD78F0882, 78F0885 CCH 08H
μ
PD78F0883, 78F0886
CFH 08H
64
User’s Manual U17555EJ4V0UD
Page 65

CHAPTER 3 CPU ARCHITECTURE
3.3 Instruction Address Addressing
An instruction address is determined by program counter (PC) contents and is normally incremented (+1 for each
byte) automatically according to the number of bytes of an instruction to be fetched each time another instruction is
executed. When a branch instruction is executed, the branch destination information is set to the PC and branched by
the following addressing (for details of instructions, refer to 78K/0 Series Instructions User’s Manual (U12326E).
3.3.1 Relative addressing
[Function]
The value obtained by adding 8-bit immediate data (displacement value: jdisp8) of an instruction code to the
start address of the following instruction is transferred to the program counter (PC) and branched. The
displacement value is treated as signed two’s complement data (−128 to +127) and bit 7 becomes a sign bit.
In other words, relative addressing consists of relative branching from the start address of the following
instruction to the −128 to +127 range.
This function is carried out when the BR $addr16 instruction or a conditional branch instruction is executed.
[Illustration]
15 0
PC
+
15 0
876
PC indicates the start address
...
of the instruction after the BR instruction.
α
15 0
PC
When S = 0, all bits of are 0.
When S = 1, all bits of are 1.
α
α
S
jdisp8
User’s Manual U17555EJ4V0UD
65
Page 66

CHAPTER 3 CPU ARCHITECTURE
3.3.2 Immediate addressing
[Function]
Immediate data in the instruction word is transferred to the program counter (PC) and branched.
This function is carried out when the CALL !addr16 or BR !addr16 or CALLF !addr11 instruction is executed.
CALL !addr16 and BR !addr16 instructions can be branched to the entire memory space. The CALLF !addr11
instruction is branched to the 0800H to 0FFFH area.
[Illustration]
In the case of CALL !addr16 and BR !addr16 instructions
70
CALL or BR
Low Addr.
High Addr.
15 0
PC
In the case of CALLF !addr11 instruction
70
15 0
PC
00001
643
10–8
fa
CALLF
fa
7–0
11 10
87
87
66
User’s Manual U17555EJ4V0UD
Page 67

CHAPTER 3 CPU ARCHITECTURE
3.3.3 Table indirect addressing
[Function]
Table contents (branch destination address) of the particular location to be addressed by bits 1 to 5 of the
immediate data of an operation code are transferred to the program counter (PC) and branched.
This function is carried out when the CALLT [addr5] instruction is executed.
This instruction references the address stored in the memory table from 40H to 7FH, and allows branching to
the entire memory space.
[Illustration]
765 10
Operation code
ta
4–0
111
Effective address
Effective address+1
15 1
01
00000000
Memory (Table)
70
Low Addr.
High Addr.
15 0
PC
87
65 0
87
0
3.3.4 Register addressing
[Function]
Register pair (AX) contents to be specified with an instruction word are transferred to the program counter (PC)
and branched.
This function is carried out when the BR AX instruction is executed.
[Illustration]
70
07
rp
15 0
PC
AX
87
User’s Manual U17555EJ4V0UD
67
Page 68

CHAPTER 3 CPU ARCHITECTURE
3.4 Operand Address Addressing
The following methods are available to specify the register and memory (addressing) to undergo manipulation
during instruction execution.
3.4.1 Implied addressing
[Function]
The register that functions as an accumulator (A and AX) among the general-purpose registers is automatically
(implicitly) addressed.
Of the 78K0/FC2 instruction words, the following instructions employ implied addressing.
Instruction Register to Be Specified by Implied Addressing
MULU A register for multiplicand and AX register for product storage
DIVUW AX register for dividend and quotient storage
ADJBA/ADJBS A register for storage of numeric values that become decimal correction targets
ROR4/ROL4 A register for storage of digit data that undergoes digit rotation
[Operand format]
Because implied addressing can be automatically employed with an instruction, no particular operand format is
necessary.
[Description example]
In the case of MULU X
With an 8-bit × 8-bit multiply instruction, the product of A register and X register is stored in AX. In this example,
the A and AX registers are specified by implied addressing.
68
User’s Manual U17555EJ4V0UD
Page 69

