Page 1

Page 2

Page 3

Technical Information Updates
As we continue to make engineering enhancements to our products, the information in our
Service Manuals need to be updated accordingly. If you wish to be informed of these
updates, kindly fill in and fax us your details.
Fax to: 6-04-6194467
The Technical Publications Coordinator,
Global Customer Documentation,
R&D Department,
Motorola Penang.
Your Details
N a m e / C o n t a c t P e r s o n :
Company Name:
Address:
Telephone No.:
Fax No.:
Email Address:
How would you like to receive the update notification?
Through:
Manual No.:6878419A01
Kindly complete the Service Manual Feedback Form on the next page to help us ensure
that you receive the most accurate and complete information.
mail email fax
Page 4

Service Manual Feedback Form
We believe that reports from users provide valuable information for producing quality
manuals. Kindly take a few moments to provide feedback on this manual. Thank you for
your cooperation.
Fax to: 6-04-6194467
The Technical Publications Coordinator,
Global Customer Documentation,
R&D Department,
Motorola Penang.
1. Please check all the appropriate boxes:
Complete
Disassembly
Procedures
Alignment
Procedures
Exploded
Views
Schematic
Diagrams
Circuit Board
Details
Electrical Parts
List
Exploded View
Parts List
Incomplete
Correct
Incorrect
Clear
Confusing
Size
Adequate
Size
Too Small
Not Covered
2. How do you rate this particular Service Manual?
excellent very good good fair poor
3. Did this Service manual provide you with the information necessary to service and
maintain the specific equipment?
very much so generally yes to some extent no
4. We would appreciate any corrections or recommendations for improving this manual.
Please include the specific page number(s) of the diagram or procedure in question.
in this Manual
5. General comments/suggestions:
Manual No.:6878419A01
Page 5

COPYRIGHT
Copyrights
© 2009 by Motorola, Inc. All rights reserved.
No part of this manual may be reproduced, transmitted, stored in a retrieval system, or translated into
any language or computer language, in any form or by any means, without the prior written
permission of Motorola Inc.
Computer Software Copyrights
The Motorola products described in this manual may include copyrighted Motorola computer
programs stored in semiconductor memories or other media. Laws in the United States and other
countries preserve for Motorola certain exclusive rights for copyrighted computer programs including,
but not limited to, the exclusive right to copy or reproduce in any form the copyrighted computer
program. Accordingly, any copyrighted Motorola computer programs contained in the Motorola
products described in this manual may not be copied, reproduced, modified, reverse-engineered, or
distributed in any manner without the express written permission of Motorola. Furthermore, the
purchase of Motorola products shall not be deemed to grant either directly or by implication, estoppel,
or otherwise, any license under the copyrights, patents or patent applications of Motorola, except for
the normal non-exclusive royalty-free license to use that arises by operation of law in the sale of a
product.
i
Trademarks
MOTOROLA and the Stylized M Logo are registered in the U.S.Patent and Trademark Office. All
other product or service names are the property of their respective owners.
Page 6

ii
SAFETY
Product Safety and RF Exposure Compliance
These servicing instructions are for use by qualified personnel only. To reduce the
risk of electric shock, do not perform any servicing other than that contained in the
Operating Instructions unless you are qualified to do so. Refer all servicing to
qualified service personnel.
Before using this product, read the operating instructions for safe usage contained
in the Product Safety and RF Exposure booklet enclosed with your radio.
ATTENTION!
This is restricted to occupational use only to satisfy ICNIRP RF energy exposure
requirements. Before using this product, read the RF energy awareness information and
operating instructions in the Product Safety and RF Exposure booklet enclosed with your
radio (Motorola Publication part number 68007024010) to ensure compliance with RF energy
exposure limits.
For a list of Motorola-approved antennas, and other accessories, visit the following web site
which lists approved accessories: http://www.motorola.com/governmentandenterprise
Page 7

DOCUMENT HISTORY
The following major changes have been implemented in this manual since the previous edition:
Edition Description Date
6878419A01-A Initial edition Feb. 2009
6878419A01-B Added UHF1 403 – 447 MHz information Sept. 2009
CHAPTER 1 : Model Charts and Test Specifications
Updated UHF1 range to 403 – 447 MHz
Added UHF1 model chart and specifications
Updated Receiver, Transmitter, PLL Synthesizer, TX Audio
Block Diagrams
CHAPTER 3 : Test Equipment, Service Aids, and Service Tools
Updated “Wiring of the Connectors” diagram
CHAPTER 5 : Radio Programming and Tuning
Updated “CPS Programming Setup” diagram
Updated “Radio Tuning Setup diagram
Added UHF1 band in “Transmitter Alignment Options” table
iii
CHAPTER 6 : Maintenance (FKP)
Added UHF1 PCB parts list
Updated Exploded View (Remove Tanapa Label)
Updated Quantity in Parts List
CHAPTER 7: Maintenance (LKP)
Added UHF1 PCB parts list
Updated Exploded View (Remove Tanapa Label)
Updated Quantity in Parts List
Page 8

iv
Notes
Page 9

Table of Contents v
Table of Contents
Copyright ........................................................................................................ i
Safety ............................................................................................................. ii
Document History ........................................................................................ iii
Chapter 1 Model Charts and Test Specifications .............................. 1-1
1.1 Radio Model Information................................................................................................................ 1-1
1.2 Model Chart for UHF2, 435–480 MHz ........................................................................................... 1-2
1.3 Model Chart for VHF, 136–174 MHz .............................................................................................1-3
1.4 Model Chart for UHF1, 403–447 MHz ........................................................................................... 1-4
1.5 UHF2 Specifications ...................................................................................................................... 1-5
1.6 VHF Specifications ........................................................................................................................ 1-6
1.7 UHF1 Specifications ...................................................................................................................... 1-7
Chapter 2 Theory Of Operation ........................................................... 2-1
2.1 Introduction .................................................................................................................................... 2-1
2.2 Major Assemblies .......................................................................................................................... 2-1
2.2.1 Receiver............................................................................................................................ 2-1
2.2.1.1 RX Front End..................................................................................................... 2-2
2.2.1.2 RX Back End ..................................................................................................... 2-2
2.2.1.3 RX Squelch........................................................................................................ 2-3
2.2.2 Transmitter........................................................................................................................ 2-4
2.2.3 Phase Lock Loop Synthesizer .......................................................................................... 2-5
2.2.4 RX Audio Circuit ............................................................................................................... 2-6
2.2.5 TX Audio Circuit................................................................................................................ 2-7
2.2.6 Microcontroller .................................................................................................................. 2-8
2.2.7 Power Supply.................................................................................................................... 2-8
Chapter 3 Test Equipment, Service Aids, and Service Tools........... 3-1
3.1 Test Equipment.............................................................................................................................. 3-1
3.2 Service Aids................................................................................................................................... 3-2
Chapter 4 Performance Checks .......................................................... 4-1
4.1 General .......................................................................................................................................... 4-1
4.2 Power–Up Self Test....................................................................................................................... 4-1
4.3 LCD/LED/Button/Volume Knob Test Mode.................................................................................... 4-1
Chapter 5 Radio Programming and Tuning ....................................... 5-1
5.1 Introduction .................................................................................................................................... 5-1
5.2 CPS Programming Setup .............................................................................................................. 5-1
5.3 Radio-to-Radio Cloning ................................................................................................................. 5-1
Page 10

vi Table of Contents
5.4 Radio Tuning Setup ....................................................................................................................... 5-2
5.4.1 Initial Test Equipment Control Settings............................................................................. 5-3
5.5 Transmitter Alignment Options ......................................................................................................5-3
5.5.1 Transmit High Power Tuning ............................................................................................ 5-3
5.5.2 Transmit Low Power Tuning ............................................................................................. 5-4
5.5.3 Transmit Modulation Tuning .............................................................................................5-5
5.5.3.1 Service Monitor Setting...................................................................................... 5-5
5.5.3.2 Transmit 12.5 kHz Modulation Tuning ...............................................................5-6
5.5.3.3 Transmit 25 kHz Modulation Tuning ..................................................................5-7
5.6 Receiver Tuning............................................................................................................................. 5-8
5.6.1 Service Monitor Setting..................................................................................................... 5-8
5.6.2 Receive 12.5 kHz-Band Normal Squelch Tuning.............................................................. 5-9
5.6.3 Receive 12.5 kHz-Band Tight Squelch Tuning ............................................................... 5-10
5.6.4 Receive 25 kHz-Band Normal Squelch Tuning............................................................... 5-11
5.6.5 Receive 25 kHz-Band Tight Squelch Tuning .................................................................. 5-12
5.7 Utilities ......................................................................................................................................... 5-13
5.7.1 Program Serial No. .........................................................................................................5-13
5.8 Front Panel Programming............................................................................................................ 5-14
5.8.1 Introduction ..................................................................................................................... 5-14
5.8.2 Dealer and User Configurations...................................................................................... 5-14
5.8.2.1 Switching between Dealer and User Configurations........................................ 5-14
5.8.3 Entering Programming Mode .......................................................................................... 5-15
5.8.4 Exiting Programming Mode............................................................................................. 5-15
5.8.5 Accessing Front Panel Programming Mode Parameters................................................ 5-15
5.8.6 Editing Front Panel Programming Mode Parameters ..................................................... 5-16
5.8.7 Factory Reset..................................................................................................................5-23
Chapter 6 Maintenance – EP350 (Full Keypad Model) ..................... 6-1
6.1 Introduction .................................................................................................................................... 6-1
6.2 Preventive Maintenance ................................................................................................................ 6-1
6.2.1 Inspection..........................................................................................................................6-1
6.2.2 Cleaning Procedures ........................................................................................................6-1
6.3 Safe Handling of CMOS and LDMOS Devices .............................................................................. 6-2
6.4 Repair Procedures and Techniques – General.............................................................................. 6-3
6.5 Disassembling and Reassembling the Radio ................................................................................ 6-6
6.5.1 Radio Disassembly – Detailed .......................................................................................... 6-7
6.5.1.1 Front Housing From Chassis Disassembly........................................................ 6-7
6.5.1.2 Chassis Assembly Disassembly ...................................................................... 6-10
6.5.1.3 Front Circuit Board, Display Module and Keypad Disassembly.......................6-11
6.5.1.4 Speaker Disassembly ...................................................................................... 6-12
6.5.2 Radio Reassembly – Detailed......................................................................................... 6-13
6.5.2.1 Speaker Reassembly....................................................................................... 6-13
6.5.2.2 Front Circuit Board, Display Module and Keypad Reassembly ....................... 6-14
6.5.2.3 Chassis Assembly Reassembly....................................................................... 6-15
6.5.2.4 Chassis and Front Housing Reassembly......................................................... 6-17
6.6 Torque List ................................................................................................................................... 6-17
6.7 Mechanical View and Parts List ................................................................................................... 6-18
6.7.1 EP350 (Full Keypad without Channel Knob) Exploded View and Parts List................... 6-18
Chapter 7 Maintenance – EP350 (Limited Keypad Model)............... 7-1
7.1 Introduction .................................................................................................................................... 7-1
Page 11

Table of Contents vii
7.2 Preventive Maintenance ................................................................................................................ 7-1
7.2.1 Inspection ......................................................................................................................... 7-1
7.2.2 Cleaning Procedures ........................................................................................................7-1
7.3 Safe Handling of CMOS and LDMOS Devices.............................................................................. 7-2
7.4 Repair Procedures and Techniques – General ............................................................................. 7-3
7.5 Disassembling and Reassembling the Radio ................................................................................ 7-6
7.5.1 Radio Disassembly – Detailed.......................................................................................... 7-7
7.5.1.1 Front Housing From Chassis Disassembly........................................................ 7-7
7.5.1.2 Chassis Assembly Disassembly ...................................................................... 7-10
7.5.1.3 Front Circuit Board, Display Module and Keypad Disassembly ...................... 7-12
7.5.1.4 Speaker Disassembly...................................................................................... 7-13
7.5.2 Radio Reassembly – Detailed ........................................................................................ 7-13
7.5.2.1 Speaker Reassembly....................................................................................... 7-13
7.5.2.2 Front Circuit Board, Display Module and Keypad Reassembly....................... 7-14
7.5.2.3 Chassis Assembly Reassembly....................................................................... 7-15
7.5.2.4 Chassis and Front Housing Reassembly......................................................... 7-17
7.6 Torque List................................................................................................................................... 7-18
7.7 Mechanical View and Parts List................................................................................................... 7-18
7.7.1 EP350 (Limited Keypad without Channel Knob) Exploded View and Parts List ............. 7-18
Chapter 8 Troubleshooting Tables ..................................................... 8-1
8.1 Error Codes ................................................................................................................................... 8-1
8.2 Troubleshooting Table for Receiver............................................................................................... 8-2
8.3 Troubleshooting Table for Transmitter........................................................................................... 8-3
Appendix A Accessories.........................................................................A-1
Appendix B Warranty, Service Support, and Replacement Parts .......B-1
B.1 Scope of Manual ............................................................................................................................B-1
B.2 Warranty ........................................................................................................................................B-1
B.2.1 What This Warranty Covers And For How Long...............................................................B-1
B.2.2 General Provisions ...........................................................................................................B-1
B.2.3 How To Get Warranty Service ..........................................................................................B-2
B.2.4 What This Warranty Does Not Cover ...............................................................................B-2
B.2.5 Patent And Software Provisions .......................................................................................B-3
B.2.6 Piece Parts .......................................................................................................................B-4
B.2.6.1 Basic Ordering................................................................................................... B-4
B.2.6.2 Motorola Online .................................................................................................B-4
B.2.7 Motorola Service Centers .................................................................................................B-4
Glossary of Terms .....................................................................................G-1
Page 12

viii List of Figures
List of Figures
Figure 2-1. Receiver Block Diagram ...................................................................................................2-1
Figure 2-2. Transmitter Block Diagram ...............................................................................................2-4
Figure 2-3. PLL Synthesizer Block Diagram....................................................................................... 2-5
Figure 2-4. RX Audio Block Diagram..................................................................................................2-6
Figure 2-5. TX Audio Block Diagram ..................................................................................................2-7
Figure 3-1. Programming/Test Cable (PMDN4077_R)....................................................................... 3-3
Figure 3-2. Cloning Cable (PMDN4076_R) ........................................................................................ 3-3
Figure 3-3. Wiring of the Connectors .................................................................................................. 3-3
Figure 4-4. LCD Indication.................................................................................................................. 4-1
Figure 5-5. CPS Programming Setup ................................................................................................. 5-1
Figure 5-6. Radio Tuning Setup.......................................................................................................... 5-2
Figure 5-7. Tx High Power Window (High Power) .............................................................................. 5-4
Figure 5-8. Tx Low Power Window (Low Power)................................................................................ 5-5
Figure 5-9. Tx Modulation 12.5 kHz Window ...................................................................................... 5-7
Figure 5-10. Tx Modulation 25 kHz Window .........................................................................................5-8
Figure 5-11. Rx 12.5 kHz-band Normal Squelch Tuning Window ...................................................... 5-10
Figure 5-12. Rx 12.5 kHz-band Tight Squelch Tuning Window .......................................................... 5-11
Figure 5-13. Rx 25 kHz-band Normal Squelch Tuning Window ......................................................... 5-12
Figure 5-14. Rx 25 kHz-band Tight Squelch Tuning Window .............................................................5-13
Figure 5-15. Program Radio Serial No. Window................................................................................. 5-13
Figure 6-16. Full Keypad Without Channel Knob Model....................................................................... 6-6
Figure 6-17. Battery and Antenna Removal.......................................................................................... 6-7
Figure 6-18. Knob Removal.................................................................................................................. 6-7
Figure 6-19. Chassis Removal.............................................................................................................. 6-8
Figure 6-20. Speaker Wire and Flexible Cable Connection.................................................................. 6-8
Figure 6-21. Speaker Wire Removal..................................................................................................... 6-9
Figure 6-22. Unlatch the Flexible Cable................................................................................................ 6-9
Figure 6-23. Sub-Circuit Board and Accessory Bracket Removal ...................................................... 6-10
Figure 6-24. Main Circuit Board, finger strips, O-ring and Battery Contact Seal Removal(UHF2) .....6-11
Figure 6-25. Main Circuit Board, finger strips, O-ring and Battery Contact Seal Removal(UHF1) .....6-11
Figure 6-26. Front Circuit Board Removal .......................................................................................... 6-12
Figure 6-27. LCD and Keypad Removal ............................................................................................. 6-12
Figure 6-28. Speaker Removal...........................................................................................................6-13
Figure 6-29. Speaker Reassembly ..................................................................................................... 6-13
Figure 6-30. LCD and Keypad Reassembly .......................................................................................6-14
Figure 6-31. Front Circuit Board Reassembly..................................................................................... 6-14
Figure 6-32. Main Circuit Board, finger strips, O-ring and Battery Contact Seal Reassembly(UHF2) 6-15
Figure 6-34. Sub Circuit Board and Accessory Bracket Reassembly................................................. 6-16
Figure 6-33. Main Circuit Board, finger strips, O-ring and Battery Contact Seal Reassembly(UHF1) 6-16
Figure 6-35. Chassis Assembly and Front Housing Assembly Reassembly ......................................6-17
Figure 6-36. EP350 (Full Keypad without Channel Knob)Radio Exploded View ................................6-18
Figure 7-37. Limited Keypad Without Channel Knob Model ................................................................. 7-6
Figure 7-38. Battery and Antenna Removal.......................................................................................... 7-7
Figure 7-39. Knob Removal.................................................................................................................. 7-8
Figure 7-40. Chassis Removal.............................................................................................................. 7-8
Figure 7-41. Speaker Wire and Flexible Cable Connection.................................................................. 7-9
Figure 7-42. Speaker Wire Removal..................................................................................................... 7-9
Figure 7-43. Unlatch the Flexible Cable.............................................................................................. 7-10
Figure 7-44. Sub-Circuit Board and Accessory Bracket Removal ...................................................... 7-10
Figure 7-45. Main Circuit Board, finger strips, O-ring and Battery Contact Seal Removal(UHF2) .....7-11
Page 13

List of Figures ix
Figure 7-46. Main Circuit Board, finger strips, O-ring and Battery Contact Seal Removal (UHF1) .... 7-11
Figure 7-47. Front Circuit Board Removal .......................................................................................... 7-12
Figure 7-48. LCD and Keypad Removal............................................................................................. 7-12
Figure 7-49. Speaker Removal........................................................................................................... 7-13
Figure 7-50. Speaker Reassembly ..................................................................................................... 7-14
Figure 7-51. LCD and Keypad Reassembly ....................................................................................... 7-14
Figure 7-52. Front Circuit Board Reassembly .................................................................................... 7-15
Figure 7-53. Main Circuit Board, O-ring and Battery Contact Seal Reassembly(UHF2) .................... 7-16
Figure 7-54. Main Circuit Board, finger strips, O-ring and Battery Contact Seal Reassembly(UHF1) 7-16
Figure 7-55. Sub Circuit Board and Accessory Bracket Reassembly................................................. 7-17
Figure 7-56. Chassis Assembly and Front Housing Assembly Reassembly ...................................... 7-17
Figure 7-57. EP350 (Limited Keypad without Channel Knob) – Exploded View ................................ 7-18
Page 14

x List of Tables
List of Tables
Table 1-1. Radio Model Number (Example:MDH03RDH8AA7) ........................................................ 1-1
Table 3-2. Recommended Test Equipment ....................................................................................... 3-1
Table 3-3. Service Aids......................................................................................................................3-2
Table 4-4. Radio Operation in Test Mode..........................................................................................4-1
Table 5-5. Initial Equipment Control Settings ....................................................................................5-3
Table 5-6. Transmit High/Low Power Level....................................................................................... 5-3
Table 5-7. Transmit Modulation Tuning .............................................................................................5-5
Table 5-8. Receiver Squelch Tuning ................................................................................................. 5-8
Table 5-9. Front Panel Programming Mode Parameters................................................................. 5-16
Table 6-10. Lead Free Solder Wire Part Number List ......................................................................... 6-3
Table 6-11. Lead Free Solder Paste Part Number List........................................................................6-3
Table 6-12. Torque Chart .................................................................................................................. 6-17
Table 6-13. Parts List (Full Keypad without Channel Knob) .............................................................. 6-19
Table 7-14. Lead Free Solder Wire Part Number List ......................................................................... 7-4
Table 7-15. Lead Free Solder Paste Part Number List........................................................................7-4
Table 7-16. Torque Chart .................................................................................................................. 7-18
Table 7-17. Parts List (Limited Keypad without Channel Knob) ........................................................7-19
Table 8-18. Error Code Display ........................................................................................................... 8-1
Table 8-19. Receiver Troubleshooting Table.......................................................................................8-2
Table 8-20. Transmitter Troubleshooting Table................................................................................... 8-3
Table B-1. Portable Radios and Product Accessories Warranty........................................................B-1
Related Publications
LACR
EP350 Series Radios User Guide
(English, Latin American Spanish, Brazilian Portuguese)...............................................6878081A01
EP350 Series Radios Quick Reference Card
(English, Latin American Spanish, Brazilian Portuguese)............................................. 68007024010
EP350 Basic Service Manual .................................................................................................. 6878419A01
EP350 Detailed Service Manual ..............................................................................................6878422A01
Product Safety and RF Exposure Booklet ................................................................................6881095C98
Page 15
Notations Used in This Manual xi
Notations Used in This Manual
Throughout the text in this publication, you will notice the use of the following notations. These notations
are used to emphasize that safety hazards exist, and due care must be taken and observed.
Note
An operational procedure, practice, or condition that isessential to emphasize.
CAUTION indicates a potentially hazardous situation which, if not avoided,
might result in equipment damage.
Page 16

xii Summary of Bands Available
Summary of Bands Available
Table below lists all the bands available in this manual. For details, please refer to the Model Charts section.
Frequency Band Bandwidth Power Level
UHF2 435–480 MHz 1W or 4W
VHF 136– 74 MHz 1W or 5W
UHF1 403–447 MHz 1W or 4W
Page 17

