SUPERSCRIPT 870
NETWORK USER’S GUIDE
Click Here to Go to
Table of Contents
Click Here to
Go to Index
June, 1998

Proprietary Notice and Liability Disclaimer
The information disclosed in this document, including all
designs and related materials, is the valuable property of
NEC Technologies and/or its licensors, as appropriate,
reserve all patent, copyright and other proprietary rights to
this document, including all design, manufacturing,
reproduction, use and sales rights thereto, except to the
extent said rights are expressly granted to others.
The NEC Technologies product(s) discussed in this
document are warranted in accordance with the terms of the
Limited Warranty Statement accompanying each product.
However, actual performance of each such product is
dependent upon factors such as system configuration,
customer data and operator control. Since implementation
by customers of each product may vary, the suitability of
specific product configurations and applications must be
determined by the customer and is not warranted by NEC
Technologies.
To allow for design and specification improvements, the
information in this document is subject to change at any
time without notice. Reproduction of this document or
portions thereof without prior approval of NEC
Technologies is prohibited.
Microsoft, Windows, Windows 95, Windows 98,
Windows NT, Windows for Workgroups, and MS-DOS are
registered trademarks of Microsoft Corporation.
Adobe PrintGear®, the Adobe PrintGear® logo, and
Memory Booster Technology, are trademarks of Adobe
Systems Incorporated.
All other product, service, brand, or trade names used in
this publication are the trademarks or registered trademarks
of their respective companies or organizations. NEC
disclaims any responsibility for specifying which marks are
owned by which companies or organizations.
Copyright 1998
NEC Technologies, Inc.
1250 N. Arlington Heights Rd.
Itasca, IL 60143
All Rights Reserved.
Copyright 1998
NEC Corporation
7-1 Shiba 5-Chome, Minato-Ku
Tokyo 108-01, Japan
All Rights Reserved.
© NEC Technologies, Inc., 1998.
ii SuperScript 870 — Network User’s Guide

How to Use This Online Guide
Read the Getting Started section to
understand NIC requirements.
Introduction and Package Contents
Hardware and Software Requirements
Printing Tools on the
870
Network Options CD
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3
Then install the NIC in your printer.
Preparing the Printer
Installing the NIC
Testing the NIC
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4
Read about NIC Features.
Network Settings Page
Resetting the NIC
Restoring Factory Defaults
NIC Status Lights
Using the NIC Home Page for
Network Printer Administration
Using the Management Access
Program (MAP)
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
Configure the NIC and your network to work
together. This Guide gives examples of basic
setups for the most popular systems.
. . . . . . . . . 2
. . . . . . . 3
. . . . . . . . . . . 8
Follow the instructions in this guide that are
appropriate for your system.
Windows Setup
Basic Setup for Windows
TCP/IP Setup for Windows 95/98 and
Windows NT 4.0
TCP/IP Setup for Windows for Workgroups
Windows Peer to Peer Printing
Setting lpr Printing
Using the ARP Command
Using DHCP
NetWare 4.x Setup
NetWare 3.x Setup
MacOS Setup and Printing
UNIX Setup
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 36
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .18
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .19
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
. . 15
. . . . . . . . . . . . 16
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .18
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 24
If you have difficulties printing, see the
Troubleshooting section.
Identifying the Problem
Troubleshooting for NetWare
Troubleshooting for MacOS
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 43
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . 44
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 46
If you still need help, contact NEC Printer
Technical Support at their web site
(www.nec.com/nectechsupport)
or phone 1-800-632-4650
.
GETTING STARTED
Click on Any Page Number to Go to That Page
1
Introduction
What’s In This Package
The NEC SuperScript™ 870 Network Interface Upgrade Kit
contains a network interface card (NIC) that allows you to
connect your SuperScript 870 printer to a network. This
makes it the ideal printer for workgroups and small offices.
Supported Printing Environments
The NIC comes with software for using the printer on
several network operating systems or protocols, including
• Microsoft® Windows® 95/98, Windows NT® 4.0, and
Windows for Workgroups
• NetWare® versions 3.x and 4.x
• Mac™ OS 7.x and 8.x using AppleTalk
®
• Peer to peer printing for Windows 95/98,
and Windows NT 4.0.
• UNIX®
Your Starting Point
The instructions in this guide assume that you are familiar
with your network operating system and layout, that your
system is configured and operating properly, and that your
SuperScript 870 printer drivers are already properly
installed.
See the SuperScript 870
about your 870 printer and its drivers.
User’s Guide
for more information
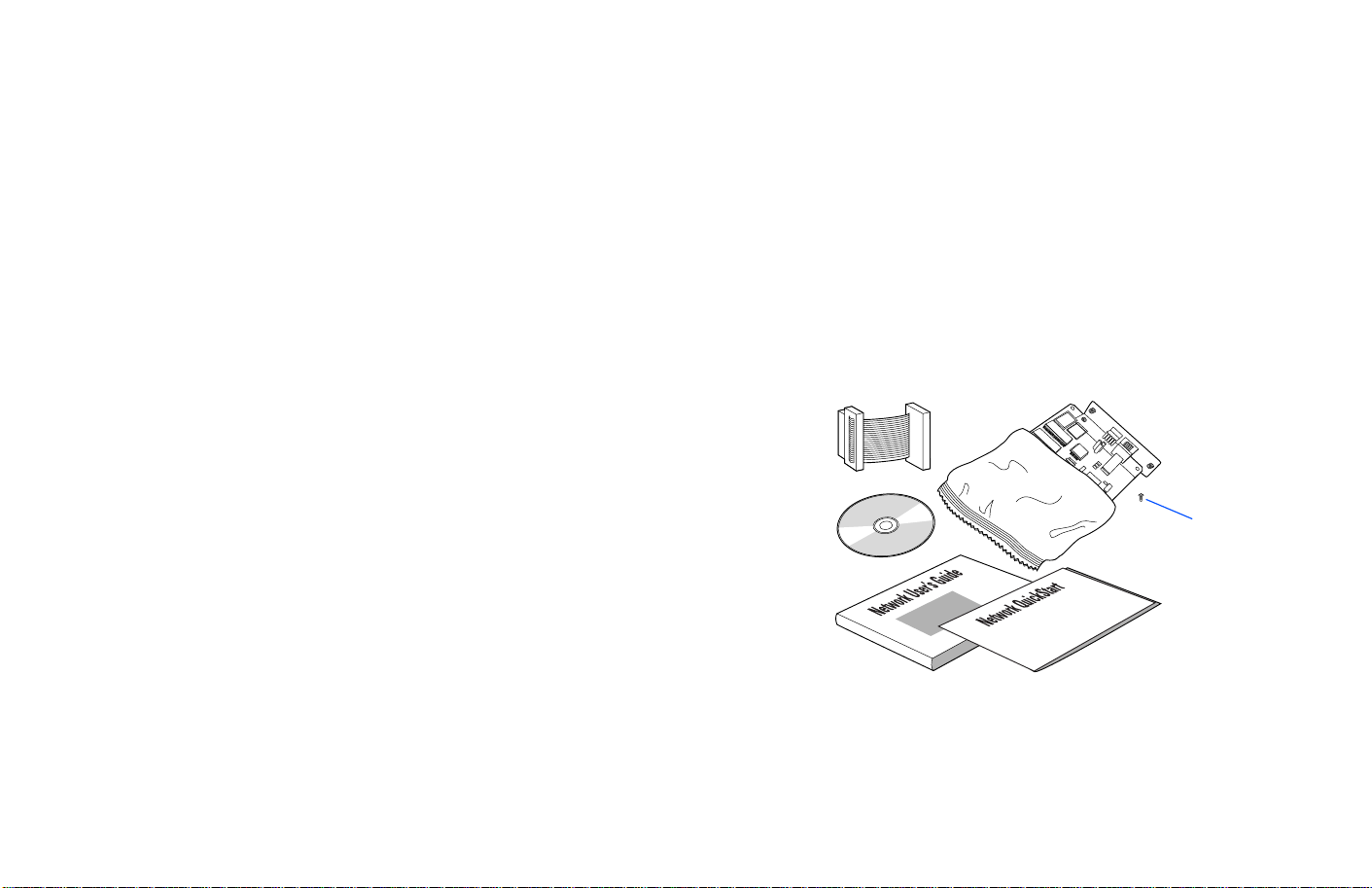
Your SuperScript 870 Network Interface Upgrade Kit
includes the following items
• One network interface card (NIC)
• One NIC interface cable
• One mounting screw
• The SuperScript 870
Network Options CD
with network
printer software (described on page 3).
• This SuperScript 870
• The SuperScript 870
NIC
Interface
Cable
Network
Options CD
Network User’s Guide
Network User’s Guide
Network QuickStart
NIC
Mounting
Screw
Network QuickStart
2 SuperScript 870 — Network User’s Guide

What You’ll Need
Hardware Requirements
You need to provide the following additional hardware to
install the NIC in your printer and connect it to your
network.
• A phillips-head screwdriver
• A Category 5 twisted pair cable with RJ-45 connectors
for 10/100Base-T Ethernet®, shown here.
note:
have a 10 Mbps or 100 Mbps Ethernet connection. For
better performance, NEC recommends that you use
shielded cable and connectors when connecting to
100 Mbps Ethernet.
Software Requirements
Your workstation and network operating system should
be configured and operating correctly. Your SuperScript
870 printer drivers should already be properly installed.
Printer drivers are on the
870 printer.
To use the NIC Home Page for network administration,
you need to have a web browser, such as Netscape
Navigator™ or Microsoft’s Internet Explorer.
The NIC automatically detects whether you
Solutions CD
that comes with the
Network Printing Tools On CD
NEC provides network printing tools on the 870
Options CD
• SuperScript MAP utility for Windows 95/98, and
Windows NT 4.0 setup
• Windows IPX peer to peer software for
Windows 95/98 and Windows NT 4.0
• Windows IP peer to peer software for
Windows 95/98 and Windows NT 4.0
• BOOTP Lite-32 for Windows 95/98 and
Windows NT 4.0
• BOOTP Lite-16 for Windows for Workgroups
• Utilities and drivers for MacOS
• Network Utilities for UNIX
that comes with this kit. These include
Network
User Information On CD
User documentation is available on the 870
Options CD
onscreen or print out, including
• This SuperScript 870
NICguide.pdf
Network User’s Guide
• Read Me files
note:
Network Options CD
in Adobe Acrobat® PDF format for you to view
Network User’s Guide
for Windows users, and
for MacOS users).
Adobe Acrobat Reader is provided on the
.
Network
(named
GETTING STARTED
3