CHAPTER 3 CPU ARCHITECTURE
3.4.2 Register addressing
[Function]
The general-purpose register to be specified is accessed as an operand with the register bank select flags
(RBS0 to RBS1) and the register specify codes (Rn and RPn) of an operation code.
Register addressing is carried out when an instruction with the following operand format is executed. When an
8-bit register is specified, one of the eight registers is specified with 3 bits in the operation code.
[Operand format]
Identifier Description
r X, A, C, B, E, D, L, H
rp AX, BC, DE, HL
‘r’ and ‘rp’ can be described by absolute names (R0 to R7 and RP0 to RP3) as well as function names (X, A, C,
B, E, D, L, H, AX, BC, DE, and HL).
[Description example]
MOV A, C; when selecting C register as r
Operation code 01100010
Register specify code
INCW DE; when selecting DE register pair as rp
Operation code 10000100
Register specify code
User’s Manual U17555EJ4V0UD
69
Page 70

CHAPTER 3 CPU ARCHITECTURE
3.4.3 Direct addressing
[Function]
The memory to be manipulated is directly addressed with immediate data in an instruction word becoming an
operand address.
[Operand format]
Identifier Description
addr16 Label or 16-bit immediate data
[Description example]
MOV A, !0FE00H; when setting !addr16 to FE00H
Operation code 10001110 OP code
00000000 00H
11111110 FEH
[Illustration]
07
OP code
addr16 (lower)
addr16 (upper)
Memory
70
User’s Manual U17555EJ4V0UD
Page 71

CHAPTER 3 CPU ARCHITECTURE
3.4.4 Short direct addressing
[Function]
The memory to be manipulated in the fixed space is directly addressed with 8-bit data in an instruction word.
This addressing is applied to the 256-byte space FE20H to FF1FH. Internal RAM and special function registers
(SFRs) are mapped at FE20H to FEFFH and FF00H to FF1FH, respectively.
The SFR area (FF00H to FF1FH) where short direct addressing is applied is a part of the overall SFR area.
Ports that are frequently accessed in a program and compare and capture registers of the timer/event counter
are mapped in this area, allowing SFRs to be manipulated with a small number of bytes and clocks.
When 8-bit immediate data is at 20H to FFH, bit 8 of an effective address is set to 0. When it is at 00H to 1FH,
bit 8 is set to 1. Refer to the [Illustration] shown below.
[Operand format]
Identifier Description
saddr Immediate data that indicate label or FE20H to FF1FH
saddrp Immediate data that indicate label or FE20H to FF1FH (even address only)
[Description example]
MOV 0FE30H, A; when transferring value of A register to saddr (FE30H)
Operation code 11110010 OP code
00110000 30H (saddr-offset)
[Illustration]
07
OP code
saddr-offset
15
Effective address
1
111111
When 8-bit immediate data is 20H to FFH,
When 8-bit immediate data is 00H to 1FH,
87
α
α
= 0
α
= 1
User’s Manual U17555EJ4V0UD
Short direct memory
0
71
Page 72

CHAPTER 3 CPU ARCHITECTURE
3.4.5 Special function register (SFR) addressing
[Function]
A memory-mapped special function register (SFR) is addressed with 8-bit immediate data in an instruction word.
This addressing is applied to the 240-byte spaces FF00H to FFCFH and FFE0H to FFFFH. However, the SFRs
mapped at FF00H to FF1FH can be accessed with short direct addressing.
[Operand format]
Identifier Description
sfr Special function register name
sfrp
16-bit manipulatable special function register name (even address
only)
[Description example]
MOV PM0, A; when selecting PM0 (FF20H) as sfr
Operation code 1 1110110 OP code
0 0100000 20H (sfr-offset)
[Illustration]
07
Effective address
OP code
sfr-offset
15
1
111111
87
1
SFR
0
72
User’s Manual U17555EJ4V0UD
Page 73

CHAPTER 3 CPU ARCHITECTURE
3.4.6 Register indirect addressing
[Function]
Register pair contents specified by a register pair specify code in an instruction word and by a register bank
select flag (RBS0 and RBS1) serve as an operand address for addressing the memory. This addressing can be
carried out for all the memory spaces.
[Operand format]
Identifier Description
[DE], [HL]
−
[Description example]
MOV A, [DE]; when selecting [DE] as register pair
Operation code 10000101
[Illustration]
16 08D7
DE
The contents of the memory
addressed are transferred.
A
7 0
E
Memory
The memory address
07
specified with the
register pair DE
User’s Manual U17555EJ4V0UD
73
Page 74