Chapter 1 Model Charts and Test Specifications
1.1 Radio Model Information
The model number and serial number are located on a label attached to the back of your radio. You
can determine the RF output power, frequency band, protocols, and physical packages. The example
below shows one portable radio model number and its specific characteristics.
Table 1-1. Radio Model Number (Example:MDH03RDH8AA7)
Regional
Prefix
Type o f
Unit
Model
Series
LA H 03 R
LA = LACR
H = Portable
03 = CP Family Model Series
Freq. Band
UHF
(435–480 MHz)
K
VHF
(136–174 MHz)
M
200MHz
(216–223 MHz)
N
200MHz
(245–247 MHz)
E
300MHz
(350–390 MHz)
Q
UHF
(403–447 MHz)
S
UHF
(470–512 MHz)
Power
Level
D
4 W
C
2 W
E
5 W
Physical
Packages
H
Limited
Keypad
without
Channel
Knob
K
Full Keypad
without
Channel
Knob
T
Full Keypad
RTTE Model
U
Limited
Keypad
RTTE Model
Channel
Spacing
8
12.5/25k
4
12.5k
6
20/25k
9
12.5/20/
25k
Protocol
AA 7
AA = Conventional
Feature
Level
No
Front Panel
Prog.
with
Scrambling
1
Fixed Freq.
Tier 1
2
Fixed Freq.
Tier 2
3
Fixed Freq.
Tier 3
4
Fixed Freq.
Tier 4
5
Fixed Freq.
Tier 5
9
Front Panel
Prog.
with
Scrambling
Page 18
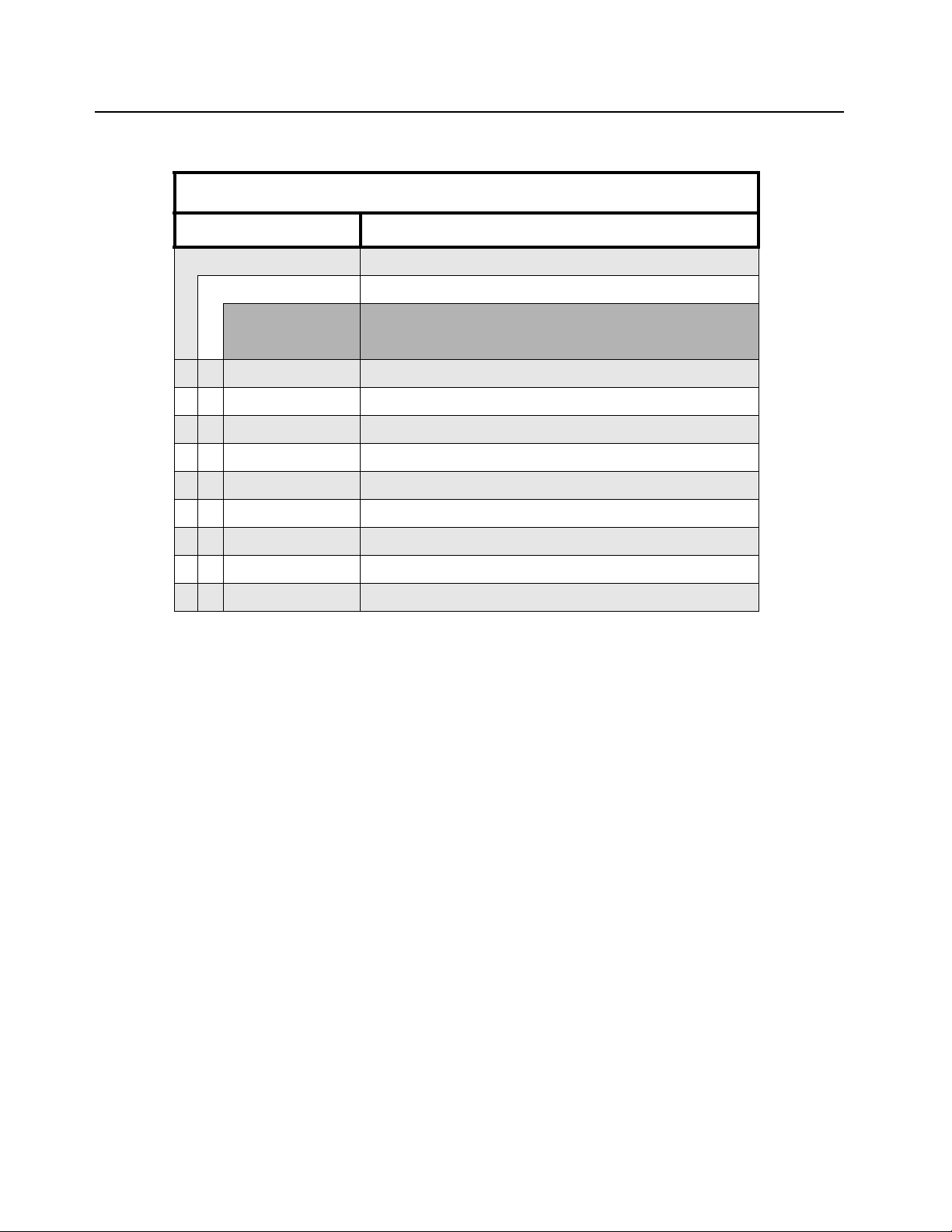
1-2 Model Charts and Test Specifications: Model Chart for UHF2, 435–480 MHz
1.2 Model Chart for UHF2, 435–480 MHz
EP350, UHF2, 435–480 MHz
Model Description
LAH03RDK8AA9AN EP350 435 – 480M 4W 12.5/25K 99C Full Keypad
LAH03RDH8AA7AN EP350 435 – 480M 4W 12.5/25K 99C Limited Keypad
Item Description
X PMUE3148_ 435 – 480M 4W 12.5/25K 99C FKPFPP SCR
X PMUE3144_ 435 – 480M 4W 12.5/25K 99C LKP SCR
X PMDE4010_R 435 – 480M 4W PCB – PMUE3148_AL
X PMDE4012_R 435 – 480M 4W PCB – PMUE3144_AL
X PMDN4130_R Front Circuit Board, FKP
X PMDN4131_R Front Circuit Board, LKP
X X PMDN4129_R Sub Circuit Board, w/o Channel
X X 6878419A01 EP350 BASIC SERVICE MANUAL
X X 6878422A01 EP350 DETAILED SERVICE MANUAL
X = Indicates compatibility with model(s)
Page 19
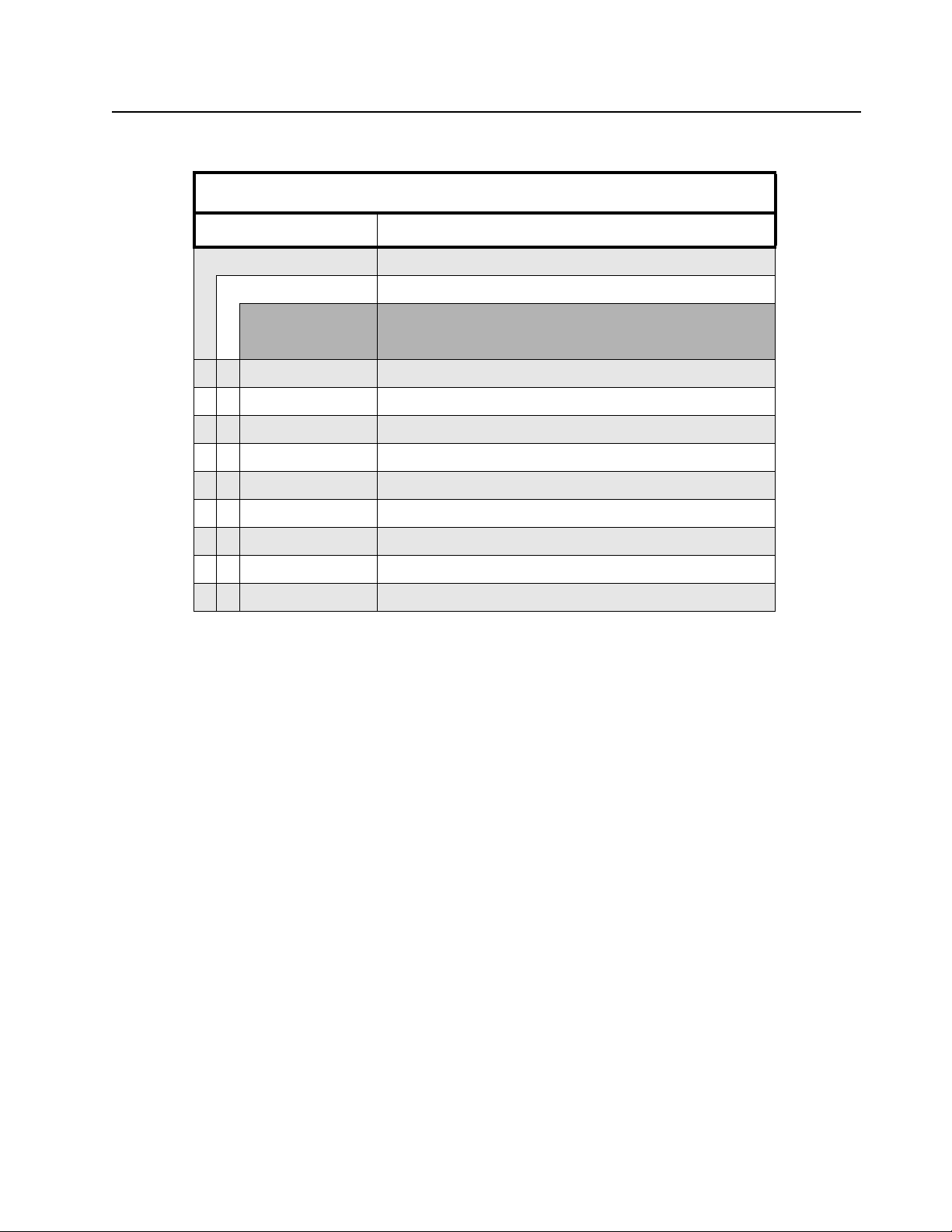
Model Charts and Test Specifications: Model Chart for VHF, 136–174 MHz 1-3
1.3 Model Chart for VHF, 136–174 MHz
EP350, VHF, 136–174 MHz
Model Description
LAH03KEK8AA9AN EP350 136 – 174M 5W 12.5/25K 99C Full Keypad
LAH03KEH8AA7AN EP350 136 – 174M 5W 12.5/25K 99C Limited Keypad
Item Description
X PMUD2437_ 136 – 174M 5W 12.5/25K 99CH FKPFPP SCR
X PMUD2441_ 136 – 174M 5W 12.5/25K 99CH LKP SCR
X PMDD4011_R 136 – 174M 5W PCB – PMUD2437_AL
X PMDD4017_R 136 – 174M 5W PCB – PMUD2441_AL
X PMDN4130_R Front Circuit Board, FKP
X PMDN4131_R Front Circuit Board, LKP
X X PMDN4129_R Sub Circuit Board, w/o Channel
X X 6878419A01 EP350 BASIC SERVICE MANUAL
X X 6878422A01 EP350 DETAILED SERVICE MANUAL
X = Indicates compatibility with model(s)
Page 20

1-4 Model Charts and Test Specifications: Model Chart for UHF1, 403–447 MHz
1.4 Model Chart for UHF1, 403–447 MHz
EP350, UHF1, 403–447 MHz
Model Description
LAH03QDK8AA9AN EP350 403 – 447M 4W 12.5/25K 99C Full Keypad
LAH03QDH8AA7AN EP350 403 – 447M 4W 12.5/25K 99C Limited Keypad
Item Description
PMUE3320_ 403 – 447M 4W 12.5/25K 99C FKPFPP
PMUE3323_ 403 – 447M 4W 12.5/25K 99C LKP
PMDE4028_R 403 – 447M 4W PCB – PMUE3320_AL
PMDE4034_R 403 – 447M 4W PCB – PMUE3323_AL
PMDN4130_R Front Circuit Board, FKP
PMDN4131_R Front Circuit Board, LKP
PMDN4129_R Sub Circuit Board, w/o Channel
6878419A01 EP350 BASIC SERVICE MANUAL
6878422A01 EP350 DETAILED SERVICE MANUAL
X = Indicates compatibility with model(s)
Page 21
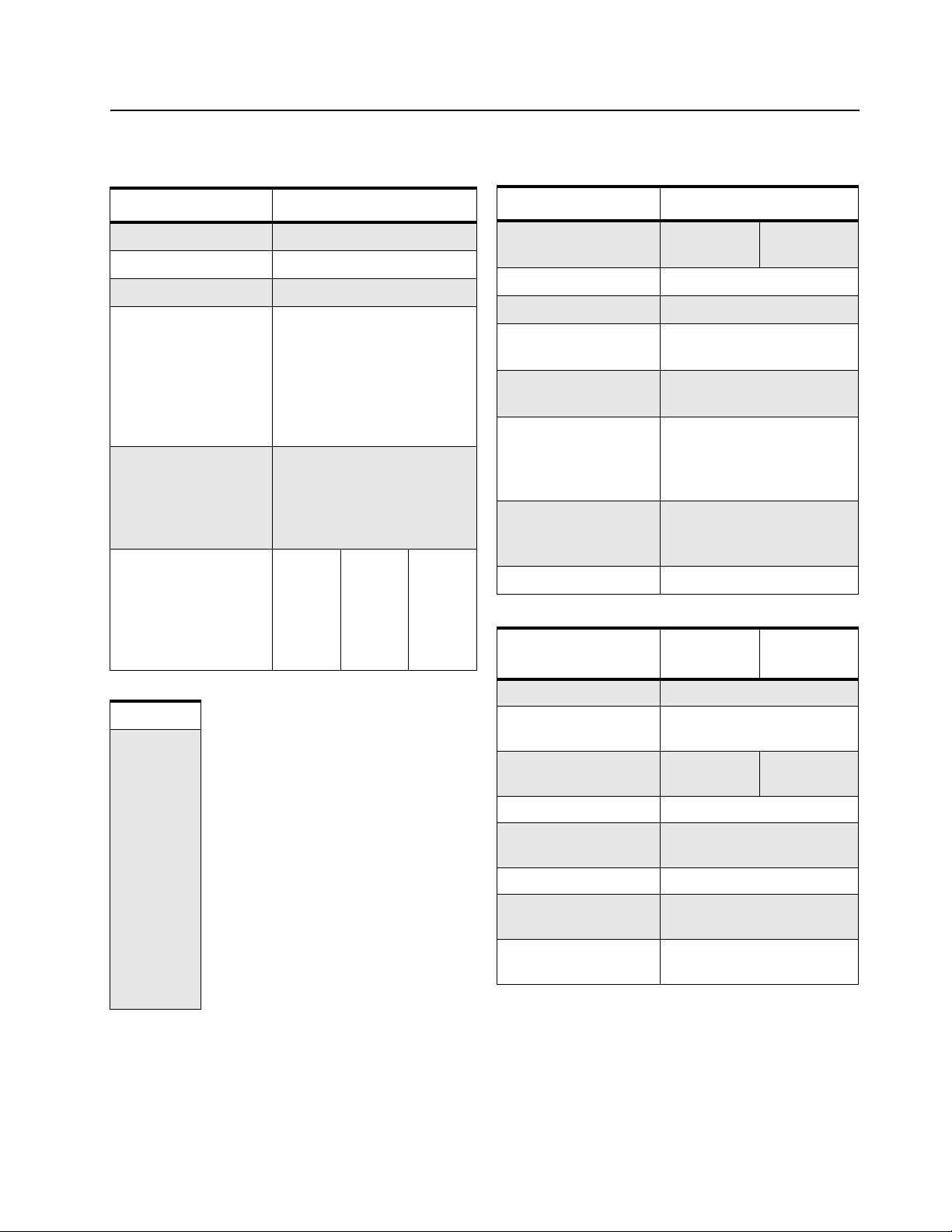
Model Charts and Test Specifications: UHF2 Specifications 1-5
1.5 UHF2 Specifications
General
UHF2
Frequency: 435 – 480 MHz
Channel Capacity: 99 Channels
Power Supply: 7.5 Volts ±20%
Dimensions:
(H x W x D)
with
High Capacity Li-Ion
NiMH Std
Li-Ion Std
Batteries:
Weight:
Battery:
High Capacity Li-Ion
NiMH Std
Li-Ion Std
Average Battery Life
@ (5-5-90 Duty
Cycle):
High Capacity Li-Ion
NiMH Std
Li-Ion Std
120 mm x 55 mm x 40.7 mm
120 mm x 55 mm x 36.5 mm
120 mm x 55 mm x 35.5 mm
342.0g
394.5g
335.0g
Capacity
(mAh)
2150
1300
1500
4 W
12 Hrs.
8 Hrs.
8 Hrs.
Self-Quieter Frequencies
UHF2
446.440
446.445
455.895
456.010
456.015
456.125
458.195
460.000
467.785
467.900
468.010
468.125
468.240
470.000
479.900
1 W
14 Hrs.
10 Hrs.
10 Hrs.
Transmitter
UHF2
RF Output
NiMH @ 7.5 V:
Frequency: 435 – 480 MHz
Channel Spacing: 12.5/25 kHz
Freq. Stability:
(-30°C to +60°C)
Spurs/Harmonics: -36 dBm < 1 GHz
Audio Response:
(from 6 dB/oct.
Pre-emphasis, 300 to
3000 Hz)
Audio Distortion:
@ 1000 Hz, 60%
Rated Max. Dev.
FM Noise: <-40 dB
Low
1 W
0.00025%
-30 dBm > 1 GHz
+1, -3 dB
<5%
High
4 W
Receiver
UHF2
12.5 kHz
Frequency: 435 – 480 MHz
Sensitivity
12 dB EIA SINAD:
Adjacent Channel
Selectivity:
Intermodulation: -70 dB
Freq. Stability
(-30°C to +60°C):
Spur Rejection: -70 dB
Image and 1/2 I-F
Rejection:
Audio Output
@ <5% Distortion:
All specifications are subject to change without notice.
0.25 μV (typical)
-65 dB -70 dB
0.00025%
-70 dB
500 mW
UHF2
25kHz
Page 22

1-6 Model Charts and Test Specifications: VHF Specifications
1.6 VHF Specifications
General
VHF
Frequency: 136 – 174 MHz
Channel Capacity: 99 Channels
Power Supply: 7.5 Volts ±20%
Dimensions:
(H x W x D)
with
High Capacity Li-Ion
NiMH Std
Li-Ion Std
Batteries:
Weight:
Battery:
High Capacity Li-Ion
NiMH Std
Li-Ion Std
Average Battery Life
@ (5-5-90 Duty
Cycle):
High Capacity Li-Ion
NiMH Std
Li-Ion Std
120 mm x 55 mm x 40.7 mm
120 mm x 55 mm x 36.5 mm
120 mm x 55 mm x 35.5 mm
342.0g
394.5g
335.0g
Capacity
(mAh)
2150
1300
1500
5 W
12 Hrs.
8 Hrs.
8 Hrs.
Self-Quieter Frequencies
VHF
140.000
155.010
155.020
155.030
155.015
155.170
155.180
155.175
155.505
159.995
160.000
160.005
161.450
167.025
167.030
169.995
170.000
170.005
173.985
173.990
1 W
14 Hrs.
10 Hrs.
10 Hrs.
Transmitter
VHF
RF Output
NiMH @ 7.5 V:
Frequency: 136 – 174 MHz
Channel Spacing: 12.5/25 kHz
Freq. Stability:
(-30°C to +60°C)
Spurs/Harmonics: -36 dBm < 1 GHz
Audio Response:
(from 6 dB/oct.
Pre-emphasis, 300 to
3000 Hz)
Audio Distortion:
@ 1000 Hz, 60%
Rated Max. Dev.
FM Noise: <-40 dB
Low
1 W
0.00025%
-30 dBm > 1 GHz
+1, -3 dB
<5%
High
5 W
Receiver
VHF
12.5 kHz
Frequency: 136 – 174 MHz
Sensitivity
12 dB EIA SINAD:
Adjacent Channel
Selectivity:
Intermodulation: -70 dB
Freq. Stability
(-30°C to +60°C):
Spur Rejection: -70 dB
Image and 1/2 I-F
Rejection:
Audio Output
@ <5% Distortion:
All specifications are subject to change without notice.\
0.25 μV (typical)
-65 dB -70 dB
0.00025%
-70 dB
500 mW
VHF
25kHz
Page 23
Model Charts and Test Specifications: UHF1 Specifications 1-7
1.7 UHF1 Specifications
General
UHF1
Frequency: 403 – 447 MHz
Channel Capacity: 99 Channels
Power Supply: 7.5 Volts ±20%
Dimensions:
(H x W x D)
with
High Capacity Li-Ion
NiMH Std
Li-Ion Std
Batteries:
Weight:
Battery:
High Capacity Li-Ion
NiMH Std
Li-Ion Std
Average Battery Life
@ (5-5-90 Duty
Cycle):
High Capacity Li-Ion
NiMH Std
Li-Ion Std
120 mm x 55 mm x 40.7 mm
120 mm x 55 mm x 36.5 mm
120 mm x 55 mm x 35.5 mm
342.0g
394.5g
335.0g
Capacity
(mAh)
2150
1300
1500
4 W
12 Hrs.
8 Hrs.
8 Hrs.
Self-Quieter Frequencies
UHF1
424.355
424.810
442.360
442.365
442.370
444.010
444.015
443.900
444.125
446.030
446.035
446.445
446.450
446.455
446.460
446.675
446.680
1 W
14 Hrs.
10 Hrs.
10 Hrs.
Transmitter
UHF1
RF Output
NiMH @ 7.5 V:
Frequency: 403 – 447 MHz
Channel Spacing: 12.5/25 kHz
Freq. Stability:
(-30°C to +60°C)
Spurs/Harmonics: -36 dBm < 1 GHz
Audio Response:
(from 6 dB/oct.
Pre-emphasis, 300 to
3000 Hz)
Audio Distortion:
@ 1000 Hz, 60%
Rated Max. Dev.
FM Noise: <-40 dB
Low
1 W
0.00025%
-30 dBm > 1 GHz
+1, -3 dB
<5%
High
4 W
Receiver
UHF1
12.5 kHz
Frequency: 403 – 447 MHz
Sensitivity
12 dB EIA SINAD:
Adjacent Channel
Selectivity:
Intermodulation: -70 dB
Freq. Stability
(-30°C to +60°C):
Spur Rejection: -70 dB
Image and 1/2 I-F
Rejection:
Audio Output
@ <5% Distortion:
All specifications are subject to change without notice.
0.25 μV (typical)
-65 dB -70 dB
0.00025%
-70 dB
500 mW
UHF1
25 kHz
Page 24