Installing the NIC in the
Printer
The instructions on this page are illustrated on page 5.
First, Prepare the Printer
1. Turn off the printer, remove the power cord from the
rear panel of the printer, and disconnect the printer
parallel cable from the port
you are facing the side and back corner where the
parallel cable port is located. Make sure that you have
enough room to work.
2. Press the Top Cover Release button and lift Cover
3. Remove the two screws that hold on the printer’s side
cover
pulling it out and then up
4. Remove the two small screws from the expansion slot
on the rear of the printer
(C)
. Then remove the side cover completely by
Second, Install the NIC
5. Remove the NIC from its protective bag.
6. Carefully align the pins and connect one end of the
interface cable to the connector on the NIC
7. Hold the NIC so that its circuitry faces inside the printer ,
its LED lights face the back of the printer, and the
mounting tab is up. Connect the free end of the interface
cable to the connector on the controller board
(A)
. Position the printer so
(D)
.
(E)
, and remove the plate.
(F)
.
(G)
.
(B)
.
8. Align the NIC with the expansion slot and reinstall the
two smaller screws removed in step 4. Use the mounting
screw to fasten the mounting tab to the brace in the
printer. Tighten all three screws to firmly attach the NIC
to the printer
9. Replace the side cover by aligning the clips with the
bottom of the printer and bringing the top into place
with the screw holes aligned (make sure that the parallel
cable port clip is not pinned back by the side cover)
Reinstall and tighten the screws
10. Close the Top Cover of the printer.
(H)
.
(I)
.
(J)
.
Third, Test the NIC
Follow these steps to verify that the NIC is installed and
operating properly.
1. Connect the network’s twisted pair cable with
RJ-45 connectors to the new network port on your
printer. Reattach the power cord to the printer, plug in
the printer.
2. Turn on the printer. It may take up to 90 seconds to
warm up, and then it prints a Network Settings page
with NIC status information (shown on page 6).
note:
this information when configuring the NIC for your
network.
Your 870 Printer is now a network printer. The rest of this
Network User’s Guide
your systems to use the network printer.
Keep the Network Settings page. You will need
gives information for configuring
4 SuperScript 870 — Network User’s Guide

Installing the NIC
NIC INSTALLATION
A B
Top Cover
Release
Button
E
F
H
C
Interface
Cable
G
Mounting
Tab
I
J
D
Brace
5
NIC Features
Network Settings Page
Each time you turn on the printer , the NIC prints a Network
Settings page.
Three ways to print a Network Settings page are
• Hold down the
seconds.
• Go to the NIC Home Page, click
Administration
Generate Now
beginning on page 8.)
• In the SuperScript 870 Utility for MacOS, select
Settings Page
described on page 30.)
The Network Settings page provides information about the
NIC’s settings and network connections. You should review
this page immediately after NIC installation and any time
you change the configuration to verify that the procedure
was done properly.
In the illustration at the right, important features are circled.
The
Unit Serial No.
used for printer identification in peer to peer and NetWare
protocols. The
MAC address. The
assign the NIC. You can set a new
using the SuperScript 870 Utility for MacOS.
Operator Panel
, click
Configure Status Page
button for about 10
Network
. (The NIC Home Page is described
from the
Utilities
menu. (This utility is
(which is also on the back of the NIC), is
Network Address
Protocol Address
is the hardware address or
is the IP address you
AppleTalk Printer Name
, then click
Print
The Network Settings Page
- - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - Unit Serial No: 991655 Version: 05.06
Network Address: 00:40:af:79:0d:38
Network Topology: Ethernet Connector:RJ45
Network Speed: 100 Megabits
Novell Network Information enabled
Print Server Name: NEC_991655
Password Defined: No
Preferred File Server Name not defined
Directory Services Tree not defined
Directory Services Context not defined
Frame Type: Novell 802.3
Peer-to-Peer Information enabled
Frame Type: 802.03
Network ID: 32803
TCP/IP Network Information enabled
Frame Type: Ethernet II Protocol Address: 131.241.45.189
Subnet Mask: 255.255.255.0 Default Gateway: 131.241.45.254
AppleTalk Network Information enabled
Frame Type: 802.2 SNAP On 802.3
Preferred Appletalk Zone:*
- - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -
Novell Connection Information
Printer Name: NEC_991655_P
File Server: NW410
Queue: NEC_991655_Q Priority: 2 Attached: Yes
Queue: NEC_991655_Q2 Priority: 1 Attached: Yes
No Notify Defined
File Server: NW312
Queue: NEC_991655_Q Priority: 1 Attached: Yes
No Notify Defined
File Server: PPD
Queue: NEC_991655_Q Priority: 1 Attached: Yes
No Notify Defined
Peer-to-Peer Connection Information
Printer Name: NEC_991655
AppleTalk Connection Information
AppleTalk Printer Name: Jane’s 870
TCP/IP Connection Information
Port Number: 10001
- - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -
6 SuperScript 870 — Network User’s Guide

Resetting the NIC
If you change NIC settings, you may need to reset the NIC
for the new settings to take effect. To reset
• Go to the NIC Home Page, click Network
Administration, then click Reset in the System
column,
or
• Turn the printer off and then on again.
Restoring Factory Default Settings
You can reset the NIC to its factory default settings. This
means that the NIC clears data such as names and IP
addresses. It does not lose its serial number or Network
Address. If you have changed the printer’s name, it will
revert to its default name.
note:
printer is moved to a different network.
Two ways to reset the NIC to factory default settings are
• Go to the NIC Home Page, click Network
Administration, then click Factory Defaults in the
System column. You will need to enter a password
(the default is sysadm). (The NIC Home Page is
described beginning on page 8, passwords are
explained on page 10.)
You should restore factory defaults when the
• Turn the printer off. Press the Operator Panel button
and hold it while turning the printer on again.
Continue holding the Operator Panel button down
for about 20 seconds until all status lights begin to
double-blink.
note:
network you will have to turn the printer off, then on
again (without pressing anything else) in order to rebroadcast the AppleTalk name on the network.
If you are using this printer on an AppleTalk
NIC Status Lights
When the NIC is installed, its two status lights, amber and
green, are located on the interface panel on the back of the
printer. Light patterns for normal operation are
Green light is on solid: This shows normal
operation while the printer is awaiting print jobs.
Amber light blinks continuously: This shows that
the NIC is receiving a print job.
Green light blinks 3 times and stays on: This
occurs when the printer has performed a successful
self-test. It then prints a Network Settings page.
Light patterns that identify error conditions are
described on page 43.
NIC FEATURES
7

Using the NIC Home Page
Your NIC has a built-in web server and home page. The NIC
Home Page allows you to perform network administration
tasks, including monitoring and configuration. It contains
links to online documentation and the NEC web site for
more information about the SuperScript 870 printer and the
latest printer drivers.
Going to the NIC Home Page
You must assign an IP address to your NIC. Then you can
use a web browser, such as Navigator or Internet Explorer,
to access the NIC Home Page.
note:
for instructions on assigning the NIC IP address. The NIC
IP address then appears on the Network Settings page
under TCP/IP Network Information/Protocol Address.
To access the NIC Home Page, open your browser by
double-clicking on its icon. Enter the NIC IP address as the
URL of the NIC. For example, http://155.100.100.25.
(The IP address is shown as the “Protocol Address” on the
Network Settings page.)
Monitoring Printer Status
The SuperScript 870 Status Monitor only works with
NetWare bindery queues. To monitor printer status on all
other networks, use the NIC Home Page.
See the
Windows Setup or UNIX Setup
sections
When you first open the NIC Home Page, it reports your
current printer status. Later, you must click the Get Current
Status button to update it.
Network Administration Options
Click on the Network Administration link to display
network administration options (shown on page 9).
System Functions
Reset: Click here to reset the NIC and allow new
settings to take effect. The NIC’s connection with the
network is fully reinitialized, but its connection with the
printer controller is not. To reset the connection with the
printer controller, turn the printer off and on.
Factory Defaults: Click here to restore factory default
values on all NIC parameters. You should restore
factory defaults if you move the NIC to a new network
or if the NIC was set up improperly the first time.
Remember that this option clears all settings you have
defined for the NIC. You must Reset the printer for the
factory default settings to take effect.
Unit Status: Click here to view the current state for
each protocol and NIC port available on your NIC. For
each supported protocol (Novell NetWare, TCP/IP, or
AppleTalk), the top line displays the protocols
supported and if the protocol is enabled or disabled.
Network Address: Click here to view the serial number
and the Ethernet MAC (Media Access Control) address
for the NIC.
8 SuperScript 870 — Network User’s Guide

The NIC Home Page
Printer Status
NIC HOME PAGE
Setup Printer
Network Print Details
How To Use This Printer
Supplies
Network Administration
Status
Energy Saving
You can view the NIC Home Page from Windows,
MacOS, or UNIX. Use a web browser, such as
Netscape Navigator or Internet Explorer.
The URL is the IP address you assign to the NIC, for
example, http://131.241.45.65.
Network Administration Options
System
Reset
Factory Defaults
Unit Status
Network Address
Change Password
Protocols
Setup NetWare
Setup TCP/IP
Setup AppleTalk
Others
Test Printer
Configure Status Page
Printer Status
9

Change Password: Changing any NIC parameters
using the NIC Home Page requires a password. Click
here to change your password. The default password is
sysadm. Your password can contain letters, numbers,
and punctuation, and is case sensitive.
note:
factory defaults manually. See page 7.
If you forget your password, you can restore
Protocol Functions
The Protocols feature is for setting up network options and
parameters. It provides extensive access to NIC parameters,
and allows you to setup IP parameters (IP address, subnet
mask, and default gateway). You can enable/disable
AppleTalk and NetWare, but not TCP/IP. (We recommend
that you disable any protocol that you are not using.)
Other Functions
Test Printer: Click here, and then click on the Start Test
button in the dialog box that appears, to send a test
document to the printer.
Configure Status Page: Click here to configure
Network Settings page options. In the dialog box that
appears, select the checkbox by Print Status Page on
Startup to generate a status page (the Network Settings
page) each time you turn on the printer or reset the NIC.
note:
checked to print at power-on.
We recommend that you leave this setting
To print out a Network Settings page immediately, click
Generate Now.
Printer Status: Click here to display status information
for the printer and NIC, as well as errors and messages.
More NIC Home Page Options
Setup Printer: Click here to download the latest
version of your SuperScript 870 printer drivers from the
NEC website. You will specify the operating system you
are using to link to the appropriate driver and
installation instructions. Then, you will need to know
the network location of your printer before you install
the software.
Network Print Details: Click here for information you
can use during printer setup to specify the location of
your printer on the network.
How To Use This Printer: Click here for answers to
FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions), reference material,
and an option to send email to NEC Printer Technical
Support. Information for both Windows and MacOS
users is included to increase your productivity and
enhance your printed page.
Supplies: Click here for information on NEC
SuperScript 870 printer supplies, accessories, and how
to order them.
10 SuperScript 870 — Network User’s Guide