CHAPTER 3 CPU ARCHITECTURE
3.4.7 Based addressing
[Function]
8-bit immediate data is added as offset data to the contents of the base register, that is, the HL register pair in
the register bank specified by the register bank select flag (RBS0 and RBS1), and the sum is used to address
the memory. Addition is performed by expanding the offset data as a positive number to 16 bits. A carry from
the 16th bit is ignored. This addressing can be carried out for all the memory spaces.
[Operand format]
Identifier Description
[HL + byte]
−
[Description example]
MOV A, [HL + 10H]; when setting byte to 10H
Operation code 10101110
00010000
[Illustration]
16 08H7
HL
The contents of the memory
addressed are transferred.
7 0
A
L
Memory
07
+10
74
User’s Manual U17555EJ4V0UD
Page 75

CHAPTER 3 CPU ARCHITECTURE
3.4.8 Based indexed addressing
[Function]
The B or C register contents specified in an instruction word are added to the contents of the base register, that
is, the HL register pair in the register bank specified by the register bank select flag (RBS0 and RBS1), and the
sum is used to address the memory. Addition is performed by expanding the B or C register contents as a
positive number to 16 bits. A carry from the 16th bit is ignored. This addressing can be carried out for all the
memory spaces.
[Operand format]
Identifier Description
[HL + B], [HL + C]
−
[Description example]
In the case of MOV A, [HL + B]; (selecting B register)
Operation code 10101011
[Illustration]
16 0
78
HL
The contents of the memory
addressed are transferred.
7 0
A
H
+
L
B
Memory
07
07
User’s Manual U17555EJ4V0UD
75
Page 76

CHAPTER 3 CPU ARCHITECTURE
3.4.9 Stack addressing
[Function]
The stack area is indirectly addressed with the stack pointer (SP) contents.
This addressing method is automatically employed when the PUSH, POP, subroutine call and return
instructions are executed or the register is saved/reset upon generation of an interrupt request.
With stack addressing, only the internal high-speed RAM area can be accessed.
[Description example]
In the case of PUSH DE; (saving DE register)
Operation code 10110101
[Illustration]
Memory 07
SP
SP
FEE0H
FEDEH
FEE0H
FEDFH
FEDEH
D
E
76
User’s Manual U17555EJ4V0UD
Page 77

CHAPTER 4 PORT FUNCTIONS
4.1 Port Functions
There are two types of pin I/O buffer power supplies: AV
supplies and the pins is shown below.
Table 4-1. Pin I/O Buffer Power Supplies
Power Supply Corresponding Pins
AVREF P80 to P87, P90
EVDD/VDD • Port pins other than P80 to P87, P90
• Non-port pins
Note
Note P90 is μPD78F0884, 78F0885, 78F0886 only.
78K0/FC2 products are provided with the ports shown in Figure 4-1 and 4-2, which enable variety of control
operations.
In addition to the function as digital I/O ports, these ports have several alternate functions. For details of the
alternate functions, refer to CHAPTER 2 PIN FUNCTIONS.
μ
PD78F0881, 78F0882, 78F0883 have a total of 37 I/O ports, ports 0, 1, 3, 4, 6 to 8, 12 and 13. The port
configuration is shown below.
Figure 4-1. Port Types (
μ
P70
Port 7
P73
REF, EVDD/VDD. The relationship between these power
Note
PD78F0881, 78F0882, 78F0883)
P00
P01
P10
Port 0
Port 8
Port 12
Port 13
P80
P87
P120
P124
P130
P17
P30
P33
P40
P41
P60
P62
Port 1
Port 3
Port 4
Port 6
User’s Manual U17555EJ4V0UD
77
Page 78

CHAPTER 4 PORT FUNCTIONS
μ
PD78F0884, 78F0885, 78F0886 have a total of 41 I/O ports, ports 0, 1, 3, 4, 6 to 9, 12 and 13. The port
configuration is shown below.
μ
Figure 4-2. Port Types (
PD78F0884, 78F0885, 78F0886)
P00
P01
P06
P10
P17
P30
P33
P40
P41
P60
P63
Port 0
Port 1
Port 3
Port 4
Port 6
Port 7
Port 8
Port 12
Port 13
P70
P73
P80
P87
P90Port 9
P120
P124
P130
P131
4.2 Port Configuration
Ports include the following hardware.
Table 4-2. Port Configuration (
μ
PD78F0881, 78F0882, 78F0883)
Item Configuration
Control registers
Port Total: 37 (CMOS I/O: 33, CMOS output: 1, N-ch open drain I/O: 3)
Pull-up resistor Total: 21
Port mode register (PM0, PM1, PM3, PM4, PM6 to PM8, PM12, PM13)
Port register (P0, P1, P3, P4, P6 to P8, P12, P13)
Pull-up resistor option register (PU0, PU1, PU3, PU4, PU7, PU12)
Table 4-3. Port Configuration (μPD78F0884, 78F0885, 78F0886)
Item Configuration
Control registers
Port Total: 41 (CMOS I/O: 36, CMOS output: 1, N-ch open drain I/O: 4)
Pull-up resistor Total: 23
Port mode register (PM0, PM1, PM3, PM6 to PM9, PM12, PM13)
Port register (P0, P1, P3, P4 to P9, P12, P13)
Pull-up resistor option register (PU0, PU1, PU3, PU4, PU7, PU12, PU13)
78
User’s Manual U17555EJ4V0UD
Page 79