1-8 Model Charts and Test Specifications: UHF1 Specifications
Notes
Page 25
Chapter 2 Theory Of Operation
A
2.1 Introduction
This chapter provides a basic theory of operation for the radio components.
2.2 Major Assemblies
• Main PCB – Contains the RF circuits which comprises receiver, transmitter, phase-locked loop
(PLL) frequency synthesizer, micro controller, power supply, audio and digital circuits
• Display and Keypad PCB (Limited and Full Keypad models only) – 8 characters (14 segments
star burst) and 10 icons with backlighting, liquid-crystal display (LCD)
• Volume Knob PCB (PMDN4129AR) – Rotary Volume Knob
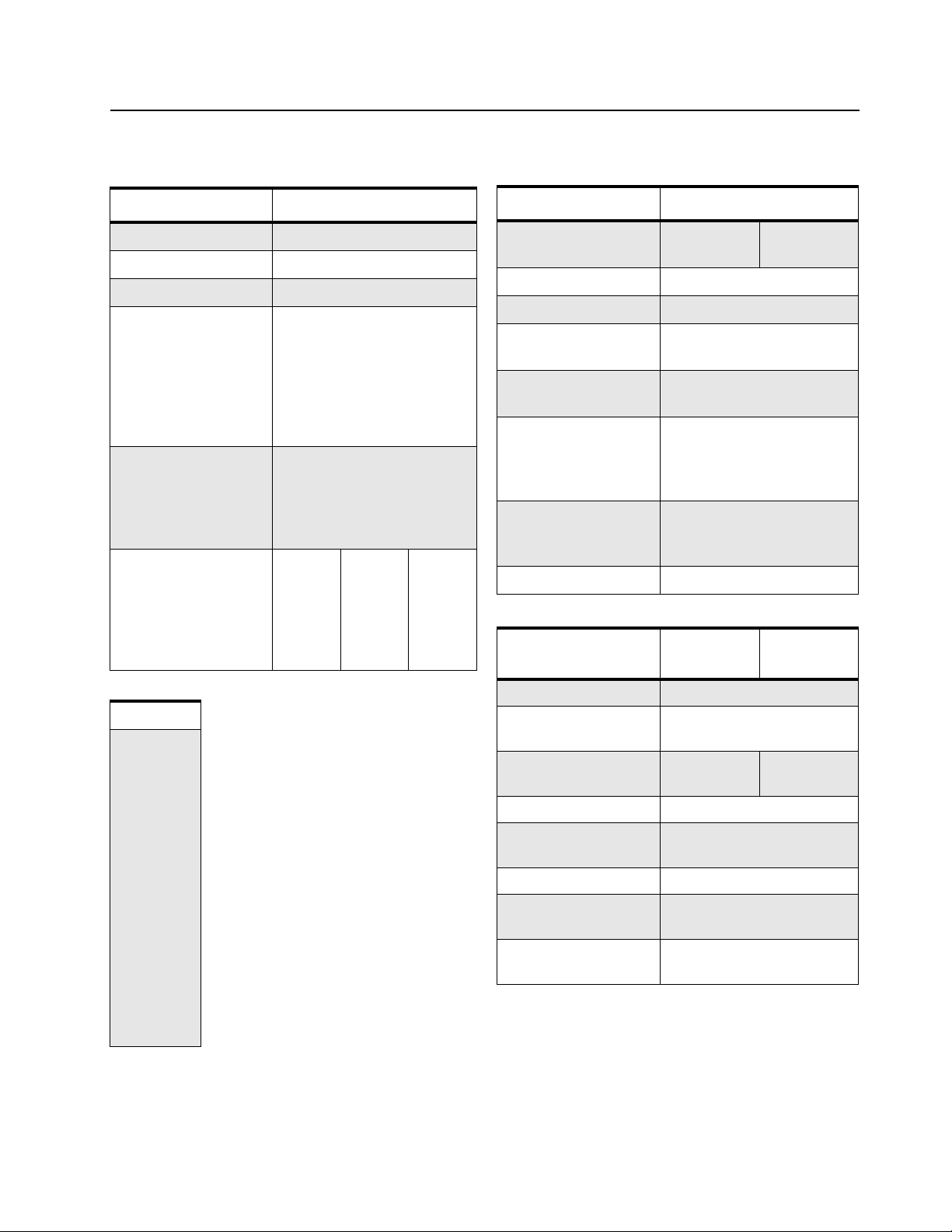
2.2.1 Receiver
The radio's receiver is a double conversion super heterodyne with 1st IF of 45.1 MHz and 2nd IF of
455 kHz.
UHF1 receiver design covers the frequency range of 403 – 447 MHz.
UHF2 receiver design covers the frequency range of 435 – 480 MHz.
VHF receiver design covers the frequency range of 136 – 174 MHz.
Preselector
Filter
RX from
ntenna Switch
from Synthesizer
First LO
N/S_SW
Recovered Audio
Amp
RSSI
RF
Postselector
Filter
Inj Filter
Descriminator
LPF
1st Mixer
455C24
Quadrature
Detector
Crystal
Filter
Ceramic
Filter
IF
Amp
IF
Amp
455FW
455HW
Crystal
44.645MHz
Figure 2-1. Receiver Block Diagram
Page 26

2-2 Theory Of Operation: Major Assemblies
2.2.1.1 RX Front End
UHF1 : Receiver Front-end consists of a low pass filter, a pre-selector filter, a low noise RF Amplifier
and a Post-selector filter. Incoming RF signal from the antenna is applied through the Harmonics
Low Pass Filter (L409, L410, L411, C426, C427, C428, C429, C445, C446) and passes through the
transmit/receive switch (CR301) and a varactor-tuned 2-pole pre-selector filter (L320, L324, C351,
C361, CR314 and CR307) before routed to an RF amplifier (Q301). The pre-selector filter is an
8 step Band-shift filter, and the frequency shifting is controlled by varactor diodes (CR314 and
CR307) connected to the CPU. The filter output is coupled to a 13 dB RF amplifier Q301 which
outputs the RF signal to the post-selector filter (L323, L328, C379, and C355) which is also a band
shift filter configured to provide steeper low-side attenuation. The 2 varactor diodes (CR313 and
CR305) with 8 frequency steps are also controlled by the CPU.
UHF
2 : Receiver Front-end consists of a low pass filter, a pre-selector filter, a low noise RF Amplifier
and a Post-selector filter. Incoming RF signal from the antenna is applied through the Harmonics
Low Pass Filter (L409, L410, L411, C426, C427, C428, C429, C445, C446) and passes through the
transmit/receive switch (CR301) and a varactor-tuned 2-pole pre-selector filter (L320, L324, C351,
C361, CR314 and CR307) before routed to an RF amplifier (Q301). The pre-selector filter is an 8
step Band-shift filter, and the frequency shifting is controlled by varactor diodes (CR314 and CR307)
connected to the CPU. The filter output is coupled to a 13 dB RF amplifier Q301 which outputs the
RF signal to the post-selector filter (L323, L322, L328, C379, C354 and C355) which is also a band
shift filter configured to provide steeper low-side attenuation. The 3 varactor diodes (CR313, CR304
and CR305) with 8 frequency steps are also controlled by the CPU.
VHF
: Receiver Front-end consists of a low pass filter, a pre-selector filter, a low noise RF Amplifier,
a Post-selector filter. Incoming RF signal from antenna is applied through the Harmonics Low Pass
Filter (L409, L410, L411, C426, C427, C428, C429, C430, C445, C446) and passes the transmit/
receive switch (CR301) and a varactor-tuned 2-pole pre-selector filter (L301, L302, L303, L304,
C301, CR302, CR303, C304, C305, C307, C308) before routed to an RF amplifier (Q301). The preselector filter is a 6 step Band-shift filter, and the frequency shifting is controlled by varactor diodes
(CR302 & CR303) connected to the CPU. The filter output is coupled to a 13 dB RF amplifier Q301
which outputs the RF signal to the post-selector filter (L308, L309, L311, C315 and C354) which is
also a band shift filter configured to provide steeper low-side attenuation. The 2 units of 6 step
frequency varactor diodes (CR305, CR307) are also controlled by the CPU.
2.2.1.2 RX Back End
UHF1 : RF signal from RX front-end is then directed to a Double Balanced Mixer (L329, L333 and
CR316). 1st LO signal from VCO is filtered by an injection filter (L310, L331, C325, C326 and C387)
to remove harmonics.
After passing through a pair of 45.1 MHz Crystal filter, the 1st IF signal is amplified by 15 dB via an
IF amp (Q303) and channeled to IF IC (U201) to be mixed thus producing the 2nd IF Frequency
(455 kHz):
Depending on channel spacing, the 2nd IF frequency passes through the wide (CF1) and/or narrow
(CF2) filters to eliminate undesired signals before being finally demodulated by demodulator in U201
with Recovered Audio as the final output.
1st IF (45.1 MHz) - 2nd LO (44.645 MHz) = 2nd IF (455 kHz)
Page 27

Theory Of Operation: Major Assemblies 2-3
UHF2 : RF signal from RX front-end is then directed to a Single Balanced Mixer (L329, L333, Q306,
and Q307). 1st LO signal from VCO is filtered by an injection filter (L310, L331, C325, C326, C327)
to remove harmonics.
After passing through a pair of 45.1 MHz Crystal filter, the 1st IF signal is amplified by 15 dB via an
IF amp (Q303) and channeled to IF IC (U201) to be mixed thus producing the 2nd IF Frequency
(455 kHz):
1st IF (45.1 MHz) - 2nd LO (44.645 MHz) = 2nd IF (455 kHz)
Depending on channel spacing, the 2nd IF frequency passes through the wide (CF1) and/or narrow
(CF2) filters to eliminate undesired signals before being finally demodulated by demodulator in U201
with Recovered Audio as the final output.
VHF
: RF signal from RX front-end is then directed to a Single Balanced Mixer (L329, L333, Q306,
and Q307). 1st LO signal from VCO is filtered by an injection filter (L310, L331, C325, C326 and
C333) to remove harmonics.
After passing through a pair of 45.1 MHz Crystal filter, The 1st IF signal is amplified by 15 dB via an
IF amp (Q303) and channeled to IF IC (U201) to be mixed thus producing 2nd IF Frequency
(455 kHz)
1st IF (45.1 MHz) - 2nd LO (44.645 MHz) = 2nd IF (455 kHz)
Depending on channel spacing, the 2nd IF frequency passes through wide (CF1) or narrow (CF2)
filter to eliminate undesired signals before being finally demodulated by demodulator in U201 with
Recovered Audio as the final output.
2.2.1.3 RX Squelch
The mute (squelch) circuitry switches off the audio amplifier when no audio is detected from the
recovered audio. The squelch circuit main components are U202 & U201.
U202 will adjust the squelch circuit sensitivity depending on Noise level from recovered audio. Noise
level is amplified by internal amplifier of U201 to help U202 decide the squelch circuit sensitivity. If
the noise level is over the set threshold, the microprocessor mutes the radio.
Note
Perform squelch tuning after any RX part replacement. Refer Chapter 5.6: Receiver Tuning
on page 5-8.
Page 28
2-4 Theory Of Operation: Major Assemblies
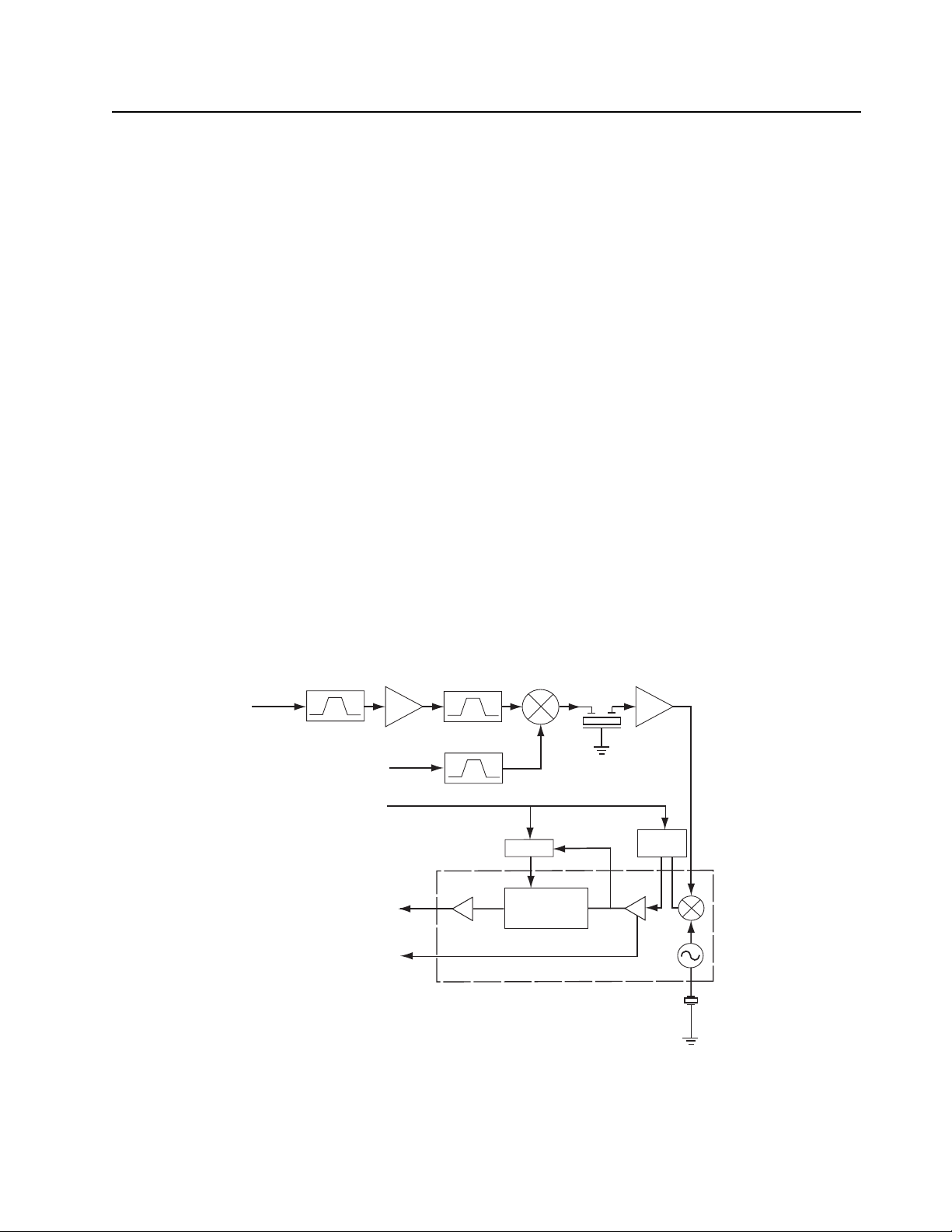
2.2.2 Transmitter
The radio's TX Power Amplifier system is a three stage amplifier which is able to amplify the VCO
output up to the permitted maximum transmit power levels (UHF: 4W, VHF: 5W).
From VCO
Attenuator
Circuit
SWB+
Power Control
Pre Driver
Amp
Driver
Amp
BAT+
Current Detect
Final
Amp
To Receiver
Strip Line
CR401
Antenna
Switch
Antenna
Harmonic
Filter
Figure 2-2. Transmitter Block Diagram
TX VCO output signal passes thru a 3 dB, pie style resistor, attenuator before going into the TX
power stage acting as isolation between the low power VCO and high power amps. The next stage
consists of a pre-driver (Q401) and a driver amplifier (Q402). The TX RF signal (UHF1: -4 dBm,
UHF2 : -4 dBm, VHF : -3 dBm) from the attenuator is amplified to +25 dBm (UHF1), +25 dBm
(UHF2) or +28 dBm (VHF) by the pre-driver and driver amp. This is followed by the final PA, an
enhancement-mode N-channel MOSFET device (Q403), which provides a 12 dB gain.
The final PA draws current directly from the DC battery supply voltage input via L413.
The PA matching network consists of C416, C417, C418, C419, C420, C422, C451 (UHF1 & UHF2)
or C417, C418, C420, C455 (VHF) and a strip line, which matches the TX Power impedance to
approximately 50 ohm. Antenna switch is shared between TX and RX circuit. In TX mode, PIN
diodes (CR401, CR301) are forward biased which enable the High Power RF signal to pass through
the antenna. In RX mode, both diodes are off. Signals applied to the antenna jack are routed, via the
Harmonics LPF in to the RX circuit. The High Power RF Signal finally passes through a TX Low Pass
Filter, a 7th order Chebyshev filter (L409, L410, L411, C426, C427, C428, C429, C445, C446).
The APC (Auto Power Control) keeps the current supplied to Final PA (Q403) constant. Resistor,
R417 is used for current sensing. The voltage difference ratio of R423 to R417 is amplified through
U401 and passed to Q404 and Q405 to produce constant power output to the antenna. Do not
exceed the maximum allowed bias voltage of the device.
Note:
Retune the TX Power if Final PA (Q403) is replaced. Refer Chapter 5.5: Transmitter
Alignment Options on page 5-3.
Page 29
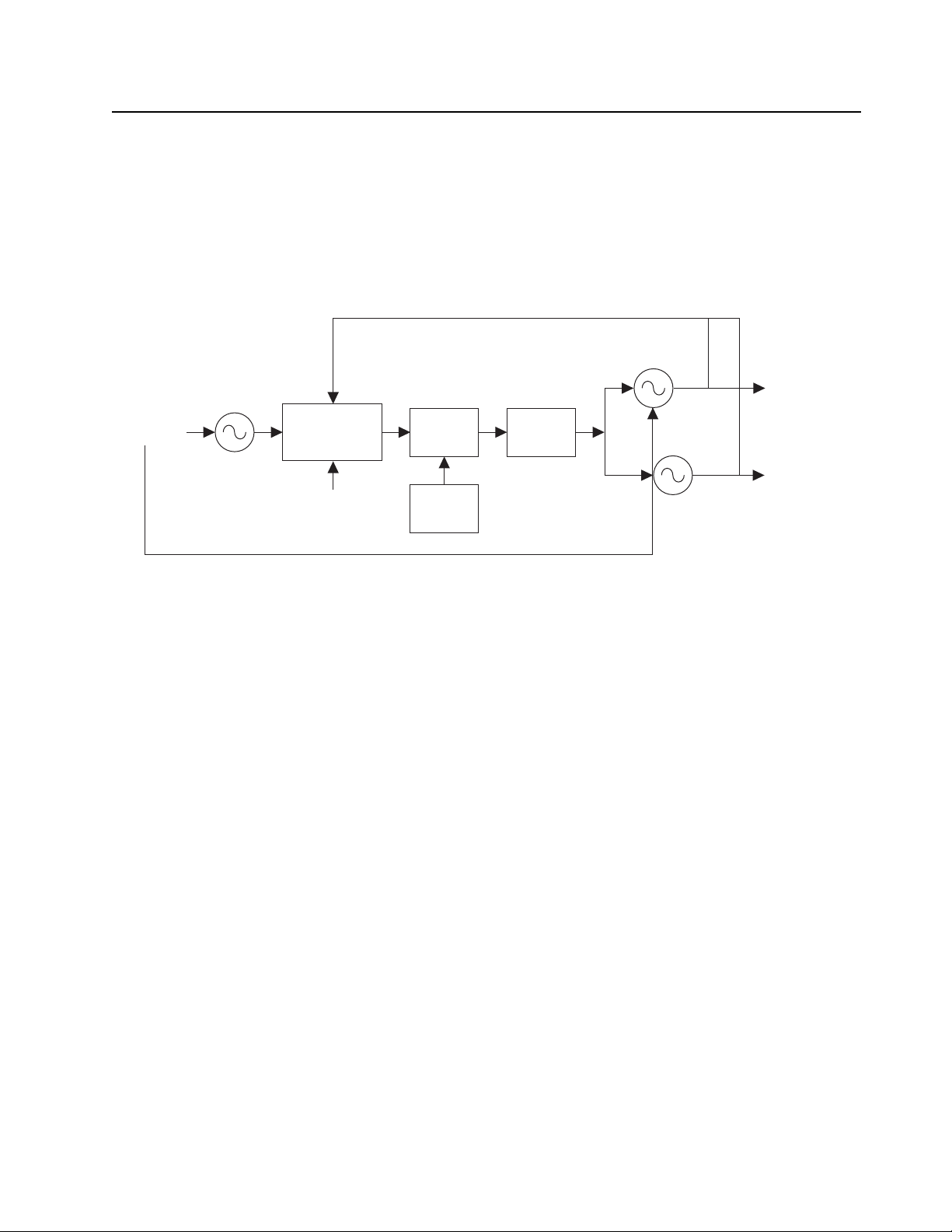
Theory Of Operation: Major Assemblies 2-5
r
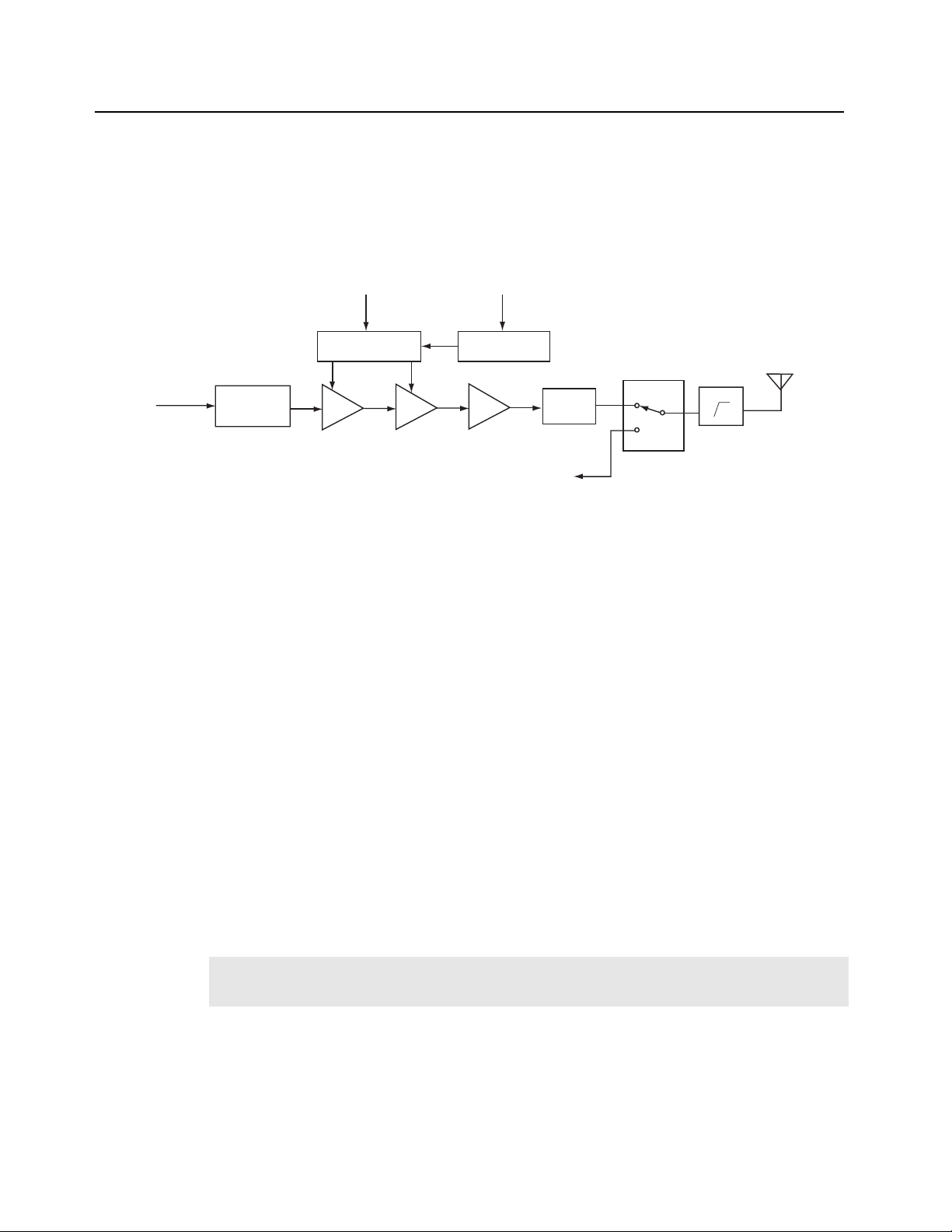
2.2.3 Phase Lock Loop Synthesizer
The Phase Lock Loop (PLL) synthesizer subsystem consists of the reference oscillator (VCTCXO),
VCO, PLL IC, Charge pump and Loop filter.
TX VCO
Circuit
Modulating
Signal
VCTCXO (Voltage Controlled Temperature Compensated crystal Oscillator) reference frequency
(12.8 MHz) provides reference to PLL IC, with stability of +/-2.5PPM at -30° to +60°C. This reference
frequency is divided to 6.25 kHz or 5 kHz by PLL IC. PLL IC outputs 2 Signals (P & R) depending on
phase difference. A charge pump is used to charge these output signals from 0 – 3.3 V up to
0 – 10 V which is required to control the VCO. A voltage doubler (U507) converts 5 V to 10 V to
supply the necessary voltage for a higher frequency resolution in VCO. The Loop filter is a Low Pass
filter (C751 – C754, R726 – R728) to reduce the residual side-band noise of VCO Reference
Frequency for the best signal-to-noise ratio. The VCO module contains both RX VCO and TX VCO,
configured as Collpits oscillators and connects to DC power through cascaded buffers. Q705 and
Q305 enable RX VCO when RX_EN is high. Q706 and Q503 enable TX VCO when TX_EN1 is high.
FL701
12.8MHz
Ref.OSC.
Synthesizer
U701
PLL Data
from μP
Charge
Pump
Voltage
Doubler
Loop
Filter
Figure 2-3. PLL Synthesizer Block Diagram
TX Out
RX Out
RX VCO
Circuit
To PA Drive
To Mixer
The input audio signal for TX VCO is from (U501-B) and applied to a varactor diodes (CR703) in
TX VCO to be modulated into TX RF signal.
Page 30