Using MAP
The Management Access Program (MAP), runs only
under Windows 95/98 and Windows NT 4.0. You use
MAP to list SuperScript 870 network printers connected to
your network. Then you select one to go to its NIC Home
Page for network administration options.
note:
you need Administrator rights. You may want to load
the program to an area of the file server restricted to
users with Administrator rights.
MAP Operating Requirements
To use MAP, you must have installed on your PC
• Netscape Navigator or Internet Explorer
• The Microsoft TCP/IP protocol stack. (It is not
necessary for the network to support TCP/IP.)
For IPX Search Functions: The IPX protocol must be
installed and enabled on your PC. Both Microsoft and
the NetWare 32-bit stacks are supported.
For IP Peer to Peer Printing: Both your workstation
and printer must have an IP address and subnet mask
entered. If communicating across subnets, the default
gateway must also be identified.
To have full use of the NIC Home Page or MAP,
Installing MAP
NIC HOME PAGE
MAP is available on the Network Options CD that is
included in the 870 Network Interface Upgrade Kit. MAP
must be installed from Windows 95/98 or Windows NT
4.0. It cannot be installed from the MS-DOS® command
prompt.
a. Insert the 870 Network Options CD.
b. In Windows 95/98 or NT 4.0, click the W indows Start
button and select Run.
c. Type <Drive>:\MAP\SETUP.EXE and click OK.
For IPX Peer to Peer Printing: Your PC must have
the IPX/SPX compatible protocol installed and
enabled .
11

Running MAP and Selecting a NIC
a. In Windows 95/98 or Windows NT 4.0, press the Start
button. Select MAP from the program group you
specified during installation.
When MAP starts, a list of all available units on the
network is displayed by unit serial number.
The unit listing will be divided by TCP/IP units and
IPX/SPX units. See the illustration at right.
note:
appear in both lists.
If a unit is enabled for both IP and IPX, it will
b. Click on a unit in the list to display its NIC Home Page.
c. Click the Network Administration button to display
options for configuring the NIC.
The NIC Home Page network administration options are
explained beginning on page 8.
An example using MAP and the NIC Home Page to
configure a NIC for NetWare 4.x is shown on page 21.
Management Access Program 3.20
[Refresh] [Help]
Units supporting TCP/IP
http://131.241.45.61/NEC_991142 NEC870
http://131.241.45.203/NEC_991149 NEC870
http://131.241.45.64/NEC_991151 NEC870
http://131.241.45.83/NEC_991650 Print Server Card
http://131.241.45.191/NEC_991653 Print Server Card
http://131.241.45.189/NEC_991655 NEC870
http://131.241.45.127/NEC_999999 Print Server Card
Units supporting IPX/SPX
NEC 991142 NEC Ethernet Option Supporting Novell (NDS), TCP/IP and AppleTalk
NEC 991149
NEC 991151
NEC 991650
NEC 991653
NEC 991655
NEC 999999
NEC Ethernet Option Supporting Novell (NDS), TCP/IP and AppleTalk
NEC Ethernet Option Supporting Novell (NDS), TCP/IP and AppleTalk
NEC Ethernet Option Supporting Novell (NDS), TCP/IP and AppleTalk
NEC Ethernet Option Supporting Novell (NDS), TCP/IP and AppleTalk
NEC Ethernet Option Supporting Novell (NDS), TCP/IP and AppleTalk
NEC Ethernet Option Supporting Novell (NDS), TCP/IP and AppleTalk
The MAP lists the 870 NICs on your network.
Select one to display its NIC Home Page.
12 SuperScript 870 — Network User’s Guide

Basic Windows Setup
Network Configuration Options
WINDOWS SETUP
There are several ways you can configure your Windows
workstation to access the 870 network printer, depending
on which version of Windows you are using and your
system configuration. To the right, under “Network
Configuration Options,” are possible scenarios.
Installing SuperScript 870 Printer Drivers
As you configure your network operating system, you
will need to install a copy of the SuperScript 870 printer
driver onto each workstation that will be accessing the
network printer. It is not necessary to install the
SuperScript Status Monitor, because it will not operate
over networks (except for NetWare bindery systems). To
view printer status, you can use the NIC Home Page.
note:
the
SuperScript 870 printer drivers are provided on
Solutions CD
that comes with the 870 printer.
TCP/IP Requirements for Windows
Configuration
TCP/IP is required for Windows 95/98, Windows NT 4.0
and Windows for Workgroups, if you want to access and
use the NIC Home Page to view printer status and
manage network printers. TCP/IP is also required to
operate the printer in an IP protocol network (such as for
peer to peer printing). TCP/IP setup for Windows 95/98
and Windows NT 4.0 is explained on page 14. TCP/IP
setup for Windows for Workgroups is explained
on page 15.
Windows 95/98
• If you have a NetWare network, see page 20 for
NetWare 4.x setup, or page 22 for Netware 3.x setup.
• If you have no network server, you can print directly
to the network printer using the peer to peer software
provided on the Network Options CD. See page 16.
Windows NT 4.0
• If you have a NetWare network, see page 20 for
NetWare 4.x setup, or page 22 for Netware 3.x setup.
• In a Windows NT network you can use lpr printing.
See page 18.
• If you have no network server, you can print directly
to the network printer using the peer to peer software
provided on the Network Options CD. See page 16.
Windows for Workgroups
• If you have a NetWare network, see page 20 for
NetWare 4.x setup, or page 22 for Netware 3.x setup.
13

TCP/IP Setup in Windows
95/98 and Windows NT 4.0
First, Install the TCP/IP Protocol
1. In Windows, open the Network control panel.
2. If TCP/IP Protocol is not installed, add it, and configure
the workstation’s TCP/IP settings.
3. Restart. The new protocols and services will not be
available until the system is restarted.
Second, Assign the IP Address and Other
TCP/IP Parameters to the NIC
If you have a DHCP server, the NIC will retrieve an IP
address automatically from the network server when you
turn on the printer. Here we provide instructions for using
BOOTP Lite to set the IP address manually. You can also use
ARP/ping commands if you prefer.
note:
or DHCP to set the IP address, see the
Information
1. Launch BOOTP Lite.
a. Insert the 870 Network Options CD.
b. Press the Windows Start button and select Run.
c. Type <Drive>:\BOOTP\BOOTPL32.EXE and click OK
to launch the utility.
For information about using the ARP command
More Windows
section, beginning on page 18.
2. Select Configure from the Admin menu.
a. Enter the IP address to assign to the NIC.
b. Enter the subnet mask. If you are unsure of the correct
subnet mask, and the first number in the NIC’s address
is from 192 to 254, then use 255.255.255.0 as the
subnet mask.
c. Enter the default gateway address (if applicable) or
leave blank.
d. Enter the hardware address of the NIC. This address is
listed on the Network Settings page under Network
Address, for example, 00:40:af:c9:f0:d8. Enter it
exactly as it appears on the Network Settings page.
3. Click on Go to send the new settings to the NIC.
After a few minutes (usually between 1 and 2 minutes, but
possibly up to 5 minutes on very large or busy networks),
the NIC will reset and print its Network Settings page. The
new IP settings will be listed in the TCP/IP Network
Information section of the Network Settings page.
If the new IP address does not appear on the Network
Settings page under “Protocol Address,” you may have
entered the hardware address incorrectly in BOOTP Lite.
Repeat Steps 2 and 3, and check the IP address on the new
Network Settings page.
The new IP address can also be verified in BootP Lite by
turning the printer off and on, and selecting Verify from the
Admin menu. It should report that the Unit is Active.
14 SuperScript 870 — Network User’s Guide

TCP/IP Setup in
Windows for Workgroups
Accessing the 870 network printer from Windows for
Workgroups is only supported over a NetWare network.
First, Install the TCP/IP Protocol
You must obtain from Microsoft a special TCP/IP protocol
stack that is compatible with Windows for Workgroups.
Follow the instructions provided with that utility to
install it.
Second, Assign the IP Address and Other
TCP/IP Parameters to the NIC
Here we provide instructions for using BOOTP Lite to set
the IP address manually. You can also use ARP/ping
commands if you prefer.
note:
to set the IP address, see page 18.
1. Launch BOOTP Lite.
a. Insert the 870 Network Options CD.
b. In the Windows Program Manager window, select
Run from the File menu.
c. Type <Drive>:\BOOTP\BOOTPL16.EXE and click
OK to launch the utility.
note:
16 Bit TCP/IP Stack only.
For information about using the ARP command
The BOOTPL16.EXE program will work with a
2. Select Configure from the Admin menu.
WINDOWS SETUP
a. Enter the IP address to assign to the NIC.
b. Enter the subnet mask. If you are unsure of the corr ect
subnet mask, and the first number in the NIC’s
address is from 192 to 254, then use 255.255.255.0
as the subnet mask.
c. Enter the default gateway address (if applicable) or
leave blank.
d. Enter the hardware address of the NIC. This address
is listed on the Network Settings page under Network
Address, for example, 00:40:af:c9:f0:d8. Enter
it exactly as it appears on the Network Settings page.
3. Click on Go to send the new settings to the NIC.
You will get a message that the program is verifying,
and then it will tell you whether the printer is active or
not. Wait for about two minutes for the printer and
NIC to reset. The Network Settings page should report
the newly entered IP information.
4. Verify Operation
Start an MS-DOS session. At the command prompt
enter: ping <IP address of NIC>
(continue until you get a reply). If you are getting a
timeout, verify that TCP/IP is enabled on the
Network Settings page. If the Network Settings page
does not show the IP information, then repeat the
above procedures.
15

Windows Peer to Peer
Printing Setup
Peer to peer printing allows Windows 95/98 and Windows
NT 4.0 computers to print directly to a networked printer
without an intervening file server. Below are the main
features of peer to peer printing.
• Runs on Windows 95/98 and Windows NT 4.0
workstations or servers “out of the box.”
• Runs on networks with or without a NetWare file server.
• Implements peer to peer direct printing between
Windows computers and networked printers.
• You can configure network printers the same way you
configure printers directly attached to a computer.
note:
be used with its factory default settings.
In isolated, serverless networks, the NIC should
IP vs. IPX Peer to Peer Printing
Your network configuration will dictate whether IP or IPX is
more appropriate. However, we recommend you use IP peer
to peer printing if possible.
For IP Peer to Peer Printing: You must install P2P-IP.
This protocol allows you to access the network printer
over an IP network. The Microsoft TCP/IP protocol
stack must also be installed and properly configured on
your workstation. The network and the network print
servers must support IP.
For IPX Peer to Peer Printing: You must install
PeerToPeer-IPX. It is not necessary to have a NetW ar e file
server on the network to use this IPX protocol.
First, Install Peer to Peer Software
Follow these steps to install the correct software.
1. Insert the 870 Network Options CD into the drive.
2. In Windows 95/98 or NT 4.0, press the Start button and
select Run.
3. At Run, type:
<drive>:\IP-P2P\SETUP.EXE (for IP),
or,
<drive>:\IPX-P2P\SETUP.EXE (for IPX)
16 SuperScript 870 — Network User’s Guide
4. Then click OK. Follow the Install wizard prompts.
When installation is complete, click OK.