CHAPTER 4 PORT FUNCTIONS
4.2.1 Port 0
Port 0 is a 3-bit I/O port with an output latch. Port 0 can be set to the input mode or output mode in 1-bit units
using port mode register 0 (PM0). When the P00, P01 and P06 pins are used as an input port, use of an on-chip pull-
up resistor can be specified in 1-bit units by pull-up resistor option register 0 (PU0).
This port can also be used for timer I/O.
Reset signal generation sets port 0 to input mode.
Figures 4-3 and 4-4 show block diagrams of port 0.
Caution P06 is
μ
PD78F0884, 78F0885, 78F0886 only.
Figure 4-3. Block Diagram of P00
EV
DD
WR
PU
PU0
PU00
Alternate function
RD
WR
PORT
Internal bus
WR
PM
P0
Output latch
(P00)
PM0
PM00
P0: Port register 0
PU0: Pull-up resistor option register 0
PM0: Port mode register 0
RD: Read signal
WR××: Write signal
P-ch
Selector
P00/TI000
User’s Manual U17555EJ4V0UD
79
Page 80

CHAPTER 4 PORT FUNCTIONS
Figure 4-4. Block Diagram of P01 and P06
EVDD
WR
PU
PU0
RD
WR
PORT
Internal bus
WRPM
P0: Port register 0
PU0: Pull-up resistor option register 0
PM0: Port mode register 0
RD: Read signal
WR××: Write signal
Caution P06 is
PU01, PU06
Alternate
function
Selector
P0
Output latch
(P01, P06)
PM0
PM01, PM06
Alternate
function
μ
PD78F0884, 78F0885, 78F0886 only.
P-ch
P01/TI010/TO00,
P06/TI011/TO01
80
User’s Manual U17555EJ4V0UD
Page 81

CHAPTER 4 PORT FUNCTIONS
4.2.2 Port 1
Port 1 is an 8-bit I/O port with an output latch. Port 1 can be set to the input mode or output mode in 1-bit units
using port mode register 1 (PM1). When the P10 to P17 pins are used as an input port, use of an on-chip pull-up
resistor can be specified in 1-bit units by pull-up resistor option register 1 (PU1).
This port can also be used for external interrupt request input, serial interface data I/O, clock I/O, and timer I/O.
Reset signal generation sets port 1 to input mode.
Figures 4-5 to 4-7 show block diagrams of port 1.
Caution To use P10/SCK10/TxD61, P11/SI10/RxD61 and P12/SO10 as general-purpose ports, set serial
operation mode register 10 (CSIM10) and serial clock selection register 10 (CSIC10) to the
default status (00H).
Figure 4-5. Block Diagram of P10, P16 and P17
EV
DD
WR
PU
PU1
PU10, PU16
and PU17
P-ch
Internal bus
Alternate
function
RD
WR
PORT
P1
Output latch
(P10, P16, P17)
WR
PM
PM1
PM10, PM16
and PM17
Alternate
function
P1: Port register 1
PU1: Pull-up resistor option register 1
PM1: Port mode register 1
RD: Read signal
WR××: Write signal
Selector
P10/SCK10/TxD61,
P16/TOH1/INTP5,
P17/TI50/TO50
User’s Manual U17555EJ4V0UD
81
Page 82

CHAPTER 4 PORT FUNCTIONS
Figure 4-6. Block Diagram of P11 and P14
EV
DD
WR
PU
PU1
Internal bus
PU11, PU14
Alternate
function
RD
WR
PORT
P1
Output latch
(P11, P14)
WR
PM
PM1
PM11, PM14
P1: Port register 1
PU1: Pull-up resistor option register 1
PM1: Port mode register 1
RD: Read signal
WR××: Write signal
P-ch
Selector
P11/SI10/RxD61,
P14/RxD60
82
User’s Manual U17555EJ4V0UD
Page 83