2-6 Theory Of Operation: Major Assemblies
2.2.4 RX Audio Circuit
The RX audio circuit consists of Audio Processor IC, Audio amp, speakers & Sub-tone system.
Audio Processor IC (AK2347)
Audio IN
(from IF IC)
pin 24
RXA1
VR3
-4 to +3.5dB /
0.5dB
Programmable
Sub audio
LPF
Sub audio
HPF
RX LPF TX/RX HPF
-6 to +6dB /
0.5dB
VR5
pin 18
U105-A,B
Compar
ator
U105-C
To CPU
(tone detect)
Scrambler /
Descrambler
U102
INT SPK.
EXT SPK.
J601
De-
emphasis
Expander VR4 SMF
-18, -4.5 to + 4.5dB /
0.25dB
Audio Amp.
OUT-
OUT+
U601
IN-
IN+
SVR
pin 21
Vol1
Audio Mute
control
Figure 2-4. RX Audio Block Diagram
The RX Audio from U201 is channeled to Audio processor IC. VR3 controls the received
demodulated signal level from -4.0 dB to +3.5 dB in 0.5 dB steps. RX LPF eliminates high-frequency
audio components > 3 kHz. TX/RX HPF eliminates low-frequency audio components lower < 250Hz.
Descrambler (if ON) inverts the spectrum distribution of audio signals with respect to scrambling
frequency. De-emphasis (if ON) restores high-frequency component of audio signal which has been
emphasized by the pre-emphasis circuit in transmitting radio. Expander (if ON) expands audio signal
by 0.5 dB to restore the original signal compressed by transmitting radio. VR4 amplifies RX audio
level by -18.0 dB, with -4.5 dB to +4.5 dB in 0.25 dB steps adjustment range. Smoothing filter (SMF)
eliminates high-frequency and clock components, generated by ASIC.
Sub-audio Programmable LPF totally eliminates voice audio from Audio signal to extract sub-audio
tone. VR5 regulates the output level of extracted sub-audio tone and sends it to a high pass filter
(U105-A,B) with 4 selectable cut-off frequencies and finally passes through a comparator (U105-C),
to square the signal and sends it to the MCU.
The output audio signal of Audio Processor IC is directed to volume control switch (SW/VOL1) which
is controlled by user and is finally amplified by U601BTL Audio Amplifier to a sufficient level to drive
either the external or internal speaker.
Page 31

Theory Of Operation: Major Assemblies 2-7
2.2.5 TX Audio Circuit
The TX audio circuit is comprised of microphones, LPF, Audio Processor IC, and TX Sub-tone
system.
4 Order LPF
(Fc=4KHz)
Mic
(Audio IN)
U501-C,D
Audio Processor IC (AK2347)
LPF
TX/RX HPF
Fc=300Hz
-6 to +6dB/
0.5dB
VR5
pin17
Scrambler/
Descrambler
U102
2 Order LPF
(Fc=300Hz)
U502-A
Limiter
To VCO &
VCTC XO
-9.6 to +3dB/
6 Order LPF
(Fc=3KHz)
U501-A,B
VR2
0.2dB
Splatter SMF
Fc=2.55KHz/
3KHz
Mod.Adj,
U508
pin8
TX AF Amp.
U502-C
pin4
TXA1
-6 to +4.5dB/
Tone IN
(from CPU)
VR1
(HPF)
1.5dB
Com-
pressor
pin19
DTA1
Pre-
Emphasis
Sub audio
Programmable
Figure 2-5. TX Audio Block Diagram
The TX audio enters the radio via the internal MIC or external MIC. This TX Audio is filtered through
a 4th order 4 kHz Low-pass filter (U501-C & D) which prevents aliasing noise from ASIC. TX Audio
enters the Audio Processor IC which is then directed to an internal Amplifier (TX A1) for gain
adjustment of audio signal. A HPF (VR1) controls the input level of TX audio signal from -6.0 dB to
+4.5 dB in 1.5 dB steps. A Compressor (if ON) compresses the amplitude of TX audio signal by
0.5 dB. A Pre-emphasis circuit (if ON) emphasizes the high frequency component of TX audio signal
to improve Signal to Noise ratio before modulation. A shared High-pass filter (TX/RX HPF)
eliminates low-frequency components <250 Hz from TX audio signal. A Limiter is used to limit the
signal amplitude and suppress frequency deviation during modulation. VR2 controls the output level
from -9.6 dB to +3.0 dB in 0.2 dB steps. A Splatter (LPF) eliminates high-frequency components
>3 kHz. A Smoothing filter (SMF) eliminates high-frequency and clock components generated
internally by ASIC.
For sub-tone data from CPU, DTA1 amplifies the signal, sends it through a Sub-audio Programmable
LPF to eliminate components of DAT1 amplification, and finally the signal is regulated by VR5 from -
6.0 dB to +6.0 dB in 0.5 dB steps. The final sub-tone data passes through a 2nd order LPF (U502-A)
before it is mixed with TX Audio for modulation.
The processed TX audio signal from Audio Processor IC is amplified by TX audio frequency amplifier
(U502-C) to increase limiting range and then adjusted to a proper level for modulation by U508.
Final TX Audio signal passes through a 6th order 3 kHz low pass filter (U501-A & B) before sent to
VCO for modulation.
Note:
Retune the TX modulation if U508 is replaced. Refer Chapter 5.5: Transmitter Alignment
Options on page 5-3.
Page 32

2-8 Theory Of Operation: Major Assemblies
The output audio signal of Audio Processor IC is directed to volume control switch (SW/VOL1)
controlled by user and is finally amplified by U601BTL Audio Amplifier to a sufficient level to drive
either the external or internal speaker.
2.2.6 Microcontroller
The microprocessor or CPU includes Microprocessor (U101), EEPROM and support components.
Radio operation is controlled by software in internal Flash ROM memory.
Radio parameters and customer specific information is stored in External EEPROM (U104). Pins 35
& 36 controls the Sub-PCB mounted LED indicators. PTT button (PB501) is linked to CPU via pin 44.
Side programmable buttons 1 & 2 (PB502 & PB503) is linked via pin 21 & 32, respectively.
Customer Programming Software (CPS) connects to the radio via a USB Programming cable
(PMDN4077_R) through the microphone port (J601 pin 6) to pin 34 & 33 (PRG/CLONE_RX & PRG/
CLONE_TX port). A 7.3728 MHz clock signal (X-in) is provided by FL101 to CPU. A voltage divider
system (R153 & R154) is used by CPU to sense battery level.
2.2.7 Power Supply
There are 4 voltage supplies in this radio: SWB+, 3.3 V, 5 V & 10 V.
SWB+ voltage is distributed to SW/Vol 1, Final PA (Q403 via R417) & APC circuit (U401).
The 3.3 V regulated supply (U506) is applied to CPU (U101), EEPROM (U104), DTMF IC (U103),
Audio processor IC (U102), microphone biasing circuit and LCD/keypad driver.
The 5.0 V regulated source (U505) is distributed to RX back end circuit, RX/TX audio filters,
1/2 VCC generator, VCO (Q705, Q706), RX B+ (Q304), TXvB (Q407) & VCTCXO.
The 10.0 V regulated source (U507) is solely applied for Charge pump use.
Page 33

Chapter 3 Test Equipment, Service Aids, and Service
Tools
3.1 Test Equipment
Table 3-2. lists test equipment required to service the radios.
Table 3-2. Recommended Test Equipment
Motorola Part No. Description Characteristics Application
R2600 series System analyzer This item will substitute
for items with an asterisk
(*)
*R1074A Fluke 87 digital
multi-meter
*R1377A AC voltmeter 1 mV to 300 mV, 10
R1611A Dual channel
100 MHz
oscilloscope
(Agillent)
S1339A RF millivolt meter 100 μV to 3V RF, 10 kHz
*R1013B or
*R1370A
SINAD meter or
SINAD meter with
RMS
True RMS metering,
200 kHz frequency
counter, 32-segment bar
graph with backlit display
mega-ohm input
impedance
Two-channel, 100 MHz
bandwidth, 200 M sample
rate/sec, 2 MB memory/
channel
to 1 GHz frequency range
Without RMS audio
voltmeter or
With RMS audio voltmeter
Frequency/deviation meter and
signal generator for wide-range
troubleshooting and alignment
Digital voltmeter is recommended
for AC/DC voltage and current
measurements
Audio voltage measurements
Waveform measurements
RF level measurements
Receiver sensitivity
measurements
Page 34

3-2 Test Equipment, Service Aids, and Service Tools: Service Aids
3.2 Service Aids
Table 3-3. lists service aids recommended for working on the EP350 Series Radios. While all of these
items are available from Motorola, most are standard shop equipment items, and any equivalent item
capable of the same performance may be substituted for the item listed.
Table 3-3. Service Aids
Motorola Part
No.
PMDN4038_R Knob Remover/Chassis Opener Used to remove the front cover assembly.
PMDN4039_R Crab Eye Nut Opener Used to remove the crab eye nut.
1
PMDN4040_R
PMDN4041_R RF Adaptor Adapts radio’s antenna port to BNC cabling of test
PMDN4076_R Radio to Radio Cloning Cable Allows a radio to be duplicated from a master radio by
PMDN4077_R Programming Cable Used to program the radio through Customer
PMDN4079_R GND Plate Interconnects radio’s chassis to RF Adaptor.
PMDN4080_R Battery Eliminator Interconnects radio to power supply.
Note: 1.Use PMDN4040BR or higher for tuning the EP350 Series radios as PMDN4040AR cannot be used to
perform this function.
Radio Test Box Enables communication between the radio, test
Description Application
equipment and the computer's USB port.
equipment.
transferring programmed data from the master radio to
the other.
Programming Software and Radio Tuner.
Page 35

Test Equipment, Service Aids, and Service Tools: Service Aids 3-3
Programming/Test Cable
2.5mm stereo
USB connection type
Figure 3-1. Programming/Test Cable (PMDN4077_R)
2.5mm stereo
2.5mm stereo >
12
RX / TX data GND
~
Figure 3-2. Cloning Cable (PMDN4076_R)
D-D+
VBUS
1
2
GND
TX_D
RX_D
IC : CP2102
2.5mm stereo
1
VBUS
2
D-
3
D+
GND
4, 5, 6
To Computor
USB_CONNECTOR
Figure 3-3. Wiring of the Connectors
Page 36

3-4 Test Equipment, Service Aids, and Service Tools: Service Aids
Notes
Page 37

Chapter 4 Performance Checks
4.1 General
These radios meet published specifications through their manufacturing process by utilizing high
accuracy laboratory-quality test equipment. The recommended field service equipment is as accurate
as the manufacturing equipment with few exceptions. This accuracy must be maintained in
compliance with the manufacturer’s recommended calibration schedule.
4.2 Power–Up Self Test
Whenever the radio is turn on, it initiates a self-test routine which checks the RAM, EEPROM
hardware and EEPROM checksum. If Self Test passes, the green LED flashes once and a Self-Test
Pass Tone is generated. If unsuccessful, the red LED flashes rapidly and a Self-Test Fail Tone is
heard.
4.3 LCD/LED/Button/Volume Knob Test Mode
1. Make sure the radio is turned off.
2. Turn on the radio and immediately press 3 times. The LED turns solid amber. The LCD
displays the following indication (Figure 4-1) andthe backlight is activated.
Figure 4-4. LCD Indication
3. The radio will operate as shown in Table 4-1 if any key is pressed while in test mode.
Table 4-4. Radio Operation in Test Mode
Button LED LCD Indication Backlight Tone
, Right
, Left
Solid Green • ON when button is
pressed.
• OFF following
button released
(after a short period
of inactivity).
Solid Red – same as above –
Page 38

4-2 Performance Checks: LCD/LED/Button/Volume Knob Test Mode
Table 4-4. Radio Operation in Test Mode (Continued)
Button LED LCD Indication Backlight Tone
SPB1
(Side
Programmable
Button 1)
SPB2
(Side
Programmable
Button 2)
, FPB1
(Front
Programmable
Button 1)
, FPB2
(Front
Programmable
Button 2)
OFF • ON when button is
pressed.
• OFF after a short
period of inactivity
(even if the button is
continuously being
pressed).
• OFF when button is
released.
OFF – same as above –
OFF – same as above – Continuous tone; volume
increases/decreases by
turning the Volume Knob
clockwise/
counterclockwise.
Note: Press to turn
continuous tone OFF.
OFF – same as above –
, FPB3
(Front
Programmable
Button 3)
Numeric (Full
Keypad Model
Only)
1
2 (a b c)
3 (d e f)
4 (g h i)
5 (j k l)
6 (m n o)
7 (p q r s)
8 (t u v)
9 (w x y z)
* (DEL)
0
# ( )
OFF – same as above – Continuos tone OFF if
previously ON.
• ON when button is
pressed.
• OFF following
button released
(after a short period
of inactivity).
Page 39

Performance Checks: LCD/LED/Button/Volume Knob Test Mode 4-3
Table 4-4. Radio Operation in Test Mode (Continued)
Button LED LCD Indication Backlight Tone
PTT Button
(Push–To–Talk
Button)
Solid Amber • ON when button is
pressed.
• OFF following
button released
(After a short period
of inactivity)
Page 40

4-4 Performance Checks: LCD/LED/Button/Volume Knob Test Mode
Notes
Page 41

Chapter 5 Radio Programming and Tuning
5.1 Introduction
This chapter provides an overview of the EP350 Series Customer Programming Software (CPS) and
the CP/EP/P Tuner as designed for use in a Windows
functions of the traditional Radio Service Software (RSS) package.
They are both available in the CPS CDROM (PMVN4161_) and Entry Level Radio Tuner
CDROM (PMVN4165_).
5.2 CPS Programming Setup
Refer to online help files for the CPS Programming procedures.
(See Figure 5-5. CPS Programming Setup for CPS Programming Setup).
Program Cable PMDN4077_R
USB connec tion
Same Cable
®
2000/XP/Vista environment. Both cover all the
2.5mm stereo
USB
Figure 5-5. CPS Programming Setup
5.3 Radio-to-Radio Cloning
1. Cloning is the process of copying the content of one radio (source radio) into another radio
(destination radio). Radio content refers to system-type features such as frequency, squelch type
option, etc.
2. The cloning can be done only if all the following conditions are met:
a. The source radio's serial number cannot be blank.
b. The source radio and the destination radio must have the same model number.
c. The source radio and the destination radio must have an identical major codeplug
version.
3. Radio functionality inherent in one radio cannot be cloned to another radio that does not contain
the same functionality. Tuning and alignment information are not transferable and are not
affected by cloning.
Page 42