Second, Add the Peer to Peer Printer in
Windows
1. In Windows 95/98 or Windows NT 4.0, press the Start
button, select Settings, then select Printers.
2. In the Printers window , double-click Add Printer. This
launches the Add Printer wizard which prompts you
to make selections.
note:
the
When the Add Printer wizard asks how the printer is
attached, select Local printer.
Specify NEC as the Manufacturer and NEC
SuperScript 870 as the Printer.
3. Your peer to peer network printer will be listed under
local printer ports and identified using the NIC serial
number. For example, NEC_911499.
Select your new peer to peer printer.
4. Continue responding to the Add Printer wizard until
the process is complete.
SuperScript 870 printer drivers are provided on
Solutions CD
that comes with the 870 printer.
Moving a Peer to Peer Printer
If you move your printer to a new network, you must
restore the NIC to its factory defaults (see page 7). If you
have changed your printer’s name, it will revert to its
original factory name.
Removing Peer to Peer Software
You should delete all printers which have been installed to
use peer to peer printing before you delete the peer to peer
software. Follow these steps.
1. Press the Windows Start button, select Settings, then
select Printers.
2. In the Printers window, select a printer to delete.
3. Select Delete from the File menu.
Removing
To remove the IP peer to peer software from your
computer, use the Add/Remove Programs control panel.
1. Press the Windows Start button, select Settings, then
select Control Panel.
2. Open Add/Remove Programs. Select P2P-IP in the list
and click Remove.
Removing
To remove the IPX peer to peer software from your
computer, use the PeerToPeer-IPX Uninstall program.
Follow these steps.
1. Insert the 870 Network Options CD into the drive.
2. Press the Windows Start button and select Run.
3. At Run, type:
<drive>:\IPX-P2P\UNINSTAL.EXE
Then click OK.
Follow the Uninstall wizard prompts. When removal
is complete, click OK.
P2P-IP
PeerToPeer-IPX
WINDOWS SETUP
17

More Windows Information
This section has additional information you may find
useful as you configure your Windows system for the
870 network printer.
Setting lpr Printing on an NT Network
The following procedure can be used to set up the lpr
spooler for a Windows NT 4.0 workstation/server.
field, enter PORT1 (the word “PORT” must be in
uppercase). Click OK, then click Close to assign that
newly created port to the SuperScript 870.
10. Click on the Sharing tab in the NEC SuperScript 870
Properties window.
11. Click on the radio button Shared and enter a name for
your SuperScript 870 printer.
12. Click OK to apply these settings to your printer.
1. In the Windows Network control panel, install the
Microsoft TCP/IP Printing service.
2. Use the Windows Add Printer wizard to install the
SuperScript 870 printer driver for Windows NT 4.0.
note:
the
3. In Windows NT 4.0, click the Start button, select
Settings, then select Printers.
4. Select the NEC SuperScript 870 printer icon, and then
select Properties from the File menu.
5. Click on the Ports tab (the SuperScript 870 driver
installs to LPT1 by default).
6. Then select Add Port.
7. Under Available Printer Port select LPR Port and click
the New Port button.
8. In the Name or address of server providing lpd field,
enter the IP (Protocol) address of the printer, for
example, 128.191.184.50. Then click OK.
9. In the Name of printer or print queue on that server
18 SuperScript 870 — Network User’s Guide
SuperScript 870 printer drivers are provided on
Solutions CD
that comes with the 870 printer.
Using ARP to set the IP Address
You can use the following procedure to set the IP address on
the NIC. Then, you can set the other IP parameters from the
NIC Home Page. The printer and the NIC must be on the
same network segment as the workstation that you are
using to configure it. The TCP/IP stack must be installed
and operating.
1. From Windows, start an MS DOS session.
2. At the command prompt enter: arp -s
[NIC IP address] [NIC Hardware Address]
(for the hardware address, use hyphens as separators,
instead of colons.)
Then enter ping [NIC IP address]
(request should time out)
3. Turn the printer off and on, and use the ping command
again to verify that the NIC has its IP address. If the NIC
has the address, the result is a confirmation message:
[NIC IP address] is alive
4. Remove the entry from the ARP cache using this
command: arp -d [NIC IP address]

Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol
Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) allows
automatic assignment of IP address and other IP
parameters for attached devices. The NIC works with
DHCP in the following way.
At power-up, the NIC broadcasts a DHCP request for an
IP address. If a DHCP server is pr esent, the r equest will be
processed, and an IP address will be returned to the NIC.
Upon receipt of the IP address, the NIC r esets, and prints a
Network Settings page. This shows the new IP address
(and subnet mask, and default gateway, if any). Under
factory default settings, once an IP address has been assigned to
it, the NIC will no longer broadcast DHCP requests. Therefore,
NIC IP address assignment with DHCP will only work when
the NIC does not have an existing IP address.
The DHCP server may grant a temporary IP address,
called a temporary lease or temporary reservation, which
expires later, or may grant a permanent or unlimited lease
or reservation which does not expire.
Devices that are granted a temporary lease will be notified
before the lease expires and asked if they would like to
extend the lease. The NIC will continue extending its lease
indefinitely (unless prohibited by your DHCP server
configuration), and thus maintain a consistent IP address.
Important: If the NIC is not turned on or is not connected to
the network when the DHCP server is sending requests to
extend the lease, the lease will not be extended. The DHCP
server will cancel the lease and may assign the IP address to
another device. Therefore, it is highly recommended to explicitly
WINDOWS SETUP
specify the NIC lease as permanent or unlimited in your DHCP
server configuration.
DHCP Settings in the NIC Home Page
You can control the way the NIC handles DHCP from the
NIC Home Page.
1. On the NIC Home Page, click the Network
Administration button.
2. Under Protocols, click Setup TCP/IP. The two DHCP
Settings are shown here.
The factory default is that both settings are checked.
If there is not an IP address alr eady stored in NVRAM,
the NIC will make a DHCP request. If there is an IP
address, it will not.
When Enable DHCP is not checked, the NIC will not
make DHCP requests.
When IP Address in NVRAM is not checked, the NIC
will always make a new DHCP address request at
startup, regardless of whether or not it has an IP
address stored in NVRAM.
19

Basic Setup for NetWare 4.x
First, use NWADMIN to attach the Printer
1. Log in to NetWare 4.x with administrator rights and
open the NetWare Administrator window.
2. Create Printer Object.
a. Highlight the Organizational Unit or Organization
where you want to create the print service in the
Directory Tree. From the Object menu, select Create.
b. In the New Object window that appears, scroll down
the Class of New Object list, select the Printer icon and
click the OK button.
c. When the Create Printer window appears, type a name
in the Printer Name field and click on the Create button.
3. Create Print Server Object.
a. Highlight the Organizational Unit. From the Object
menu, select Create.
b. In the New Object window appears, scroll down the
Class of New Object list, select the Print Server icon,
and click the OK button.
c. At the Create Print Server window, type a name in the
Print Server Name field and click the Create button.
note:
the name shown on the Network Settings page under
Novell Network Information.
The Print Server name you enter should match
4. Create Print Queue Object.
a. Highlight the Organizational Unit. From the Object
menu, select Create.
b. In the New Object window that appears, scroll down
the Class of New Object list, select the Print Queue
icon, and click the OK button.
c. At the Create Print Queue window, click the Directory
Service Queue button, then type in a name for Print
Queue Name.
d. Click the icon to the right of Print Queue Volume field
to display the browser, and select a specific Print Queue
Volume (or type the name in the field).
e. Click the Create button.
5. Assign Printer Object
a. In the Directory Tree, double click on the printer object
just created to open its Printer window. Click on the
Assignments button on the right-side of the window
and click on the Add button.
b. In the Select Object window that appears, find the print
queue object just created among the choices listed in the
Objects box and select it by clicking on it.
c. Click on the OK button and the print queue is added to
the Print Queues: box in the Printer: window. Click on
the OK button again.
20 SuperScript 870 — Network User’s Guide

6. Assign Print Server Object
a. In the Directory Tree, double-click on the print server
object you just created to open its Print Server
window.
b. In the Print Server window that appears, click on the
Assignments button and Add button to bring up the
Select Object window. Select the printer object just
created from the Objects box and click on the OK
button. Now the printer (with its context) appears in
the Printers: box of the Print Server window. Click on
the OK button.
7. Check Assignments
a. At the Directory Tree, double click on the Print
Queue object you just created. At the Print Queue
window, click on the Assignments button.
b. If you configured the print queue and printer
correctly they will appear in the proper boxes on the
Print Queue window. Press the Cancel button.
Second, Install the Printer Driver
In Windows, use the Add Printer feature to install and
configure a SuperScript 870 printer driver in each
workstation that will access the network printer.
note:
Solutions CD
Specify that the printer will be attached as a Network
Printer, and set the Port to the printer queue you just
SuperScript 870 printer drivers are on the
that comes with the printer.
created. (The Windows NT 4.0 driver installs
automatically to LPT1:. After installation, you can
manually reset the port to your NetWare queue.)
Third, use MAP and the NIC Home Page to
Configure the NIC
Now you must specify the Print Server Name, Preferred
NDS Context, and Preferred NDS Tree using the NIC
Home Page network administration options. Continue
with the instructions below, to do this.
1. Run MAP.
a. If you have not yet installed MAP, follow the
instructions on page 11.
b. In Windows 95/98 or Windows NT 4.0, click the Start
button. Select MAP from the program group you
specified during installation. When MAP starts, a list
of all available units on the network is displayed by
unit serial number.
2. Select the NIC to configure.
a. Click on a NIC in the list to display its NIC Home
Page.
note:
Netscape Navigator or Internet Explorer, to access the
NIC Home Page. Enter the NIC’s IP address as the URL,
for example, http://131.241.54.16. The IP address is
listed as “Protocol Address” on the Network Settings
page.
You can also use a web browser such as
NETWARE 4.X SETUP
21