WR
RD
PORT
WR
Internal bus
WR
CHAPTER 4 PORT FUNCTIONS
Figure 4-7. Block Diagram of P12, P13 and P15
EV
DD
PU
PU1
PU12, ,PU13
and PU15
Selector
P1
Output latch
(P12, PU13, P15)
PM
PM1
PM12, PM13
and PM15
P-ch
P12/SO10,
P13/TxD60,
P15/TOH0
Alternate
function
P1: Port register 1
PU1: Pull-up resistor option register 1
PM1: Port mode register 1
RD: Read signal
WR××: Write signal
User’s Manual U17555EJ4V0UD
83
Page 84

CHAPTER 4 PORT FUNCTIONS
4.2.3 Port 3
Port 3 is a 4-bit I/O port with an output latch. Port 3 can be set to the input mode or output mode in 1-bit units
using port mode register 3 (PM3). When used as an input port, use of an on-chip pull-up resistor can be specified in
1-bit units by pull-up resistor option register 3 (PU3).
This port can also be used for external interrupt request input and timer I/O.
Reset signal generation sets port 3 to input mode.
Figures 4-8 and 4-9 show block diagrams of port 3.
<R>
Cautions 1. Be sure to pull the P31 pin down before a reset release, to prevent malfunction.
2. Connect P31/INTP2 as follows when writing the flash memory with a flash programmer.
- P31/INTP2: Connect to EV
SS via a resistor (10 kΩ: recommended).
The above connection is not necessary when writing the flash memory by means of self
programming.
Remark P31/INTP2 and P32/INTP3 can be used for on-chip debug mode setting when the on-chip debug
function is used. For details, refer to CHAPTER 24 ON-CHIP DEBUG FUNCTION.
Figure 4-8. Block Diagram of P30 to P32
EV
DD
WR
PU
PU3
PU30 to PU32
Alternate
function
RD
Internal bus
WR
PORT
P3
Output latch
(P30 to P32)
WR
PM
PM3
PM30 to PM32
P3: Port register 3
PU3: Pull-up resistor option register 3
PM3: Port mode register 3
RD: Read signal
WR××: Write signal
P-ch
Selector
P30/INTP1,
P31/INTP2,
P32/INTP3
84
User’s Manual U17555EJ4V0UD
Page 85

CHAPTER 4 PORT FUNCTIONS
Figure 4-9. Block Diagram of P33
EV
DD
PU
WR
PU3
Internal bus
PU33
Alternate
function
RD
WR
PORT
P3
Output latch
(P33)
WR
PM
PM3
PM33
Alternate
function
P3: Port register 3
PU3: Pull-up resistor option register 3
PM3: Port mode register 3
RD: Read signal
WR××: Write signal
P-ch
Selector
P33/INTP4/TI51/TO51
User’s Manual U17555EJ4V0UD
85
Page 86

CHAPTER 4 PORT FUNCTIONS
4.2.4 Port 4
Port 4 is a 2-bit I/O port with an output latch. Port 4 can be set to the input mode or output mode in 1-bit units
using port mode register 4 (PM4). Use of an on-chip pull-up resistor can be specified in 1-bit units with pull-up resistor
option register 4 (PU4).
Reset signal generation sets port 4 to input mode.
Figure 4-10 shows a block diagram of port 4.
Figure 4-10. Block Diagram of P40, P41
EV
DD
WR
PU
PU4
RD
WR
PORT
Internal bus
WR
PM
PU40, PU41
Selector
P4
Output latch
(P40, P41)
PM4
PM40, PM41
P-ch
P40, P41
P4: Port register 4
PU4: Pull-up resistor option register 4
PM4: Port mode register 4
RD: Read signal
WR××: Write signal
86
User’s Manual U17555EJ4V0UD
Page 87

CHAPTER 4 PORT FUNCTIONS
4.2.5 Port 6
Port 6 is a 4-bit I/O port with an output latch. Port 6 can be set to the input mode or output mode in 1-bit units
using port mode register 6 (PM6).
The P60 to P63 pins are N-ch open-drain pins (6 V tolerance).
Reset signal generation sets port 6 to input mode.
Figures 4-11 shows block diagrams of port 6.
Caution P63 is
μ
PD78F0884, 78F0885, 78F0886 only.
Figure 4-11. Block Diagram of P60 to P63
RD
Selector
WR
PORT
Internal bus
P6
Output latch
(P60 to P63)
P60 to P63
WR
PM
PM6
PM60 to PM63
P6: Port register 6
PM6: Port mode register 6
RD: Read signal
WR××: Write signal
User’s Manual U17555EJ4V0UD
87
Page 88