5-2 Radio Programming and Tuning: Radio Tuning Setup
Procedure:
1. Turn source and destination radios off.
2. Connect cloning cable (PMDN4076_R) to programming port of the two radios.
3. Turn on the destination radio.
4. Press and hold on the source radio and power up. "MASTER" and programming mode
icon are displayed on the source radio and at the same time LED of the radio turns solid amber.
5. "SLAVE" and programming mode icon are displayed on the destination radio and at the same
time LED of the radio turns solid amber.
6. During the cloning process, LED flashes in amber and source radio displays "CLONING" while
destination radio displays "PROG ON".
7. When cloning is completed, the source and destination radios display "COMPLETE". To exit
cloning mode, radios should be turn off.
8. Turn both radios off.
9. Disconnect the cloning cable from both radios and turn them on for normal operation.
5.4 Radio Tuning Setup
A Windows 2000/XP/Vista PC (personal computer) and Entry Level Radio Tuner are required to tune
the radio. To perform the tuning procedures, the radio must be connected to the PC, Test box and
Universal Test Set as shown in Figure 5-6. Radio Tuning Setup below. Refer to online help files for the
tuning procedures.
System Analyzer
TX
Service Monitor
or Counter
Watt Meter
Power
Supply
RF adaptor
PMDN4041_R
RADIO
GND plate
PMDN4079_R
Battery Eliminator
PMDN4080_R
BNC
Test Box
PMDN4040_R
Program/Test Cable
Audio IN
1
RX
RX Low
PMDN4077_R
RX
TX
Audio
Transformer /
Combiner
PMDN4171_R
RX/TX data
GND
Audio Out
RF Generator
Audio Generator
Audio Analyzer
Note: 1. Use PMDN4040BR or higher for tuning the EP350 Series radios as PMDN4040AR cannot be used to
perform this function.
2. Use PMDN4171_R for tuning the EP350 Series radios when using the service monitor R2600 series.
Figure 5-6. Radio Tuning Setup
Page 43

Radio Programming and Tuning: Transmitter Alignment Options 5-3
5.4.1 Initial Test Equipment Control Settings
The initial test equipment control settings are listed in Table 5-5.
Table 5-5. Initial Equipment Control Settings
Service Monitor Test Set Power Supply
Monitor Mode: Power Monitor Impedance: 24
RF Attenuation:
AM, CW, FM: FM PTT: OFF Volt Range: 0 – 10 V
Oscilloscope Source: Mod
Oscilloscope Horizontal: 10 mSec/Div
Oscilloscope Vertical: 2.5 kHz/Div
Oscilloscope Trigger: Auto
Monitor Image: Hi
Monitor BW: Nar
Monitor Squelch: mid CW
Monitor Volume: 1/4 CW
-70 Speaker/load:
5.5 Transmitter Alignment Options
Note: The maximum available power level given in the table below must NOT be exceeded.
There are separate alignment procedures for High and Low power.
Note:
When checking the RF power output of the radio with a test set, always use a pad of
at least 30 dB attached to the radio end of the RF cable. This will avoid an RF
mismatch and ensure a stable RF reading that will not change with varying lengths of
connecting cable.
Voltage: 7.5 Vdc
Ohm
DC on/standby: Standby
Load
Current: 3.0 A
Table 5-6. Transmit High/Low Power Level
RF Band (MHz) Model Number
High Power
(W)
Low Power
435 – 480M 4W 12.5/25K 99C FKPFPP SCR _H03RDK8AA_ 4.10 – 4.35 1.05 – 1.25
435 – 480M 4W 12.5/25K 99C LKP SCR _H03RDH8AA_ 4.10 – 4.35 1.05 – 1.25
136 – 174M 5W 12.5/25K 99C SCR _H03KEK8AA_ 5.00 – 5.30 1.00 – 1.30
136 – 174M 5W 12.5/25K 99C SCR _H03KEH8AA_ 5.00 – 5.30 1.00 – 1.30
403 – 447M 4W 12.5/25K 99C FKPFPP SCR _H03QDK8AA_ 4.10 – 4.35 1.05 – 1.25
403 – 447M 4W 12.5/25K 99C LKP SCR _H03QDH8AA_ 4.10 – 4.35 1.05 – 1.25
5.5.1 Transmit High Power Tuning
1. Click the Read icon to initiate communication with the radio.
2. Under the Alignment menu, select Tx Power, then select High (Figure 5-7. Tx High Power
Window (High Power)).
(W)
Page 44

5-4 Radio Programming and Tuning: Transmitter Alignment Options
3. Press PTT Toggle. This will key up the radio at the 1st test frequency (F1).
4. Read the Transmit Power from the Service Monitor.
5. Adjust the High Power Level as shown in Table 5-6 on page 3 by using either the Left/Right
arrows on the slider or Up/Down arrows on the Working Softpot box.
6. Press PTT Toggle to dekey the radio.
7. Goto the next frequency point by clicking on the next Working Softpot value and press PTT
Toggle.
8. Repeat steps 4 – 6 for the remaining test frequencies (F2–F5).
9. Press Program to commit the softpot values into the codeplug.
10. Exit the Transmit High Power function.
11. If the radio uses only high power channels, proceed to adjust modulation. If low power channels
are used, perform Transmit Low Power Tuning as defined.
F1
F2
F3
F4
F5
Figure 5-7. Tx High Power Window (High Power)
5.5.2 Transmit Low Power Tuning
1. Click the Read icon to initiate communication with the radio.
2. Under the Alignment menu, select Tx Power, then select Low (Figure 5-8. Tx Low Power
Window (Low Power)).
3. Press PTT Toggle. This will key up the radio at the 1st test frequency (F1).
4. Read the Transmit Power from the Service Monitor.
5. Adjust the Low Power Level as shown in Table 5-6 on page 3 by using either the Left/Right
arrows on the slider or Up/Down arrows on the Working Softpot box.
6. Press PTT Toggle to dekey the radio.
7. Goto the next frequency point by clicking on the next Working Softpot value and press PTT
Toggle.
8. Repeat steps 4–6 for the remaining test frequencies (F2–F5).
9. Press Program to commit the softpot values into the codeplug.
10. Exit the Transmit Low Power function.
11. Proceed to Adjust Modulation.
Page 45

Radio Programming and Tuning: Transmitter Alignment Options 5-5
F1
F2
F3
F4
F5
Figure 5-8. Tx Low Power Window (Low Power)
5.5.3 Transmit Modulation Tuning
There are 2 variations of Transmit Modulation Tuning, namely 12.5 kHz and 25 kHz.
Table 5-7. Transmit Modulation Tuning
Channel Spacing (kHz) Tuning Range (kHz)
12.5 2.25 ± 0.05
25 4.5 ± 0.1
5.5.3.1 Service Monitor Setting
1. Initial setup using the 8920A RF Communications Test Set
a. Connect “RF IN/OUT” port on 8920A to RF adaptor on radio’s antenna port using a N-Type to
BNC cable. Connect “AUDIO OUT” on 8920A to “Tx MOD” on test box using a BNC to BNC
cable. Connect the rest according to Figure 5-6. Radio Tuning Setup.
b. On 8920A, select “Tx” under “SCREEN CONTROL”.
c. Using the “CURSOR CONTROL”, key in the following items:
i. Tune Mode: Auto
ii. Tune Freq: Depends on Tune Mode
- Once “Auto” is selected, the centre frequency is set to the strongest RF signal
- Once “Manual” is selected, desired frequency has to be entered manually
iii. Tx Pwr Zero: Zero
iv. Input Port: RF In
v. Ext Tx Key: Off
Page 46

5-6 Radio Programming and Tuning: Transmitter Alignment Options
vi. AF An1 In: FM Demod
vii. Filter 1: 50 Hz HPF
viii. Filter 2: 15 kHz LPF
ix. De-Emphasis: 750us
x. Detector: Pk+-Max
xi. AFGen1 Freq: 1.0000 kHz
xii. AFGen1 Lvl: 100mV
2. Initial setup using the R2600 series RF Communications Test Set
a. Connect “RF IN/OUT” port on R2600 series to RF adaptor on radio’s antenna port using a N-
Type to BNC cable. Connect “MOT OUT” on R2600 series to “Tx MOD” on test box using a
BNC to BNC cable. Connect the rest according to Figure 5-6. Radio Tuning Setup.
b. On R2600, select “DISP” under “CURSOR ZONE”:
i. Meter: RF DISPLAY
ii. Mode: STANDARD
iii. Dev: (Reading for Transmit Modulation)
c. On R2600, select “RF” under “CURSOR ZONE”:
i. RF Control: MONITOR
ii. Preset: --
iii. B/W: NB
iv. Freq: Frequency Point (F1–F5) on Tuner
v. Output Lvl: 20dBm
vi. Gen RF Out: RF I/O
vii. Modulation Type: FM
d. On R2600, select “AUD” under “CURSOR ZONE”:
i. Fixed 1kHz: 0.100V. Enable (~)
ii. Synth: Disable (x)
iii. DTMF: Disable (x)
iv. External: Disable (x)
5.5.3.2 Transmit 12.5 kHz Modulation Tuning
1. Under the Alignment menu, select Tx Modulation, then select Mod. 12.5 kHz (Figure 5-9. Tx
Modulation 12.5 kHz Window).
2. Press PTT Toggle and switch to PTT on the test box. This will key up the radio at the F1.
3. Read the Modulation from the Service Monitor.
4. Change the modulation setting until the Tx deviation value (in Service Monitor) lies in the range of
the 12.5 kHz channel (as shown in Table 5-7.) by using either the Left/Right arrows on the slider
or Up/Down arrows on the Working Softpot box.
5. Press PTT Toggle to dekey the radio.
Page 47

Radio Programming and Tuning: Transmitter Alignment Options 5-7
6. Go to the next frequency point by clicking on the next Working Softpot value and press PTT
Toggle.
7. Repeat steps 3–5 for the remaining test frequencies (F2–F5).
8. Press Program to commit the softpot values into the codeplug.
9. Exit the Transmit 12.5 kHz Modulation function.
10. If 25 kHz channels are used, perform Transmit 25 kHz Modulation Tuning.
F1
F2
F3
F4
F5
Figure 5-9. Tx Modulation 12.5 kHz Window
5.5.3.3 Transmit 25 kHz Modulation Tuning
1. Under the Alignment menu, select Tx Modulation, then select Mod. 25 kHz (Figure 5-10. Tx
Modulation 25 kHz Window).
2. Press PTT Toggle and switch to PTT on the test box. This will key up the radio at the F1.
3. Read the Modulation from the Service Monitor.
4. Change the modulation setting until the Tx deviation value (in Service Monitor) lies in the range of
the 25 kHz channel (as shown in Table 5-7.) by using either the Left/Right arrows on the slider or
Up/Down arrows on the Working Softpot box.
5. Press PTT Toggle to dekey the radio.
6. Goto the next frequency point by clicking on the next Working Softpot value and press PTT
Toggle.
7. Repeat steps 3–5 for the remaining test frequencies (F2–F5).
8. Press Program to commit the softpot values into the codeplug.
9. Exit the Transmit 25 kHz Modulation function.
Page 48

5-8 Radio Programming and Tuning: Receiver Tuning
F1
F2
F3
F4
F5
Figure 5-10. Tx Modulation 25 kHz Window
5.6 Receiver Tuning
There are 4 variations of Receive Squelch Tuning: 12.5 kHz-Band Normal Squelch, 12.5 kHz-Band
Tight Squelch, 25 kHz-Band Normal Squelch and 25 kHz-Band Tight Squelch.
Table 5-8. Receiver Squelch Tuning
Squelch Type Tuning Range (dB)
Normal 6 – 8
Tight 15 – 17
5.6.1 Service Monitor Setting
1. Initial setup using the 8920A RF Communications Test Set
a. Connect “RF IN/OUT” port on 8920A to RF adaptor on radio’s antenna port using a N-Type to
BNC cable. Connect “AUDIO IN” HI and LO on 8920A to “Rx Audio” on test box using two
BNC to BNC cables. Connect the rest according to Figure 5-6. Radio Tuning Setup.
b. On 8920A, press “Rx” under “SCREEN CONTROL”.
c. Using the “CURSOR CONTROL”, key in the items below:
i. RF Gen Freq: Frequency Point (F1 – F5) on Tuner
ii. Amplitude: -128dBm
iii. Atten Hold: Off
iv. Output Port: RF Out
v. AFGen1 Freq: 1.0000 kHz
vi. AFGen1 To: 1.5 kHz for 12.5 kHz channel spacing, 3.0 kHz for 25 kHz channel spacing
vii. AFGen2 Freq: 0.0000 kHz
viii. AFGen2 To: Off
ix. Filter 1: 50 Hz HPF
Page 49

Radio Programming and Tuning: Receiver Tuning 5-9
x. Filter 2: 15 kHz LPF
xi. Ext Load R: 24 Ω
2. Initial setup using the R2600 series RF Communications Test Set
a. Connect “RF IN/OUT” port on R2600 series to RF adaptor on radio’s antenna port using a N-
Type to BNC cable. Connect “VERT/SINAD DIST/DVM COUNTER IN” on R2600 series to
the single input on audio transformer using one BNC to BNC cable. Connect the rest
according to Figure 5-6. Radio Tuning Setup.
b. On R2600, select “DISP” under “CURSOR ZONE”
i. Meter: SINAD
ii. Mode: STANDARD
c. On R2600, select “RF” under “CURSOR ZONE”:
i. RF Control: GENERATE
ii. Preset: --
iii. B/W: NB
iv. Freq: Frequency Point (F1–F5) on Tuner
v. Output Lvl: -128dBm (refer to step 2 in Section 5.6.2) and increase slowly (-127dBm,
-126dBm…) (refer to step 3 in Section 5.6.2)
vi. Gen RF Out: RF I/O
vii. Modulation Type: FM
d. On R2600, select “AUD” under “CURSOR ZONE”:
i. Fixed 1kHz: 1.50 kHz for 12.5kHz channel spacing and 3.0 kHz for 25kHz channel
spacing. Enable (~)
ii. Synth: Disable (x)
iii. DTMF: Disable (x)
iv. External: Disable (x)
5.6.2 Receive 12.5 kHz-Band Normal Squelch Tuning
1. Under the Alignment menu, select Rx Squelch, then select Squelch 12.5 kHz-band Normal.
(Figure 5-11. Rx 12.5 kHz-band Normal Squelch Tuning Window).
2. Apply a RF signal (with 1 kHz tone at 1.5 kHz deviation) for current frequency point with minimum
amplitude, -128 dBm (F1 being the first).
3. Set softpot to minimum (0) and adjust the amplitude of RF signal to the range of normal squelch
tuning (as shown in Table 5-8.) on the test equipment.
4. Adjust the softpot value by using either the Left/Right arrows on the slider or Up/Down arrows on
the Working Softpot box until the radio is totally muted.
5. Repeat steps 2–4 for F2–F5.
6. Press Program to commit the softpot values into the codeplug.
Page 50

5-10 Radio Programming and Tuning: Receiver Tuning
F1
F2
F3
F4
F5
Figure 5-11. Rx 12.5 kHz-band Normal Squelch Tuning Window
5.6.3 Receive 12.5 kHz-Band Tight Squelch Tuning
1. Under the Alignment menu, select Rx Squelch, then select Squelch 12.5 kHz-band Tight.
(Figure 5-12. Rx 12.5 kHz-band Tight Squelch Tuning Window).
2. Apply a RF signal (with 1 kHz tone at 1.5 kHz deviation) for current frequency point with minimum
amplitude, -128 dBm (F1 being the first).
3. Set softpot to minimum (0) and adjust the amplitude of RF signal to the range of tight squelch
tuning (as shown in Table 5-8.) on the test equipment.
4. Adjust the softpot value by using either the Left/Right arrows on the slider or Up/Down arrows on
the Working Softpot box until the radio is totally muted.
5. Repeat steps 2–4 for F2–F5.
6. Press Program to commit the softpot values into the codeplug.
Page 51

Radio Programming and Tuning: Receiver Tuning 5-11
F1
F2
F3
F4
F5
Figure 5-12. Rx 12.5 kHz-band Tight Squelch Tuning Window
5.6.4 Receive 25 kHz-Band Normal Squelch Tuning
1. Under the Alignment menu, select Rx Squelch, then select Squelch 25 kHz-band Normal.
(Figure 5-13. Rx 25 kHz-band Normal Squelch Tuning Window).
2. Apply a RF signal (with 1 kHz tone at 3.0 kHz deviation) for current frequency point with minimum
amplitude, -128 dBm (F1 being the first).
3. Set softpot to minimum (0) and adjust the amplitude of RF signal to the range of normal squelch
tuning (as shown in Table 5-8.) on the test equipment.
4. Adjust the softpot value by using either the Left/Right arrows on the slider or Up/Down arrows on
the Working Softpot box until the radio is totally muted.
5. Repeat steps 2–4 for F2–F5.
6. Press Program to commit the softpot values into the codeplug.
Page 52

5-12 Radio Programming and Tuning: Receiver Tuning
F1
F2
F3
F4
F5
Figure 5-13. Rx 25 kHz-band Normal Squelch Tuning Window
5.6.5 Receive 25 kHz-Band Tight Squelch Tuning
1. Under the Alignment menu, select Rx Squelch, then select Squelch 25 kHz-band Tight.
(Figure 5-14. Rx 25 kHz-band Tight Squelch Tuning Window).
2. Apply a RF signal (with 1 kHz tone at 3.0 kHz deviation) for current frequency point with minimum
amplitude, -128 dBm (F1 being the first).
3. Set softpot to minimum (0) and adjust the amplitude of RF signal to the range of tight squelch
tuning (as shown in Table 5-8.) on the test equipment.
4. Adjust the softpot value by using either the Left/Right arrows on the slider or Up/Down arrows on
the Working Softpot box until the radio is totally muted.
5. Repeat steps 2–4 for F2–F5.
6. Press Program to commit the softpot values into the codeplug.
Page 53

Radio Programming and Tuning: Utilities 5-13
F1
F2
F3
F4
F5
Figure 5-14. Rx 25 kHz-band Tight Squelch Tuning Window
5.7 Utilities
5.7.1 Program Serial No.
The Program Serial No. option under the Utilities heading allow the radio serial number to be
programmed. However, the serial number of a particular radio can only be programmed if it was
originally blank. Only New Service Boards have a blank serial number. Once a new serial number is
programmed into the board, it is NO longer changeable. If the serial number of the radio is not blank,
access to the screen will be denied. The serial number programming screen is shown in
Figure 5-15. Program Radio Serial No. Window. For the new radio serial number to take effect, close
the screen and then read the radio again.
Figure 5-15. Program Radio Serial No. Window
Page 54

5-14 Radio Programming and Tuning: Front Panel Programming
5.8 Front Panel Programming
5.8.1 Introduction
This mode allows you to change the feature parameters to enhance the use of your radio.
Note
To program your radio using the front panel, you need to enter Programming Mode in Dealer
Configuration. This configuration/mode allows you to edit a number of features to enhance the use of
this radio.
In user configuration, a user will have a limited choice to program the radio.
Note
Please use the CPS to program additional setting on the radio.
Some EP350 Series models do not have Dealer Configuration enabled. (EP350 Series
radio with the following Regional Super Tanapa: PMUE3144_AL, PMUD2441_AL and
PMUE3323_AL only have User Configuration enabled). Please use the CPS to program
additional setting on the radio.
5.8.2 Dealer and User Configurations
Your radio is shipped out from the factory configured according to the User Configuration. In this
configuration, users can only access a limited number of features. Channels and other radio settings
can ONLY be programmed when the radio is operating in Dealer Configuration.
To prepare radios for the users, the dealer should:
1. Set the radio to Dealer Configuration (if the radio is configured in User Configuration).
2. Enter Programming Mode.
3. Program the radio with all the necessary parameters, according to the users' requirements.
4. Set the radio back to User Configuration.
Clone the radio's parameters to all the users' radios.
Note:
CPS can enable/disable the access for performing the User/Dealer mode switch function. If
the access is disabled, then the radio cannot enter the User/Dealer mode switch function.
5.8.2.1 Switching between Dealer and User Configurations
5.8.2.1.1 From Dealer to User
1. Turn off the radio.
2. Press the Side Programmable Button 2 (bottom side programmable button) 5 times within 3
seconds after turning on the radio.
3. LCD will display the current front panel programming mode.
4. If the LCD does not display "USER",
a. Press Left-arrow or Right-arrow buttons to scroll to "USER" mode.
b. Press PTT to confirm "USER" mode selection.
c. The LCD displays "USER MODE ON" for a while before showing “USER”.
5. Turn off the radio. The radio is now operating in USER MODE.
Page 55

Radio Programming and Tuning: Front Panel Programming 5-15
5.8.2.1.2 From User to Dealer
1. Turn off the radio.
2. Press the Side Programmable Button 2 (bottom side programmable button) 5 times within 3
seconds after turning on the radio.
3. LCD will display the current front panel programming mode.
4. If the LCD does not display "DEALER",
a. Press Left-arrow or Right-arrow buttons to scroll to "DEALER" mode.
b. Press PTT to confirm "DEALER" mode selection.
c. The LCD displays "DEALER MODE ON" for a while before showing “DEALER”.
5. Turn off the radio. The radio is now operating in DEALER MODE.
Important:
If the radio is to be given to the customer, REMEMBER to switch it back to operate in
User Configuration.
5.8.3 Entering Programming Mode
Make sure the radio is turn off. Press Side Programmable Button 1 (top side programmable button),
and turn ON the radio. A tone is heard, indicating that the radio is in Programming Mode. The
indicator illuminates and the "BCKLIGHT" is displayed on the radio LCD.
5.8.4 Exiting Programming Mode
Turn off the radio to exit Programming Mode.
5.8.5 Accessing Front Panel Programming Mode Parameters
Press or to scroll through the parameters for each menu or sub-menu item, or
Press PTT to select the menu or sub-menu item, or
Press Side Programmable Button 1 to either return to previous menu level or to exit the selection
parameter without change.
Page 56