3. NetWare 4.x (NDS) Configuration
a. On the NIC Home Page, click the Network
Administration button to display options for
configuring the NIC.
b. Click on NetWare Setup in the Protocols column.
c. In the NetWare Configuration dialog box that appears,
enter a name in the Print Server Name field, enter a
name in the Preferred NDS Context field, and enter a
name in the Preferred NDS Tree field. (Leave the
Preferred File Server field blank.)
d. Enter the password and click on the Accept Settings
button. (The default password is sysadm.)
4. Confirm Successful Configuration.
a. In the Systems column, click on Reset.
After the Reset, the program advises waiting 2 minutes
before reconnecting, but the NIC may be available
sooner.
b. Go back to the NIC Home Page, click the Network
Administration button. Then, in the System column,
click on Unit Status.
c. In the dialog box that appears, scroll down to display
the NetWare Status. The Queue Status should be
Attached.
d. If the Queue Status is not shown as Attached, please
verify that the entries for Print Server Name, Preferred
NDS Context, and Print Server Password match those
defined in NWADMIN.
Basic Setup for NetWare 3.x
Complete these basic tasks to configure NetWare 3.x
bindery-based services for your printer.
1. Log in to NetWare 3.x with Administrator rights and
start PCONSOLE.
2. Define the Print Queue.
a. Select Print Queue Information from the Available
Options menu and press ENTER.
b. Press INSERT, type a name for the new queue to be
serviced by the NIC and press ENTER. Press ESCAPE to
return to the Available Options Menu.
3. Define the Print Server.
a. Select Print Server Information from the Available
Options menu and press
b. Press INSERT, type the NIC Print Server Name and pr ess
ENTER.
note:
the name shown on the Network Settings page under
Novell Network Information.
The Print Server Name you enter should match
ENTER.
22 SuperScript 870 — Network User’s Guide

4. Define the Printer.
a. Press ENTER with the new Print Server Highlighted,
select Print Server Configuration and press ENTER,
then select Printer Configuration and press ENTER.
b. In the Configured Printers list, select an unused
printer number and press ENTER. In the Printer <#>
Configuration screen, define a new name for the
printer if desired. (The printer name is displayed in
various NetWare printing messages.)
c. Press ESCAPE to exit and select Yes to save the
changes. Press ESCAPE again to return to the Printer
Server Configuration menu.
5. Assign the Print Queue.
a. Select Queues Serviced By Printer and press ENTER.
Highlight the desired printer on the Defined Printers
list and press ENTER.
b. Press INSERT to display the Available Queues list.
Select the desired queue and press ENTER. Assign a
Priority level (recommended choice is 1) and press
ENTER.
c. Press
Alt-F10 to exit PCONSOLE.
6. Confirm Successful Configuration.
a. Turn the printer off and on and wait for a Network
Settings page to print. If the network is large, this may
take several minutes.
b. The Novell Connection Information area on the
Network Settings page displays the printer name, file
server, queue, etc. If it displays Attached: Yes, this
confirms that the NIC Print Server is ready to accept
print jobs. If not, verify that the Print Server name
matches exactly the Print Server name that was
entered in PCONSOLE.
7. Install and Configure Your Printer Driver
In Windows, use the Add Printer feature to install and
configure a SuperScript 870 printer driver in each
workstation that will access the network printer.
note:
Solutions CD
SuperScript 870 printer drivers are on the
that comes with the printer.
Specify that the printer will be attached as a Network
Printer, and set the Port to the printer queue you just
created. (The Windows NT 4.0 driver installs
automatically to LPT1:. After installation, you can
manually reset the port to your NetWare queue.)
NETWARE 3.X SETUP
23

Basic Setup for MacOS
Complete these basic tasks to begin printing.
1. Install SuperScript 870 MacOS Software
a. Insert the 870 Network Options CD in your drive and
double-click the SuperScript 870 Installer icon.
b. The installer prompts you to select installation
preferences and creates the SuperScript 870 Folder on
your hard drive.
You will have to turn the printer off and then on again
for the new name to take effect.
5. Checking Printer Status
You can view active information about your printer’s status.
In the SuperScript 870 Folder, double-click the SuperScript
870 Utilities icon. From the Utility menu, select Check
Printer Status.
2. Choose the Printer
a. Select Chooser from the Apple menu and make sur e the
AppleTalk Active button is selected.
b. In the Chooser, select the SuperScript 870 printer icon,
select the AppleTalk zone your printer is on, then select
the printer’s name in the printer list.
3. Set Background Printing
In the Chooser, set Background Printing to On or Off.
Background Printing allows you to continue working while
a job is printing.
4. Rename Your Printer
If you have more than one SuperScript 870 printer on your
network, you should rename your printer.
a. In the SuperScript 870 Folder on your hard drive,
double-click the SuperScript 870 Utilities icon.
b. From the Utilities menu, select Name Printer and follow
the directions in the dialog box.
24 SuperScript 870 — Network User’s Guide
The MacOS Chooser

Printing with MacOS
The Network Options CD contains MacOS driver software
that allows your printer to deliver high-speed
performance at lower cost than competing printers. Adobe
Memory Booster™ helps your printer handle most
complex print jobs without added memory.
Printer software provided for MacOS users includes
• SuperScript 870 Printer Driver for print job and page
setup
• SuperScript 870 Spooler for background printing and
managing print jobs
• SuperScript 870 Utility for monitoring and managing
the printer
Additional software is available on the Solutions CD that
comes with your 870 printer . This includes 78 Type 1 fonts,
Adobe Type Manager®, Adobe Acrobat® Reader, clip art,
and an Acrobat PDF document, How to Look Good on Paper,
that helps you choose and use fonts.
System Requirements
The SuperScript 870 Printer Driver for MacOS requires the
following hardware and software to operate correctly.
• 4 MB of RAM. Additional memory may be requir ed to
print complex files or to print with the Spooler.
• 2 MB of hard disk space available to install the printer
driver and related utilities from the Network Options
CD. Additional hard disk space is required to install
Adobe Type Manager and fonts from the Solutions CD.
• EtherTalk® network adapter.
MACOS PRINTING
25

Print Job Setup
Printing a document
To print a document from your MacOS computer
1. Select Print from the File menu.
2. A Print dialog box appears that allows you to select the
options you want (shown below).
3. Select options and click Print to print the document.
The print options are described below.
Number of Copies
In the Copies field enter a value from 1 to 999 to specify the
number of copies to print.
Print Dialog Box
Page Range
Use the Pages fields to specify which pages of the document
to print. To print the whole document, click All (the default).
To print a range of pages, type the first page you want in the
From field, and the last page in the To field.
Resolution
Use the Resolution dropdown menu to set the printing
resolution, in dots per inch (dpi). For best printing results,
select 600 dpi—Highest Quality (the default). For faster
printing but lower quality, select 300 dpi—Faster Printing.
Toner Usage
Conserve printer toner by selecting Save toner . This r educes
the amount of toner used to print the page image.
Print Options
note: Any additional settings that appear in the Print dialog box
are specific to the application you are using.
26 SuperScript 870 — Network User’s Guide

Paper Source
The Paper Source option lets you choose which paper to
use based on your current printer configuration setup.
Paper source options vary, depending on whether you
have the optional 500-sheet cassette installed.
Destination
Select the print job destination here.
Printer: Your document is printed out on your printer
(the default).
File: The print job is saved as a SuperScript 870 file
under a name and location you specify. You can then
print the file from a remote system with an 870 printer
attached. To print it out from MacOS, select Print
SuperScript 870 File from the SuperScript 870 Utilities
menu. To print from Windows or DOS, use the
command
copy /b <filename>
Additional Print Options
Click the Options button on the Print dialog box to
display additional settings, including print order, cover or
trailer pages, print color handling, imaging mode, and
halftone settings, described below.
Print Order
MACOS PRINTING
Front to Back: Select this to print multiple-page
documents from the first page to the last.
Back to Front: Select this to print multiple-page
documents from the last page to the first.
Cover or Trailer Page
A cover page shows information including the document
name, user name, date, and time printed. A cover or trailer
page is recommended in a large network environment.
None: Select this to print the document without a
cover page (the default).
First: Select this to print a cover page as the first page
of the document.
Last: Select this to print a trailer page as the last page
of the document.
Print Colors As
This setting controls the appearance of a color document
on this monochrome printer.
Grayscale: Maps colors to equivalent grayscale
shades (the default).
Black & White: Limits printing to monochrome only,
which speeds up the printing process slightly.
27

Imaging Modes
This setting controls the printing of text and graphics. You
can select an imaging method from the menu, or allow
SuperScript 870 to select the best method automatically.
To manually control the imaging mode, choose one of the
following menu options:
Page Setup
To view and change Page Setup settings
1. Select Page Setup from the File menu.
2. A Print dialog box appears that allows you to select the
options you want (shown on page 29).
3. Select options and click OK to return to the document.
Auto Select Best Mode: Allows SuperScript 870 to
select the imaging method automatically. This option
works well for most print jobs.
Optimize for Word Processing: Ensures the fastest
printing for documents that contain mostly text.
Image Entire Page as Graphic: Ensures the best
possible match between what you see on the screen and
what is printed. When this option is selected, the entire
page, including fonts, is sent as a single graphic image
to the printer.
Halftone Settings
This setting allows you to fine tune the way SuperScript 870
converts grayscale or color images into black-and-white dot
patterns (halftones).
Fine: Provides smoother grays and fills.
Standard (Faster Output): Results in coarser grays but
faster printing.
Photocopy Reduction: Produces images using a
different dot pattern that is optimized for reproduction
on photocopy machines.
Page Setup settings are described on the pages that follow.
Paper Size
Select a supported paper size here.
Orientation
Orientation describes the position of images on a page with
respect to the long and short edges of the paper. Portrait
means the page is taller than wide as you view it; landscape
means the page is wider than tall.
Page Scaling
Select Page Scaling options here.
Reduce or Enlarge: Enter a value from 20 to 400.
Use Entire Print Area: If you check this, a reduced or
enlarged page image is placed in the top left corner of
the page (the default).
Photocopy Reduction: Check this to center a reduced
image on the page.
28 SuperScript 870 — Network User’s Guide

Print Page Border: Check this to print a border
around the printable area of the page.
The Page Preview icon shows the results of your
selections.
Page Setup Options
MACOS PRINTING
Click the Options button on the Page Setup dialog box to
display these settings.
Flip Horizontal: Check this to print a mirror image of
the page image.
Page Setup Dialog Box
Page Preview and Printable Area
This icon shows the effect of the selections you
make. Click it to display the dimensions of paper you
select. The inner rule shows the printable area for
that paper size. Click again to see the values in other
units (inches or millimeters). Click a third time to
return to the page preview.
Options
Default Settings
29