CHAPTER 4 PORT FUNCTIONS
4.2.6 Port 7
Port 7 is a 4-bit I/O port with an output latch. Port 7 can be set to the input mode or output mode in 1-bit units
using port mode register 7 (PM7). When the P70 to P73 pins are used as an input port, use of an on-chip pull-up
resistor can be specified in 1-bit units by pull-up resistor option register 7 (PU7).
This port can also be used for external interrupt request input, and clock output pins, buzzer output pins, CAN I/F
I/O.
Reset signal generation sets port 7 to input mode.
Figures 4-12 and 4-13 show block diagrams of port 7.
<R>
Figure 4-12. Block Diagram of P70
EV
DD
WR
PU
PU7
PU70
RD
PORT
WR
P7
Internal bus
WR
PM
Output latch
(P70)
PM7
PM70
Alternate
function
P7: Port register 7
PU7: Pull-up resistor option register 7
PM7: Port mode register 7
RD: Read signal
WR××: Write signal
P-ch
Selector
P70/CTxD
88
User’s Manual U17555EJ4V0UD
Page 89

CHAPTER 4 PORT FUNCTIONS
Figure 4-13. Block Diagram of P71
EV
DD
PU
WR
PU7
PU71
Alternate function
RD
WR
PORT
Internal bus
P7
Output latch
(P71)
WR
PM
PM7
PM71
P7: Port register 7
PU7: Pull-up resistor option register 7
PM7: Port mode register 7
RD: Read signal
WR××: Write signal
P-ch
Selector
P71/CRxD
User’s Manual U17555EJ4V0UD
89
Page 90

CHAPTER 4 PORT FUNCTIONS
Figure 4-14. Block Diagram of P72 and P73
EV
DD
WR
PU
PU7
Internal bus
PU72 and PU73
Alternate
function
RD
WR
PORT
P7
Output latch
(P72 and P73)
WR
PM
PM7
PM72 and PM73
Alternate
function
P7: Port register 7
PU7: Pull-up resistor option register 7
PM7: Port mode register 7
RD: Read signal
WR××: Write signal
P-ch
Selector
P72/PCL/INTP6
P73/BUZ/INTP7
90
User’s Manual U17555EJ4V0UD
Page 91
CHAPTER 4 PORT FUNCTIONS
4.2.7 Port 8
Port 8 is an 8-bit I/O port with an output latch. Port 8 can be set to the input mode or output mode in 1-bit units
using port mode register 8 (PM8).
This port can also be used for A/D converter analog input.
To use P80/ANI0 to P87/ANI7 as digital input pins, set them in the digital I/O mode by using the A/D port
configuration register (ADPC) and in the input mode by using PM8. Use these pins starting from the lower bit.
To use P80/ANI0 to P87/ANI7 as digital output pins, set them in the digital I/O mode by using ADPC and in the
output mode by using PM8 (for details, see 12.3 (5) A/D port configuration register (ADPC)).
Table 4-4. Setting Functions of P80/ANI0 to P87/ANI7 Pins
ADPC PM8 ADS P80/ANI0 to P87/ANI7 Pin
Analog input selection
Input mode
Output mode
Output mode
−
−
Selects ANI. Analog input (to be converted) Input mode
Does not select ANI. Analog input (not to be converted)
Selects ANI.
Does not select ANI.
Digital input Digital I/O selection
Digital output
Setting prohibited
All P80/ANI0 to P87/ANI7 are set in the analog input mode when the reset signal is generated.
Figure 4-15 shows a block diagram of port 8.
Caution Make the AV
REF pin the same potential as the VDD pin when port 8 is used as a digital port.
Figure 4-15. Block Diagram of P80 to P87
RD
Selector
PORT
WR
P8
Internal bus
WR
PM
Output latch
(P80 to P87)
PM8
PM80 to PM87
P80/ANI0 to
P87/ANI7
A/D converter
P8: Port register 8
PM8: Port mode register 8
RD: Read signal
WR××: Write signal
User’s Manual U17555EJ4V0UD
91
Page 92