5-16 Radio Programming and Tuning: Front Panel Programming
5.8.6 Editing Front Panel Programming Mode Parameters
Table 5-9. Front Panel Programming Mode Parameters
Main Menu
BCKLIGHT
(Backlight)
BATTERY SAVER
ACCESORY
(Accessory)
TONE VOL
(Alert Tone
Volum e)
1st Level
Sub-Menu
(Battery Saver)
TYPE
(Battery Type)
SPK GAIN
(External
Speaker
Gain)
MIC GAIN
(External
Microphone
Gain)
VOX GAIN
(VOX
Microphone
Gain)
VOX CH CH-001 ...
2nd Level
Sub-Menu
CH-099
Setting Remarks
AUTO
TOGGLE
OFF
NORMAL
ENHANCED
NIMH
LI-ION
H LI-ION
+2
+1
0
-1
-2
+2
+1
0
-1
-2
VERY HIGH
HIGH
MIDDLE
LOW
ENABLE
DISABLE
ON
OFF
AUTO – Backlight Off if no keypress for more
than 5 seconds.
Pressing the Backlight button again prolongs
illumination time.
TOGGLE – Allows Backlight Button to toggle
control the ON/OFF status of the backlight.
Helps to extend battery life. When enabled, turns
off the radio receiver circuitry periodically when
no activity is detected.
NORMAL – turns off radio less frequently; select
this to save battery when expecting to receive
Selective Call or Call Alert.
ENHANCED – turns off receiver for a longer
duration; select this to maximize battery saving
with no Selective Call or Call Alert.
Type of battery radio uses.
NIMH – Nickel Metal Hydride
LI-ION – Lithium-Ion
H LI-ION – High Capacity Lithium-Ion
Volume Adjustment – External Speaker.
+2: maximum external speaker gain
-2: minimum external speaker gain
Sensitivity Adjustment – External microphone.
+2: maximum external microphone sensitivity
gain
-2: minimum external microphone sensitivity gain
VOX microphone sensitivity adjustment – VOX
accessories
VERYHIGH: maximum VOX microphone
sensitivity gain.
LOW: minimum VOX microphone sensitivity gain.
Enable or Disable VOX feature for the selected
channel.
Selects the alert tone volume preference.
OFF: no alert tone.
ON: Alert tone is on.
Page 57

Radio Programming and Tuning: Front Panel Programming 5-17
Table 5-9. Front Panel Programming Mode Parameters (Continued)
Main Menu
PROG BTN
(Programmable
Button)
1st Level
Sub-Menu
SIDE 1S
(Side Button 1
– Short Press
SIDE 1L
(Side Button 1
– Long Press)
SIDE 2S
(Side Button 2
– Short Press)
SIDE 2L
(Side Button 2
– Long Press)
FRONT 1S
(Front Button 1
– Short Press)
2nd Level
Sub-Menu
Setting Remarks
UNASSIGN (Unassigned)
BCKLIGHT (Backlight)
CH ALIAS (Channel Alias)
PTT ID (PTT ID Enable)
TPL/DPL (TPL/DPL Enable)
PRIME CH (Prime Channel)
POWER (Power Level)
SCAN
SQUELCH (Squelch Level)
TALKARND (Talkaround)
MONITOR
PHONE (Phone Mode)
SCM CODE (Scrambling
Code Select)
VOX (Voice Operated
Transmit)
RV BURST (Reverse Burst)
SEL CALL (Selective Call)
CL ALERT (Call Alert)
UNASSIGN (Unassigned)
BCKLIGHT (Backlight)
CH ALIAS (Channel Alias)
KEY LOCK (Keypad Lock)
NUIS DEL (Nuisance
Channel Delete)
PTT ID (PTT ID Enable)
TPL/DPL (TPL/DPL Enable)
PRIME CH (Prime Channel)
POWER (Power Level)
SCAN
SQUELCH (Squelch Level)
TALKARND (Talkaround)
STKY MONITOR (Sticky
Monitor)
PHONE (Phone Mode)
SCRAMBLE (Scrambling
Enable)
SCM CODE (Scrambling
Code Select)
VOX (Voice Operated
Transmit)
RV BURST (Reverse Burst)
SEL CALL (Selective Call)
CL ALERT (Call Alert)
VOL SET (Volume Set)
- same as above - Program Side Button 2 – Short Press.
- same as above - Program Side Button 2 – Long Press.
- same as above - Program Front Button 1 – Short Press.
Program Side Button 1 – Short Press.
Program Side Button 1 – Long Press.
Page 58

5-18 Radio Programming and Tuning: Front Panel Programming
Table 5-9. Front Panel Programming Mode Parameters (Continued)
Main Menu
CHANNEL
1st Level
Sub-Menu
FRONT 1L
(Front Button 1
– Long Press)
FRONT 2S
(Front Button 2
– Short Press)
FRONT 2L
(Front Button 2
– Long Press)
FRONT 3S
(Front Button 3
– Short Press)
FRONT 3L
(Front Button 3
– Long Press)
AC TIVATE
ALIAS
BANDWDTH
(Bandwidth)
RX FREQ
(Rx Frequency)
TX FREQ
(Tx Frequency)
PL DSPLY
(PL Display
Type)
RX PL
(Receive TPL/
DPL)
TX PL
(Transmit TPL/
DPL)
TPL 1
**
**
**
**
**
**
**
**
**
2nd Level
Sub-Menu
CH-001 ...
CH-099
CH-001 ...
CH-099
CH-001 ...
CH-099
CH-001 ...
CH-099
CH-001 ...
CH-099
CH-001 ...
CH-099
CH-001 ...
CH-099
Setting Remarks
- same as above - Program Front Button 1 – Long Press.
- same as above - Program Front Button 2 – Short Press.
- same as above - Program Front Button 2 – Long Press.
- same as above - Program Front Button 3 – Short Press.
- same as above - Program Front Button 3 – Long Press.
ENABLE
DISABLE
YYYYYYYY Set alias for the channel.
12.5 KHZ
25.0 KHZ
XXX. XXXX Set receiving frequency (in MHz) for the current
XXX. XXXX Set transmitting frequency (in MHz) for the
FREQ
CODE
CSQ CSQ
TPL 067.0 ... 001 ...
TPL 254.1 042
DPL 023 or 043
DPL 754 127
TPL 1 TPL 1
TPL 2 TPL 2
TPL 3 TPL 3
CSQ CSQ
TPL 067.0 001 ...
TPL 254.1 042
DPL 023 or 043
DPL 754 127
TPL 1 TPL 1
TPL 2 TPL 2
TPL 3 TPL 3
067.0
067.1 ...
254.9
255.0
Enable or disable a channel.
Set channel bandwidth at 12.5 kHz or 25 kHz.
The selection will depending on the bandwidth
setting allowed for a particular mode
channel.
current channel.
PL display type – in frequency or code.
Receive PL
•Frequency: CSQ, TPL 67.0 – TPL 254.1,
DPL 023 – DPL 754, user defined TPL 1, user
defined TPL 2, & user defined TPL 3
•Code: CSQ, 001 – 127, user defined TPL 1,
user defined TPL 2, & user defined TPL 3
Transmit PL
•Frequency: CSQ, TPL 67.0 – TPL 254.1,
DPL 023 – DPL 754, user defined TPL 1, user
defined TPL 2, & user defined TPL 3
•Code: CSQ, 001 – 127, user defined TPL 1,
user defined TPL 2, & user defined TPL 3
Non-standard private line (TPL) frequency.
67.0 Hz – 255.0 Hz with 0.1 Hz step.
Page 59

Radio Programming and Tuning: Front Panel Programming 5-19
Table 5-9. Front Panel Programming Mode Parameters (Continued)
Main Menu
1st Level
Sub-Menu
**
TPL 2
**
TPL 3
RXDPL TY
(RX DPL Type)
TXDPL TY
(TX DPL Type)
RV BURST
(Reverse Burst)
TOC
(Turn Off Code)
SQUELCH
(Squelch Level)
TIME OUT
(Time
Out Timer)
POWER
(Power Level)
PRIME CH
(Prime
Channel
PR CH HT
(Prime Channel
Hang Time)
BCL
(Busy Channel
Lockout)
COPY CH
(Copy Channel)
**
**
**
**
**
**
**
2nd Level
Sub-Menu
CH-001 ...
CH-099
CH-001 ...
CH-099
CH-001 ...
CH-099
CH-001 ...
CH-099
CH-001 ...
CH-099
CH-001 ...
CH-099
CH-001 ...
CH-099
CH-001 ...
CH-099
Setting Remarks
067.0
067.1 ...
254.9
255.0
067.0
067.1 ...
254.9
255.0
DPL
INV DPL (Invert DPL)
DPL
INV DPL (Invert DPL)
NONE
180
240
ENABLE
DISABLE
NORMAL
TIGHT
OFF
010
020
...
590
600
HIGH
LOW
OFF
001...
099
010
011...
059
060
ENABLE
DISABLE
TO CH XXX Copy setting of a channel to a new channel.
Non-standard private line (TPL) frequency.
67.0 Hz – 255.0 Hz with 0.1 Hz step.
Non-standard private line (TPL) frequency.
67.0 Hz – 255.0 Hz with step size of 0.1 Hz.
Receive DPL Type – DPL or Invert DPL.
Transmit DPL Type – DPL or Invert DP.
Reverse burst setting – None, 180° or 240°.
Turn Off Code setting – enable or disable.
NORMAL squelch level – receive weak signals.
TIGHT squelch level – receive strong signals and
eliminates unwanted noise.
Maximum duration (in seconds) the radio can
transmit continuously.
Power level – High or Low.
The channel that you wish to spend most of your
time monitoring.
The radio will always switch back to the Prime
Channel if it is idle for more than the
preprogrammed hang-time in other channels.
Prime Channel Hang Time – duration the radio
will stay in another channel before reverting back
to the prime channel.
10 sec. – 60 sec. with step size of 1 sec.
Busy channel lockout – enable or disable.
SIGNALNG
(Signaling)
**
PTT ID XXXXXXXX Set PTT ID.
Page 60

5-20 Radio Programming and Tuning: Front Panel Programming
Table 5-9. Front Panel Programming Mode Parameters (Continued)
Main Menu
SCAN
1st Level
Sub-Menu
PTTID TY
(PTT ID Type)
PTTID CH
(PTT ID
Channel)
PTT TONE
(PTT Side
Tone)
TXPRTIME
(TX Pretime)
IND ID
(Individual ID)
GRP ID
(Group ID)
ALL ID XXXXXXXX Set All ID.
ACK ID
(Acknowledge
ID)
ACK IND
(Acknowledge
for Individual
Call)
SEL CAL
(Selective Call
Channel)
CALL PL
(PL Required
for Call)
CL ALERT
(Call Alert
Channel)
HANGTIME
(Scan Hang
Time)
**
2nd Level
Sub-Menu
CH-001 ...
CH-099
CH-001 ...
CH-099
CH-001 ...
CH-099
CH-001 ...
CH-099
CH-001 ...
CH-099
Setting Remarks
NONE
PRE
POST
BOTH
ENABLE
DISABLE
NONE
LONG
SHORT
0000
0025...
3975
4000
XXXXXXXX Set Individual ID.
XXXXXXXX Set Group ID.
XXXXXXXX Set Acknowledge ID.
ENABLE
DISABLE
ENABLE
DISABLE
ENABLE
DISABLE
ENABLE
DISABLE
500
1000 ...
9500
10000
PTT ID type – None, Pre, Post or Both.
Set channel with PTT ID enabled.
PTT side tone – No side tone, Long side tone or
Short side tone.
Transmit pretime – duration radio waits, after a
Push-to-Talk (PTT) button press, before
transmitting the DTMF signaling.
0ms – 4000ms with step size of 25ms.
Set channel that enable Acknowledge ID
transmission upon receiving Individual Call.
Set channel that enable Selective Call
transmission.
Set channel that enable PL required for call
feature.
When enabled, the radio needs to receive a
matching Call ID as well as a TPL/DPL code in
order to unmute on the current channel.
Set channel that enable Call Alert transmission.
Scan hang time: 500ms – 10000ms with step size
of 500ms.
INT TIME
(Scan Interval
Time)
LIST 1
(Scan List 1)
**
01-XXX
02-XXX ...
15-XXX
16-XXX\
750
1000 ...
4750
5000
_ _ _
001 ...
099
Scan interval time: 750ms - 5000ms with step
size of 250ms.
Set Scan List 1 members.
xxx – selected scan list member
_ _ _ – no scan list member is selected
Page 61

Radio Programming and Tuning: Front Panel Programming 5-21
Table 5-9. Front Panel Programming Mode Parameters (Continued)
Main Menu
SCRMBLIN
(Voice Inversion
Scrambling)
1st Level
Sub-Menu
LIST 2
(Scan List 2)
LIST 3
(Scan List 3)
LIST SEL
(Scan List
Select)
SCAN TYP
(Scan Type
Select)
PRIORITY
(Priority
Channel
Select)
CHANNEL
(Scrambling
Channel
Select)
CODE
(Scrambling
Code
Select)
2nd Level
Sub-Menu
01-XXX
02-XXX ...
15-XXX
16-XXX\
01-XXX
02-XXX ...
15-XXX
16-XXX\
CH-001 ...
CH-099
CH-001 ...
CH-099
LIST1
(Scan List 1)
LIST2
(Scan List 2)
LIST3
(Scan List 3)
CH-001 ...
CH-099
Setting Remarks
_ _ _
001 ...
099
_ _ _
001 ...
099
LIST1 (Scan List 1)
LIST2 (Scan List 2)
LIST3 (Scan List 3)
NORMAL
PRIORITY
_ _ _
001 ...
099
_ _ _
001 ...
099
_ _ _
001 ...
099
ENABLE
DISABLE
3.29
3.39
Set Scan List 2 members.
xxx – selected scan list member
_ _ _ – no scan list member is selected
Set Scan List 3 members.
xxx – selected scan list member
_ _ _ – no scan list member is selected
Set scan list for a selected channel.
Scan type for selected channel – Normal Scan,
Priority Scan
Set Priority Channel for Scan List 1.
xxx – selected priority channel
_ _ _ – no priority channel is selected
Set Priority Channel for Scan List 2.
xxx – selected priority channel
_ _ _ – no priority channel is selected
Set Priority Channel for Scan List 3.
xxx – selected priority channel
_ _ _ – no priority channel is selected
Scrambling – Enable or disable
Scrambling code – 3.29 or 3.39.
Page 62

5-22 Radio Programming and Tuning: Front Panel Programming
Table 5-9. Front Panel Programming Mode Parameters (Continued)
Main Menu
PHONE
CALL LST
(Call List
*
**
*
*
Applicable to Keypad Models only.
Only applicable to radio that supports Dealer Mode.
1st Level
Sub-Menu
ACC CODE
(Access Code)
DEACCCODE
(Deaccess
Code)
PHONE 01 NUMBER01 Set Phone No 1.
ALIAS
(Assigned
name
PHONE XX
(XX = 01 to 16)
ALIAS EDIT XXXXXXXX Allows you to edit call ID. XXXXXXXX denotes
CALL XX
(XX= 01 to 16)
2nd Level
Sub-Menu
EDIT Edit phone number – XXXXXXXX.
DELETE Delete the phone entry.
DELETE Selecting DELETE option will delete the call list
Setting Remarks
XXXXXXXX Access code for phone – XXXXXXXX.
Use radio keypad to enter up to 16 characters
consisting of 0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,#,*
XXXXXXXX Deaccess code for phone – XXXXXXXX.
Use radio keypad to enter up to 16 characters
consisting of 0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,#,*
Use radio keypad to enter up to16 characters
consisting of 0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,#,*
Note: NUMBER01 will appear if the phone list
entry is empty.
NAME 01 Set alias for Phone No 1.
User can use radio keypad to enter up to 8
characters consisting of A – Z, 0 – 9, \, #, < >, *, +,
_, /, Note: NAME 01 will appear if the phone list entry
is empty.
Note: The alias will appear at 1st menu level if the
phone list entry is not empty.
NUMBERXX Set Phone No X.
User can use radio keypad to enter up to16
characters consisting of 0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,#,*
Note: NUMBERXX will appear if the phone list
entry is empty.
NAMEXX Set alias for Phone No X.
User can use radio keypad to enter up to 8
characters consisting of A – Z, 0 – 9, \, #, < >, *, +,
_, /, Note: NAMEXX will appear if the phone list entry
is empty.
the
call ID numbers.
Note: The alias will appear at 1st menu level if the
call list entry is not empty.
entry.
ID XX Set call list ID X.
Use radio keypad to enter up to 8 characters
consisting of 0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,#,*
Note: ID XX will appear if the call list entry is
empty.
ALIAS XX Set alias for call list ID X.
Use radio keypad to enter up to 8 characters
consisting of A - Z, 0 - 9, \, #, < >, *, +, _, /, Note: Alias XX will appear if the call list entry is
empty.
Page 63

Radio Programming and Tuning: Front Panel Programming 5-23
5.8.7 Factory Reset
This feature allows you to erase certain programmable parameters and restore the radio to the
factory default settings. The radio, upon reset, clears all memory channels, and restores the default
settings of radio wide parameters.
1. Set the radio in Dealer Configuration (if it is operating in User Configuration).
2. Press and hold Side Programming Button 2 and PTT button together, while turning on the radio.
3. A good key tone is heard and “FA RESET” is displayed on the LCD
4. Proceed to step 8 to Cancel Factory Reset.
5. Press . “YES” is displayed.
6. Press PTT to confirm Factory Reset. “RESET OP” is shown while factory reset operation is in
progress.
7. Upon completion, “FACTORY RESET COMPLETED” is shown and the radio automatically turn
off and on again. The radio is now restored to its default factory setting.
8. Press . “NO” is displayed.
9. Press PTT to confirm Cancellation. “CANCELLED” is shown and the radio automatically turn off,
and on again.
Note:
Factory Reset function is only available for Software Mode 1 radio.
Page 64

5-24 Radio Programming and Tuning: Front Panel Programming
Notes
Page 65

Chapter 6 Maintenance – EP350 (Full Keypad Model)
6.1 Introduction
This section provides details about the following:
• Preventive maintenance (inspection and cleaning)
• Safe handling of CMOS and LDMOS devices
• Disassembly and reassembly of the radio
• Repair procedures and techniques
• Mechanical View and Parts List
6.2 Preventive Maintenance
The radios do not require a scheduled preventive maintenance program; however, periodic visual
inspection and cleaning is recommended.
6.2.1 Inspection
Check that the external surfaces of the radio are clean, and that all external controls and switches are
functional. It is not recommended to inspect the interior electronic circuitry.
6.2.2 Cleaning Procedures
The following procedures describe the recommended cleaning agents and the methods to be used
when cleaning the external and internal surfaces of the radio. External surfaces include the front
cover, housing assembly and battery case. These surfaces should be cleaned whenever a periodic
visual inspection reveals the presence of smudges, grease, and/or grime.
Note:
The only recommended agent for cleaning the external radio surfaces is a 0.5% solution of a mild
dishwashing detergent in water. The only factory recommended liquid for cleaning the printed circuit
boards and their components is isopropyl alcohol (100% by volume).
The effects of certain chemicals and their vapors can have harmful results on certain plastics.
Avoid using aerosol sprays, tuner cleaners, and other chemicals.
Internal surfaces should be cleaned only when the radio is disassembled for service or
repair.
Page 66

6-2 Maintenance – EP350 (Full Keypad Model): Safe Handling of CMOS and LDMOS Devices
Cleaning External Plastic Surfaces
Apply the 0.5% detergent-water solution sparingly with a stiff, non-metallic, short-bristled brush to
work all loose dirt away from the radio. Use a soft, absorbent, lintless cloth or tissue to remove the
solution and dry the radio. Make sure that no water remains entrapped near the connectors, cracks,
or crevices.
Cleaning Internal Circuit Boards and Components
Isopropyl alcohol (100%) may be applied with a stiff, non-metallic, short-bristled brush to dislodge
embedded or caked materials located in hard-to-reach areas. The brush stroke should direct the
dislodged material out and away from the inside of the radio. Make sure that controls or tunable
components are not soaked with alcohol. Do not use high-pressure air to hasten the drying process
since this could cause the liquid to collect in unwanted places. After completing the cleaning process,
use a soft, absorbent, lintless cloth to dry the area. Do not brush or apply any isopropyl alcohol to the
frame, front cover, or back cover.
Note:
Always use a fresh supply of alcohol and a clean container to prevent contamination by
dissolved material (from previous usage).
6.3 Safe Handling of CMOS and LDMOS Devices
Complementary metal-oxide semiconductor (CMOS) devices are used in this family of radios, and are
susceptible to damage by electrostatic or high voltage charges. Damage can be latent, resulting in
failures occurring weeks or months later. Therefore, special precautions must be taken to prevent
device damage during disassembly, troubleshooting, and repair.
Handling precautions are mandatory for CMOS circuits and are especially important in low humidity
conditions. DO NOT attempt to disassemble the radio without first referring to the following CAUTION
statement.
This radio contains static-sensitive devices. Do not open the radio unless you are properly
grounded. Take the following precautions when working on this unit:
• Store and transport all CMOS devices in conductive material so that all exposed
leads are shorted together. Do not insert CMOS devices into conventional plastic
“snow” trays used for storage and transportation of other semiconductor devices.
• Ground the working surface of the service bench to protect the CMOS device. We
recommend using a wrist strap, two ground cords, a table mat, and a floor mat.
• Wear a conductive wrist strap in series with a 100k resistor to ground. (Replacement
wrist straps that connect to the bench top covering are Motorola part number
4280385A59.)
• Do not wear nylon clothing while handling CMOS devices.
• Do not insert or remove CMOS devices with power applied. Check all power supplies
used for testing CMOS devices to be certain that there are no voltage transients
present.
• When straightening CMOS pins, provide ground straps for the apparatus used.
• When soldering, use a grounded soldering iron.
• If at all possible, handle CMOS devices by the package and not by the leads. Prior to
touching the unit, touch an electrical ground to remove any static charge that you
may have accumulated. The package and substrate may be electrically common. If
so, the reaction of a discharge to the case would cause the same damage as touching
the leads.
Page 67