Flip Vertical: Check this to print the page image
upside-down.
Invert Image: Check this to print the white areas of the
document black, and the black areas of the document
white.
Precision Bitmap Alignment: Check this to improve
the quality of screen resolution bitmap images placed in
your document.
The Page Preview icon shows the results of your selections.
Default Options
You can set default page setup options to be used for all
documents printed on your NEC SuperScript 870 printer.
Click the Settings button on the Page Setup dialog box to
display these settings.
Save the Current Settings as the User Default:
Check this to save the page setup settings you just
entered and use them as the defaults for all new
documents.
Restore User Default Settings: Check this to return
the page setup defaults to the most recent settings that
were saved.
Printer Management
The SuperScript 870 Utility for MacOS allows you to
manage printer operations and print information pages. To
display the utility
1. In the SuperScript 870 Folder on your hard drive,
double-click the SuperScript 870 Utility icon.
2. From the Utilities menu, select the operation you want
to perform.
SuperScript 870 Utility dialog boxes are shown on the facing
page. SuperScript 870 Utility operations are described
below.
Change Printer
To choose another printer:
1. Click the Change Printer button on the SuperScript 870
Utility title screen.
2. In the dialog box that appears, select the appropriate
AppleTalk zone, and then select a new printer name in
the printer list.
Restore Factory Default Settings: Check this to
return the Page Setup defaults to the original
SuperScript 870 printer driver settings.
30 SuperScript 870 — Network User’s Guide

SuperScript 870 Utility for Printer Management
MACOS PRINTING
Change Printer Settings
Check Printer Status
31

Name Printer
If you have more than one SuperScript 870 printer on your
network, you should rename your printer.
From the Utilities menu, select Name Printer and enter a
new name in the dialog box. You will have to turn your
printer off and then on again before continuing.
Change Printer Settings
From the Utilities menu, select Change Printer Settings. In
the dialog box that appears, select from the options
described below. To restore all settings to their default
values, click the Defaults button.
Energy Saving: Controls the amount of time the
printer waits without receiving data before going into
energy saving mode. When the printer is in energy
saving mode, it “sleeps” until it receives a print job.
Enter a value from 1 to 255 minutes (the default setting
is 15). Select Off to deactivate energy saving mode. The
default setting is 15 minutes.
Manual Feed Time Out: This setting determines how
long the printer waits for you to insert paper in the
manual feed slot when manual feed has been selected. If
you exceed this period, the printer prints the job using
paper from the paper tray. The default setting is Off (the
printer waits indefinitely for paper to be inserted into
the manual feed slot).
Wait Time Out: This setting determines how long the
printer waits for data before ejecting a partially printed
page. By default, this setting is turned off but you can
change it if complex print jobs (documents containing a
lot of graphics, gradations, or shading) are not printing
because the printer driver is taking too long to process
them. You may also want to change this setting if you
have a very slow computer or you are using an
application that is slow to retrieve data (such as a
database program).
Auto Continue: This setting controls whether the
printer continues printing after it detects an error. When
this feature is Off, the printer waits for you to press the
Operator Panel button of the printer before it resumes
printing. The default is On
Jam Recovery: This setting controls whether the
printer automatically reprints pages that did not print
because of a jam. With jam recovery On, printing may
take a little longer. The default is Off.
Horizontal Offset: Select Custom, and enter a value to
shift the page image right or left on the paper. Setting a
negative value moves the image to the left; a positive
value moves it to the right. You can set a value from -127
to +127. Each increment is equal to one three-hundredth
of an inch. The default setting is zero.
Vertical Offset: Select Custom, and enter a value to
shift the page image up or down on the paper. Setting a
negative value moves the image up; a positive value
moves it down. You can set a value from -127 to +127.
Each increment is equal to one three-hundredth of an
inch. The default setting is zero.
32 SuperScript 870 — Network User’s Guide

Check Printer Status
You can view online information about your printer’s
status. In the SuperScript 870 Folder, double-click the
SuperScript 870 Utilities icon. From the Utility menu,
select Check Printer Status.
Print Demo Page
Select this command from the Utilities menu to print a
demonstration page that illustrates your SuperScript 870’s
capabilities.
Print Settings Page
Select this command from the Utilities menu to print
pages that provide a summary of your printer’s settings
and network information.
Print SuperScript 870 File
Select this command from the Utilities menu to print a
document that was previously saved as a SuperScript 870
file, using the Destination/File option in the Print dialog
box. A file browser appears that you use to locate the file.
The Spooler and Background Printing
MACOS PRINTING
You can use the SuperScript 870 Spooler to print
documents in the background, to check the status of your
print jobs, and to reorder and cancel jobs.
To use the Spooler, you need to activate Background
Printing. This allows you to continue working while your
print job is processing.
Activate Background Printing
1. Select the Chooser in the Apple menu.
2. Click on the SuperScript 870 printer for which you
want to enable background printing. (You may have
to scroll through the list of zones and printers to find
the one you want.)
3. Set Background Printing to On for that printer.
Viewing Print Status Information
Status information is available with both foreground and
background printing. During foreground printing (when
background printing is disabled), this information is
displayed in a status window. During background
printing, it is displayed in the SuperScript 870 Spooler
window.
33

Launching the Spooler
The Spooler is launched automatically when you print a
document (if background printing is on). To view the
Spooler window, select SuperScript 870 Spooler from the
Finder menu in the upper right corner of your screen.
You can also open this window when there are no
documents being printed (or when background printing is
off), by double-clicking on the SuperScript 870 Spooler icon
in the Extensions Folder inside the System Folder.
The Spooler shows information about the job currently
being printed and lists jobs waiting in the print queue.
SuperScript 870 Spooler
Canceling an Active Print Job
To stop the job that is currently printing, display the Spooler
window, select the current job, if necessary, and click Cancel
Printing.
Removing a Print Job
You can remove a print job from the Spooler Waiting list.
Just select the name of any document listed under Waiting
and click Remove From List.
Reordering Print Jobs
You can reorder print jobs in the Spooler . Use your mouse to
drag and rearrange print job names in the Waiting list.
Spooler Preferences
34 SuperScript 870 — Network User’s Guide

Stopping the Printer
You can pause the printer temporarily to remove a print
job from the Waiting list or change the order of print jobs.
If a document is being printed when you pause the print
queue, the printer finishes it before stopping.
To stop the printer: Select Stop Printing from the
File menu when the Spooler window is displayed.
To resume printing: Select Resume Printing from
the File menu when the Spooler window is displayed.
Setting Spooler Preferences
You can control how and when status information, errors,
and alerts are displayed by setting Spooler preferences.
1. With the SuperScript 870 Spooler window displayed,
select Preferences from the File menu.
2. Select or change the status message display options in
the Preferences dialog box, and click OK.
Preference settings are shown in the illustration on
page 34.
MACOS PRINTING
35

Basic Setup for UNIX
UNIX setup consists of 1) setting the IP Addr ess on the NIC,
and 2) setting up one of two printing modes, either
The SuperScript NIC printer supports
• Solaris 2.x
• SCO Openserver Release 5
Printer-based lpd: Here, the printer appears as a
resident host running a line printer daemon. The printer
can print the username and filename on its banner page.
In this mode, a printing daemon must be installed on
each host that you want to print jobs.
Host-based lpd: Here, a supplied line printer daemon
is run on one or more workstations and print data is
communicated to the NIC using a TCP/IP port. The
printer can print a banner page with the host’s name
only. You configure the printer only one time, when you
install the print server. The 870 Network Options CD
contains the tools you need to setup host-based lpd
printing for UNIX.
In general, printer-based lpd is easiest to use on BSD UNIX
systems, requiring an entry in the printcap file once the NIC
has its IP information. Some UNIX System V systems have
restrictions on support of remote LPD printers, requiring
that the host-based LPD approach be used. For many
operating systems, you have the option of using either
method.
This section includes setup for these supported systems
using printer-based lpd or host-based lpd.
The 870 should also work with all UNIX systems that
support lpd, and operate with other host-resident print
supervisor/spooler programs that present a print image to
the printer over a TCP/IP port. Additional UNIX setup
procedures can be found in your system administration
manuals.
First, Configure the IP Address on the NIC
Regardless of the printing mode selected, the NIC must be
assigned an IP address and routing parameters.
The example below uses ARP and ping commands.
note:
You will need to provide the Ethernet MAC address of the
NIC. This is the 12-character code that is listed as Network
Address on the Network Settings page. A Network Settings
page is printed out each time the printer is turned on or
reset.
You can also use BOOTP or RARP.
36 SuperScript 870 — Network User’s Guide

Assigning the IP Address using arp and ping
1. Turn off the printer.
2. Log in as superuser on a host on the same subnet as the
printer NIC.
3. Find the Ethernet address of the NIC. The address is
printed on the Network Settings page.
4. Edit the hosts file (usually /etc/hosts) or use NIS
or DNS to add the IP address and printer NIC name.
See the network administrator for the IP address. For
example, a printer NIC with the name superscript and
an IP address of 192.9.200.200 has the following
entry:
192.9.200.200 superscript
5. Add an entry to the ARP cache for the printer NIC’s IP
address and Ethernet address. For example:
arp -s 192.9.200.200 00:40:c8:80:04:ff
6. Check the printer to see that the host is on the same
subnet/network as the printer. Turn on the printer.
7. Use a ping command to start the IP address
assignment. For example:
ping 192.9.200.200 or ping superscript
address, the result is a confirmation message:
192.9.200.200 is alive
9. Remove the entry from the ARP cache using the
following command. Specify the printer NIC either by
its IP address or by its name. For example:
arp -d superscript
Second, Set Up Your Printing Mode
To set up printer-based lpd for SCO UNIX remote
printers and Solaris 2.x, continue below.
To set up TCP/IP and host-based lpd for Solaris 2.x and
SCO UNIX systems, proceed to page 39.
Printer-Based lpd Setup
lpd is an implementation of the standard UNIX line
printer daemon which lets you print across a TCP/IP
network, without the need to install software on your
workstation, and with all filtering and banners done by
the NIC. Remote printing uses the same commands (lpr,
lpq, lpc) as local printing.
UNIX SETUP
The printer NIC will not respond to this ping
command but it will read its IP address from the
packets.
8. Turn the printer off and back on again and then use
the ping command again to verify that the printer NIC
obtained its IP address. If the printer NIC has the
The process begins when the lpr call finds a printer on a
remote system by looking at the remote (rm) entry in the
/etc/printcap file for that printer. lpr handles a print
job for a remote printer by opening a connection with the
lpd process on the remote system and sending the data file
(followed by the control file containing control
information for this job) to the remote system. The printer-
37

based lpd then filters the data and prints the job according
to information contained in the control file and its own
printcap file.
The NIC lpd recognizes printer emulations, such as PCL and
ASCII, and formats the data so it can be printed on the 870
printer. Using the NIC Home Page, you can set the NIC port
to PCL, ASCII, or Other. The SuperScript 870 cannot print
PostScript files.
The following sections give specific lpd setup instructions
for various systems. You must log in as a superuser in order
to execute the commands.
Setting Up Remote Printing on SCO UNIX
1. Set up the SuperScript 870 printer with the NIC as a
remote printer on a host that sends jobs to a Print Server
using lpd. Use the following procedures to do this:
At the prompt, type: mkdev rlp
note:
additional printers to be configured, use the
command.
You cannot run
mkdev rlp
twice. If you have
rlpconf
2. You will now be asked a series of questions. Respond as
follows. Do you want to install or remove a remote
printer? Type: I
3. Do you want to change printer description file
/etc/printcap? Type: Y
4. Write a printer name. For example,
type: lprprinter1
5. Is lprprinter1 a remote printer or a local printer? Type: R
6. Enter remote host name: type host name entered in
printcap for the NIC. For example, type: lprprinter
7. Confirm the information you have entered. Type: Y
8. Confirm the preceding connection as your system
default. Type: Y
9. Enter another printer name or quit setup. Type: Q
10. Do you want to start the remote daemon now? Type: Y
Using a line editor of your choice, add the following to
your /etc/printcap file.
lprprinter1:\
:lp=:\
:rm=lprprinter:\
:rp=PORT1:\
:sd=/usr/spool/lpd/lprprinter1:
note:
in the earlier steps. Actual parameters may vary
depending on prior setup.
This information was based on the sample input
38 SuperScript 870 — Network User’s Guide