CHAPTER 4 PORT FUNCTIONS
4.2.8 Port 9
Port 9 is a 1-bit I/O port with an output latch. Port 9 can be set to the input mode or output mode in 1-bit units
using port mode register 9 (PM9).
This port can also be used for A/D converter analog input.
To use P90/ANI8 as digital input pin, set them in the digital I/O mode by using the A/D port configuration register
(ADPC) and in the input mode by using PM9. Use these pins starting from the lower bit.
To use P90/ANI8 as digital output pin, set them in the digital I/O mode by using ADPC and in the output mode by
using PM9 (for details, see 12.3 (5) A/D port configuration register (ADPC)).
Table 4-5. Setting Function of P90/ANI8 Pin
ADPC PM9 ADS P90/ANI8
Analog input selection
Input mode
Output mode
Output mode
−
−
Selects ANI. Analog input (to be converted) Input mode
Does not select ANI. Analog input (not to be converted)
Selects ANI.
Does not select ANI.
Digital input Digital I/O selection
Digital output
Setting prohibited
All P90/ANI8 are set in the analog input mode when the reset signal is generated.
Figure 4-16 shows a block diagram of port 9.
Cautions 1. P90 is
2. Make the AV
μ
PD78F0884, 78F0885, 78F0886 only.
REF pin the same potential as the VDD pin when port 9 is used as a digital port.
3. When using P90/ANI80 in the input mode, not only PM9 (input/output) but also the A/D port
configuration register (ADPC) (analog input/digital input)must be set (for details, see 12.3 (5)
A/D port configuration register (ADPC)). The reset value of ADPC is 00H (P90/ANI8 is
analog input pin).
92
User’s Manual U17555EJ4V0UD
Page 93

CHAPTER 4 PORT FUNCTIONS
Figure 4-16. Block Diagram of P90
RD
Selector
PORT
WR
P9
Internal bus
WR
PM
Output latch
(P90)
PM9
PM90
P90/ANI8
A/D converter
P9: Port register 9
PM9: Port mode register 9
RD: Read signal
WR××: Write signal
User’s Manual U17555EJ4V0UD
93
Page 94

CHAPTER 4 PORT FUNCTIONS
4.2.9 Port 12
Port 12 is a 5-bit I/O port with an output latch. Port 12 can be set to the input mode or output mode in 1-bit units
using port mode register 12 (PM12). When used as an input port only for P120, use of an on-chip pull-up resistor can
be specified by pull-up resistor option register 12 (PU12).
This port can also be used for external interrupt input, potential input for external low-voltage detector, connecting
resonator for main system clock, connecting resonator for subsystem clock, external clock input for main system clock,
external clock input for subsystem clock.
Reset signal generation sets port 12 to input mode.
Figures 4-17 and 4-18 show block diagrams of port 12.
Cautions 1. When using the P121 to P124 pins to connect a resonator for the main system clock (X1, X2)
or subsystem clock (XT1, XT2), or to input an external clock for the main system clock
(EXCLK) or subsystem clock (EXCLKS), the X1 oscillation mode, XT1 oscillation mode, or
external clock input mode must be set by using the clock operation mode select register
(OSCCTL) (for detail, see 5.3 (5) Clock operation mode select register (OSCCTL)). The reset
value of OSCCTL is 00H (all of the P121 to P124 pins are I/O port pins). At this time, setting
of the PM121 to PM124 and P121 to P124 pins is not necessary.
2. Connect P121/X1 as follows when writing the flash memory with a flash programmer.
- P121/X1: When using this pin as a port, connect it to V
SS via a resistor (10 kΩ:
recommended) (in the input mode) or leave it open (in the output mode).
The above connection is not necessary when writing the flash memory by means of self
programming.
94
User’s Manual U17555EJ4V0UD
Page 95

CHAPTER 4 PORT FUNCTIONS
Figure 4-17. Block Diagram of P120
EVDD
WR
PU
PU12
Internal bus
PU120
Alternate
function
RD
WR
PORT
P12
Output latch
(P120)
WRPM
PM12
PM120
P12: Port register 12
PU12: Pull-up resistor option register 12
PM12: Port mode register 12
RD: Read signal
WR××: Write signal
P-ch
Selector
P120/INTP0/EXLVI
User’s Manual U17555EJ4V0UD
95
Page 96

WR
WR
RD
PORT
PM
Figure 4-18. Block Diagram of P121 to P124
P12
Output latch
(P122/P124)
PM12
PM122/PM124
OSCCTL
OSCSEL/
OSCSELS
CHAPTER 4 PORT FUNCTIONS
OSCCTL
OSCSEL/
OSCSELS
Selector
P122/X2/EXCLK,
P124/XT2/EXCLKS
OSCCTL
EXCLK, OSCSEL/
EXCLKS, OSCSELS
Internal bus
RD
Selector
WR
PORT
WR
PM
OSCSEL/OSCSELS
EXCLK/EXCLKS
P12
Output latch
(P121/P123)
PM12
PM121/PM123
OSCCTL
OSCCTL
P121/X1,
P123/XT1
P12: Port register 12
PU12: Pull-up resistor option register 12
PM12: Port mode register 12
RD: Read signal
WR××: Write signal
96
User’s Manual U17555EJ4V0UD
Page 97