Maintenance – EP350 (Full Keypad Model): Repair Procedures and Techniques – General 6-3
6.4 Repair Procedures and Techniques – General
Note
Environmentally Preferred Products (EPP) (refer to the marking on the printed circuit
boards - examples shown below) were developed and assembled using environmentally
preferred components and solder assembly techniques that meet or exceed compliance
to the European Union’s ROHS and WEEE directives (Waste Electrical and Electronic
Equipment (WEEE) Directive 2002/96/EC and Restriction of Hazardous Substances
(ROHS) Directive 2002/95/EC). To maintain product compliance and reliability, use only
the Motorola specified parts in this manual.
For the identification of lead (Pb) free assemblies, all EPP products will carry the EPP
Marking, shown below, on the printed circuit board (PCB). This marking provides
information to those performing assembly, servicing and recycling operation on this
product, adhering to the JEDEC standard #97. The EPP Marking takes the form of a
label or marking on the PCB.
Any rework or repair on Environmentally Preferred Products must be done using the appropriate
lead-free solder wire and solder paste as stated in the following tables:
Table 6-10. Lead Free Solder Wire Part Number List
Motorola
Part Number
1088929Y01 95.5Sn/3.8Ag/0.7Cu RMA Version 2.7-3.2% 217C 52171 0.015” 1lb spool
Alloy Flux Type
Flux Content
by Weight
Melting
Point
Supplier Part
number
Diameter Weight
Table 6-11. Lead Free Solder Paste Part Number List
Motorola
Part Number
10-856-
74C03
Manufacturer Part
Number
NC-SMQ230 900-1000KCPs
Viscosity Type Composition & Percent Metal
Brookfield(5rpm)
Type 3
-325/+500)
(
95.5%Sn-3.8%Ag-0.7%Cu
89.3%
Liquidus
Temperature
217 Degree C
Parts Replacement and Substitution
When damaged parts are replaced, identical parts should be used. If the identical
replacement part is not locally available, check the parts list for the proper Motorola part number.
Orders for replacement parts which are listed in the “Parts List” section of this manual, should be
placed directly on Motorola’s local distribution organization or via Motorola Online
Rigid Circuit Boards
This family of radios uses bonded, multi-layer, printed circuit boards. Since the inner layers are not
accessible, some special considerations are required when soldering and unsoldering components.
The printed-through holes may interconnect multiple layers of the printed circuit. Therefore, exercise
care to avoid pulling the plated circuit out of the hole.
When soldering near the connector pins:
Page 68

6-4 Maintenance – EP350 (Full Keypad Model): Repair Procedures and Techniques – General
• Avoid accidentally getting solder in the connector.
• Be careful not to form solder bridges between the connector pins.
• Examine your work closely for shorts due to solder bridges.
Chip Components
Use the RLN4062 Hot-Air Repair Station for chip component replacement. Adjust the temperature
control to 390 °C (735 °F), and adjust the airflow to a minimum setting. Airflow can vary due to
component density.
• To remove a chip component:
1. Use a hot-air hand piece and position the nozzle of the hand piece approximately 0.3 cm
(1/8") above the component to be removed.
2. Begin applying the hot air. Once thde solder reflows, remove the component using a pair
of tweezers.
3. Using a solder wick and a soldering iron or a power desoldering station, remove the
excess solder from the pads.
• To replace a chip component using a soldering iron:
1. Select the appropriate micro-tipped soldering iron and apply fresh solder to one of the
solder pads.
2. Using a pair of tweezers, position the new chip component in place while heating the
fresh solder.
3. Once solder wicks onto the new component, remove the heat from the solder.
4. Heat the remaining pad with the soldering iron and apply solder until it wicks to the
component. If necessary, touch up the first side. All solder joints should be smooth and
shiny.
• To replace a chip component using hot air:
1. Use the hot-air hand piece and reflow the solder on the solder pads to smooth it.
2. Apply a drop of solder paste flux to each pad.
3. Using a pair of tweezers, position the new component in place.
4. Position the hot-air hand piece approximately 0.3 cm (1/8") above the component and
begin applying heat.
5. Once the solder wicks to the component, remove the heat and inspect the repair. All
joints should be smooth and shiny.
Page 69

Maintenance – EP350 (Full Keypad Model): Repair Procedures and Techniques – General 6-5
Shields
Removing and replacing shields is recommended to be done with the Air Blower,
BOSCH GHG 603 or equivalent.
• To remove the shield:
1. Place the circuit board in the circuit board holder.
2. Add solder paste flux around the base of the shield.
3. Position the heat-focus head onto the shield.
4. Turn on the heater and wait until the shield lifts off the circuit board.
5. Once the shield is off, turn off the heat, and grab the part with a pair of tweezers.
6. Remove the circuit board from the circuit board holder.
• To replace the shield:
1. Add solder to the shield if necessary, using a micro-tipped soldering iron.
2. Next, rub the soldering iron tip along the edge of the shield to smooth out any excess
solder. Use solder wick and a soldering iron to remove excess solder from the solder
pads on the circuit board.
3. Place the circuit board back in the circuit board holder.
4. Place the shield on the circuit board using a pair of tweezers.
5. Position the heat-focus head over the shield.
6. Turn on the heater and wait for the solder to reflow.
7. Once complete, turn off the heat, raise the heat-focus head and wait approximately one
minute for the part to cool.
8. Remove the circuit board and inspect the repair. No cleaning should be necessary.
Page 70

6-6 Maintenance – EP350 (Full Keypad Model): Disassembling and Reassembling the Radio
6.5 Disassembling and Reassembling the Radio – General
When disassembling and reassembling the radio, it is important to pay particular attention to the snaps and
tabs, and how parts align with each other.
The following tools are required for disassembling and reassembling the radio (see Chapter 3 for a list
of service aids):
• Phillips Screwdriver
• Flat Head Screwdriver
• Torque Driver
• Crab Eye Nut Opener (PMDN4039_R)
• Chassis and Knob Opener (PMDN4038_R)
• Tweezers
If a unit requires further testing or service than is customarily performed at the basic level, please
send the unit to a Motorola Authorized Service Center listed in Appendix B.
Note:
Numbers in parentheses ( ) refer to item numbers in Table 6-13 on page 6-19.
Figure 6-16. Full Keypad Without Channel Knob Model
Page 71

Maintenance – EP350 (Full Keypad Model): Disassembling and Reassembling the Radio 6-7
6.5.1 Radio Disassembly – Detailed
6.5.1.1 Front Housing From Chassis Disassembly
1. Turn off the radio.
2. Remove the Battery (29):
a. Release the battery latch by moving it into the unlock position.
b. Slide the Battery downwards.
c. Remove the Battery from the radio.
Belt Clip
Antenna
Battery Latch
Battery
Figure 6-17. Battery and Antenna Removal
3. Remove the Antenna (21) by turning it counterclockwise.
4. Remove the Volume Knob (7) from its shaft using the Chassis and Knob Opener.
(Refer Figure 6-18).
Volume Knob
Chassis and Knob Opener
Figure 6-18. Knob Removal
Page 72

6-8 Maintenance – EP350 (Full Keypad Model): Disassembling and Reassembling the Radio
Note:
The Volume Knob can be turned clockwise and counterclockwise. However, it is designed to
fit very tightly on the shaft.
5. Separate the Chassis (25) from the Front Housing Assembly (1):
a. Insert the Chassis and Knob Opener in between the thin retaining wall and the chassis
at the bottom of the radio. Do not mar the O-ring sealing area on the housing.
b. Slowly pry the bottom of the chassis from the housing by pushing the Chassis and Knob
Opener downwards, and prying the handle of the tool over and behind the base of the
radio. This forces the thin inner plastic wall toward the base of the radio thus releasing
the two chassis base tabs. (Refer Figure 6-19).
Figure 6-19. Chassis Removal
Marring the front cover O-ring sealing area will prevent the radio from sealing properly. If the
O-ring (23) is damaged, replace it with a new one.
c. Slide the rear chassis downwards, and away from the front housing. Be careful not to
damage the Flexible Cable (37) and speaker wire underneath. (Refer Figure 6-20).
Speaker Wire
Flexible Cable
Figure 6-20. Speaker Wire and Flexible Cable Connection
Page 73

Maintenance – EP350 (Full Keypad Model): Disassembling and Reassembling the Radio 6-9
Note:
The speaker wire and flexible cable connector connecting the Front Housing Assembly (1)
and the Chassis (25) prevent the two units from being completely separated
d. Remove the speaker wire connector connecting the main circuit board and the internal
speaker on the front housing with the tweezers. (Refer Figure 6-21)
Speaker Connector
Figure 6-21. Speaker Wire Removal
e. Lay the front housing down. Rotate the chassis sideways from the Front Housing
Assembly (1) and lay it down.
f. Push the latches on the Front Circuit Board (39) sideways to the right to release the
flexible cable from the connector. (Refer Figure 6-22).
Latches
Figure 6-22. Unlatch the Flexible Cable
Page 74

6-10 Maintenance – EP350 (Full Keypad Model): Disassembling and Reassembling the Radio
6.5.1.2 Chassis Assembly Disassembly
1. Remove the Accessory Bracket (33).
2. Remove the nut (16) on the On/Off Volume Knob Shaft with the Crab Eye Nut Opener.
3. Remove the screw holding the Sub Circuit Board (15) to the Chassis (25) with a Phillips
screwdriver.
4. Push the latches on the Main Circuit Board (18) to release the Flexible Cable (37) from the
connector.
5. Remove the Sub Circuit Board from the Chassis. (Refer Figure 6-23).
Nut
Latch
Sub Circuit Board
Accessory Bracket
Figure 6-23. Sub-Circuit Board and Accessory Bracket Removal
6. Remove the six screws (35) holding the Main Circuit Board to the Chassis with a Phillips
screwdriver. Remove the RF Support Screw (19) with a flat head screwdriver.
7. Remove the Main Circuit Board from the Chassis.
Refer to the CMOS CAUTION paragraph under Section 6.3 before removing the main board. Be
sure to use ESD protection when handling the circuit boards.
8. Remove the seven small O-ring retainers from their slots in the Chassis. Note the alignment of
the retainers for reassembly.
9. Remove the O-ring (22) and the Battery Contact Seal (26). (Refer Figure 6-24).
10. Remove the finger strips from the Chassis. Reuse the finger strips if chassis change is required
only. Note the alignment of the finger strips for assembly.
Page 75

Maintenance – EP350 (Full Keypad Model): Disassembling and Reassembling the Radio 6-11
Finger Strip
O-Ring
Battery Contact Seal
Figure 6-24. Main Circuit Board, finger strips, O-ring and Battery Contact Seal Removal(UHF2)
Finger Strip
O-Ring
Battery Contact Seal
Figure 6-25. Main Circuit Board, finger strips, O-ring and Battery Contact Seal Removal(UHF1)
6.5.1.3 Front Circuit Board, Display Module and Keypad Disassembly
1. Push the latches on the Front Circuit Board (39) to release the Liquid Crystal Display (LCD)
flexible cable from the connector.
2. Remove the five screws holding the Front Circuit Board to the front housing with a Phillips
screwdriver.
Page 76

6-12 Maintenance – EP350 (Full Keypad Model): Disassembling and Reassembling the Radio
3. Remove the Front Circuit Board from the Front Housing. (Refer Figure 6-26).
Circuit Board
Figure 6-26. Front Circuit Board Removal
4. Remove the LCD (36) and Keypad (41) from the Front Housing. (Refer Figure 6-27).
LCD
6.5.1.4 Speaker Disassembly
1. Remove the screw holding the Speaker Retainer (10) to the Front Housing with a Phillips
screwdriver.
2. Remove the Speaker Retainer from the Housing.
Note:
3. Remove the Speaker from the Housing with a flat head screwdriver.
4. Remove the Speaker Insulator (11) from the speaker.
Be careful not to damage the Speaker Wire when removing the Retainer Bracket.
Keypad
Figure 6-27. LCD and Keypad Removal
Page 77

Maintenance – EP350 (Full Keypad Model): Disassembling and Reassembling the Radio 6-13
5. Remove the Speaker Felt (8) from the grille area (Refer Figure 6-28).
Speaker Retainer
Speaker Insulator
Speaker
Speaker Felt
Figure 6-28. Speaker Removal
6.5.2 Radio Reassembly – Detailed
6.5.2.1 Speaker Reassembly
1. Place the Speaker Felt (8) onto the grille area.
2. Align the speaker wire at three o'clock position and push down the speaker until fully adhere onto
the front housing.
3. Align the Speaker Insulator (11) at twelve o'clock position and push down until fully adhere onto
the speaker.
4. Install the Speaker Retainer (10).
5. Tighten the Speaker Retainer to the housing with a Phillips screw torque to (Refer Table 6-12 on
page 6-17 for torque in other units).
Speaker Retainer
Speaker Insulator
Speaker
Speaker Felt
Figure 6-29. Speaker Reassembly
Page 78

6-14 Maintenance – EP350 (Full Keypad Model): Disassembling and Reassembling the Radio
6.5.2.2 Front Circuit Board, Display Module and Keypad Reassembly
1. Place and align the LCD (36) onto the front housing.
2. Place and align the Keypad (41) onto the keypad slot. Apply force around the keypad and ensure
the keypad sealing rib is perfectly seated onto the keypad slot. (Refer Figure 6-30).
LCD
Keypad
Figure 6-30. LCD and Keypad Reassembly
3. Place the Front Circuit Board (39) straight down on top of the LCD and keypad. Align the front
circuit board to the four housing ribs. Press the top right edge of the front circuit board to ensure
the microphone sealing rubber is fully seated in place.
4. Tighten the five screws holding the front circuit board with a Phillips screwdriver torque to
(Refer Table 6-12 on page 6-17 for torque in other units).
Figure 6-31. Front Circuit Board Reassembly
5. Insert the LCD flexible cable into the connector on the front circuit board.
6. Push the latches into the connectors.
Circuit Board
Page 79

Maintenance – EP350 (Full Keypad Model): Disassembling and Reassembling the Radio 6-15
6.5.2.3 Chassis Assembly Reassembly
1. Fit the Battery Contact Seal (26) onto the battery contact slot.
2. Align and assemble the finger strips for assembly.
3. Fit the main O-ring (22) onto the chassis as follow:
a. Ensure that the main O-ring is not twisted. Untangle to original form if necessary.
b. Secure A into the bottom two notches on the chassis. (Refer Figure 6-32).
c. Fit the bottom section of the main O-ring around the bottom two grooves.
d. Insert B into the top two catches on the chassis.
e. Fit the top section of the main O-ring around the top two corners of the chassis.
f. Secure C into the remaining three notches on the chassis.
4. Place the main circuit board straight down on top of the chassis.
Note:
Make sure the battery contact seal protrudes through the chassis and is not squeezed
under the chassis. Ensure the O-ring is also not squeezed under main circuit board.
5. Tighten the six screws holding the main circuit board with a Phillips screwdriver torque to
(Refer Table 6-12 on page 6-17 for torque in other units).
6. Tighten the RF Support Screw (19) with a flat head screw torque to (Refer Table 6-12 on page 6-
17 for torque in other units)..
B
C
A
Figure 6-32. Main Circuit Board, finger strips, O-ring and Battery Contact Seal Reassembly(UHF2)
Page 80

6-16 Maintenance – EP350 (Full Keypad Model): Disassembling and Reassembling the Radio
B
C
A
Figure 6-33. Main Circuit Board, finger strips, O-ring and Battery Contact Seal Reassembly(UHF1)
7. Insert the Sub Circuit Board Flexible Cable (14) into the respective connectors at the top of the
main circuit board.
8. Push the latches into the connectors.
9. Place the sub circuit board straight down on top of the chassis.
10. Tighten the screw that is holding the sub circuit with a Phillips screwdriver torque to
(Refer Table 6-12 on page 6-17 for torque in other units).
11. Tighten the nut on the On/Off Volume Knob Shaft with the Crab Eye Nut Opener.
12. Align and Insert the Accessory Bracket (33) into the audio jack hole. (Refer Figure 6-34).
Accessory Bracket
Audio Jack
Figure 6-34. Sub Circuit Board and Accessory Bracket Reassembly
Page 81

Maintenance – EP350 (Full Keypad Model): Torque List 6-17
6.5.2.4 Chassis and Front Housing Reassembly
1. Assembly the Chassis Assembly to the Front Housing Assembly (1) as follow:
a. Lay the Chassis Assembly beside to the Front Housing Assembly.
b. Insert the Flexible Cable (37) from the main circuit board into the connector on the front
circuit board.
c. Push the latches into the Front Housing Assembly.
d. Connect the speaker wire to the connector.
Note:
2. Slide the On/Off Volume Knob Shaft into the respective holes in the front cover.
3. Insert top chassis tabs into the recesses on the front cover and apply some force until the tabs
4. Be sure the O-ring (22) is properly seated so that the radio is properly sealed.
5. Snap the bottom of the chassis into the front housing.
6. Reassemble the Knob (7), Dust Cover (40), Antenna (21), and Battery (29). (Refer Figure 6-35).
For re-use Flexible Cable (37), please ensure that it is properly folded. For new Flexible
Cable (37), please ensure pre-folded flexible cable was provided and used.
are fully inserted.
Radio Chassis
Figure 6-35. Chassis Assembly and Front Housing Assembly Reassembly
6.6 Torque List
Table 6-12 lists the various screws by part number and description, followed by the torque values in
different units of measure. Torque all screws to the recommended value when assembling the radio.
Table 6-12. Torque Chart
Torque
Part Number Description Quantity
N-mIb-in kgf-cm
PMDN4099_R Retainer, Speaker, with screw 1 0.11±0.01 0.95±0.09 1.10±0.10
PMDN4119_R Screw, Tapping 5 0.13±0.01 1.17±0.13 1.35±0.15
PMDN4107_R Screw, Machine 7 0.23±0.01 2.04±0.13 2.35±0.15
PMDN4114_R Screw, RF Support 1 0.23±0.01 2.04±0.13 2.35±0.15
Page 82

6-18 Maintenance – EP350 (Full Keypad Model): Mechanical View and Parts List
6.7 Mechanical View and Parts List
6.7.1 EP350 (Full Keypad without Channel Knob) Exploded View and Parts List
21
27
26
25
7
6
5
8
4
11
10
9
12
16
15
13
14
20
18
19
17
22
24
23
42
28
29
30
2
3
36
35
39
1
41
40
37
38
32
34
33
43
31
Figure 6-36. EP350 (Full Keypad without Channel Knob)Radio Exploded View
Page 83

Maintenance – EP350 (Full Keypad Model): Mechanical View and Parts List 6-19
Table 6-13. Parts List (Full Keypad without Channel Knob)
Item Motorola Kit Number Description Quantity
1 PMDN4087_R Front Housing, Full Keypad 1
2 PMDN4086_R Name Plate (EP350) 1
3 PMDN4124_R Double Molded Cover, PTT 1
4 PMDN4090_R Seal, Volume Knob 1
5 PMDN4088_R Adhesive, Top Control 1
6 PMDN4104_R Escutcheon, Top without Channel knob 1
7 PMDN4102_R Knob, Volume 1
8 PMDN4100_R Felt, Speaker 1
9 PMDN4067_R Speaker 1
10 PMDN4099_R Retainer, Speaker, with screw 1
11 PMDN4098_R Insulator, Speaker 1
12 PMDN4135_R Seal, Microphone 1
13 PMDN4139_R Microphone 1
14 PMDN4111_R Flexible Cable, Sub Circuit Board 1
15 PMDN4129_R Sub Circuit Board, w/o Channel 1
16 PMDN4112_R
17 PMDN4134_R Switch, Tact 3
*
PMDE4010_R
18
PMDD4011_R
PMDE4028_R
19 PMDN4114_R Screw, RF Support 1
20 PMDN4138_R Bracket, Antenna 1
21 See Appendix A Antenna 1
22 PMDN4116_R
^
PMDN4120_R Finger Strip, Chassis 2 (UHF2 and VHF)
23
24 PMDN4121_R Pad, Thermal 1
25 PMDN4122_R Chassis 1
26 PMDN4105_R Seal, Battery Contact 1
27 PMDN4110_R Label, Caution 1
28 See Appendix A Belt Clip 1
29 See Appendix A Battery 1
30 PMDN4028_R Tuning Hole Sticker (Small) 1
Crab-Eye Nut, Volume and Channel
Main Circuit Board (EP350 – PMUE3148_AL)
Main Circuit Board (EP350 – PMUD2437_AL)
Main Circuit Board (EP350 – PMUE3320_AL)
-ring
O
1
1
1
3 (UHF1)
31 PMDN4106_R Gel Pad, Ceramic Filter 1
32 0915184H01 Contact, Battery 1
33 PMDN4108_R Bracket, Accessory 1
34 0980683Z01 Jack, Audio 1
Page 84