Setting Up Solaris 2.X to Use lpd
If your system recognizes the lpsystem command, you
can use lpd. Another option is the admintool if your
system supports it.
Use the following steps to install, using lpsystem:
1. lpsystem -t bsd <IP_address_of_NIC>
Enter the NIC print server host name from the
/etc/hosts file. Your system may want its IP
address instead of the remote host name.
2. lpadmin -p <local printername> -s
<remote host name or IP address>!PORT1
note:
3. Enable<local printername>
4. Accept<local printername>
There is no space after the remote host name.
Host-based lpd Setup
UNIX SETUP
Once the NIC has its IP address assigned, the following
steps are necessary for Host-Side TCP/IP printing.
1. Load the provided print server software, Network
Utilities for UNIX on your workstation.
Loading the Software
The 870 Network Options CD contains install scripts for
host-based printing on various UNIX systems. (Loading
the software is not necessary if printer-based lpr is used.)
1. Log in as superuser to the system that spools directly to
the print server.
2. Insert the 870 Network Options CD in the host drive.
3. Mount your CD-ROM and go to the UNIX directory.
Now you can run the appropriate installation script and
complete the configuration for your operating system. In
this section we provide examples for SCO UNIX and
Solaris 2.x.
39

Installing and Printing on Solaris 2.x
1. Run the Installation script by typing: nicinst. Once
the operating system has been identified, the script
downloads the files for your particular system, to the
/usr/nic directory, and prompts you for information
as needed.
2. Type
cp /usr/spool/lp/model/standard
/usr/nic/port1_interface
note:
suffice for generic or routine printing of most PCL and
ASCII files. To use a printer specific interface other than
the default interface script (named standard), you must
have a copy of that printer interface edited and installed
in the /usr/nic directory.
Use of this default interface in most cases will
Next, you will need to edit the printer interface program
you created.
3. Type
cd /usr/nic and using an editor, open and edit the
port1_interface file.
4. Search for FILTER= and insert the following line above
or below the # FILTER="${LPCAT} section of the file.
Comment (using the # sign) any other FILTER entries
present in this section of the file.
FILTER="/usr/nic/infilter| /usr/nic/
nicfilter <printer NIC name> 10001"
The <printer NIC name> must be the same as the
one present in the /etc/hosts file. Optional
arguments to be inserted after the 10001 entry and
before the trailing <“>are
${banner}
${user_name}
${request_ID}
${files}.
For further explanation of these and the statement
above, refer to the System 5 Release 4 System
Administration Manual.
5. Save the file and close the editor.
You need to configure the host-side printer using
lpadmin.
40 SuperScript 870 — Network User’s Guide

6. Type the following command.
lpadmin -p <printer name>
-v /dev/null -i /usr/nic/port1_interface
note:
associates it with a given device and printer interface
program. There is no
method of configuration.
lpadmin configures the printer name and
/etc/printcap
file involved with this
Next, you need to initialize the printer.
7. Type the following commands.
accept <printer name>
enable <printer name>
note: After each entry, lpadmin should provide an
acknowledgment of the command invoked.
8. Type the following command.
lp -d <printer name> /etc/hosts, and
press ENTER.
9. Check for output, or type the following:
lpstat <printer name> or -t.
and press ENTER.
and press ENTER.
Installing and Printing on SCO UNIX
UNIX SETUP
After loading the software from the 870 Network Options
CD, you must configure the printer and make it known to
the lp system.
Follow the steps below.
1. Run the Installation script by typing: nicinst. The
script automatically downloads the correct NIC print
server utilities for your particular system and prompts
you for information as needed.
One of the questions posed by the install script is
whether the printer is a PostScript printer . You have to
answer no because the 870 printer does not support
PostScript language. Then the install script uses an
input filter (infilter) that supplies CR/LF translation to
print ASCII files on a PCL printer.
2. Select your system. Choose one of these options.
1) AT&T/SVR4; 386
2) SCO UNIX System V
3) None of the above
Type: 1, 2, or 3 and press ENTER.
3. Enter the IP nodename of this Network Interface
Card.
Type the name assigned in the /etc/hosts file and press
ENTER. For example: superscript
4. Enter the Printer Name to be used by this printer:
Type a printer name and press ENTER.
41

5. Your screen will now display the information you
provided the install script. For example,
Node name of the NIC: superscript
Printer name to be used: <printer_name>
Do you want to accept this configuration?
Type: yes and press ENTER.
6. The script automatically starts the daemon for the newly
configured printer. It also displays the path you should
use if you ever need to restart the daemon. In the
preceding example, the path would be:
/usr/nic/nic_print /dev/nic/printer_name superscript
10001 &
note:
reload the daemon manually using the command
mentioned above.
When you reboot your PC, it may be necessary to
This example reflects names supplied in the script
earlier.
When the installation script is complete, you must still
configure the printer and make it known to the lp system.
The SCO UNIX lp system uses the lpadmin maintenance
command to configure a printer (there is no
/etc/printcap file). The specific commands to do this
are:
lpadmin -p printer_name
-v /dev/nic/printer_name
note:
by using the -i command.
Your host may require you to specify the model
enable <printer_name>
accept <printer_name>
You can also use other options for the lpadmin command.
See your system documentation for details. Note that the
printer name must be the same as the one you entered
during NIC installation. SCO supplies the sam program as
an alternative to configure the printer.
When using sam, specify everything as if the printer were
directly connected to /dev/nic/printer_name.
The software installed with your SCO system can satisfy
most of your printing needs. Use the lpfilter command
to define new filters and content types if necessary.
42 SuperScript 870 — Network User’s Guide

Identifying the Problem
Use the checklists in this section to identify the cause of
printing problems. If a problem persists, contact NEC
Printer Technical Support at their web site
(www.nec.com/nectechsupport) or phone 1-800-632-4650.
Check the Printer Operation
Verify that the printer is plugged in, turned on, and
online—the green Online light on the Operator Panel
should be lit (or blinking slowly if in energy saving mode),
or nothing will print.
Check NIC Status Lights
TROUBLESHOOTING
Check the NIC’s status lights to ensure that there is no
error condition. The two status lights, amber and green,
are located on the interface panel on the back of the
printer. The green light should be lit and steady. Light
patterns that indicate serious hardware problems or
software errors are shown below. If you see one of these
patterns, you should contact NEC Printer Technical
Support.
Green light blinks rapidly: This occurs when the
printer performs a self-test and detects bad SIMM.
Check the Network Settings Page
On power-up, the NIC prints out a Network Settings page
which has useful information for troubleshooting. Check
the Network Settings page to see which protocols are
enabled and active. Confirm that the network protocol
you configured appears on the page. If not, it should be
reconfigured correctly for the NIC. (For instructions on
printing a Network Settings page, see page 6.)
Check Printer Status on NIC Home Page
Go to the NIC Home Page and click the Get Current
Status button to view the printer status. (For instructions
on how to browse to the NIC Home Page, see page 8.)
Check other Network Users
Determine if other users can print. If they cannot and they
are all on the same network operating system, the problem
is most likely in the network configuration.
Green light blinks rapidly 4 times, pauses: This
occurs when the printer performs a self-test and
detects a problem in the Ethernet hardware.
Amber light blinks short for 10 seconds, then goes
out, and the green light blinks continuously: This
occurs when the printer performs a flash memory selftest and the checksum fails.
Green light blinks slowly: When this happens after
power-on completes, it indicates an interface error.
Green light blinks rapidly: When this happens while
the printer awaits print jobs, it indicates that the
NetWare connection has been lost.
Green and amber lights blink alternately: This
would occur when you turn on the printer after
restoring factory defaults, and indicates an error.
43

Review Recent System Changes
Verify that any hardware changes (installations,
modifications, removals), to the printer or network, were
done correctly. If you added a new software application,
make sure the program is compatible and installed correctly
on the network. See your network protocol documentation
to confirm.
Check Hardware Connections
• Be sure that your cable is a Category 5 twisted pair cable
with RJ-45 connectors for 10/100Base-T ethernet.
• Check that the network connector is plugged into the
RJ-45 connector on the NIC.
• Try another cable to make sure you do not have a bad
cable.
• If you are using a 10/100Base-T concentrator hub that
does not support the link signal, use Manual Ethernet
Port selection instead of the factory default, Automatic
Ethernet Port selection.
Troubleshooting for NetWare
Use MAP and the NIC Home Page/Network
Administration options to troubleshoot in an IPX
environment (see page 8 for instructions on using the NIC
Home Page). The checklists in this section show what to
look for.
NetWare Checklist
• Is the NIC name entered correctly? The factory-default
name is NEC_<serial number>
The serial number is on the back of the NIC and also
shown at the top of the Network Settings page.
• Did you assign print queues to the printer? It is
recommended you assign each print queue to a specific
printer NIC. If print queues are assigned to other
network printers, the print jobs may be going to another
network printer.
• Did you assign the printer to the type Remote Other /
Unknown?
If the PCONSOLE NWAdmin settings are correct, the
connection between the printer and network may have been
broken. Turn the printer off and, using PCONSOLE, wait for
the status message Not Connected. Turn the printer on and
the status should change to Waiting for Job.
44 SuperScript 870 — Network User’s Guide