CHAPTER 4 PORT FUNCTIONS
4.2.10 Port 13
Port 130 is a 1-bit output-only port.
Port 131 is 1-bit I/O port. P131 can be set to the input mode or output mode in 1-bit units using port mode register
13 (PM13). When used as an input port, use of an on-chip pull-up resistor can be specified in 1-bit units by pull-up
resistor option register 13 (PU13).
Figures 4-19 and 4-20 show block diagrams of port 13.
Caution P131 is
μ
PD78F0884, 78F0885, 78F0886 only.
Figure 4-19. Block Diagram of P130
RD
WR
PORT
Internal bus
P13
Output latch
(P130)
P130
P13: Port register 13
RD: Read signal
WR××: Write signal
Remark When reset is effected, P130 outputs a low level. If P130 is set to output a high level before reset is
effected, the output signal of P130 can be dummy-output as the CPU reset signal.
Reset signal
P130
Set by software
User’s Manual U17555EJ4V0UD
97
Page 98

CHAPTER 4 PORT FUNCTIONS
Figure 4-20. Block Diagram of P131
EV
DD
WR
PU
PU13
Internal bus
P13: Port register 13
PU13: Pull-up resistor option register 13
PM13: Port mode register 13
RD: Read signal
WR××: Write signal
Caution P131 is
PU131
RD
WR
PORT
WR
PM
μ
PD78F0884, 78F0885, 78F0886 only.
P13
Output latch
(P131)
PM13
PM131
P-ch
Selector
P131
98
User’s Manual U17555EJ4V0UD
Page 99

CHAPTER 4 PORT FUNCTIONS
4.3 Registers Controlling Port Function
Port functions are controlled by the following three types of registers.
• Port mode registers (PM0, PM1, PM3, PM4, PM6 to PM9, PM12, PM13)
• Port registers (P0, P1, P3, P4, P6 to P9, P12, P13)
• Pull-up resistor option registers (PU0, PU1, PU3, PU4, PU7, PU12, PU13)
• A/D port configuration register (ADPC)
Caution P06, P63, P90, P131, PM06, PM63, PM90, PM131, PU06 and PU131 are
78F0886 only.
(1) Port mode registers (PM0, PM1, PM3, PM4, PM6 to PM9, PM12, PM13)
These registers specify input or output mode for the port in 1-bit units.
These registers can be set by a 1-bit or 8-bit memory manipulation instruction.
Reset signal generation sets these registers to FFH except for PM13. PM13 is set to FEH.
When port pins are used as alternate-function pins, set the port mode register and output latch as shown in Table
4-6.
μ
PD78F0884, 78F0885,
User’s Manual U17555EJ4V0UD
99
Page 100

Symbol
PM0
CHAPTER 4 PORT FUNCTIONS
Figure 4-21. Format of Port Mode Register
7
1
6
PM06
Note
5
1
4
1
3
1
2
1
1
PM010PM00
Address
FF20H
After reset
FFH
R/W
R/W
PM1
PM3
PM4
PM6
PM7
PM8
PM9
PM12
7
PM17
7
1
7
1
7
1
7
1
7
PM87
7
1
7
1
6
PM165PM154PM143PM132PM121PM110PM10 FF21H FFH R/W
6
1
6
1
6
1
6
1
5
1
5
1
5
1
5
1
4
1
4
1
4
1
4
1
3
PM332PM321PM310PM30 FF23H FFH R/W
3
1
2
1
1
PM410PM40 FF24H FFH R/W
3
Note
PM632PM621PM610PM60 FF26H FFH R/W
3
PM732PM721PM710PM70 FF27H FFH R/W
6
PM865PM854PM843PM832PM821PM810PM80 FF28H FFH R/W
6
1
6
1
5
1
5
1
4
1
3
1
2
1
1
1
0
Note
PM90 FF29H FFH R/W
4
PM1243PM1232PM1221PM1210PM120 FF2CH FFH R/W
PM13
7
1
6
1
5
1
4
1
3
1
2
1
1
PM131
0
Note
0 FF2DH FEH R/W
Note Be sure to clear bit 6 of PM0, bit 3 of PM6, bit 0 of PM9 and bit 1 of PM13 to 1 at μPD78F0881, 78F0882,
78F0883.
PMmn
0 Output mode (output buffer on)
1 Input mode (output buffer off)
Pmn pin I/O mode selection
(m = 0, 1, 3, 4, 6 to 9, 12, 13; n = 0 to 7)
100
User’s Manual U17555EJ4V0UD
 Loading...
Loading...