6-20 Maintenance – EP350 (Full Keypad Model): Mechanical View and Parts List
Table 6-13. Parts List (Full Keypad without Channel Knob) (Continued)
Item Motorola Kit Number Description Quantity
35 PMDN4107_R Screw, Machine 7
36 PMDN4123_R Module, Liquid Crystal Display 1
37 PMDN4109_R Flexible Cable, Main Circuit Board 1
38 PMDN4119_R Screw, Tapping 5
‡
PMDN4130_R Front Circuit Board, FKP 1
39
40 PMDN4113_R Cover, Dust 1
41 PMDN4115_R Keypad, Full Keypad 1
#
PMDN4148_R Finger Strip RX 2
42
#
PMDN4150_R Finger Strip, T PCB 1
43
Note:
*
This kit consists of tact switch, antenna bracket, PCB finger strip, battery contact and audio jack.
‡
This kit consists of microphone and microphone seal.
^
This kit is applicable for VHF, UHF1 and UHF2.
#
This kit is only applicable for UHF1.
Page 85

Chapter 7 Maintenance – EP350 (Limited Keypad
Model)
7.1 Introduction
This section provides details about the following:
• Preventive maintenance (inspection and cleaning)
• Safe handling of CMOS and LDMOS devices
• Disassembly and reassembly of the radio
• Repair procedures and techniques
• Mechanical View and Parts List
7.2 Preventive Maintenance
The radios do not require a scheduled preventive maintenance program; however, periodic visual
inspection and cleaning is recommended.
7.2.1 Inspection
Check that the external surfaces of the radio are clean, and that all external controls and switches are
functional. It is not recommended to inspect the interior electronic circuitry.
7.2.2 Cleaning Procedures
The following procedures describe the recommended cleaning agents and the methods to be used
when cleaning the external and internal surfaces of the radio. External surfaces include the front
cover, housing assembly and battery case. These surfaces should be cleaned whenever a periodic
visual inspection reveals the presence of smudges, grease, and/or grime.
Note:
The only recommended agent for cleaning the external radio surfaces is a 0.5% solution of a mild
dishwashing detergent in water. The only factory recommended liquid for cleaning the printed circuit
boards and their components is isopropyl alcohol (100% by volume).
The effects of certain chemicals and their vapors can have harmful results on certain plastics.
Avoid using aerosol sprays, tuner cleaners, and other chemicals.
Internal surfaces should be cleaned only when the radio is disassembled for service or
repair.
Page 86

7-2 Maintenance – EP350 (Limited Keypad Model): Safe Handling of CMOS and LDMOS Devices
Cleaning External Plastic Surfaces
Apply the 0.5% detergent-water solution sparingly with a stiff, non-metallic, short-bristled brush to
work all loose dirt away from the radio. Use a soft, absorbent, lintless cloth or tissue to remove the
solution and dry the radio. Make sure that no water remains entrapped near the connectors, cracks, or
crevices.
Cleaning Internal Circuit Boards and Components
Isopropyl alcohol (100%) may be applied with a stiff, non-metallic, short-bristled brush to dislodge
embedded or caked materials located in hard-to-reach areas. The brush stroke should direct the
dislodged material out and away from the inside of the radio. Make sure that controls or tunable
components are not soaked with alcohol. Do not use high-pressure air to hasten the drying process
since this could cause the liquid to collect in unwanted places. After completing the cleaning process,
use a soft, absorbent, lintless cloth to dry the area. Do not brush or apply any isopropyl alcohol to the
frame, front cover, or back cover.
Note:
Always use a fresh supply of alcohol and a clean container to prevent contamination by
dissolved material (from previous usage).
7.3 Safe Handling of CMOS and LDMOS Devices
Complementary metal-oxide semiconductor (CMOS) devices are used in this family of radios, and are
susceptible to damage by electrostatic or high voltage charges. Damage can be latent, resulting in
failures occurring weeks or months later. Therefore, special precautions must be taken to prevent
device damage during disassembly, troubleshooting, and repair.
Handling precautions are mandatory for CMOS circuits and are especially important in low humidity
conditions. DO NOT attempt to disassemble the radio without first referring to the following CAUTION
statement.
Page 87

Maintenance – EP350 (Limited Keypad Model): Repair Procedures and Techniques – General 7-3
This radio contains static-sensitive devices. Do not open the radio unless you are properly
grounded. Take the following precautions when working on this unit:
• Store and transport all CMOS devices in conductive material so that all exposed
leads are shorted together. Do not insert CMOS devices into conventional plastic
“snow” trays used for storage and transportation of other semiconductor devices.
• Ground the working surface of the service bench to protect the CMOS device. We
recommend using a wrist strap, two ground cords, a table mat, and a floor mat.
• Wear a conductive wrist strap in series with a 100k resistor to ground. (Replacement
wrist straps that connect to the bench top covering are Motorola part number
4280385A59.)
• Do not wear nylon clothing while handling CMOS devices.
• Do not insert or remove CMOS devices with power applied. Check all power supplies
used for testing CMOS devices to be certain that there are no voltage transients
present.
• When straightening CMOS pins, provide ground straps for the apparatus used.
• When soldering, use a grounded soldering iron.
• If at all possible, handle CMOS devices by the package and not by the leads. Prior to
touching the unit, touch an electrical ground to remove any static charge that you
may have accumulated. The package and substrate may be electrically common. If
so, the reaction of a discharge to the case would cause the same damage as touching
the leads.
7.4 Repair Procedures and Techniques – General
Note
Any rework or repair on Environmentally Preferred Products must be done using the appropriate
lead-free solder wire and solder paste as stated in the following tables:
Environmentally Preferred Products (EPP) (refer to the marking on the printed circuit
boards - examples shown below) were developed and assembled using environmentally
preferred components and solder assembly techniques that meet or exceed compliance
to the European Union’s ROHS and WEEE directives (Waste Electrical and Electronic
Equipment (WEEE) Directive 2002/96/EC and Restriction of Hazardous Substances
(ROHS) Directive 2002/95/EC). To maintain product compliance and reliability, use only
the Motorola specified parts in this manual.
For the identification of lead (Pb) free assemblies, all EPP products will carry the EPP
Marking, shown below, on the printed circuit board (PCB). This marking provides
information to those performing assembly, servicing and recycling operation on this
product, adhering to the JEDEC standard #97. The EPP Marking takes the form of a
label or marking on the PCB.
Page 88

7-4 Maintenance – EP350 (Limited Keypad Model): Repair Procedures and Techniques – General
Table 7-14. Lead Free Solder Wire Part Number List
Motorola
Part Number
1088929Y01 95.5Sn/3.8Ag/0.7Cu RMA Version 2.7-3.2% 217C 52171 0.015” 1lb spool
Alloy Flux Type
Flux Content
by Weight
Melting
Point
Supplier Part
number
Diameter Weight
Table 7-15. Lead Free Solder Paste Part Number List
Motorola
Part Number
10-856-
74C03
Manufacturer Part
Number
NC-SMQ230 900-1000KCPs
Viscosity Type Composition & Percent Metal
Brookfield(5rpm)
Type 3
-325/+500)
(
95.5%Sn-3.8%Ag-0.7%Cu
89.3%
Liquidus
Temperature
217 Degree C
Parts Replacement and Substitution
When damaged parts are replaced, identical parts should be used. If the identical
replacement part is not locally available, check the parts list for the proper Motorola part number.
Orders for replacement parts which are listed in the “Parts List” section of this manual, should be
placed directly on Motorola’s local distribution organization or via Motorola Online
Rigid Circuit Boards
This family of radios uses bonded, multi-layer, printed circuit boards. Since the inner layers are not
accessible, some special considerations are required when soldering and unsoldering components.
The printed-through holes may interconnect multiple layers of the printed circuit. Therefore, exercise
care to avoid pulling the plated circuit out of the hole.
When soldering near the connector pins:
• Avoid accidentally getting solder in the connector.
• Be careful not to form solder bridges between the connector pins.
• Examine your work closely for shorts due to solder bridges.
Chip Components
Use the RLN4062 Hot-Air Repair Station for chip component replacement. Adjust the temperature
control to 390 °C (735 °F), and adjust the airflow to a minimum setting. Airflow can vary due to
component density.
• To remove a chip component:
1. Use a hot-air hand piece and position the nozzle of the hand piece approximately 0.3 cm
(1/8") above the component to be removed.
2. Begin applying the hot air. Once thde solder reflows, remove the component using a pair
of tweezers.
3. Using a solder wick and a soldering iron or a power desoldering station, remove the
excess solder from the pads.
• To replace a chip component using a soldering iron:
1. Select the appropriate micro-tipped soldering iron and apply fresh solder to one of the
solder pads.
2. Using a pair of tweezers, position the new chip component in place while heating the
fresh solder.
Page 89

Maintenance – EP350 (Limited Keypad Model): Repair Procedures and Techniques – General 7-5
3. Once solder wicks onto the new component, remove the heat from the solder.
4. Heat the remaining pad with the soldering iron and apply solder until it wicks to the
component. If necessary, touch up the first side. All solder joints should be smooth and
shiny.
• To replace a chip component using hot air:
1. Use the hot-air hand piece and reflow the solder on the solder pads to smooth it.
2. Apply a drop of solder paste flux to each pad.
3. Using a pair of tweezers, position the new component in place.
4. Position the hot-air hand piece approximately 0.3 cm (1/8") above the component and
begin applying heat.
5. Once the solder wicks to the component, remove the heat and inspect the repair. All
joints should be smooth and shiny.
Shields
Removing and replacing shields is recommended to be done with the Air Blower,
BOSCH GHG 603 or equivalent.
• To remove the shield:
1. Place the circuit board in the circuit board holder.
2. Add solder paste flux around the base of the shield.
3. Position the heat-focus head onto the shield.
4. Turn on the heater and wait until the shield lifts off the circuit board.
5. Once the shield is off, turn off the heat, and grab the part with a pair of tweezers.
6. Remove the circuit board from the circuit board holder.
• To replace the shield:
1. Add solder to the shield if necessary, using a micro-tipped soldering iron.
2. Next, rub the soldering iron tip along the edge of the shield to smooth out any excess
solder. Use solder wick and a soldering iron to remove excess solder from the solder
pads on the circuit board.
3. Place the circuit board back in the circuit board holder.
4. Place the shield on the circuit board using a pair of tweezers.
5. Position the heat-focus head over the shield.
6. Turn on the heater and wait for the solder to reflow.
7. Once complete, turn off the heat, raise the heat-focus head and wait approximately one
minute for the part to cool.
8. Remove the circuit board and inspect the repair. No cleaning should be necessary.
Page 90

7-6 Maintenance – EP350 (Limited Keypad Model): Disassembling and Reassembling the Radio
7.5 Disassembling and Reassembling the Radio – General
When disassembling and reassembling the radio, it is important to pay particular attention to the snaps and
tabs, and how parts align with each other.
The following tools are required for disassembling and reassembling the radio (see Chapter 3 for a list
of service aids):
• Phillips Screwdriver
• Flat Head Screwdriver
• Torque Driver
• Crab Eye Nut Opener (PMDN4039_R)
• Chassis and Knob Opener (PMDN4038_R)
• Tweezers
If a unit requires further testing or service than is customarily performed at the basic level, please
send the unit to a Motorola Authorized Service Center listed in Appendix B.
Note:
Numbers in parentheses ( ) refer to item numbers in Table 7-17 on page 7-19.
Figure 7-37. Limited Keypad Without Channel Knob Model
Page 91

Maintenance – EP350 (Limited Keypad Model): Disassembling and Reassembling the Radio 7-7
7.5.1 Radio Disassembly – Detailed
7.5.1.1 Front Housing From Chassis Disassembly
1. Turn off the radio.
2. Remove the Battery (29):
a. Release the battery latch by moving it into the unlock position.
b. Slide the Battery downwards.
c. Remove the Battery from the radio
Belt Clip
Antenna
Battery
Figure 7-38. Battery and Antenna Removal
3. Remove the Antenna (21) by turning it counterclockwise.
Battery Latch
Page 92

7-8 Maintenance – EP350 (Limited Keypad Model): Disassembling and Reassembling the Radio
4. Remove the Volume Knob (7) from its shaft using the Chassis and Knob Opener.
(Refer Figure 7-39.
Volume Knob
Chassis and Knob Opener
Figure 7-39. Knob Removal
Note:
The Volume Knob can be turned clockwise and counterclockwise. However, it is designed
to fit very tightly on the shaft.
5. Separate the Chassis (25) from the Front Housing Assembly (1):
a. Insert the Chassis and Knob Opener in between the thin retaining wall and the chassis
at the bottom of the radio. Do not mar the O-ring sealing area on the housing.
b. Slowly pry the bottom of the chassis from the housing by pushing the Chassis and Knob
Opener downwards, and prying the handle of the tool over and behind the base of the
radio. This forces the thin inner plastic wall toward the base of the radio thus releasing
the two chassis base tabs. (Refer Figure 7-40).
Figure 7-40. Chassis Removal
Marring the front cover O-ring sealing area will prevent the radio from sealing properly. If the
O-ring (23) is damaged, replace it with a new one.
Page 93

Maintenance – EP350 (Limited Keypad Model): Disassembling and Reassembling the Radio 7-9
c. Slide the rear chassis downwards, and away from the front housing. Be careful not to
damage the Flexible Cable (37) and speaker wire underneath. (Refer Figure 7-41).
Speaker Wire
Flexible Cable
Figure 7-41. Speaker Wire and Flexible Cable Connection
Note:
The speaker wire and flexible cable connector connecting the Front Housing Assembly (1)
and the Chassis (25) prevent the two units from being completely separated
d. Remove the speaker wire connector connecting the main circuit board and the internal
speaker on the front housing with the tweezers. (Refer Figure 7-42).
Speaker Connector
Figure 7-42. Speaker Wire Removal
e. Lay the front housing down. Rotate the chassis sideways from the Front Housing
Assembly (1) and lay it down.
Page 94

7-10 Maintenance – EP350 (Limited Keypad Model): Disassembling and Reassembling the Radio
f. Push the latches on the Front Circuit Board (39) sideways to the right to release the
flexible cable from the connector. (Refer Figure 7-43).
Latches
Figure 7-43. Unlatch the Flexible Cable
7.5.1.2 Chassis Assembly Disassembly
1. Remove the Accessory Bracket (33).
2. Remove the nut (16) on the On Off Volume Knob Shaft with the Crab Eye Nut Opener.
3. Remove the screw holding the Sub Circuit Board (15) to the Chassis (25) with a Phillips
screwdriver.
4. Push the latches on the Main Circuit Board (18) to release the Flexible Cable (37) from the
connector.
5. Remove the Sub Circuit Board from the Chassis. (Refer Figure 7-44).
Nut
Latch
Sub Circuit Board
Accessory Bracket
Figure 7-44. Sub-Circuit Board and Accessory Bracket Removal
6. Remove the six screws (35) holding the Main Circuit Board to the Chassis with a Phillips
screwdriver. Remove the RF Support Screw (19) with a flat head screwdriver.
Page 95

Maintenance – EP350 (Limited Keypad Model): Disassembling and Reassembling the Radio 7-11
7. Remove the Main Circuit Board from the Chassis.
Refer to the CMOS CAUTION paragraph under Section 7.3 before removing the main board. Be
sure to use ESD protection when handling the circuit boards.
8. Remove the seven small O-ring retainers from their slots in the Chassis. Note the alignment of
the retainers for reassembly.
9. Remove O-ring (23) and the Battery Contact Seal (26). (Refer Figure 7-45).
10. Remove the finger strips from the Chassis. Reuse the finger strips if chassis change is required
only. Note the alignment of the finger strips for assembly.
Finger Strip
O-Ring
Battery Contact Seal
Figure 7-45. Main Circuit Board, finger strips, O-ring and Battery Contact Seal Removal(UHF2)
Finger Strip
O-Ring
Battery Contact Seal
Figure 7-46. Main Circuit Board, finger strips, O-ring and Battery Contact Seal Removal (UHF1)
Page 96

7-12 Maintenance – EP350 (Limited Keypad Model): Disassembling and Reassembling the Radio
7.5.1.3 Front Circuit Board, Display Module and Keypad Disassembly
1. Push the latches on the Front Circuit Board (39) to release the Liquid Crystal Display (LCD)
flexible cable from the connector.
2. Remove the five screws holding the Front Circuit Board to the front housing with a Phillips
screwdriver.
3. Remove the Front Circuit Board from the Front Housing. (Refer Figure 7-47).
Circuit Board
Figure 7-47. Front Circuit Board Removal
4. Remove the LCD (36) (37), Poron Pad (42) and Keypad (41) from the Front Housing.
(Refer Figure 7-48).
LCD
Keypad
Poron Pad
Figure 7-48. LCD and Keypad Removal
Note:
The poron pad will be damaged during disassembly. A new poron pad is needed for
reassembly.
Page 97

Maintenance – EP350 (Limited Keypad Model): Disassembling and Reassembling the Radio 7-13
7.5.1.4 Speaker Disassembly
1. Remove the screw holding the Speaker Retainer (10) to the Front Housing with a Phillips
screwdriver.
2. Remove the Speaker Retainer from the Housing.
Note:
3. Remove the Speaker from the Housing with a flat head screwdriver.
4. Remove the Speaker Insulator (11) from the speaker.
5. Remove the Speaker Felt (8) from the grille area (Refer Figure 7-49).
Be careful not to damage the Speaker Wire when removing the Retainer Bracket.
Speaker Retainer
Speaker Insulator
Speaker
Speaker Felt
Figure 7-49. Speaker Removal
7.5.2 Radio Reassembly – Detailed
7.5.2.1 Speaker Reassembly
1. Place the Speaker Felt (8) onto the grille area.
2. Align the speaker wire at three o'clock position and push down the speaker until fully adhere onto
the front housing.
3. Align the Speaker Insulator (11) at twelve o'clock position and push down until fully adhere onto
the speaker.
4. Install the Speaker Retainer (10).
5. Tighten the Speaker Retainer to the housing with a Phillips screwdriver torque to (Refer Table 7-
16 on page 7-18 for torque in other units)
Page 98

7-14 Maintenance – EP350 (Limited Keypad Model): Disassembling and Reassembling the Radio
Speaker Retainer
Speaker Insulator
Speaker
Speaker Felt
Figure 7-50. Speaker Reassembly
7.5.2.2 Front Circuit Board, Display Module and Keypad Reassembly
1. Place and align the LCD (36) onto the front housing.
2. Place and align the Keypad (41) onto the keypad slot. Apply force around the keypad and ensure
the keypad sealing rib is perfectly seated onto the keypad slot. (Refer Figure 7-51).
LCD
Keypad
Keypad Poron Pad
Figure 7-51. LCD and Keypad Reassembly
3. Place the Front Circuit Board (39) straight down on top of the LCD and keypad. Align the front
circuit board to the four housing ribs. Press the top right edge of the front circuit board to ensure
the microphone sealing rubber is fully seated in place.
4. Tighten the five screws holding the front circuit board with a Phillips screwdriver torque to
(Refer Table 7-16 on page 7-18 for torque in other units)
Page 99

Maintenance – EP350 (Limited Keypad Model): Disassembling and Reassembling the Radio 7-15
.
Circuit Board
Figure 7-52. Front Circuit Board Reassembly
5. Insert the LCD flexible cable into the connector on the front circuit board.
6. Push the latches into the connectors.
7.5.2.3 Chassis Assembly Reassembly
1. Fit the Battery Contact Seal (26) onto the battery contact slot.
2. Align and assemble the finger strips for assembly.
3. Fit the main O-ring (23) onto the chassis as follow:
a. Ensure that the main O-ring is not twisted. Untangle to original form if necessary.
b. Secure A into the bottom two notches on the chassis. (Refer Figure 7-53).
c. Fit the bottom section of the main O-ring around the bottom two grooves.
d. Insert B into the top two catches on the chassis.
e. Fit the top section of the main O-ring around the top two corners of the chassis.
f. Secure C into the remaining three notches on the chassis.
4. Place the main circuit board straight down on top of the chassis.
Note:
Make sure the battery contact seal protrudes through the chassis and is not squeezed
under the chassis. Ensure the O-ring is also not squeezed under main circuit board.
Page 100

7-16 Maintenance – EP350 (Limited Keypad Model): Disassembling and Reassembling the Radio
5. Tighten the six screws holding the main circuit board with a Phillips screwdriver torque to
(Refer Table 7-16 on page 7-18 for torque in other units).
6. Tighten the RF Support Screw (19) with a flat head screwdriver torque to (Refer Table 7-16 on
page 7-18 for torque in other units).
B
C
A
Figure 7-53. Main Circuit Board, O-ring and Battery Contact Seal Reassembly(UHF2)
B
C
A
Figure 7-54. Main Circuit Board, finger strips, O-ring and Battery Contact Seal Reassembly(UHF1)
7. Insert the Sub Circuit Board Flexible Cable (14) into the respective connectors at the top of the
main circuit board.
8. Push the latches into the connectors.
9. Place the sub circuit board straight down on top of the chassis.
10. Tighten the screw that is holding the sub circuit with a Phillips screwdriver torque to
. (Refer Table 7-16 on page 7-18 for torque in other units).
11. Tighten the nut on the On/Off Volume Knob Shaft with the Crab Eye Nut Opener.
 Loading...
Loading...