File Server Checklist
• Is there enough disk space on the file server and is it
running?
• Is the correct file server associated with the printer?
Use PCONSOLE to check.
• Did you have the proper rights to configure the
printer?
Computer Checklist
• Is the network loaded onto the computer? See your
NetWare documentation.
• Is the application set up to print to the printer? Are
you using the correct driver?
• Is the workstation connected to the correct print
queue? Print a file and verify that the file goes to the
queue.
• Are the print queues assigned to the NIC-connected
printer also assigned to another network printer? If
they are, the print jobs may be going to that printer.
• Is AUTO ENDCAP enabled? AUTO ENDCAP lets you
send data to a network printer. If it is not enabled,
enable it.
• Are text files printing but graphic files not? The
printing may be timing out. Use NetWare's
PRINTCON or CAPTURE to set a longer timeout
period. Set the time to at least two minutes for
graphics applications.
NIC Configuration Checklist
TROUBLESHOOTING
If all your hardware connections are correct, check the
following
• Use the NIC Home Page to check the status of the
NIC. The NIC Network Settings page shows the status
for the selected network interface card. This report
includes the status of file servers and queues assigned
to a printer along with a description of any problems.
• The printer may not be assigned to the correct print
queues. Use PCONSOLE to direct print jobs to the
correct queues, then check to see if the print job is in
the queue.
• If devices were added or changed, use PCONSOLE to
make sure you configured the new devices correctly.
• Make sure the NIC name has been entered correctly. If
you changed the name using the NIC Home Page, you
must also change the name in PCONSOLE.
• You cannot use PCONSOLE Version 1.0 to configure
the NIC. Contact Novell for an upgrade.
NIC/File Server/Printer Checklist
Check the following to see if the NIC and file server are
sending data to the printer. If the NIC cannot log onto the
file server, or cannot service jobs from a file server
• The NIC is not created on that file server. Use
PCONSOLE to create the print server on the correct
file server.
45

• The password assigned to the NIC through PCONSOLE
does not match the password assigned using the NIC
Home Page. Use the NIC Home Page to update the
password stored in the NIC’s memory.
• Use PCONSOLE to check if the print jobs are being sent
to the printer. Be sure the print job is in the print queue
and waiting to be printed.
Computer to NIC Connection Checklist
To make sure the computer is communicating with the NIC,
perform these tests.
• Print a file from the workstation and make sure the print
job gets to the print queue using PCONSOLE. If the
print job does get to the queue, the problem is not with
the workstation/NIC connection.
• Use CAPTURE to send data to the printer from a
workstation software application. See your NetWare
print server manual for information.
• Make sure another printer is not taking the print jobs
from the queues before the NIC can service the job. To
do this, disable the other printer and send another
print job.
NIC Loses Its File Server Connection: If the NIC loses
its connection to the file server, it will take
approximately five to 10 minutes to reconnect. If the
connection is not made after a reasonable amount of
time, check the error conditions to troubleshoot the
problem.
Unable to Print from a Different Context: The NIC
does not support printing from a context other than the
one you specified using the MAP utility on your Web
browser. To do this, you must create an alias queue. See
your NetWare Manual for more info.
Troubleshooting for MacOS
• Is the Macintosh computer connected to the network
through Ethernet, and has the correct network port been
selected?
• Did you select the correct printer driver, zone, and
printer name in the Chooser?
• If you renamed the printer in the SuperScript 870 Utility,
you must power the printer off then on, and then
reselect the printer under its new name in the Chooser.
• If you placed the printer in a new zone, be sure you
reselected the zone and the printer name in the Chooser.
• The default name for the SuperScript 870 printer is
SuperScript 870N #, where # is the sequential number of
870 printers installed. If a user changes the name of
SuperScript 870 2 to Mary’s Printer, the last printer in
line will be reassigned the name Superscript 870 2, and
the print path must be changed using the Chooser for
the system to work again.
46 SuperScript 870 — Network User’s Guide

Numerics
10/100 Base-T connection 3
870 NIC 2
A
ARP 18
B
BOOTP Lite-16 15
BOOTP Lite-32 14
C
cable specifications 3
category 5 cable 3
CD contents 3
configuring a NIC for NetWare 21
connecting the NIC to the network 4
cover page (in MacOS) 27
D
default password 10
DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration
Protocol)
assigning IP address 19
NIC configuration 19
E
ethernet address 36
F
factory defaults, restoring 7
H
hardware connections
troubleshooting 44
hardware requirements 3
I
installation requirements
hardware 3
software 3
systems 2
installing the NIC 4
IP address
assigning in UNIX 36
assigning in Windows 95/98 14
assigning in Windows for
Workgroups 15
assigning in Windows NT 4.0 14
assigning using ARP 18
assigning using BOOTP Lite-16 15
assigning using BOOTP Lite-32 14
assigning using DHCP 19
assigning using ping 37
L
lpr printing 18
M
MAC address 36
MacOS
background printing 24, 33
basic setup 24
canceling a print job 34
checking printer status 24, 33
how to print 26
monitoring print jobs 33
print demo page 33
print job setup 26
print settings pages 33
print SuperScript 870 file 33
printer management 30
change printer settings 32
change printers 30
rename printer 32
printing 25
renaming the printer 24
reordering print jobs 34
resolution setting 26
stopping the printer 35
system requirements 25
the chooser 24
the spooler 33
troubleshooting 46
MacOS page setup
default options 30
dialog boxes 29
flip horizontal 29
flip vertical 30
invert image 30
Click on Any Page Number to Go to That Page
Index i

orientation 28
page scaling 28
page size 28
precision bitmap alignment 30
print preview 29
printable area 29
MacOS print job settings
cover page 27
destinations 27
halftones 28
imaging 28
number of copies 26
page range 26
paper source 27
print colors as 27
print order 27
resolution 26
toner usage 26
trailer page 27
MacOS printer settings
auto continue 32
energy saving 32
horizontal offset 32
jam recovery 32
manual feed time out 32
vertical offset 32
wait time out 32
MAP
configuring a NIC for NetWare 21
installing 11
operating requirements 11
selecting a NIC 12
monitoring printer status 8
mounting screw 2
N
NetWare
3.x basic setup 22
4.x basic setup 20
troubleshooting 44
NetWare 4.x
MAP configuration 21
network address 8
network administration 8, 21
configuring the network settings
page 10
displaying printer status 10
downloading printer drivers 10
online help 10
ordering supplies 10
password 10
protocols 10
resetting the NIC 8
restoring factory defaults 8
setting up the printer 10
testing the printer 10
viewing network address 8
viewing network information 10
viewing unit status 8
network connection status 8
Network Options CD 3
network print details 10
network protocols 10
network settings page
configuration 10
how to print 6
network upgrade kit
package contents 2
NIC home page 8
DHCP settings 19
getting technical support 10
monitoring printer status 8
network administration options 8
ordering supplies 10
NIC interface cable 2
NIC status information 8
NIC status lights
error conditions 43
normal operations 7
NWADMIN 20
O
operator panel button 6
ii SuperScript 870 — Network User’s Guide
Click on Any Page Number to Go to That Page

P
password 10
PCONSOLE 22
peer to peer printing
adding the printer in Windows 17
installing software 16
IP 16
IPX 16
moving a printer 17
removing software 17
printer drivers
SuperScript 870 for Windows 2
printer status 10
printing to file 27
protocols 10
R
resetting the NIC 7
restoring factory defaults 7
RJ-45 connectors 3
S
setup printer 10
shielded twisted pair cable 3
software requirements 3
Spooler (MacOS)
setting preferences 35
spooler (MacOS) 33
status page (see network settings
page) 6
SuperScript 870 files
creating 27
printing 33
SuperScript 870 Utility for MacOS 31
supplies, ordering 10
supported printing environments 2
supported UNIX environments 36
T
TCP/IP
requirements for Windows
Windows 95/98 and
Windows NT 4.0 14
Windows for Workgroups 15
technical support
from the NIC home page 10
ordering supplies 10
testing the NIC 4
testing the printer 10
trailer page (in MacOS) 27
troubleshooting
hardware connections 44
identifying the problem 43
MacOS 46
NetWare 44
twisted pair cable 3
13
U
UNIX
assigning IP address 36
basic setup 36
host-based lpd 36
host-based lpd setup 39
installing TCP/IP 39
loading utilities 39
Network Utilities for UNIX 36
printer-based lpd 36
printer-based lpd setup 37
supported environments 36
UNIX host-based setup
SCO UNIX
Solaris 2.x setup 40
UNIX printer-based setup
SCO UNIX remote printing 38
Solaris 2.x setup 39
user information
on the CD 3
on the NIC home page 10
41
W
Windows
network printing options 13
peer to peer printing 16
setting lpr printing 18
using ARP to assign IP address 18
Windows 95/98 14
Windows for Workgroups 15
Windows NT 4.0 14
Click on Any Page Number to Go to That Page
Index iii

FCC Statement
(For United States Use Only)
Federal Communications Commission Radio Frequency Interference
Statement.
WARNING: Changes or modifications to this unit not expressly
approved by the party responsible for compliance could void the user’s
authority to operate the equipment.
NOTE: This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the
limits for a Class A digital device, pursuant to Part 15 of the FCC Rules.
These limits are designed to provide reasonable protection against
harmful interference in a residential installation. This equipment
generates, uses, and can radiate radio frequency energy and, if not
installed and used in accordance with the instructions, may cause
harmful interference to radio communications.
However, there is no guarantee that interference will not occur in a
particular installation. If this equipment does cause harmful interference
to radio or television reception, which can be determined by turning the
equipment off and on, the user is encouraged to try to correct the
interference by one or more of the following measures.
• Reorient or relocate the receiving antenna.
• Increase the separation between the equipment and receiver.
• Connect the equipment to an outlet on a circuit different from the
one to which the receiver is connected.
• Consult the dealer or an experience radio or TV technician for help
Use a shielded and properly grounded I/O cable to ensure compliance of
this unit to the specified limits of the rules.
Your 870 SuperScript printer with optional Network Interface Card (NIC)
installed meets the requirements of FCC Class A when connected to an
Ethernet cable.
(For Canadian Use Only)
This digital apparatus does not exceed the Class A limits for radio noise
emissions from digital apparatus as set out in the radio interference
regulations of the Canadian Department of Communications.
Le présent appareil numérique n’émet pas de bruits radioélectriques
dépassants les limites applicables aux appareils numériques de Classe
A présentes dans le règlement sur le brouillage radioélectrique édictaté
par le Ministère des Communications du Canada.
Declaration of Conformity
This device complies with part 15 of the FCC Rules. Operation is subject
to the following two conditions:
1. This device may not cause harmful interference.
2. This device must accept any interference received, including
interference that may cause undesired operation.
U.S. Responsible Party: NEC Technologies, Inc.
Address:
Telephone Number: 630-467-5000
Type of product: Laser Printer.
Equipment Classification: Class A Peripheral.
Model: SuperScript 870 with Network Interface Card (NIC) installed.
We hereby declare that the equipment specified
above conforms to the technical standards as
specified in the FCC rules.
1250 N. Arlington Heights Road,
Itasca, Illinois 60143
iv SuperScript 870 — Network User’s Guide
 Loading...
Loading...